Page 1
Novell®
www.novell.com
AUTHORIZED DOCUMENTATION
Administration Guide
XDASv2 for eDirectory, IDM, and NMAS
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
v1
October 15, 2010
Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 2

Legal Notices
Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to the contents or use of this documentation, and
specifically disclaims any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose.
Further, Novell, Inc., reserves the right to revise this publication and to make changes to its content, at any time,
without obligation to notify any person or entity of such revisions or changes.
Further, Novell, Inc., makes no representations or warranties with respect to any software, and specifically disclaims
any express or implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for any particular purpose. Further, Novell, Inc.,
reserves the right to make changes to any and all parts of Novell software, at any time, without any obligation to
notify any person or entity of such changes.
Any products or technical information provided under this Agreement may be subject to U.S. export controls and the
trade laws of other countries. You agree to comply with all export control regulations and to obtain any required
licenses or classification to export, re-export or import deliverables. You agree not to export or re-export to entities on
the current U.S. export exclusion lists or to any embargoed or terrorist countries as specified in the U.S. export laws.
You agree to not use deliverables for prohibited nuclear, missile, or chemical biological weaponry end uses. See the
Novell International Trade Services Web page (http://www.novell.com/info/exports/) for more information on
exporting Novell software. Novell assumes no responsibility for your failure to obtain any necessary export
approvals.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Copyright © 2010 Novell, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, photocopied,
stored on a retrieval system, or transmitted without the express written consent of the publisher.
Novell, Inc.
404 Wyman Street, Suite 500
Waltham, MA 02451
U.S.A.
www.novell.com
Online Documentation: To access the latest online documentation for this and other Novell products, see
the Novell Documentation Web page (http://www.novell.com/documentation).
Page 3

Novell Trademarks
For Novell trademarks, see the Novell Trademark and Service Mark list (http://www.novell.com/company/legal/
trademarks/tmlist.html).
Third-Party Materials
All third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Page 4

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
4 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 5

Contents
About This Guide 7
1Overview 9
1.1 Key Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.2 XDASv2 Server Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2 Configuring XDASv2 11
2.1 Installing eDirectory XDASv2 Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2 Configuring XDASv2 Property File. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.3 Configuring XDAS Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.4 Loading the Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
3 iManager Plug-In for XDASv2 13
3.1 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.2 Installing iManager Plug-In for XDASv2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.3 Using iManager Plug-In Console for XDASv2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.4 Configuring XDASv2 Events for Auditing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.4.1 Configuring Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.4.2 Configuring XDASv2 Roles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3.4.3 Configuring XDASv2 Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.5 Securing the iManager Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4 Troubleshooting 19
A XDASv2 Events 21
A.1 Account Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
A.2 Session Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
A.3 Data Item and Resource Element Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
A.4 Service or Application Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
A.5 Service or Application Utilization Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
A.6 Peer Association Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
A.7 Data Item or Resource Element Content Access Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
A.8 Work Flow Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
A.9 Role Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
A.10 Exceptional Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
A.11 Audit Service Management Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
A.12 Authentication Event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
B XDASv2 Schema 33
B.1 XDAS V2 JSON Schema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
B.2 XDAS Field Definitions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
B.3 Outcome Codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
B.4 Example of an Event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Contents 5
Page 6

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
6 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 7

About This Guide
This guide describes how to configure and use XDASv2 to audit Novell eDirectory 8.8 and Novell
Identity Manager.
Chapter 1, “Overview,” on page 9
Chapter 2, “Configuring XDASv2,” on page 11
Chapter 3, “iManager Plug-In for XDASv2,” on page 13
Chapter 4, “Troubleshooting,” on page 19
Chapter A, “XDASv2 Events,” on page 21
Appendix B, “XDASv2 Schema,” on page 33
Audience
This guide is intended for Administrators.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Feedback
We want to hear your comments and suggestions about this manual and the other documentation
included with this product. Please use the User Comments feature at the bottom of each page of the
online documentation, or go to www.novell.com/documentation/feedback.html and enter your
comments there.
Documentation Updates
For the most recent version of the XDASv2 Administration Guide, visit the eDirectory Web site
(http://www.novell.com/documentation/edir88).
Additional Documentation
For documentation on eDirectory documentation, see the following:
Novell eDirectory 8.8 Administration Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/edir88/
index.html).
Novell eDirectory 8.8 Installation Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/edir88/
index.html).
Novell iManager 2.7 Administration Guide (http://www.novell.com/documentation/
imanager27/index.html).
About This Guide 7
Page 8

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
8 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 9

1
Overview
The XDASv2 specification provides a standardized classification for audit events. It defines a set of
generic events at a global distributed system level. XDASv2 provides a common portable audit
record format to facilitate the merging and analysis of audit information from multiple components
at the distributed system level. The XDASv2 events are encapsulated within a hierarchical
notational system that helps to extend the standard or existing event identifier set.The XDASv2
taxonomy defines a set of fields, of these the primary fields are observer, initiator and target.
XDASv2 events helps you easily understand the audit trails of heterogeneous applications
Section 1.1, “Key Benefits,” on page 9
Section 1.2, “XDASv2 Server Architecture,” on page 9
1.1 Key Benefits
Provides secured audit services for a distributed system.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
1
Defines a set of generic events at a global distributed system level.
Defines a common portable audit record format to help merge and analyse the audit
information from multiple components of a distributed system.
Defines a common format for audit events that analysis applications can use.
Records XDASv2 audit trail.
Configures event preselection criteria and event disposition actions.
Provides a common audit format regardless of the platform on which the XDASv2 service is
running.
Supports heterogeneous environments without the necessity to reengineer the current operating
system or application-specific audit service implementations.
Supports adequate separation of duties for users.
Protects the audit log by making it accessible only to principals acting in specific
administrative or security roles.
1.2 XDASv2 Server Architecture
Overview
9
Page 10
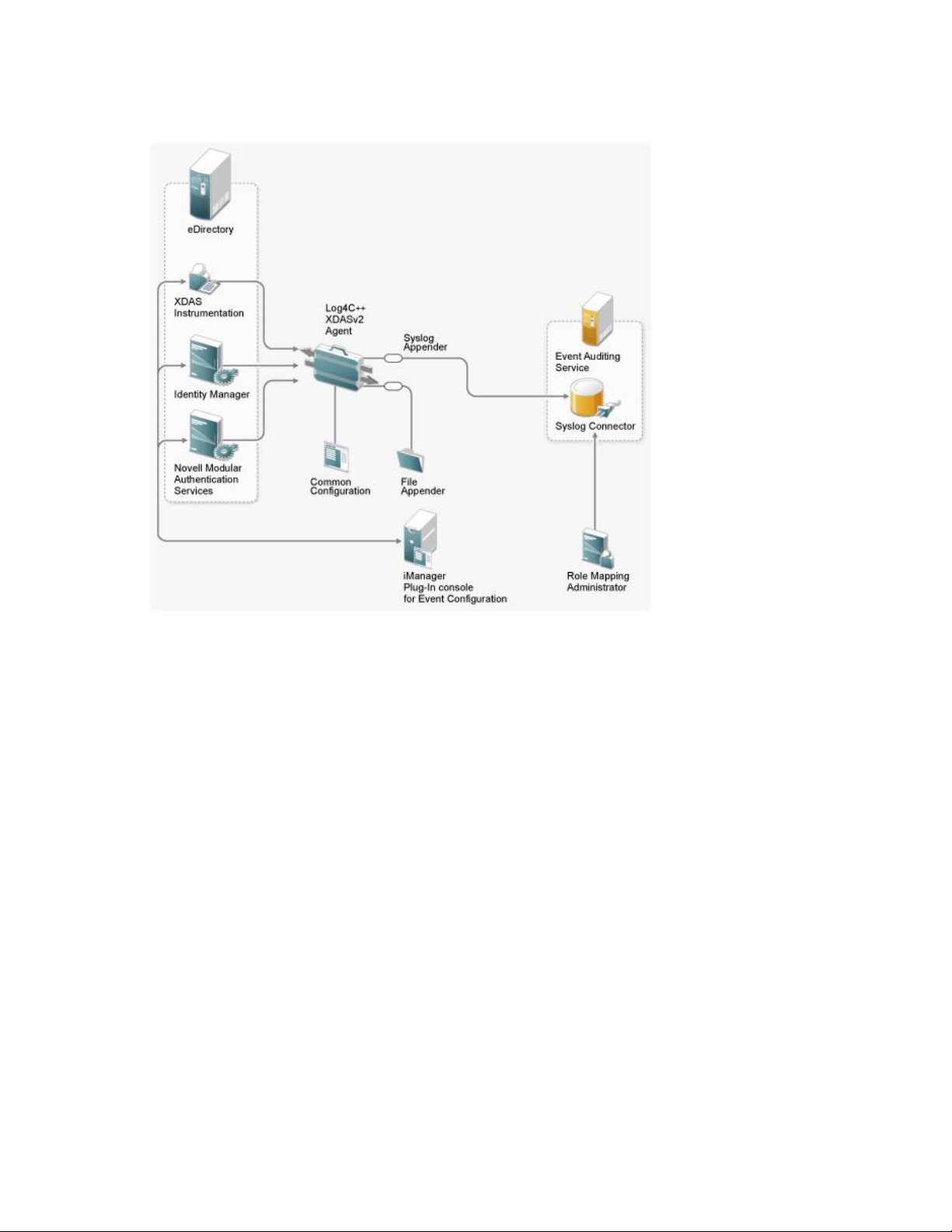
Figure 1-1 XDASv2 Server Architecture
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
10 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 11

2
Configuring XDASv2
This chapter contains the following information:
Section 2.1, “Installing eDirectory XDASv2 Files,” on page 11
Section 2.2, “Configuring XDASv2 Property File,” on page 11
Section 2.3, “Configuring XDAS Events,” on page 12
Section 2.4, “Loading the Modules,” on page 12
2.1 Installing eDirectory XDASv2 Files
The following eDirectory XDASv2 files are, by default, installed as part of eDirectory.
Linux:
novell-edirectory-xdaslog
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
2
novell-edirectory-xdaslog-conf
novell-edirectory-xdasinstrument
Solaris:
NOVLlog
NOVLedirxdasin
Windows
xdasauditds.dlm
xdaslog.dll
2.2 Configuring XDASv2 Property File
The XDASv2 property file is located at
xdasconfig.properties
The following is the content of the XDASv2 property file:
# Set the level of the root logger to DEBUG and attach appenders.
#log4j.rootLogger=debug, S, R
# Defines appender S to be a SyslogAppender.
#log4j.appender.S=org.apache.log4j.net.SyslogAppender
# Defines location of Syslog server.
#log4j.appender.S.Host=localhost
#log4j.appender.S.Port=port
. You can customize the file according to your requirement.
/etc/opt/novell/configuration/
# Specify protocol to be used (UDP/TCP/SSL)
#log4j.appender.S.Protocol=UDP
# Specify SSL certificate file for SSL connection.
# File path should be given with double backslash.
#log4j.appender.S.SSLCertFile=/etc/opt/novell/mycert.pem
Configuring XDASv2
11
Page 12

# Minimum log-level allowed in syslog.
#log4j.appender.S.Threshold=INFO
# Defines the type of facility.
#log4j.appender.S.Facility=USER
# Layout definition for appender Syslog S.
#log4j.appender.S.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
#log4j.appender.S.layout.ConversionPattern=%c : %p%m%n
# Defines appender R to be a Rolling File Appender.
#log4j.appender.R=org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender
# Log file for appender R.
#log4j.appender.R.File=/var/opt/novell/eDirectory/log/xdas-events.log
# Max size of log file for appender R.
#log4j.appender.R.MaxFileSize=100MB
# Set the maximum number of backup files to keep for appender R.
# Max can be 13. If set to zero, then there will be no backup files.
#log4j.appender.R.MaxBackupIndex=10
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
# Layout definition for appender Rolling log file R.
#log4j.appender.R.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
#log4j.appender.R.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{MMM dd HH:mm:ss} %c : %p%m%n
Table 2-1 XDASv2 Property File
Options ID Description
Syslog Appender S
Rolling File Appender R
2.3 Configuring XDAS Events
See Chapter 3, “iManager Plug-In for XDASv2,” on page 13 for information on configuring
XDASv2 events for eDirectory.
2.4 Loading the Modules
After you have configured the XDASv2 events, run the following command to load the XDASv2
modules:
Linux/Solaris: Run the following command to load the XDASv2 modules:
ndstrace -c "load xdasauditds"
Windows: Run
ndscons.exe
then click Start.
If you have installed NMAS and enabled NMAS auditing, the NMAS server automatically loads the
XDASv2 library.
12 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
, select xdasauditds option from the list of available modules,
Page 13

3
iManager Plug-In for XDASv2
You can manage and configure eDirectory for XDASv2 auditing by using Novell iManager. Novell
iManager is a Web-based application that is used to manage, maintain, and monitor Novell
eDirectory through wired and wireless devices.The XDASv2 iManager plug-in is included with the
eDirectory installation.
NOTE: iManager plug-in is only for enabling and configuring XDASv2 events for eDirectory. This
plug-in does not apply to NMAS and Identity Manager.
Section 3.1, “System Requirements,” on page 13
Section 3.2, “Installing iManager Plug-In for XDASv2,” on page 13
Section 3.3, “Using iManager Plug-In Console for XDASv2,” on page 13
Section 3.4, “Configuring XDASv2 Events for Auditing,” on page 14
Section 3.5, “Securing the iManager Connection,” on page 18
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
3
3.1 System Requirements
Installing and using the Novell Audit iManager Plug-in requires iManager 2.7.4. See Novell
iManager Product Page (http://www.novell.com/products/consoles/) for requirements and download
instructions.
3.2 Installing iManager Plug-In for XDASv2
iManager plug-in for XDASv2 is, by default, installed with eDirectory.
3.3 Using iManager Plug-In Console for XDASv2
1 Log in to the iManager console.
1a Open iManager from a Web browser, using the following URL:
https://ip_address_or_DNS/nps/iManager.html
where ip_address_or_DNS is the IP address or DNS name of your iManager server.
For example:
http://192.168.0.5/nps/iManager.html
1b Log in using your username and password.
In iManager, you have access only to those roles for which you have assigned rights. To
have full access to all Novell iManager features, you must log in as a user with Admin
rights to the tree.
For more information, see Accessing iManager (http://www.novell.com/documentation/
imanager27/imanager_admin_273/data/bsxrjzp.html)
2 Select Audit Configuration from Roles and Tasks.
3 Specify the NCP Server.
iManager Plug-In for XDASv2
13
Page 14

Click the Object Selector icon to browse for the NCP server.
4 Click OK.
The XDASv2 Audit page is displayed. Continue with Section 3.4.1, “Configuring Events,” on
page 14.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
3.4 Configuring XDASv2 Events for Auditing
Section 3.4.1, “Configuring Events,” on page 14
Section 3.4.2, “Configuring XDASv2 Roles,” on page 16
Section 3.4.3, “Configuring XDASv2 Accounts,” on page 17
3.4.1 Configuring Events
Use this page to configure XDASv2 events.
14 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 15

Figure 3-1 XDASv2 Events
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
1 You can select both or either of the following components for XDASv2 event settings:
DS: Specifies an eDirectory™ object. For each DS object, a corresponding LDAP object
exists.
LDAP: Specifies an LDAP object.
2 Log event values:
The events are logged into a text file. Event values with more than 768 bytes in size are
considered as large values. You can log events of any size.
Log Large Values: Select this option to log events that are more than 768 bytes in size.
Do Not Log Large Values: Select this option to log events that are less than 768 Byte in size.
If the event size is more, the event value is truncated and saved to the log file.
3 Specify the following based on your requirement:
iManager Plug-In for XDASv2 15
Page 16

Options Description
Account Management Events Select the account management events for which you
want to log events. You can log events to create, delete,
enable, disable, and query accounts, and also to modify
account security token.
Session Management Events Select the session management events for which you
want to log events. You can log events to create,
terminate, and modify sessions.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Data Item or Resource Element
Management Events
Service or Application Management
Events
Service or Application Utilization Events Select the service or application utilization events for
Peer Association Management Events Select the peer association events for which you want to
Data Item or Resource Element Content
Access Events
Role Management Events Select the role management events for which you want
Exceptional Management Events Select the exceptional management events for which
Select the data item or resource element management
events for which you want to log events. You can log
events to create and delete data items and to modify
and query data item attributes.
Select the service or application management events
for which you want to log events. You can log events for
enabling and disabling services.
which you want to log events. You can log events to
start and terminate services, and to modify process
contexts.
log events. You can log events for creating and
terminating peer associations.
Select the data item or resource element content
access events for which you want to log events. You can
log events to create, terminate, and modify data item
associations.
to log events. You can log events to create, delete,
query, and modify roles.
you want to log events. You can log events to start and
shut down systems and also to back up and recover
data stores.
Authentication Management Events Select the authentication management events for which
Operational Events Select the operational management events for which
For more information on events, see Chapter A, “XDASv2 Events,” on page 21.
3.4.2 Configuring XDASv2 Roles
Configure XDASv2 roles for the objects for which you want to collect XDASv2 events. You can
select object classes and set attributes for them.
16 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
you want to log events. You can log events to
authenticate sessions and create access tokens.
you want to log events. You can log events to generate
eDirectory operation IDs.
Page 17

Figure 3-2 XDASv2 Roles
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
1 Select object classes for which you want to collect events.
2 Set any number of attributes for the object classes you have selected. Click the attribute and
click the arrow to add the attribute to the selected list of attributes.
3 Click OK after you add the attributes. Click Apply to confirm the modifications.
The selected attributes appear in this list.
3.4.3 Configuring XDASv2 Accounts
Configure XDASv2 accounts by selecting available object classes. Click OK to exit the application.
iManager Plug-In for XDASv2 17
Page 18

Figure 3-3 XDASv2 Accounts
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
1 Select object classes from the list for which you want to collect events.
2 Selected object classes appear in this list.
3 Click Apply after adding the object classes.
3.5 Securing the iManager Connection
When you log in to iManager, your connection is automatically forwarded to a secure port. The
default HTTPS port for iManager is 443.
For more information on running iManager over an SSL connection, see “Configuring and Using
SSL for LDAP Connections” in the iManager Administration Guide. (http://www.novell.com/
documentation/imanager27)
18 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 19

4
Troubleshooting
Keep in mind the following information when you install Novell XDASv2:
Initializing XDAS module error
Possible Cause: You cannot connect to the server IP or the port number mentioned in
xdasconfig.properties file when you initialize the XDASv2 module. It displays
the followng message:
log4cxx: Could not instantiate TCP Socket to <IP>. All
logging will FAIL.
log4cxx: IO Exception : status code = 111
Action: To work around this issue,
1 Check whether the sever IP or the port number given in the
xdasconfig.properties file is correct.
2 Check whether the remote server is reachable and is accepting the
connection on the given port.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
4
3 Reload the xdasauditds module.
The TCP connection is lost
Possible Cause: If the remote server is not reachable or does not accept connection on the given
port, the following error is displayed:
log4cxx: Detected problem with TCP connection to <IP>. All
logging will FAIL.
log4cxx: IO Exception : status code = 32
Action: To work around this issue:
1 Check whether remote server is reachable and is accepting the connection
on the given port.
2 Reload the xdasauditds module.
The SSL certificate file issue
Possible Cause: The SSL certificate file is either not valid or not present at the given location in
the xdasconfig.properties file. The following error is displayed:
log4cxx: could not load verify locations for SSL
Action: To work around this issue,
1 Specify the absolute path to a valid certificate file.
2 Reload the xdasauditds module.
Troubleshooting
19
Page 20

The network connection to the remote server is lost
Source: The following error is displayed:
log4cxx: SSL write failed for <IP>. All logging will FAIL.
Action: To work around this issue,
1 Check whether remote server is reachable and is accepting the connection
on the given port.
2 Reload the xdasauditds module.
The SSL connection has failed
Possible Cause: The SSL connection fails because either the TLS/SSL handshake fails or a
connection failure occurs. The following error message is displayed:
log4cxx: SSL Connect Failed to <IP>
Action: To work around this issue,
1 Check whether remote server is reachable and is listening on the given
port.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
2 Check whether the certificate is valid.
3 Reload the xdasauditds module.
20 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 21

A
XDASv2 Events
The XDASv2 events are classified into the following categories:
Section A.1, “Account Management Events,” on page 21
Section A.2, “Session Management Events,” on page 22
Section A.3, “Data Item and Resource Element Management Events,” on page 23
Section A.4, “Service or Application Management Events,” on page 24
Section A.5, “Service or Application Utilization Events,” on page 25
Section A.6, “Peer Association Management Events,” on page 25
Section A.7, “Data Item or Resource Element Content Access Events,” on page 26
Section A.8, “Work Flow Management Events,” on page 27
Section A.9, “Role Management Events,” on page 28
Section A.10, “Exceptional Events,” on page 28
Section A.11, “Audit Service Management Events,” on page 29
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
A
Section A.12, “Authentication Event,” on page 30
A.1 Account Management Events
An identity is a token used to represent a particular user or entity. Blame or credit for an action goes
to the identity for a set of activities within a system. Accounts exist in the application domains to
associate attributes with the set of identifiers typically associated with identities. Identities can be a
a human being or an automated identity, such as another service, which is acting on behalf of a
human or a regularly scheduled system activity. In both the cases, account management is
considered as persistent account creation, wherein an identity with some limited or unlimited set of
system rights is associated with attributes.
NOTE: The
Modify Account
security, and is thus given its own event.
Table A-1 Account Management Event Taxonomy
Event Name
Create Account 0.0.0.0 DSE_CREATE
Modify Account Security Token
, but modification of account security tokens is considered critical to audit
Event
Identifier
Corres. eDir
Event
_ENTRY
event could have been defined in terms of
Description Use
Create a new
account
Consider this event as
appropriate for any situation
wherein an account, as
defined above, is to be
created.
XDASv2 Events
21
Page 22

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Delete Account 0.0.0.1 DSE_DELETE
Disable Account 0.0.0.2 DSE_LOGIN Disable an existing
Enable Account 0.0.0.3 Enable an existing
Query Account 0.0.0.4 DSE_SEARCH Query an existing
Event
Identifier
Corres. eDir
Event
_ENTRY
Description Use
Delete an existing
account
account
account
account
This event has the opposite
semantic meaning of account
creation. Use this event
wherever such an account,as
described above, is to be
deleted.
Consider this event relevant
for any situation where a
particular record in an identifier
database is disabled by an
administrator or an automated
security process such that it
can no longer be used until it is
re-enabled
This is the counterpart event to
the disable account event
defined above.
Consider the Query account
events whenever a request for
the attribute information ofa
particular account is made.
Modify Account 0.0.0.5 DSE_MERGE_
ENTRIES
Modify Account
Security Token
Query Account
Security Token
Delete Account
Security Token
0.0.0.6 DSE_CHGPASSModify an existing
Modify an existing
account
account security
token
Consider the Modify account
events whenever a request to
change attribute information of
a particular account is made.
An account security token may
be a password, or any other
type of authentication
materials associated with a
user account. Here, a user
account means any type of
account by which a user,
application, or system service
may authenticate, and then act
with the rights of that account.
A.2 Session Management Events
A session is the association of an initiator with a stream of communication. A session may represent
a user's connection to server, as in the case of logging into a Unix or Windows host, or a set of
related transactions in a connection-less environment, as in the case of using a cookie to maintain
persistent transactions between a browser client and a Web server.
22 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 23

Table A-2 Session Management Event Taxonomy
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Create Session 0.0.1.0 Create a new
Terminate Session 0.0.1.1 Terminate an
Query Session 0.0.1.2 Query user session
Modify Session 0.0.1.3 DSE_CHANGE
Event
Identifier
Corres. eDir
Event
_CONN_STAT
E
Description Use
This event should be reported
session
existing session
attributes
Modify user session
attributes
whenever a new session (as
defined above) is created.
This event should be reported
whenever an existing session
(as defined above) is
terminated.
This event should be reported
whenever attribute information
is requested on an existing
session.
This event should be reported
whenever attribute information
is modified on an existing
session.
A.3 Data Item and Resource Element Management Events
This set of events relate to the creation and management of data items and resource elements within
a domain. The type of data item or resource element is dependent upon the domain. For example,
files and directories, device special files, and shared memory segments within an operating system,
tables and records within a database, messages within an email system. The term data item is used in
this context to refer to any type of resource element.
Table A-3 Data Item and Resource Element Management Event Taxonomy
Event Name
Create Data Item 0.0.2.0 DSE_CREATE
Delete Data Item 0.0.2.1 DSE_DELETE
Query Data Item
Attribute
Event
Identifier
0.0.2.2 DSE_COMPA
Corresponding
eDir Event
_ENTRY
_ENTRY
RE_ATTR_VA
LUE
Dexription Use
Create a data item This event is reported whenever a
Delete a data item This event is reported whenever a
Query data item
attributes
security-relevant data item or
resource element is created.
security-relevant data item or
resource element is deleted
This event is reported whenever a
security-relevant data item or
resource element is queried –
either for value, or for an attribute
of the data item.
XDASv2 Events 23
Page 24

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Modify Data Item
Attribute
Event
Identifier
0.0.2.3 DSE_DEFINE
Corresponding
eDir Event
_ATTR_DEF
DSE_REMOV
E_ATTR_DEF
DSE_REMOV
E_CLASS_DE
F
DSE_DEFINE
_CLASS_DEF
DSE_MODIFY
_CLASS_DEF
Dexription Use
Modify data item
attributes
This event is reported whenever a
security-relevant data item or
resource element is modified –
either the value, or an attribute of
the data item
A.4 Service or Application Management Events
This set of events relates to the management of services or applications. For example, the RPM
package manager might throw these events as packages are installed or removed from a Linux
system. Windows 32 Service Control Manager (SCM) events sent to the Windows 32 System Event
Log may be translated into these events as they are imported into OpenXDASv2. This set of events
could also be much more domain-specific, including concepts such as installing, removing, or
configuring installable executable-modules within a single application domain. The key idea is to
ensure that reported events have security significance.
Table A-4 Service or Application Management Event Taxonomy
Event Name
Install Service 0.0.3.0 DSE_CHANG
Remove Service 0.0.3.1 DSE_CHANG
Query Service
Configuration
Modify Service
Configuration
Disable Service 0.0.3.4 DSE_CLOSE_
Event
Identifier
0.0.3.2 Query the
0.0.3.3 Modify
Corresponding
eDir Event
E_MODULE_
STATE
E_MODULE_
STATE
BINDERY
Description Use
Install a service or
application
Remove a service
or application
configuration of a
service or
application
configuration of a
service or
application
Disable a service
or application
This event is reported when a
service or application is installed
This event is reported when a
service or application is removed.
This event is reported when service
or application configuration
information is requested.
This event is reported when service
or application configuration
information is modified.
This event is reported when a
service, operation or function is
disabled.
24 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 25

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Enable Service 0.0.3.5 DSE_OPEN_B
Event
Identifier
Corresponding
eDir Event
INDERY
Description Use
Enable a service
or application
This event ise reported when a
service, operation or function is
enabled.
A.5 Service or Application Utilization Events
This class of events relates to the use of services and applications. They typically map to the
execution of a program or a procedure and manipulation of the processing environment.
Table A-5 Service or Application Utilization Events Taxonomy
Event Name
Invoke Service 0.0.4.0 DSE_START_
Terminate Service 0.0.4.1 DSE_END_UP
Event
Identifier
Corresponding
eDir Event
UPDATE_SCH
EMA
DATE_SCHE
MA
Description Use
Invoke a service or
application
Terminate a service
or application
This event is reported when a
security-relevant service is
invoked.
This event is reported when a
service is terminated.
Query Process
Context
Modify Process
Context
0.0.4.2 Query a processing
context
0.0.4.3 DSE_SERVE
R_RENAME
DSE_SYNTHE
TIC_TIME
DSE_SERVE
R_ADDRESS_
CHANGE
Modify processing
context
This event is reported when any
attributes of a process context
are queried – this event is
somewhat specific to operating
systems, but some use can be
found in other domain-specific
applications.
This event is reported when any
attributes of a process context
are modified – this event is
somewhat specific to operating
systems, but some use can be
found in other domain-specific
applications.
A.6 Peer Association Management Events
Peer association events are related to the association of a user or identity with a group, or the
association of two users in some domain-specific context. For example, adding an LDAP user to a
group, or associating two users for a domain-specific purpose in an application's identity association
database.These events are also related to the association of identities within disparate authentication
domains for purposes of federation.
For example, when an identity in domain A makes a request to a service governed by domain B,
then a peer association is required between these domains – often this is called a trust relationship.
From an implementation perspective, setting up a trust relationship is often done by establishing an
XDASv2 Events 25
Page 26

identity in domain B, which is used as a proxy for any request coming from any identity in domain
A. Trust relationships can be much more complex, however, as individual identities in domain A can
have individual associations with specific domain B identities.
Table A-6 Peer Association Management Events Taxonomy
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Create Peer
Association
Terminate Peer
Association
Query Association
Context
Modify Association
Context
Receive Data Via
Association
Send Data Via
Association
Event
Identifier
0.0.5.0 Create an
0.0.5.1 Terminate an
0.0.5.2 Query an
0.0.5.3 Modify an
0.0.5.4 Receive data via an
0.0.5.5 Send data via an
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
association with a
peer
association with a
peer
association context
association context
association
association
This event is reported when a
new peer association is created.
This event is reported when an
existing peer association is
destroyed.
This event is reported when the
attributes of a peer association
are queried.
This event is reported when the
attributes of a peer association
are modified.
This event is reported when data
is received from a service in an
authentication domain
specifically via a trust
relationship or peer association.
This event is reported when data
is sent to a service in an
authentication domain
specifically via a trust
relationship or peer association.
A.7 Data Item or Resource Element Content Access Events
Resource content-access events are related to access of any data files protected by an authentication
domain. This could be file system files, database records, Web pages etc. While instrumenting
applications, consider securing access to the resources. Resource access can be a high-bandwidth
process. Therefore, only security-relevant events should be reported. Such instrumentation should
be configurable at the application level by the application administrator, thus must be policy driven.
This implies that such applications add additional infrastructure and user interface to allow
administrators to manage the resource-access events that has to be audited, and determine the
unimportant events within the security context.
26 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 27

Table A-7 Data Item or Resource Element Content Access Events Taxonomy
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Create Data Item
Association
Terminate Data
Item Association
Query Data Item
Association
Modify Data Item
Association
Query Data Item
Contents
Event
Identifier
0.0.6.0 Create association
0.0.6.1 Terminate
0.0.6.2 Query context of
0.0.6.3 Modify context of
0.0.6.4 Query data item
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
with a data item
association with a
data item
association with a
data item
association with
data item
contents
This event is reported when rights
are granted by an identity to a
specific data item – when a trust
relationship is established between
an identity and a data item.
This event is reported when rights
are revoked from an identity to a
specific data item – when a trust
relationship is revoked between an
identity and a data item.
This event is reported when rights
are queried for an identity on a
specific data item – when trust
relationship attributes are queried
for a specific identity and data item.
This event is reported when rights
are modified on the previously
established relationship between
an identity and specific data item.
This event isreported when a data
item is read on behalf of an identity.
Modify Data Item
Contents
0.0.6.5 Modify data item
contents
This event is reported when a data
item is written on behalf of an
identity.
A.8 Work Flow Management Events
Even though work flow events can be classified in terms of data items, work flow has its own
category of events within the XDASv2 taxonomy. Work flow events is used whenever a work flow
process is instrumented for audit events.
Table A-8 Workflow Management Event Taxonomy
Event Name
Request Work
Flow Approval
Receive Work
Flow Approval
Escalate Work
Flow Request
Event
Identifier
0.0.7.0 Initiate a workflow
0.0.7.1 Receive a work
0.0.7.2 A work flow item
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
Approval for a work flow item has
approval request
flow approval
notice
was escalated
been requested.
Approval for a work flow item has
been received by appropriate
authority.
A work flow request has been
escalated.
XDASv2 Events 27
Page 28

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Send Work Flow
Notification
Event
Identifier
0.0.7.3 A work flow
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
Sent a work flow change
notification was
sent
notification.
A.9 Role Management Events
Role management event may also be classified in terms of data items, but role management is key to
systems that manage identity, so these were also given their own category within the XDASv2
taxonomy.
Table A-9 Role Management Event Taxonomy
Event Name
Create Role 0.0.8.0 Create a new role Creates a new role , or an attempt
Delete Role 0.0.8.1 Delete an existing
Event
Identifier
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
is made to create a new role.
An existing role is deleted, or an
role
attempt is made to delete an
existing role.
Disable Role 0.0.8.2 Disable an
existing role
Enable Role 0.0.8.3 Enable an
existing role
Query Role 0.0.8.4 Query role
attributes
Modify Role 0.0.8.5 Modify a role
attribute
An existing role is disabled, or an
attempt is made to disable an
existing role.
A previously disabled role is reenabled, or an attempt is made to
enable a previously disabled role.
Role attributes are queried, or an
attempt is made to query role
attributes.
Role attributes are modified, or an
attempt is made to modify role
attributes.
A.10 Exceptional Events
Exceptional events are generated very rarely, and are considered important because they are
generated. For instance, shutting down an enterprise-critical server is exceptional because it can’t
happen without someone's permission.
28 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 29

Table A-10 Exceptional Event Taxonomy
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Start System 0.0.9.0 Start a system This event is reported when a
Shutdown System 0.0.9.1 Shutdown a
Resource
Exhaustion
Resource
Corruption
Resource
Unavailable
Event
Identifier
0.0.9.2 Resource
0.0.9.3 Resource
0.0.9.4 Resource
Corresponding
eDir Event
Description Use
server, system, or mission-critical
application starts up.
This event is reported when a
system
exhaustion
Corruption
Unavailable
server, system, or mission critical
application shuts down.
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application runs out of some
critical resource, like memory or
disk space. It is often difficult to
report such events because often
the critical resource in question is
required in order to report the
event.
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application detects a resource
corruption (memory, disk file, etc).
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application becomes unavailable.
Resource
Available
Back up Data
Store
Recover Data
Store
0.0.9.5 Resource
Available
0.0.9.6 Back up Data
Store
0.0.9.7 Recover Data
Store
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application becomes available.
This event is usually reported if
the resource has been unavalable
for a period of time.
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application backs up a critical
data store.
This event is reported when a
server, system, or mission critical
application restores a critical data
store.
A.11 Audit Service Management Events
Audit services have traditionally been classified by themselves because auditing represents a lower
level activity than the security events which themselves are being audited. By classifying audit
events separately, an entire category of endless-loop defects can be avoided. Developers
instrumenting applications will probably never need to report these events, as they are generally
reported by systems like OpenXDAS itself. However, they are documented here for the sake of
completeness.
XDASv2 Events 29
Page 30

Table A-11 Audit Service Management Event Taxonomy
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Name
Configure Audit
Service
Audit Data Store
Full
Audit Data Store
Corrupted
Event
Identifier
Corres. eDir
Event
Description Use
0.0.10.0 Configure audit
service
0.0.10.1 Audit datastore is
full
0.0.10.2 Audit datastore is
corrupted
Configuration data has been
changed for an audit subsystem.
OpenXDAS reports this event when
a SIGHUP is received, indicating
that the xdasd configuration file has
been modified and should be reread.
This event is reported by
OpenXDAS when an audit log is
full, and can no longer accept
additional audit records. Where
possible, space is reserved for this
event, in case it must be reported.
This event is reported by
OpenXDAS when the data store
reports that an audit log has been
corrupted. Generally, this condition
is not detected unless a request is
made to read an audit stream, and
the audit log reports that it cannot
be read due to corruption.
A.12 Authentication Event
XDASv1 specified authentication as a modification of session attributes. XDASv2 makes
authentication a first class event because authentication is critical to an audit.
Table A-12 Authentication Events Taxonomy
Event Names
Authenticate
Event
Identifier
0.0.11.0 A new identity is
Session
Unauthenticate
0.0.11.1 A user has actively
Session
Federate Identity 0.0.11.2 A remote identity is
eDirectory
Events
Description Use
When a user authenticates a
associated with a
session
session, a new identity is
associated with that session. This
identity is then used to authorize
requests for protected resources.
When a user clicks the "Logout"
disassociated his
identity from an
existing
authenticate
button on his or her web browser,
the previously authenticated identity
is removed from an existing
authenticated session.
session.
An identity relationship is
associated with a
local identity.
established between a user at
XYZ.COM and the local identity
provider.
30 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 31

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event Names
Event
Identifier
eDirectory
Events
Description Use
Unfederate Identity 0.0.11.3 A remote identity is
disassociated from
a local identity.
Create Access
Token
0.0.11.4 A SAMLv2, WS-*,
OAuth, or other
access token was
provided upon
request.
An existing identity relationship
between a user at an external
identity provider and the local
identity provier is removed.
A resource access token was
created by a service (or identity)
provider to send to a service
consumer. Access is limited by time
frame, specifically requested
resources, or other limiting criteria,
in terms of a contract specified by
previously agreed upon name/value
pairs in the token. The act of
creating and sending an access
token is the start of a new pseudoidentity with limited and specific
rights to protected resources. This
pseudo-identity can be used as a
correlation identifier between this
and future authorization events. The
actually identity of the system user
behind the access token may or
may not be hidden from the
consumer.
Destroy Access
Token
0.0.11.5 An existing
SAMLv2, WS-*,
OAuth, or other
access token was
destroyed or
decommissioned.
A previously created access token
was decommissioned such that it is
no longer allowed to be used for
access to protected resources.
Future requests for access to
protected resources, based on this
access token should be denied.
XDASv2 Events 31
Page 32

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
32 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 33

B
XDASv2 Schema
Section B.1, “XDAS V2 JSON Schema,” on page 33
Section B.2, “XDAS Field Definitions,” on page 36
Section B.3, “Outcome Codes,” on page 39
Section B.4, “Example of an Event,” on page 39
The XDAS schema is defined as follows:
B.1 XDAS V2 JSON Schema
{
"id":"XDASv2",
"title":"XDAS Version 2 JSON Schema",
"description":"A JSON representation of an XDASv2 event record.",
"type":"objectr",
"properties":{
"Source":{
"description":"The original source of the event, if applicable.",
"type":"string",
"optional":true
},
"Observer":{
"description":"The recorder (ie., the XDASv2 service) of the event.",
"type":"object",
"optional":false,
"properties":{
"Account":{"$ref":"account"},
"Entity":{"$ref":"entity"}
}
},
"Initiator":{
"description":"The authenticated entity or access token that causes an
event.",
"type":"object",
"optional":false,
"properties":{
"Account":{"$ref":"account","optional":true},
"Entity":{"$ref":"entity"},
"Assertions":{
"description":"Attribute/value assertions about an identity.",
"type":"object",
"optional":true
}
}
},
"Target":{
"description":"The target object, account, data item, etc of the
event.",
"type":"object",
"optional":true,
"properties":{
"Account":{"$ref":"account"},
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
B
XDASv2 Schema
33
Page 34

"Entity":{"$ref":"entity"},
"Data":{
"description":"A set attribute/value pairs describing the target
object.", *
"type":"object",
"optional":true
}
}
},
"Action":{
"description":"The action describes the event in a uniform manner.",
"type":"object",
"optional":false,
"properties":{
"Event":{
"description":"The event identifier in standard XDASv2 taxonomy.",
"type":"object",
"optional":false,
"properties":{
"Id":{
"description":"The XDASv2 taxonomy event identifier.",
"type":"string",
"optional":false,
"pattern":"/^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]+)*$/"
},
"Name":{
"description":"A short descriptive name for the specific
event.", eg. a new replica is added
"type":"string",
"optional":true
},
"CorrelationID":{
"description":"Correlation ID, source#uniqueID#connID",
"type":"string",
"optional":true
}
},
"SubEvent":{
"type":object
"description": "Describes the actual domain specific event that has
occured.",
"optional":true,
"properties":{
"Name"":{
"description":"A short descriptive name for this event.",
"type":"string",
"optional":true
},
}
}
}
"Log":{
"description":"Client-specified logging attributes.",
"optional":true,
"properties":{
"Severity":{"type":"integer", "optional":true},
"Priority":{"type":"integer", "optional":true},
"Facility":{"type":"integer", "optional":true}
}
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
34 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 35

}
"Outcome":{
"description":"The XDASv2 taxonomy outcome identifier.",
"type":"string",
"optional":false,
"pattern":"/^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]+)*$/"
}
"Time":{
"description":"The time the event occurred.",
"type":"object",
"optional":false,
"properties":{
"Offset":{
"description":"Seconds since Jan 1, 1970.",
"type":"integer"
},
"Sequence":{
"description":"Milliseconds since last integral second.",
"type":"integer",
"optional":true
},
"Tolerance":{
"description":"A tolerance value in milliseconds.",
"type":"integer",
"optional":true
},
"Certainty":{
"description":"Percentage certainty of tolerance.",
"type":"integer",
"optional":true,
"minimum":0,
"maximum":100,
"default":100,
},
"Source":{
"description":"The time source (eg., ntp://time.nist.gov).",
"type":"string",
"optional":true
},
"Zone":{
"description":"A valid timezone symbol (eg., MST/MDT).",
"type":"string",
"optional":true
}
}
"ExtendedOutcome":{
"description":"The XDASv2 taxonomy outcome identifier.",
"type":"string",
"optional":false,
"pattern":"/^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]+)*$/"
}
}
}
}
},
{
"id":"account",
"description":"A representation of an XDAS account.",
"type":"object",
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
XDASv2 Schema 35
Page 36

"properties":{
"Domain":{
"description":"A (URL) reference to the authority managing this
account.", /* lets take it as the partition?
"type":"string"
},
"Name":{
"description":"A human-readable account name.", - DN
"type":"string",
"optional":true
},
"Id":{
"description":"A machine-readable unique account identifier value.", EntryID
"type":"integer"
}
}
},
{
"id":"entity", - Server details for Target, client
address details for the initiator
"description":"A representation of an addressable entity.",
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"SysAddr":{"type":"string","optional":true},
"SysName":{"type":"string","optional":true},
"SvcName":{"type":"string","optional":true},
"SvcComp":{"type":"string","optional":true},
}
}
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
B.2 XDAS Field Definitions
These fields in the schema are the XDASv2 fields defined specifically for audit events. Some or all
of these fields may also be relevant to other types of event, but information of this sort is required
for auditing services. The XDASv2 JSON record format is open. By that, we mean that any
additional fields may be added to the record at any place, as long as they don't conflict with the field
values defined for audit by the XDASv2 standard.
Thus, if there is a particular type of correlation data, such as a workflow identifier, or a session
identifier that can be used as correlation data points between events within a particular workflow or
client session, you may add these fields. Simply choose a non-conflicting name for your field.
Table B-1 XDAS Field Definitions
XDAS Field Description
Source (Optional) The source of an event identifies the event service of another system from
which this event was originally defined and converted to an XDAS event.
Since many events are generated directly by XDAS clients, the source field is
optional.
36 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 37

XDAS Field Description
Initiator The initiator of an event is the authenticated entity that initially provoked
creation of the event. Note that an initiator need not be identified. If the entity
can't be identified - perhaps an entity is attempting to login, thus provoking the
generation of a login event by an observer - then as much information about
the origin of the event as possible should be specified. NOTE: In the special
case of a login event, the authenticated identity of the initiator is not yet known
until after the login attempt has succeeded. Therefore a failed login event
should not give the identity of the target account as the identity of the initiator.
An intiator is described in terms of an account and an entity (described below),
as well as an optional set of assertions. These assertions describe, in terms of
a set of name/value pairs, the attributes of the initiator identity. Some initiators
are not known by a specific account, but are known only by a set of assertions
(SAML2, for instance) that describe the rights of the actor. The schema is not
defined for these assertions, as they will be different for each class and
potentially for each individual object.
Action The action identifies the event that is being recorded. This field provides the
XDASv2 event identifier, as well as an outcome code (success, or failure
class), and the time the event occurred, with as much accuracy as possible.
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Event The event field is the key to XDAS events. Event encapsulates a taxonomical
identifier and a short descriptive name for human readability.
Id The event Id code represents the event identifier, defined by the XDASv2
standard event taxonomy, and extensions defined by the Novell CSS product.
Name The event name is a human readable representation of the event identifier.
The event name is optional, but recommended for readability.
Data The event data provides additional descriptive information about the event.
Log The log field contains standard syslog-like log-level values, in terms of
Severity and Facility numeric identifiers. The log field is optional, as well as
every sub-field within the log field. These values should only be used when
necessary, as they generally represent judgment calls on the part of the
instrumentor. Such judgment calls are best left to analysis software or
engineers once the event data is collected.
Outcome For details on outcome codes, see Section B.3, “Outcome Codes,” on
page 39.
Time The event time is the time recorded by the observer at the point the event was
committed to the event service. Time values are gathered by the XDAS client
helper library. Thus, there is no reason to be concerned about values stored in
this field, as the helper library will attempt to be as accurate as possible when
generating time information.
Offset The offset field contains a value representing the number of seconds since
midnight, January 1, 1970 - otherwise known as the Unix epoch.
Sequence The sequence field contains a unique numeric value identifying this event from
another event which may have been recorded within the same second. For
the most part, this value should be taken as a monotonically increasing
numeric value that begins at zero and continues until the next second
boundary, at which point, it begins again at zero.
XDASv2 Schema 37
Page 38

XDAS Field Description
Tolerance The tolerance value is a value between 0 and 100, indicating the tolerance of
the clock used to record the time in offset. Values of zero indicate the clock is
very accurate. Values of 100 indicate that the clock should not be trusted.
Certainty The certainty value is a value between 0 and 100, indicating the percentage
certainty of the tolerance value. Zero means there is no certainty of the
tolerance, and thus, it shouldn't be trusted to any degree of accuracy. A value
of 100 indicates that the tolerance value is very accurate.
Source The time source is information indicating the source of time for the observer
system. This may be a URL for a time server, or simply a local time source,
such as a hardware clock.
Zone The time zone is the new time zone string representing the time zone of this
clock.
Target (Optional) The target of an event is the account or protected resource upon which the
initiator is attempting to act, thereby provoking the generation of an event. A
target is described in terms of an account and an entity (described below), as
well as an optional and unspecified Data object. The Data object is a set of
name/value pairs describing class-specific attributes of the actor. The schema
does not define the actual fields, as different classes will have a unique set of
data attributes (if any).
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
Observer The observer of an event is the authenticated identity of an entity (service) that
is monitoring the system, and generating events based on initiator actions. An
observer is described in terms of an account and an entity (described below).
Referenced Classes The observer, initiator, and target fields contain references to the account and
entity classes defined separately within the schema. These other classes
identify key attributes of the three primary actors within an audit event.
Account Class The account class represents the identity of the actor. This identity is relative
to an authentication realm or Domain. Both an account name and an account
Id are provides, although only the Id is really required. The Name is for human
readability.
Account Domain The account Domain defines the authentication authority of the actor. Account
identifiers mean very little without an authentication authority.
Account Name The account Name is optional, providing human readability.
Account Id The account Id is a unique identifier of the account within the authentication
Domain.
Entity Class The entity class describes the location of the actor. This location is defined in
terms of a system access end point (IP network) address and a system
access end point (host/domain) name. Additional fields are also available to
describe the service and component names within the software that manages
the above end points.
Entity SysAddr An IP address describing the access end point of the software actor.
Entity SysName A host/domain name describing the access end point of the software actor.
Entity SvcName A service name further describing the service that manages the above end
point.
Entity SvcComp A service component name describing the component within the above
service.
38 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
Page 39

B.3 Outcome Codes
The outcome code is a hierarchical numeric value much like the event code. Outcome codes indicate
success or a failure class and reason. The success hierarchy is encapsulated by the 0.x sub-arc.
Failure classes are represented by the 1.x hierarchy. Denial codes are represented by the 2.x
hierarchy.
B.4 Example of an Event
An example event is given below:
{"Source" : "eDirectory#DS",
"Observer" : {"Account" : {"Domain" : "TREE_NAME","Name" :
"CN=server1,O=novell"},
"Entity" : {"SysAddr" : "164.99.90.129","SysName" : "blr-edir-phoenix"}},
"Initiator" : {"Account" : {"Domain" : "TREE_NAME","Name" :
"CN=server1,O=novell"},"Assertions" : {"NetAddress" :
"164.99.90.129"}},"Target" : {"Data" : {"Name" :
"CN=server1,O=novell","newFlags" : "262178","oldFlags" : "35"}},"Action" :
{"Event" : {"Id" : "0.0.1.3","Name" : "MODIFY_SESSION","CorrelationID" :
"eDirectory#-1#","SubEvent" : "DSE_CHANGE_CONN_STATE"},"Time" : {"Offset" :
1286430957},"Log" : {"Severity" : 7},"Outcome" : "0","ExtendedOutcome" : "0"}}
novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
XDASv2 Schema 39
Page 40

novdocx (en) 16 April 2010
40 Novell XDASv2 Administration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...