LM2670
SIMPLE SWITCHER
®
High Efficiency 3A Step-Down
Voltage Regulator with Sync
General Description
The LM2670 series of regulators are monolithic integrated
circuits which provide all of the active functions for a
step-down (buck) switching regulator capable of driving up to
3A loads with excellent line and load regulation characteristics. High efficiency (
>
90%) is obtained through the use of a
low ON-resistance DMOS powerswitch. The series consists
of fixed output voltages of 3.3V, 5V and 12V and an adjustable output version.
The SIMPLE SWITCHER concept provides for a complete
design using a minimum number of external components.
The switching clock frequency can be provided by an internal fixed frequency oscillator (260KHz) or from an externally
provided clock in the range of 280KHz to 400Khz which allows the use of physically smaller sized components.Afamily of standard inductors for use with the LM2670 are available from several manufacturers to greatly simplify the
design process. The external Sync clock provides direct and
precise control of the output ripple frequency for consistent
filtering or frequency spectrum positioning.
The LM2670 series also has built in thermal shutdown, current limiting and an ON/OFF control input that can power
down the regulator to a low 50µA quiescent current standby
condition. The output voltage is guaranteed to a
±
2%toler-
ance.
Features
n Efficiency up to 94
%
n Simple and easy to design with (using off-the-shelf
external components)
n 150 mΩ DMOS output switch
n 3.3V, 5V and 12V fixed output and adjustable (1.2V to
37V ) versions
n 50µA standby current when switched OFF
n
±
2%maximum output tolerance over full line and load
conditions
n Wide input voltage range: 8V to 40V
n External Sync clock capability (280KHz to 400KHz)
n 260 KHz fixed frequency internal oscillator
n −40 to +125˚C operating junction temperature range
Applications
n Simple to design, high efficiency (>90%) step-down
switching regulators
n Efficient system pre-regulator for linear voltage
regulators
n Battery chargers
n Communications and radio equipment regulator with
synchronized clock frequency
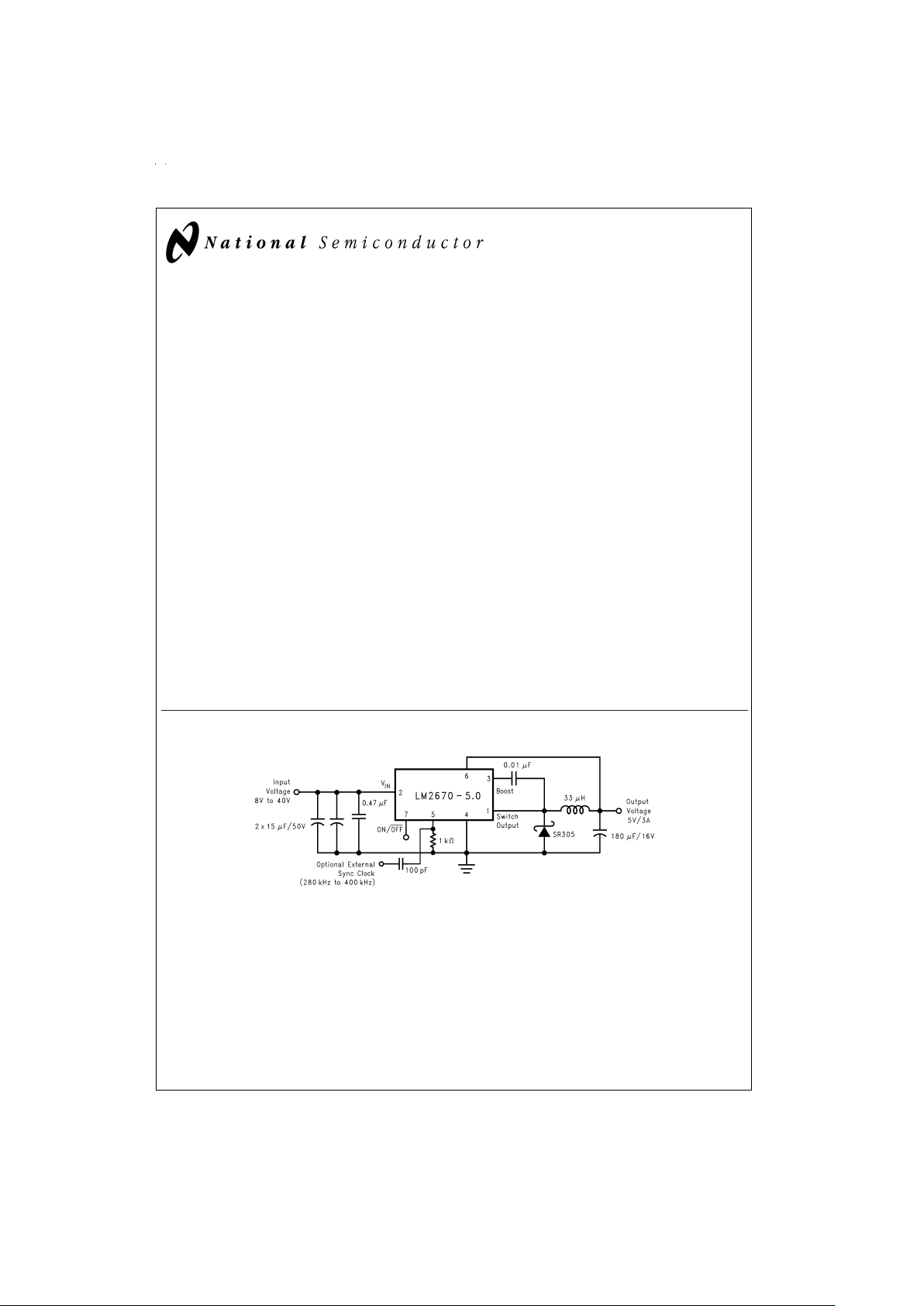
Typical Application
SIMPLE SWITCHER®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
DS100942-3
August 1998
LM2670 SIMPLE SWITCHER High Efficiency 3A Step-Down Voltage Regulator with Sync
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100942 www.national.com
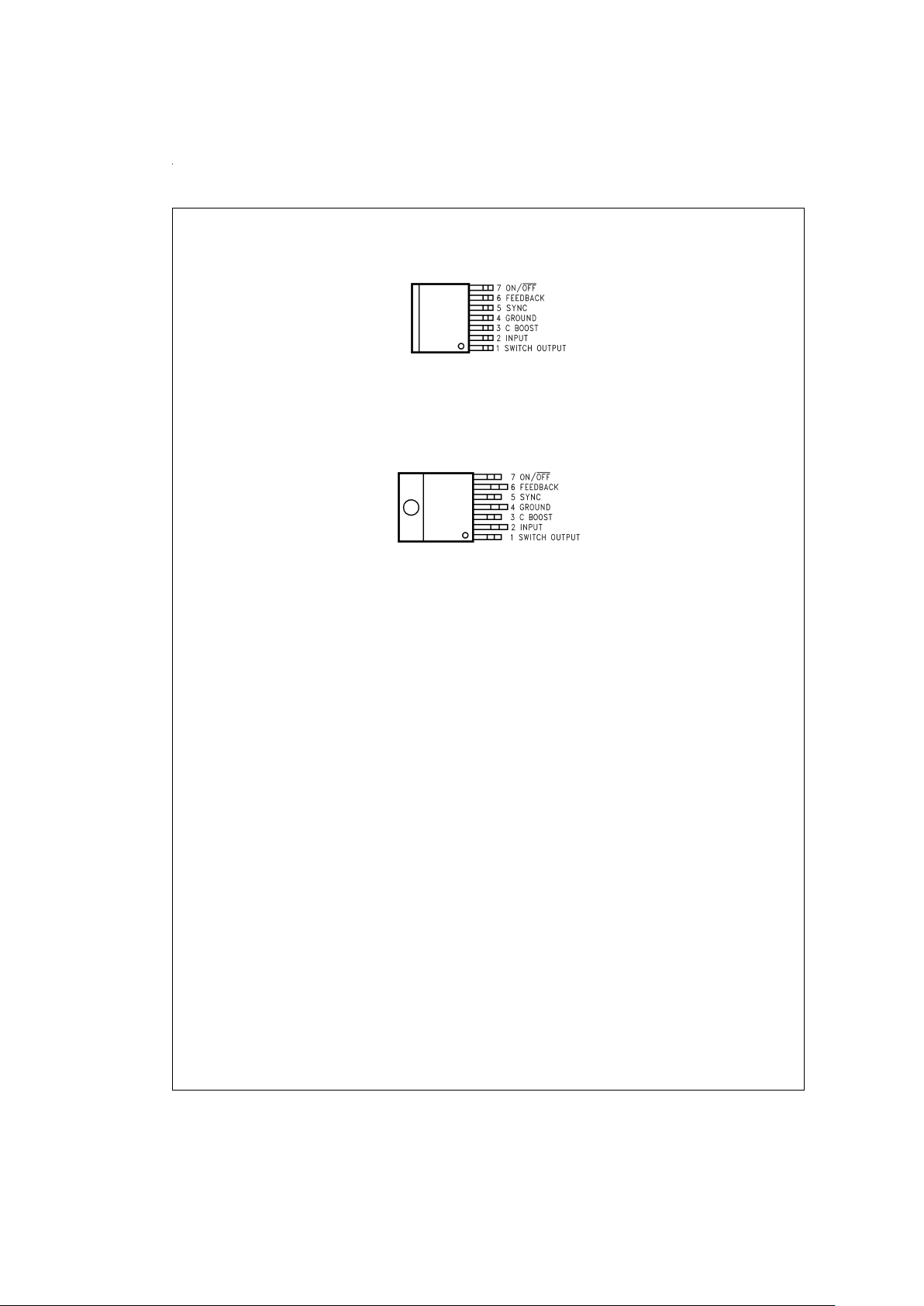
Connection Diagram and Ordering Information
TO-263 Package
Top View
DS100942-1
Order Number
LM2670S-3.3, LM2670S-5.0,
LM2670S-12 or LM2670S-ADJ
See NSC Package Number TS7B
TO-220 Package
Top View
DS100942-2
Order Number
LM2670T-3.3, LM2670T-5.0,
LM2670T-12 or LM2670T-ADJ
See NSC Package Number TA07B
www.national.com 2

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Input Supply Voltage 45V
ON/OFF Pin Voltage −0.1V to 6V
Switch Voltage to Ground −1V to V
IN
Boost Pin Voltage VSW+8V
Feedback Pin Voltage −0.3V to 14V
Power Dissipation Internally Limited
ESD (Note 2) 2 kV
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to 150˚C
Soldering Temperature
Wave 4 sec, 260˚C
Infrared 10 sec, 240˚C
Vapor Phase 75 sec, 219˚C
Operating Ratings
Supply Voltage 8V to 40V
Junction Temperature Range (T
J
) −40˚C to 125˚C
Thermal Resistance (θ
JA
) 30˚C/W
Thermal Resistance (θ
JC
) 2˚C/W
Electrical Characteristics Limits appearing in bold type face apply over the entire junction temperature
range of operation, −40˚C to 125˚C. Specifications appearing in normal type apply for T
A
=
T
J
=
25˚C. Sync pin open cir-
cuited.
LM2670-3.3
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Min Max Units
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 4)
V
OUT
Output Voltage V
IN
=
8V to 40V, 100mA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 3A 3.3 3.234/3.201 3.366/3.399 V
η Efficiency V
IN
=
12V, I
LOAD
=
3A 86
%
LM2670-5.0
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Min Max Units
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 4)
V
OUT
Output Voltage V
IN
=
8V to 40V, 100mA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 3A 5.0 4.900/4.850 5.100/5.150 V
η Efficiency V
IN
=
12V, I
LOAD
=
3A 88
%
LM2670-12
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Min Max Units
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 4)
V
OUT
Output Voltage V
IN
=
15V to 40V, 100mA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 3A 12 11.76/11.64 12.24/12.36 V
η Efficiency V
IN
=
24V, I
LOAD
=
3A 94
%
LM2670-ADJ
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Min Max Units
(Note 3) (Note 4) (Note 4)
V
FB
Feedback
Voltage
V
IN
=
8V to 40V, 100mA ≤ I
OUT
≤ 3A
V
OUT
Programmed for 5V
1.21 1.186/1.174 1.234/1.246 V
η Efficiency V
IN
=
12V, I
LOAD
=
3A 88
%
www.national.com3

All Output Voltage Versions
Electrical Characteristics
Limits appearing in bold type face apply over the entire junction temperature range of operation, −40˚C to 125˚C.
Specifications appearing in normal type apply for T
A
=
T
J
=
25˚C. Unless otherwise specified V
IN
=
12V for the 3.3V, 5V and
Adjustable versions and V
IN
=
24V for the 12V version, Sync pin open circuited..
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typ Min Max Units
DEVICE PARAMETERS
I
Q
Quiescent
Current V
FEEDBACK
=
8V 4.2 6 mA
For 3.3V, 5.0V, and ADJ Versions
V
FEEDBACK
=
15V
For 12V Versions
I
STBY
Standby
Quiescent
Current
ON/OFF Pin=0V
50 100/150 µA
I
CL
Current Limit 4.5 3.8/3.6 5.25/5.4 A
I
L
Output
Leakage
Current
V
IN
=
40V, ON/OFF Pin=0V
V
SWITCH
=
0V
V
SWITCH
=
−1V
16
200
15
µA
mA
R
DS(ON)
Switch
On-Resistance
I
SWITCH
=
3A
0.15 0.17/0.29 Ω
f
O
Oscillator
Frequency
Measured at Switch Pin
260 225 280 kHz
D Duty Cycle Maximum Duty Cycle 91
%
Minimum Duty Cycle 0
%
I
BIAS
Feedback Bias
Current
V
FEEDBACK
=
1.3V
ADJ Version Only
85 nA
V
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
Threshold
Voltage
1.4 0.8 2.0 V
I
ON/OFF
ON/OFF Input
Current
ON/OFF Input=0V
20 45 µA
F
SYNC
Synchronization
Frequency
V
SYNC
(Pin 5)=3.5V, 50%Duty Cycle
400 KHz
V
SYNC
SYNC
Threshold
Voltage
1.4 V
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions under which of the device is
guaranteed. Operating Ratings do not imply guaranteed performance limits. For guaranteed performance limits and associated test condition, see the electrical Characteristics tables.
Note 2: ESD was applied using the human-body model, a 100pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor into each pin.
Note 3: Typical values are determined with T
A
=
T
J
=
25˚C and represent the most likely norm.
Note 4: All limits are guaranteed at room temperature (standard type face) and at temperature extremes (bold type face). All room temperature limits are 100
%
tested during production with T
A
=
T
J
=
25˚C. All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard standard Quality Control (SQC) meth-
ods. All limits are used to calculateAverage Outgoing Quality Level (AOQL).
www.national.com 4
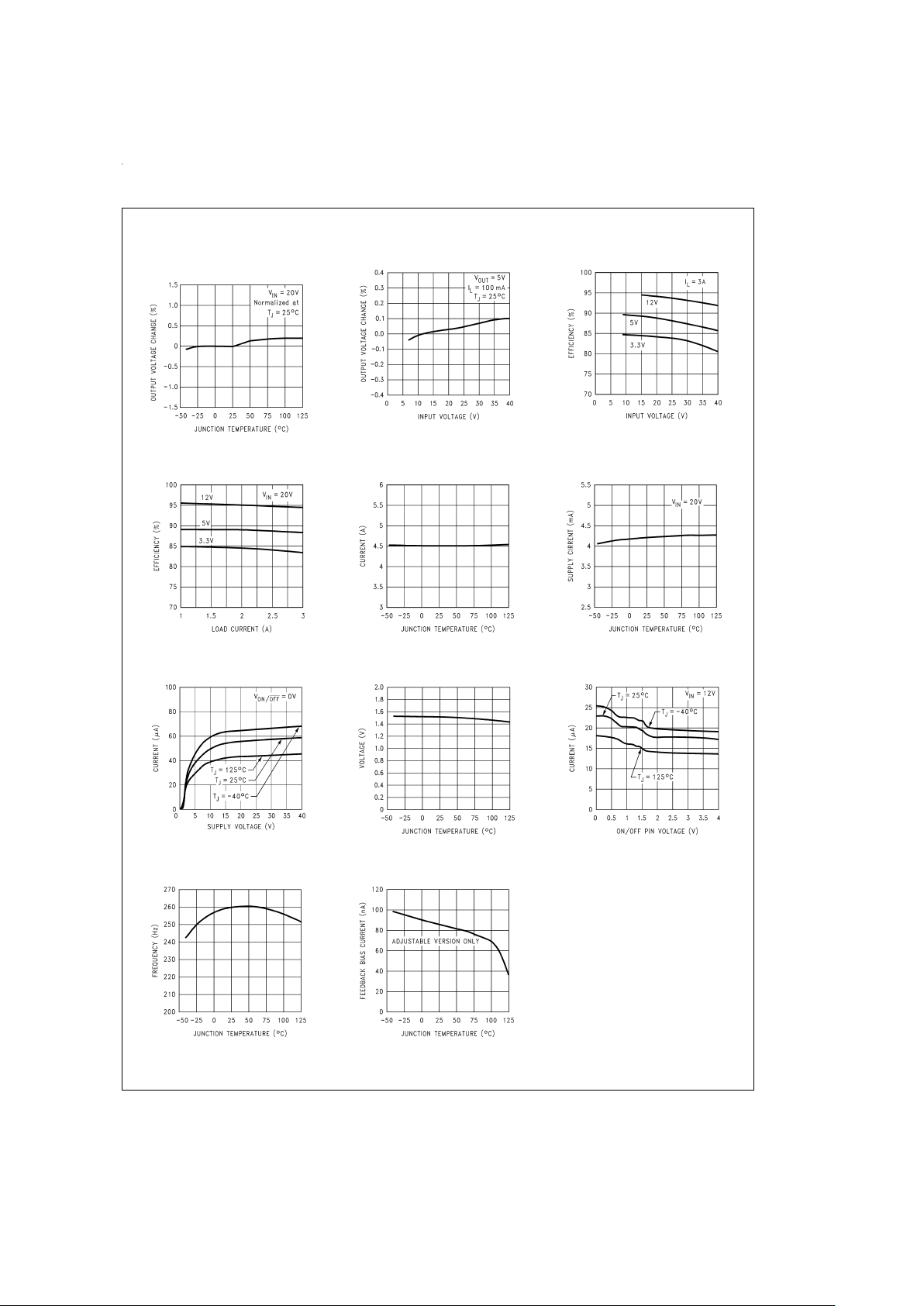
Typical Performance Characteristics
Normalized
Output Voltage
DS100942-9
Line Regulation
DS100942-10
Efficiency vs Input Voltage
DS100942-11
Efficiency vs I
LOAD
DS100942-12
Switch Current Limit
DS100942-4
Operating Quiescent Current
DS100942-5
Standby Quiescent Current
DS100942-40
ON/OFF Threshold Voltage
DS100942-13
ON/OFF Pin Current (Sourcing)
DS100942-14
Switching Frequency
DS100942-15
Feedback Pin Bias Current
DS100942-16
www.national.com5
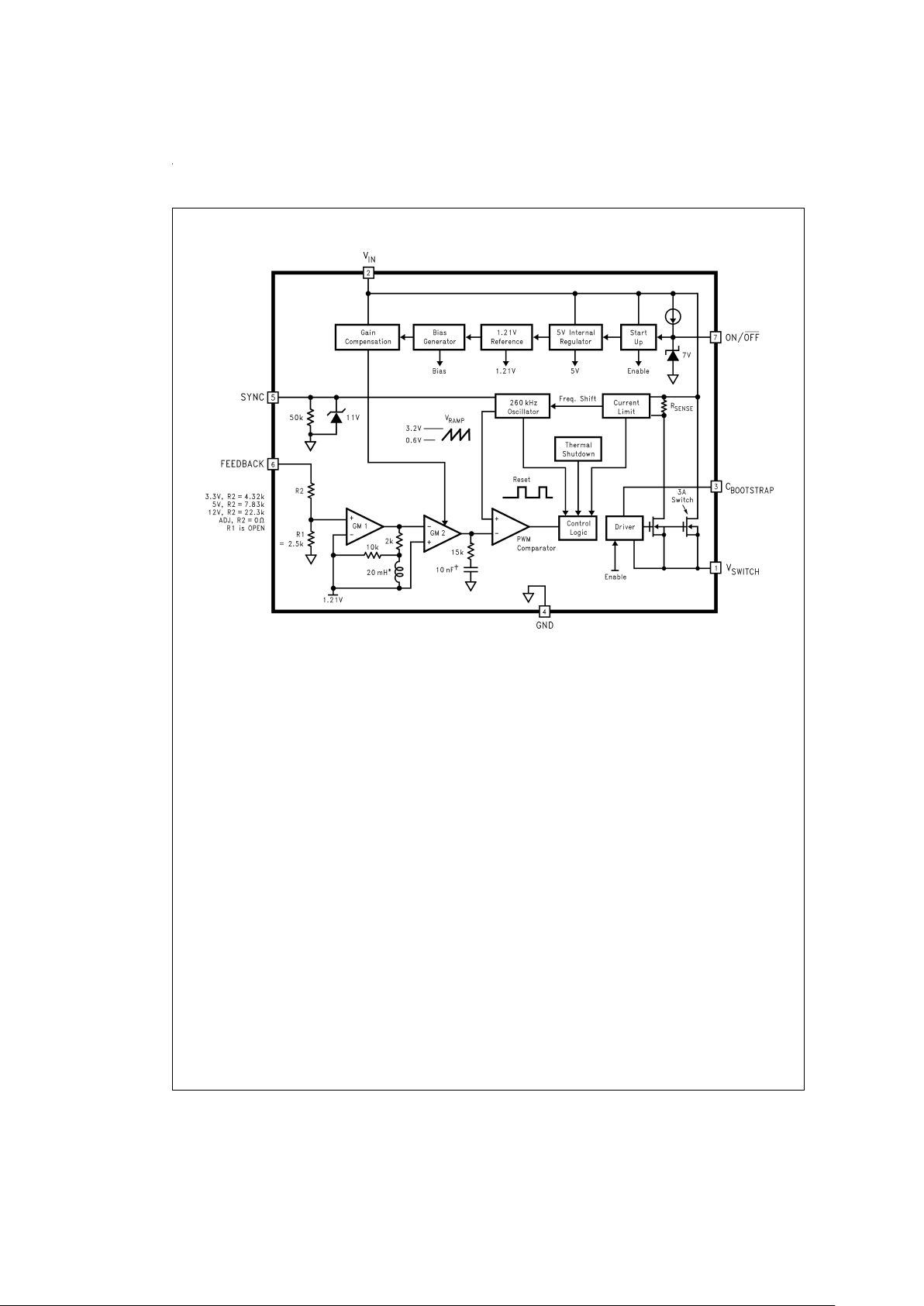
Block Diagram
DS100942-6
* Active Inductor Patent Number 5,514,947
†
Active Capacitor Patent Number 5,382,918
www.national.com 6
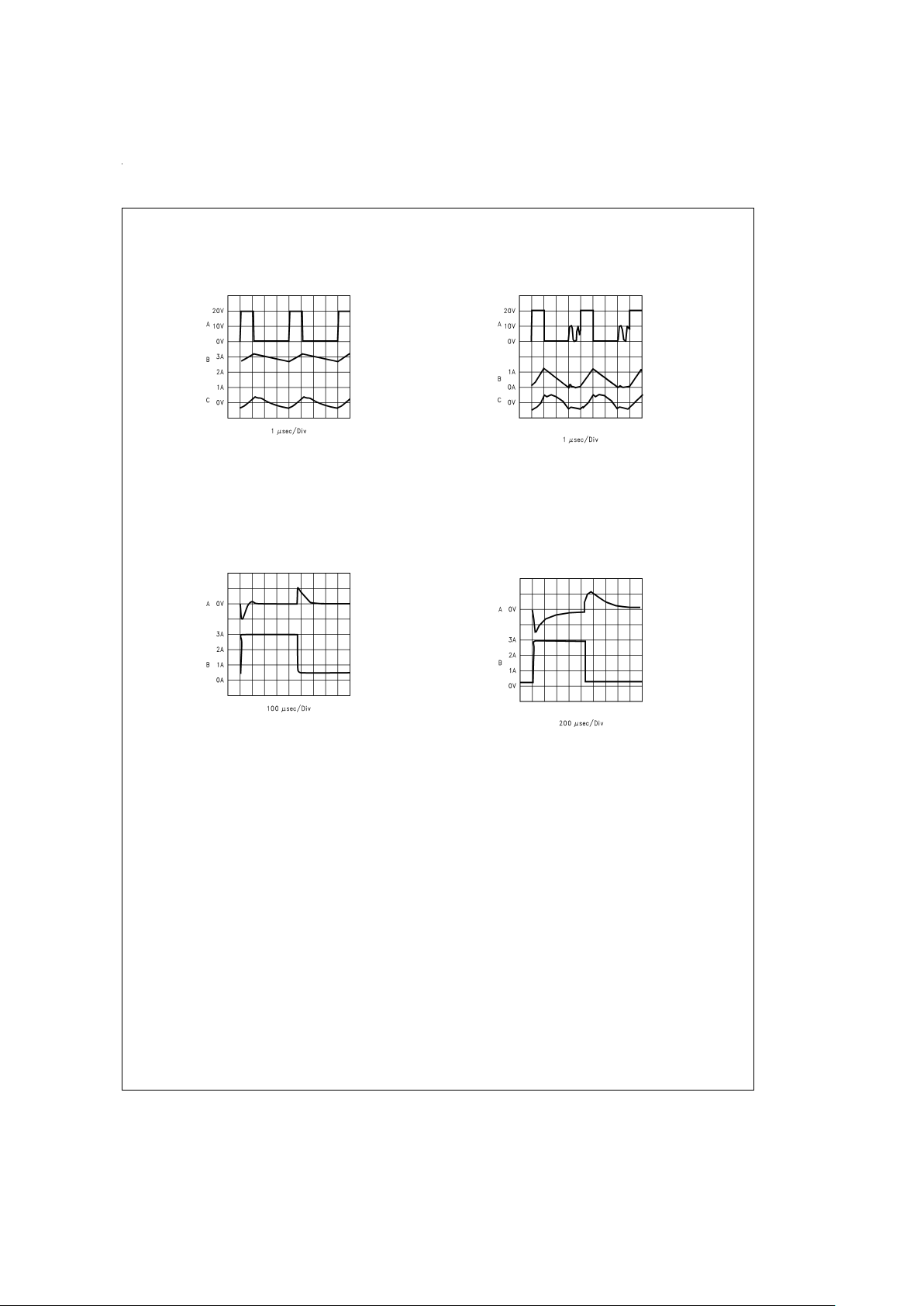
Typical Performance Characteristics
Continuous Mode Switching Waveforms
V
IN
=
20V, V
OUT
=
5V, I
LOAD
=
3A
L=33 µH, C
OUT
=
200 µF, C
OUT
ESR=26 mΩ
DS100942-17
A: VSWPin Voltage, 10 V/div.
B: Inductor Current, 1 A/div
C: Output Ripple Voltage, 20 mV/div AC-Coupled
Horizontal Time Base: 1 µs/div
Discontinuous Mode Switching Waveforms
V
IN
=
20V, V
OUT
=
5V, I
LOAD
=
500 mA
L=10 µH, C
OUT
=
400 µF, C
OUT
ESR=13 mΩ
DS100942-18
A: VSWPin Voltage, 10 V/div.
B: Inductor Current, 1 A/div
C: Output Ripple Voltage, 20 mV/div AC-Coupled
Horizontal Time Base: 1 µs//iv
Load Transient Response for Continuous Mode
V
IN
=
20V, V
OUT
=
5V
L=33 µH, C
OUT
=
200 µF, C
OUT
ESR=26 mΩ
DS100942-19
A: Output Voltage, 100 mV//div, AC-Coupled.
B: Load Current: 500 mA to 3A Load Pulse
Horizontal Time Base: 100 µs/div
Load Transient Response for Discontinuous Mode
V
IN
=
20V, V
OUT
=
5V,
L=10 µH, C
OUT
=
400 µF, C
OUT
ESR=13 mΩ
DS100942-20
A: Output Voltage, 100 mV/div, AC-Coupled.
B: Load Current: 200 mA to 3A Load Pulse
Horizontal Time Base: 200 µs/div
www.national.com7

Application Hints
The LM2670 provides all of the active functions required for
a step-down (buck) switching regulator. The internal power
switch is a DMOS power MOSFET to provide power supply
designs with high current capability, up to 3A, and highly efficient operation.
The LM2670 is part of the SIMPLE SWITCHER family of
power converters. A complete design uses a minimum number of external components, which have been
pre-determined from a variety of manufacturers. Using either
this data sheet or a designsoftware program called
LM267X
Made Simple
(version 2.0) a complete switching powersupply can be designed quickly. The software is providedfree of
charge and can be downloaded from National Semiconductor’s Internet site located at http://www.national.com.
PIN 1 - Switch Output
This is the output of a power MOSFETswitch connected directly to the input voltage. The switch provides energy to an
inductor, an output capacitor and the load circuitry under
control of an internal pulse-width-modulator (PWM). The
PWM controller is internally clocked by afixed 260KHz oscillator. In a standard step-down application the duty cycle
(Time ON/Time OFF) of the power switch is proportional to
the ratio of the power supply output voltage to the input voltage. The voltage on pin1 switchesbetween Vin (switchON)
and below ground by the voltage dropof the external Schottky diode (switch OFF).
PIN 2 - Input
The input voltage for the power supplyis connected topin 2.
In addition to providing energy to the load the input voltage
also provides bias for the internal circuitry of the LM2670.
For guaranteed performance the input voltage must be in the
range of 8V to 40V. For best performance of the power supply the input pin should always be bypassed with an input capacitor located close to pin 2.
PIN3-CBoost
A capacitor must be connected from pin 3 to the switch output, pin 1. This capacitor boosts thegate drive tothe internal
MOSFET above Vin to fully turn it ON. This minimizes conduction losses in the power switch to maintain high efficiency. The recommended value for C Boost is 0.01µF.
PIN 4 - Ground
This is the ground reference connection for all components
in the power supply. In fast-switching, high-current applica-
tions such as those implemented with the LM2670, it is recommended that a broad ground plane be used to minimize
signal coupling throughout the circuit
PIN 5 - Sync
This input allows control of the switching clock frequency. If
left open-circuited the regulator will be switched at the internal oscillator frequency, between 225KHz and 280KHz. An
external clock can be used to force the switching frequency
and thereby control the output ripple frequency of the regulator.This capability provides for consistent filtering of the output ripple from system to system as well as precise frequency spectrum positioning of theripple frequency whichis
often desired in communications and radio applications. This
external frequency must be greater than the LM2670 internal
oscillator frequency, which could be as high as 280KHz, to
prevent an erroneous reset of the internal ramp oscillator
and PWM control of the power switch. The ramp oscillator is
reset on the positive goingedge of thesync input signal.It is
recommended that the external TTL or CMOS compatible
clock (between 0V and a level greater than 3V) be ac
coupled to the sync input through a 100pf capacitor and a
1KΩ resistor to ground at pin 5 as shown in
Figure 1
.
PIN 6 - Feedback
This is the input to a two-stage high gain amplifier, which
drives the PWM controller. It is necessary to connectpin 6 to
the actual output of the power supply to set the dc output
voltage. For the fixed output devices (3.3V, 5V and 12V outputs), a direct wire connection to the output is all that is required as internal gain setting resistors are provided inside
the LM2670. For the adjustable output version two external
resistors are required to set thedc output voltage.For stable
operation of the power supply it is important to prevent coupling of any inductor flux to the feedback input.
PIN 7 - ON/OFF
This input provides an electrical ON/OFF control of the
power supply. Connecting this pin to ground or to any voltage less than 0.8V will completely turn OFF the regulator.
The current drain from the input supply when OFF is only
50µA. Pin 7 has an internal pull-up current source of approximately 20µA and a protection clamp zener diode of 7V to
ground. When electrically driving the ON/OFF pin the high
voltage level for the ON condition should not exceed the 6V
absolute maximum limit. When ON/OFF control is not required pin 7 should be left open circuited.
www.national.com 8

Application Hints (Continued)
DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS
Power supply design using the LM2670 is greatly simplified
by using recommended external components. A wide range
of inductors, capacitors and Schottky diodes from several
manufacturers have been evaluated for use in designs that
cover the full rangeof capabilities (input voltage, output voltage and load current) of the LM2670.Asimple design procedure using nomographs and component tables provided in
this data sheet leads to a working design with very little effort. Alternatively, the design software,
LM267X Made
Simple
(version 2.0), can also be used to provide instant
component selection, circuit performance calculations for
evaluation, a bill of materials component list and a circuit
schematic.
The individual components from the various manufacturers
called out for use are still just a small sample of the vast array of components available in the industry. While these
components are recommended, they are not exclusively the
only components for use in a design. After a close comparison of component specifications, equivalent devices from
other manufacturers could besubstituted for use in an application.
Important considerations for each external component and
an explanation of how the nomographs and selection tables
were developed follows.
INDUCTOR
The inductor is the key component in a switching regulator.
For efficiency the inductor stores energy during the switch
ON time and then transfers energy to the load while the
switch is OFF.
Nomographs are used to select the inductance value required for a given set of operating conditions. The nomographs assume that the circuit is operating in continuous
mode (the current flowing through the inductor never falls to
zero). The magnitude of inductance isselected to maintain a
maximum ripple current of 30%of the maximum load current. If the ripple current exceeds this 30%limit the next
larger value is selected.
The inductors offered have been specifically manufactured
to provide proper operation under all operating conditions of
input and output voltage and load current. Severalpart types
are offered for a given amount of inductance. Both surface
DS100942-7
FIGURE 1. Basic circuit for fixed output voltage applications.
DS100942-8
FIGURE 2. Basic circuit for adjustable output voltage applications
www.national.com9

Application Hints (Continued)
mount and through-hole devices are available. The inductors
from each of the three manufacturers have unique characteristics.
Renco: ferrite stick core inductors; benefits are typically lowest cost and can withstand ripple and transient peak currents
above the rated value. These inductors have an external
magnetic field, which may generate EMI.
Pulse Engineering: powdered iron toroid core inductors;
these also can withstandhigher than rated currents and, being toroid inductors, will have low EMI.
Coilcraft: ferrite drum core inductors; these are the smallest
physical size inductors and are available only as surface
mount components. These inductors also generate EMI but
less than stick inductors.
OUTPUT CAPACITOR
The output capacitor acts to smooth the dc output voltage
and also provides energy storage.Selection of anoutput capacitor, with an associated equivalent series resistance
(ESR), impacts both the amount of output ripple voltage and
stability of the control loop.
The output ripple voltage of the power supply is the product
of the capacitor ESR and the inductorripple current. Thecapacitor types recommended in the tables were selected for
having low ESR ratings.
In addition, both surface mount tantalum capacitors and
through-hole aluminum electrolytic capacitors are offered as
solutions.
Impacting frequency stability of the overall control loop, the
output capacitance, in conjunction with the inductor, creates
a double pole inside the feedback loop. In addition the capacitance and the ESR value create a zero. These frequency response effects together with the internalfrequency
compensation circuitry of the LM2670 modify the gain and
phase shift of the closed loop system.
As a general rule for stable switching regulator circuits it is
desired to have the unity gain bandwidth of the circuit to be
limited to no more than one-sixth of the controller switching
frequency.With the fixed 260KHz switching frequency of the
LM2670, the output capacitor is selected to provide a unity
gain bandwidth of 40KHz maximum. Each recommended capacitor value has been chosen to achieve this result.
In some cases multiple capacitors are required either to reduce the ESR of the output capacitor, to minimize output
ripple (a ripple voltage of 1%of Vout or less is the assumed
performance condition), or to increase the output capacitance to reduce the closed loop unitygain bandwidth (to less
than 40KHz). When parallel combinations of capacitors are
required it has been assumed that each capacitor is the exact same part type.
The RMS current and working voltage (WV) ratings of the
output capacitor are also important considerations. In a typical step-down switching regulator, the inductor ripple current
(set to be no more than 30%of the maximum load current by
the inductor selection) is the current that flows through the
output capacitor. The capacitor RMS current rating must be
greater than this ripple current.The voltage rating of theoutput capacitor should begreater than 1.3 times the maximum
output voltage of the power supply.If operation of the system
at elevated temperatures is required, the capacitor voltage
rating may be de-rated to less than the nominal room temperature rating. Careful inspection of the manufacturer’s
specification for de-rating of working voltage with temperature is important.
INPUT CAPACITOR
Fast changing currents in high current switching regulators
place a significant dynamic load on the unregulated power
source.An input capacitor helpsto provide additional current
to the power supply as well as smooth out input voltage
variations.
Like the output capacitor, the key specifications for the input
capacitor are RMS current rating and working voltage. The
RMS current flowing through the input capacitor is equal to
one-half of the maximum dc load current so the capacitor
should be rated to handle this. Paralleling multiple capacitors
proportionally increases the current rating of the total capacitance. The voltage rating should also be selected to be 1.3
times the maximum input voltage. Depending on the unregulated input power source, under light load conditions the
maximum input voltage could be significantly higher than
normal operation and should be considered when selecting
an input capacitor.
The input capacitor should be placed very close to the input
pin of the LM2670. Due to relative high current operation
with fast transient changes, the series inductance of input
connecting wires or PCB tracescan create ringing signals at
the input terminal whichcould possibly propagate to the output or other parts of the circuitry. It may be necessary in
some designs to add a small valued (0.1µF to 0.47µF) ceramic type capacitor in parallel with the input capacitor to
prevent or minimize any ringing.
CATCH DIODE
When the power switch in the LM2670 turns OFF,the current
through the inductor continues to flow.The path for this current is through the diode connected between the switch output and ground. This forward biased diode clamps the switch
output to a voltage less than ground. This negative voltage
must be greater than −1V so a low voltage drop (particularly
at high current levels) Schottky diodeis recommended. Total
efficiency of the entire powersupply is significantlyimpacted
by the power lost in the output catch diode. The average current through the catch diode isdependent on theswitch duty
cycle (D) and isequal tothe load current times (1-D). Use of
a diode rated formuch higher current than is required by the
actual application helps to minimize the voltage drop and
power loss in the diode.
During the switch ON time the diode will be reversed biased
by the input voltage. The reverse voltage rating of the diode
should be at least 1.3 times greater than the maximum input
voltage.
BOOST CAPACITOR
The boost capacitor creates a voltage used to overdrive the
gate of the internal power MOSFET.This improves efficiency
by minimizing the on resistance of the switchand associated
power loss. For all applications it is recommended to use a
0.01µF/50V ceramic capacitor.
SYNC COMPONENTS
When synchronizing the LM2670 with an external clock it is
recommended to connect the clock to pin5 through a series
100pf capacitor and connect a 1KΩ resistor to ground from
pin 5. This RC networkcreates a short 100nS pulseon each
positive edge of the clock to reset the internal ramp oscillator. The reset time of the oscillator is approximately 300nS.
www.national.com 10

Application Hints (Continued)
SIMPLE DESIGN PROCEDURE
Using the nomographs and tables in this data sheet (or use
the available design software at http://www.national.com) a
complete step-down regulator can be designed in a few
simple steps.
Step 1: Define the power supply operating conditions:
Required output voltage
Maximum DC input voltage
Maximum output load current
Step 2: Set the output voltage by selecting a fixed output
LM2670 (3.3V, 5V or 12V applications) or determine the required feedback resistors for use with the adjustable
LM2670−ADJ
Step 3: Determine the inductor required by using one of the
four nomographs,
Figure 3
through
Figure 6
. Table 1 provides a specific manufacturer andpart number for the inductor.
Step 4: Using Table 3 (fixed output voltage) or Table 6 (adjustable output voltage), determine the output capacitance
required for stable operation. Table 2 provides the specific
capacitor type from the manufacturer of choice.
Step 5: Determine an input capacitor from Table 4 for fixed
output voltage applications. Use Table 2 to find the specific
capacitor type. For adjustable output circuits select a capacitor from Table 2 with a sufficientworking voltage(WV) rating
greater than Vin max, andan rms current rating greaterthan
one-half the maximum load current (2 or more capacitors in
parallel may be required).
Step 6: Select a diode from Table5. The current rating of the
diode must be greater thanI load max andthe Reverse Voltage rating must be greater than Vin max.
Step 7: Include a 0.01µF/50V capacitor forCboost in the design.
FIXED OUTPUT VOLTAGE DESIGN EXAMPLE
A system logic power supply bus of 3.3V is to be generated
from a wall adapter which provides an unregulated DC voltage of 13V to 16V. The maximum load current is 2.5A.
Through-hole components are preferred.
Step 1: Operating conditions are:
Vout=3.3V
Vin max=16V
Iload max=2.5A
Step 2: Select an LM2670T-3.3. The output voltage will have
a tolerance of
±
2%at room temperature and±3%over the full operating
temperature range.
Step 3: Use the nomograph for the 3.3V device ,
Figure 3
.
The intersection of the 16V horizontal line (V
in
max) and the
2.5A vertical line (I
load
max) indicates that L33, a 22µH in-
ductor, is required.
From Table 1, L33 in a through-hole component is available
from Renco with part number RL-1283-22-43or part number
PE-53933 from Pulse Engineering.
Step 4: Use Table3 to determine an outputcapacitor. With a
3.3V output and a 22µH inductor there are four through-hole
output capacitor solutions with the number of same type capacitors to be paralleled and an identifying capacitor code
given. Table 2 provides the actual capacitor characteristics.
Any of the following choices will work in the circuit:
1 x 220µF/10V Sanyo OS-CON (code C5)
1 x 1000µF/35V Sanyo MV-GX (code C10)
1 x 2200µF/10V Nichicon PL (code C5)
1 x 1000µF/35V Panasonic HFQ (code C7)
Step 5: Use Table 4 to select an input capacitor. With 3.3V
output and 22µH there are three through-hole solutions.
These capacitors provide a sufficient voltage rating and an
rms current rating greater than 1.25A (1/2 I
load
max). Again
using Table 2 for specific component characteristics the following choices are suitable:
1 x 1000µF/63V Sanyo MV-GX (code C14)
1 x 820µF/63V Nichicon PL (code C24)
1 x 560µF/50V Panasonic HFQ (code C13)
Step 6: From Table5a3ASchottky diode must be selected.
For through-hole components 20V rated diodes are sufficient
and 2 part types are suitable:
1N5820
SR302
Step 7: A 0.01µF capacitor will be used for Cboost.
ADJUSTABLE OUTPUT DESIGN EXAMPLE
In this example it is desired toconvert the voltage from atwo
battery automotive power supply (voltage range of 20V to
28V,typical in largetruck applications) to the 14.8VDC alternator supply typically used to power electronic equipment
from single battery 12V vehicle systems. The load current required is 2A maximum. It is also desired to implement the
power supply with all surface mount components.
Step 1: Operating conditions are:
Vout=14.8V
Vin max=28V
Iload max=2A
Step 2: Select an LM2670S-ADJ. To set the output voltage
to 14.9V two resistors need to be chosen (R1 and R2 in
Fig-
ure 2
). For the adjustable device the output voltage is set by
the following relationship:
Where VFBis the feedback voltage of typically 1.21V.
A recommended value to use for R1 is 1K. In this example
then R2 is determined to be:
R2=11.23KΩ
The closest standard 1%tolerance value to use is 11.3KΩ
This will set the nominal output voltage to 14.88V which is
within 0.5%of the target value.
Step 3: To use the nomograph for the adjustable device,
Fig-
ure 6
, requires a calculation of the inductor
Volt
•
microsecond constant (E•T expressed in V•µS) from
the following formula:
where V
SAT
is the voltage drop across the internal power
switch which is R
ds(ON)
times I
load
. In this example this would
be typically 0.15Ω x 2A or 0.3V and V
D
is the voltage drop
across the forward bisased Schottky diode, typically 0.5V.
The switching frequency of 260KHz is the nominal value to
use to estimate the ON time of the switch during which energy is stored in the inductor.
www.national.com11

Application Hints (Continued)
For this example E
•
T is found to be:
Using
Figure 6
, the intersection of 27V•µS horizontally and
the 2A vertical line (I
load
max) indicates that L38 , a 68µH in-
ductor, should be used.
From Table1, L38 in a surface mount component is available
from Pulse Engineering with part number PE-54038S.
Step 4: Use Table6 to determine an outputcapacitor. With a
14.8V output the 12.5 to 15V row is used and witha 68µH inductor there are three surface mount output capacitor solutions. Table 2 provides the actual capacitor characteristics
based on the C Code number. Any of the following choices
can be used:
1 x 33µF/20V AVX TPS (code C6)
1 x 47µF/20V Sprague 594 (code C8)
1 x 47µF/20V Kemet T495 (code C8)
Important Note:
When using the adjustable device in low
voltage applications (less than3V output), if the nomograph,
Figure 6, selects an inductance of 22µH or less, Table6 does
not provide an output capacitor solution. With these conditions the number of output capacitors required for stable operation becomes impractical. It is recommended to use either a 33µH or 47µHinductor and the output capacitorsfrom
Table 6.
Step 5: An input capacitor for this example will require at
least a 35V WV rating with an rms current rating of 1A (1/2
Iout max). From Table2 it can be seenthat C12, a 33µF/35V
capacitor from Sprague, has the required voltage/current rating of the surface mount components.
Step 6: From Table5a3ASchottky diode must be selected.
For surface mount diodes with a margin ofsafety on the voltage rating one of five diodes can be used:
SK34
30BQ040
30WQ04F
MBRS340
MBRD340
Step 7: A 0.01µF capacitor will be used for Cboost.
www.national.com 12

Application Hints (Continued)
INDUCTOR VALUE SELECTION GUIDES (For Continuous Mode Operation)
DS100942-21
FIGURE 3. LM2670-3.3
DS100942-22
FIGURE 4. LM2670-5.0
DS100942-23
FIGURE 5. LM2670-12
DS100942-24
FIGURE 6. LM2670-ADJ
www.national.com13

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 1. Inductor Manufacturer Part Numbers
Inductor
Reference
Number
Inductance
(µH)
Current
(A)
Renco Pulse Engineering Coilcraft
Through Hole Surface
Mount
Through
Hole
Surface
Mount
Surface Mount
L23 33 1.35 RL-5471-7 RL1500-33 PE-53823 PE-53823S DO3316-333
L24 22 1.65 RL-1283-22-43 RL1500-22 PE-53824 PE-53824S DO3316-223
L25 15 2.00 RL-1283-15-43 RL1500-15 PE-53825 PE-53825S DO3316-153
L29 100 1.41 RL-5471-4 RL-6050-100 PE-53829 PE-53829S DO5022P-104
L30 68 1.71 RL-5471-5 RL6050-68 PE-53830 PE-53830S DO5022P-683
L31 47 2.06 RL-5471-6 RL6050-47 PE-53831 PE-53831S DO5022P-473
L32 33 2.46 RL-5471-7 RL6050-33 PE-53932 PE-53932S DO5022P-333
L33 22 3.02 RL-1283-22-43 RL6050-22 PE-53933 PE-53933S DO5022P-223
L34 15 3.65 RL-1283-15-43 — PE-53934 PE-53934S DO5022P-153
L38 68 2.97 RL-5472-2 — PE-54038 PE-54038S —
L39 47 3.57 RL-5472-3 — PE-54039 PE-54039S —
L40 33 4.26 RL-1283-33-43 — PE-54040 PE-54040S —
L41 22 5.22 RL-1283-22-43 — PE-54041 P0841 —
L44 68 3.45 RL-5473-3 — PE-54044 — —
L45 10 4.47 RL-1283-10-43 — — P0845 DO5022P-103HC
Inductor Manufacturer Contact Numbers
Coilcraft Phone (800) 322-2645
FAX (708) 639-1469
Coilcraft, Europe Phone +44 1236 730 595
FAX +44 1236 730 627
Pulse Engineering Phone (619) 674-8100
FAX (619) 674-8262
Pulse Engineering, Phone +353 93 24 107
Europe FAX +353 93 24 459
Renco Electronics Phone (800) 645-5828
FAX (516) 586-5562
www.national.com 14

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 2. Input and Output Capacitor Codes
Capacitor
Reference
Code
Surface Mount
AVX TPS Series Sprague 594D Series Kemet T495 Series
C
(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)C(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)C(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)
C1 330 6.3 1.15 120 6.3 1.1 100 6.3 0.82
C2 100 10 1.1 220 6.3 1.4 220 6.3 1.1
C3 220 10 1.15 68 10 1.05 330 6.3 1.1
C4 47 16 0.89 150 10 1.35 100 10 1.1
C5 100 16 1.15 47 16 1 150 10 1.1
C6 33 20 0.77 100 16 1.3 220 10 1.1
C7 68 20 0.94 180 16 1.95 33 20 0.78
C8 22 25 0.77 47 20 1.15 47 20 0.94
C9 10 35 0.63 33 25 1.05 68 20 0.94
C10 22 35 0.66 68 25 1.6 10 35 0.63
C11 15 35 0.75 22 35 0.63
C12 33 35 1 4.7 50 0.66
C13 15 50 0.9
www.national.com15

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 2. Input and Output Capacitor Codes (continued)
Capacitor
Reference
Code
Through Hole
Sanyo OS-CON SA
Series
Sanyo MV-GX Series Nichicon PL Series Panasonic HFQ Series
C (µF) WV
(V)
Irms
(A)C(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)C(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)C(µF)WV(V)
Irms
(A)
C1 47 6.3 1 1000 6.3 0.8 680 10 0.8 82 35 0.4
C2 150 6.3 1.95 270 16 0.6 820 10 0.98 120 35 0.44
C3 330 6.3 2.45 470 16 0.75 1000 10 1.06 220 35 0.76
C4 100 10 1.87 560 16 0.95 1200 10 1.28 330 35 1.01
C5 220 10 2.36 820 16 1.25 2200 10 1.71 560 35 1.4
C6 33 16 0.96 1000 16 1.3 3300 10 2.18 820 35 1.62
C7 100 16 1.92 150 35 0.65 3900 10 2.36 1000 35 1.73
C8 150 16 2.28 470 35 1.3 6800 10 2.68 2200 35 2.8
C9 100 20 2.25 680 35 1.4 180 16 0.41 56 50 0.36
C10 47 25 2.09 1000 35 1.7 270 16 0.55 100 50 0.5
C11 220 63 0.76 470 16 0.77 220 50 0.92
C12 470 63 1.2 680 16 1.02 470 50 1.44
C13 680 63 1.5 820 16 1.22 560 50 1.68
C14 1000 63 1.75 1800 16 1.88 1200 50 2.22
C15 220 25 0.63 330 63 1.42
C16 220 35 0.79 1500 63 2.51
C17 560 35 1.43
C18 2200 35 2.68
C19 150 50 0.82
C20 220 50 1.04
C21 330 50 1.3
C22 100 63 0.75
C23 390 63 1.62
C24 820 63 2.22
C25 1200 63 2.51
Capacitor Manufacturer Contact Numbers
Nichicon Phone (847) 843-7500
FAX (847) 843-2798
Panasonic Phone (714) 373-7857
FAX (714) 373-7102
AVX Phone (845) 448-9411
FAX (845) 448-1943
Sprague/Vishay Phone (207) 324-4140
FAX (207) 324-7223
Sanyo Phone (619) 661-6322
FAX (619) 661-1055
Kemet Phone (864) 963-6300
FAX (864) 963-6521
www.national.com 16

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 3. Output Capacitors for Fixed Output Voltage Application
Output
Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Surface Mount
AVX TPS Series Sprague 594D
Series
Kemet T495 Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
3.3
10 4C23C14C4
15 4C23C14C4
22 3C22C73C4
33 2C22C62C4
5
10 4C24C64C4
15 3C22C73C4
22 3C22C73C4
33 2C22C32C4
47 2C21C72C4
12
10 4C53C65C9
15 3C52C74C8
22 2C52C63C8
33 2C51C72C8
47 2C41C62C8
68 1C51C52C7
100 1C41C51C8
Output
Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Through Hole
Sanyo OS-CON SA
Series
Sanyo MV-GX
Series
Nichicon PL Series
Panasonic HFQ
Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
3.3
10 1 C3 1 C10 1 C6 2 C6
15 1 C3 1 C10 1 C6 2 C5
22 1 C5 1 C10 1 C5 1 C7
33 1 C2 1 C10 1 C13 1 C5
5
10 2 C4 1 C10 1 C6 2 C5
15 1 C5 1 C10 1 C5 1 C6
22 1 C5 1 C5 1 C5 1 C5
33 1 C4 1 C5 1 C13 1 C5
47 1 C4 1 C4 1 C13 2 C3
12
10 2 C7 1 C5 1 C18 2 C5
15 1 C8 1 C5 1 C17 1 C5
22 1 C7 1 C5 1 C13 1 C5
33 1 C7 1 C3 1 C11 1 C4
47 1 C7 1 C3 1 C10 1 C3
68 1 C7 1 C2 1 C10 1 C3
100 1 C7 1 C2 1 C9 1 C1
No. represents the number of identical capacitor types to be connected in parallel
C Code indicates the Capacitor Reference number in Table 2 for identifying the specific component from the manufacturer.
www.national.com17

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 4. Input Capacitors for Fixed Output Voltage Application
(Assumes worst case maximum input voltage and load current for a given inductance value)
Output
Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Surface Mount
AVX TPS Series Sprague 594D
Series
Kemet T495 Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
3.3
10 2C51C72C8
15 3 C9 1 C10 3 C10
22
**
2 C13 3 C12
33
**
2 C13 2 C12
5
10 2C51C72C8
15 2C51C72C8
22 3 C10 2 C12 3 C11
33
**
2 C13 3 C12
47
**
1 C13 2 C12
12
10 2C72C102C7
15 2C72C102C7
22 3 C10 2 C12 3 C10
33 3 C10 2 C12 3 C10
47
**
2 C13 3 C12
68
**
2 C13 2 C12
100
**
1 C13 2 C12
Output
Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Through Hole
Sanyo OS-CON SA
Series
Sanyo MV-GX
Series
Nichicon PL Series
Panasonic HFQ
Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
3.3
10 1 C7 2 C4 1 C5 1 C6
15 1 C10 1 C10 1 C18 1 C6
22
**
1 C14 1 C24 1 C13
33
**
1 C12 1 C20 1 C12
5
10 1 C7 2 C4 1 C14 1 C6
15 1 C7 2 C4 1 C14 1 C6
22
**
1 C10 1 C18 1 C13
33
**
1 C14 1 C23 1 C13
47
**
1 C12 1 C20 1 C12
12
10 1 C9 1 C10 1 C18 1 C6
15 1 C10 1 C10 1 C18 1 C6
22 1 C10 1 C10 1 C18 1 C6
33
**
1 C10 1 C18 1 C6
47
**
1 C13 1 C23 1 C13
68
**
1 C12 1 C21 1 C12
100
**
1 C11 1 C22 1 C11
*
Check voltage rating of capacitors to be greater than application input voltage.
No. represents the number of identical capacitor types to be connected in parallel
C Code indicates the Capacitor Reference number in Table 2 for identifying the specific component from the manufacturer.
www.national.com 18

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 5. Schottky Diode Selection Table
Reverse
Voltage
(V)
Surface Mount Through Hole
3A 5A or More 3A 5A or More
20V SK32 1N5820
SR302
30V SK33 MBRD835L 1N5821
30WQ03F 31DQ03
40V SK34 MBRB1545CT 1N5822
30BQ040 6TQ045S MBR340 MBR745
30WQ04F 31DQ04 80SQ045
MBRS340 SR403 6TQ045
MBRD340
50V or
More
SK35 MBR350
30WQ05F 31DQ05
SR305
Diode Manufacturer Contact Numbers
International Rectifier Phone (310) 322-3331
FAX (310) 322-3332
Motorola Phone (800) 521-6274
FAX (602) 244-6609
General
Semiconductor
Phone (516) 847-3000
FAX (516) 847-3236
Diodes, Inc. Phone (805) 446-4800
FAX (805) 446-4850
www.national.com19

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 6. Output Capacitors for Adjustable Output Voltage Applications
Output Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Surface Mount
AVX TPS Series Sprague 594D
Series
Kemet T495 Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
1.21 to 2.50
33
*
7C16C27C3
47
*
5C14C25C3
2.5 to 3.75
33
*
4C13C24C3
47
*
3C12C23C3
3.75 to 5
22 4C13C24C3
33 3C12C23C3
47 2C12C22C3
5 to 6.25
22 3C21C33C4
33 2C22C32C4
47 2C22C32C4
68 1C21C31C4
6.25 to 7.5
22 3C21C43C4
33 2C21C32C4
47 1C31C41C6
68 1C21C31C4
7.5 to 10
33 2C51C62C8
47 1C51C62C8
68 1C51C61C8
100 1C41C51C8
10 to 12.5
33 1C51C62C8
47 1C51C62C8
68 1C51C61C8
100 1C51C61C8
12.5 to 15
33 1C61C81C8
47 1C61C81C8
68 1C61C81C8
100 1C61C81C8
15 to 20
33 1 C8 1 C10 2 C10
47 1C81C92C10
68 1C81C92C10
100 1C81C91C10
20 to 30
33 2 C9 2 C11 2 C11
47 1 C10 1 C12 1 C11
68 1 C9 1 C12 1 C11
100 1 C9 1 C12 1 C11
30 to 37
10 4 C13 8 C12
15 3 C13 5 C12
22 No Values Available 2 C13 4 C12
33 1 C13 3 C12
47 1 C13 2 C12
68 1 C13 2 C12
www.national.com 20

Application Hints (Continued)
Table 6. Output Capacitors for Adjustable Output Voltage Applications
(continued)
Output Voltage
(V)
Inductance
(µH)
Through Hole
Sanyo OS-CON SA
Series
Sanyo MV-GX
Series
Nichicon PL Series
Panasonic HFQ
Series
No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code No. C Code
1.21 to 2.50
33
*
2C35C15C33 C
47
*
2C24C13C32C5
2.5 to 3.75
33
*
1C33C13C12C5
47
*
1C22C12C31C5
3.75 to 5
22 1 C3 3 C1 3 C1 2 C5
33 1 C2 2 C1 2 C1 1 C5
47 1 C2 2 C1 1 C3 1 C5
5 to 6.25
22 1 C5 2 C6 2 C3 2 C5
33 1 C4 1 C6 2 C1 1 C5
47 1 C4 1 C6 1 C3 1 C5
68 1 C4 1 C6 1 C1 1 C5
6.25 to 7.5
22 1 C5 1 C6 2 C1 1 C5
33 1 C4 1 C6 1 C3 1 C5
47 1 C4 1 C6 1 C1 1 C5
68 1 C4 1 C2 1 C1 1 C5
7.5 to 10
33 1 C7 1 C6 1 C14 1 C5
47 1 C7 1 C6 1 C14 1 C5
68 1 C7 1 C2 1 C14 1 C2
100 1 C7 1 C2 1 C14 1 C2
10 to 12.5
33 1 C7 1 C6 1 C14 1 C5
47 1 C7 1 C2 1 C14 1 C5
68 1 C7 1 C2 1 C9 1 C2
100 1 C7 1 C2 1 C9 1 C2
12.5 to 15
33 1 C9 1 C10 1 C15 1 C2
47 1 C9 1 C10 1 C15 1 C2
68 1 C9 1 C10 1 C15 1 C2
100 1 C9 1 C10 1 C15 1 C2
15 to 20
33 1 C10 1 C7 1 C15 1 C2
47 1 C10 1 C7 1 C15 1 C2
68 1 C10 1 C7 1 C15 1 C2
100 1 C10 1 C7 1 C15 1 C2
20 to 30
33 1 C7 1 C16 1 C2
47 No Values 1 C7 1 C16 1 C2
68 Available 1 C7 1 C16 1 C2
100 1 C7 1 C16 1 C2
30 to 37
10 1 C12 1 C20 1 C10
15 1 C11 1 C20 1 C11
22 No Values 1 C11 1 C20 1 C10
33 Available 1 C11 1 C20 1 C10
47 1 C11 1 C20 1 C10
68 1 C11 1 C20 1 C10
* Set to a higher value for a practical design solution. See Applications Hints section
No. represents the number of identical capacitor types to be connected in parallel
C Code indicates the Capacitor Reference number in Table 2 for identifying the specific component from the manufacturer.
www.national.com21

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
TO-263 Surface Mount Power Package
Order Number LM2670S-3.3, LM2670S-5.0,
LM2670S-12 or LM2670S-ADJ
NS Package Number TS7B
www.national.com 22

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
www.national.com
TO-220 Power Package
Order Number LM2670T-3.3, LM2670T-5.0,
LM2670T-12 or LM2670T-ADJ
NS Package Number TA07B
LM2670 SIMPLE SWITCHER High Efficiency 3A Step-Down Voltage Regulator with Sync
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...