Page 1
Novell®
www.novell.com
Users Guide
ZENworks® Network Access Control
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION
5.0
September 22, 2008
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 2

Legal Notices
Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and
specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Further, Novell, Inc., reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes to its content, at any time,
without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
Further, Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to any software, and specifically disclaims
any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc.,
reserves the right to make changes to any and all parts of Novell software, at any time, without any obligation to
notify any person or entity of such changes.
Any products or technical information provided under this Agreement may be subject to U.S. export controls and the
trade laws of other countries. You agree to comply with all export control regulations and to obtain any required
licenses or classification to export, re-export or import deliverables. You agree not to export or re-export to entities on
the current U.S. export exclusion lists or to any embargoed or terrorist countries as specified in the U.S. export laws.
You agree to not use deliverables for prohibited nuclear, missile, or chemical biological weaponry end uses. See the
Novell International Trade Services Web page (http://www.novell.com/info/exports/) for more information on
exporting Novell software. Novell assumes no responsibility for your failure to obtain any necessary export
approvals.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Copyright © 2008 Novell, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, photocopied,
stored on a retrieval system, or transmitted without the express written consent of the publisher.
Novell, Inc., has intellectual property rights relating to technology embodied in the product that is described in this
document. In particular, and without limitation, these intellectual property rights may include one or more of the U.S.
patents listed on the Novell Legal Patents Web page (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/patents/) and one or
more additional patents or pending patent applications in the U.S. and in other countries.
Novell, Inc.
404 Wyman Street, Suite 500
Waltham, MA 02451
U.S.A.
www.novell.com
Online Documentation: To access the latest online documentation for this and other Novell products, see
the Novell Documentation Web page (http://www.novell.com/documentation).
Page 3

Novell Trademarks
For Novell trademarks, see the Novell Trademark and Service Mark list (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/
trademarks/tmlist.html).
Third-Party Materials
All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
This Novell software product includes open-source software components. Novell conforms to the terms and
conditions that govern the use of the open source components included in this product. Users of this product have
the right to access the open source code and view all applicable terms and conditions governing opens source
component usage. Visit http://www.novell.com/products/zenworks/networkaccesscontrol/opensource to access
open source code, applicable terms and conditions, and related information.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Page 4

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
4 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 5

Contents
1 Introduction 15
1.1 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Home Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1.2 System Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
1.3 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control v5.0 for v4.x Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
1.4 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
1.4.1 The Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.4.2 About Novell ZENworks Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
1.5 Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.6 Additional Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.7 Installing and Upgrading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
1.8 Conventions Used in This Document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.1 Navigation Paragraph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.2 Tip Paragraph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.3 Note Paragraph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.4 Important Paragraph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.5 Warning Paragraph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
1.8.6 Italic Text . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.8.7 Courier Font. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.8.8 Angled Brackets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
1.8.9 Square Brackets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.8.10 Terms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.9 Copying Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.9.1 SCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.9.2 PSCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
1.10 Users’ guide online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Clusters and Servers 33
2.1 Single-server Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
2.2 Multiple-server Installations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3 System Configuration 37
3.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3.2 Enforcement Clusters and Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.3 Enforcement Clusters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
3.3.1 Adding an Enforcement Cluster. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.3.2 Editing Enforcement Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3.3.3 Viewing Enforcement Cluster Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
3.3.4 Deleting Enforcement Clusters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3.4 Enforcement Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
3.4.1 Adding an ES. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.4.2 Cluster and Server Icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3.4.3 Editing ESs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
3.4.4 Changing the ES Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
3.4.5 Changing the ES Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
3.4.6 Modifying the ES SNMP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
3.4.7 Modifying the ES root Account Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3.4.8 Viewing ES Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3.4.9 Deleting ESs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Contents 5
Page 6

3.4.10 ES Recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.5 Management Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3.5.1 Viewing Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
3.5.2 Modifying MS Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
3.5.3 Selecting a Proxy Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3.5.4 Setting the Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
3.5.5 Automatically Setting the Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3.5.6 Manually Setting the Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
3.5.7 Selecting the Time Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.5.8 Enabling SNMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.5.9 Modifying the MS root Account Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.5.10 Checking for Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrades . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
3.5.11 Changing the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrade Timeout. . . . . . . 56
3.6 User Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.6.1 Adding a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
3.6.2 Searching for a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.6.3 Sorting the User Account Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
3.6.4 Copying a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.6.5 Editing a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3.6.6 Deleting a User Account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3.7 User Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
3.7.1 Adding a User Role . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
3.7.2 Editing User Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3.7.3 Deleting User Roles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
3.7.4 Sorting the User Roles Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
3.8 License. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
3.8.1 Updating Your License Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3.9 Test Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
3.9.1 Manually Checking for Test Updates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3.9.2 Selecting Test Update Times. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3.9.3 Viewing Test Update Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3.10 Quarantining, General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
3.10.1 Selecting the Quarantine Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
3.10.2 Selecting the Access Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
3.11 Quarantining, 802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
3.11.1 Entering Basic 802.1X Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3.11.2 Authentication Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
3.11.3 Adding 802.1X Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
3.11.4 Testing the Connection to a Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
3.11.5 Cisco IOS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
3.11.6 Cisco CatOS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
3.11.7 Enterasys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
3.11.8 Extreme ExtremeWare . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
3.11.9 Extreme XOS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
3.11.10 Foundry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
3.11.11 HP ProCurve Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
3.11.12 HP ProCurve WESM xl or HP ProCurve WESM zl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
3.11.13 HP ProCurve 420 AP or HP ProCurve 530 AP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
3.11.14 Nortel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
3.11.15 Other . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
3.12 Quarantining, DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
3.12.1 DHCP Server Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
3.12.2 Setting DHCP Enforcement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
3.12.3 Adding a DHCP Quarantine Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
3.12.4 Sorting the DHCP Quarantine Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
3.12.5 Editing a DHCP Quarantine Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
3.12.6 Deleting a DHCP Quarantine Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
3.13 Quarantining, Inline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
6 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 7

3.14 Post-connect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
3.14.1 Allowing the Post-connect Service Through the Firewall. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
3.14.2 First Time Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
3.14.3 Setting Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
3.14.4 Configuring a Post-connect System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
3.14.5 Launching Post-connect Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
3.14.6 Post-connect in the Endpoint Activity Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
3.14.7 Adding Post-connect System Logos and Icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
3.15 Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
3.15.1 Initiating a New Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
3.15.2 Restoring From a Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
3.16 Downloading Support Packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
3.17 Cluster Setting Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
3.17.1 Testing Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
3.17.2 Selecting End-user Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.17.3 Accessible Services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
3.17.4 Exceptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
3.17.5 Notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
3.17.6 End-user Screens . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
3.17.7 Agentless Credentials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
3.18 Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
3.18.1 Setting ES Logging Levels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
3.18.2 Setting 802.1X Devices Logging Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
3.19 Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
3.19.1 Setting the Agent Read Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
3.19.2 Setting the RPC Command Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
4 Endpoint Activity 137
4.1 Filtering the Endpoint Activity Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
4.1.1 Filtering by Access Control or Test Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
4.1.2 Filtering by Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
4.1.3 Limiting Number of Endpoints Displayed. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
4.1.4 Searching. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
4.2 Access Control States . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
4.3 Endpoint Test Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
4.4 Enforcement Cluster Access Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
4.5 Viewing Endpoint Access Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
4.6 Selecting Endpoints to Act on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
4.7 Acting on Selected Endpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
4.7.1 Manually Retest an Endpoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
4.7.2 Immediately Grant Access to an Endpoint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
4.7.3 Immediately Quarantine an Endpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
4.7.4 Clearing Temporary Endpoint States. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
4.8 Viewing Endpoint Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
4.9 Troubleshooting Quarantined Endpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
5 End-user Access 157
5.1 Test Methods Used . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
5.1.1 Agent Callback. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
5.2 Endpoints Supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
5.3 Browser Version. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
5.4 Firewall Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
5.4.1 Managed Endpoints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
5.4.2 Unmanaged Endpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Contents 7
Page 8

5.4.3 Making Changes to the Firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
5.5 Windows Endpoint Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
5.5.1 IE Internet Security Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
5.5.2 Agent-based Test Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
5.5.3 Agentless Test Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
5.5.4 ActiveX Test Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
5.6 Mac OS X Endpoint Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
5.6.1 Ports Used for Testing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
5.6.2 Allowing Novell ZENworks Network Access Control through the OS X Firewall . . . 171
5.7 End-user Access Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
5.7.1 Opening Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
5.7.2 Windows NAC Agent Test Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
5.7.3 Mac OS Agent Test Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
5.7.4 ActiveX Test Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
5.7.5 Agentless Test Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
5.7.6 Testing Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
5.7.7 Test Successful Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
5.7.8 Testing Cancelled Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
5.7.9 Testing Failed Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
5.7.10 Error Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
5.8 Customizing Error Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
6 NAC Policies 201
6.1 Standard NAC Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
6.2 NAC Policy Group Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
6.2.1 Add a NAC Policy Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
6.2.2 Editing a NAC Policy Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
6.2.3 Deleting a NAC Policy Group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
6.3 NAC Policy Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
6.3.1 Enabling or Disabling a NAC Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
6.3.2 Selecting the Default NAC Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
6.3.3 Creating a New NAC Policy. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
6.3.4 Editing a NAC Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.5 Copying a NAC Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.6 Deleting a NAC Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.7 Moving a NAC Policy Between NAC Policy Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
6.3.8 Assigning Endpoints and Domains to a Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
6.3.9 NAC Policy Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
6.3.10 Setting Retest Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
6.3.11 Setting Connection Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 210
6.3.12 Defining Non-supported OS Access Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.3.13 Setting Test Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.3.14 Selecting Action Taken . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
6.4 About Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
6.4.1 Viewing Information About Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
6.4.2 Selecting Test Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
6.4.3 Test Icons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
7 Quarantined Networks 217
7.1 Endpoint Quarantine Precedence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
7.2 Using Ports in Accessible Services and Endpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 218
7.3 Always Granting Access to an Endpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
7.4 Always Quarantining an Endpoint . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
7.5 New Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
8 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 9

7.6 Shared Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
7.7 Untestable Endpoints and DHCP Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
7.8 Windows Domain Authentication and Quarantined Endpoints. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
8 High Availability and Load Balancing 225
8.1 High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
8.2 Load Balancing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
9 Inline Quarantine Method 229
10 DHCP Quarantine Method 231
10.1 Configuring Novell ZENworks Network Access Control for DHCP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
10.1.1 Setting up a Quarantine Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
10.1.2 Router Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 232
10.1.3 Configuring Windows Update Service for XP SP2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
11 802.1X Quarantine Method 235
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
11.1 About 802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
11.2 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control and 802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
11.3 Setting up the 802.1X Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 239
11.3.1 Setting up the RADIUS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 240
11.3.2 Enabling Novell ZENworks Network Access Control for 802.1X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 264
11.3.3 Setting up the Supplicant. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 265
11.3.4 Setting up the Authenticator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 272
12 API 283
12.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 283
12.2 Setting Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
12.3 Setting Firewall Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
12.4 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Events Generated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 285
12.4.1 Examples of Events Generated . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 286
12.4.2 Java Program and Command for Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 288
12.5 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Requests Supported. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
12.5.1 Examples of Requests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
12.5.2 Post-connect Request Example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
12.5.3 Java Program and Command for Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
13 Remote Device Activity Capture 295
13.1 Creating a DAC Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 295
13.1.1 Downloading the EXE File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
13.1.2 Running the Windows Installer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
13.1.3 Adding Additional Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 302
13.1.4 Configuring the MS and ES for DAC . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 303
13.1.5 Adding Additional ESs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 304
13.1.6 Starting the Windows Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
13.1.7 Viewing Version Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 305
13.1.8 Removing the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 306
13.2 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control to Infoblox Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
13.2.1 Configuring the Infoblox Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
13.2.2 Configuring Novell ZENworks Network Access Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 308
Contents 9
Page 10

14 Reports 311
14.1 Generating Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
14.2 Viewing Report Details . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
14.3 Printing Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
14.4 Saving Reports to a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
14.5 Converting an HTML Report to a Word Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
15 DHCP Plug-in 317
15.1 Installation Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
15.2 DHCP Plug-in and the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control User Interface . . . . . . . . 320
15.2.1 Installing the Plug-in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
15.2.2 Enabling the Plug-in and Adding Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 323
15.2.3 Viewing DHCP Server Plug-in Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 325
15.2.4 Editing DHCP Server Plug-in Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
15.2.5 Deleting a DHCP Server Plug-in Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 326
15.2.6 Disabling a DHCP Server Plug-in Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
15.2.7 Enabling a DHCP Server Plug-in Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
16 System Administration 329
16.1 Launching Novell ZENworks Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 329
16.1.1 Launching and Logging into Novell ZENworks Network Access Control. . . . . . . . . 330
16.1.2 Logging out of Novell ZENworks Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
16.1.3 Important Browser Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
16.2 Restarting Novell ZENworks Network Access Control System Processes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
16.3 Managing your Novell ZENworks Network Access Control License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
16.3.1 Entering a New License Key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 331
16.4 Downloading New Tests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
16.5 System Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 332
16.5.1 DNS/Windows Domain Authentication and Quarantined Endpoints . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
16.5.2 Matching Windows Domain Policies to NAC Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
16.5.3 Setting the Access Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 334
16.5.4 Naming Your Enforcement Cluster . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
16.5.5 Changing the MS Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
16.5.6 Changing the ES Host Name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
16.5.7 Changing the MS or ES IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
16.5.8 Resetting your System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
16.5.9 Resetting your Test Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
16.5.10 Changing Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
16.5.11 Specifying an Email Server for Sending Notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
16.6 Entering Networks Using CIDR Format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 338
16.7 Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
16.7.1 Creating a Backup File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
16.7.2 Restoring from Backup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 339
16.7.3 Restoring the Original Database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
16.7.4 Generating a Support Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
16.8 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 341
16.9 Supported VPNs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
16.10 Adding Custom Tests. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
16.10.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
16.10.2 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 343
16.10.3 Changing the Error Messages in a Test Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 344
16.10.4 Creating a Custom Test Class Script from Scratch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
16.10.5 BasicTests API . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
10 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 11

16.11 End-user Access Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
16.12 How Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Handles Static IP Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . 362
16.13 Managing Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
16.13.1 Resetting the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Server Password . . . . . . 364
16.13.2 Resetting the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Database Password. . . . 365
16.13.3 Changing the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Administrator Password. 365
16.14 NTLM 2 Authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 366
16.15 Working with Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 367
16.16 Creating and Replacing SSL Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
16.16.1 Creating a New Self-signed Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 368
16.16.2 Using an SSL Certificate from a known Certificate Authority (CA) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
16.17 Moving an ES from One MS to Another. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 370
16.18 Recovering Quickly from a Network Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
16.19 VLAN Tagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 371
16.20 iptables Wrapper Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
16.21 Supporting Network Management System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
16.21.1 Enabling ICMP Echo Requests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 374
16.21.2 Changing the Community Name for SNMPD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
16.21.3 SNMP MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 376
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
17 Patch Management 379
17.1 Flagging a Test to Launch a Patch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
17.2 Selecting the Patch Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 380
17.3 Specifying the Number of Retests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
17.4 Specifying the Retest Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
17.5 SMS Patch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
17.6 SMS Concepts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
17.7 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control/SMS/Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
Process . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
17.8 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Setup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
17.9 Learning More About SMS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 382
A Configuring the Post-connect Server 385
A.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
A.2 Extracting the ZIP File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 385
A.2.1 Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
A.2.2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
A.3 ZIP File Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 386
A.4 Setting up a Post-connect Host . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
A.4.1 Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 387
A.4.2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 388
A.5 Viewing Logs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
A.6 Testing the Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
A.6.1 Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
A.6.2 Linux . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 390
A.7 Configuring Your Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
A.8 Allowing Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Through the Firewall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 391
B Tests Help 393
B.1 Browser Security Policy — Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 393
B.1.1 Browser Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 395
Contents 11
Page 12

B.1.2 Internet Explorer (IE) Internet Security Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 396
B.1.3 Internet Explorer (IE) Local Intranet Security Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 397
B.1.4 Internet Explorer (IE) Restricted Site Security Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
B.1.5 Internet Explorer (IE) Trusted Sites Security Zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 399
B.2 Operating System — Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
B.2.1 IIS Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
B.2.2 Internet Explorer Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
B.2.3 Microsoft Office Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 402
B.2.4 Microsoft Applications Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
B.2.5 Microsoft Servers Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
B.2.6 Microsoft Tools Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
B.2.7 Service Packs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
B.2.8 Windows 2000 SP4 Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 405
B.2.9 Windows 2003 SP1 Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
B.2.10 Windows 2003 SP2 Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 407
B.2.11 Windows Automatic Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 408
B.2.12 Windows Media Player Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
TM
B.2.13 Windows Vista
SP0 Hotfixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 409
B.2.14 Windows XP SP1 Hotfixes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 410
B.2.15 Windows XP SP2 Hotfixes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
B.3 Security Settings — OS X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 411
B.3.1 Mac AirPort WEP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
B.3.2 Mac AirPort Preference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 412
B.3.3 Mac AirPort User Prompt . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
B.3.4 Mac Anti-virus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
B.3.5 Mac Bluetooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 414
B.3.6 Mac Firewall. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 415
B.3.7 Mac Internet Sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
B.3.8 Mac QuickTime
®
Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 416
B.3.9 Mac Security Updates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 417
B.3.10 Mac Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
B.4 Security Settings — Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
B.4.1 Allowed Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 418
B.4.2 Microsoft Excel Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 419
B.4.3 Microsoft Outlook Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
B.4.4 Microsoft Word Macros . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 421
B.4.5 Services Not Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 422
B.4.6 Services Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
B.4.7 Windows Bridge Network Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 424
B.4.8 Windows Wireless Network SSID Connections. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
B.4.9 Windows Security Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
B.4.10 Windows Startup Registry Entries Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 427
B.4.11 Wireless Network Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
B.5 Software — Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
B.5.1 Anti-spyware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 429
B.5.2 Anti-virus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 430
B.5.3 High-risk Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
B.5.4 Microsoft Office Version Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 431
B.5.5 P2P . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 432
B.5.6 Personal Firewalls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
B.5.7 Software Not Allowed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 433
B.5.8 Software Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 434
B.5.9 Worms, Viruses, and Trojans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 435
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
C HA Bypass Card 437
C.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 437
C.2 Location and Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
12 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 13

C.3 HA Bypass Supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
C.4 Installing the Bypass Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 438
C.5 Configuring the Bypass Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439
C.6 Operating the Bypass Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 441
D Database Design (Data Dictionary) 443
D.1 test_result table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 443
D.2 Device table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
D.3 sa_cluster. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
D.4 sa_node . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
D.5 sa_user . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
D.6 cluster_to_user. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 448
D.7 user_group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 448
D.8 user_to_groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 448
D.9 group_to_permission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 448
E Ports used in Novell ZENworks Network Access Control 451
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
F MS Disaster Recovery 457
F.1 Installation Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
F.2 Installing the Standby MS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 457
F.3 Ongoing Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 458
F.4 Failover process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 458
G Licenses 461
G.1 Novell End-user License Agreement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 461
G.2 Other licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
G.2.1 Apache License Version 2.0, January 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
G.2.2 ASM 2.2.3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 471
G.2.3 Open SSH 4.5p1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 472
G.2.4 Postgresql 8.1.8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 476
G.2.5 Postgresql jdbc 8.1-408. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 476
G.2.6 xstream 1.2.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
G.2.7 Libeay (Open SSL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
G.2.8 Junit 4.4 Common Public License - v 1.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 479
G.2.9 Open SSL 1.1.2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
G.2.10 The following license applies to SAPQ 2.0, samba-tng 0.4 and bridgeutil 1.1 . . . . 485
G.2.11 Pullparser 2.1.10 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 490
G.2.12 Xpp3 1.1.3.4d . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 491
G.2.13 jcifs 1.2.15, mm.mysql 2.0.14, P0f 2.06, jarapac,ncacn_np, ntlm-security jpcap
07.1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 492
G.2.14 Ojdbc 14.10g . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 499
G.2.15 JavaMail 1.3.1 Sun Microsystems, Inc. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
G.2.16 jcharts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
G.2.17 PyXML 0.8.4 Python License (CNRI Python License). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
G.2.18 IO-Stty .02 and IO-Tty1.02. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 508
G.2.19 Concurrent 1.3.4.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
G.2.20 Crypto ++ 5.2.1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 510
G.2.21 WinPcap 4.0.1a . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
G.2.22 Activation 1.0.2 package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 516
G.2.23 JAVA OPTIONAL PACKAGE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 518
G.2.24 jsp-api package.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 519
Contents 13
Page 14

Glossary 525
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
14 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 15
1
Introduction
This section contains the following information:
Section 1.1, “Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Home Window,” on page 15
Section 1.2, “System Monitor,” on page 16
Section 1.3, “Novell ZENworks Network Access Control v5.0 for v4.x Users,” on page 17
Section 1.4, “Overview,” on page 20
Section 1.5, “Technical Support,” on page 25
Section 1.6, “Additional Documentation,” on page 25
Section 1.7, “Installing and Upgrading,” on page 25
Section 1.8, “Conventions Used in This Document,” on page 26
Section 1.9, “Copying Files,” on page 28
Section 1.10, “Users’ guide online help,” on page 29
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1
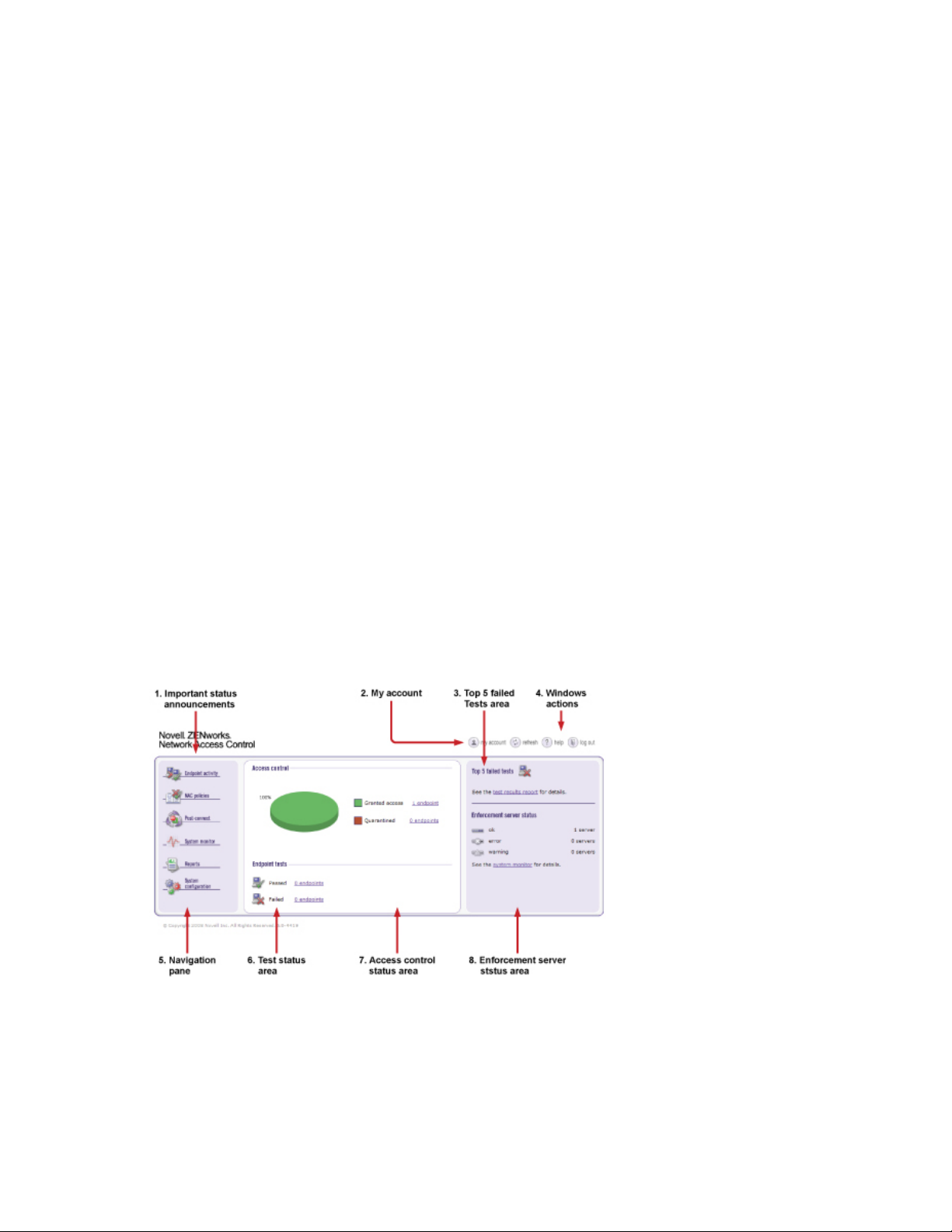
1.1 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Home Window
The Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Home window is a centralized management user
interface that allows you to quickly assess the status of your network. The following figure and list
describe and show the key features:
Figure 1-1 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Home Window
1. Important status announcements — If there is anything that needs your immediate attention,
a status announcement is displayed at the top of the window. Click clear to remove the
announcement.
Introduction
15
Page 16

2. My account — Click this icon to open the user account editing window. See Section 3.6, “User
Accounts,” on page 57 for details on creating and editing user accounts. You must have
administrator privileges to create user accounts; however, any user can edit their own account.
3. Top 5 failed tests area — The Top 5 failed tests area indicates the tests that fail the
most. Click on an endpoint number or the Test results report option to view details.
4. Window actions — Use these buttons to refresh the window, log out of the user interface, and
access online help.
5. Navigation pane — The menu items shown in this pane vary depending on your permission
level. See Section 3.7, “User Roles,” on page 63 for more information on permissions. You
must have administrator privileges to create and edit user roles. Once you select a menu item
from the navigation pane, use the bread crumbs at the top of the windows to navigate
throughout the user interface (Figure 1-1 on page 15).
6. Endpoint test status area — The Endpoint tests area displays the total number of
endpoints that Novell ZENworks Network Access Control has attempted to test, and what the
test status is for each endpoint. Click the number of endpoints to view details.
7. Access control status area — The Access control area displays the total number of
endpoints that have attempted to connect to your network, and what the access state is as a
percentage and as a number. Click on the number of endpoints to view details.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
8. Enforcement server (ES) status area — The Enforcement server status area
provides status on your ESs. Click the System monitor option to view details.
1.2 System Monitor
The System monitor window provides the following information:
Enforcement cluster name — The Enforcement clusters are listed by name in the order they
were created. Click on a cluster name to view cluster details. You must have cluster-editing
permissions to view and edit cluster details.
Server name by cluster — The servers for each cluster are listed by name in the order they
were created. Click on a server name to view server details. You must have cluster-editing
permissions to view and edit server details.
Cluster access mode — The cluster access mode is either normal or allow all. See
Section 3.2, “Enforcement Clusters and Servers,” on page 39 for instructions on making the
access mode selection.
Health status — Health status shows ok for servers with no problems, and either warning or
error for servers with problems. Click the server name to view details.
Upgrade status — Upgrade status shows the status of any upgrades in process.
% memory used — The amount of memory currently used by each server is shown as a
percentage of total memory available.
Endpoints tested/minute — The number of endpoints tested over the last 15 minutes or less.
Endpoints queued — The number of tests running or scheduled to run on that ES.
System load average — The number of processes waiting to run (top command). In Linux,
entering top at the command line returns a real-time look at processor activity.
16 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 17
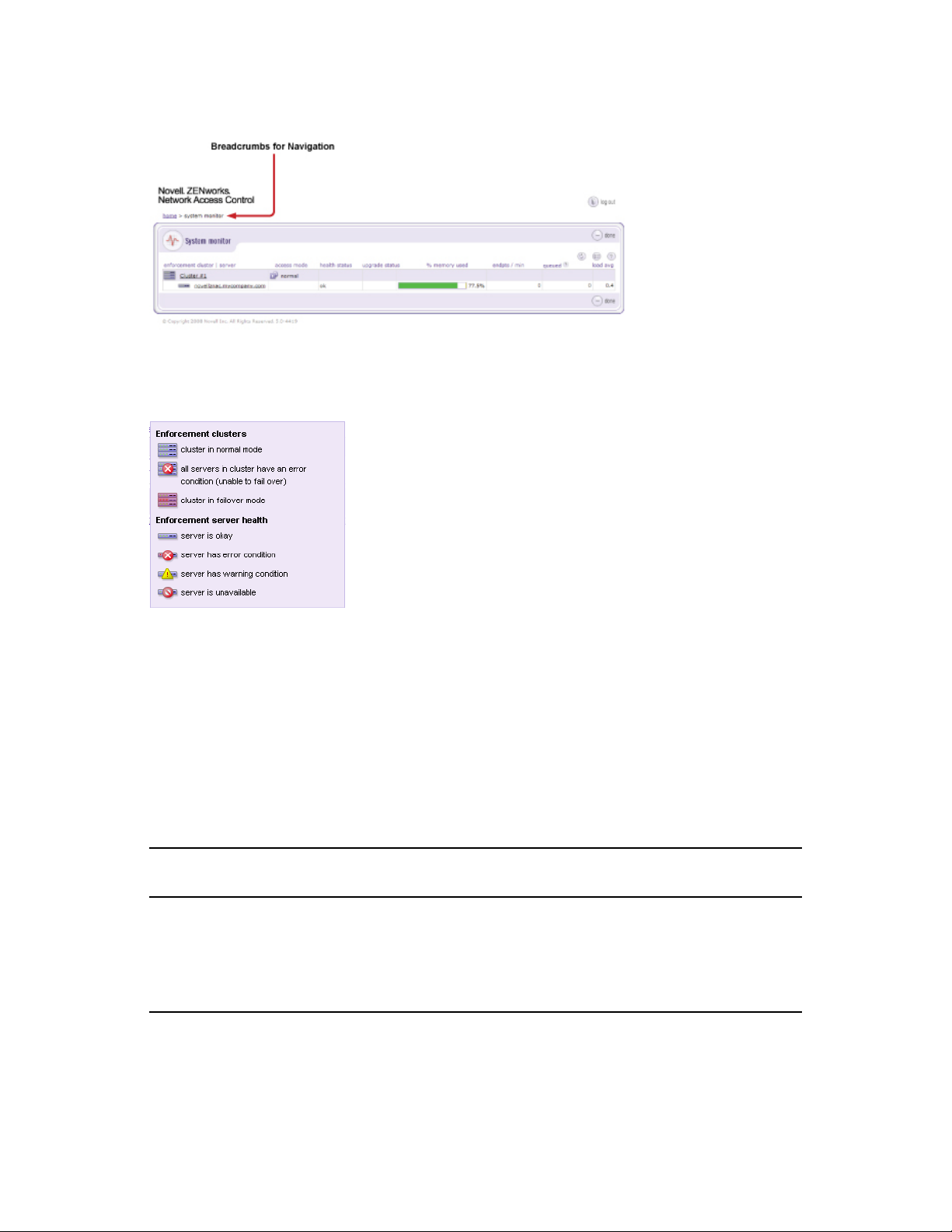
Figure 1-2 System Monitor Window
The following figure shows the legend for the System monitor window icons:
Figure 1-3 System Monitor Window Legend
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1.3 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control v5.0 for v4.x Users
The user interface has been completely redesigned in this release of Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control. The following table provides a quick-reference for users familiar with Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control v4.x. The first column shows the v4.x task with the
corresponding v5.0 user interface location in the second column.
Table 1-1 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control v5.0 for v4.x Users
Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control 4.x
System configuration
button
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control 5.0 Notes
System configuration menu option The System configuration
button was previously towards
the top right of the main window.
The System configuration menu
option is now at the bottom left
of the home window.
Introduction 17
Page 18

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control 4.x
General tab License key — System
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control 5.0 Notes
configuration>>License
Name of network — System
configuration>>Enforcement clusters
& servers
Default NAC policy — NAC policy
Administrator login — System
configuration>>User accounts
System tab
Interface and DNS configuration —
System configuration>>Select a
server>>Configuration
Date & time settings — System
configuration>>Management server
Quarantine tab
Accessible services and endpoints —
System configuration>>Accessible
services
configuration>>Enforcement clusters
& servers>>Select add an
Enforcement cluster or Select an
existing cluster>>Accessible services
OR System
Quarantine method — System
configuration>>Quarantining>>Select
a cluster to override the default setting
Quarantine area — System
configuration>>Quarantining>>DHCP
quarantine method>>Add a quarantine
area
Routing on the endpoint — System
configuration>>Quarantining>>DHCP
quarantine method>>Add a quarantine
area
The General tab tasks are now
on two different windows:
System configuration and NAC
policies.
The Network name no longer
applies; use cluster and server
names instead.
System tab tasks are on the
System configuration window.
Accessible services are set as
cluster defaults. These defaults
can be overridden when
creating or editing a cluster.
The default quarantine method
for all clusters is 802.1X. This
default can be overridden for all
clusters and per cluster.
The DHCP quarantine option
has two selections now: Static
routes on the endpoints or
Router access control lists.
Notification tab System configuration>>Notifications
System configuration>>Select an
Enforcement cluster>>Notifications
Tests tab
Check for test updates — System
configuration>>Test updates
Endpoint testing exemptions —
System configuration>>Exceptions
Thresholds tab The thresholds and stoplight have been
removed.
18 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
OR
Notifications are set as cluster
defaults, but can be overridden
when creating or editing a
cluster.
Exemptions is now called
exceptions.
The home window now provides
system status.
Page 19

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control 4.x
End-user access tab End-user testing methods — System
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control 5.0 Notes
End-user tab tasks are on the
configuration>>Testing methods
End-user testing options — System
configuration>>Testing methods
System configuration window.
They are set as cluster defaults,
but can be overridden when
creating or editing a cluster.
End-user testing screen customization
— System configuration>>End-user
screens
Enable test failed pop-up — System
configuration>>End-user screens
Credentials tab System configuration>>Agentless
credentials
Monitor and report zone Home window System status is shown on the
Windows domain credentials
are on the System configuration
window (Agentless credentials).
They are set as cluster defaults,
but can be overridden when
creating or editing a cluster.
RDBMS and LDAP credentials
have been removed.
home window and on the
System monitor window.
Manage system
zone>>System mode
Access policies zone Home window>>NAC policies Access policies are now called
View activity tab Home window>>Endpoint activity Devices are now called
N/A Home window>>System monitor
Access policy
editor>>Viewing last
device results
Reports tab Home window>>Reports
Proxy settings
(command line)
nac.properties file
updates
Backing up data
(command line)
System configuration>>Enforcement
clusters & servers>>Select or add an
Enforcement cluster>>General
Endpoint activity
System configuration>>Management server
and via the command line for times when
the license has not yet been validated.
Use a script to update properties files (nac-
es.properties and nacms.properties).
System configuration>>Maintenance
NAC policies.
Endpoints.
Proxy servers can be configured
for test updates and license
validation only.
Property file updates should no
longer be made directly, but
imported using the
setProperty.py script.
Introduction 19
Page 20

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control 4.x
Restoring data
(command line)
Diagnostics link Not currently available. May be added in a
Tests tab>>View test
update logs
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control 5.0 Notes
System configuration>>Maintenance
future release.
System configuration>>Test
updates>>View test update log.
1.4 Overview
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control protects the network by ensuring that endpoints are free
from threats and in compliance with the organization's IT security standards. Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control systematically tests endpoints—with or without the use of a client or
agent—for compliance with organizational security policies, quarantining non-compliant machines
before they damage the network.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control ensures that the applications and services running on
endpoints (such as LAN, RAS, VPN, and WiFi endpoints) are up-to-date and free of worms, viruses,
trojans, P2P and other potentially damaging software. It dramatically reduces the cost and effort of
securing your network's weakest links—the endpoints your IT group might not adequately control.
There are advantages and disadvantages inherent with each of the test method technologies. Having
a choice of testing solutions enables you to maximize the advantages and minimize the
disadvantages.
TIP: Agentless testing uses an existing Windows service (RPC). ActiveX testing uses an ActiveX
control. Novell agent testing installs an agent (NAC Agent) and runs as a new Windows service.
20 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 21
The trade-offs in the test methods are described in the following table:
Table 1-2 Test Methods
Trade-offs
Tes t method
Pros Cons
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Agentless Truly agentless, no install or
download.
No extra memory load on the client
machine.
Can begin testing, view test results,
and give network access without any
end-user interaction for endpoints on
your Windows domains.
Easiest of the three test methods to
deploy.
Saves administration time and is
therefore less expensive than
agent-based solutions.
ActiveX plug-in
No installation or upgrade to
maintain.
Supports all Windows operating
systems.
Only Internet Explorer application
access required through personal
firewall. Must open port 1500.
Requires RPC Service to be
available to the Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control server
(ports 139 or 445).
Requires file and print sharing to be
enabled.
Not supported by legacy Windows
operating systems and non-Windows
operating systems.
TM
If the endpoint is not on a domain,
the user must specify local
credentials. A user often does not
know what credentials to enter.
No retesting of endpoint once
browser is closed.
Not supported by non-Windows
operating systems.
Browser security settings must allow
ActiveX control operation of signed
and safe controls. This is the default
for the Internet zone. Raise the
Internet zone setting and make
Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control part of the trusted zone.
Requires interaction from
end-users—they must download the
control before they can access
network.
NAC Agent
Always available for retesting.
The agent is automatically updated
with product updates.
Supports all Windows platforms.
Install and upgrade to maintain.
Requires one-time interaction from
end-users—they must download and
install before they can access
network.
The following list highlights key features:
Enforcement options — Novell ZENworks Network Access Control provides multiple
enforcement options for quarantining endpoints that do not comply with your security policy
(Inline, DHCP, and 802.1X). This enables Novell ZENworks Network Access Control to
enforce compliance across complex, heterogeneous networks.
High availability and load balancing — A multi-server Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control deployment is mutually supporting. Should one server fail, other nodes within a cluster
will automatically provide coverage for the affected network segment.
Introduction 21
Page 22

Load balancing is achieved by an algorithm that spreads the endpoint testing load across all
ESs in a cluster.
Multiple-user, role-based access — In enterprise deployments numerous individuals, each
with varying responsibilities, typically require access to information within Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control. Role-based access enables system administrators to control who has
access to the data, the functions they are allowed to perform, and the information they can view
and act on. Role-based access ensures the integrity of the enterprise-wide Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control deployment and creates the separation of duties that conforms to
security best-practices.
Extensible — Novell ZENworks Network Access Control’s easy-to-use open API allows
administrators to create custom tests for meeting unique organizational requirements. The API
is fully exposed and thoroughly documented. Custom tests are created using scripts and can be
seamlessly added to existing policies.
Compatible with existing heterogeneous network infrastructure — No upgrades to your
existing network infrastructure are required.
Variety of enforcement options — Permit, deny, or quarantine based on test results.
Self-remediation — Reduces IT administration by empowering users to bring their machines
into compliance.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Subscription-based licensing — Includes all test updates and software upgrades.
1.4.1 The Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Process
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control administrators create NAC policies that define which
applications and services are permitted, and specify the actions to be taken when endpoints do not
comply. Novell ZENworks Network Access Control automatically applies the NAC policies to
endpoints as they log into the network, and periodically as the endpoints remain logged into the
network. Based on results, endpoints are either permitted or quarantined to a specific part of the
network, thus enforcing the organizational security standards. Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control tracks all testing and connection activity and produces a range of reports for auditors,
managers, and IT staff.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control performs pre-connect testing; when an endpoint passes
the NAC policy tests (or is otherwise granted access), the endpoint is allowed access to the network.
If you have external Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS) systems
that monitor your network for attacks, you can configure these external systems in Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control so they can request that Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control quarantine an endpoint after it has been connected (post-connect).
1.4.2 About Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
The following sections contain more information:
“NAC Policy Definition” on page 23
“Endpoint Testing” on page 23
“Compliance Enforcement” on page 24
“Automated and Manual Repair” on page 24
“Targeted Reporting” on page 24
22 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 23

NAC Policy Definition
NAC policies consist of individual tests that evaluate the security status of endpoints attempting to
access the network. Specific tests assess operating systems, verify that key hotfixes and patches
have been installed, ensure antivirus and other security applications are present and up-to-date,
detect the presence of worms, trojans, and viruses, and check for potentially dangerous applications
such as file sharing, peer-to-peer (P2P), or spyware. See Appendix B, “Tests Help,” on page 393 for
more information.
Key features include:
Out-of-the-box NAC policies — High, medium, and low security are ready to use with no
additional configuration required.
Standard and custom tests — Novell ZENworks Network Access Control comes with a
broad range of tests. You can also create custom tests through the Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control application programming interface (API).
Automatic test updates — Novell ZENworks Network Access Control is automatically
updated with tests that cover newly released patches, hotfixes, software updates, worms, and
trojans, and recommended security settings for common applications. New tests are
automatically added to the test database as frequently as hourly, ensuring immediate protection
against newly discovered threats.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Organization-specific policies — Any number of NAC policies can be created and tailored to
your organizational needs. Create policies for like endpoints (for example, all Windows 2000
workstations), for an IP range or specific IPs, or by geographic location.
Endpoint Testing
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control automatically tests all endpoints attempting to access
your network through a LAN, RAS, VPN, or WiFi connection. Tests are fast and you are kept
informed of test progress and results. After the initial compliance tests, Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control periodically tests endpoints that have been granted access to ensure that real-time
system changes do not violate the NAC policy.
TIP: Novell ZENworks Network Access Control passes approximately 9 to 16 kilobytes of total
data between a single endpoint and a single Novell ZENworks Network Access Control server for a
single testing session with the High Security NAC policy (approximately 20 tests). It typically takes
between 5 and 10 seconds to all tests in a policy on a 100Mb LAN. If your endpoints are taking
longer to test, there might be a configuration problem with DNS on the Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control server.
NOTE: If the end-user selects ActiveX test and then closes the browser, their endpoint is not
retested until the end-user opens another browser session, reloading the ActiveX agent.
Key features include:
Multiple test method options — Agentless, ActiveX, or NAC Agent. Select the most
appropriate method for your environment or endpoint.
Introduction 23
Page 24

Rapid testing and robust endpoint management — Thousands of endpoints can be tested
and managed simultaneously.
Continual testing — Endpoints are retested on an administrator-defined interval as long as
they remain connected to the network.
Compliance Enforcement
Based on endpoint test results, Novell ZENworks Network Access Control takes the appropriate
action. Endpoints that test compliant with the applied policy are permitted access. Non-compliant
endpoints are either quarantined, or are given access for a temporary period. Implement the
necessary fixes during this period.
Key features include:
Flexible enforcement options — Grant or quarantine access criteria is designated by the
administrator and driven by the criticality of selected tests and corporate security standards.
Manual overrides — Administrators can retest, quarantine, or grant access to endpoints on
demand.
User notifications — Users of non-compliant endpoints receive immediate notification about
the location of the endpoint deficiencies, as well as step-by-step information about
implementing the corrections to achieve compliance.
Administrator notifications — Administrators receive a variety of notifications and alerts
based on testing and access activity.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Graduated enforcement — Allows controlled system rollout.
Automated and Manual Repair
Self-remediation — End-users are notified of where their endpoints are deficient and provided
with remediation instructions.
Access grace period — Non-compliant endpoints are granted access for a temporary,
administrator-defined period to facilitate remediation.
Patch Management — Novell ZENworks Network Access Control can integrate with patch
management software, automating the process to get an endpoint updated and on the network.
Targeted Reporting
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control reports provide concise security status information on
endpoint compliance and access activity. Specific reports are available for auditors, managers, and
IT staff members.
For more information, seeChapter 14, “Reports,” on page 311.
24 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 25

1.5 Technical Support
Table 1-3 on page 25 lists the available technical support options.
Table 1-3 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Technical Support
Option Contact Hours
Call Novell Support (800) 858-4000 Monday - Friday
8:00 AM - 6:00 PM Mountain Time
Web support http://www.novell.com/support
(http://www.novell.com/support)
1.6 Additional Documentation
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control documentation is available in a number of media
formats and is accessible in a variety of ways:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Quick-start card — The Quick-start card provides a high-level overview of the physical
deployment options, software installation, post-installation configuration, the Users’ Guide,
and how to get support.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Installation Guide — The Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control Installation Guide is designed to get Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control up and running on your network quickly. It provides instructions on installation
and on system configuration. The Installation Guide is available on the installation CD in the /
docs directory.
Online help — Online help is an essential component that assists in the installation,
configuration, and ongoing management of Novell ZENworks Network Access Control. You
can access the online help by clicking the question mark displayed in the upper-right corner of
the primary interface elements. See Section 1.10, “Users’ guide online help,” on page 29 for
additional information.
1.7 Installing and Upgrading
Installation instructions are provided in the Installation Guide.
Upgrading is described in Section 3.5.10, “Checking for Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
Upgrades,” on page 56.
IMPORTANT: Installing third-party software on the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
server is not supported. If you install additional software on the Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control server, you need to remove it in order to troubleshoot any Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control issues, and it will likely be partially or fully overwritten during Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control release upgrades or patch installs, compromising the third-party software
functionality. Additionally, installing third-party software and/or modifying the Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control software can violate your license agreement. Please refer to the Novell
EULA: “Licenses” on page 461.
Introduction 25
Page 26

1.8 Conventions Used in This Document
The conventions used in this document are described in this section:
1.8.1 Navigation Paragraph
Navigation paragraphs provide a quick visual on how to get to the screen or area discussed.
Example:
Home window>>Configure system
1.8.2 Tip Paragraph
Tips provide helpful, but not required information.
Example:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
TIP: Hover the cursor over the “x dhcp servers with errors” text to get additional information in a
pop-up window.
1.8.3 Note Paragraph
Notes notify you of important information.
Example:
NOTE: If there is no activity for 30 minutes, the configuration window times out and you must log
in again.
1.8.4 Important Paragraph
Importants notify you of conditions that can cause errors or unexpected results.
Example:
IMPORTANT: Do not rename the files or they will not be seen by Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control.
1.8.5 Warning Paragraph
Warnings notify you of conditions that can lock your system or cause damage to your data.
Example:
WARNING: Do not log in using SSH—this kills your session and causes your session to hang.
26 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 27

1.8.6 Italic Text
Italic text is used in the following cases:
Showing emphasis —
Low — You are not protected from potentially unsafe macros. (Not recommended).
Introducing new terms —
The SMS server contains a database of logical groups with common attributes called
collections. SMS operates only on clients (endpoints) that are members of a collection.
Indicating document titles —
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Installation Guide
Indicating a variable entry in a command —
https://<IP_address>
/index.html
In this case, you must replace <IP_address> with the actual IP address, such as
10.0.16.99. Do not type the angled brackets.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1.8.7 Courier Font
Courier font is used in the following cases:
Indicating path names —
Change the working directory to the following:
C:\Program Files\<MyCompany>\
Indicating text; enter exactly as shown —
NAC Agent
Enter the following URL in the browser address field:
https://<IP_address>/index.html
In this case, you must replace <IP_address> with the actual IP address, such as
10.0.16.99. Do not type the angled brackets.
Indicating file names —
SAIASConnector.ini
1.8.8 Angled Brackets
Angled brackets enclose variable text that needs to be replaced with your specific values.
Example:
https://<IP_address>/index.html
In this case, you must replace <IP_address> with the actual IP address, such as 10.0.16.99. Do
not type the angled brackets.
Introduction 27
Page 28
1.8.9 Square Brackets
Square brackets are used in the following cases:
Indicating keys to press on the keyboard —
[Ctrl]+[Shift]+[r]
Indicating a variable section in a *.INI file —
[Global]
NASList=192.168.200.135
Indicating a list in a properties file —
Compliance.ObjectManager.DHCPConnectorServers=[192.168.51.130, 192.168.99.1]
1.8.10 Terms
Terms are defined in the “Glossary” on page 525.
Example:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
MAC Media Access Control — The unique number that identifies a physical
endpoint. Generally referred to as the MAC address.
1.9 Copying Files
Whenever you copy a file from one machine to another, copy it using a secure copy utility that uses
the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. The exact syntax of the copy command will vary based on the
utility you use.
Example:
1 Copy the /usr/local/nac/properties/NACAVPs.txt file from the Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control server to the ACS server using PSCP (or other secure copy
utility).
1.9.1 SCP
scp is a Linux/UNIX command used to copy files between Linux/UNIX machines. It has the
following syntax:
scp user@source:/directory/file user@destination:/directory/file
scp is included with Linux/UNIX.
1.9.2 PSCP
pscp is a program used to copy files between Windows and Linux/UNIX machines.
To use pscp, you must first save it from the following location to the Windows machine:
28 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 29

http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html (http://
www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html)
Next, open a DOS (command) window on the Windows machine, and enter the commands as
follows:
To copy a file from a Linux machine to a Windows machine, enter the following:
<pscp directory>\pscp fred@example.com:/etc/hosts c:\temp\examplehosts.txt
You will be prompted to enter a password for the Linux/UNIX machine.
To copy a file from a Windows machine to a Linux machine, enter the following:
<pscp directory>\pscp c:\documents\foo.txt fred@example.com:/tmp/foo
You will be prompted to enter a password for the Linux/UNIX machine.
NOTE: You can either enter the path to the PSCP.EXE file as part of the command, or cd to the
directory where you saved the PSCP.EXE file before entering the pscp command.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1.10 Users’ guide online help
In Novell ZENworks Network Access Control, the help links in the product open an HTML version
of the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control documents. The PDF version is still available in
the /docs directory on the CD, and by clicking the Open Users’ guide or Open
Installation guide PDF links in the HTML document. This section briefly describes the key
components to the HTML version. The online help contains the same content as this Users’ guide.
Introduction 29
Page 30
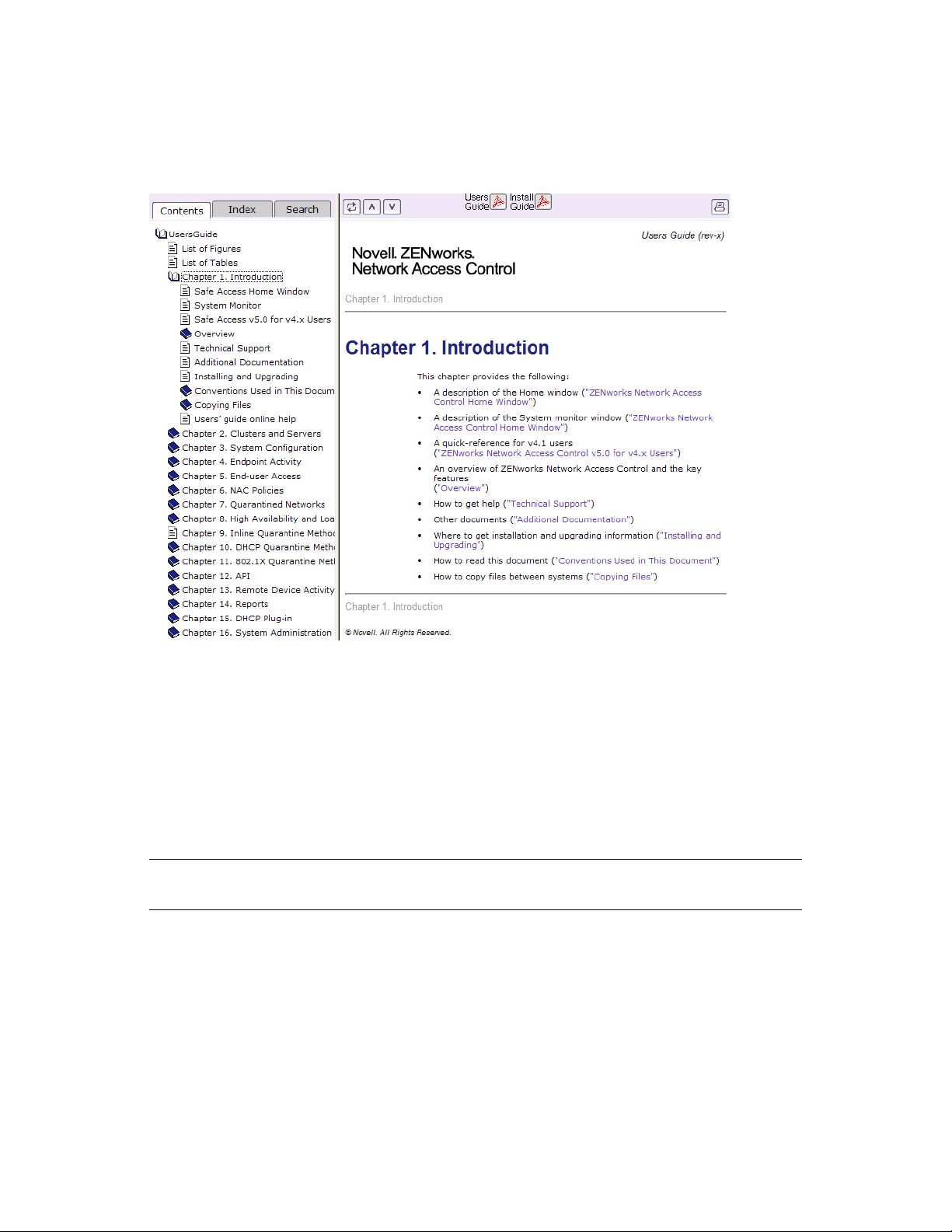
When you click a help link from within Novell ZENworks Network Access Control, the help topic
opens in a new window, as shown in the following figure:
Figure 1-4 Online Help
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
The following options are available:
Previous — Click the upward pointing icon to go to the previous page.
Next — Click the downward pointing icon to go to the next page.
Print topic — Click the printer icon to print the current topic.
Bread crumbs — Click on any of the non-graylinks in the bread crumbs trail to go to that
section.
Open PDF — Click the Open PDF file link to open the PDF file.
TIP: To print the entire document, open and print the PDF file. Selecting the print icon in the HTML
version will print only the topic you are viewing.
Click anywhere in the Contents pane to navigate through the document.
30 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 31

To view the index:
Online help document>>Show navigation icon>>Index tab
Figure 1-5 Index Tab
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click on a letter link at the top of the index column to see the index entries.
2 Click on an index entry to see the location in the text.
3 Click on cross reference items in highlighted text to see more information on these items.
Introduction 31
Page 32

To search for a term:
Online help document>>Shown navigation icon>>Search tab
Figure 1-6 Search tab
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter a term in the search box.
2 Click Go.
3 Click on one of the results returned to display it in the right-side pane.
4 Click on the red arrow to see the contents of the collapsed section of the document.
NOTE: Red arrows that point to the right denote collapsed sections. The default is for these sections
to show as closed. Clicking on these red arrows turns them downward to open their content.
32 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 33

2
Clusters and Servers
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control introduces clusters and servers. A cluster is a logical
grouping of one or more ESs that are managed by one MS.
A single-server installation is one where the MS and ES are on one server. The ES is assigned to a
Default cluster. This configuration is illustrated in Figure 2-1 on page 34.
A multiple-server installation is one where the MS is on one server and there are one or more ESs on
separate servers. Each ES must be assigned to a cluster. This configuration is illustrated in Figure 2-
2 on page 35.
The responsibilities of the MS and ES are as follows:
MS
Configuration
NAC policies
Quarantining
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2
Endpoint activity
License
Test updates
ES
Testing
Access control
The quarantine method is defined per cluster; all of the ESs in a given cluster use the same
quarantine method (Inline, DHCP, or 802.1X). When using multiple clusters, each cluster can have a
different quarantine method. Clusters cooperate to test and control access to the network, although
the ESs in each cluster are not able to communicate with any ES in any other cluster.
The following sections contain more information:
Section 2.1, “Single-server Installation,” on page 34
Section 2.2, “Multiple-server Installations,” on page 34
Clusters and Servers
33
Page 34

2.1 Single-server Installation
The simplest installation is where the MS and ES are installed on the same physical server as shown
in the following figure:
Figure 2-1 Single-server Installation
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2.2 Multiple-server Installations
By using at least three servers, one for the MS and two for ESs, you gain the advantage of high
availability and load balancing.
High availability is where ESs take over for any other ES or servers that become unavailable. Load
balancing is where the testing of endpoints is spread evenly over all of the ESs. A three-server
installation is shown in the following figure:
34 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 35

Figure 2-2 Multiple-server Installation
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
When your network is more complex, you can continue to add clusters as shown in the following
figure:
Figure 2-3 Multiple-server, Multiple-cluster Installation
The system configuration area allows you to select default settings for all clusters, as well as
override the default settings on a per-cluster basis. See Chapter 3, “System Configuration,” on
page 37 for task-based instructions.
Clusters and Servers 35
Page 36

The following recommendations should be followed when configuring your network for best
performance results:
A maximum of 300,000 endpoints per MS (4 GB RAM required)
A maximum of five ESs per cluster
A maximum of 3000 endpoints per ES
There is no inherent limitation in the number of clusters per MS
When these recommendations are followed, the following applies:
80% of the 3000 endpoints will be tested in 30 seconds or less
All endpoints are returned to the proper status within 15 minutes after a network recovery
(power failure, all endpoints attempting to reconnect, 3000 endpoints per ES)
NOTE: The minimum and recommended hardware requirements are listed in Section 16.8, “System
Requirements,” on page 341; however, Novell has tested and certified Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control on the following systems:
Dell Xeon 5130, 2 GB RAM, 73 GB Hard drive, 15 k SAS, 3 NICs
Dell Xeon E5335, 4 GB RAM, 146 GB Hard drive, 15 k SAS, 3 NICs
Dell Xeon E5335, 8 GB RAM, 300 GB Hard drive, 15 k SAS, 3 NICs
Dell Dual Xeon E5335, 8 GB RAM, 600 GB Hard drive, RAID 10, 3 NICs, 2 PSU
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
36 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 37

3
System Configuration
The System configuration window allows the system administrator to set the operating
parameters for Novell ZENworks Network Access Control.
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.1, “Introduction,” on page 38
Section 3.2, “Enforcement Clusters and Servers,” on page 39
Section 3.3, “Enforcement Clusters,” on page 39
Section 3.4, “Enforcement Servers,” on page 43
Section 3.5, “Management Server,” on page 50
Section 3.6, “User Accounts,” on page 57
Section 3.7, “User Roles,” on page 63
Section 3.8, “License,” on page 67
Section 3.9, “Test Updates,” on page 68
Section 3.10, “Quarantining, General,” on page 70
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3
Section 3.11, “Quarantining, 802.1X,” on page 72
Section 3.12, “Quarantining, DHCP,” on page 104
Section 3.13, “Quarantining, Inline,” on page 108
Section 3.14, “Post-connect,” on page 109
Section 3.15, “Maintenance,” on page 114
Section 3.16, “Downloading Support Packages,” on page 116
Section 3.17, “Cluster Setting Defaults,” on page 116
Section 3.18, “Logging,” on page 131
Section 3.19, “Advanced Settings,” on page 133
System Configuration
37
Page 38

3.1 Introduction
User logins and associated user roles determine the access permissions for specific functionality
within Novell ZENworks Network Access Control. The following table shows the default home
window menu options that are available by user role:
Table 3-1 Default Menu Options
User role Home window menu options available
System Administrator Endpoint activity
NAC policies
System monitor
Reports
System configuration
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Cluster Administrator
Help Desk Technician
View-Only User
Endpoint activity
System monitor
Reports
Enforcement clusters & servers
Endpoint activity
Reports
Endpoint activity
Reports
Only a system administrator can assign access permissions and access the System
configuration window. See Figure 1-1 on page 15 for the Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control home window of a user with system administration permissions. If you do not see the
System configuration menu option, you do not have system administrator permissions.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control configuration includes the following:
Enforcement clusters & servers — Section 3.2, “Enforcement Clusters and Servers,” on
page 39
MS — Section 3.5, “Management Server,” on page 50
User accounts — Section 3.6, “User Accounts,” on page 57
User roles — Section 3.7, “User Roles,” on page 63
License — Section 3.8, “License,” on page 67
Test updates — Section 3.9, “Test Updates,” on page 68
Quarantining — Section 3.10, “Quarantining, General,” on page 70
Maintenance — Section 3.15, “Maintenance,” on page 114
Cluster setting defaults
Testing Methods — Section 3.17.1, “Testing Methods,” on page 117
Accessible services — Section 3.17.3, “Accessible Services,” on page 119
Exceptions — Section 3.17.4, “Exceptions,” on page 121
38 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 39

Notifications — Section 3.17.5, “Notifications,” on page 123
End-user screens — Section 3.17.6, “End-user Screens,” on page 125
Agentless credentials — Section 3.17.7, “Agentless Credentials,” on page 127
Logging — Section 3.18, “Logging,” on page 131
Advanced — Section 3.19, “Advanced Settings,” on page 133
NOTE: You can override any of the cluster default settings on a per-cluster basis.
3.2 Enforcement Clusters and Servers
The Enforcement clusters & servers menu option (Figure 3-2 on page 43) is where
you configure Enforcement clusters and servers. You can perform the following tasks:
Enforcement clusters
Add, edit, or delete Enforcement clusters
Set operating parameters for specific Enforcement clusters, which differ from the default
Enforcement cluster and server settings set up on the System configuration
window
View available Enforcement clusters and associated servers
View status of Enforcement clusters and servers
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Select cluster access mode (normal or allow all)
ESs
Add, edit, or delete ESs
Set ES network settings, date and time, and password
View available ESs
View status, memory usage, and disk space usage of ESs
3.3 Enforcement Clusters
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.3.1, “Adding an Enforcement Cluster,” on page 40
Section 3.3.2, “Editing Enforcement Clusters,” on page 42
Section 3.3.3, “Viewing Enforcement Cluster Status,” on page 42
Section 3.3.4, “Deleting Enforcement Clusters,” on page 43
System Configuration 39
Page 40

3.3.1 Adding an Enforcement Cluster
To add an Enforcement cluster:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
Figure 3-1 System Configuration, Enforcement Clusters & Servers
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click Add an Enforcement cluster in the Enforcement clusters &
servers area. The Add Enforcement cluster window appears. The General area is
displayed by default.
40 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 41

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1a Enter a name for the Enforcement cluster in the Cluster name field.
1b Select a NAC policy group from the NAC policy group drop-down list (see
Chapter 6, “NAC Policies,” on page 201).
2 Click Quarantining in the Add Enforcement cluster window. Complete the steps
described in Section 3.10, “Quarantining, General,” on page 70.
TIP: You can also access the quarantine area Enforcement cluster by clicking Quarantining in
the System configuration window (see Section 3.10, “Quarantining, General,” on page 70 for
more information).
3 The following cluster settings take on default values set from the System configuration
window. To set up operating parameters that differ from those default settings, select the menu
item of the settings you want to change, then select the For this cluster, override
the default settings check box, and make the desired changes. Refer to the sections
listed below to set up the default values, or for more information on the specific settings.
Testing methods — See Section 3.17.1, “Testing Methods,” on page 117
Accessible services — See Section 3.17.3, “Accessible Services,” on page 119
Exceptions — See Section 3.17.4, “Exceptions,” on page 121
Notifications — See Section 3.17.5, “Notifications,” on page 123
End-user screens — See Section 3.17.6, “End-user Screens,” on page 125
Agentless credentials — See Section 3.17.7, “Agentless Credentials,” on page 127
Logging — See Section 3.18, “Logging,” on page 131
Advanced — See Section 3.19, “Advanced Settings,” on page 133
System Configuration 41
Page 42

3.3.2 Editing Enforcement Clusters
To edit the Enforcement clusters settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
1 Click the cluster you want to edit. The Enforcement cluster window appears, as shown
in Figure 3-2 on page 43.
2 Click a menu option to access the cluster settings:
General
Quarantining
Testing methods
Accessible services
Exceptions
Notifications
End-user screens
Agentless credentials
Logging
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Advanced
3 Enter or change information in the fields you want to modify, as described in Section 3.3.1,
“Adding an Enforcement Cluster,” on page 40.
4 Click ok.
3.3.3 Viewing Enforcement Cluster Status
There are two ways Novell ZENworks Network Access Control provides Enforcement cluster
status:
The icons next to the cluster name (see Figure 3-3 on page 44)
The Enforcement cluster window (see the following steps)
To view Enforcement cluster statistics:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
42 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 43

Click a cluster name, for example Austin. The Enforcement cluster window appears:
Figure 3-2 Enforcement Cluster, General
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
The statistics shown in this window are per cluster, where the statistics shown in the Home window
are system-wide. See Section 1.2, “System Monitor,” on page 16 for column descriptions.
3.3.4 Deleting Enforcement Clusters
NOTE: Enforcement clusters need to be empty before the delete option appears next to the name in
the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control user interface.
To delete Enforcement clusters:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
1 Click delete next to the cluster you want to remove. The Delete Enforcement
cluster confirmation window appears.
2 Click yes. The System configuration window appears (Figure 3-3 on page 44).
3.4 Enforcement Servers
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.4.1, “Adding an ES,” on page 44
Section 3.4.2, “Cluster and Server Icons,” on page 45
Section 3.4.3, “Editing ESs,” on page 45
Section 3.4.4, “Changing the ES Network Settings,” on page 46
Section 3.4.5, “Changing the ES Date and Time,” on page 47
Section 3.4.6, “Modifying the ES SNMP Settings,” on page 47
Section 3.4.7, “Modifying the ES root Account Password,” on page 48
Section 3.4.8, “Viewing ES Status,” on page 48
System Configuration 43
Page 44

Section 3.4.9, “Deleting ESs,” on page 49
Section 3.4.10, “ES Recovery,” on page 49
3.4.1 Adding an ES
To add an ES :
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
Figure 3-3 System Configuration, Enforcement Clusters & Servers
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click Add an Enforcement server in the Enforcement clusters & servers
area. The Add Enforcement server window appears.
Figure 3-4 Add Enforcement Server
44 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 45

2 Select a cluster from the Cluster drop-down list.
3 Enter the IP address for this ES in the IP address text box.
4 Enter the fully qualified hostname to set on this server in the Host name text box.
5 Enter one or more DNS resolver IP addresses, separated by a commas, semicolons, or spaces in
the DNS IP addresses text box. For example, 10.0.16.100,10.0.1.1
6 Enter the password to set for the root user of the ES server’s operating system in the Root
password text box.
7 Re-enter the password to set for the root user of the ES server’s operating system in the Re-
enter root password text box.
8 Click ok.
3.4.2 Cluster and Server Icons
To view the cluster and server icons:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Move the mouse over the legend icon. The legend pop-up window appears.
2 Move the mouse away from the legend icon to hide pop-up window.
Figure 3-5 Enforcement Cluster Legend
3.4.3 Editing ESs
To edit ES settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
1 Click the ES you want to edit. The Enforcement server window appears, as shown in
Figure 3-6 on page 46.
System Configuration 45
Page 46

2 Click the Configuration menu option to access the Enforcement Server’s settings. The
Configuration area is displayed:
Figure 3-6 Enforcement Server
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3 Edit the following settings:
ES Network settings — Section 3.4.4, “Changing the ES Network Settings,” on page 46
ES Date and time — Section 3.4.5, “Changing the ES Date and Time,” on page 47
ES SNMP settings — Section 3.4.6, “Modifying the ES SNMP Settings,” on page 47
Other settings — Section 3.4.7, “Modifying the ES root Account Password,” on page 48
4 Click ok.
3.4.4 Changing the ES Network Settings
IMPORTANT: Back up your system immediately after changing the MS or ES IP address. If you
do not back up with the new IP address, and later restore your system, it will restore the previous IP
address which can show an ES error condition and cause authentication problems. See Section 3.15,
“Maintenance,” on page 114 for instructions on backing up and restoring your system.
To change the ES network settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers>>Select an
ES>>Configuration
46 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 47

Modify any of the following Network settings you want to change:
Enter a new ES in the Host name text field. For example, garp.mycompany.com
Enter a new ES address in the IP address text field. For example, 192.168.153.35
Enter a new netmask in the Network mask text field. For example, 255.255.255.0
Enter a new gateway in the Gateway IP address text field. For example
192.168.153.2
Enter one or more DNS resolver IP addresses, separated by commas, semicolons, or spaces in
the DNS IP addresses text box. For example: 10.0.16.100,10.0.1.1
NOTE: The Novell ZENworks Network Access Control ESs host name must be a fully qualified
domain name (FQDN). For example, the FQDN should include the host and the domain name—
including the top-level domain.
For example, waldo.mycompany.com. Select names that are short, easy to remember, have no
spaces or underscores, and the first and last character cannot be a dash (-).
NOTE: You cannot change the ES IP address for a single-server installation. You can change the
MS IP address for a single-server installation.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3.4.5 Changing the ES Date and Time
To change the ES date and time:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers>>Select an
ES>>Configuration
1 Select a Region from the Region drop-down list in the Date and time area.
2 Select a time zone from the Time zone drop-down list.
3 Click ok.
NOTE: See Section 3.5.7, “Selecting the Time Zone,” on page 55 for information on changing the
time zone settings for the MS.
WARNING: Manually changing the date/time by a large amount (other than a time zone change)
will require a restart of all servers. Rolling back the clock will have adverse effects on the system.
3.4.6 Modifying the ES SNMP Settings
To change the ES SNMP settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers>>Select an
ES>>Configuration
1 Select the Enable SNMP check box.
System Configuration 47
Page 48

2 Enter a Read community string, such as Public2.
3 Enter the Allowed source network. This value must be either default or a network
specified in CIDR notation.
3.4.7 Modifying the ES root Account Password
To change the ES root account password:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers>>Select an
ES>>Configuration
1 Enter the new password in the Root password text box in the Other settings area.
2 Re-enter the password in the Re-enter root password text box.
3 Click ok.
3.4.8 Viewing ES Status
There are two ways Novell ZENworks Network Access Control provides ES status:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
The icons next to the server name (see Figure 3-5 on page 45)
The Status window (see the following steps). The Enforcement server window
allows you to view the following information:
Health status
Upgrade status
Process/thread status
System load average for the server
Current endpoints being tested/minute for the server
Percentage of memory used on the server
Disk space usage for the server
48 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 49

To view ES status:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
1 Click the server for which you want to view the status. The Enforcement server window
appears:
Figure 3-7 Enforcement Server, Status
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Click ok or cancel.
3.4.9 Deleting ESs
NOTE: Servers need to be powered down for the delete option to appear next to the name in the
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control user interface.
To delete ESs:
Home window>>System configuration>>Enforcement clusters & servers
1 Click delete next to the server you want to remove from the cluster. The Delete
Enforcement server confirmation window appears.
2 Click yes. The System configuration window appears.
3.4.10 ES Recovery
If an existing ES goes down and comes back up, it can participate in its assigned cluster, even if the
MS is not available.
When a new ES is created, the MS must be available before the ES can participate in a cluster.
System Configuration 49
Page 50

3.5 Management Server
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.5.1, “Viewing Network Settings,” on page 51
Section 3.5.2, “Modifying MS Network Settings,” on page 52
Section 3.5.3, “Selecting a Proxy Server,” on page 53
Section 3.5.4, “Setting the Date and Time,” on page 53
Section 3.5.5, “Automatically Setting the Time,” on page 54
Section 3.5.6, “Manually Setting the Time,” on page 54
Section 3.5.7, “Selecting the Time Zone,” on page 55
Section 3.5.8, “Enabling SNMP,” on page 55
Section 3.5.9, “Modifying the MS root Account Password,” on page 55
Section 3.5.10, “Checking for Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrades,” on
page 56
Section 3.5.11, “Changing the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrade Timeout,”
on page 56
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
50 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 51

3.5.1 Viewing Network Settings
To view MS status:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
Figure 3-8 System Configuration, Management Server
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 51
Page 52

1 Server status is shown in the Network settings area.
2 Click ok or cancel.
3.5.2 Modifying MS Network Settings
IMPORTANT: Back up your system immediately after changing the MS or ES IP address. If you
do not back up with the new IP address, and later restore your system, it will restore the previous IP
address which can show an ES error condition and cause authentication problems. See Section 3.15,
“Maintenance,” on page 114 for instructions on backing up and restoring your system.
To modify MS network settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
WARNING: Changing the MS network settings will cause the network interface to restart.
1 Click edit network settings in the Network settings area.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Figure 3-9 Management Server Network Settings
2 Enter the values you want to modify:
Enter a new name in the Host name text field. For example, garp.mycompany.com
NOTE: Select names that are short, easy to remember, have no spaces or underscores, and
the first and last character cannot be a dash (-).
Enter a new address in the IP address text field. For example, 192.168.153.35
Enter a new netmask in the Network mask text field. For example, 255.255.255.0
Enter a new gateway in the Gateway IP address text field. For example
192.168.153.2
Enter one or more DNS resolver IP addresses, separated by commas, semicolons, or
spaces in the DNS IP addresses text box. For example:
10.0.16.100,10.0.1.1
3 Click ok.
52 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 53

3.5.3 Selecting a Proxy Server
Connecting to the Internet is necessary for updating tests, validating license keys, and sending
support packages.
To select a proxy server:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Select Use a proxy server for Internet connections.
2 Enter the IP address or hostname of the server that will act as the proxy for Internet connections
in the Proxy server IP address text field.
3 Enter the port used for connecting to the proxy server in the Proxy server port text field.
4 If your proxy server requires authentication, select the Proxy server is
authenticated check box.
4a Authentication method — Select the scheme used to authenticate credentials on the
proxy server. The following methods are supported:
Basic (not recommended) — The original and most compatible authentication
scheme for HTTP. Also the least secure because it sends the user ID and password to
the server unencrypted.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Digest — Added in the HTTP 1.1 protocol, this scheme is significantly more secure
than basic authentication because it never transfers the actual password across the
network, but instead uses it to encrypt a "nonce" value sent from the server.
Negotiable — Using this scheme, the client and the proxy server negotiate a scheme
for authentication. Ultimately, either the basic or digest scheme will be used.
4b Enter the ID of a user account on the proxy server in the User name text box.
4c Enter the password of the user account specified in the User name text box in the
Password text box.
4d Re-enter the password.
5 Click ok.
3.5.4 Setting the Date and Time
The Date and time area allows you to configure the following:
Allow automatic synchronization with an NTP server
Manually set date and time for the MS
Edit date and time:
Set time zone
Set date
Set time
NOTE: Date and time settings are applied to the MS; however, you can set the time zone for each
ES.
System Configuration 53
Page 54

3.5.5 Automatically Setting the Time
To automatically set the time:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Select Automatically receive NTP updates from and enter one or more
Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers, separated by commas. The NTP protocol allows Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control to synchronize its date and time with other endpoints on
your network. For example, time.nist.gov.
2 Click ok.
TIP: Use of NTP is strongly recommended.
3.5.6 Manually Setting the Time
To manually set the time:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Select Manually set date & time.
2 Click edit. The Date and time window appears:
Figure 3-10 Date & Time
3 Select the correct date and time.
4 Click ok.
5 Click ok.
IMPORTANT: Manually changing the date/time (other than a time zone change) a large amount
will require a restart of all servers. Rolling back the clock will have adverse effects on the system.
54 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 55

3.5.7 Selecting the Time Zone
To set the time zone:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Select the following:
1a Select a region from the Region drop-down list in the Date and time area.
1b Select a time zone from the Time zone drop-down list.
2 Click ok.
3.5.8 Enabling SNMP
To select SNMP settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server>>SNMP settings
1 Select the Enable SNMP check box to select the SNMP settings.
1a Enter the SNMP read community string.
1b Enter the SNMP allowed source network. The value must be either “default” or a network
specified in CIDR notation.
2 Select the Outgoing SNMP notifications check box.
3 Enter a comma-separated list of IP address or hostnames that can receive the SNMP
notifications.
4 Enter the community string used to authorize SNMP notifications from Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
5 Select one or both of the following:
5a Select the Resend notifications check box and enter the resend interval, for
example 60.
NOTE: NAC policy tests can be configured such that if an endpoint fails the test, it will
be granted network access temporarily. In these cases, it might be desirable not to send an
SNMP notification.
5b Select the Do not send notifications when an endpoint has been
granted temporary network access check box to disable these
notifications.
3.5.9 Modifying the MS root Account Password
To change the MS root account password:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Enter the new password in the Root password text box in the Other settings area.
2 Re-enter the password in the Re-enter root password text box.
3 Click ok.
System Configuration 55
Page 56

3.5.10 Checking for Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrades
To check for system upgrades:
Home window>>System configuration>>Management server
1 Click check for upgrades in the System upgrade area. A progress window appears.
2 If your license is expired, you will get a System upgrade error window that provides
instructions on how to renew your license.
3 A status window appears indicating if upgrades are available.
3a If no upgrades are available, click ok to clear the status window.
3b Click ok to return to System configuration.
3c If an upgrade is available, click yes to upgrade your system.
IMPORTANT: Installation of an upgrade can take several hours to download all the software. You
can continue to use Novell ZENworks Network Access Control during the download process.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control will automatically shutdown and restart after the
software downloads.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
TIP: Since upgrading can take longer than the default timeout (45 minutes) setting of the Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control Update, Novell recommends that you increase the timeout
value when you have limited bandwidth by performing the steps described in Section 3.5.11,
“Changing the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrade Timeout,” on page 56.
3.5.11 Changing the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Upgrade Timeout
Since upgrading can take longer than the default timeout (45 minutes) setting of the Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control Update, Novell recommends that you increase the timeout
value when you have limited bandwidth by performing these steps.
To change the inactivity timeout value for upgrades:
Command window
1 Log in to the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control server as root, either using SSH or
directly with a keyboard.
2 Enter the following at the command line:
setProperty.py -m Compliance.UpgradeManager.UpgradeTimeout=<minutes>
Where:
<minutes> is the number of minutes of inactivity Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
will wait before assuming the upgrade failed. For example, 30. The default value is 45.
56 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 57

3.6 User Accounts
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control allows you to create multiple user accounts. User
accounts provide and limit access to Novell ZENworks Network Access Control functions based on
permissions (user roles) and clusters assigned. See Section 3.7, “User Roles,” on page 63 for more
information on setting permissions for the user roles.
The User accounts menu option allows you to do the following:
View user accounts
Search by user ID, user name, or email address
Add a user account
Edit a user account
Delete a user account
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.6.1, “Adding a User Account,” on page 58
Section 3.6.2, “Searching for a User Account,” on page 60
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Section 3.6.3, “Sorting the User Account Area,” on page 60
Section 3.6.4, “Copying a User Account,” on page 61
Section 3.6.5, “Editing a User Account,” on page 62
Section 3.6.6, “Deleting a User Account,” on page 62
System Configuration 57
Page 58

3.6.1 Adding a User Account
To add a user account:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
Figure 3-11 System Configuration, User Accounts
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click Add a user account. The Add user account window appears:
58 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 59

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Enter the following information:
User ID — The user ID used to log into Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
Password — The password used to log into Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
Full name — The name associated with the user account
Email address — The email address used for notifications
3 Select an Account status:
enabled — This status allows an account to log into the user interface
disabled — This status prevents an account from logging into the user interface
4 In the User roles area, select one of the following default roles for the user account: (See
Section 3.7, “User Roles,” on page 63 for more information about user roles and permissions
associated with user roles.)
Cluster Administrator
View-Only User
System Administrator
Help Desk Technician
You can select a custom user role if you have created any.
NOTE: Users must be assigned at least one role.
5 In the Clusters area, select a cluster or clusters.
System Configuration 59
Page 60

NOTE: Users must be assigned at least one Enforcement cluster.
6 Click ok.
Table 3-2 Default User Roles
User Role Name Description
Cluster Administrator For their clusters, users having this role can configure their assigned
clusters, view endpoint activity, change endpoint access control, retest
endpoints, and generate reports.
View-Only User Users having this role can view endpoint activity and generate reports
about their clusters.
System Administrator Users having this role have all permissions.
Help Desk Technician For their clusters, users having this role can view endpoint activity,
change endpoint access control, retest endpoints, and run reports.
User-defined role Create your own user roles and definitions.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3.6.2 Searching for a User Account
To search for a user account:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
1 Select one of the following from the Search drop-down list:
user ID
full name
email address
2 Enter the text to search for in the for field.
3 Click search.
TIP: Click reset to clear the text field and to refresh the display to show all accounts after a
search.
3.6.3 Sorting the User Account Area
To sort the user account area:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
Click the column heading for user id, full name, email address, user roles, or
clusters. The user accounts reorder according to the column heading selected. Click the column
heading again to change from ascending to descending.
60 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 61

3.6.4 Copying a User Account
To copy a user account:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
1 Click copy next to the user account you want to duplicate. The Copy user account
window appears. The account information is duplicated from the original account.
Figure 3-12 Copy User Account
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Enter the User ID of the new account.
3 Enter the Password.
4 Re-enter the password.
5 Select the Account status (enable or disable).
6 Select the User role for the account.
7 Select the Clusters that the user account can access.
8 Click ok.
System Configuration 61
Page 62

3.6.5 Editing a User Account
To edit a user account:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
1 Click the name of the user account that you want to edit. The User account window
appears:
Figure 3-13 User Account
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Change or enter information in the fields you want to change. See Section 3.6.1, “Adding a
User Account,” on page 58 for information on user account settings.
3 Click ok.
3.6.6 Deleting a User Account
You must always have at least one account with System Administrator permissions.
IMPORTANT: Do not delete or edit the account with which you are currently accessing the
interface. Doing so can produce an error and lock you out of the interface until your session has
timed out.
62 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 63

To delete a user account:
Home window>>System configuration>>User accounts
1 Click delete next to the user account you want to remove. The Delete user account
confirmation window appears.
2 Click yes.
3.7 User Roles
The User roles menu option allows you to configure the following:
View current user roles and details associated with those roles
Add a new user role
Name the new user role
Provide a detail description for the new user role
Assign permissions to the new user role
Edit a user role
Edit the name of the user role
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Edit the detail description of the user role
Edit the assigned permissions for the user role
Delete a user role
System Configuration 63
Page 64

3.7.1 Adding a User Role
To add a user role:
Home window>>System configuration>>User roles
Figure 3-14 System Configuration, User Roles
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click add a user role in the User roles area. The Add user role window
appears.
64 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 65

novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Enter a descriptive name in the Role name field.
3 Enter a description of the role in the Description field.
4 Select the permissions for the user role. For more information about permissions, the following
table:
Table 3-3 User Role Permissions
Permission Description
Configure clusters Allows you to add clusters, configure the settings of all your
assigned clusters, and delete any of your clusters.
Configure servers Allows you to configure all servers within your clusters
Configure the system Allows you to configure all system-level settings
View system alerts Allows you to view system alerts on your home screen
Generate reports Allows you to generate reports about any of your assigned clusters
Manage NAC policies Allows you to manage the NAC policies for all of your clusters
View endpoint activity Allows you to view details about all endpoints in your clusters
Monitor system status Allows you to monitor the system status
Control Access Allows you to quarantine or grant network access to endpoints in
your clusters
Retest endpoints Allows you to have endpoints in your clusters retested
System Configuration 65
Page 66

3.7.2 Editing User Roles
NOTE: You cannot edit the System Administrator user role.
To edit user roles:
Home window>>System configuration>>User roles
1 Click the role you want to edit. The user role window appears:
Figure 3-15 User Role
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
2 Enter the information in the fields you want to change. See Section 3.7.1, “Adding a User
Role,” on page 64 for information on user role settings.
3 Click ok.
3.7.3 Deleting User Roles
NOTE: You cannot delete the System Administrator role.
To delete user roles:
Home window>>System configuration>>User roles
1 Click delete next to the user role you want to remove. The Delete user role
confirmation window appears.
2 Click yes.
66 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 67

3.7.4 Sorting the User Roles Area
To sort the user roles area:
Home window>>System configuration>>User roles
1 Click user role name or description column heading. The selected category sorts in
ascending or descending order.
2 Click ok.
3.8 License
The License menu option allows you to configure the following:
Enter and submit a new license key
View license start and end dates
View number of days remaining on license, and associated renewal date
View remaining endpoints and servers available under license
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.8.1, “Updating Your License Key,” on page 68
System Configuration 67
Page 68

3.8.1 Updating Your License Key
To update your license key:
Home window>>System configuration>>License
Figure 3-16 System Configuration, License
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 The license key should be pre-populated from the first-time login (as described in the
Installation Guide). If you need to update your license key, in the New license key field,
enter your Novell ZENworks Network Access Control license key, which Novell sends to you
by email. Copy and paste the license key directly from the text file.
TIP: The double-equal sign (==) is part of the license key. Include it with the rest of the
numbers.
2 Click Submit Now.
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control is enabled through the license key. The license key
is validated, and it appears in the Registered license key field.
3 Click ok on the license validated pop-up window.
3.9 Test Updates
The Test updates menu option allows you to configure the following:
View last successful test update date/time
Check for test updates (forces an immediate check for test updates)
Set time or times for downloading test updates
View test update logs
68 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 69

The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.9.1, “Manually Checking for Test Updates,” on page 69
Section 3.9.2, “Selecting Test Update Times,” on page 70
Section 3.9.3, “Viewing Test Update Logs,” on page 70
3.9.1 Manually Checking for Test Updates
To manually check for test updates:
Home window>>System configuration>>Test updates
Figure 3-17 System Configuration, Test Updates
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 In the Last successful test update area, click check for test updates.
2 Click ok.
NOTE: It is important to check for test updates during the initial configuration of Novell
ZENworks Network Access Control.
System Configuration 69
Page 70

3.9.2 Selecting Test Update Times
To select test update times:
Home window>>System configuration>>Test updates
1 Using the hour check boxes, select the time periods in which you would like Novell ZENworks
Network Access Control to check for available test updates.
By default, Novell ZENworks Network Access Control checks once every hour using the
Novell Secure Rule Distribution Center. All times listed are dependent upon the clock setting
and time zone of the hardware on which Novell ZENworks Network Access Control is running.
2 Click ok.
3.9.3 Viewing Test Update Logs
To view test update logs:
Home window>>System configuration>>Test updates
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Click the View test update log link just to the right of the Check for test
updates button. The Test update log window appears:
Figure 3-18 Test Update Log
The Test update log window legend is shown in the following figure:
Figure 3-19 Test Update Log Window Legend
3.10 Quarantining, General
The Quarantining menu option allows you to configure the following by cluster:
Select the quarantine method
Select the access mode
Basic 802.1X settings
70 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 71

Authentication settings
Add, edit, delete 802.1X devices
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.10.1, “Selecting the Quarantine Method,” on page 71
Section 3.10.2, “Selecting the Access Mode,” on page 72
3.10.1 Selecting the Quarantine Method
To select the quarantine method:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining
Figure 3-20 System Configuration, Quarantining
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Select a cluster.
System Configuration 71
Page 72

2 In the Quarantine method area, select one of the following quarantine methods:
802.1X — When using the 802.1X quarantine method, Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control must sit in a place on the network where it can communicate with your
RADIUS server, which communicates with your switch or router, which performs the
quarantining.
DHCP — When configured with a DHCP quarantine area, Novell ZENworks Network
Access Control must sit inline with your DHCP server. All endpoints requesting a DHCP
IP address are issued a temporary address on a quarantine subnetwork. Once the endpoint
is allowed access, the IP address is renewed, and the main DHCP server assigns an
address to the main LAN. With a multiple subnetwork or VLAN network, one quarantine
area must be configured for each subnetwork. See Chapter 13, “Remote Device Activity
Capture,” on page 295 for information on using multiple DHCP servers.
Inline — When using the inline quarantine method, Novell ZENworks Network Access
Control must be placed on the network where all traffic to be quarantined passes through
Novell ZENworks Network Access Control. It must be inline with an endpoint like a
VPN.
3 Click ok.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3.10.2 Selecting the Access Mode
To select the access mode:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining
1 Select one of the following in the Access mode area:
normal — Either allows or quarantines endpoints depending on the setup of the
enforcement sever.
allow all — Endpoints are tested; however, they are always given access to the production
network.
NOTE: If you are setting up a cluster for the first time, and you have not yet added an ES, select
allow all until you have finished configuring Novell ZENworks Network Access Control.
3.11 Quarantining, 802.1X
The 802.1X quarantine (enforcement) method is enabled by default.
To select the 802.1X quarantine method:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining
1 Select a cluster.
2 In the Quarantine method area, select the 802.1X radio button.
3 Click ok.
The following sections contain more information:
Section 3.11.1, “Entering Basic 802.1X Settings,” on page 73
72 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 73

Section 3.11.2, “Authentication Settings,” on page 74
Section 3.11.3, “Adding 802.1X Devices,” on page 79
Section 3.11.4, “Testing the Connection to a Device,” on page 80
Section 3.11.5, “Cisco IOS,” on page 82
Section 3.11.6, “Cisco CatOS,” on page 84
Section 3.11.7, “Enterasys,” on page 86
Section 3.11.8, “Extreme ExtremeWare,” on page 88
Section 3.11.9, “Extreme XOS,” on page 90
Section 3.11.10, “Foundry,” on page 92
Section 3.11.11, “HP ProCurve Switch,” on page 94
Section 3.11.12, “HP ProCurve WESM xl or HP ProCurve WESM zl,” on page 97
Section 3.11.13, “HP ProCurve 420 AP or HP ProCurve 530 AP,” on page 99
Section 3.11.14, “Nortel,” on page 101
Section 3.11.15, “Other,” on page 103
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
3.11.1 Entering Basic 802.1X Settings
To enter basic 802.1X settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X quarantine method radio button
1 In 802.1X enforcement mode, the Enforcement servers must be able monitor DHCP
conversations and detect endpoints by sniffing network traffic as it flows between the DHCP
server and the endpoints. Select an Endpoint detection location radio button as
follows:
Remote — In more complex deployments, it is often impossible (in the case of multiple
Enforcement servers or multiple DHCP servers) or undesirable to span switch ports. In
this case the DHCP traffic monitoring and endpoint detection can be run remotely by
installing and configuring the endpoint activity capture software on each DHCP server
involved in the 802.1X deployment. In this case, choose the remote option.
Local — In simple configurations, it is possible to span, or mirror, the switch port into
which the DHCP server is connected. The eth1 interface of the Enforcement server is then
plugged into the spanned port and endpoint traffic is monitored on the eth1 interface. In
this case, choose the local option.
2 Enter one or more non-quarantined subnets, separated by commas in the Quarantine
subnets text field. All subnets should be entered using CIDR addresses.
3 Select a RADIUS server type by selecting one of the following radio buttons:
Local — Enables a local RADIUS server on the ES which can be configured to perform
authentication itself or proxy to another server.
Remote IAS — Disables the local RADIUS server so that an IAS server configured with
the NAC IAS plug-in to point to an ES can be used instead. When possible, a local
RADIUS server that proxies to the IAS server should be the preferred configuration.
4 Click ok.
System Configuration 73
Page 74

3.11.2 Authentication Settings
The following sections contain more information:
“Selecting the RADIUS Authentication method” on page 74
“Configuring Windows Domain Settings” on page 75
“Configuring OpenLDAP Settings” on page 77
Selecting the RADIUS Authentication method
To select the RADIUS authentication method:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X quarantine method radio button
1 Select the Local radio button in the Basic 802.1X settings area.
2 Select an End-user authentication method:
Manual — RADIUS server authentication settings are configured manually from the
command line. See Section 11.3.2, “Enabling Novell ZENworks Network Access Control
for 802.1X,” on page 264 for configuration information.
Windows domain — Authentication requests are handled by a Windows domain through
NTLM protocol. The ES must be able to join to the domain for this to work. See
“Configuring Windows Domain Settings” on page 75 for more information.
OpenLDAP — User credentials are queried from an OpenLDAP directory service. See
“Configuring OpenLDAP Settings” on page 77 for more information.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Proxy — Authentication requests are proxied to a remote RADIUS server configured to
allow the ES as a client NAS.
3 Click ok.
74 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 75

Configuring Windows Domain Settings
To configure Windows domain settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Local radio button
1 Select Windows domain from the End-user authentication method drop-down
list.
Figure 3-21 System Configuration, Windows Domain
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 75
Page 76

2 Enter the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the domain to be joined in the Domain
name text field.
3 Enter the user name of an account with sufficient administrative rights to join an ES to the
domain in the Administrator user name text field.
4 Enter the password of the account entered into the Administrator user name field in
the Administrator password text field.
5 Enter the list of domain controllers, separated by commas, for this domain in the Domain
controllers text field.
6 To test the Windows domain settings:
6a Select one of the following from the Server to test from drop-down list in the
Test Windows domain settings area:
The ES in this cluster to test from, or
The MS
NOTE: If you have a single-server installation, the Server to test from drop-down
list is not available.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
6b To verify a specific set of user credentials in addition to the Windows domain settings,
select the Verify credentials for an end-user check box, and specify the
following:
1. Enter the user name of the end-user in the User name text box.
2. Enter the password of the end-user in the Password text box.
3. Re-enter the password of the end-user in the Re-enter password text box.
6c Click test settings.
7 Click ok.
76 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 77

Configuring OpenLDAP Settings
To configure OpenLDAP settings:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Local radio button
1 Select OpenLDAP from the End-user authentication method drop-down list.
Figure 3-22 System Configuration, OpenLDAP
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 77
Page 78

2 Enter the LDAP server hostname or IP address and optional port number in the Server text
field. For example: 10.0.1.2:636
3 Enter the DN under which LDAP searches should be done in the Identity text field. For
example: cn=admin,o=My Org,c=UA
4 Enter the password that authenticates the DN entered into the Identity text field in the
Password text field.
5 Type the same password you entered into the Password field in the Re-enter password
field.
6 Enter the base DN of LDAP searches in the Base DN text field. For example: o=My
Org,c=UA
7 Enter the LDAP search filter used to locate user objects from name supplied by endpoint in the
Filter text field. For example: (uid=%u)
8 Enter the LDAP attribute which contains end-user passwords in the Password attribute
text field. This is initially set to userPassword to use the universal password of the
eDirectory user.
9 To use a secure Transport Layer Security (TLS) connection with the LDAP server that is
verified with a certificate authority:
9a Select the Use a secure connection (TLS) check box.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
9b Enter a PEM-encoded file name that contains the CA certificate used to sign the LDAP
server's TLS certificate in the New certificate text field. Click Browse to search
for file names. The current certificate selected is shown by Current certificate.
10 To test the OpenLDAP settings:
10a Select one of the following from the Server to test from drop-down list in the
Test Windows domain settings area:
The ES in this cluster to test from, or
The MS
10b To verify a specific set of user credentials in addition to the OpenLDAP settings, select the
Verify credentials for an end-user check box, and specify the following:
1. Enter the user name of the end-user in the User name text box.
2. Enter the password of the end-user in the Password text box.
3. Re-enter the password of the end-user in the Re-enter password text box.
10c Click test settings.
11 Click ok.
78 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 79

3.11.3 Adding 802.1X Devices
To add an 802.1X device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-23 Add 802.X Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the 802.1X device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
NOTE: See your system administrator to obtain the shared secret for your switch.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select an 802.1X device from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Enter the configuration settings for the specific device:
Cisco IOS — See Section 3.11.5, “Cisco IOS,” on page 82.
Cisco CatOS — See Section 3.11.6, “Cisco CatOS,” on page 84.
Enterasys — See Section 3.11.7, “Enterasys,” on page 86.
Extreme ExtremeWare — See Section 3.11.8, “Extreme ExtremeWare,” on page 88.
Extreme XOS — See Section 3.11.9, “Extreme XOS,” on page 90.
Foundry — See Section 3.11.10, “Foundry,” on page 92.
HP ProCurve switch — See Section 3.11.11, “HP ProCurve Switch,” on page 94.
HP ProCurve WESM — See Section 3.11.12, “HP ProCurve WESM xl or HP ProCurve
WESM zl,” on page 97.
HP ProCurve 420/530 AP — See Section 3.11.13, “HP ProCurve 420 AP or HP
ProCurve 530 AP,” on page 99.
System Configuration 79
Page 80

Nortel — See Section 3.11.14, “Nortel,” on page 101.
Other — See Section 3.11.15, “Other,” on page 103.
7 Click ok.
3.11.4 Testing the Connection to a Device
The test connection area has different options based on the switch you select:
Cisco CATOS, Cisco IOS, Enterasys, Extreme, Foundry switches — See Figure 3-24 on
page 80.
ProCurve, Nortel, Other switches — See Figure 3-25 on page 80.
To test the connection to an 802.1X device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio button
NOTE: You must have already added devices for them to appear in the 802.1X devices area. You
can also test the device as you add it.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 In the 802.1X devices area, click edit next to the device you want to test. The 802.1X
device window appears. The Test connection to this device area is near the
bottom of the window:
Figure 3-24 Add 802.X Device, Test Connection Area Option 1
Figure 3-25 Add 802.X Device, Test Connection Area Option 2
2 For ProCurve, Nortel, Other switches (Figure 3-24 on page 80),:
2a Select the Method to execute the re-authentication command in test:
802.1X
MAC auth
2b Enter the port of the endpoint being tested in the Port text field.
2c Enter the MAC address of the endpoint being tested in the MAC address text field.
80 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 81

3 For Cisco CATOS, Cisco IOS, Enterasys, Extreme, Foundry switches (Figure 3-25 on
page 80) if you want to include the re-authentication command as part of the test, select the
Re-authenticate an endpoint during test check box and:
3a Enter the port of the endpoint being tested in the Port text field.
3b Enter the MAC address of the endpoint being tested in the MAC address text field.
NOTE: You must enter the port, the MAC address, or both, depending on the reauthentication OID.
4 Click test connection to this device.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 81
Page 82

3.11.5 Cisco IOS
To add a Cisco IOS device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-26 Add Cisco IOS Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the Cisco IOS device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Cisco IOS from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
82 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 83

8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
9 Re-enter the console password.
10 Enter the Cisco port mask in the text field. This specifies which characters within the
endpoint identifier returned by the Cisco device contain the bank and port information of the
endpoint. All offsets start at 0, so a mask of 2/34 indicates character 3 for the bank and
characters 4 and 5 for the port. If the Cisco device were to return 50210 for an endpoint, a port
mask of 2/34 would indicate that the endpoint is on bank 2 and port 10 (2/10), where 210 are
the third, fourth and fifth bytes in the identifier.
11 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
12 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
13 Click ok.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
System Configuration 83
Page 84

3.11.6 Cisco CatOS
To add a Cisco CatOS device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-27 Add Cisco CatOS Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the Cisco CatOS device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Cisco CatOS from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
84 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 85

8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
9 Re-enter the console password.
10 Enter the password with which to enter enable mode.
11 Re-enter the enable mode password.
12 Enter the networks (using CIDR notation) that this device is in direct control over in the
Network list text field. This is only necessary if the device does not send its IP address
with its supplicant request.
13 Enter the Cisco port mask in the text field. This specifies which characters within the
endpoint identifier returned by the Cisco device contain the bank and port information of the
endpoint. All offsets start at 0, so a mask of 2/34 indicates character 3 for the bank and
characters 4 and 5 for the port. If the Cisco device were to return 50210 for an endpoint, a port
mask of 2/34 would indicate that the endpoint is on bank 2 and port 10 (2/10), where 210 are
the third, fourth and fifth bytes in the identifier.
14 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
15 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
16 Click ok.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
CatOS User Name in Enable Mode
If you have your CatOS switch configured to run in enable mode with a user name, the expect script
supplied with Novell ZENworks Network Access Control will not run “out of the box.”
Workaround: Do not use a user name with your switch, or modify the expect script in the console to
include the user name.
To modify the expect script in the Novell ZENworks Network Access Control user
interface:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining menu option
1 Click edit next to an 802.1X device. (You can also perform these steps while you are adding an
802.1X device.)
2 Click the plus sign next to Show scripts.
3 Add the correct expect script syntax to the text box for enable mode user name. See your switch
documentation for more information on the correct syntax.
4 Click ok.
System Configuration 85
Page 86

3.11.7 Enterasys
To add an Enterasys device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-28 Add Enterasys Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the Enterasys device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Enterasys from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
9 Re-enter the console password.
86 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 87

10 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
11 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
12 Click ok.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 87
Page 88

3.11.8 Extreme ExtremeWare
To add an ExtremeWare device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-29 Add ExtremeWare Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the ExtremeWare device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Extreme ExtremeWare from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
9 Re-enter the console password.
88 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 89

10 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
11 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
12 Click ok.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 89
Page 90

3.11.9 Extreme XOS
To add an Extreme XOS device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-30 Add Extreme XOS Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the Extreme XOS device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Extreme XOS from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
9 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
90 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 91

10 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
11 Click ok.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 91
Page 92

3.11.10 Foundry
To add a Foundry device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-31 Add Foundry Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the Foundry device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select Foundry from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select telnet or SSH from the Connection method drop-down list.
7 Enter the User name with which to log into the device's console.
8 Enter the Password with which to log into the device's console.
92 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 93

9 Re-enter the console password.
10 Enter the password with which to enter enable mode.
11 Re-enter the enable mode password.
12 Enter the Reconnect idle time. This is the amount of time in milliseconds that a telnet /
SSH console can remain idle or unused before it is reset.
13 Select the Show scripts plus symbol to show the following scripts:
Initialization script — The expect script used to log into the console and enter enable
mode.
Re-authentication script — The expect script used to perform endpoint re-
authentication.
Exit script — The expect script used to exit the console.
14 Click ok.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
System Configuration 93
Page 94

3.11.11 HP ProCurve Switch
To add an HP ProCurve switch:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-32 Add HP ProCurve Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the HP ProCurve device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select ProCurve Switch from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Select whether to connect to this device using telnet, SSH, or SNMPv2 in the
Connection method drop-down list.
94 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 95

7 SSH settings:
7a Enter the User name used to log into this device's console.
7b Enter the Password used to log into this device's console.
7c To help confirm accuracy, type the same password you entered into the Password field
in the Re-enter Password field.
7d Enter the Enable mode user name that is used to enter enable mode on this device.
7e Enter the Password used to enter enable mode on this device.
7f To help confirm accuracy, type the same password you entered into the Enable password
field in the Re-enter Password field.
7g Enter the amount of time, in milliseconds, before an idle open SSH session is reset. The
default is 60000 (60 seconds) in the Reconnect idle time field.
8 Telnet settings:
8a Enter the User name used to log into this device's console.
8b Enter the Password used to log into this device's console.
8c To help confirm accuracy, type the same password you entered into the Password field
in the Re-enter Password field.
8d Enter the Enable mode user name that is used to enter enable mode on this device.
8e Enter the Password used to enter enable mode on this device.
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
8f To help confirm accuracy, type the same password you entered into the Enable password
field in the Re-enter Password field.
8g Enter the amount of time, in milliseconds, before an idle open telnet session is reset. The
default is 60000 (60 seconds) in the Reconnect idle time field.
9 SNMPv2 settings:
9a Enter the Community string used to authorize writes to SNMP objects.
9b Enter the OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the Re-authenticate OID text
field. The strings "${Port}" and "${MAC}" will be substituted for the port and MAC
address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
9c Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the
INTEGER
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
NULLOBJ
OID type drop-down list:
System Configuration 95
Page 96

9d Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID
value text field.
9e Select the Use a different OID for MAC authentication check box to re-
authenticate using a different OID when the supplicant request is for a MAC authenticated
device.
1. Enter the Re-authenticate OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint. The
strings "${PORT}" and "${MAC_DOTTED_DECIMAL}" are substituted for the
port and MAC address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
2. Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the OID type drop-down list:
INTEGER
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
NULLOBJ
3. Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID
value text field.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
96 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 97

3.11.12 HP ProCurve WESM xl or HP ProCurve WESM zl
To add an HP ProCurve WESM xl or HP ProCurve WESM zl device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-33 Add HP ProCurve WESM xl/zl Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the HP ProCurve WESM device in the IP address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select ProCurve WESM from the Device type drop-down list.
6 Enter the Community string used to authorize writes to SNMP objects.
7 Enter the OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the Re-authenticate OID text field.
The strings "${Port}" and "${MAC_DOTTED_DECIMAL}" will be substituted for the port
and MAC address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
System Configuration 97
Page 98

NOTE: Figure 3-33 on page 97 shows an example for WESM zl.
8 Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the OID type drop-down list:
INTEGER
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
NULLOBJ
9 Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID value
text field.
10 Select the Use a different OID for MAC authentication check box to re-
authenticate using a different OID when the supplicant request is for a MAC authenticated
device.
10a Enter the Re-authenticate OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint. The strings
"${Port}" and "${MAC_DOTTED_DECIMAL}" are substituted for the port and MAC
address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
10b Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the OID type drop-down list:
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
INTEGER
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
NULLOBJ
10c Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID
value text field.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
98 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
Page 99

3.11.13 HP ProCurve 420 AP or HP ProCurve 530 AP
To add an HP ProCurve 420 AP or HP ProCurve 530 AP device:
Home window>>System configuration>>Quarantining>>802.1X Quarantine method radio
button>>Add an 802.1X device
Figure 3-34 Add HP ProCurve 420/530 AP Device
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
1 Enter the IP address of the HP ProCurve AP or HP ProCurve 530 AP device in the IP
address text field.
2 Enter a shared secret in the Shared secret text field. The shared secret is used to encrypt
and sign packets between the device and RADIUS server.
3 Re-enter the shared secret in the Re-enter shared secret text field.
4 Enter an alias for this device that appears in log files in the Short name text field.
5 Select ProCurve 420 AP or ProCurve 530 AP from the Device type drop-
down list.
6 Enter the Community string used to authorize writes to SNMP objects.
System Configuration 99
Page 100

7 Enter the OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the Re-authenticate OID text field.
The strings "${Port}" and "${MAC_DOTTED_DECIMAL}" will be substituted for the port
and MAC address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
8 Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the OID type drop-down list:
INTEGER
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
NULLOBJ
9 Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID value
text field.
10 Select the Use a different OID for MAC authentication check box to re-
authenticate using a different OID when the supplicant request is for a MAC authenticated
device.
10a Enter the Re-authenticate OID used to re-authenticate an endpoint. The strings
"${Port}" and "${MAC_DOTTED_DECIMAL}" are substituted for the port and MAC
address of the endpoint to be re-authenticated.
10b Select the type of the re-authentication OID from the OID type drop-down list:
INTEGER
novdocx (en) 24 March 2009
unsigned INTEGER
TIMETICKS
IPADDRESS
OBJID
STRING
HEX STRING
DECIMAL STRING
BITS
NULLOBJ
10c Enter the OID re-authentication value used to re-authenticate an endpoint in the OID
value text field.
TIP: Click revert to defaults to restore the default settings.
100 Novell ZENworks Network Access Control Users Guide
 Loading...
Loading...