Page 1
AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION
Administration Guide
Novell®
ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
3.5
March 31, 2009
www.novell.com
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 2

Legal Notices
Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and
specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Further, Novell, Inc., reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes to its content, at any time,
without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
Further, Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to any software, and specifically disclaims
any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc.,
reserves the right to make changes to any and all parts of Novell software, at any time, without any obligation to
notify any person or entity of such changes.
Any products or technical information provided under this Agreement may be subject to U.S. export controls and the
trade laws of other countries. You agree to comply with all export control regulations and to obtain any required
licenses or classification to export, re-export or import deliverables. You agree not to export or re-export to entities
on the current U.S. export exclusion lists or to any embargoed or terrorist countries as specified in the U.S. export
laws. You agree to not use deliverables for prohibited nuclear, missile, or chemical biological weaponry end uses.
See the Novell International Trade Services Web page (http://www.novell.com/info/exports/) for more information
on exporting Novell software. Novell assumes no responsibility for your failure to obtain any necessary export
approvals.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Copyright © 2007-2009 Novell, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, photocopied,
stored on a retrieval system, or transmitted without the express written consent of the publisher.
Novell, Inc., has intellectual property rights relating to technology embodied in the product that is described in this
document. In particular, and without limitation, these intellectual property rights may include one or more of the U.S.
patents listed on the Novell Legal Patents Web page (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/patents/) and one or
more additional patents or pending patent applications in the U.S. and in other countries.
Novell, Inc.
404 Wyman Street, Suite 500
Waltham, MA 02451
U.S.A.
www.novell.com
Online Documentation: To access the latest online documentation for this and other Novell products, see
the Novell Documentation Web page (http://www.novell.com/documentation).
Page 3

Novell Trademarks
For Novell trademarks, see the Novell Trademark and Service Mark list (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/
trademarks/tmlist.html).
Third-Party Materials
All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Page 4

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
4 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide 9
1 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management 11
1.1 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.2 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1.2.1 ASP.NET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.2.2 Reliable Time Stamp . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.3 About the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Manuals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
1.4 USB/Wireless Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2 Policy Distribution Service 17
2.1 About the Policy Distribution Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.1.1 Server Selection and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.1.2 Server Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.1.3 Upgrading the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.1.4 Uninstall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.2 Securing Server Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.2.1 Physical Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.2.2 Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.2.3 High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.3 Running the Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
3 Configuring the Directory Service 21
3.1 Configuring the Directory Service for Novell eDirectory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.2 Configuring the Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4 Using the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Service 37
4.1 About the Management Service. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.1.1 Server Selection and Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
4.1.2 Server Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.3 Upgrading the Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.1.4 Uninstall . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2 Securing Server Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2.1 Physical Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
4.2.2 Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.2.3 High Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.2.4 Running the Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
4.3 Distributing and Renewing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Credentials . . . . . . . . 39
4.3.1 Distributing Endpoint Security Management Credentials (Key Management Key) . . 39
4.3.2 Periodic Renewal of the Key Management Key (KMK) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5 Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 41
5.1 Using the Console Taskbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.1.1 Policy Tasks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5.1.2 Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Contents 5
Page 6

5.1.3 Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.1.4 Endpoint Auditing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.2 Using the Console Menu Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
5.3 Using the Configuration Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.3.1 Infrastructure and Scheduling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
5.3.2 Authenticating Directories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
5.3.3 Service Synchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5.4 Using Alerts Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
5.4.1 Configuring Endpoint Security Management for Alerts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
5.4.2 Configuring Alert Triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
5.4.3 Managing Alerts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
5.5 Using Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.5.1 Using the Reports Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.5.2 Adherence Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
5.5.3 Alert Drill-Down Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
5.5.4 Application Control Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
5.5.5 Endpoint Activity Reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
5.5.6 Encryption Solutions Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
5.5.7 Client Self Defense Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
5.5.8 Integrity Enforcement Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
5.5.9 Location Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
5.5.10 Outbound Content Compliance Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
5.5.11 Administrative Overrides Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
5.5.12 Endpoint Updates Reports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
5.5.13 USB Devices Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
5.5.14 Wireless Enforcement Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
5.6 Generating Custom Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
5.6.1 Software Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
5.6.2 Creating a ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Compliant Report. . . . . . . . . 61
5.6.3 Available Reporting Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
5.6.4 Creating a Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
5.7 Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
5.7.1 Understanding the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
5.7.2 Sharing Encrypted Files. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
5.8 Managing Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
5.8.1 Exporting Encryption Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
5.8.2 Importing Encryption Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
5.8.3 Generating a New Key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
6 Creating and Distributing Security Policies 75
6.1 Navigating the Management Console UI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
6.1.1 Using the Policy Tabs and Tree. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
6.1.2 Using the Policy Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
6.2 Creating Security Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
6.2.1 Global Policy Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
6.2.2 Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
6.2.3 Integrity and Remediation Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
6.2.4 Compliance Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
6.2.5 Publishing Security Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
6.3 Managing Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
6.3.1 Show Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
6.3.2 Error Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
6.3.3 Custom User Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
6.3.4 Hyperlinks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
6.3.5 Defined Location Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
6.3.6 Network Environments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
6 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 7

6.3.7 Firewall Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
6.3.8 TCP/UDP Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
6.3.9 Access Control Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
6.3.10 Application Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
6.3.11 Rule Scripting Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
6.4 Importing and Exporting Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
6.4.1 Importing Policies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
6.4.2 Exporting a Policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
6.4.3 Exporting Policies to Unmanaged Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
6.5 Sample Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
6.5.1 Create Registry Shortcut (VB Script) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
6.5.2 Allow Only One Connection Type (JScript) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
6.5.3 Stamp Once Script. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
7 Managing the Endpoint Security Client 3.5 175
7.1 Understanding the Endpoint Security Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
7.2 Installing and Uninstalling the ZENworks Security Agent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
7.2.1 Installing the Endpoint Security Client 3.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
7.2.2 Uninstalling the Endpoint Security Client 3.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
7.3 Understanding Client Self Defense . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
7.4 Upgrading the Endpoint Security Client 3.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
7.4.1 Setting the Upgrade Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
7.5 Running the Endpoint Security Client 3.5 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
7.5.1 Multiple User Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
7.5.2 Machine-Based Policies (Active Directory Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
7.5.3 Distributing Unmanaged Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
7.6 Using the Endpoint Security Client Diagnostics Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
7.6.1 Creating a Diagnostics Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
7.6.2 Administrator Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
7.6.3 Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
7.6.4 Reporting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
8 Managing the Endpoint Security Client 4.0 191
8.1 Understanding the Endpoint Security Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
8.2 Installing and Uninstalling the ZENworks Security Agent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
8.2.1 Installing the Endpoint Security Client 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
8.2.2 Uninstalling the Endpoint Security Client 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
8.3 Running the Endpoint Security Client 4.0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
8.3.1 Multiple User Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
8.3.2 Machine-Based Policies (Active Directory Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
8.3.3 Distributing Unmanaged Policies. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
8.4 Using the Endpoint Security Client Diagnostics Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
8.4.1 Creating a Diagnostics Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
8.4.2 Administrator Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
8.4.3 Module List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
8.4.4 Logging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
9 Using ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Utilities 203
9.1 Using the ZENworks File Decryption Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
9.1.1 Using the File Decryption Utility. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
9.1.2 Using the Administrator Configured Decryption Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
9.2 Using the Override-Password Key Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Contents 7
Page 8

A Acronym Glossary 207
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
8 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 9

About This Guide
This Novell® ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide is written for
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administrators who are required to manage the
Endpoint Security Management services, create security policies for the enterprise, generate and
analyze reporting data, and provide troubleshooting for end users. Instructions for completing these
tasks are provided in this manual.
The information in this guide is organized as follows:
Chapter 1, “ZENworks Endpoint Security Management,” on page 11
Chapter 2, “Policy Distribution Service,” on page 17
Chapter 3, “Configuring the Directory Service,” on page 21
Chapter 4, “Using the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Service,” on page 37
Chapter 5, “Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console,” on
page 41
Chapter 6, “Creating and Distributing Security Policies,” on page 75
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Chapter 7, “Managing the Endpoint Security Client 3.5,” on page 175
Chapter 8, “Managing the Endpoint Security Client 4.0,” on page 191
Chapter 9, “Using ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Utilities,” on page 203
Appendix A, “Acronym Glossary,” on page 207
Audience
This guide is written for the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management administrators.
Feedback
We want to hear your comments and suggestions about this manual and the other documentation
included with this product. Please use the User Comments feature at the bottom of each page of the
online documentation, or go to the Novell Documentation Feedback site (http://www.novell.com/
documentation/feedback.html) and enter your comments there.
Additional Documentation
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management is supported by other documentation (in both PDF and
HTML formats) that you can use to learn about and implement the product. For additional
documentation, see the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management 3.5 documentation Web site
(http://www.novell.com/documentation/zesm35).
Documentation Conventions
In Novell documentation, a greater-than symbol (>) is used to separate actions within a step and
items in a cross-reference path.
®
A trademark symbol (
trademark.
, TM, etc.) denotes a Novell trademark. An asterisk (*) denotes a third-party
About This Guide 9
Page 10

When a single pathname can be written with a backslash for some platforms or a forward slash for
other platforms, the pathname is presented with a backslash. Users of platforms that require a
forward slash, such as Linux*, should use forward slashes as required by your software.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
10 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 11

1
ZENworks Endpoint Security
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Management
Novell® ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management provides complete, centralized security
management for all endpoints in the enterprise. Because ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
applies security at the most vulnerable point, the endpoint, all security settings are applied and
enforced regardless of whether the user is connecting to the network directly, dialing in remotely, or
even not connecting to corporate infrastructure at all. This is critical to not only protect the data
within the corporate perimeter, but also to protect the critical data that resides on the endpoint device
itself.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management automatically adjusts security settings and user
permissions based on the current network environment characteristics. A sophisticated engine is
used to determine the user's location and automatically adjusts firewall settings and permissions for
applications, adapters, hardware, etc.
Security is enforced through the creation and distribution of ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management security policies. Each location (Work, Home, Alternate, Airport, etc.) listed in a
security policy is assigned to a network environment (or multiple network environments). A location
determines which hardware is available and the degree of firewall settings that are activated within
the network environment. The firewall settings determine which networking ports, access control
lists (ACLs), and applications are accessible/required. Various integrity checks and scripts can be
run at location change to ensure that all required security software is up to date and running.
1
Figure 1-1 Effectiveness of NDIS-Layer Firewall
In securing mobile devices, ZENworks Endpoint Security Management is superior to typical
personal firewall technologies, which operate only in the application layer or as a firewall-hook
driver. ZENworks Endpoint Security Management client security is integrated into the Network
Driver Interface Specification (NDIS) driver for each network interface card (NIC), providing
security protection from the moment traffic enters the computer. Differences between ZENworks
Endpoint Security Management and application-layer firewalls and filter drivers are illustrated in
Figure 1-1, “Effectiveness of NDIS-Layer Firewall,” on page 11.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
11
Page 12
Security decisions and system performance are optimized when security implementations operate at
the lowest appropriate layer of the protocol stack. With the ZENworks Security Management
Endpoint Security Client, unsolicited traffic is dropped at the lowest levels of the NDIS driver stack
by means of Adaptive Port Blocking (stateful packet inspection) technology. This approach protects
against protocol-based attacks, including unauthorized port scans, SYN Flood, NetBIOS, and
DDOS attacks.
1.1 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Overview
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management consists of four high-level functional components:
Policy Distribution Service
Management Service
Management Console
Endpoint Security Client
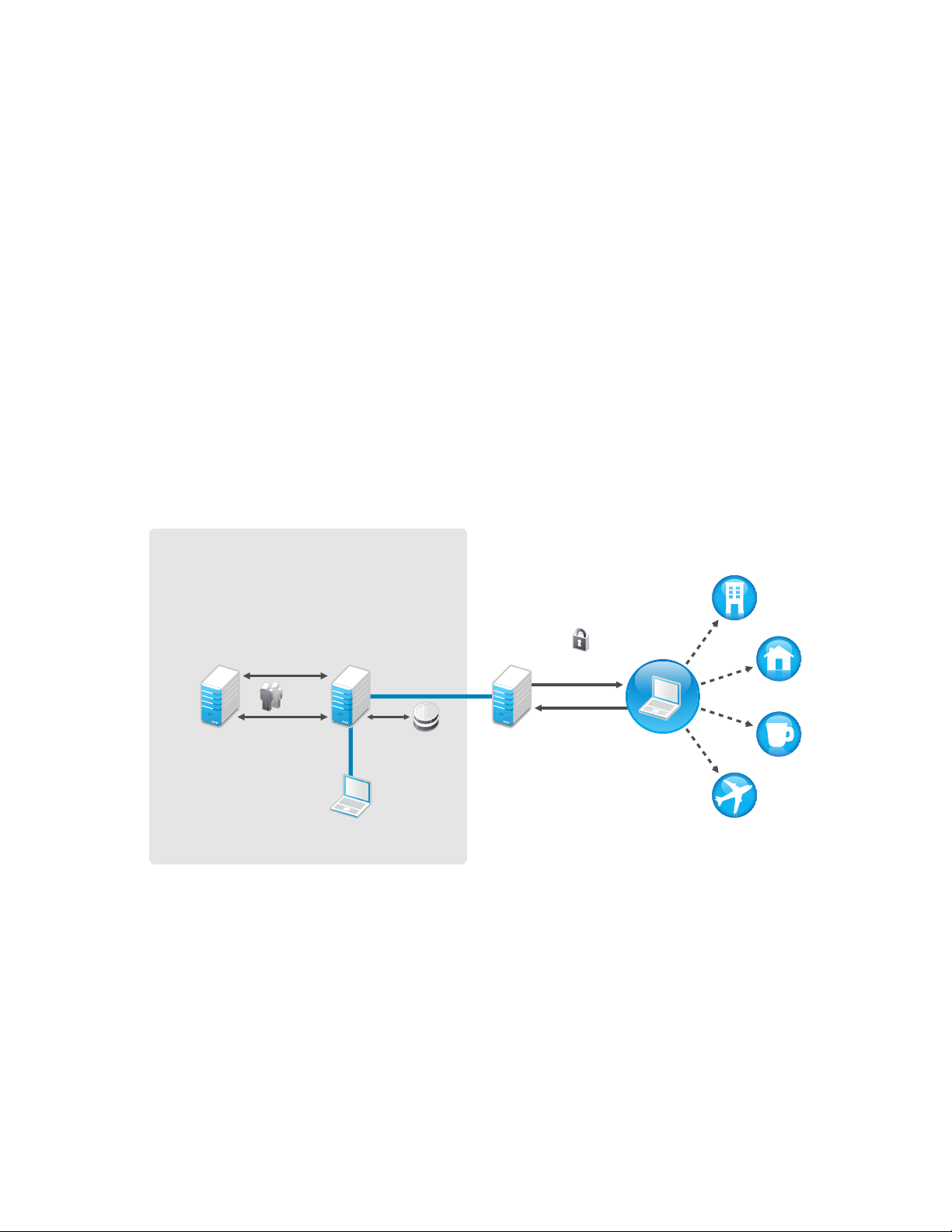
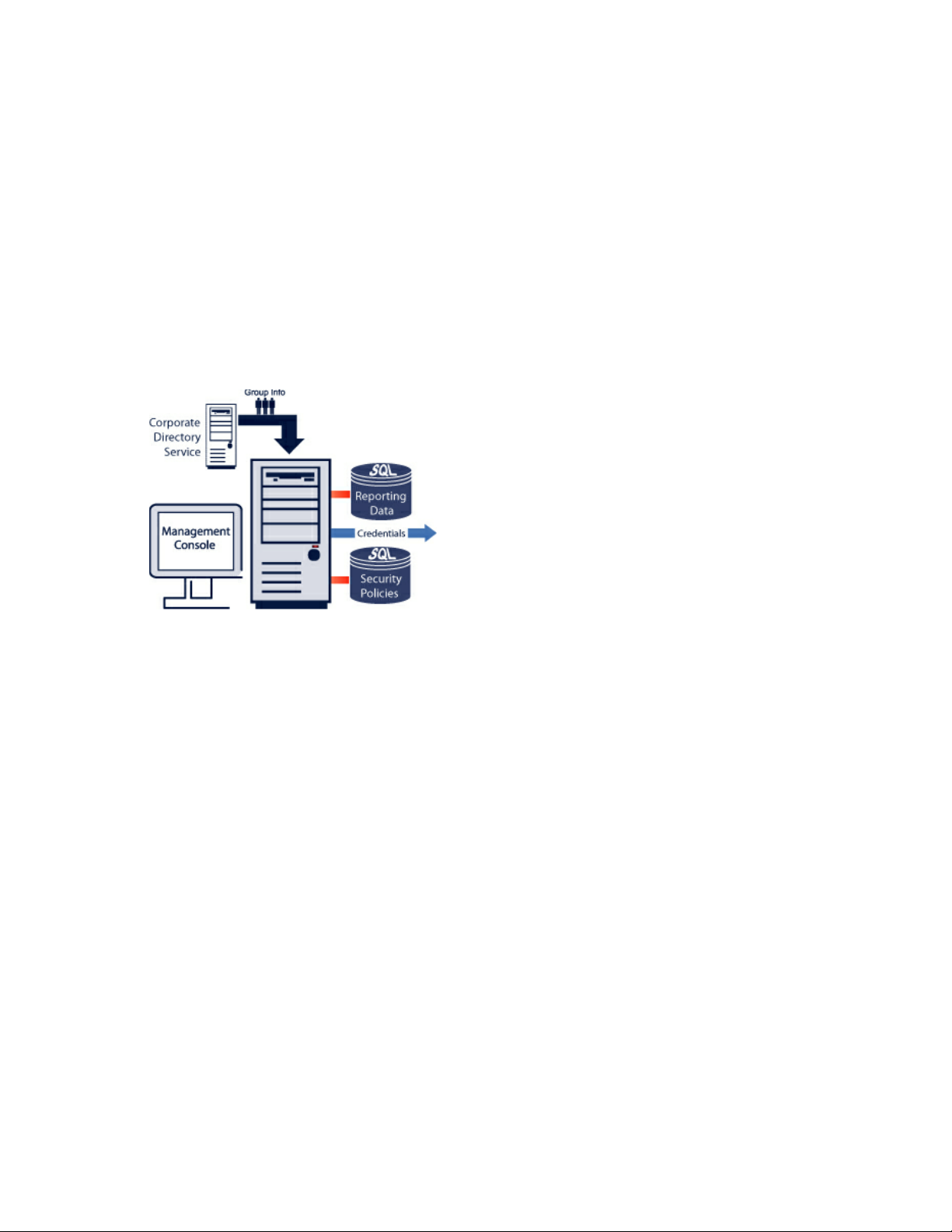
The figure below shows these components in the architecture:
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Figure 1-2 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Architecture
Endpoint Security Management
Central Management
Location Secure
Active Directory,
LDAP, or NT Domain
Directory Service
Enterprise Perimeter
ZENworks
Management
Group
Info
Management
Service
Console
SSL Link
SQL
Database
Policy
Distribution
Service
Enterprise
Web Server
DMZ
(Demilitarized Zone)
Encrypted
Policy
Reporting
Information
ZENworks
Security
Client
Office
Home
Coffee
Shop
On The
Road
The Endpoint Security Client is responsible for enforcement of the distributed security policies on
the endpoint system. When the Endpoint Security Client is installed on all enterprise computers,
these computers (endpoints) can now travel outside the corporate perimeter and maintain their
security, while endpoints inside the perimeter receive additional security checks within the perimeter
firewall.
12 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 13

Each Central Management component is installed separately, the following components are installed
on servers that are secured inside the corporate perimeter:
Policy Distribution Service: Responsible for the distribution of security policies to the
Endpoint Security Client, and retrieval of reporting data from the Endpoint Security Clients.
The Policy Distribution Service can be deployed in the DMZ or outside the enterprise firewall,
to ensure regular policy updates for mobile endpoints.
Management Service: Responsible for user policy assignment and component authentication;
reporting data retrieval, creation and dissemination of ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management reports; and security policy creation and storage.
Management Console: The visible user interface, which can run directly on the server hosting
the Management Service or on a workstation residing inside the corporate firewall with
connection to the Management Service server. The Management Console is used to configure
the Management Service and to create and manage user and group security policies. Policies
can be created, copied, edited, disseminated, or deleted using the Management Console.
1.2 System Requirements
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Server System Requirements Client System Requirements
Operating Systems:
Microsoft* Windows* 2003 Server
Processor:
3.0 GHz Pentium* 4 HT (or greater)
756 MB RAM minimum (1 GB+ Recommended)
Disk Space:
500 MB - Without local Microsoft SQL database
5 GB - With local MS SQL database (SCSI
recommended)
Required Software:
Supported RDBMS (SQL Server Standard, SQL
Server Enterprise, Microsoft SQL Server 2000
SP4, or SQL 2005)
Microsoft Internet Information Services (configured
for SSL)
Supported Directory Services (eDirectory, Active
Directory, or NT Domains*)
.NET framework 3.5 (servers and Management
Control only)
Operating Systems for Endpoint Security Client 3.5:
Windows XP SP1
Windows XP SP2
Windows 2000 SP4
Operating Systems for Endpoint Security Client 4.0:
Windows Vista SP1 (32-bit)
Processor:
600MHz Pentium 3 (or greater)
Minimum 128 MB RAM (256 MB or greater
recommended
Disk Space:
5 MB required, 5 additional MB recommended for
reporting data
Required Software:
Windows 3.1 Installer
All Windows updates should be current
Standalone Management Control:
Supported RDBMS (SQL Server Standard, SQL
Server Enterprise, Microsoft SQL Server 2000
SP4, SQL 2005, SQL Express)
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management 13
Page 14

1.2.1 ASP.NET
The Policy Distribution and Management services require a LOCAL account of ASP.NET to be
enabled. If this is disabled, the services will not work correctly.
1.2.2 Reliable Time Stamp
The Novell ZENworks Endpoint Security Management solution gathers data from multiple sources
and collates this data to create a wide variety of security and audit reports. The utility and probative
value of these reports is greatly diminished if disparate sources disagree as to times, and so it is
strongly recommended that anyone installing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management provide
for enterprise-wide time synchronization (such as that provided by Active Directory* or through the
use of Network Time Protocol).
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administrators should follow all installation, operation,
and maintenance recommendations provided in this document and the ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management Installation Guide in order to ensure a strong security environment.
1.3 About the ZENworks Endpoint Security
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Management Manuals
The ZENworks Endpoint Security Management manuals provide three levels of guidance for the
users of the product.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide: This guide is written for the
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administrators who manage the ZENworks
Endpoint Security Management services, create security policies for the enterprise, generate
and analyze reporting data, and provide troubleshooting for users. Instructions for completing
these tasks are provided in this manual. This is the guide you are currently reading.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide: This guide provides complete
installation instructions for the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management components and
assists the administrator in getting those components up and running.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Client 3.5 User Guide: This manual is written to instruct the end
user on the operation of the Endpoint Security Client running on Windows XP and Windows
2000. This guide can be sent to all employees in the enterprise to help them understand how to
use the Endpoint Security Client.
ZENworks Endpoint Security Client 4.0 User Guide: This manual is written to instruct the end
user on the operation of the Endpoint Security Client running on Windows Vista. This guide
can be sent to all employees in the enterprise to help them understand how to use the Endpoint
Security Client.
1.4 USB/Wireless Security
ZENworks USB/Wireless Security (UWS) is a simplified version of the product that provides
comprehensive USB control, connectivity security, and file encryption features. ZENworks USB/
Wireless Security does not include some of the additional security features that are available in
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management. If you have purchased USB/Wireless Security rather
than ZENworks Endpoint Security Management, all functionality described in this manual will be
essentially the same, with only certain policy features unavailable in the Management Console.
14 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 15

The unavailable features have been marked with the following notation on their respective pages:
NOTE: This feature is only available in the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management installation,
and cannot be used for USB/Wireless Security security policies.
Features without this notation are available for both ZENworks Endpoint Security Management and
UWS security policies.
To verify which version you are running, open the “About” screen from the Help menu in
Management Console (see Section 5.2, “Using the Console Menu Bar,” on page 43).
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management 15
Page 16

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
16 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 17

2
Policy Distribution Service
The Policy Distribution Service in Novell® ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management is a web
service application that, when requested, distributes security policies and other necessary data to
Endpoint Security Clients on endpoint computers in your enterprise. Endpoint Security Management
security policies are created and edited with the Management Service's Management Console, then
published to the Policy Distribution Service, from where they are downloaded by the client at checkin.
The following graphic illustrates the role of the Policy Distribution Service:
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
2
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 2.1, “About the Policy Distribution Service,” on page 17
Section 2.2, “Securing Server Access,” on page 18
Section 2.3, “Running the Service,” on page 19
2.1 About the Policy Distribution Service
The Policy Distribution Service authenticates Endpoint Security Clients based on the user ID
credentials obtained from the Management Service, and supplies each client with the designated
security policy.
Reporting data is collected by Endpoint Security Clients and passed up to the Policy Distribution
Service. This data is periodically collected by the Management Service and then deleted from the
Policy Distribution Service.
The Policy Distribution Service does not initiate any communications with the other Endpoint
Security Management components, and only responds to others. It does not hold sensitive data in the
clear, nor does it hold the keys needed to decrypt the sensitive data. It does not hold user credentials
or any other user-specific data.
Section 2.1.1, “Server Selection and Installation,” on page 18
Section 2.1.2, “Server Maintenance,” on page 18
Section 2.1.3, “Upgrading the Software,” on page 18
Section 2.1.4, “Uninstall,” on page 18
Policy Distribution Service
17
Page 18

2.1.1 Server Selection and Installation
See the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide for selection and installation
instructions.
2.1.2 Server Maintenance
It is recommended that regular disk cleanup tasks be configured to run on this server to remove
temporary files from the
generate an inordinate amount of temporary files that needlessly consume disk space.
Windows\temp
folder. Under extreme load conditions, Windows can
2.1.3 Upgrading the Software
To upgrade your software from one release to another, you must uninstall the old release and install
the new release. Complete instructions are provided in “Upgrading” in the ZENworks Endpoint
Security Management Installation Guide.
2.1.4 Uninstall
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To uninstall the Policy Distribution Service, use the Add/Remove Programs function in the
Windows Control Panel, or run the installation again from the ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management installation CD.
2.2 Securing Server Access
The following sections contain information to help you secure access to your ZENworks Endpoint
Security Management server:
Section 2.2.1, “Physical Access Control,” on page 18
Section 2.2.2, “Network Access Control,” on page 19
Section 2.2.3, “High Availability,” on page 19
2.2.1 Physical Access Control
Physical access to the Distribution Service Server should be controlled to prevent access by
unauthorized parties. Measures taken should be appropriate to the risks involved. There are multiple
available standards and guidelines available, including NIST recommendations, HIPAA
requirements, ISO/IEC 17799, and less formal collections of recommendations such as CISSP or
SANS guidelines. Even when a given regulatory frameworks is not applicable, it may still act as a
valuable resource and planning guide.
Likewise, Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity mechanisms to protect the Distribution Server
should be put in place to protect the server if an organizational risk assessment identifies a need for
such steps. The mechanisms best used will depend on the specifics of the organization and its
desired risk profile, and cannot be described in advance. The same standards and guidelines sources
listed above can be helpful in this decision as well.
18 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 19

2.2.2 Network Access Control
The Distribution Server can be further protected from unauthorized access by restricting network
access to it. This may take the form of some or all of the following:
Restricting incoming connection attempts to those ports and protocols from which a valid
access attempt might be expected
Restricting outgoing connection attempts to those IP addresses to which a valid access attempt
might be expected
Restricting outgoing connection attempts to those ports and protocols to which a valid access
attempt might be expected
Such measures can be imposed through the use of standard firewall technology.
2.2.3 High Availability
High Availability mechanisms for the Distribution Server should be put in place if an organizational
risk assessment identifies a need for such steps. There are multiple alternative mechanisms for
building high availability solutions, ranging from the general (DNS round-robining, layer 3
switches, etc.) to the vendor specific (the Microsoft* web site has multiple resources on high
availability web services and clustering issues). Those implementing and maintaining a ZENworks
Endpoint Security Management solution should determine which class of high availability solution
is most appropriate for their context. Note that the Distribution Server has been architected to
function in non-high-availability situations, and does not require High Availability to provide its
services.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
2.3 Running the Service
The Policy Distribution Service launches immediately following installation, with no reboot of the
server required. The Management Console can adjust upload times for the Distribution Service
using the Configuration feature (see Section 5.3.1, “Infrastructure and Scheduling,” on page 44).
Policy Distribution Service 19
Page 20

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
20 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 21

3
Configuring the Directory Service
After you install ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management, you must create and configure a
directory service before you can start managing devices in your system.
The New Directory Service Configuration Wizard lets you create a directory service configuration
that defines the scope of your ZENworks Endpoint Security Management client installations. The
new configuration uses your existing directory service to define the logical boundary for your userbased and computer-based client installations.
The wizard guides you through the process of selecting the directory service and the containers
where current and future client accounts reside.
The wizard also lets you synchronize the directory entries included in the new configuration. This
synchronization is performed in the background so you can immediately begin using your new
configuration.
The following sections contain more information:
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
3
Section 3.1, “Configuring the Directory Service for Novell eDirectory,” on page 21
Section 3.2, “Configuring the Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory,” on page 28
3.1 Configuring the Directory Service for Novell eDirectory
After installing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management, the New Directory Service
Configuration Wizard automatically displays. If you have just installed the product and the
Welcome page is displayed, skip to Step 4 in the following procedure.
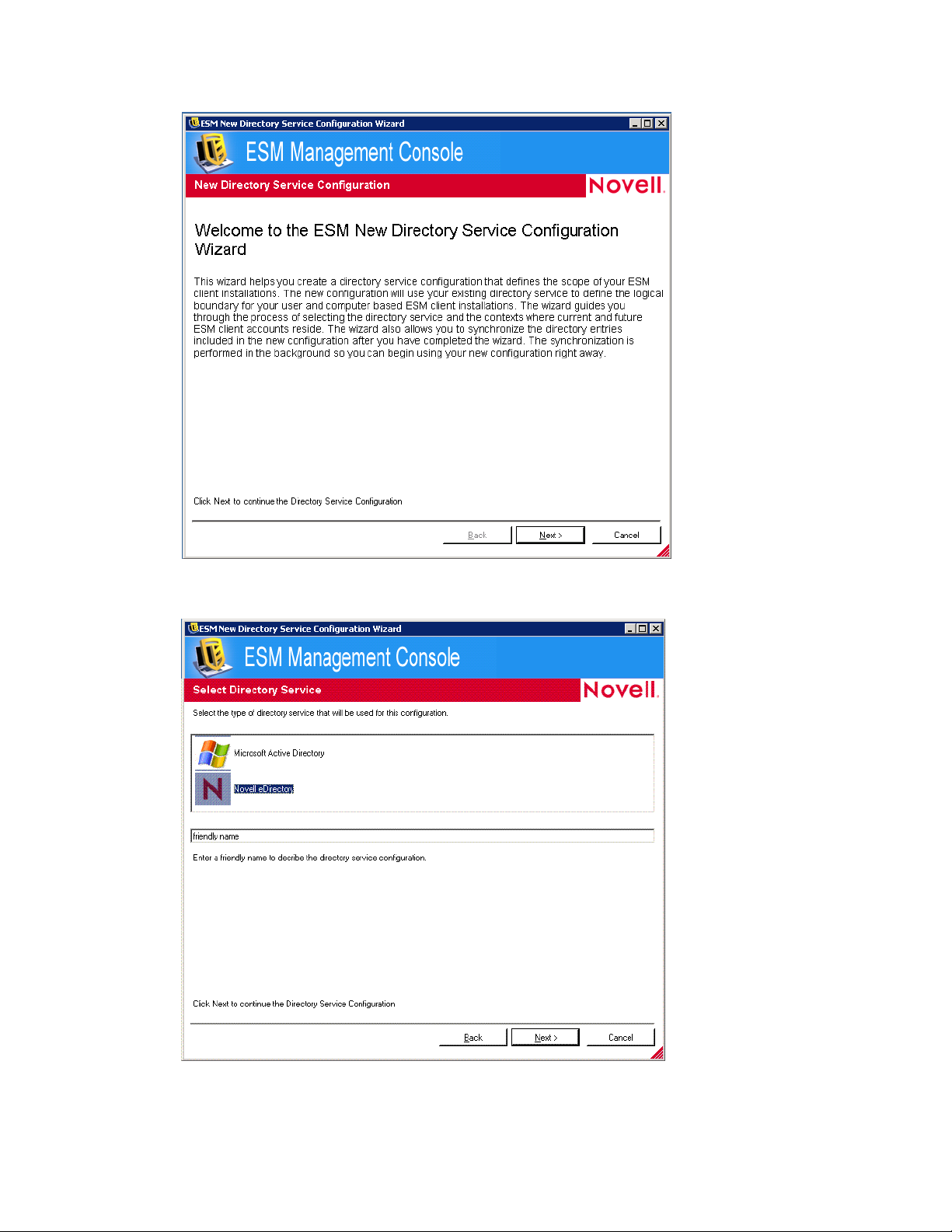
To configure the directory service:
1 In the Management Console, click Too ls > Configuration.
2 Click Authenticating Directories.
3 Click New to launch the New Directory Service Configuration Wizard.
Configuring the Directory Service
21
Page 22
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
4 Click Next to display the Select Directory Service page.
5 Select Novell eDirectory as the directory service.
22 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 23
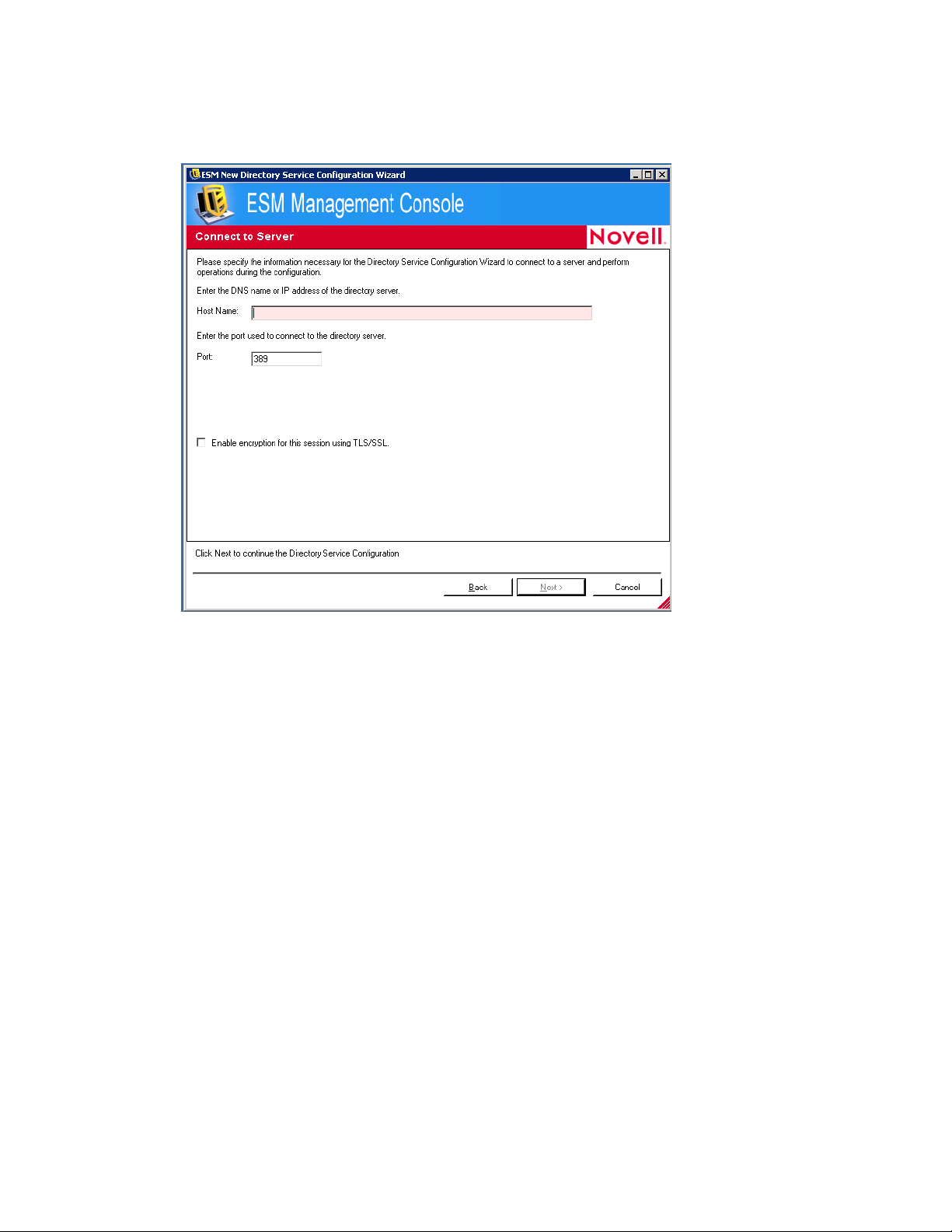
6 Specify a friendly name to describe the directory service configuration, then click Next to
display the Connect to Server page.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
7 Fill in the fields:
Host Name: Specify the DNS name or IP address of the directory server. If the DNS name
or IP address cannot be authenticated, a bind error message displays.
Port: Specify the port used to connect to the directory server.
Port 389 is the default. If you use a different port to connect to the directory server, you
can specify that port.
Enable Encryption for this Session using TLS/SSL: Select to enable encryption. If you
select this option, the port is automatically changed to 636.
8 Click Next to display the Provide Credentials page.
Configuring the Directory Service 23
Page 24
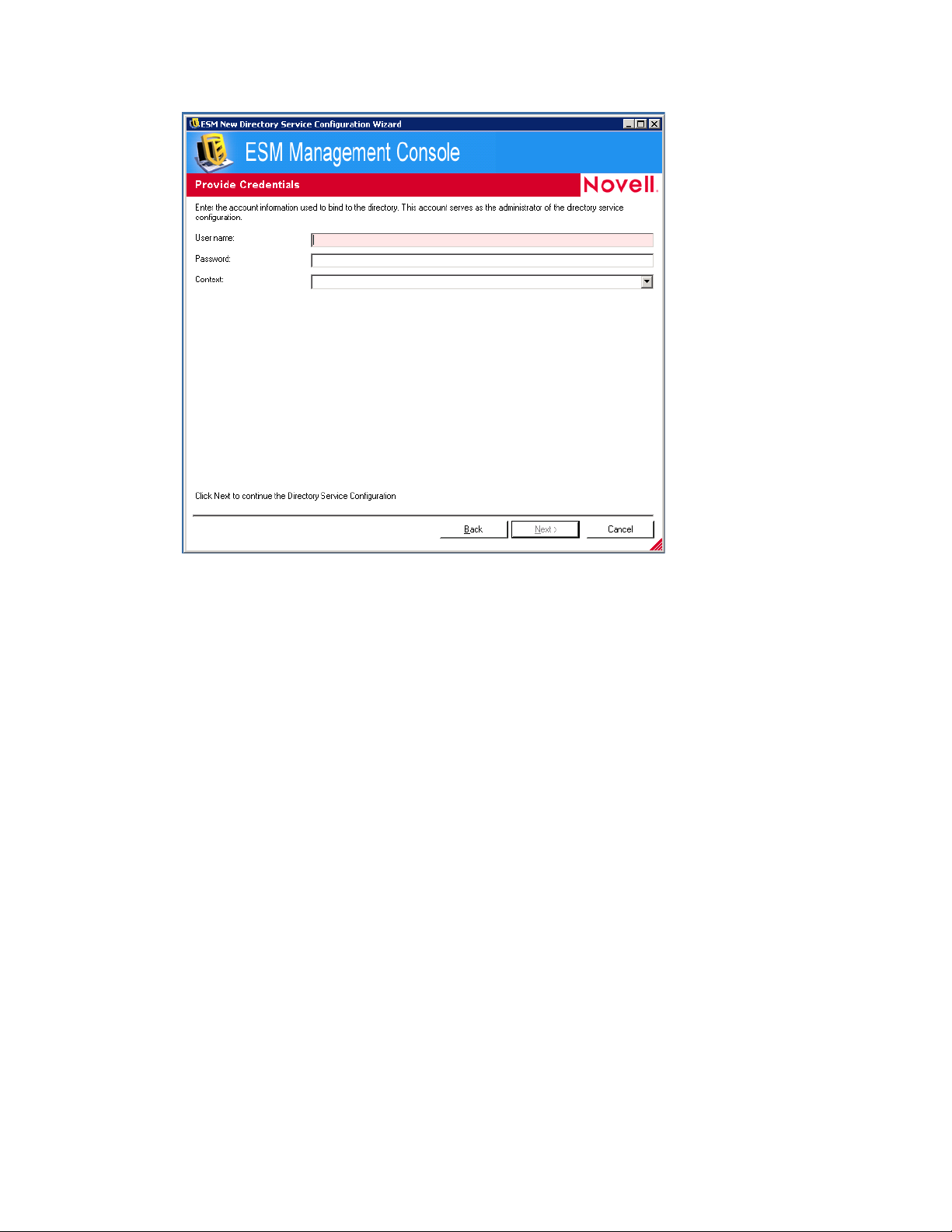
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
9 Fill in the fields:
User name: Specify the account administrator to bind to the directory.
This account serves as the administrator of the directory service configuration. The login
name must be a user who has permission to view the entire directory tree. It is
recommended that this user be the OU administrator.
Password: Specify the password for the account administrator.
This account serves as the administrator of this directory service configuration.
The password should not be set to expire, and this account should never be disabled.
Context: Specify the context in which the account administrator is a member.
10 Click Next to display the Select Directory Partitions page.
24 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 25
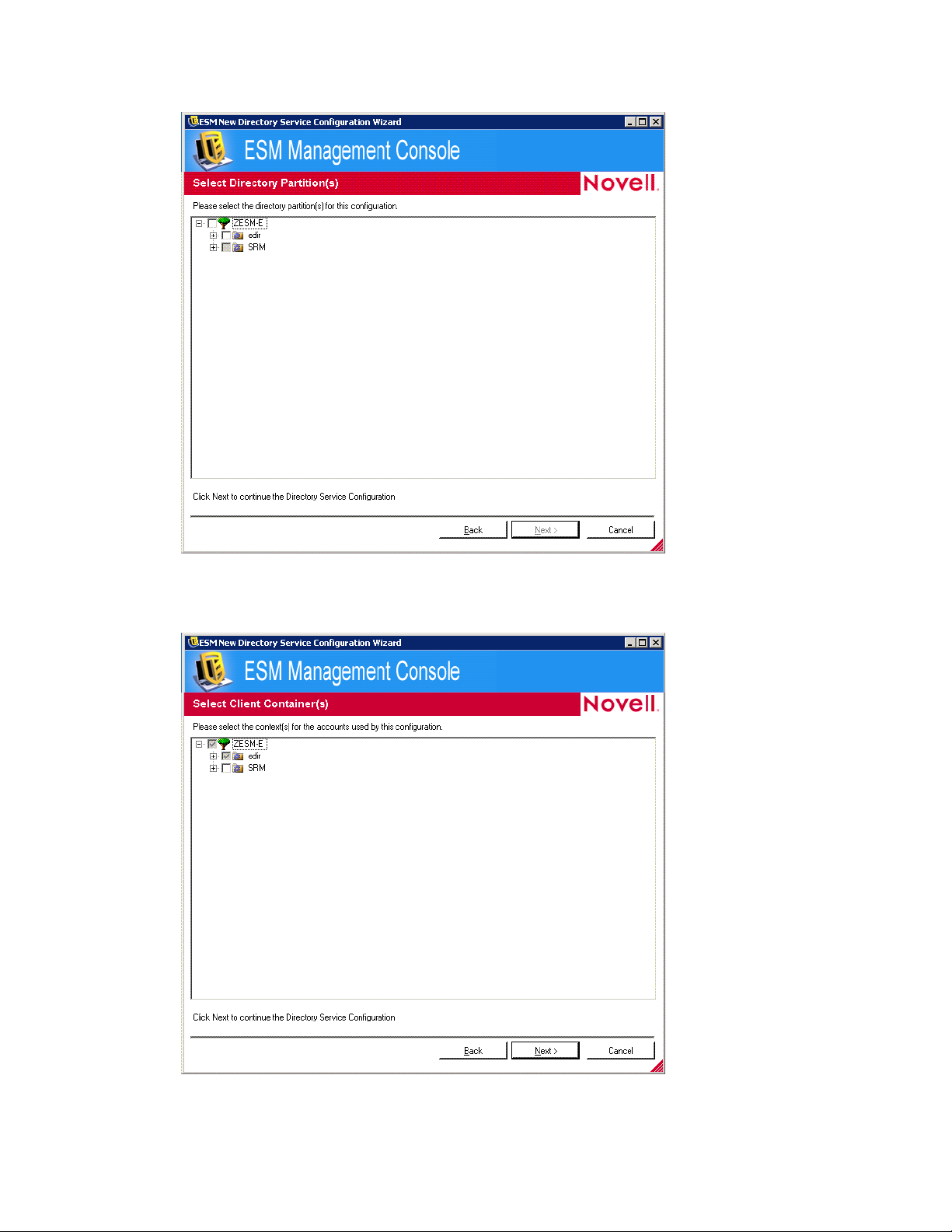
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
11 Browse to and select the directory partitions for this configuration, then click Next to display
the Select Client Contexts page.
12 Browse to and select the context(s) for the accounts used in this configuration.
Configuring the Directory Service 25
Page 26
The Select Client Context(s) page lets you narrow the search to only those contexts that contain
managed users and computers, which improves performance.
Any client installation that attempts to check in with the management server the does not reside
in a selected context results in longer search times.
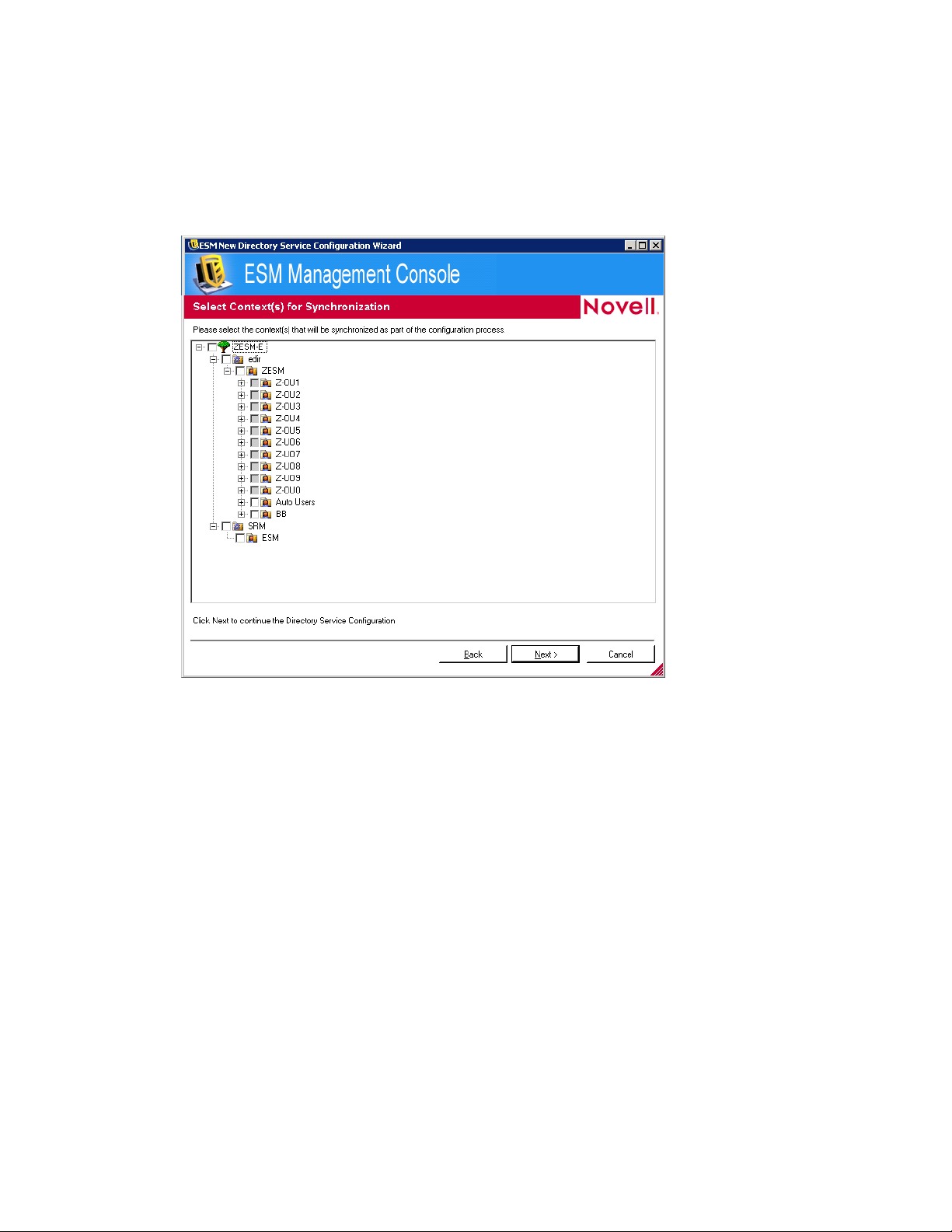
13 Click Next to display the Select Context(s) for Synchronization page.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
14 (Optional) Select the contexts to synchronize as part of the configuration process.
The synchronization is performed in the background so you can immediately begin using your
new configuration. If you have many users and computers to synchronize, this might take a few
hours.
If you do not specify contexts to synchronize, the users and computers in those contexts are
populated in the Management Console when they check in.
Synchronizing contexts pre-populates the Management Console with those users and
computers so that you can immediately perform actions such as creating security policies.
When the users or computers check in to the system, those policies are pushed down and
applied. By pre-populating the Management Console, you can immediately begin creating
policies that are specific to individual users or computers, rather than creating a policy that
applies to all users and computers in the context. If you do not synchronize the context, you
must wait until those users and computers check in to the system before creating unique
policies for different users or computers.
15 Click Next to display the Save Configuration page.
26 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 27
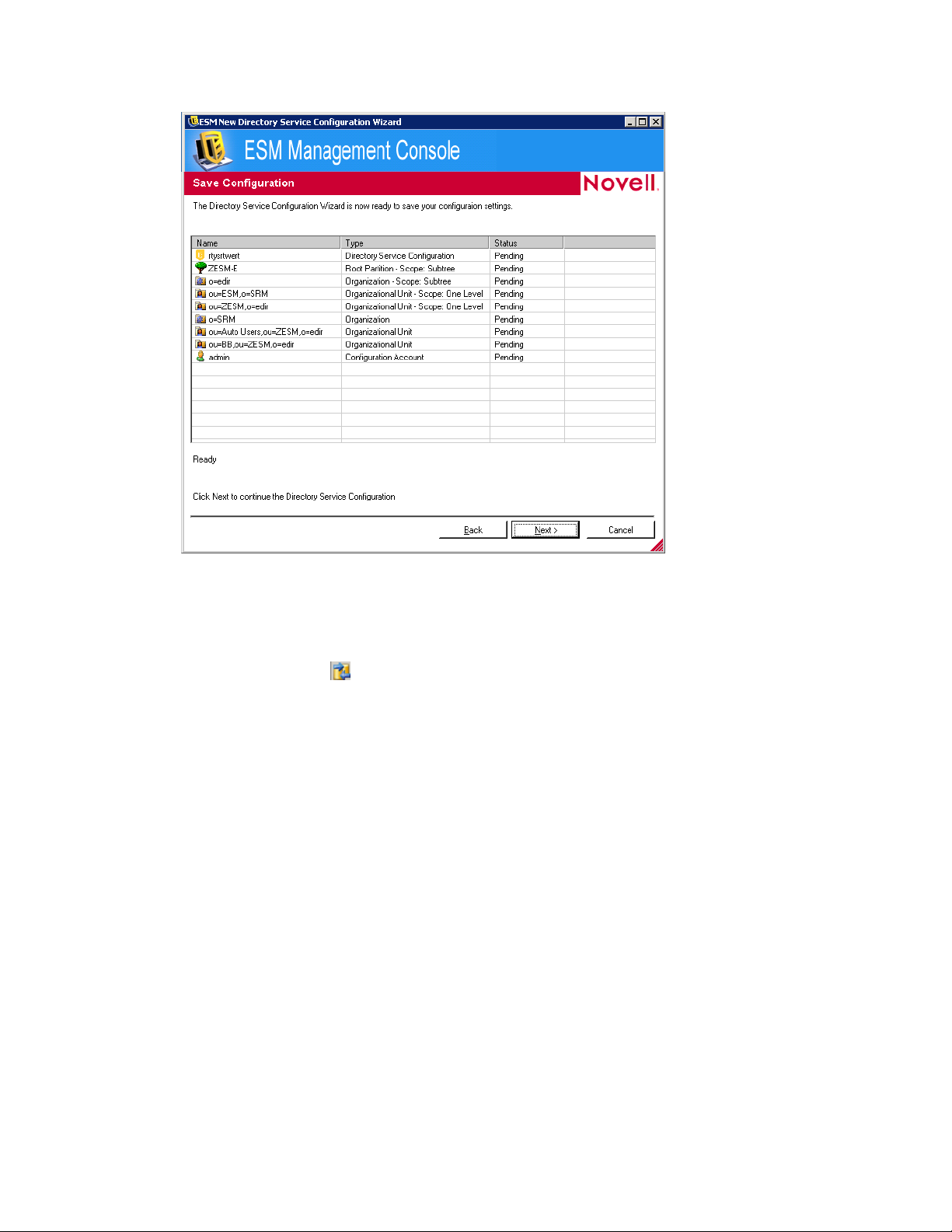
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
16 Review the information, then click Next.
You can click Back to change any settings, if necessary.
17 Click Finish.
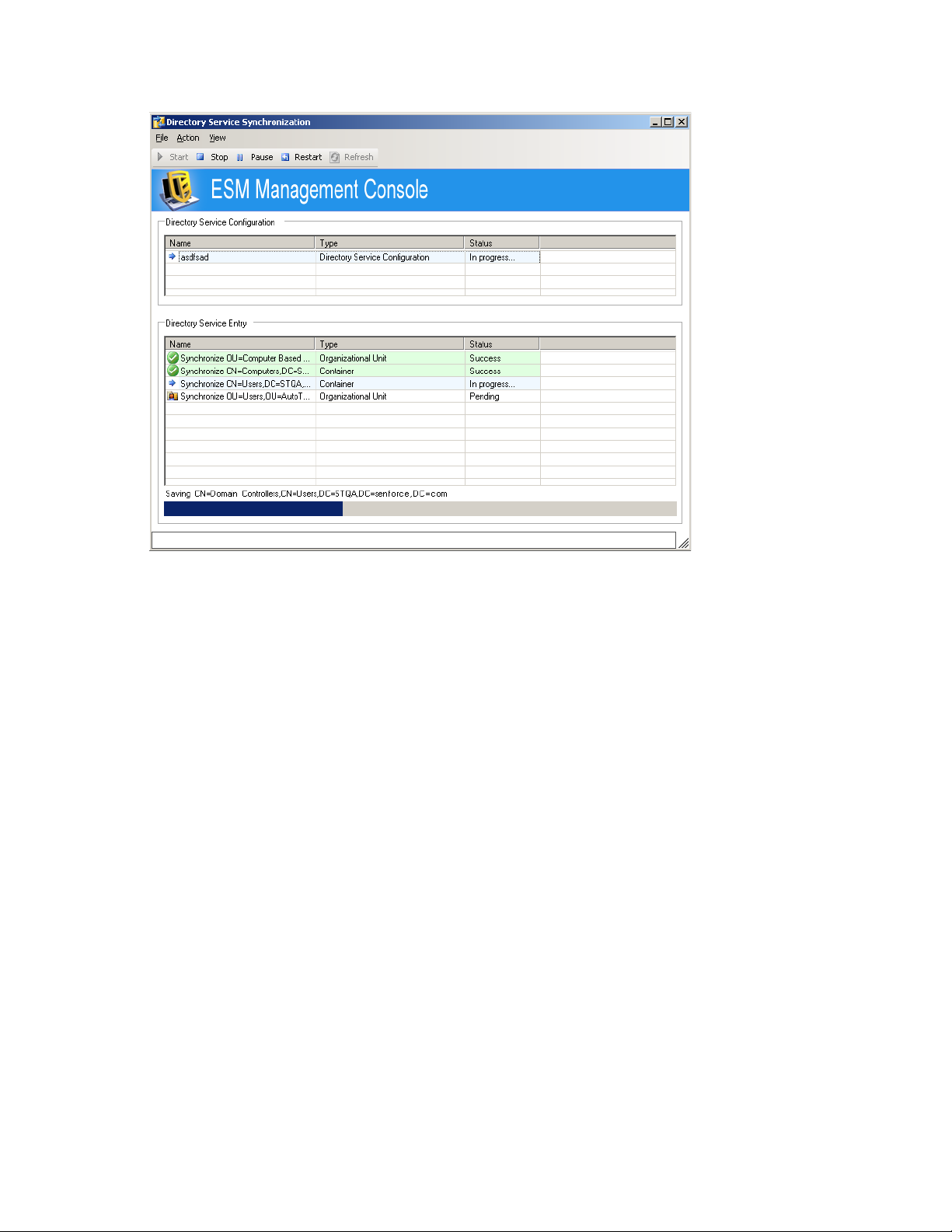
When you click Finish, the icon displays in your Windows notification area and the
synchronization begins. You can double-click the icon to display the Directory Services
Synchronization dialog box.
Configuring the Directory Service 27
Page 28
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The synchronization occurs in the background. If you exit the Management Console, the
synchronization stops. When you open the Management Console again, the synchronization
resumes where it left off.
3.2 Configuring the Directory Service for Microsoft Active Directory
After installing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management, the New Directory Service
Configuration Wizard automatically displays. If you have just installed the product and the
Welcome page is displayed, skip to Step 4 in the following procedure.
To configure the directory service:
1 In the Management Console, click Too ls > Configuration.
2 Click Authenticating Directories.
3 Click New to launch the New Directory Service Configuration Wizard.
28 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 29
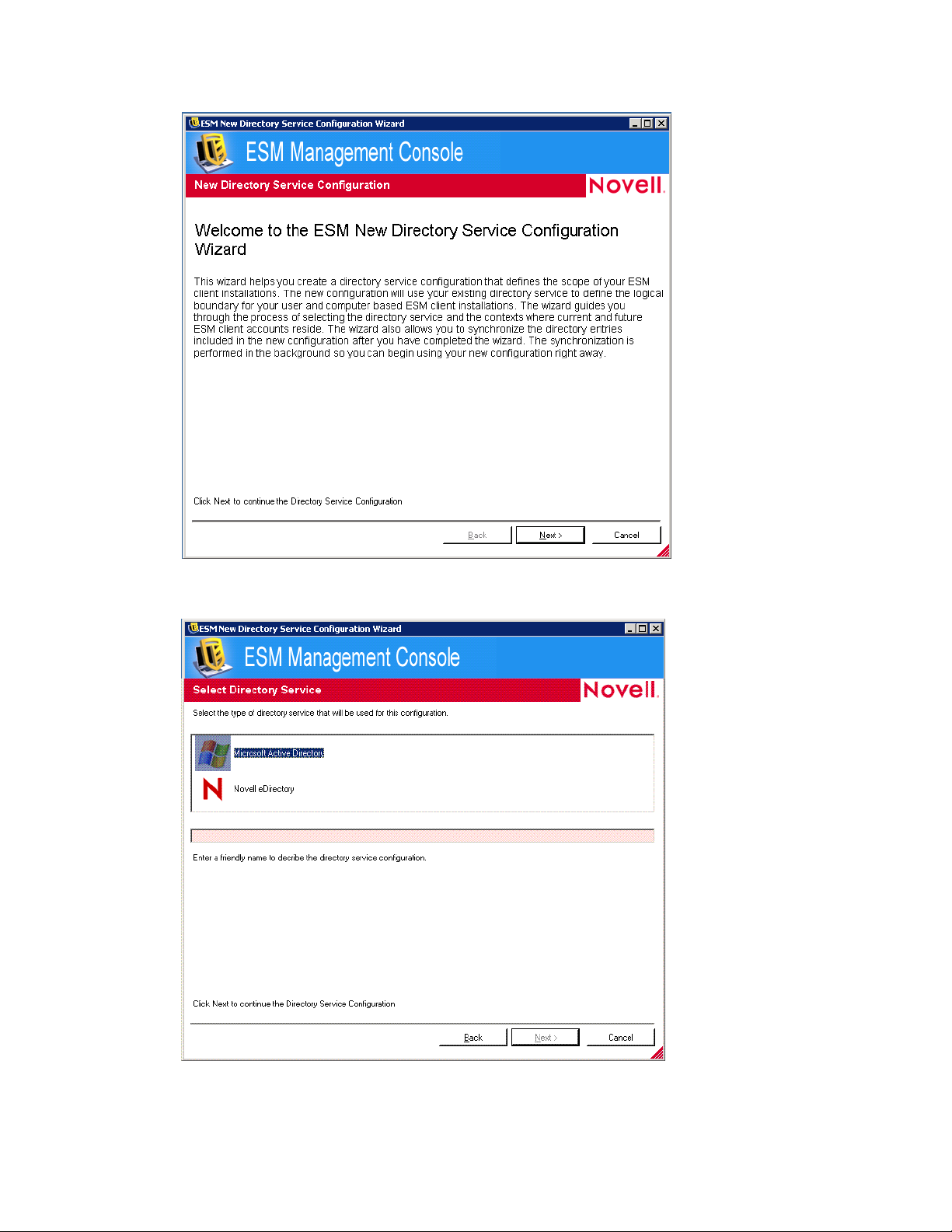
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
4 Click Next to display the Select Directory Service page.
5 Select Microsoft Active Directory as the directory service.
Configuring the Directory Service 29
Page 30
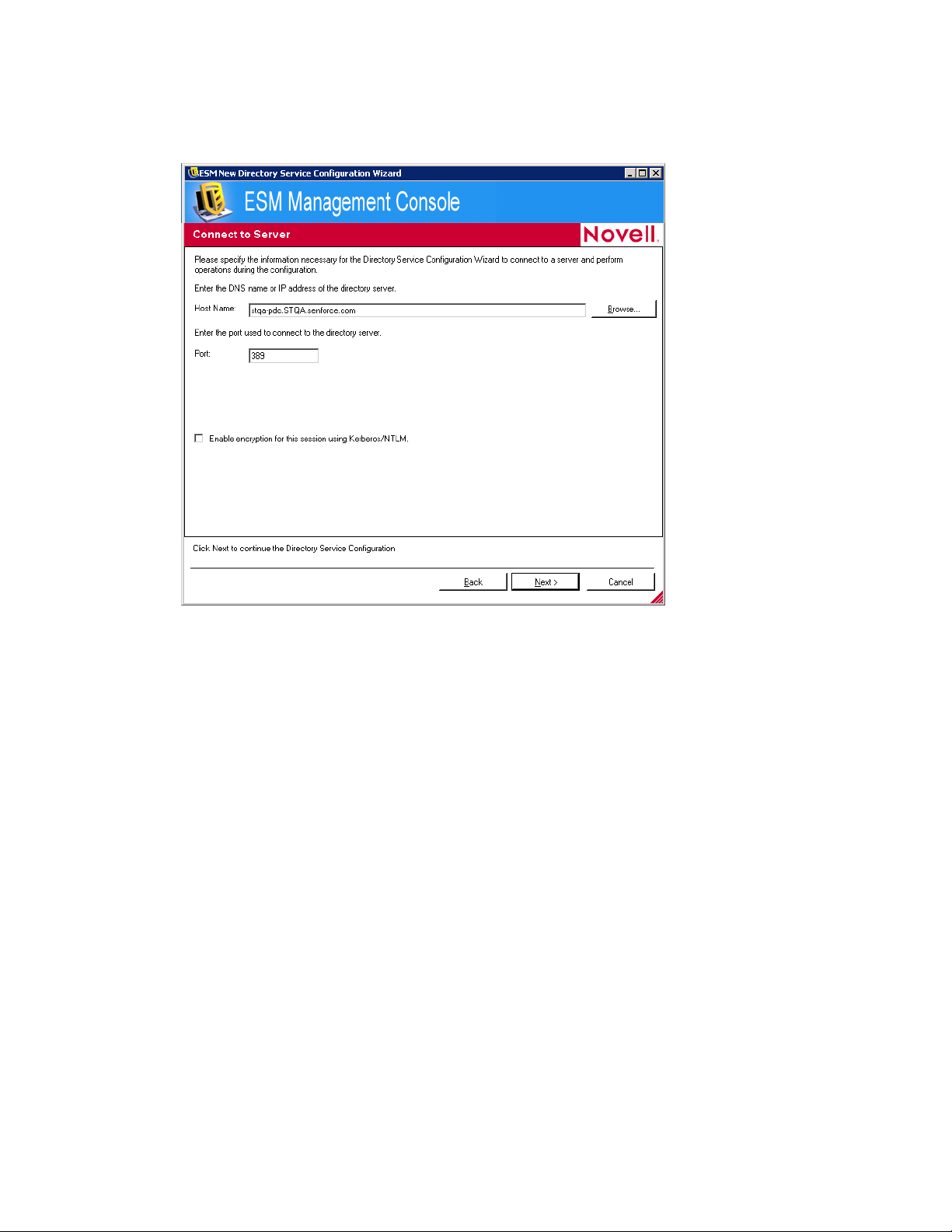
6 Specify a friendly name to describe the directory service configuration, then click Next to
display the Connect to Server page.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
7 Fill in the fields:
Host Name: Specify the DNS name or IP address of the directory server. If the DNS name
or IP address cannot be authenticated, a bind error message displays.
Port: Specify the port used to connect to the directory server.
Port 389 is the default. If you use a different port to connect to the directory server, you
can specify that port.
Enable Encryption for this Session using Kerberos/NTLM: Select to enable
encryption.
8 Click Next to display the Provide Credentials page.
30 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 31

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
9 Fill in the fields:
User name: Specify the account administrator to bind to the directory.
This account serves as the administrator of the directory service configuration. The login
name must be a user who has permission to view the entire directory tree. It is
recommended that this user be the domain administrator.
Password: Specify the password for the account administrator.
This account serves as the administrator of this directory service configuration.
The password should not be set to expire, and this account should never be disabled.
Domain: Specify the domain in which the account administrator is a member.
Authentication Method: Select an authentication method:
Negotiate
Kerberos
NTLM
10 If the configuration administrator user you specified in Step 9 cannot be found in the domain,
the Locate Account Entry page displays.
Configuring the Directory Service 31
Page 32

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Specify the container where the administrator is located.
11 Click Next to display the Select Authenticating Domain(s) page.
32 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 33

12 Browse to and select the authenticating domains for this configuration, then click Next to
display the Select Client Container(s) page.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
13 Browse to and select the containers for the accounts used in this configuration.
The Select Client Container(s) page lets you narrow the search to only those containers that
contain managed users and computers, which improves performance.
Any client installation that attempts to check in with the management server the does not reside
in a selected container results in longer search times.
14 Click Next to display the Select Container(s) for Synchronization page.
Configuring the Directory Service 33
Page 34

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
15 (Optional) Select the containers to synchronize as part of the configuration process.
The synchronization is performed in the background so you can immediately begin using your
new configuration. If you have many users and computers to synchronize, this might take a few
hours.
If you do not specify containers to synchronize, the users and computers in those contexts are
populated in the Management Console when they check in.
Synchronizing contexts pre-populates the Management Console with those users and
computers so that you can immediately perform actions such as creating security policies.
When the users or computers check in to the system, those policies are pushed down and
applied. By pre-populating the Management Console, you can immediately begin creating
policies that are specific to individual users or computers, rather than creating a policy that
applies to all users and computers in the context. If you do not synchronize the context, you
must wait until those users and computers check in to the system before creating unique
policies for different users or computers.
16 Click Next to display the Save Configuration page.
34 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 35

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
17 Review the information, then click Next.
You can click Back to change any settings, if necessary.
18 Click Finish.
When you click Finish, the icon displays in your Windows notification area and the
synchronization begins. You can double-click the icon to display the Directory Services
Synchronization dialog box.
Configuring the Directory Service 35
Page 36
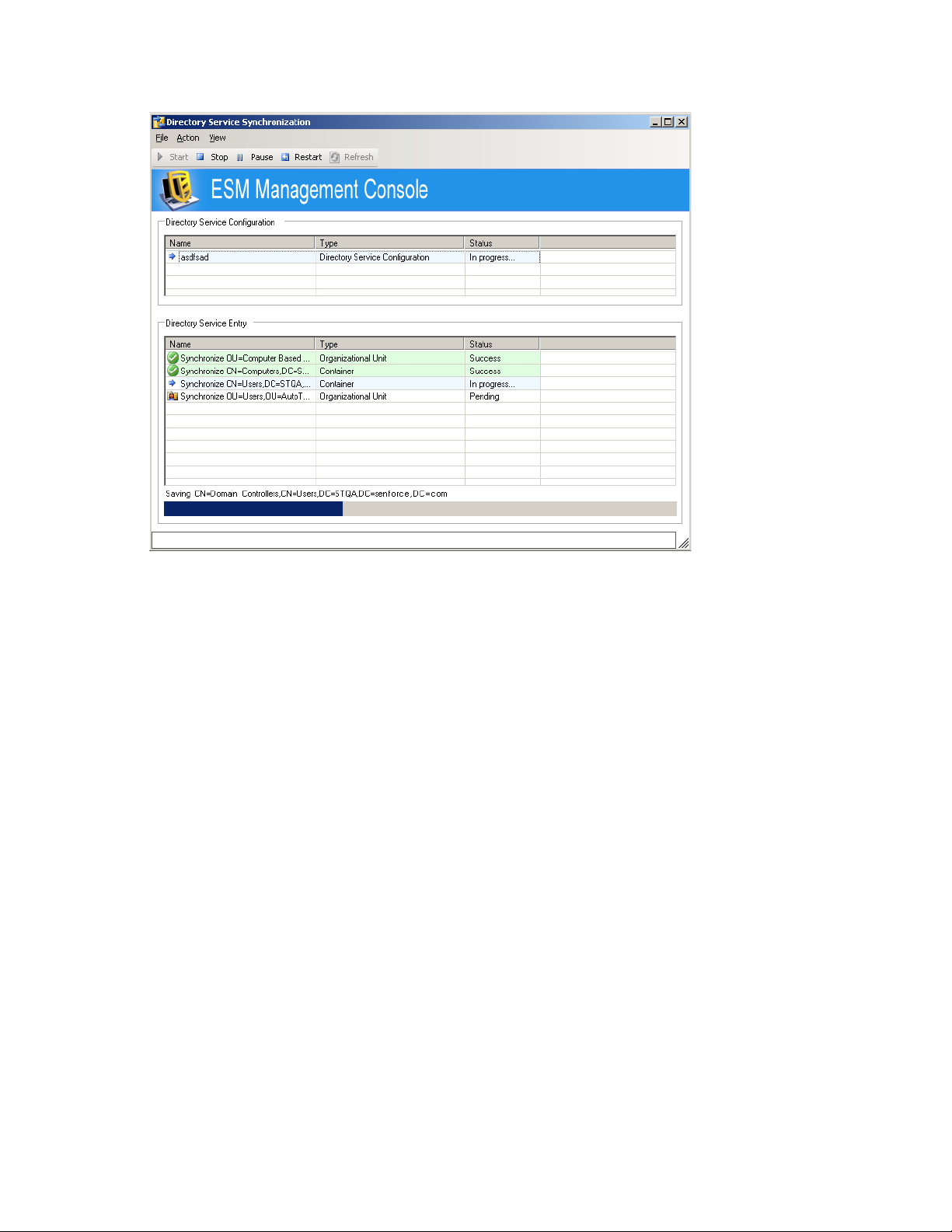
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The synchronization occurs in the background. If you exit the Management Console, the
synchronization stops. When you open the Management Console again, the synchronization
resumes where it left off.
36 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 37
4
Using the ZENworks Endpoint
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Security Management Service
The Management Service in Novell® ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management is the central
service for Endpoint Security Management. It is used to create authentication credentials, design and
store security policies and their components, and provide remediation through a robust reporting
service. It provides security policies and user information to the Policy Distribution Service, as well
as providing opaque credentials to Endpoint Security Clients.
The following graphic illustrates the role of the Management Service:
4
Security policies, credentials, and reports are stored in an SQL database(s), which may reside on the
same server as the Management Service or on remote servers.
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 4.1, “About the Management Service,” on page 37
Section 4.2, “Securing Server Access,” on page 38
Section 4.3, “Distributing and Renewing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
Credentials,” on page 39
4.1 About the Management Service
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 4.1.1, “Server Selection and Installation,” on page 37
Section 4.1.2, “Server Maintenance,” on page 38
Section 4.1.3, “Upgrading the Software,” on page 38
Section 4.1.4, “Uninstall,” on page 38
4.1.1 Server Selection and Installation
See ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide for selection and installation
instructions.
Using the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Service
37
Page 38

4.1.2 Server Maintenance
It is recommended that regular disk cleanup tasks be configured to run on this server to remove
temporary files out of the
generate an inordinate amount of temporary files that needlessly consume disk space.
Windows\temp
folder. Under extreme load conditions, Windows can
4.1.3 Upgrading the Software
To upgrade your software from one release to another, you must uninstall the old release and install
the new release. Complete instructions are provided in “Upgrading” in the ZENworks Endpoint
Security Management Installation Guide.
4.1.4 Uninstall
To uninstall the Management Service, use the Add/Remove Programs function in the Windows
Control Panel.
To uninstall the Management Console (when run on a separate computer), use the Add/Remove
Programs function in the Windows Control Panel.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
4.2 Securing Server Access
The following sections contain information to help you secure access to your ZENworks Endpoint
Security Management server:
Section 4.2.1, “Physical Access Control,” on page 38
Section 4.2.2, “Network Access Control,” on page 39
Section 4.2.3, “High Availability,” on page 39
Section 4.2.4, “Running the Service,” on page 39
4.2.1 Physical Access Control
Physical access to the Management Server should be controlled to prevent access by unauthorized
parties. Measures taken should be appropriate to the risks involved. There are multiple available
standards and guidelines available, including NIST recommendations, HIPAA requirements, ISO/
IEC 17799, and less formal collections of recommendations such as CISSP or SANS guidelines.
Even when a given regulatory frameworks is not applicable, it may still act as a valuable resource
and planning guide.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity mechanisms to protect the Management Server should
be put in place to protect the server if an organizational risk assessment identifies a need for such
steps. The mechanisms best used will depend on the specifics of the organization and its desired risk
profile, and cannot be described in advance. There are multiple available standards and guidelines
available, including NIST recommendations, HIPAA requirements, ISO/IEC 17799, and less formal
collections of recommendations such as CISSP or SANS guidelines.
38 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 39

4.2.2 Network Access Control
The Management Server can be further protected from unauthorized access by restricting network
access to it. This may take the form of some or all of the following:
Restricting incoming connection attempts to those IP addresses from which a valid access
attempt might be expected
Restricting incoming connection attempts to those ports and protocols from which a valid
access attempt might be expected
Restricting outgoing connection attempts to those IP addresses to which a valid access attempt
might be expected
Restricting outgoing connection attempts to those ports and protocols to which a valid access
attempt might be expected.
Such measures can be imposed through the use of standard firewall technology.
4.2.3 High Availability
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
High Availability mechanisms for the Management Server should be put in place if an
organizational risk assessment identifies a need for such steps. There are multiple alternative
mechanisms for building high availability solutions, ranging from the general (DNS round-robining,
layer 3 switches, etc.) to the vendor specific (the Microsoft web site has multiple resources on high
availability web services). Those implementing and maintaining an Endpoint Security Management
solution should determine which class of high availability solution is most appropriate for their
context. Note that the Management Server has been architected to function in non-high-availability
situations, and does not require High Availability to provide its services.
4.2.4 Running the Service
The Management Service launches immediately following installation, with no reboot of the server
required. The Management Console is used to manage the data on the Management Service. See
Section 5.3.1, “Infrastructure and Scheduling,” on page 44 for more details.
4.3 Distributing and Renewing ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Credentials
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 4.3.1, “Distributing Endpoint Security Management Credentials (Key Management
Key),” on page 39
Section 4.3.2, “Periodic Renewal of the Key Management Key (KMK),” on page 40
4.3.1 Distributing Endpoint Security Management Credentials (Key Management Key)
The Management Service automatically distributes credentials to each Endpoint Security Client
when it is installed and checks in to the Management Service for the first time. After this credential
is distributed, the Endpoint Security Client is permitted to receive policies from the Policy
Distribution Service, and provide reporting data to the Reporting Service.
Using the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Service 39
Page 40

4.3.2 Periodic Renewal of the Key Management Key (KMK)
Cryptographic best practices dictate that the KMK be renewed at regular intervals to prevent certain
cryptographic attacks from being practical. This need only take place on a relatively long cycle:
typically on the order of once every year, and should not be done too frequently because the changeover does involve some effort and bandwidth costs.
To renew the KMK, perform the following steps:
1 Open the Communications Console on the Management Service (Start/Programs/Novell/
Management Service/Endpoint Security Management Communications Console).
NOTE: Running the Communications Console causes the Management Service to lose user
and log data; however, policy data is not deleted.
2 Allow the Communications Console to run a complete check.
3 Have all end users authenticate to the Management Service (either via VPN or while inside the
appropriate firewall), by right-clicking the Endpoint Security Client taskbar icon, then clicking
Check for Policy Update.
4 The Management Console automatically passes the new KMK credentials down. In some
cases, the user must authenticate to the domain (username and password).
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Until the endpoints renew their KMK, they will not be able to communicate with the Policy
Distribution Service.
40 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 41

5
Using the ZENworks Storage
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Encryption Solution Management
Console
The Management Console in Novell® ZENworks® Endpoint Security Management is the central
access and control mechanism for the Management Service.
Double-click the ESM Management Console icon on the desktop to launch the login window. Log in
to the console by entering the administrator name and password. The username entered must be an
authorized user on the Management Service.
NOTE: It is recommended that the console be closed or minimized when not in use.
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 5.1, “Using the Console Taskbar,” on page 41
Section 5.2, “Using the Console Menu Bar,” on page 43
Section 5.3, “Using the Configuration Window,” on page 44
Section 5.4, “Using Alerts Monitoring,” on page 47
Section 5.5, “Using Reports,” on page 51
Section 5.6, “Generating Custom Reports,” on page 60
5
Section 5.7, “Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution,” on page 71
Section 5.8, “Managing Keys,” on page 72
5.1 Using the Console Taskbar
The taskbar on the left provides access to the Management Console tasks. If the taskbar is not
visible, click the Tas ks button.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console
41
Page 42

Figure 5-1 The Management Console
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The functions available in the taskbar are described in the following sections:
Section 5.1.1, “Policy Tasks,” on page 42
Section 5.1.2, “Resources,” on page 43
Section 5.1.3, “Configuration,” on page 43
Section 5.1.4, “Endpoint Auditing,” on page 43
5.1.1 Policy Tasks
The primary function of the Management Console is the creation and dissemination of security
policies. The Policy Tasks guide the administrator through creating and editing security policies that
are used by the Endpoint Security Client to apply centrally managed security to each endpoint.
The Policy Tasks include the following:
Active Policies: Displays a list of current policies, which can be reviewed and edited. Click the
policy to open it.
Create Policy: Starts the policy creation process. For more information, see Chapter 6,
“Creating and Distributing Security Policies,” on page 75.
Import Policy: Imports policies created using other management services. For more
information, see Section 6.4.1, “Importing Policies,” on page 169.
Clicking any of the policy tasks minimizes the taskbar. Click the Tasks button left side of the
Management Console to display it again.
42 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 43

5.1.2 Resources
The following resources are available to help you:
Contact Support: Launches a browser to display the Novell Contacts and Offices page.
Online Technical Help: Launches a browser to display the Novell Training and Support page.
Management Console Help: Launches Help.
5.1.3 Configuration
The Management Service Configuration tasks provide controls for both the ZENworks Endpoint
Security Management server infrastructure and controls for monitoring additional enterprise
directory services. See Section 5.3, “Using the Configuration Window,” on page 44 for details. This
control is not available when running a "Stand-Alone" Management Console. See the ZENworks
Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide for more information.
5.1.4 Endpoint Auditing
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Endpoint Auditing gives you access to Endpoint Security Management Reporting and Alerting.
Alerts monitoring ensures that any attempts to compromise corporate security policies are reported
in the Management Console. This allows the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
administrator to know of potential problems and take any appropriate remedial actions. The Alerts
dashboard is completely configurable, granting total control over when and how frequently alerts are
triggered. See Section 5.4, “Using Alerts Monitoring,” on page 47 for details.
Reporting is critical in assessing and implementing strong security policies. Reports can be accessed
through the Management Console by clicking Reporting. The endpoint security information
gathered and reported back is also completely configurable, and can be gathered by domain, group,
or individual user. See Section 5.5, “Using Reports,” on page 51 for details.
5.2 Using the Console Menu Bar
The menu bar gives you access to all functions of the Management Console. As with all Windows
menus, simply click the menu link to display the menu items. The menu items are described below.
Figure 5-2 Menu Bar
File: Lets you create and manage policies.
Create New Policy: Starts the process to create a new policy.
Refresh Policy List: Updates the list to display all active policies.
Delete Policy: Deletes the selected policy.
Import Policy: Imports a policy into the Management Console.
Export Policy: Exports a policy and the required
outside of the Management Service database.
Exit: Closes the Management Console software, logging out the user.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 43
setup.sen
file to a specified location
Page 44

To ol s: Lets you control the Management Service.
Configuration: Opens the Configuration window.
Export Encryption Keys: Displays the Export Encryption Keys(s) dialog box.
Import Encryption Keys: Displays the Import Encryption Keys(s) dialog box.
Generate New Key: Creates and activates a new encryption key for policies enforcing
data protection.
View: Lets you change access key policy tasks without using the taskbar.
Active Policies: When a policy is open, switches the view to that policy.
Alerts: Displays the Alerts dashboard.
Reporting: Displays the Reporting dashboard.
Help: Lets you access to the Management Console Help and the About box.
Help: Launches the Management Console Help tool, which guides you through policy
creation as well as all Management Console tasks (also available by pressing the F1 key
on your keyboard).
About: Launches the About window, which displays the installation type (ESM or UWS
(see Section 1.4, “USB/Wireless Security,” on page 14) and the current version number
for the Management Console. This window is also where the license key is entered if you
purchase the product after installation.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
5.3 Using the Configuration Window
The Configuration window gives the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management administrator
access to the Infrastructure and Scheduling, Authenticating Directories, and Server Synchronization
controls.
NOTE: This function is not available if this is a Stand-Alone Management Console.
To access the Configuration window:
1 Click Too ls > Configuration.
2 Click one of the following options in the left pane:
Section 5.3.1, “Infrastructure and Scheduling,” on page 44
Section 5.3.2, “Authenticating Directories,” on page 46
Section 5.3.3, “Service Synchronization,” on page 47
5.3.1 Infrastructure and Scheduling
The Infrastructure and Scheduling module allows the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management
administrator to designate and change the Policy Distribution Service URL and control the
synchronization intervals for the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management components.
44 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 45

Figure 5-3 Infrastructure and Scheduling Window
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain more information about the Infastructure and Scheduling options:
“Distribution Service URL” on page 45
“Scheduling” on page 45
Distribution Service URL
Use this option to update the Policy Distribution Service location for both the Management Service
and all Endpoint Security Clients (without requiring them to be reinstalled) if the Policy Distribution
Service is moved to a new server. The URL for the current server is listed in the text field. Only the
server name should be changed to point to the new server. Do not change any information after the
server name.
Example:
NOTE: If the current URL is listed as
http:\\ACME\PolicyServer\ShieldClient.asmx
and
the Policy Distribution Service has been installed on a new server, ACME 43, the URL should be
updated as follows:
http:\\ACME43\PolicyServer\ShieldClient.asmx
.
After the URL has been updated, click OK to update all policies and send an automatic update of the
Policy Distribution Service. This also updates the Management Service.
When changing the server URL, it is recommended that the old Policy Distribution Service not be
terminated until the updated policies have a 100 percent adherence level. For more information, see
Section 5.5, “Using Reports,” on page 51).
Scheduling
The Scheduling components permit the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management administrator to
designate when the Management Service will synchronize with other ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management components, to ensure that all data and queued jobs match any recent activity, and to
schedule the SQL maintenance jobs. All time increments are listed in minutes.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 45
Page 46

The following scheduling options are available:
Distribution Service: Sets the synchronization schedule with the Policy Distribution Service.
Policy Data and Activity: Sets the synchronization schedule with policy updates.
Management Data: Sets the policy synchronization with the Management Service.
Enterprise Structure: Sets the synchronization schedule with the enterprise directory service
(eDirectory, Active Directory, NT Domain, and LDAP). Changes in the enterprise directory
service are monitored so that corresponding changes in user-policy assignments are detected
and sent to the Policy Distribution Service for Client authentication.
Client Reporting: Sets the frequency that the Management Service interrogates for and
downloads reporting data from the Policy Distribution Service.
Keep Alert Data for x Days: Configures alerts based on a snapshot of data reported by the
endpoints. To optimize performance, and to ensure that alerts are relevant to recent activity,
you can se the storage threshold based on a number of days.
5.3.2 Authenticating Directories
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Policies are distributed to end users by interrogating the Enterprise's existing directory service
(eDirectory, Active Directory, and NT Domains). The Authenticating Directories service is
responsible for handling end-user credentials and authentication issues for the Policy Distribution
Service.
NT Domain is supported only when the Management Service is installed on a Windows 2000 or
Windows 2000 advanced server (SP4).
An initial directory service is normally detected and monitored during the Management Service
communication check at installation. Authenticating Directories can, if required, manage users from
multiple directories and multiple directory platforms.
Figure 5-4 Authenticating Directories Window
All information, with the exception of the directory type may be updated.
46 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 47

To add a new directory service:
1 Click New to launch the New Directory Service Configuration Wizard.
2 Follow the prompts to complete the wizard. For detailed steps to complete the wizard, see
Chapter 3, “Configuring the Directory Service,” on page 21.
5.3.3 Service Synchronization
The Service Synchronization control lets you to force a synchronization of the Management Service
and Policy Distribution Service. This updates all alerting, reporting, and policy distribution.
Figure 5-5 Service Synchronization
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To update the current service status, click Refresh.
To restart the services and process the currently queued activities, click Synchronize.
5.4 Using Alerts Monitoring
Alerts monitoring allows the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management administrator to
effortlessly gauge the security state of all ZENworks Endpoint Security Management managed
endpoints throughout the enterprise. Alerts triggers are fully configurable and can report either a
warning or a full emergency alert. This tool is accessed either through Endpoint Auditing on the
taskbar or by using the View menu.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 47
Page 48

Figure 5-6 Alerts Dashboard
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Alerts monitoring is available for the following areas:
Client Integrity: Notifies the administrator of unremediated integrity test results.
Communication Port Security: Notifies the administrator of potential port scan attempts.
Data Protection: Notifies the administrator of files that are copied to removable storage
devices within a one-day period.
Security Client Configuration: Notifies the administrator of incorrect security client versions
and incorrect policies.
Security Client Tampering: Notifies the administrator of user hack attempts, uninstall
attempts, and usage of the override password.
Wireless Security: Notifies the administrator of unsecure access points, both detected and
connected to by the end user.
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 5.4.1, “Configuring Endpoint Security Management for Alerts,” on page 48
Section 5.4.2, “Configuring Alert Triggers,” on page 49
Section 5.4.3, “Managing Alerts,” on page 50
5.4.1 Configuring Endpoint Security Management for Alerts
Alerts monitoring requires reporting data be collected and uploaded at regular intervals to give the
most accurate picture of the current endpoint security environment. Unmanaged Endpoint Security
Clients do not provide reporting data, and will therefore, not be included in the Alerts monitoring.
48 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 49
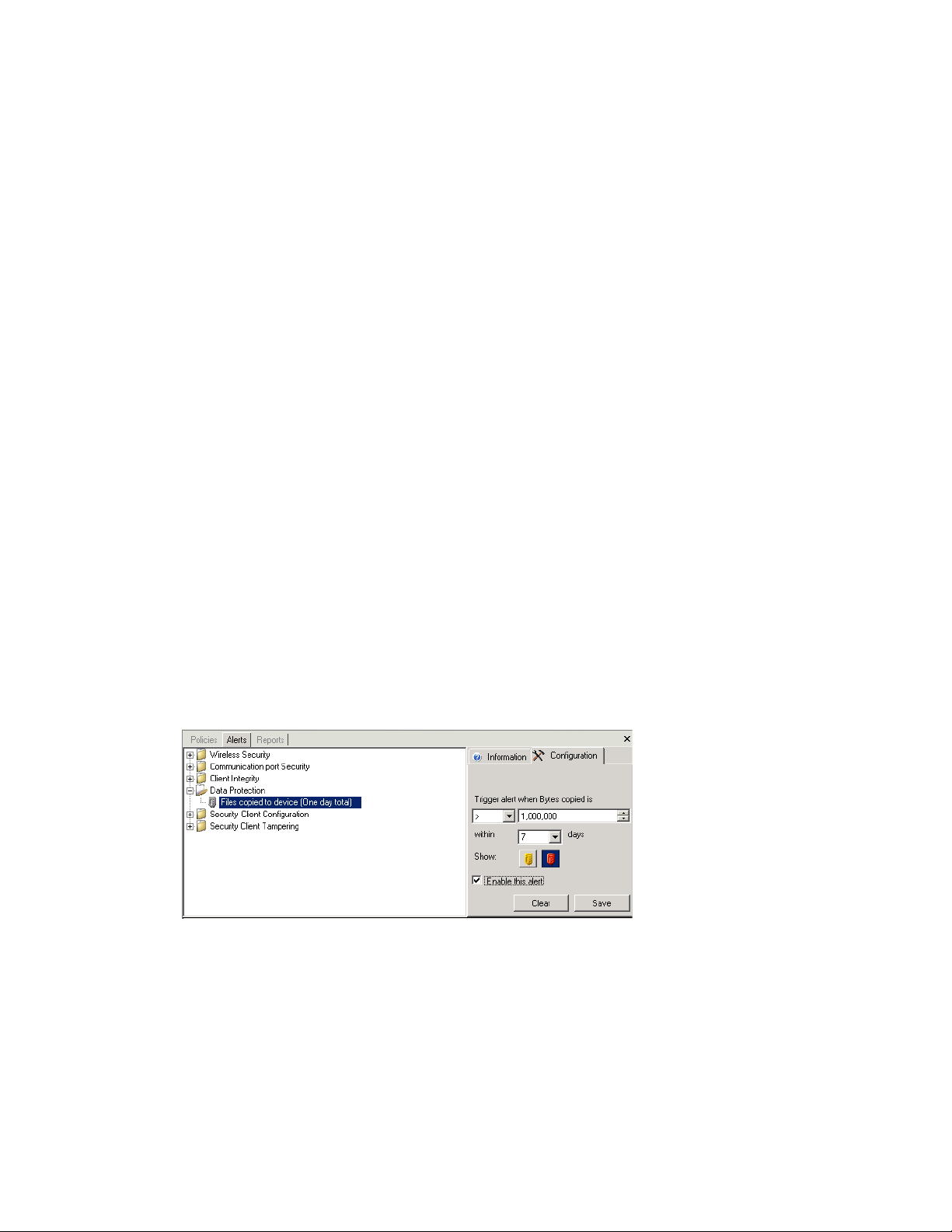
The following sections contain more information:
“Activating Reporting” on page 49
“Optimizing Synchronization” on page 49
Activating Reporting
Reporting should be activated in each security policy. See Section 6.2.4, “Compliance Reporting,”
on page 118 for details on setting up reporting for a security policy. Adjust report send times to an
interval that will give you consistent updates on endpoint status. Additionally, an alert will not
activate without a report. Any activity you want to be alerted to must have an appropriate report
assigned to it in the security policy.
Optimizing Synchronization
By default, the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Reporting Service syncs every 12 hours.
This means that reporting and alerts data are not ready until 12 hours have passed from installation.
To adjust this time, open the Configuration tool (see “Scheduling” on page 45) and adjust the Client
Reporting time to the number of minutes appropriate for your needs and your environment.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
When data is needed immediately, the Service Synchronization option in the Configuration tool
immediately lynches the Policy Distribution Service (which collects the reporting data from the
endpoints) and the Reporting Service, which updates all alerts based on the newly collected data.
See Section 5.3.3, “Service Synchronization,” on page 47 for details.
5.4.2 Configuring Alert Triggers
Alert triggers can be adjusted to thresholds that fit your corporate security needs.
To adjust alerts from their defaults:
1 Select an alert from the list and click the Configuration tab.
2 Adjust the trigger threshold by selecting the condition from the drop-down list. This states
whether the trigger number is:
Equal to (=)
Greater than (<)
Greater than or equal to (<=)
Less than (>)
Less than or equal to (>=)
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 49
Page 50

3 Adjust the trigger number. This number varies, depending upon the type of alert.
4 Select the number of days that this number must be met.
5 Select the trigger type, whether it’s the warning icon ( ) or the emergency icon ( ).
6 Click Enable this alert.
7 Click Save.
5.4.3 Managing Alerts
Alerts notify you of issues that need to be remedied within the endpoint security environment.
Remediation is normally handled on a case-by-case and individual or group basis. To help identify
the issue, Alert reports are displayed when the alert is selected.
Figure 5-7 Alert Reporting
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
This report displays the current trigger results, displaying information by affected user or device.
The data provides the necessary information to take remediation actions to correct any potential
corporate security issues. Additional information can be found by opening Reporting.
Once remediation actions have been taken, the alert remains active until the next reporting update.
To clear an alerts:
1 Select an alert from the list, then click the Configuration tab on the right.
50 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 51

2 Click Clear to clear the reporting data from Alerts (this data is still available in the reporting
database), and will not reactivate until new data is received.
5.5 Using Reports
The Reporting Service provides Adherence and Status reports for the enterprise. The available data
is provided for directories and user groups within a directory. Novell reports provide feedback on the
effects individual policy components can have on enterprise endpoints. Requests for these reports
are set in the Security Policy (see Section 6.2.4, “Compliance Reporting,” on page 118) and provide
useful data to determine policy updates.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain more information:
Section 5.5.1, “Using the Reports Tools,” on page 51
Section 5.5.2, “Adherence Reports,” on page 53
Section 5.5.3, “Alert Drill-Down Reports,” on page 55
Section 5.5.4, “Application Control Reports,” on page 56
Section 5.5.5, “Endpoint Activity Reports,” on page 56
Section 5.5.6, “Encryption Solutions Reports,” on page 57
Section 5.5.7, “Client Self Defense Reports,” on page 57
Section 5.5.8, “Integrity Enforcement Reports,” on page 57
Section 5.5.9, “Location Reports,” on page 58
Section 5.5.10, “Outbound Content Compliance Reports,” on page 58
Section 5.5.11, “Administrative Overrides Reports,” on page 59
Section 5.5.12, “Endpoint Updates Reports,” on page 59
Section 5.5.13, “USB Devices Reports,” on page 60
Section 5.5.14, “Wireless Enforcement Reports,” on page 60
5.5.1 Using the Reports Tools
You can select Reporting from either the Endpoint Auditing taskbar or from the View menu. The list
of available reports displays (click on the "plus" sign icons next to each report type to expand the
list).
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 51
Page 52

Figure 5-8 Reports Menu
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Reports are configured by identifying the date range and other parameters (for example, user or
location). To set the dates, select the report, click Configure, click the date selector to expand to the
calendar view, then select the month and day (be sure to click on the day to change the date
parameter).
Figure 5-9 Use calendar tool to set the date-range
Click Vie w to generate the report.
After a report is generated, it can be viewed through the Management Console, printed, e-mailed, or
.pdf
or exported as a
Figure 5-10 Report Toolbar
file by using the Report toolbar.
52 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 53
When reviewing reports, the arrow buttons help you navigate through each page of the report.
Reports typically have charts and graphs on the first page, with the gathered data on the remaining
pages, ordered by date and type.
Use the Printer button to print the full report using the default printer for this computer.
Use the Export button to save the report as a PDF file, Excel spreadsheet, Word document, or RTF
file for distribution.
Use the Group Tree button to toggle a list of parameters to the side of the report. Select any of these
parameters to drill down farther into the report. Click the Group Tree button to close the sidebar.
Use the Magnifying Glass button to display a drop-down menu to adjust the current view size.
Use the Binoculars button to open a search window.
When you mouse over a certain parameter, such as a user name or device name, the mouse pointer
changes to a magnifying glass. You can double-click that particular item and display a new report
for just that object. Click the X button to close the current view and return to the original report.
To return to the report list, click the Show Report List icon above the report window.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Figure 5-11 Report list icon
Reports are not available until data has been uploaded from the Endpoint Security Clients. By
default, the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Reporting service syncs every 12 hours.
This means that reporting and alerts data will not be ready until 12 hours have passed from
installation. To adjust this time frame, open the Configuration tool (see “Scheduling” on page 45),
and adjust the Client Reporting time to the number of minutes appropriate for your needs and your
environment.
Reports that do not have data available will have the Configure or Preview button grayed out, with
the words No data underneath.
Figure 5-12 No data
5.5.2 Adherence Reports
Adherence Reports provide compliance information about the distribution of security policies to
managed users. A score of 100 percent adherence indicates that all managed users have checked in
and received the current policy.
Click the plus sign next to Adherence to expand the list to display the following reports:
“Endpoint Check-In Adherence” on page 54
“Endpoints that Never Checked-In” on page 54
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 53
Page 54

“Endpoint Client Versions” on page 54
“Group Policy Non-Compliance” on page 54
“Endpoint State History by Machine” on page 54
“Policy Assignment” on page 54
“Endpoint State History by User” on page 54
Endpoint Check-In Adherence
Provides a summary of the days since check-in by enterprise endpoints, and the age of their
respective current policy. These numbers are averaged to summarize the report. This report requires
no variables be entered. The report displays the users by name, which policies have been assigned to
them, the days since their last check-in, and the age of the policy.
Endpoints that Never Checked-In
Lists the user accounts that have registered with the Management Service but have never checked
with the Distribution Service for a policy update. Select one or more groups to generate the report.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
NOTE: These may be Management Console users who don't have a Security Client installed in their
names.
Endpoint Client Versions
Lists the most recently reported version of the client on each endpoint. Set the date parameters to
generate this report.
Group Policy Non-Compliance
Lists groups in which some users do not have the correct policy. Selections can be made for one or
more groups to generate the report.
Endpoint State History by Machine
Lists the most recent status (in a given date-range) of ZENworks Endpoint Security Managementprotected endpoints, grouped by machine name. It displays the logged-on user name, current policy,
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management client version, and network location. This report
requires a range of dates to be entered. The administrator can drill down by double-clicking any
entry to see a complete list of status reports for a particular machine.
Policy Assignment
Lists the users or groups (accounts) that have received the specified policy. Select the desired policy
from the list and click Vie w to run the report.
Endpoint State History by User
Lists the most recent status (in a given date-range) of ZENworks Endpoint Security Managementprotected endpoints, grouped by user name. It displays the machine name, current policy, Endpoint
Security Management client version, and network location. This report requires a range of dates to
be entered. The administrator can drill down by double-clicking any entry to see a complete list of
status reports for a particular user.
54 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 55

5.5.3 Alert Drill-Down Reports
Additional alert information is available in these drill-down reports. These reports only display data
when an alert has been triggered. Clearing an alert also clears the alert report; however, the data is
still available in a standard report.
Click the plus sign next to Alert Drill-Down Reports to expand the list to display the following
reports:
“Client Tampering Alert Data” on page 55
“Files Copied Alert Data” on page 55
“Incorrect Client Version Alert Data” on page 55
“Incorrect Client Policy Alert Data” on page 55
“Override Attempts Alert Data” on page 55
“Integrity Failures Alert Data” on page 55
“Port Scan Alert Data” on page 55
“Uninstall Attempt Alert Data” on page 56
“Unsecure Access Point Alert Data” on page 56
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
“Unsecure Access Point Connection Alert Data” on page 56
Client Tampering Alert Data
Lists instances where a user has made an unauthorized attempt to modify or disable the Endpoint
Security Client.
Files Copied Alert Data
Lists accounts that have copied data to removable storage.
Incorrect Client Version Alert Data
Displays the history of the status of the ZENworks Security Client Update process.
Incorrect Client Policy Alert Data
Lists users who do not have the correct policy.
Override Attempts Alert Data
Lists instances where client self-defense mechanisms have been administratively overridden,
granting privileged control over the Endpoint Security Client.
Integrity Failures Alert Data
Displays the history of success/failure client integrity checks.
Port Scan Alert Data
Lists the number of blocked packets on the number of different ports (a large number of ports may
indicate a port scan occurred).
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 55
Page 56

Uninstall Attempt Alert Data
Lists users who have attempted to uninstall the Endpoint Security Client.
Unsecure Access Point Alert Data
Lists unsecured access points detected by the Endpoint Security Client.
Unsecure Access Point Connection Alert Data
Lists unsecured access points connected to by the Endpoint Security Client.
5.5.4 Application Control Reports
Lists all unauthorized attempts by blocked applications to access the network or run when not
permitted by the policy.
Click the plus sign next to Alert Drill-Down Reports to expand the list to display the following
report:
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
“Application Control Details” on page 56
Application Control Details
Lists the date, location, the action taken by the Endpoint Security Client, the application that
attempted run, and the number of times this was attempted. Dates display in UTC.
Enter the date parameters, select the application names from the list, select the user accounts, and
click Vie w to run the report.
5.5.5 Endpoint Activity Reports
Endpoint Activity reports provide feedback for individual policy components and the effect they
have on the operation of the endpoint.
Click the plus sign next to Endpoint Activity to expand the list to display the following reports:
“Blocked Packets by IP Address” on page 56
“Blocked Packets by User” on page 56
“Network Usage Statistics by User” on page 57
“Network Usage Statistics by Adapter Type” on page 57
Blocked Packets by IP Address
Lists blocked packets filtered by the destination IP address. Dates display in UTC.
Select the destination IP from the list and set the date parameters. The report displays the dates,
locations, affected ports, and the name of the blocked packets.
Blocked Packets by User
Lists blocked packets filtered by users. Dates display in UTC. The data provided is essentially the
same as Blocked Packets by IP Address, but arranged by user.
56 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 57

Network Usage Statistics by User
Lists packets sent, received, or blocked; and network errors, filtered by users. This report requires a
range of dates to be entered. Dates display in UTC.
Network Usage Statistics by Adapter Type
Lists packets sent, received, or blocked; and network errors, filtered by adapter type. This report
requires a range of dates to be entered and the Location. Dates display in UTC.
5.5.6 Encryption Solutions Reports
When endpoint encryption is activated, reports on the transference of files to and from the encrypted
folders is monitored and recorded.
Click the plus sign next to Encryption Solutions to expand the list to display the following reports:
“File Encryption Activity” on page 57
“Encryption Exceptions” on page 57
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
File Encryption Activity
Lists files that have had encryption applied.
Encryption Exceptions
Lists errors from the encryption subsystem (for example, a protected file could not be decrypted
because the user did not have the right keys).
5.5.7 Client Self Defense Reports
Client Self Defense reports provide feedback about users trying to prevent the Endpoint Security
Client from doing its job.
Click the plus sign next to Client Self Defense to expand the list to display the following report:
“Endpoint Security Client Hack Attempts” on page 57
Endpoint Security Client Hack Attempts
Lists instances where a user has made an unauthorized attempt to modify or disable the Endpoint
Security Client. Dates display in UTC.
Specify the date parameters, then click View to run the report.
5.5.8 Integrity Enforcement Reports
Provides reporting for anti-virus/anti-spyware integrity results.
Click the plus sign next to Integrity Enforcement to expand the list to display the following reports:
“Client Integrity History” on page 58
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 57
Page 58

“Unremediated Integrity Failures by Rule” on page 58
“Unremediated Integrity Failures by User” on page 58
Client Integrity History
Lists the success and failure of client integrity checks. Dates display in UTC.
Select the date range for the report, integrity rule(s), and user name(s).
Unremediated Integrity Failures by Rule
Reports on integrity rules and tests that have failed and not yet been remediated.
Select the integrity rules, then click View to run the report.
Unremediated Integrity Failures by User
Reports on users that have failed integrity tests and not yet been remediated.
Select the user names, then click Vie w to run the report.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
5.5.9 Location Reports
Provides data for common location usage (which locations are most commonly used by users).
Click the plus sign next to Location to expand the list to display the following report:
“Location Usage Data by Date and User” on page 58
Location Usage Data by Date and User
Displays information gathered from individual clients about what locations are used and when.
Dates display in UTC. The locations displayed are the locations used by the user. Unused locations
are not displayed. Select the date range to generate the report.
5.5.10 Outbound Content Compliance Reports
Provides information regarding the use of removable drives and identifies which files have been
uploaded to such drives.
Click the plus sign next to Outbound Content Compliance to expand the list to display the following
reports:
“Removable Storage Activity by Account” on page 59
“Removable Storage Activity by Device” on page 59
“Copies from Removable Storage by Account” on page 59
“Detected Removable Storage Devices” on page 59
“Chart 7 Days of Removable Storage Activity by Account” on page 59
58 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 59

Removable Storage Activity by Account
Lists accounts that have copied data to removable storage. No parameters are required to generate
this report.
Removable Storage Activity by Device
Shows removable storage devices to which files have been copied. Select the date range, user
names, and locations to generate this report.
Copies from Removable Storage by Account
Shows accounts that have copied data from removable storage to fixed drives.
Detected Removable Storage Devices
Lists removable storage devices that have been detected on the endpoint. Select the date range, user
names, and locations to generate this report.
Chart 7 Days of Removable Storage Activity by Account
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Displays a chart listing accounts that have recently copied data to removable storage. Enter the date
range to generate this report.
5.5.11 Administrative Overrides Reports
Reports instances where client self-defence mechanisms have been administratively overridden,
granting privileged control over the Endpoint Security Client.
Click the plus sign next to Administrative Overrides to expand the list to display the following
report:
“Security Client Overrides” on page 59
Security Client Overrides
Displays successful override attempts by user and date. Dates display in UTC.
Select the user and date range, then click View to run the report.
5.5.12 Endpoint Updates Reports
Shows the status of the ZENworks Security Client Update process (see “ZSC Update” on page 94).
Dates display in UTC.
Click the plus sign next to Endpoint Updates to expand the list to display the following reports:
“Chart Percentage of ZSC Update Failures” on page 60
“History of ZSC Update Status” on page 60
“Chart Types of Failed ZSC Updates” on page 60
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 59
Page 60

Chart Percentage of ZSC Update Failures
Lists the percentage of ZENworks Security Client Update that have failed (and not been
remediated). No parameters are required to generate this report.
History of ZSC Update Status
Shows the history of the status of the ZENworks Security Client Update process. Select the date
range and click Vie w to run the report. The report displays the users that have checked in and
received the update.
Chart Types of Failed ZSC Updates
Shows ZENworks Security Client Updates that have failed (and not been remediated). Select the
date range and click Vie w to run the report. The report displays the users that have checked in, but
had a failed update installation.
5.5.13 USB Devices Reports
Shows security client USB device inventory that is listed by user or machine. This report shows
whatever a user has plugged into a USB port and is recorded for either the user or the machine.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
5.5.14 Wireless Enforcement Reports
Provides reports regarding Wi-Fi environments the endpoint is exposed to.
Click the plus sign next to Wi-Fi Enforcement to expand the list to display the following reports:
“Wireless Connection Availability” on page 60
“Wireless Connection Attempts” on page 60
“Wireless Environment History” on page 60
Wireless Connection Availability
Displays the access points available for connection by policy and location. Includes the channel,
SSID, MAC address, and whether or not the access point was encrypted.
Wireless Connection Attempts
Displays the access points connection attempts, by location and by ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management account.
Wireless Environment History
Provides a survey of all detected access points, regardless of ownership. Includes the frequency,
signal strength, and whether or not the access point was encrypted. Dates display in UTC. Select the
desired locations and the date range to generate this report.
5.6 Generating Custom Reports
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management lets you create custom reports to better manage endpoint
computers in your system.
60 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 61

The following sections contain more information:
Section 5.6.1, “Software Requirements,” on page 61
Section 5.6.2, “Creating a ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Compliant Report,” on
page 61
Section 5.6.3, “Available Reporting Information,” on page 62
Section 5.6.4, “Creating a Report,” on page 65
5.6.1 Software Requirements
You can use ODBC-compliant reporting tools (for example, Crystal Reports*, Brio*, and Actuate*)
to create custom reports not included in the Novell reports list. These reporting tools can view and
query the reporting information from a common data warehouse, star format.
The reports included with ZENworks Endpoint Security Management were created using Crystal
Reports for Visual Studio .NET (SP2). This version of Crystal Reports is bundled with Visual
Studio .NET and is available as an optional component. To learn more, visit http://
msdn.microsoft.com/vstudio/team/crystalreports/default.aspx (http://msdn.microsoft.com/vstudio/
team/crystalreports/default.aspx).
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
5.6.2 Creating a ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Compliant Report
Before you begin, please review the report creation process outlined at: http://msdn.microsoft.com/
vstudio/team/crystalreports/gettingstarted/default.aspx (http://msdn.microsoft.com/vstudio/team/
crystalreports/gettingstarted/default.aspx).
The first phase implementation of the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management reporting
framework has the following requirements of every report to be integrated into the system:
The report must be based on only one data source. That data source must be a single table or
view residing within the source database.
Figure 5-13 Browse the Reporting Data Source
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 61
Page 62

The report must have a title specified and saved with the report. The optional title, subject,
author, and comments display if specified.
Figure 5-14 Report Document Properties
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The report cannot contain any sub-reports.
Filtering parameters must be named the same as the target columns within the database fields
of the table or view.
Figure 5-15 Available Database Fields
5.6.3 Available Reporting Information
The ZENworks Endpoint Security Management reporting database is designed to closely model the
star schema format. The star schema is a single "fact" table containing a compound primary key,
with one segment for each dimension and additional columns of additive, numeric facts.
The Reporting Service includes the following two dimension tables:
ORGANIZATION_DIM: The organization table, defining the instances of users, groups,
organizational units, containers, and services in a hierarchal relationship. Each row represents one of
these units.
62 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 63

UNIT_MEMBER_DIM: Association of organization units to other organization units. For
example, although a user can be stored within a specific container within Active Directory, the user
might also be a member of an organization unit or security groups. Each row represents a
relationship of organization units.
The data source must be defined to the reporting tool, typically for most third-party applications the
following steps are necessary:
1 Define an OLEDB ADO connection to the server hosting the Management Service.
2 Select the Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server.
3 Enter the Management Service server as the server.
4 Enter the SQL account name and password.
5 Enter the Reporting Service database name (default name is STRSDB) as the database.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 63
Page 64

The following views are available for report generation:
EVENT_ACCESSPOINT_FACT_VW: This view describes the access points observed by
user, day, policy, location, and access point instance.
EVENT_BLOCKEDPACKETS_FACT_VW: This view describes the summarized instances
of port activity that was blocked due to policy configuration by the endpoint. The information
included is logged user, day, policy, location, and source/destination IP/port.
EVENT_CLIENTACTIVITY_FACT_VW: This view describes the summarized instances
of port activity at the endpoint. The information included is logged user, day, policy, location
and device.
EVENT_CLIENTAPPLICATIONS_FACT_VW: This view describes the summarized
instances of application use (duration) by user, day, policy, location and application.
EVENT_CLIENTDEFENSE_HACK_FACT_VW: This view describes the instances of
hack attempts against the endpoint client. Active users, applications, and services are included
within the report. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location, and attack result.
EVENT_CLIENTDEFENSE_OVERRIDES_FACT_VW: This view describes the instances
of policy override and the affected devices. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location,
and override type.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
EVENT_CLIENTDEFENSE_UNINSTALL_FACT_VW: This view describes the instances
of attempts to remove the endpoint client. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location,
and attack result.
EVENT_CLIENTDEVICE_FACT_VW: This view describes the types of devices in use by
an endpoint. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location, and device type.
EVENT_CLIENTENVIRONMENTS_FACT_VW: This view describes the custom
(stamped) network environments used for location detection. The data is grouped by user, day,
policy, location, device type, and environment data.
EVENT_CLIENTINTEGRITY_FACT_VW: This view describes the results of integrity
rules applied at the endpoint. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location, and rule.
EVENT_CLIENTLOCATION_FACT_VW: This view describes the time at location as well
as adapter (configuration and type) used at the location. The data is grouped by user, day,
policy, and location.
EVENT_CLIENTRULE_FACT_VW: This view describes the generic reporting mechanism
for integrity and scripting rules. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, location, and rule.
EVENT_COMPONENTACTION_FACT_VW: This view describes the Management
Console activity performed on specific components. For example, you could see when the
policy update interval was changed for a specific location in a policy. The data is grouped by
user, day, policy, and component and defines the new and old value.
EVENT_MANGERIO_FACT_VW: This view describes when a component has been created
or edited. The data is grouped by user, day, component, and action.
EVENT_ORGANIZATIONACTION_FACT_VW: This view describes the user activity as
it relates to ZENworks Endpoint Security Management integration with an Enterprise
information repository. All user management activities are reflected within this table.
64 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 65
EVENT_POLICYCOMPONENT_FACT_VW: This view describes the interaction of
components and policies. For example, when a location is added to a policy, an audit row
reflects that change. The data is grouped by user, day, policy, component, and action.
EVENT_PUBLISHACTION_FACT_VW: This view describes the policy and component
assignment to an organization.
EVENT_SERVERACTION_FACT_VW: This view describes the user activity with the
Distribution Service (Check In, for example).
EVENT_USERACTION_FACT_VW: This view describes the user policy activity with the
Distribution Service (Policy, Key, EFS Key, Schema downloads).
5.6.4 Creating a Report
The following steps describe the creation of a simple report. The following example uses the Visual
Studio.NET 2003 Enterprise Architect IDE.
1 From the IDE, select Add New Item and add a new Crystal Report.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
2 Create a report using the wizard.
3 Define the data source. Access the Management Service reporting service database within data.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 65
Page 66

4 Using the connection definition wizard, define an OLEDB ADO connection to the Reporting
Service database. Select Microsoft OLE DB Provider for SQL Server, then click Next.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
5 Select the Reporting server. Enter the User ID, password, and database name for the Reporting
Service (see the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide for more
information). Click Next, then click Finish.
6 Select the desired source table or view for your report by expanding the tree nodes as shown
below.
66 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 67

7 Under the Fields tab, select the table or view columns that you want to include within your
report. Click Next to continue.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
8 If you are planning to group or summarize your data, click the Group tab and select the
columns you want to group. Click Next or select the Style tab.
9 Title the report and select the style.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 67
Page 68

The Report Builder displays.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
10 To set up a filter, right-click Parameter Fields in the field explorer, then click New.
68 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 69

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
11 The following filter allows you to select multiple users to filter by with the prompting text of
"User Name:" displayed within the UI. The parameter is named the same as the column.
12 Right-click the report, then click Report > Edit Selection Formula > Records.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 69
Page 70

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
13 Using the new parameter, specify only the records where the field equals the values selected in
the parameter. Select the column and then a comparison (=) and then the parameter. Press
CTRL-S to save the filter
14 Repeat Step 10 to Step 13 for each filter. Edit the design of the report and the save the report.
15 After a custom report is generated, the report can be dropped into the
Files\Novell\Management Service\Reports\Reports\
directory on the Management
\Program
Service Server. Once there, the new report displays in the reports list in the Reporting Service
web interface (click Refresh List to display the new reports).
70 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 71

5.7 Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution
The ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution provides complete, centralized security management of
all mobile data by actively enforcing a corporate encryption policy on the endpoint itself.
The ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution lets you do the following:
Centrally create, distribute, enforce, and audit encryption policies on all endpoints and
removable storage devices.
Encrypt all files saved to, or copied to, a specific directory on all fixed disc partitions on the
hard drive.
Encrypt all files copied to removable storage devices.
Share files freely within an organization, while blocking unauthorized access to files.
Share password-protected, encrypted files with people outside the organization through an
available decryption utility.
Easily update, back up, and recover keys via policy without losing data.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 5.7.1, “Understanding the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution,” on page 71
Section 5.7.2, “Sharing Encrypted Files,” on page 71
5.7.1 Understanding the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution
Data encryption is enforced on fixed disk volumes and removable storage devices through the
creation and distribution of data encryption security policies.
When a data encryption policy is activated on an endpoint device, an encrypted Safe Harbor folder is
added to the root directory of any fixed disk volumes on the endpoint. Any data stored in a Safe
Harbor folder is encrypted. Attempts to read the data by anyone who is not an authorized user for
that endpoint device are unsuccessful.
Any removable storage device connected to the device is encrypted. Data placed on the removable
storage device is immediately encrypted and can only be read on endpoint devices in the same
policy group. If desired, you can configure the policy to provide a sharing folder (the default name is
Password Encrypted Files) on the removable storage devices. This folder enables users to share the
folder’s files with persons outside their policy group via a password (see “Data Encryption” on
page 91).
5.7.2 Sharing Encrypted Files
Each Management Console contains its own encryption key. Users assigned policies created by the
same Management Console can access encrypted files created by each other. For example, if User A
and User B are assigned data encryption policies created with the same Management Console, User
A can log in to User B’s machine (as User A) and access User B’s encrypted files. User A can also
read any files on an encrypted removable storage device supplied by User B.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 71
Page 72

Users assigned policies created by different Management Consoles cannot access each other’s fixed
disk encrypted files unless you share (export and import) encryption keys between consoles. The
same is true of files on an encrypted removable storage device, with the exception of files located in
the Password Encrypted Files (shared) folder. For files located in the shared folder, the user must
provide the access password.
If an endpoint device does not have the Security client installed, users of the device can access
shared folder files from an encrypted removable device if 1) they have the ZENworks File
Decryption Utility and 2) they know the file access password. For information about the File
Decryption Utility, see Section 9.1, “Using the ZENworks File Decryption Utility,” on page 203.
5.8 Managing Keys
Key management permits you to back up, import, and update an encryption key. We recommend the
following key management practices:
Export and save your encryption keys. This ensures that, in the case of a systems failure or an
inadvertent policy change, data can be decrypted. Each Management Console has its own
encryption key. If you have multiple Management Consoles, you need to export the encryption
key from each console.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
If you believe that an encryption key is compromised, update to a new key. Generating a new
key results in a temporary performance decrease on endpoint devices while the Security client
reencrypts data.
If you have used multiple Management Consoles to create Data Encryption policies, you
should export the key from each Management Console and import it into the other consoles so
that all Management Consoles have all keys. This allows the Management Console to include
all keys in each Data Encryption policy. The result is that all Security client users, regardless of
their Data Encryption policy, can access encrypted policies created by other Security client
users in your environment.
Encryption Key controls are accessed through the Too ls menu of the ZENworks Endpoint Security
Management Console.
72 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 73
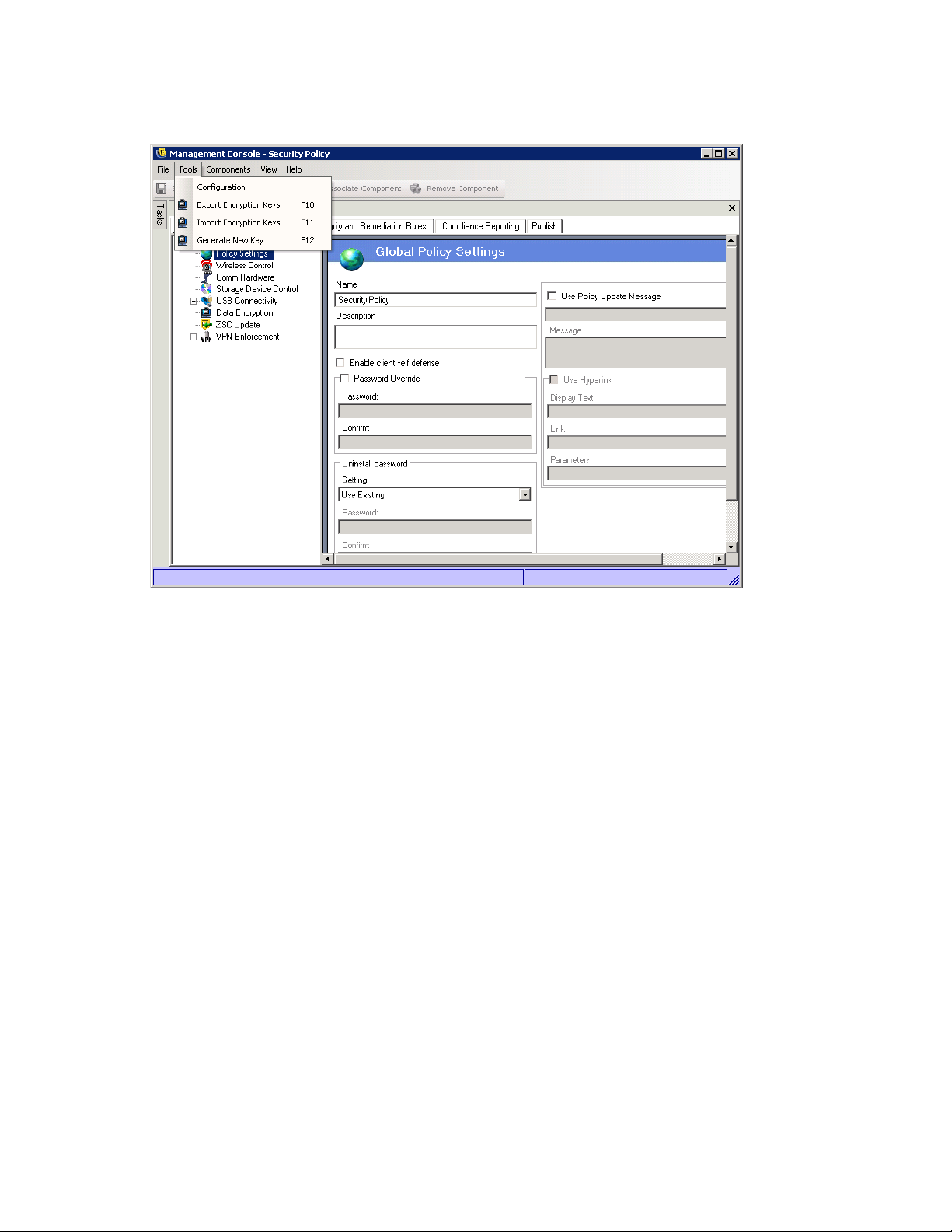
Figure 5-16 Access Encryption Keys through the tools menu
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain additional information:
Section 5.8.1, “Exporting Encryption Keys,” on page 73
Section 5.8.2, “Importing Encryption Keys,” on page 74
Section 5.8.3, “Generating a New Key,” on page 74
5.8.1 Exporting Encryption Keys
For back up purposes, and to send the key to another Management Console, the current encryption
key set can be exported to a designated file location.
1 In the Management Console, click Too ls , then click Export Encryption Keys.
2 Specify the path and filename for the exported file.
3 Specify a password in the provided field. The key cannot be imported without this password.
4 Click OK.
All key files in the database are included in the exported file.
Using the ZENworks Storage Encryption Solution Management Console 73
Page 74

5.8.2 Importing Encryption Keys
You can import keys from a backup or another Management Console. Importing keys from another
Management Console allows endpoints managed by this console to read files protected by Data
Encryption policies created in the other Management Console. When importing keys, duplicates are
ignored. Imported keys become part of your “key set” and do not replace the current common key.
All keys are passed down when a new policy is published.
1 In the Management Console, click Too ls , then click Import Encryption Keys.
2 Browse to or specify the file to be imported.
3 Specify the password for the encryption key.
4 Click OK.
5.8.3 Generating a New Key
1 In the Management Console, click Too ls , then click Generate New Key.
All previous keys are stored in the policy.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
74 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 75

6
Creating and Distributing Security
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Policies
The ZENworks® Endpoint Security Client uses security policies to apply location security to mobile
users. Decisions on networking port availability, network application availability, file storage device
access, and wired or Wi-Fi connectivity are determined by the administrator for each location.
Security policies can be custom-created for the enterprise, individual user groups, or individual
users/machines. Security policies can allow full employee productivity while securing the endpoint,
or can restrict the employee to only running certain applications and having only authorized
hardware available to them.
IMPORTANT: Information in this section that pertains to the Endpoint Security Client has been
written for the Endpoint Security Client 3.5. For the features that are supported in Endpoint Security
Client 4.0, see the “Novell ZENworks Endpoint Security Client 4.0” Readme.
The following sections contain more information:
Section 6.1, “Navigating the Management Console UI,” on page 75
Section 6.2, “Creating Security Policies,” on page 79
Section 6.3, “Managing Policies,” on page 122
Section 6.4, “Importing and Exporting Policies,” on page 169
Section 6.5, “Sample Scripts,” on page 170
6
6.1 Navigating the Management Console UI
To begin a security policy:
1 In the Management Console, click File > Create New Policy.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies
75
Page 76

2 Specify the name for the new policy, then click Create to display the Management Console
with the Policy toolbar and the Policy tab displayed.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections describe the Management Console’s user interface as it relates to creating
and distributing security policies using ZENworks Endpoint Security Management:
Section 6.1.1, “Using the Policy Tabs and Tree,” on page 76
Section 6.1.2, “Using the Policy Toolbar,” on page 78
6.1.1 Using the Policy Tabs and Tree
A security policy is configured by navigating through the available tabs at the top of the
Management Console and by using the options in the Global Settings tree in the left pane.
76 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 77

Figure 6-1 Management Console
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The available tabs include the following:
Global Policy Settings: The Global Policy Settings are applied as defaults throughout the
policy and are not location specific.
The Global Policy Settings let you configure the following settings:
Policy Settings
Wireless Control
Communication Hardware
Storage Device Control
USB Connectivity
Data Encryption
Endpoint Security Client
VPN Enforcement
Locations: These policy rules are applied within a specific location type, whether specified as
a single network or a type of network, such as a coffee shop or airport.
Integrity and Remediation Rules: These rules ensure that essential software (such as
antivirus and spyware) is running and up-to-date on the device.
Compliance Reporting: Instructs the policy whether reporting data (including the type of
data) is gathered for this particular policy.
Publish: Publishes the completed policy to individual users, directory service user groups, and
individual machines.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 77
Page 78

The Policy Tree displays the available subset components for the tabbed categories. For example,
Global Policy Settings include subsets of Wireless Control, ZENworks Security Client Update, and
VPN Enforcement. Only the items contained on the primary subset page are required to define a
category, the remaining subsets are optional components.
6.1.2 Using the Policy Toolbar
The policy toolbar provides four controls. The Save control is available throughout policy creation;
the component controls are only available under the Locations and Integrity and Remediation tabs.
Figure 6-2 Policy Toolbar
Explanations of the tools are provided below:
Save Polic: Saves the policy in its current state. As you complete each component subset, it is
highly recommended that you click the Save icon on the Policy toolbar. If incomplete or
incorrect data is entered into a component, the error notification screen displays (see
Section 6.3.2, “Error Notification,” on page 122 for more details).
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
New Component: Creates a new component in a Location or Integrity subset. After the policy
is saved, a new component is available to associate in other policies.
Associate Component: Opens the Select Component screen for the current subset. The
available components include any pre-defined components included at installation and all
components created in other policies.
Figure 6-3 Select Component Window
78 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 79

Changes made to associated components affect all other instances of that component. For
example, you can create a single Location component named Work that defines the corporate
network environment and security settings to be applied whenever an endpoint enters that
environment. This component can now be applied to all security policies. Updates to the
environment or security settings can be changed in the component in one policy and will update
the same component in all other policies that its associated to.
Use the Show Usage command to view all other policies associated with this component.
Remove Component: Removes a component from the policy. The component is still available
for association in this and other policies.
6.2 Creating Security Policies
To begin a security policy:
1 In the Management Console, click File > Create New Policy.
2 Specify the name for the new policy, then click Create to display the Management Console
with the Policy toolbar and the Policy tabs displayed.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
3 Configure the policy settings using the following tabs (click each link for detailed information
about each tab and its options):
Section 6.2.1, “Global Policy Settings,” on page 80
Section 6.2.2, “Locations,” on page 98
Section 6.2.3, “Integrity and Remediation Rules,” on page 109
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 79
Page 80
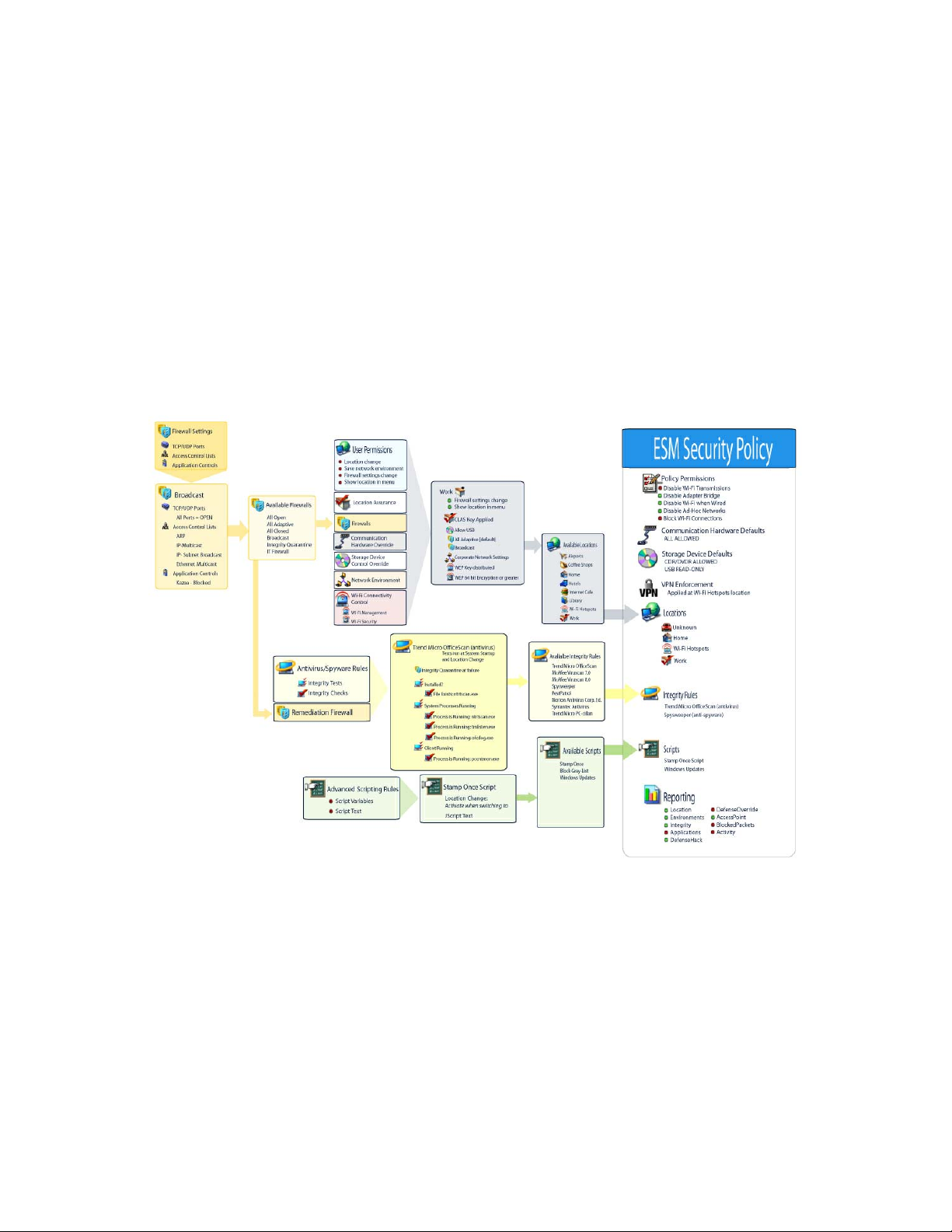
Section 6.2.4, “Compliance Reporting,” on page 118
Section 6.2.5, “Publishing Security Policies,” on page 121
Security policies are built by defining all the Global Settings (default behaviors), then creating and
associating existing components for that policy, such as locations, firewalls and integrity rules, and
finally establishing compliance reporting for the policy.
The components are created either within a dummy policy or are associated from other policies. It is
assumed that for your first few policies you are creating all of the unique locations, firewall settings
and integrity rules for the enterprise. These components are stored in the Management Service’s
database for possible later use in other policies.
The diagram below shows the components for each level and a resulting policy taken from the
selections.
Figure 6-4 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Security Policy creation process
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
6.2.1 Global Policy Settings
The global policy settings are applied as basic defaults for the policy. To access this control, in the
Management Console, click the Global Policy Settings tab.
80 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 81

Figure 6-5 Global Policy Settings
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain more information about the settings you can configure on a global
basis:
“Policy Settings” on page 81
“Wireless Control” on page 82
“Communication Hardware” on page 84
“Storage Device Control” on page 85
“USB Connectivity” on page 88
“Data Encryption” on page 91
“ZSC Update” on page 94
“VPN Enforcement” on page 95
Policy Settings
The primary global settings include:
Name and Description: The policy name was specified at the beginning of the policy creation
process. You can edit the name or provide a description of the policy.
Enable client self defense: Client Self Defense can be enabled or disabled by policy. Leaving
this box checked ensures that Client Self Defense is active. Unchecking the box deactivates
Client Self Defense for all endpoints using this policy.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 81
Page 82
Password Override: This feature allows an administrator to set a password override that can
temporarily disable the policy for a specified period of time. Check the Password Override box
and enter the password in the provided field. Enter the password again in the confirmation
field. Use this password in the Override Password Generator to generate the password key for
this policy.
WARNING: It is highly recommended that end users are not given this password, rather the
Override Password Generator should be used to generate a temporary key for them.
Uninstall Password: We recommend that every Endpoint Security Client be installed with an
uninstall password to prevent users from uninstalling the software. This password is normally
configured at installation; however, the password can be updated, enabled, or disabled via
policy.
The default setting is Use Existing, which will not change the uninstall password.
Enabled is used to either activate an uninstall password or to change it. Enter the new
password and confirm it.
Disabled is used to deactivate the uninstall password requirement.
Use Policy Update Message: You can display a custom user message whenever the policy is
updated. Click on the check box, then specify the message information in the provided boxes.
Use Hyperlink: A hyperlink to additional information, corporate policy, or other related
information can be included at the bottom of the custom message (see Section 6.3.4,
“Hyperlinks,” on page 124 for more information). The following is an example of the dialog
box displayed to the user.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Figure 6-6 Updated Policy Custom Message with Hyperlink
Wireless Control
Wireless Control globally sets adapter connectivity parameters to secure both the endpoint and the
network. To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, then click the Wireless Control
icon in the policy tree on the left.
82 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 83

Figure 6-7 Wireless Control Policy
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The wireless control settings include the following:
Disable Wi-Fi Transmissions: This setting globally disables all Wi-Fi adapters, up to and
including complete silencing of a built-in Wi-Fi radio.
You can choose to display a custom user message and hyperlink when the user attempts to
activate a Wi-Fi connection. See Section 6.3.3, “Custom User Messages,” on page 123 for
more information.
Disable Adapter Bridge: This setting globally disables the networking bridge functionality
included with Windows XP, which allows the user to bridge multiple adapters and act as a hub
on the network.
You can choose to display a custom user message and hyperlink when the user attempts a WiFi connection. See Section 6.3.3, “Custom User Messages,” on page 123 for more information.
Disable Wi-Fi When Wired: This setting globally disables all Wi-Fi Adapters when the user
has a wired (LAN through the NIC) connection.
Disable AdHoc Networks: This setting globally disables all AdHoc connectivity; thereby,
enforcing Wi-Fi connectivity over a network (for example, via an access point) and restricts all
peer-to-peer networking of this type.
Block Wi-Fi Connections: This setting globally blocks Wi-Fi connections without silencing
the Wi-Fi radio. Use this setting when you want to disable Wi-Fi connection, but want to use
access points for location detection. See Section 6.2.2, “Locations,” on page 98 for more
information.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 83
Page 84
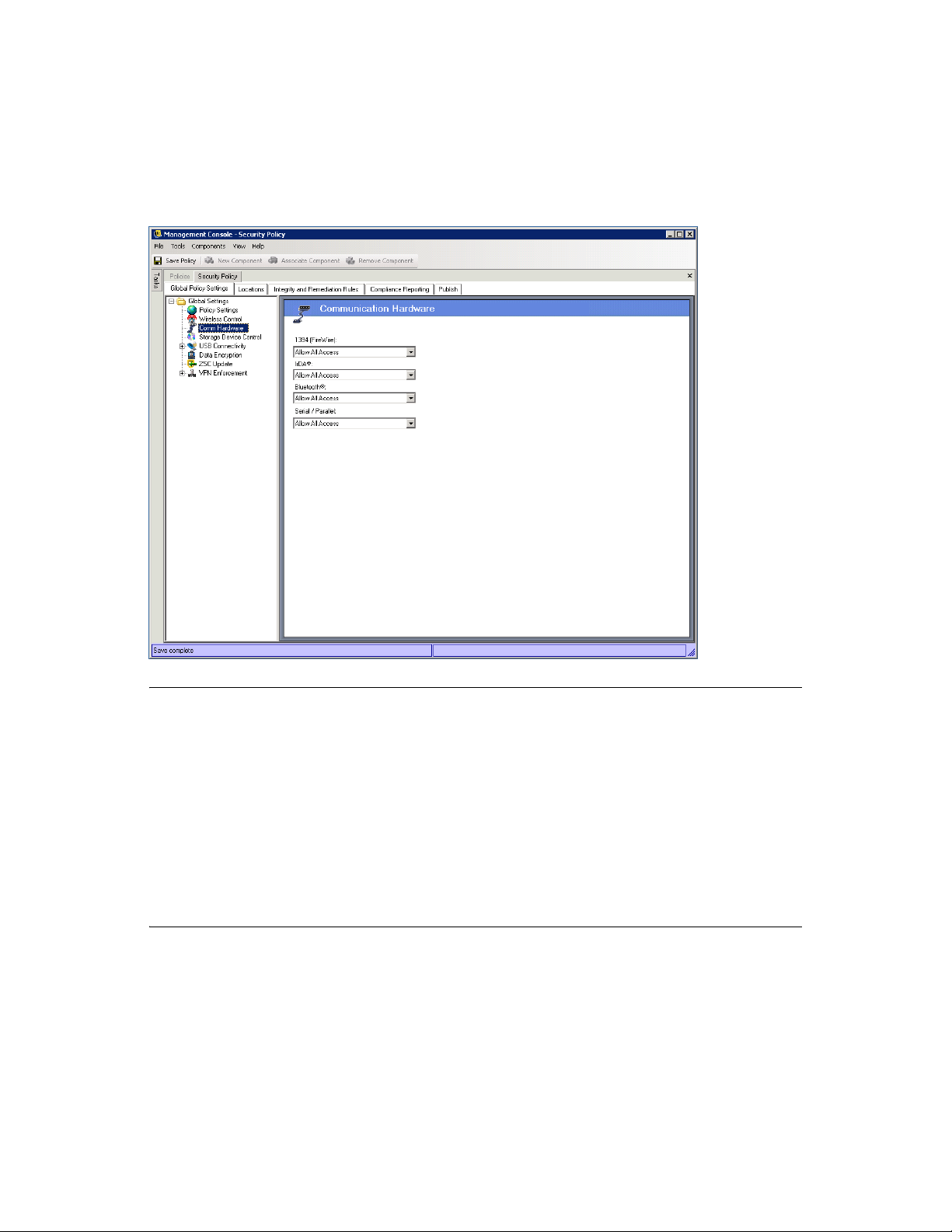
Communication Hardware
Communication hardware controls, by location, which hardware types are permitted a connection
within this network environment.
Figure 6-8 Communication Hardware Policy
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
NOTE: You can set the communication hardware controls globally on the Global Policy Settings
tab or for individual locations on the Locations tab.
To access this control:
To set the communication hardware controls on a global basis, click the Global Policy Settings tab,
expand Global Settings in the tree, then click Comm Hardware.
or
To set the communication hardware controls for a location, click the Locations tab, expand the
desired location in the tree, then click Comm Hardware. For more information about setting the
communication hardware settings for a location, see “Communication Hardware” on page 100.
Select to either allow or disable the global setting for each communication hardware device listed:
1394 (FireWire): Controls the FireWire access port on the endpoint.
IrDA: Controls the infrared access port on the endpoint.
Bluetooth: Controls the Bluetooth access port on the endpoint.
Serial/Parallel: Controls serial and parallel port access on the endpoint.
84 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 85
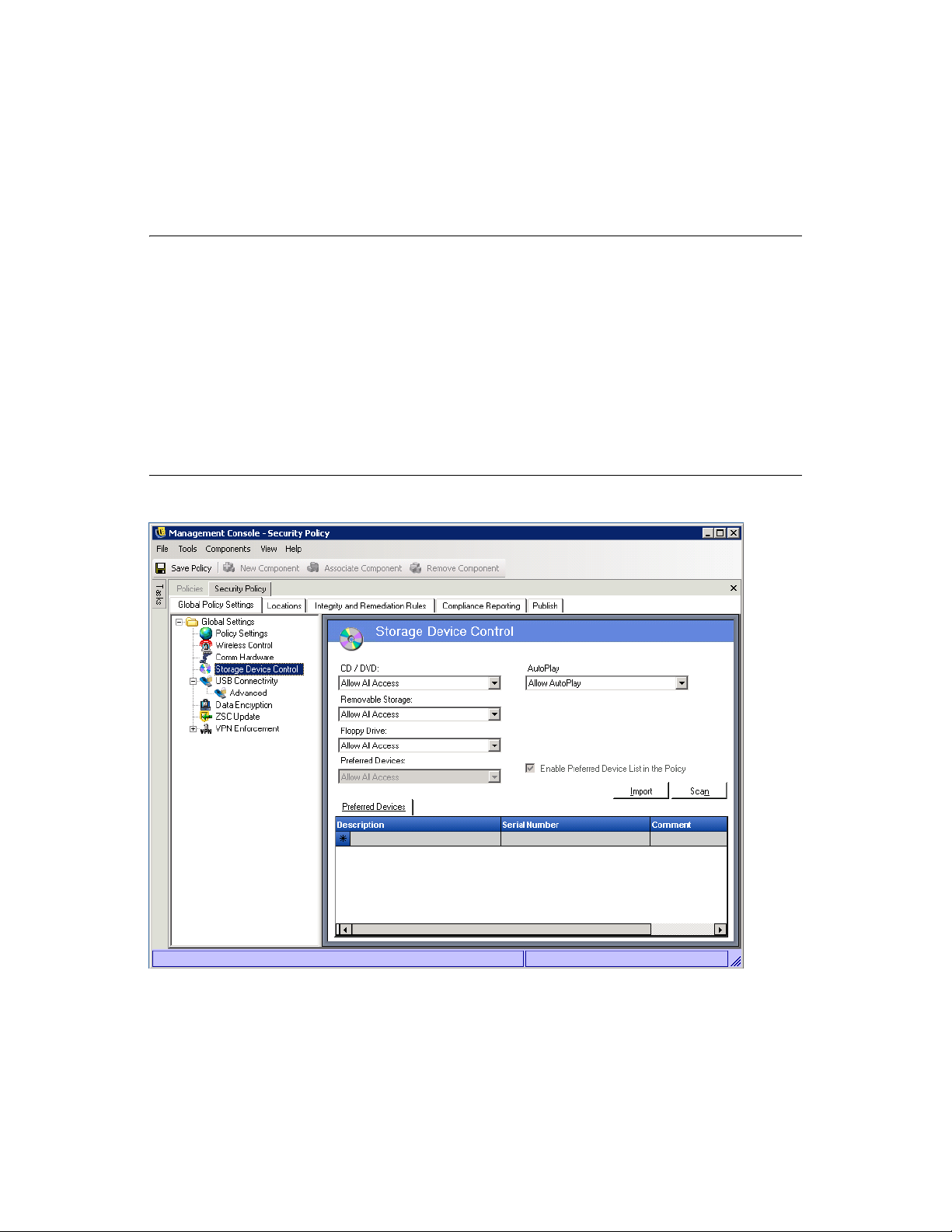
Storage Device Control
Storage device controls set the default storage device settings for the policy, where all external file
storage devices are either allowed to read/write files, function in a read-only state, or be fully
disabled. When disabled, these devices are rendered unable to retrieve any data from the endpoint;
while the hard drive and all network drives remain accessible and operational.
NOTE: You can set the storage device controls globally on the Global Policy Settings tab or for
individual locations on the Locations tab.
To access this control:
To set the storage device controls on a global basis, click the Global Policy Settings tab, expand
Global Settings in the tree, then click Storage Device Control.
or
To set the storage device controls for a location, click the Locations tab, expand the desired location
in the tree, then click Storage Device Control. For more information, see “Communication
Hardware” on page 100.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Figure 6-9 Global Storage Device
Storage Device Control is differentiated into the following categories:
CD/DVD: Controls all devices listed under DVD/CD-ROM drives in Windows Device
Manager.
Removable Storage: Controls all devices reporting as Removable storage under Disk drives in
Windows Device Manager.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 85
Page 86

Floppy Drive: Controls all devices listed under Floppy disk drives in Windows Device
Manager.
Preferred Devices: Allows only Removable Storage devices included in the Preferred Devices
list. All other devices reporting as removable storage are not allowed. For information about
adding preferred devices, see “Preferred Devices” on page 87.
AutoPlay: Controls the Windows AutoPlay feature. AutoPlay performs two processes. First, it
launches the AutoRun process, which looks for an autorun.inf in the root directory and
executes the instructions in the file. Second, it looks for specific content (music, video, and
pictures) and launches the appropriate application to display or play the content. Select one of
the following options:
Allow AutoPlay: Allows the AutoPlay feature, including AutoRun.
Block AutoPlay: Blocks the AutoPlay feature, including AutoRun.
Block AutoRun: Blocks the AutoRun feature so that autorun.inf instructions are not
executed. Launching of applications for music, video and pictures is not blocked.
Fixed storage (hard disk drives) and network drives (when available) are always allowed.
To set the policy default for a category, select from the following options:
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Allow All Access: The device type is allowed by default.
Disable All Access: The device type is disallowed. When users attempt to access files on a
defined storage device, they receive an error message from the operating system, or the
application attempting to access the local storage device, that the action has failed
Read-Only Access: The device type is set as Read-Only. When users attempt to write to the
device, they receive an error message from the operating system, or the application attempting
to access the local storage device, that the action has failed
NOTE: If you want to disable CD-ROM drives or floppy drives on a group of endpoints or set them
as Read-Only, the Local Security Settings (passed down through a directory service group policy
object) must have both Devices: Restrict CD-ROM access to locally logged-on user only and
Devices: Restrict floppy access to locally logged-on user only set as Disabled. To verify this, open
either the group policy object, or open Administrative Tools on a machine. Look in Local Security
Settings - Security Options and verify both devices are disabled (see Figure 6-10). Disabled is the
default.
86 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 87
Figure 6-10 Verify Local Storage Device Options are set as Disabled
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Preferred Devices
Preferred Removable Storage Devices may be optionally entered into a list, permitting only the
authorized devices access when the global setting is used at a location. Devices entered into this list
must have a serial number.
To add a preferred device:
1 Manually enter the device information. To do so, click a field (Description, Serial Number,
Comment) and type the information.
or
Scan the device information. To do so, insert the device into a USB port on the Manangement
Console’s machine, then click Scan.
2 Select one of the following settings from the Preferred Devices list. All Removable Storage
devices use the same setting:
Allow All Access: The devices in the Preferred Devices list are permitted full read/write
capability. All other Removable Storage devices are disabled.
Read-Only Acess: The devices on the Preferred Devices list are permitted read-only
capability. All other Removable Storage devices are disabled.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 87
Page 88
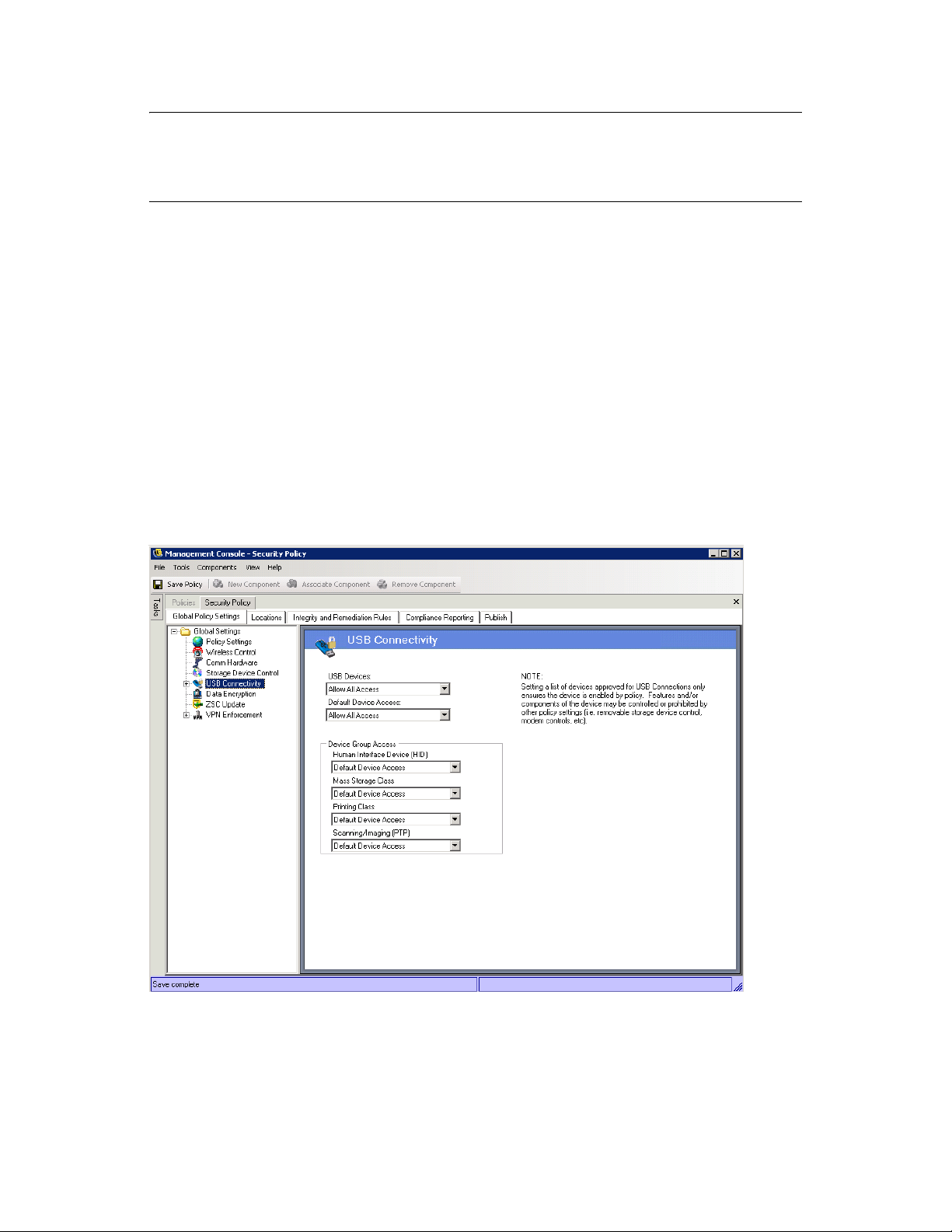
NOTE: Location-based Storage Device Control settings override the global settings. For example,
you might define that at the Work location, all external storage devices are permitted, while
allowing only the global default at all other locations, limiting users to the devices on the preferred
list.
USB Connectivity
All devices that connect via the USB BUS can be allowed or denied by policy. These devices can be
scanned into the policy from the USB Device Inventory report or by scanning all devices currently
connected to a machine. These devices can be filtered based on manufacturer, product name, serial
numbers, type, and so forth.
For support purposes, the administrator can configure the policy to accept a set of devices, either by
manufacturer type, (for example, all HP devices are allowed), or by product type (all USB-human
interface devices [mouse and keyboard] are allowed). Additionally, individual devices can be
permitted to prevent non-supported devices from being introduced into the network (for example, no
printers are allowed except for this one).
To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, then click USB Connectivity in the policy
tree on the left.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Figure 6-11 USB Connectivity page.
Access is first evaluated based on whether the bus is active or not. This is determined by the USB
Devices setting. If this setting is set to Disable All Access, the device is disabled and evaluation
stops. If this setting is set to Allow All Access, the client continues the evaluation and set looking for
88 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 89

filter matches. As with many other fields in the ZENworks Management Console, when being set on
a location, the USB Devices value can also be set to Apply Global Settings and the global value of
this field will be used instead.
The client gathers the filters that are applied from the policy, based on the location and global
settings.
The client will then group the filters based on access into the following groups:
Always Block: Always block the device. This setting cannot be overridden.
Always Allow: Always allow access unless the device matches an Always Block filter.
Block: Block access unless the device matches an Always Allow filter.
Allow: Allow access unless the device matches an Always Block or a Block filter.
Default Device Access: Give the device the same access level as Default Device Access if no
other match is found.
A device is evaluated against each group in the above order (first the Always Block group, followed
by Always Allow, and so forth). When a device matches at least one filter in a group, the device's
access is set to that level and evaluation stops. If the device is evaluated against all filters, and no
match is found, the Default Device Access level is applied.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Device Access set in the Device Group Access area is considered along with all other filters being
used at that location. This is done by generating matching filters for each of the grouping when the
policy is published to the client. These filters are as follows:
Device Group Access: Filter:
Human Interface Device(HID) "Device Class" is equal to 3.
Mass Storage Class "Device Class" is equal to 8.
Printing Class "Device Class" is equal to 7.
Scanning/Imaging (PTP) "Device Class" is equal to 6.
Advanced
In most situations, the four device groups listed on the USB Connectivity page (Human Interface
Device, Mass Storage Class, Printing Class, and Scanning/Imaging) are sufficient to allow or deny
access to most USB devices. If you have devices that do not register in one of these groups, you can
configure settings on the USB Connectivity Advanced page. You can also use the settings on the
Advanced page to provide whitelist access to certain devices even though they might be denied
access because of the settings on the USB Connectivity page.
To access the Advanced USB Connectivity options, click the plus sign next to USB Connectivity in
the Global Settings tree, then click Advanced. You can use the USB Device Audit report as a means
of getting all the information you could potentially use on the USB Connectivity Control Advanced
page.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 89
Page 90

Figure 6-12 USB Connectivity Advanced page.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To add a device to the list, fill in the following fields:
Access: Select an access level:
Always Block: Always block the device. This setting cannot be overridden.
Always Allow: Always allow access unless the device matches an Always Block filter.
Block: Block access unless the device matches an Always Allow filter.
Allow: Allow access unless the device matches an Always Block or a Block filter.
Default Device Access: Give the device the same access level as Default Device Access if
no other match is found.
Manufacturer: Click the Manufacturer column then type the name of the manufacturer you
want to include in the filter (Canon, for example).
Product: Click the Product column then type the name of the product you want to include in
the filter.
Friendly Name: Click the Friendly Name column then type the friendly name of the device
you want to include in the filter.
Serial Number: Click the Serial Number column then type the serial number of the device you
want to include in the filter.
Comment: Click the Comment column then type the comment you want to include in the filter
(Canon, for example).
You can click the Advanced Columns box to add the following columns: USB Version, Device
Class, Device Sub-Class, Device Protocol, Vendor ID, Product ID, BCD Device, O/S Device ID, and
O/S Device Class.
90 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 91

A device makes available a set of attributes to the OS. These attributes are matched by the client to
the fields required by a filter. All fields in the filter must match an attribute provided by the device in
order to have a match. If the device does not provide an attribute or field that is required by the filter,
that filter fails to match.
For example, suppose a device provides the following attributes: Manufacture: Acme Class: 8,
Serial Number: "1234".
The filter: Class == 8 would match this device. The filter: Product == "Acme" would not match
because the device did not provide a Product attribute to the OS.
The following fields are sub-string matched: Manufacturer, Product, and Friendly Name. All other
fields are exact matches.
As a matter of interest, USB serial number(SN) field by spec. is only unique when considered when
specifying the following fields along with the SN: USB Version, Vendor ID, Production ID, and
BCD Device.
Current valid values for USB version in decimal are: 512 - USB 2.0, 272 - USB 1.1, 256 - USB 1.0.
Data Encryption
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Data Encryption determines whether file encryption is enforced on the endpoint and what type of
encryption is available. Data can be encrypted to permit file sharing (with password protection) or
can set encrypted data to be read-only on computers running the Storage Encryption Solution.
NOTE: Encryption is supported only on Windows XP SP2. The encryption portion of the security
policy is ignored on devices that do not meet this OS requirement.
To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, then click Data Encryption in the policy
tree on the left.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 91
Page 92

Figure 6-13 Data Encryption controls
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To activate the individual controls, click the Enable Data Encryption check box.
NOTE: Encryption keys are distributed to all machines that receive policies from the Policy
Distribution Service, regardless of whether data encryption is activated or not. However, this control
instructs the Endpoint Security Client to activate its encryption drivers, which allows users to read
files sent to them without requiring the File Decryption Utility. See Section 9.1, “Using the
ZENworks File Decryption Utility,” on page 203 for more details.
Determine what levels of encryption are permitted by this policy:
Policy password to allow decryption: Entering a password here to require all users using this
policy to enter this password prior to decrypting any encrypted files stored in their Safe Harbor
folders.
This is an optional setting, leave blank to not require the password.
Enable “Safe Harbor” encrypted folder for fixed disks: Generates a folder at the root of all
volumes on the endpoint, named
Encryption Protected Files
. All files placed in this
folder are encrypted and managed by the Endpoint Security Client. Data placed in this folder is
automatically encrypted and can only be accessed by authorized users on this machine.
The folder name can be changed by clicking in the Folder Name field, selecting the current
text, and entering the name you desire.
Encrypt User’s “My Documents” Folder: Select this option to encrypt all files in the
user’s My Documents folder. As with the Safe Harbor folder, data placed in this folder is
automatically encrypted and can only be accessed by authorized users on this machine.
92 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 93

Allow user specified folders: Select this option to allow users to select which folders on
their computer are encrypted. This is for local folders only; no removable storage devices
nor network drives can be encrypted.
WARNING: Before disabling data encryption, ensure that all data stored in these folders has
been extracted by the user and stored in another location.
Enable encryption for removable storage devices: All data written to removable storage
devices from an endpoint protected by this policy is encrypted. Users with this policy on their
machines are able to read the data; therefore, file sharing via removable storage device within a
policy group is available. Users outside this policy group are not able to read the files encrypted
on the drive, and will only be able to access files within the Password Encrypted Files folder (if
activated) with a provided password.
Enable encryption via user-defined password: This setting gives the user the ability to
store files in a Password Encrypted Files folder on the removable storage device (this
folder will be generated automatically when this setting is applied).
When a user adds files to this folder, the files are encrypted with a password that the user
supplies. The user can then access the files from any device that is not running the
Security client. To decrypt the files, the user needs the ZENworks File Decryption utility
and the encryption password. You must supply this utility to the user; it is not part of the
Security client (see Section 9.1, “Using the ZENworks File Decryption Utility,” on
page 203).
For example, assume that a user is working on encrypted files at work. The user wants to
take the files home to work on them, but the home computer does not have the Security
client installed. The user copies the files to the Password Encrypted Files folder on a USB
thumb drive, takes the files home, then accesses them using the ZENworks File
Decryption utility you provided.
If desired, you can change the default folder name (Password Encrypted Files) to another
name.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Require strong password: This setting forces the user to set a strong password for the
Password Encrypted Files folder. A strong password requires the following:
seven or more characters
at least one of each of the four types of characters:
uppercase letters from A to Z
lowercase letters from a to z
numbers from 0 to 9
at least one special character ~!@#$%^&*()+{}[]:;<>?,./
For example: y9G@wb?
WARNING: Before disabling data encryption, ensure that all data stored on removable
storage devices has been extracted by the user and stored in another location.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 93
Page 94

Force client reboot when required: When encryption is added to a policy, it does not become
active until the endpoint is rebooted. This setting forces the required reboot by displaying a
countdown timer, warning the user that the machine will reboot in the specified number of
seconds. The user has that amount of time to save work before the machine reboots.
Reboots are required when encryption is first activated in a policy, and again when either “Safe
Harbor” or removable storage encryption is activated (if activated separately from encryption
activation). For example, when an encryption policy is applied for the first time, two reboots
are required: one reboot to initialize the drivers and another reboot to put any safe harbors into
encryption. If additional safe harbors are subsequently selected after the policy has been
applied, only one reboot is required to put the safe harbor into policy.
ZSC Update
Patches to repair any minor defects in the Endpoint Security Client are made available with regular
ZENworks Endpoint Security Management updates. Rather than providing a new installer, which
needs to be distributed through MSI to all endpoints, ZENworks Security Client Update allows the
administrator to dedicate a zone on the network that distributes update patches to end users when
they associate to that network environment.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, then click ZSC Update in the policy tree
on the left.
Figure 6-14 ZSC Update
To facilitate simple and secure distribution of these patches to all Endpoint Security Client users:
1 Check Enable to activate the screen and the rule.
94 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 95

2 Specify the location where the Endpoint Security Client looks for the updates. Due to the
recommendations in the next step, the location associated with the enterprise environment (i.e.:
the "Work" location) is the recommended candidate.
3 Enter the URI where the patch has been stored. This needs to point to the patch file, which can
be either the
.exe
file). For security purposes, it is recommended that these files be stored on a secure server
setup.exe
file for the Endpoint Security Client, or an MSI file created from the
behind the corporate firewall.
4 Enter the version information for this file in the provided fields. Version information is found
by installing the Endpoint Security Client and opening the About screen (see the ZENworks
Endpoint Security Management Installation Guide for details). The version number for
STEngine.exe
is the version number you want to use in the fields.
Each time the user enters the assigned location, the Endpoint Security Client checks the URI for an
update that matches that version number. If an update is available, the Endpoint Security Client
downloads and installs it.
VPN Enforcement
This rule enforces the use of either an SSL or a client-based VPN (Virtual Private Network). This
rule is typically applied at wireless hotspots, allowing the user to associate and connect to the public
network, at which time the rule attempts to make the VPN connection, then switches the user to a
defined location and firewall setting. All parameters are at the discretion of the administrator. All
parameters override existing policy settings. The VPN-Enforcement component requires the user be
connected to a network prior to launching.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
NOTE: This feature is only available in the ZENworks Endpoint Security Management installation,
and cannot be used for UWS security policies.
To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, then click VPN Enforcement in the
policy tree on the left.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 95
Page 96
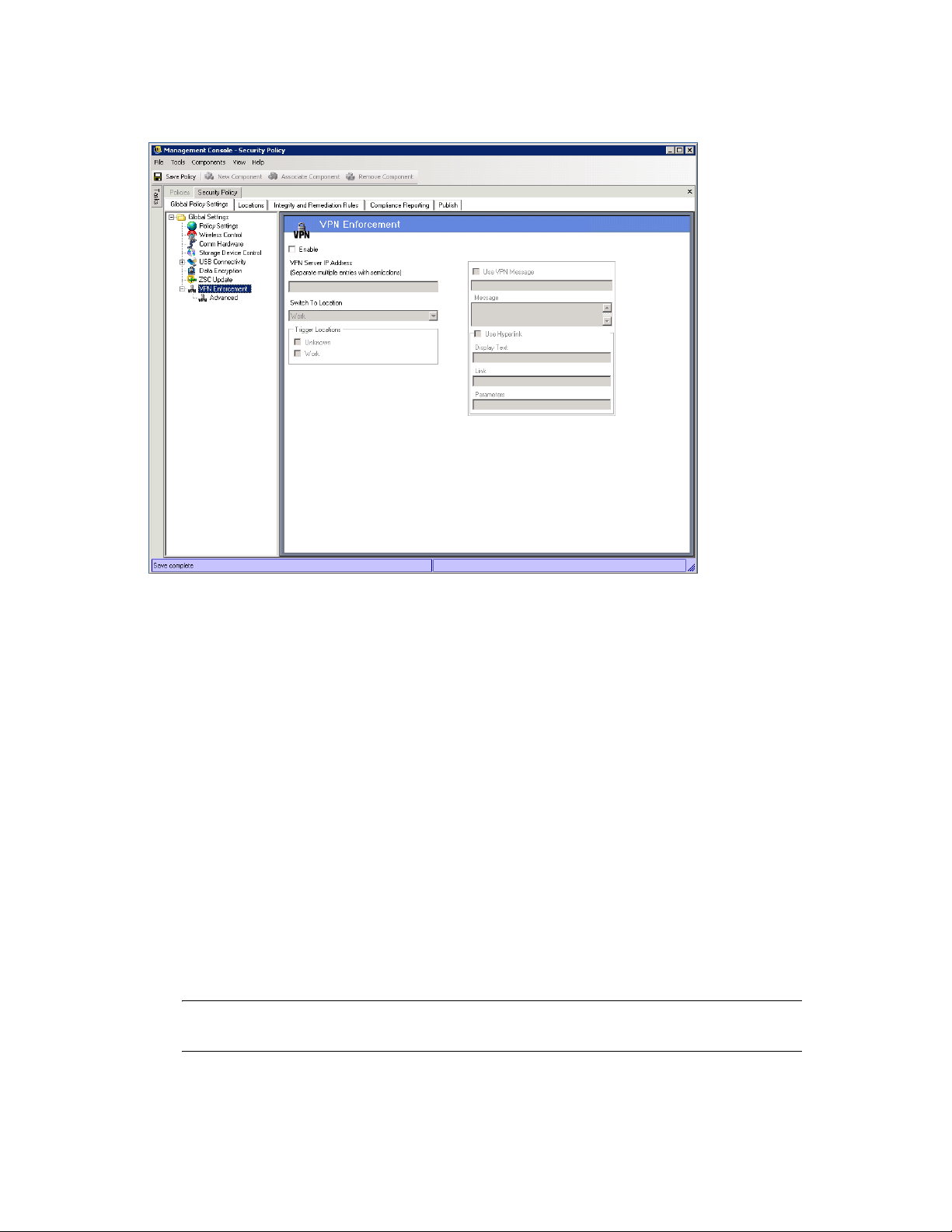
Figure 6-15 Basic VPN Enforcement
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
To use the VPN Enforcement rule, at least two locations must exist.
To add VPN enforcement to a new or existing security policy:
1 Select Enable to activate the screen and the rule.
2 Specify the IP addresses for the VPN Server in the provided field. If multiple addresses are
specified, separate each with a semi-colon (for example: 10.64.123.5;66.744.82.36).
3 Select the Switch To Location from the drop-down list. The Endpoint Security Client switches
to this location after the VPN authenticates.
The Switch To location is the location the Endpoint Security Client switches to when the VPN
is activated. It is recommended that this location contain some restrictions, and only a single
restrictive firewall setting as its default.
The All-Closed firewall setting, which closes all TCP/UDP ports, is recommend for strict VPN
enforcement. This setting prevents any unauthorized networking, while the VPN IP address
acts as an ACL to the VPN server, and permits network connectivity.
4 Select the Trigger locations where the VPN enforcement rule is applied. For strict VPN
enforcement, it is recommended the default Unknown location be used for this policy. After the
network has authenticated, the VPN rule activates and switches to the assigned Switch To
Location.
NOTE: The location switch occurs before the VPN connection, after the network has
authenticated.
5 Enter a Custom User Message to display when the VPN has authenticated to the network. For
non-client VPNs, this should be suffiClient.
96 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 97
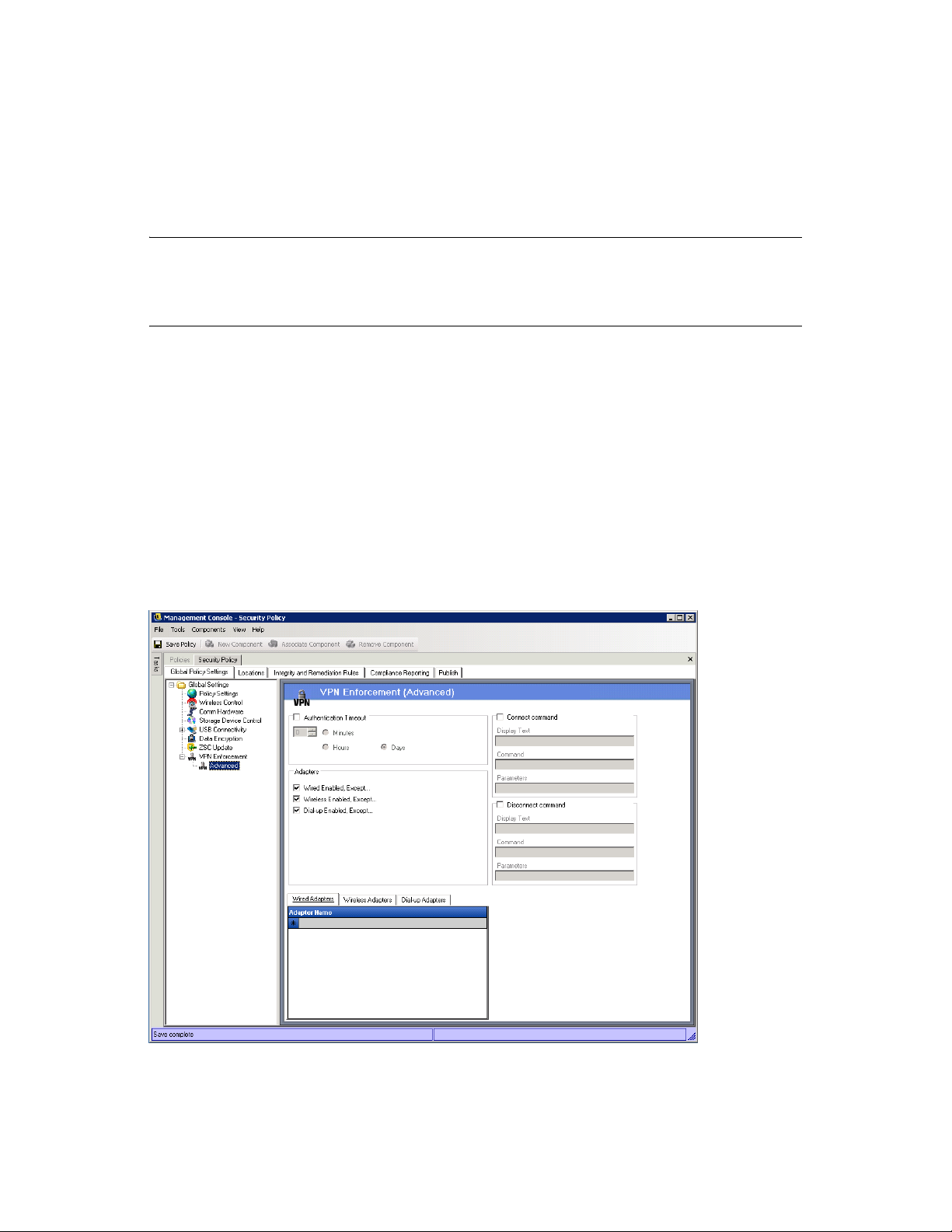
For VPNs with a client, include a hyperlink that points to the VPN Client.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Example:
C:\Program Files\Cisco Systems\VPN Client\ipsecdialer.exe
This link launches the application, but the user stills need to log in. A switch can be entered into
the Parameters field, or a batch file could be created and pointed to, rather than the client
executable).
NOTE: VPN clients that generate virtual adapters (for example, Cisco Systems* VPN Client 4.0)
display the: "Policy Has Been Updated" message. The Policy has not been updated, the Endpoint
Security Client is simply comparing the virtual adapter to any adapter restrictions in the current
policy.
The standard VPN Enforcement settings described above make VPN connectivity an option. Users
are granted connectivity to the current network whether they launch their VPN or not. For stricter
enforcement, see Advanced VPN Settings below.
Advanced VPN Settings
Advanced VPN controls are used to set Authentication Timeouts to secure against VPN failure,
connect commands for client-based VPNs, and use Adapter controls to control the adapters
permitted VPN access.
To access this control, click the Global Policy Settings tab, click the “+” symbol next to VPN
Enforcement, then click
Figure 6-16 Advanced VPN Enforcement
Advanced
in the policy tree on the left.
The following advanced VPN enforcement settings can be configured:
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 97
Page 98

Authentication Timeout: Administrators can place the endpoint in a secured firewall setting (the
firewall Switch To Location setting) to secure against any failure of VPN connectivity. The
Authentication Timeout is the amount of time the Endpoint Security Client waits to gain
authentication to the VPN server. It is recommended that this parameter be set above 1 minute to
allow authentication over slower connections.
Connect/Disconnect Commands: When using the Authentication timer, the Connect and
Disconnect commands control client-based VPN activation. Specify the location of the VPN client
and the required switches in the Parameters fields. The Disconnect command is optional, and
provides for VPN clients that require that the user disconnects before logging off of the network.
NOTE: VPN clients that generate virtual adapters (for example, Cisco Systems VPN Client 4.0)
display the: "Policy Has Been Updated" message, and may switch away from the current location
temporarily. The Policy has not been updated, the Endpoint Security Client is simply comparing the
virtual adapter to any adapter restrictions in the current policy. It is recommended that when running
VPN clients of this type that the Disconnect command hyperlink not be used.
Adapters: This is essentially a mini Adapter policy specific to the VPN Enforcement.
If an adapter is checked (changing it to Enabled, Except), those adapters (Wireless being specific to
card type) are permitted connectivity to the VPN.
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
Adapters entered into the exception lists below, are denied connectivity to the VPN, while all others
of that type will be given connectivity.
If an adapter is not checked (Disabled, Except), then only the adapters entered into the exception list
are permitted to connect to the VPN; all others are denied connectivity.
This control can be used for adapters incompatible to the VPN, for example, or adapters not
supported by the IT department.
This rule overrides the adapter policy set for the switch-to location.
6.2.2 Locations
Locations are rule-groups assigned to network environments. These environments can be set in the
policy (see Section 6.3.6, “Network Environments,” on page 126), or by the user, when permitted.
Each location can be given unique security settings, denying access to certain kinds of networking
and hardware in more hostile network environments, and granting broader access within trusted
environments.
To access Location controls, click the Locations tab.
98 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
Page 99
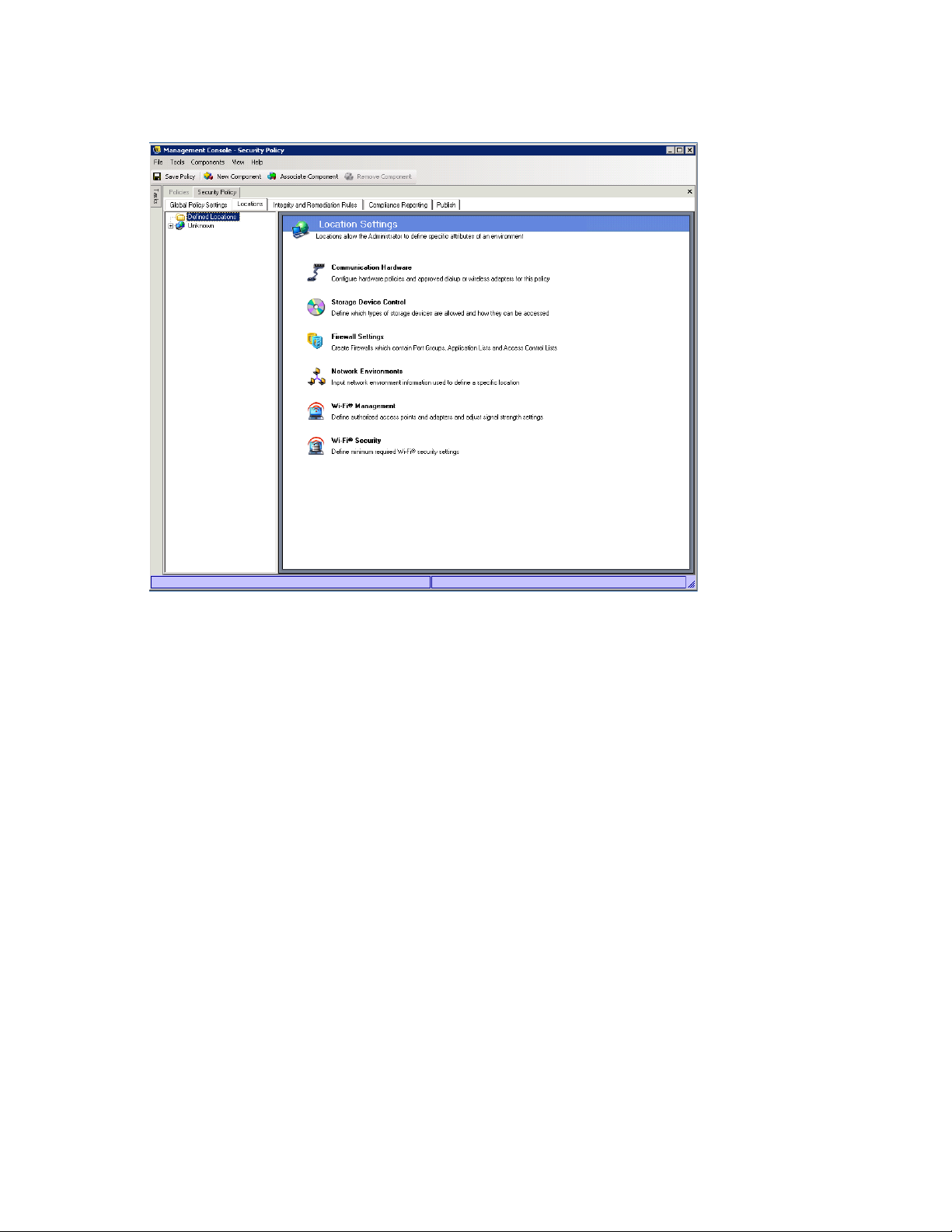
Figure 6-17 Location Settings
novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
The following sections contain more information:
“About Locations” on page 99
“Communication Hardware” on page 100
“Storage Device Control” on page 102
“Wi-Fi Management” on page 104
“Wi-Fi Security” on page 108
About Locations
The following types of locations can be configured:
The Unknown Location: All policies have a default Unknown location. This is the location the
Endpoint Security Client switches users to when they leave a known network environment. This
Unknown location is unique for each policy and is not available as a shared component. Network
Environments cannot be set nor saved for this location.
To access the Unknown Location controls, click the Locations tab, then click the Unknown location
in the policy tree on the left.
Defined Locations: Defined locations can be created for the policy, or existing locations (those
created for other policies) can be associated.
To create a new location:
1 Click Defined Locations, then click the New Component button on the toolbar.
Creating and Distributing Security Policies 99
Page 100

novdocx (en) 17 September 2009
2 Name the location and provide a description.
3 Define the location settings (see below).
4 Click Save Policy.
To associate an existing location:
1 Click Defined Locations, then click the Associate Component button on the toolbar.
2 Select the desired locations from the list.
3 Edit the settings, if desired.
NOTE: Changing the settings in a shared component will affect all other instances of this same
component. Use the Show Usage command to view all other policies associated with this
component.
4 Click Save Policy.
It is recommended that multiple defined locations (beyond simple Work and Unknown locations) be
defined in the policy to provide users with varying security permissions when they connect outside
the enterprise firewall. Keeping the location names simple (for example, Coffee Shops, Airports,
Home) and providing a visual cue through the location's Taskbar icon, which helps users easily
switch to the appropriate security settings required for each network environment.
Communication Hardware
Communication hardware controls, by location, which hardware types are permitted a connection
within this network environment.
100 ZENworks Endpoint Security Management Administration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...