NXP Semiconductors ColdFire MCF52235, ColdFire MCF52230, ColdFire MCF52231, ColdFire MCF52233, ColdFire MCF52234 Reference Manual
Page 1

MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated
Microcontroller Reference Manual
Devices Supported:
MCF52230
MCF52231
MCF52233
MCF52234
MCF52235
Document Number:
MCF52235RM
Rev. 0
04/2006
Page 2

How to Reach Us:
Home Page:
www.freescale.com
E-mail:
support@freescale.com
USA/Europe or Locations Not Listed:
Freescale Semiconductor
Technical Information Center, CH370
1300 N. Alma School Road
Chandler, Arizona 85224
+1-800-521-6274 or +1-480-768-2130
support@freescale.com
Europe, Middle East, and Africa:
Freescale Halbleiter Deutschland GmbH
Technical Information Center
Schatzbogen 7
81829 Muenchen, Germany
+44 1296 380 456 (English)
+46 8 52200080 (English)
+49 89 92103 559 (German)
+33 1 69 35 48 48 (French)
support@freescale.com
Japan:
Freescale Semiconductor Japan Ltd.
Headquarters
ARCO Tower 15F
1-8-1, Shimo-Meguro, Meguro-ku,
Tokyo 153-0064, Japan
0120 191014 or +81 3 5437 9125
support.japan@freescale.com
Asia/Pacific:
Freescale Semiconductor Hong Kong Ltd.
Technical Information Center
2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate
Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
+800 26668334
support.asia@freescale.com
For Literature Requests Only:
Freescale Semiconductor Literature Distribution Center
P.O. Box 5405
Denver, Colorado 80217
1-800-441-2447 or 303-675-2140
Fax: 303-675-2150
LDCForFreescaleSemiconductor@hibbertgroup.com
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and
software implementers to use Freescale Semiconductor products. There are
no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design or
fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the
information in this document.
Freescale Semiconductor reserves the right to make changes without further
notice to any products herein. Freescale Semiconductor makes no warranty,
representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for any
particular purpose, nor does Freescale Semiconductor assume any liability
arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and specifically
disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or
incidental damages. “Typical” parameters that may be provided in Freescale
Semiconductor data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different
applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating
parameters, including “Typicals”, must be validated for each customer
application by customer’s technical exper ts. Freescale Semiconductor does
not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Freescale Semiconductor products are not designed, intended, or authorized
for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body,
or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other
application in which the failure of the Freescale Semico nductor product could
create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer
purchase or use Freescale Semicondu ctor products for any such unintended
or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Freescale
Semiconductor and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and
distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of
personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized
use, even if such claim alleges that Freescale Semiconductor was negligent
regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Freescale™ and the Freescale logo are trademarks of Freescale
Semiconductor, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of their
respective owners.
© Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. 2006. All rights reserved.
Document Number: MCF52235RM
Rev. 0
04/2006
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1
Overview
1.1 MCF52235 Family Configurations ...................................................................................................2
1.2 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................2
1.3 Part Numbers and Packaging ............................................................................................................4
1.4 Features .............................................................................................................................................4
Chapter 2
Signal Descriptions
2.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
2.2 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................1
2.3 Reset Signals .....................................................................................................................................8
2.4 PLL and Clock Signals ......................................................................................................................8
2.5 Mode Selection ..................................................................................................................................8
2.6 External Interrupt Signals ..................................................................................................................8
2.7 Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI) .......................................................................................9
2.8 Fast Ethernet Controller PHY Signals ............................................................................................10
2.9 I2C I/O Signals ................................................................................................................................10
2.10 UART Module Signals ....................................................................................................................11
2.11 DMA Timer Signals ........................................................................................................................11
2.12 ADC Signals ....................................................................................................................................11
2.13 General Purpose Timer Signals .......................................................................................................12
2.14 Pulse Width Modulator Signals .......................................................................................................12
2.15 Debug Support Signals ....................................................................................................................12
2.16 EzPort Signal Descriptions ..............................................................................................................13
2.17 Power and Ground Pins ...................................................................................................................14
Chapter 3
ColdFire Core
3.1 Processor Pipelines ............................................................................................................................1
3.2 Memory Map/Register Description ...................................................................................................2
3.3 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA_A+) .............................................................................................8
3.4 Exception Processing Overview ........................................................................................................8
3.5 Exception Stack Frame Definition ..................................................................................................10
3.6 Processor Exceptions .......................................................................................................................11
3.7 Instruction Execution Timing ..........................................................................................................18
3.8 Standard One Operand Instruction Execution Times ......................................................................20
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor iii
Preliminary
Page 4

3.9 Standard Two Operand Instruction Execution Times ......................................................................21
3.10 Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times ...................................................................................22
3.11 EMAC Instruction Execution Times ...............................................................................................23
3.12 Branch Instruction Execution Times ...............................................................................................24
Chapter 4
Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
4.1 Multiply-Accumulate Unit ................................................................................................................1
4.2 Introduction to the MAC ...................................................................................................................2
4.3 General Operation .............................................................................................................................2
4.4 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................5
4.5 EMAC Instruction Set Summary ....................................................................................................11
Chapter 5
Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
5.1 CAU Registers ...................................................................................................................................1
5.2 CAU Operation .................................................................................................................................2
5.3 CAU Commands ...............................................................................................................................2
5.4 CAU Equate Values ...........................................................................................................................7
Chapter 6
Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
6.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................1
6.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................2
6.3 Modes of Operation ...........................................................................................................................2
6.4 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................3
6.5 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................11
6.6 Initialization/Application Information ............................................................................................12
Chapter 7
Clock Module
7.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
7.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
7.3 Modes of Operation ...........................................................................................................................1
7.4 Low-power Mode Operation .............................................................................................................2
7.5 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................2
7.6 Signal Descriptions ...........................................................................................................................4
7.7 Memory Map and Registers ..............................................................................................................5
7.8 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................11
Chapter 8
Real Time Clock
8.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
8.2 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................2
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
iv Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 5

8.3 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................12
8.4 Initialization/Application Information ............................................................................................13
Chapter 9
Power Management
9.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
9.2 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................1
9.3 IPS Bus Timeout Monitor ...............................................................................................................10
9.4 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................11
Chapter 10
Reset Controller Module
10.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
10.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
10.3 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................1
10.4 Signals ...............................................................................................................................................2
10.5 Memory Map and Registers ..............................................................................................................2
10.6 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................5
Chapter 11
Static RAM (SRAM)
11.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
11.2 Memory Map/Register Description ...................................................................................................1
11.3 Initialization/Application Information ..............................................................................................3
Chapter 12
Chip Configuration Module (CCM)
12.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
12.2 External Signal Descriptions .............................................................................................................2
12.3 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................2
12.4 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................5
12.5 Reset ..................................................................................................................................................6
Chapter 13
System Control Module (SCM)
13.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
13.2 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................1
13.3 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
13.4 Memory Map and Register Definition ..............................................................................................2
13.5 Register Descriptions ........................................................................................................................3
13.6 Internal Bus Arbitration ..................................................................................................................11
13.7 System Access Control Unit (SACU) .............................................................................................14
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor v
Preliminary
Page 6

Chapter 14
General Purpose I/O Module
14.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
14.2 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................2
14.3 Features .............................................................................................................................................3
14.4 Signal Descriptions ...........................................................................................................................3
14.5 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................4
14.6 Register Descriptions ........................................................................................................................6
14.7 Ports Interrupts ................................................................................................................................15
Chapter 15
Interrupt Controller Module
15.1 68K/ColdFire Interrupt Architecture Overview ................................................................................1
15.2 Memory Map .....................................................................................................................................4
15.3 Register Descriptions ........................................................................................................................5
15.4 Low-Power Wakeup Operation .......................................................................................................18
Chapter 16
Edge Port Module (EPORT)
16.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
16.2 Low-Power Mode Operation .............................................................................................................2
16.3 Interrupt/GPIO Pin Descriptions .......................................................................................................2
16.4 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................3
Chapter 17
ColdFire Flash Module (CFM)
17.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
17.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................3
17.3 Memory Map and Register Definition ..............................................................................................3
17.4 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................14
Chapter 18
Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC)
18.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................1
18.2 Modes of Operation ...........................................................................................................................1
18.3 FEC Top-Level Functional Diagram .................................................................................................3
18.4 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................4
18.5 Programming Model .......................................................................................................................17
18.6 Buffer Descriptors ...........................................................................................................................42
Chapter 19
Ethernet Physical Transceiver (EPHY) Block Description
19.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
19.2 External Signal Descriptions .............................................................................................................3
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
vi Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 7

19.3 Memory Map and Register Descriptions ..........................................................................................5
19.4 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................21
Chapter 20
DMA Controller Module
20.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
20.2 M-bus Priority Level (MPL) .............................................................................................................4
20.3 DMA Transfer Overview ..................................................................................................................4
20.4 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................5
20.5 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................16
Chapter 21
EzPort
21.1 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
21.2 Modes of Operation ...........................................................................................................................1
21.3 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................2
21.4 Command Definition .........................................................................................................................3
21.5 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................7
21.6 Initialization/Application Information ..............................................................................................8
Chapter 22
Programmable Interrupt Timer Modules (PIT0–PIT1)
22.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
22.2 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................2
22.3 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................5
Chapter 23
General Purpose Timer Module (GPT)
23.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
23.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
23.3 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................2
23.4 Low-Power Mode Operation .............................................................................................................3
23.5 Signal Description .............................................................................................................................3
23.6 Memory Map and Registers ..............................................................................................................4
23.7 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................17
23.8 Reset ................................................................................................................................................21
23.9 Interrupts .........................................................................................................................................21
Chapter 24
DMA Timers (DTIM0–DTIM3)
24.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
24.2 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................2
24.3 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................8
24.4 Initialization/Application Information ..............................................................................................8
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor vii
Preliminary
Page 8

Chapter 25
Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
25.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
25.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................2
25.3 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................3
25.4 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................10
25.5 Initialization/Application Information ............................................................................................16
Chapter 26
UART Modules
26.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
26.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................3
26.3 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................4
26.4 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................18
Chapter 27
2
C Interface
I
27.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
27.2 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................1
27.3 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
27.4 I2C System Configuration .................................................................................................................3
27.5 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................7
27.6 I2C Programming Examples ............................................................................................................12
Chapter 28
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
28.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
28.2 Features .............................................................................................................................................1
28.3 Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................................1
28.4 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................2
28.5 Register Definitions .........................................................................................................................18
Chapter 29
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Module
29.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
29.2 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................2
29.3 Functional Description ....................................................................................................................12
Chapter 30
FlexCAN
30.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
30.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................5
30.3 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................5
30.4 Functional Overview .......................................................................................................................20
30.5 FlexCAN Initialization Sequence ....................................................................................................28
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
viii Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 9

Chapter 31
Debug Module
31.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
31.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................2
31.3 Real-Time Trace Support ..................................................................................................................3
31.4 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................6
31.5 Background Debug Mode (BDM) ...................................................................................................17
31.6 Real-Time Debug Support ...............................................................................................................37
31.7 Processor Status, DDATA Definition ..............................................................................................40
31.8 Freescale-Recommended BDM Pinout ...........................................................................................44
Chapter 32
IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port (JTAG)
32.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................1
32.2 External Signal Description ..............................................................................................................2
32.3 Memory Map/Register Definition .....................................................................................................4
32.4 Functional Description ......................................................................................................................6
32.5 Initialization/Application Information ............................................................................................10
Appendix A
Register Memory Map Quick Reference
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor ix
Preliminary
Page 10

MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
x Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 11

Chapter 1 Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the major features and functional components of the MCF52235
family of microcontrollers. The MCF52235 family is a highly integrated implementation of the ColdFire®
family of reduced instruction set computing (RISC) microcontrollers that also includes the MC52230,
MCF52231, MC52233 and MC52234 . The differences between these parts are summarized in Tab le 1-1.
This document is written from the perspective of the MC52235 .The MC52235 represents a family of
highly-integrated 32-bit microcontrollers based on the V2 ColdFire microarchitecture. Featuring up to 32
Kbytes of internal SRAM and 256 Kbytes of Flash memory, four 32-bit timers with DMA request
capability, a 4-channel DMA controller, fast Ethernet, a CAN module, an I2C™ module, 3 UARTs and a
queued SPI, the MC52235 family has been designed for general-purpose industrial control applications.
n enhanced multiply-accumulate unit (EMAC) and divider providing 56Drystone 2.1 MIPS at a frequency
up to 60MHz from internal Flash. On-chip modules include the following:
• V2 ColdFire core with enhanced multiply-accumulate unit (EMAC)
• Cryptographic Acceleration Unit (CAU)
• 32 Kbytes of internal SRAM
• 256 Kbytes of on-chip Flash memory
• Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC) with on-chip transceiver (ePHY)
• Three universal asynchronous receiver/transmitters (UARTs)
• Controller area network 2.0B (FlexCAN) module
• Inter-integrated circuit (I2C) bus controller
• 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
• Queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI) module
• Four-channel, 32-bit direct memory access (DMA) controller
• Four-channel, 32-bit input capture/output compare timers with optional DMA support
• Two 16-bit periodic interrupt timers (PITs)
• Programmable software watchdog timer
• Two interrupt controllers, each capable of handling up to 63 interrupt sources (126 total)
These devices are ideal for cost-sensitive applications requiring significant control processing for
connectivity, data buffering, and user interface, as well as signal processing in a variety of key markets
such as security, imaging, networking, gaming, and medical. This leading package of integration and high
performance allows fast time to market through easy code reuse and extensive third party tool support.
To locate any published errata or updates for this document, refer to the ColdFire products website at
http://www.freescale.com/coldfire.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-1
Preliminary
Page 12
Overview
1.1 MCF52235 Family Configurations
Table 1. MCF52235 Family Configurations
Module 52230 52231 52233 52234 52235
ColdFire Version 2 Core with EMAC (Enhanced
Multiply-Accumulate Unit)
System Clock 60 MHz
Performance (Dhrystone 2.1 MIPS) 56
Flash / Static RAM (SRAM) 128/32 Kbytes 128/32 Kbytes 256/32 Kbytes
Interrupt Controllers (INTC0/INTC1) x x x x x
Fast Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) x x x x x
Random Number Generator and Crypto
Acceleration Unit (CAU)
FlexCAN 2.0B Module - x - x x
Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC) with on-chip
interface (EPHY)
Four-channel Direct-Memory Access (DMA) x x x x x
Software Watchdog Timer (WDT) x x x x x
Programmable Interrupt Timer 2 2 2 2 2
Four-Channel General Purpose Timer x x x x x
32-bit DMA Timers 4 4 4 4 4
QSPI x x x x x
UART(s) 3 3 3 3 3
2
Cxxxxx
I
Eight/Four-channel 8/16-bit PWM Timer x x x x x
xxxxx
----x
xxxxx
General Purpose I/O Module (GPIO) x x x x x
Chip Configuration and Reset Controller Module x x x x x
Background Debug Mode (BDM) x x x x x
JTAG - IEEE 1149.1 Test Access Port
Package 80, 112-pin
1
The full debug/trace interface is available only on the 112- and 121-pin packages. A reduced debug
1
xxxxx
LQFP
80, 112-pin
LQFP
80, 112-pin
LQFP
121 MAPBGA
80, 112-pin
LQFP
121 MAPBGA
112-pin LQFP
121 MAPBGA
interface is bonded on the 80-pin package.
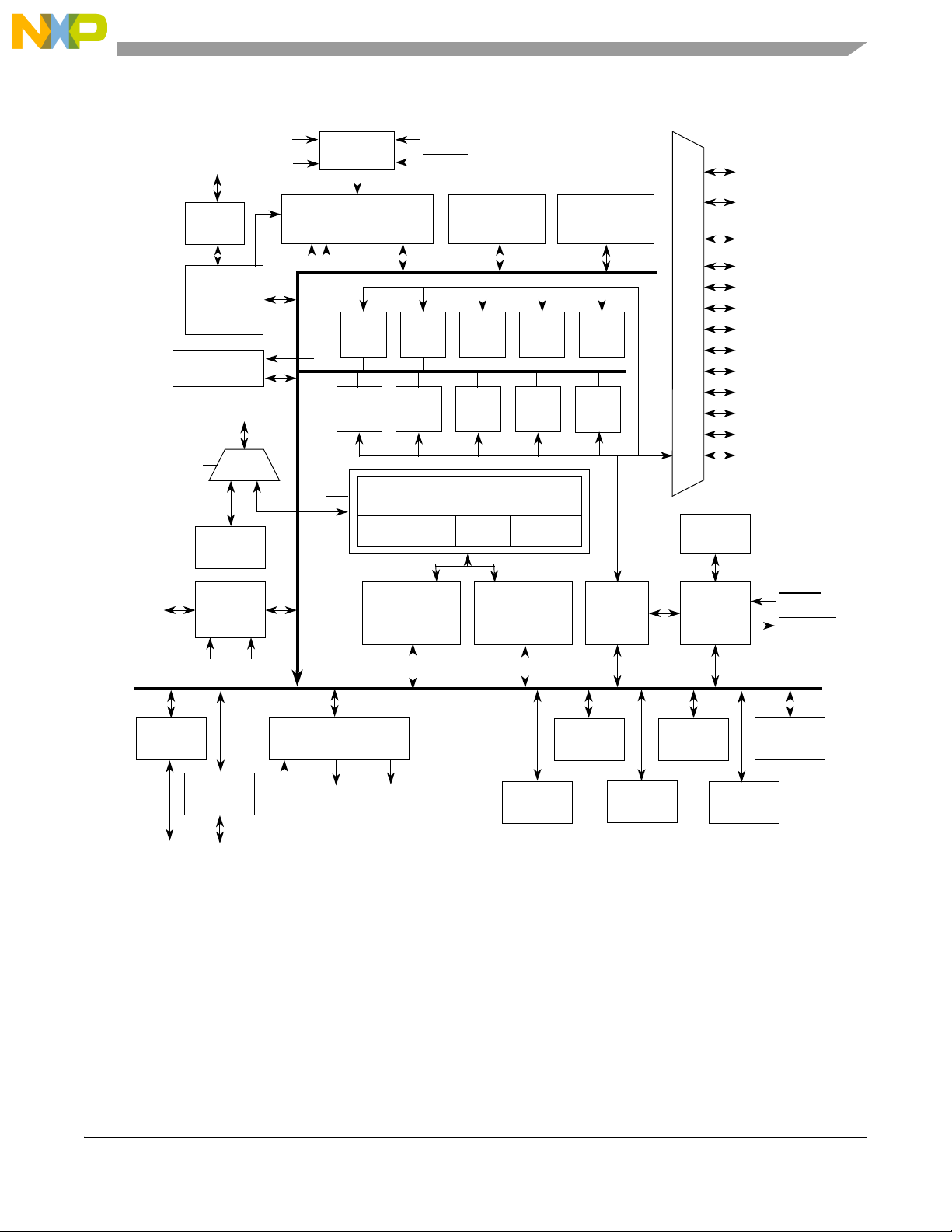
1.2 Block Diagram
The superset device in the MCF52235 family comes in a 112-leaded quad flat package (LQFP) and a 121
pin MAPBGA. Figure 1-1 shows a top-level block diagram of the MCF52235 .
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 13
Overview
EPHY_TX
EPHY_RX
JTAG_EN
EPHY
Fast
Ethernet
Controller
(FEC)
4 CH DMA
To/From PADI
MUX
JTAG
TAP
EzPD EzPCK
EzPQ
EzPort
EzPCS
Arbiter
UART
UART
0
1
DTIM0DTIM1DTIM2DTIM
V2 ColdFire CPU
OEP
IFP
Interrupt
Controller 1
UART
2
CAU
I2C
3
EMAC
Interrupt
Controller 2
QSPI
RTC
PADI – Pin Muxing
PMM
ICOCn
QSPI_DIN,
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_SCK,
QSPI_PCSn
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
UnTXD
UnRXD
UnRTS
UnCTS
DTINn/DTOUTn
CANRX
CANTX
PWMn
ADCAN[7:0]
V
RHVRL
Edge
Port 1
Edge
Port 2
EXTAL XTAL CLKOUT
To/From Interrupt Controller
32 Kbytes
SRAM
(4Kx16)x4
256 Kbytes
Flash
(32Kx16)x4
PLL
CLKGEN
RNGA
Figure 1-1. MCF52235 Block Diagram
PORTS
(GPIO)
FlexCAN
PIT0
PIT1
CIM
RSTIN
RSTOUT
PWM
GPT
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-3
Preliminary
Page 14
Overview
1.3 Part Numbers and Packaging
Table 1-2. Part Number Summary
Part Number Flash / SRAM Key Features Package Speed
MCF52230 128 Kbytes / 32 Kbytes 3 UARTs, I
MCF52231 128 Kbytes / 32 Kbytes 3 UARTs, I
MCF52233 256 Kbytes / 32 Kbytes 3 UARTs, I
MDCF52234 256 Kbytes / 32 Kbytes 3 UARTs, I
MCF52235 256 Kbytes / 32 Kbytes 3 UARTs, I
EPHY, DMA, 16-/32-bit/PWM Timers, CAN
Table 1-2 summarizes the features of the MCF52235 product family. Several speed/package options are
available to match cost- or performance-sensitive applications.
2
C, QSPI, A/D, FEC EPHY, DMA,
16-/32-bit/PWM Timers
2
C, QSPI, A/D, FEC EPHY, DMA,
16-/32-bit/PWM Timers, CAN
2
C, QSPI, A/D, FEC EPHY, DMA,
16-/32-bit/PWM Timers
2
C, QSPI, A/D, FEC, EPHY, DMA,
16-/32-bit/PWM Timers, CAN
2
C, QSPI, A/D, Crypto, FEC,
80-pin TQFP
112-pin LQFP
80-pin TQFP
112-pin LQFP
80-pin TQFP
112-pin LQFP
80-pin TQFP 112-pin LQFP 121 MAPBGA
112-pin LQFP 121 MAPBGA
60 MHz
60 MHz
60 MHz
60 MHz
60 MHz
1.4 Features
The MCF52235 family includes the following features:
• Version 2 ColdFire variable-length RISC processor core
— Static operation
— 32-bit address and data paths on-chip
— Up to 60 MHz processor core frequency
— Sixteen general-purpose, 32-bit data and address registers
— Implements ColdFire ISA_A with extensions to support the user stack pointer register and four
new instructions for improved bit processing (ISA_A+)
— Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate (EMAC) unit with 32-bit accumulator to support
16 × 16 → 32 or 32 × 32 → 32 operations
— Cryptography Acceleration Unit (CAU)
– Tightly-coupled coprocessor to accelerate software-based encryption and message digest
functions
– FIPS-140 compliant random number generator
— Support for DES, 3DES, AES, MD5, and SHA-1 algorithms
— Illegal instruction decode that allows for 68K emulation support
• System debug support
— Real time trace for determining dynamic execution path
— Background debug mode (BDM) for in-circuit debugging (DEBUG_B+)
— Real time debug support, with six hardware breakpoints (4 PC, 1 address and 1 data) that can
be configured into a 1- or 2-level trigger
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 15

• On-chip memories
— 32-Kbyte dual-ported SRAM on CPU internal bus, supporting core and DMA access with
standby power supply support
— 256 Kbytes of interleaved Flash memory supporting 2-1-1-1 accesses
• Power management
— Fully static operation with processor sleep and whole chip stop modes
— Very rapid response to interrupts from the low-power sleep mode (wake-up feature)
— Clock enable/disable for each peripheral when not used
• Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC)
— 10/100 BaseT/TX capability, half duplex or full duplex
— On-chip transmit and receive FIFOs
— Built-in dedicated DMA controller
— Memory-based flexible descriptor rings
• On-chip Ethernet Transceiver (EPHY)
— Digital adaptive equalization
— Supports auto-negotiation
Overview
— Baseline wander correction
— Full-/Half-duplex support in all modes
— Loopback modes
— Supports MDIO preamble suppression
— Jumbo packet
• FlexCAN 2.0B module
— Based on and includes all existing features of the Freescale TouCAN module
— Full implementation of the CAN protocol specification version 2.0B
– Standard Data and Remote Frames (up to 109 bits long)
– Extended Data and Remote Frames (up to 127 bits long)
– 0–8 bytes data length
– Programmable bit rate up to 1 Mbit/sec
— Flexible Message Buffers (MBs), totalling up to 16 message buffers of 0–8 byte data length
each, configurable as Rx or Tx, all supporting standard and extended messages
— Unused Message Buffer space can be used as general purpose RAM space
— Listen only mode capability
— Content-related addressing
— No read/write semaphores required
— Three programmable mask registers: global for MBs 0-13, special for MB14, and special for
MB15
— Programmable transmit-first scheme: lowest ID or lowest buffer number
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-5
Preliminary
Page 16

Overview
— “Time stamp” based on 16-bit free-running timer
— Global network time, synchronized by a specific message
— Maskable interrupts
• Three universal asynchronous/synchronous receiver transmitters (UARTs)
— 16-bit divider for clock generation
— Interrupt control logic with maskable interrupts
— DMA support
— Data formats can be 5, 6, 7 or 8 bits with even, odd or no parity
— Up to 2 stop bits in 1/16 increments
— Error-detection capabilities
— Modem support includes request-to-send (RTS) and clear-to-send (CTS) lines for two UARTs
— Transmit and receive FIFO buffers
•I2C module
— Interchip bus interface for EEPROMs, LCD controllers, A/D converters, and keypads
— Fully compatible with industry-standard I2C bus
— Master and slave modes support multiple masters
— Automatic interrupt generation with programmable level
• Queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI)
— Full-duplex, three-wire synchronous transfers
— Up to four chip selects available
— Master mode operation only
— Programmable bit rates up to half the CPU clock frequency
— Up to 16 pre-programmed transfers
• Fast analog-to-digital converter (ADC)
— Eight analog input channels
— 12-bit resolution
— Minimum 1.125 µs conversion time
— Simultaneous sampling of two channels for motor control applications
— Single-scan or continuous operation
— Optional interrupts on conversion complete, zero crossing (sign change), or under/over
low/high limit
— Unused analog channels can be used as digital I/O
• Four 32-bit DMA timers
— 16.7-ns resolution at 60 MHz
— Programmable sources for clock input, including an external clock option
— Programmable prescaler
— Input capture capability with programmable trigger edge on input pin
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 17

— Output compare with programmable mode for the output pin
— Free run and restart modes
— Maskable interrupts on input capture or output compare
— DMA trigger capability on input capture or output compare
• Four-channel general purpose timer
— 16-bit architecture
— Programmable prescaler
— Output pulse widths variable from microseconds to seconds
— Single 16-bit input pulse accumulator
— Toggle-on-overflow feature for pulse-width modulator (PWM) generation
— One dual-mode pulse accumulation channel
• Pulse-width modulation timer
— Operates as eight channels with 8-bit resolution or four channels with 16-bit resolution
— Programmable period and duty cycle
— Programmable enable/disable for each channel
— Software selectable polarity for each channel
Overview
— Period and duty cycle are double buffered. Change takes effect when the end of the current
period is reached (PWM counter reaches zero) or when the channel is disabled.
— Programmable center or left aligned outputs on individual channels
— Four clock sources (A, B, SA, and SB) provide for a wide range of frequencies
— Emergency shutdown
• Real-Time Clock (RTC)
— Maintains system time-of-day clock
— Provides stopwatch and alarm interrupt functions
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-7
Preliminary
Page 18

Overview
• Two periodic interrupt timers (PITs)
— 16-bit counter
— Selectable as free running or count down
• Software watchdog timer
— 32-bit counter
— Low power mode support
• Clock Generation Features
— 25 MHz crystal input
— On-chip PLL can generate core frequencies up to maximum 60MHz operating frequency
— Provides clock for integrated EPHY
• Dual Interrupt Controllers (INTC0/INTC1)
— Support for multiple interrupt sources organized as follows:
– Fully-programmable interrupt sources for each peripheral
– 7 fixed-level interrupt sources
– Seven external interrupt signals
— Unique vector number for each interrupt source
— Ability to mask any individual interrupt source or all interrupt sources (global mask-all)
— Support for hardware and software interrupt acknowledge (IACK) cycles
— Combinatorial path to provide wake-up from low power modes
• DMA controller
— Four fully programmable channels
— Dual-address transfer support with 8-, 16-, and 32-bit data capability, along with support for
16-byte (4 x 32-bit) burst transfers
— Source/destination address pointers that can increment or remain constant
— 24-bit byte transfer counter per channel
— Auto-alignment transfers supported for efficient block movement
— Bursting and cycle steal support
— Software-programmable DMA requesters for the UARTs (3) and 32-bit timers (4)
•Reset
— Separate reset in and reset out signals
— Seven sources of reset:
– Power-on reset (POR)
– External
– Software
– Watchdog
– Loss of clock
– Loss of lock
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 19

Overview
– Low-voltage detection (LVD)
— Status flag indication of source of last reset
• Chip integration module (CIM)
— System configuration during reset
— Selects one of three clock modes
— Configures output pad drive strength
— Unique part identification number and part revision number
• General purpose I/O interface
— Up to 56 bits of general purpose I/O
— Bit manipulation supported via set/clear functions
— Programmable drive strengths
— Unused peripheral pins may be used as extra GPIO
• JTAG support for system level board testing
1.4.1 V2 Core Overview
The version 2 ColdFire processor core is comprised of two separate pipelines that are decoupled by an
instruction buffer. The two-stage instruction fetch pipeline (IFP) is responsible for instruction-address
generation and instruction fetch. The instruction buffer is a first-in-first-out (FIFO) buffer that holds
prefetched instructions awaiting execution in the operand execution pipeline (OEP). The OEP includes
two pipeline stages. The first stage decodes instructions and selects operands (DSOC); the second stage
(AGEX) performs instruction execution and calculates operand effective addresses, if needed.
The V2 core implements the ColdFire instruction set architecture revision A+ with added support for a
separate user stack pointer register and four new instructions to assist in bit processing. Additionally, the
MCF52235 core includes the enhanced multiply-accumulate (EMAC) unit for improved signal
processing capabilities. The MAC implements a three-stage arithmetic pipeline, optimized for 16 x 16 bit
operations, with support for one 32-bit accumulator. Supported operands include 16- and 32-bit signed and
unsigned integers, signed fractional operands, and a complete set of instructions to process these data
types. The EMAC provides support for execution of DSP operations within the context of a single
processor at a minimal hardware cost.
1.4.2 Integrated Debug Module
The ColdFire processor core debug interface is provided to support system debugging in conjunction with
low-cost debug and emulator development tools. Through a standard debug interface, users can access
debug information and real-time tracing capability is provided on 112-and 121-lead packages. This allows
the processor and system to be debugged at full speed without the need for costly in-circuit emulators.
The on-chip breakpoint resources include a total of nine programmable 32-bit registers: an address and an
address mask register, a data and a data mask register, four PC registers, and one PC mask register. These
registers can be accessed through the dedicated debug serial communication channel or from the
processor’s supervisor mode programming model. The breakpoint registers can be configured to generate
triggers by combining the address, data, and PC conditions in a variety of single- or dual-level definitions.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-9
Preliminary
Page 20

Overview
The trigger event can be programmed to generate a processor halt or initiate a debug interrupt exception.
The MCF52235 implements revision B+ of the coldfire Debug Architecture.
The MCF52235 ’s interrupt servicing options during emulator mode allow real-time critical interrupt
service routines to be serviced while processing a debug interrupt event, thereby ensuring that the system
continues to operate even during debugging.
To support program trace, the V2 debug module provides processor status (PST[3:0]) and debug data
(DDATA[3:0]) ports. These buses and the PSTCLK output provide execution status, captured operand
data, and branch target addresses defining processor activity at the CPU’s clock rate. The MCF52235
includes a new debug signal, ALLPST. This signal is the logical ‘AND’ of the processor status (PST[3:0])
signals and is useful for detecting when the processor is in a halted state (PST[3:0] = 1111).
The full debug/trace interface is available only on the 112 and 121-pin packages. However, every product
features the dedicated debug serial communication channel (DSI, DSO, DSCLK) and the ALLPST signal.
1.4.3 JTAG
The MCF52235 supports circuit board test strategies based on the Test Technology Committee of IEEE
and the Joint Test Action Group (JTAG). The test logic includes a test access port (TAP) consisting of a
16-state controller, an instruction register, and three test registers (a 1-bit bypass register, a -bit
boundary-scan register, and a 32-bit ID register). The boundary scan register links the device’s pins into
one shift register. Test logic, implemented using static logic design, is independent of the device system
logic.
The MCF52235 implementation can do the following:
• Perform boundary-scan operations to test circuit board electrical continuity
• Sample MCF52235 system pins during operation and transparently shift out the result in the
boundary scan register
• Bypass the MCF52235 for a given circuit board test by effectively reducing the boundary-scan
register to a single bit
• Disable the output drive to pins during circuit-board testing
• Drive output pins to stable levels
1.4.4 On-Chip Memories
1.4.4.1 SRAM
The dual-ported SRAM module provides a general-purpose 32-Kbyte memory block that the ColdFire
core can access in a single cycle. The location of the memory block can be set to any 32-Kbyte boundary
within the 4-Gbyte address space. This memory is ideal for storing critical code or data structures and for
use as the system stack. Because the SRAM module is physically connected to the processor's high-speed
local bus, it can quickly service core-initiated accesses or memory-referencing commands from the debug
module.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 21

Overview
The SRAM module is also accessible by the DMA. The dual-ported nature of the SRAM makes it ideal
for implementing applications with double-buffer schemes, where the processor and a DMA device
operate in alternate regions of the SRAM to maximize system performance.
1.4.4.2 Flash
The ColdFire Flash module (CFM) is a non-volatile memory (NVM) module that connects to the
processor’s high-speed local bus. The CFM is constructed with four banks of 32K x 16-bit Flash arrays to
generate 256 Kbytes of 32-bit Flash memory. These arrays serve as electrically erasable and
programmable, non-volatile program and data memory. The Flash memory is ideal for program and data
storage for single-chip applications, allowing for field reprogramming without requiring an external high
voltage source. The CFM interfaces to the ColdFire core through an optimized read-only memory
controller which supports interleaved accesses from the 2-cycle Flash arrays. A backdoor mapping of the
Flash memory is used for all program, erase, and verify operations, as well as providing a read datapath
for the DMA. Flash memory may also be programmed via the EzPort, which is a serial Flash programming
interface that allows the Flash to be read, erased and programmed by an external controller in a format
compatible with most SPI bus Flash memory chips. This allows easy device programming via Automated
Test Equipment or bulk programming tools.
1.4.5 Cryptography Acceleration Unit
The MCF52235 device incorporates two hardware accelerators for cryptographic functions. First, the
CAU is a coprocessor tightly-coupled to the V2 ColdFire core that implements a set of specialized
operations to increase the throughput of software-based encryption and message digest functions,
specifically the DES, 3DES, AES, MD5 and SHA-1 algorithms. Second, a random number generator
provides FIPS-140 compliant 32-bit values to security processing routines. Both modules supply critical
acceleration to software-based cryptographic algorithms at a minimal hardware cost.
1.4.6 Power Management
The MCF52235 incorporates several low power modes of operation which are entered under program
control and exited by several external trigger events. An integrated power-on reset (POR) circuit monitors
the input supply and forces an MCU reset as the supply voltage rises. The low voltage detector (LVD)
monitors the supply voltage and is configurable to force a reset or interrupt condition if it falls below the
LVD trip point.
1.4.7 FlexCAN
The FlexCAN module is a communication controller implementing version 2.0 of the CAN protocol parts
A and B. The CAN protocol can be used as an industrial control serial data bus, meeting the specific
requirements of reliable operation in a harsh EMI environment with high bandwidth. This instantiation of
FlexCAN has 16 message buffers.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-11
Preliminary
Page 22

Overview
1.4.8 UARTs
The MCF52235 has three full-duplex UARTs that function independently. The three UARTs can be
clocked by the system bus clock, eliminating the need for an external clock source. On smaller packages,
the third UART is multiplexed with other digital I/O functions.
1.4.9 I2C Bus
The I2C bus is a two-wire, bidirectional serial bus that provides a simple, efficient method of data exchange
and minimizes the interconnection between devices. This bus is suitable for applications requiring
occasional communications over a short distance between many devices on a circuit board.
1.4.10 QSPI
The queued serial peripheral interface (QSPI) provides a synchronous serial peripheral interface with
queued transfer capability. It allows up to 16 transfers to be queued at once, minimizing the need for CPU
intervention between transfers.
1.4.11 Fast ADC
The Fast ADC consists of an eight-channel input select multiplexer and two independent sample and hold
(S/H) circuits feeding separate 12-bit ADCs. The two separate converters store their results in accessible
buffers for further processing.
The ADC can be configured to perform a single scan and halt, perform a scan whenever triggered, or
perform a programmed scan sequence repeatedly until manually stopped.
The ADC can be configured for either sequential or simultaneous conversion. When configured for
sequential conversions, up to eight channels can be sampled and stored in any order specified by the
channel list register. Both ADCs may be required during a scan, depending on the inputs to be sampled.
During a simultaneous conversion, both S/H circuits are used to capture two different channels at the same
time. This configuration requires that a single channel may not be sampled by both S/H circuits
simultaneously.
Optional interrupts can be generated at the end of the scan sequence if a channel is out of range (measures
below the low threshold limit or above the high threshold limit set in the limit registers) or at several
different zero crossing conditions.
1.4.12 DMA Timers (DTIM0–DTIM3)
There are four independent, DMA transfer capable 32-bit timers (DTIM0, DTIM1, DTIM2, and DTIM3)
on the each device. Each module incorporates a 32-bit timer with a separate register set for configuration
and control. The timers can be configured to operate from the system clock or from an external clock
source using one of the DTINx signals. If the system clock is selected, it can be divided by 16 or 1. The
input clock is further divided by a user-programmable 8-bit prescaler which clocks the actual timer counter
register (TCRn). Each of these timers can be configured for input capture or reference (output) compare
mode. Timer events may optionally cause interrupt requests or DMA transfers.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 23

Overview
1.4.13 General Purpose Timer (GPT)
The general purpose timer (GPT) is a 4-channel timer module consisting of a 16-bit programmable counter
driven by a 7-stage programmable prescaler. Each of the four channels can be configured for input capture
or output compare. Additionally, one of the channels, channel 3, can be configured as a pulse accumulator.
A timer overflow function allows software to extend the timing capability of the system beyond the 16-bit
range of the counter. The input capture and output compare functions allow simultaneous input waveform
measurements and output waveform generation. The input capture function can capture the time of a
selected transition edge. The output compare function can generate output waveforms and timer software
delays. The 16-bit pulse accumulator can operate as a simple event counter or a gated time accumulator.
1.4.14 Periodic Interrupt Timers (PIT0 and PIT1)
The two periodic interrupt timers (PIT0 and PIT1) are 16-bit timers that provide interrupts at regular
intervals with minimal processor intervention. Each timer can either count down from the value written in
its PIT modulus register, or it can be a free-running down-counter.
1.4.15 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Timers
The MCF52235 has an 8-channel, 8-bit PWM timer. Each channel has a programmable period and duty
cycle as well as a dedicated counter. Each of the modulators can create independent continuous waveforms
with software-selectable duty rates from 0% to 100%. The PWM outputs have programmable polarity, and
can be programmed as left aligned outputs or center aligned outputs. For higher period and duty cycle
resolution, each pair of adjacent channels ([7:6], [5:4], [3:2], and [1:0]) can be concatenated to form a
single 16-bit channel. The module can thus be configured to support 8/0, 6/1, 4/2, 2/3, or 0/4 8-/16-bit
channels.
1.4.16 Software Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer is a 32-bit timer that facilitates recovery from runaway code. The watchdog counter
is a free-running down-counter that generates a reset on underflow. To prevent a reset, software must
periodically restart the countdown.
1.4.17 Phase Locked Loop (PLL)
The clock module contains a crystal oscillator, 8 MHz on-chip relaxation oscillator (OCO), phase-locked
loop (PLL), reduced frequency divider (RFD), low-power divider status/control registers, and control
logic. In order to improve noise immunity, the PLL, crystal oscillator, and relaxation oscillator have their
own power supply inputs: VDDPLL and VSSPLL. All other circuits are powered by the normal supply
pins, VDD and VSS.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 1-13
Preliminary
Page 24

Overview
1.4.18 Interrupt Controller (INTC0/INTC1)
There are two interrupt controllers on the MCF52235. These interrupt controllers are organized as seven
levels with up to nine interrupt sources per level. Each interrupt source has a unique interrupt vector, and
provide each peripheral with all necessary interrupts. Each internal interrupt has a programmable level
[1-7] and priority within the level. The seven external interrupts have fixed levels/priorities.
1.4.19 DMA Controller
The direct memory access (DMA) controller provides an efficient way to move blocks of data with
minimal processor intervention. It has four channels that allow byte, word, longword, or 16-byte burst line
transfers. These transfers are triggered by software explicitly setting a DCRn[START] bit or by the
occurrence of certain UART or DMA timer events.
1.4.20 Reset
The reset controller determines the source of reset, asserts the appropriate reset signals to the system, and
keeps track of what caused the last reset. There are seven sources of reset:
• External reset input
• Power-on reset (POR)
• Watchdog timer
• Phase locked-loop (PLL) loss of lock
• PLL loss of clock
• Software
• Low-voltage detector (LVD)
Control of the LVD and its associated reset and interrupt are handled by the reset controller. Other registers
provide status flags indicating the last source of reset and a control bit for software assertion of the RSTO
pin.
1.4.21 GPIO
Nearly all pins on the MCF52235 have general purpose I/O capability in addition to their primary
functions, and are grouped into 8-bit ports. Some ports do not utilize all 8 bits. Each port has registers that
configure, monitor, and control the port pins.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
1-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 25

Signal Descriptions
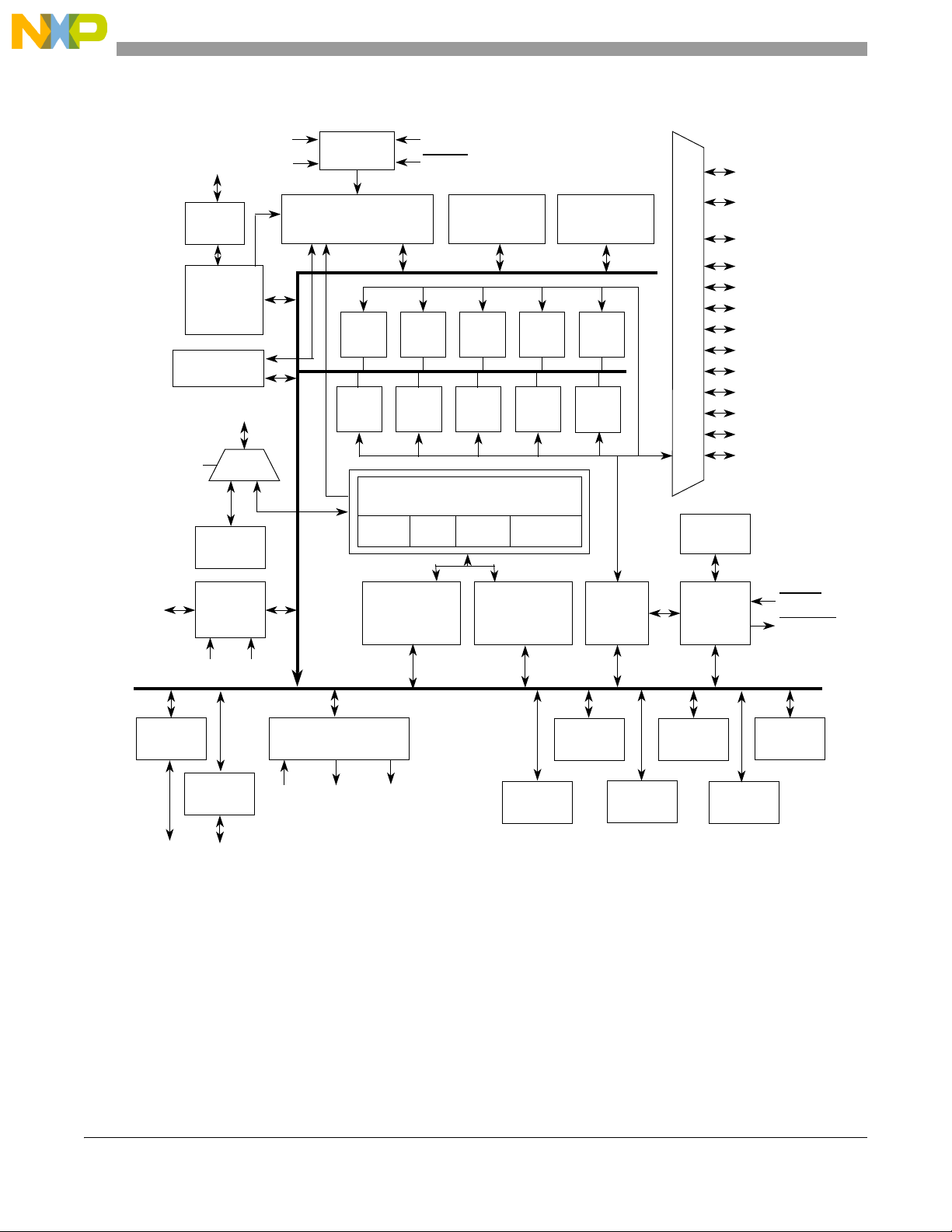
Chapter 2 Signal Descriptions
2.1 Introduction
This chapter describes signals implemented on this device and includes an alphabetical listing of signals
that characterizes each signal as an input or output, defines its state at reset, and identifies whether a
pull-up resistor should be used.
NOTE
The terms ‘assertion’ and ‘negation’ are used to avoid confusion when
dealing with a mixture of active-low and active-high signals. The term
‘asserted’ indicates that a signal is active, independent of the voltage level.
The term ‘negated’ indicates that a signal is inactive.
Active-low signals, such as SRAS and TA, are indicated with an overbar.
2.2 Overview
Figure 2-1 shows the block diagram of the device with the signal interface.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-1
Preliminary
Page 26
Signal Descriptions
EPHY_TX
EPHY_RX
JTAG_EN
EPHY
Fast
Ethernet
Controller
(FEC)
4 CH DMA
To/From PADI
MUX
JTAG
TAP
EzPD EzPCK
EzPQ
EzPort
Arbiter
UART
0
DTIM0DTIM1DTIM2DTIM
EzPCS
UART
1
V2 ColdFire CPU
OEP
IFP
Interrupt
Controller 1
UART
2
CAU
I2C
3
EMAC
Interrupt
Controller 2
QSPI
RTC
PADI – Pin Muxing
PMM
ICOCn
QSPI_DIN,
QSPI_DOUT
QSPI_SCK,
QSPI_PCSn
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
UnTXD
UnRXD
UnRTS
UnCTS
DTINn/DTOUTn
CANRX
CANTX
PWMn
ADCAN[7:0]
V
RHVRL
Edge
Port 1
Edge
Port 2
To/From Interrupt Controller
EXTAL XTAL CLKOUT
32 Kbytes
SRAM
(4Kx16)x4
PLL
CLKGEN
256 Kbytes
Flash
(32Kx16)x4
RNGA
PORTS
(GPIO)
FlexCAN
PIT0
PIT1
CIM
RSTIN
RSTOUT
PWM
GPT
Figure 2-1. Block Diagram with Signal Interfaces
Table 2-1 shows the pin functions by primary and alternate purpose, and illustrates which packages contain
each pin.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 27
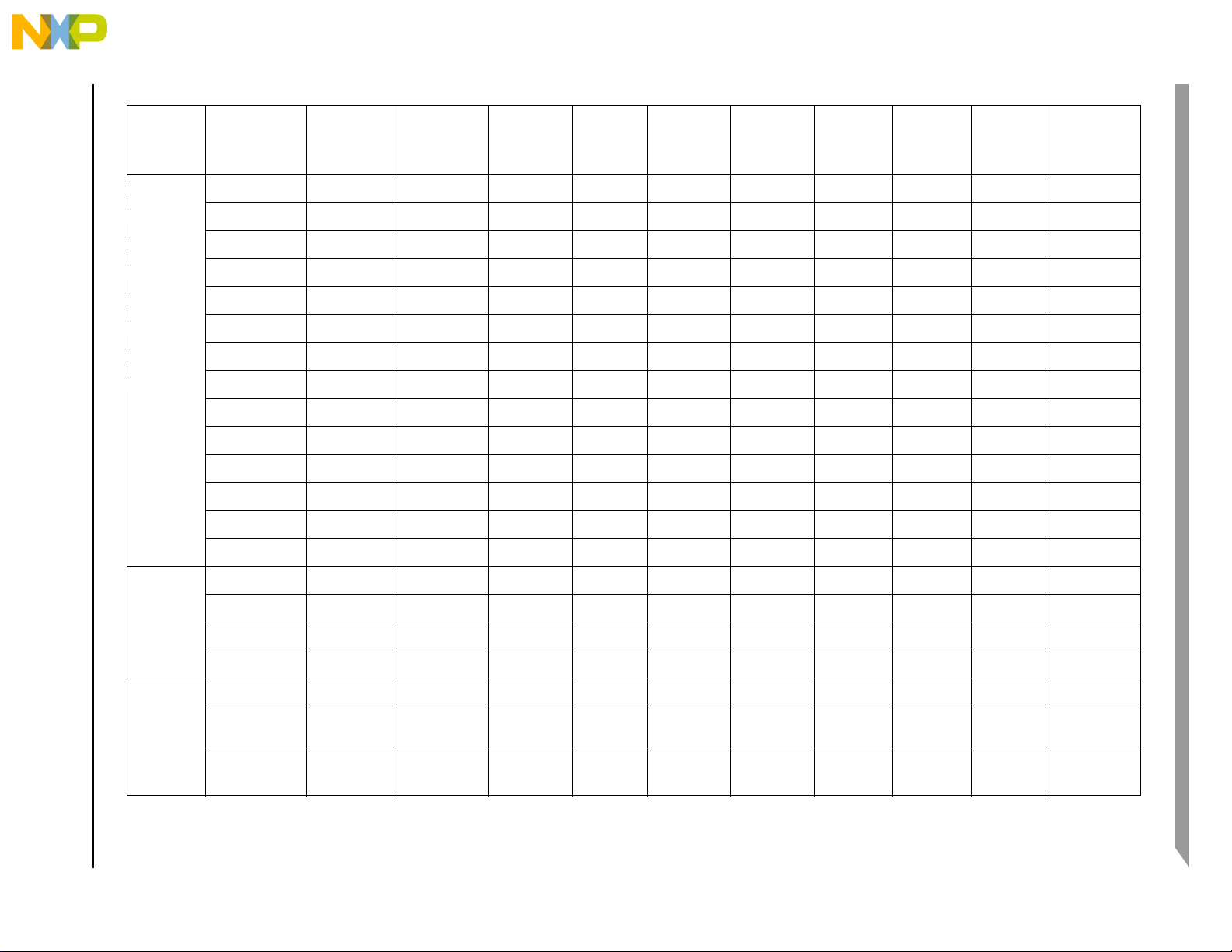
Freescale Semiconductor 2-3
Table 2-1. Pin Functions by Primary and Alternate Purpose
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tiary
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
Wired OR
1
Control
Pull-up /
Pull-down
Pin on121
2
MAPBGA
Pin on 112
LQFP
Pin on 80
LQFP
Notes
ADC AN7 — — PAN[7] Low — — — 88 64
AN6 — — PAN[6] Low — — — 87 63
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
AN5 — — PAN[5] Low — — — 86 62
AN4 — — PAN[4] Low — — — 85 61
AN3 — — PAN[3] Low — — — 89 65
AN2 — — PAN[2] Low — — — 90 66
AN1 — — PAN[1] Low — — — 91 67
AN0 — — PAN[0] Low — — — 92 68
3
SYNCA CANTX
Preliminary
SYNCB CANRX
FEC_MDIO PAS[3] PDSR[39] — — — 28 20
3
FEC_MDC PAS[2] PDSR[39] — — — 27 19
VDDA — — — N/A N/A — — 93 69
VSSA — — — N/A N/A — — 94 72
VRH — — — N/A N/A — — 95 70
VRL — — — N/A N/A — — 96 71
Clock
Generation
Debug
Data
EXTAL — — — N/A N/A — — 48 36
XTAL — — — N/A N/A — — 49 37
VDDPLL — — — N/A N/A — — 45 33
VSSPLL — — — N/A N/A — — 47 35
ALLPST — — — High — — — 7 7
DDATA[3:0] — — PDD[7:4] High — — — 12,13,
16,17
PST[3:0] — — PDD[3:0] High — — — 80,79,
78,77
—
Signal Descriptions
—
Page 28
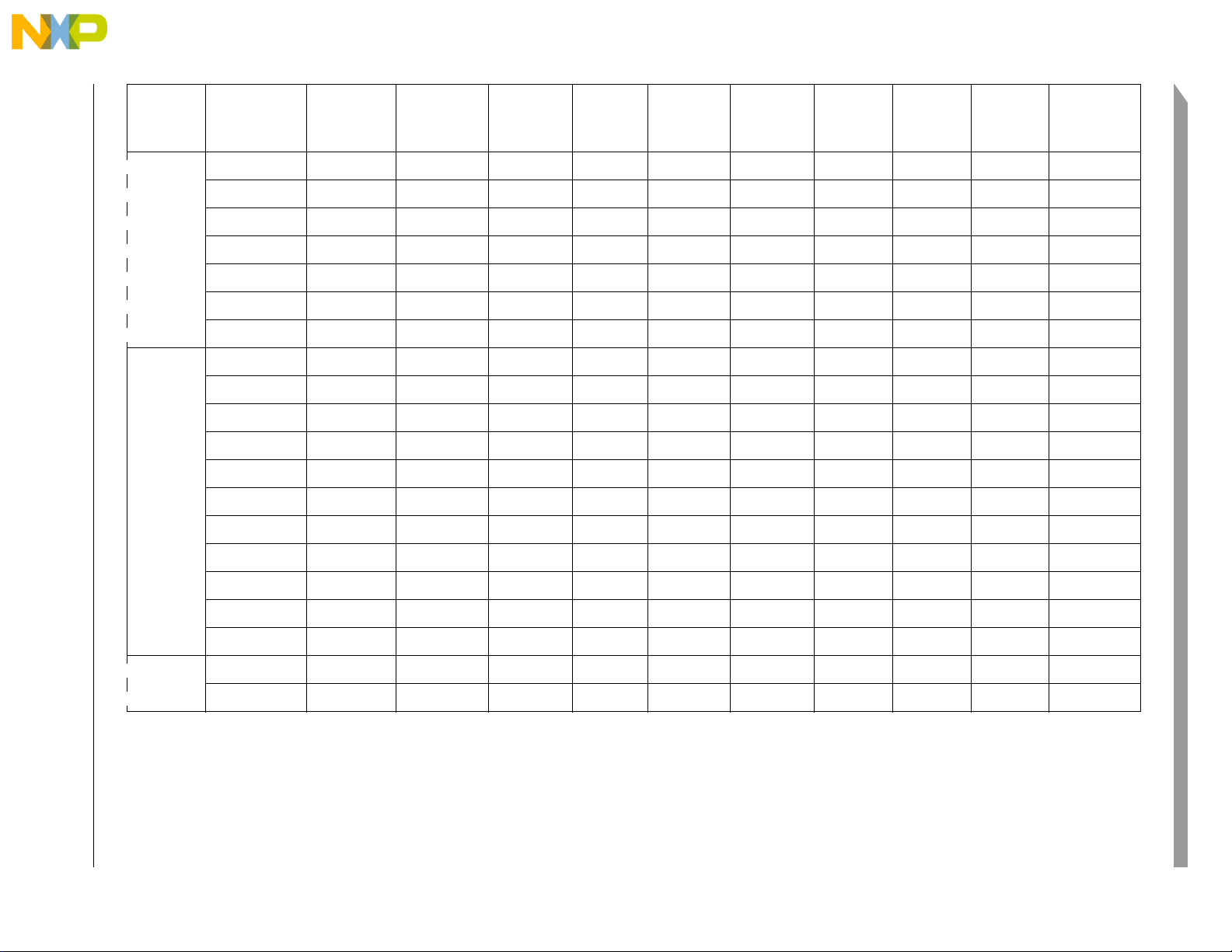
2-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tiary
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
Wired OR
1
Control
Pull-up /
Pull-down
Pin on121
2
MAPBGA
Pin on 112
LQFP
Pin on 80
LQFP
Signal Descriptions
Notes
Ethernet
LEDs
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
ACTLED — — PLD[0] PDSR[32] PWOR[8] — — 84 60
COLLED — — PLD[4] PDSR[36] PWOR[12] — — 58 42
DUPLED — — PLD[3] PDSR[35] PWOR[11] — — 59 43
LNKLED — — PLD[1] PDSR[33] PWOR[9] — — 83 59
SPDLED — — PLD[2] PDSR[34] PWOR[10] — — 81 57
RXLED — — PLD[5] PDSR[37] PWOR[13] — — 52 —
TXLED — — PLD[6] PDSR[38] PWOR[14] — — 51 —
Ethernet
PHY
PHY_RBIAS — — — — — — 66 46
PHY_RXN — — — — — — 74 54
PHY_RXP — — — — — — 73 53
Preliminary
PHY_TXN — — — — — — 71 51
PHY_TXP — — — — — — 70 50
PHY_VDDA — — — N/A — 68 48
PHY_VDDRX — — — N/A — 75 55
PHY_VDDTX — — — N/A — 69 49
PHY_VSSA — — — N/A — 67 47
PHY_VSSRX — — — N/A — 76 56
PHY_VSSTX — — — N/A — 72 52
I2C SCL CANTX
SDA CANRX
3
3
TXD2 PAS[0] PDSR[0] — pull-up
RXD2 PAS[1] PDSR[0] — pull-up
4
4
— 111 79
— 112 80
Page 29
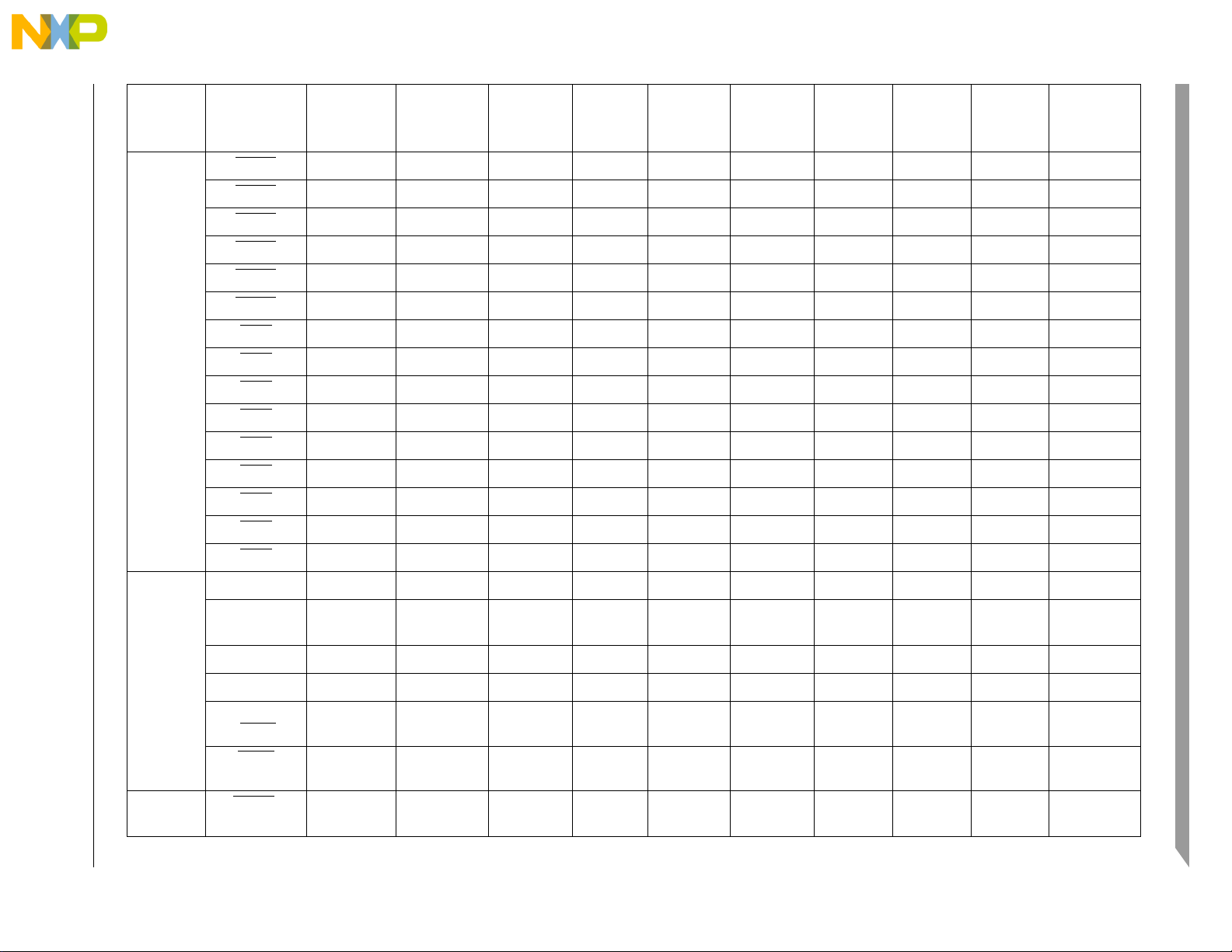
Freescale Semiconductor 2-5
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tiary
Function
Quaternary
Function
Interrupts IRQ15 — — PGP[7] PSDR[47] — pull-up
IRQ14 — — PGP[6] PSDR[46] — pull-up
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
IRQ13 — — PGP[5] PSDR[45] — pull-up
IRQ12 — — PGP[4] PSDR[44] — pull-up
IRQ11 — — PGP[3] PSDR[43] — pull-up
IRQ10 — — PGP[2] PSDR[42] — pull-up
IRQ9 — — PGP[1] PSDR[41] — pull-up
IRQ8 — — PGP[0] PSDR[40] — pull-up
IRQ7 — — PNQ[7] Low — pull-up
IRQ6 — FEC_RXER PNQ[6] Low — pull-up
Preliminary
IRQ5 — FEC_RXD[1] PNQ[5] Low — pull-up
IRQ4 — — PNQ[4] Low — pull-up
IRQ3 — FEC_RXD[2] PNQ[3] Low — pull-up
IRQ2 — FEC_RXD[3] PNQ[2] Low — pull-up
IRQ1 SYNCA PWM1 PNQ[1] High — pull-up
Drive
Strength /
Control
Wired OR
1
Control
Pull-up /
Pull-down
2
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
Pin on121
MAPBGA
Pin on 112
LQFP
Pin on 80
LQFP
— 106 —
— 105 —
—98—
—97—
—57—
—29—
—11—
—10—
—5640
—19—
—20—
—4129
—53—
—54—
—5539
Notes
JTAG/BDM JTAG_EN — — — N/A N/A pull-down — 18 12
TCLK/
CLKOUT — — High — pull-up
5
—1 1
PSTCLK
TDI/DSI — — — N/A N/A pull-up
5
—4 4
TDO/DSO — — — High N/A — — 5 5
TMS
— — — N/A N/A pull-up
5
—2 2
/BKPT
TRST
— — — N/A N/A pull-up
5
—6 6
/DSCLK
Mode
Selection
RCON
EZPCS
/
— — — N/A N/A pull-up — 3 3
Signal Descriptions
Page 30
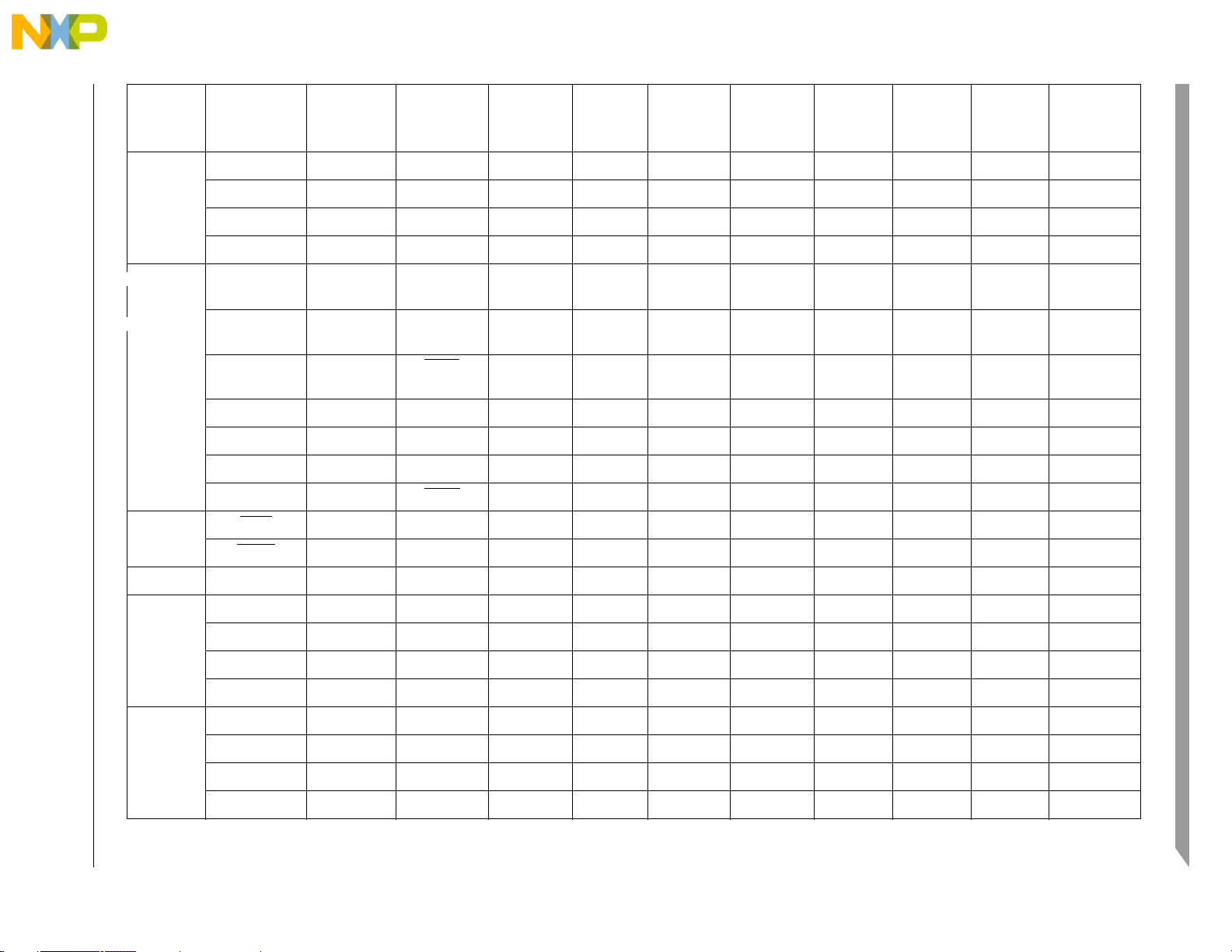
Freescale Semiconductor 2-6
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tiary
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
Wired OR
1
Control
Pull-up /
Pull-down
Pin on121
2
MAPBGA
Pin on 112
LQFP
Pin on 80
LQFP
PWM PWM7 — — PTD[3] PDSR[31] — — — 104 —
PWM5 — — PTD[2] PDSR[30] — — — 103 —
Notes
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
PWM3 — — PTD[1] PDSR[29] — — — 100 —
PWM1 — — PTD[0] PDSR[28] — — — 99 —
QSPI QSPI_DIN/
CANRX
3
RXD1 PQS[1] PDSR[2] PWOR[4] — — 34 25
EZPD
QSPI_DOUT/
CANTX
3
TXD1 PQS[0] PDSR[1] PWOR[5] — — 35 26
EZPQ
QSPI_SCK/
SCL RTS1 PQS[2] PDSR[3] PWOR[6] pull-up
6
—3627
EZPCK
QSPI_CS3 SYNCA SYNCB PQS[6] PDSR[7] — — — 40 —
Preliminary
QSPI_CS2 — — PQS[5] PDSR[6] — — — 39 —
QSPI_CS1 — — PQS[4] PDSR[5] — — — 38 —
6
7
—3758
—4432
Reset
QSPI_CS0 SDA CTS1
7
RSTI — — — N/A N/A pull-up
PQS[3] PDSR[4] PWOR[7] pull-up
RSTO — — — high — — — 46 34
Test TEST — — — N/A N/A pull-down — 50 38
Timers,
16-bit
GPT3 FEC_TXD[3] PWM7 PTA[3] PDSR[23] — pull-up
GPT2 FEC_TXD[2] PWM5 PTA[2] PDSR[22] — pull-up
GPT1 FEC_TXD[1] PWM3 PTA[1] PDSR[21] — pull-up
GPT0 FEC_TXER PWM1 PTA[0] PDSR[20] — pull-up
8
8
8
8
— 107 75
— 108 76
— 109 77
— 110 78
Timers,
32-bit
TIN3 TOUT3 PWM6 PTC[3] PDSR[19] — — — 22 14
TIN2 TOUT2 PWM4 PTC[2] PDSR[18] — — — 21 13
TIN1 TOUT1 PWM2 PTC[1] PDSR[17] — — — 9 9
TIN0 TOUT0 PWM0 PTC[0] PDSR[16] — — — 8 8
Signal Descriptions
Page 31

Freescale Semiconductor 2-7
Pin
Group
Primary
Function
Secondary
Function
Ter tiary
Function
Quaternary
Function
Drive
Strength /
Control
Wired OR
1
Control
Pull-up /
Pull-down
Pin on121
2
MAPBGA
Pin on 112
LQFP
Pin on 80
LQFP
UART 0 CTS0 CANRX3FEC_RXCLK PUA[3] PDSR[11] — — — 26 18
RTS0 CANTX
3
FEC_RXDV PUA[2] PDSR[10] — — — 25 17
Notes
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
RXD0 — FEC_RXD[0] PUA[1] PDSR[9] PWOR[0] — — 30 21
TXD0 — FEC_CRS PUA[0] PDSR[8] PWOR[1] — — 31 22
UART 1 CTS1 SYNCA RXD2 PUB[3] PDSR[15] — — — 24 16
RTS1 SYNCB TXD2 PUB[2] PDSR[14] — — — 23 15
RXD1 — FEC_TXD[0] PUB[1] PDSR[13] PWOR[2] — — 32 23
TXD1 — FEC_COL PUB[0] PDSR[12] PWOR[3] — — 33 24
UART 2 CTS2 — — PUC[3] PDSR[27] — — — 61 —
RTS2 — — PUC[2] PDSR[26] — — — 60 —
Preliminary
RXD2 — — PUC[1] PDSR[25] — — — 62 —
TXD2 — — PUC[30] PDSR[24] — — — 63 —
FlexCAN SYNCA CANTX
SYNCB CANRX
10
VDD
VDD — — — N/A N/A — 14,43,65,
VSS VSS — — — N/A N/A — 15,42,
1
The PDSR and PSSR registers are described in Chapter 14, “General Purpose I/O Module. All programmable signals default to 2mA drive in normal (single-chip)
mode.
2
All signals have a pull-up in GPIO mode.
3
The multiplexed CANTX and CANRX signals do not have dedicated pins, but are available as muxed replacements for other signals.
4
For primary and GPIO functions only.
5
Only when JTAG mode is enabled.
6
For secondary and GPIO functions only.
7
RSTI has an internal pull-up resistor, however the use of an external resistor is very strongly recommended
8
For GPIO function. Primary Function has pull-up control within the GPT module
9
The multiplexed CANTX and CANRX signals do not have dedicated pins, but are available as muxed replacements for other signals.
10
This list for power and ground does not include those dedicated power/ground pins included elsewhere, e.g. in the ethernet PHY.
9
FEC_MDIO PAS[3] PDSR[39] — — — — — See Note
3
FEC_MDC PAS[2] PDSR[39] — — — — — See Note
10,31,45,
82,102
58,74
11,30,
64,101
44,73
3
3
Signal Descriptions
Page 32

Signal Descriptions
2.3 Reset Signals
Table 2-2 describes signals that are used to either reset the chip or as a reset indication.
Table 2-2. Reset Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Reset In RSTI
Reset Out RSTO Driven low for 512 CPU clocks after the reset source has deasserted
Primary reset input to the device. Asserting RSTI immediately resets
the CPU and peripherals.
and PLL locked.
2.4 PLL and Clock Signals
Table 2-3 describes signals that are used to support the on-chip clock generation circuitry.
Table 2-3. PLL and Clock Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
External Clock In EXTAL Crystal oscillator or external clock input. I
Crystal XTAL Crystal oscillator output. O
Clock Out CLKOUT This output signal reflects the internal system clock. O
2.5 Mode Selection
Table 2-4 describes signals used in mode selection, Table 2- 5 describes particular clocking modes.
Table 2-4. Mode Selection Signals
I
O
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Reset Configuration RCON
Test TEST Reserved for factory testing only and in normal modes of operation
The serial Flash programming mode is entered by asserting the
RCON pin (with the TEST pin negated) as the chip comes out of
reset. During this mode, the EzPort has access to the Flash memory
which can be programmed from an external device.
I
should be connected to VSS to prevent unintentional activation of
test functions.
2.6 External Interrupt Signals
Table 2-5 describes the external interrupt signals.
Table 2-5. External Interrupt Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
External Interrupts IRQ
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-8 Freescale Semiconductor
[15:1] External interrupt sources. I
Preliminary
Page 33

2.7 Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI)
Table 2-6 describes the QSPI signals.
Table 2-6. Queued Serial Peripheral Interface (QSPI) Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Signal Descriptions
QSPI Synchronous
Serial Output
QSPI Synchronous
Serial Data Input
QSPI Serial Clock QSPI_CLK Provides the serial clock from the QSPI. The polarity and phase of
Synchronous Peripheral
Chip Selects
QSPI_DOUT Provides the serial data from the QSPI and can be programmed to be
driven on the rising or falling edge of QSPI_CLK.
QSPI_DIN Provides the serial data to the QSPI and can be programmed to be
sampled on the rising or falling edge of QSPI_CLK.
QSPI_CLK are programmable.
QSPI_CS[3:0] QSPI peripheral chip selects that can be programmed to be active
high or low.
O
I
O
O
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-9
Preliminary
Page 34

Signal Descriptions
2.8 Fast Ethernet Controller PHY Signals
Table 7 describes the Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC) Signals.
Table 7. Fast Ethernet Controller (FEC) Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Twisted Pair Input + RXP Differential Ethernet twisted-pair input pin. This pin is high-impedance
out of reset.
Twisted Pair Input - RXN Differential Ethernet twisted-pair input pin. This pin is high-impedance
out of reset.
Twisted Pair Output + TXN Differential Ethernet twisted-pair output pin. This pin is
high-impedance out of reset.
Twisted Pair Output - TXP Differential Ethernet twisted-pair output pin. This pin is
high-impedance out of reset.
Bias Control Resistor RBIAS Connect a 12.4 kΩ (1.0%) external resistor, RBIAS, between the
PHY_RBIAS pin and analog ground.
Place this resistor as near to the chip pin as possible. Stray
capacitance must be kept to less than 10 pF
(>50 pF will cause instability). No high-speed signals can be permitted
in the region of RBIAS.
Activity LED ACT_LED Indicates when the EPHY is transmitting or receiving O
Link LED LINK_LED Indicates when the EPHY has a valid link O
Speed LED SPD_LED Indicates the speed of the EPHY connection O
Duplex LED DUPLED Indicates the duplex (full or half) of the EPHY connection O
Collision LED COLLED Indicates if the EPHY detects a collision O
Transmit LED TXLED Indicates if the EPHY is transmitting O
I
I
O
O
I
Receive LED RXLED Indicates if the EPHY is receiving O
2.9 I2C I/O Signals
Table 2-8 describes the I2C serial interface module signals.
Table 2-8. I2C I/O Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Serial Clock SCL Open-drain clock signal for the for the I2C interface. Either it is driven
Serial Data SDA Open-drain signal that serves as the data input/output for the I2C
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-10 Freescale Semiconductor
2
by the I
clock input when the I
interface.
C module when the bus is in master mode or it becomes the
Preliminary
2
C is in slave mode.
I/O
I/O
Page 35

2.10 UART Module Signals
Table 2-9 describes the UART module signals.
Table 2-9. UART Module Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Signal Descriptions
Transmit Serial Data Output UTXDn Transmitter serial data outputs for the UART modules. The output is
held high (mark condition) when the transmitter is disabled, idle, or in
the local loopback mode. Data is shifted out, LSB first, on this pin at
the falling edge of the serial clock source.
Receive Serial Data Input URXDn Receiver serial data inputs for the UART modules. Data is received on
this pin LSB first. When the UART clock is stopped for power-down
mode, any transition on this pin restarts it.
Clear-to-Send UCTS
Request-to-Send URTSn Automatic request-to-send outputs from the UART modules. This
n Indicate to the UART modules that they can begin data transmission. I
signal can also be configured to be asserted and negated as a
function of the RxFIFO level.
2.11 DMA Timer Signals
Table 2-10 describes the signals of the four DMA timer modules.
Table 2-10. DMA Timer Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
DMA Timer Input DTIN Event input to the DMA timer modules. I
DMA Timer Output DTOUT Programmable output from the DMA timer modules. O
O
I
O
2.12 ADC Signals
Table 2-11 describes the signals of the analog-to-digital converter.
Table 2-11. ADC Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Analog Inputs AN[7:0] Inputs to the A-to-D converter. I
Analog Reference V
Analog Supply V
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-11
V
V
DDA
SSA
RH
RL
Reference voltage high and low inputs. I
I
Isolate the ADC circuitry from power supply noise —
—
Preliminary
Page 36

Signal Descriptions
2.13 General Purpose Timer Signals
Table 2-12 describes the general purpose timer signals.
Table 2-12. GPT Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
General Purpose Timer
Input/Output
GPT[3:0] Inputs to or outputs from the general purpose timer module I/O
2.14 Pulse Width Modulator Signals
Table 2-13 describes the PWM signals.
Table 2-13. PWM Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
PWM Output Channels PWM[7:0] Pulse width modulated output for PWM channels O
2.15 Debug Support Signals
The signals in Table 2-14 are used as the interface to the on-chip JTAG controller and also to interface to
the BDM logic.
Table 2-14. Debug Support Signals
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
JTAG Enable JTAG_EN Select between debug module and JTAG signals at reset I
Test Reset TRST This active-low signal is used to initialize the JTAG logic
asynchronously.
I
Test Clock TCLK Used to synchronize the JTAG logic. I
Test Mode Select TMS Used to sequence the JTAG state machine. TMS is sampled on the
rising edge of TCLK.
Test Data Input TDI Serial input for test instructions and data. TDI is sampled on the rising
edge of TCLK.
Test Data Output TDO Serial output for test instructions and data. TDO is three-stateable and
is actively driven in the shift-IR and shift-DR controller states. TDO
changes on the falling edge of TCLK.
Development Serial
Clock
Breakpoint BKPT
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-12 Freescale Semiconductor
DSCLK Development Serial Clock. Internally synchronized input. (The logic
level on DSCLK is validated if it has the same value on two
consecutive rising bus clock edges.) Clocks the serial communication
port to the debug module during packet transfers. Maximum frequency
is PSTCLK/5. At the synchronized rising edge of DSCLK, the data
input on DSI is sampled and DSO changes state.
Breakpoint. Input used to request a manual breakpoint. Assertion of
BKPT puts the processor into a halted state after the current
instruction completes. Halt status is reflected on processor status
signals () as the value 0xF.
Preliminary
I
I
O
I
I
Page 37

Signal Descriptions
Table 2-14. Debug Support Signals (continued)
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
Development Serial
Input
Development Serial
Output
Debug Data DDATA[3:0] Debug data. Displays captured processor data and breakpoint status.
Processor Status Clock PSTCLK Processor Status Clock. Delayed version of the processor clock. Its
Processor Status
Outputs
DSI Development Serial Input. Internally synchronized input that provides
data input for the serial communication port to the debug module,
once the DSCLK has been seen as high (logic 1).
DSO Development Serial Output. Provides serial output communication for
debug module responses. DSO is registered internally. The output is
delayed from the validation of DSCLK high.
The CLKOUT signal can be used by the development system to know
when to sample DDATA[3:0].
rising edge appears in the center of valid PST and DDATA output.
PSTCLK indicates when the development system should sample PST
and DDATA values.
If real-time trace is not used, setting CSR[PCD] keeps PSTCLK, and
PST and DDATA outputs from toggling without disabling triggers.
Non-quiescent operation can be reenabled by clearing CSR[PCD],
although the external development systems must resynchronize with
the PST and DDATA outputs.
PSTCLK starts clocking only when the first non-zero PST value (0xC,
0xD, or 0xF) occurs during system reset exception processing.
PST[3:0] Indicate core status. Debug mode timing is synchronous with the
processor clock; status is unrelated to the current bus transfer. The
CLKOUT signal can be used by the development system to know
when to sample PST[3:0].
I
O
O
O
O
All Processor Status
Outputs
ALLPST Logical “AND” of PST[3.0] O
2.16 EzPort Signal Descriptions
Table 2-15 contains a list of EzPort external signals
Table 2-15. EzPort Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
EzPort Clock EZPCK Shift clock for EzPort transfers I
EzPort Chip Select EZPCS Chip select for signaling the start and end of
serial transfers
EzPort Serial Data In EZPD EZPD is sampled on the rising edge of EZPCK I
EzPort Serial Data Out EZPQ EZPQ transitions on the falling edge of EZPCK O
I
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-13
Preliminary
Page 38

Signal Descriptions
2.17 Power and Ground Pins
The pins described in Table 2-16 provide system power and ground to the chip. Multiple pins are provided
for adequate current capability. All power supply pins must have adequate decoupling (bypass
capacitance) for high-frequency noise suppression.
Table 2-16. Power and Ground Pins
Signal Name Abbreviation Function I/O
PLL Analog Supply VDDPLL,
VSSPLL
Positive Supply VDD These pins supply positive power to the core logic. I
Ground VSS This pin is the negative supply (ground) to the chip.
Dedicated power supply signals to isolate the sensitive PLL analog
circuitry from the normal levels of noise present on the digital power
supply.
I
Some of the VDD and VSS pins on the device are only to be used for noise bypass. Figure 2 shows a typical
connection diagram. Pay particular attention to those pins which show only capacitor connections. Do not
connect power supply voltage directly to these pins unless the desire is to send the device into a slow but
certain death spiral.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 39

Signal Descriptions
MCF52235
Pin numbering is shown
for the 80-lead TQFP
DDRX
DDTX
VDDPLL
VSSPLL
V
V
V
V
DDR
V
SSX1
V
DDX1
V
DDX2
V
SSX2
V
V
V
V
DDA
DDA
RH
V
RL
SSA
DD2
SS2
DD1
SS1
33
35
69
70
71
72
58
11
10
31
30
45
44
74
73
0.22µF 1000pF
0.1µF
0.1µF 10µH
*
0.1µF
0.1µF
0.1µF
0.22µF
0.22µF
3.3V
10µF
10V
Tantalum
PHY_V
48
0.22µF
12.4KΩ
PHY_RBIAS
46
55
PHY_V
PHY_V
49
0.22µF0.22µF
1%
Figure 2. Suggested connection scheme for Power and Ground
optional
*
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 2-15
Preliminary
Page 40

Signal Descriptions
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
2-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 41

Chapter 3 ColdFire Core
This section describes the organization of the Version 2 (V2) ColdFire® processor core and an overview
of the program-visible registers. For detailed information on instructions, see the ISA_A+ definition in the
ColdFire Family Programmer’s Reference Manual.
3.1 Processor Pipelines
Figure 3-1 is a block diagram showing the processor pipelines of a V2 ColdFire core.
Instruction
IAG
Address
Generation
Instruction
Fetch
Pipeline
Operand
Execution
Pipeline
IC
IB
DSOC
AGEX
Instruction
Fetch Cycle
FIFO
Instruction Buffer
Decode & Select,
Operand Fetch
Address
Generation,
Execute
Figure 3-1. V2 ColdFire Core Pipelines
Address [31:0]
Data[31:0]
As with all ColdFire cores, the V2 ColdFire core is comprised of two separate pipelines that are decoupled
by an instruction buffer.
The instruction fetch pipeline (IFP) is a two-stage pipeline for prefetching instructions. The prefetched
instruction stream is then gated into the two-stage operand execution pipeline (OEP), which decodes the
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-1
Preliminary
Page 42

ColdFire Core
instruction, fetches the required operands and then executes the required function. Since the IFP and OEP
pipelines are decoupled by an instruction buffer which serves as a FIFO queue, the IFP is able to prefetch
instructions in advance of their actual use by the OEP thereby minimizing time stalled waiting for
instructions.
The V2 ColdFire core pipeline stages include the following:
• Two-stage instruction fetch pipeline (IFP) (plus instruction buffer stage)
— Instruction address generation (IAG)—Calculates the next prefetch address
— Instruction fetch cycle (IC)—Initiates prefetch on the processor’s local bus
— Instruction buffer (IB)—Buffer stage minimizes effects of fetch latency using FIFO queue
• Two-stage operand execution pipeline (OEP)
— Decode and select/operand fetch cycle (DSOC)—Decodes instructions and fetches the
required components for effective address calculation, or the operand fetch cycle
— Address generation/execute cycle (AGEX)—Calculates operand address or executes the
instruction
When the instruction buffer is empty, opcodes are loaded directly from the IC cycle into the operand
execution pipeline. If the buffer is not empty, the IFP stores the contents of the fetch cycle in the IB until
it is required by the OEP.
For register-to-register and register-to-memory store operations, the instruction passes through both OEP
stages once. For memory-to-register and read-modify-write memory operations, an instruction is
effectively staged through the OEP twice: the first time to calculate the effective address and initiate the
operand fetch on the processor’s local bus, and the second time to complete the operand reference and
perform the required function defined by the instruction.
The resulting pipeline and local bus structure allows the V2 ColdFire core to deliver sustained high
performance across a variety of demanding embedded applications.
3.2 Memory Map/Register Description
The following sections describe the processor registers in the user and supervisor programming models.
The appropriate programming model is selected based on the privilege level (user mode or supervisor
mode) of the processor as defined by the S bit of the status register (SR). Table 3-1 lists the processor
registers.
The user programming model is the same as the M68000 family microprocessors, consisting of the
following registers:
• 16 general-purpose 32-bit registers (D0–D7, A0–A7)
• 32-bit program counter (PC)
• 8-bit condition code register (CCR)
The supervisor programming model is intended to be used only by system control software to implement
restricted operating system functions, I/O control, and memory management. All accesses that affect the
control features of ColdFire processors are in the supervisor programming model, which consists of
registers available in user mode as well as the following control registers:
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 43

• 16-bit status register (SR)
• 32-bit supervisor stack pointer (SSP)
• 32-bit vector base register (VBR)
• Two 32-bit memory base address registers (RAMBAR, FLASHBAR)
Table 3-1. ColdFire Core Programming Model
ColdFire Core
DRc[4–0]
Load: 0x080
Store: 0x180
Load: 0x081
Store: 0x181
Load: 0x082–7
Store: 0x182–7
Load: 0x088–8E
Store: 0x188–8E
Load: 0x08F Store: 0x18F
0x804 MAC Status Register (MACSR) 32 R/W 0x0000_0000 No 3.2.4/3-5
0x805 MAC Address Mask Register (MASK) 32 R/W 0xFFFF_FFFF No 3.2.4/3-5
0x806, 0x809, 0x80A, 0x80B
0x807 MAC Accumulator 0,1 Extension Bytes
1
Data Register 0 (D0) 32 R/W 0xCF20_6089 No 3.2.1/3-4
Data Register 1 (D1) 32 R/W 0x10A0_1070 No 3.2.1/3-4
Data Register 2–7 (D2–D7) 32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.1/3-4
Address Register 0–6 (A0–A6) 32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.2/3-4
Supervisor/User A7 Stack Pointer (A7) 32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.3/3-4
MAC Accumulators 0–3 (ACC0–3) 32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.4/3-5
(ACCext01)
Register
Supervisor/User Access Registers
Width
(bits)
Access Reset Value
32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.4/3-5
Written with
MOVEC
Section/Page
0x808 MAC Accumulator 2,3 Extension Bytes
(ACCext23)
0x80E Condition Code Register (CCR) 8 R/W Undefined No 3.2.5/3-5
0x80F Program Counter (PC) 32 R/W Undefined Yes 3.2.6/3-6
Supervisor Access Only Registers
0x800 User/Supervisor A7 Stack Pointer (OTHER_A7) 32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.3/3-4
0x801 Vector Base Register (VBR) 32 R/W 0x0000_0000 Yes 3.2.7/3-6
0x80E Status Register (SR) 16 R/W 0x27-- No 3.2.8/3-7
0xC04 Flash Base Address Register (FLASHBAR) 32 R/W 0x0000_0000 Yes 3.2.9/3-8
0xC05 RAM Base Address Register (RAMBAR) 32 R/W 0x0000_0000 Yes 3.2.9/3-8
1
The addresses listed in this column represent the value of the DRc field used when accessing the core registers via the BDM port. For more information see Chapter 31, “Debug Module.”
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-3
Preliminary
32 R/W Undefined No 3.2.4/3-5
Page 44

ColdFire Core
3.2.1 Data Registers (D0–D7)
Registers D0–D7 are used as data registers for bit (1-bit), byte (8-bit), word (16-bit) and longword (32-bit)
operations; they can also be used as index registers.
NOTE
Registers D0 and D1 contain hardware configuration details after reset. See
Section 3.6.14, “Reset Exception,” for more details.
DRc[4:0]: Load: 0x080 + n; n = 0-7 (Dn)
Store: 0x180 + n; n = 0-7 (Dn)
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset
(D2-D7)
(D0, D1)
––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Reset
Figure 3-2. Data Registers (D0–D7)
Data
See Section 3.6.14, “Reset Exception”
Access: User read/write
3.2.2 Address Registers (A0–A6)
These registers can be used as software stack pointers, index registers, or base address registers; they can
also be used for word and longword operations.
DRc[4:0]: Load: 0x088 + n; n =0–6 (An)
Store: 0x188 + n; n =0–6 (An)
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Address
Access: User read/write
Figure 3-3. Address Registers (A0–A6)
3.2.3 Supervisor/User Stack Pointers (A7 and OTHER_A7)
This ColdFire architecture supports two independent stack pointer (A7) registers—the supervisor stack
pointer (SSP) and the user stack pointer (USP). The hardware implementation of these two
programmable-visible 32-bit registers does not identify one as the SSP and the other as the USP. Instead,
the hardware uses one 32-bit register as the active A7 and the other as OTHER_A7. Thus, the register
contents are a function of the processor operation mode, as shown in the following:
if SR[S] = 1
then A7 = Supervisor Stack Pointer
OTHER_A7 = User Stack Pointer
else A7 = User Stack Pointer
OTHER_A7 = Supervisor Stack Pointer
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 45

ColdFire Core
The BDM programming model supports direct reads and writes to A7 and OTHER_A7. It is the
responsibility of the external development system to determine, based on the setting of SR[S], the mapping
of A7 and OTHER_A7 to the two program-visible definitions (SSP and USP).
To support dual stack pointers, the following two supervisor instructions are included in the ColdFire
instruction set architecture to load/store the USP:
move.l Ay, USP; move to USP
move.l USP, Ax; move from USP
These instructions are described in the ColdFire Family Programmer’s Reference Manual.
NOTE
The USP must be initialized using the mov.l Ay,USP instruction before any
entry into user mode.
DRc[4:0]: Load: 0x08F (A7)
Store: 0x18F (A7)
0x800 (OTHER_A7)
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Figure 3-4. Stack Pointer Registers (A7 and OTHER_A7)
Address
Access: A7: User read/write
OTHER_A7: Supervisor read/write
3.2.4 EMAC Register Description
The registers in the EMAC portion of the user programming model, are described in Chapter 4, “Enhanced
Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC),” and include the following registers:
• Four 48-bit accumulator registers partitioned as follows:
— Four 32-bit accumulators (ACC0–ACC3)
— Eight 8-bit accumulator extension bytes (two per accumulator). These are grouped into two
32-bit values for load and store operations (ACCEXT01 and ACCEXT23).
Accumulators and extension bytes can be loaded, copied, and stored, and results from EMAC
arithmetic operations generally affect the entire 48-bit destination.
• Eight 8-bit accumulator extensions (two per accumulator), packaged as two 32-bit values for load
and store operations (ACCext01 and ACCext23)
• One 16-bit mask register (MASK)
• One 32-bit status register (MACSR) including four indicator bits signaling product or
accumulation overflow (one for each accumulator: PAV0–PAV3)
3.2.5 Condition Code Register (CCR)
The CCR is the LSB of the processor status register (SR). Bits 4–0 act as indicator flags for results
generated by processor operations. The extend bit (X) is also used as an input operand during
multiprecision arithmetic computations.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-5
Preliminary
Page 46

ColdFire Core
DRc[4:0]: LSB of Status Register (SR) Access: User read-only
76543210
R 0 0 0 X N Z V C
W
Reset:0 0 0 —————
Figure 3-5. Condition Code Register (CCR)
Table 3-2. CCR Field Descriptions
Field Description
7–5 Reserved, should be cleared.
4
Extend condition code bit. Set to the value of the C-bit for arithmetic operations; otherwise not affected or set to a
X
specified result.
3
Negative condition code bit. Set if the most significant bit of the result is set; otherwise cleared.
N
2
Zero condition code bit. Set if the result equals zero; otherwise cleared.
Z
1
Overflow condition code bit. Set if an arithmetic overflow occurs implying that the result cannot be represented in the
V
operand size; otherwise cleared.
0
Carry condition code bit. Set if a carry out of the operand msb occurs for an addition, or if a borrow occurs in a
C
subtraction; otherwise cleared
Set to the value of the C bit for arithmetic operations; otherwise not affected.
3.2.6 Program Counter (PC)
The PC contains the address of the currently executing instruction. During instruction execution and
exception processing, the processor automatically increments the contents of the PC or places a new value
in the PC, as appropriate. The PC is used as a base address for PC-relative operand addressing.
DRc[4:0]: 0x80F (PC) Access: User read/write
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Figure 3-6. Program Counter Register (PC)
Address
3.2.7 Vector Base Register (VBR)
The VBR contains the base address of the exception vector table in memory. To access the vector table,
the displacement of an exception vector is added to the value in VBR. The lower 20 bits of the VBR are
not implemented by ColdFire processors; they are assumed to be zero, forcing the table to be aligned on a
1 MByte boundary.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 47

ColdFire Core
DRc[4:0]: 0x801 (VBR) Access: Supervisor read/write
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset00000000000000000000000000000000
Base Address
Figure 3-7. Vector Base Register (VBR)
3.2.8 Status Register (SR)
The SR stores the processor status and includes the CCR, the interrupt priority mask, and other control
bits. In supervisor mode, software can access the entire SR. In user mode, only the lower 8 bits are
accessible (CCR). The control bits indicate the following states for the processor: trace mode (T bit),
supervisor or user mode (S bit), and master or interrupt state (M bit). All defined bits in the SR have
read/write access when in supervisor mode. The SR register must be explicitly loaded after reset and before
any compare, Bcc, or Scc instructions are executed.
DRc[4:0]: 0x80E (SR) Access: Supervisor read/write
System Byte Condition Code Register (CCR)
1514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset00100111000—————
0
T
S M
0
I
000XN ZVC
Figure 3-8. Status Register (SR)
Table 3-3. SR Field Descriptions
Field Description
15TTrace enable. When set, the processor performs a trace exception after every instruction.
14 Reserved, should be cleared.
13SSupervisor/user state. Denotes whether the processor is in supervisor mode (S = 1) or user mode (S = 0).
12MMaster/interrupt state. This bit is cleared by an interrupt exception, and can be set by software during execution of
the RTE or move to SR instructions.
11 Reserved, should be cleared.
10–8IInterrupt level mask. Defines the current interrupt level. Interrupt requests are inhibited for all priority levels less than
or equal to the current level, except the edge-sensitive level 7 request, which cannot be masked.
7–5 Reserved, should be cleared.
4–0
CCR
Refer to Ta bl e 3 -2 .
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-7
Preliminary
Page 48

ColdFire Core
3.2.9 Memory Base Address Registers (RAMBAR, FLASHBAR)
The memory base address registers are used to specify the base address of the internal SRAM and Flash
modules and indicate the types of references mapped to each. Each base address register includes a base
address, write-protect bit, address space mask bits, and an enable bit. FLASHBAR determines the base
address of the on-chip Flash, and RAMBAR determines the base address of the on-chip RAM. For more
information, refer to Section 11.2.1, “SRAM Base Address Register (RAMBAR).”
3.3 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA_A+)
The original ColdFire instruction set architecture (ISA) was derived from the M68000-family opcodes
based on extensive analysis of embedded application code. After the initial ColdFire compilers were
created, developers identified ISA additions that would enhance both code density and overall
performance. Additionally, as users implemented ColdFire-based designs into a wide range of embedded
systems, they identified frequently used instruction sequences that could be improved by the creation of
new instructions. This observation was especially prevalent in development environments that made use
of substantial amounts of assembly language code.
Table 3-4 summarizes the instructions added to revision ISA_A to form revision ISA_A+. For more details
see the ColdFire Family Programmer’s Reference Manual.
Table 3-4. Instruction Enhancements over Revision ISA_A
Instruction Description
BITREV The contents of the destination data register are bit-reversed; that is, new Dn[31] = old Dn[0],
new Dn[30] = old Dn[1], ..., new Dn[0] = old Dn[31].
BYTEREV The contents of the destination data register are byte-reversed; that is, new Dn[31:24] = old
Dn[7:0], ..., new Dn[7:0] = old Dn[31:24].
FF1 The data register, Dn, is scanned, beginning from the most-significant bit (Dn[31]) and ending
with the least-significant bit (Dn[0]), searching for the first set bit. The data register is then
loaded with the offset count from bit 31 where the first set bit appears.
MOVE FROM
USP
MOVE TO USP Source → USP
STLDSR Pushes the contents of the status register onto the stack and then reloads the status register
USP → Destination
with the immediate data value.
3.4 Exception Processing Overview
Exception processing for ColdFire processors is streamlined for performance. The ColdFire processors
differ from the M68000 family in that they include:
• A simplified exception vector table
• Reduced relocation capabilities using the vector base register
• A single exception stack frame format
• Use of a single self-aligning stack pointer (for ISA_A implementations only)
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 49

ColdFire Core
All ColdFire processors use an instruction restart exception model. However, Version 2 ColdFire
processors require more software support to recover from certain access errors. See Section 3.6.1, “Access
Error Exception” for details.
Exception processing includes all actions from the detection of the fault condition to the initiation of fetch
for the first handler instruction. Exception processing is comprised of four major steps.
First, the processor makes an internal copy of the SR and then enters supervisor mode by setting the S bit
and disabling trace mode by clearing the T bit. The occurrence of an interrupt exception also forces the M
bit to be cleared and the interrupt priority mask to be set to the level of the current interrupt request.
Second, the processor determines the exception vector number. For all faults except interrupts, the
processor performs this calculation based on the exception type. For interrupts, the processor performs an
interrupt-acknowledge (IACK) bus cycle to obtain the vector number from the interrupt controller. The
IACK cycle is mapped to a special acknowledge address space with the interrupt level encoded in the
address.
Third, the processor saves the current context by creating an exception stack frame on the system stack.
Processors implementing ISA_A support a single stack pointer in the A7 address register; therefore, there
is not notion of separate supervisor and user stack pointer. As a result, the exception stack frame is created
at a 0-modulo-4 address on top of the current system stack. For processors implementing all other ISA
revisions and supporting 2 stack pointers, the exception stack frame is created at a 0-modulo-4 address on
top of the system stack defined by the supervisor stack pointer (SSP). Additionally, the processor uses a
simplified fixed-length stack frame for all exceptions. The exception type determines whether the program
counter placed in the exception stack frame defines the location of the faulting instruction (fault) or the
address of the next instruction to be executed (next).
Fourth, the processor calculates the address of the first instruction of the exception handler. By definition,
the exception vector table is aligned on a 1 Mbyte boundary. This instruction address is generated by
fetching an exception vector from the table located at the address defined in the vector base register. The
index into the exception table is calculated as (4 × vector number). Once the exception vector has been
fetched, the contents of the vector determine the address of the first instruction of the desired handler. After
the instruction fetch for the first opcode of the handler has been initiated, exception processing terminates
and normal instruction processing continues in the handler.
All ColdFire processors support a 1024-byte vector table aligned on any 1 Mbyte address boundary (see
Table 3-5 ). The table contains 256 exception vectors; the first 64 are defined by Freescale and the
remaining 192 are user-defined interrupt vectors.
Table 3-5. Exception Vector Assignments
Vector
Number(s)
0 0x000 — Initial stack pointer
1 0x004 — Initial program counter
2 0x008 Fault Access error
3 0x00C Fault Address error
Vector
Offset (Hex)
Stacked
Program
Counter
Assignment
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-9
Preliminary
Page 50

ColdFire Core
Table 3-5. Exception Vector Assignments (continued)
Vector
Number(s)
4 0x010 Fault Illegal instruction
5 0x014 Fault Divide by zero
6–7 0x018–0x01C — Reserved
8 0x020 Fault Privilege violation
9 0x024 Next Trace
10 0x028 Fault Unimplemented line-a opcode
11 0x02C Fault Unimplemented line-f opcode
12 0x030 Next Debug interrupt
13 0x034 — Reserved
14 0x038 Fault Format error
15–23 0x03C–0x05C — Reserved
24 0x060 Next Spurious interrupt
25–31 0x064–0x07C — Reserved
32–47 0x080–0x0BC Next Trap # 0-15 instructions
48–63 0x0C0–0x0FC — Reserved
64–255 0x100–0x3FC Next User-defined interrupts
“Fault” refers to the PC of the instruction that caused the exception; “Next” refers to the PC
of the next instruction that follows the instruction that caused the fault.
Vector
Offset (Hex)
Stacked
Program
Counter
Assignment
All ColdFire processors inhibit interrupt sampling during the first instruction of all exception handlers.
This allows any handler to effectively disable interrupts, if necessary, by raising the interrupt mask level
contained in the status register. In addition, the ISA_A+ architecture includes an instruction (STLDSR)
that stores the current interrupt mask level and loads a value into the SR. This instruction is specifically
intended for use as the first instruction of an interrupt service routine which services multiple interrupt
requests with different interrupt levels. For more details see the ColdFire Family Programmer’s Reference
Manual.
3.5 Exception Stack Frame Definition
The exception stack frame is shown in Figure 3-9. The first longword of the exception stack frame contains
the 16-bit format/vector word (F/V) and the 16-bit status register, and the second longword contains the
32-bit program counter address.
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
SSP → FORMAT FS[3:2] VECTOR FS[1:0] Status Register
+ 0x4
Figure 3-9. Exception Stack Frame Form
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Program Counter
3-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 51

ColdFire Core
The 16-bit format/vector word contains 3 unique fields:
• A 4-bit format field at the top of the system stack is always written with a value of 4, 5, 6, or 7 by
the processor indicating a two-longword frame format. See Table 3-6 .
Table 3-6. Format Field Encodings
Original SSP @ Time
of Exception, Bits 1:0
00 Original SSP - 8 4
01 Original SSP - 9 5
10 Original SSP - 10 6
11 Original SSP - 11 7
SSP @ 1st
Instruction of
Handler
Format Field
• There is a 4-bit fault status field, FS[3:0], at the top of the system stack. This field is defined for
access and address errors only and written as zeros for all other types of exceptions. See Tabl e 3-7.
Table 3-7. Fault Status Encodings
FS[3:0] Definition
00xx Reserved
0100 Error on instruction fetch
0101 Reserved
011x Reserved
1000 Error on operand write
1001 Attempted write to write-protected space
101x Reserved
1100 Error on operand read
1101 Reserved
111x Reserved
• The 8-bit vector number, vector[7:0], defines the exception type and is calculated by the processor
for all internal faults and represents the value supplied by the interrupt controller in the case of an
interrupt. Refer to Table 3-5 .
3.6 Processor Exceptions
3.6.1 Access Error Exception
The exact processor response to an access error depends on the type of memory reference being performed.
For an instruction fetch, the processor postpones the error reporting until the faulted reference is needed
by an instruction for execution. Therefore, faults that occur during instruction prefetches that are then
followed by a change of instruction flow do not generate an exception. When the processor attempts to
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-11
Preliminary
Page 52

ColdFire Core
execute an instruction with a faulted opword and/or extension words, the access error is signaled and the
instruction aborted. For this type of exception, the programming model has not been altered by the
instruction generating the access error.
If the access error occurs on an operand read, the processor immediately aborts the current instruction’s
execution and initiates exception processing. In this situation, any address register updates attributable to
the auto-addressing modes, (for example, (An)+,-(An)), have already been performed, so the programming
model contains the updated An value. In addition, if an access error occurs during the execution of a
MOVEM instruction loading from memory, any registers already updated before the fault occurs contain
the operands from memory.
The V2 ColdFire processor uses an imprecise reporting mechanism for access errors on operand writes.
Because the actual write cycle may be decoupled from the processor’s issuing of the operation, the
signaling of an access error appears to be decoupled from the instruction that generated the write.
Accordingly, the PC contained in the exception stack frame merely represents the location in the program
when the access error was signaled. All programming model updates associated with the write instruction
are completed. The NOP instruction can collect access errors for writes. This instruction delays its
execution until all previous operations, including all pending write operations, are complete. If any
previous write terminates with an access error, it is guaranteed to be reported on the NOP instruction.
3.6.2 Address Error Exception
Any attempted execution transferring control to an odd instruction address (that is, if bit 0 of the target
address is set) results in an address error exception.
Any attempted use of a word-sized index register (Xn.w) or a scale factor of 8 on an indexed effective
addressing mode generates an address error as does an attempted execution of a full-format indexed
addressing mode.
3.6.3 Illegal Instruction Exception
Any attempted execution of an illegal 16-bit opcode (except for line-A and line-F opcodes) generates an
illegal instruction exception (vector 4). Additionally, any attempted execution of any non-MAC line-A and
most line-F opcode generates their unique exception types, vector numbers 10 and 11, respectively.
ColdFire cores do not provide illegal instruction detection on the extension words on any instruction,
including MOVEC.
3.6.4 Divide-By-Zero
Attempting to divide by zero causes an exception (vector 5, offset = 0x014).
3.6.5 Privilege Violation
The attempted execution of a supervisor mode instruction while in user mode generates a privilege
violation exception. See the ColdFire Programmer’s Reference Manual for a list of supervisor-mode
instructions.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 53

ColdFire Core
3.6.6 Trace Exception
To aid in program development, all ColdFire processors provide an instruction-by-instruction tracing
capability. While in trace mode, indicated by setting of the T bit in the status register (SR[15] = 1), the
completion of an instruction execution (for all but the STOP instruction) signals a trace exception. This
functionality allows a debugger to monitor program execution.
The STOP instruction has the following effects:
1. The instruction before the STOP executes and then generates a trace exception. In the exception stack frame, the PC points to the STOP opcode.
2. When the trace handler is exited, the STOP instruction is executed, loading the SR with the immediate operand from the instruction.
3. The processor then generates a trace exception. The PC in the exception stack frame points to the instruction after the STOP, and the SR reflects the value loaded in the previous step.
If the processor is not in trace mode and executes a STOP instruction where the immediate operand sets
SR[T], hardware loads the SR and generates a trace exception. The PC in the exception stack frame points
to the instruction after the STOP, and the SR reflects the value loaded in step 2.
Because ColdFire processors do not support any hardware stacking of multiple exceptions, it is the
responsibility of the operating system to check for trace mode after processing other exception types. As
an example, consider the execution of a TRAP instruction while in trace mode. The processor will initiate
the TRAP exception and then pass control to the corresponding handler. If the system requires that a trace
exception be processed, it is the responsibility of the TRAP exception handler to check for this condition
(SR[T] in the exception stack frame asserted) and pass control to the trace handler before returning from
the original exception.
3.6.7 Unimplemented Line-A Opcode
A line-A opcode is defined when bits 15-12 of the opword are 0b1010. This exception is generated by the
attempted execution of an undefined line-A opcode.
3.6.8 Unimplemented Line-F Opcode
A line-F opcode is defined when bits 15-12 of the opword are 0b1111. This exception is generated by
attempted execution of an undefined line-F opcode.
3.6.9 Debug Interrupt
This special type of program interrupt is discussed in detail in Chapter 31, “Debug Module.” This
exception is generated in response to a hardware breakpoint register trigger. The processor does not
generate an IACK cycle but rather calculates the vector number internally (vector number 12).
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-13
Preliminary
Page 54

ColdFire Core
3.6.10 RTE and Format Error Exception
When an RTE instruction is executed, the processor first examines the 4-bit format field to validate the
frame type. For a ColdFire core, any attempted RTE execution where the format is not equal to {4,5,6,7}
generates a format error. The exception stack frame for the format error is created without disturbing the
original RTE frame and the stacked PC pointing to the RTE instruction.
The selection of the format value provides some limited debug support for porting code from M68000
applications. On M68000 family processors, the SR was located at the top of the stack. On those
processors, bit 30 of the longword addressed by the system stack pointer is typically zero. Thus, if an RTE
is attempted using this “old” format, it generates a format error on a ColdFire processor.
If the format field defines a valid type, the processor: (1) reloads the SR operand, (2) fetches the second
longword operand, (3) adjusts the stack pointer by adding the format value to the auto-incremented address
after the fetch of the first longword, and then (4) transfers control to the instruction address defined by the
second longword operand within the stack frame.
3.6.11 TRAP Instruction Exception
The TRAP #n instruction always forces an exception as part of its execution and is useful for implementing
system calls.
3.6.12 Interrupt Exception
Interrupt exception processing includes interrupt recognition and the fetch of the appropriate vector from
the interrupt controller using an IACK cycle. See Chapter 12, “Interrupt Controller Module,” for details
on the interrupt controller.
3.6.13 Fault-on-Fault Halt
If a ColdFire processor encounters any type of fault during the exception processing of another fault, the
processor immediately halts execution with the catastrophic “fault-on-fault” condition. A reset is required
to force the processor to exit this halted state.
3.6.14 Reset Exception
Asserting the reset input signal to the processor causes a reset exception. The reset exception has the
highest priority of any exception; it provides for system initialization and recovery from catastrophic
failure. Reset also aborts any processing in progress when the reset input is recognized. Processing cannot
be recovered.
The reset exception places the processor in the supervisor mode by setting the S bit and disables tracing
by clearing the T bit in the SR. This exception also clears the M bit and sets the processor’s interrupt
priority mask in the SR to the highest level (level 7). Next, the VBR is initialized to zero (0x00000000).
The control registers specifying the operation of any memories (e.g., cache and/or RAM modules)
connected directly to the processor are disabled.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 55

ColdFire Core
NOTE
Other implementation-specific registers are also affected. Refer to each of
the modules in this user’s manual for details on these registers.
Once the processor is granted the bus, it then performs two longword read bus cycles. The first longword
at address 0 is loaded into the stack pointer and the second longword at address 4 is loaded into the program
counter. After the initial instruction is fetched from memory, program execution begins at the address in
the PC. If an access error or address error occurs before the first instruction is executed, the processor
enters the fault-on-fault halted state.
ColdFire processors load hardware configuration information into the D0 and D1 general-purpose
registers after system reset. The hardware configuration information is loaded immediately after the
reset-in signal is negated. This allows an emulator to read out the contents of these registers via BDM to
determine the hardware configuration.
Information loaded into D0 defines the processor hardware configuration as shown in Figure 3-10.
DRc[4:0]: Load: 0x080 (D0)
Store: 0x180 (D0)
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
R PF VER REV
W
Reset110011110010 0000
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R MAC DIVEMACFPUMMU000 ISA DEBUG
W
Reset 0 1 1 0000010001 001
Access: User read-only
Figure 3-10. D0 Hardware Configuration Info
Table 3-8. D0 Hardware Configuration Info Field Description
Field Description
31–24PFProcessor family. This field is fixed to a hex value of 0xCF indicating a ColdFire core is present.
23–20
VER
ColdFire core version number. Defines the hardware microarchitecture version of the ColdFire core.
0010 V2 ColdFire core (This is the value used for this device.)
0011 V3 ColdFire core
0100 V4 ColdFire core
0101 V5 ColdFire core
Else Reserved for future use.
19–16
REV
MAC
Freescale Semiconductor 3-15
Processor revision number. The default is 0b0000.
15
MAC present.This bit signals if the optional multiply-accumulate (MAC) execution engine is present in the processor
core.
0 MAC execute engine not present in core. (This is the value used for this device.)
1 MAC execute engine is present in core.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Preliminary
Page 56

ColdFire Core
Table 3-8. D0 Hardware Configuration Info Field Description (continued)
Field Description
14
Divide present. This bit signals if the hardware divider (DIV) is present in the processor core.
DIV
0 Divide execute engine not present in core.
1 Divide execute engine is present in core. (This is the value used for this device.)
13
EMAC present. This bit signals if the optional enhanced multiply-accumulate (EMAC) execution engine is present in
EMAC
FPU
MMU
10–8 Reserved.
the processor core.
0 EMAC execute engine not present in core.
1 EMAC execute engine is present in core.(This is the value used for this device.)
12
FPU present. This bit signals if the optional floating-point (FPU) execution engine is present in the processor core.
0 FPU execute engine not present in core. (This is the value used for this device.)
1 FPU execute engine is present in core.
11
MMU present. This bit signals if the optional virtual memory management unit (MMU) is present in the processor core.
0 MMU execute engine not present in core. (This is the value used for this device.)
1 MMU execute engine is present in core.
7–4
ISA revision. This 4-bit field defines the instruction set architecture (ISA) revision level implemented in the ColdFire
ISA
processor core.
0000 ISA_A
0001 ISA_B
0010 ISA_C
1000 ISA_A+ (This is the value used for this device)
Else Reserved
3–0
Debug module revision number. This 4-bit field defines the revision level of the debug module implemented in the
DEBUG
ColdFire processor core.
0000 DEBUG_A
0001 DEBUG_B
0010 DEBUG_C
0011 DEBUG_D
0100 DEBUG_E
1001 DEBUG_B+ (This is the value used for this device)
Else Reserved
Information loaded into D1 defines the local memory hardware configuration as shown in the figure below.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 57

ColdFire Core
DRc[4:0]: Load: 0x081 (D1)
Access: User read-only
Store: 0x181 (D1)
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
RCLSZ CCAS CCSZ FLASHSZ 0000
W
Reset 0001000010100000
1514131211109876543210
RMBSZ UCAS 0000 SRAMSZ 0000
W
Reset 0001000001110000
Figure 3-11. D1 Hardware Configuration Info
Table 3-9. D1 Hardware Configuration Information Field Description
Field Description
31–30
CLSZ
29–28
CCAS
Cache line size. This field is fixed to a hex value of 0x0 indicating a 16-byte cache line size.
Configurable cache associativity.
00 Four-way
01 Direct mapped (This is the value used for this device)
Else Reserved for future use
27–24
CCSZ
Configurable cache size. Indicates the amount of instruction/data cache.
0000 No configurable cache (This is the value used for this device)
0001 512B configurable cache
0010 1KB configurable cache
0011 2KB configurable cache
0100 4KB configurable cache
0101 8KB configurable cache
0110 16KB configurable cache
0111 32KB configurable cache
1000 64KB configurable cache
Else Reserved
23–20
FLASHSZ
Flash bank size.
0000-0111 No flash
1000 64KB Flash
1001 128KB Flash
1010 256KB Flash (This is the value used for this device)
1011 512KB Flash
Else Reserved for future use.
19–16 Reserved
15–14
MBSZ
Bus size. Defines the width of the ColdFire master Bus datapath.
00 32-bit system bus datapath (This is the value used for this device)
01 64-bit system bus datapath
Else Reserved
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-17
Preliminary
Page 58

ColdFire Core
Table 3-9. D1 Hardware Configuration Information Field Description (continued)
Field Description
13–12
UCAS
11–8 Reserved.
7–4
SRAMSZ
3-0 Reserved
Unified cache associativity. Defines the unified cache set-associativity.
00 Four-way
01 Direct mapped (This is the value used for this device)
Else Reserved for future use
SRAM bank size.
0000 No SRAM
0001 512 bytes
0010 1 Kbytes
0011 2 Kbytes
0100 4 Kbytes
0101 8 Kbytes
0110 16 Kbytes
0111 32 Kbytes (This is the value used for this device)
1000 64 Kbytes
1001 128 Kbytes
Else Reserved for future use
3.7 Instruction Execution Timing
This section presents processor instruction execution times in terms of processor core clock cycles. The
number of operand references for each instruction is enclosed in parentheses following the number of
processor clock cycles. Each timing entry is presented as C(R/W) where:
•C is the number of processor clock cycles, including all applicable operand fetches and writes, and
all internal core cycles required to complete the instruction execution.
• R/W is the number of operand reads (R) and writes (W) required by the instruction. An operation
performing a read-modify-write function is denoted as (1/1).
This section includes the assumptions concerning the timing values and the execution time details.
3.7.1 Timing Assumptions
For the timing data presented in this section, the following assumptions apply:
1. The OEP is loaded with the opword and all required extension words at the beginning of each instruction execution. This implies that the OEP does not wait for the IFP to supply opwords and/or extension words.
2. The OEP does not experience any sequence-related pipeline stalls.The most common example of
this type of stall involves consecutive store operations, excluding the MOVEM instruction. For all
STORE operations (except MOVEM), certain hardware resources within the processor are marked
as “busy” for two clock cycles after the final decode and select/operand fetch cycle (DSOC) of the
store instruction. If a subsequent STORE instruction is encountered within this 2-cycle window, it
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-18 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 59

ColdFire Core
is stalled until the resource again becomes available. Thus, the maximum pipeline stall involving
consecutive STORE operations is 2 cycles. The MOVEM instruction uses a different set of
resources and this stall does not apply.
3. The OEP completes all memory accesses without any stall conditions caused by the memory itself. Thus, the timing details provided in this section assume that an infinite zero-wait state memory is attached to the processor core.
4. All operand data accesses are aligned on the same byte boundary as the operand size, i.e., 16-bit operands aligned on 0-modulo-2 addresses, 32-bit operands aligned on 0-modulo-4 addresses.
The processor core decomposes misaligned operand references into a series of aligned accesses as shown
in Table 3-10.
Table 3-10. Misaligned Operand References
address[1:0] Size
01 or 11 Word Byte, Byte 2(1/0) if read
01 or 11 Long Byte, Word,
10 Long Word, Word 2(1/0) if read
Bus
Operations
Byte
Additional
C(R/W)
1(0/1) if write
3(2/0) if read 2(0/2) if write
1(0/1) if write
3.7.2 MOVE Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-11 lists execution times for MOVE.{B,W} instructions; Table 3-12 lists timings for MOVE.L. For
all tables in this section, the execution time of any instruction using the PC-relative effective addressing
modes is the same for the comparable An-relative mode.The nomenclature “xxx.wl” refers to both forms
of absolute addressing, xxx.w and xxx.l.
Table 3-11. MOVE Byte and Word Execution Times
Destination
Source
Rx (Ax) (Ax)+ -(Ax) (d16,Ax) (d8,Ax,Xi*SF) xxx.wl
Dy 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1)
Ay 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1)
(Ay) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1)) 3(1/1)
(Ay)+ 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1)) 3(1/1)
-(Ay) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1)
(d16,Ay) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — —
(d8,Ay,Xi*SF) 4(1/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1)) — — —
xxx.w 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — — —
xxx.l 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — — —
(d16,PC) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 31/1) 3(1/1) — —
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-19
Preliminary
Page 60

ColdFire Core
Table 3-11. MOVE Byte and Word Execution Times (continued)
Destination
Source
Rx (Ax) (Ax)+ -(Ax) (d16,Ax) (d8,Ax,Xi*SF) xxx.wl
(d8,PC,Xi*SF) 4(1/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1)) — — —
#xxx 1(0/0) 3(0/1) 3(0/1) 3(0/1) — — —
Table 3-12. MOVE Long Execution Times
Destination
Source
Rx (Ax) (Ax)+ -(Ax) (d16,Ax) (d8,Ax,Xi*SF) xxx.wl
Dy 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1)
Ay 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1)
(Ay) 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 3(1/1) 2(1/1)
(Ay)+ 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 3(1/1) 2(1/1)
-(Ay) 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 3(1/1) 2(1/1)
(d16,Ay) 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) — —
(d8,Ay,Xi*SF) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — — —
xxx.w 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) — — —
xxx.l 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) — — —
(d16,PC) 2(1/0) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) 2(1/1) — —
(d8,PC,Xi*SF) 3(1/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — — —
#xxx 1(0/0) 2(0/1) 2(0/1) 2(0/1) — — —
3.8 Standard One Operand Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-13. One Operand Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An) (d8,An,Xn*SF) xxx.wl #xxx
bitrevDx1(0/0)———— — ——
byterevDx1(0/0)———— — ——
clr.b <ea> 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1) —
clr.w <ea> 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1) —
clr.l <ea> 1(0/0) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 1(0/1) 2(0/1) 1(0/1) —
ext.wDx1(0/0)———— — ——
ext.lDx1(0/0)———— — ——
extb.lDx1(0/0)———— — ——
ff1Dx1(0/0)———— — ——
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-20 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 61

ColdFire Core
Table 3-13. One Operand Instruction Execution Times (continued)
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An) (d8,An,Xn*SF) xxx.wl #xxx
neg.lDx1(0/0)———— — ——
negx.l Dx 1(0/0) ———— — ——
not.lDx1(0/0)———— — ——
sccDx1(0/0)———— — ——
swapDx1(0/0)———— — ——
tst.b <ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
tst.w <ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
tst.l <ea> 1(0/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 3(1/0) 2(1/0) 1(0/0)
3.9 Standard Two Operand Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-14. Two Operand Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An)
(d16,An)
(d16,PC)
(d8,An,Xn*SF)
(d8,PC,Xn*SF)
xxx.wl #xxx
add.l <ea>,Rx 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
add.l Dy,<ea> — 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
addi.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
addq.l #imm,<ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
addx.l Dy,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
and.l <ea>,Rx 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
and.l Dy,<ea> — 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
andi.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
asl.l <ea>,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
asr.l <ea>,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
bchg Dy,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 5(1/1) 4(1/1) —
bchg #imm,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) — — —
bclr Dy,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 5(1/1) 4(1/1) —
bclr #imm,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) — — —
bset Dy,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 41/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 5(1/1) 4(1/1) —
bset #imm,<ea> 2(0/0) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) 4(1/1) — — —
btst Dy,<ea> 2(0/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
btst #imm,<ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) — — 1(0/0)
cmp.l <ea>,Rx 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
cmpi.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-21
Preliminary
Page 62

ColdFire Core
Opcode <EA>
divs.w <ea>,Dx 20(0/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 24(1/0) 23(1/0) 20(0/0)
divu.w <ea>,Dx 20(0/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 23(1/0) 24(1/0) 23(1/0) 20(0/0)
divs.l <ea>,Dx ≤35(0/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) — — —
divu.l <ea>,Dx ≤35(0/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) — — —
eor.l Dy,<ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
eori.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
lea <ea>,Ax — 1(0/0) — — 1(0/0) 2(0/0) 1(0/0) —
lsl.l <ea>,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
lsr.l <ea>,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
moveq #imm,Dx — — — — — — — 1(0/0)
or.l <ea>,Rx 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
or.l Dy,<ea> — 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
ori.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
rems.l <ea>,Dx ≤35(0/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) — — — remu.l <ea>,Dx ≤35(0/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) ≤38(1/0) — — —
sub.l <ea>,Rx 1(0/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 1(0/0)
sub.l Dy,<ea> — 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
subi.l #imm,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
subq.l #imm,<ea> 1(0/0) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 3(1/1) 4(1/1) 3(1/1) —
subx.l Dy,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
Table 3-14. Two Operand Instruction Execution Times (continued)
Effective Address
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An)
(d16,An)
(d16,PC)
(d8,An,Xn*SF)
(d8,PC,Xn*SF)
xxx.wl #xxx
3.10 Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-15. Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
link.w Ay,#imm 2(0/1) — — — — — — —
move.l Ay,USP 3(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.l USP,Ax 3(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.w CCR,Dx 1(0/0) ———— — ——
move.w <ea>,CCR 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
move.w SR,Dx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.w <ea>,SR 7(0/0) — — — — — — 7(0/0)
movec Ry,Rc 9(0/1) — — — — — — —
movem.l <ea>,&list — 1+n(n/0) — — 1+n(n/0) — — —
3-22 Freescale Semiconductor
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An) (d8,An,Xn*SF) xxx.wl #xxx
2
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Preliminary
Page 63

Table 3-15. Miscellaneous Instruction Execution Times (continued)
ColdFire Core
Opcode <EA>
Effective Address
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An) (d8,An,Xn*SF) xxx.wl #xxx
movem.l &list,<ea> — 1+n(0/n) — — 1+n(0/n) — — —
nop 3(0/0) — — — — — — —
pea <ea> — 2(0/1) — — 2(0/1)
4
3(0/1)
5
2(0/1) —
pulse 1(0/0)———— — ——
stldsr#imm————— — —5(0/1)
stop#imm————— — —3(0/0)
3
trap#imm————— — —15(1/2)
trapf 1(0/0)———— — ——
trapf.w 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
trapf.l 1(0/0)———— — ——
unlk Ax 2(1/0) — — — — — — —
wddata <ea> — 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0) 4(1/0) 3(1/0) 3(1/0)
wdebug <ea> — 5(2/0) — — 5(2/0) — — —
1
n is the number of registers moved by the MOVEM opcode.
2
If a MOVE.W #imm,SR instruction is executed and imm[13] = 1, the execution time is 1(0/0).
3
The execution time for STOP is the time required until the processor begins sampling continuously for interrupts.
4
PEA execution times are the same for (d16,PC).
5
PEA execution times are the same for (d8,PC,Xn*SF).
3.11 EMAC Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-16. EMAC Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An)
muls.w <ea>y, Dx 4(0/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 71/0) 6(1/0) 4(0/0)
mulu.w <ea>y, Dx 4(0/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 71/0) 6(1/0) 4(0/0)
muls.l <ea>y, Dx 4(0/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) — — —
mulu.l <ea>y, Dx 4(0/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) 6(1/0) — — —
mac.w Ry, Rx, Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
mac.l Ry, Rx, Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
msac.w Ry, Rx, Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
msac.l Ry, Rx, Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
mac.w Ry, Rx, <ea>, Rw, Raccx — 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0)
mac.l Ry, Rx, <ea>, Rw, Raccx — 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0)
(d8,An,
Xn*SF)
1
1
xxx.wl #xxx
———
———
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-23
Preliminary
Page 64

ColdFire Core
Opcode <EA>
msac.w Ry, Rx, <ea>, Rw — 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0)
msac.l Ry, Rx, <ea>, Rw, Raccx — 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0) 2(1/0)
move.l <ea>y, Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
move.l Raccy,Raccx 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.l <ea>y, MACSR 5(0/0) — — — — — — 5(0/0)
move.l <ea>y, Rmask 4(0/0) — — — — — — 4(0/0)
move.l <ea>y,Raccext01 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
move.l <ea>y,Raccext23 1(0/0) — — — — — — 1(0/0)
move.l Raccx,<ea>x 1(0/0)
move.l MACSR,<ea>x 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.l Rmask, <ea>x 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
Table 3-16. EMAC Instruction Execution Times (continued)
Effective Address
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An) (d16,An)
2
——— — ———
(d8,An,
Xn*SF)
1
———
1
———
xxx.wl #xxx
move.l Raccext01,<ea.x 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
move.l Raccext23,<ea>x 1(0/0) — — — — — — —
1
Effective address of (d16,PC) not supported
2
Storing an accumulator requires one additional processor clock cycle when saturation is enabled, or
fractional rounding is performed (MACSR[7:4] = 1---, -11-, --11)
3.12 Branch Instruction Execution Times
Table 3-17. General Branch Instruction Execution Times
Effective Address
Opcode <EA>
Rn (An) (An)+ -(An)
bsr — — — — 3(0/1) — — —
jmp <ea> — 3(0/0) — — 3(0/0) 4(0/0) 3(0/0) —
jsr <ea> — 3(0/1) — — 3(0/1) 4(0/1) 3(0/1) —
rte — — 10(2/0) — — — — —
rts ——5(1/0)—————
(d16,An)
(d16,PC)
(d8,An,Xi*SF)
(d8,PC,Xi*SF)
xxx.wl #xxx
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-24 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 65

Table 3-18. BRA, Bcc Instruction Execution Times
ColdFire Core
Opcode
Forward
Taken
Forward
Not Taken
Backward
Taken
Backward
Not Taken
bra 2(0/0) — 2(0/0) —
bcc 3(0/0) 1(0/0) 2(0/0) 3(0/0)
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 3-25
Preliminary
Page 66

ColdFire Core
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
3-26 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 67

Chapter 4 Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
This chapter describes the functionality, microarchitecture, and performance of the enhanced
multiply-accumulate (EMAC) unit in the ColdFire family of processors.
4.1 Multiply-Accumulate Unit
The MAC design provides a set of DSP operations that can be used to improve the performance of
embedded code while supporting the integer multiply instructions of the baseline ColdFire architecture.
The MAC provides functionality in three related areas:
1. Signed and unsigned integer multiplies
2. Multiply-accumulate operations supporting signed and unsigned integer operands as well as signed, fixed-point, fractional operands
3. Miscellaneous register operations
The ColdFire family supports two MAC implementations with different performance levels and
capabilities. The original MAC features a three-stage execution pipeline optimized for 16-bit operands,
with a 16x16 multiply array and a single 32-bit accumulator. The EMAC features a four-stage pipeline
optimized for 32-bit operands, with a fully pipelined 32 × 32 multiply array and four 48-bit accumulators.
The first ColdFire MAC supported signed and unsigned integer operands and was optimized for 16x16
operations, such as those found in a variety of applications including servo control and image compression.
As ColdFire-based systems proliferated, the desire for more precision on input operands increased. The
result was an improved ColdFire MAC with user-programmable control to optionally enable use of
fractional input operands.
EMAC improvements target three primary areas:
• Improved performance of 32 × 32 multiply operation.
• Addition of three more accumulators to minimize MAC pipeline stalls caused by exchanges
between the accumulator and the pipeline’s general-purpose registers
• A 48-bit accumulation data path to allow the use of a 40-bit product, plus the addition of 8
extension bits to increase the dynamic number range when implementing signal processing
algorithms
The three areas of functionality are addressed in detail in following sections. The logic required to support
this functionality is contained in a MAC module, as shown in Figure 4-1.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-1
Preliminary
Page 68

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
Operand Y Operand X
X
Shift 0,1,-1
+
-
/
Accumulator(s)
Figure 4-1. Multiply-Accumulate Functionality Diagram
4.2 Introduction to the MAC
The MAC is an extension of the basic multiplier found in most microprocessors. It is typically
implemented in hardware within an architecture and supports rapid execution of signal processing
algorithms in fewer cycles than comparable non-MAC architectures. For example, small digital filters can
tolerate some variance in an algorithm’s execution time, but larger, more complicated algorithms such as
orthogonal transforms may have more demanding speed requirements beyond the scope of any processor
architecture and may require full DSP implementation.
To strike a balance between speed, size, and functionality, the ColdFire MAC is optimized for a small set
of operations that involve multiplication and cumulative additions. Specifically, the multiplier array is
optimized for single-cycle pipelined operations with a possible accumulation after product generation.
This functionality is common in many signal processing applications. The ColdFire core architecture also
has been modified to allow an operand to be fetched in parallel with a multiply, increasing overall
performance for certain DSP operations.
Consider a typical filtering operation where the filter is defined as in Equation 4-1.
N1–
yi() ak()yi k–()
∑
k1=
N1–
bk()xi k–()
+=
∑
k0=
Eqn. 4-1
Here, the output y(i) is determined by past output values and past input values. This is the general form of
an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter. A finite impulse response (FIR) filter can be obtained by setting
coefficients a(k) to zero. In either case, the operations involved in computing such a filter are multiplies
and product summing. To show this point, reduce the above equation to a simple, four-tap FIR filter, shown
in Equation 4-2, in which the accumulated sum is a sum of past data values and coefficients.
3
yi() bk()xi k–()
∑
k0=
b0()xi() b1()xi 1–()b2()xi 2–()b3()xi 3–()+++==
Eqn. 4-2
4.3 General Operation
The MAC speeds execution of ColdFire integer multiply instructions (MULS and MULU) and provides
additional functionality for multiply-accumulate operations. By executing MULS and MULU in the MAC,
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 69

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
execution times are minimized and deterministic compared to the 2-bit/cycle algorithm with early
termination that the OEP normally uses if no MAC hardware is present.
The added MAC instructions to the ColdFire ISA provide for the multiplication of two numbers, followed
by the addition or subtraction of the product to or from the value in an accumulator. Optionally, the product
may be shifted left or right by 1 bit before addition or subtraction. Hardware support for saturation
arithmetic can be enabled to minimize software overhead when dealing with potential overflow conditions.
Multiply-accumulate operations support 16- or 32-bit input operands of the following formats:
• Signed integers
• Unsigned integers
• Signed, fixed-point, fractional numbers
The EMAC is optimized for single-cycle, pipelined 32 × 32 multiplications. For word- and
longword-sized integer input operands, the low-order 40 bits of the product are formed and used with the
destination accumulator. For fractional operands, the entire 64-bit product is calculated and either
truncated or rounded to the most-significant 40-bit result using the round-to-nearest (even) method before
it is combined with the destination accumulator.
For all operations, the resulting 40-bit product is extended to a 48-bit value (using sign-extension for
signed integer and fractional operands, zero-fill for unsigned integer operands) before being combined
with the 48-bit destination accumulator.
Figure 4-2 and Figure 4-3 show relative alignment of input operands, the full 64-bit product, the resulting
40-bit product used for accumulation, and 48-bit accumulator formats.
32
32
“0”
8
Accumulator [31:0] Extension Byte Lower [7:0]
Product
Extended Product
+
Accumulator
OperandY
OperandX
X
40 23
8
840
Extension Byte Upper [7:0]
Figure 4-2. Fractional Alignment
40
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-3
Preliminary
Page 70

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
Product
Extended Product
+
Accumulator
OperandY
X
OperandX
24
8
8
Extension Byte Upper [7:0]
Extension Byte Lower [7:0]
Figure 4-3. Signed and Unsigned Integer Alignment
8
8
8
32
32
32
32
32
Accumulator [31:0]
Thus, the 48-bit accumulator definition is a function of the EMAC operating mode. Given that each 48-bit
accumulator is the concatenation of 16-bit accumulator extension register (ACCextn) contents and 32-bit
ACCn contents, the specific definitions are as follows:
if MACSR[6:5] == 00 /* signed integer mode */
Complete Accumulator[47:0] = {ACCextn[15:0], ACCn[31:0]}
if MACSR[6:5] == 01 or 11 /* signed fractional mode */
Complete Accumulator [47:0] = {ACCextn[15:8], ACCn[31:0], ACCextn[7:0]}
if MACSR[6:5] == 10 /* unsigned integer mode */
Complete Accumulator[47:0] = {ACCextn[15:0], ACCn[31:0]}
The four accumulators are represented as an array, ACCn, where n selects the register.
Although the multiplier array is implemented in a four-stage pipeline, all arithmetic MAC instructions
have an effective issue rate of 1 cycle, regardless of input operand size or type.
All arithmetic operations use register-based input operands, and summed values are stored internally in an
accumulator. Thus, an additional move instruction is needed to store data in a general-purpose register.
One new feature found in EMAC instructions is the ability to choose the upper or lower word of a register
as a 16-bit input operand. This is useful in filtering operations if one data register is loaded with the input
data and another is loaded with the coefficient. Two 16-bit multiply accumulates can be performed without
fetching additional operands between instructions by alternating the word choice during the calculations.
The EMAC has four accumulator registers versus the MAC’s single accumulator. The additional registers
improve the performance of some algorithms by minimizing pipeline stalls needed to store an accumulator
value back to general-purpose registers. Many algorithms require multiple calculations on a given data set.
By applying different accumulators to these calculations, it is often possible to store one accumulator
without any stalls while performing operations involving a different destination accumulator.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 71

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
The need to move large amounts of data presents an obstacle to obtaining high throughput rates in DSP
engines. New and existing ColdFire instructions can accommodate these requirements. A MOVEM
instruction can move large blocks of data efficiently by generating line-sized burst references. The ability
to simultaneously load an operand from memory into a register and execute a MAC instruction makes
some DSP operations such as filtering and convolution more manageable.
The programming model includes a mask register (MASK), which can optionally be used to generate an
operand address during MAC + MOVE instructions. The application of this register with auto-increment
addressing mode supports efficient implementation of circular data queues for memory operands.
4.4 Memory Map/Register Definition
The following table and sections explain the MAC registers:
Table 4-1. EMAC Memory Map
CPU Space
(Rc)
0x804 MAC Status Register (MACSR) 32 R/W 0x0000_0000 4.4.1/4-5
0x805 MAC Address Mask Register (MASK) 32 R/W 0xFFFF_FFFF 4.4.2/4-9
0x806, 0x809,
0x80A, 0x80B
0x807 MAC Accumulator 0,1 Extension Bytes (ACCext01) 32 R/W Undefined 4.4.4/4-10
0x808 MAC Accumulator 2,3 Extension Bytes (ACCext23) 32 R/W Undefined 4.4.4/4-10
MAC Accumulators 0–3 (ACC0–3) 32 R/W Undefined 4.4.3/4-10
Register
Width
(bits)
Access Reset Value Section/Page
4.4.1 MAC Status Register (MACSR)
The MAC status register (MACSR) contains a 4-bit operational mode field and condition flags.
Operational mode bits control whether operands are signed or unsigned and whether they are treated as
integers or fractions. These bits also control the overflow/saturation mode and the way in which rounding
is performed. Negative, zero, and multiple overflow condition flags are also provided.
Address: CPU @ 0x804 Access: User read/write
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0PAVn
W
Reset000000000000000000000000 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
OMC
S/U F/I R/T
N Z VEV
Figure 4-4. MAC Status Register (MACSR)
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-5
Preliminary
Page 72

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
Table 4-2. MACSR Field Descriptions
Field Description
31–12 Reserved, should be cleared.
11–8
PAV n
7
OMC
6
S/U
Product/accumulation overflow flags. Contains four flags, one per accumulator, that indicate if past MAC or
MSAC instructions generated an overflow during product calculation or the 48-bit accumulation. When a
MAC or MSAC instruction is executed, the PAVn flag associated with the destination accumulator is used
to form the general overflow flag, MACSR[V]. Once set, each flag remains set until V is cleared by a
MOV.L, MACSR instruction or the accumulator is loaded directly.
Overflow/saturation mode. Used to enable or disable saturation mode on overflow. If set, the accumulator
is set to the appropriate constant on any operation which overflows the accumulator. Once saturated, the
accumulator remains unaffected by any other MAC or MSAC instructions until either the overflow bit is
cleared or the accumulator is directly loaded.
Signed/unsigned operations.
In integer mode:
S/U determines whether operations performed are signed or unsigned. It also determines the accumulator
value during saturation, if enabled.
0 Signed numbers. On overflow, if OMC is enabled, an accumulator saturates to the most positive
(0x7FFF_FFFF) or the most negative (0x8000_0000) number, depending on both the instruction and the
value of the product that overflowed.
1 Unsigned numbers. On overflow, if OMC is enabled, an accumulator saturates to the smallest value
(0x0000_0000) or the largest value (0xFFFF_FFFF), depending on the instruction.
In fractional mode:
S/U controls rounding while storing an accumulator to a general-purpose register.
0 Move accumulator without rounding to a 16-bit value. Accumulator is moved to a general-purpose
register as a 32-bit value.
1 The accumulator is rounded to a 16-bit value using the round-to-nearest (even) method when it is moved
to a general-purpose register. See Section 4.4.1.1.1, “Rounding.” The resulting 16-bit value is stored in
the lower word of the destination register. The upper word is zero-filled. The accumulator value is not
affected by this rounding procedure.
5
F/I
4
R/T
3
N
2
Z
Fractional/integer mode Determines whether input operands are treated as fractions or integers.
0 Integers can be represented in either signed or unsigned notation, depending on the value of S/U.
1 Fractions are represented in signed, fixed-point, two’s complement notation. Values range from -1 to
-15
for 16-bit fractions and -1 to 1 - 2
1-2
-31
for 32-bit fractions. See Section 4.5.2, “Data
Representation."
Round/truncate mode. Controls the rounding procedure for MOV.L ACCx,Rx, or MSAC.L instructions when
operating in fractional mode.
0 Truncate. The product’s lsbs are dropped before it is combined with the accumulator. Additionally, when
a store accumulator instruction is executed (MOV.L ACCx,Rx), the 8 lsbs of the 48-bit accumulator logic
are simply truncated.
1 Round-to-nearest (even). The 64-bit product of two 32-bit, fractional operands is rounded to the nearest
40-bit value. If the low-order 24 bits equal 0x80_0000, the upper 40 bits are rounded to the nearest even
(lsb = 0) value. See Section 4.4.1.1.1, “Rounding.” Additionally, when a store accumulator instruction is
executed (MOV.L ACCx,Rx), the lsbs of the 48-bit accumulator logic are used to round the resulting 16or 32-bit value. If MACSR[S/U] = 0 and MACSR[R/T] = 1, the low-order 8 bits are used to round the
resulting 32-bit fraction. If MACSR[S/U] = 1, the low-order 24 bits are used to round the resulting 16-bit
fraction.
Negative. Set if the msb of the result is set, otherwise cleared. N is affected only by MAC, MSAC, and load
operations; it is not affected by MULS and MULU instructions.
Zero. Set if the result equals zero, otherwise cleared. This bit is affected only by MAC, MSAC, and load
operations; it is not affected by MULS and MULU instructions.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 73

Table 4-2. MACSR Field Descriptions (continued)
Field Description
Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
1
V
0
EV
Overflow. Set if an arithmetic overflow occurs on a MAC or MSAC instruction indicating that the result
cannot be represented in the limited width of the EMAC. V is set only if a product overflow occurs or the
accumulation overflows the 48-bit structure. V is evaluated on each MAC or MSAC operation and uses the
appropriate PAVn flag in the next-state V evaluation.
Extension overflow. Signals that the last MAC or MSAC instruction overflowed the 32 lsbs in integer mode
or the 40 lsbs in fractional mode of the destination accumulator. However, the result is still accurately
represented in the combined 48-bit accumulator structure. Although an overflow has occurred, the correct
result, sign, and magnitude are contained in the 48-bit accumulator. Subsequent MAC or MSAC operations
may return the accumulator to a valid 32/40-bit result.
Table 4-3 summarizes the interaction of the MACSR[S/U,F/I,R/T] control bits.
Table 4-3. Summary of S/U, F/I, and R/T Control Bits
S/U F/I R/T Operational Modes
0 0 x Signed, integer
0 1 0 Signed, fractional
Truncate on MAC.L and MSAC.L
No round on accumulator stores
0 1 1 Signed, fractional
Round on MAC.L and MSAC.L
Round-to-32-bits on accumulator stores
1 0 x Unsigned, integer
1 1 0 Signed, fractional
Truncate on MAC.L and MSAC.L
Round-to-16-bits on accumulator stores
1 1 1 Signed, fractional
Round on MAC.L and MSAC.L
Round-to-16-bits on accumulator stores
4.4.1.1 Fractional Operation Mode
This section describes behavior when the fractional mode is used (MACSR[F/I] is set).
4.4.1.1.1 Rounding
When the processor is in fractional mode, there are two operations during which rounding can occur:
1. Execution of a store accumulator instruction (MOV.L ACCx,Rx). The lsbs of the 48-bit
accumulator logic are used to round the resulting 16- or 32-bit value. If MACSR[S/U] is cleared,
the low-order 8 bits are used to round the resulting 32-bit fraction. If MACSR[S/U] is set, the
low-order 24 bits are used to round the resulting 16-bit fraction.
2. Execution of a MAC (or MSAC) instruction with 32-bit operands. If MACSR[R/T] is zero, multiplying two 32-bit numbers creates a 64-bit product that is truncated to the upper 40 bits; otherwise, it is rounded using round-to-nearest (even) method.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-7
Preliminary
Page 74

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
To understand the round-to-nearest-even method, consider the following example involving the rounding
of a 32-bit number, R0, to a 16-bit number. Using this method, the 32-bit number is rounded to the closest
16-bit number possible. Let the high-order 16 bits of R0 be named R0.U and the low-order 16 bits be R0.L.
• If R0.L is less than 0x8000, the result is truncated to the value of R0.U.
• If R0.L is greater than 0x8000, the upper word is incremented (rounded up).
• If R0.L is 0x8000, R0 is half-way between two 16-bit numbers. In this case, rounding is based on
the lsb of R0.U, so the result is always even (lsb = 0).
— If the lsb of R0.U = 1 and R0.L = 0x8000, the number is rounded up.
— If the lsb of R0.U = 0 and R0.L =0x8000, the number is rounded down.
This method minimizes rounding bias and creates as statistically correct an answer as possible.
The rounding algorithm is summarized in the following pseudocode:
if R0.L < 0x8000
then Result = R0.U
else if R0.L > 0x8000
then Result = R0.U + 1
else if lsb of R0.U = 0 /* R0.L = 0x8000 */
then Result = R0.U
else Result = R0.U + 1
The round-to-nearest-even technique is also known as convergent rounding.
4.4.1.1.2 Saving and Restoring the EMAC Programming Model
The presence of rounding logic in the output datapath of the EMAC requires that special care be taken
during the EMAC’s save/restore process. In particular, any result rounding modes must be disabled during
the save/restore process so the exact bit-wise contents of the EMAC registers are accessed. Consider the
following memory structure containing the EMAC programming model:
struct macState {
int acc0;
int acc1;
int acc2;
int acc3;
int accext01;
int accext02;
int mask;
int macsr;
} macState;
The following assembly language routine shows the proper sequence for a correct EMAC state save. This
code assumes all Dn and An registers are available for use and the memory location of the state save is
defined by A7.
EMAC_state_save:
move.l macsr,d7 ; save the macsr
clr.l d0 ; zero the register to ...
move.l d0,macsr ; disable rounding in the macsr
move.l acc0,d0 ; save the accumulators
move.l acc1,d1
move.l acc2,d2
move.l acc3,d3
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 75

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
move.l accext01,d4 ; save the accumulator extensions
move.l accext23,d5
move.l mask,d6 ; save the address mask
movem.l #0x00ff,(a7) ; move the state to memory
The following code performs the EMAC state restore:
EMAC_state_restore:
movem.l (a7),#0x00ff ; restore the state from memory
move.l #0,macsr ; disable rounding in the macsr
move.l d0,acc0 ; restore the accumulators
move.l d1,acc1
move.l d2,acc2
move.l d3,acc3
move.l d4,accext01 ; restore the accumulator extensions
move.l d5,accext23
move.l d6,mask ; restore the address mask
move.l d7,macsr ; restore the macsr
By executing this type of sequence, the exact state of the EMAC programming model can be correctly
saved and restored.
4.4.1.1.3 MULS/MULU
MULS and MULU are unaffected by fractional mode operation; operands are still assumed to be integers.
4.4.1.1.4 Scale Factor in MAC or MSAC Instructions
The scale factor is ignored while the MAC is in fractional mode.
4.4.2 Mask Register (MASK)
The 32-bit MASK implements the low-order 16 bits to minimize the alignment complications involved
with loading and storing only 16 bits. When the MASK is loaded, the low-order 16 bits of the source
operand are actually loaded into the register. When it is stored, the upper 16 bits are all forced to ones.
This register performs a simple AND with the operand address for MAC instructions. That is, the
processor calculates the normal operand address and, if enabled, that address is then ANDed with
{0xFFFF, MASK[15:0]} to form the final address. Therefore, with certain MASK bits cleared, the operand
address can be constrained to a certain memory region. This is used primarily to implement circular queues
in conjunction with the (An)+ addressing mode.
This feature minimizes the addressing support required for filtering, convolution, or any routine that
implements a data array as a circular queue. For MAC + MOVE operations, the MASK contents can
optionally be included in all memory effective address calculations. The syntax is as follows:
MAC.sz Ry,RxSF,<ea>y&,Rw
The & operator enables the use of MASK and causes bit 5 of the extension word to be set. The exact
algorithm for the use of MASK is as follows:
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-9
Preliminary
Page 76

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
if extension word, bit [5] = 1, the MASK bit, then
if <ea> = (An)
oa = An & {0xFFFF, MASK}
if <ea> = (An)+
oa = An
An = (An + 4) & {0xFFFF, MASK}
if <ea> =-(An)
oa = (An - 4) & {0xFFFF, MASK}
An = (An - 4) & {0xFFFF, MASK}
if <ea> = (d16,An)
oa = (An + se_d16) & {0xFFFF0x, MASK}
Here, oa is the calculated operand address and se_d16 is a sign-extended 16-bit displacement. For
auto-addressing modes of post-increment and pre-decrement, the calculation of the updated An value is
also shown.
Use of the post-increment addressing mode, {(An)+} with the MASK is suggested for circular queue
implementations.
Address: CPU @ 0x805 (MASK) Access: User read/write
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset11111111111111111111111111111111
Mask
Figure 4-5. Mask Register (MASK)
4.4.3 Accumulator Registers (ACC0–3)
The accumulator registers store 32-bits of the MAC operation result. The accumulator extension registers
are used to form the entire 48-bit result.
Address: CPU @ 0x806 (ACC0)
CPU @ 0x809 (ACC1)
CPU @ 0x80A (ACC2)
CPU @ 0x80B (ACC3)
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Accumulator
Figure 4-6. Accumulator Registers (ACC0–3)
Access: User read/write
4.4.4 Accumulator Extension Registers (ACCext01, ACCext23)
Each pair of 8-bit accumulator extension fields are concatenated with the corresponding 32-bit
accumulator register to form the 48-bit accumulator. For more information on their use, see Section 4.3,
“General Operation.”
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-10 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 77

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
Address: CPU @ 0x807 (ACCext01) Access: User read/write
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
Accumulator 0 Upper
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Extension Byte
Accumulator 0 Lower
Extension Byte
Accumulator 1 Upper
Extension Byte
Accumulator 1 Lower
Extension Byte
Figure 4-7. Accumulator Extension Register (ACCext01)
Address: CPU @ 0x808 (ACCext23) Access: User read/write
313029282726252423222120191817161514131211109876543210
R
Accumulator 2 Upper
W
Reset––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Extension Byte
Accumulator 2 Lower
Extension Byte
Accumulator 3 Upper
Extension Byte
Accumulator 3 Lower
Extension Byte
Figure 4-8. Accumulator Extension Register (ACCext23)
4.5 EMAC Instruction Set Summary
Table 4-4 summarizes EMAC unit instructions.
Table 4-4. EMAC Instruction Summary
Command Mnemonic Description
Multiply Signed MULS <ea>y,Dx Multiplies two signed operands yielding a signed result
Multiply Unsigned MULU <ea>y,Dx Multiplies two unsigned operands yielding an unsigned result
Multiply Accumulate MAC Ry,RxSF,ACCx
MSAC Ry,RxSF,ACCx
Multiply Accumulate
with Load
Load Accumulator MOV.L {Ry,#imm},ACCx Loads an accumulator with a 32-bit operand
Store Accumulator MOV.L ACCx,Rx Writes the contents of an accumulator to a CPU register
Copy Accumulator MOV.L ACCy,ACCx Copies a 48-bit accumulator
Load MACSR MOV.L {Ry,#imm},MACSR Writes a value to MACSR
Store MACSR MOV.L MACSR,Rx Write the contents of MACSR to a CPU register
Store MACSR to CCR MOV.L MACSR,CCR Write the contents of MACSR to the CCR
Load MAC Mask Reg MOV.L {Ry,#imm},MASK Writes a value to the MASK register
Store MAC Mask Reg MOV.L MASK,Rx Writes the contents of the MASK to a CPU register
Load AccExtensions01 MOV.L {Ry,#imm},ACCext01 Loads the accumulator 0,1 extension bytes with a 32-bit
MAC Ry,Rx,<ea>y,Rw,ACCx
MSAC Ry,Rx,<ea>y,Rw,ACCx
Multiplies two operands and adds/subtracts the product
to/from an accumulator
Multiplies two operands and combines the product to an
accumulator while loading a register with the memory operand
operand
Load AccExtensions23 MOV.L {Ry,#imm},ACCext23 Loads the accumulator 2,3 extension bytes with a 32-bit
operand
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-11
Preliminary
Page 78

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
Table 4-4. EMAC Instruction Summary (continued)
Command Mnemonic Description
Store AccExtensions01 MOV.L ACCext01,Rx Writes the contents of accumulator 0,1 extension bytes into a
CPU register
Store AccExtensions23 MOV.L ACCext23,Rx Writes the contents of accumulator 2,3 extension bytes into a
CPU register
4.5.1 EMAC Instruction Execution Times
The instruction execution times for the EMAC can be found in Section 3.11, “EMAC Instruction
Execution Times.”
The EMAC execution pipeline overlaps the AGEX stage of the OEP; that is, the first stage of the EMAC
pipeline is the last stage of the basic OEP. EMAC units are designed for sustained, fully-pipelined
operation on accumulator load, copy, and multiply-accumulate instructions. However, instructions that
store contents of the multiply-accumulate programming model can generate OEP stalls that expose the
EMAC execution pipeline depth, as in the following:
mac.w Ry, Rx, Acc0
mov.l Acc0, Rz
The mov.l instruction that stores the accumulator to an integer register (Rz) stalls until the program-visible
copy of the accumulator is available. Figure 4-9 shows EMAC timing.
Three-cycle
regBusy stall
DSOC
AGEX
EMAC EX1
EMAC EX2
EMAC EX3
EMAC EX4
Accumulator 0
mac
mac
mac
mac
mac
old
movmov
mov
mov
mac
new
Figure 4-9. EMAC-Specific OEP Sequence Stall
In Figure 4-9, the OEP stalls the store-accumulator instruction for 3 cycles: the depth of the EMAC
pipeline minus 1. The minus 1 factor is needed because the OEP and EMAC pipelines overlap by a cycle,
the AGEX stage. As the store-accumulator instruction reaches the AGEX stage where the operation is
performed, the just-updated accumulator 0 value is available.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-12 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 79

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
As with change or use stalls between accumulators and general-purpose registers, introducing intervening
instructions that do not reference the busy register can reduce or eliminate sequence-related store-MAC
instruction stalls. In fact, a major benefit of the EMAC is the addition of three accumulators to minimize
stalls caused by exchanges between the accumulator(s) and the general-purpose registers.
4.5.2 Data Representation
MACSR[S/U,F/I] selects one of the following three modes, where each mode defines a unique operand
type:
1. Two’s complement signed integer: In this format, an N-bit operand value lies in the range -2
< operand < 2
(N-1)
- 1. The binary point is right of the lsb.
2. Unsigned integer: In this format, an N-bit operand value lies in the range 0 < operand < 2N - 1. The binary point is right of the lsb.
3. Two’s complement, signed fractional: In an N-bit number, the first bit is the sign bit. The remaining
bits signify the first N-1 bits after the binary point. Given an N-bit number, a
N-1aN-2aN-3
its value is given by the equation in Equation 4-3.
N2–
value 1 a
⋅()–2
N1–
+=
This format can represent numbers in the range -1 < operand < 1 - 2
∑
i0=
i1N–+()
ai⋅
(N-1)
.
(N-1)
... a2a1a0,
Eqn. 4-3
For words and longwords, the largest negative number that can be represented is -1, whose internal
representation is 0x8000 and 0x8000_0000, respectively. The largest positive word is 0x7FFF or (1 - 2
the most positive longword is 0x7FFF_FFFF or (1 - 2
-31
).
4.5.3 MAC Opcodes
MAC opcodes are described in the ColdFire Programmer’s Reference Manual.
Note the following:
• Unless otherwise noted, the value of MACSR[N,Z] is based on the result of the final operation that
involves the product and the accumulator.
• The overflow (V) flag is handled differently. It is set if the complete product cannot be represented
as a 40-bit value (this applies to 32 × 32 integer operations only) or if the combination of the
product with an accumulator cannot be represented in the given number of bits. The EMAC design
includes an additional product/accumulation overflow bit for each accumulator that are treated as
sticky indicators and are used to calculate the V bit on each MAC or MSAC instruction. See
Section 4.4.1, “MAC Status Register (MACSR).”
• For the MAC design, the assembler syntax of the MAC (multiply and add to accumulator) and
MSAC (multiply and subtract from accumulator) instructions does not include a reference to the
single accumulator. For the EMAC, it is expected that assemblers support this syntax and that no
explicit reference to an accumulator is interpreted as a reference to ACC0. These assemblers would
also support syntaxes where the destination accumulator is explicitly defined.
-15
);
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-13
Preliminary
Page 80

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
• The optional 1-bit shift of the product is specified using the notation {<< | >>} SF, where <<1
indicates a left shift and >>1 indicates a right shift. The shift is performed before the product is
added to or subtracted from the accumulator. Without this operator, the product is not shifted. If the
EMAC is in fractional mode (MACSR[F/I] is set), SF is ignored and no shift is performed. Because
a product can overflow, the following guidelines are implemented:
— For unsigned word and longword operations, a zero is shifted into the product on right shifts.
— For signed, word operations, the sign bit is shifted into the product on right shifts unless the
product is zero. For signed, longword operations, the sign bit is shifted into the product unless
an overflow occurs or the product is zero, in which case a zero is shifted in.
— For all left shifts, a zero is inserted into the lsb position.
The following pseudocode explains basic MAC or MSAC instruction functionality. This example is
presented as a case statement covering the three basic operating modes with signed integers, unsigned
integers, and signed fractionals. Throughout this example, a comma-separated list in curly brackets, {},
indicates a concatenation operation.
switch (MACSR[6:5]) /* MACSR[S/U, F/I] */
{
case 0: /* signed integers */
if (MACSR.OMC == 0 || MACSR.PAVn == 0)
then {
MACSR.PAVn = 0
/* select the input operands */
if (sz == word)
then {if (U/Ly == 1)
then operandY[31:0] = {sign-extended Ry[31], Ry[31:16]}
else operandY[31:0] = {sign-extended Ry[15], Ry[15:0]}
if (U/Lx == 1)
then operandX[31:0] = {sign-extended Rx[31], Rx[31:16]}
else operandX[31:0] = {sign-extended Rx[15], Rx[15:0]}
}
else {operandY[31:0] = Ry[31:0]
operandX[31:0] = Rx[31:0]
}
/* perform the multiply */
product[63:0] = operandY[31:0] * operandX[31:0]
/* check for product overflow */
if ((product[63:39] != 0x0000_00_0) && (product[63:39] != 0xffff_ff_1))
then { /* product overflow */
MACSR.PAVn = 1
MACSR.V = 1
if (inst == MSAC && MACSR.OMC == 1)
then if (product[63] == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0x0000_7fff_ffff
else result[47:0] = 0xffff_8000_0000
else if (MACSR.OMC == 1)
then /* overflowed MAC,
saturationMode enabled */
if (product[63] == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0xffff_8000_0000
else result[47:0] = 0x0000_7fff_ffff
}
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-14 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 81

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
/* sign-extend to 48 bits before performing any scaling */
product[47:40] = {8{product[39]}} /* sign-extend */
/* scale product before combining with accumulator */
switch (SF) /* 2-bit scale factor */
{
case 0: /* no scaling specified */
break;
case 1: /* SF = “<< 1” */
product[40:0] = {product[39:0], 0}
break;
case 2: /* reserved encoding */
break;
case 3: /* SF = “>> 1” */
product[39:0] = {product[39], product[39:1]}
break;
}
if (MACSR.PAVn == 0)
then {if (inst == MSAC)
then result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] - product[47:0]
else result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] + product[47:0]
}
/* check for accumulation overflow */
if (accumulationOverflow == 1)
then {MACSR.PAVn = 1
MACSR.V = 1
if (MACSR.OMC == 1)
then /* accumulation overflow,
saturationMode enabled */
if (result[47] == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0x0000_7fff_ffff
else result[47:0] = 0xffff_8000_0000
}
/* transfer the result to the accumulator */
ACCx[47:0] = result[47:0]
}
MACSR.V = MACSR.PAVn
MACSR.N = ACCx[47]
if (ACCx[47:0] == 0x0000_0000_0000)
then MACSR.Z = 1
else MACSR.Z = 0
if ((ACCx[47:31] == 0x0000_0) || (ACCx[47:31] == 0xffff_1))
then MACSR.EV = 0
else MACSR.EV = 1
break;
case 1,3: /* signed fractionals */
if (MACSR.OMC == 0 || MACSR.PAVn == 0)
then {
MACSR.PAVn = 0
if (sz == word)
then {if (U/Ly == 1)
then operandY[31:0] = {Ry[31:16], 0x0000}
else operandY[31:0] = {Ry[15:0], 0x0000}
if (U/Lx == 1)
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-15
Preliminary
Page 82

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
then operandX[31:0] = {Rx[31:16], 0x0000}
else operandX[31:0] = {Rx[15:0], 0x0000}
}
else {operandY[31:0] = Ry[31:0]
operandX[31:0] = Rx[31:0]
}
/* perform the multiply */
product[63:0] = (operandY[31:0] * operandX[31:0]) << 1
/* check for product rounding */
if (MACSR.R/T == 1)
then { /* perform convergent rounding */
if (product[23:0] > 0x80_0000)
then product[63:24] = product[63:24] + 1
else if ((product[23:0] == 0x80_0000) && (product[24] == 1))
then product[63:24] = product[63:24] + 1
}
/* sign-extend to 48 bits and combine with accumulator */
/* check for the -1 * -1 overflow case */
if ((operandY[31:0] == 0x8000_0000) && (operandX[31:0] == 0x8000_0000))
then product[71:64] = 0x00 /* zero-fill */
else product[71:64] = {8{product[63]}} /* sign-extend */
if (inst == MSAC)
then result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] - product[71:24]
else result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] + product[71:24]
/* check for accumulation overflow */
if (accumulationOverflow == 1)
then {MACSR.PAVn = 1
MACSR.V = 1
if (MACSR.OMC == 1)
then /* accumulation overflow,
saturationMode enabled */
if (result[47] == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0x007f_ffff_ff00
else result[47:0] = 0xff80_0000_0000
}
/* transfer the result to the accumulator */
ACCx[47:0] = result[47:0]
}
MACSR.V = MACSR.PAVn
MACSR.N = ACCx[47]
if (ACCx[47:0] == 0x0000_0000_0000)
then MACSR.Z = 1
else MACSR.Z = 0
if ((ACCx[47:39] == 0x00_0) || (ACCx[47:39] == 0xff_1))
then MACSR.EV = 0
else MACSR.EV = 1
break;
case 2: /* unsigned integers */
if (MACSR.OMC == 0 || MACSR.PAVn == 0)
then {
MACSR.PAVn = 0
/* select the input operands */
if (sz == word)
then {if (U/Ly == 1)
then operandY[31:0] = {0x0000, Ry[31:16]}
else operandY[31:0] = {0x0000, Ry[15:0]}
if (U/Lx == 1)
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-16 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 83

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
then operandX[31:0] = {0x0000, Rx[31:16]}
else operandX[31:0] = {0x0000, Rx[15:0]}
}
else {operandY[31:0] = Ry[31:0]
operandX[31:0] = Rx[31:0]
}
/* perform the multiply */
product[63:0] = operandY[31:0] * operandX[31:0]
/* check for product overflow */
if (product[63:40] != 0x0000_00)
then { /* product overflow */
MACSR.PAVn = 1
MACSR.V = 1
if (inst == MSAC && MACSR.OMC == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0x0000_0000_0000
else if (MACSR.OMC == 1)
then /* overflowed MAC,
saturationMode enabled */
result[47:0] = 0xffff_ffff_ffff
}
/* zero-fill to 48 bits before performing any scaling */
product[47:40] = 0 /* zero-fill upper byte */
/* scale product before combining with accumulator */
switch (SF) /* 2-bit scale factor */
{
case 0: /* no scaling specified */
break;
case 1: /* SF = “<< 1” */
product[40:0] = {product[39:0], 0}
break;
case 2: /* reserved encoding */
break;
case 3: /* SF = “>> 1” */
product[39:0] = {0, product[39:1]}
break;
}
/* combine with accumulator */
if (MACSR.PAVn == 0)
then {if (inst == MSAC)
then result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] - product[47:0]
else result[47:0] = ACCx[47:0] + product[47:0]
}
/* check for accumulation overflow */
if (accumulationOverflow == 1)
then {MACSR.PAVn = 1
MACSR.V = 1
if (inst == MSAC && MACSR.OMC == 1)
then result[47:0] = 0x0000_0000_0000
else if (MACSR.OMC == 1)
then /* overflowed MAC,
saturationMode enabled */
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 4-17
Preliminary
Page 84

Enhanced Multiply-Accumulate Unit (EMAC)
}
/* transfer the result to the accumulator */
ACCx[47:0] = result[47:0]
}
MACSR.V = MACSR.PAVn
MACSR.N = ACCx[47]
if (ACCx[47:0] == 0x0000_0000_0000)
then MACSR.Z = 1
else MACSR.Z = 0
if (ACCx[47:32] == 0x0000)
then MACSR.EV = 0
else MACSR.EV = 1
break;
}
result[47:0] = 0xffff_ffff_ffff
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
4-18 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 85

Chapter 5 Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
This chapter describes the Cryptographic Acceleration Unit (CAU) programming model. The CAU is an
instruction level coprocessor that is accessed with ColdFire coprocessor instructions (see section XX). The
CAU supports acceleration of the following cryptographic algorithms: DES, 3DES, AES, MD5 and
SHA-1.
NOTE
To enhance readability, this chapter shows the CAU as coprocessor 0.
Future implementations could have the CAU designated as coprocessor 1.
5.1 CAU Registers
The CAU register file consists of eight, 32-bit registers as shown in Table 5-1. All registers can be read
with the coprocessor store instruction (cp0st.l) and written with the coprocessor load instruction (cp0ld.l).
However, only bits 0-1 of the CASR are writable. Bits 2-27 of CASR loads should be 0 for compatibility
with future versions of the CAU. The CAU only supports long word accesses and register codes 0x8-0xF
are reserved.
Table 5-1. CAU Register File
Code Name Description DES AES SHA-1 MD5
0 CASR status register -- -- -- --
1 CAA accumulator -- -- T a
2 CA0 general purpose 0 C W0 A --
3 CA1 general purpose 1 D W1 B b
4 CA2 general purpose 2 L W2 C c
5 CA3 general purpose 3 R W3 D d
6 CA4 general purpose 4 -- -- E --
7 CA5 general purpose 5 -- -- W --
5.1.1 CAU Status Register
The status register (CASR) contains all of the status and configuration for the CAU. It has three defined
fields and 26 bits reserved as shown in Figure 5-1<f-helvetica><st-bold>Figure 5-1..
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 5-1
Preliminary
Page 86

Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16
R VER 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
W
RESET: 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
W
RESET: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
= Read Only or Reserved
Figure 5-1. Status Register (CASR)
DPE IC
IC — Illegal Command
1 = Illegal coprocessor command issued
0 = No illegal commands issued
DPE — DES Parity Error
1 = DES key parity error detected
0 = No error detected
VER — CAU Version
Indicates CAU version; only version 1 is defined.
5.2 CAU Operation
The cp0ld.l instruction is used to write to CAU registers and specify CAU operations. Operand 1 of the
instruction is the source operand (if any) and the CAU destination register is encoded in the CMD field.
All CAU load instruction commands have an execution time specifier of 0.
The cp0st.l instruction is used to read CAU registers. The CAU source register is encoded in the CMD.
The CAU only supports long word stores. The CAU store instruction command has an execution time
specifier of 0.
5.3 CAU Commands
The CAU supports 22 commands as shown in Table 5-2 and described in the following sections, (see
section Section 5.4, “CAU Equate Values “ for assembly constant definitions). All other encodings are
reserved. The IC bit in the CASR will be set if any command is issued that is not defined in the encodings
described in this section. A specific illegal command (ILL) is defined to allow for software self checking.
Reserved commands should not be issued to ensure compatibility with future implementations.
NOTE
The value CAx is any CAU register (CASR, CAA, CA0-CA5).
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
5-2 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 87

Table 5-2. CAU Commands
Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
Inst Type
cp0ld.l CNOP No Operation 0x00 0x0 ---
cp0ld.l LDR Load Reg 0x01 CAx Op1 -> CAx
cp0st.l STR Store Reg 0x02 CAx CAx -> Destination
cp0ld.l ADR Add 0x03 CAx CAx + Op1 -> CAx
cp0ld.l RADR Reverse and Add 0x04 CAx CAx + ByteRev(Op1) -> CAx
cp0ld.l ADRA Add Reg to Acc 0x05 CAx CAx + CAA -> CAA
cp0ld.l XOR Exclusive Or 0x06 CAx CAx ^ Op1 -> CAx
cp0ld.l ROTL Rotate Left 0x07 CAx CAx <<< Op1 -> CAx
cp0ld.l MVRA Move Reg to Acc 0x08 CAx CAx -> CAA
cp0ld.l MVAR Move Acc to Reg 0x09 CAx CAA -> CAx
cp0ld.l AESS AES Sub Bytes 0x0A CAx SubBytes(CAx) -> CAx
cp0ld.l AESIS AES Inv Sub Bytes 0x0B CAx InvSubBytes(CAx) -> CAx
cp0ld.l AESC AES Column Op 0x0C CAx MixColumns(CAx)^Op1 -> CAx
cp0ld.l AESIC AES Inv Column Op 0x0D CAx InvMixColumns(CAx^Op1) -> CAx
cp0ld.l AESR AES Shift Rows 0x0E 0x0 ShiftRows(CA0-CA3) -> CA0-CA3
cp0ld.l AESIR AES Inv Shift Rows 0x0F 0x0 InvShiftRows(CA0-CA3) -> CA0-CA3
cp0ld.l DESR DES Round 0x10 IP FP KS[1:0] DES Round(CA0-CA3)->CA0-CA3
cp0ld.l DESK DES Key Setup 0x11 0 0 CP DC DES Key Op(CA0-CA1)->CA0-CA1
cp0ld.l HASH Hash Function 0x12 0 HF[2:0] Hash Func(CA1-CA3)+CAA->CAA
cp0ld.l SHS Secure Hash Shift 0x13 0x0 CAA <<< 5 -> CAA,
cp0ld.l MDS Message Digest Shift 0x14 0x0 CA3-> CAA, CAA->CA1, CA1->CA2,
cp0ld.l ILL Illegal Command 0x1F 0x0 0x1->CASR[0]
Command
Name
Description CMD[8:4] CMD[3:0] Operation
Key Parity Error & CP -> CASR[1]
CAA->CA0, CA0->CA1,
CA1 <<< 30 -> CA2,
CA2->CA3, CA3->CA4
CA2->CA3,
5.3.1 CNOP - coprocessor no operation
cp0ld.l #CNOP
The CNOP command is the coprocessor cp0nop instruction defined for synchronization.
5.3.2 LDR - load register
cp0ld.l <ea>,#LDR+CAx
The LDR command loads CAx with the source data specified by <ea>.
5.3.3 STR - store register
cp0st.l <ea>,#STR+CAx
The STR command stores the value from CAx to the destination specified by <ea>.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 5-3
Preliminary
Page 88

Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
5.3.4 ADR - add to register
cp0ld.l <ea>,#ADR+CAx
The ADR command adds the source operand specified by <ea> to CAx and stores the result in CAx.
5.3.5 RADR - reverse and add to register
cp0ld.l <ea>,#RADR+CAx
The RADR command does a byte reverse on the source operand specified by <ea>, adds that value to CAx
and stores the result in CAx. An example is shown in Table 5-3.
Table 5-3. RADR Command Example
Operand CAx Before CAx After
01020304 A0B0C0D0 A4B3C2D1
5.3.6 ADRA - add register to accumulator
cp0ld.l #ADRA+CAx
The ADRA command adds CAx to CAA and stores the result in CAA.
5.3.7 XOR - exclusive or
cp0ld.l <ea>,#XOR+CAx
The XOR command does an exclusive or of the source operand specified by <ea> with CAx and stores the
result in CAx.
5.3.8 ROTL - rotate left
cp0ld.l <ea>,#ROTL+CAx
The ROTL rotates the bits of CAx to the left with the result stored back to CAx. The number of bits to
rotate is the value specified by <ea> modulo 32.
5.3.9 MVRA - move register to accumulator
cp0ld.l #MVRA+CAx
The MVRA moves the value from the source register CAx to the destination register CAA.
5.3.10 MVAR - move accumulator to register
cp0ld.l #MVAR+CAx
The MVRA command moves the value from source register CAA to the destination register CAx.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
5-4 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 89

Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
5.3.11 AESS - AES substitution
cp0ld.l #AESS+CAx
The AESS command performs the AES byte substitution operation on CAx and stores the result back to
CAx.
5.3.12 AESIS - AES inverse substitution
cp0ld.l #AESIS+CAx
The AESIS command performs the AES inverse byte substitution operation on CAx and stores the result
back to CAx.
5.3.13 AESC - AES column operation
cp0ld.l <ea>,#AESC+CAx
The AESC command performs the AES columns operation on the contents of CAx then performs an
exclusive or of that result with the source operand specified by <ea> and stores the result in CAx.
5.3.14 AESIC - AES inverse column operation
cp0ld.l <ea>,#AESIC+CAx
The AESIC command performs an exclusive or operation of the source operand specified by <ea> on the
contents of CAx followed by the AES inverse mix columns operation on that result and stores the result
back in CAx.
5.3.15 AESR - AES shift rows
cp0ld.l #AESR
The AESR command performs the AES shift rows operation on registers CA0, CA1, CA2 and CA3. An
example is shown in Table 5-4 .
Table 5-4. AESR Command Example
Register Before After
CA0 01020304 01060B00
CA1 05060708 050A0F04
CA2 090A0B0C 090E0308
CA3 0D0E0F00 0D02070C
5.3.16 AESIR - AES inverse shift rows
cp0ld.l #AESIR
The AESR command performs the AES inverse shift rows operation on registers CA0, CA1, CA2 and
CA3. An example is shown in Table 5-5 .
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 5-5
Preliminary
Page 90

Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
Table 5-5. AESIR Command Example
Register Before After
CA0 01060B00 01020304
CA1 050A0F04 05060708
CA2 090E0308 090A0B0C
CA3 0D02070C 0D0E0F00
5.3.17 DESR - DES round
cp0ld.l #DESR+{IP}+{FP}+{KSx}
The DESR command performs a round of the DES algorithm and a key schedule update with the following
source and destination designations: CA0=C, CA1=D, CA2=L, CA3=R. If the IP bit is set then the DES
initial permutation is performed on CA2 and CA3 before the round operation. If the FP bit is set then the
DES final permutation (inverse initial permutation) is performed on CA2 and CA3 after the round
operation. The round operation uses the source values from registers CA0 and CA1 for the key addition
operation. The KSx field specifies the shift to use for the key schedule operation used to update the values
in CA0 and CA1. The specific shift function performed is based on the KSx field as defined in Table 5-6 .
Table 5-6. Key Shift Function Codes
KSx
Code
0 KSL1 Left 1
1 KSL2 Left 2
2 KSR1 Right 1
3 KSR2 Right 2
KSx
Define
Shift Function
5.3.18 DESK - DES key setup
cp0ld.l #DESK+{CP}+{DC}
The DESK command performs the initial key transformation (permuted choice 1) defined by the DES
algorithm on CA0 and CA1 with CA0 containing bits 1-32 of the key and CA1 containing bits 33-64 of
the key1. If the DC bit is set then no shift operation is performed and the values C0 and D0 are stored back
to CA0 and CA1 respectively. The DC bit should be set for decrypt operations. If the DC bit is not set then
a left shift by 1 is also performed and the values C
and D1 are stored back to CA0 and CA1 respectively.
1
The DC bit should be 0 for encrypt operations. If the CP bit is set and a key parity error is detected then
the DPE bit of the CASR is set, otherwise it is cleared.
5.3.19 HASH - hash function
cp0ld.l #HASH+HFx
The HASH command performs a hashing operation on CA1, CA2 and CA3 and adds that result to the
value in CAA and stores the result in CAA. The specific hash function performed is based on the HFx field
as defined in Table 5-7.
1.The DES algorithm numbers the most significant bit of a block as bit1 and the least significant as bit 64.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
5-6 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 91

Table 5-7. Hash Function Codes
Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
HFx
Code
0 HFF MD5 F() CA1&CA2 | ~CA1&CA3
1 HFG MD5 G() CA1&CA3 | CA2&~CA3
2 HFH MD5 H(), SHA Parity() CA1^CA2^CA3
3 HFI MD5 I() CA2^(CA1|~CA3)
4 HFC SHA Ch() CA1&CA2 ^ ~CA1&CA3
5 HFM SHA Maj() CA1&CA2 ^ CA1&CA3 ^ CA2&CA3
HFx
Define
Hash Function Hash Logic
5.3.20 SHS - secure hash shift
cp0ld.l #SHS
The SHS command does a set of register to register move and shift operations in parallel that is useful for
implementing SHA-1. The following source and destination assignments are made: CAA=CAA<<<5,
CA0=CAA, CA1=CA0, CA2=CA1<<<30, CA3=CA2, CA4=CA3.
5.3.21 MDS - message digest shift
cp0ld.l #MDS
The MDS command does a set of register to register move operations in parallel that is useful for
implementing MD5. The following source and destination assignments are made: CAA=CA3,
CA1=CAA, CA2=CA1, CA3=CA2.
5.3.22 ILL - illegal command
cp0ld.l #ILL
The ILL command is a specific illegal command that sets the IC bit in the CASR. All undefined commands
are reserved for use in future implementations.
5.4 CAU Equate Values
; CAU Registers (CAx)
.set CASR,0x0
.set CAA,0x1
.set CA0,0x2
.set CA1,0x3
.set CA2,0x4
.set CA3,0x5
.set CA4,0x6
.set CA5,0x7
; CAU Commands
.set CNOP,0x000
.set LDR,0x010
.set STR,0x020
.set ADR,0x030
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor 5-7
Preliminary
Page 92

Cryptographic Acceleration Unit
.set RADR,0x040
.set ADRA,0x050
.set XOR,0x060
.set ROTL,0x070
.set MVRA,0x080
.set MVAR,0x090
.set AESS,0x0A0
.set AESIS,0x0B0
.set AESC,0x0C0
.set AESIC,0x0D0
.set AESR,0x0E0
.set AESIR,0x0F0
.set DESR,0x100
.set DESK,0x110
.set HASH,0x120
.set SHS,0x130
.set MDS,0x140
.set ILL,0x1F0
; DESR Fields
.set IP,0x08 ; initial permutation
.set FP,0x04 ; final permutation
.set KSL1,0x00 ; key schedule left 1 bit
.set KSL2,0x01 ; key schedule left 2 bits
.set KSR1,0x02 ; key schedule right 1 bit
.set KSR2,0x03 ; key schedule right 2 bits
; DESK Field
.set DC,0x01 ; decrypt key schedule
.set CP,0x02 ; check parity
; HASH Functions Codes
.set HFF,0x0 ; MD5 F() CA1&CA2 | ~CA1&CA3
.set HFG,0x1 ; MD5 G() CA1&CA3 | CA2&~CA3
.set HFH,0x2 ; MD5 H(), SHA Parity() CA1^CA2^CA3
.set HFI,0x3 ; MD5 I() CA2^(CA1|~CA3)
.set HFC,0x4 ; SHA Ch() CA1&CA2 ^ ~CA1&CA3
.set HFM,0x5 ; SHA Maj() CA1&CA2 ^ CA1&CA3 ^ CA2&CA3
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
5-8 Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary
Page 93

Chapter 6 Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
A top level block diagram of the RNGA is shown in Figure 6-1. The module is connects to the IP Bus
defined in SRS version 3.1.1 IP Interface Specification.
Output Register
RNGA Core/Control
Logic
Figure 6-1. RNGA Block Diagram
Internal
Bus
6.1 Overview
The RNGA (Random Number Generator Accelerator) module is a digital integrated circuit capable of
generating 32-bit random numbers. It is designed to comply with FIPS-140 standards for randomness and
non-determinism. The random bits are generated by clocking shift registers with clocks derived from ring
oscillators. The configuration of the shift registers ensures statistically good data (i.e. data that looks
random). The oscillators with their unknown frequencies provide the required entropy needed to create
random data.
It is important to note that there is no known cryptographic proof showing that this is a secure method of
generating random data. In fact, there may be an attack against the random number generator described in
this document if its output is used directly in a cryptographic application (the attack is based on the
linearity of the internal shift registers). In light of this, it is highly recommended that the random data
produced by this module be used as an input seed to a NIST approved (based on DES or SHA-1) or
cryptographically secure (RSA Generator or BBS Generator) random number generation algorithm. It is
also recommended that other sources of entropy be used along with the RNGA to generate the seed to the
pseudorandom algorithm. The more random sources combined to create the seed the better. The following
is a list of sources which could be easily combined with the output of this module.
• Current time using highest precision possible.
• Mouse and keyboard motions (or equivalent if being used on a cell phone or PDA).
• Other entropy supplied directly by the user.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor Preliminary 6-1
Page 94

Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
6.2 Features
The RNGA includes these distinctive features:
• 32-bit interface
• 32-bit Output Register
• secure mode
• power saving mode
6.3 Modes of Operation
Although the RNGA has several modes, only one is intended for use during normal operation. The other
modes were created to aid in verification and testability of the module. The Normal and Oscillator
Frequency Test Modes are entered by setting the appropriate bits in the RNGA Mode register. The Sleep
Mode is entered by setting the appropriate bit in the RNGA Control register. These registers are described
in more detail in Section 6.4.1, “.Register Descriptions.
• Normal Mode
In this mode the RNGA generates random data. Since this is the default mode of operation, the user
is not required to change the mode before requesting random data. This is also the only valid mode
when in the secure state. While in this mode, the internal shift registers are driven by internally
generated clocks with unknown frequency. Depending on the internal state of the RNGA, these
clocks are derived from either the RNGA’s oscillators or a deterministic clock (based on the system
clock). For simplicity sake, throughout the rest of this document these clocks will be referred to as
the oscillator clocks.
• Secure Mode
In this mode the RNGA is forced into the Normal mode described above. Secure Mode is equivalent
to the condition where the RNGA is in Normal mode and is unable to exit that mode. The low power
Sleep Mode can be entered while in the Secure Mode.
• Verification Mode
This mode is provided for verification and testing of the module. While in this mode, the random
output is generated by a counter rather than the usual shift registers. The deterministic result allows
for easy verification of the surrounding RNGA control logic.
• Oscillator Frequency Test Mode
This mode is provided for testing of the RNGA’s ring oscillators. While in this mode, the shift
registers are clocked exclusively by the oscillator clocks (this may not be the case in the Normal
Mode) allowing the oscillator frequency counters (described in Section 6.4.1, “.Register
Descriptions) to accurately count the pulses received from the oscillator clocks during a given
amount of time.
• Sleep Mode
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
6-2 Preliminary Freescale Semiconductor
Page 95

Memory Map/Register Definition
In this mode the RNGA’s oscillator clocks are shut off. The mode is entered by writing to the Sleep
bit in the Control Register. When in this mode, the Output Register will not be loaded.
• Scan Mode
In this mode the RNGA reconfigures much of its untestable logic so it is testable by scan. The mode
is entered by driving the block input ipt_mode active. This mode should only be used when scan is
used to test the module.
These are high level descriptions only, detailed descriptions of operating modes are contained in later
sections.
6.4 Memory Map/Register Definition
The address map for the RNGA is shown in Table 6-1. The following subsections describe each
addressable register in more detail.
Table 6-1. Module Memory Map1
Address Use Access
0x00 Control R/W
0x04 Status R
0x08 Entropy Register W
0x0c Output Register R
0x10 Mode R/W
0x14 Verification Control R/W
0x18 Oscillator Control Counter R/W
0x1c Oscillator #1 Counter R
0x20 Oscillator #2 Counter R
0x24 Oscillator Counter Status R
= Registers which are inaccessible in secure mode
1
Shaded registers are intended for factory test purposes only. Access to these registers is blocked when
the RNGA is in Secure Mode
6.4.1 .Register Descriptions
This section consists of register descriptions in address order. All RNGA_32IP registers are 32-bit access
only.
6.4.1.1 Control Register
Immediately after reset the RNGA begins generating entropy in its internal shift registers. Random data is
not pushed to the Output Register until after the Go bit in the Control register is set to a one. After this, a
random 32-bit word is pushed to the Output Register every 256 cycles. If the Output Register is full, then
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Freescale Semiconductor
Preliminary 6-3
Page 96

Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
no push will occur. In this way the Output Register will be kept as full as possible. The fields in the Control
Register are defined in Figure 6-2.
31:5 4 3 2 1 0
R 0x0000000
W
RESET: 0x0000000 0 0 0 0 0
REG
ADDR
Sleep
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Figure 6-2. Control Register
0
Clear Inter-
rupt
0x001F_0000
Interrupt
Mask
High Assur-
ance
Go
Go
The Go Bit must be set before the RNGA will begin loading data into the Output Register. This bit is
sticky and can only be cleared by a hardware reset or by changing to Secure Mode. Setting the Go bit
will not bring the RNGA out of Sleep Mode. Furthermore, the Go bit does not need to be reset after
exiting Sleep Mode.
1 = Output Register will be loaded with random data.
0 = Output Register is not loaded with random data.
High Assurance
While this bit is high, the RNGA will notify the SCC if a security violation occurs (i.e. the Output
Register is read while empty). This bit enables Security Violation bit in the Status Register as well as
the output rnga_scc_debug port. This bit is sticky and can only be cleared through a hardware reset.
1 = Enable notification of security violations.
0 = Disable notification of security violations.
Interrupt Mask
This bit masks the error interrupt, ipi_error_int.
1 = Interrupt ipi_error_int is masked.
0 = Interrupt ipi_error_int is enabled.
Clear Interrupt
Writing a one to this bit clears the error interrupt as well as the error status bit in the Status Register.
The bit is self clearing.
1 = Clear interrupt ipi_error_int.
0 = Do not clear interrupt ipi_error_int.
Sleep
The RNGA can be placed in low power mode by either asserting the module input ipg_doze, or by
setting this Sleep bit. If either of these conditions are met, the oscillators are disabled. De-asserting
ipg_doze and resetting the Sleep Bit will cause the RNGA to exit Sleep Mode. The Output Register
will not be pushed while the RNGA is in Sleep Mode.
1 = RNGA is in Sleep Mode.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
6-4 Preliminary Freescale Semiconductor
Page 97

Memory Map/Register Definition
0 = RNGA is not in Sleep Mode.
6.4.1.2 Status Register
The Status Register shown in Figure 6-3 is a read only register which reflects the internal status of the
RNGA. Only 32-bit reads of this register is supported.
31 30:24 23-16 15:8 7:5 4 3 2 1 0
R
W
RESET: 0 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x0 0 0 0 0 0
REG
ADDR
Osc.
Dead
0x00
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Output
Register
Size
Security Violation
When enabled by the High Assurance bit in the Control Register, this bit signals that a security
violation has occurred. Currently, Output Register underflow is the only condition which is considered
a security violation. The bit is sticky and can only be cleared by a hardware reset. The output
rnga_scc_debug is driven off this bit.
1 = A security violation has occurred.
0 = No security violations have occurred or the High Assurance bit in the Control Register is not set.
Output
Register
Level
Figure 6-3. Status Register
0x0 Sleep
0x001F_0004
Error In-
terrupt
Output
Register
Underflow
Last Read
Status
Security
Violation
Last Read Status
This bit is always enabled and reflects the status of the most recent read of the Output Register.
1 = Last read was performed while the Output Register was empty (underflow condition).
0 = Last read was performed while the Output Register was not empty.
Output Register Underflow
This bit is always enabled and signals a Output Register underflow condition. The bit is reset by
reading the Status Register.
1 = The Output Register has been read while empty since last read of the Status Register.
0 = The Output Register has not been read while empty since last read of the Status Register.
Error Interrupt
This bit is always enabled and signals a Output Register underflow condition. This bit is different from
the previous two bits in that it is only reset by a write to the clear interrupt bit in the Control Register.
This bit is not masked by the Interrupt Mask bit of the Control Register.
1 = The Output Register has been read while empty.
0 = The Output Register has not been read while empty.
Sleep
Freescale Semiconductor
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
Preliminary 6-5
Page 98

Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
This bit reflects whether the RNGA is in Sleep mode (i.e. either the Sleep bit in the Control Register
is set or the ipg_doze input is asserted). When this bit is a one, the RNGA is in Sleep Mode and the
oscillator clocks are inactive. While in this mode, the Output Register will not be loaded and the Output
Register Level will not increase.
1 = The RNGA is in Sleep Mode.
0 = The RNGA is not in Sleep Mode.
Output Register Level
Signals how many random words are currently resident in the Output Register. The bits should be
interpreted as an integer (the value 0b00001001 = signals that 0x09 random words are in the Output
Register)
Output Register Size
Signals the actual size of the Output Register. In other words, this is the maximum possible Output
Register Level. The bits should be interpreted as an integer.
Osc. Dead
Indicates that at least one of the shift registers is stuck in its reset state. This information can be used
to determine whether the oscillator clocks are operational (i.e. not dead or broken). Verification of the
oscillator clocks is achieved through a sequence of commands written to the Verification Control
Register (see Section 6.4.1.6, “Verification Control Register). First, the oscillator clocks should be
turned off. Second, the shift registers should be reset. At this point, the oscillator dead bit will assert
since the shift registers are in their reset state. Finally, the oscillators should be turned back on. If the
oscillator dead bit does not de-assert within a few clock cycles, the oscillators are dead.
1 = At least one oscillator is broken
0 = Both oscillators are operational
Note: This bit is intended to be used for silicon (production) test purposes and the
above sequence should be followed to determine if the RNGA oscillators are
functional. For simulation purposes, this bit will not be deterministic and should be
masked or “don’t cared”.
6.4.1.3 Entropy Register
The Entropy Register is a write-only register which allows the user to insert entropy into the RNGA. This
register allows an external user to continually seed the RNGA with externally generated random data.
Although the use of this register is recommended, it is also optional. The Entropy Register can be written
at any time during operation and cannot be written too quickly.
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
6-6 Preliminary Freescale Semiconductor
Page 99

Memory Map/Register Definition
Each time the Entropy Register is written, the written value is used to update the internal state of the
RNGA. The update is performed in such a way that the entropy in the RNGA’s internal state is preserved.
Use of the Entropy Register can increase the entropy but never decrease it.
31:0
R 0x00000000
W External Entropy
RESET: 0x00000000
REG
ADDR
Figure 6-4. Entropy Register
0x001F_0008
= Unimplemented or Reserved
External Entropy
The bits in this field are used to update the internal state of the RNGA.
6.4.1.4 Output Register
The Output Register provides temporary storage for random data generated by the RNGA. The output of
the Output Register is accessible through address 0x0c in the RNGA_32IP’s address map. As long as the
Output Register is not empty, a read of this address will return 32 bits of random data. If the Output
Register is read when it is empty, Error Interrupt, Output Register Underflow and Last Read bits in the
Status Register will be set. If the interrupt is enabled in the Control Register ipi_error_int will also be
driven active. If the High Assurance bit in the Control Register is set, then rnga_scc_debug will also be
driven high. The Output Register Level field in the Status Register, described in Section 6.4.1.2, “Status
Register, can be polled to monitor how many 32-bit words are currently resident in the Output Register.
When in Normal Mode, a new random word is pushed into the Output Register every 256 clock cycles (as
long as the Output Register is not full). It is very important that the host polls the Status Register to make
sure random values are present before reading from the Output Register.
Random Output
32 bits of random data.
Freescale Semiconductor
31:0
R Random Output
W
RESET: 0x00000000
REG
ADDR
Figure 6-5. Output Register
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
0x001F_000C
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Preliminary 6-7
Page 100

Random Number Generator Accelerator (RNGA)
6.4.1.5 Mode Register
This register cannot be accessed when the RNGA is in the Secure Mode. The Mode register is used to
configure the RNGA’s mode of operation. Figure 6-6 shows the valid fields in the Mode Register.
31:2 1 0
R 0
W
RESET: 0x00000000 0 0
REG
ADDR
Figure 6-6. Mode Register
Verification
When this bit is active, the RNGA is in Verification Mode. While in this mode, the pseudorandom
output of the shift registers is ignored and replaced with a counter value that increments every time the
output is sampled. This allows the deterministic logic around the shift registers and oscillators to be
verified easily.
1 = RNGA is in Verification Mode
0 = RNGA is not in Verification Mode
Oscillator Frequency
Test
0x001F_0010
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Verification
Oscillator Frequency Test
When this bit is active, the RNGA is in Oscillator Frequency Test Mode. While in this mode, the
RNGA drives the shift registers with the oscillator clocks 100% of the time (while in Normal Mode,
the oscillator clocks are occasionally disabled). This allows the approximate frequencies of the
oscillators to be calculated accurately.
1 = RNGA is in Oscillator Frequency Test Mode
0 = RNGA is not in Oscillator Frequency Test Mode
6.4.1.6 Verification Control Register
Through use of this register, the RNGA can placed in a deterministic mode allowing verification of the
design. A diagram of the register is shown in Figure 6-7.
31:3 2 1 0
R 0x0000000 0
W
RESET: 0x00000 0 0 0
REG
ADDR
= Unimplemented or Reserved
Reset Shift
Registers
0x14
Force Sys-
tem Clock
Shift Clock
Off
Figure 6-7. Verification Control Register‘
MCF52235 ColdFire® Integrated Microcontroller Reference Manual, Rev. 0
6-8 Preliminary Freescale Semiconductor
 Loading...
Loading...