Page 1

Novatel Wireless, Inc.
PCI Express Mini-card
Integration & Design Guidelines
Version 1. A
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page1
Page 2
Notice: Restricted Proprietary Information
© Copyright Novatel Wireless, Inc. (2005)
The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of Novatel Wireless, Inc. All
rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction of this manual in any form without the expressed
written approval of Novatel Wireless, Inc. is strictly prohibited. This manual may not, in whole or in
part, be copied, reproduced, translated, or reduced to any electronic or magnetic storage medium
without the written consent of a duly authorized officer of Novatel Wireless Inc.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be
construed as a commitment by Novatel Wireless Inc. unless such commitment is expressly given
in a covering document.
Novatel Wireless Inc. makes no warranties, either expressed or implied, regarding this document,
its merchantability, or its fitness, for any particular purpose.
Printed and produced in United States of America.
Document Revision History
Rev. Date Brief Description of Change Originator Approved by
1.0 March 28,
Initial Draft John Ross
2005
1.1 August
Added SDK and AT Commands Matt Golden
1,2005
1. A September
Second Draft Sharon Lee
30,2005
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page2
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introduction.................................................................................................................................. 14
PCI Express Mini Card.......................................................................................................... 14
www.pcisig.com/home .......................................................................................................... 14
Getting Started............................................................................................................................. 15
Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 15
Windows Platforms ...............................................................................................................15
S a f e t y W a r n in g ................................................................................................................. 15
F C C R F I n t e r fe r e n c e S t a t e me n t................................................................................... 16
Radio Frequency Exposure Evaluation Requirements......................................................... 16
Technical Support Contacts..................................................................................................16
Device Specifications.................................................................................................................. 17
Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 17
Product Overview............................................................................................................. 17
Hardware................................................................................................................................... 17
Card Specifications............................................................................................................... 17
Mechanical Specification ...................................................................................................... 18
Shielding / Mechanical enclosure ......................................................................................... 20
Host Interface connector....................................................................................................... 20
Interface Specification............................................................................................................... 21
Host Interface........................................................................................................................ 21
USB Interface........................................................................................................................ 22
RF Interface .......................................................................................................................... 22
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Interface.................................................................. 22
USIM Interface...................................................................................................................... 22
LED Interface........................................................................................................................ 22
Power Supply........................................................................................................................ 23
Power Class.......................................................................................................................... 25
WDISABLE............................................................................................................................ 26
Electrostatic Discharge and Electro-Magnetic Interference.................................................. 27
Firmware ................................................................................................................................... 27
Overview............................................................................................................................... 27
Memory................................................................................................................................. 27
EU730/740 Firmware Features............................................................................................. 27
EV620 Firmware Features.................................................................................................... 32
Application Software ................................................................................................................. 34
Environmental ........................................................................................................................... 35
Provisioning with IOTA.............................................................................................................. 36
eIOTA.................................................................................................................................... 36
Enabling, disabling, and starting eIOTA ............................................................................... 36
Checking eIOTA status......................................................................................................... 37
Development Board..................................................................................................................... 38
Fixture Diagram/Assembly Diagram......................................................................................... 38
Photo of Top View..................................................................................................................... 39
Schematic.................................................................................................................................. 40
Hardware Design Guidelines......................................................................................................41
Power Supply Requirements for GSM Bursting........................................................................ 41
SIM Card Socket Location ........................................................................................................42
Antenna..................................................................................................................................... 42
1XEV-DO Diversity Antenna Requirements ......................................................................... 42
FCC Implications – Mobile vs. Portable Devices.................................................................. 43
TRP (Total Radiated Power) Requirements......................................................................... 43
MobiLink Phoenix SDK ............................................................................................................... 45
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page3
Page 4

Introduction ........................................................................................................................... 45
Requirements........................................................................................................................ 45
SDK MODULES........................................................................................................................ 45
Phoenix & Blaze.................................................................................................................... 45
NetMonkey............................................................................................................................ 46
Profile Manager..................................................................................................................... 46
Hotspot Finder....................................................................................................................... 46
Menu..................................................................................................................................... 46
Utilities................................................................................................................................... 46
PHOENIX SERVER Software design....................................................................................... 47
Single Server and Multiple Clients........................................................................................ 47
Novatel Wireless Product Line Support................................................................................ 48
State Machine with 2-Way Communication.......................................................................... 48
MobiLink Connection Manager.................................................................................................. 49
Overview............................................................................................................................... 49
Purpose................................................................................................................................. 49
Applicable Documents .......................................................................................................... 49
GENERAL FEATURES............................................................................................................. 49
User Interface Functionality.................................................................................................. 49
Layout ................................................................................................................................... 50
Mouse Over........................................................................................................................... 51
Snap to Edge ........................................................................................................................ 51
Hot Swapping........................................................................................................................ 51
Skinning Customization ........................................................................................................ 51
Localization........................................................................................................................... 52
File ........................................................................................................................................ 52
MOBILINK™ FEATURES......................................................................................................... 53
Main Display Window............................................................................................................ 53
Indicators............................................................................................................................... 57
Connect/Disconnect Button .................................................................................................. 58
Menu..................................................................................................................................... 58
SIM/Lock Management......................................................................................................... 70
Quick Access Buttons........................................................................................................... 71
Software Web Upgrade......................................................................................................... 71
SMS Client............................................................................................................................ 71
Addressbook Features.......................................................................................................... 75
Phoenix API Interface to PCI Express Mini Card...................................................................... 78
Overview............................................................................................................................... 78
Client Object.............................................................................................................................. 78
ChangeLockCode method.................................................................................................... 79
Connect method.................................................................................................................... 79
DebugPrint method...............................................................................................................80
DeleteMessage method........................................................................................................ 80
Disconnect method ...............................................................................................................81
GetAdapter method...............................................................................................................81
GetAdapterList method......................................................................................................... 82
GetConnectStatus method.................................................................................................... 82
GetContact method...............................................................................................................83
GetContactInfo method......................................................................................................... 83
GetDeviceId method ............................................................................................................. 84
GetDeviceModel method ...................................................................................................... 84
GetDeviceNetwork method................................................................................................... 85
GetDeviceState method........................................................................................................ 85
GetDeviceTechnology method.............................................................................................. 87
GetFID method...................................................................................................................... 87
GetHardwareVersion method ............................................................................................... 87
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page4
Page 5

GetLockStatus method ......................................................................................................... 88
GetMessage method............................................................................................................. 88
GetMessageCount method................................................................................................... 89
GetMessageStatus method .................................................................................................. 89
GetMobileNumber method.................................................................................................... 90
GetNetworkOperatorList method.......................................................................................... 90
GetNetworkPreference method ............................................................................................ 91
GetNewMessageCount method............................................................................................ 91
GetOSVersionInfo method.................................................................................................... 92
GetPRLVersion method........................................................................................................ 92
GetRasErrorString method ................................................................................................... 93
GetSigStr method.................................................................................................................. 93
GetSoftwareVersion method................................................................................................. 94
IsDormant method ................................................................................................................94
IsMessageMemoryFull method............................................................................................. 95
IsRoaming method................................................................................................................95
SendMessage method.......................................................................................................... 95
SetAdapter method...............................................................................................................96
SetAutoLock method............................................................................................................. 96
SetCallSettings method ........................................................................................................ 97
SetContact method ...............................................................................................................97
SetMessageStatus method................................................................................................... 98
SetNetworkOperator method................................................................................................ 99
SetNetworkPreference method............................................................................................. 99
SetProxy method................................................................................................................. 100
SetSMSC method............................................................................................................... 100
Shutdown method............................................................................................................... 101
Unlock method.................................................................................................................... 101
IEventPhoenixNotifySink object.............................................................................................. 102
FireEventDeviceState method............................................................................................ 102
FireEventDormant method.................................................................................................. 102
FireEventIncomingCall method........................................................................................... 102
FireEventNetwork method .................................................................................................. 102
FireEventRoaming method................................................................................................. 103
FireEventSigStr method...................................................................................................... 103
FireEventSMSStatus method.............................................................................................. 103
QoS object............................................................................................................................... 103
deliveryofSDUError property............................................................................................... 104
deliveryOrder property........................................................................................................ 104
guarBitDL property.............................................................................................................. 104
guarBitUL property.............................................................................................................. 104
maxBitDL property.............................................................................................................. 105
maxBitUL property.............................................................................................................. 105
maxSDUSize property ........................................................................................................ 105
ResBitErrorRatio property................................................................................................... 105
SDUErrorRatio property...................................................................................................... 106
trafficClass property............................................................................................................ 106
trafficHandling property....................................................................................................... 106
transferDelay property ........................................................................................................ 106
Blaze object............................................................................................................................. 107
EventDeviceState event...................................................................................................... 107
EventDormant event........................................................................................................... 107
EventIncomingCall event.................................................................................................... 107
EventNetwork event............................................................................................................ 108
EventRoaming event........................................................................................................... 108
EventSigStr event ............................................................................................................... 108
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page5
Page 6

EventSMSStatus event....................................................................................................... 108
Attach method..................................................................................................................... 108
Detach method.................................................................................................................... 109
Hotspots object ....................................................................................................................... 109
AboutBox method ............................................................................................................... 109
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 109
ViewHotspots method......................................................................................................... 109
Menu object............................................................................................................................. 110
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 110
ShowAbout method............................................................................................................. 110
ShowActivation method ...................................................................................................... 110
ShowConfig method............................................................................................................ 111
ShowDebug method ........................................................................................................... 111
ShowProp method .............................................................................................................. 111
ShowReport method........................................................................................................... 111
ShowUnlock method........................................................................................................... 112
Language object...................................................................................................................... 112
GetLanguageCount method................................................................................................ 112
GetLanguageIndex method ................................................................................................ 112
GetString method................................................................................................................ 113
GetStringTableCount method............................................................................................. 113
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 113
ProfileManager object............................................................................................................. 114
AboutBox method ............................................................................................................... 114
CreateProfile method.......................................................................................................... 114
GetDefaultProfileName method.......................................................................................... 114
GetProfile method............................................................................................................... 115
GetProfileNameList method................................................................................................ 115
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 115
SetDefaultProfile method.................................................................................................... 116
ShowProfileList method...................................................................................................... 116
Profile object............................................................................................................................ 116
APN property....................................................................................................................... 116
AuthenticationType property............................................................................................... 117
CarrierName property......................................................................................................... 117
ConnectType property ........................................................................................................ 117
DataSpeed property............................................................................................................ 118
DefaultGateway property.................................................................................................... 118
DeliveryofSDUError property.............................................................................................. 118
DeliveryOrder property........................................................................................................ 119
DialString property.............................................................................................................. 119
Fallback2GProfile property ................................................................................................. 119
IPAddress property............................................................................................................. 120
MaxSDUSize property ........................................................................................................ 120
Password property.............................................................................................................. 120
PDPAddress property......................................................................................................... 120
PDPType property .............................................................................................................. 121
PrimaryDNS property.......................................................................................................... 121
PrimaryWINS property........................................................................................................ 121
ProfileName property.......................................................................................................... 122
ProxyAddress property ....................................................................................................... 122
ProxyPort property.............................................................................................................. 122
ResErrorRatio property....................................................................................................... 123
SDUErrorRatio property...................................................................................................... 123
SecondaryDNS property..................................................................................................... 123
SecondaryWINS property................................................................................................... 124
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page6
Page 7

SetProxy property ............................................................................................................... 124
SMSC property.................................................................................................................... 124
SMSEmailNumber property................................................................................................ 125
StaticIP property.................................................................................................................. 125
SubnetMask property.......................................................................................................... 125
Technology property........................................................................................................... 125
TrafficClass property........................................................................................................... 126
TrafficHandling property...................................................................................................... 126
TransferDelay property....................................................................................................... 126
UseDNS property................................................................................................................ 127
Username property............................................................................................................. 127
UseVPN property................................................................................................................ 127
UseWINS property.............................................................................................................. 128
VPNEntryName property .................................................................................................... 128
NetMonkey Lib objects............................................................................................................ 128
EventAdapterFound event.................................................................................................. 128
EventAdapterUpdate event................................................................................................. 128
LAN object............................................................................................................................... 129
GetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 129
GetAdapterList method....................................................................................................... 129
GetBytesIn method............................................................................................................. 129
GetBytesOut method .......................................................................................................... 130
GetConnectState method ................................................................................................... 130
GetDefaultGateway method................................................................................................ 130
GetDuration method............................................................................................................ 130
GetFriendlyName method................................................................................................... 131
GetIPAddress method......................................................................................................... 131
GetLinkSpeed method........................................................................................................ 131
GetMacAddress method..................................................................................................... 132
GetNdisName method ........................................................................................................ 132
GetSubnetMask method..................................................................................................... 132
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 132
SetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 133
WLAN object ........................................................................................................................... 133
AddWepKey method........................................................................................................... 133
Disassociate method........................................................................................................... 133
FindProfile method.............................................................................................................. 134
GetAccessPoints method.................................................................................................... 134
GetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 134
GetAdapterList method....................................................................................................... 135
GetBssid method................................................................................................................. 135
GetBytesIn method............................................................................................................. 135
GetBytesOut method .......................................................................................................... 135
GetConnectState method ................................................................................................... 136
GetDefaultGateway method................................................................................................ 136
GetDuration method............................................................................................................ 136
GetFriendlyName method................................................................................................... 137
GetIPAddress method......................................................................................................... 137
GetLinkSpeed method........................................................................................................ 137
GetMacAddress method..................................................................................................... 137
GetNdisName method ........................................................................................................ 138
GetRssi method .................................................................................................................. 138
GetSigStr method................................................................................................................ 138
GetSubnetMask method..................................................................................................... 138
GetSupportedRates method............................................................................................... 139
GetWZCServiceState method............................................................................................. 139
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page7
Page 8

Init method .......................................................................................................................... 139
IsAdminUser method .......................................................................................................... 140
RemoveWepKey method.................................................................................................... 140
Scan method....................................................................................................................... 140
SetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 140
StartWZCService method................................................................................................... 141
StopWZCService method ................................................................................................... 141
WWAN object.......................................................................................................................... 141
DisableDevice method........................................................................................................ 141
EnableDevice method......................................................................................................... 141
GetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 142
GetAdapterList method....................................................................................................... 142
GetBytesIn method............................................................................................................. 142
GetBytesOut method .......................................................................................................... 143
GetConnectState method ................................................................................................... 143
GetDefaultGateway method................................................................................................ 143
GetDuration method............................................................................................................ 143
GetFriendlyName method................................................................................................... 144
GetIPAddress method......................................................................................................... 144
GetLinkSpeed method........................................................................................................ 144
GetNdisName method ........................................................................................................ 145
GetSubnetMask method..................................................................................................... 145
Init method .......................................................................................................................... 145
InitDevice method ............................................................................................................... 145
IsDeviceEnabled method.................................................................................................... 146
SetAdapter method............................................................................................................. 146
UpdateDeviceParam method.............................................................................................. 146
AT Commands ........................................................................................................................... 148
Introduction ......................................................................................................................... 148
NW PCI AT Command Set...................................................................................................... 148
A/......................................................................................................................................... 148
ATA..................................................................................................................................... 149
ATD..................................................................................................................................... 149
ATE..................................................................................................................................... 151
ATH..................................................................................................................................... 151
ATV..................................................................................................................................... 151
ATZ ..................................................................................................................................... 152
AT&C................................................................................................................................... 152
AT&D................................................................................................................................... 153
AT&V................................................................................................................................... 153
AT+CFC.............................................................................................................................. 154
AT+CRM ............................................................................................................................. 155
AT+CSQ.............................................................................................................................. 155
AT+CSS.............................................................................................................................. 156
AT+CXT .............................................................................................................................. 156
AT+ER................................................................................................................................. 157
AT+ETBM ........................................................................................................................... 157
AT+FCLASS ....................................................................................................................... 158
AT+GCAP........................................................................................................................... 158
AT+GMI............................................................................................................................... 158
AT+GMM............................................................................................................................. 159
AT+GMR............................................................................................................................. 159
AT+GSN.............................................................................................................................. 159
AT$QCQNC........................................................................................................................ 160
AT$QCPREV ...................................................................................................................... 160
AT$QCCLR......................................................................................................................... 160
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page8
Page 9

AT$QCPKND...................................................................................................................... 161
AT$QCVAD......................................................................................................................... 161
AT$QCMDR........................................................................................................................ 162
AT$QCMIP.......................................................................................................................... 162
AT$QCMIPP ....................................................................................................................... 163
AT$QCMIPT........................................................................................................................ 163
AT$QCMIPEP..................................................................................................................... 164
AT$QCMIPGETP................................................................................................................ 164
AT$QCMIPNAI.................................................................................................................... 164
AT$QCMIPRT..................................................................................................................... 165
AT$QCMIPMASS................................................................................................................ 165
AT$QCMIPMHSS ............................................................................................................... 166
AT$QCMIPMASSX............................................................................................................. 167
AT$QCMIPMHSSX............................................................................................................. 167
AT$QCMIPMASPI .............................................................................................................. 168
AT$QCMIPMHSPI .............................................................................................................. 168
AT$NW................................................................................................................................ 169
AT$NVTLLTIME.................................................................................................................. 169
AT$NVTLMDN.................................................................................................................... 169
AT+IOTA............................................................................................................................. 170
AT$NWACTIVATION.......................................................................................................... 170
AT+PZID ............................................................................................................................. 171
AT$SPNAI........................................................................................................................... 171
Novatel Wireless Developer Network Library ......................................................................... 172
AT+COPS ........................................................................................................................... 172
AT+CSPN ........................................................................................................................... 173
AT$NWATR ........................................................................................................................ 174
AT$NWCID ......................................................................................................................... 174
AT$NWFLASH.................................................................................................................... 175
AT$NWHLR ........................................................................................................................ 175
AT$NWICCID...................................................................................................................... 178
AT$NWNPC........................................................................................................................ 178
AT$NWPDN........................................................................................................................ 179
AT$NWPINR....................................................................................................................... 180
AT$NWRAT ........................................................................................................................ 180
Additional AT Commands ....................................................................................................... 181
ATH..................................................................................................................................... 181
ATI....................................................................................................................................... 182
ATL...................................................................................................................................... 182
ATO..................................................................................................................................... 182
ATP..................................................................................................................................... 182
ATQ..................................................................................................................................... 182
ATS0................................................................................................................................... 183
ATS3................................................................................................................................... 183
ATS4................................................................................................................................... 183
ATS5................................................................................................................................... 183
ATS6................................................................................................................................... 183
ATS7................................................................................................................................... 184
ATS8................................................................................................................................... 184
ATS10................................................................................................................................. 184
ATT ..................................................................................................................................... 184
ATX..................................................................................................................................... 184
AT&F................................................................................................................................... 185
AT+CBC.............................................................................................................................. 185
AT+CBST............................................................................................................................ 185
AT+CCFC ........................................................................................................................... 186
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page9
Page 10

AT+CCUG........................................................................................................................... 186
AT+CCWA .......................................................................................................................... 186
AT+CFUN ........................................................................................................................... 186
AT+CGACT......................................................................................................................... 186
AT+CGATT......................................................................................................................... 187
AT+CGCLASS.................................................................................................................... 187
AT+CGDCONT................................................................................................................... 187
AT+CGDSCO...................................................................................................................... 187
AT+CGEQMIN.................................................................................................................... 188
AT+CGEQREQ................................................................................................................... 188
AT+CGEREP...................................................................................................................... 189
AT+CGMI............................................................................................................................ 189
AT+CGMM.......................................................................................................................... 189
AT+CGMR .......................................................................................................................... 190
AT+CGQMIN....................................................................................................................... 190
AT+CGQREQ ..................................................................................................................... 190
AT+CGREG........................................................................................................................ 191
AT+CGSMS........................................................................................................................ 191
AT+CGSN........................................................................................................................... 191
AT+CGTFT ......................................................................................................................... 191
AT+CHLD............................................................................................................................ 192
AT+CHSN ........................................................................................................................... 192
AT+CHUP ........................................................................................................................... 193
AT+CIMI.............................................................................................................................. 193
AT+CLCK............................................................................................................................ 193
AT+CMEE........................................................................................................................... 193
AT+CMGC .......................................................................................................................... 193
AT+CMGD .......................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMGF........................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMGL........................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMGR .......................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMGS........................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMGW.......................................................................................................................... 194
AT+CMMS .......................................................................................................................... 195
AT+CMOD .......................................................................................................................... 195
AT+CMSS........................................................................................................................... 195
AT+CNMA........................................................................................................................... 195
AT+CNMI ............................................................................................................................ 195
AT+CPAS............................................................................................................................ 196
AT+CPBF............................................................................................................................ 196
AT+CPBR ........................................................................................................................... 196
AT+CPBS............................................................................................................................ 196
AT+CPBW........................................................................................................................... 196
AT+CPIN............................................................................................................................. 197
AT+CPMS........................................................................................................................... 197
AT+CPWD .......................................................................................................................... 197
AT+CR ................................................................................................................................ 197
AT+CRC.............................................................................................................................. 197
AT+CREG........................................................................................................................... 198
AT+CRLP............................................................................................................................ 198
AT+CSCA ........................................................................................................................... 198
AT+CSCB ........................................................................................................................... 198
AT+CSCS ........................................................................................................................... 199
AT+CSDH ........................................................................................................................... 199
AT+CSIM ............................................................................................................................ 199
AT+CSMP........................................................................................................................... 199
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page10
Page 11

AT+CSMS........................................................................................................................... 199
AT+CSTA............................................................................................................................ 200
AT+CUSD ........................................................................................................................... 200
AT+DR ................................................................................................................................ 200
AT+DS................................................................................................................................. 200
AT+ES................................................................................................................................. 200
AT+ESA .............................................................................................................................. 201
AT+FAR .............................................................................................................................. 201
AT+FCL............................................................................................................................... 201
AT+FDD.............................................................................................................................. 201
AT+FIT................................................................................................................................ 202
AT+FRH.............................................................................................................................. 202
AT+FRM.............................................................................................................................. 202
AT+FRS .............................................................................................................................. 202
AT+FTH............................................................................................................................... 203
AT+FTM.............................................................................................................................. 203
AT+FTS............................................................................................................................... 203
AT+ICF................................................................................................................................ 203
AT+IFC................................................................................................................................ 203
AT+IPR................................................................................................................................ 204
CME ERROR Codes for CDMA Commands .......................................................................... 204
CMS Error Codes for CDMA Commands ............................................................................... 205
Regulatory Approval Requirements........................................................................................ 207
FCC (Federal Communication Commission).......................................................................... 207
GCF (Global Certification Forum) ........................................................................................... 207
PTCRB (PCS Type Certification Review Board)..................................................................... 207
CE (Conformance European).................................................................................................. 207
IOT .......................................................................................................................................... 209
Compliance Certification Process........................................................................................... 210
EV-DO FCC Accreditation....................................................................................................... 210
EV-DO CDG Interoperability................................................................................................... 210
EV-DO Verizon Certification Process ..................................................................................... 211
HDSPA FCC Accreditation...................................................................................................... 211
GCF Compliance Process....................................................................................................... 211
PTCRB Compliance Process.................................................................................................. 212
CE Mark Certification Process................................................................................................ 213
Infrastructure IOT Process...................................................................................................... 214
Carrier Certification Process................................................................................................... 214
Test Laboratories.................................................................................................................... 215
FCC / CE Test Houses ....................................................................................................... 215
PTCRB / GCF Test Houses................................................................................................ 215
Reference Parts Specifications................................................................................................ 216
RF Connector...................................................................................................................... 216
Mini Card Connector........................................................................................................... 217
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)......................................................................................... 218
References ................................................................................................................................. 219
Glossary ..................................................................................................................................... 220
Table of Figures
Figure 1:
Figure 2: EU730/EU740 Module......................................................................................... 19
Figure 3: PCIe Minicard Module Envelope ......................................................................... 20
Figure 4: W_Disable Pull-up Configuration......................................................................... 26
EV620 Module ..................................................................................................... 18
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page11
Page 12

Figure 5:
Figure 6: Up-Ramp for Lowest Power Levels..................................................................... 41
Figure 7: Up-Ramp for Lowest Power Levels (Scheme 2) ................................................. 42
Figure 8: Total Radiated Power .......................................................................................... 43
Figure 9: Applications.......................................................................................................... 45
Figure 10: Module Design..................................................................................................... 47
Figure 11: Automation Server............................................................................................... 47
Figure 12: State Machine...................................................................................................... 48
Figure 13: Main MobiLink Display......................................................................................... 50
Figure 14: Skin Design.......................................................................................................... 51
Figure 15: On-Line Help........................................................................................................ 52
Figure 16: Status Indication .................................................................................................. 53
Figure 17: 3G Wireless View................................................................................................. 54
Figure 18: WiFi View............................................................................................................. 55
Figure 19: HotSpot Activation ............................................................................................... 56
Figure 20: Network Connection............................................................................................. 56
Figure 21: Ethernet View....................................................................................................... 57
Figure 22: Connection Button ............................................................................................... 58
Figure 23: 3G Profiles ........................................................................................................... 59
Figure 24: Profile Settings..................................................................................................... 60
Figure 25: Different Tab Settngs........................................................................................... 60
Figure 26: Profile Wizard Step 1........................................................................................... 61
Figure 27: Profile Wizard Step #2......................................................................................... 62
Figure 28: Profile Wizard Step #3......................................................................................... 62
Figure 29: General Tab......................................................................................................... 63
Figure 30: Mobile Tab ........................................................................................................... 64
Figure 31: WiFi Tab............................................................................................................... 65
Figure 32: WAP Window....................................................................................................... 65
Figure 33: Ethernet Tab........................................................................................................ 66
Figure 34: AP Window .......................................................................................................... 66
Figure 35: CDMA................................................................................................................... 67
Figure 36: UMTS/HSDPA ..................................................................................................... 67
Figure 37: Report Log........................................................................................................... 68
Figure 38: Desktop Transparency......................................................................................... 69
Figure 39: About Dialogue .................................................................................................... 70
Figure 40: Enter PUK............................................................................................................ 70
Figure 41: Configuration Menu.............................................................................................. 70
Figure 42: Quick Access Button Default Functions............................................................... 71
Figure 43: MobiLink SMS Client............................................................................................ 72
Figure 44: Compose Message.............................................................................................. 74
Figure 45: Address Book....................................................................................................... 76
Figure 46: Select Group Contacts......................................................................................... 77
Figure 47: RF Connector..................................................................................................... 216
Figure 48: Mini PCI Express Connector.............................................................................. 217
Up-ramp for Highest Power Levels...................................................................... 41
Table of Tables
Table 1:
Table 2: LED Function....................................................................................................... 22
Table 3: EV620 DC Specifications..................................................................................... 23
Table 4: EU740 DC Specifications..................................................................................... 23
Table 5: EU730 DC Specifications.................................................................................... 24
Table 6: GPRS/GSM Duty Cycles and Typical power consumption ................................. 24
Table 7: EV620 Power Class............................................................................................. 25
Host Interface specification.................................................................................. 21
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page12
Page 13

Table 8:
Table 9: EU730 Power Classes......................................................................................... 26
Table 10: EU730/740 Environmental Specification ............................................................. 35
Table 11: EV620 Environmental Specification..................................................................... 35
Table 12: Suggested Ramp Timing for Scheme 2............................................................... 42
Table 13: Design specifications for the Diversity EVDO antenna........................................ 42
Table 14: CDMA Test Frequencies...................................................................................... 44
Table 15: GSM-1900 Test Frequencies............................................................................... 44
Table 16: Status Indication .................................................................................................. 53
Table 17: 3G Indicators........................................................................................................ 57
Table 18: Menu Subjects..................................................................................................... 58
Table 19: General Tab Features.......................................................................................... 63
Table 20: Mobile Tab Features............................................................................................ 64
Table 21: Identity Properties................................................................................................ 67
Table 22: Report Values...................................................................................................... 68
Table 23: Mailbox List.......................................................................................................... 72
Table 24: Fields List............................................................................................................. 73
Table 25: Tool Bar Button.................................................................................................... 74
Table 26: Destination Addresses......................................................................................... 75
Table 27: Address Books..................................................................................................... 76
Table 28: CME Error Codes............................................................................................... 204
Table 29: CMS Error Codes............................................................................................... 205
Table 30: R&TTE ............................................................................................................... 208
Table 31: GSM/GPRS European Regulations................................................................... 209
EU740 Power Classes......................................................................................... 25
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page13
Page 14

Introduction
PCI Express Mini Card
Novatel Wireless has designed a line of embedded broadband access modules around the PCI
Express Mini Card standard. This product line provides platform developers and system
integrators with the ability to enable global 3G broadband access. The governing body for PCI
Express standardization is PCI SIG (Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group.)
The website for PCI SIG can be found at the following URL:
www.pcisig.com/home
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page14
Page 15

Getting Started
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide advance design and integration information to assist
in the integration planning and evaluation of Novatel Wireless PCI Express Mini-cards. This
document is intended to specify key components of the integration tools available for the Novatel
Wireless line of PCI Express Mini-cards.
The EV620 is Novatel Wireless’s versatile module to add WLAN capability to other devices. It
was developed to be integrated into other devices such as kiosks or vending machines based on
the PCI Express Mini-card specification 1.0.
The EU730™ and EU740™ are Novatel Wireless’s mini-card developed for small form factor PCI
Express cards specifically used for Wide Area Wireless (WAN, i.e. cellular) technology.
Therefore, the EU730™ and EU740™ will work with all Windows driven laptops given the drivers
are properly installed. When you install MobiLink™ on a Windows OS system it will automatically
include the drivers necessary to communicate with the PCI Express Mini Card. MobiLink™ is
Novatel’s Windows application manager for the PCI Express Mini Card. MobiLink provides an
easy interface to make a data connection, change operating parameters, and view alerts such as
SMS or signal strength indicator. However, anyone can still install the drivers manually and so will
be discussed in the following sections. In addition, once the drivers are installed, following the
Phoenix Client API functions, anyone could develop their Client side software manager to interact
with the PCI Express Mini Card.
When using any of these devices, EU730, EU740™ or the EV620, activation is required for the
device to be allowed on the operator’s network. For example, Sprint requires the customer to run
IOTA, Internet Over-The-Air, provisioning to prepare the device to work on the wireless network.
Activation is required for the EV620 while the EU730™ and EU740™ require a valid SIM card
before it can be used on the operator’s wireless network. Please refer to section on provisioning
with IOTA for assistance.
Windows Platforms
The Phoenix API will interface with your top level applications and provide the abstraction of the
module specifics to the upper applications. Please refer to the Phoenix API Interface Chapter for
details.
Please refer to the MobiLink Phoenix SDK chapter for details on developing applications and
communicating with the modem on Windows platforms.
Safety Warning
Neither the EV620 nor EU730 / EU740 products may be used in an environment where radio
frequency equipment is prohibited or restricted in its use. This includes aircraft/airports, hospitals,
and other sensitive electronic areas.
Under extended operation the EU730™ and EU740™ modem will generate a noticeable amo unt
of heat. Like all PC Cards, the modem generates heat during normal operation and will be heated
by the host computer. For this reason it is recommended that after extended periods of operation,
prior to removal and handling, you allow the modem to cool down.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page15
Page 16
FCC RF Interference Statement
FCC applies to EV630 and EU730/740. Refer to sections on Regulatory Compliance for more
details.
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference Statement: The EV620
product has been certified to comply within the limits of a class B digital device pursuant to Part
15, Part 22 and Part 24 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in residential situations. This equipment generates, uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy, and, if not properly installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, or to laptop
computers and PDA's. This can be determined by turning the equipment on and off. You are
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna of the television, radio or cordless telephone.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/television technician for additional
suggestions.
Radio Frequency Exposure Evaluation Requirements
The radio frequency exposure evaluation requirements for the embedded module are spe cified in
the module Product Specification. In general, for the United States market, the embedded
modules are treated as “mobile devices” as per FCC CFR47 paragraph 2.1091.
A mobile device is defined as “a transmitting device designed to be used in other than fixed
locations and to generally be used in such a way that a separation distance of at least 20 cm is
normally maintained between the transmitter’s radiating structure(s) and the body of the user or
nearby persons.” The antenna type used for the radio frequency exposure evaluation must be
specified in the documentation and sold with the module. If the module is used with a different
antenna type and/or in a design where the separation distance of 20 cm is not normally
maintained, the radio frequency exposure evaluation should be repeated for the new
configuration. In some cases the module use may fit the definition of “portable devices” as per
FCC CFR47 paragraph 2.1093.
Some devices are not subject to radio frequency exposure evaluation prior to equipment
authorization, depending on the transmitter power level and frequency band of operation.
Technical Support Contacts
WWW: http://www.nvtl.com/support/index.html
Email: support@novatelwireless.com
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page16
Page 17

Device Specifications
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the specifications for the EU730/EU740 and the
EV620 module. This section is intended to specify electrical, mechanical and software interfaces
and performance; and to provide the information necessary to integrate the module into an overall
product design.
Product Overview
The EV620 will operate in the 800/1900 CDMA bands. The EV620 is primarily targeted for the
North American market.
The EU730 and EU740 are wireless modem modules designed to be embedded into laptop
computers and other host devices.
The EU730 & EU740 provide for quad band GSM support as well as UMTS/HSDPA operation at
800MHz, 1900MHz & 2100MHz. The EU730 is primarily targeted for the North American market
and the EU740 is primarily targeted for EMEA (Europe, Middle East and African) markets.
• The EU740 will operate in the 850/900/1800/1900 GPRS/EDGE bands and 2100
UMTS/HSDPA band.
• The EU730 will operate in the 850/900/1800/1900 GPRS/EDGE bands, and 1900
MTS/HSDPA band.
The modules will be compatible with Windows™ compliant applications including VPN, e-mail,
and web browsing.
The core protocol stack will be supplied by Qualcomm and contains UMTS, HSDPA, GPRS and
EDGE technologies for EU730/740, and CDMA, CDMA 1XRTT, and CDMA 1XEV-DO
technologies for EV620. Around this core, Novatel Wireless has created the firmware drivers that
provide access to the hardware on the embedded modem. The feature set is comprised of the
data device features supported in the Qualcomm protocol stack.
The hardware consists of a PCI Express Mini Card compliant interface (except as detailed
herein), a baseband chipset from Qualcomm™, an RF radio chipset from Qualcomm™, and the
various other components used to support these major components. The baseband and firmware
are based on the MSM6275 series chipset for EU730/740 and MSM6500 se ries chipset for
EV620.
Hardware
Card Specifications
The EV620, EU730 and EU740 are designed to meet the PCI Express Mini Card electromechanical card standard with some exceptions to accommodate the power requirements. The
EU730 and EU740 are USB only cards.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page17
Page 18
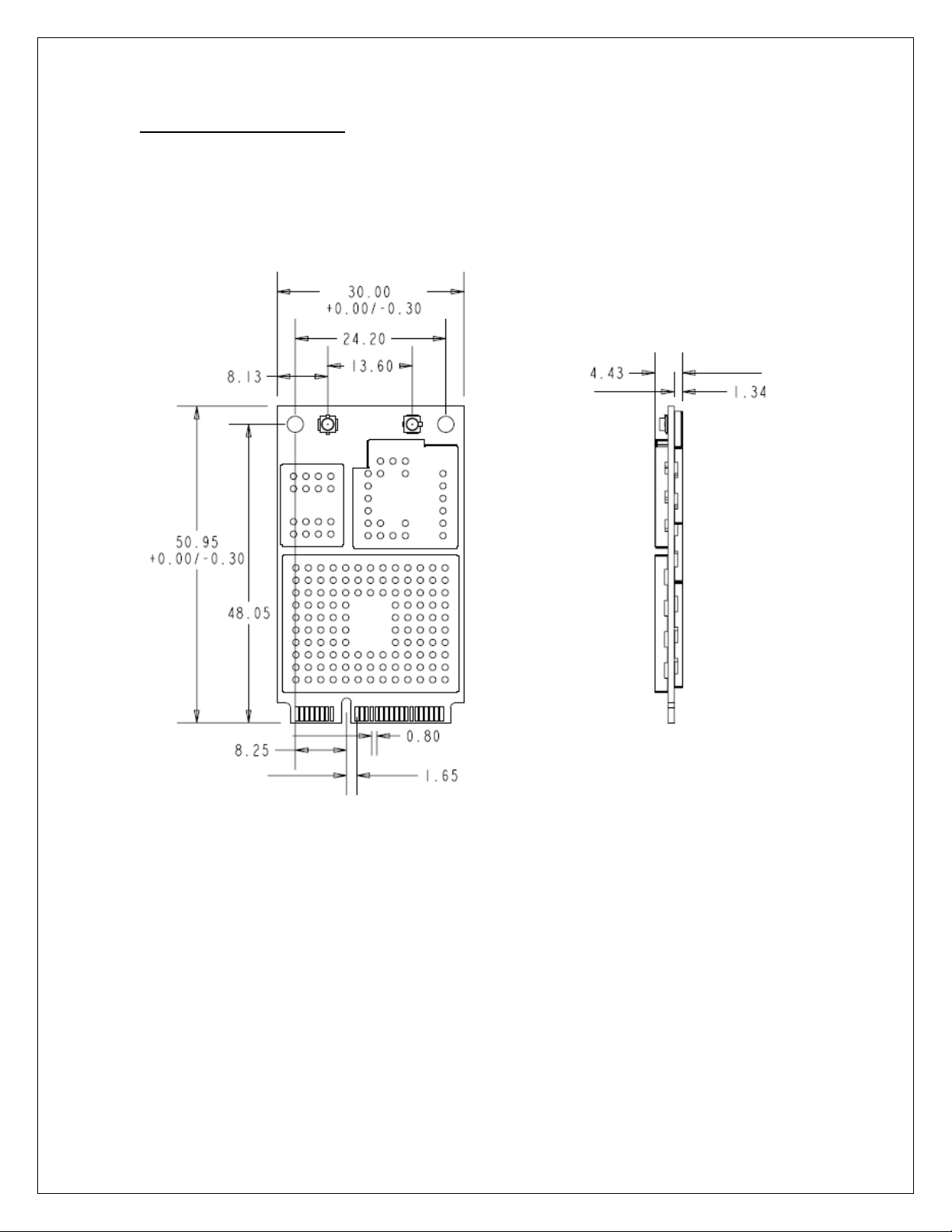
Mechanical Specification
The drawing below shows the dimensions of the EV620 module. The measurements given below
are typical. Consider thickness to be 5.0 max in designing.
Figure 1: EV620 Module
The drawing below shows the dimensions of the EU730/EU740 module.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page18
Page 19
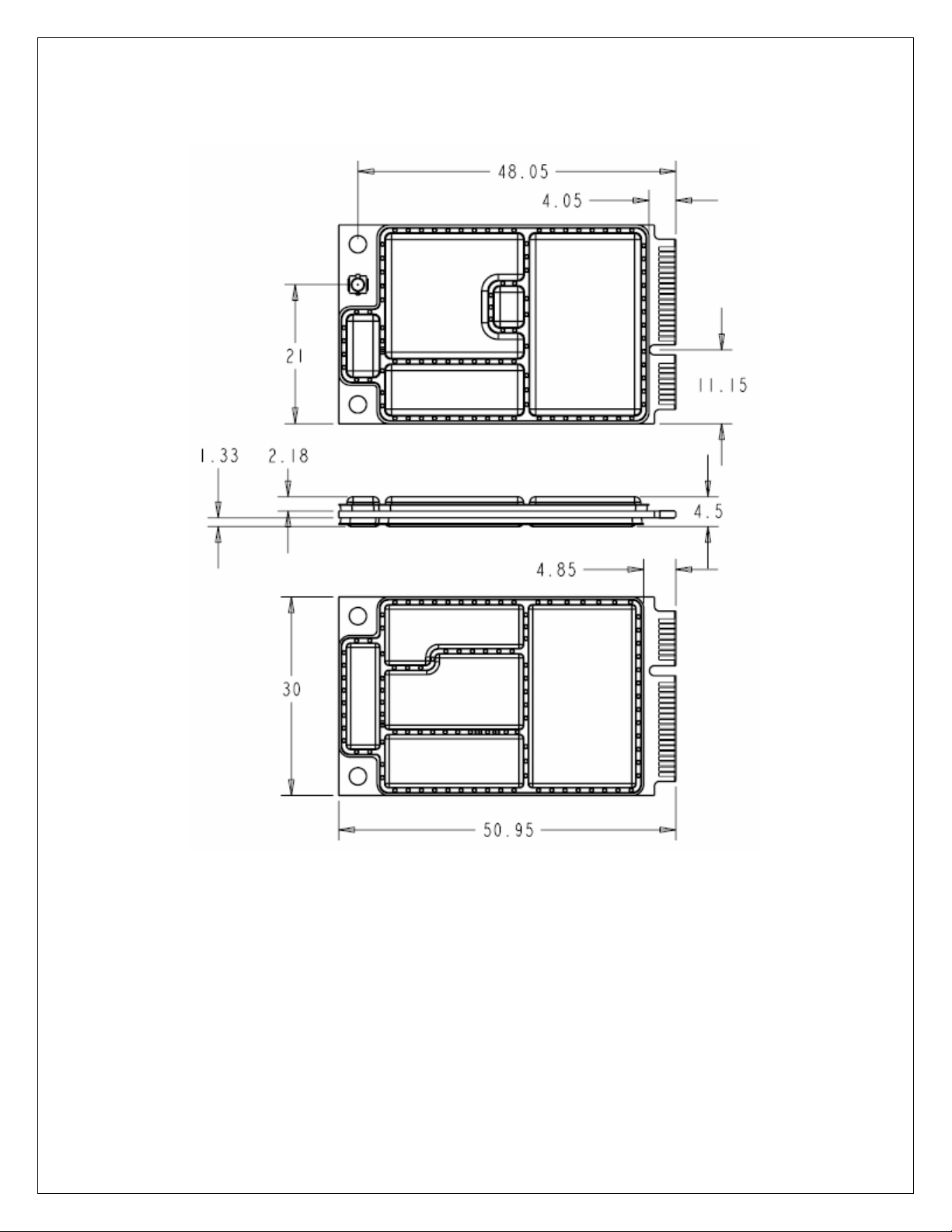
Figure 2: EU730/EU740 Module
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page19
Page 20

Figure 3: PCIe Minicard Module Envelope
5.0 mm
1.35 mm
Shielding / Mechanical enclosure
The EU730 and 740 use a metalized plastic shield technology. The shields are held in place
using solder balls.
The EV620 will use a stamped sheet metal shield technology. The shields are held in place with
solder.
Host Interface connector
The host interface connector is a 1 mm wide card edge connector. This is compatible with the
following host connectors:
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page20
Page 21
Molex 67910-0002
FCI 10019331-001
The host connector should be compliant with the Mini PCI express Electromecha nical
specification.
Interface Specification
Host Interface
The EV620 and EU730/740 is designed to meet the PCI Express Mini-Card specification. The
table below gives a description of the pin-out and usage. The USB option of the specification is
supported. Deviations from the Mini PCI Express card specification are noted.
The PCI Express Mini Card provides two power sources: one at 3.3V (+3.3V) and one
at 1.5V (+1.5V). The auxiliary voltage source (+3.3Vaux) is sourced over the same pins as the
primary voltage (+3.3V) and is available during the system’s stand-by/suspend state to support
wake event 5 processing on the communications card.
Table 1: Host Interface specification
Pin PCIe Spec EV620 EU730/740 Pin PCIe Spec EV620 EU730/740
1 WAKE # N C N C 2 3.3 V 3.3 V 3.3 V
3 Reserved NC NC 4 G ND GND GN D
5 Reserved NC NC 6 1.5V NC NC
7 CLKREQ# NC NC 8 UIM_PWR UIM_PWR UIM_PWR
9 GND GND GND 10 UIM_DATA UIM_DATA UIM_DATA
11 REFCLK - NC NC 12 UIM _CLK UIM_C LK UIM_C LK
13 REFCLK+ N C NC 14 UIM_RESET UIM_RESET UIM_RESET
15 GND GND GND 16 UIM_VPP NC NC
Mechanical Key
17 Reserved NC NC 18 GND GND GND
19 Reserved NC NC 20 W_DISABLE# W_DISABLE# W_DISABLE#
21 GN D GND GND 22 PER ST# NC NC
23 PER n0 NC NC 24 +3.3Vaux NC NC
25 PERp0 NC NC 26 GND GND GND
27 GN D GND GND 28 +1.5V NC NC
29 GN D GND GND 30 SMB _CLK NC NC
31 PETn0 NC NC 32 SMB_DA TA NC NC
33 PETp0 NC NC 34 GND GND GND
35 GND GND GND 36 USB_D- USB_D- USB_D37 Reserved GND GND 38 USB_D+ USB_D+ USB_D+
39 Reserved 3.3V 3.3V 40 GND GND GND
41 Reserved 3.3V 3.3V 42 LED _WWA N# LED_WWA N# LED_WWAN #
43 Reserved G ND GND 44 LED_WLAN # NC NC
45 Reserved NC NC 46 LED_W PAN # NC NC
47 Reserved NC NC 48 +1.5V NC NC
49 Reserved NC NC 50 GND GND GND
51 Reserved NC NC 52 3.3V 3.3V 3.3V
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page21
Page 22

USB Interface
The Mini card acts as a peripheral device and supports the USB 2.0 standard at low speed (1.5
Mbps) and full speed (12 Mbps). It does not support the high speed (480 Mbps) mode of
operation.
RF Interface
The EV620 and EU730/740 are designed to be connected to an external antenna integrated into
the laptop. The antenna port presents a nominal 50Ω impedance.
Subscriber Identification Module (SIM) Interface
A 5 line SIM interface is provided on the mini-card edge connector for the EU730/740. The signal
levels comply with the ETSI standard Specification of the 3 Volt Subscriber Identity Module Mobile Equipment (SIM-ME) interface (GSM 11.12 version 4.3.1). Note that no ESD protection
will be provided on the card. The host device is expected to provide the ESD protection at the
SIM connector.
The OEM Module supports a 3.3V SIM as described in ETSI 11.12. The relevant signals are
brought out on the 70 pin connector.
The ETSI specification also dictates that the system be made aware if the SIM card is
disconnected during operation. This function is handled by the SIM_IN signal. This line should be
asserted high when a SIM is present. The SIM_IN signal is pulled low on the OEM Module by a
4.7kΩ resistor so that when a SIM is not present the line will be low. Care should be taken not to
use a weak pull-up for the SIM_IN signal. If the OEM Module will be integrated into a system in
which the SIM cannot be removed.
USIM Interface
The USIM will be provided by the host. A SIM connector is not included on the card. The interface
to the USIM is provided on the host interface connector.
LED Interface
The LED_WWAN signal provides an LED driver as per the Mini Express PCI card specification.
The LED operation is outlined in the table below.
Table 2: LED Function
State LED function
On The WWAN radio is on, and capable of transmitting.
Off The WWAN radio is not capable of transmitting
Slow Blink Powered but not associated or authenticated; searching
Intermittent blink Activity proportional to transmitting/ receiving speed
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page22
Page 23

Power Supply
Power is drawn from the 3.3V pins on the Mini Card connector as shown in tables following. The
current in the various operating modes in given.
Table 3: EV620 DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typical Max Units
Vcc Supply Voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
Icc max maximum supply current 1000 mA
Icc stdby Target Standby supply current TBD mA
Table 4: EU740 DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
Vcc Supply Voltage 3.04 3.3 3.56 V
Icc max maximum supply current 2750 mA
Icc stdby Target Standby supply current 180 mA
Icc csd Target CSD supply current 500 TBD mA
Icc grps avg
Icc grps
peak
Icc WCDMA Target WCDMA supply current 900 TBD mA
Target GPRS supply current
average
Target GPRS supply current peak 2200 TBD mA
750 TBD mA
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page23
Page 24
Table 5: EU730 DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
Vcc Supply Voltage 3.04 3.3 3.56 V
Icc max maximum supply current 2750 mA
Icc stdby Target Standby supply current 180 mA
Icc csd Target CSD supply current 500 TBD mA
Icc grps avg
Target GPRS supply current
750 TBD mA
average
Icc grps
Target GPRS supply current peak 2200 TBD mA
peak
Icc WCDMA Target WCDMA supply current mA
Table 6: GPRS/GSM Duty Cycles and Typical power consumption
Mode Average battery power Peak & duty cycle
GPRS Transmitting 2.3 W average 7.0 W / 25%
GPRS Receiving 2.3 W average 7.0 W / 25%
GSM Transmitting 1.7 W average 7.7 W / 12.5%
GSM Receiving 1.7 W average 7.7 W / 12.5%
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page24
Page 25
Power Class
The power classes are shown in following tables.
Table 7: EV620 Power Class
Band (MHz) Power Class Comment
800 CDMA Class III +23dBm ERP
CDMA 1XRTT Class III +23dBm ERP
CDMA 1XEV-DO Class III +23dBm ERP
1900 CDMA Class II +23dBm EiRP
CDMA 1XRTT Class II +23dBm EiRP
CDMA 1XEV-DO Class II +23dBm EiRP
Table 8: EU740 Power Classes
Band (MHz) Power Class Comment
850 GPRS 4 +33 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +27 dBm nominal
900 GPRS 4 +33 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +27 dBm nominal
1800 GPRS 1 +30 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +26 dBm nominal
1900 GPRS 1 +30 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +26 dBm nominal
2100 UMTS/HSDPA 3 +24 dBm nominal
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page25
Page 26
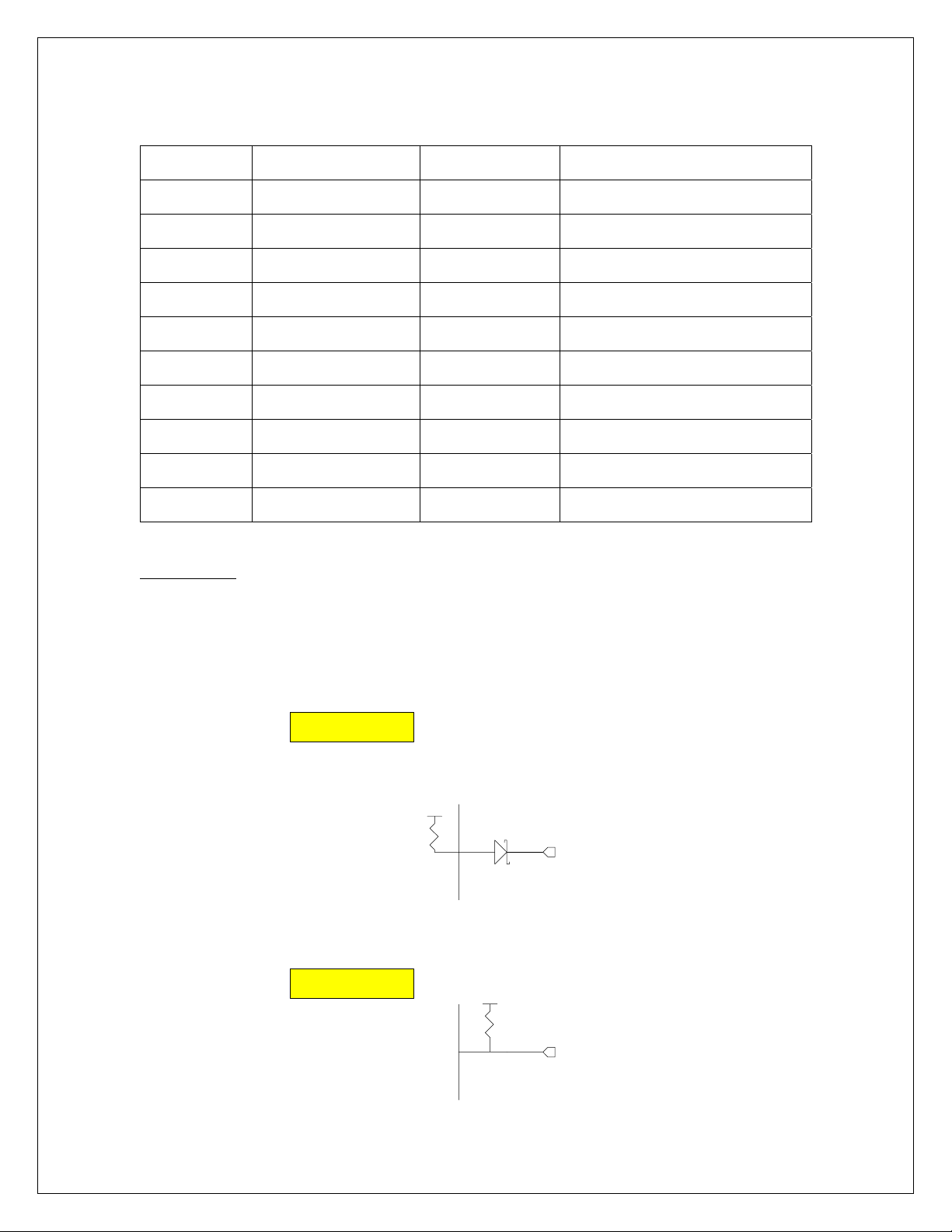
Table 9: EU730 Power Classes
Band (MHz) Power Class Comment
850 GPRS 4 +33 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +27 dBm nominal
900 GPRS 4 +33 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +27 dBm nominal
1800 GPRS 1 +30 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +26 dBm nominal
1900 GPRS 1 +30 dBm nominal
EDGE E2 +26 dBm nominal
1900 UMTS/HSDPA 4 +21 dBm nominal
850 UMTS/HSDPA 4 +21 dBm nominal
WDISABLE
The modem is made incapable of transmitting when the WDISABLE pin is pulled low. The
following diagram illustrates the Pull-Up resistor configuration:
Figure 4: W_Disable Pull-up Configuration
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page26
Page 27

Electrostatic Discharge and Electro-Magnetic Interference
The modem does not protect itself from ESD. It is the responsibility of the host to ensure that
there will not be any harmful discharges to the modem.
With regard to EMI, the modem will meet FCC part 15 for North American markets, and ETSI EN
301 489-1 for European markets. This device when incorporated in any other product may require
FCC and/or other approvals. It is the user’s responsibility to do this.
Firmware
Overview
The firmware for the EU730/740 is comprised of the Qualcomm supplied UMTS/GPRS protocol
stack (Advanced Mobile Subscriber Station (AMSS) 6275 Software) with additional Novatel
Wireless firmware specific to the Mini Card implementation. The firmware runs on ARM9 core in
the MSM6275 ASIC.
The firmware for the EV620 is comprised of the Qualcomm supplied CDMA2000 protocol stac k
(Advanced Mobile Subscriber Station (AMSS) 6500 Software) with additional Novatel Wireless
firmware specific to the PC card implementation. The firmware runs on ARM9 core in the
MSM6500 ASIC.
Memory
In order to reduce the MSM6275 and the MSM6500 firmware memory footprint, unused
application features, drivers and services are removed. The network protocol layers (Mobility
Management, Data services, Radio Resource Control, Radio Link Control, Media Access Control,
Physical Layer control and Drivers to Qualcomm’s RF chipsets) remains unaltered.
EU730/740 Firmware Features
Protocol of HSDPA Features for EU730/740
• UMTS: 3GPP Release 5, June 2004
• UE Category 12, QPSK, 1.8 Mbps Peak Rate
• QTC Release 2 will support 384 Ul and 1.8 M DL
• PS RAB (DL: up to 1.8M and UL: up to 384 K) on HSDPA channel
• DCCH 3.4 Kbps
• Establish/ Release/ Reconfigure of HSDPA channel
• HSDPA channel re- pointing (Synchronized and non- synchronized cell change ) for
mobility.
• Up switching and Down switching of PS RAB between DPCH and HS- DSCH
• Switching between HSDPA channel and common channel
• Integrity protection and ciphering
• Primary PDP context.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page27
Page 28

GPRS/EGPRS Protocol and Feature Rollout for EU730/740
GPRS
• channel coding schemes CS1-4
• link adaptation
• multislot class 10
• One-phase packet access
• Two-phase packet access
• GPRS test modes ( ETSI test mode A and B)
• Attach / Detach
• GPRS detach only
• Combined GPRS/IMSI detach
• MS-initiated detach
• NW-initiated detach
• Automatic GPRS attach at power-up
• GPRS attach status indication
EGPRS
• Uplink modulation and coding schemes MCS 1-4
• downlink modulation and coding schemes MCS 1-9
• 8PSK modulation on both uplink and downlink for MCS 5-9
• multislot class 1
• One-phase packet access
• Two-phase packet access
• EGPRS test modes (ETSI test mode A and B)
• EGPRS link adaptation
• EGPRS incremental redundancy
• EGPRS multislot class 10
NC0
Medium access modes – dynamic allocation
RLC-acknowledged operation mode
RLC unacknowledged operation mode
LLC-acknowledged transmission mode
LLC-unacknowledged transmission mode
GSM network operation mode I
GSM network operation mode II
PBCCH/PCCCH support in NOM I
PDP Context
• Mobile-originated PDP context activation
• Mobile-originated PDP context deactivation
• Network-originated PDP context deactivation
• Network-originated PDP context activation
• PDP context modification (NW initiated)
• Active PDP context indication
• PDP address (IPv4)
• PDP address (IPv6)
• PDP context type – IP
• Static IP
• Dynamic IP
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page28
Page 29

• RFC1144 TCP/IP header compression
• WINS address support-primary and secondary
• QoS
• Support QoS profile (release 97)
• Enhanced QoS (refer to 3GPP TS 22.060, Section 5.6.2; TS 24.008, Section
10.5.6.5)
• Support QoS profile (release 99, EGPRS-capable terminals)
• Background QoS class supported
• Interactive QoS class supported
• Streaming QoS class supported
V.42bis data compression
Carrier will be able to program GPRS service parameters (PDP context) (via Application Profile)
Data counter (time and transferred bytes per session and cumulative sessions)
Packet enhanced measurement report (PEMR)
Network-assisted cell change (R4 GERAN Feature Set 1)
Extended UL TBF mode (R4 GERAN Feature Set 1)
UMTS
• Cell_PCH and URA_PCH
• WCDMA-to-GPRS reselection in CELL_FACH
• 64K Sync CSD
• Radio link failure (RRC)
• Inter-frequency reselection in Cell_FACH
• CLTD mode 1
• SIB scheduling
• Path loss measurements
• 6F/6G (UE internal)
• Re-establishment procedure
• SIB modification
• SIB 7
• Inter-frequency redirection
• Inter-RAT redirection (RRC connection reject to GSM)
• HCS
Security
• Support of encryption A5/1
• Support of encryption A5/2
• GPRS ciphering algorithm GEA1
• GPRS ciphering algorithm GEA2
• PAP for RADIUS authentication - GPRS/EGPRS
• CHAP for RADIUS authentication - GPRS/EGPRS
• Support for encryption algorithm UEA1 (Kasumi)
• Support for integrity algorithm UIA1 (Kasumi)
• IMEI Security
• OMA DRM v1.0
• Forward lock
• Combined delivery
• Separate delivery
• OMA DRM v2.0
• SIM lock
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page29
Page 30

SMS
• Mobile-originated SMS (MO-SMS) over CS channel
• Mobile-originated SMS (MO-SMS) over PS channel
• Mobile-originated SMS over PS shall fall back to CS if: a) PS service is not available, or
b) there is a PS network failure
• Mobile-originated SMS (MO-SMS) concatenation (minimum of 5 segments)
• Mobile-terminated SMS (MT-SMS) over CS channel
• Mobile-terminated SMS (MT-SMS) over PS channel
• Mobile-terminated SMS (MT-SMS) concatenation (minimum of 5 segments)
• Mobile-originated SMS email
• Mobile-originated SMS email concatenation (minimum of 5 segments)
USSD
• Unstructured supplementary service data – mobile-originated (MO-USSD)
• Unstructured supplementary service data – mobile-terminated (MT-USSD)
SS
• Calling Line Identification Restriction (CLIR)
• Calling Name Presentation (CNAP)
• Barring of All Outgoing Calls (BAOC)
• Barring of Outgoing International Calls (BOIC)
• Barring of Outgoing International Calls except to Home PLMN (BOIC-exHC)
• Barring of All Incoming Calls (BAIC)
• Barring of All Incoming Calls when Roaming outside the Home PLMN (BIC-Roam)
• International Access Function “+“
Network Selection
• Support for the network selection procedures described in 3G 22.011, R4 minimum
• Support for the network selection procedures described in 3G 23.122, R4 minimum
• Support for the RRC connection reject message to redirect from a 3G system to a 2G
system, according to 25.331, R4 minimum
• Support for the network selection procedures described in 3G 43.022, R4 minimum
• Support for an initial HPLMN scan at a 2mins after power on
• Support for a HPLMN rescan irrespective of the serving MCC
• Support of equivalent PLMN
• Network selection within 30 seconds upon power up
Inter-RAT and Inter-Frequency
• GSM900 1 WCDMA2100 handover – blind mode
• GSM1800 1 WCDMA2100 handover – blind mode
• GSM900 " WCDMA2100 handover – idle frame measurements
• GSM1800 " WCDMA2100 handover – idle frame measurements
• GSM900 1 WCDMA2100 cell reselection
• GSM1800 1 WCDMA2100 cell reselection
• GSM900 1 WCDMA2100 CCO
• GSM900 1 WCDMA 2100 CCO
• GSM900 (w/BCCH/ PBCCH) " WCDMA2100 reselection in packet transfer
• GSM1800 (w/BCCH/ PBCCH) " WCDMA2100 reselection in packet transfer
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page30
Page 31

• PS data continuity during OOS and RAT change
• PS data continuity with MPDP (primary and secondary contexts) and RAT change
• EDGE 1 WCDMA cell reselection in packet transfer
• Inter-RAT NACC 2G 1 3G
• 3G background PLMN search while in 2G
• 3G background PLMN search while in 3G
HSPDA
• Category 12 (QPSK)
• Code Rates
• Rate ¼
• Rate ½
• Rate 1/3
• HSDPA Logical Channels
• HS-SCCH
• HS-DPCCH
• HS-PDSCH
• Up to 5 HS-PDSCH channels support
• HSPDPA Transport Channels
• HS-DSCH
. 120 kbps
•
. 240 kbps
•
. 360 kbps
•
• Fast L1 HARQ
• Incremental redundancy
• Chase combining retransmission scheme
• Multi-Code Operation 1 code
• 5 codes
• 480 kbps
• 600 kbps
• 720 kbps
• 1.2 Mbps
• 1.8 Mbps
• Fast link adaptation
• Vary the effective code rate
• HARQ, MAC-HS disassembly
• MAC-HS reordering queue distribution and processing support
• Synchronous and non-synchronous cell change support
• Intra-NodeB (softer re-pointing) cell change support
• Inter-NodeB (soft re-pointing) cell change support
• Up-switching and down-switching of PS RAB between HS-PDSCH and DPCH
• Ciphering on the HS channel
• Support to not resume the HS channel if inter-RAT handover fails, but save the RB
mapping information
• Support to not resume the HS channel if a radio link failure occurs, but save the RB
mapping information
• QoS
• Background QoS class supported
• Interactive QoS class supported
• Streaming QoS class supported
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page31
Page 32

System
• Network Selection
• Enhanced Network Selection (ENS)
• Supplementary Services
SIM
• Dual IMSI
Fixes to Feature and Protocol deficiencies identified through testing of Beta Release
HSDPA Compressed mode with active HS channel
Video on DPCH
MAC-d de-multiplexing
EV620 Firmware Features
Firmware Naming Convention
There are two firmware release strings that can be retrieved from the device, a short form
consisting of a three digit decimal starting at 100 and run sequentially and a long string M6500CBBIRD-XXXXX.YYY [MMM DD HH:MM:SS]. XXXXX is the Qualcomm base release and patch
level, YYY is identical to the three digit decimal from the short form, [] contains the release date
and time.
The starting version of firmware is 136.
Standards Support
• IS-707: 14.4 kbps Data Services
• TSB-74: 14.4 kbps Radio Link Protocol and Interband Operations
• TIA/EIA/IS-2000 PN-4756 (Ballot Version): Addendum 1 (to the IS-2000 standard)
• IS-707A: CDMA Data Services Revision for IS-95B
• IS-707A-1: CDMA Data Services Revision for cdma2000 Rel. 0
• IS-95A, IS-95B: CDMA Dual-Mode Air Interface Standard
• PN-4430 (Ballot Resolution Version 0.14, to be published as TIA/EIA-IS-2000.4):
cdma2000: Signaling Layer 2 Standard for Spread Spectrum Systems
• J-STD-008: IS-95 adapted for 1900 MHz frequency band
• PN-4429 (Ballot Resolution Version, to be published as TIA/ EIA-IS-2000.3): Medium
Access Control (MAC) for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
• TIA/EIA-95-B: Mobile Station-Base Station Compatibility Standard for Dual-Mode Spread
Spectrum Systems
• IS-683A: OTA Update: Roaming System Selection and Programming Block
• PN-4428 (Ballot Resolution Version, to be published as TIA/ EIA-IS-2000.2): Physical
Layer Standard for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
• IS-637A: Short Message Service including mobile-origination
• PN-4431 (Ballot Resolution Version 1.06, to be published as TIA/EIA-IS-2000.5): Upper
Layer (Layer 3) Signaling Standard for cdma2000 Spread Spectrum Systems
• IS-856-2 (3GPP2 C.S0024): cdma2000® High Rate Packet Data Air Interface
Specification
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page32
Page 33

Frequency Band Support
• Band Class 0 – Cellular 800 MHz
• Band Class 1 – PCS 1.9 GHz
CDMA Air Interface
• TIA/EIA/IS-95-A Air Interface
• TIA/EIA-95-B Air Interface
• J-STD-008 + TSB74 Air Interface
• TIA/EIA/IS-2000-0 Air Interface
• TIA/EIA/IS-2000-A Air Interface
• TIA/EIA/IS-2001 Data Session Handoff
• TIA/EIA-126 Loop back Services
• TIA/EIA/IS-870 Test Data Services
• TIA/EIA/IS-871 Markov Services
• TIA/EIA/IS-707-A Data Services
• TIA/EIA-637-A Short Message Services
• TIA/EIA/IS-683-A OTASP Services
• Traffic State Receiver Diversity Combining
• Idle State Low-Power Slotted Mode
• Dynamic P_REV Specification
• Dynamic Feature Selection
1XEV-DO Air Interface
• TIA/EIA/IS-856-2 Air Interface
• TIA/EIA-878 Authentication and Session Handoff
• TIA/EIA/IS-890-1 Test Application
• Connected State Receiver Diversity Combining
• Idle State Low-Power Slotted Mode
• Acquisition State Micro Searching
• Connected State Off-Frequency Neighbor Searching
• Extended Username and Password for AN Authentication
• System Access Inhibit Response
• Air Interface Session Association With PPP Session
• 1xEV-DO to 1x Hand-Down Algorithm DRC Filter
• 1xEV-DO Suspend timer disabled
Multimode Services
• System Determination 2.0
• Multimode Call Manager
• TIA/EIA/IS-683C Preferred Roaming List
• CDMA-Only Mode
• HDR-Only Mode
• CDMA+HDR Mode
• CDMA+HDR Hybrid Mode
• CDMA QPCH in Hybrid Idle State
• Hybrid in CDMA Power-Save
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page33
Page 34

Data Services
• TIA/EIA/IS-707 AT Command Processing
• TIA/EIA/IS-835 Wireless IP Networking
• Internet Protocol Stack (TCP/UDP/IP/PPP)
• Simple IP Address Management
• Mobile IP Address Management
• RFC1750 Dynamic Mobile IP Key Update (DMU)
• Embedded internet over the air (eIOTA) activation Client
• Relay Mode Operation
• Network Mode Operation
• Sockets Mode Operation
• Socket Layer API
UIM Card Services
• No R-UIM Support will be provided.
Universal Serial Bus Interface
• USB Specification 2.0
• Full Speed Device Operation
• Communications Device Class Profile
• Composite Device Profile
• Data Service Interface
• Diagnostics Service Interface
• Download Service Interface
Application Software
Novatel provides Mobilink™ application software . The software is defined in later Chapter.
MobiLink™ connection manager software to install and configure modem (for all supported
platforms)
AT Command Set Support per IS-707
Fully compatible and interoperable with current Microsoft OS platforms: PPC 2000/2002/HPC,
Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows ME, & Windows XP
Integrated drivers for Windows OS, configurable as either a modem or network card
PCI Express Mini-card
Compatibility with all major brands of PC's and PPC computing platforms
Sleep Mode capabilities
Uses common base technology shared with OEM Module
IS-683A compliant - Over-The-Air activation and parameter update capabilities.
On-line help, getting started guide, documentation
All software applications necessary to communicate with the PCI Express Mini Card will operate
with the following platforms: PPC 200/2002/HPC, Windows 98, Windows 2000, Windows ME, &
Windows XP
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page34
Page 35

All software shall support 640x480, 640x240, and 800x600 color and monochrome displays
MobiLink™ allows the user to configure the modem easily
MobiLink provides diagnostic capability
MobiLink provides a Help menu that is Context Sensitive
Environmental
The EU730/740 and EV620 will be compliant with the Mini PCI Express Electromechanical
specification as detailed in the table below.
It should be noted that Novatel Wireless cannot guarantee that the host device (laptop; PDA;
notebook etc.) will be able to endure these same environmental conditions. Users are advised to
consult the host device documentation for specifications and observe any restrictions of use.
Table 10: EU730/740 Environmental Specification
Parameter Condition
Low Temperature Storage -20 °C
High Temperature Storage 85 °C
Low Temperature Operating 0 °C
High Temperature Operating (within spec) 65 °C1
High Temperature Operating (relaxed spec) 85 °C
Relative Humidity 95% maximum (non condensing)
Vibration and High Frequency 147m/s2 (15G) peak; 10 to 2000 Hz
Drop 75 cm
Table 11: EV620 Environmental Specification
Parameter Condition
Low Temperature Storage -30 °C
High Temperature Storage 85 °C
Low Temperature Operating -20 °C
High Temperature Operating 65 °C2
Relative Humidity 95% maximum (non condensing)
ESD 8kV Air / 4kV Contact
1
It is required that the shield temperature not exceed 80°C at anytime. It may be necessary for
the system integrator to provide some method to insure this surface temperature is not exceeded.
2
It is required that the shield temperature not exceed 80°C at anytime. It may be necessary for
the system integrator to provide some method to insure this surface temperature is not exceeded.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page35
Page 36

Vibration and High Frequency 147m/s
Drop 75 cm
The EV620 product operates in a reliable fashion consistent with CDMA (IS-98C) and PCMCIA
V2.1 standards. It will withstand three-foot drop and still remain functional.
2
(15G) peak; 10 to 2000 Hz
Provisioning with IOTA
This applies only to the EV620. The EU730 & 740 use SIM cards and don’t require any type of
IOTA.
Sprint PCS uses IOTA to perform their provisioning before a wireless device is allowed on the
data network. This process is operator specific so there maybe variations as to how provisioning
is done. In all cases, please contact the network operator if you have questions concerning
activation and subscriber related questions.
When using the PCI Express Mini Card, the activation is done by MobiLink™. MobiLink™ will
automatically detect if the EV620 module needs to perform any provisioning on Sprint’s network.
Since the EV620 module does not use MobiLink, you must run IOTA from the primary port on the
EV620 module. Novatel Wireless has developed an embedded IOTA Client calle d, eIOTA that
interfaces through AT commands. This Client will allow the subscriber to execute an IOTA
session to perform provisioning of the EV620. Once this is done, the EV620 can access the
1xRTT and 1xEVDO networks.
For use with Sprint PCS, the subscriber first needs to contact a sales representative to activate
the EV620. The Sprint PCS representative will present to the subscriber the MDN or MIN
numbers with the SPC. These parameters need to be entered into the EV620 if it does not
already exist. Upon the time of receiving these parameters, Sprint PCS has a time provisioning
requirement of 1.5 days to 2 days for the EV620 to perform and complete an IOTA session. If the
subscriber does not complete the IOTA provisioning within this time, the subscriber will have to
call Sprint PCS again to reset the provisioning timer.
At the end of this section, there is a flowchart diagram that further explains the process of using
eIOTA.
eIOTA
eIOTA is a subscriber unit provisioning Client, or Provisioning Service Agent. Embedded in the
CDMA wireless modem, the Client communicates with Handset Configuration Manager, the
operator’s IOTA server, to download provisioning data to the subscriber unit or upload settings
per server's request. It allows the operator to remotely perform provisioning without having to
bring the wireless device into a sales location.
eIOTA is disabled by default from the factory. This is done because if eIOTA was active, it would
automatically attempt an eIOTA session if the EV620 has not already completed provisioning.
When the subscriber finishes entering the MDN or MIN, they could either enable eIOTA and have
the EV620 automatically attempt an IOTA session after a power cycle or initiate a manual IOTA
session.
Enabling, disabling, and starting eIOTA
eIOTA Client can be enabled or disabled by issuing the AT commands:
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page36
Page 37

• To enable: AT+IOTA=1
• To disable: AT+IOTA=0
• To force start: AT+IOTA=2
There are two ways to start eIOTA, NIIP(Network Initiated Initial Provisioning) or CIIP(Client
Initiated Initial Provisioning). In NIIP, operator’s IOTA server pushes a special SMS message to
the Client to trigger an IOTA session. In CIIP, a session can be triggered by locally issuing an AT
command: AT+IOTA=2.
Checking eIOTA status
The AT command: AT+IOTA=? Is used to query the eIOTA status while IOTA is active.
Please refer to AT+IOTA in the AT Commands Chapter for details.
Cautions that need to be taken when eIOTA is active
DO NOT power off the unit until IOTA session is finished.
DO NOT remove the antenna from the unit.
DO NOT disconnect the data call issued by eIOTA.
When running eIOTA, to ensure no power lost, make sure to use the AC power and NOT the
battery power.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page37
Page 38

Development Board
Fixture Diagram/Assembly Diagram
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page38
Page 39

Photo of Top View
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page39
Page 40

Schematic
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page40
Page 41

Hardware Design Guidelines
Power Supply Requirements for GSM Bursting
One power ramping scheme uses two timings for high and low power levels, as sho wn in the
following representative ramps.
Figure 5: Up-ramp for Highest Power Levels
Figure 6: Up-Ramp for Lowest Power Levels
The Second power ramping scheme uses one timing for all power levels. A representative ramp
for low power levels is shown, with suggested ramp timings.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page41
Page 42

TX_Enable high Vramp start Vramp length (to full
GSM PL 5 – 16
GSM PL 17 – 19
DCS PL 0 – 10
DCS PL 11 –15
Table 12: Suggested Ramp Timing for Scheme 2
power)
-17 us -15 us 14 us
-17 us -8 us 7 us
-17 us -15 us 14 us
-17 us -8 us 7 us
Figure 7: Up-Ramp for Lowest Power Levels (Scheme 2)
SIM Card Socket Location
SIM Card must be placed so as to minimize trace length between SIM Card and Connector. If
there is too much distance this will impede good performance.
Antenna
1XEV-DO Diversity Antenna Requirements
Table 13: Design specifications for the Diversity EVDO antenna
Description Minimum Maximum Unit
Primary Antenna (Transmit & Receive)
Peak Antenna Gain 1.0 dBi
Average Gain -3.0 dBi
Efficiency -4.0 (40) dB (%)
Polarization (Ratio Gv:Gh) 0.0 dB
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page42
Page 43

Input VSWR 2.5:1
Average Power Handling 2.0 Watt
Secondary Antenna (Receive Only Diversity)
Average Gain -9.0 dBi
Efficiency -10.0 (10) dB (%)
Polarization (Ratio Gv:Gh) 0.0 dB
Input VSWR 2.5:1
Antenna to Antenna Requirements
Isolation -8.0 dB
Fading Correlation Coefficient 0.5 dB (%)
FCC Implications – Mobile vs. Portable Devices
Testing for SAR for Portable Device must be done if within 20 cm of body. SAR testing is not
necessary for Mobile Devices.
TRP (Total Radiated Power) Requirements
Good radiated performance is critical to the effective operation of a mobile in networks. A
comprehensive characterizing of radiated performance enables carriers to know how well mobiles
work within the specific network design constraints. Generally , peak EIRP (Effective Isotropic
Radiated Power) is not a good indication of mobile performance in the field. From a field
performance perspective, measurement of the average and peak EIRP on a head model is more
meaningful than measurement of peak EIRP in free-space conditions. This spherical effective
isotropic radiated power is termed TRP (Total Radiated Power.) The TRP is the sum of all po wer
radiated by the antenna, regardless of direction or polarization, as illustrated below.
Figure 8: Total Radiated Power
Tests shall be carried out for three different frequency pairs across the bands supported by the
device, as defined for CDMA TIA/EIA-98-D and for GSM 1900 3GPP TS 51.010 in the tables
below.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page43
Page 44

Table 14: CDMA Test Frequencies
Table 15: GSM-1900 Test Frequencies
Radiated power measurements will be recorded in the “free-space” configuration on all applica ble
frequencies. For portable units , TPR measurements are repeated on all appli ca ble frequencies.
TPR will be reported using the Figure of Merit for industry analysis. Device power shall comply
with the power levels specified in the relevant industry standards.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page44
Page 45

MobiLink Phoenix SDK
Introduction
This document describes the high-level architecture and design of the Phoenix SDK. This SDK is
meant for Novatel Wireless data products.
Requirements
• Single Server
• Multiple Clients
• Support Novatel Wireless product line
• Single, Internal State Machine
• Event Driven support for 2-way communication
SDK MODULES
Any number of Client applications can take full advantage of the Phoenix SDK.
Figure 9: Applications
Phoenix &
Blaze
MobiLink
UCM
NetMonke
y
SMS Client Address
book
Applications
ActiveX
Profile
Manager
Hotspot
Finder
Web Update
Menu
Utilities
Phoenix & Blaze
Phoenix is the brains of the SDK. Phoenix maintains a single state machine which all Clients
communicate with. Anything and everything involving communication to the device takes places
through the Phoenix server. Implemented as a Document/View executable supporting
automation, the Phoenix server automatically keeps a count of how many Clients are attached to
it via COM interfacing. The server is initialized automatically once the first Client is instantiated
and shut down once the last Client instance is terminated. With the beauty of OLE Automation,
the Phoenix server can be utilized using many different programming languages, including C++,
MFC, JavaScript, VBScript, etc. Refer to Phoenix.chm for API documentation. If wanting to use
Phoenix in Visual Studio, import the type library Phoenix.tlb and create a wrapper class for it.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page45
Page 46

Blaze ActiveX control helps Client applications to receive events fired by the Phoenix server.
This allows for simple 2-way communication, replacing redundant loop checking used in the past.
Refer to Blaze.chm for API documentation. If wanting to use Blaze ActiveX control in Visual
Studio, add the NVTL Blaze control from the registered Components and Controls Gallery and
create a wrapper class for it.
Sample Code: Refer to PhoenixClient VC++/MFC Project
NetMonkey
NetMonkey ActiveX control provides interfaces to some very useful networking components for
managing WLAN, LAN, & WWAN. The WLAN component utilizes Windows XP’s Wireless Zero
Config when managing and configuring Wi-Fi access points for seamless and easy-to-use
access. Currently, the WWAN component supports only Novatel Wireless products, given the
proper NDIS drivers. Refer to NetMonkey.chm for API documentation.
Profile Manager
Profile Manager ActiveX control helps to manage many types of WWAN network configurations
needed in order to make successful connections to a network. Mostly utilized by UMTS/HSDPA
networks, it provides a means to store settings like PDP type, PDP Address, APN, Quality of
Services settings, IP addresses, proxy settings and more. Each profile is maintained in a local
database in a proprietary XML format. Profile properties allow for seamless use via the Phoenix
server API. Refer to ProfileManager.chm for API documentation.
Hotspot Finder
Hotspot Finder ActiveX control, given a database directory of Wi-Fi hotspots, provides a simple
GUI which allows the end-user to easily refine searches in order to find the closest Wi-Fi hotspot.
Refer to Hotspots.chm for API documentation.
Menu
Menu ActiveX control, currently used in MobiLink, provides a set of GUI’s for the end-user. The
Properties dialog displays details relating to the currently selected device. The Configuration
dialog provides a means to change certain UI settings, as well as change a limi t ed amount of
WWAN, WLAN, and LAN settings. The Report dialog shows connection logs and statistics, while
the Unlock dialog provides a UI for unlocking the current device. Lastly, the Activation dialog
provides a step-by-step Wizard for the user to activate his or her device, while the Debug dial og
provides immediate network debugging information for technical support. Refer to Menu.chm for
API documentation. (Debug Info and Activation work in progress)
Utilities
Utilities ActiveX control mainly provides a set of Novatel Wireless proprietary utility components.
Currently available is the Language component, which provides a set of translations for a nu mber
of languages. Components involving any kind of UI take advantage of the Language component
in order to support localization. Refer to Utilities.chm for API documentation.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page46
Page 47

PHOENIX SERVER Software design
d
Overall module design is shown below.
Figure 10: Module Design
Phoenix
ActiveX
Modules
Main
State
DebugLog
PnP
Detection
RAS
SMS Address
Book
Universal
Loader
Single Server and Multiple Clients
Server-Client design has been implemented using COM and OLE Automation.
Figure 11: Automation Server
Menu
MobiLink
##Debug
r
3
Party
App
Automation
Server
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page47
Page 48

Novatel Wireless Product Line Support
Server
Client Communication Layer
Methods, Prope
rties, and Events
d
Customer driven product line will be support via the Universal Loader which will allow Phoenix a
generic means of communication to all products.
State Machine with 2-Way Communication
Figure 12: State Machine
Main Thread maintaining device
status and states
Phoenix server
Address Book
Caching
Thread
SMS
message
caching
Universal
Loader
Events
MobiLink
Menu ActiveX
SMS Client
-
r
3
Party Application
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page48
Page 49

MobiLink Connection Manager
Overview
Firmware is installed in all modems prior leaving the manufacturing facility. Firmware updates in
the EV620 can be performed by using the EV620 Development Kit Interface Board and Novatel’s
MobiLink. However in the EU730™ and EU740™, all that is necessary is the MobiLink software.
The MobiLink tool can also be used to change CDMA parameters and many other settings. All
these actions will be explained in the following sections.
These instructions may change for future product release.
The Novatel Wireless MobiLink™ Communications Software Suite is a family of wireless
connectivity applications that connect mobile devices using wireless wide area networks (WWAN)
as well as WiFi and Ethernet in a single application to allow quick and easy access to email, the
Internet and corporate networks anytime, anywhere. With MobiLink and a wide area wireless
device, mobile users can stay productive and connected to customers and colleagues while out of
the office. MobiLink is optimally engineered to work with all of Novatel Wireless' Wireless
Modems for best in class 3G wireless broadband access solutions.
The MobiLink Communications Software Suite of applications contains a messaging Client that
manages 2 way SMS operations, an addressbook Client that manages contacts and phone
number, connection manager that manages the connectivity, and a customization utility to
manage and generate install customization settings. The following section will detail the features
of each application.
Purpose
This section provides high level user interface information regarding the appearance and
operation of the MobiLink™ Connection Manager application developed for Windows 2000, XP
Pro, and XP Home.
Applicable Documents
All software names and version numbers displayed should meet the requirements outlined in the
Consistency & Naming Conventions Requirements Document. This document also covers
the requirements for the desktop, including the necessary icons and the use of the Start menu.
For more details on meeting the requirements for Microsoft Windows certification, refer to the
document entitled, Application Specification for Microsoft Windows 2000 and Windows XP
for Desktop Applications, which can be found on Microsoft’s web site.
GENERAL FEATURES
User Interface Functionality
The first design principle for MobiLink applications is that the basic information and co ntrols
needed for day-to-day operations are quickly and easily accessible while less frequently used
functions are located deeper in the menu system. The user interface is designed to be intuitive to
use and will not require a large learning curve for the average user. The second design principle
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page49
Page 50

for MobiLink is to be easily customizable in order to be able to meet the various requirements of a
global market.
Layout
The general layout of the main windows is designed to display important information for
connectivity while making it easy to navigate to other functions. The main function such as mobile
status and signal strength display is shown in the main window. The connection button is
prominently displayed and easily accessible. The main MobiLink display is shown below.
Figure 13: Main MobiLink Display
The Dashboard Area in the layout is designed as a launching area for other applications. The
default applications in the current design are internet browser, SMS Client, Addressbook, and
Help file. Other applications can be launched.
The Active Profile Selection is a list that allows for easy access to choose the active profile to use
for connection. For 3G, this list is a list of connection profiles while for WiFi, this is a list of access
points found. For WiFi, this list also shows the signal quality and whether the access point is
encrypted.
Lastly, there are the standard minimize and close buttons that are the main stay of any
application. The minimize button hides the application as a tray icon and the close button
gracefully closes the application.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page50
Page 51

Mouse Over
Mouse over is a feature of the application that displays helpful hint about the function of the
application as the mouse is moved over an active area of the application such as the menu
button.
Snap to Edge
Snap to edge is a feature that makes the MobiLink application window snap to the sides of the
Windows desktop as the user drags the application close to the edge.
Hot Swapping
The design of MobiLink allows for hot swapping of the 3G device. Users can plug and unplug a
3G wireless device and MobiLink will automatically recognize the technology and dynamically
change the display to show the relevant information.
Skinning Customization
Due to the software design and the underlying graphics engine used, the main “skin” of MobiLink
is completely customizable. The skin is contained in separate resource files that can be easily
changed for branding or function. One design is shown below and more can be developed.
Figure 14: Skin Design
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page51
Page 52

Localization
It is the intent of the MobiLink™ connection manager design to be able to support localization.
Double byte Unicode is used and all the text used by MobiLink is kept in resource files that can
easily be translated and added. Currently MobiLink supports the following languages:
• Chinese Simplified
• Chinese Traditional
• Danish
• English
• French
• German
• Italian
• Spanish
• Swedish
• Polish
File
The MobiLink™ connection manager shall contain a help file that can be accessed through a help
button or via F1 key. The help file is also localizable and is in HTML format as shown below:
Figure 15: On-Line Help
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page52
Page 53

MOBILINK™ FEATURES
The following sections describe the various features of MobiLink.
Main Display Window
The main display area of MobiLink is used for status indication of the different types of
connections. The following information is displayed.
Figure 16: Status Indication
Table 16: Status Indication
Number
Reference
1 Signal Strength Bar This is the quality of the signal for the selected
2 Connection Status This is a text indicating the connection status
3 Connect Duration This indicates the number of hours, minutes, and
4 Bytes Out/Packets Out This indicates the number of bytes sent for the
Status Information Description
seconds the current connection ha s been up
current connection
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page53
Page 54

5 Bytes In/Packet In This indicates the number of bytes received for the
current connection
6 Network Name For UMTS/HSDPA, this would show the network
name received from the AT+COPS command
7 Profile List This is the list of supported profiles that contains the
connection settings such as username and
password and QoS for 3G. This is a list of the 3G
profiles for the 3G networks and a list of WiFi
profiles for the WiFi network. The displayed profile is
the active profile.
8 Indicators The indicators are icons that show additional status
of the 3G wireless. Each indicator will be described
below.
9 Connection Type Selection
Bar
This is a navigation bar that selects which
connection information is displayed in the main
window. As the connection is selected, the main
window will slide to show the right information. Each
of the connection icons for this navigation bar also
shows the signal strength of the respective
connection.
The connection navigation bar was added to support the universal connection management
functionality. By having a navigation bar, the user is presented with just the information that is
required for the connection of interest. The pictures below show t he three views for each
connection type.
Figure 17: 3G Wireless View
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page54
Page 55

With the 3G Wireless view, connection button can be used to connect to the chosen profile
displayed. The status icons for 3G will be displayed on the top right corner and when connected,
byte count and time displayed will be shown. The vertical bar next to the navigation bar indicates
which view is currently active. When the user clicks on the WiFi navigation button, the WiFi view
will be shown.
Figure 18: WiFi View
The WiFi view does not have a connection button since WiFi is a connectionless ada ptor. The
view does show signal strength, packet count, and connection time as well as connection stat us.
Since MobiLink’s WiFi is developed using Windows zero configur ation, MobiLink WiFi control can
coexist with Windows wireless network connection. The default hotspot is shown in the selection
list in the same place as the 3G profile list. The list of hotspots is dynamically generated based on
a WiFi network scan of the area. Users can chose to make another hotspot active by clicking on
the selection list shown below.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page55
Page 56

Figure 19: HotSpot Activation
The connection list displays all the available hotspots seen by the WiFi adaptor. The list is
arranged in alphabetical order and the signal level for each is shown on the side. Also, if the
hotspot is WEP protected, a lock icon will be shown. To change hotspot, users can select one
from the list. If the hotspot is WEP protected the following dialog will be displayed to query for the
network key.
Figure 20: Network Connection
Lastly, the user can view the Ethernet connection by clicking on the Ethernet navigation bar icon.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page56
Page 57

Figure 21: Ethernet View
The Ethernet view shows the connection status, the packet count, and the connection duration.
Indicators
3G indicators are shown on the right upper corner of the main status display. The design of these
indicators is based on standard 3G indicators used on mobile devices. The following table
describes all the indicators.
Table 17: 3G Indicators
Indicator Status/Description
3G radio is roaming
3G in dormant mode (May not be applicable for all MAs)
New SMS is available
3G device is locked
WWAN
Network
This is the type of WWAN protocol that is acquired. The types are:
• HSDPA • UMTS
• GPRS • GSM
• IS95a • 1XRTT
• EVDO
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page57
Page 58

Connect/Disconnect Button
Since the main purpose of MobiLink’s connection manager is for connecting the user to the
internet, the connection button is prominently placed. The Connection button is used to initiate a
3G data connection. The connection button is not used for WiFi or Ethernet since the network
adaptors are connectionless and will automatically connect as long as there is a valid connection.
Figure 22: Connection Button
Menu
When the Menu button is clicked, the following menu subjects are displayed:
Table 18: Menu Subjects
Menu Item Description
Profile Manager This menu item opens up the dialog for creating, editing, and deleting
profiles
Configuration This menu item opens up a dialog for changing MobiLink settings
Properties This menu item opens up a dialog that displays the properties of the
3G modem
Report This menu item opens up a dialog that displays the connections
statistics and connection history
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page58
Page 59

Transparency This menu item is to set the application display transparency. This
feature allows the desktop items below the application to be shown
through the transparency
About This menu item bring s up i nformation about the MobiLink application
Exit This menu item will quit the MobiLink application
Profile Manager
The profile manager allows the user to manage the connection profiles for both the 3G
connection and WiFi connection. The user can create a profile using the New, edit or view the
profile, and delete a profile.
3G Wireless Profiles
The first tab shows the 3G wireless profiles as shown below.
Figure 23: 3G Profiles
The wireless profiles can be selected for viewing in the case of a locked profile and for editing in
the case of an unlocked profile. Locked profiles are preset and can not be deleted or altered.
This is to reduce the incidence of connection problems related to incorrect settings due to user
error. The dialog below shows the actual profile settings. For locked profiles, the settings are
grayed out and cannot be modified.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page59
Page 60

Figure 24: Profile Settings
The profile settings are categorized under different tabs and can be different for UMTS and
CDMA. In the case of CDMA, the QoS tab does not apply. The following screens show the
various settings under each tab.
Figure 25: Different Tab Settngs
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page60
Page 61

When changes are made to any of the tabs, the user must click the Apply button to effect the
changes. Cancel can be clicked to cancel the settings. The exception is the on the last VPN tab.
When creating a new VPN, the VPN entry is created when the user clicks the New button with an
entry name. The apply button is used to change the associated VPN for the profile. VPN
association is used to automatically establish a VPN session after a successful 3G connection.
When creating a profile by clicking on the New button, the profile wizard is used to guide the user
through some simple steps for creating a new profile. The advanced settings are preset based on
a template profile for the carrier network and hidden from the user. In the rare case where
advanced parameters need to be changed, the user can then select the newly created profile and
click on Edit to edit the parameters.
Figure 26: Profile Wizard Step 1
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page61
Page 62

Figure 27: Profile Wizard Step #2
Figure 28: Profile Wizard Step #3
WiFi Profiles
TBD
Configuration
The configuration menu has all the available settings for MobiLink. The configuration window is
broken down in to four functional tabs. The General tab is for the user interface settings and
language selection. The Mobile tab is used to set parameters for the 3G device. The WiFi tab
has settings for WiFi adaptor, and the Ethernet tab is used to set the Ethernet adaptor. Each of
the tabs is shown below.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page62
Page 63

Figure 29: General Tab
Table 19: General Tab Features
General Tab Feature Description
Always on top When checked, the application is always the top most
application on the desktop
Sound Effects On When checked, sounds will be played on user actions
Language This is a selection list for choosing the language to be
used for MobiLink. Windows Default will base the
language on what Windows uses as the native language
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page63
Page 64

Figure 30: Mobile Tab
Table 20: Mobile Tab Features
Feature Description
Auto-Connect when
launch
This feature is for MobiLink to automatically connect to the
network when launched
Network Selection This selection is used to select the network preference.
For CDMA, this is to select the operating network and for
UMTS/HSDPA, it’s for selection the radio access
technology
Auto-Lock on power up Check to lock the SIM upon power up. A 4 to 8 digits code
must be supplied to turn on and off the auto lock feature.
Change Lock Code Chick this button to change the lock code. This button is
only active if the auto-lock SIM feature is turned on.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page64
Page 65

Figure 31: WiFi Tab
The WiFi tab allows user to choose the WiFi adaptor from a list of detected adaptors. Also, the
adaptor properties can be modified by clicking on the properties button. The wireless adaptor
properties window is shown below.
Figure 32: WAP Window
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page65
Page 66

Figure 33: Ethernet Tab
The Ethernet tab allows user to choose the Ethernet adaptor from a list of detected adaptors.
Also, the adaptor properties can be modified by clicking on the properties button. The adaptor
properties window is shown below.
Figure 34: AP Window
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page66
Page 67

Properties Menu
The properties menu displays some of the key properties of the UMTS and EVDO devices.
Figure 35: CDMA
Figure 36: UMTS/HSDPA
Table 21: Identity Properties
Property
Firmware Version Firmware version of the 3G device
IMEI/ESN International Mobile Equipment Identity (UMTS)/ Electronic
Description
Serial Number (CDMA)
Mobil Number Number for the mobile
Manufacturer Who produced the modem
Modem Type Modem technology
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page67
Page 68

Technology 3G technology
PRL version Preferred Roaming List version number(CDMA)
FID Factory ID. This is a unique tracking number for factory
builds
Report Log
The report log has statistic information about the current connection as well as a history list of
past connections.
Figure 37: Report Log
Table 22: Report Values
Value Description
Instant downlink This is most recent measured downlink throughput
Average downlink This is the average of all the measured downlink
throughput
Max downlink This is the maximum achieved downlink throughput
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page68
Page 69

Total data This is the total data that has been ever sent since
MobiLink has been installed on the machine
Connection time The is the amount of time the conne ction has lasted
MB per month This is a resettable counter of how many bytes since the
last reset
Minutes per month This is a resettable counter of how many minutes since the
last reset
Transparency
This menu feature allows the user to select the percent transparency for MobiLink. The choices
range from 0% to 90% with 0% being solid and 90% being very transparent. Transparency
allows desktop items below MobiLink to be displayed for better multitasking. Below is an
example of MobiLink transparency on a desktop.
Figure 38: Desktop Transparency
About
The About dialog displays MobiLink information such as version number, release date, and
copyright.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page69
Page 70

Figure 39: About Dialogue
SIM/Lock Management
Upon Mobilink startup, ff the device is locked on power up, a small dialog will be displayed such
as below to ask the user to enter the unlock code prior to continuing with MobiLi nk.
Figure 40: Enter PUK
The lock setting and code can be managed in the Mobile tab of the configuration menu shown
below.
Figure 41: Configuration Menu
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page70
Page 71

Quick Access Buttons
The quick access buttons are designed to provide a launch pad for other applications. Four
buttons are provided and can be remapped to other applications. The picture below shows the
default functions assigned to the quick access buttons.
Figure 42: Quick Access Button Default Functions
Software Web Upgrade
TBD
SMS Client
The MobiLink SMS Client is used to manage reading and sending SMS messages. The SMS
Client is an application that is part of the MobiLink application suite. The design of this
application is to emulate an email Client to reduce the amount of new learning that is required to
start using this application. This application is launched from the main connection manager Quick
Access button. The following features are supported.
• Send new messages
• Reply to message
• Forward message
• Email interworking
• Concatenated SMS
• Set priority of message
• Rich text editing functions
• Printing
• Support for embedded hyper links and email links in message
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page71
Page 72

• Auto language selection
• Send to multiple recipients
• Status receipt of sent messages
• Status bar to indicate number of messages, character count, etc…
Figure 43: MobiLink SMS Client
SMS Mailboxes
Very much like an email Client, the SMS Client has multiple mail boxes to store different types of
messages.
Table 23: Mailbox List
Mailbox Description
Inbox All incoming SMS is delivered to this mail box
and will be highlighted if unread.
Outbox All outgoing SMS will be put into this mailbox.
If the SMS has not been sent to the card, it will
be held here until it can be sent.
Sent All sent SMS messages are placed here.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page72
Page 73

SIM All SMS messages that are still stored on the
SIM.
The message panel contains the key information for a list of messages. The messages can be
reorder in the message panel by clicking on the fields located on the top strip. The fields are the
following:
Table 24: Fields List
Field Description
! Importance
From Where the message is from. Only shown when
Inbox is selected.
To Where the message is sent. Only shown in
when Outbox or Sent box is selected.
Message Displays the first few characters of the
message
Received Time when the message is received
Sent Time when the message is sent
Callback Callback number
Menu Bar
The menu bar contains the following items:
Menu Item Description
• File o Exit Exits the application
• Edit o Undo Undo last text editing
o Cut Cut the selected text
o Copy Copy the selected text
o Paste Paste text on clipboard
o Select All Select all text in message content panel
• View o Toolbar Display tool bar
o Statusbar Display Status bar
• Help o About SMSClient Display About dialog
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page73
Page 74

Toolbar
The tool bar is accessible across the top and gives user quick access to common tasks. The tool
bar contains the following buttons:
Table 25: Tool Bar Button
Button Description
New SMS Message Opens up dialog to create a new SMS message
Delete Deletes the highlighted message or group of messages.
Reply Reply to the highlighted message.
Forward Forward the contents of the highlighted message.
Status Bar
The status bar displays information about each of the mailbox selected. It will give the number of
messages and the number of unread messages. The status bar is located on the bottom strip.
Compose Message Window
Clicking on the New SMS Message button will bring up the following dialog: This window allows
the user to enter the destination address, SMS message, a callback number for CDMA, and a
subject text. Standard text editing such as cutting, copying, pasting is supported in the message
box. In addition, the user can use the tool bar or the menu to set the priority and encoding of the
message. Both Unicode and ASCII are supported. Unicode is used to send characters not in the
standard ASCII character set.
Figure 44: Compose Message
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page74
Page 75

For the destination address, users can chose to select from the address book by clicking on the
To button. Also, multiple destinations can be entered separated by a comma or semicolon.
The toolbar supports the following functions: Clicking on the “To” button or the Addressbo ok
button will bring up the following dialog to select the contact to insert into the destination field.
Multiple destination addresses can be selected.
Table 26: Destination Addresses
Button Description
Send Send the SMS message
! Emergency priority
! Urgent priority
Print the SMS message
Editing functions. Cut, copy, and paste text
Open the addressbook to select from
Set Unicode encoding for message
Email Interworking
A new feature added to this version of MobiLink is the ability for email interworking. What this
feature does is to allow an email message to be sent over an SMS message. If the user types in
an email address in the To filed, the application will automatically format the SMS message so
that the SMSC on the network side will forward it as an email.
The recipient of this email can simply reply to the message and the message will be forwarded
back to the wireless device.
Concatenated SMS
With the addition of email interworking, the ability to send an SMS that is longer than the limited
160 characters is very important. To address that issue, the SMS Client will allow the user to
enter a long message and automatically segment the message and send it as separate SMS with
a special tag to indicate the messages are segments of a long message.
Addressbook Features
The MobiLink address book allows the management of phone numbers on the S I M, Windows
Address Book and Outlook. The following screen shows the address book Client.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page75
Page 76

Figure 45: Address Book
The address book Client has a selection box that allow the user to chose which address book to
view. The following addresses can be selected:
Table 27: Address Books
Addressbook Description
Windows Address
Book
Outlook Address
Book
SIM
Global Group
Contact
User can create, delete, and view contact properties as well as send an SMS message using the
selected contact by clicking on one of the buttons on the bottom of the Address Book Client.
This is the native Windows Addressbook that is part of
Windows Accessories folder
This is the local Outlook Addressbook. This is only
accessible if Outlook is installed on the computer
This is the address book located on the 3G device or the
SIM of the device
This is the group contacts that contain distribution lists
created by the user. This list can contain contacts from
any of the above address books
Global Group Contact
Global Group Contact feature allows users to create distribution lists for sending SMS.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page76
Page 77

Figure 46: Select Group Contacts
When the user chooses to create a Global Group Contact, a new dialog will be opened up to
allow the user to select from the different address books and move them to create a new
distribution list. The total number in a distribution list is up to 100. The list can contain a mixture
from different address books and can contain both mobile numbers as well as email addre sses.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page77
Page 78

Phoenix API Interface to PCI Express Mini Card
Overview
This is the Phoenix API Command Set Reference for the Novatel Wireless CDMA Modem
product. This document describes the modem API used by host applications running on Windows
2000, and Windows XP.
The SDK provides universal API support for both 1XEV-DO and HSDPA mini-cards. This
provides interfaces through the Windows XP and Windows 2000 operating systems. It includes
API support as well as sample code to provide for ease of application development.
Phoenix is the brains of the SDK. Phoenix maintains a single state machine that all Clients
communicate with. Anything and everything involving communication to the device takes places
through the Phoenix server. Implemented as a Document/View executable supporting
automation, the Phoenix server automatically keeps a count of how many Clients are attached to
it via COM interfacing. The server is initialized automatically once the first Client is instantiated
and shut down once the last Client instance is terminated. With the beauty of OLE Automation,
the Phoenix server can be utilized using many different programming languages, including C++,
MFC, JavaScript, VBScript, etc. Refer to Phoenix.chm for API documentation. If you want to
use Phoenix in Visual Studio, import the type library Phoenix.tlb and create a wrapper class for it.
Blaze ActiveX control helps Client applications to receive events fired by the Phoenix server.
This allows for simple 2-way communication, replacing redundant loop checking used in the past.
Refer to Blaze.chm for API documentation. If you want to use Blaze ActiveX control in Visual
Studio, add the NVTL Blaze control from the registered Components and Controls Gallery and
create a wrapper class for it.
Phoenix API is the communication engine between host applications and a Novatel Wireless
CDMA modem. It is a DLL library that provides an interface for user/host applications to
communicate commands to the modem for purposes of serial access, general diagnostic, NV
programming, SMS messaging, and general modem functions. It provides the hardware
abstraction that the host applications don’t need to involve itself with.
The following facts and conventions are applicable across the whole document unless specially
specified.
• All API calls are synchronous. The calling thread will be blocked until the function call
returns.
• HANDLE hCom is used in most Loader functions as the first argument. It will not be
repeated in the Parameters section for every function. The com port handle must be
obtained by calling function Open_Output_Handles( ). NULL is not a valid handle value.
The handle should be closed before applications quit.
• Modem: Novatel Wireless CDMA Modem
• Loader: Novatel Wireless CDMA Modem Loader API
• Applications: Host applications using Loader API to access Novatel Wireless CDMA PC
Card Modem
Client Object
The Client object uses the following methods:
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page78
Page 79

ChangeLockCode method
Description: Used to change the lock code of the device.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.ChangeLockCode(lpszLockCode As String, lpszNewLockCode As
String)
The ChangeLockCode method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
lpszLockCode String
lpszNewLockCode String
Sample Code using ChangeLockCode Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::ChangeLockCode(LPCTSTR lpszLockCode, LPCTSTR
lpszNewLockCode)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_BSTR VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x18, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
lpszLockCode, lpszNewLockCode);
return result;
}
Connect method
Description: To initiate a PS or CS (if supported by device) call.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax:
object.Connect(lpszUsername As String, lpszPassword As String, lpszNumber As String,
varErrorMsg As Variant, nIPAddress As Long, nPrimaryDNS As Long, nSecond aryDNS As L ong,
nPrimaryWINS As Long, nSecondaryWINS As Long, nPapChap As Long, lpszVPN As String)
The Connect method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
lpszUsername String
lpszPassword String
lpszNumber String
varErrorMsg Variant
nIPAddress Long
nPrimaryDNS Long
nSecondaryDNS Long
nPrimaryWINS Long
nSecondaryWINS Long
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page79
Page 80

nPapChap Long
lpszVPN String
Sample Code using Connect Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::Connect(LPCTSTR lpszUsername, LPCTSTR lpszPassword, LPCTSTR
lpszNumber, VARIANT* varErrorMsg, long nIPAddress, long nPrimaryDNS, long
nSecondaryDNS, long nPrimaryWINS, long nSecondaryWINS, long nPapChap, LPCTSTR
lpszVPN)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_BSTR VTS_BSTR VTS_BSTR VTS_PVARIANT VTS_I4
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x5, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
lpszUsername, lpszPassword, lpszNumber, varErrorMsg,
nIPAddress, nPrimaryDNS, nSecondaryDNS, nPrimaryWINS, nSecondaryWINS, nPapChap,
lpszVPN);
return result;
}
DebugPrint method
Description: Used to write out to the log file.
Syntax: object.DebugPrint(nModule As Long, nLevel As Long, lpszDebug As String)
The DebugPrint method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nModule Long
nLevel Long
lpszDebug String
Sample Code using DebugPrint Method:
void IPhoenixWrapper::DebugPrint(long nModule, long nLevel, LPCTSTR lpszDebug)
{
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x1e, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_EMPTY, NULL, parms,
nModule, nLevel, lpszDebug);
}
DeleteMessage method
Description: Delete a message.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.DeleteMessage(nMsgBoxEnum As Long, nIndex As Long)
The DeleteMessage method syntax has these parts:
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page80
Page 81

Part Description
Object An expression evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMsgBoxEnum Long
nIndex Long
Sample Code using DeleteMessage Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::DeleteMessage(long nMsgBoxEnum, long nIndex)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x21, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMsgBoxEnum, nIndex);
return result;
}
Disconnect method
Description: To terminate call.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.Disconnect
The Disconnect method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
Object An expression evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using Disconnect Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::Disconnect()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x6, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetAdapter method
Description: Get the name of the currently selected/active device.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetAdapter
The GetAdapter method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
Object An expression evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetAdapter Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetAdapter()
{
Cstring result;
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page81
Page 82

InvokeHelper(0x1b, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetAdapterList method
Description: Get a list of currently available devices.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetAdapterList(varAdapterList As Variant)
The GetAdapterList method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
Object An expression evaluating to an object of type Client.
varAdapterList Variant
Sample Code using GetAdapterList Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetAdapterList(VARIANT* varAdapterList)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x1d, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varAdapterList);
return result;
}
GetConnectStatus method
Description: Once connected, get RAS status info of the current connection.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax:
object.GetConnectStatus(varState As Variant, varError As Variant, varBytesIn As Variant,
varBytesOut As Variant, varDuration As Variant)
The GetConnectStatus method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
Object An expression evaluating to an object of type Client.
varState Variant
varError Variant
varBytesIn Variant
varBytesOut Variant
varDuration Variant
Sample Code using ConnectStatus Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetConnectStatus(VARIANT* varState, VARIANT* varError, VARIANT*
varBytesIn, VARIANT* varBytesOut, VARIANT* varDuration)
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page82
Page 83

{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x8, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varState, varError, varBytesIn, varBytesOut, varDuration);
return result;
}
GetContact method
Description: Get the contact’s name and details by index.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetContact(nIndex As Long, varContactName As Variant,
varContactDetails As Variant)
The GetContact method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nIndex Long
varContactName Variant
varContactDetails Variant
Sample Code using GetContact Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetContact(long nIndex, VARIANT* varContactName, VARIANT*
varContactDetails)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x28, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nIndex, varContactName, varContactDetails);
return result;
}
GetContactInfo method
Description: Get phonebook’s max size, contact name’s max length, and contact detail’s max
length.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetContactInfo(varPhonebookMax As Variant, varContactNameMax As
Variant, varContactDetailsMax As Variant)
The GetContactInfo method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
varPhonebookMax Variant
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page83
Page 84

varContactNameMax Variant
varContactDetailsMax Variant
Sample Code using GetContactInfo Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetContactInfo(VARIANT* varPhonebookMax, VARIANT*
varContactNameMax, VARIANT* varContactDetailsMax)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x27, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varPhonebookMax, varContactNameMax,
varContactDetailsMax);
return result;
}
GetDeviceId method
Description: Get the device ID (ESN/IMEI) of the device
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetDeviceId
The GetDeviceId method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetDeviceID Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetDeviceId()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0xe, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetDeviceModel method
Description: Get the model name of the device.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetDeviceModel
The GetDeviceModel method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetDeviceModel Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetDeviceModel()
{
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page84
Page 85

Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0xc, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetDeviceNetwork method
Description: Get currently attached network type.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetDeviceNetwork
The GetDeviceNetwork method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetDeviceNetwork Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetDeviceNetwork()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0x3, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetDeviceState method
Description: Get device state. Refer to SDK.h for possible states.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetDeviceState
The GetDeviceState method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetDeviceState Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetDeviceState()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x11, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
Possible States
typedef enum _PX_DEVICE_STATE
{
// PX_STATE_MIN = 0,
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page85
Page 86

PX_STATE_UNKNOWN = 0, // State of device cannot be
determined
PX_STATE_NOCARD = 1,
PX_STATE_INITIALIZING = 2,
PX_STATE_DISABLED = 3, // Disabled by
Fn-F2 or user intervention
PX_STATE_LOCKED = 4,
PX_STATE_SEARCHING = 5,
PX_STATE_IDLE = 6,
PX_STATE_CONNECTING = 7,
PX_STATE_AUTHENTICATING = 8,
PX_STATE_CONNECTED = 9,
PX_STATE_NDIS = 10,
PX_STATE_SHUTDOWN = 11,
PX_STATE_STANDBY = 12,
// PX_STATE_MAX
}PX_DEVICE_STATE;
// States that all public SMS functions will return
typedef enum {
SMS_STATE_EMPTY = 60000,
SMS_STATE_UNREAD,
SMS_STATE_UNREAD_PRIORITY,
SMS_STATE_READ,
SMS_STATE_FORWARDED,
SMS_STATE_REPLIED,
SMS_STATE_SENDING,
SMS_STATE_SENT,
SMS_STATE_DELIVERED,
SMS_STATE_FAILED_SEND
} SMSMessageState;
typedef enum {
SMSInbox,
SMSOutbox,
SMSSentbox,
SMSSIM
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page86
Page 87

} SMSBoxEnum;
GetDeviceTechnology method
Description: Get device technology defined by NovatelModemAPI.h.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetDeviceTechnology
The GetDeviceTechnology method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetDeviceTechnology Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetDeviceTechnology()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x2, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetFID method
Description: Get the FID of the device. (CDMA/EVDO Only)
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetFID
The GetFID method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetFID Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetFID()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0x10, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetHardwareVersion method
Description: Get the hardware version of the device
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetHardwareVersion
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page87
Page 88

The GetHardwareVersion method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetHardwareVersion Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetHardwareVersion()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0xb, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetLockStatus method
Description: Determine whether the device is locked, including autolock setting.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetLockStatus(varLockStatus As Variant, varAutoLockOn As Variant)
The GetLockStatus method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
varLockStatus Variant
varAutoLockOn Variant
Sample Code using GetLockStatus Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetLockStatus(VARIANT* varLockStatus, VARIANT* varAutoLockOn)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x17, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varLockStatus, varAutoLockOn);
return result;
}
GetMessage method
Description: Retrieve message given which message box and an index.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetMessage(nMsgBoxEnum As Long, nIndex As Long, varState As
Variant, varMsg As Variant, nMsgSize As Long)
The GetMessage method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMsgBoxEnum Long
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page88
Page 89

nIndex Long
varState Variant
varMsg Variant
nMsgSize Long
Sample Code using GetMessage Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetMessage(long nMsgBoxEnum, long nIndex, VARIANT* varState,
VARIANT* varMsg, long nMsgSize)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x20, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMsgBoxEnum, nIndex, varState, varMsg, nMsgSize);
return result;
}
GetMessageCount method
Description: Get current count given which message box.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetMessageCount(nMsgBoxEnum As Long)
The GetMessageCount method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMsgBoxEnum Long
Sample Code using GetMessageCount Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetMessageCount(long nMsgBoxEnum)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x24, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMsgBoxEnum);
return result;
}
GetMessageStatus method
Description: Get a message status. Refer to SDK.h for possible states.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetMessageStatus(nMsgBoxEnum As Long, nIndex As Long, varState
As Variant)
The GetMessageStatus method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page89
Page 90

object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMsgBoxEnum Long
nIndex Long
varState Variant
Sample Code using GetMessageStatus Method:
long IphoenixWrapper::GetMessageStatus(long nMsgBoxEnum, long nIndex, VARIANT*
varState)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x22, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMsgBoxEnum, nIndex, varState);
return result;
}
GetMobileNumber method
Description: Get the mobile number (MDN) of the device.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetMobileNumber
The GetMobileNumber method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GeMobileNumber Method:
Cstring IphoenixWrapper::GetMobileNumber()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0xd, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetNetworkOperatorList method
Description: Get a list of operators. (UMTS/HSDPA Only)
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetNetworkOperatorList(varOperatorList As Variant)
The GetNetworkOperatorList method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page90
Page 91

varOperatorList Variant
Sample Code using GetNetworkOperatorList Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::GetNetworkOperatorList(VARIANT* varOperatorList)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x1a, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varOperatorList);
return result;
}
GetNetworkPreference method
Description: Get network mode: RAT_MODE_AUTO (0), RAT_MODE_GSM (1),
RAT_MODE_WCDMA (2) (UMTS/HSDPA Only)
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetNetworkPreference(varMode As Variant)
The GetNetworkPreference method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
varMode Variant
Sample Code using GetNetworkPreference Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::GetNetworkPreference(VARIANT* varMode)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x2d, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varMode);
return result;
}
GetNewMessageCount method
Description: Get new message count.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetNewMessageCount
The GetNewMessageCount method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page91
Page 92

Sample Code using GetNewMessageCount Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::GetNewMessageCount()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x1f, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetOSVersionInfo method
Description: Get the OS versioning info.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetOSVersionInfo(varMajorVersion As Variant, varMinorVersion As
Variant, varCSDVersion As Variant)
The GetOSVersionInfo method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
varMajorVersion Variant
varMinorVersion Variant
varCSDVersion Variant
Sample Code using GetOSVersionInfo Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::GetOSVersionInfo(VARIANT* varMajorVersion, VARIANT*
varMinorVersion, VARIANT* varCSDVersion)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x9, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varMajorVersion, varMinorVersion, varCSDVersion);
return result;
}
CString IPhoenixWrapper::GetSoftwareVersion()
{
CString result;
InvokeHelper(0xa, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetPRLVersion method
Description: Get the PRL version of the device. (CDMA/EVDO Only)
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetPRLVersion
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page92
Page 93

The GetPRLVersion method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code:
CString IphoenixWrapper::GetPRLVersion()
{
Cstring result;
InvokeHelper(0xf, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
GetRasErrorString method
Description: Pass a RAS error code and get a RAS error string.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetRasErrorString(nErrorCode As Long)
The GetRasErrorString method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nErrorCode Long
Sample Code using GetRasErrorString Method:
CString IPhoenixWrapper::GetRasErrorString(long nErrorCode)
{
CString result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x1, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, parms,
nErrorCode);
return result;
}
GetSigStr method
Description: Get Signal Strength. Values: 0 – 5
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.GetSigStr
The GetSigStr method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page93
Page 94

Sample Code using GetSigStr Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::GetSigStr()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x4, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
GetSoftwareVersion method
Description: Get the software (firmware) version of the device.
Return Type: A String value.
Syntax: object.GetSoftwareVersion
The GetSoftwareVersion method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using GetSoftwareVersion Method:
CString IPhoenixWrapper::GetSoftwareVersion()
{
CString result;
InvokeHelper(0xa, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_BSTR, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
IsDormant method
Description: Determine whether the device is currently dormant.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.IsDormant
The IsDormant method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using IsDormat Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::IsDormant()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x14, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page94
Page 95

IsMessageMemoryFull method
Description: Check to see if the message box memory is full.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.IsMessageMemoryFull
The IsMessageMemoryFull method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using IsMessageMemoryFull Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::IsMessageMemoryFull()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x26, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
IsRoaming method
Description: Determine whether the device is currently roaming.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.IsRoaming
The IsRoaming method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
Sample Code using IsRoaming Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::IsRoaming()
{
long result;
InvokeHelper(0x13, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, NULL);
return result;
}
SendMessage method
Description: To send a message.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SendMessage(varMsg As Variant, nMsgSize As Long, varMsgIndex As
Variant)
The SendMessage method syntax has these parts:
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page95
Page 96

Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
varMsg Variant
nMsgSize Long
varMsgIndex Variant
Sample Code using SendMessage Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SendMessage(VARIANT* varMsg, long nMsgSize, VARIANT*
varMsgIndex)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_PVARIANT VTS_I4 VTS_PVARIANT;
InvokeHelper(0x25, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
varMsg, nMsgSize, varMsgIndex);
return result;
}
SetAdapter method
Description: To select a new active device.
Syntax: object.SetAdapter(lpszAdapter As String)
The SetAdapter method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
lpszAdapter String
Sample Code using SetAdapter Method:
void IPhoenixWrapper::SetAdapter(LPCTSTR lpszAdapter)
{
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x1c, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_EMPTY, NULL, parms,
lpszAdapter);
}
SetAutoLock method
Description: To turn ON or OFF the autolock setting.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetAutoLock(nAutoOn As Long, lpszLockCode As String)
The SetAutoLock method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nAutoOn Long
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page96
Page 97

lpszLockCode String
Sample Code using SetAutoLock Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetAutoLock(long nAutoOn, LPCTSTR lpszLockCode)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x16, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nAutoOn, lpszLockCode);
return result;
}
SetCallSettings method
Description: Set the call settings, including quality of service settings. (UMTS/HSDPA Only)
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetCallSettings(nPDPType As Long, lpszAPN As String, nPDPAddress
As
Long, lpdQoS As Object)
The SetCallSettings method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nPDPType Long
lpszAPN String
nPDPAddress Long
lpdQoS Object
Sample Code using SetCallSettings Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetCallSettings(long nPDPType, LPCTSTR lpszAPN, long nPDPAddress,
LPDISPATCH lpdQoS)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR VTS_I4 VTS_DISPATCH;
InvokeHelper(0x12, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nPDPType, lpszAPN, nPDPAddress, lpdQoS);
return result;
}
SetContact method
Description: Set the contact’s name and details by index.
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page97
Page 98

Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetContact(nIndex As Long, lpszContactName As String,
lpszContactDetails As String)
The SetContact method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nIndex Long
lpszContactName String
lpszContactDetails String
Sample Code using SetContact Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetContact(long nIndex, LPCTSTR lpszContactName, LPCTSTR
lpszContactDetails)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x29, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nIndex, lpszContactName, lpszContactDetails);
return result;
}
SetMessageStatus method
Description: Set the state of a message.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax:
object.SetMessageStatus(nMsgBoxEnum As Long, nIndex As Long, nState As Long)
The SetMessageStatus method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMsgBoxEnum Long
nIndex Long
nState Long
Sample Code using SetMessageStatus Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetMessageStatus(long nMsgBoxEnum, long nIndex, long nState)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x23, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMsgBoxEnum, nIndex, nState);
return result;
}
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page98
Page 99

SetNetworkOperator method
Description: To set the network operator provided by GetNetworkOperatorList. (UMTS/HSDPA
Only)
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetNetworkOperator(nMode As Long, nFormat As Long, lpszOperator
As String)
The SetNetworkOperator method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMode Long
nFormat Long
lpszOperator String
Sample Code using SetNeworkOperator Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetNetworkOperator(long nMode, long nFormat, LPCTSTR lpszOperator)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4 VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x19, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nMode, nFormat, lpszOperator);
return result;
}
SetNetworkPreference method
Description: Set network mode: RAT_MODE_AUTO (0), RAT_MODE_GSM (1),
RAT_MODE_WCDMA (2) (UMTS/HSDPA Only)
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetNetworkPreference(nMode As Long)
The SetNetworkPreference method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nMode Long
Sample Code using SetNetworkPreference Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetNetworkPreference(long nMode)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x2c, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page99
Page 100

nMode);
return result;
}
SetProxy method
Description: Set proxy settings given a proxy IP address and port.
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetProxy(nProxy As Long, nPort As Long)
The SetProxy method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
nProxy Long
nPort Long
Sample Code using SetProxy Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetProxy(long nProxy, long nPort)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_I4 VTS_I4;
InvokeHelper(0x7, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
nProxy, nPort);
return result;
}
SetSMSC method
Description: Setting the SMSC is required for proper SMS functionality
Return Type: A Long value.
Syntax: object.SetSMSC(lpszSMSC As String)
The SetSMSC method syntax has these parts:
Part Description
object An expressio n evaluating to an object of type Client.
lpszSMSC String
Sample Code using SetSMSC Method:
long IPhoenixWrapper::SetSMSC(LPCTSTR lpszSMSC)
{
long result;
static BYTE parms[] =
VTS_BSTR;
InvokeHelper(0x2a, DISPATCH_METHOD, VT_I4, (void*)&result, parms,
lpszSMSC);
Novatel Wireless, Proprietary & Confidential
Page100
 Loading...
Loading...