NSC DS92LV1210TMSA, DS92LV1210MDC Datasheet
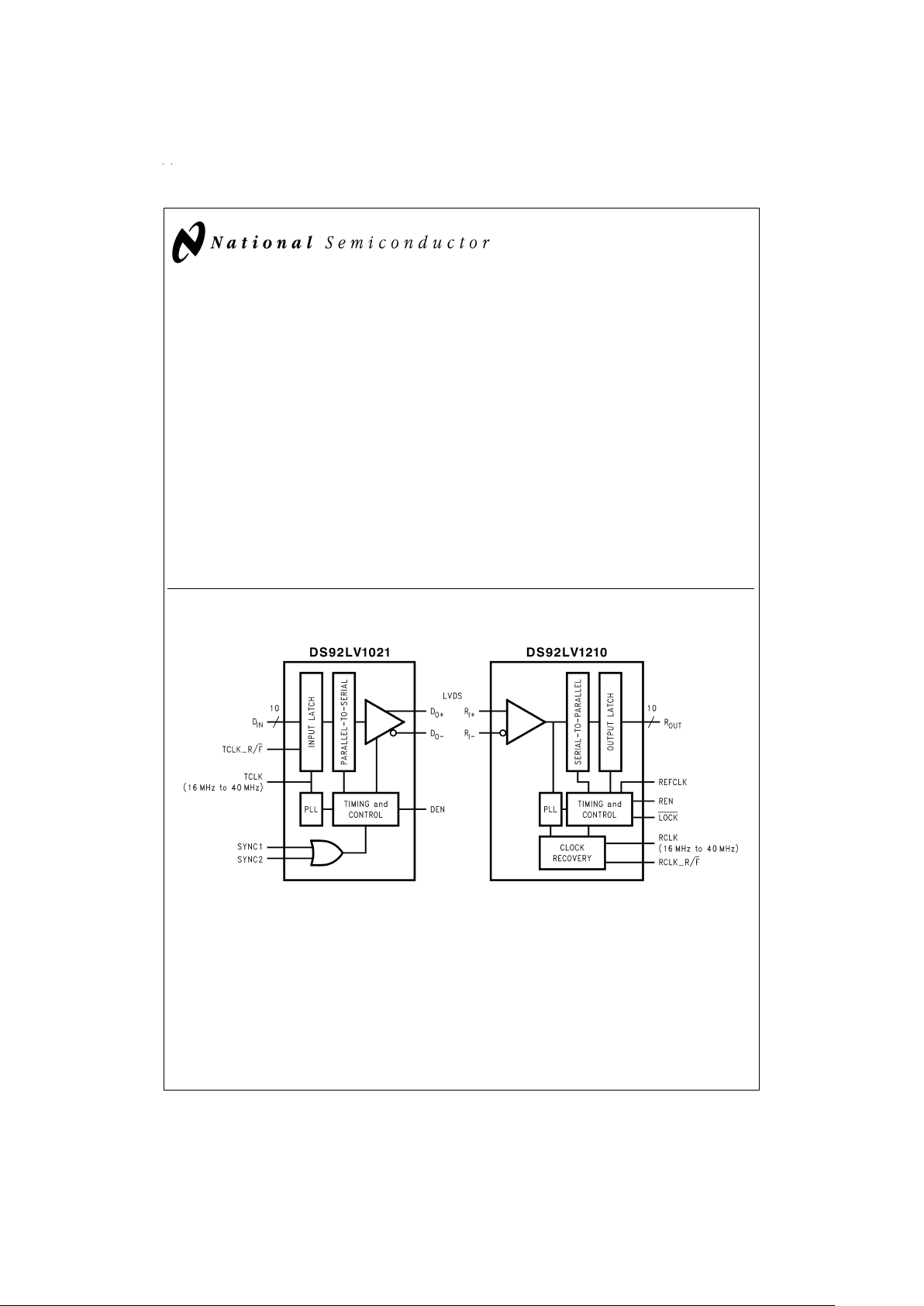
DS92LV1021 and DS92LV1210
16-40 MHz 10 Bit Bus LVDS Serializer and Deserializer
General Description
The DS92LV1021 transforms a 10-bit wide parallel CMOS/
TTL data bus into a single high speed Bus LVDS serial data
stream with embedded clock.TheDS92LV1210 receives the
Bus LVDS serial data stream and transforms it back into a
10-bit wide parallel data bus and separates clock. The
DS92LV1021 may transmit data over heavily loaded backplanes or 10 meters of cable. The reduced cable, PCB trace
count and connector sizesavescostandmakesPCB design
layout easier. Clock-to-data and data-to-data skew are eliminated since one output will transmit both clock and all data
bits serially. The powerdown pin is used to save power, by
reducing supply current when either device is not in use. The
Serializer has a synchronization mode that should be activated upon power-up of the device. The Deserializer will establish lock to this signal within 1024 cycles, and will flag
Lock status. The embedded clock guarantees a transition on
the bus every 12-bit cycle; eliminating transmission errors
due to charged cable conditions. The DS92LV1021 output
pins may be TRI-STATE
®
to achieve a high impedance
state. The PLL can lock to frequencies between 16 MHz and
40 MHz.
Features
n Guaranteed transition every data transfer cycle
n Single differential pair eliminates multi-channel skew
n Flow-through pinout for easy PCB layout
n 400 Mbps serial Bus LVDS bandwidth (at 40 MHz clock)
n 10-bit parallel interface for 1 byte data plus 2 control bits
n Synchronization mode and LOCK indicator
n Programmable edge trigger on clock
n High impedance on receiver inputs when power is off
n Bus LVDS serial output rated for 27Ω load
n Small 28-lead SSOP package-MSA
Block Diagrams
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
DS100110-1
March 1999
DS92LV1021/DS92LV1210 16-40 MHz 10 Bit Bus LVDS Serializer and Deserializer
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100110 www.national.com

Block Diagrams (Continued)
Functional Description
The DS92LV1021 and DS92LV1210 is a 10-bit Serializer /
Deserializer chipset designed to transmit data over a heavily
loaded differential backplanes at clock speeds from 16 to
40MHz. It may also be used to drive data over Unshielded
Twisted Pair (UTP) cable.
The chipset has three active states of operation: Initialization, Data Transfer,and Resynchronization; and two passive
states: Powerdown and TRI-STATE
®
.
The following sections describe each operation and passive
state.
Initialization
Before data can be transferred both devices must be initialized. Initialization refers to synchronization of the Serializer
and the Deserializer PLL’s to local clocks that may be the
same or separate. Afterward, synchronization of Deserializer
to Serializer occurs as the second step of initialization.
Step 1: When V
CC
is applied to both Serializer and/or Dese-
rializer, the respective outputs are held in TRI-STATE
®
and
internal circuitry is disabled by on-chip power-on circuitry.
When V
CC
reaches VCCOK (2.5V) the PLL in each device
begins locking to a local clock. For the Serializer, the local
clock is the transmit clock, TCLK, provided by the source
ASIC or other device. For the Deserializer, the local clock is
provided by an on-board oscillator or other source and applied to the REFCLK pin. After V
CC
OK is reached the de-
vice’s PLL will lock.
The Serializer outputs are held in TRI-STATE while the PLL
locks to the TCLK. The Serializer is now ready to send data
or SYNC patterns depending on the levels of the SYNC1 and
SYNC2 inputs. The SYNC pattern is composed of six ones
and six zeros switching at the input clock rate.
The Deserializer LOCK output will remain high while its PLL
is locking to the local clock- the REFCLK input and then to
SYNC patterns on the input.
Step 2: The Deserializer PLL must synchronize to the Serializer to complete the initialization. The transmission of SYNC
patterns to the Deserializer enables the Deserializer to lock
to the Serializer signal.
Control of the sync pins is left to the user. A feedback loop
between the LOCK pin is one recommendation. Another op-
tion is that one or both of the Serializer SYNC inputs are asserted for at least 1024 cycles of TCLK to initiate transmission of SYNC patterns. The Serializer will continue to send
SYNC patterns after the minimum of 1024 if either of the
SYNC inputs remain high.
When the Deserializer detects edge transitions at the Bus
LVDS input it will attempt to lock to the embedded clock information. When the Deserializer locks to the Bus LVDS
clock, the LOCK output will go low. When LOCK is low the
Deserializer outputs represent incoming Bus LVDS data.
Data Transfer
After initialization, the Serializer inputs DIN0–DIN9 may be
used to input data to the Serializer. Data is clocked into the
Serializer by the TCLK input. The edge of TCLK used to
strobe in data is selectable via the TCLK_R/F pin. TCLK_R/F
high selects the rising edge for clocking data and low selects
the falling edge. If either of the SYNC inputs is high for
5*TCLK cycles the data at DIN 0-DIN9 is ignored regardless
of the clock edge.
A start bit and a stop bit, appended internally,frame the data
bits in the register. The start bit is always high and the stop
bit is always low. The start and stop bits function as the embedded clock bits in the serial stream.
Serialized data and clock bits (10+2 bits) are transmitted
from the serial data output (DO) at 12 times the TCLK frequency.For example, if TCLK is 40 MHz, the serial rate is 40
x 12 = 480 Mega bits per second. Since only 10 bits are from
input data, the serial “payload” rate is 10 times the TCLK frequency. For instance, if TCLK = 40 MHz, the payload data
rate is 40 x 10 = 400 Mbps. TCLK is provided by the data
source and must be in the range 16 MHz to 40 MHz nominal.
The outputs (DO
±
) can drive a heavily loaded backplane or
a point-to-point connection. The outputs transmit data when
the enable pin (DEN) is high, PWRDN = high and SYNC1
and SYNC2 are low. The DEN pin may be used to TRISTATE the outputs when driven low.
The LOCK pin on the Deserializer is driven low when it is
synchronized with the Serializer. The Deserializer locks to
the embedded clock and uses it to recover the serialized
data. ROUT data is valid when LOCK is low. Otherwise
ROUT0–ROUT9 is invalid.
Application
DS100110-2
www.national.com 2
Data Transfer (Continued)
RCLK pin is the reference to data on the ROUT0-ROUT9
pins. The polarity of the RCLK edge is controlled by the
RCLK_R/F input.
ROUT(0-9), LOCK and RCLK outputs will drive a minimum
of three CMOS input gates (15 pF load) with 40 MHz clock.
Resynchronization
The Deserializer LOCK pin driven low indicates that the Deserializer PLL is locked to the embedded clock edge. If the
Deserializer loses lock, the LOCK output will go high and the
outputs (including RCLK) will be TRI-STATE.
The LOCK pin must be monitored by the system to detect a
loss of synchronization and the system must arrange to
pulse the Serializer SYNC1 or SYNC2 pin to resynchronize.
There are multiple approaches possible. One recommendation is to provide a feedback loop using the LOCK pin itself to
control the sync request of the Serializer (SYNC1 or
SYNC2). Otherwise, LOCK pin needs to be monitored and
when it is a high, the system needs to ensure that one or
both of the Serializer SYNC inputs area asserted for at least
1024 cycles of TCLK. A minimum of 1024 sync patterns are
needed to resynchronize. Dual SYNC pins are provided for
multiple control in a multi-drop application.
Powerdown
The Powerdown state is a low power sleep mode that the
Serializer and Deserializer may use to reduce power when
there is no data to be transferred. Powerdown is entered
when PWRDN and REN are driven low on the Deserializer,
and when the PWRDN is driven low on the Serializer. In
Powerdown, the PLL is stopped and the outputs go into TRISTATE, disabling load current and also reducing supply current to the milliamp range. To exit Powerdown, PWRDN is
driven high.
Both the Serializer and Deserializer must reinitialize and resynchronize before data can be transferred. Initialization of
the Serializer takes 1024 TCLK cycles. The Deserializer will
initialize and assert LOCK high until it is locked to the Bus
LVDS clock.
TRI-STATE
For the Serializer, TRI-STATE is entered when the DEN pin
is driven low. This will TRI-STATE both driver output pins
(DO+ and DO−). When DEN is driven high the serializer will
return to the previous state as long as all other control pins
remain static (SYNC1, SYNC2, PWRDN, TCLK_R/F).
For the Deserializer, TRI-STATE is entered when the REN
pin is driven low. This will TRI-STATE the receiver output
pins (ROUT0–ROUT9), LOCK and RCLK.
Order Numbers
NSID Function Package
DS92LV1021TMSA Serializer MSA28
DS92LV1210TMSA Deserializer MSA28
www.national.com3
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) −0.3V to +4V
CMOS/TTL Input Voltage −0.3V to (V
CC
+0.3V)
CMOS/TTL Output Voltage −0.3V to (V
CC
+0.3V)
Bus LVDS Receiver Input
Voltage −0.3V to +3.9V
Bus LVDS Driver Output
Voltage −0.3V to +3.9V
Bus LVDS Output Short
Circuit Duration Continuous
Junction Temperature +150˚C
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 4 seconds) +260˚C
Maximum Package Power Dissipation Capacity
@
25˚C Package:
28L SSOP 1.27 W
Package Derating:
28L SSOP
10.2 mW/˚C above
+25˚C
ESD Rating (HBM)
>
5kV
Recommended Operating
Conditions
Min Nom Max Units
Supply Voltage (V
CC
) 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Operating Free Air
Temperature (T
A
)
−40 +25 +85 ˚C
Receiver Input Range 0 2.4 V
Supply Noise Voltage
(V
CC
)
100 mV
P-P
Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
SERIALIZER CMOS/TTL DC SPECIFICATIONS (apply to DIN0-9, TCLK, PWRDN, TCLK_R/F, SYNC1, SYNC2, DEN)
V
IH
High Level Input Voltage 2.0 V
CC
V
V
IL
Low Level Input Voltage GND 0.8 V
V
CL
Input Clamp Voltage ICL= −18 mA −1.5 V
I
IN
Input Current VIN= 0V or 3.6V −10
±
2 +10 µA
DESERIALIZER CMOS/TTL DC SPECIFICATIONS (apply to pins PWRDN, RCLK_R/ F, REN, REFCLK = inputs; apply to pins
ROUT, RCLK, LOCK = outputs)
V
IH
High Level Input Voltage 2.0 V
CC
V
V
IL
Low Level Input Voltage GND 0.8 V
V
CL
Input Clamp Voltage ICL= −18 mA −0.62 −1.5 V
I
IN
Input Current VIN= 0V or 3.6V −10
±
1 +10 µA
V
OH
High Level Output Voltage IOH= −9 mA 2.1 2.93 V
CC
V
V
OL
Low Level Output Voltage IOL= 9 mA GND 0.33 0.6 V
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current VOUT = 0V −15 −38 −85 mA
I
OZ
TRI-STATE Output Current PWRDN or REN = 0.8V, V
OUT
=0VorVCC −10±0.4 +10 µA
SERIALIZER Bus LVDS DC SPECIFICATIONS (apply to pins DO+ and DO−)
V
OD
Output Differential Voltage
(DO+)–(DO−)
RL=27Ω
200 270 mV
∆V
OD
Output Differential Voltage
Unbalance
35 mV
V
OS
Offset Voltage 0.78 1.1 1.3 V
∆V
OS
Offset Voltage Unbalance 35 mV
I
OS
Output Short Circuit Current D0 = 0V, DIN = High,PWRDN and DEN = 2.4V −10 −15 mA
I
OZ
TRI-STATE Output Current PWRDN or DEN = 0.8V, DO = 0V or VCC −10
±
1 +10 µA
I
OX
Power-Off Output Current VCC = 0V, DO = 0V or VCC −20
±
1 +20 µA
DESERIALIZER Bus LVDS DC SPECIFICATIONS (apply to pins RI+ and RI−)
VTH Differential Threshold High
Voltage
VCM = +1.1V
+19 +100 mV
VTL Differential Threshold Low
Voltage
−100 −7 mV
www.national.com 4

Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
DESERIALIZER Bus LVDS DC SPECIFICATIONS (apply to pins RI+ and RI−)
I
IN
Input Current VIN= +2.4V, VCC= 3.6V or 0V −10
±
1 +10 µA
V
IN
= 0V, VCC= 3.6V or 0V −15
±
1 +15 µA
SERIALIZER SUPPLY CURRENT (apply to pins DVCC and AVCC)
I
CCD
Serializer Supply Current RL = 27Ω f = 40 MHz 32 55 mA
Worst Case
Figure 1
f = 16 MHz 25 45 mA
I
CCXD
Serializer Supply Current
Powerdown
PWRDN = 0.8V
410mA
DESERIALIZER SUPPLY CURRENT (apply to pins DVCC and AVCC)
I
CCR
Deserializer Supply Current CL= 15 pF f = 40 MHz 44 75 mA
Worst Case
Figure 2
f = 16 MHz 31 55 mA
I
CCXR
Deserializer Supply Current
Powerdown
PWRDN = 0.8V, REN = 0.8V
1.5 5.0 mA
Serializer Timing Requirements for TCLK
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
TCP
Transmit Clock Period 25 T 62.5 ns
t
TCIH
Transmit Clock High Time 0.4T 0.5T 0.6T ns
t
TCIL
Transmit Clock Low Time 0.4T 0.5T 0.6T ns
t
CLKT
TCLK Input Transition Time 3 6 ns
t
JIT
TCLK Input Jitter 150 ps
Serializer Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
LLHT
Bus LVDS Low-to-High
Transition Time
RL=27Ω
Figure 3
CL=10pF to GND
0.2 1 ns
t
LHLT
Bus LVDS High-to-Low
Transition Time
0.25 1 ns
t
DIS
DIN (0-9) Setup to TCLK
Figure 6
RL=27Ω,
C
L
=10pF to GND
1.0 0 ns
t
DIH
DIN (0-9) Hold from TCLK
6.5 4.5 ns
t
HZD
DO±HIGH to
TRI-STATE Delay
Figure 7
(Note 4)
R
L
=27Ω,
C
L
=10pF to GND
3.5 10 ns
t
LZD
DO±LOW to TRI-STATE
Delay
2.9 10 ns
t
ZHD
DO±TRI-STATE to HIGH
Delay
2.5 10 ns
t
ZLD
DO±TRI-STATE to LOW
Delay
2.7 10 ns
t
SPW
SYNC Pulse Width
Figure 8
RL=27Ω
1024*t
TCP
1029*t
TCP
ns
t
PLD
Serializer PLL Lock Time 2048*t
TCP
2049*t
TCP
ns
t
SD
Serializer Delay
Figure 9
RL=27Ω t
TCP
t
TCP
+ 2.5 t
TCP
+5 ns
t
BIT
Bus LVDS Bit Width RL=27Ω,
C
L
=10pF to GND
t
CLK
/12 ns
www.national.com5
Deserializer Timing Requirements for REFCLK
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
t
RFCP
REFCLK Period 25 T 62.5 ns
t
RFDC
REFCLK Duty Cycle 50
%
t
RFCP/tTCP
Ratio of REFCLK to TCLK
Periods
0.83 1 1.03
t
RFTT
REFCLK Transition Time 3 6 ns
Deserializer Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Pin/Freq. Min Typ Max Units
t
RCP
Receiver out Clock
Period
Figure 9
t
RCP=tTCP
RCLK
25 62.5 ns
t
CLH
CMOS/TTL Low-to-High
Transition Time
CL=15pF
Figure 4
Rout(0-9),
25ns
t
CHL
CMOS/TTL High-to-Low
Transition Time
LOCK, RCLK
25ns
t
DD
Deserializer Delay
Figure 10
1.75*t
RCP
1.75*t
RCP
+3 1.75*t
RCP
+7 ns
t
ROS
ROUT (0-9) Setup Data to
RCLK
Figure 11
RCLK
0.4*t
RCP
0.5*t
RCP
ns
t
ROH
ROUT (0-9) Hold Data to
RCLK
−0.4*t
RCP
−0.5*t
RCP
ns
t
RDC
RCLK Duty Cycle 40 50 60
%
t
HZR
HIGH to TRI-STATE Delay
Figure 12
Rout(0-9),
LOCK
4+0.5*t
RCP
10+t
RCP
ns
t
LZR
LOW to TRI-STATE Delay 4.2+0.5*t
RCP
10+t
RCP
ns
t
ZHR
TRI-STATE to HIGH Delay 6+0.5*t
RCP
12+t
RCP
ns
t
ZLR
TRI-STATE to LOW Delay 6.5+0.5*t
RCP
12+t
RCP
ns
t
DSR1
Deserializer PLL Lock Time
from PWRDWN (with
SYNCPAT)
(Note 5)
Figure 13
Figure 14
16MHz
715µs
40MHz
4.8 25.6 µs
t
DSR2
Deserializer PLL Lock time
from SYNCPAT
16MHz 7 10 µs
40MHz 4.5 7 µs
t
ZHLK
TRI-STATE to HIGH Delay
(power-up)
LOCK
1.5 12 ns
t
RNM
Deserializer Noise Margin
Figure 15
(Note 6)
16 MHz 400 1100 ps
40 MHz 100 400 ps
Note 1: “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the devices
should be operated at these limits. The table of “Electrical Characteristics” specifies conditions of device operation.
Note 2: Typical values are given for V
CC
= 3.3V and TA= +25˚C.
Note 3: Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of device pins is defined as negative. Voltages are referenced to ground except VOD, ∆VOD, VTH
and VTL which are differential voltages.
Note 4: Due to TRI-STATE of the Serializer, the Deserializer will lose PLL lock and have to resynchronize before data transfer.
Note 5: For the purpose of specifying deserializer PLL performance tDSR1 and tDSR2 are specified with the REFCLK running and stable, and specific conditions
of the incoming data stream (SYNCPATs). It is recommended that the derserializer be initialized using either tDSR1 timing or tDSR2 timing. tDSR1 is the time required
for the deserializer to indicate lock upon power-up or when leaving the power-down mode. Synchronization patterns should be sent to the device before initiating either condition. tDSR2 is the time required to indicate lock for the powered-up and enabled deserializer when the input (RI+ and RI-) conditions change from not receiving data to receiving synchronization patterns (SYNCPATs).
Note 6: tRNM is a measure of how much phase noise (jitter) the deserializer can tolerate in the incoming data stream before bit errors occur.
www.national.com 6
 Loading...
Loading...