Datasheet LMC6442IMX, LMC6442IMMX, LMC6442AIN, LMC6442AIMX, LMC6442AIMMX Datasheet (NSC)
...
LMC6442
Dual Micropower Rail-to-Rail Output Single Supply
Operational Amplifier
General Description
The LMC6442 is ideal for battery powered systems, where
very low supply current (less than one microamp per amplifier) and Rail-to-Rail output swing is required. It is characterized for 2.2V to 10V operation, and at 2.2V supply, the
LMC6442 is ideal for single (Li-Ion) or two cell (NiCad or alkaline) battery systems.
The LMC6442 is designed for battery powered systems that
require long service life through low supply current, such as
smoke and gas detectors, and pager or personal communications systems.
Operation from single supply is enhanced by the wide common mode input voltage range which includes the ground (or
negative supply) for ground sensing applications. Very low
(5fA, typical) input bias current and near constant supply current over supply voltage enhance the LMC6442’s performance near the end-of-life battery voltage.
Designed for closed loop gains of greater than plus two (or
minus one), the amplifier has typically 9.5 KHz GBWP (Gain
Bandwidth Product). Unity gain can be used with a simple
compensation circuit, which also allows capacitive loads of
up to 300 pF to be driven, as described in the Application
Notes section.
For compact assembly the LMC6442 is available in the
MSOP 8 pin package, about one half the size required by the
SOIC 8 pin package. 8 pin DIP and 8 pin SOIC are also
available.
Key Specifications
Features
(Typical, V
S
=
2.2V)
n Output Swing to within 30 mV of supply rail
n High voltage gain 103 dB
n Gain Bandwidth Product 9.5 KHz
n Guaranteed for: 2.2V, 5V, 10V
n Low Supply Current 0.95 µA/Amplifier
n Input Voltage Range −0.3V to V
+
-0.9V
n Power consumption 2.1 µW/Amplifier
n Stable for A
V
≥+2 or AV≤ −1
Applications
n Portable instruments
n Smoke/gas/CO/fire detectors
n Pagers/cell phones
n Instrumentation
n Thermostats
n Occupancy sensors
n Cameras
n Active badges
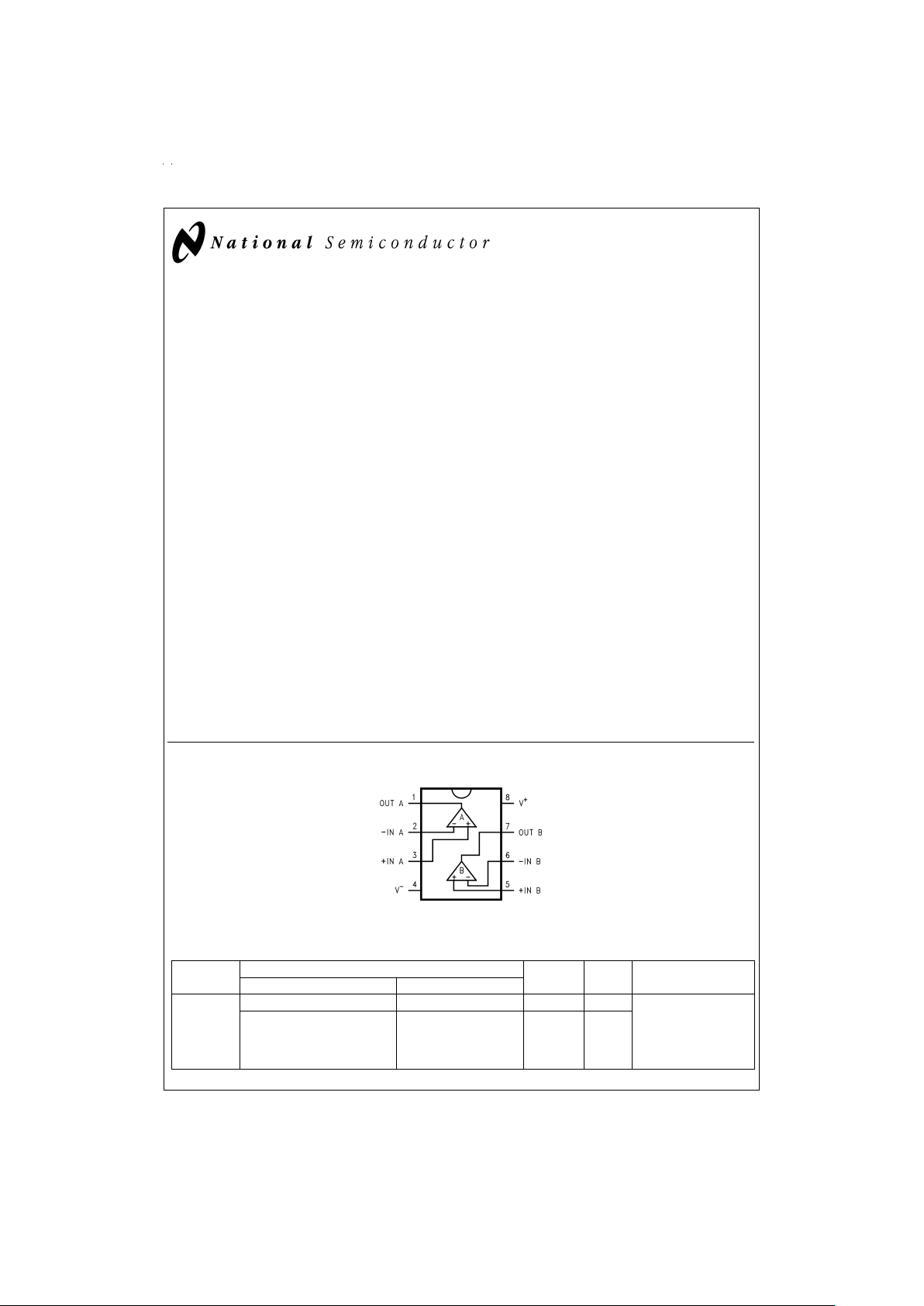
Connection Diagram
Ordering Information
Package
Temperature Range
NSC
Drawing
Supplied
AS
Package Marking
Industrial −40˚C to +85˚C Military −55˚C to +125˚C
8-pin SO-8 LMC6442AIM, LMC6442IM - M08A Rails
LMC6442AIM
LMC6442IM
LMC6442AIMX, LMC6442IMX - M08A
2.5K
Tape
and
Reel
DS100064-40
Top View
September 1997
LMC6442 Dual Micropower Rail-to-Rail Output Single Supply Operational Amplifier
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100064 www.national.com
Ordering Information (Continued)
Package
Temperature Range
NSC
Drawing
Supplied
AS
Package Marking
Industrial −40˚C to +85˚C Military −55˚C to +125˚C
MSOP LMC6442AIMM, LMC6442IMM - MUA08A Rails
A08A
LMC6442AIMMX,
LMC6442IMMX
- MUA08A
3K Tape
and
Reel
8-pin DIP
LMC6442AIN, LMC6442IN - N08E
Rails LMC6442AIN,
LMC6442IN
8-pin CDIP
-
5962-9761301QPA J08A Rails LMC6442AMJ-QML
5962-976130IQPA
10-pin SO
-
5962-9761301QXA WG10A Trays LMC6442AMWG-Q
9761301QXA
www.national.com 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
ESD Tolerance (Note 2) 2 kV
Differential Input Voltage
±
Supply Voltages
Voltage at Input/Output Pin (V
+
) + 0.3V, (V−) − 0.3V
Supply Voltage (V
+−V−
): 16V
Current at Input Pin (Note 10)
±
5mA
Current at Output Pin(Notes 3, 7)
±
30 mA
Lead Temp. (soldering 10 sec) 260˚C
Storage Temp. Range: −65˚C to +150˚C
Junction Temp. (Note 4) 150˚C
Operating Ratings(Note 1)
Supply Voltage 1.8V ≤ V
S
≤ 11V
Junction Temperature −40˚C
<
T
J
<
+85˚C
Range: LMC6442AI, LMC6442I
Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
)
M Package, 8-pin Surface
Mount
193˚C/W
MSOP Package 235˚C/W
N Package, 8-pin Molded
DIP
115˚C/W
2.2V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
J
=
25˚C, V
+
=
2.2V, V
−
=
0V, V
CM
=
V
O
=
V
+
/2, and R
L
=
1MΩto V
+
/2.
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typ
(Note 5)
LMC6442AI
Limit
(Note 6)
LMC6442I
Limit
(Note 6)
Units
DC Electrical Characteristics
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage
−0.75
±
3
±
4
±
7
±
8
mV
max
TCV
OS
Temp. coefficient of input
offset voltage
0.4 µV/˚C
I
B
Input Bias Current (Note 14)
0.005 44
pA
max
I
OS
Input Offset Current (Note 14)
0.0025 22
pA
max
CMRR Common Mode Rejection
Ratio
−0.1V ≤ V
CM
≤0.5V 92 67
67
67
67
dB min
C
IN
Common Mode Input
Capacitance
4.7 pF
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
S
=
2.5 V to 10V
95
75
75
75
75
dB
min
V
CM
Input Common-Mode Voltage
Range
CMRR ≥ 50 dB
1.3
1.05
0.95
1.05
0.95
V
min
−0.3 −0.2
0
−0.2
0
V
max
A
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain Sourcing (Note 11) 100
dB
min
Sinking(Note 11) 94
V
O
=
0.22V to 2V 103 80 80
V
O
Output Swing V
ID
=
100 mV (Note 13)
2.18
2.15
2.15
2.15
2.15
V
min
V
ID
=
−100 mV (Note 13) 22 60
60
60
60
mV
max
I
SC
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing, V
ID
=
100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
50 18
17
18
17
µA
min
Sinking, V
ID
=
−100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
50 20
19
20
19
I
S
Supply Current (2 amplifiers) R
L
=
open 1.90 2.4
3.0
2.6
3.2
µA
max
V
+
=
1.8V, R
L
=
open 2.10
AC Electrical Characteristics
SR Slew Rate (Note 8) 2.2 V/ms
www.national.com3

2.2V Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
J
=
25˚C, V
+
=
2.2V, V
−
=
0V, V
CM
=
V
O
=
V
+
/2, and R
L
=
1MΩto V
+
/2.
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typ
(Note 5)
LMC6442AI
Limit
(Note 6)
LMC6442I
Limit
(Note 6)
Units
AC Electrical Characteristics
GBWP Gain-Bandwidth Product 9.5 KHz
φ
m
Phase Margin (Note 15) 63 Degree
5V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
J
=
25˚C, V
+
=
5V, V
−
=
0V, V
CM
=
V
O
=
V
+
/2, and R
L
=
1MΩto V
+
/2.
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typ
(Note 5)
LMC6442AI
Limit
(Note 6)
LMC6442I
Limit
(Note 6)
Units
DC Electrical Characteristics
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage
−0.75
±
3
±
4
±
7
±
8
mV
max
TCV
OS
Temp. coefficient of input
offset voltage
0.4 µV/˚C
I
B
Input Bias Current (Note 14)
0.005 44
pA
max
I
OS
Input Offset Current (Note 14)
0.0025 22
pA
max
CMRR Common Mode Rejection
Ratio
−0.1V ≤ V
CM
≤3.5V 102 70
70
70
70
dB min
C
IN
Common Mode Input
Capacitance
4.1 pF
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
S
=
2.5 V to 10V
95
75
75
75
75
dB
min
V
CM
Input Common-Mode Voltage
Range
CMRR ≥ 50 dB
4.1
3.85
3.75
3.85
3.75
V
min
−0.4 −0.2
0
−0.2
0
V
max
A
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain Sourcing (Note 11) 100
dB
min
Sinking (Note 11) 94
V
O
=
0.5V to 4.5V 103 80 80
V
O
Output Swing V
ID
=
100 mV
(Note 13)
4.99 4.95
4.95
4.95
4.95
V
min
V
ID
=
−100 mV
(Note 13)
20 50
50
50
50
mV
max
I
SC
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing, V
ID
=
100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
500 300
200
300
200
µA
min
Sinking, V
ID
=
−100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
350 200
150
200
150
I
S
Supply Current (2 amplifiers) R
L
=
open 1.90 2.4
3.0
2.6
3.2
µA
max
AC Electrical Characteristics
SR Slew Rate (Note 8) 4.1 2.5 2.5 V/ms
GBWP Gain-Bandwidth Product 10 KHz
φ
m
Phase Margin (Note 15) 64 Degree
THD Total Harmonic Distortion A
V
=
+2, f=100 Hz,
R
L
=
10MΩ,V
OUT
=
1 Vpp
0.08
%
www.national.com 4

10V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
J
=
25˚C, V
+
=
10V, V
−
=
0V, V
CM
=
V
O
=
V
+
/2, and R
L
=
1MΩto V
+
/2.
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions
Typ
(Note 5)
LMC6442AI
Limit
(Note 6)
LMC6442I
Limit
(Note 6)
Units
DC Electrical Characteristics
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage
−1.5
±
3
±
4
±
7
±
8
mV
max
TCV
OS
Temp. coefficient of input
offset voltage
0.4 µV/˚C
I
B
Input Bias Current (Note 14)
0.005 44
pA
max
I
OS
Input Offset Current (Note 14)
0.0025 22
pA
max
CMRR Common Mode Rejection
Ratio
−0.1V ≤ V
CM
≤8.5V 105 70
70
70
70
dB min
C
IN
Common Mode Input
Capacitance
3.5 pF
PSRR Power Supply Rejection Ratio V
S
=
2.5 V to 10V
95
75
75
75
75
dB
min
V
CM
Input Common-Mode Voltage
Range
CMRR ≥ 50 dB
9.1
8.85
8.75
8.85
8.75
V
min
−0.4 −0.2
0
−0.2
0
V
max
A
V
Large Signal Voltage Gain Sourcing (Note 11) 120
dB
min
Sinking (Note 11) 100
V
O
=
0.5V to 9.5V 104 80 80
V
O
Output Swing V
ID
=
100 mV
(Note 13)
9.99 9.97
9.97
9.97
9.97
V
min
V
ID
=
−100 mV(Note 13) 22 50
50
50
50
mV
max
I
SC
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing, V
ID
=
100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
2100 1200
1000
1200
1000
µA
min
Sinking, V
ID
=
−100 mV
(Notes 12, 13)
900 600
500
600
500
I
S
Supply Current (2 amplifiers) R
L
=
open 1.90 2.4
3.0
2.6
3.2
µA
max
AC Electrical Characteristics
SR Slew Rate(Note 8) 4.1 2.5 2.5 V/ms
GBWP Gain-Bandwidth Product 10.5 KHz
φ
m
Phase Margin (Note 15) 68 Degree
e
n
Input-Referred Voltage Noise R
L
=
open
f=10 Hz
170 nV/
√
Hz
i
n
Input-Referred Current Noise R
L
=
open
f=10 Hz
0.0002 pA/
√
Hz
Crosstalk Rejection (Note 9) 85 dB
www.national.com5

Electrical Characteristics (continued)
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF.
Note 3: Applies to both single-supply and split-supply operation. Continuous short circuit operation at elevated ambient temperature can result in exceeding the
maximum allowed junction temperature of 150˚C. Output currents in excess of
±
30 mA over long term may adversely affect reliability.
Note 4: The maximumpowerdissipation is a function of T
J(max)
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD=(T
J
-
(max)
-TA)/ θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
Note 5: Typical Values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 6: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis unless otherwise specified.
Note 7: Do not short circuit output to V
+
,when V+is greater than 13V or reliability will be adversely affected.
Note 8: Slew rate is the slower of the rising and falling slew rates.
Note 9: Input referred, V
+
=
10V and R
L
=
10 MΩ connected to 5V. Each amp excited in turn with 1 KHz to produce about 10 Vpp output.
Note 10: Limiting input pin current is only necessary for input voltages that exceed absolute maximum input voltage ratings.
Note 11: R
L
connected to V+/2. For Sourcing Test, V
O
>
V+/2. For Sinking tests, V
O
<
V+/2.
Note 12: Output shorted to ground for sourcing, and shorted to V+ for sinking short circuit current test.
Note 13: V
ID
is differential input voltage referenced to inverting input.
Note 14: Limits guaranteed by design.
Note 15: See the Typical Performance Characteristics and Application Notes sections for more details.
Typical Performance Characteristics V
S
=
5V, Single Supply, T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise specified
Total Supply Current
vs Supply Voltage
DS100064-8
Total Supply Current
vs Supply Voltage
(Negative Input Overdrive)
DS100064-9
Total Supply Current
vs Supply Voltage
(Positive Input Overdrive)
DS100064-10
Input Bias Current
vs Temperature
DS100064-41
Offset Voltage vs
Common Mode Voltage
(V
S
=
2.2V)
DS100064-6
Offset Voltage vs
Common Mode Voltage
(V
S
=
5V)
DS100064-7
www.national.com 6

Typical Performance Characteristics V
S
=
5V, Single Supply, T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise
specified (Continued)
Offset Voltage vs
Common Mode Voltage
(V
S
=
10V)
DS100064-42
Swing Towards V−vs
Supply Voltage
DS100064-3
Swing Towards V+vs
Supply Voltage
DS100064-2
Swing From Rail(s)
vs Temperature
DS100064-1
Output Source Current
vs Output Voltage
DS100064-49
Output Sink Current
vs Output Voltage
DS100064-48
Maximum Output Voltage
vs Load Resistance
DS100064-24
Large Signal Voltage
Gain vs Supply Voltage
DS100064-52
Open Loop
Gain/Phase vs
Frequency
DS100064-19
www.national.com7

Typical Performance Characteristics V
S
=
5V, Single Supply, T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise
specified (Continued)
Open Loop
Gain/Phase vs
Frequency For Various C
L
(Z
L
=
1MΩII C
L
)
DS100064-26
Open Loop
Gain/Phase vs
Frequency For Various C
L
(Z
L
=
100 KΩ II C
L
)
DS100064-25
Gain Bandwidth Product
vs Supply Voltage
DS100064-21
Phase Margin
(Worst Case)
vs Supply Voltage
DS100064-23
CMRR vs Frequency
DS100064-34
PSRR vs Frequency
DS100064-15
Positive Slew Rate vs
Supply Voltage
DS100064-12
Negative Slew Rate vs
Supply Voltage
DS100064-11
Cross-Talk Rejection
vs Frequency
DS100064-18
www.national.com 8

Typical Performance Characteristics V
S
=
5V, Single Supply, T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise
specified (Continued)
Input Voltage Noise
vs Frequency
DS100064-16
Output Impedance
vs Frequency
DS100064-33
THD+N vs Frequency
DS100064-28
THD+N vs Amplitude
DS100064-27
Maximum Output
Swing vs Frequency
DS100064-53
Small Signal Step
Response
(A
V
=
+2) (C
L
=
12 pF, 100 pF)
DS100064-29
Large Signal Step
Response
(A
V
=
+2) (C
L
=
100 pF)
DS100064-30
Small Signal Step
Response
(A
V
=
−1)(C
L
=
1MΩ II 100 pF, 200
pF)
DS100064-51
Small Signal Step
Response
(A
V
=
+ 1) For Various C
L
DS100064-31
www.national.com9

Typical Performance Characteristics V
S
=
5V, Single Supply, T
A
=
25˚C unless otherwise
specified (Continued)
Application Notes
Using LMC6442 in unity gain applications: LMC6442 is
optimized for maximum bandwidth and minimal external
components when operating at a minimum closed loop gain
of +2 (or −1). However, it is also possible to operate the device in a unity gain configuration by adding external compensation as shown in Figure 1:
Using this compensation technique it is possible to drive capacitive loads of up to 300 pF without causing oscillations
(see the Typical Performance Characteristics for step response plots). This compensation can also be used with
other gain settings in order to improve stability, especially
when driving capacitive loads (for optimum performance, R
c
and Ccmay need to be adjusted).
Using “T” Network:
Compromises need to be made whenever high gain inverting stages need to achieve a high input impedance as well.
This is especially important in low current applications which
tend to deal with high resistance values. Using a traditional
inverting amplifier, gain is inversely proportional to the resistor value tied between the inverting terminal and input while
the input impedance is equal to this value. For example, in
order to build an inverting amplifier with an input impedance
of 10MΩ and a gain of 100, one needs to come up with a
feedback resistor of 1000MΩ -an expensive task.
An alternate solution is to use a “T” Network in the feedback
path, as shown in Fig. 2.
Closed loop gain, A
V
is given by:
It must be noted, however, that using this scheme, the realizable bandwidth would be less than the theoretical maximum. With feedback factor, β, defined as:
BW(−3 dB)≈GBWP
•
β
In this case, assuming a GBWP of about 10 KHz, the expected BW would be around 50 Hz (vs 100 Hz with the conventional inverting amplifier).
Looking at the problem from a different view, with R
F
defined
by A
V
•
Rin, one could select a value for R in the “T” Network
and then determine R1 based on this selection:
Large Signal Step
Response
(A
V
=
+1) (C
L
=
200pF)
DS100064-32
DS100064-35
FIGURE 1. A
V
=
+1 Operation by adding C
c
and R
c
DS100064-36
FIGURE 2. “T” Network Used to Replace High Value
Resistor
DS100064-22
FIGURE 3. “T” Network Values for Various Values of R
www.national.com 10

Application Notes (Continued)
For convenience, Fig. 3 shows R1 vs R
F
for different values
of R.
Design Considerations for Capacitive Loads: As with
many other opamps, the LMC6442 is more stable at higher
closed loop gains when driving a capacitive load. Figure 4
shows minimum closed loop gain versus load capacitance,
to achieve less than 10%overshoot in the output small signal response. In addition, the LMC6442 is more stable when
it provides more output current to the load and when its output voltage does not swing close to V
−
.
The LMC6442 is more tolerant to capacitive loads when the
equivalent output load resistance is lowered or when output
voltage is 1V or greater from the V
−
supply. The capacitive
load drive capability is also improved by adding an isolating
resistor in series with the load and the output of the device.
Figure 5 shows the value of this resistor for various capacitive loads (A
V
=
−1), while limiting the output to less than 10
%
overshoot.
Referring to the Typical Performance Characteristics plot of
Phase Margin (Worst Case) vs Supply Voltage, note that
Phase Margin increases as the equivalent output load resistance is lowered. This plot shows the expected Phase Margin when the device output is very close to V
−
, which is the
least stable condition of operation. Comparing this Phase
Margin value to the one read off the Open Loop Gain/Phase
vs Frequency plot, one can predict the improvement in
Phase Margin if the output does not swing close to V
−
. This
dependence of Phase Margin on output voltage is minimized
as long as the output load, R
L
, is about 1MΩ or less.
Output Phase Reversal: The LMC6442 is immune against
this behavior even when the input voltages exceed the common mode voltage range.
Output Time Delay: Due to the ultra low power consumption of the device, there could be as long as 2.5 ms of time
delay from when power is applied to when the device output
reaches its final value.
DS100064-47
FIGURE 4. Minimum Operating Gain vs Capactive Load
DS100064-43
FIGURE 5. Isolating Resistor Value vs Capactive Load
www.national.com11

Application Circuits
Micropower Single Supply Voltage to Frequency Converter
DS100064-45
V
+
=
5V: I
S
<
10µA, f/V
C
=
4.3 (Hz/V)
DS100064-46
www.national.com 12

Application Circuits (Continued)
Gain Stage with Current Boosting
DS100064-54
Offset Nulling Schemes
DS100064-44
www.national.com13

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
8-Lead (0.150″ Wide) Molded Small Outline Package, JEDEC
Order Number LMC6442AIM or LMC6442IM or LMC6442AIMX or LMC6442IMX
NS Package Number M08A
8-Lead (0.300″ Wide) Molded Dual-In-Line Package
Order Number LMC6442AIN or LMC6442IN or LMC6442AINX or LMC6442INX
NS Package Number N08E
www.national.com 14

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL
SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
8-Lead (0.118″ Wide) Molded Mini Small Outline Package
Order Number LMC6442AIMM or LMC6442IMM or LMC6442AIMMX or LMC6442IMMX
NS Package Number MUA08A
LMC6442 Dual Micropower Rail-to-Rail Output Single Supply Operational Amplifier
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...