Novogo 0S30000CF222 Users Manual


Plug & Go – as simple as that
Thank you for choosing NOVOGO as your door-to-door in-car navigator. This
document is the detailed description of the software. Although NOVOGO can easily
be discovered by experience, it is still recommended that you read through this
manual to clearly understand the exact function of each button and icon.
2

Table of contents
Copyright note........................................................................................1
Table of contents.................................................................................... 3
1 Warnings and safety information ...................................................6
2 General information .........................................................................7
3 Operating NOVOGO (Controls)....................................................... 8
3.1 Hardware buttons ( Please refer to Hardware User Manual ) ................. 8
3.1.1 Tilt up and down.................................................................................... 8
3.1.2 Zoom in and out .................................................................................... 8
3.1.3 Voice instruction announcement ........................................................... 9
3.1.4 The Route Information screen............................................................... 9
3.2 Screen buttons and controls..................................................................... 9
3.2.1 List selectors ......................................................................................... 9
3.2.2 Sliders ................................................................................................. 10
3.2.3 Switches.............................................................................................. 10
3.2.4 Switches in the Quick menu................................................................ 10
3.2.5 Virtual keyboards ................................................................................ 11
4 Discovering the program through the screens ........................... 13
4.1 Main menu ................................................................................................ 13
4.2 GPS Data screen ...................................................................................... 14
4.2.1 GPS data displayed ............................................................................ 14
4.2.2 GPS connection indicator.................................................................... 14
4.2.3 GPS data quality indicator................................................................... 15
4.2.4 Time synchronization .......................................................................... 15
4.3 The map .................................................................................................... 16
4.3.1 2D and 3D map views ......................................................................... 16
4.3.2 Zoom levels......................................................................................... 17
4.3.3 Daylight and night colour schemes ..................................................... 17
4.3.4 Streets and roads................................................................................ 18
4.3.5 Other objects....................................................................................... 19
4.3.6 Current position and Lock-on-Road .................................................... 20
4.3.7 Selected map point, also known as the Cursor ................................... 20
4.3.8 Marked map points (Pin) ..................................................................... 21
4.3.9 Visible POIs (Points of Interest) .......................................................... 22
4.3.10 Elements of the Active Route.............................................................. 23
3

4.4 Screens with map..................................................................................... 25
4.4.1 Turn preview (No. 1) ........................................................................... 26
4.4.2 Zoom in and out (No. 2 & 3)................................................................ 26
4.4.3 Tilt up and down (No. 4 & 5)................................................................ 27
4.4.4 Lock to GPS position and heading (No. 6) .......................................... 27
4.4.5 Cursor (No. 7) ..................................................................................... 28
4.4.6 Map scale (No. 8)................................................................................ 28
4.4.7 Menu (No. 9) ....................................................................................... 29
4.4.8 Map orientation and Overview (No. 10)............................................... 29
4.4.9 GPS position quality (No. 11) .............................................................. 30
4.4.10 Battery status (No. 12) ........................................................................ 30
4.4.11 Sound muting (No. 13) ........................................................................ 30
4.4.12 Track Log recording/playback indicator (No. 14)................................. 31
4.4.13 Cursor menu (No. 15) ......................................................................... 31
4.4.14 Current street (No. 16) ........................................................................ 33
4.4.15 Travel and Route data (No. 17)........................................................... 33
4.4.16 Distance to next turn (No. 18) ............................................................. 34
4.4.17 Next street / Next settlement (No. 19) ................................................. 34
4.5 Route Information screen........................................................................ 34
4.5.1 Route data displayed (for destination and via points).......................... 34
4.5.2 Warning icons ..................................................................................... 36
4.5.3 Fit to screen ........................................................................................ 37
4.5.4 Parameters.......................................................................................... 38
4.6 Menu.......................................................................................................... 38
4.6.1 Find tab ............................................................................................... 38
4.6.2 Quick tab............................................................................................. 38
4.6.3 Route tab ............................................................................................ 45
4.6.4 Main button ......................................................................................... 50
5 Settings ...........................................................................................51
5.1 General settings ....................................................................................... 51
5.1.1 Safety Mode........................................................................................ 51
5.1.2 Set Favourite Destinations .................................................................. 52
5.1.3 Automatic Night Colours ..................................................................... 52
5.1.4 Warn When Speeding ......................................................................... 52
5.1.5 Off-route Recalculation ....................................................................... 54
5.2 Map settings ............................................................................................. 54
5.2.1 Daylight / Night colour profile .............................................................. 55
5.2.2 Cockpit / Map mode map details ......................................................... 55
5.2.3 Alternative Road Names ..................................................................... 55
5.2.4 Show Street Labels ............................................................................. 55
5.2.5 Textured Polygons .............................................................................. 56
5.3 Sound settings ......................................................................................... 56
5.3.1 Master sound volume/switch............................................................... 56
5.3.2 Voice guidance volume/switch ............................................................ 56
5.3.3 Key sound volume/switch.................................................................... 56
5.3.4 Dynamic Volume ................................................................................. 57
5.3.5 Attention Tone..................................................................................... 57
5.4 Route parameter settings ........................................................................ 57
5.4.1 Method ................................................................................................ 58
4

5.4.2 Route .................................................................................................. 58
5.4.3 Vehicle ................................................................................................ 58
5.4.4 Road types to include/exclude ............................................................ 59
5.5 Language & Units..................................................................................... 60
5.5.1 Program language............................................................................... 60
5.5.2 Voice language ................................................................................... 61
5.5.3 Units.................................................................................................... 61
5.5.4 Set Date & Time Format ..................................................................... 61
5.6 Advanced settings ................................................................................... 61
5.6.1 Display options.................................................................................... 62
5.6.2 Backlight settings ................................................................................ 63
5.6.3 Smart Zoom ........................................................................................ 63
5.6.4 Route options ...................................................................................... 65
5.6.5 User data management....................................................................... 67
6 Find.................................................................................................. 68
6.1 Find (Main menu)...................................................................................... 68
6.2 Selection by tapping the map.................................................................. 68
6.3 Using the Find menu................................................................................ 69
6.3.1 Find an Address, Street, Intersection or City....................................... 69
6.3.2 Find in History ..................................................................................... 74
6.3.3 Find Coordinates................................................................................. 74
6.3.4 Find a POI........................................................................................... 75
6.3.5 Find one of the Favourites (Home/Work) ............................................ 77
7 Examples of using NOVOGO ........................................................78
7.1 Navigated route (2 destinations, reverse order) .................................... 78
7.2 Off-line route planning (4 destinations, mixed order, optimised) ........ 86
8 Troubleshooting guide ..................................................................92
9 Glossary..........................................................................................94
5

1 Warnings and safety information
NOVOGO is a navigation system that helps you find your way to your selected
destination. The position information obtained from the GPS receiver will not be
transmitted anywhere, so others will not be able to track you by the help of this
program.
If you are the driver of the vehicle, we recommend that you operate NOVOGO before
beginning your journey. The driver’s attention should be on the road. Plan your route
before departure and pull over if you need to change route parameters. NOVOGO
has a built-in (optional) Safety Mode that will prevent you from using the screen
functions if your car is in motion. Unless a passenger will be the only one to operate
NOVOGO, we strongly encourage you to turn on the Safety Mode.
It is also important that you look at the display only if it is absolutely safe to do so.
You should always observe traffic signs and road geometry before you obey any
instruction from NOVOGO. If you need to deviate from the recommended direction,
NOVOGO will suggest a modified route according to the new situation.
Never place the PND where it can obstruct the view of the driver, is within the
deployment zone of airbags, or where it can cause injuries in case of an accident.
6

2 General information
NOVOGO is a navigation system optimised for in-car use. It provides door-to-door
navigation for both single and multi-point routes using adaptable route parameters.
NOVOGO is capable of planning routes throughout the whole map region installed on
the memory card. Unlike some other products, NOVOGO does not require that you
change maps or switch to a poorly detailed general map to navigate between map
segments or countries. You always have complete freedom to go wherever you wish.
Just insert the memory card and go.
You do not need a stylus to use NOVOGO. All screen buttons and controls are
designed so that you can operate them with your fingertips.
NOVOGO does not contain pop-up or pull-down menus. You can access all functions
of the program by using hardware and screen buttons. With the help of these buttons
you can travel through all the screens of the program. Most of the screens (especially
menu functions and settings) can be accessed from several other screens,
minimising the number of actions needed to reach the desired function.
When using NOVOGO, you do not need to ‘double tap’ or ‘tap & hold’ the touch
screen as these functions cannot be used reliably in a moving vehicle. A single tap
triggers most of the screen controls. The only exceptions are ‘drag & drop’ for moving
the map, or scaling it in Map mode (4.4.6).
Most of the screens have a Return (
returns to the previous screen or directly to one of the map screens.
Settings screens also have a Help (
a detailed description of the current settings screen.
) button in the top left corner. This arrow
) button in the top right corner. This will show
7

3 Operating NOVOGO (Controls)
NOVOGO is designed for easy operation. All controls are operable by fingertips.
Wherever possible, pushbuttons and lists are provided to make accessing functions
or changing settings as easy as possible.
3.1 Hardware buttons ( Please refer to Hardware User Manual )
3.1.1 Tilt up and down
This function modifies the vertical view angle of the map in 3D mode. NOVOGO
offers a wide range of view angles starting from a top down view (a seamlessly
integrated 2D view) down to a flat view that lets you see far ahead.
The automatic Smart Zoom function will do the necessary tilting for you when
navigating (gives a flat view if the next turn is at a distance to let you see far ahead
and raises the angle when approaching a turn to give you a better view of the
upcoming manoeuvre). If you manually change the view angle, Smart Zoom will no
longer tilt the map by itself (automatic zooming and rotating remains active). Tap the
Lock button (4.4.4) to return the tilt control to Smart Zoom. You can also set
NOVOGO to do this automatically after a few seconds (5.6.3.3).
3.1.2 Zoom in and out
Zoom will change the scale of the map. If you zoom out, you will see a larger part of
the map, while zooming in shows a smaller part of the map in more detail.
The automatic Smart Zoom function will do the necessary zooming for you when
navigating (zooms out if the next turn is at a distance to let you see far ahead and
zooms in when approaching a turn to give you a better view of the upcoming
manoeuvre). If you manually change the zoom level, Smart Zoom will no longer scale
the map by itself (automatic tilting and rotating remains active). Tap the Lock button
(4.4.4) to return the zoom control to Smart Zoom. You can also set NOVOGO to do
this automatically after a few seconds (5.6.3.3).
8

3.1.3 Voice instruction announcement
When using either the Map or the Cockpit screen, you can repeat the latest voice
instruction by pressing the speak button
Tip: Use this button any time during your journey if you need the distance and type of
the next route event.
Note: In order to receive voice instructions, sound should not be muted (4.4.11),
voice guidance must be enabled (5.3.2), and a route must be active.
Note: If you have disabled Smart Zoom by using the functions above or moved the
map during navigation (i.e. the Lock button appears on the screen), Enter will first reenable normal navigation (Lock-to-Position and Smart Zoom), and will say the
instruction only after being pushed again.
3.1.4 The Route Information screen
To give easy access to the most important data screen during navigation, tap the
bottom section of the Cockpit screen (4.4.14) or the Info button (4.6.3.6) in the Route
menu) to display this screen.
3.2 Screen buttons and controls
The primary input channel of NOVOGO is the touch screen. If you read on, you will
realise that most parts of the screen are not only used to display information but also
to initiate functions by tapping. Below you will find a list of the most frequently used
controls in the program.
3.2.1 List selectors
When the values in the list need to be named, only the current value is shown
(sometimes together with a short description) in a horizontal stripe with arrows at
both ends.
The arrows are buttons. Tap to move left in the list or tap to move right. You
need not confirm your selection. As soon as you leave the screen, the selected value
becomes effective.
9

Note: The only exception for this is the Manual GPS Configuration screen where you
can confirm your new set of selections by tapping the button, or leave the
previous settings untouched by exiting with the button in the top left corner.
3.2.2 Sliders
When a feature has several different unnamed (numeric) values, NOVOGO will show
sliders that look like analogue potentiometers to set the desired value.
If the value limits are not displayed at the ends of the slider, the leftmost position
means the minimum value, while the rightmost position represents the maximum
value.
This control can be operated in two ways. Either drag the handle to move the slider
to its new position, or tap the slider where you want the handle to appear (the thumb
jumps there immediately). As with the list selectors, there is no need to confirm your
selection. As soon as you leave the screen, the selected value becomes effective.
3.2.3 Switches
When a function can only have two values (mainly Enabled and Disabled), a switch is
used. Unlike with list selectors, the horizontal line contains the name of the function
and not the actual status. There is a lamp on the left to show whether the function is
active or not.
When the lamp is dark ( ), the function is not selected. When it is lit ( ), the
function is enabled. The whole strip works as a button. Tap anywhere to toggle
between the enabled and disabled status.
3.2.4 Switches in the Quick menu
The switches of the Quick menu (4.6.2) behave as normal switches but they look
different in order to fit in with the other menu buttons.
10

Tap the button to toggle between the enabled and disabled states.
3.2.5 Virtual keyboards
NOVOGO is designed in a way that you only need to enter letters or numbers when it
is inevitable. In these cases a full screen keyboard pops up that can easily be
operated with your fingertips. You can choose between a separate ABC and numeric
keypad, or a set of QWERTY-type keyboards that contain both letters and numbers.
NOVOGO will remember your last choice and offer it the next time you need to enter
data.
The alphabetic keyboards in NOVOGO do not contain special characters, because
you do not need to enter accents when searching for a destination. Type only the
base letters (the letter most similar to the accented one) and NOVOGO will search for
all their combinations in the database (e.g. for the Hungarian street ‘Révász’ you only
need to type ‘Revasz’, and the rest is done by the program).
When you type in POI or track log names, NOVOGO will automatically turn all initials
into capitals to create names that look pleasant.
3.2.5.1 ABC-type keyboards
These keyboards contain only letters (Latin, Hebraic, Greek or Cyrillic). If you wish to
enter numbers, you need to tap the Keys (
keyboard.
Use Backspace (
mistake, tap Space (
the text.
This type of keyboard has large, finger-friendly buttons.
If you are used to computer keyboards, you may consider trying one of the
QWERTY-type keypads.
) to delete the last letter you have entered if you have made a
) to enter more words, and hit Done ( ) to finish entering
) button to switch to the numeric
11

3.2.5.2 QWERTY-type keyboards
QWERTY-type keyboards have both letters and numbers on them. Their layout is the
same as of the standard QWERTY, QWERTZ (German) and AZERTY (French)
keyboards. To switch to your desired QWERTY-type keyboard, press the Keys button
repeatedly until the appropriate keyboard appears.
Due to the high number of buttons to be displayed in one line, in portrait and square
modes these keyboards have narrow buttons. Still, with some practice they can be
easily fingertip operated.
The special keys described in the previous section are also available here.
3.2.5.3 The numeric keyboard
The numeric keyboard only contains numbers, on huge buttons. The special keys
you find on the other keyboards (except Space) are available here as well.
Although QWERTY-type keyboards also contain number keys, when entering a
house number, the program offers the more convenient numeric keypad.
12

4 Discovering the program through the screens
The best way to discover NOVOGO is to explore each screen in detail, and to find
out how to move from one to another. Read this chapter for a guided tour.
If you have already discovered some basic functions of the program, you may
choose to jump to Chapter 7 to read real-life examples that touch as many of the
basic features as possible (for advanced functions you should still consult Chapter 5).
Should any of the functions mentioned there look unfamiliar, use the references to
get to the specific part of this manual describing the concerned feature.
NOVOGO starts by displaying the Main menu. This is the root of the screen hierarchy,
but you only need to return here in a few cases. Many of the screens are also
accessible from each other to reduce the number of actions needed to initiate a
function or change a setting.
4.1 Main menu
The Main menu is the first screen of NOVOGO. Most parts of the program are
directly accessible from here by using the buttons described below.
13

4.2 GPS Data screen
The GPS Data screen is a collection of information received from the GPS device
and it also serves as the entry point to the GPS Setup and Time Sync screens.
4.2.1 GPS data displayed
The virtual sky on the left represents the currently visible part of the sky above you,
with your position as the centre. The satellites are shown at their current positions.
The GPS receives data from the green and grey satellites but not from the red ones.
Signals from the grey satellites are only received, while green ones are used by the
GPS to calculate your current location. On the right you can see the satellite signal
strength bars. Grey bars are for the grey and black bars are for the green satellites.
To identify satellites use their numbers also shown in the virtual sky. The more
satellites your GPS tracks (the green ones), the better your calculated position will be.
Additional pieces of information on this screen are: current position in
latitude/longitude format, elevation, speed, date, time and calculated accuracy.
Note: Accuracy can be affected by several factors the GPS cannot take into account.
Use this accuracy information only as estimation.
There are two icons on the left to show the status of the GPS connection and the
quality of reception.
4.2.2 GPS connection indicator
In the middle to the left there is a lamp similar to the ones used for switches. This one
has more colours and represents more values:
x
x
- dark lamp means there is no communication on the selected port,
- red lamp means connection to any GPS receiver has not been
established yet, so you need to set it up by using the Detect or Config. buttons,
x
- a slowly blinking yellow lamp means that there is no connection to the
GPS receiver, but NOVOGO is trying to connect,
14

x
- a fast blinking green lamp means that there is communication with the
GPS and data is being received.
4.2.3 GPS data quality indicator
In the top left corner there is a satellite dish to show the quality of the GPS position.
Different colours represent different signal quality:
x
x
x
x
- black with a red cross means there is no connection with the GPS
device,
- red means the GPS is connected but no GPS position is available,
- yellow means 2D reception. A GPS position has been aquired,
NOVOGO is ready for navigation, but the GPS is using enough satellites for
calculating the horizontal position only. Elevation data is not provided, and the
position error may be significant.
- green means 3D reception. The GPS receiver has enough satellites to
calculate altitude. Position is generally correct (yet it can still be inaccurate due
to different environmental factors). NOVOGO is ready for navigation.
4.2.4 Time synchronization
In the top right corner of the screen you have another button that leads to a new
screen where you can synchronize the clock of your PND to the very accurate time
provided by the connected GPS.
Turn on the Auto Correction switch to let NOVOGO frequently check and correct the
PND time with the GPS time.
Below that button you will see the current values of the GPS and the PND clocks.
You can check here whether any correction is needed. Tap the
manually synchronize the time.
button to
15
Below the PND time you have
or without a valid GPS time. It also gives you the chance to correct the time after
synchronization if your PND does not support time zones or daylight saving time.
You can also use these buttons if you prefer to set the PND time from this screen
instead of using the time setup features of the operating system.
and controls to manually correct the time with
4.3 The map
The most important and most frequently used screens of NOVOGO are the two
screens with the map (Map screen and Cockpit screen). They are similar in look and
in possible controls but are optimised for different uses. The map they display is
common. The elements of the map are described here. For the controls and special
functions of the two map screens see 4.4.
The current version of NOVOGO is primarily intended for land navigation. That is why
maps in NOVOGO look similar to paper roadmaps (when using daytime colours and
2D map mode). However, NOVOGO provides much more than regular paper maps
can. The look and the contents can be changed.
4.3.1 2D and 3D map views
Besides the classical top down view of the map (called 2D mode), you have the
possibility to tilt the map to have a perspective view (3D mode) that gives a view
similar to that seen through the windscreen with the possibility to see far ahead.
It is easy to change between 2D and 3D modes. You have two options. You can use
hardware buttons (3.1.1) or the semi-transparent screen icons (4.4.3) to tilt the map
seamlessly between 2D and all 3D angles, or you can use the switch in the Quick
menu (4.6.2.1) to quickly switch between the two modes.
Note: You may find that 2D mode is more useful in North-up Map mode when looking
for a certain part of the map or an object to select as destination. On the other hand,
3D mode in Track-up Cockpit mode with Smart Zoom makes navigation very
comfortable. The description of these modes will come later in this manual.
Note: Using the Advanced settings, you can force Map mode to always start in 2D
North-up view and/or Cockpit mode to always start in 3D Track-up view (5.6.1). You
16

can still rotate and tilt the maps in either mode, but the next time you enter this
screen, the preset look will reappear.
4.3.2 Zoom levels
NOVOGO uses high quality vector maps that let you see the map at various zoom
levels, always with optimised content (the density of the map details can be
independently set for Map and Cockpit screens in Map settings (5.2.2)). Street
names and other text objects are always displayed with the same font size, never
upside down, and you only see as many streets and objects as needed to find your
way around the map. Zoom in and out to see how the map changes in either the 2D
or 3D view.
Changing the scale of the map is very easy. You can drag and stretch the scale
(4.4.6) at the bottom of the Map screen, use hardware buttons (3.1.2) or semitransparent screen icons (4.4.2) on both Map and Cockpit screens.
Note: If you need to zoom out briefly to locate your position on the map, use the
Overview mode instead of zooming out and back in. The Overview mode is a 2D
North-up view that can be started by tapping the compass button on the right (see
4.4.8).
Note: NOVOGO has a special Smart Zoom function for navigation that automatically
rotates, scales and tilts the map in 3D map mode to always give you the optimal view
in your current situation. When approaching a turn, it will zoom in and raise the view
angle to let you easily recognise your manoeuvre at the next junction. If the next turn
is at a distance, it will zoom out and lower the view angle to flat in order to let you see
the road in front of you.
4.3.3 Daylight and night colour schemes
The different colour schemes let you adjust NOVOGO to the brightness of the
environment. Use the daylight and night colour schemes accordingly. Daylight
colours are similar to paper roadmaps, while the night colour schemes use dark tints
for large objects to keep the average brightness of the screen low, with carefully
selected colours to still keep you informed about all the necessary information on the
screen.
17

You can change between day and night views manually in the Quick Menu (4.6.2.3)
or let NOVOGO do it automatically (5.1.3) for you.
Note: The automatic day/night mode is based upon the current date and GPS
position by which NOVOGO calculates the exact sunrise and sunset times on the
particular day at the particular location. Using that information NOVOGO can
automatically switch between the colour schemes a few minutes before sunrise,
when the sky has already turned bright, and a few minutes after sunset before it gets
dark.
Tip: There are several daytime and night colour schemes included with NOVOGO. To
select the one that suits your needs the best, make your selection in Settings (5.2.1).
Note: The colours mentioned and screenshots included in this manual refer to the
default daytime and night colour schemes. They may not look the same in the
schemes you have chosen.
Tip: If you use NOVOGO after sunrise or before sunset, look for the sun in the sky in
the map background using a flat 3D view. It is displayed at its actual position to give
you another way to orientate, and also to provide some eye candy.
4.3.4 Streets and roads
The similarity of NOVOGO to paper roadmaps is also convenient when it comes to
streets, the most important elements of the map concerning navigation. NOVOGO
uses similar colour codes to those you are accustomed to, and the width of the
streets also refers to their importance, so it will not be difficult to tell a highway from a
small street.
18

Streets and roads have names or numbers for identification. Of course, this
information can be displayed on the map. NOVOGO uses two different ways to show
street labels. The conventional way is the same as a roadmap – it displays the name
of the street aligned with the street. The alternative is a kind of virtual signpost stuck
into the street itself.
You need not choose between the two modes. NOVOGO will use the one best for
the current tilt and zoom level. Zoom in to have only a few streets on the map, and
start tilting up and down to see how NOVOGO switches between the two modes in
an instant.
Note: The automatic switching is on even when using Smart Zoom. At first you may
find it odd, but later you will discover how it adjusts the displayed information to the
current view of the map. It is important, as the driver must be able to read the map at
a glance.
Tip: If you do not want to be bothered by street names during navigation, turn them
off on the Map Settings screen (5.2.4).
Tip: Major roads usually have alternative names (numbering) besides the primary
name. You can choose whether to display these alternative names or not. You can
set this in Map settings (5.2.3).
4.3.5 Other objects
To help orientate you, the map also contains objects that have no other navigating
function than to help you recognise your location on the map. These are surfacewaters, large buildings, forests, etc.
Tip: These objects are normally displayed using textured polygons that look natural
to the eye. You may wish to switch the textured display off (5.2.5) to free some of the
resources of your PND by replacing textures with plain coloured surfaces.
19
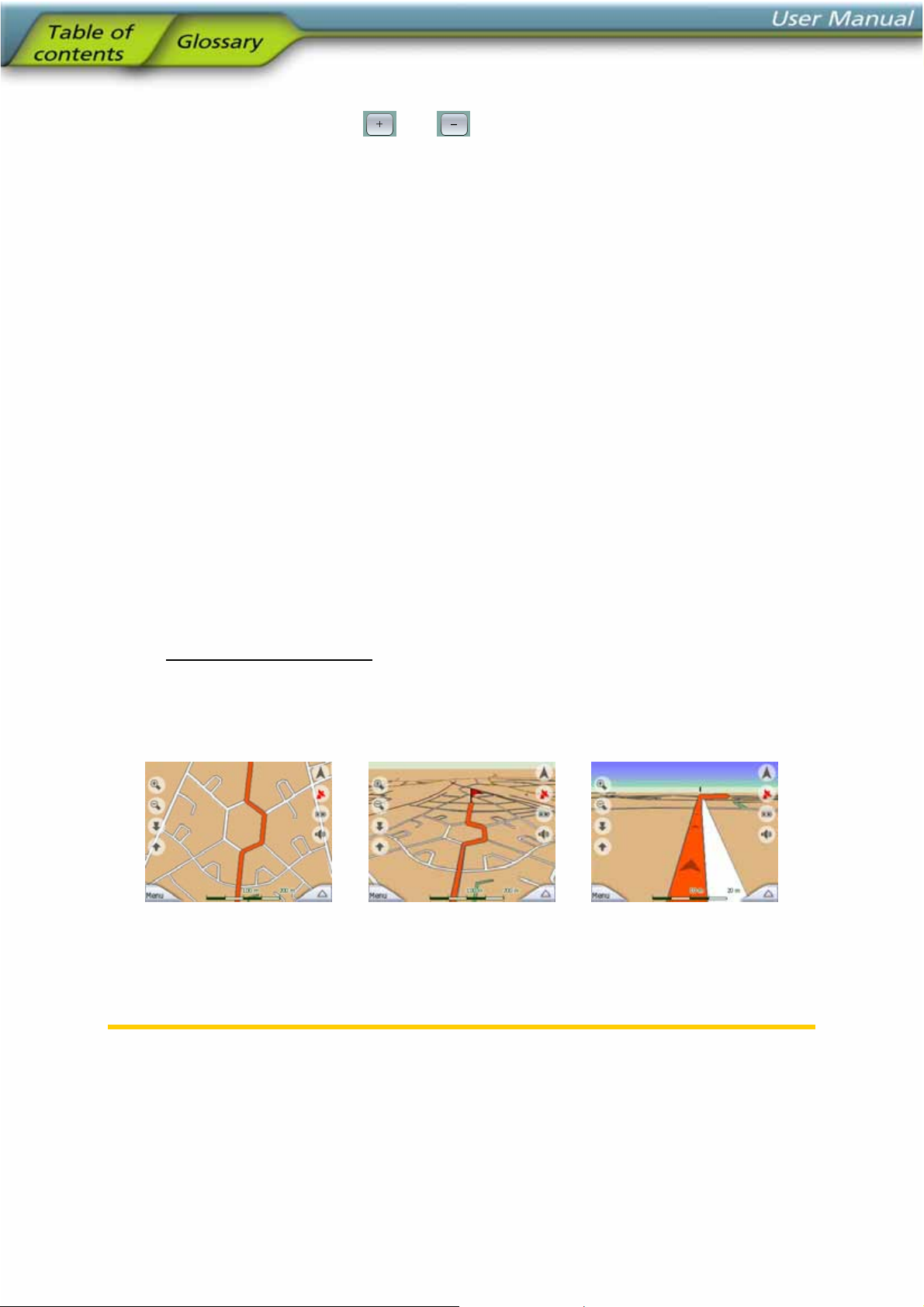
4.3.6 Current position and Lock-on-Road
When your GPS position is available, a blue arrow (yellow when using night colours)
shows your location on the map. The direction of the arrow represents your heading.
The arrow is sized and vertically rotated with the zoom and tilt levels to always look
realistic.
NOVOGO has a built-in Lock-on-Road feature that always puts the position arrow on
the road, on the axis of the street in case of one-way streets, or on the side of the
road where you drive (e.g. on the right in Germany and on the left in the U.K.) on
two-way roads.
The location received from the GPS receiver is shown as a blue dot on the map. This
can help you locate your position if the GPS accuracy is poor, and the Lock-on-Road
system puts you on the wrong street. It is also the location saved in the track log
(4.6.2.6).
Note: the Lock-on-Road feature can be turned off in Advanced settings (5.6.4.4) for
pedestrian use. When switched off, the arrow is displayed where the blue dot would
be with active Lock-on-Road.
When the GPS position is lost, the arrow turns grey and jumps to the last known
position, disabling Lock-on-Road (the last position before losing the reception is
usually inaccurate, and there is a chance that Lock-on-Road may choose the wrong
street).
4.3.7 Selected map point, also known as the Cursor
If you tap the map somewhere or select a specific item in Find, it will become the
selected point on the map, marked with a small red dot and permanently radiating
red circles to make it conspicuous at all zoom levels, even when it is in the
background of a 3D map view. You can use this point as starting point, via point, or
destination of your route, you can search for a POI near to it, mark it with a drawing-
20

pin, or save it as a POI. The cursor, when visible, is also the reference point for map
scaling.
Note: When your GPS position is available, and Lock-to-Position is active, the cursor
is always the current GPS position. When you select another point by tapping the
map, or using Find, the new Cursor is shown on the display, Lock-to-Position
becomes disabled, and the Lock button appears on the screen. Now the Cursor is
the newly selected point. As soon as you tap the Lock button, or after the given
timeout NOVOGO restores Lock-to-Position (5.6.3.3), and the Cursor jumps back to
the current GPS position.
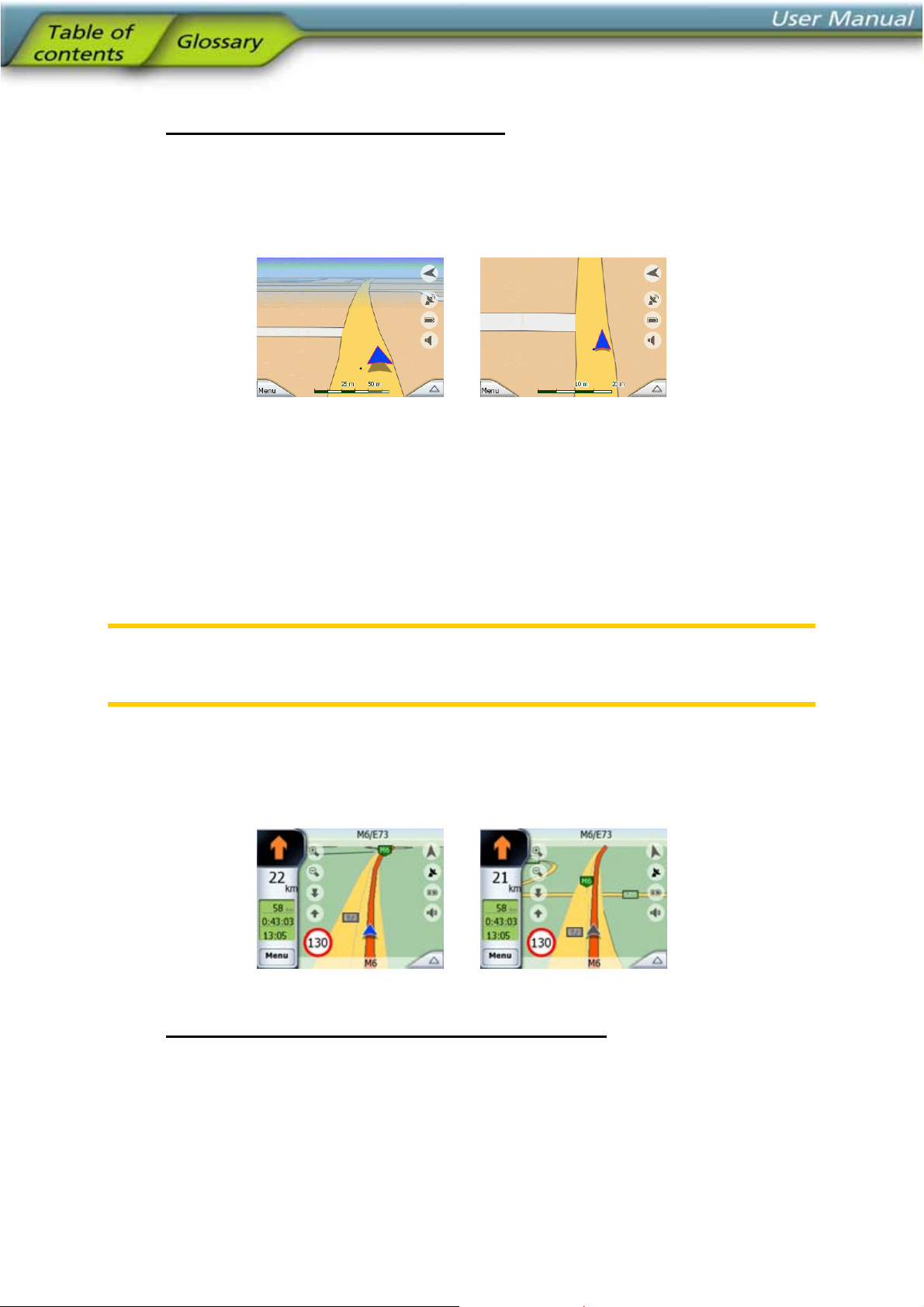
4.3.8 Marked map points (Pin)
The Cursor can be marked with a pin. Pins are shown as being stuck in the map. A
pin is visible at all zoom levels and remains in its position until you unpin it, or delete
all pins in Advanced settings (5.6.5.1).
The colour of the pin is automatically selected by NOVOGO. Different colours help
you identify a pin in the History list (6.3.2) later. There they are shown together with
their address and GPS coordinates.
Tip: There is a quick way to save the current GPS position as a pin. Press the Record
button (hardware button with an audio cassette icon on it) to save the pin instantly.
Tip: A quick way to tell the coordinates of a location you found on the map is to pin it,
and then look for the coordinates in the History list (6.3.2). This way you also save
the coordinates with the pin for later reference. If you do not need the coordinates
later, just select the point and start Find Coordinates (6.3.3).
21
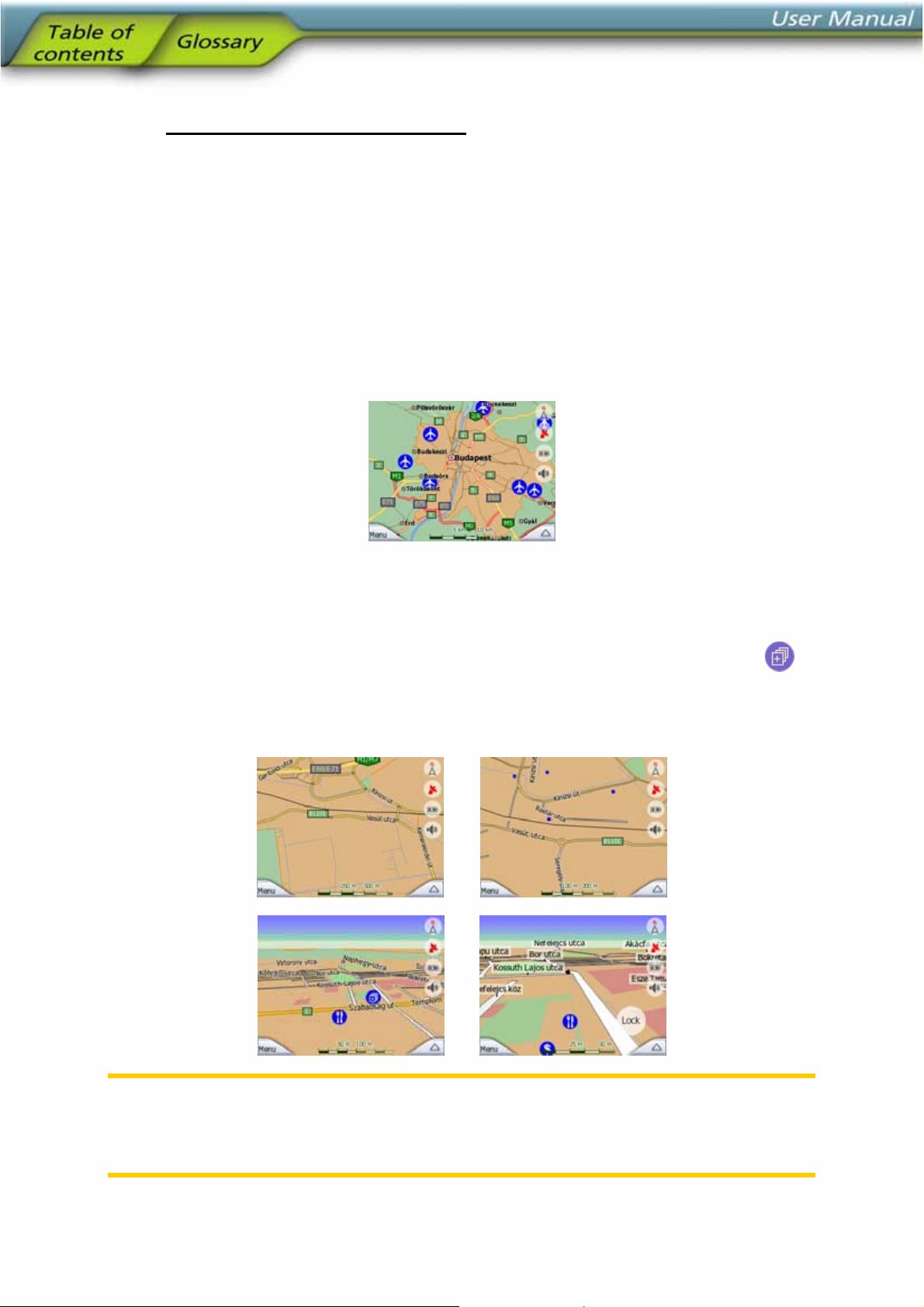
4.3.9 Visible POIs (Points of Interest)
NOVOGO comes with thousands of built-in POIs, and you can create your own POI
database as well. Having all of them displayed on the map would make the map too
crowded. To avoid this, NOVOGO lets you select which POIs to show and which
ones to hide (4.6.2.4) using their categories and subcategories.
POIs are represented by icons on the map. For a built-in POI it is the icon of the
subcategory of the actual POI. For points you create, it is the icon you had chosen
when you created the POI (it can be changed later).
These icons are large enough to recognise the symbol, and semi-transparent so as
not to cover the streets and junctions behind them.
When the map is zoomed out, the icons are not shown. As you zoom in, small dots
appear at the locations of visible POIs. Zooming in further makes the full icons
appear.
If two points are too close to each other so that icons overlap, a multi-POI icon
shown instead of individual ones. Zoom in more to see them separately. (Should the
two POIs have the same icon, this icon will be displayed instead of the multi-POI
icon.)
Note: When navigating, POI icons can be disabled together with street names (5.2.4).
If you still need this information during your journey, just drag the map to disable
Lock-to-Position (4.4.4). This will restore street names and POI icons immediately.
Now press Enter or tap Lock to reactivate Lock-to-Position.
is
22
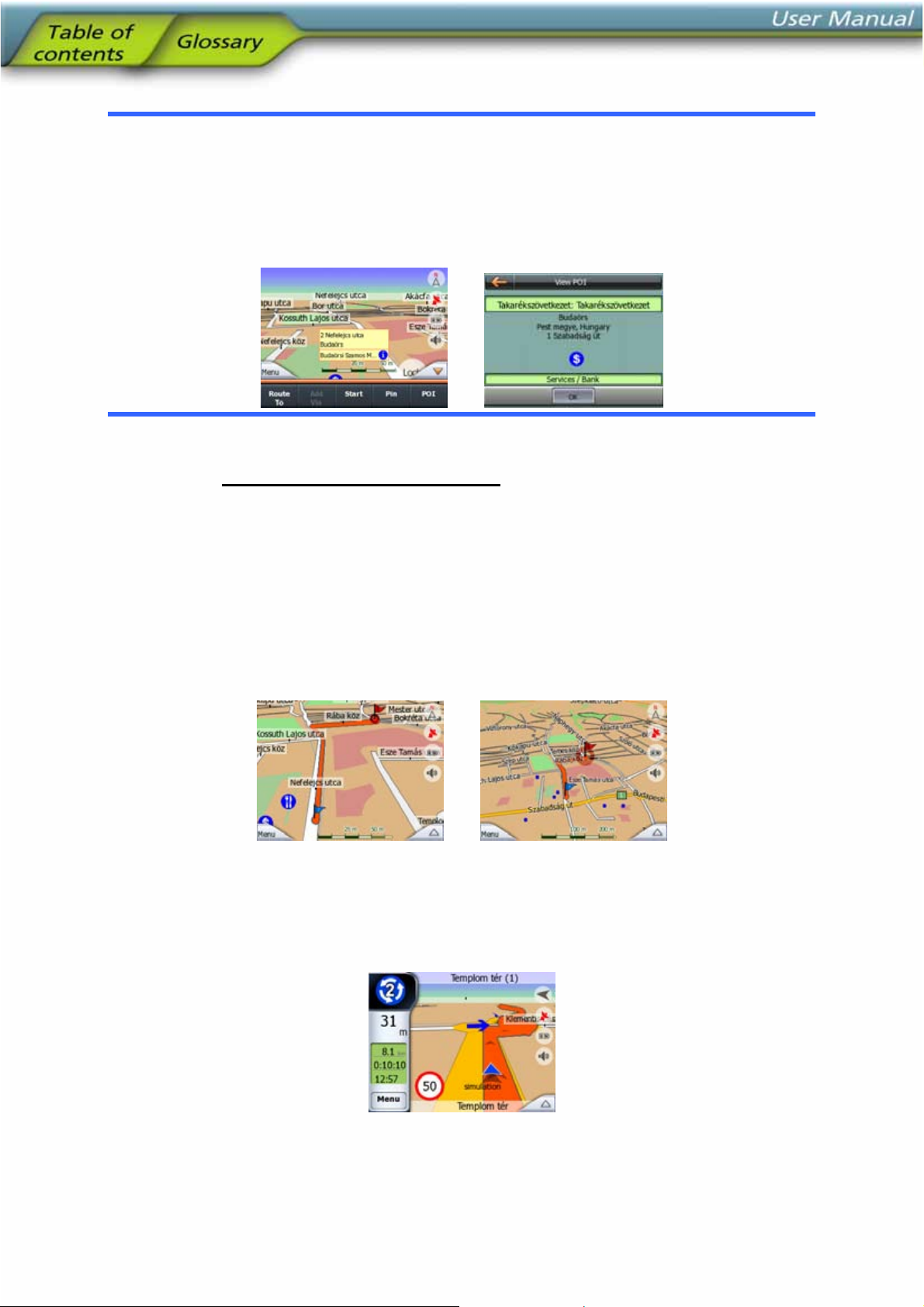
Tip: Tap the map on or near a POI item to see the list of the names of the nearest
POIs in a popup list, if it is enabled (4.6.2.5). To see the details of a particular POI in
the list, tap the blue ’i’ icon on the right. If you have too may POIs nearby, this list
may not be complete. In the Cursor menu (4.4.13) there is a button called POI that
leads you to the screen of all nearby POI items. There you can open them one by
one to see their details, and select any of them as a route point.
4.3.10 Elements of the Active Route
NOVOGO uses a multi-destination routing system in which you have a start point
(your current location if GPS position is available), a destination, the line of the active
leg of the route, and optionally via points and inactive legs. They are all shown on the
map.
4.3.10.1 The start point, via points and the destination
These points are represented by flags.
4.3.10.2 Animated turn guidance
Animated arrows represent all route events other than the above-mentioned special
points. These arrows show the direction in which you need to continue your journey.
23
4.3.10.3 The active leg of the route
The active leg is the section of the route you are currently driving. If you have not
added any via points, the whole route will be the active leg. When via points are
present, the active leg is the part leading from your location to the next via point.
The active section is displayed in light green when the sun is up, and in red during
the night. In both cases it is the most conspicuous part of the map even when in the
background of a 3D map view.
The line of the route is displayed on the driving side of the road for two-way and on
the axis in case of one-way streets. When the map is zoomed in and the line is wide
enough, small arrows show the direction of the route. This can be useful if you
preview the route before starting the journey or when entering a complex junction.
4.3.10.4 Inactive legs of the route
Future sections of a route are inactive. They are also shown on the map with the
same colour but a darker tint than the active one. An inactive route section becomes
active as soon as you reach its starting via point.
4.3.10.5 Roads in the route excluded by your preferences
Although you can choose whether to include or avoid some road types in Route
parameter settings (5.4.4), sometimes they are impossible to avoid near the starting
point, via points or the destination. If so, NOVOGO will display those segments of the
route with an alternate colour. They are shown in red with daylight colours, and
yellow with the night colour scheme, both in active and inactive legs of the route.
24
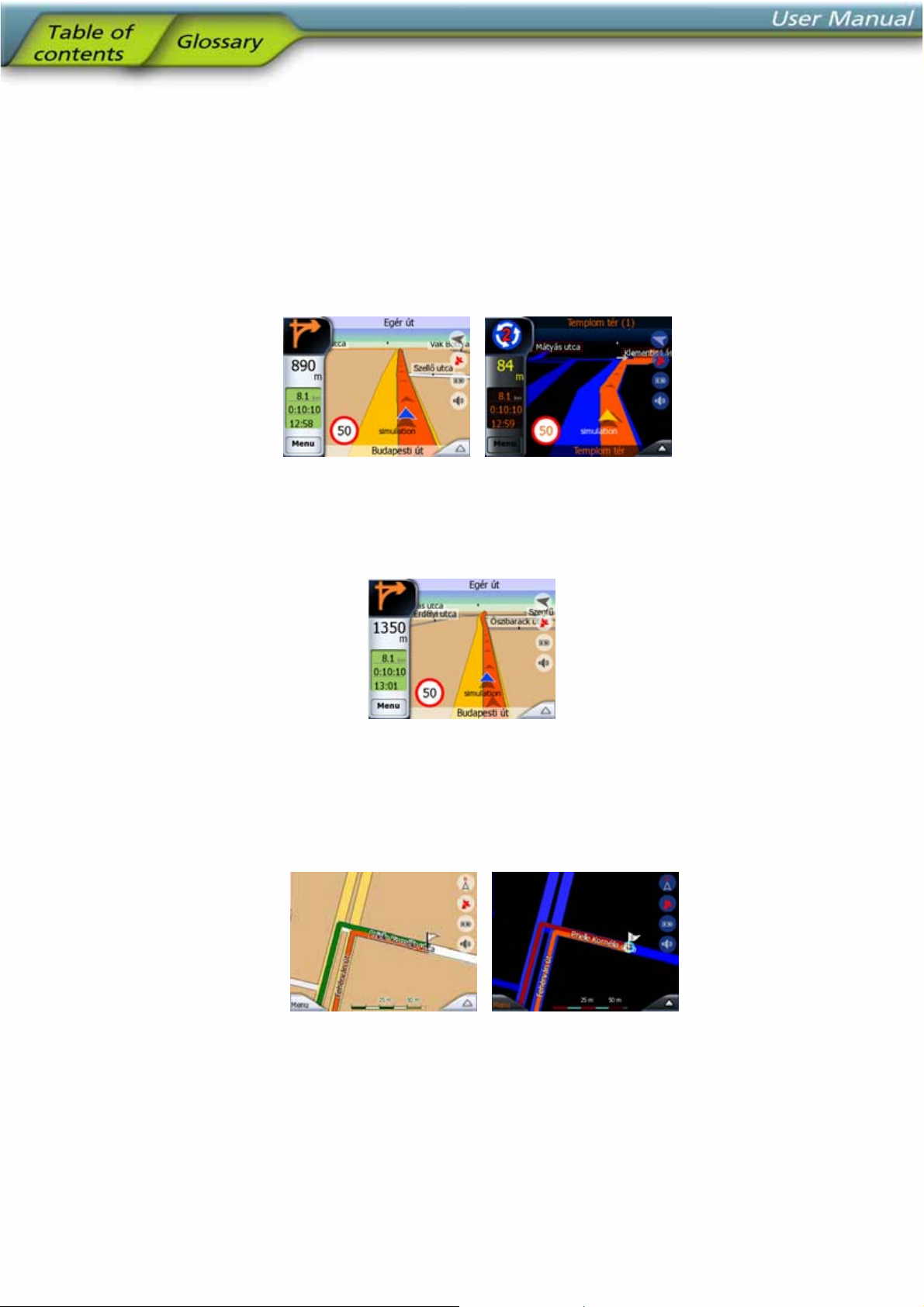
4.4 Screens with map
Having explained the contents of the map, the description of the other parts of the
map screens follows. There are two map screens: the Map screen and the Cockpit
screen. The way they show the map is the same but their look and controls are
optimised for different purposes.
The Map screen is to be used mainly without a GPS, to browse the map, create user
POI items, or to plan your route based on map points. The Map screen is designed to
give you the maximum map area. This screen is usually used in 2D North-up mode
(you can set NOVOGO so it always opens the Map screen like that – see 5.6.1.1).
The Cockpit screen is for driving purposes. Besides showing the map, it contains
some additional travel information if you are just cruising (speed, current street your
are driving in, speed limit for the current street), and some more route data if you are
navigating (e.g. next street in your route, distance to travel, type of the next route
event). This screen is typically used in 3D Track-up mode (you can make NOVOGO
always open the Cockpit screen like that – see 5.6.1.2).
There are several controls that function in a similar fashion on the two screens. They
are described on the following pages.
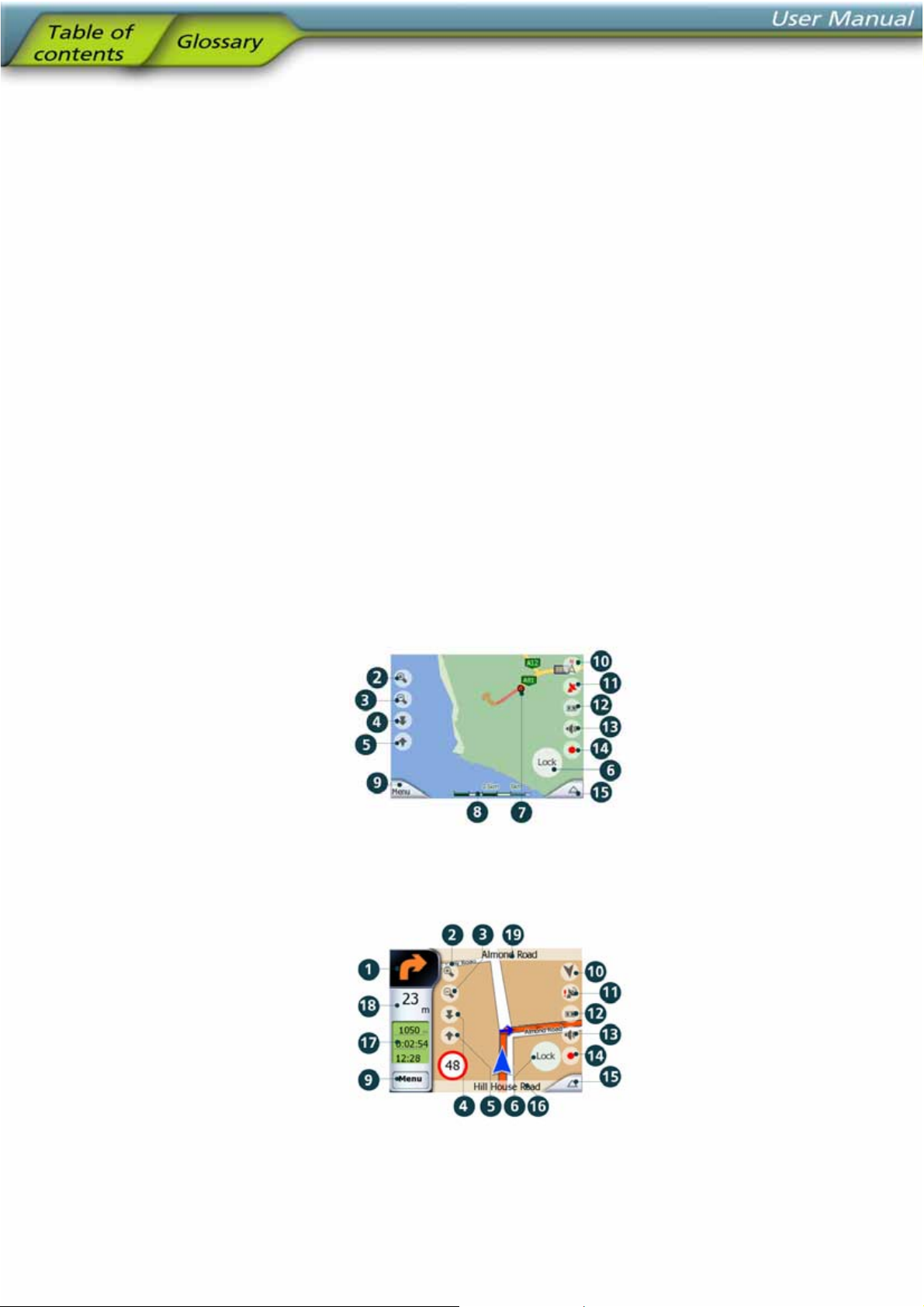
Map screen contents:
Cockpit screen contents:
No. Display Control
1 (Cockpit only) Turn preview* Opens Route menu*
25

2 n/a Zooms in (optional)
3 n/a Zooms out (optional)
4 n/a Tilts down (optional)
5 n/a Tilts up (optional)
6 Indicates that Lock to GPS position and
heading is inactive
7 Selected map point (Cursor) Opens Popup Info and Cursor menu
8 (Map only) Map scale Zooms in/out by dragging
9 n/a Menu (Find, Quick, Route, Main)
10 Map orientation and Overview Switches North-up, Track-up and Overview
11 GPS position quality Opens GPS Data screen
12 Battery status Opens settings
13 Sound on or muted Enables/disables muting
14 Track Log recording or playback Opens Track Log screen
15 n/a Opens Cursor menu
16 (Cockpit only) Current street Opens Route Information screen
17 (Cockpit only) Travel and Route data** Opens Route Information screen
18 (Cockpit only) Distance to next turn*** n/a
19 (Cockpit only) Next street*** n/a
Re-enables Lock-to-Position / Smart Zoom
* On Map screen only when a route is active
** Contents differ when a route is active
*** Only appears when a route is active
**** Only appears when a route is active and the next turn is near
4.4.1 Turn preview (No. 1)
On the Cockpit screen this field shows a graphic illustration of the next manoeuvre.
For example when you approach a turn, an arrow will show whether it is a slight,
normal or sharp turn. When showing a roundabout, the number of the exit is also
given in the picture.
This field also serves as a button. Tap it to get to the Route menu (4.6.3). The Map
screen will show a button called Route here if there is an active route. This also leads
to the Route menu.
4.4.2 Zoom in and out (No. 2 & 3)
These semi-transparent buttons are only displayed if ‘Zoom & Tilt’ is enabled in the
Quick menu (4.6.2.2).
26
As already described in 3.1.2, zoom will change the scale of the map. Zoom out
shows a larger part of the map, while Zoom in shows a smaller part of the map in
more detail.
The automatic Smart Zoom function will do the necessary zooming for you when
navigating (zooms out if the next turn is at a distance to let you see far ahead and
zooms in when approaching a turn to give you a better view of the upcoming
manoeuvre). If you manually change the zoom level, Smart Zoom will no longer scale
the map by itself (automatic tilting and rotating remains active). You need to tap the
Lock button (4.4.4) to return the zoom control to Smart Zoom. You can also set
NOVOGO to do this automatically after a few seconds (5.6.3.3).
4.4.3 Tilt up and down (No. 4 & 5)
These semi-transparent buttons are only displayed if ‘Zoom & Tilt’ is enabled in the
Quick menu (4.6.2.2).
As already described in 3.1.1, this function modifies the vertical viewing angle of the
map in 3D mode. You can change the angle in a wide range starting from a top down
view (2D view is seamlessly integrated) all the way to a flat view that lets you see far
ahead.
The automatic Smart Zoom function will do the necessary tilting for you when
navigating (gives a flat view if the next turn is at a distance to let you see far ahead
and raises the angle when approaching a turn to give you a better view of the
upcoming manoeuvre). If you manually change the view angle, Smart Zoom will no
longer tilt the map by itself (automatic zooming and rotating remains active). You
need to tap the Lock button (4.4.4) to return the tilt control to Smart Zoom. You can
also set NOVOGO to do this automatically after a few seconds (5.6.3.3).
4.4.4 Lock to GPS position and heading (No. 6)
This semi-transparent icon is displayed if GPS position is available, and the map has
been moved or rotated. It also appears when you scale or tilt the map while Smart
Zoom is enabled.
27
Normally NOVOGO positions the map to keep the GPS position visible somewhere
on the map (when North-up orientation is selected), or always at the bottom centre of
the map (when Track-up orientation is selected).
If you manually move the map, it will freeze the map in the new position. To return to
the GPS position, use this Lock button. Rotating the map in any direction will only
freeze the orientation of the map, but it keeps on moving to keep the GPS position
visible. Use Lock to return to North-up or Track-up orientation (the one previously
selected).
When Smart Zoom is enabled, scaling or tilting the map also stops the automatic
zooming or automatic tilting respectively. To reactivate Smart Zoom, tap this button.
Tip: In Advanced settings you can set a delay time after which NOVOGO pushes the
Lock button for you automatically (5.6.3.3). This can be turned on for re-enabling
both Lock-to-Position and Smart Zoom.
4.4.5 Cursor (No. 7)
As described in 4.3.7, if you tap the map somewhere or select one specific item in
Find, it will become the selected point on the map, marked with a small red dot and
radiating red circles to make it conspicuous. You can use this point as starting point,
via point or destination for your route, you can search for a POI near it, mark it with a
pin, or save it as a POI.
Note: When GPS position is available, the Lock button will appear indicating that you
have disabled Lock-to-Position. Tapping the Lock button will re-enable the position
lock and move the cursor back to the current GPS position. The same happens when
NOVOGO restores Lock-to-Position automatically, if it is set in Advanced settings
(5.6.3.3).
4.4.6 Map scale (No. 8)
The scale indicator is only available on the Map screen. In 2D map view it represents
the scale of the map. In 3D view it is the scale of the nearest part of the map only.
You can use it in both 2D and 3D modes to scale the map. Drag and pull it right to
zoom in, or left to zoom out.
28

4.4.7 Menu (No. 9)
This button opens the Menu with the Find engine, the Quick menu, the Route menu
and the exit button that takes you to the Main menu screen. The Menu will be
described in detail later in 4.6.
4.4.8 Map orientation and Overview (No. 10)
You can view the map screens in three different presentation modes. This switch will
cycle through them in the following order.
The usual map orientation for navigation is Track-up. It means NOVOGO rotates the
map during navigation to always face the direction of your travel. In this mode an
arrow (compass) points towards North.
Tap this icon to switch to North-up mode. Now the map is fixed to keep facing North.
The icon changes to show the new rotation mode.
Tap the icon again to enter Overview mode. This mode looks similar to the North-up
mode with one difference: the zoom level in this mode has a fixed default to give you
a better look of where you are on the map. You can change the zoom level at any
time, this will not cause the Lock button to appear, but when entering Overview mode
later, the default zoom level will be restored.
The arrow representing your position will be fixed in the middle of the screen. When
you move the map in Overview mode, the Lock button will appear, and when pushed,
it will move the map to have your current position in the middle of the map again.
You cannot rotate the map in Overview mode. This mode is strictly north-up.
You can set up NOVOGO so that it will switch to Overview mode during navigation
when the next turn is far away. You can specify this distance and the fixed zoom
level of Overview in Advanced settings (5.6.3.2). An airplane icon indicates Overview
mode.
Tap the icon again to return to Track-up (automatic rotation) mode.
29

4.4.9 GPS position quality (No. 11)
Similarly to the icon found on the GPS Data screen (4.2.3), the map screens also
inform you about the GPS signal. They can show the same four values:
x
x
x
x
The black satellite dish with the red exclamation mark shows there is no
connection with the GPS receiver. GPS navigation is not possible.
Red shows there is a connection, but the signal is too weak to give a
position. GPS navigation is not possible.
Black shows there is a GPS position, and navigation is possible. When
only one arc is shown, the position is 2D (no altitude available), and position
error may be significant, yet NOVOGO is ready to navigate.
A black dish and two arcs represent a 3D GPS position. NOVOGO is
ready to navigate.
4.4.10 Battery status (No. 12)
The status of the PND battery is also shown by NOVOGO. You can estimate the
available power reserve from the length of the bar inside. Some examples:
x
x
x
x
The thunderbolt in the battery shows the battery is being charged.
Battery is not charging, but it is at full capacity.
Battery in not full, but there is sufficient reserve capacity.
When the inside of the battery turns red, the battery needs recharging.
4.4.11 Sound muting (No. 13)
By tapping this button you can quickly mute all sounds of the PND. This will not
modify the volume level and the enabled or disabled status of the voice guidance or
the key sounds (all to be set on the Sound Settings screen: 5.3), just mutes the
sound output. When muting is enabled, the speaker icon is crossed out.
30
 Loading...
Loading...