Page 1

UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 User manual
Document information
Info Content
Keywords LPC55S16, LPC55S1x, LPCXpresso55S16, LPC55S16-EVK
Abstract LPCXpresso55S16 development board user manual
Page 2

NXP Semiconductors
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Revision history
Rev Date Description
1.3 20201019 Updated description of JP12 to include an explanation of establishing an external USART
1.2 20200619 Added Section 10.2 “Proper termination resistors required between the MCU and the USB
1.1 20200306 Updated information about crystals.
1.0 20201002 Initial internal release.
connection using JP3. Corrected miscellaneous typos.
connector”.
Updated information about 1.8V operation.
Added clarifications about labeling of external serial connector.
Added section 10 to Errata.
Added information about regulator errata.
Contact information
For more information, please visit: http://www.nxp.com
For sales office addresses, please send an email to: salesaddresses@nxp.com
UM11423
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 2 of 20
All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
Page 3

NXP Semiconductors
1. Introduction
The LPCXpresso™ family of boards provides a powerful and flexible development system
for NXP's LPC Cortex®-M family of MCUs. They can be used with a wide range of
development tools, including NXP's MCUXpresso IDE, Keil uVISION and IAR Embedded
Workbench. The LPCXpresso55S06 board (order code LPC55S06-EVK) is the evaluation
and development platform for the LPC55S1x families of MCUs.
See https://www.nxp.com/demoboard/LPC55S06-EVK for more information on these
boards, including tutorial videos, development software and board hardware design files.
The abbreviation LPC55S1x is used to collectively refer to the LPC55S16 family device on
the board.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Fig 1. LPCXpresso55S16
The LPCXpresso55S16 board includes the following features:
• LPC55S16 Cortex-M33 processor
• Onboard, high-speed USB, Link2 debug probe with CMSIS-DAP and SEGGER J-Link
protocol options
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 3 of 20
Page 4

NXP Semiconductors
• UART and SPI port bridging from LPC55Sxx target to USB via the onboard debug
probe
• Optional external debug probes with trace option (10 or 20 pin Cortex-M connectors)
• External crystal oscillators
• RGB user LED
• Reset, ISP, User/Wakeup and user buttons
• Multiple Expansion options, including Arduino UNO, Mikroe Click and PMod
• CAN-FD controller and onboard CAN transceiver
• NXP FXOS8700 accelerometer
• Stereo audio codec with line in/out
• High / full speed USB port with micro A/B connector for the host or device functionality
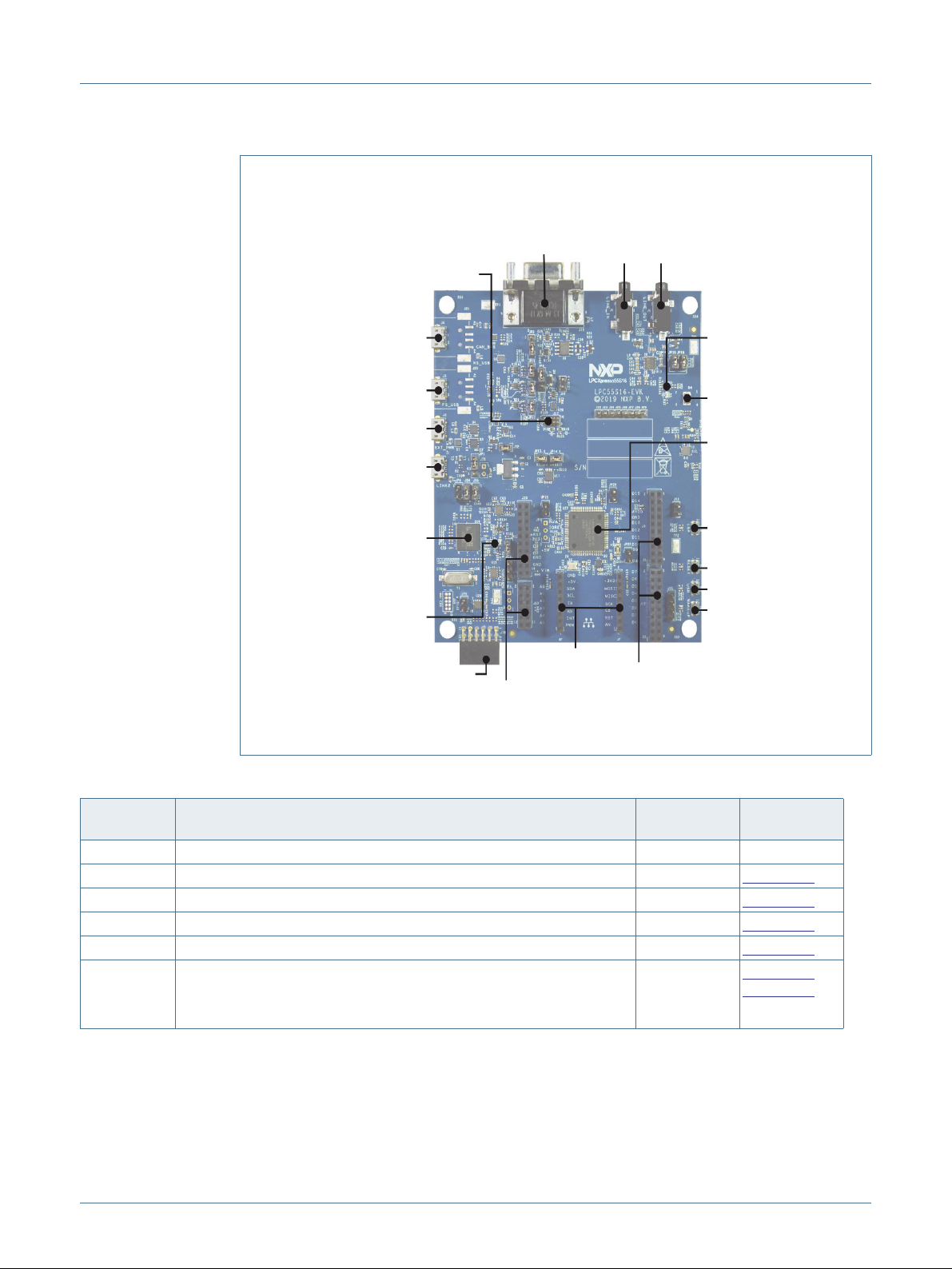
2. Board layout and Settings
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Figure 2 shows the layout of the board (top side), indicating the default location of the
jumpers, while Figure 3 shows locations of the connectors and headers. Table 1 provides
a description of connectors, jumpers, LEDs and buttons.
JP2: USB Host power enable
(1-2 closed, USB0)
JP 15, JP16, J P17: Link2 SWD
(closed)
JS2: USB host selection
(1-2 closed USB0)
JP1: Power Selection
(1-2 closed, 3.3V)
JP6: DFU mode on-board
debugger (open)
JS4: PM OD I2C enable
(closed)
JS5: PM OD I2C enable
(closed)
JP12: UART (closed)
JP9: PMOD SPI/Flexcomm0
UART (open)
JP3: E xternal UART
(1 RXD 2 TXD, 3 GND)
JP21: VDDA power (closed)
JP 18, JP19: C odec (closed)
JP8: Buer power (1-2 closed)
JP7: O n-board debug
target (open)
JP13: Link2 SWD (closed)
JP14: Link2 SWD (closed)
JP20: VDD power (closed)
JS3: Force target M CU
into ISP mode (open)
JP22: VBAT power (closed)
J11: Analog comparator
Input/O utput (open)
Fig. Default jumper locations
Fig 2. Default jumper positions
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 4 of 20
Page 5
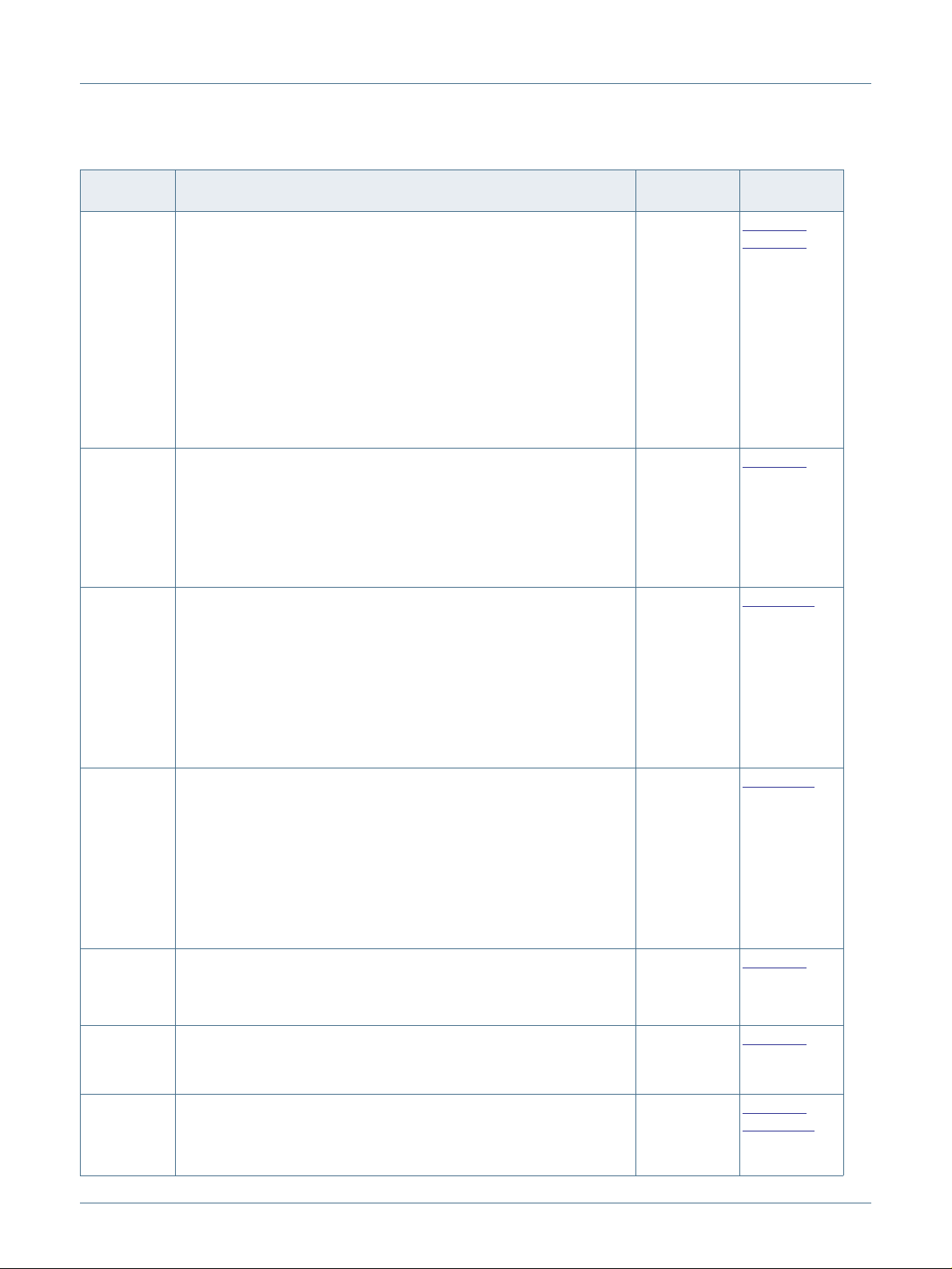
NXP Semiconductors
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
J4
J3
J2
J1
U16
D8
J17
J18
J10, J13
J19
J5D4J6
D5
U27
SW4
SW2
SW3
SW1
J8, J7
J9, J12
Fig 3. Board connectors and headers
Table 1. Indicators, buttons, connectors and LEDs
Circuit
Description Default Reference
reference
D5 Target power indicator LED n/a n/a
D8 Link2 boot LED n/a
Section 4.1
D4 RGB User LED (Tri-color Red/Green/Blue) n/a Section 7.5
J5 Audio codec line input jack. n/a Section 7.5
J6 Audio codec line output jack. n/a Section 7.5
JP8 Buffer Power Selection
For On-board Target place in position 1-2 (default)
1-2
Section 3.1,
Section 4.4
For Off-board Target place in position 2-3
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 5 of 20
Page 6
NXP Semiconductors
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Table 1. Indicators, buttons, connectors and LEDs
Circuit
reference
JP6 Link2 (LPC43xx) force DFU boot.
JP7 Target processor selection for the on-board Debug Probe.
JP2 USB host Vbus selection
JS2 USB host power control selection
JP9 When open (default), the "Bridge" UART and SPI connections from the
JP1 Target VDD power selection. An external supply voltage to the
Description Default Reference
Leave this jumper open (default) for Link2 to follow the normal boot
sequence. The Link2 will boot from internal flash if image is found
there. With the internal flash erased the Link2 normal boot sequence
will fall through to DFU boot.
Install this jumper to force the Link2 to DFU boot mode. Use this setting
to reprogram the Link2 internal flash with a new image (using the
LPCScrypt utility) or to use the MCUXpresso IDE with CMSIS-DAP
protocol.
Note that the Link2 flash is pre-programmed with a version of
CMSIS-DAP firmware by default.
Jumper open (default) the LPC55Sxx Target SWD interface enabled.
Normal operating mode where the Target SWD is connected to either
the on-board Link2 Debug Probe or an external Debug Probe.
Jumper shunted, the LPC55Sxx Target SWD interface is disabled. Use
this setting only when the on-board Link2 Debug Probe is used to
debug an off-board target MCU.
Note that only one of USB0 or USB1 can be configured as a USB host
port at any given time (this is a board restriction, not a limitation of the
LPC55Sxx.)
Install jumper in position 1-2 for USB0 (Full Speed) to provide Vbus (i.e.
enable USB host capability) (Default)
Install jumper in position 2-3 for USB1 (High Speed) to provide Vbus
(i.e. enable USB host capability)
This jumper selects routing of USB port power and overcurrent detect
from either the USB0 or USB1 ports of the LPC55Sxx. Note that only
one of USB0 or USB1 can be configured as a USB host port at any
given time (this is a board restriction, not a limitation of the LPC55Sxx.)
Leave open when using USB1 (High Speed) as a USB host (Default)
Install jumper for USB0 (Full Speed) to provide Vbus (i.e. enable USB
host capability).
Link2 probe are driven to the LPC55Sxx target. Install JP9 when using
the SPI interface at connector J18 and/or FC0 UART at JP3. Note that
this disables the Link2 SPI and UART (bridge) connections.
LPC55Sxx can also be applied through pin 2 of this header.
UM11423
Open
Open Section 4.
1-2 (USB0)
Installed
(USB1)
Open
1-2 (3.3V)
2-3 (1.8V)
Section 3.,
Section 4.
Section 6.1
Section 6.1
Section 4.
Section 5.
J2 External +5V power
Micro USB connection for power to the LPC55Sxx target and peripheral
circuitry (excluding Link2 Debug Probe). Must be installed for the USB
host to work.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 6 of 20
n/a Section 5.
Section 6.1
Page 7

NXP Semiconductors
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Table 1. Indicators, buttons, connectors and LEDs
Circuit
reference
J1 Link2 Debug Probe connector
J17 10 pin external debug probe / off board target connector
JP3 Serial port header
J4 LPC55Sxx USB1 (high speed) micro AB port connector n/a LPC55Sxx
J3 LPC55Sxx USB0 (full speed) micro AB port connector n/a LPC55Sxx
JP20 Power to MCU VDD, once removed, it can be used to measure VDD
JP21 Power to MCU VDDA, once removed, it can be used to measure VDDA
JP22 Power to MCU VBAT, once removed, it can be used to measure VBAT
JP5 ADC reference connector
J9,J10,J12,J13LPCXpresso expansion connectors, including Arduino R3 compatible
J18 PMod expansion connector / Host interface connector This connector
J19 CAN-FD controller
J7, J8 Mikroe Click site
J22 - J29 Miscellaneous GPIO pins for debugging purposes. n/a
Description Default Reference
n/a Section 4.
Micro USB type B connection for the on-board Link2 Debug Probe.
Note: do not use this connection when using an external Debug Probe.
This standard Cortex-M debug connector is used either to (1) connect
and off-board debug probe or (2) to connect an external debug target.
0.1” header providing convenient access to Flexcom 0 USART (the
USART used for ISP boot). When using this port install jumper JP9 to
disable the Link2 connection to this port.
current.
current.
current.
This header provides an access point to inject positive and negative
voltage references for the LPC55Sxx ADC.
site. Provides connectivity to SPI (high-speed SPI), USART (Flexcom
1), I2C (Flexcom 3 and Flexcom 1), I2S (Flexcom 7), ADC0, GPIO and
PLU pins.
provides access to the SPI (Flexcom 3) and I2C (Flexcom 1) ports that
support LPC55Sxx ISP mode, along with 2 GPIO lines. When using the
SPI port at this connector ensure jumper JP9 is installed to disable the
connection to the Link2 debug probe.
DB9 Male connector to CAN-FD network.
Provides connectivity to standard Mikroe Click connectors. Shares SPI,
ADC, I2C and USART connections with the J9, J10, J12, J13
expansion connectors.
n/a
n/a Section 3.1.3
Installed Measuring
Installed Measuring
Installed Measuring
Open
n/a
n/a Expansion
n/a
n/a Section 8.
Section 3.1.3
USB Ports
USB Ports
LPC55Sxx
device supply
current
LPC55Sxx
device supply
current
LPC55Sxx
device supply
current
Section 8.
connectors
Section 7.3
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 7 of 20
Page 8

NXP Semiconductors
Table 1. Indicators, buttons, connectors and LEDs
Circuit
reference
SW4 ISP/User button
SW1 Wake/User button
SW3 User button
SW2 Reset button
Description Default Reference
When pressed, this button connect sport pin P0_5 to ground. Hold this
button down while pressing and releasing Reset (SW2) to force the
LPC55Sxx into ISP mode. Port P0_5 may also be reconfigured as a
GPIO in user application code to enable this button to be used for other,
user-defined purposes.
This button, when pressed, pulls P1_18 to ground. A 330K ohm pull up
to VDD is connected to P1_18.
This button, when pressed, pulls P1_9 to ground. A 100K ohm pull up
to VDD is connected to P1_9, and this port is also connected to pin 2 of
expansion connector J12.
When pressed, reset is applied to the LPC55Sxx, expansion connector
(Arduino reset) J10, the Mikroe Click site reset, and U18 (debug
connector J17 reset when debugging an off-board target).
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
n/a
n/a Section 7.6.2
n/a Section 7.6.2
n/a
Section 7.6.1
Section 7.6.3
3. Getting started
This section describes how to first power up the board and then how to start a first debug
session using the MCUXpresso SDK. The board is pre-programmed with a simple
program indicating that the target MCU is running. Connect a micro USB cable from
connector J2 to a host computer or power supply to power-up the board and run this
program.
The following debug probes can be used with those development and the board (check
compatibility between debug probe and IDE used, including support for Arm Cortex M33
cores):
• On-board debug probe (LPC4322 “Link2”) from connector J1
• LPC-Link2 (OM13054) debug probe from NXP or Embedded Artists
• P&E Micro probes
• Keil ULINK2 probes
• IAR I-Jet probes
Other debug probes may also be supported by IAR and Keil tools and by other
IDEs/debug tools; refer the websites of these companies for further information.
3.1 Starting a debug session using the on-board (Link2) Debug Probe
By default, the Board is configured to use the on-board Debug Probe (Link2) to debug the
on-board target (LPC55Sxx), using the CMSIS-DAP debug protocol pre-programmed into
the Link2 Flash memory. The MCUXpresso IDE or other development tools that support
the CMSIS-DAP protocol can be used in the default configuration. Check with your
toolchain vendor for availability of specific device support packs for the LPC55Sxx series
devices.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 8 of 20
Page 9

NXP Semiconductors
Note that when using the MCUXpresso IDE, the on-board Link2 can also be booted in
DFU mode by installing a jumper on JP6; if this is done then the IDE will download
CMSIS-DAP to the probe as needed. Using DFU boot mode will ensure that the most
up-to-date / compatible firmware image is used with the MCUXpresso IDE.
Note: if the Debug Probe is set up to boot in DFU mode, the USB bridge functions (virtual
COM port) and Debug Probe features will not be available if the board is not first initialized
by the MCUXpresso IDE.
3.1.1 Installation steps for use with MCUXpresso IDE
Download and install the MCUXpresso IDE.
Configure and download an SDK package (with the MCUXpresso IDE tool chain option
selected) from the MCUXpresso SDK Builder utility (http://mcuxpresso.nxp.com).
Ensure jumper JP8 is fitted in position 1 - 2 (local target powered), and JP7 is not installed
(target SWD enabled). These are the default positions set during board manufacture.
Connect the board to the USB port of your host computer, connecting a micro USB cable
to connector J1. The board will boot and run the pre-installed demo.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
The board is now ready to be used with the MCUXpresso SDK examples for the
LPCXpresso55S16.
When the board is used for the first time, it is recommended to force the LPC55Sxx target
into a known state by performing an ISP boot before attempting to run your first example
code. This can be achieved by pressing and holding down the ISP button while pressing
and releasing the reset button or installing the LPC55Sxx ISP jumper.
3.1.2 Installation steps to use Keil and IAR tools with on-board debug probe
Download and install LPCScrypt (https://www.nxp.com/lpcscrypt). This will install required
drivers for the board. Note that the Link2 (LPC4322 device) is pre-programmed with
CMSIS-DAP firmware. If you have previously installed LPCScrypt please ensure version
2.1 or later is installed.
Ensure jumper JP8 is fitted in position 1-2 (local target powered), and J7 is not installed
(target SWD enabled). These are the default positions set during board manufacture.
The Link2 Debug Probe on the board will have been programmed with CMSIS-DSP
firmware during manufacture, but can also be updated with J-link OB for LPC-Link2. To
start the board with this firmware running, ensure JP6 is not installed as power is
connected, so the Link2 Debug Probe boots from internal flash. If you wish to
update/change the Link2 firmware please follow the steps described in Section 4.2.
Connect the Board to the USB port of your host computer, connecting a micro USB cable
to connector J1 ("Debug-Link"). The board will boot and run the pre-installed demo. Allow
about 30 seconds for the Link2 devices to enumerate for the first time. It is not necessary
to check the Hardware Manager on your host computer, however if this is done there will
be five devices (if using CMSIS-DAP protocol); four under Human Interface Devices
(CMSIS-DAP, LPC-SIO, two HID Compliant Devices, and a USB Input Device) and one
under Ports (LPC-LinkII Ucom).
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 9 of 20
Page 10

NXP Semiconductors
Your board is now ready to use with your 3rd party tool. Follow the instructions for those
tools for using a CMSIS-DAP probe. MCUXpresso IDE can also be used with the board
after setting up the board this way.
When the board is used for the first time, it is recommended to force the target into known
state by performing an ISP boot before attempting to run your first example code. This can
be achieved by pressing and holding down the ISP button while pressing and releasing
the reset button.
3.1.3 Starting a debug session using an external Debug Probe
Code running on the LPC55Sxx target can be debugged using an external Debug Probe
that conforms to the standard ARM Cortex-M debug connector. To use an external Debug
Probe connect the probe to the SWD connector (J17) and connect power via the micro
USB connector J2.
Note: The Debug link USB connector J1 must be left unconnected so that the Link2
Debug Probe is left unpowered and does not contend with the SWD interface signals from
the external Debug Probe. Also note that the VCOM function provided by the on-board
Debug Probe is not available when using an external debug probe. Then, J3 serial port
header can be served as an alternative to provide convenient access to Flexcomm 0
USART. When using this port, ensure jumper JP9 is installed and JP12 is open.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 10 of 20
Page 11

NXP Semiconductors
4. On-board (Link2) Debug probe
This section describes the features provided by the on-board Link2 Debug Probe,
including how to use this to debug an external target.
The Link2 Debug Probe is implemented using an LPC432x MCU (circuit reference U16),
which provides a high speed USB port interface to the host computer that runs the
development tools. This device is not intended for developer use, and should only be used
with approved firmware images from NXP. The Link2 on-chip flash memory is factory
programmed with a firmware image that supports CMSIS-DAP debug protocol, but also
includes other USB end point functions:
• Virtual COM (VCOM) port: a serial device that can be used with any host computer
application design for serial port communication (e.g. Teraterm, puTTY, etc.) Set the
terminal program for baud rate to 115200, no parity, 8 bit data, 1 stop bit, no flow
control.
• SWO trace end point: this virtual device is used by MCUXpresso to retrieve SWO
trace data. See the MCUXpresso IDE documentation for more information.
• I2S/SPI bridges: bridge device from I2C and SPI ports of the LPC target.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
All of these devices are independent of each other and of the CMSIS-DAP debug device
that is enumerated when the board is connected to a host computer; for example, the
VCOM port can be used if the board is running an application when no debugger is
running.
In order to correctly install and use the Link2 device on the LPCXpresso55S16 (required
for any debugging purpose) for Windows host computers, install the drivers first. These
drivers will automatically be installed when MCUXpresso IDE has already been installed.
If these IDEs are not being used, it is recommended LPCScrypt be installed as this also
includes the required drivers. All these tools and utilities are available for free download at
https://www.nxp.com/lpcscrypt.
The CMSIS-DAP firmware image installed at the factory (and by LPCScrypt) will uniquely
identify itself to the host computer so that more than one board can be connected to that
host computer at any time. Some toolchains cannot discern between multiple debug
devices; refer to your toolchain documentation for more information (note the
MCUXpresso IDE does support multiple LPCXpresso board targets.)
Note: The Link2 only boots when the board is power cycled; the reset button on the board
does not reset the Link2.
When using MCUXpresso IDE, the Link2 can be automatically booted with the latest /
most appropriate firmware for that IDE version by installing JP6 (DFU jumper) before
powering up the board. This is the recommended approach for the MCUXpresso IDE.
Note that if JP6 is installed when powering the board then the VCOM port (and other
devices mentioned above) device will not appear until the MCUXpresso IDE boots the
Debug Probe. The Debug Probe is booted once a debug session is started (that is, the
IDE attempts to download code to the target).
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 11 of 20
Page 12

NXP Semiconductors
4.1 Link2 boot LED
LED D8 is the Link2 MCU BOOT0_LED indicator. This LED reflects the state of Link2
MCU pin P1_1. When the boot process fails, D8 will toggle at a 1 Hz rate for 60 seconds.
After 60 seconds, the Link2 MCU is reset.
4.2 Programming the Link2 firmware
As mentioned earlier in this section, it is not normally necessary to program the Link2
firmware. However, this can easily be accomplished using the supporting utility,
LPCScrypt.
To program the Link2 Flash the Link2 device (LPC432x) must be in DFU mode. If the
Link2 already has a valid image in the flash, it will need to be forced into DFU mode by
placing a jumper shunt on JP6 (DFU), and power cycling (disconnecting then
reconnecting power via J1.) Link2 MCU programming is performed using the LPCScrypt
utility (see http://www.nxp.com/lpcscrypt). Instructions for using the tool are located at the
same web page.
After installing LPCScrypt, use either the “Program LPC-Link2 with CMSIS-DAP” or
“Program LPC-Link2 with JLink” utilities provided in that installation to update the
firmware, following on-screen instructions.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
4.3 VCOM port
The identifier of the VCOM port will vary between boards and hosts as each board will
enumerate with a unique identifier. On Windows, to determine the COM port, open the
Windows operating system Device Manager. This can be achieved by going to the
Windows operating system Start menu and typing "Device Manager" in the search bar. In
the device manager look under "Ports"; the LPC-LinkII UCom Port device and its name
should be visible. NOTE: this VCOM port will only appear if (a) the Debug Probe has been
programmed with the CMSIS-DAP firmware and the Debug Probe DFU link (JP6) is
removed at power up, or (b) if the Debug Probe has been configured for DFU boot (JP6
installed) at power up and MCUXpresso IDE has booted it (by starting a debug session.
If the J-Link firmware image has been programmed into the Debug Probe and DFU boot
mode is not being used, then a VCOM device called J-Link CDC UART port will appear
instead of the LPC-LinkII UCom port.
Note that the VCOM port is not available when the Link2 Debug Probe is not powered.
When using an external debug probe. Then, J3 serial port header can be served as an
alternative to provide convenient access to Flexcomm 0 USART. When using this port,
ensure jumper JP9 is installed and JP12 is open.
4.4 Configuring the LPCXpresso55S16 to debug an off-board target
The LPCXpresso55S16 board's Link2 Debug Probe may be used to debug an off-board
target MCU. The on-board Link2 Debug Probe is capable of debugging target MCU's with
a VDDIO range of 1.6V to 3.6V. To keep the on-board target LPC55Sxx MCU from
interfering with the SWD interface, JP7 must be closed. The Link2 Debug Probe SWD
should be connected by a ribbon cable between the J17 connector to the off-board target
MCU SWD interface. Power the LPCXpresso55S16 board from the Link USB connector
J1, and fit jumper JP8 across pins 2 - 3 (External Target).
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 12 of 20
Page 13

NXP Semiconductors
5. Board Power
The LPCXpresso55S16 board requires +5V input to power the on-board voltage low
dropout linear regulators, of which there are 3, circuit reference U1, U3 and U4.
The Link2 Debug probe has a 2.5V regulator (U1) which draws power from USB
connector J1 ("Debug Link") only.
There are two other regulators, providing the option of 1.8V (U4) or 3.3V (U3) to the other
devices on the board; these regulators can be powered by any of the following (+5V)
sources:
• USB Debug Link connector (J1)
• USB +5V Power only connector (J2)
• USB Full Speed connector for LPC55Sxx (J3)
• USB High Speed connector for LPC55Sxx (J4)
The +5V sources above are connected via protection diodes to prevent reverse powering
of any of them by another source. The +5V output of these combined sources is also
connected to the Arduino and Mikroe expansion sites. Note that if J3 or J4 is configured
as a USB host port then those connectors will not supply power to the board and another
power source must be provided through J2.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Note that the FXOS8700 Accelerometer requires the board to be configured for 3.3V
operation.
CAN-FD transceiver, circuit reference U9, TJA1044, is populated to support CAN-FD
communication. CAN-FD transceiver requires +5V supply.
For further details, refer to the board schematics.
5.1 Measuring LPC55Sxx device supply current
Current supply to the LPC55Sxx Core can be measured via JP20 for VDD, JP21 for
VDDA, and JP22 for VBAT.
5.2 1.8V operation
Please note the minimum voltage supply for the LPC55S1x/LPC551X devices is 1.8 V, so
variations in the 1.8V regulator tolerance and/or loading on the regulator may cause the
brown-out detect (BOD) to trigger, especially when using the device at higher operating
frequencies (when current draw is higher). The default BOD settings may be changed to
avoid this problem, before higher clock speeds and/or higher current draw I/Os are
enabled (e.g. at the start of main()) with a function call to the power library, as shown
below:
POWER_SetBodVbatLevel(kPOWER_BodVbatLevel1650mv, kPOWER_BodHystLevel50mv,
false);
It should be noted that this workaround may not work in all cases due to the regulator
used on the board has a tolerance that does not guarantee the minimum required voltage
output; see: Section 10 “Errata”.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 13 of 20
Page 14

NXP Semiconductors
6. Board serial connections
This section describes connections between LPC55Sxx on-board serial peripherals and
connectors for use with off-board devices.
6.1 LPC55Sxx USB Ports
The Board incorporates micro AB connectors for both of USB0 (Full Speed, connector J3)
and USB1 (High Speed, connector J4) ports of the LPC55S16. Both of these ports are
capable of operating as a device or a host, and this is why micro AB connectors are used.
The Board can only be configured to support one of these ports as a host at a time (this is
a limitation of the board, not the LPC55Sxx). When either port is used as a host, power
must be supplied to the board via the +5V power only micro B USB port. Jumper JP2 is
used to connect power from a load switch to the VBUS signal of the port selected; JP2
should be placed in position 1-2 for USB0 or position 2-3 for USB1. If neither USB port is
being used as a USB host this jumper is not required.
6.2 USART header
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
Header JP3 is provided as a convenient way to use an LPC55Sxx USART with a serial to
USB cable. Flexcom 0 ports (P0_29 and P0_30) are used for this feature, since these
ports are assigned for USART ISP mode. Note that these ports are shared with the Link2
debug probe (LPC4322) and PMod connector; when using this header ensure that there
is no conflicting device connected to the PMod connector and that jumper JP9 is installed
to disable the connection to the Link2 and JP12 jumper should be open. Always ensure
the serial cable is only connected when the board is powered to prevent the LPC55S16
being powered through this TXD/RXD pins.
Note: the silkscreen on the board is labeled from the perspective of a serial cable
connected to the board, so JP3 pin 3 (labeled “RXD” on the board silkscreen) is
connected to PIO0_30 (Flexcomm0 TXD), and JP3 pin 2 (labeled “TXD” on the board
silkscreen) is connected to PIO0_29 (Flexcomm0 RXD).
7. On-board peripherals
This section describes how the on-board peripheral devices of the Board are connected to
the LPC55Sxx and relevant configuration options. For full details of these devices please
refer to the individual device datasheets. For circuit further details, refer to the board
schematics.
7.1 Audio Codec
The LPCXpresso55S16 board incorporates a Cirrus Logic (Wolfson) WM8904 audio
codec. This codec has both I2C (for control) and I2S (for data) interfaces.
The I2C interface of the codec is routed to Flexcomm 4 of the LPC55Sxx, the same
connection as used for the other I2C devices on the board; the Codec has an address of
0b0011010x.
The Flexcomm 6 and Flexcomm 7 interfaces of the LPC55Sxx are connected respectively
to the Codec for data sent to / receive from the Codec. The board design assumes pad
sharing between Flexcom 6 and Flexcom 7 for I2S connections.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 14 of 20
Page 15

NXP Semiconductors
Table 2. Audio Codec port connections
Circuit reference Port Flexcoms
I2S SCK P0_21 Flexcom 6 & 7, pad shared
I2S TX Data P0_20 Flexcom 7
I2S RX Data P1_13 Flexcom 6
I2S WS P0_19 Flexcom 6 & 7, pad shared
I2C SDA P1_21 Flexcom 4
I2C SCL P1_20 Flexcom 4
I2S_MCLK P1_31
I2S connections from the LPC55Sxx are also connected to the Expansion connectors;
solder jumpers may be removed to disconnect the on-board codec if an external I2S
device is to be used instead.
Line input (J5) and line output (J6) 1/4" stereo jack sockets provide analog I/O
connections to the Codec. See schematic for further information.
7.2 CAN-FD Connector
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
The LPC55S16 MCU includes a CAN-FD controller. On LPCXpresso55S16 board, P1.22
(IOCON Function 9) and P1.27 (IOCON Function 9) are configured as CAN_RXD and
CAN_TXD respectively. A CAN-FD transceiver, U9, TJA1044, is populated on the board
with level shifters between LPC55S16 target and CAN-FD transceiver to support both
1.8V and 3.3V. LPCXpresso55S16 board incorporates a DB9 connector (J19) to support
CAN-FD communication.
CAN-FD software driver examples are provided as part of the MCUXpresso SDK.
7.3 Accelerometer
The board includes an NXP FXOS8700 accelerometer, interfaced to Flexcom 4 (ports
P1_21 and P1_20) with its interrupt output connected to P1_26 (this signal is also shared
with the Expansion connector J12 via a 100 ohm resistor (R36).) The accelerometer has
an I2C address of 0b0001111X.
I2C software drivers are provided as part of the MCUXpresso SDK, and example code is
provided to illustrate how to read values from the accelerometer.
7.4 Crystals
For applications requiring high-speed communication such as high-speed USB and
accurate clock such as real-time clock (RTC), two external crystal oscillators are provided
on the board, 16MHz crystal for XTAL32M and 32.768KHz for XTAL32K.
External capacitors are not required on the crystal pins, but are installed on board. These
may be removed for better performance if issues are observed. See the
"LPC55S1x/LPC551x Cap Bank API” chapter of the LPC55S1x/LPC551x User manual for
further information.
7.5 RGB User LED
An User controlled RGB LED is provided on the Board. The LEDs in this device are
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 15 of 20
Page 16

NXP Semiconductors
controlled by LPC55Sxx ports P1_4 (Red), P1_6 (Blue), P1_7 (Green) with the LEDs
being illuminated when the respective GPIO pin is set to high. Note that these port lines
are also connected to expansion connector J12.
7.6 Buttons
Four buttons are provided on the LPCXpresso55S16 board, as described in this section.
7.6.1 ISP (SW4)
P0_5 is pulled up to VDD via a 100kohm resistor; pressing this button will pull P0_5 low.
This port is read by the LPC55Sxx boot code to determine if the MCU should enter In
System Programming (ISP) mode. The main purpose of this button is to force the
LPC55Sxx into ISP mode at boot time; to do this hold down this button while pressing and
releasing the Reset button, or while connecting power to the board. While the main
purpose of ISP mode is to program the flash of the LPC55Sxx, forcing the MCU into this
mode places it into a known state in which development tools can gain debug control. If an
application in flash is crashing or disabling the SWD port unintentionally, then ISP mode
can be useful to recover control of the board. Refer to the LPC55S1x User Manual for
more information on ISP mode.
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
The ISP button can also be used in user application code. Care should be taken if P0_5 is
configured as an output driving high, since pressing this button will short it to ground.
Note that jumper JS3 may also be used as a convenient way to always assert ISP when
the LPC55Sxx is reset or powered up.
7.6.2 User (SW3) and Wakeup (SW1) buttons
The User (SW3) and Wakeup (SW1) buttons are intended for user application use. These
buttons pull ports P1_9 (User) with 100kohm pull-up resistor and P1_18 (Wakeup) with
330kohm pull-up resistor low when the button is pressed.
7.6.3 Reset (SW2)
Pressing this button will assert reset to the LPC55Sxx and to the Mikroe and Arduino
connector sites. Note that the Link2 Debug Probe (LPC4322) is not reset when this button
is pressed.
8. Expansion connectors
The LPCXpresso55S16 includes 3 expansion connector sets, incorporating support for
Arduino UNO R3, Mikroe Click and PMod standards. The Arduino UNO connector
footprint is surrounded by additional connectors that are compatible with other
LPCXpresso V3 boards. For further details, refer to the board schematics.
8.1 Mikroe Click Site
The connectors J7 and J8 provide a Mikroe Click module site for the wide range of
add-on modules available from MikroElektronika. Note that this site shares the same SPI,
I2C and UART connections as the Arduino/LPCXpresso V3 expansion connectors.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 16 of 20
Page 17

NXP Semiconductors
8.2 Host / PMod Connector
Connector J18 is a connector which provide convenient access for a remote host to the
SPI and I2C ports of the LPC55Sxx that support ISP mode. When setting up the Board to
be used with a host, jumper JP9 must be installed to prevent conflict with the Link2 (which
can also emulate an SPI or I2C host).
8.3 Arduino and LPCXpresso V3 expansion connectors
The connectors J9, J10, J12, J13, provide Arduino UNO R3 compatibility and access to
several other signals for use in prototyping. The overall footprint is compatible with the
LPCXpresso V3 expansion connector footprint used on other LPCXpresso boards of this
type. Note that some ports used on these connectors are shared with other
devices/connectors on the board, including the Mikroe Click site, audio codec and RGB
LED. Refer to the schematic for further information.
When using an Arduino shield with the Board, align the Arduino shield (SCL) with pin 1 of
connector J9 on the LPCXpresso55S16 board.
Table 3. Arduino and LPCXpresso V3 expansion connections
Expansion connector Port
J9 The odd number pins are compatible with Arduino Uno rev3 Digital
J12 The odd numbered pins 1 – 15 are compatible with Arduino Uno rev3
J10 The even numbered pins 6 – 20 are compatible with the Arduino Uno
P13 The even numbered pins 2 – 12 are compatible with Arduino Uno
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
15:8, AREF, SDA & SCL connector. The even numbered pins are
used for external access and expansion of LPC55Sxx signals not
used by the Arduino Uno rev3 compatible interface.
Digital 7:0 connector. The even numbered pins, and odd numbered
pins 17 and 19, are used for external access and expansion of
LPC55Sxx signals not used by the Arduino Uno rev3 compatible
interface.
rev3 Power connector standard.
rev3 Analog connector. The odd numbered pins are used for external
access and expansion of LPC55Sxx signals not used by the Arduino
Uno rev3 compatible interface.
9. Board Power
This section describes miscellaneous board features that we not covered elsewhere in
this manual.
9.1 LPC55Sxx ADC references and inputs
By default, the LPC55Sxx ADC positive reference is connected to VDDA and the negative
reference to ground. Different reference voltages may be used by removing R65 zero
resistor and connecting an external reference to JP5 (pin 1 for positive, pin 3 for negative).
An external differential ADC input signal can be applied at J13 or at the JP4 expansion
connector. This connection is routed to PIO0_16 and PIO0_23.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 17 of 20
Page 18

NXP Semiconductors
10. Errata
This section provides errata for commonly known issues that may occur during device
processing.
10.1 Brown-out detect (BOD) may be triggered during boot (code execution from ROM)
Boards have a 1.8V regulator installed that has a 2% tolerance. This can result in the
supply voltage being below the specification of the LPC55S1x/LPC551x device and thus
in some cases the brown-out detect (BOD) of the device may trigger during boot (code
execution from ROM). If this occurs it will prevent an application programmed in SRAM or
flash from executing. In this situation, an external 1.8V supply may be connected to the
center pin of P4 to power the LPC55S1x/LPC551x device. Note that board designs should
use a regulator that guarantees a minimum 1.8V supply; alternative regulators with 1.9V
or 2V outputs are available from Torex in their XC6203 family in the same footprint, and
also in the XC6503 range, and other alternatives are available from other suppliers.
Some boards have passive components installed that are not necessary and should be
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
omitted in application designs; see: Section 6.1 “LPC55Sxx USB Ports” and Section 7.4
“Crystals”.
10.2 Proper termination resistors required between the MCU and the USB connector
USB0 port uses the FS/LS driver which needs to have 33 Ohm external series termination
resistors between the MCU and the USB connector. Without proper termination, a failure
in the USB signal quality during USB compliance testing may occur. Zero Ohm resistors
on R6 and R8 should be replaced with 33 Ohm resistors.
11. Board operating conditions
These boards have been designed for use in laboratory conditions (0 to 50 degrees
Celsius) and should not be used for extended temperature testing. Refer to the data sheet
of the LPC55xx MCU being used for full operating conditions for that device.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 18 of 20
Page 19

NXP Semiconductors
12. Legal information
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
12.1 Definitions
Draft — The document is a draft version only. The content is still under
internal review and subject to formal approval, which may result in
modifications or additions. NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties as to the accuracy or completeness of
information included herein and shall have no liability for the consequences of
use of such information.
12.2 Disclaimers
Limited warranty and liability — Information in this document is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, NXP Semiconductors does not give any
representations or warranties, expressed or implied, as to the accuracy or
completeness of such information and shall have no liability for the
consequences of use of such information.
In no event shall NXP Semiconductors be liable for any indirect, incidental,
punitive, special or consequential damages (including - without limitation - lost
profits, lost savings, business interruption, costs related to the removal or
replacement of any products or rework charges) whether or not such
damages are based on tort (including negligence), warranty, breach of
contract or any other legal theory.
Notwithstanding any damages that customer might incur for any reason
whatsoever, NXP Semiconductors’ aggregate and cumulative liability towards
customer for the products described herein shall be limited in accordance
with the Terms and conditions of commercial sale of NXP Semiconductors.
Right to make changes — NXP Semiconductors reserves the right to make
changes to information published in this document, including without
limitation specifications and product descriptions, at any time and without
notice. This document supersedes and replaces all information supplied prior
to the publication hereof.
Suitability for use — NXP Semiconductors products are not designed,
authorized or warranted to be suitable for use in life support, life-critical or
safety-critical systems or equipment, nor in applications where failure or
malfunction of an NXP Semiconductors product can reasonably be expected
to result in personal injury, death or severe property or environmental
damage. NXP Semiconductors accepts no liability for inclusion and/or use of
NXP Semiconductors products in such equipment or applications and
therefore such inclusion and/or use is at the customer’s own risk.
Applications — Applications that are described herein for any of these
products are for illustrative purposes only. NXP Semiconductors makes no
representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the
specified use without further testing or modification.
Customers are responsible for the design and operation of their applications
and products using NXP Semiconductors products, and NXP Semiconductors
accepts no liability for any assistance with applications or customer product
design. It is customer’s sole responsibility to determine whether the NXP
Semiconductors product is suitable and fit for the customer’s applications and
products planned, as well as for the planned application and use of
customer’s third party customer(s). Customers should provide appropriate
design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks associated with their
applications and products.
NXP Semiconductors does not accept any liability related to any default,
damage, costs or problem which is based on any weakness or default in the
customer’s applications or products, or the application or use by customer’s
third party customer(s). Customer is responsible for doing all necessary
testing for the customer’s applications and products using NXP
Semiconductors products in order to avoid a default of the applications and
the products or of the application or use by customer’s third party
customer(s). NXP does not accept any liability in this respect.
Export control — This document as well as the item(s) described herein
may be subject to export control regulations. Export might require a prior
authorization from national authorities.
12.3 Trademarks
Notice: All referenced brands, product names, service names and trademarks
are the property of their respective owners.
UM11423 All information provided in this document is subject to legal disclaimers. © NXP B.V. 2020. All rights reserved.
User manual Rev. 1.3 — 20 October 2020 19 of 20
Page 20

NXP Semiconductors
13. Contents
UM11423
LPCXpresso55S16 Development Boards
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Board layout and Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3 Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1 Starting a debug session using the on-board
(Link2) Debug Probe. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.1.1 Installation steps for use with MCUXpresso IDE 9
3.1.2 Installation steps to use Keil and IAR tools with
on-board debug probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3.1.3 Starting a debug session using an external Debug
Probe . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 On-board (Link2) Debug probe. . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.1 Link2 boot LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.2 Programming the Link2 firmware . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.3 VCOM port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
4.4 Configuring the LPCXpresso55S16 to debug an
off-board target . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Board Power. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5.1 Measuring LPC55Sxx device supply current . 13
5.2 1.8V operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 Board serial connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.1 LPC55Sxx USB Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
6.2 USART header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
7 On-board peripherals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
7.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Audio Codec 14
7.2 CAN-FD Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.3 Accelerometer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.4 Crystals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.5 RGB User LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
7.6 Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7.6.1 ISP (SW4). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7.6.2 User (SW3) and Wakeup (SW1) buttons . . . . 16
7.6.3 Reset (SW2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
8 Expansion connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
8.1 Mikroe Click Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
8.2 Host / PMod Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
8.3 Arduino and LPCXpresso V3 expansion
connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
9 Board Power. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
9.1 LPC55Sxx ADC references and inputs. . . . . . 17
10 Errata. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
10.1 Brown-out detect (BOD) may be triggered during
boot (code execution from ROM) . . . . . . . . . . 18
10.2 Proper termination resistors required between the
MCU and the USB connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
11 Board operating conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
12 Legal information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
12.1 Definitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
12.2 Disclaimers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
12.3 Trademarks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
13 Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Please be aware that important notices concerning this document and the product(s)
described herein, have been included in section ‘Legal information’.
© NXP B.V. 2020 All rights reserved.
For more information, please visit: http://www.nxp.com
For sales office addresses, please send an email to: salesaddresses@nxp.com
Date of release: 20 October 2020
Document identifier: UM11423
 Loading...
Loading...