Page 1

S12 MagniV
Microcontrollers
nxp.com
MC9S12VRP-Series
Reference Manual and
Datasheet
MC9S12VRP64
Rev. 1.3
19 Sep 2017
Page 2

Your printed copy may be an earlier revision. To verify you have the latest information available, refer to:
http://nxp.com
A full list of family members and options is included in the device overview section.
The following revision history table summarizes changes contained in this document.
This document contains information for all constituent modules, with the exception of the CPU. For CPU
information please refer to CPU12-1 in the CPU12 & CPU12X Reference Manual.
Revision History
Date Revision Description
• Updated Data-Flash size for S12VRP48 option, Ta bl e 1 -2
01 MAR 2017 1.0
7 AUG 2017 1.1A
18 AUG 2017 1.1 • Official release
• Removed internal register bit reference 13.3.4/13-376
• Updated NVM timing for Erase D-Flash Sector Ta bl e I -1
• Removed Preliminary marking
• Minor corrections in Chapter 1, “Device Overview S12VRP-Series”, Chapter 2, “Port
Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)”, and Chapter 14, “Low-Side Driver - LS2DRV
(S12LS2DRV_V1)”
• Updated electrical specifications in Appendix A to Appendix H
14 SEP 2017 1.2A • Updated electrical specifications in Appendix A and Appendix D
15 SEP 2017 1.2 • Official release
19 SEP 2017 1.3 • Block diagram added to Chapter 15, “Current Sense Amplifier Module (ISENSEV1)
Page 3

Chapter 1
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.3 S12VRP-Series Comparison . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
1.4 Chip-Level Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
1.5 Module Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.5.1 HCS12 16-Bit Central Processor Unit (CPU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.5.2 On-Chip Flash with ECC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.5.3 On-Chip SRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.5.4 Main External Oscillator (XOSCLCP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.5.5 Internal RC Oscillator (IRC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.5.6 Internal Phase-Locked Loop (IPLL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.5.7 Clock and Power Management Unit (CPMU) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
1.5.8 System Integrity Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5.9 Timer (TIM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5.10 Pulse Width Modulation Module (PWM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5.11 LIN physical layer transceiver (LINPHY) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5.12 Serial Communication Interface Module (SCI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5.13 Analog-to-Digital Converter Module (ADC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.5.14 Supply Voltage Sense (BATS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.5.15 On-Chip Voltage Regulator system (VREG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
1.5.16 Low-side driver (LSDRV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.5.17 Low-side driver (LS2DRV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.5.18 Current Sense Amplifier . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.5.19 High-side drivers (HSDRV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.5.20 Background Debug (BDM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
1.5.21 Debugger (DBG) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.6 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.7 Family Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.7.1 Part ID Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.8 Signal Description and Device Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.8.1 Pin Assignment Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.8.2 Detailed Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
1.8.3 Power Supply Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
1.8.4 Device Pinouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
1.8.5 MC9S12VRP Pinout 48-pin LQFP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
1.9 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
1.9.1 Chip Configuration Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
1.9.2 Low Power Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
1.10 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
1.11 Resets and Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
1.11.1 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
1.11.2 Interrupt Vectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
1.11.3 Effects of Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 3
Page 4

1.12 Module Device level Dependencies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
1.12.1 ADC External Trigger Input Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
1.12.2 ADC Special Conversion Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.12.3 HVI Digital input enables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.12.4 API external clock output (API_EXTCLK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.12.5 COP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
1.12.6 CPMU High Temperature Trimming . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
1.12.7 Flash IFR Mapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Chapter 2
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2.1.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
2.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
2.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
2.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
2.3.1 Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
2.3.2 Device Specific PIM Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
2.3.3 PIM Generic Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
2.3.4 PIM Generic Register Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
2.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
2.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
2.4.2 Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
2.4.3 Pin I/O Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
2.4.4 Pull Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
2.4.5 Increased Drive Strength on PP2, PP1 and PP0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
2.4.6 High Side Drivers and Low Side Drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
2.4.7 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
2.4.8 High-Voltage Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
2.5 Initialization and Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
2.5.1 Port Data and Data Direction Register writes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
2.5.2 SCI Baud Rate Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
2.5.3 Over-Current Protection on PP2 and PP0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
2.5.4 Open Input Detection on PL[5:0] (HVI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Chapter 3
S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
3.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
3.1.2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
3.1.3 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3.1.4 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3.1.5 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
4 NXP Semiconductors
Page 5

3.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
3.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
3.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
3.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
3.4.1 MCU Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
3.4.2 Memory Map Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
3.4.3 Unimplemented and Reserved Address Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
3.4.4 Prioritization of Memory Accesses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
3.4.5 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Chapter 4
S12 Clock, Reset and Power Management Unit (S12CPMU_UHV_V8)
4.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
4.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
4.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
4.1.3 S12CPMU_UHV_V8 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
4.2 Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.1 RESET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.2 EXTAL and XTAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.3 VSUP — Regulator Power Input Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.4 VDDA, VSSA — Regulator Reference Supply Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.5 VDDX, VSSX— Pad Supply Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.2.6 VSS— Ground Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.2.7 API_EXTCLK — API external clock output pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.2.8 VDD— Internal Regulator Output Supply (Core Logic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.2.9 VDDF— Internal Regulator Output Supply (NVM Logic) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.2.10 TEMPSENSE — Internal Temperature Sensor Output Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
4.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
4.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
4.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
4.4.1 Phase Locked Loop with Internal Filter (PLL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
4.4.2 Startup from Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
4.4.3 Stop Mode using PLLCLK as source of the Bus Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
4.4.4 Full Stop Mode using Oscillator Clock as source of the Bus Clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
4.4.5 External Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
4.4.6 System Clock Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
4.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
4.5.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
4.5.2 Description of Reset Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
4.5.3 Oscillator Clock Monitor Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
4.5.4 PLL Clock Monitor Reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
4.5.5 Power-On Reset (POR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4.5.6 Low-Voltage Reset (LVR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
4.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 5
Page 6

4.6.1 Description of Interrupt Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
4.7 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
4.7.1 General Initialization information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
4.7.2 Application information for COP and API usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
Chapter 5
Background Debug Module (S12SBDMV1)
5.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
5.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
5.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
5.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
5.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
5.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
5.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
5.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
5.3.3 Family ID Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.4.1 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.4.2 Enabling and Activating BDM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.4.3 BDM Hardware Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
5.4.4 Standard BDM Firmware Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
5.4.5 BDM Command Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
5.4.6 BDM Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
5.4.7 Serial Interface Hardware Handshake Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
5.4.8 Hardware Handshake Abort Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
5.4.9 SYNC — Request Timed Reference Pulse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
5.4.10 Instruction Tracing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
5.4.11 Serial Communication Time Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Chapter 6
S12S Debug Module (S12DBGV2)
6.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
6.1.1 Glossary Of Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
6.1.2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
6.1.3 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
6.1.4 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
6.1.5 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
6.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
6.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
6.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
6.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
6.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
6.4.1 S12DBGV2 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 214
6.4.2 Comparator Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
6 NXP Semiconductors
Page 7

6.4.3 Match Modes (Forced or Tagged) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
6.4.4 State Sequence Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
6.4.5 Trace Buffer Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
6.4.6 Tagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 227
6.4.7 Breakpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
6.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
6.5.1 State Machine scenarios . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
6.5.2 Scenario 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
6.5.3 Scenario 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
6.5.4 Scenario 3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
6.5.5 Scenario 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
6.5.6 Scenario 5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
6.5.7 Scenario 6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
6.5.8 Scenario 7 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
6.5.9 Scenario 8 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
6.5.10 Scenario 9 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
6.5.11 Scenario 10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Chapter 7
Interrupt Module (S12SINTV1)
7.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
7.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
7.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
7.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
7.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
7.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
7.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
7.3.1 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
7.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
7.4.1 S12S Exception Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
7.4.2 Interrupt Prioritization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
7.4.3 Reset Exception Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
7.4.4 Exception Priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 241
7.5 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
7.5.1 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
7.5.2 Interrupt Nesting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
7.5.3 Wake Up from Stop or Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 242
Chapter 8
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC12B12CV2)
Block Description
8.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
8.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
8.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 7
Page 8

8.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
8.2 Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
8.2.1 Detailed Signal Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
8.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
8.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 249
8.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 252
8.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
8.4.1 Analog Sub-Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
8.4.2 Digital Sub-Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 268
8.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
8.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 270
Chapter 9
Pulse-Width Modulator (S12PWM8B8CV2)
9.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
9.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
9.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 271
9.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
9.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
9.2.1 PWM7 - PWM0 — PWM Channel 7 - 0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
9.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
9.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
9.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
9.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
9.4.1 PWM Clock Select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
9.4.2 PWM Channel Timers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 291
9.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 299
9.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 300
Chapter 10
Serial Communication Interface (S12SCIV6)
10.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
10.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 301
10.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
10.1.3 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
10.1.4 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
10.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
10.2.1 TXD — Transmit Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
10.2.2 RXD — Receive Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
10.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
10.3.1 Module Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
10.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
10.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
10.4.1 Infrared Interface Submodule . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
8 NXP Semiconductors
Page 9

10.4.2 LIN Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
10.4.3 Data Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
10.4.4 Baud Rate Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
10.4.5 Transmitter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
10.4.6 Receiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
10.4.7 Single-Wire Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
10.4.8 Loop Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
10.5 Initialization/Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
10.5.1 Reset Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
10.5.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
10.5.3 Interrupt Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
10.5.4 Recovery from Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
10.5.5 Recovery from Stop Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
Chapter 11
Timer Module (TIM16B2CV3)
11.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
11.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
11.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
11.1.3 Block Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
11.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
11.2.1 IOC1 - IOC0 — Input Capture and Output Compare Channel 1-0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 342
11.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
11.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
11.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
11.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
11.4.1 Prescaler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
11.4.2 Input Capture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
11.4.3 Output Compare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
11.5 Resets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
11.6 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
11.6.1 Channel [1:0] Interrupt (C[1:0]F) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
11.6.2 Timer Overflow Interrupt (TOF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Chapter 12
High-Side Driver Module - HSDRV2C (HSDRV2CV3)
12.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
12.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
12.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
12.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 360
12.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
12.2.1 HS[0], HS[1] — High Side Driver Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
12.2.2 VSUPHS — High Side Driver Power Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
12.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 9
Page 10

12.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
12.3.2 Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
12.3.3 Port HS Data Register (HSDR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
12.3.4 HSDRV2C Configuration Register (HSCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
12.3.5 HSDRV2C Slew Rate Control Register (HSSLR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 365
12.3.6 Reserved Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
12.3.7 HSDRV2C Status Register (HSSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
12.3.8 HSDRV2C Interrupt Enable Register (HSIE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
12.3.9 HSDRV2C Interrupt Flag Register (HSIF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
12.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
12.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
12.4.2 Open Load Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
12.4.3 Over-Current Shutdown . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
12.4.4 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
Chapter 13
Low-Side Drivers - LSDRV (S12LSDRV2)
13.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
13.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
13.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
13.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
13.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
13.2.1 LS0, LS1— Low Side Driver Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
13.2.2 LSGND — Low Side Driver Ground Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
13.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
13.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
13.3.2 Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
13.3.3 Port LS Data Register (LSDR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
13.3.4 LSDRV Configuration Register (LSCR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
13.3.5 Reserved Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
13.3.6 Reserved Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
13.3.7 LSDRV Status Register (LSSR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
13.3.8 LSDRV Interrupt Enable Register (LSIE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
13.3.9 LSDRV Interrupt Flag Register (LSIF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
13.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
13.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
13.4.2 Open-Load Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
13.4.3 Over-Current Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
13.4.4 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
Chapter 14
Low-Side Driver - LS2DRV (S12LS2DRV_V1)
14.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
14.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
10 NXP Semiconductors
Page 11

14.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 383
14.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 384
14.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
14.2.1 LS2 — Low Side Driver Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
14.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
14.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
14.3.2 Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
14.3.3 Port LS Data Register (LS2DR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
14.3.4 LS2DRV Configuration Register (LS2CR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
14.3.5 Reserved Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
14.3.6 LS2DRV Interrupt Enable Register (LS2IE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
14.3.7 LS2DRV Interrupt Flag Register (LS2IF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
14.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
14.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
14.4.2 Over-Current Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
14.4.3 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 392
Chapter 15
Current Sense Amplifier Module (ISENSEV1)
15.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
15.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
15.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
15.4 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
15.4.1 AMPP — Current Sense Amplifier Non-Inverting Input Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
15.4.2 AMPM — Current Sense Amplifier Inverting Input Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
15.4.3 AMP — Current Sense Amplifier Output Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 394
15.5 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
15.5.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
15.5.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
15.6 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
15.6.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
15.6.2 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
Chapter 16
LIN Physical Layer (S12LINPHYV2)
16.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
16.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
16.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
16.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
16.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
16.2.1 LIN — LIN Bus Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
16.2.2 LGND — LIN Ground Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
16.2.3 VLINSUP — Positive Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
16.2.4 LPTxD — LIN Transmit Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 11
Page 12

16.2.5 LPRxD — LIN Receive Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
16.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
16.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
16.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
16.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
16.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
16.4.2 Slew Rate and LIN Mode Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
16.4.3 Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
16.4.4 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 419
16.5 Application Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
16.5.1 Module Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
16.5.2 Interrupt handling in Interrupt Service Routine (ISR) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
Chapter 17
Supply Voltage Sensor - (BATSV2)
17.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
17.1.1 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
17.1.2 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
17.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
17.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
17.2.1 VSENSE — Supply (Battery) Voltage Sense Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
17.2.2 VSUP — Voltage Supply Pin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
17.3 Memory Map and Register Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
17.3.1 Register Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
17.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
17.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
17.4.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
17.4.2 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
Chapter 18
64 KByte Flash Module (S12FTMRG64K4KV2)
18.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
18.1.1 Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
18.1.2 Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
18.1.3 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
18.2 External Signal Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 440
18.3 Memory Map and Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
18.3.1 Module Memory Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
18.3.2 Register Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
18.4 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
18.4.1 Modes of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
18.4.2 IFR Version ID Word . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
18.4.3 Internal NVM resource (NVMRES) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
18.4.4 Flash Command Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 464
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
12 NXP Semiconductors
Page 13

18.4.5 Allowed Simultaneous P-Flash and D-Flash Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
18.4.6 Flash Command Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
18.4.7 Interrupts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
18.4.8 Wait Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
18.4.9 Stop Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
18.5 Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
18.5.1 Unsecuring the MCU using Backdoor Key Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
18.5.2 Unsecuring the MCU in Special Single Chip Mode using BDM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
18.5.3 Mode and Security Effects on Flash Command Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
18.6 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
Appendix A
MCU Electrical Specifications
A.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
A.1.1 Parameter Classification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
A.1.2 Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
A.1.3 Current Injection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
A.1.4 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
A.1.5 ESD Protection and Latch-up Immunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 492
A.1.6 Recommended Capacitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
A.1.7 Operating Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
A.1.8 Power Dissipation and Thermal Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
A.2 General Purpose I/O Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
A.2.1 High Voltage Inputs (HVI) Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
A.3 Supply Currents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
A.3.1 Measurement Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 500
Appendix B
CPMU Electrical Specifications (VREG, OSC, IRC, PLL)
B.1 VREG Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
B.2 Reset and Stop Timing Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
B.3 OSC Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
B.4 IRC Electrical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
B.5 Phase Locked Loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
B.5.1 Jitter Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 505
Appendix C
ADC Electrical Specifications
C.1 ADC Operating Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 508
C.1.1 Factors Influencing Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 508
C.2 ADC Analog Input Parasitics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
C.3 ADC Accuracy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
C.3.1 ADC Accuracy Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 13
Page 14

Appendix D
HSDRV Electrical Specifications
D.1 Static Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 515
D.2 Dynamic Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 516
Appendix E
LINPHY Electrical Specifications
E.1 Static Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 517
E.2 Dynamic Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 518
Appendix F
LSDRV/LS2DRV Electrical Specifications
F.1 LSDRV Static Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 520
F.2 LSDRV Dynamic Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
F.3 LS2DRV Static Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 521
Appendix G
ISENSE Electrical Specifications
G.1 Operating Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 522
Appendix H
BATS Electrical Specifications
H.1 Static Electrical Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 523
H.2 Dynamic Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 524
Appendix I
NVM Electrical Parameters
I.1 NVM Timing Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 525
I.2 NVM Reliability Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 527
Appendix J
Package Information
Appendix K
Ordering Information
Appendix L
Detailed Register Address Map
L.1 0x0000-0x0009 Port Integration Module (PIM) Map 1 of 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
L.2 0x000A-0x000B Module Mapping Control (MMC) Map 1 of 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
L.3 0x000C-0x000D Port Integration Module (PIM) Map 2 of 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
L.4 0x000E-0x000F Reserved . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 536
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
14 NXP Semiconductors
Page 15

L.5 0x0010-0x0017 Module Mapping Control (MMC) Map 2 of 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 536
L.6 0x0018-0x0019 Reserved . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 536
L.7 0x001A-0x001B Part ID Registers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
L.8 0x001C-0x001F Port Integration Module (PIM) Map 3 of 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
L.9 0x0020-0x002F Debug Module (S12SDBG) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
L.10 0x0030-0x0033 Reserved . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 538
L.11 0x0034-0x003F Clock Reset and Power Management (CPMU) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 538
L.12 0x0040-0x006F Timer Module (TIM0) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 539
L.13 0x0070-0x009F Analog to Digital Converter (ATD) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 540
L.14 0x00A0-0x00C7 Pulse Width Modulator 6-Channels (PWM) Map. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 542
L.15 0x00C8-0x00CF Serial Communication Interface (SCI0) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
L.16 0x00D0-0x00D7 Serial Communication Interface (SCI1) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
L.17 0x0100-0x0113 NVM Control Register (FTMRG) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 545
L.18 0x0120 Interrupt Vector Base Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
L.19 0x0140-0x0147 High Side Drivers (HSDRV2C) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
L.20 0x0150-0x0157 Low Side Drivers (LSDRV) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
L.21 0x0158-0x015F Low Side Driver (LS2DRV). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 547
L.22 0x0170-0x0177 Supply Voltage Sense (BATS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 548
L.23 0x0178-0x017F Current Sense Amplifier (ISENSE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
L.24 0x0180-0x01AF Timer Module (TIM1) Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
L.25 0x0240 -0x027F Port Integration Module (PIM) Map 4 of 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
L.26 0x02F0-0x02FF Clock and Power Management Unit (CPMU) Map 2 of 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 554
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 15
Page 16

MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
16 NXP Semiconductors
Page 17
Chapter 1 Device Overview S12VRP-Series
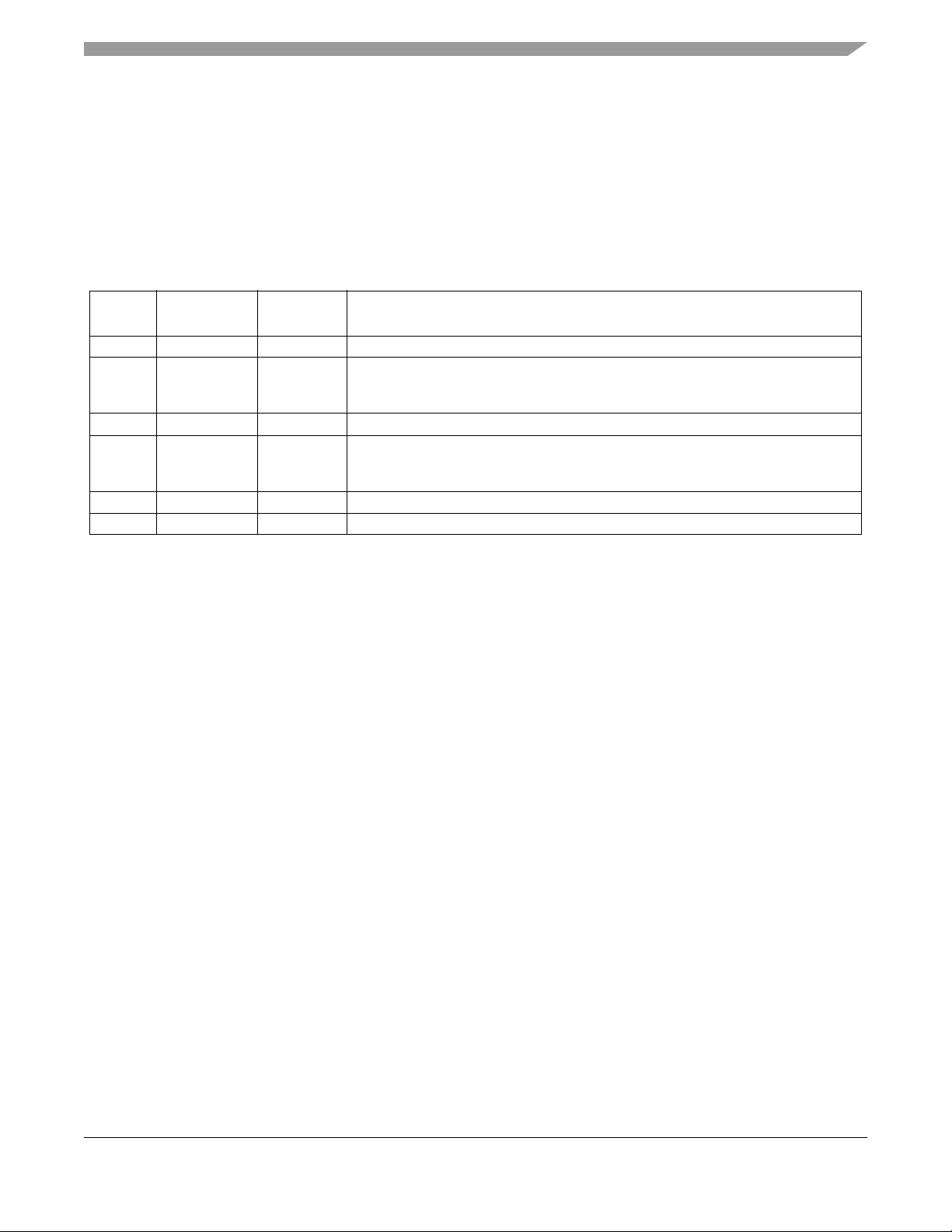
Table 1-1. Revision History
Version
Number
0.1A 8-Apr-2016 All • Initial Draft
0.2 28-Apr-2016 All • Moved API_EXTCLK from PS2 to PT2 following DFT feedback
0.3 02-Jun-2016 All • Minor corrections based on shared review feedback
0.4 08-Jul-2016 Various
0.5 05-Sep-2016 • Removed ADC calibration information
0.6 02-Aug-2017 • Corrected typos and formatting
Revision
Date
Sections
Affected
1.12.3/1-44
Various
Description of Changes
• Removed VSUPHS and specified high-side drive is supplied by VSUP
• Minor corrections from initial draft shared review
• Corrections based on V1.0A shared review feedback
• Documented HVI digital inputs are controlled by PortL DIENL not ATDDIENx
• Removed SC part information
1.1 Introduction
The S12VRP-Series is an optimized automotive 16-bit microcontroller product line focused on low-cost,
high-performance, and low pin-count. Like other MagniV devices, the S12VRP-Series integrates key
components such as a LIN physical interface and a voltage regulator system to supply the microcontroller
directly from the vehicle battery. Being part of the existing MC9S12VR-Family, the S12VRP-Series
integrates key analog blocks to control other elements of the system which operate at vehicle battery level
(e.g. relay drivers, high-side driver outputs, wake up inputs). The S12VRP-Series extends the existing
MC9S12VR-Family with more RAM, more high-voltage inputs, current sensing capabilities and some
other enhancements.
The S12VRP-Series uses many features already found in the MagniV family, including error correction
code (ECC) on flash memory, a separate data-flash module for diagnostic or data storage, a fast
analog-to-digital converter (ADC) and a frequency modulated phase locked loop (IPLL) that improves the
EMC performance.
The S12VRP-Series delivers an optimized solution with the integration of several key system components
into a single device, optimizing system architecture and achieving significant space savings. The
S12VRP-Series delivers all the advantages and efficiencies of a 16-bit MCU while retaining the low cost,
power consumption, EMC, and code-size efficiency advantages currently enjoyed by users of NXP’s
existing 8-bit and 16-bit MCU families. The S12VRP-Series is offered in a 48-pin LQFP package. In
addition to the I/O ports available in each module, further I/O ports are available with interrupt capability
allowing wake-up from stop or wait modes.
The S12VRP-Series is targeted at relay based motor control automotive applications requiring single node
LIN communications. Typical examples of these applications include:
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 17
Page 18
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Window lift modules
• Door modules
• Seat controllers
• Smart actuators
• Sun roof modules
1.2 Features
This section describes the key features of the S12VRP-Series.
1.3 S12VRP-Series Comparison
Table 1-2 provides a summary of different members of the S12VRP-Series and their features.
S12VRP is part of NXP S12VR-family, commonalities & differences are outlined in AN5328, also
including a comparison to MM912_634.
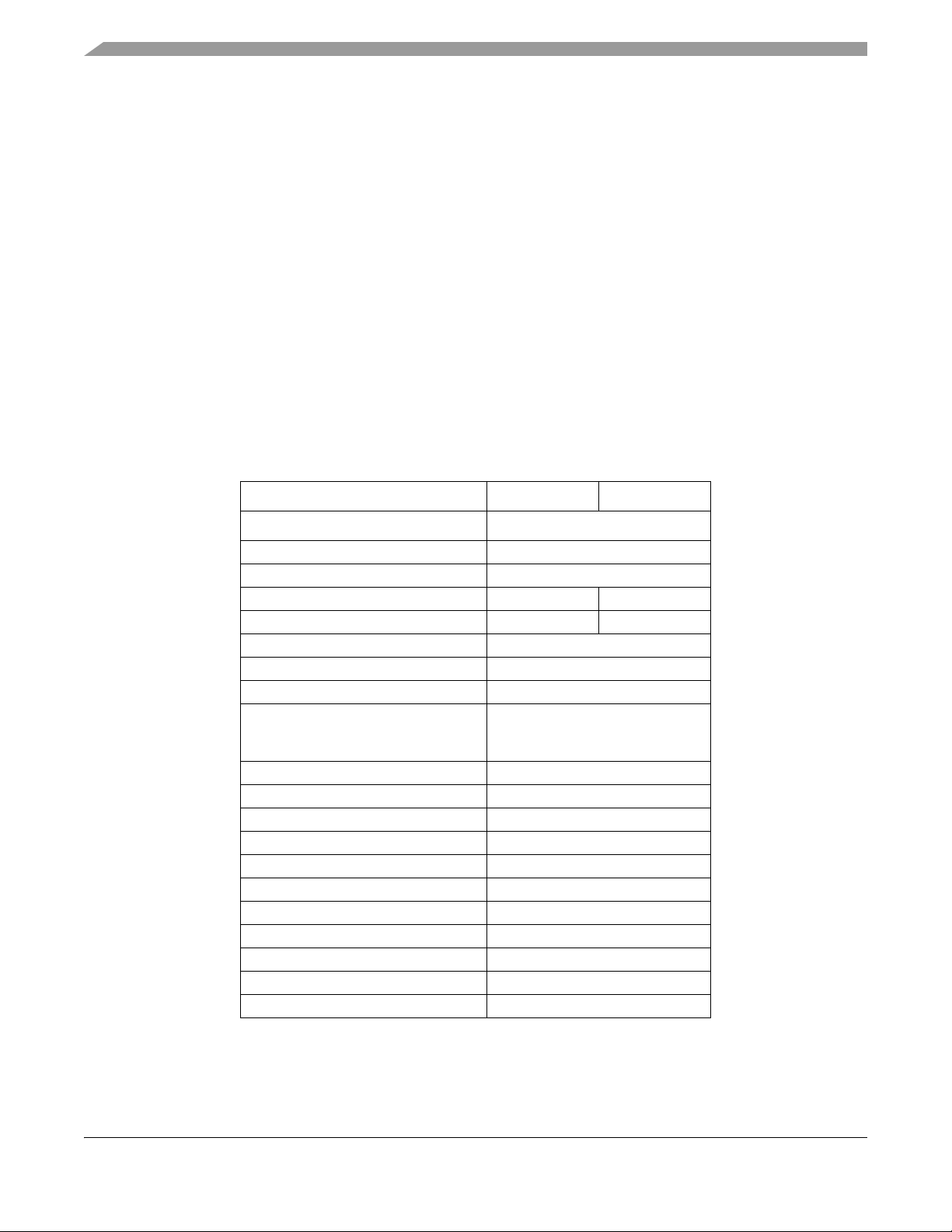
Table 1-2. S1 2 V R P-Serie s
Feature S12VRP48 S12VRP64
Package option 48LQFP
Core HCS12
Bus frequency 25 MHz
Flash memory (ECC) 48 KB 64 KB
Data-Flash 2 KB 4 KB
RAM 6 KB
LIN Physical layer 1
1
SCI
Timer
- TIM0
- TIM1
PWM 8ch x 8-bit or 4ch x 16-bit
10-bit ADC channels 12
Frequency modulated PLL Yes
Internal 1 MHz RC oscillator Yes
Autonomous window watchdog 1
Low side driver (relay driver) 2
Low side driver (general) 1
High side driver 2
Current sense amplifier 1
High voltage Inputs 6
Direct Battery sense pin, Vsense Yes
2
2ch x16-bit
2ch x16-bit
2
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
18 NXP Semiconductors
Page 19
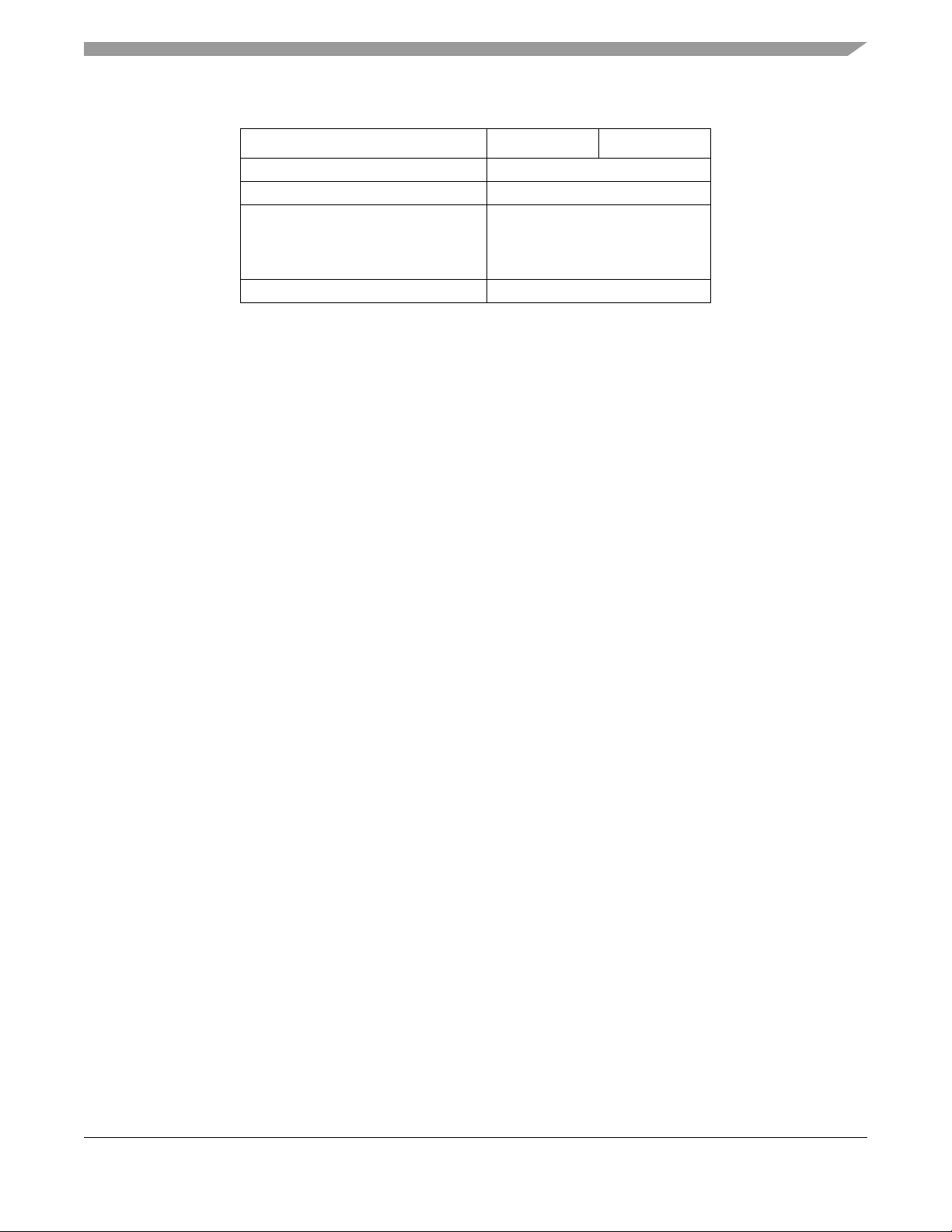
Table 1-2. S1 2 V R P-Serie s
Feature S12VRP48 S12VRP64
Supply voltage sense, Vsup Yes
Chip temperature sensor 1
3
General purpose I/O
- 10mA Driver pin
- 20mA EVDD (e.g. Hall Sensor supply)
- 20mA @5V LL-FET Driver
Interrupt capable pins (5V/12V) 12/6
1
SCI0 is routed to LIN PHY by default
2
6 mapped to PAD pins, 6 mapped to HVI pins
3
All port pins (including PADx and PLx)
including:-
28
1
1
1
1.4 Chip-Level Features
On-chip modules available within the family include the following features:
• HCS12 CPU core
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• 64 KB or 48 KB on-chip Program-FLASH with ECC
• 4 KB or 2KB Data-FLASH with ECC
• 6 KB on-chip SRAM
• Phase locked loop (IPLL) frequency multiplier with internal filter
• 1 MHz internal RC oscillator with +/-1.3% accuracy over rated temperature range
• 4-20 MHz amplitude controlled pierce oscillator
• Internal COP (watchdog) module (with separate clock source)
• Two timer modules (TIM) supporting input/output channels that provide a range of 16-bit input
capture & output compare (up to 4 channels)
• Pulse width modulation (PWM) module (up to 8x 8-bit channels or 4x 16-bit channels)
• 10-bit resolution successive approximation analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with up to 6
channels mapped to external PAD pins and 6 channels mapped to HVI pins
• One serial communication interface (SCI) module supporting LIN communications (with RX
connected to a timer channel for internal oscillator calibration purposes, if desired)
• One on-chip LIN physical layer transceiver fully compliant with the LIN 2.2A & SAE J2602-2
standards routed to the SCI module supporting LIN communications
• One additional SCI (not connected to LIN physical layer)
• On-chip voltage regulator (VREG) for regulation of input supply and all internal voltages
• Autonomous periodic interrupt (API) (combined with watchdog)
• Two protected low-side driver outputs to drive inductive loads (VSUP domain)
• One further 20mA low-side driver output (VSUP domain)
• Two protected high-side driver outputs (VSUP domain)
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 19
Page 20

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Six high-voltage inputs (HVI) with wake-up capability and interface to internal ADC
• 20mA high-current 5V output for use as Hall sensor supply (PP2, EVDD)
• 20mA high-current 5V output to drive external logic level FET (PP0, Power GPIO)
• 10mA high current 5V output (PP1)
• Current sense circuits for over-current detection
• Battery voltage sense with low battery warning, internally reverse battery protected
• Chip temperature sensor
1.5 Module Features
The following sections provide more details of the modules implemented on the S12VRP-Series.
1.5.1 HCS12 16-Bit Central Processor Unit (CPU)
The HCS12 CPU is a high-speed, 16-bit processing unit that has a programming model identical to that of
the industry standard M68HC11 central processor unit (CPU).
• Full 16-bit data paths supports efficient arithmetic operation and high-speed math execution
• Supports instructions with odd byte counts, including many single-byte instructions. This allows
much more efficient use of ROM space.
• Extensive set of indexed addressing capabilities, including:
— Using the stack pointer as an indexing register in all indexed operations
— Using the program counter as an indexing register in all but auto increment/decrement mode
— Accumulator offsets using A, B, or D accumulators
— Automatic index predecrement, preincrement, postdecrement, and postincrement (by –8 to +8)
1.5.2 On-Chip Flash with ECC
On-chip flash memory on the S12VRP-Series features the following:
• 64 or 48 KB of program flash memory
— 32 data bits plus 7 syndrome ECC (error correction code) bits allowing single bit fault
correction and double fault detection
— Erase sector size 512 bytes
— Automated program and erase algorithm
— User margin level setting for reads
— Protection scheme to prevent accidental program or erase
• 4 KB of data flash memory
— Single bit error correction and double fault detection within a word during read operations
— Erase sector size 256 bytes
— Automated program and erase algorithm with verify and generation of ECC parity bits
— Protection scheme to prevent accidental program or erase
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
20 NXP Semiconductors
Page 21

— User margin level setting for reads
1.5.3 On-Chip SRAM
• 6 KB of general-purpose RAM
1.5.4 Main External Oscillator (XOSCLCP)
• Loop control Pierce oscillator using 4 MHz to 20 MHz crystal
— Current gain control on amplitude output
— Signal with low harmonic distortion
— Low power
— Good noise immunity
— Eliminates need for external current limiting resistor
— Transconductance sized for optimum start-up margin for typical crystals
— Oscillator pins shared with GPIO functionality
1.5.5 Internal RC Oscillator (IRC)
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Factory trimmed internal reference clock
— 1 MHz internal RC oscillator with 1.3% accuracy over rated temperature range
1.5.6 Internal Phase-Locked Loop (IPLL)
• Phase-locked-loop clock frequency multiplier
— No external components required
— Reference divider and multiplier allow large variety of clock rates
— Automatic bandwidth control mode for low-jitter operation
— Automatic frequency lock detector
— Configurable option to spread spectrum for reduced EMC radiation (frequency modulation)
— Reference clock sources:
– Internal 1 MHz RC oscillator (IRC)
– External crystal oscillator
1.5.7 Clock and Power Management Unit (CPMU)
• Real time interrupt (RTI)
• Clock monitor (CM)
• System reset generation
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 21
Page 22

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.5.8 System Integrity Support
• Power-on reset (POR)
• Illegal address detection with reset
• Low-voltage detection with interrupt or reset
• Computer operating properly (COP) watchdog with option to run on internal RC oscillator
— Configurable as window COP for enhanced failure detection
— Can be initialized out of reset using option bits located in flash memory
• Clock monitor supervising the correct function of the oscillator
1.5.9 Timer (TIM)
• Two modules with 2x 16-bit channels each, for input capture or output compare
• 16-bit free-running counter with 8-bit precision prescaler
1.5.10 Pulse Width Modulation Module (PWM)
• Up to eight 8-bit channels or reconfigurable four 16-bit channel PWM resolution
• Programmable period and duty cycle per channel
• Center-aligned or left-aligned outputs
• Programmable clock select logic with a wide range of frequencies
1.5.11 LIN physical layer transceiver (LINPHY)
• Compliant with LIN Physical Layer 2.2A specification
• Compliant with the SAE J2602-2 LIN standard
• Standby mode with glitch-filtered wake-up
• Slew rate selection optimized for the baud rates: 10.4kBit/s, 20kBit/s and Fast Mode (up to
250kBit/s)
• Switchable 34k/330k pull-ups (in shutdown mode, 330konly
• Current limitation for LIN Bus pin falling edge
• Over-current protection
• LIN TxD-dominant timeout feature monitoring the LPTxD signal
• Automatic transmitter shutdown in case of an over-current or TxD-dominant timeout
• Fulfills the OEM “Hardware Requirements for LIN, CAN and FlexRay Interfaces in Automotive
Applications” v1.3
• Internal connection to one SCI
1.5.12 Serial Communication Interface Module (SCI)
• Full-duplex or single-wire operation
• Standard mark/space non-return-to-zero (NRZ) format
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
22 NXP Semiconductors
Page 23

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Selectable IrDA 1.4 return-to-zero-inverted (RZI) format with programmable pulse widths
• 16-bit baud rate selection
• Programmable character length
• Programmable polarity for transmitter and receiver
• Active edge receive wake-up
• Break detect and transmit collision detect supporting LIN
1.5.13 Analog-to-Digital Converter Module (ADC)
• 12-channel, 10-bit analog-to-digital converter
— 6 channels mapped to 5V GPIO pins
— 6 channels mapped to high voltage input (HVI) pins
— 8-/10-bit resolution
— 3 us, 10-bit single conversion time
— Left or right justified result data
— Internal oscillator for conversion in stop modes
— Continuous conversion mode
— Multiple channel scans
• GPIO pins can also be used as digital I/O; HVI pins can also be used as high voltage inputs
• Pins can be used as keyboard wake-up interrupt (KWI)
• Internal voltages monitored with the ADC module:
—V
SUP
or V
SENSE
— Chip temperature sensor (VHT) or band gap voltage (VBG)
—VRH, VRL
—(V
—V
DDF
RH +VRL
/2)
1.5.14 Supply Voltage Sense (BATS)
• VSENSE & VSUP pin low or high voltage interrupt
• VSENSE & VSUP pin can be routed via an internal divider to the internal ADC
1.5.15 On-Chip Voltage Regulator system (VREG)
• Voltage regulator
— Linear voltage regulator directly supplied by VSUP (protected VBAT)
— Low-voltage detect with low-voltage interrupt on VSUP
— Capable of supplying both the MCU internally and providing additional external current
(approximately 20mA) to supply other components within the electronic control unit.
— Over-temperature interrupt
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 23
Page 24

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Internal Voltage regulator
— Linear voltage regulator with bandgap reference
— Low-voltage detect with low-voltage interrupt on VDDA
— Power-on reset (POR) circuit
— Low-voltage reset (LVR)
1.5.16 Low-side driver (LSDRV)
• Two low-side drivers targeted for up to 180mA current capability
• Internal Timer or PWM channels can be routed to control the low-side drivers
• Open-load detection
• Over-current protection with shutdown and interrupt
• Active clamp (for driving relays)
• Recirculation detection
1.5.17 Low-side driver (LS2DRV)
• Additional low-side driver targeted for up to 20mA current capability
• Internal Timer or PWM channels can be routed to control the low-side driver
• Over-current protection with shutdown and interrupt
1.5.18 Current Sense Amplifier
• One channel, integrated op-amp functionality
1.5.19 High-side drivers (HSDRV)
• Two high-side drivers targeted for up to 50mA current capability
• Internal Timer or PWM channels can be routed to control the high-side drivers
• Up to 20KHz operating frequency
• Over-current protection with shutdown and interrupt
• Open load detection
• Programmable slew rate control
1.5.20 Background Debug (BDM)
• Background debug module (BDM) with single-wire interface
— Non-intrusive memory access commands
— Supports in-circuit programming of on-chip nonvolatile memory
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
24 NXP Semiconductors
Page 25
1.5.21 Debugger (DBG)
4 or 2 KB Data-Flash with ECC
RESET
EXTAL
XTAL
6 KB RAM
BKGD
VSUP
Real Time Interrupt
Clock Monitor
Single-wire Background
TEST
Debug Module
Interrupt Module
SCI1
PS0
PS1
PTS
16-bit 2-channel Timer
TIM0
Asynchronous Serial IF
8-bit 8 channel
Pulse Width Modulator
PWM
64 or 48 KB Program-Flash with ECC
CPU12-V1
COP Watchdog
PLL with Frequency
Modulation option
Debug Module
3 comparators
64 Byte Trace Buffer
Reset Generation
and Test Entry
RXD
TXD
Auton. Periodic Int.
PT3
PT0
PT1
PT2
PTT
PP0 / PGPIO
PP1
PP2 / EVDD
PTP
IOC1_1
IOC0_0
IOC0_1
IOC1_0
VDDX1/VSSX1
VDDX2/VSSX2
HS0
HS1
5V IO Supply Output
VSS
Low Power Pierce
Oscillator
SCI0
Asynchronous Serial IF
RXD
TXD
PS2
PS3
Voltage Regulator
Input: 6V – 18V
Block Diagram shows the maximum configuration!
HS1
HS0
HSDRV
High Side Driver
LS0
LSDRV
Low Side (Relay) Driver
Not all pins or all peripherals are available on all devices and packages.
Rerouting options are not shown.
PE0
PTE
PE1
Internal RC Oscillator
PWM0
PWM1
PP3
PP4
PP5
PL0
PL1
PL2
PL3
LIN
LINPHY
LIN Physical Layer
PTL
LIN
LGND
VSUPHS
VSUP
LSGND
LSGND
LS1
LS0
LS1
VSENSE
BATS
VSENSE
Battery Sensor
LGND
PWM2
PWM3
PWM4
PWM5PWM[7:6]
see Pinout
PL4
PL5
LS2DRV
Low Side Driver
LS2
LS2
Isense-AMP
Current Sense Circuit
AMPP0
AMPM0
AMP0
ADC
AN[11:0]
PAD0
10-bit / 8-bit
VDDA
VSSA
PTAD
Analog-Digital
Converter
PAD 4
PAD 1
PAD 2
PAD 3
16-bit 2-channel Timer
TIM1
PAD 5
• Trace buffer with depth of 64 entries
• Three comparators (A, B and C)
— Access address comparisons with optional data comparisons
— Program counter comparisons
— Exact address or address range comparisons
• Two types of comparator matches
— Tagged This matches just before a specific instruction begins execution
— Force This is valid on the first instruction boundary after a match occurs
• Four trace modes
• Four stage state sequencer
1.6 Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows a high-level block diagram of the S12VRP-Series.
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Figure 1-1. S12VRP-Series Block Diagram
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 25
Page 26
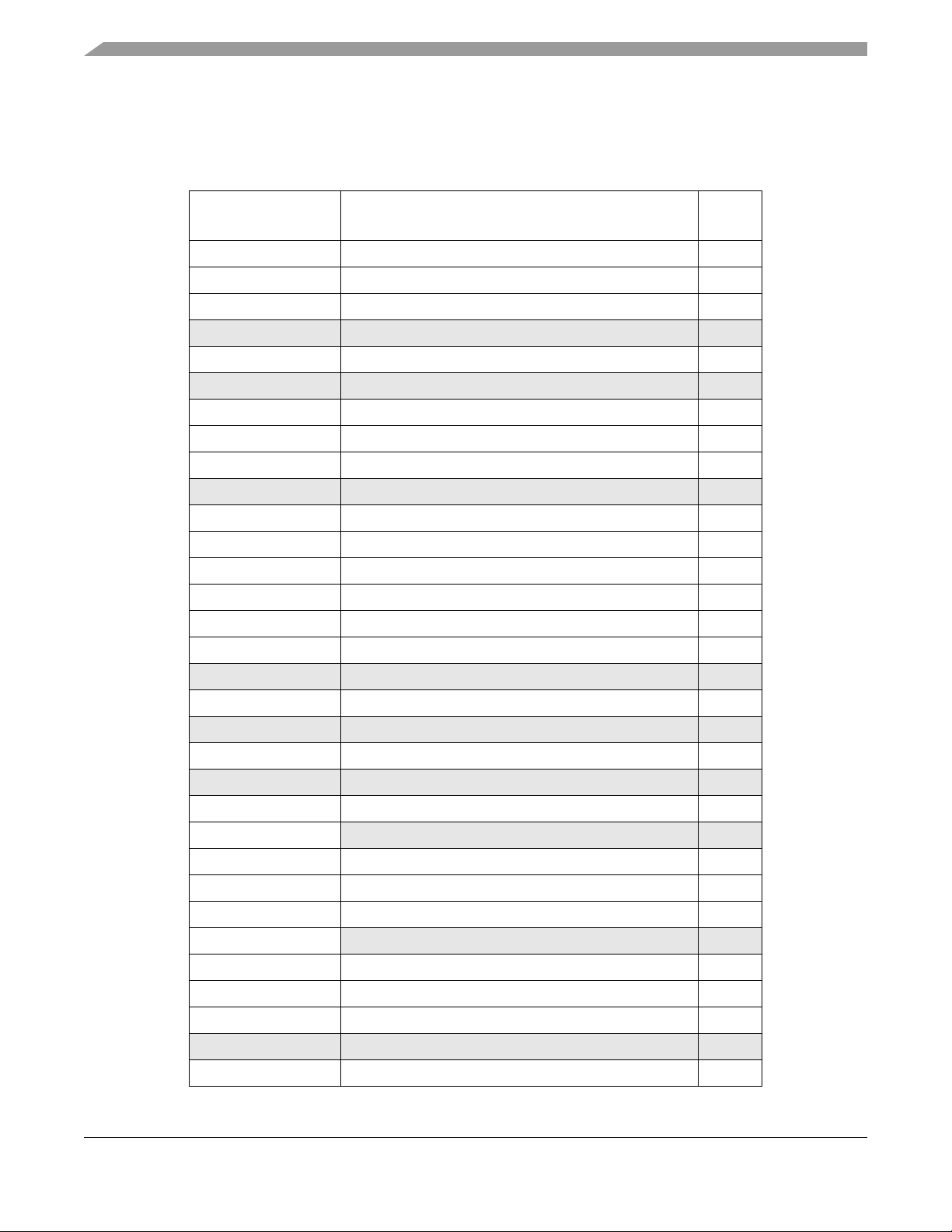
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.7 Family Memory Map
Table 1-3 shows the S12VRP-Series register memory map.
Table 1-3. Device Register Memory Map
Address Module
0x0000–0x0009 PIM (port integration module
0x000A–0x000B MMC (memory map control) 2
0x000C–0x000D PIM (port integration module) 2
0x000E–0x000F Reserved 2
0x0010–0x0017 MMC (memory map control) 8
0x0018–0x0019 Reserved 2
0x001A–0x001B Device ID register 2
0x001C–0x001F PIM (port integration module) 4
0x0020–0x002F DBG (debug module) 16
0x0030–0x0033 Reserved 4
0x0034–0x003F CPMU (clock and power management) 12
0x0040–0x006F TIM0 (timer module <= 8 channels) 48
0x0070–0x009F ADC (analog to digital converter <= 16 channels) 48
0x00A0–0x00C7 PWM (pulse-width modulator <= 8 channels) 40
0x00C8–0x00CF SCI0 (serial communication interface) 8
0x00D0–0x00D7 SCI1 (serial communication interface) 8
0x00D8–0x00FF Reserved 40
) 10
Size
(Bytes)
0x0100–0x0113 FTMRG control registers 20
0x0114–0x011F Reserved 12
0x0120 INT (interrupt module) 1
0x0121–0x013F Reserved 31
0x0140–0x0147 HSDRV (high-side driver) 8
0x0148–0x014F
0x0150–0x0157 LSDRV (low-side driver) 8
0x0158–0x015F LS2DRV 8
0x0160–0x0167 LINPHY (LIN physical layer) 8
0x0168–0x016F Reserved 8
0x0170–0x0177 BATS (supply voltage sense) 8
0x0178–0x017F ISENSE (current sense amplifier) 8
0x0180–0x01AF TIM1 (timer module) 48
0x01B0–0x023F Reserved 144
0x0240–0x027F PIM (port integration module) 64
26 NXP Semiconductors
Reserved 8
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 27
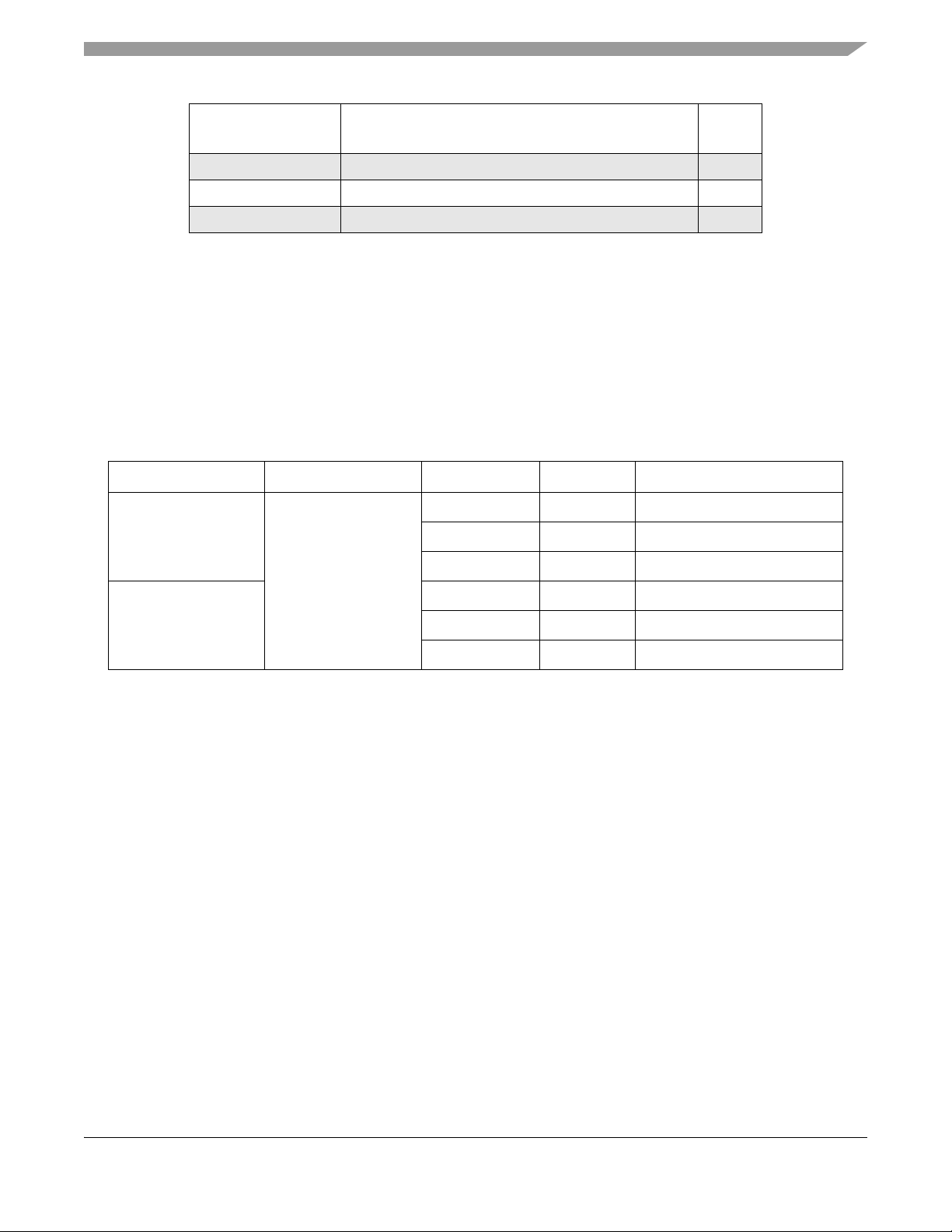
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Address Module
0x0280–0x02EF Reserved 112
0x02F0–0x02FF CPMU (clock and power management) 16
0x0300–0x03FF Reserved 256
Size
(Bytes)
Reserved register space shown in Tab le 1-3 is not allocated to any module.
This register space is reserved for future use. Writing to these locations has
no effect. Read access to these locations returns zero.
Figure 1-2 shows S12VRP-Series CPU and BDM local address translation to the global memory map as
a graphical representation. The whole 256K global memory space is visible through the P-Flash window
located in the 64k local memory map located at 0x8000 - 0xBFFF using the PPAGE register.
Table 1-4. S12VRP-Series Memory Address Ranges
Device Memory Size Address
SRAM 6 KB 0x2800-0x3FFF
S12VRP48
4 KB Data-Flash
Data Flash 2 KB 0x0400-0x0BFF
Program Flash 48 KB Page D, E and F
SRAM 6 KB 0x2800-0x3FFF
S12VRP64
Data Flash 4 KB 0x0400-0x13FF
Program Flash 64KB Page C, D, E and F
NOTE
Flash space on page 0xC in Figure 1-2 is not available on S12VRP48.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 27
Page 28
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Paging Window
0x3_FFFF
Local CPU and BDM
Memory Map Global Memory Map
0xFFFF
0xC000
0x0_0400
0x0_0000
0x3_C000
0x0000
0x8000
0x0400
0x4000
0x0_4000
Paging Window
RAM
RAM
Unimplemented
Unimplemented
Register Space
Register Space
Internal
NVM
Resources
Internal
NVM
Resources
P-Flash Space
P-Flash Space
P-Flash Space
P-Flash Space
EEPROM
Data-Flash
EEPROM
Data-Flash
Register Space
Register Space
Page 0xE
Page 0xE
Page 0xF
Page 0xF
Page 0xD
Page 0xD
Page 0xC
Page 0xC
NVMRES=1
0x3_0000
0x3_4000
0x3_8000
RAM
RAM
Unimplemented
Unimplemented
0x1400
0x2800
P-Flash Space
P-Flash Space
P-Flash Space
Page 0xF
Page 0xF
Page 0xC
Page 0xC
Page 0xD
Page 0xD
Figure 1-2. S12VRP-Series Global Memory Map.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
28 NXP Semiconductors
Page 29
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.7.1 Part ID Assignments
The part ID is located in two 8-bit registers PARTIDH and PARTIDL (addresses 0x001A and 0x001B).
The read-only value is a unique part ID for each revision of the chip. Tab le 1-5 shows the assigned part ID
number and mask set number.
Table 1-5. Assigned Part ID Numbers
Device Mask Set Number Part ID
S12VRP48 0N80T $3A80
S12VRP64 0N80T $3A80
1.8 Signal Description and Device Pinouts
This section describes signals that connect off-chip. It includes a pinout diagram, a table of signal
properties, and detailed discussion of signals. It is built from the signal description sections of the
individual IP blocks on the device.
1.8.1 Pin Assignment Overview
Table 1-6 provides a summary of which ports are available for the 48-pin package option.
Table 1-6. Port Availability by Package Option
Port 48 LQFP
Port AD PAD[5:0]
Port E PE[1:0]
Port P PP[5:0]
Port S PS[3:0]
Port T PT[3:0]
Port L PL[5:0]
Sum of ports 28
I/O power pairs VDDX/VSSX 2/2
NOTE
To avoid current drawn from floating inputs, all non-bonded pins should be
configured as output or configured as input with a pull up or pull down
device enabled
1.8.2 Detailed Signal Descriptions
This section describes the signal properties.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 29
Page 30

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.8.2.1 RESET — External Reset Signal
The RESET signal is an active low, bidirectional control signal. It acts as an input to initialize the MCU to
a known start-up state, and an output when an internal MCU function causes a reset. The RESET pin has
an internal pull-up device.
1.8.2.2 TEST — Test Pin
This input only pin is reserved for factory test. This pin has an internal pull-down device.
NOTE
The TEST pin must be tied to ground in all applications.
1.8.2.3 BKGD / MODC — Background Debug Signal
The BKGD/MODC pin is used as a pseudo-open-drain pin for the background debug communication. It
is used as an MCU operating mode select pin during reset. The state of this pin is latched to the MODC bit
at the rising edge of RESET. The BKGD pin has an internal pull-up device.
1.8.2.4 PAD[5:0] / KWAD[5:0] — Port AD Input Signals of ADC
PAD[5:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals can be configured on a per signal basis
as interrupt inputs with wake-up capability (KWAD[5:0]).These signals can have a pull-up or pull-down
device selected and enabled on a per signal basis. Out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
1.8.2.5 PE[1:0] — Port E I/O Signals
PE[1:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals each have pull-down device, enabled by
a single control bit for this signal group. Out of reset the pull-down devices are enabled.
1.8.2.6 PP[5:0] / KWP[5:0] — Port P I/O Signals
PP[5:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. The signals can be configured on a per signal basis as
interrupt inputs with wake-up capability (KWP[5:0]). PP[2:0] have high current drive strength. PP[2] and
PP[0] have an over-current interrupt feature. They can have a pull-up or pull-down device selected and
enabled on per signal basis. Out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
1.8.2.7 PS[3:0] — Port S I/O Signals
PS[3:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. They can have a pull-up or pull-down device selected
and enabled on per signal basis. Out of reset the pull-up devices are enabled.
1.8.2.8 PT[3:0] — Port T I/O Signals
PT[3:0] are general-purpose input or output signals. They can have a pull-up or pull-down device selected
and enabled on per signal basis. Out of reset the pull devices are disabled.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
30 NXP Semiconductors
Page 31

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.8.2.9 PL[5:0] / KWL[5:0] — Port L Input Signals
PL[5:0] are high voltage input ports. The signals can be configured on per signal basis as interrupt inputs
with wake-up capability (KWL[5:0]).
1.8.2.10 LIN — LIN Physical Layer Signal
This pad is connected to the single-wire LIN data bus.
1.8.2.11 HS[1:0] — High-Side Drivers Output Signals
Outputs of the two high-side drivers intended to drive incandescent bulbs or LEDs.
1.8.2.12 LS[1:0] — Low-Side Drivers Output Signals
Outputs of the two low-side drivers intended to drive inductive loads (relays).
1.8.2.13 LS2 — Low-Side Driver Output Signal
Output of the general purpose (20mA) low-side driver.
1.8.2.14 VSENSE — Voltage Sensor Input
This pin can be connected to the supply (Battery) line for voltage measurements. The voltage present at
this input is scaled down by an internal voltage divider, and can be routed to the internal ADC via an analog
multiplexer. The pin itself is protected against reverse battery connections. To protect the pin from external
fast transients an external resistor is needed.
1.8.2.15 AN[11:0] — ADC Input Signals
AN[11:0] are the analog inputs of the Analog-to-Digital Converter. The channels AN[5:0] are connected
to PAD[5:0] port pins. The channels AN[11:6] are connected to HVI[5:0] respectively.
1.8.2.16 VRH, VRL — ADC Reference Signals
VRH and VRL are the reference voltage inputs for the analog-to-digital converter. VRH is internally
connected to VDDA. VRL is internally connected to VSSA.
1.8.2.17 LINPHY Signals
1.8.2.17.1 VLINSUP — Positive Power Supply
This is the power supply to the LINPHY. VLINSUP is connected internally to VSUP.
1.8.2.17.2 LPTXD Signal
This signal is the LINPHY transmit input.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 31
Page 32

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.8.2.17.3 LPRXD Signal
This signal is the LINPHY receive output.
1.8.2.18 SCI Signals
1.8.2.18.1 RXD[1:0] Signals
These signals are associated with the receive functionality of the serial communication interfaces SCI1-0.
1.8.2.18.2 TXD[1:0] Signals
These signals are associated with the transmit functionality of the serial communication interfaces SCI1-0.
1.8.2.19 PWM[7:0] Signals
The signals PWM[7:0] are associated with the PWM module outputs.
1.8.2.20 Internal Clock outputs
1.8.2.20.1 ECLK
This signal is associated with the output of the divided bus clock (ECLK).
NOTE
This feature is only intended for debug purposes at room temperature.
It must not be used for clocking external devices in an application.
1.8.2.21 ETRIG[1:0]
These signals are inputs to the Analog-to-Digital Converter. Their purpose is to trigger ADC conversions.
1.8.2.22 IOC0_[1:0] Signals
The signals IOC0_[1:0] are associated with the input capture or output compare functionality of the timer
(TIM0) module.
1.8.2.23 IOC1_[1:0] Signals
The signals IOC1_[1:0] are associated with the input capture or output compare functionality of the timer
(TIM1) module.
1.8.3 Power Supply Pins
S12VRP-Series power and ground pins are described below. Because fast signal transitions place high,
short-duration current demands on the power supply, use bypass capacitors with high-frequency
characteristics and place them as close to the MCU as possible.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
32 NXP Semiconductors
Page 33

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
NOTE
All ground pins must be connected together in the application.
1.8.3.1 VDDX1, VDDX2, VSSX1, VSSX2 — Power Pins and Ground Pins
VDDX1 and VDDX2 are the 5V power supply output for the I/O drivers. This voltage is generated by the
on chip voltage regulator. Bypass requirements on VDDX1 and VDDX2 pins depend on how heavily the
MCU pins are loaded. All VDDX pins are connected together internally. All VSSX pins are connected
together internally.
1.8.3.2 VDDA, VSSA — Power Supply Pins for ADC
These are the power supply and ground input pins for the analog-to-digital converter and the voltage
regulator.
NOTE
The reference voltages VRH and VRL are internally connected to VDDA
and VSSA.
1.8.3.3 VSS — Core Ground Pin
The voltage supply of nominally 1.8V is generated by the internal voltage regulator. The return current
path is through the VSS pin.
1.8.3.4 LGND — LINPHY Ground Pin
LGND is the ground pin for the LIN physical layer LINPHY.
1.8.3.5 LSGND — Ground Pin for Low-Side Drivers
LSGND is the shared ground pin for the low-side drivers.
1.8.3.6 VSUP — Voltage Supply Pin for Voltage Regulator
VSUP is the 12V/18V shared supply voltage pin for the on chip voltage regulator. This pin is also used as
the high-side driver supply.
1.8.3.7 Power and Ground Connection Summary
Table 1-7. Power and Ground Connection Summary
Mnemonic Nominal Voltage Description
VSS 0V Ground pin for 1.8V core supply voltage generated by on chip voltage regulator
VDDX1 5.0 V 5V power supply output for I/O drivers generated by on chip voltage regulator
VSSX1 0V Ground pin for I/O drivers
VDDX2 5.0 V 5V power supply output for I/O drivers generated by on chip voltage regulator
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 33
Page 34

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Mnemonic Nominal Voltage Description
VSSX2 0V Ground pin for I/O drivers
VDDA 5.0 V External power supply for the analog-to-digital converter and for the reference circuit of the
internal voltage regulator
VSSA 0V Ground pin for VDDA analog supply
LGND 0V Ground pin for LIN physical
LSGND 0V Ground pin for low-side driver
VSUP 12V/18V External power supply for voltage regulator and high-side driver supply
1.8.4 Device Pinouts
S12VRP-Series is available in a 48-pin package. Signals in parentheses in denote alternative module
routing options.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
34 NXP Semiconductors
Page 35

1.8.5 MC9S12VRP Pinout 48-pin LQFP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
1314151617181920212223
24
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
4847464544434241403938
37
S12VRP-Series
48-pin LQFP
PAD5 / KWAD5 / AN5
PL5 / HVI5 / KWL5 / AN11
PL4 / HVI4 / KWL4 / AN10
PL3 / HVI3 / KWL3 / AN9
PL2 / HVI2 / KWL2 / AN8
PL1 / HVI1 / KWL1 / AN7
PL0 / HVI0 / KWL0 / AN6
VSENSE
HS1
VSSX2
HS0
VSUP
TEST
RESET
PWM3 / KWP3 / PP3
PWM4 / ETRIG0 / KWP4 / PP4
PWM5 / ETRIG1 / IRQ
/ KWP5 / PP5
VSS
EXTAL / PE0
XTAL / PE1
VDDX2
PGPIO / PWM0 / KWP0 / PP0
XIRQ
/ PWM1 / KWP1 / PP1
EVDD / PWM2 / KWP2 / PP2
LGND
LIN
LS0
LSGND
LS1
LS2
VSSX1
VDDX1
RXD1 / (RXD0) / PS0
TXD1 / (LPDR1) / (TXD0) / PS1
(RXD1) / (PWM4) / (ETRIG0) / PS2
MODC / BKGD
PS3 / ECLK / (TXD1) / (PWM5) / (ETRIG1)
PT3 / IOC1_1 / (LPTXD)
PT2 / API_EXTCLK / IOC1_0 / (LPRXD)
PT1 / IOC0_1 / PWM7 / (TXD0) / (LPDR)
PT0 / IOC0_0 / PWM6 / (RXD0)
PAD0 / KWAD0 / AN0 / AMP0
PAD1 / KWAD1 / AN1 / AMPM0
PAD2 / KWAD2 / AN2 / AMPP0
PAD3 / KWAD3 / AN3
PAD4 / KWAD4 / AN4
VDDA
VSSA
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Figure 1-3. MC9S12VRP 48-pin LQFP pinout
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 35
Page 36

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Table 1-8. Pin Summary
Package Function
48 LQFP Pin
st
1
Func.
nd
2
Func.
rd
3
Func.
th
4
Func.
Power
Supply
Internal Pull
Resistor
CTRL
Reset
State
1 LGND————— — —
2 LIN————— — —
3 LS0 OC0_0 PWM5 PWM6 — — — —
4LSGND————— — —
5LS1OC0_1PWM7———— —
6LS2OC1_1PWM2———— —
7 VSSX1 — — — — — — —
8VDDX1————V
9 PS0 RXD0 RXD1 — — V
DDX
DDX
——
PERS/
Up
PPSS
10 PS1 TXD0 LPDR1 TXD1 — V
DDX
PERS/
Up
PPSS
11 PS2 ETRIG0 PWM4 RXD1 — V
DDX
PERS/
Up
PPSS
12 BKGD MODC — — — V
DDX
PUCR/
Up
BKPUE
13 TEST — — — — N.A TEST pin Down
14 RESET
15 PP3 KWP3 PWM3 — — V
————V
DDX
DDX
RESET pin Up
PERP/
Off
PPSP
16 PP4 KWP4 ETRIG0 PWM4 — V
DDX
PERP/
Off
PPSP
17 PP5 KWP5 ETRIG1 PWM5 IRQ
V
DDX
PERP/
Off
PPSP
18 VSS — — — — — — —
19 PE0 EXTAL — — — V
DDX
PUCR/
Down
PUPEE
20 PE1 XTAL — — — V
DDX
PUCR/
Down
PUPEE
21VDDX2————— — —
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
36 NXP Semiconductors
Page 37

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Package Function
48 LQFP Pin
st
1
Func.
nd
2
Func.
22 PP0 KWP0 PWM0 PGPIO
rd
3
Func.
th
4
Func.
1
—V
Power
Supply
DDX
Internal Pull
Resistor
CTRL
PERP/
PPSP
23 PP1 KWP1 PWM1 XIRQ
—V
DDX
PERP/
PPSP
24 PP2 KWP2 PWM2 EVDD — V
DDX
PERP/
PPSP
25 VSUP — — — — — — —
26 HS0 OC1_0 PWM3 — — V
SUP
——
27 VSSX2 — — — — — — —
28 HS1 OC1_1 PWM1 PWM4 — V
SUP
——
29 VSENSE — — — — — — —
30 PL0 HVI0 KWL0 AN6 — V
31 PL1 HVI1 KWL1 AN7 — V
32 PL2 HVI2 KWL2 AN8 — V
33 PL3 HVI3 KWL3 AN9 — V
34 PL4 HVI4 KWL4 AN10 — V
35 PL5 HVI5 KWL5 AN11 — V
36 PAD5 KWAD5 AN5 — — V
DDX
DDX
DDX
DDX
DDX
DDX
DDA
——
——
——
——
——
——
PER1AD/
PPS1AD
Reset
State
Off
Off
Off
Off
37 VSSA — — — — — — —
38 VDDA — — — — — — —
39 PAD4 KWAD4 AN4 — — V
DDA
PER1AD/
Off
PPS1AD
40 PAD3 KWAD3 AN3 — — V
DDA
PER1AD/
Off
PPS1AD
41 PAD2 KWAD2 AN2 AMPP0 — V
DDA
PER1AD/
Off
PPS1AD
42 PAD1 KWAD1 AN1 AMPM0 — V
DDA
PER1AD/
Off
PPS1AD
43 PAD0 KWAD0 AN0 AMP0 — V
DDA
PER1AD/
Off
PPS1AD
44 PT0 IOC0_0 PWM6 RXD0 — V
DDX
PERT/
Off
PPST
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 37
Page 38

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Package Function
48 LQFP Pin
st
1
Func.
nd
2
Func.
rd
3
Func.
th
4
Func.
45 PT1 IOC0_1 PWM7 TXD0 LPDR1 V
46 PT2 IOC1_0 LPRXD API_EX
—V
TCLK
47 PT3 IOC1_1 LPTXD — — V
48 PS3 ETRIG1 PWM5 TXD1 ECLK V
1
PGPIO is EVDD type, capable of driving up to 20KHz into logic level FET.
Power
Supply
DDX
DDX
DDX
DDX
Internal Pull
Resistor
CTRL
PERT/
PPST
PERT/
PPST
PERT/
PPST
PERS/
PPSS
Reset
State
Off
Off
Off
Up
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
38 NXP Semiconductors
Page 39

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.9 Modes of Operation
The MCU can operate in different modes. These are described in 1.9.1 Chip Configuration Summary.
The MCU can operate in different power modes to facilitate power saving when full system performance is not required. These are described in 1.9.2 Low Power Operation.
Some modules feature a software programmable option to freeze the module status whilst the background
debug module is active to facilitate debugging.
1.9.1 Chip Configuration Summary
The different modes and the security state of the MCU affect the debug features (enabled or disabled).
The operating mode out of reset is determined by the state of the MODC signal during reset (see
Table 1-9). The MODC bit in the MODE register shows the current operating mode and provides limited
mode switching during operation. The state of the MODC signal is latched into this bit on the rising edge
of RESET.
Table 1-9. Chip Modes
Chip Modes MODC
Normal single chip 1
Special single chip 0
1.9.1.1 Normal Single-Chip Mode
This mode is intended for normal device operation. The opcode from the on-chip memory is being
executed after reset (requires the reset vector to be programmed correctly). The processor program is
executed from internal memory.
1.9.1.2 Special Single-Chip Mode
This mode is used for debugging single-chip operation, boot-strapping, or security related operations. The
background debug module BDM is active in this mode. The CPU executes a monitor program located in
an on-chip ROM. BDM firmware waits for additional serial commands through the BKGD pin.
1.9.2 Low Power Operation
The S12VRP-Series has two dynamic-power modes (run and wait) and two static low-power modes stop
and pseudo stop). For a detailed description refer to Chapter 4, “S12 Clock, Reset and Power Management
Unit (S12CPMU_UHV_V8).
• Dynamic power mode: Run
— Run mode is the main full performance operating mode with the entire device clocked. The user
can configure the device operating speed through selection of the clock source and the phase
locked loop (PLL) frequency. To save power, unused peripherals must not be enabled.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 39
Page 40

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
• Dynamic power mode: Wait
— This mode is entered when the CPU executes the WAI instruction. In this mode the CPU does
not execute instructions. The internal CPU clock is switched off. All peripherals can be active
in system wait mode. For further power consumption the peripherals can individually turn off
their local clocks. Asserting RESET
system wait mode.
• Static power mode Pseudo-stop:
— In this mode the system clocks are stopped but the oscillator is still running and the real time
interrupt (RTI) and watchdog (COP), Autonomous Periodic Interrupt (API) and ATD modules
may be enabled. Other peripherals are turned off. This mode consumes more current than
system STOP mode but, as the oscillator continues to run, the full speed wake up time from this
mode is significantly shorter. Asserting XIRQ
RXEDGIF), or key wake-up (incl. HVI) can wake the device if enabled.
• Static power mode: Stop
— The oscillator is stopped in this mode. By default, all clocks are switched off and all counters
and dividers remain frozen. The autonomous periodic interrupt (API), COP (if clocked from
API clock source and enabled), XIRQ, IRQ, key wake-up (incl. HVI) and the LIN physical
layer transceiver modules (SCI0 RXEDGIF) may be enabled to wake the device.
, XIRQ, IRQ, or any other interrupt that is not masked ends
, IRQ, LIN physical layer activity (SCI0
1.10 Security
The MCU security mechanism prevents unauthorized access to the Flash memory. Refer to Section 5.4.1
Security and Section 18.5 Security.
1.11 Resets and Interrupts
Consult the S12 CPU manual and the S12SINT section for detailed information on exception processing.
1.11.1 Resets
Table 1-10. lists all Reset sources and the vector locations. Resets are explained in detail in the Chapter 4,
“S12 Clock, Reset and Power Management Unit (S12CPMU_UHV_V8)”.
Table 1-10. Reset Sources and Vector Locations
Vector Address Reset Source
Power-On Reset (POR) None None
$FFFE
Low Voltage Reset (LVR) None None
$FFFE
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
External pin RESET
$FFFE
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
40 NXP Semiconductors
None None
Page 41

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Vector Address Reset Source
Illegal Address Reset None None
$FFFE
Clock monitor reset None
$FFFC
COP watchdog reset None
$FFFA
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
OSCE Bit in CPMUOSC register
CR[2:0] in CPMUCOP register
1.11.2 Interrupt Vectors
Table 1-11 lists all interrupt sources and vectors in the default order of priority. The interrupt module (see
Chapter 7, “Interrupt Module (S12SINTV1)”) provides an interrupt vector base register (IVBR) to relocate
the vectors.
Table 1-11. Interrupt Vector Locations (Sheet 1 of 3)
Vector Address Interrupt Source
Vector base + $F8 Unimplemented instruction trap None None - -
Vector base+ $F6 SWI None None - -
Vector base+ $F4 XIRQ
Vector base+ $F2 IRQ
CCR
Mask
X Bit None Yes Yes
I bit IRQCR (IRQEN) Yes Yes
Local Enable
Wake up
from STOP
Wake up
from WAIT
Vector base+ $F0 RTI time-out interrupt I bit CPMUINT (RTIE)
Vector base+ $EE TIM0 timer channel 0 I bit TIM0TIE (C0I) No Yes
Vector base + $EC TIM0 timer channel 1 I bit TIM0TIE (C1I) No Yes
Vector base+ $EA TIM1 timer channel 0 I bit TIM1TIE (C0I) No Yes
Vector base+ $E8 TIM1 timer channel 1 I bit TIM1TIE (C1I) No Yes
Vector base+ $E6
to
Vector base + $E0
Vector base + $DE TIM0 timer overflow I bit TIM0TSCR2(TOF) No Yes
Vector base + $DC TIM1 timer overflow I bit TIM1TSCR2(TOF) No Yes
Vector base + $DA
to
Vector base + $D8
Vector base+ $D6 SCI0 I bit SCI0CR2
Reserved
Reserved
(TIE, TCIE, RIE, ILIE)
SCI0ACR1
(RXEDGIE, BERRIE, BKDIE)
see
Section
4.1.2.3
Stop Mode
RXEDGIF
only
Yes
Yes
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 41
Page 42

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Table 1-11. Interrupt Vector Locations (Sheet 2 of 3)
Vector Address Interrupt Source
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
Vector base + $D4 SCI1 I bit SCI1CR2
(TIE, TCIE, RIE, ILIE)
Wake up
from STOP
RXEDGIF
only
Wake up
from WAIT
Yes
SCI1ACR1
(RXEDGIE, BERRIE, BKDIE)
Vector base + $D2 ADC I bit ATDCTL2 (ASCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $D0
Vector base + $CE Port L I bit PIEL (PIEL5-PIEL0)
Reserved
Yes
Yes
Vector base + $CC
to
Reserved
Vector base + $CA
Vector base + $C8 Oscillator status interrupt I bit CPMUINT (OSCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $C6 PLL lock interrupt I bit CPMUINT (LOCKIE) No Yes
Vector base + $C4
to
Reserved
Vector base + $BC
Vector base + $BA FLASH error I bit FERCNFG (SFDIE, DFDIE) No No
Vector base + $B8 FLASH command I bit FCNFG (CCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $B6
to
Reserved
Vector base + $B0
Vector base + $AE HSDRV over-current interrupt I bit HSIE (HSOCIE)
No
Yes
Vector base + $AC LSDRV over-current interrupt I bit LSIE (LSOCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $AA LINPHY over-current interrupt or
I bit LPIE (LPDTIE & LPOCIE) No Yes
TXD-dominant timeout interrupt
Vector base + $A8 BATS low & high battery voltage
I bit BATIE (BVHIE,BVLIE) No Yes
interrupt
Vector base + $A6 LS2DRV over-current interrupt I bit LS2IE (LS2OCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $A4 Reserved
Vector base + $A2 Current Sense Interrupt I bit CSIE (OCIE) No Yes
Vector base + $A0
to
Reserved
Vector base + $90
Vector base + $8E Port P interrupt I bit PIEP (PIEP[5:0])
Yes
Yes
Vector base+ $8C Port P2 and P0 over-current interrupt I bit PIEP (OCIEP2, OCIEP0) No Yes
Vector base + $8A Low-voltage interrupt (LVI) I bit CPMUCTRL (LVIE) No Yes
Vector base + $88 Autonomous periodical interrupt (API) I bit CPMUAPICTRL (APIE)
Yes
Yes
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
42 NXP Semiconductors
Page 43

Table 1-11. Interrupt Vector Locations (Sheet 3 of 3)
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
Vector Address Interrupt Source
Vector base + $86 High temperature interrupt I bit CPMUHTCTL(HTIE) No Yes
Vector base + $84 ADC compare interrupt I bit ATDCTL2 (ACMPIE) No Yes
Vector base + $82 Port AD interrupt I bit PIE1AD(PIE1AD[5:0])
Vector base + $80 Spurious interrupt — None - -
CCR
Mask
Local Enable
Wake up
from STOP
Yes
Wake up
from WAIT
Yes
1.11.3 Effects of Reset
When a reset occurs, MCU registers and control bits are initialized. Refer to the respective block sections
for register reset states.
On each reset, the Flash module executes a reset sequence to load Flash configuration registers.
1.11.3.1 Flash Configuration Reset Sequence Phase
On each reset, the Flash module halts CPU activity while loading Flash module registers from the Flash
memory. If double faults are detected in the reset phase, Flash module protection and security may be
active on leaving reset. This is explained in more detail in the Flash module Chapter 18, “64 KByte Flash
Module (S12FTMRG64K4KV2)”.
1.11.3.2 Reset While Flash Command Active
If a reset occurs while any Flash command is in progress, that command is immediately aborted. The state
of the word being programmed or the sector/block being erased is not guaranteed.
1.11.3.3 I/O Pins
Refer to the PIM section for reset configurations of all peripheral module ports.
1.11.3.4 RAM
The RAM arrays are not initialized out of reset.
1.12 Module Device level Dependencies
1.12.1 ADC External Trigger Input Connection
The ADC module includes external trigger inputs ETRIG0, ETRIG1, ETRIG2, and ETRIG3. The external
trigger allows the user to synchronize ADC conversion to external trigger events. On the S12VRP-Series
ETRIG0 is connected to PP4 / PWM4 and ETRIG1 is connected to PP5 / PWM5. ETRIG2 and ETRIG3
are not used. ETRIG0 can be routed to PS2 and ETRIG1 can be routed to PS3.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 43
Page 44

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
1.12.2 ADC Special Conversion Channels
Whenever the ADC’s Special Channel Conversion Bit (SC) in ATD Control Register 5 (ATDCTL5) is set,
it is capable of running conversion on a number of internal channels. Table 1-12 lists the internal sources
which are connected to these special conversion channels.
Table 1-12. Usage of ADC Special Conversion Channels
ATDCTL5 Register Bits Usage
SC CD CC CB CA ADC Channel
1 0 0 0 1 Internal_7 Bandgap Voltage V
sensor V
Temperature Control Register (CPMUHTCTL)
1 0 0 1 0 Internal_0 Flash Supply Voltage VDDF
11010 Internal_4 V
SENSE
or V
see Section 4.3.2.13, “High
HT
selectable in BATS module see
SUP
Section 17.1.1 Features
or Chip temperature
BG
1.12.3 HVI Digital input enables
The HVI digital input enables of the MC9S12VRP-Series are controlled by the Port L DIENL register. The
corresponding ADC digital input enable bits in ATDDIENx are redundant.
1.12.4 API external clock output (API_EXTCLK)
The API_EXTCLK option which is described 4.3.2.15 Autonomous Periodical Interrupt Control Register
(CPMUAPICTL) is available on PT2.
1.12.5 COP Configuration
The COP time-out rate bits CR[2:0] and the WCOP bit in the CPMUCOP register at address 0x003C are
loaded from the Flash configuration field byte at global address 0x3_FF0E during the reset sequence. See
Table 1-13 and Table 1-14 for coding.
Table 1-13. Initial COP Rate Configuration
NV[2:0] in
FOPT Register
000 111
001 110
010 101
011 100
100 011
101 010
110 001
111 000
CR[2:0] in
COPCTL Register
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
44 NXP Semiconductors
Page 45

Table 1-14. Initial WCOP Configuration
Device Overview S12VRP-Series
NV[3] in
FOPT Register
10
01
WCOP in
COPCTL Register
1.12.6 CPMU High Temperature Trimming
The value loaded from the flash into the CPMUHTTR register is a default value for the device. There is
no device specific trimming carried out during production. The specified VHT value is a typical value that
is part dependent and should thus be calibrated.
1.12.7 Flash IFR Mapping
Table 1-15. Flash IFR Mapping
IFR Byte Address FEDCBA 9 876543210
0x40B8 - 0x40B9
0x40BA -0x40BB
FL
G
ACLKTR[5:0]
TCTRIM[4:0]
1
3
IRCTRIM[9:0]
HTTR[3:0]
4
2
1
see Section 4.3.2.16 Autonomous Clock Trimming Register (CPMUACLKTR)
2
see Section 4.3.2.19 High Temperature Trimming Register (CPMUHTTR)
3
see Section 4.3.2.20 S12CPMU_UHV_V8 IRC1M Trim Registers (CPMUIRCTRIMH / CPMUIRCTRIML)
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 45
Page 46

Device Overview S12VRP-Series
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
46 NXP Semiconductors
Page 47

Chapter 2 Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-1. Revision History
Rev. No. Date
V00.01 23 Feb 2016 • Initial Version
V00.02 10 Mar 2016 • Changed PERS[3:0] reset value to 0xF
V00.03 11 Mar 2016 • Added PIMTEST1 for PP2:0 routing to ADC channel for test
V00.04 21 Mar 2016 • Added rerouting options to default pins in pin function and priority tables
V00.05 01 Apr 2016 • Added PWM[5:4] routing dependencies Table 2-6
V00.06 28 Apr 2016 • Moved API_EXTCLK to PS2 following DFT feedback
V00.07 10 May 2016 2.3.2.8/68 • Specified pin interrupt and ETRIG timing specs. invalid if RCOEN is set
V00.08 07 Jul 2016 Various
Sections
Affected
Table 2-6
Table 2-7
Table 2-8
Table 2-9
Ta bl e 2 -1 0
Table 2-11
Ta bl e 2 -1 2
Substantial Change(s)
• Added LREPORT
• Spec tag updates from verification engineer review
• Renamed PIMTEST to PIMTEST0
• Prevented PWM[5:4] rerouting to 2 pins simultaneously
• Prevented OC1_1 rerouting to LS2 and HS1 simultaneously
• Specified that functions cannot be routed to 2 pins simultaneously
• Replaced PT2 with PS2 in DFT port following DFT feedback
• Minor enhancements and fixes from RM V1.0A shared review
• Documented PP0, PP2 over current interrupts
• Included all PS0 RXD0 routing bits
• Included all PT3 IOC1_1 routing bits
• Included all routing bits
• Differentiated between LSDRV and LS2DRV, included all routing bits
• Changed reference from LSDRV to LS2DRV
• Clarified bit still affect ETRIG[1:0] when PWM channels routed to LS0,HS1
V00.09 10 Aug 2016 • Internal test feature update
V00.10 11 Aug 2016 2.4.7.2/86 • Specified RC OSC not dependent on interrupt enables
V00.11 02 Aug 2017 Table 2-3
Ta bl e 2 -1 0
Table 2-11
Ta bl e 2 -1 3
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 47
• Corrected typos and formating
Page 48

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.1 Introduction
2.1.1 Overview
The S12VRP-family port integration module establishes the interface between the peripheral modules and
the I/O pins for all ports. It controls the electrical pin properties as well as the signal prioritization and
multiplexing on shared pins.
This document covers:
•Port AD
GPIO/KWU ADC AMP Pins
PTAD5 AN5 PAD5
PTAD4 AN4 PAD4
PTAD3 AN3 PAD3
PTAD2 AN2 AMPP0 PAD2
PTAD1 AN1 AMPM0 PAD1
PTAD0 AN0 AMP0 PAD0
• Port E
GPIO
PTE1 XTAL PE1
PTE0 EXTAL PE0
External
Oscillator
• Port L
HVI/KWU ADC Pins
PTIL5 AN11 PL5
Pins
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
48 NXP Semiconductors
Page 49

PTIL4 AN10 PL4
PTIL3 AN9 PL3
PTIL2 AN8 PL2
PTIL1 AN7 PL1
PTIL0 AN6 PL0
• Port P
GPIO/KWU ETRIG PWM IRQ/XIRQ Pins
PTP5 ETRIG1 PWM5 IRQ PP5
PTP4 ETRIG0 PWM4 PP4
PTP3 PWM3 PP3
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
PTP2 PWM2 PP2
PTP1 PWM1 XIRQ
PTP0 PWM0 PP0
•Port S
GPIO ETRIG PWM SCI0 LINPHY SCI1 CLOCK Pins
PTS3 ETRIG1 PWM5 TXD1 ECLK PS3
PTS2 ETRIG0 PWM4 RXD1 PS2
PTS1 TXD0 LPDR1 TXD1 PS1
PTS0 RXD0 RXD1 PS0
PP1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 49
Page 50

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
•Port T
GPIO TIM0 TIM1 PWM SCI0 LINPHY CLOCK Pins
PTT3 IOC1_1 LPTXD PT3
PTT2 IOC1_0 LPRXD API PT2
PTT1 IOC0_1 PWM7 TXD0 LPDR1 PT1
PTT0 IOC0_0 PWM6 RXD0 PT0
Most I/O pins can be configured by register bits to select data direction and to enable and select pull-up or
pulldown devices.
NOTE
This document shows the superset of all available features offered by the
S12VRP device family. Refer to the device overview information for
functions not available for a particular device or package option.
2.1.2 Features
The PIM includes these distinctive registers:
• Data registers for ports AD, E, S, T, P when used as general-purpose I/O
• Data direction registers for ports AD, E, S, T, P when used as general-purpose I/O
• Control registers to enable pull devices on ports AD, S, T, P
• Control register to enable pull devices on port E and on BKGD pin
• Control registers to select pullups or pulldowns on ports AD, S, T, P
• Control registers to enable open-drain (wired-or) mode on port S
• Control register to enable/disable reduced output drive on port P high-current pins
• Control register to enable digital input buffers on port L
• Interrupt enable register for pin interrupts and key-wakeup (KWU) on ports AD, P and L
• Interrupt flag register for pin interrupts and key-wakeup (KWU) on ports AD, P and L
• Control register to configure IRQ pin operation
• Control register to enable ECLK output
• Routing registers to map peripheral module signal to external pins and to control internal routing:
— PWM channels to alternative pins
— ETRIG channels to alternative pins
— SCI0 and SCI1 to alternative pins
— Various SCI0-LINPHY routing options for standalone use and conformance testing
— Internal SCI0/LINPHY link to TIM1 input capture channel (IC1_1) for baud rate detection
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
50 NXP Semiconductors
Page 51

— Internal HVI to ADC link
— HSDRV driven from PWM, TIM OC or related register bit
— LSDRV, LS2DRV driven from PWM, TIM OC or related register bit
A standard port pin has the following minimum features:
• Input/output selection
• 5V output drive
• 5V digital and analog input
• Input with selectable pull-up or pulldown device
Optional features supported on dedicated pins:
• Interrupt input with glitch filtering
• Open drain for wired-or connections
• High current drive strength from VDDX with over-current protection
• High-voltage input
2.2 External Signal Description
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
This section lists and describes the signals that connect off-chip.
Table 2-10 shows all pins and functions that are controlled by the PIM. Routing options are denoted in
parentheses. Specific functions cannot be routed to 2 pins simultaneously.
NOTE
If there is more than one function associated with a pin, the output priority
is indicated by the position in the table from top (highest priority) to bottom
(lowest priority). Inputs do not arbitrate priority unless noted differently in
Table 2-40.
Table 2-2. BKGD Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
— BKGD MODC
1
Function active when RESET asserted
Pin Function
& Priority
1
BKGD I/O BDM communication pin —
I/O Description
I MODC input during RESET
Routing
Register Bit
— BKGD
Func.
after
Reset
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 51
Page 52

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-3. Port AD Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
AD PAD5-3 AN[5:3] I ADC analog input — GPIO
PTAD[5:3]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWAD[5:3]
PAD2 AMPP0 I ISENSE AMP0 non-inverting input (+) —
AN2 I ADC analog input —
PTAD[2]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWAD[2]
PAD1 AMPM0 I ISENSE AMP0 inverting input (-) —
AN1 I ADC analog input —
PTAD[1]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWAD[1]
PAD0 AMP0 O ISENSE AMP0 output —
AN0 I ADC analog input —
PTAD[0]/
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
KWAD[0]
1
Digital input buffers are disabled after reset. See Section 8.3.2.4, “ATD Control Register 3 (ATDCTL3)”
Table 2-4. Port E Pin Functions and Priorities
Func.
after
Reset
1
Func.
after
Reset
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
E PE1 XTAL — CPMU OSC signal — GPIO
PTE[1] I/O GPIO —
PE0 EXTAL — CPMU OSC signal —
PTE[0] I/O GPIO —
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
52 NXP Semiconductors
Page 53

Table 2-5. Port L Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
L PL5 PTL[5]/
KWL[5]/
AN11
PL4 PTL[4]/
KWL[4]/
AN10
PL3 PTL[3]/
KWL[3]/
AN9
PL2 PTL[2]/
KWL[2]/
AN8
PL1 PTL[1]/
KWL[1]/
AN7
PL0 PTL[0]/
KWL[0]/
AN6
I/O Description
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
I HVI with pin-interrupt with
key-wakeup and
ADC analog input
Routing
Register Bit
Func.
after
Reset
—HVI
—
—
—
—
—
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 53
Page 54

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-6. Port P Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
P PP5 IRQ
PWM5 O
ETRIG1 I ADC external trigger input PWM5ET1
PTP[5]/
KWP[5]
PP4 PWM4 O
ETRIG0 I ADC external trigger input PWM4ET0
PTP[4]/
KWP[4]
PP3 PWM3 O PWM channel 3 HS0RR1-0
PTP[3]/
KWP[3]
PP2 PWM2 O PWM channel 2 with over current interrupt LS2RR1-0
PTP[2]/
KWP[2]
EVDD
PP1 XIRQ
PWM1 O PWM channel 1 HS1RR1-0
PTP[1]/
KWP[1]/
EVDD
PP0 PWM0 O PWM channel 0 with over current interrupt —
PTP[0]/
KWP[0]/
EVDD
I/O Description
I Maskable level or falling edge-sensitive
Routing
Register Bit
—GPIO
interrupt
PWM channel 5
PWM5ET1
LS0RR1-0
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
PWM channel 4
PWM4ET0
HS1RR1-0
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
I/O GPIO with pin-interrupt and key-wakeup —
I/O
GPIO with interrupt and wakeup
—
Switchable external power supply output
(20mA) with over-current interrupt
I Non-maskable level-sensitive interrupt —
I/O
GPIO with interrupt and wakeup
—
Switchable external power supply output
(10mA)
I/O
GPIO with interrupt and wakeup
—
Switchable external power supply output
(20mA) with over-current interrupt
Func.
after
Reset
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
54 NXP Semiconductors
Page 55

Table 2-7. Port S Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Func.
after
Reset
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
S PS3 ECLK O Free running clock — GPIO
(TXD1) I/O SCI1 transmit MODRR24
(PWM5) O PWM channel 5 PWM5ET1
(ETRIG1) I ADC external trigger input PWM5ET1
PTS[3] I/O GPIO —
PS2 (RXD1) I SCI1 receive MODRR24
(PWM4) O PWM channel 4 PWM4ET0
(ETRIG0) I ADC external trigger input PWM4ET0
PTS[2] I/O GPIO —
PS1 TXD1 I/O SCI1 transmit MODRR24
(LPDR1) O LINPHY register LPDR[LPDR1] MODRR23-20
(TXD0) I/O SCI0 transmit MODRR23-20
PTS[1] I/O GPIO —
PS0 RXD1 I SCI1 receive MODRR24
(RXD0) I SCI0 receive MODRR23-20
PTS[0] I/O GPIO —
Table 2-8. Port T Pin Functions and Priorities
Func.
after
Reset
Port Pin
Pin Function
& Priority
I/O Description
Routing
Register Bit
T PT3 (LPTXD) I LINPHY transmit pin MODRR23-20 GPIO
IOC1_1 I/O TIM1 channel 1 HS1RR1-0 (OC1_1)
LS2RR1-0 (OC1_1)
MODRR27 (IC1_1)
PTT[3] I/O GPIO —
PT2 API
1
O CPMU API external clock output —
(LPRXD) O LINPHY receive output MODRR23-20
IOC1_0 I/O TIM1 channel 0 HS0RR1-0 (OC1_0)
PTT[2] I/O GPIO —
PT1 (LPDR1) O LINPHY register LPDR[LPDR1] MODRR23-20
(TXD0) I/O SCI0 transmit MODRR23-20
PWM7 O PWM channel 7 LS1RR1-0
IOC0_1 I/O TIM0 channel 1 LS1RR1-0 (OC0_1)
PTT[1] I/O GPIO —
PT0 (RXD0) I SCI0 receive MODRR23-20
PWM6 O PWM channel 6 LS0RR1-0
IOC0_0 I/O TIM0 channel 0 LS0RR1-0 (OC0_0)
PTT[0] I/O GPIO —
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 55
Page 56

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
1
Not a PIM feature; listed here only for priority information.
Table 2-9. HSDRV Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
2
N/A
HS1 (PWM1) O PWM channel 1 HS1RR1-0 HSDRV
Pin Function
(No Priority)
I/O Description
1
(PWM4) O PWM channel 4 HS1RR1-0
(OC1_1) O TIM1 output compare channel 1 HS1RR1-0, LS2RR1-0
HSDR[HSDR1] O High-side driver 1 HS1RR1-0
HS0 (PWM3) O PWM channel 3 HS0RR1-0 HSDRV
(OC1_0) O TIM1 output compare channel 0 HS0RR1-0
HSDR[HSDR0] O High-side driver 0 HS0RR1-0
1
No priority. The routing is selected solely by MODRR1 bits.
2
Not a PIM port. Listed here for routing information only. Refer to section S12HSDRV.
Table 2-10. LSDRV and LS2DRV Pin Functions and Priorities
Port Pin
2
N/A
LS2
(LS2DRV)
LS1
(LSDRV)
LS0
(LSDRV)
Pin Function
(No Priority)
(PWM2) O PWM channel 2 LS2RR1-0 LS2DRV
(OC1_1) O TIM1 output compare channel 1 HS1RR1-0, LS2RR1-0
LS2DR[LSDR] O Low-side driver 2 LS2RR1-0
(PWM7) O PWM channel 7 LS1RR1-0 LSDRV
(OC0_1) O TIM0 output compare channel 1 LS1RR1-0
LSDR[LSDR1] O Low-side driver 1 LS1RR1-0
(PWM5) O PWM channel 5 LS0RR1-0
(PWM6) O PWM channel 6 LS0RR1-0
(OC0_0) O TIM0 output compare channel 0 LS0RR1-0
LSDR[LSDR0] O Low-side driver 0 LS0RR1-0
I/O Description
1
Routing
Register Bit
Routing
Register Bit
Func.
after
Reset
Func.
after
Reset
1
No priority. The routing is selected solely by MODRR0 bits.
2
Not a PIM port. Listed here for routing information only. Refer to section S12LSDRV/S12LS2DRV.
2.3 Memory Map and Register Definition
This section provides a detailed description of all port integration module registers. Subsection 2.3.1
shows all registers and bits at their related addresses within the global device register map. A detailed
description of every register bit is given in subsections 2.3.2 to 2.3.4.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
56 NXP Semiconductors
Page 57

2.3.1 Register Map
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Global
Address
0x0000–
0x0007
0x0008 PORTE
0x0009 DDRE
0x000A–
0x000B
0x000C PUCR
0x000D Reserved
0x000E–
0x001B
0x001C ECLKCTL
Register
Name
Reserved
Non-PIM
Address Range
Non-PIM
Address Range
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R00000000
W
R000000
W
R000000
W
R
W
R0
W
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
R
W
R
NECLK
W
BKPUE
0000000
Non-PIM Address Range
0
PDPEE
Non-PIM Address Range
0000
PTE1 PTE0
DDRE1 DDRE0
0x001D PPOCPE
0x001E IRQCR
0x001F Reserved
0x0020–
0x023F
0x0240 PTT
0x0241 PTIT
0x0242 DDRT
Non-PIM
Address Range
R
OCPEP2 OCPEP0
W
R
IRQE IRQEN
W
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
R
W
R0000
W
R 0 0 0 0 PTIT3 PTIT2 PTIT1 PTIT0
W
R0000
W
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
000000
000000
Non-PIM Address Range
PTT3 PTT2 PTT1 PTT0
DDRT3 DDRT2 DDRT1 DDRT0
NXP Semiconductors 57
Page 58

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x0243 Reserved
0x0244 PERT
0x0245 PPST
0x0246 MODRR0
0x0247 MODRR1
0x0248 PTS
0x0249 PTIS
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R00000000
W
R0000
W
R0000
W
R0 0
W
LS2RR1 LS2RR0 LS1RR1 LS1RR0 LS0RR1 LS0RR0
PERT3 PERT2 PERT1 PERT0
PPST3 PPST2 PPST1 PPST0
R0 0
W
R0000
W
PWM5ET1 PWM4ET0 HS1RR1 HS1RR0 HS0RR1 HS0RR0
PTS3 PTS2 PTS1 PTS0
R 0 0 0 0 PTIS3 PTIS2 PTIS1 PTIS0
W
0x024A DDRS
0x024B Reserved
0x024C PERS
0x024D PPSS
0x024E WOMS
0x024F MODRR2
0x0250–
0x0257
Reserved
0x0258 PTP
R0000
W
DDRS3 DDRS2 DDRS1 DDRS0
R00000000
W
R0000
W
R0000
W
R0000
W
R
MODRR27
W
00
MODRR24 MODRR23 MODRR22 MODRR21 MODRR20
PERS3 PERS2 PERS1 PERS0
PPSS3 PPSS2 PPSS1 PPSS0
WOMS3 WOMS2 WOMS1 WOMS0
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
PTP5 PTP4 PTP3 PTP2 PTP1 PTP0
0x0259 PTIP
R 0 0 PTIP5 PTIP4 PTIP3 PTIP2 PTIP1 PTIP0
W
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
58 NXP Semiconductors
Page 59

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x025A DDRP
0x025B RDRP
0x025C PERP
0x025D PPSP
0x025E PIEP
0x025F PIFP
0x0260 Reserved
0x02610x0264
Reserved
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R0 0
W
R00000
W
R0 0
W
R0 0
W
R
OCIEP2 OCIEP0 PIEP5 PIEP4 PIEP3 PIEP2 PIEP1 PIEP0
W
R
OCIFP2 OCIFP0 PIFP5 PIFP4 PIFP3 PIFP2 PIFP1 PIFP0
W
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
DDRP5 DDRP4 DDRP3 DDRP2 DDRP1 DDRP0
RDRP2 RDRP1 RDRP0
PERP5 PERP4 PERP3 PERP2 PERP1 PERP0
PPSP5 PPSP4 PPSP3 PPSP2 PPSP1 PPSP0
R00000000
W
0x0265 PTAENL
0x0266 PTADIRL
0x0267 PTABYPL
0x0268 PTPSL
0x0269 PTIL
0x026A DIENL
0x026B PTTEL
0x026C PIRL
0 0
W
W
W
W
R
R
R
R
0 0
0 0
0 0
PTAENL5 PTAENL4 PTAENL3 PTAENL2 PTAENL1 PTAENL0
PTADIRL5 PTADIRL4 PTADIRL3 PTADIRL2 PTADIRL1 PTADIRL0
PTABYPL5 PTABYPL4 PTABYPL3 PTABYPL2 PTABYPL1 PTABYPL0
PTPSL5 PTPSL4 PTPSL3 PTPSL2 PTPSL1 PTPSL0
R 0 0 PTIL5 PTIL4 PTIL3 PTIL2 PTIL1 PTIL0
W
R0 0
W
R0 0
W
R0 0
W
DIENL5 DIENL4 DIENL3 DIENL2 DIENL1 DIENL0
PTTEL5 PTTEL4 PTTEL3 PTTEL2 PTTEL1 PTTEL0
PIRL5 PIRL4 PIRL3 PIRL2 PIRL1 PIRL0
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 59
Page 60

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Global
Address
Register
Name
0x026D PPSL
0x026E PIEL
0x026F
PIFL
0x0270 Reserved
0x0271 PT1AD
0x0272 Reserved
0x0273 PTI1AD
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R0 0
W
PPSL5 PPSL4 PPSL3 PPSL2 PPSL1 PPSL0
R0 0
W
R0 0
W
PIEL5 PIEL4 PIEL3 PIEL2 PIEL1 PIEL0
PIFL5 PIF4 PIFL3 PIFL2 PIFL1 PIFL0
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
PT1AD5 PT1AD4 PT1AD3 PT1AD2 PT1AD1 PT1AD0
R00000000
W
R 0 0 PTI1AD5 PTI1AD4 PTI1AD3 PTI1AD2 PTI1AD1 PTI1AD0
W
0x0274 Reserved
0x0275 DDR1AD
0x0276–
0x0278
Reserved
0x0279 PER1AD
0x027A Reserved
0x027B PPS1AD
0x027C Reserved
0x027D PIE1AD
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
DDR1AD5 DDR1AD4 DDR1AD3 DDR1AD2 DDR1AD1 DDR1AD0
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
PER1AD5 PER1AD4 PER1AD3 PER1AD2 PER1AD1 PER1AD0
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
PPS1AD5 PPS1AD4 PPS1AD3 PPS1AD2 PPS1AD1 PPS1AD0
R00000000
W
R0 0
W
PIE1AD5 PIE1AD4 PIE1AD3 PIE1AD2 PIE1AD1 PIE1AD0
0x027E Reserved
W
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
60 NXP Semiconductors
R00000000
Page 61

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Global
Address
0x027F PIF1AD
Register
Name
Bit 7654321Bit 0
R0 0
W
= Unimplemented
PIF1AD5 PIF1AD4 PIF1AD3 PIF1AD2 PIF1AD1 PIF1AD0
2.3.2 Device Specific PIM Registers
This section describes registers for device specific related functions not part of the generic port registers.
• If not stated differently, writing to reserved bits has no effect and reading returns zero.
• All register read accesses are synchronous to internal clocks.
• Register bits can be written at any time if not stated differently.
2.3.2.1 Module Routing Register 0 (MODRR0)
Address 0x0246 Access: User read/write
76543210
R0 0
W
LS2RR1 LS2RR0 LS1RR1 LS1RR0 LS0RR1 LS0RR0
1
Reset00000000
Figure 2-1. Module Routing Register 0
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
Table 2-11. Module Routing Register 0 Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-4
LS2RR1-0
MODule Routing Register 0 — LS2
This register controls the routing of PWM and TIM channels to pin LS2 of LS2DRV module. By default the pin is
controlled by the related LS2DRV port register bit.
11 PWM channel 2 routed to LS2 if enabled
10 PWM channel 2 routed to LS2 if enabled
01 TIM1 output compare channel 1 routed to LS2 if enabled. If OC1_1 is routed to HS1 then this bit has no effect.
00 LS2 controlled by register bit LS2DR[LSDR]. See Chapter 14, “Low-Side Driver - LS2DRV (S12LS2DRV_V1)”
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 61
Page 62

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-11. Module Routing Register 0 Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
3-2
LS1RR1-0
1-0
LS0RR1-0
MODule Routing Register 0 — LS1
This register controls the routing of PWM and TIM channels to pin LS1 of LSDRV module. By default the pin is
controlled by the related LSDRV port register bit.
11 PWM channel 7 routed to LS1 if enabled
10 PWM channel 7 routed to LS1 if enabled
01 TIM0 output compare channel 1 routed to LS1 if enabled
00 LS1 controlled by register bit LSDR[LSDR1]. Refer to LSDRV section
MODule Routing Register 0 — LS0
This register controls the routing of PWM and TIM channels to pin LS0 of LSDRV module. By default the pin is
controlled by the related LSDRV port register bit.
11 PWM channel 5 routed to LS0 if enabled
10 PWM channel 6 routed to LS0 if enabled
01 TIM0 output compare channel 0 routed to LS0 if enabled
00 LS0 controlled by register bit LSDR[LSDR0]. Refer to LSDRV section.
2.3.2.2 Module Routing Register 1 (MODRR1)
Address 0x0247 Access: User read/write
76543210
R0 0
W
Reset00000000
PWM5ET1 PWM4ET0 HS1RR1 HS1RR0 HS0RR1 HS0RR0
1
Figure 2-2. Module Routing Register 1 (MODRR1)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
Table 2-12. MODRR1 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5
PWM5ET1
4
PWM4ET0
MODule Routing Register 1 — PWM5, ETRIG1
If PWM channel 5 is routed to LS0, then this bit has no effect on PWM mapping but ETRIG1 is still mapped by this
bit.
1 PWM channel 5 on PS3; ETRIG1 on PS3.
0 PWM channel 5 on PP5; ETRIG1 on PP5
MODule Routing Register 1 — PWM4, ETRIG0
If PWM channel 4 is routed to HS1, then this bit has no effect on PWM mapping but ETRIG0 is still mapped by this
bit.
1 PWM channel 4 on PS2; ETRIG0 on PS2
0 PWM channel 4 on PP4; ETRIG0 on PP4
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
62 NXP Semiconductors
Page 63

Table 2-12. MODRR1 Routing Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
3-2
HS1RR1-0
1-0
HS0RR1-0
MODule Routing Register 1 — HS1
This register controls the routing of PWM and TIM channels to pin HS1 of HSDRV module. By default the pin is
controlled by the related HSDRV port register bit.
11 PWM channel 1 routed to HS1 if enabled
10 PWM channel 4 routed to HS1 if enabled
01 TIM1 output compare channel 1 routed to HS1 if enabled
00 HS1 controlled by register bit HSDR[HSDR1]. Refer to HSDRV section
MODule Routing Register 1 — HS0
This register controls the routing of PWM and TIM channels to pin HS0 of HSDRV module. By default the pin is
controlled by the related HSDRV port register bit.
11 PWM channel 3 routed to HS0 if enabled
10 PWM channel 3 routed to HS0 if enabled
01 TIM1 output compare channel 0 routed to HS0 if enabled
00 HS0 controlled by register bit HSDR[HSDR0]. Refer to HSDRV section.
2.3.2.3 Module Routing Register 2 (MODRR2)
Address 0x024F Access: User read/write
76543210
W
Routing
Option
R
MODRR27
LPRXD to
TIM1
00
MODRR24 MODRR23 MODRR22 MODRR21 MODRR20
— — SCI1 SCI0 SCI0-to-LINPHY interface
1
Reset00000000
Figure 2-3. Module Routing Register 2 (MODRR2)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Once in normal, anytime in special mode
Table 2-13. Module Routing Register 2 Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
MODRR27
4
MODRR22
MODule Routing Register 2 — TIM1 routing
1 TIM1 input capture channel 1 is connected to RXD0
0 TIM1 input capture channel 1 is connected to PT3
MODule Routing Register 2 — SCI1 routing
1 TXD1 on PS3; RXD1 on PS2
0 TXD1 on PS1; RXD1 on PS0
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 63
Page 64

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
MODRR27
PT2 / LPRXD
PT3 / LPTXD
PT1 / TXD0 / LPDR1
PT0 / RXD0
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
0
TIM1 input
capture
channel 1
MODRR22MODRR21
MODRR20
SCI0
LINPHY
TXD0
RXD0
LPTXD
LPRXD
1
0
1
0
MODRR23
PS0 / RXD0
PS1 / TXD0 / LPDR1
LPDR1
LIN
Table 2-13. Module Routing Register 2 Field Descriptions
Field Description
3
MODRR23
2-0
MODRR2
[2:0]
MODule Routing Register 2 — SCI0 TXD0 and RXD0 routing
1 TXD0 or LPDR1 mapped to PT1; RXD0 mapped to PT0
0 TXD0 or LPDR1 mapped to PS1; RXD0 mapped to PS0
MODule Routing Register 2 — SCI0-to-LINPHY routing
Selection of SCI0-to-LINPHY interface routing options to support probing and conformance testing. Refer to
Figure 2-4 for an illustration and Ta b le 2 - 14 for preferred settings. SCI0 must be enabled for TXD0 routing to take
effect on pins. LINPHY must be enabled for LPRXD and LPDR[LPDR1] routings to take effect on pins.
MODRR2[2:0] Description
Figure 2-4. SCI0 to LINPHY Routing Options Illustration
Table 2-14. Preferred Interface Configurations
000 Default setting:
001 Direct control setting:
SCI0 connects to LINPHY, interface internal only
LPDR[LPDR1] register bit controls LPTXD, interface internal only
64 NXP Semiconductors
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 65

MODRR2[2:0] Description
100 Probe setting:
SCI0 connects to LINPHY, interface accessible on 2 external pins
110 Conformance test setting:
Interface opened and all 4 signals routed externally
NOTE
For standalone usage of SCI0 on external pins set MODRR[2:0]=0b110 and
disable LINPHY (LPCR[LPE]=0). This releases the LINPHY associated
pins to other shared functions.
2.3.2.4 Port E, BKGD pin Pull Control Register (PUCR)
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Address 0x000C Access: User read/write
76543210
R0
BKPUE
W
Reset01010000
0
PDPEE
0000
Figure 2-5. Port E, BKGD pin Pull Control Register (PUCR)
1
Read:Anytime
Write:Anytime, except BKPUE, which is writable in special mode only
Table 2-15. PUCR Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
6
BKPUE
4
PDPEE
BKGD pin Pullup Enable — Activate pullup device on pin
This bit configures whether a pull-up device is activated, if the pin is used as input. If a pin is used as output this bit
has no effect.
1 Pullup device enabled
0 Pullup device disabled
Pull-Down Port E Enable — Activate pulldown devices on all port input pins
This bit configures whether a pulldown device is activated on all associated port input pins. If a pin is used as output
or used with the CPMU OSC function this bit has no effect. Out of reset the pulldown devices are enabled.
1 Pullup devices enabled
0 Pullup devices disabled
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 65
Page 66

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.2.5 Reserved Register
Address 0x000D Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
Resetxxxxxxxx
Figure 2-6. Reserved Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and is not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the module’s functionality.
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
66 NXP Semiconductors
Page 67

2.3.2.6 ECLK Control Register (ECLKCTL)
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Address 0x001C Access: User read/write
76543210
R
0000000
1
NECLK
W
Reset:10000000
Figure 2-7. ECLK Control Register (ECLKCTL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-16. ECLKCTL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
NECLK
No ECLK — Disable ECLK output
This bit controls the availability of a free-running clock on the ECLK pin. This clock has a fixed rate equivalent to the
internal bus clock.
1 ECLK disabled
0 ECLK enabled
2.3.2.7 IRQ Control Register (IRQCR)
Address 0x001E Access: User read/write
76543210
R
000000
IRQE IRQEN
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-8. IRQ Control Register (IRQCR)
1
Read: Anytime
Write:
IRQE: Once in normal mode, anytime in special mode
IRQEN: Anytime
Table 2-17. IRQCR Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
IRQE
6
IRQEN
IRQ select edge sensitive only —
1 IRQ
pin configured to respond only to falling edges. Falling edges on the IRQ pin are detected anytime when
IRQE=1 and are cleared only upon a reset or the servicing of the IRQ
interrupt.
0 IRQ configured for low level recognition
IRQ enable —
pin is connected to interrupt logic
1 IRQ
0 IRQ pin is disconnected from interrupt logic
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 67
Page 68

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.2.8 Reserved Register
Address 0x001F Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
Resetxxxxxxxx
Figure 2-9. Reserved Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode
NOTE
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and are not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the module’s functionality.
2.3.2.9 Reserved Register
Address 0x0260 Access: User read/write
76543210
R
Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved Reserved
W
1
1
Reset00000000
Figure 2-10. Reserved Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Only in special mode after previously writing the unlocking code 0xE3 to the same address
NOTE
This reserved register is designed for factory test purposes only and are not
intended for general user access. Writing to this register when in special
modes can alter the module’s functionality.
2.3.3 PIM Generic Registers
This section describes the details of PIM generic registers.
• Writing to reserved bits has no effect and read returns zero.
• All register read accesses are synchronous to internal clocks.
• All registers can be written at any time, however a specific configuration might not become active.
E.g. a pull-up device does not become active while the port is used as a push-pull output.
• General-purpose data output availability depends on prioritization; input data registers always
reflect the pin status independent of the use.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
68 NXP Semiconductors
Page 69

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
• Pull-device availability, pull-device polarity, wired-or mode, key-wake up functionality are
independent of the prioritization unless noted differently.
NOTE
This is a generic description of the standard PIM registers. For availability
of individual bits refer to Section 2.3.1, “Register Map” and Table 2-39
2.3.3.1 Port Data Register
Address 0x0008 PTE
0x0271 PT1AD
0x0258 PTP
0x0248 PTS
0x0240 PTT
76543210
R
PTx7 PTx6 PTx5 PTx4 PTx3 PTx2 PTx1 PTx0
W
Reset00000000
Access: User read/write
Figure 2-11. Port Data Register
1
Read: Anytime. The data source is depending on the data direction value.
Write: Anytime
Table 2-18. Port Data Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PTx7-0
Port Data — General purpose input/output data
This register holds the value driven out to the pin if the pin is used as a general purpose output.
When not used with the alternative function (refer to Ta b le 2 - 10 ), these pins can be used as general purpose I/O.
If the associated data direction bits of these pins are set to 1, a read returns the value of the port register, otherwise
the buffered pin input state is read.
1
2.3.3.2 Port Input Register
Address 0x0273 PTI1AD
0x0259 PTIP
0x0249 PTIS
0x0241 PTIT
76543210
R PTIx7 PTIx6 PTIx5 PTIx4 PTIx3 PTIx2 PTIx1 PTIx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-12. Port Input Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write:Never
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 69
Access: User read only
1
Page 70

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-19. Port Input Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PTIx7-0
Port Input — Data input
A read always returns the buffered input state of the associated pin. It can be used to detect overload or short circuit
conditions on output pins.
2.3.3.3 Data Direction Register
Address 0x0009 DDRE
0x0275 DDR1AD
0x025A DDRP
0x024A DDRS
0x0242 DDRT
76543210
R
DDRx7 DDRx6 DDRx5 DDRx4 DDRx3 DDRx2 DDRx1 DDRx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-13. Data Direction Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-20. Data Direction Register Field Descriptions
Access: User read/write
1
Field Description
7-0
DDRx7-0
Data Direction — Select general-purpose data direction
This bit determines whether the pin is a general-purpose input or output. If a peripheral module controls the pin the
content of the data direction register is ignored. Independent of the pin usage with a peripheral module this register
determines the source of data when reading the associated data register address.
Note: Due to internal synchronization circuits, it can take up to two bus clock cycles until the correct value is read on
port data and port input registers, when changing the data direction register.
1 Associated pin is configured as output
0 Associated pin is configured as input
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
70 NXP Semiconductors
Page 71

2.3.3.4 Pull Device Enable Register
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Address 0x0279 PER1AD
Access: User read/write
1
0x025C PERP
0x024C PERS
0x0244 PERT
76543210
R
PERx7 PERx6 PERx5 PERx4 PERx3 PERx2 PERx1 PERx0
W
PERS Reset00001111
Others Reset00000000
Figure 2-14. Pull Device Enable Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-21. Pull Device Enable Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PERx7-0
Pull Enable — Activate pull device on input pin
This bit controls whether a pull device on the associated port input or open-drain output pin is active.
The PERS[3:0] reset value is 0xF. All other bits reset to 0.
If a pin is used as push-pull output this bit has no effect. The polarity is selected by the related polarity select register
bit. On open-drain output pins only a pull-up device can be enabled.
1 Pull device enabled
0 Pull device disabled
2.3.3.5 Polarity Select Register
Address 0x027B PPS1AD
0x025D PPSP
0x024D PPSS
0x0245 PPST
76543210
R
PPSx7 PPSx6 PPSx5 PPSx4 PPSx3 PPSx2 PPSx1 PPSx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-15. Polarity Select Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Access: User read/write
1
NXP Semiconductors 71
Page 72

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-22. Polarity Select Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
PPSx7-0
Pull Polarity Select — Configure pull device and pin interrupt edge polarity on input pin
This bit selects a pull-up or a pulldown device if enabled on the associated port input pin.
If a port has interrupt functionality this bit also selects the polarity of the active edge.
1 Pulldown device selected; rising edge selected
0 Pullup device selected; falling edge selected
2.3.3.6 Port Interrupt Enable Register
Address 0x027D PIE1AD
0x026E PIEL
76543210
R
PIEx7 PIEx6 PIEx5 PIEx4 PIEx3 PIEx2 PIEx1 PIEx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-16. Port Interrupt Enable Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-23. Port Interrupt Enable Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
Access: User read/write
1
7-0
PIEx7-0
Port Interrupt Enable — Activate pin interrupt (KWU)
This bit enables or disables the edge sensitive pin interrupt on the associated pin. An interrupt can be generated if
the pin is operating in input or output mode when in use as general-purpose I/O or a related peripheral function.
1 Interrupt is enabled
0 Interrupt is disabled (interrupt flag masked)
2.3.3.7 Port Interrupt Flag Register
Address 0x027F PIF1AD
0x026F PIFL
76543210
R
PIFx7 PIFx6 PIFx5 PIFx4 PIFx3 PIFx2 PIFx1 PIFx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-17. Port Interrupt Flag Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime, write 1 to clear
Access: User read/write
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
72 NXP Semiconductors
Page 73

Table 2-24. Port Interrupt Flag Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
7-0
PIFx7-0
Port Interrupt Flag — Signal pin event (KWU)
This flag asserts after a valid active edge was detected on the related pin (see Section 2.4.7.2, “Pin Interrupts and
Key-Wakeup (KWU)”). This can be a rising or a falling edge based on the state of the polarity select register. An
interrupt will occur if the associated interrupt enable bit is set.
Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 Active edge on the associated bit has occurred
0 No active edge occurred
2.3.3.8 Reduced Drive Register
Address 0x025B RDRP Access: User read/write
76543210
R
RDRx7 RDRx6 RDRx5 RDRx4 RDRx3 RDRx2 RDRx1 RDRx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-18. Reduced Drive Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-25. Reduced Drive Register Field Descriptions
1
Field Description
7-0
RDRx7-0
Reduced Drive Register — Select reduced drive for output pin
This bit configures the drive strength of the associated output pin as either full or reduced. If a pin is used as input
this bit has no effect. The reduced drive function is independent of which function is being used on the pin.
1 Reduced drive selected
0 Full drive strength enabled
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 73
Page 74

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.3.9 Wired-Or Mode Register
Address 0x024E WOMS Access: User read/write
76543210
R
WOMx7 WOMx6 WOMx5 WOMx4 WOMx3 WOMx2 WOMx1 WOMx0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-19. Wired-Or Mode Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-26. Wired-Or Mode Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7-0
WOMx7-0
Wired-Or Mode register — Enable open-drain output
This bit configures an output pin as wired-or. If enabled the output is driven active-low only (open drain) while the
active high drive is disabled. This allows a multi-point connection of several serial modules. The bit has no influence
on pins used as inputs.
1 Output buffer operates as open-drain output
0 Output buffer operates as push-pull output
2.3.3.10 PIM Reserved Register
1
Address (any reserved) Access: User read
76543210
R00000000
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-20. PIM Reserved Register
1
Read: Always reads 0x00
Write: Unimplemented
2.3.4 PIM Generic Register Exceptions
This section lists registers with deviations from the generic description in one or more register bits.
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
74 NXP Semiconductors
Page 75

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.4.1 Port P Over-Current Protection Enable Register (PPOCPE)
Address 0x001D Access: User read/write
76543210
R
000000
OCPEP2 OCPEP0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-21. Port P Over -Current Protection Enable Register (PPOCPE)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-27. PPOCPE Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
OCPEP2
6
OCPEP0
Over-Current Protection Enable Port P 2 — Activate over-current detector on PP2 (refer to 2.5.3, “Over-Current
Protection on PP2 and PP0)
1 PP2 over-current detector enabled
0 PP2 over-current detector disabled
Over-Current Protection Enable Port P 0 — Activate over-current detector on PP0(refer to 2.5.3, “Over-Current
Protection on PP2 and PP0)
1 PP0 over-current detector enabled
0 PP0 over-current detector disabled
1
2.3.4.2 Port P Interrupt Enable Register (PIEP)
Address 0x025E PIEP Access: User read/write
76543210
R
OCIEP2 OCIEP0 PIEP5 PIEP4 PIEP3 PIEP2 PIEP1 PIEP0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-22. Port P Interrupt Enable Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 75
Page 76

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-28. PIEP Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
OCIEP2
6
OCIEP0
5-0
PIEP5-0
Over-Current Interrupt Enable —
This bit enables or disables the over-current interrupt on PP2.
1 PP2 over-current interrupt enabled
0 PP2 over-current interrupt disabled (interrupt flag masked)
Over-Current Interrupt Enable —
This bit enables or disables the over-current interrupt on PP0.
1 PP0 over-current interrupt enabled
0 PP0 over-current interrupt disabled (interrupt flag masked)
Port Interrupt Enable — Activate pin interrupt (KWU)
This bit enables or disables the edge sensitive pin interrupt on the associated pin. An interrupt can be generated if
the pin is operating in input or output mode when in use with the general-purpose or related peripheral function.
1 Interrupt is enabled
0 Interrupt is disabled (interrupt flag masked)
2.3.4.3 Port P Interrupt Flag Register (PIFP)
Address 0x025F PIFP Access: User read/write
76543210
R
OCIFP2 OCIFP0 PIFP5 PIFP4 PIFP3 PIFP2 PIFP1 PIFP0
W
Reset00000000
1
Figure 2-23. Port P Interrupt Flag Register
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime, write 1 to clear
Table 2-29. PIFP Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
OCIFP2
Over-Current Interrupt Flag —
This flag asserts if an over-current condition is detected on PP2 (Section 2.4.7.3, “Over-Current Interrupt and
Protection”). Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 PP2 over-current event occurred
0 No PP2 over-current event occurred
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
76 NXP Semiconductors
Page 77

Table 2-29. PIFP Register Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
6
OCIFP0
Over-Current Interrupt Flag —
This flag asserts if an over-current condition is detected on PP0 (Section 2.4.7.3, “Over-Current Interrupt and
Protection”). Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 PP0 over-current event occurred
0 No PP0 over-current event occurred
5-0
PIFP5-0
Port Interrupt Flag — Signal pin event (KWU)
This flag asserts after a valid active edge was detected on the related pin (see Section 2.4.7.2, “Pin Interrupts and
Key-Wakeup (KWU)”). This can be a rising or a falling edge based on the state of the polarity select register. An
interrupt will occur if the associated interrupt enable bit is set.
Writing a logic “1” to the corresponding bit field clears the flag.
1 Active edge on the associated bit has occurred
0 No active edge occurred
2.3.4.4 Port L ADC Connection Enable Register (PTAENL)
Address 0x0265 Access: User read/write
76543210
R 0 0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-24. Port L ADC Connection Enable Register (PTAENL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
PTAENL5 PTAENL4 PTAENL3 PTAENL2 PTAENL1 PTAENL0
1
Table 2-30. PTAENL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTAENL
5-0
Port L ADC Connection Enable —
These bits enable the analog signal link to an ADC channel. If set to 1 the analog input function takes precedence
over the digital input in run mode by disabling the input buffer unless overridden by PTTEL=1.
Note: When enabling the resistor paths to ground by setting PTAENL=1, a delay of t
be accounted for.
1 ADC connection enabled
0 ADC connection disabled
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
UNC_HVI
+ two bus cycles must
NXP Semiconductors 77
Page 78

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.4.5 Port L ADC Direct Register (PTADIRL)
Address 0x0266 Access: User read/write
76543210
R 0 0
PTADIRL5 PTADIRL4 PTADIRL3 PTADIRL2 PTADIRL1 PTADIRL0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-25. Port L ADC Direct Register (PTADIRL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-31. PTADIRL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTADIRL
5-0
Port L ADC Direct Connection —
This bit connects the analog input signal directly to the ADC channel, bypassing the voltage divider. This bit takes
effect only in analog mode (PTAENL=1).
1 Input pin directly connected to ADC channel
0 Input voltage divider active on analog input to ADC channel
2.3.4.6 Port L ADC Bypass Register (PTABYPL)
1
Address 0x0267 Access: User read/write
76543210
R 0 0
PTABYPL5 PTABYPL4 PTABYPL3 PTABYPL2 PTABYPL1 PTABYPL0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-26. Port L ADC Bypass Register (PTABYPL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-32. PTABYPL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTABYPL
5-0
Port L ADC Connection Bypass —
This bit bypasses and powers down the impedance converter stage in the signal path from the analog input pin to
the ADC channel input. This bit takes effect only if using direct input connection to the ADC channel (PTADIRL=1).
1 Impedance converter bypassed
0 Impedance converter used
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
78 NXP Semiconductors
Page 79

2.3.4.7 Port L Pull Select Register (PTPSL)
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Address 0x0268 Access: User read/write
76543210
R 0 0
PTPSL5 PTPSL4 PTPSL3 PTPSL2 PTPSL1 PTPSL0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-27. Port L Pull Select Register (PTPSL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-33. PTPSL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTPSL5-0
Port L Pull Select —
This bit selects a pull device on the corresponding HVI pin in analog mode for open input detection. By default a
pulldown device is active as part of the input voltage divider. If this bit set to 1 and PTTEL=1 and not in stop mode a
pull-up to a level close to V
takes effect and overrides the weak pulldown device.
DDX
1 Pullup enabled
0 Pulldown enabled
2.3.4.8 Port L Input Register (PTIL)
1
Address 0x0269 Access: User read only
76543210
R 0 0 PTIL5 PTIL4 PTIL3 PTIL2 PTIL1 PTIL0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-28. Port L Input Register (PTIL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Never
Table 2-34. PTIL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTIL5-0
1
Refer to PTTEL bit description in Section 2.3.4.10, “Port L Test Enable Register (PTTEL) for an override condition.
Port Input Data Register Port L —
A read returns the synchronized input state if the related DIENL bit is set to 1 (digital mode) and the pin is not
used in analog mode (PTAENL=0). See Section 2.3.4.11, “Port L Input Divider Ratio Selection Register
(PIRL)”. A one is read in any other case
1
.
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 79
Page 80

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.4.9 Port L Digital Input Enable Register (DIENL)
Address 0x26A Access: User read/write
76543210
R0 0
DIENL5 DIENL4 DIENL3 DIENL2 DIENL1 DIENL0
W
Reset00000000
Figure 2-29. Port L Digital Input Enable Register (DIENL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-35. DIENL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
DIENL5-0
1
Refer to PTTEL bit description in Section 2.3.4.10, “Port L Test Enable Register (PTTEL) for an override condition.
Digital Input Enable Port L — Input buffer control
This bit controls the HVI digital input function. If set to 1 the input buffer is enabled and the HVI pin can be used with
the digital function. If the analog input function is enabled (PTAENL=1) the input buffer of the selected HVI pin is
forced off
1 Associated pin digital input is enabled if not used as analog input in run mode
0 Associated pin digital input is disabled
1
in run mode and is released to be active in stop mode only if DIENL=1.
1
1
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
80 NXP Semiconductors
Page 81

2.3.4.10 Port L Test Enable Register (PTTEL)
Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Address 0x026B Access: User read/write
76543210
R0 0
W
Reset00000000
PTTEL5 PTTEL4 PTTEL3 PTTEL2 PTTEL1 PTTEL0
Figure 2-30. Port L Test Enable Register (PTTEL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-36. PTTEL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PTTEL5-0
Port L Test Enable —
This bit forces the input buffer of the HVI pin active while using the analog function to support open input detection
in run mode. Refer to Section 2.5.4, “Open Input Detection on PL[5:0] (HVI)”). In stop mode this bit has no effect.
Note: In direct mode (PTADIRL=1) the digital input buffer is not enabled.
1 Input buffer enabled when used with analog function and not in direct mode (PTADIRL=0)
0 Input buffer disabled when used with analog function
NOTE
When enabling the resistor paths to ground by setting PTAENL=1 or, a
settling time of t
UNC_HVI
+ two bus cycles must be considered to let internal
nodes be loaded with correct values.
1
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 81
Page 82

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.3.4.11 Port L Input Divider Ratio Selection Register (PIRL)
Address 0x026C Access: User read/write
76543210
R0 0
W
Reset00000000
PIRL5 PIRL4 PIRL3 PIRL2 PIRL1 PIRL0
Figure 2-31. Port L Input Divider Ratio Selection Register (PIRL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-37. PIRL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PIRL5-0
Port L Input Divider Ratio Select —
This bit selects one of two voltage divider ratios for the associated HVI pin in analog mode.
1Ratio
0Ratio
L_HVI
H_HVI
selected
selected
2.3.4.12 Port L Polarity Select Register (PPSL)
Address 0x026D Access: User read/write
1
1
76543210
R 0 0
W
Reset00000000
PPSL5 PPSL4 PPSL3 PPSL2 PPSL1 PPSL0
Figure 2-32. Port L Polarity Select Register (PPSL)
1
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
Table 2-38. PPSL Register Field Descriptions
Field Description
5-0
PPSL5-0
Polarity Select —
This bit selects the polarity of the active interrupt edge on the associated HVI pin.
1 Rising edge selected
0 Falling edge selected
2.4 Functional Description
2.4.1 General
Each pin except BKGD and port L pins can act as general-purpose I/O. In addition each pin can act as an
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
82 NXP Semiconductors
Page 83

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
output or input of a peripheral module.
2.4.2 Registers
Table 2-39 lists the implemented configuration bits which are available on each port. These registers
except the pin input registers can be written at any time, however a specific configuration might not
become active. For example a pull-up device does not become active while the port is used as a push-pull
output.
Unimplemented bits read zero.
Table 2-39. Bit Indices of Implemented Register Bits per Port
Port Data
Register
Port PT PTI DDR PER PPS PIE PIF DIE RDR WOM
E1-0—1-0 PDPEE——————
S3-03-03-03-03-0————3-0
AD 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 —
T3-03-03-03-03-0—————
P 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 5-0 — 2-0 —
L—5-0——5-0
1
Digital input enable bits are located in the ADC register ATDDIEN
2
The PPSL bits select the active interrupt edge. They do not select the polarity of the pull device.
Port
Input
Register
Data
Direction
Register
Pull
Device
Enable
Register
Polarity
Select
Register
2
Port
Interrupt
Enable
Register
5-0 5-0 5-0 — —
Port
Interrupt
Flag
Register
Digital
Input
Enable
Register
1
Reduced
Drive
Register
——
Wired-Or
Mode
Register
2.4.3 Pin I/O Control
Figure 2-33 illustrates the data paths to and from an I/O pin. Input and output data can always be read via
the input register (PTIx, Section 2.3.3.2, “Port Input Register”) independent of if the pin is used as
general-purpose I/O or with a shared peripheral function. If the pin is configured as input (DDRx=0,
Section 2.3.3.3, “Data Direction Register”), the pin state can also be read through the data register (PTx,
Section 2.3.3.1, “Port Data Register”).
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 83
Page 84

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
PTx
DDRx
output enable
port enable
1
0
1
0
Pin
data out
Periph.
data in
Module
1
0
synch.
PTIx
Figure 2-33. Illustration of I/O pin functionality
The general-purpose data direction configuration can be overruled by an enabled peripheral function
shared on the same pin (Table 2-40). If more than one peripheral function is available and enabled at the
same time, the highest ranked module according the predefined priority scheme in the tables of
Section 2.2, External Signal Description will take precedence on the pin.
Table 2-40. Effect of Enabled Features
Enabled Feature
CPMU OSC EXTAL, XTAL CPMU takes control
TIMx output compare y IOCx_y Forced output
TIMx input capture y IOCx_y None
SCIx TXDx SCI takes control
PWM channel x PWMx Forced output
ADC channel x ANx None
AMPx AMPx, AMPPx, AMPMx None
IRQ IRQ Forced input
XIRQ XIRQ Forced input
LINPHY LPTXD Forced input
1
If applicable the appropriate routing configuration must be set for the signals to take effect on the pins.
2
DDR maintains control
3
To use the digital input function the related bit in Digital Input Enable Register (DIENAD) must be set to logic
level “1”.
1
Related Signal(s) Effect on I/O state
2
RXDx Forced input
2 3
2
LPRXD, LPDR1 Forced output
84 NXP Semiconductors
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 85

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.4.4 Pull Devices
I/O pins provide an individually selectable pull-up and pulldown device to avoid current consumption
caused by floating inputs. A pull device is enabled with pull enable register bits PERx (Section 2.3.3.4,
“Pull Device Enable Register”; 0=disabled; 1=enabled) and the pull direction is selected with port polarity
select register bits PPSx (Section 2.3.3.5, “Polarity Select Register”; 0=pullup, 1=pulldown). The reset
states are given in the individual register descriptions.
If a pin is used as an output either by setting the data direction bit (DDRx=1) or by an enabled peripheral
feature the pull devices are disabled in order to avoid increased current consumption.
If a pin is used as open-drain output (WOMx=1) then the pulldown device is disabled.
2.4.5 Increased Drive Strength on PP2, PP1 and PP0
Pins PP[2:0] feature increased current driving capability. For each pin the increased drive strength is the
state configured at reset. It can be reduced for each pin individually by setting the corresponding bit in the
RDRP register, Section 2.3.3.8, Reduced Drive Register. The drive strength is independent of the pin being
used by peripheral modules.
These pins can be used as general purpose I/O or due to increased current capability in output mode as
switchable external power supply (EVDD) pins for external devices like Hall sensors.
PP2 is a nominally 20mA capable pin on high and low sides. It includes an over-current flag and interrupt.
PP0 is a nominally 20mA capable pin, on both high and low sides, with low voltage drop on the high side
when configured for full drive. It includes an over-current flag and interrupt.
PP1 is a nominally 10mA capable pin, symmetric drive on high and low sides. It does not include
over-current flag/interrupt.
The device electrical parameter specification provides more detailed drive strength information.
2.4.6 High Side Drivers and Low Side Drivers
The High Side and Low Side Drivers are described in documentation dedicated to them. The PIM only
provides rerouting options, as listed in Table 2-9 and Table 2-10.
2.4.7 Interrupts
This section describes the interrupts generated by the PIM and their individual sources. Vector addresses
and interrupt priorities are defined at MCU level.
Table 2-41. PIM Interrupt Sources
Module Interrupt Sources Local Enable
XIRQ
IRQ IRQCR[IRQEN]
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 85
None
Page 86

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Table 2-41. PIM Interrupt Sources
Module Interrupt Sources Local Enable
Port AD pin interrupt PIE1AD[PIE1AD]
Port P pin interrupt PIEP[PIEP]
Port L pin interrupt PIEL[PIEL]
Port P over-current interrupt OCIEP[OCIEP]
2.4.7.1 XIRQ, IRQ Interrupts
The XIRQ pin allows requesting non-maskable interrupts after reset initialization. During reset, the X bit
in the condition code register is set and any interrupts are masked until software enables them.
The IRQ pin allows requesting asynchronous interrupts. The interrupt input is disabled out of reset. To
enable the interrupt the IRQCR[IRQEN] bit must be set and the I bit cleared in the condition code register.
The interrupt can be configured for level-sensitive or falling-edge-sensitive triggering. If IRQCR[IRQEN]
is cleared while an interrupt is pending, the request will de-assert.
Both interrupts are able to wake-up the device from stop mode. Means for glitch filtering are not provided
on these pins.
2.4.7.2 Pin Interrupts and Key-Wakeup (KWU)
Ports AD, P and L offer pin interrupt and key-wakeup capability. The related interrupt enable (PIE) as well
as the sensitivity to rising or falling edges (PPS) can be individually configured on a per-pin basis. All
bits/pins in a port share the same interrupt vector. Interrupts can be used with the pins configured as inputs
or outputs.
An interrupt is generated when a bit in the port interrupt flag (PIF) and its corresponding port interrupt
enable (PIE) are both set. The pin interrupt feature is also capable of waking up the CPU when it is in stop
or wait mode (key-wakeup).
A digital filter on each pin prevents short pulses from generating an interrupt. A valid edge on an input is
detected if 4 consecutive samples of a passive level are followed by 4 consecutive samples of an active
level. Else the sampling logic is restarted.
In run and wait mode the filters are continuously clocked by the bus clock. Pulses with a duration of
t
PULSE<nP_MASK/fbus
are assuredly filtered out while pulses with a duration of t
PULSE>nP_PASS/fbus
guarantee a pin interrupt.
In stop mode the filter clock is generated by an RC-oscillator. The minimum pulse length varies over
process conditions, temperature and voltage. Pulses with a duration of t
filtered out while pulses with a duration of t
PULSE>tP_PASS
guarantee a wakeup event (Figure 2-34).
PULSE<tP_MASK
are assuredly
Please refer to the “Pin Interrupt Characteristics” in the device electrical specification for pulse length
limits.
To reduce current consumption the RC oscillator is active only for a short phase following a detected edge
on any pin whose interrupt flag is not set (PIF[x]=0).
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
86 NXP Semiconductors
Page 87

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
Glitch, filtered out, no interrupt flag set
Valid pulse, interrupt flag set
uncertain
t
P_MASK
t
P_PASS
Figure 2-34. Interrupt Glitch Filter (here: active low level selected)
2.4.7.3 Over-Current Interrupt and Protection
In case of an over-current condition on high-current capable outputs, the related over-current interrupt flag
OCIF[OCIF] asserts. This flag generates an interrupt if the related enable bit OCIE[OCIE] is set.
An asserted flag immediately forces the related output independent of its driving source (port data register
or peripheral module) to its disabled level to protect the device. The flag must be cleared to re-enable the
driver.
2.4.8 High-Voltage Input
A high-voltage input (HVI) on port L has the following features:
• Input voltage range up to V
• Digital input function
• Pin interrupt and wakeup from stop capability
• Analog input function with selectable divider ratio and interface to ADC channels. Optional direct
input bypassing voltage divider and impedance converter. Able to wakeup from stop (pin interrupts
in run mode not available).
• Open input detection.
Figure 2-35 shows a block diagram of the HVI.
The term stop mode (STOP) is limited to voltage regulator operating in
reduced performance mode (RPM). Refer to device overview information.
LX
NOTE
NXP Semiconductors 87
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 88

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
PL (HVI)
PTIL
PIRL
ADC
R
EXT_HVI
PTAENL
V
HVI
(DIENL & (PTAENL | STOP))
Input Buffer
Impedance
Converter
PTAENL
& STOP
& PTADIRL
PTAENL
& STOP & PTADIRL
VDDX
& STOP
PTAENL
| (PTAENL & PTADIRL & PTTEL & STOP)
140K
400K
110K
440K
PTAENL
& PTTEL
& PTPSL
& PTADIRL
& PTABYPL
10K
& PTADIRL
& STOP
Figure 2-35. HVI Block Diagram
An external resistor R
EXT_HVI
NOTE
must always be connected to the
high-voltage input to protect the device pins from fast transients and to
Voltages up to V
to logic level. There are two modes, digital and analog, where these signals can be processed.
2.4.8.1 Digital Mode Operation
In digital mode (PTAENL=0) the input buffer is enabled if DIENL=1. The synchronized pin input state
determined at threshold level V
achieve the specified pin input divider ratios when using the HVI in analog
mode.
can be applied to the HVI pin. Internal voltage dividers scale the input signals down
HVI
TH_HVI
can be read in register PTIL. An interrupt flag (PIFL) is set on input
transitions if enabled (PIEL=1) and configured for the related edge polarity (PPSL). Wakeup from stop
mode is supported.
88 NXP Semiconductors
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 89

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2.4.8.2 Analog Mode Operation
In analog mode (PTAENL=1) the input buffer is forced off (except if HVI test enabled, PTTEL=1, and not
in direct mode PTADIRL=0). The voltage applied to a selectable HVI pin can be measured on its related
ADC channel (refer to device overview information for channel assignment). One of two input divider
ratios (Ratio
bypassed (PTADIRL=1). Additionally, in the latter case, the impedance converter in the ADC signal path
can be used or bypassed in direct input mode (PTABYPL).
In run mode the digital input buffer of the selected pin is disabled to avoid shoot-through current unless
PTTEL is set and PTDIRL is clear (the voltage divider is not bypassed). Thus pin interrupt can only be
generated if PTTEL is set and PTDIRL is clear.
In stop mode (RPM) the digital input buffer is enabled only if DIENL=1 to support wakeup functionality.
Table 2-42 shows the HVI input configuration depending on register bits and operation mode.
Mode DIENL PTAENL Digital Input Analog Input Resulting Function
Run 0 0 off off Input disabled (Reset state)
2
Stop
H_HVI
, Ratio
01off
1 0 enabled off Digital input, interrupt supported
11off
0 0 off off Input disabled, wakeup from stop not
01offoff
1 0 enabled off Digital input, wakeup from stop supported
1 1 enabled off
) can be chosen (PIRL) on the analog input or the voltage divider can be
L_HVI
Table 2-42. HVI Input Configurations
1
1
enabled Analog input, interrupt not supported
enabled Analog input, interrupt not supported
supported
1
Enabled if PTTEL=1 & PTADIRL=0)
2
The term “stop mode” is limited to the voltage regulator operating in reduced performance mode (RPM) refer to “Low Power
Modes” section in device overview. In any other case the HVI configuration defaults to “run mode”.
2.5 Initialization and Application Information
2.5.1 Port Data and Data Direction Register writes
It is not recommended to write PORTx/PTx and DDRx in a word access. When changing the register pins
from inputs to outputs, the data may have extra transitions during the write access. Initialize the port data
register before enabling the outputs.
2.5.2 SCI Baud Rate Detection
The baud rate for SCI0 can be determined by using a timer channel to measure the data rate on the related
RXD signal.
1. Establish the link: set MODRR2[MODRR27]=1 to route TIM1 input capture channel 1 to internal
RXD0 signal of SCI0.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 89
Page 90

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
2. Determine pulse width of incoming data: Configure TIM1 input capture channel 1 to measure time
between incoming signal edges.
2.5.3 Over-Current Protection on PP2 and PP0
Pins PP2 and PP0 can be used as general-purpose I/O or due to increased current capability in output mode
as a switchable external power supply (EVDD) pins for external devices like Hall sensors.
An over-current monitor is implemented to protect the controller from short circuits or excess currents on
the output which can only arise if the pin is configured for full drive. Although the full drive current is
available on the high and low side, the protection is only available on the high side when sourcing current
from EVDD . There is also no protection to voltages higher than V
To power up the over-current monitor set the related OCPE bit.
In stop mode the over-current monitor is disabled for power saving. The increased current capability
cannot be maintained to supply the external device. Therefore when using the pin as power supply the
external load must be powered down prior to entering stop mode by driving the output low.
DDX
.
An over-current condition is detected if the output current level exceeds the threshold I
in run mode.
OCD
The output driver is immediately forced low and the over-current interrupt flag OCIF asserts. Refer to
Section 2.4.7.3, “Over-Current Interrupt and Protection”.
2.5.4 Open Input Detection on PL[5:0] (HVI)
The connection of an external pull device on a high-voltage input can be validated by using the built-in
pull functionality of the HVI. Depending on the application type an external pulldown circuit can be
detected with the internal pull-up device whereas an external pull-up circuit can be detected with the
internal pulldown device which is part of the input voltage divider.
Note that the following procedures make use of a function that overrides the automatic disable mechanism
of the digital input buffer when using the HVI in analog mode. Make sure to switch off the override
function when using the HVI in analog mode after the check has been completed.
2.5.4.1 External pulldown device (Figure 2-36):
1. Enable analog function on HVI in non-direct mode (PTAENL=1, PTADIRL=0)
2. Select internal pull-up device on HVI (PTPSL=1)
3. Enable function to force input buffer active on HVI in analog mode (PTTEL=1)
4. Verify PTIL=0 for a connected external pulldown device; read PTIL=1 for an open input
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
90 NXP Semiconductors
Page 91

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
HVI
140K
400K
VDDX
Digital in
110K / 550K
min. 1/4 * V
DDX
10K
PIRL=0 / PIRL=1
HV Supply
HVI
140K
510K / 950K
Digital in
max. 17/22 * V
HVI
(PIRL=0)
PIRL=0 / PIRL=1
max. 19/22 * V
HVI
(PIRL=1)
10K
HV Supply
Figure 2-36. Digital Input Read with Pullup Enabled
2.5.4.2 External pull-up device (Figure 2-37):
1. Enable analog function on HVI in non-direct mode (PTAENL=1, PTADIRL=0)
2. Select internal pulldown device on HVI (PTPSL=0)
3. Enable function to force input buffer active on HVI in analog mode (PTTEL=1)
4. Verify PTIL=1 for a connected external pull-up device; read PTIL=0 for an open input
Figure 2-37. Digital Input Read with Pulldown Enabled
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 91
Page 92

Port Integration Module (S12VRPPIMV1)
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
92 NXP Semiconductors
Page 93

Chapter 3 S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
Table 3-1. Revision History Table
Rev. No.
(Item No.)
01.04 26-Apr 2016 Added S12VRP64
Date
(Submitted By)
Sections
Affected
Substantial Change(s)
3.1 Introduction
The S12GMMC module controls the access to all internal memories and peripherals for the CPU12 and
S12SBDM module. It regulates access priorities and determines the address mapping of the on-chip
resources. Figure 3-1 shows a block diagram of the S12GMMC module.
3.1.1 Glossary
Table 3-2. Glossary Of Terms
Term Definition
Local Addresses Address within the CPU12’s Local Address Map (Figure 3-12)
Global Address Address within the Global Address Map (Figure 3-12)
Aligned Bus Access Bus access to an even address.
Misaligned Bus Access Bus access to an odd address.
NS Normal Single-Chip Mode
SS Special Single-Chip Mode
Unimplemented Address Ranges Address ranges which are not mapped to any on-chip resource.
NVM Non-volatile Memory; P-Flash or D-Flash
IFR NVM Information Row. Refer to FTMRG Block Guide
P-Flash Program Flash. Refer to FTMRG Block Guide
D-Flash Data Flash. Refer to FTMRG Block Guide
3.1.2 Overview
The S12GMMC connects the CPU12’s and the S12SBDM’s bus interfaces to the MCU’s on-chip resources
(memories and peripherals). It arbitrates the bus accesses and determines all of the MCU’s memory maps.
Furthermore, the S12GMMC is responsible for constraining memory accesses on secured devices and for
selecting the MCU’s functional mode.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 93
Page 94

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
3.1.3 Features
The main features of this block are:
• Paging capability to support a global 256 KByte memory address space
• Bus arbitration between the masters CPU12, S12SBDM to different resources.
• MCU operation mode control
• MCU security control
• Generation of system reset when CPU12 accesses an unimplemented address (i.e., an address
which does not belong to any of the on-chip modules) in single-chip modes
3.1.4 Modes of Operation
The S12GMMC selects the MCU’s functional mode. It also determines the devices behavior in secured
and unsecured state.
3.1.4.1 Functional Modes
Two functional modes are implemented on devices of the S12VRP product family:
• Normal Single Chip (NS)
The mode used for running applications.
• Special Single Chip Mode (SS)
A debug mode which causes the device to enter BDM Active Mode after each reset. Peripherals
may also provide special debug features in this mode.
3.1.4.2 Security
S12VRP devices can be secured to prohibit external access to the on-chip flash. The S12GMMC module
determines the access permissions to the on-chip memories in secured and unsecured state.
3.1.5 Block Diagram
Figure 3-1 shows a block diagram of the S12GMMC.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
94 NXP Semiconductors
Page 95

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
CPU
BDM
Target Bus Controller
DBG
MMC
Address Decoder & Priority
Peripherals
P-FlashD-Flash RAM
Figure 3-1. S12GMMC Block Diagram
3.2 External Signal Description
The S12GMMC uses two external pins to determine the devices operating mode: RESET and MODC
(Figure 3-3) See Device User Guide (DUG) for the mapping of these signals to device pins.
Table 3-3. External System Pins Associated With S12GMMC
Pin Name Pin Functions Description
RESET
(See Section
Device Overview)
MODC
(See Section
Device Overview)
3.3 Memory Map and Registers
3.3.1 Module Memory Map
RESET
MODC
The RESET pin is used the select the MCU’s operating mode.
The MODC pin is captured at the rising edge of the RESET
value determines the MCU’s operating mode.
pin. The captured
A summary of the registers associated with the S12GMMC block is shown in Figure 3-2. Detailed
descriptions of the registers and bits are given in the subsections that follow.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 95
Page 96

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
Address
0x000A Reserved R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x000B MODE R
0x0010 Reserved R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x0011 DIRECT R
0x0012 Reserved R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x0013 MMCCTL1 R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0x0014 Reserved R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Register
Name
Bit 765432 1Bit 0
W
MODC
W
W
DP15 DP14 DP13 DP12 DP11 DP10 DP9 DP8
W
W
W
W
00000 0 0
NVMRES
0x0015 PPAGE R 0 0 0 0
W
0x0016-
0x0017
ReservedR000000 0 0
W
= Unimplemented or Reserved
PIX3 PIX2 PIX1 PIX0
Figure 3-2. MMC Register Summary
3.3.2 Register Descriptions
This section consists of the S12GMMC control register descriptions in address order.
3.3.2.1 Mode Register (MODE)
Address: 0x000B
76543210
R
MODC
W
Reset MODC
1. External signal (see Table 3-3).
1
0000000
0000000
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Figure 3-3. Mode Register (MODE)
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
96 NXP Semiconductors
Page 97

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
Normal
Single-Chip
1
Special
Single-Chip
0
(SS)
RESET
(NS)
1
01
Read: Anytime.
Write: Only if a transition is allowed (see Figure 3-4).
The MODC bit of the MODE register is used to select the MCU’s operating mode.
Table 3-4. MODE Field Descriptions
Field Description
7
MODC
Mode Select Bit — This bit controls the current operating mode during RESET
mode pin MODC determines the operating mode during RESET
into the respective register bit after the RESET signal goes inactive (see Figure 3-4).
Write restrictions exist to disallow transitions between certain modes. Figure 3-4 illustrates all allowed mode
changes. Attempting non authorized transitions will not change the MODE bit, but it will block further writes to
the register bit except in special modes.
Write accesses to the MODE register are blocked when the device is secured.
low (active). The state of the pin is registered
high (inactive). The external
Figure 3-4. Mode Transition Diagram when MCU is Unsecured
3.3.2.2 Direct Page Register (DIRECT)
Address: 0x0011
76543210
R
DP15 DP14 DP13 DP12 DP11 DP10 DP9 DP8
W
Reset00000000
Figure 3-5. Direct Register (DIRECT)
Read: Anytime
Write: anytime in special SS, write-once in NS.
This register determines the position of the 256 Byte direct page within the memory map.It is valid for both
global and local mapping scheme.
NXP Semiconductors 97
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 98

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
Bit15
Bit0
Bit7
CPU Address [15:0]
Bit8
DP [15:8]
Table 3-5. DIRECT Field Descriptions
Field Description
7–0
DP[15:8]
Direct Page Index Bits 15–8 — These bits are used by the CPU when performing accesses using the direct
addressing mode. These register bits form bits [15:8] of the local address (see Figure 3-6).
Figure 3-6. DIRECT Address Mapping
Example 3-1. This example demonstrates usage of the Direct Addressing Mode
MOVB #$04,DIRECT ;Set DIRECT register to 0x04. From this point on, all memory
;accesses using direct addressing mode will be in the local
;address range from 0x0400 to 0x04FF.
LDY <$12 ;Load the Y index register from 0x0412 (direct access).
3.3.2.3 MMC Control Register (MMCCTL1)
Address: 0x0013
76543210
R0000000
W
Reset00000000
= Unimplemented or Reserved
NVMRES
Figure 3-7. MMC Control Register (MMCCTL1)
Read: Anytime.
Write: Anytime.
The NVMRES bit maps 16k of internal NVM resources (see Section FTMRG) to the global address space
0x04000 to 0x07FFF.
Table 3-6. MODE Field Descriptions
Field Description
0
NVMRES
Map internal NVM resources into the global memory map
Write: Anytime
This bit maps internal NVM resources into the global address space.
0 Program flash is mapped to the global address range from 0x04000 to 0x07FFF.
1 NVM resources are mapped to the global address range from 0x04000 to 0x07FFF.
98 NXP Semiconductors
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
Page 99

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
Bit14
Bit0
Address [13:0]
PPAGE Register [3:0]
Global Address [17:0]
Bit13
Bit17
Address: CPU Local Address
or BDM Local Address
3.3.2.4 Program Page Index Register (PPAGE)
Address: 0x0015
76543210
R0 0 0 0
W
Reset00001110
Figure 3-8. Program Page Index Register (PPAGE)
Read: Anytime
Write: Anytime
The four index bits of the PPAGE register select a 16K page in the global memory map (Figure 3-12). The
selected 16K page is mapped into the paging window ranging from local address 0x8000 to 0xBFFF.
Figure 3-9 illustrates the translation from local to global addresses for accesses to the paging window. The
CPU has special access to read and write this register directly during execution of CALL and RTC
instructions.
PIX3 PIX2 PIX1 PIX0
Figure 3-9. PPAGE Address Mapping
NOTE
Writes to this register using the special access of the CALL and RTC
instructions will be complete before the end of the instruction execution.
Table 3-7. PPAGE Field Descriptions
Field Description
3–0
PIX[3:0]
Program Page Index Bits 3–0 — These page index bits are used to select which of the 256 flash array pages
is to be accessed in the Program Page Window.
The fixed 16KB page from 0x0000 to 0x3FFF is the page number 0xC. Parts of this page are covered by
Registers, D-Flash and RAM space. See SoC Guide for details.
The fixed 16KB page from 0x4000–0x7FFF is the page number 0xD.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
NXP Semiconductors 99
Page 100

S12G Memory Map Controller (S12GMMCV1)
The reset value of 0xE ensures that there is linear P-Flash space available between addresses 0x0000 and
0xFFFF out of reset.
The fixed 16KB page from 0xC000-0xFFFF is the page number 0xF.
3.4 Functional Description
The S12GMMC block performs several basic functions of the S12VRP sub-system operation: MCU
operation modes, priority control, address mapping, select signal generation and access limitations for the
system. Each aspect is described in the following subsections.
3.4.1 MCU Operating Modes
• Normal single chip mode
This is the operation mode for running application code. There is no external bus in this mode.
• Special single chip mode
This mode is generally used for debugging operation, boot-strapping or security related operations.
The active background debug mode is in control of the CPU code execution and the BDM firmware
is waiting for serial commands sent through the BKGD pin.
3.4.2 Memory Map Scheme
3.4.2.1 CPU and BDM Memory Map Scheme
The BDM firmware lookup tables and BDM register memory locations share addresses with other
modules; however they are not visible in the memory map during user’s code execution. The BDM
memory resources are enabled only during the READ_BD and WRITE_BD access cycles to distinguish
between accesses to the BDM memory area and accesses to the other modules. (Refer to BDM Block
Guide for further details).
When the MCU enters active BDM mode, the BDM firmware lookup tables and the BDM registers
become visible in the local memory map in the range 0xFF00-0xFFFF (global address 0x3_FF00 0x3_FFFF) and the CPU begins execution of firmware commands or the BDM begins execution of
hardware commands. The resources which share memory space with the BDM module will not be visible
in the memory map during active BDM mode.
Please note that after the MCU enters active BDM mode the BDM firmware lookup tables and the BDM
registers will also be visible between addresses 0xBF00 and 0xBFFF if the PPAGE register contains value
of 0x0F.
3.4.2.1.1 Expansion of the Local Address Map
Expansion of the CPU Local Address Map
The program page index register in S12GMMC allows accessing up to 256KB of address space in the
global memory map by using the four index bits (PPAGE[3:0]) to page 16x16 KB blocks into the program
page window located from address 0x8000 to address 0xBFFF in the local CPU memory map.
MC9S12VRP Family Reference Manual Rev. 1.3
100 NXP Semiconductors
 Loading...
Loading...