Novo Nordisk NovoLog Instruction Manual
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information
needed to use NovoLog
prescribing information for NovoLog
®
NovoLog
(insulin aspart [rDNA origin] injection)
®
safely and effectively. See full
®
.
solution for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
——— INDICATIONS AND USAGE ———
®
• NovoLog
is an insulin analog indicated to improve glycemic
control in adults and children with diabetes mellitus (1.1).
——— DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ———
• The dosage of NovoLog® must be individualized.
®
•
Subcutaneous injection:
NovoLog
should generally be given
immediately (within 5-10 minutes) prior to the start of a meal
(2.2).
•
Use in pumps:
Change the NovoLog
every 6 days, change the infusion set, and the infusion set
insertion site at least every 3 days. NovoLog
®
in the reservoir at least
®
should not be
mixed with other insulins or with a diluent when it is used in
the pump (2.3).
•
Intravenous use:
from 0.05 U/mL to 1.0 U/mL insulin aspart in infusion systems
using polypropylene infusion bags. NovoLog
NovoLog
®
should be used at concentrations
®
has been shown
to be stable in infusion fluids such as 0.9% sodium chloride
(2.4).
——— DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS ———
Each presentation contains 100 Units of insulin aspart per mL
(U-100)
•
10 mL vials (3)
• 3 mL PenFill® cartridges for the 3 mL PenFill® cartridge device (3)
• 3 mL NovoLog® FlexPen® (3)
®
•
3 mL NovoLog
FlexTouch® (3)
——— CONTRAINDICATIONS ———
•
Do not use during episodes of hypoglycemia (4).
Do not use in patients with hypersensitivity to NovoLog
•
®
or one
of its excipients.
——— WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS ———
•
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse effect of insulin
therapy. Glucose monitoring is recommended for all patients with
diabetes. Any change of insulin dose should be made cautiously
and only under medical supervision (5.1, 5.2).
•
Insulin, particularly when given intravenously or in settings of
poor glycemic control, can cause hypokalemia. Use caution in
patients predisposed to hypokalemia (5.3).
Like all insulins, NovoLog
•
®
requirements may be reduced in
patients with renal impairment or hepatic impairment (5.4, 5.5).
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy
•
anaphylaxis, may occur with insulin products, including
®
NovoLog
(5.6).
•
Fluid retention and heart failure can occur with concomitant use
of thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are PPAR-gamma agonists,
and insulin, including NovoLog
®
, including
(5.10).
——— ADVERSE REACTIONS ———
®
Adverse reactions observed with NovoLog
include hypoglycemia,
allergic reactions, local injection site reactions, lipodystrophy, rash
and pruritus (6).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact
Novo Nordisk Inc. at 1-800-727-6500 or FDA at 1-800FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
——— DRUG INTERACTIONS ———
•
The following may increase the blood-glucose-lowering effect
and susceptibility to hypoglycemia: oral antidiabetic products,
pramlintide, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine,
monoamine oxidase inhibitors, propoxyphene, salicylates,
somatostatin analogs, sulfonamide antibiotics (7).
•
The following may reduce the blood-glucose-lowering effect:
corticosteroids, niacin, danazol, diuretics, sympathomimetic
agents (e.g., epinephrine, salbutamol, terbutaline), isoniazid,
phenothiazine derivatives, somatropin, thyroid hormones,
estrogens, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), atypical
antipsychotics (7).
•
Beta-blockers, clonidine, lithium salts, and alcohol may either
potentiate or weaken the blood-glucose-lowering effect of insulin
(7).
•
Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be
followed by hyperglycemia (7).
The signs of hypoglycemia may be reduced or absent in patients
•
taking sympatholytic products such as beta-blockers, clonidine,
guanethidine, and reserpine (7).
——— USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS ———
•
Pediatric: Has not been studied in children with type 2 diabetes.
Has not been studied in children with type 1 diabetes <2 years of
age (8.4).
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and
FDA approved patient labeling.
Revised: 4/2014
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing
2.2 Subcutaneous Injection
2.3 Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) by External
Pump
2.4 Intravenous Use
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4
CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Administration
5.2
Hypoglycemia
5.3
Hypokalemia
5.4 Renal Impairment
5.5 Hepatic Impairment
5.6 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
5.7 Antibody Production
5.8 Mixing of Insulins
5.9
5.10
6
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion by External
Fluid retention and heart failure with concomitant use of
PPAR-gamma agonists
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Pump
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULA
8.1
Pregnancy
TIONS
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10
OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2
Pharmacodynamics
12.3
Pharmacokinetics
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal T
CLINICAL STUDIES
14
oxicology and/or Pharmacology
14.1 Subcutaneous Daily Injections
14.2
14.3 Intravenous Administration of NovoLog
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) by External
Pump
®
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Recommended Storage
1
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Physician Instructions
17.2 Patients Using Pumps
17.3 FDA Approved Patient Labeling
* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are
not listed.

NovoLog® (insulin aspart [rDNA origin] injection)
2
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
INDICA
1
1.1 Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
NovoLog
and children with diabetes mellitus.
2
2.1 Dosing
NovoLog
human insulin. The dosage of NovoLog
given by subcutaneous injection should generally be used in regimens with an
intermediate or long-acting insulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5), How
Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. The total daily insulin requirement
may vary and is usually between 0.5 to 1.0 units/kg/day. When used in a mealrelated subcutaneous injection treatment regimen, 50 to 70% of total insulin
requirements may be provided by NovoLog
by an intermediate-acting or long-acting insulin. Because of NovoLog
comparatively rapid onset and short duration of glucose lowering activity,
some patients may require more basal insulin and more total insulin to prevent
pre-meal hyperglycemia when using NovoLog
regular insulin.
Do not use NovoLog
clear and colorless. NovoLog
date.
2.2 Subcutaneous Injection
NovoLog
region, buttocks, thigh, or upper arm. Because NovoLog
onset and a shorter duration of activity than human regular insulin, it should
be injected immediately (within 5-10 minutes) before a meal. Injection sites
should be rotated within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy.
As with all insulins, the duration of action of NovoLog
the dose, injection site, blood flow, temperature, and level of physical activity.
NovoLog
subcutaneous injection. Diluting one part NovoLog
yield a concentration one-tenth that of NovoLog
one part NovoLog
of NovoLog
2.3
NovoLog
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.9), How Supplied/Storage and Handling
(16.2)]. Diluted insulin should not be used in external insulin pumps. Because
NovoLog
regular insulin, pre-meal boluses of NovoLog
(within 5-10 minutes) before a meal. Infusion sites should be rotated within
the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy. The initial programming
of the external insulin infusion pump should be based on the total daily
insulin dose of the previous regimen. Although there is significant interpatient
variability, approximately 50% of the total dose is usually given as meal-related
boluses of NovoLog
the NovoLog
infusion sets and the infusion set insertion site at least every 3
days.
The following insulin pumps
studies conducted by Novo Nordisk, the manufacturer of NovoLog
• Medtronic Paradigm
• MiniMed 508
• Disetronic
Before using a different insulin pump with NovoLog®, read the pump label to
make sure the pump has been evaluated with NovoLog
2.4
NovoLog
glycemic control with close monitoring of blood glucose and potassium levels
to avoid hypoglycemia and hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5),
How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)]. For intravenous use, NovoLog
should be used at concentrations from 0.05 U/mL to 1.0 U/mL insulin aspart
in infusion systems using polypropylene infusion bags. NovoLog
shown to be stable in infusion fluids such as 0.9% sodium chloride.
Inspect NovoLog
administration.
3
NovoLog
contains 100 units of insulin aspart per mL (U-100).
• 10 mL vials
• 3 mL PenFill cartridges for the 3 mL PenFill
• 3 mL NovoLog
• 3 mL NovoLog® FlexTouch
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
NovoLog
• during episodes of hypoglycemia
• in patients with hypersensitivity to NovoLog
TIONS AND USAGE
®
is an insulin analog indicated to improve glycemic control in adults
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRA
®
is an insulin analog with an earlier onset of action than regular
®
that is viscous (thickened) or cloudy; use only if it is
®
should be administered by subcutaneous injection in the abdominal
®
may be diluted with Insulin Diluting Medium for NovoLog® for
®
to one part diluent will yield a concentration one-half that
®
(equivalent to U-50).
TION
®
must be individualized. NovoLog®
®
and the remainder provided
®
than when using human
®
should not be used after the printed expiration
®
has a more rapid
®
will vary according to
®
to nine parts diluent will
®
(equivalent to U-10). Diluting
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) by External
Pump
®
can also be infused subcutaneously by an external insulin pump
®
has a more rapid onset and a shorter duration of activity than human
®
and the remainder is given as a basal infusion. Change
®
in the reservoir at least every 6 days, change the
†
have been used in NovoLog® clinical or in vitro
®
512 and 712
®
D-TRON® and H-TRON
Intravenous Use
®
can be administered intravenously under medical supervision for
®
for particulate matter and discoloration prior to parenteral
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
®
is available in the following package sizes: each presentation
(with or without the addition of a NovoPen
disposable needles
®
FlexPen
®
is contraindicated
®
®
®
should be infused immediately
®
®
.
®
cartridge delivery device
®
3 PenMate®) with NovoFine®
®
or one of its excipients.
®
:
®
has been
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Administration
®
NovoLog
has a more rapid onset of action and a shorter duration of activity
than regular human insulin. An injection of NovoLog
followed by a meal within 5-10 minutes. Because of NovoLog
®
should immediately be
®
’s short duration
of action, a longer acting insulin should also be used in patients with type 1
diabetes and may also be needed in patients with type 2 diabetes. Glucose
monitoring is recommended for all patients with diabetes and is particularly
important for patients using external pump infusion therapy.
Any change of insulin dose should be made cautiously and only under medical
supervision. Changing from one insulin product to another or changing the
insulin strength may result in the need for a change in dosage. As with all
insulin preparations, the time course of NovoLog
individuals or at different times in the same individual and is dependent on many
conditions, including the site of injection, local blood supply, temperature, and
physical activity. Patients who change their level of physical activity or meal
plan may require adjustment of insulin dosages. Insulin requirements may be
altered during illness, emotional disturbances, or other stresses.
Patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy must
be trained to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy
available in case of pump failure.
®
Needles, NovoLog
’s
be shared.
5.2 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse effect of all insulin therapies,
including NovoLog
or convulsions and may result in temporary or permanent impairment of brain
function or death. Severe hypoglycemia requiring the assistance of another
person and/or parenteral glucose infusion or glucagon administration has
been observed in clinical trials with insulin, including trials with NovoLog
The timing of hypoglycemia usually reflects the time-action profile of the
administered insulin formulations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. Other
factors such as changes in food intake (e.g., amount of food or timing of
meals), injection site, exercise, and concomitant medications may also alter
the risk of hypoglycemia [see Drug Interactions (7)]. As with all insulins, use
caution in patients with hypoglycemia unawareness and in patients who may
be predisposed to hypoglycemia (e.g., patients who are fasting or have erratic
food intake). The patient’s ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as
a result of hypoglycemia. This may present a risk in situations where these
abilities are especially important, such as driving or operating other machinery.
Rapid changes in serum glucose levels may induce symptoms of
hypoglycemia in persons with diabetes, regardless of the glucose value. Early
warning symptoms of hypoglycemia may be different or less pronounced under
certain conditions, such as longstanding diabetes, diabetic nerve disease, use
of medications such as beta-blockers, or intensified diabetes control [see
Drug Interactions (7)]. These situations may result in severe hypoglycemia
(and, possibly, loss of consciousness) prior to the patient’s awareness of
hypoglycemia. Intravenously administered insulin has a more rapid onset
of action than subcutaneously administered insulin, requiring more close
monitoring for hypoglycemia.
5.3 Hypokalemia
All insulin products, including NovoLog
extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia that, if left
untreated, may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death.
Use caution in patients who may be at risk for hypokalemia (e.g., patients using
potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum
potassium concentrations, and patients receiving intravenously administered
insulin).
5.4 Renal Impairment
As with other insulins, the dose requirements for NovoLog
patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.5 Hepatic Impairment
As with other insulins, the dose requirements for NovoLog
patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.6 Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Local Reactions - As with other insulin therapy, patients may experience
redness, swelling, or itching at the site of NovoLog
usually resolve in a few days to a few weeks, but in some occasions, may
require discontinuation of NovoLog
®
be related to factors other than insulin, such as irritants in a skin cleansing
agent or poor injection technique. Localized reactions and generalized
myalgias have been reported with injected metacresol, which is an excipient
in NovoLog
Systemic Reactions - Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including
anaphylaxis, may occur with any insulin product, including NovoLog
Anaphylactic reactions with NovoLog
Generalized allergy to insulin may also cause whole body rash (including
pruritus), dyspnea, wheezing, hypotension, tachycardia, or diaphoresis. In
controlled clinical trials, allergic reactions were reported in 3 of 735 patients
(0.4%) treated with regular human insulin and 10 of 1394 patients (0.7%)
treated with NovoLog
(0.1%) NovoLog
5.7 Antibody Production
Increases in anti-insulin antibody titers that react with both human insulin and
insulin aspart have been observed in patients treated with NovoLog
in anti-insulin antibodies are observed more frequently with NovoLog
with regular human insulin. Data from a 12-month controlled trial in patients
with type 1 diabetes suggest that the increase in these antibodies is transient,
and the differences in antibody levels between the regular human insulin and
insulin aspart treatment groups observed at 3 and 6 months were no longer
evident at 12 months. In this study these antibodies did not appear to cause
deterioration in glycemic control or necessitate increases in insulin dose.
In rare cases, the presence of such insulin antibodies may necessitate
adjustment of the insulin dose in order to correct a tendency towards
hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia.
®
action may vary in different
®
FlexPen® and NovoLog® FlexTouch® must not
®
. Severe hypoglycemia may lead to unconsciousness and/
®
, cause a shift in potassium from the
®
may be reduced in
®
may be reduced in
®
injection. These reactions
®
. In some instances, these reactions may
®
.
®
have been reported post-approval.
®
. In controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials, 3 of 2341
®
-treated patients discontinued due to allergic reactions.
®
. Increases
®
5.8 Mixing of Insulins
• Mixing NovoLog
attenuates the peak concentration of NovoLog
affecting the time to peak concentration or total bioavailability of NovoLog
If NovoLog
into the syringe first, and the mixture should be injected immediately after
mixing.
• The efficacy and safety of mixing NovoLog
produced by other manufacturers have not been studied.
Insulin mixtures should not be administered intravenously
•
5.9
When used in an external subcutaneous insulin infusion pump,
NovoLog
When using NovoLog
information should be followed (e.g., in-use time, frequency of changing
infusion sets) because NovoLog
pump manual instructions.
Pump or infusion set malfunctions or insulin degradation can lead to a rapid
onset of hyperglycemia and ketosis because of the small subcutaneous depot
of insulin. This is especially pertinent for rapid-acting insulin analogs that are
more rapidly absorbed through skin and have a shorter duration of action.
Prompt identification and correction of the cause of hyperglycemia or ketosis
is necessary. Interim therapy with subcutaneous injection may be required [see
Dosage and Administration (2.3), Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.9), How
®
.
Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2), and Patient Counseling Information
(17.2)].
NovoLog
NovoLog
other insulin or with a diluent [see Dosage and Administration (2.3),
Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.9), How Supplied/Storage and Handling
(16.2), and Patient Counseling Information (17.2)].
5.10
®
with NPH human insulin immediately before injection
®
is mixed with NPH human insulin, NovoLog® should be drawn
®
, without significantly
®
with insulin preparations
.
Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion by External Pump
®
should not be mixed with any other insulin or diluent.
®
in an external insulin pump, the NovoLog®-specific
®
-specific information may differ from general
®
should not be exposed to temperatures greater than 37°C (98.6°F).
®
that will be used in a pump should not be mixed with
Fluid retention and heart failure with concomitant use of
PPAR-gamma agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention,
particularly when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to
or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin, including NovoLog
and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms
of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according
to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the
PPAR-gamma agonist must be considered.
6
ADVERSE REACTIONS
rial Experience
Clinical T
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying designs, the adverse
reaction rates reported in one clinical trial may not be easily compared to those
rates reported in another clinical trial, and may not reflect the rates actually
observed in clinical practice.
•
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most commonly obser
using insulin, including NovoLog
• Insulin initiation and glucose control intensification
Intensification or rapid improvement in glucose control has been
associated with a transitory, reversible ophthalmologic refraction disorder,
worsening of diabetic retinopathy, and acute painful peripheral neuropathy.
However, long-term glycemic control decreases the risk of diabetic
retinopathy and neuropathy.
• Lipodystrophy
Long-term use of insulin, including NovoLog
the site of repeated insulin injections or infusion. Lipodystrophy includes
lipohypertrophy (thickening of adipose tissue) and lipoatrophy (thinning of
adipose tissue), and may affect insulin absorption. Rotate insulin injection
or infusion sites within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy.
• Weight gain
eight gain can occur with some insulin therapies, including NovoLog
W
and has been attributed to the anabolic effects of insulin and the decrease
in glucosuria.
• Peripheral Edema
Insulin may cause sodium retention and edema, particularly if previously
poor metabolic control is improved by intensified insulin therapy.
®
.
• Frequencies of adverse drug reactions
The frequencies of adverse drug reactions during NovoLog
in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus are
listed in the tables below.
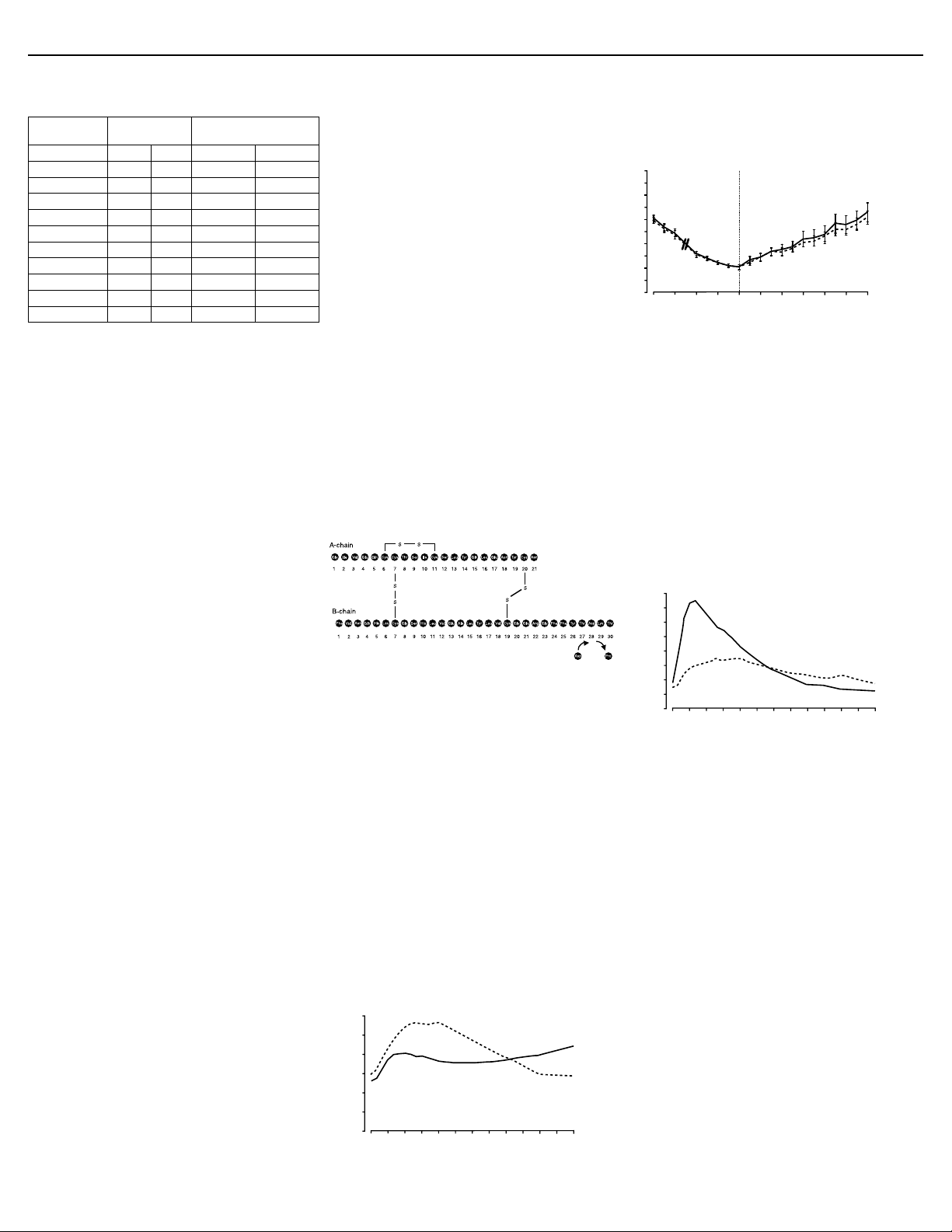
Table 1: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events in Patients with Type
1 Diabetes Mellitus (Adverse events with frequency ≥ 5% and
occurring more frequently with NovoLog
regular insulin are listed)
NovoLog® + NPH
Preferred Term N (%) N (%)
than
N= 596
ved adverse reaction in patients
®
[see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
®
, can cause lipodystrophy at
®
clinical trials
®
compared to human
Human Regular Insulin + NPH
N= 286
Hypoglycemia* 448 75% 205 72%
Headache 70 12% 28 10%
Injury accidental 65 11% 29 10%
Nausea 43 7% 13 5%
Diarrhea 28 5% 9 3%
*Hypoglycemia is defined as an episode of blood glucose concentration <45 mg/dL,
with or without symptoms. See Section 14 for the incidence of serious hypoglycemia in
the individual clinical trials.
®
.
®
,
®
,
NovoLog® (insulin aspart [rDNA origin] injection)
180
162
144
126
108
R+60
Mean Blood Glucose (mg/dL)
Note: The slashes on the mean profile indicate a jump on the time axis
80
6
Time (h)
Free serum insulin (mU/L)
300
6
Time (h)
Serum glucose (mg/dL)
3
Table 2: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events in Patients with
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (except for hypoglycemia, adverse
events with frequency ≥ 5% and occurring more frequently with
®
compared to human regular insulin are listed)
NovoLog
NovoLog® + NPH
N= 91
Human Regular Insulin + NPH
N= 91
N (%) N (%)
Hypoglycemia* 25 27% 33 36%
Hyporeflexia 10 11% 6 7%
Onychomycosis 9 10% 5 5%
Sensory disturbance 8 9% 6 7%
Urinary tract infection 7 8% 6 7%
Chest pain 5 5% 3 3%
Headache 5 5% 3 3%
Skin disorder 5 5% 2 2%
Abdominal pain 5 5% 1 1%
Sinusitis 5 5% 1 1%
*Hypoglycemia is defined as an episode of blood glucose concentration <45 mg/dL,
with or without symptoms. See Section 14 for the incidence of serious hypoglycemia in
the individual clinical trials.
Postmarketing Data
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during
postapproval use of NovoLog
voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to
reliably estimate their frequency. Medication errors in which other insulins
have been accidentally substituted for NovoLog
postapproval use [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
®
. Because these adverse reactions are reported
®
have been identified during
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
A number of substances affect glucose metabolism and may require insulin
dose adjustment and particularly close monitoring.
•
The following are examples of substances that may increase the
blood-glucose-lowering effect and susceptibility to hypoglycemia:
oral antidiabetic products, pramlintide, ACE inhibitors, disopyramide,
fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, propoxyphene,
salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), sulfonamide antibiotics.
•
The following are examples of substances that may reduce the bloodglucose-lowering effect: corticosteroids, niacin, danazol, diuretics,
sympathomimetic agents (e.g., epinephrine, salbutamol, terbutaline),
isoniazid, phenothiazine derivatives, somatropin, thyroid hormones,
estrogens, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), atypical
antipsychotics.
• Beta-blockers, clonidine, lithium salts, and alcohol may either potentiate or
weaken the blood-glucose-lowering effect of insulin.
• Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed
by hyperglycemia.
•
The signs of hypoglycemia may be reduced or absent in patients taking
sympatholytic products such as beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine,
and reserpine.
8
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULA
TIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category B. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth
defects, loss, or other adverse outcome regardless of drug exposure. This
background risk is increased in pregnancies complicated by hyperglycemia
and may be decreased with good metabolic control. It is essential for patients
with diabetes or history of gestational diabetes to maintain good metabolic
control before conception and throughout pregnancy. Insulin requirements
may decrease during the first trimester, generally increase during the second
and third trimesters, and rapidly decline after delivery. Careful monitoring of
glucose control is essential in these patients. Therefore, female patients should
be advised to tell their physician if they intend to become, or if they become
pregnant while taking NovoLog
An open-label, randomized study compared the safety and efficacy of
®
(n=157) versus regular human insulin (n=165) in 322 pregnant
NovoLog
women with type 1 diabetes. Two-thirds of the enrolled patients were already
pregnant when they entered the study. Because only one-third of the patients
enrolled before conception, the study was not large enough to evaluate the risk
of congenital malformations. Both groups achieved a mean HbA
during pregnancy, and there was no significant difference in the incidence of
maternal hypoglycemia.
Subcutaneous reproduction and teratology studies have been performed
with NovoLog
studies, NovoLog
and throughout pregnancy, and to rabbits during organogenesis. The effects
of NovoLog
human insulin. NovoLog
implantation losses and visceral/skeletal abnormalities in rats at a dose of 200
U/kg/day (approximately 32 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 U/
kg/day, based on U/body surface area) and in rabbits at a dose of 10 U/kg/
day (approximately three times the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 U/kg/day,
based on U/body surface area). The effects are probably secondary to maternal
hypoglycemia at high doses. No significant effects were observed in rats at a
dose of 50 U/kg/day and in rabbits at a dose of 3 U/kg/day. These doses are
approximately 8 times the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 U/kg/day for rats
and equal to the human subcutaneous dose of 1.0 U/kg/day for rabbits, based
on U/body surface area.
®
and regular human insulin in rats and rabbits. In these
®
®
did not differ from those observed with subcutaneous regular
®
.
of ~ 6%
1c
was given to female rats before mating, during mating,
®
, like human insulin, caused pre- and post-
Nursing Mothers
8.3
It
is unknown whether insulin aspart is excreted in human milk. Use of
®
is compatible with breastfeeding, but women with diabetes who are
NovoLog
lactating may require adjustments of their insulin doses.
Pediatric Use
8.4
®
NovoLog
is approved for use in children for subcutaneous daily injections
and for subcutaneous continuous infusion by external insulin pump.
®
has not been studied in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of
NovoLog
age. NovoLog
Please see Section 14 CLINICAL STUDIES for summaries of clinical studies.
8.5
Of the total number of patients (n= 1,375) treated with NovoLog
clinical studies, 2.6% (n=36) were 65 years of age or over. One-half of these
patients had type 1 diabetes (18/1285) and the other half had type 2 diabetes
(18/90). The HbA
not differ by age, particularly in patients with type 2 diabetes. Additional studies
in larger populations of patients 65 years of age or over are needed to permit
conclusions regarding the safety of NovoLog
patients. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic studies to assess the effect of
age on the onset of NovoLog
®
has not been studied in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes.
Geriatric Use
response to NovoLog®, as compared to human insulin, did
1c
®
in elderly compared to younger
®
action have not been performed.
®
in 3 controlled
10 OVERDOSAGE
Excess insulin administration may cause hypoglycemia and, particularly when
given intravenously, hypokalemia. Mild episodes of hypoglycemia usually
can be treated with oral glucose. Adjustments in drug dosage, meal patterns,
or exercise, may be needed. More severe episodes with coma, seizure, or
neurologic impairment may be treated with intramuscular/subcutaneous
glucagon or concentrated intravenous glucose. Sustained carbohydrate intake
and observation may be necessary because hypoglycemia may recur after
apparent clinical recovery. Hypokalemia must be corrected appropriately.
11 DESCRIPTION
®
(insulin aspart [rDNA origin] injection) is a rapid-acting human
NovoLog
insulin analog used to lower blood glucose. NovoLog
regular human insulin with the exception of a single substitution of the amino
acid proline by aspartic acid in position B28, and is produced by recombinant
DNA technology utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker’s yeast). Insulin
aspart has the empirical formula C
of 5825.8.
Figure 1. Structural formula of insulin aspart.
®
is a sterile, aqueous, clear, and colorless solution, that contains
NovoLog
insulin aspart 100 Units/mL, glycerin 16 mg/mL, phenol 1.50 mg/mL,
metacresol 1.72 mg/mL, zinc 19.6 mcg/mL, disodium hydrogen phosphate
dihydrate 1.25 mg/mL, sodium chloride 0.58 mg/mL and water for injection.
®
has a pH of 7.2-7.6. Hydrochloric acid 10% and/or sodium
NovoLog
hydroxide 10% may be added to adjust pH.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The primar
y activity of NovoLog
Insulins, including NovoLog
cells and lower blood glucose by facilitating the cellular uptake of glucose and
simultaneously inhibiting the output of glucose from the liver.
256H381N65079S6
®
is the regulation of glucose metabolism.
®
, bind to the insulin receptors on muscle and fat
®
is homologous with
and a molecular weight
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Studies in normal volunteers and patients with diabetes demonstrated that
subcutaneous administration of NovoLog
than regular human insulin.
In a study in patients with type 1 diabetes (n=22), the maximum glucoselowering effect of NovoLog
subcutaneous injection (see Figure 2). The duration of action for NovoLog
is 3 to 5 hours. The time course of action of insulin and insulin analogs such
®
as NovoLog
individual. The parameters of NovoLog
duration) as designated in Figure 2 should be considered only as general
guidelines. The rate of insulin absorption and onset of activity is affected by the
site of injection, exercise, and other variables [see Warnings and Precautions
(5.1)].
Figure 2. Serial mean serum glucose collected up to 6 hours
following a single pre-meal dose of NovoLog
regular human insulin (hatched curve) injected immediately
before a meal in 22 patients with type 1 diabetes.
may vary considerably in different individuals or within the same
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 12345
®
has a more rapid onset of action
®
occurred between 1 and 3 hours after
®
activity (time of onset, peak time and
®
(solid curve) or
A double-blind, randomized, two-way cross-over study in 16 patients with
type 1 diabetes demonstrated that intravenous infusion of NovoLog
in a blood glucose profile that was similar to that after intravenous infusion
with regular human insulin. NovoLog
the patient’s blood glucose decreased to 36 mg/dL, or until the patient
demonstrated signs of hypoglycemia (rise in heart rate and onset of sweating),
defined as the time of autonomic reaction (R) (see Figure 3).
90
72
54
36
18
0
0 10 R–20 R R+40 R+50
Figure 3. Mean blood glucose profiles following intravenous
infusion of NovoLog
(solid curve) in 16 patients with type 1 diabetes. R represents the
time of autonomic reaction.
R–10 R+10 R+20 R+30
®
(hatched curve) and regular human insulin
®
or human insulin was infused until
Time (min)
®
resulted
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The single substitution of the amino acid proline with aspartic acid at position
B28 in NovoLog
observed with regular human insulin. NovoLog
absorbed after subcutaneous injection compared to regular human insulin.
In a randomized, double-blind, crossover study 17 healthy Caucasian male
subjects between 18 and 40 years of age received an intravenous infusion of
either NovoLog
The mean insulin clearance was similar for the two groups with mean values
of 1.2 l/h/kg for the NovoLog
insulin group.
Bioavailability and Absorption - NovoLog
onset of action, and a shorter duration of action than regular human insulin
after subcutaneous injection (see Figure 2 and Figure 4). The relative
bioavailability of NovoLog
the two insulins are absorbed to a similar extent.
Figure 4. Serial mean serum free insulin concentration collected
up to 6 hours following a single pre-meal dose of NovoLog
(solid curve) or regular human insulin (hatched curve) injected
immediately before a meal in 22 patients with type 1 diabetes.
In studies in healthy volunteers (total n=107) and patients with type 1 diabetes
(total n=40), NovoLog
approximately twice as fast as regular human insulin. The median time to
maximum concentration in these trials was 40 to 50 minutes for NovoLog
versus 80 to 120 minutes for regular human insulin. In a clinical trial in patients
with type 1 diabetes, NovoLog
subcutaneously at a dose of 0.15 U/kg body weight, reached mean
maximum concentrations of 82 and 36 mU/L, respectively. Pharmacokinetic/
pharmacodynamic characteristics of insulin aspart have not been established
in patients with type 2 diabetes.
®
The intra-individual variability in time to maximum serum insulin concentration
for healthy male volunteers was significantly less for NovoLog
regular human insulin. The clinical significance of this observation has not
been established.
In a clinical study in healthy non-obese subjects, the pharmacokinetic
differences between NovoLog
were observed independent of the site of injection (abdomen, thigh, or upper
arm).
Distribution and Elimination - NovoLog
(<10%), similar to that seen with regular human insulin. After subcutaneous
administration in normal male volunteers (n=24), NovoLog
eliminated than regular human insulin with an average apparent half-life of 81
minutes compared to 141 minutes for regular human insulin.
®
reduces the molecule’s tendency to form hexamers as
®
or regular human insulin at 1.5 mU/kg/min for 120 minutes.
®
group and 1.2 l/h/kg for the regular human
®
compared to regular human insulin indicates that
60
40
20
0
012345
®
consistently reached peak serum concentrations
®
and regular human insulin, both administered
®
and regular human insulin described above,
®
is, therefore, more rapidly
®
has a faster absorption, a faster
®
has low binding to plasma proteins
®
®
than for
®
was more rapidly
Specific Populations
Children and Adolescents - The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic
properties of NovoLog
single dose study in 18 children (6-12 years, n=9) and adolescents (13-17
years [Tanner grade ≥ 2], n=9) with type 1 diabetes. The relative differences
in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in children and adolescents with
type 1 diabetes between NovoLog
those in healthy adult subjects and adults with type 1 diabetes.
Gender - In healthy volunteers, no difference in insulin aspart levels was
seen between men and women when body weight differences were taken into
®
and regular human insulin were evaluated in a
®
and regular human insulin were similar to
®
 Loading...
Loading...