Page 1

Integration Guide:
GSM0408IG001
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Integration Guide
Version: Draft
Page 2
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Document Title: Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA Modem Integration Guide
Version: 1.0x
Date: 3/3/08
Status: Draft
Document Control ID: GSM0408IG001
General
All efforts have been made to ensure the accuracy of material provided in this document at the time
of release. However, the items described in this document are subject to continuous development
and improvement. All specifications are subject to change without notice and do not represent a
commitment on the part of Enfora, Inc. Enfora, Inc. will not be responsible for any loss or damages
incurred related to the use of information contained in this document.
This product is not intended for use in life support appliances, devices or systems where a
malfunction of the product can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Enfora, Inc.
customers using, integrating, and/or selling this product for use in such applications do so at their
own risk and agree to fully indemnify Enfora, Inc. for any damages resulting from illegal use or resale.
Copyright
Complying with all applicable copyright laws is the responsibility of the user. Without limiting the
rights under copyright, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in or introduced into a
retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying,
recording or otherwise), or for any purpose, without the express written permission of Enfora, Inc.
Enfora may have patents, patent applications, trademarks, copyrights or other intellectual property
rights covering subject matter in this document. Except as expressly provided in any written license
agreement from Enfora, the furnishing of this document does not give you any license to these
patents, trademarks, copyrights or other intellectual property.
©2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008 Enfora, Inc. All rights reserved.
Enabler and Spider are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Enfora, Inc. in the United
States.
GSM0408IG002 Version 1.00 – 12/07/2007
Page 3

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Table of Contents
1. ..................................................................................................................1 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.1. ..................................................................................................... 1 IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
2. ................................................................................................1 REGULATORY COMPLIANCE FCC
2.1. ................................................... 1 INTEGRATION CONSIDERATIONS AND INSTALLATION REQUIREMENTS
2.2. ......................................................................................................................................3 DISCLAIMER
3. .......................................................................................................................4 MANUAL OVERVIEW
3.1. ........................................................................................................................... 4 REVISION HISTORY
3.2. .................................................................................................................. 5 REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
3.2.1. ..................................................................5 Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA Product Documentation
3.2.2. .....................................................................................................6 GSM Device Specifications
3.2.3. .......................................................................................................................6 US Government
................................................................................6 3.2.3.1. Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
........................................................................6 3.2.3.2. FCC Office of Engineering and Technology (OET)
3.2.4. ......................................................................................................................6 Industry Canada
3.2.5. .....................................................................................................6 Environmental Regulations
3.2.6. .......................................................................................................7 Mechanical Specifications
3.2.7. ......................................................................................................7 RF and EMI Specifications
3.2.8. ..........................................................................................................7 Joint Industry Standards
4. ................................................................................................................................8 INTRODUCTION
4.1. ........................................................................................................................ 8 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
4.2. ......................................................................... 8 KEY FEATURES OF THE ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE
4.3. ...............................................................................................10 PROVIDING MULTI-BAND OPERATION
4.4. ...................................................................................10 WIRELESS DATA APPLICATION POSSIBILITIES
4.5. .......................................................11 SUMMARY OF FEATURES FOR THE ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE
4.6. ........................................................................... 13 LAYOUT GUIDELINES FOR THE ENABLER IIIG BGA
4.6.1. ..............................................................................................................................13 Placement
4.6.2. ........................................................................................................................14 Ground Plane
4.6.3. .......................................................................................................................15 Thermal Relief
4.6.4. ...............................................................................................15 Antenna and RF Signal Trace
4.6.5. ..............................................................................................................................16 Vbat Input
4.6.6. .........................................................................................................16 I/O Routing and Fanout
4.6.7. .......................................................................................................18 Audio Reference Design
..........................................................................................................................18 4.6.7.1. Audio Schematic
................................................................................................................................19 4.6.7.2. Audio Layout
4.7. ..................................................................................20 BGA HANDLING AND SOLDERING GUIDELINES
5. .....................................................................................................21 TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
5.1. .................................................................................21 ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE BLOCK DIAGRAM
5.2. ..............................................................................................22 DETAILED PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
5.3. ........................................................................................................................23 OPERATING POWER
5.3.1. .............................................................................................................23 Typical Input Current
5.3.2. ............................................................................................................23 GSM Transmit Power
5.3.3. ......................................................................................................24 GSM Receiver Sensitivity
5.4. ....................................................................................................................24 PHYSICAL INTERFACES
5.4.1. ...................................................................................................................................24 Module
5.4.2. ...............................................................................................................24 Host PCB Footprint
5.5. .............................................................................................................25 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
5.5.1. ...............................................................................................................................30 BGA Map
5.6. .....................................................................................................................31 CIRCUIT PROTECTION
5.7. ...................................................................................32 PAD SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS AND FUNCTIONS
GSM0408IG002 Version 1.00 – 12/07/2007
Page 4

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.1. .....................................................................32 Module Power (Pads C1, C2, D1, D2, E1, E2)
5.7.2. ..................................................................................................................33 Antenna (Pad A1)
5.7.3. .................................................................33 Reset Signal (Pad F6, also known as ON_\OFF)
5.7.4. ...................................................................................34 Power Control (Pad K9) (PWR_CTL)
5.7.5. ......................................................................37 Level Translation Reference Power (Pad G5)
5.7.6. ....................................................................................................37 USB (Pads J2, J3, K1, K2)
5.7.7. ...............................................................................37 General Purpose Input/Output Interface
5.7.8. .............................................................................................................................39 RTC Sleep
5.7.9. ......................................................................................................................40 Serial Interface
5.7.10. .................................41 MCSI – Multi-Channel Serial Interface (Pads D13, D14, E13, E14)
5.7.11. .................................................................................................42 VBACKUP Input (Pad G6)
5.7.12. ...................................................................................................43 32 kHz output (Pad A11)
5.7.13. .......................................................................................43 Analog-To-Digital Input (Pad K3)
5.7.14. .........................................................................43 Handset Microphone Input (Pads K4, L4)
5.7.15. .......................................................................44 Handset Microphone Bias Output (Pad J4)
5.7.16. ..........................................................................44 Handset Speaker Output (Pads M4, M5)
5.7.17. .................................................................................45 Headset Microphone Input (Pad M2)
5.7.18. .......................................................................45 Headset Microphone Bias Output (Pad J5)
5.7.19. .......................................................46 Headset Speaker Output Left & Right (Pads M3, L3)
5.7.20. ........................................................................46 Headset Output Common Mode (Pad M6)
5.7.21. ...................................................................................................47 Headset Detect (Pad H4)
5.7.22. ..............................47 Remote Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) (Pads A7, A9, B7, B8, H5)
...........................................................................................49 5.7.22.1. Remote SIM Component Information
6. ...........................................................................................50 GSM/GPRS MODES OF OPERATION
6.1. ...........................................50 ENABLING THE TRANSMISSION MODES FOR THE GSM/GPRS SERVICES
6.2. ..................................................................................................................50 VOICE COMMUNICATION
6.3. ...............................................................................................................50 CIRCUIT-SWITCHED DATA
6.4. ..................................................................................................51 SMS: SHORT MESSAGE SERVICES
7. .............................................................................................................................52 SIM OPERATION
7.1. ..................................................................................................................52 PROVISIONING THE SIM
7.2. ...................................................52 GSM SERVICES SUPPORTED BY THE ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE
7.3. .................................................52 GPRS SERVICES SUPPORTED BY THE ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE
7.4. ..................................................................................52 SELECTING THE GSM MODES OF OPERATION
8. ...............................................................................................................54 SOFTWARE INTERFACE
8.1. ....................................................................................................................54 SOFTWARE INTERFACE
8.2. ............................................................................................................55 ENFORA AT COMMAND SET
8.3. ...............................................................55 ENFORA PACKET APPLICATION PROGRAMMING INTERFACE
8.3.1. API Architecture.....................................................................................................................55
8.4. ...............................................................................................................55 SETUP AND INITIALIZATION
8.4.1. .......................................................................................................................55 General Setup
8.4.2. ...........................................55 HyperTerminal Configuration for the Enabler IIIG BGA module
8.4.3. ...................................................................................56 Initialization (AT Command Interface)
8.4.4. ...................................................................................57 Initial Response to the AT Command
8.4.5. ..........................................57 Sending an Initialization String to the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
8.4.6. ..............................58 Setting Up the Communication Mode for the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
8.4.7. ...........................................................58 Querying the Status of the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
8.4.8. .................................................58 Setting Module Reporting Parameters for GSM and GPRS
8.5. ....................................................................................................................58 GSM/SMS EXAMPLES
8.5.1. .............58 Initialize the Enabler IIIG BGA Module to Send and Receive SMS Text Messages
8.5.2. ....................................................................................................58 Managing SMS Messages
8.5.3. .........................................................................................................58 Data Call Configuration
8.5.4. ........................................................................................................58 Voice Call Configuration
GSM0408IG002 Version 1.00 – 12/07/2007
Page 5

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8.6. ..............................................................................................................58 GPRS PACKET EXAMPLES
8.6.1. ...........................................................................................58 GPRS ATTACH and ACTIVATE
8.6.2. .............................................................................................................59 Windows PPP Setup
9. .......................................................................................................60 INTEGRATION AND TESTING
9.1. ..................................................................60 INTEGRATING THE ENFORA ENABLER IIIG BGA MODULE
10. ...........................................................................................62 APPENDIX A - LIMITED WARRANTY
10.1. ........................................................................................................................................62 SCOPE
10.2. .................................................................................................................................62 HARDWARE
10.3. .................................................................................................................................62 SOFTWARE
10.4. ............................................................................................................63 OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
11. ....................................................................64 APPENDIX B - REGULATIONS AND COMPLIANCE
11.1. .................................................................................64 GCF/PTCRB APPROVAL (FORMERLY FTA)
11.2. ......................................64 ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY (EMC) AND SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
11.3. ...............................................................................64 EMC/SAFETY REQUIREMENTS FOR THE USA
11.4. ..............................................................................65 HUMAN EXPOSURE COMPLIANCE STATEMENT
11.5. ........................................................................................65 COMPLIANCE WITH FCC REGULATIONS
11.6. .........................................................................................65 UNINTENTIONAL RADIATORS, PART 15
11.7. .....................................................................................66 INTENTIONAL RADIATORS, PART 22 & 24
11.8. ..........................................66 INSTRUCTIONS TO THE ORIGINAL EQUIPMENT MANUFACTURER (OEM)
11.8.1. .............67 OEM Responsibilities for All Products Containing the Enabler IIIG BGA module
11.8.2. ............................69 Specific OEM Responsibilities for Portable Products and Applications
11.8.3. ...............................69 Specific OEM Responsibilities for Mobile Products and Applications
11.8.4. .................................69 Specific OEM Responsibilities for Fixed Products and Applications
11.9. .....................70 EMC/SAFETY REQUIREMENTS FOR THE COUNTRIES OF THE EUROPEAN UNION (EU)
11.10. ................................................................70 EMC/SAFETY REQUIREMENTS FOR OTHER COUNTRIES
12. .............................................................................71 APPENDIX C - GLOSSARY AND ACRONYMS
13. .......................................................................................73 APPENDIX D – TABLES AND FIGURES
14. ........................................................................................74 APPENDIX E - CONTACTING ENFORA
GSM0408IG002 Version 1.00 – 12/07/2007
Page 6

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
1. Safety Precautions
1.1. Important Safety Information
The following information applies to the devices described in this manual. Always observe all
standard and accepted safety precautions and guidelines when handling any electrical device.
• Save this manual: it contains important safety information and operating instructions.
• Do not expose the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA product to open flames.
• Ensure that liquids do not spill onto the device.
• Do not attempt to disassemble the product: Doing so will void the warranty. This product
does not contain consumer-serviceable components.
2. Regulatory Compliance FCC
2.1. Integration Considerations and Installation Requirements
The Enabler IIIG BGA modem is designed for use in a variety of host units, "enabling" the host
platform to perform wireless data communications. However, there are certain criteria relative to
integrating the modem into a host platform such as a PC, laptop, handheld or PocketPC
and control unit, etc. that must be considered to ensure continued compliance with FCC
compliance requirements.
• Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may
cause undesired operation of the device.
In order to use the Enabler IIIG BGA modem without additional FCC certification approvals, the
installation must meet the following conditions:
• Maximum RF output power and antenna gain to meet Maximum Permissible Exposure
Requirements: GSM850 mode: Power at antenna port is +33 dBm, the maximum gain is 1.4
dBi. GSM1900 mode: Power at antenna port is 30 dBm, the maximum gain is 7.0 dBi.
• If used in a "portable" application such as a handheld or body worn device with the antenna
less than 20 cm (7.9 in.) from the human body when the device is operating, then the
integrator is responsible for passing additional "as installed" testing and the device will require
its own FCC ID:
i. SAR (Specific Absorption Rate) testing, with results submitted to the FCC for
approval prior to selling the integrated unit. If unable to meet SAR requirements,
then the host unit must be restricted to "mobile" use (see below).
ii. Unintentional emissions, FCC Part 15; results do not have to be submitted to the
FCC unless requested, although the test provides substantiation for required
labeling (see below).
iii. ERP and EIRP measurements for FCC Parts 22 and 24, alternatively a full retest
on FCC Parts 22 and 24 can be performed
®
, monitor
GSM0408IG001 Page 1 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 7
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
p
Modem Integration Guide
• If used in a "mobile" application where the antenna is normally separated at least 20 cm (7.9
in) from the human body during device operation, then an appropriate warning label must be
placed on the host unit adjacent to the antenna. The label should contain a statement such
as the following:
• Host unit user manuals and other documentation must also include appropriate caution and
warning statements and information.
• If the FCCID for the modem is not visible when installed in the host platform, then a
permanently attached or marked label must be displayed on the host unit referring to the
enclosed modem. For example, the label should contain wording such as:
WARNING
RF exposure. Keep at least 20 cm
(7.9 in) separation distance from
the antenna and the human body.
Contains GSM/GPRS modem transmitter module
FCC ID: MIVGSM0408
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
eration.
o
OR
Contains FCC ID: MIVGSM0408
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and
(2) This device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired
operation.
• Any antenna used with the modem must be approved by the FCC or as a Class II Permissive
Change (including MPEL or SAR data as applicable). The "professional installation"
provision of FCC Part 15.203 does not apply.
GSM0408IG001 Page 2 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 8
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
• The transmitter and antenna must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter. Violation of this would allow a user to plug another transmitter
in to the product and potentially create an RF exposure condition.
2.2. Disclaimer
The information and instructions contained within this publication comply with all FCC, GCF,
PTCRB, R&TTE, IMEI and other applicable codes that are in effect at the time of publication.
Enfora disclaims all responsibility for any act or omissions, or for breach of law, code or
regulation, including local or state codes, performed by a third party.
Enfora strongly recommends that all installations, hookups, transmissions, etc., be performed by
persons who are experienced in the fields of radio frequency technologies. Enfora acknowledges
that the installation, setup and transmission guidelines contained within this publication are
guidelines, and that each installation may have variables outside of the guidelines contained
herein. Said variables must be taken into consideration when installing or using the product, and
Enfora shall not be responsible for installations or transmissions that fall outside of the
parameters set forth in this publication.
WARNING
The transmitter and antenna must not be collocated
or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter. Failure to observe
this warning could produce an RF exposure
condition.
Enfora shall not be liable for consequential or incidental damages, injury to any person or
property, anticipated or lost profits, loss of time, or other losses incurred by Customer or any third
party in connection with the installation of the Products or Customer's failure to comply with the
information and instructions contained herein.
The Enabler IIIG BGA platform is designed with
features to support a robust connection. There are
instances where the module performance is beyond
the control of the intended design. Integrated designs
that require 24 by 7 operation must implement power
control via an external circuit or by implementing power
management as specified within this design guide.
GSM0408IG001 Page 3 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 9
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
3. Manual Overview
This document describes the available hardware interface of the Enabler IIIG BGA modem
(herein also noted as “modem” or “module”). The purpose of this document is to define the
electrical, mechanical and software interfaces while providing detailed technical information in
order to streamline the process of hardware and system integration.
3.1. Revision History
Date Rev Description
03/10/08 .01 Initial Release Draft
GSM0408IG001 Page 4 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 10

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
3.2. Reference Documents
3.2.1. Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA Product Documentation
Manuals
• GSM0308AT001 - Enfora GSM/GPRS OEM Module AT Command Set Reference
• GSM0308UG001 - Enfora GSM-GPRS Family API Reference
GSM0408IG001 Page 5 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 11
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
3.2.2. GSM Device Specifications
• 3GPP TS 51010-1 (850, 900,1800,1900 MHz devices)
To view the latest release, go to:
http://www.3gpp.org/ftp/Specs/html-info/51010-1.htm
3.2.3. US Government
3.2.3.1. Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Internet:
• FCC Rules, Part 24
• 47 CFR Subpart E--Broadband PCS
• 47 CFR § 24.52, sections 1.1307(b), 2.1091, and 2.1093
• FCC Rules, Part 22 for GSM 850
• FCC Rules, Part 15
• FCC Rules, Part 2
• Subpart J--Equipment Authorization Procedures
• Section 2.925
http://www.fcc.gov
3.2.3.2. FCC Office of Engineering and Technology (OET)
Internet:
• Bulletin Number 65 "Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure
http://www.fcc.gov/oet
to Radio Frequency Electromagnetic Fields"
• Supplement C "Additional Information for Evaluating Compliance of Mobile and
Portable Devices with FCC Limits for Exposure to Radio Frequency Emissions"
3.2.4. Industry Canada
• RSS-132
• RSS-133
• ICES-003
3.2.5. Environmental Regulations
• National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) of 1969 (Part 1, Subpart 1)
GSM0408IG001 Page 6 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 12

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
3.2.6. Mechanical Specifications
• ASTM D999
• ASTM D775
• IEC 68-2-27
• Bellcore Gr-63-CORE
• ETS 300 019-1-1 Class 1.2
• ETS 300 019-1-2 Class 2.1
• ETS 300 019-1-3 Class 3.1
3.2.7. RF and EMI Specifications
• ETSI Standards
• EN 61000-4-6
• EN 61000-4-3
• 3GPP TS 51.010-1, Section 12.2
• EN 55022 Class B
3.2.8. Joint Industry Standards
• IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020C
GSM0408IG001 Page 7 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 13
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4. Introduction
4.1. Product Overview
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA modem is a compact, wireless Ball Grid Array surface mount OEM
module that utilizes the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) and GPRS (General
Packet Radio Services) international communications standards to provide two-way wireless
capabilities via GSM services. The module is a fully Type-approved GSM/GPRS device, enabling
application-specific, two-way communication and control.
The small size of the module allows it to be integrated easily into the application and packaging.
4.2. Key Features of the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The following table summarizes the main features of the module.
Table 1 - Enabler IIIG BGA Key Features
Interface
Power
Radio Features
Regulatory
Data, RF input/output interface 167 pad soldered BGA
Primary serial port V.24 protocol, 1.8V levels, full 9-pin, UART
implementation
USB port USB – Debug only (Enfora Use only)
GPIO Up to 20 GPIO Some GPIO pins have dual-
purpose functionality.
Audio Digital audio via MCSI port
Voice Supports four vocoder modes: full-rate (FR),
enhanced full-rate (EFR), half-rate (HR), and
adaptive multi-rate (AMR)
Command protocol Enfora Packet API, GSM AT command set
Voltage backup Voltage backup pad available to maintain RTC,
battery capable
Reference clock 32kHz output reference clock
ADC 1 ADC port
Remote Subscriber Identity
Module (SIM)
Electrical power 3.3 to 4.5 Vdc (VBAT)
Peak currents and average
power consumption
Frequency bands EGSM 900, GSM1800, GSM 850 and GSM 1900
GSM/GPRS features supported Provides for all GSM/GPRS authentication,
Agency approvals
1.8/3 V compatible with SIM detect
Refer to the Operating Power table in the
Technical Specifications for peak currents and
average power consumption for various modes of
operation.
capability.
encryption, and frequency hopping algorithms.
GPRS Coding Schemes CS1-CS4 supported.
Multi-Slot Class 10 (4RX/2TX, Max 5 Slots).
• GCF Type Approval
• PTCRB Type Approval
• FCC Certification
• RTTE
• CE (European Community Certification)
• IC (Industry Canada) Approval
GSM0408IG001 Page 8 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 14
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
GSM/GPRS
Functionality
Audio Features
Outputs
• Mobile-originated and mobile-terminated SMS messages: up to 140 bytes or
up to 160 GSM 7-bit ASCII characters.
• Reception of Cell Broadcast Message
• SMS Receipt acknowledgement
• Circuit Switched Data (Transparent & Non-transparent up to 9.6 Kbps)
• Voice (EFR, FR, HR)
• Supports Unstructured Supplementary Service Data (USSD)
• Multi-Slot Class 10 Supported (4Rx/2TX), (5 Slot Max)
• PBCCH/PCCCH Supported
• Handset Microphone biasing
• Headset Microphone biasing
• Headset Plug/Unplug detection
• Headset Hook detection (call answer/end button on equipped Headset
microphone device)
• High output dynamic differential Earphone mode, using Headset outputs
• Pop Noise attenuation circuitry implemented for all single-ended output
stages
• Handset microphone input (MICIN, MICIP pads)
• Headset microphone input (HSMIC pad)
• Handset earphone outputs (EARP, EARN pads)
• Headset 32 stereo outputs (HSOL, HSOR pads)
GSM0408IG001 Page 9 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 15

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4.3. Providing Multi-Band Operation
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module provides 4 frequency bands for compatibility with worldwide
frequency standards. 850/1900 frequency bands are primarily used in North and South America,
while 900/1800 bands are used through out the world.
4.4. Wireless Data Application Possibilities
A variety of applications can use the module for transmitting/receiving data/voice, such as:
• Automated Meter Reading
• Point of Sale Applications
• E-mail and Internet access
• Automated Vehicle Location (AVL)
• Machine to Machine communication (M2M)
• Telematics
• Telemetry
• Wireless Security
• Smart Phones
• Telemedicine
GSM0408IG001 Page 10 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 16

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4.5. Summary of Features for the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The following summarizes the main features of the module.
Mechanical
Dimensions................................... 28.0 mm x 24.0 mm x 2.50 mm
Weight .......................................... 3.6g
Packet Data Transfer:
Protocol................................................................... GPRS Release 97 and 99
Coding Schemes .................................................... CS1-CS4
Multi-Slot Capability: (
Demonstrated @MS10) .............. MS10 (4RX/2TX) (Max 5 Slots)
Packet Channel Support......................................... PBCCH/PCCCH
Circuit Switched Data Transfer:
V110 ............................................. 300 bps/1200 bps/2400 bps/4800 bps/9600 bps/14,400 bps
Non-Transparent .......................... 300 bps/1200 bps/2400 bps/4800 bps/9600 bps/14,400 bps
Short Message Services:
GSM SMS .................................... MO, MT, CB, Text and PDU Modes
GPRS SMS .................................. MO, MT, CB, Text and PDU Modes
Voice Capability:
Speech Codec.............................. EFR, FR, HR, AMR
GSM/GPRS Radio Performance Multi-Band:
GSM0408 Radio Frequencies............. 850 MHz, 900 MHz, 1800 MHz, and 1900 MHz
Sensitivity ............................................ <-106 dBm (Typical GPRS CS1)
850 & 900 MHz Transmit Power ......... Class 4 (2 W)
1800 & 1900 MHz Transmit Power .....Class 1 (1 W)
System Requirements:
Host Interface............................... Serial Interface
DC Voltage................................... 3.3 to 4.5 Vdc
GSM0408IG001 Page 11 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 17

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Application Interface:
Host Protocol................................ Enfora Packet API and AT Commands
Internal Protocols ......................... UDP stack, TCP/IP stack, PPP, PAD, and CMUX
Physical Interface......................... 1 serial (primary/Default, rate auto baud), 1 USB (debug)
Audio Interface.............................. Handset microphone input (MICIN, MICIP pads); Headset
SIM Interface:
Remote SIM ................................. 1.8/3-Volt SIM Compatible
Environmental:
Compliant Operating Temp.......... -20 °C to 60 °C (Fully GSM Spec Compliant)
Operating Temperature................ -30 °C to 70 °C
Storage Temperature ................... -40 °C to 85 °C
Humidity ....................................... 5 to 95% non-condensing
MCSI (PCM Audio only)
microphone input (HSMIC pad); Handset earphone outputs
(EARP, EARN pads); Headset 32 stereo outputs (HSOL,
HSOR pads).
EMC:
Emissions ..................................... FCC Parts 15,22 & 24, Class B
3GPP TS 51010-1, Section 12.2
EN 55022 Class B
Operating Power (TYPICAL):
GSM Operation
GSM 850/900 (1 RX/1 TX, full power) .............250 mA average, 1.6 A peak
GSM 1800 (1 RX/1 TX, full power) ..................215 mA average, 1.3 A peak
GSM 1900 (1 RX/1 TX, full power) ..................204 mA average, 1.2 A peak
Idle.................................................................... <2.5 mA Average in DFX 5
Shutdown ......................................................... ≈ 55 uA
GPRS Operation Power
EGSM 850/900 (4 RX/1 TX, full power) ...........272 mA average,
EGSM 850/900 (2 RX/2 TX, full power) ...........420 mA average,
1.6 A peak
1.6 A peak
GSM 1800 (4 RX/1 TX, full power) ..................242 mA average, A peak
GSM 1800 (2 RX/2 TX, full power) ..................354 mA average, A peak
GSM 1900 (4 RX/1 TX, full power) ..................235 mA average, A peak
GSM 1900 (2 RX/2 TX, full power) ..................340 mA average, A peak
Idle.................................................................... <2.5 mA average in DFX 5
Shutdown .........................................................≈ 55 uA
GSM0408IG001 Page 12 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 18

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
GSM Transmit Power
1800/1900 MHz............................ GSM Power Class 1 (30 dBm ± 2 dB @ antenna connection)
850/900 MHz................................ GSM Power Class 4 (33 dBm ± 2 dB @ antenna connection)
GSM/GPRS Receiver Sensitivity (Typical)
1800/1900 MHz............................ <-106 dBm, GPRS Coding Scheme 1 (CS1)
850/900 MHz................................ <-106 dBm, GPRS Coding Scheme 1 (CS1)
4.6. Layout Guidelines for the Enabler IIIG BGA
The following guidelines are provided in an effort to allow Enabler IIIG BGA module users to
successfully implement their PCB layout to obtain the best performance. This includes the lowest
possible EMI emissions, maximum thermal conduction, mechanical integrity, and voice quality. The
module is a very compact, high performance design, yet it is easy to interface into the final product.
In order to realize its full potential, designers should pay close attention to ground structures, the
routing of RF and Digital traces, and the size of the power supply lines.
These design tips are strictly guidelines and are not
meant to be a complete list of items that guarantee
actual performance. Each application is different and
may require variation from these guidelines, however,
care should be given to utilize these sound engineering
principles whenever possible.
4.6.1. Placement
When integrating the Enabler IIIG BGA into a host design, it is critical for the design engineer and
system architect to take steps early on in the design to minimize the potential noise and
interference issues associated with proximity of RF sources, clock sources and receivers.
Carefully determining the optimum placement for the module will ensure the best performance for
GSM communication. All potential sources of noise and interference should be taken into
consideration before determining where each module and circuit should be physically placed in
the design. A system frequency plan is recommended in order to avoid system clock frequencies
with harmonics at 13MHz, 26MHz, or the GSM 850/900/1800/1900 operational bands.
Please refer to
trace is as short as possible. Refer to section
Bulk bypass capacitance should be placed adjacent to the power input pads as shown, and
power traces should be 0.1” (2.54mm) wide as a minimum, or wider if routing is longer than 5”
(127mm). Refer to section
Figure 1. The module should be rotated and placed such that the RF antenna
4.6.4 for more detail on RF routing.
4.6.5 for detailed discussion of power input.
GSM0408IG001 Page 13 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 19
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
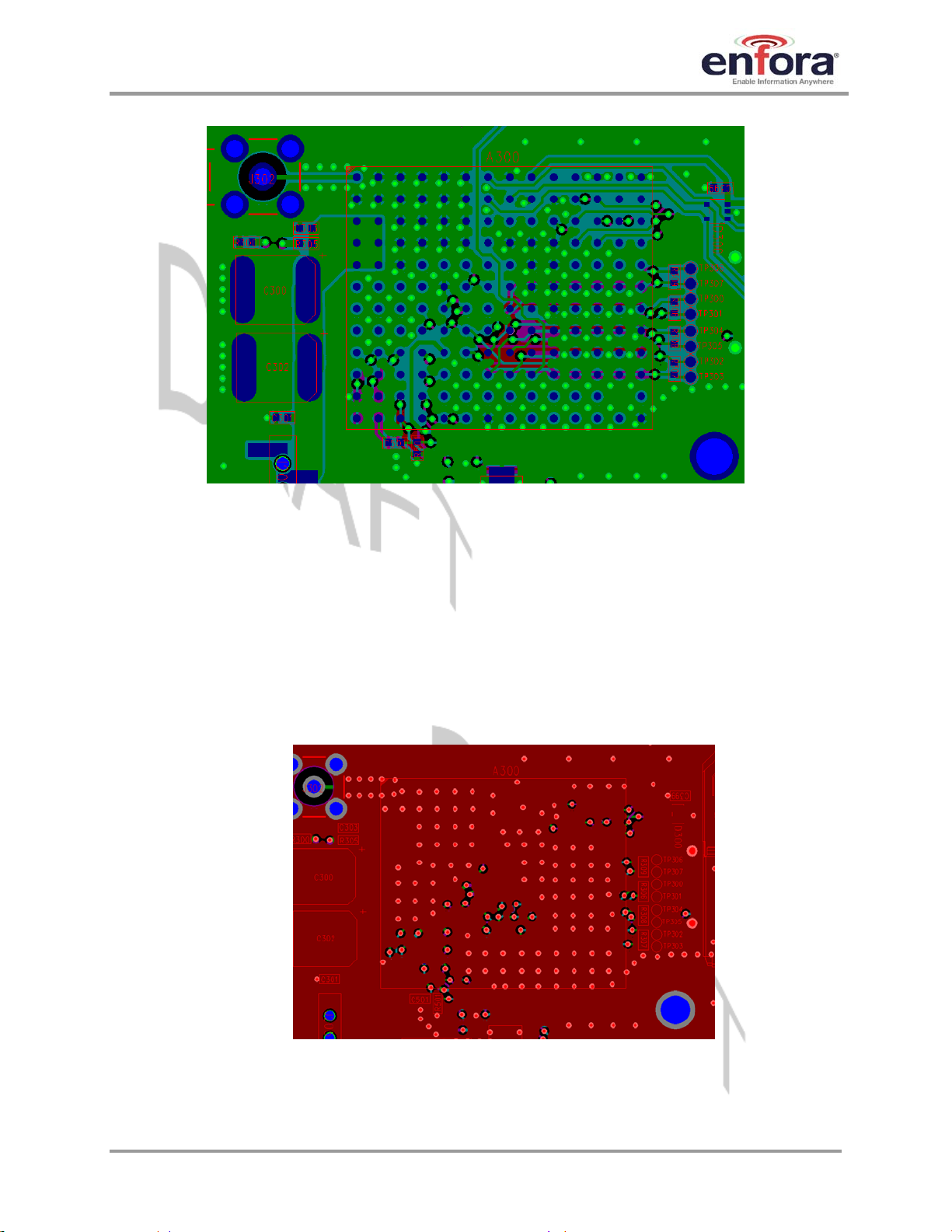
Figure 1 – Example of placement and ground plane for the module host board
4.6.2. Ground Plane
To ensure the lowest possible EMI emissions and maximum thermal conductivity, it is imperative
that all ground balls on the Enabler IIIG BGA module be soldered to a continuous ground plane.
This ground plane should cover a minimum of the RF/power quadrant of the module, as shown in
the upper left area of
Figure 1, and should be interconnected to ground flooding on other layers
so that there are no ground loops between module pads. Ground vias should be provided under
or adjacent to each ground pad to create a low impedance ground. It is recommended to
minimize the number of top-layer I/O traces under the module to allow for as much ground plane
as possible. An example of a good ground structure and pad layout is shown in
solid grounding through via interconnect in
Figure 2.
Figure 1, and
Figure 2 – Example of solid flooding on layer 4 with via interconnect
GSM0408IG001 Page 14 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 20
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4.6.3. Thermal Relief
Because the ground plane acts as a large heat sink, it can affect the solder adhesion of the
module. A common method to reduce this effect is to use thermal relief around the pad in
question. However, great care must be taken when using thermal relief for high current or high
frequency applications. Insufficient grounding caused by narrow elongated thermals will result in
poor thermal transfer, constricted ground current return, and inadequate RF grounding. Poor RF
grounding may be manifested by excessive radiated or conducted harmonics.
example of host board grounding in the RF/power area of the module. Recommended design
parameters are 10 mils (.254 mm) copper flood clearance and 15 mils (.381 mm) thermal spoke
width. A grounding via should be located either directly adjacent to the pad if using thru-hole vias
or can optionally be located in the pad for blind via design. For blind via technology with via-inpad, the vias must be filled and plated over to remove the dimple. See section ??? for process
specifications with regard to module attachment to the host.
Figure 3 shows an
Figure 3 – Example of thermal relief and Vbat feed
4.6.4. Antenna and RF Signal Trace
The PCB trace that feeds the RF output port must be designed for a 50 ohm characteristic
impedance. It should be coplanar, or routed into internal layers to keep the top layer continuous
around and underneath the Enabler module. Ample ground vias should be provided around the
RF trace and launch pad. Special care should be taken when the RF trace changes layers
between the module and the antenna port or connector, as such transitions can introduce an
additional mismatch and degrade system sensitivity. If possible, keep I/O and power traces away
from the RF port. This includes traces running parallel or orthogonal to it. The designer must pay
close attention to the thickness of the dielectric beneath the signal pad and trace. Most PCB
manufacturers can adjust the trace width to maintain 50 ohms impedance if the traces are
identified and instructions are included on the FAB drawing. This service is typically provided at
no or minimal additional cost.
For minimum RF emissions due to the fundamental frequency of operation, the Enabler module
works best with an antenna load that has a VSWR of 1.5:1 or better. The antenna should not
have gain at the harmonic frequencies; otherwise, the conducted harmonics could be amplified to
a point where the product no longer passes type approval. However, for applications where
antenna quality is less than ideal, it is recommended to have a low pass filter (Pi structure with
N=3) in the RF path to the antenna. This is a secondary plan should there be a need to lower
harmonic levels at frequencies above the PCS band. The pad structure may also be used to
GSM0408IG001 Page 15 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 21
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
match the antenna load impedance, if required. If it is not needed, a capacitor of low reactance
may be used to bridge the Pi structure.
4.6.5. Vbat Input
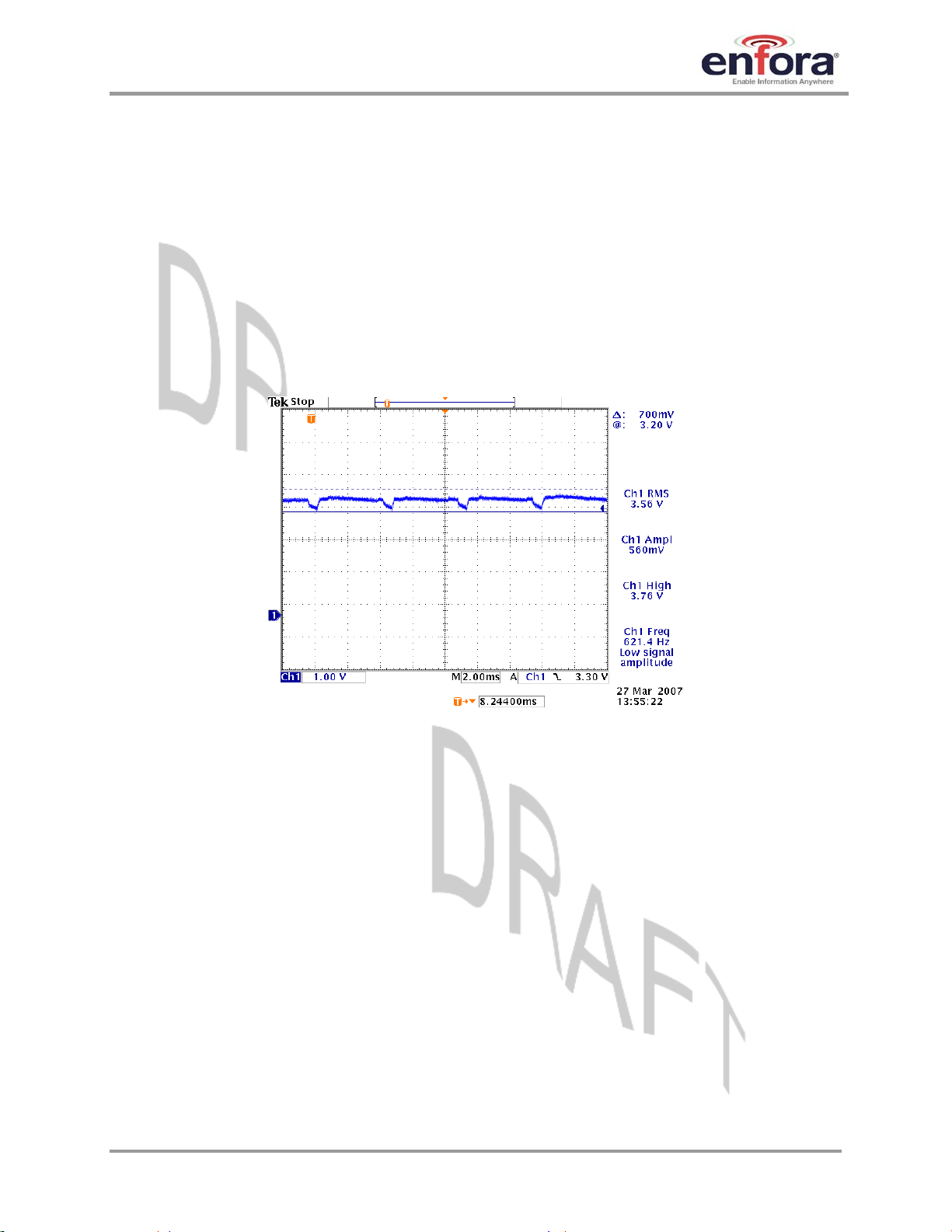
The Enabler Vbat input can have a relative high current draw that can fluctuate rapidly, especially
when transmitting at max power and burst mode. The Vbat interface must be designed to provide
the required instantaneous voltage and current with minimal voltage droop. This includes both
sufficient bulk decoupling capacitance as well as adequate layout provisions.
When routing connections to the Enabler Vbat pads, it would seem reasonable to use traces of
the same width as the pads. However, such traces will not have sufficient copper. The use of
narrow traces to connect the Vbat pads to the source voltage can act like a high impedance and
cause a significant voltage droop when higher currents are required, as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4 - Example of Vbat Voltage Droop
If Vbat drops too low, the Enabler module will reset. To minimize the trace loss, it is
recommended to use a larger trace that spans several pads as shown in
Figure 3. The layout
should provide sufficient trace width over the entire route from the module to the source of the
Vbat voltage. Any transitions between layers for this trace should utilize multiple vias.
Since even the best layout will have some impedance from the source to the Enabler module,
sufficient bulk decoupling capacitance is required at the Vbat input to the module. It is suggested
to use at least two 1000 uF low ESR tantalum capacitors located adjacent to the module Vbat
pads. Any thermal relief used on these capacitors should comply with the information given
above in order to provide the lowest impedance possible. The design should include multiple vias
to the internal ground plane, placed close to the capacitors, as grounding of these capacitors is
critical.
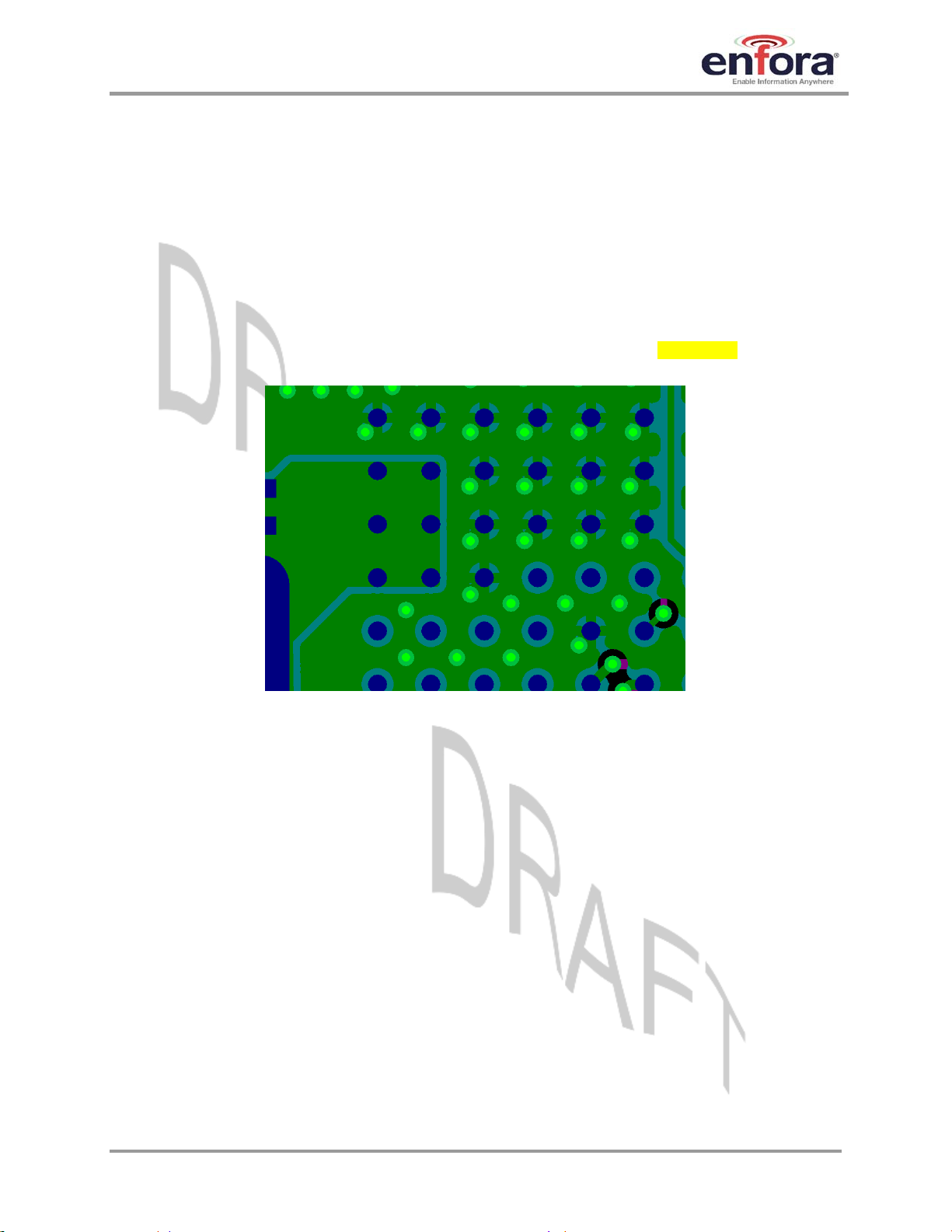
4.6.6. I/O Routing and Fanout
The Enabler IIIG BGA interface is grouped by functions, as shown in the BGA map of section
5.5.1. Each functional group should be fanned out and routed as a group from the module. It is
preferred to route as much of the I/O nets as possible on internal layers in order to maintain
continuous grounding. Pad spacing on the module allows for flexibility in placing vias adjacent to
the pads.
Figure 5 and Figure 6 are both examples of functional grouping and fanout. Note that
GSM0408IG001 Page 16 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 22
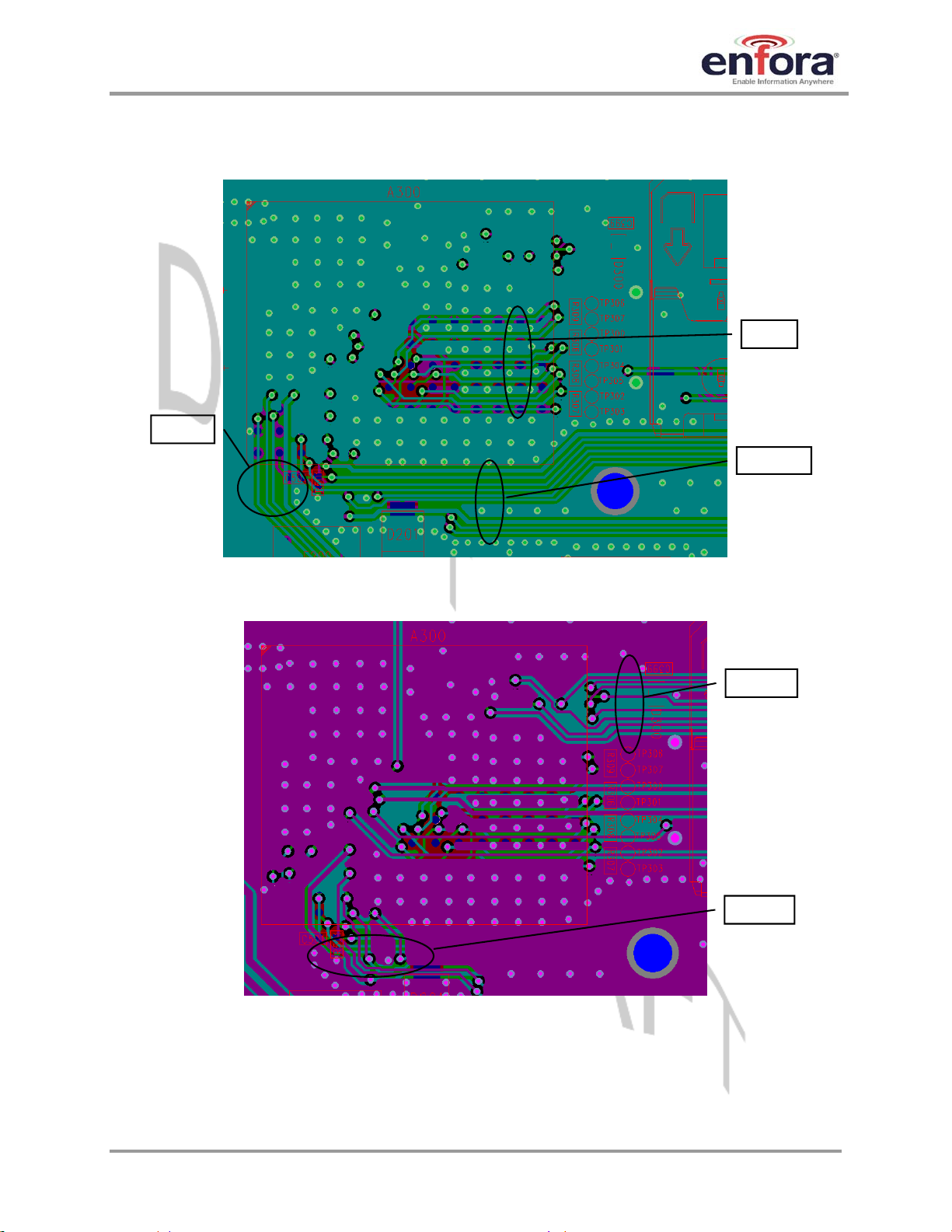
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
A
Modem Integration Guide
I/O is routed down/away from the power/RF area of the module in order to minimize interference.
Recommended audio I/O design is detailed in section
USB
4.6.7 below.
I2S
Figure 5 – Example of layer 2 routing fanout
Figure 6 – Example of layer 3 UART and audio fanout
UART
udio
GSM0408IG001 Page 17 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 23

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4.6.7. Audio Reference Design
The audio quality is very dependent on the circuit design and layout. As an aid to obtaining good
audio quality, a reference design has been included below. It has been proven to provide good
performance on the SDK module.
4.6.7.1. Audio Schematic
Figure 8 and Figure 8 show examples for both handset and headset audio connections. The
47pF capacitors should be placed as close as possible to the interface connector in order to
filter the 217Hz noise inherent in GSM mobile devices. All capacitors are low ESR ceramic;
small values are NP0, while larger values are X7R or X5R. Resistors are all 5% thick film
chip. The connector part numbers shown in the last line of each callout are available from
CUI Inc.
Figure 7– Handset Audio Reference Schematic
GSM0408IG001 Page 18 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 24
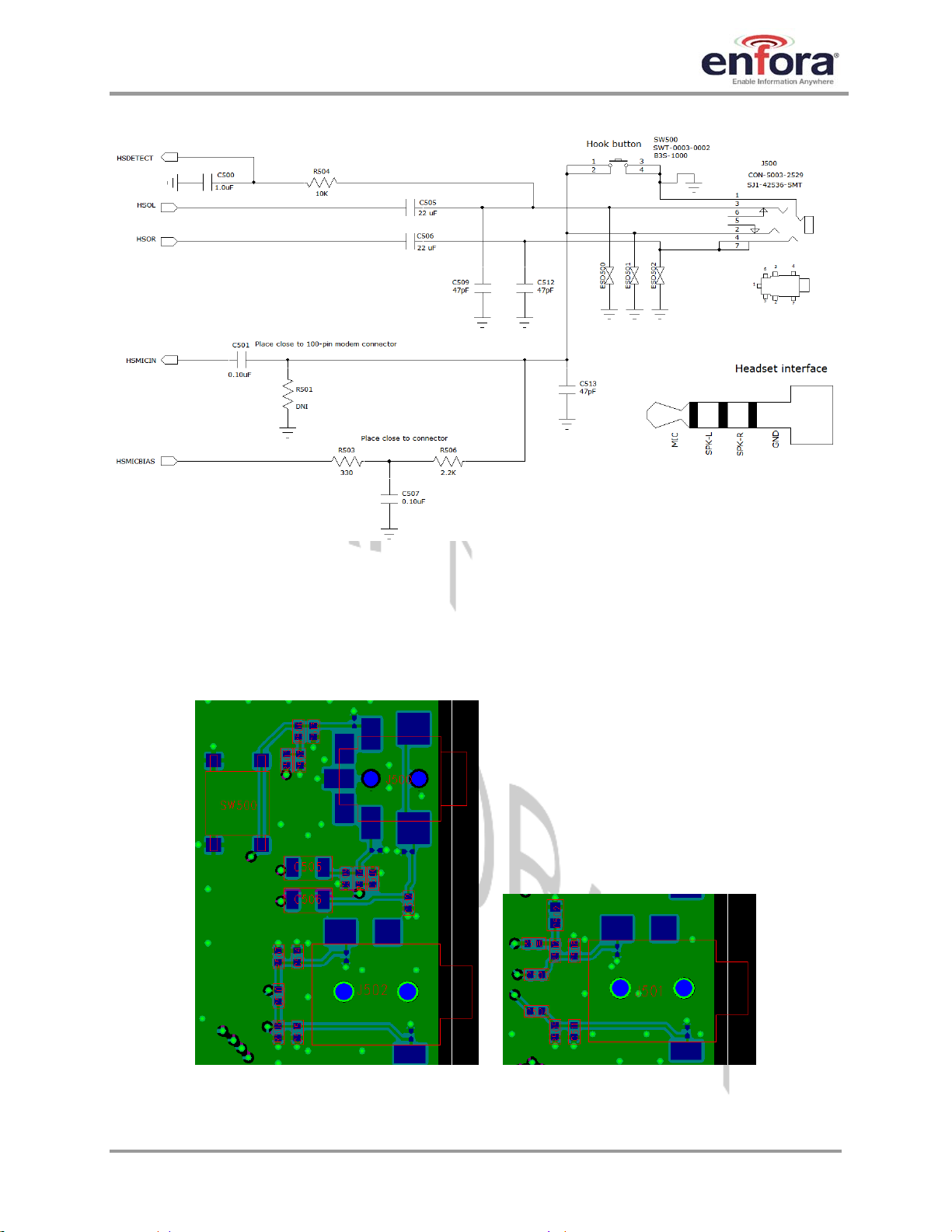
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Figure 8 – Headset Audio Reference Schematic
4.6.7.2. Audio Layout
Layout plots for the audio interface section of the SDK are shown below in
lines should be routed from the module on internal layers in groups with differential pairs
routed together. Care should be taken to isolate the audio signals from Vbat, higher speed
digital I/O, and RF. An audio routing example is shown in
Figure 5.
Figure 9. Audio
Figure 9 – Audio interface layout examples
GSM0408IG001 Page 19 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 25

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
4.7. BGA Handling and Soldering Guidelines
The guidelines presented in IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020C for handling, preparation, and reflow of leadfree devices should be applied to the Enabler IIIG BGA module. Care should be taken to minimize
module moisture exposure before reflow. The module is classified as a Type 3 MSL (moisture
sensitivity level).
Additional information forthcoming
GSM0408IG001 Page 20 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 26

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5. Technical Specifications
5.1. Enabler IIIG BGA Module Block Diagram
VBAT
32 Mbit flash/16 Mbit pSRAM
SIM Detect
BGA Pads (167)
Remote SIM (4)
GPIO (8)
Camera (6)
Serial I/O, 9 wire
I2S Digital Audio (8)
SPI (6)
JTAG (6)
MCSI (4)
I2C
Keyboard (10)
LCD (14)
Digital Signal Processing
GSM0408 GSM/GPRS
Memory
(max 128 Mb/64 Mb)
Locosto
(ARM7) & Digital RF
Transceiver
System on Chip
Pwr Rails
I/O
Clock
26 MHz
XTL
APC
TSPACT (4)
LB TX
HB TX
RX-GSM
RX-EGSM
RX-1800
RX-1900
RF Power
Amplifer
+ Switch
Module
2/22/08
8ohm Speaker w/Bias (5)
Stereo Headset w/Mic (4)
LED Drv (Paging, Backlight) (3)
PWRON
ADC In
Buffered 32KHz
Backup Battery
Reset
Microphone w/Bias (3)
Ear Speaker (2)
Aux Stereo Audio In (2)
Battery Charger (10)
USB OTG (4)
Vibrator Drv
32 kHz
XTL
Analog/Aux Processing &
Power Mgmt
(Triton Lite)
RF
Figure 10 - Enabler IIIG BGA Module Block Diagram
GSM0408IG001 Page 21 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 27

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.2. Detailed Product Specifications
Physical Dimensions and Weight
Size (L x W x H)
Weight
28.0 mm x 24.0 mm x 2.50 mm
Without SIM Connector –
< 3.6 grams
With SIM Connector (no SIM inserted) –
< 4.2 grams
Climatic: Operational
GSM Compliant temperature
Operating temperature
-20°C to +60°C
-30°C to +70°C
Relative humidity 5 - 95%
Air pressure (altitude) 70 kPa to 106 kPa (-400 m to 3000 m)
Climatic: Storage and Transportation
Duration 24 months
Ambient temperature -40°C to +85°C
Relative humidity
5% to 95%, non condensing (at 40C)
Thermal shock -50°C to +23°C, +70°C to +23°C; < 5 min
Altitude -400 m to 15,000 m
Mechanical: Operational
Operational vibration, sinusoidal
Operational vibration, random
2 3
0.1 m
/s , 2 to 200 Hz
2
, 9 to 350 Hz 3.0 mm disp, 2 to 9 Hz; 1 m/s
Mechanical: Storage and Transportation
Transportation vibration, packaged ASTM D999
Drop, packaged ASTM D775 method A, 10 drops
Shock, un-packaged 150 m/s2 , 11 ms, half-sine per IEC 68-2-27
Drop, un-packaged 4-inch drop per Bellcore GR-63-CORE
Mechanical: Proposed Standards
Transportation ETSI Standard ETS 300 019-1-2 Class 2.3
Transportation
Operational ETSI Standard ETS 300 019-1-3 Class 3.1
Operational
Storage ETSI Standard ETS 300 019-1-1 Class 1.2
Storage
Electromagnetic Emissions
Radiated spurious FCC Part 22 & 24 / Part 15 Class \ B3GPP TS
51.010-1 Section 12.2
EN 55022 Class B
GSM0408IG001 Page 22 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 28

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.3. Operating Power
The module requires an input voltage of 3.3 Vdc to 4.5 Vdc.
5.3.1. Typical Input Current
Test Conditions: Typical Results @ 3.8 V, 20 deg C, with 2000 μF at connector input on V
BAT
and
RF terminated into a 50 Ω resistive load.
GSM Operation Input Current
Band Mode Low Nom/Avg High/Peak Units
1900 21 204 1180 mA
1800 21 215 1280 mA
900 21 248 1600 mA
850
ALL Idle 600uA 2.4mA 154mA
N/A Shutdown 53uA
1 RX/1 TX, Full Power
21 250 1600 mA
GPRS Operation Input Current
Band Mode Low Nom/Avg High/Peak Units
1900
1800
900
850
ALL Idle 600uA 2.4mA 140mA
N/A Shutdown 53uA
4 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 235 1180 mA
2 RX/2TX, Full Power 15 340 1180 mA
1 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 192 1180 mA
4 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 242 1280 mA
2 RX/2TX, Full Power 15 354 1280 mA
1 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 201 1280 mA
4 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 272 1600 mA
2 RX/2TX, Full Power 15 422 1600 mA
1 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 232 1600 mA
4 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 268 1600 mA
2 RX/2TX, Full Power 15 420 1600 mA
1 RX/1TX, Full Power 15 231 1600 mA
5.3.2. GSM Transmit Power
Enfora Enabler IIIG
Power Class Transmit Power
BGA module
1900 MHz
1800 MHz
850 MHz
900 MHz
GSM Power Class 1 1-W conducted power maximum (30
dBm +/- 2 dB), measured at the
antenna port
GSM Power Class 4 2-W conducted power maximum (33
dBm +/- 2 dB), measured at the
antenna port
GSM0408IG001 Page 23 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 29

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.3.3. GSM Receiver Sensitivity
Enfora Enabler IIIG
BGA module
1900 MHz
1800 MHz
900 MHz
850 MHz
5.4. Physical Interfaces
5.4.1. Module
Sensitivity Mode
-106 dBm (typical)
-106 dBm (typical)
GPRS Coding Scheme 1 (CS1)
GPRS Coding Scheme 1 (CS1)
Figure 11 - Module Dimensions
All dimensions are in millimeters (mm).
Shield cosmetics may change.
5.4.2. Host PCB Footprint
The recommend footprint for the host PCB is shown in
Figure 12. Note that the pad dimensions
given are for a solder mask defined pad, in order to avoid irregularities due to flooding, thermals,
and routes.
GSM0408IG001 Page 24 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 30

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Figure 12 - Host PCB Footprint
(Dimensions are in millimeters.)
5.5. Electrical Connections
Pad Signal Name I/O Description Alternate Description/Function
A1 ANT I/O RF Port to Antenna
A2 GND I GND
A3 GND I GND
A4 GND I GND
A5 GND I GND
A6 GND I GND
A7 SIM_IO I/O SIM Data
A8 GND I GND
A9 VRSIM O SIM Power
A10 GPIO-2 I/O GPIO-2 *USB_BOOT: Input @ boot, I/O after
boot. Must be Tri-State or Low at boot.
A11 CLK32K_BUF O Buffered 32 kHz clock
A12 GND I GND
A13 GPIO-5 I/O GPIO-5
A14 GND I GND
GSM0408IG001 Page 25 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 31

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Pad Signal Name I/O Description Alternate Description/Function
B1 GND I GND
B2 GND I GND
B3 GND I GND
B4 GND I GND
B5 GND I GND
B6 GND I GND
B7 SIM_CLK O SIM Clock
B8 SIM_RST O SIM Reset
B9 GND I GND
B10 GND I GND
B11 UART_RX O UART Serial Data Output
B12 UART_DTR I UART Data Terminal Ready
B13** TRSTN I JTAG Test Reset Input
B14* I2C_2_SCL I/O I C Serial Clock
C1 VBAT I Main Power Input
C2 VBAT I Main Power Input
C3 GND I GND
C4 GND I GND
C5 GND I GND
C6 GND I GND
C7 TSPACT_12 O Timed Gen Purpose Output
C8* KBR3 I Keyboard Input
C9 GPIO-1 I/O GPIO-1
C10 UART_RING O UART Ring Indicator
C11 UART_DCD O UART DCD Output
C12 UART_CTS O UART CTS Output
C13 UART_RTS I UART RTS Input
C14* I2C_2_SDA I/O I2C Serial Data
D1 VBAT I Main Power Input
D2 VBAT I Main Power Input
D3 GND I GND
D4 GND I GND
D5 GND I GND
D6 GND I GND
D7 KBC0 I Keyboard Input
D8 GND I GND
D9 GND I GND
D10 GND I GND
D11 UART_TX I UART Serial Data Input
D12 UART_DSR O UART Data Set Ready
D13 GPIO-10 I/O GPIO-10 *MCSI_FSYNC: Frame Synchronization
D14 GPIO-12 I/O GPIO-12 *MCSI_RX: Serial data input
E1 VBAT I Main power input
E2 VBAT I Main power input
2
I/O
GSM0408IG001 Page 26 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 32

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Pad Signal Name I/O Description Alternate Description/Function
E3* ADCIN3 I ADCIN3 BATT_TEMP: Battery Temperature Input
E4* LED_A I LED Current Sink
E5* LED_C I LED Current Sink
E6* KBC2 I Keyboard Input
E7* KBR0 I Keyboard Input
E8 GPIO-19 I/O GPIO-19 *KBR4: Keyboard Input
E9 GND I GND
E10 GND I GND
E11 GPIO-17 I/O GPIO-17 *SPI_\CS1: MSSPI Chip Select 1 Output
E12 GPIO-8 I/O GPIO-8
E13 GPIO-11 I/O GPIO-11 *MCSI_TX: Serial Data Output
E14 GPIO-9 I/O GPIO-9 *MCSI_CLK: Serial Clock I/O
F1* ICTLUSB1 O USB External Pass Transistor Control
F2* ICTLUSB2 O USB External Pass Transistor Control
F3* BM_PRECH I Pre-Charge Boot Mode
F4* LED_B I LED Current Sink
F5* ADCIN2 I ADCIN2 BATT_TYPE: Battery Type
Module Reset; Must be driven by open collector/drain. F6 ON_\OFF I
F7* KBC1 I Keyboard Input
F8* KBR1 I Keyboard Input
F9 GND I GND
F10 GND I GND
F11 GPIO-14 I/O GPIO-14 *SPI_MISO: MSSPI Master-In Slave-Out
F12 GPIO-7 I/O GPIO-7
F13 No Connect Do not connect. Leave open.
F14 GPIO-3 I/O GPIO-3
G1* PCHGAC O AC Pre-Charge Output Current
G2* ICTLAC1 O AC External Pass-Transistor Control
G3* ICTLAC2 O AC External Pass-Transistor Control
G4* VRWLED O PWM Drive for LED Control
G5 VRIO O 1.8 V Interface Voltage
G6 VBACKUP I Battery Backup Input
G7* KBC3 I Keyboard Input
G8* KBR2 I Keyboard Input
G9** \EMU0 I/O JTAG Test Emulation 0
G10 GND I GND
G11 GPIO-13 I/O GPIO-13 *SPI_CLK: MSSPI Serial Clock
G12 GPIO-18 I/O GPIO-18 *SPI_\CS2: MSSPI Chip Select 2 Output
G13 GPIO-6 I/O GPIO-6
G14* CAM_RST I/O Camera Reset
H1* PCHGUSB O Car-Kit Pre-Charge Output Current
H2* VAC I Battery Charger Input Power Supply
H3* VBATS I Charge Current Sense
H4 HSDETECT I Headset Detect
GSM0408IG001 Page 27 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 33

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Pad Signal Name I/O Description Alternate Description/Function
H5 SIMDTC I SIM Detect
H6 CDO O I S data out from Locosto (slave mode; mode only supported when used with onboard
H7 CSCLK I I2S clock into Locosto (slave mode; mode only supported when used with onboard
H8 CDI I I2S data into Locosto (slave mode; mode only supported when used with onboard
H9 GPIO-20 I/O GPIO-20 *KBC4: Keyboard Input
H10* LCD_R\W I/O 6800 Mode: Read/write Control Pin.
H11 GPIO-16 I/O GPIO-16 *SPI_\CS0: MSSPI Chip Select 0
H12 GPIO-15 I/O GPIO-15 *SPI_MOSI: MSSPI Master-Out Slave-In
H13** TDO O JTAG Test Data Out
H14 GND I GND
J1* VCCS I Charge Current Sense
J2* USB_DP I/O USB Data I/O Positive
J4 MICBIAS O Microphone Bias Voltage
J5 HSMICBIAS O Headset Microphone bias voltage
J6 I2S_SDR I I S Serial-Data into Analog Processor (master mode); Must be connected to H6
J7 I2S_SCK O I
J8 CSYNC I I S Sync Into Base-Band Processor (slave mode; mode only supported when used with
J9 GPIO-4 I/O GPIO-4
J10* LCD_DATA3 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
J11* CCP_CKN I Serial Camera Clock, Negative.
J12* CCP_DTP I Serial Camera Data, Positive.
J13* CAM PWR DN I/O Camera Power Down
J14** TDI I JTAG Test Data In
K1* ID_USB I/O USB Connector Identification
K2* USB_DM I/O USB Data I/O Negative
K3 ADCIN I ADC Input
K4 MICIN I Negative Microphone input
K5* SPKPA O
K6* SPKNA O
K7 I2S_SDX O I
K8 I2S_WS O I
K9 \PWON I Module Power Control
K10* LCD_DATA0 I/O LCD interface I/O data bus
2
codec); Must be connected to J6 (I2S_SDR) on Host PCB if external codec is not
used.
codec); Must be connected to J7 (I2S_SCK) on Host PCB if external codec is not
used.
codec); Must be connected to K7 (I2S_SDX) on Host PCB if external codec is not
used.
High = Read; Low = Write.
8086 Mode: Write Enable Clock.
High = Read; Low = Write
Send data to the LCD controller on the RnW falling edge. Can be used as GPIO (by
default).
USB Bus Power; Must be tied to ground if not used. J3* VBUS I
2
(CDO) on Host PCB if external codec is not used.
2
S Serial-Clock from Analog Processor (master mode); Must be connected to H7
(CSCLK) on Host PCB if external codec is not used.
2
onboard codec); Must be connected to K8 (I2S_WS) on Host PCB if external codec
is not used.
8 Ω speaker amplifier positive output (A)
8 Ω speaker amplifier negative output (A)
2
S serial data from Triton (master mode); Must be connected to H8 (CDI) on Host
PCB if external codec is not used.
2
S sync from Triton (master mode); Must be connected to J8 (CSYNC) on Host PCB
if external codec is not used.
GSM0408IG001 Page 28 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 34

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Pad Signal Name I/O Description Alternate Description/Function
K11* LCD_RS I/O LCD interface register selection (by default), used also as GPIO;
K12* CCP_DTN I Serial camera data negative
K13* CCP_CKP I Serial camera clock positive
K14** TCK I JTAG Test Clock
L1 GND I GND
L2* FML I FM audio in - left
L3 HSOR O Headset Output - Right
L4 MICIP I Positive Microphone Input
L5* SPKPD O
L6* SPKND O
L7* SPKVDD I Speaker driver bias
L8* VIBDR O Vibrator driver
L9* LCD_CS0 O LCD interface chip-select for chip 0. Data I/O are available when low. When high, data
8 Ω speaker amplifier positive output (D)
8 Ω speaker amplifier negative output (D)
I/O are in a high impedance state. Bits shared with the GPIO module and used as
GPIO by default. These bits are used as outputs for LCD interface.
L10* LCD_CS1 O LCD interface chip-select for chip 1. Data I/O are available when low. When high, data
L11* LCD_DATA5 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
L12* LCD_DATA2 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
L14** TMS I JTAG Test Mode Select
M1* AUXI_FMR I Auxiliary audio/FM Input - Right
M2 HSMIC I Headset microphone input
M3 HSOL O Headset Output - Left
M4 EARN O Handset Output - Negative
M5 EARP O Handset Output - Positive
M6 HSOVMID O Headset Amplifier Pseudo-Ground
M7 GND I GND
M8* LCD_\RST O LCD Controller Reset
M9* LCD_STB I/O
M10* LCD_DATA1 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
M11* LCD_DATA6 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
M12* LCD_DATA4 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
M13* LCD_DATA7 I/O LCD Interface I/O Data Bus
M14 GND I GND
I/O are in a high impedance state. Bits shared with the GPIO module and used as
GPIO by default. These bits are used as outputs for LCD interface.
6800 Mode: Strobe enable (by default). Read data from the LCD controller on the
strobe falling edge. Send data to the LCD controller on the strobe rising edge.
8086 Mode: Read Enable (by default); Read data from the LCD controller on the strobe
rising edge. Can be used as GPIO.
Types I = Input, O = Output, P = Power, G = Ground
* Note 1: For hardware reference only. The current v ersion of gen eric firmware do es not support the
use of this pad/function. Contact Enfora for further details.
**Note 2: For Enfora Use ONLY
GSM0408IG001 Page 29 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 35

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.5.1. BGA Map
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
M
K
H
G
GND
LCD_
LCD_
LCD_
DATA7
DATA4
L
J
F
TMS
TCK
TDI
GND
RST
CAM
GPIO-3
LCD_
No-Ball
CKP
CCP_
CCP_
CCP_
DOWN
CAM PWR
TDO
GPIO-6
GPIO
(future)
DATA2
DTN
DTP
GPIO-15
GPIO-18
GPIO-7
DATA6
LCD_
DATA5
RS
LCD_
CKN
CCP_
GPIO-16
GPIO-13
GPIO-14
LCD_
LCD_
LCD_
LCD_
LCD_
GND
GND
DATA1
CS1
DATA0
DATA3
R\W
STB
LCD_
CS0
LCD_
\PWON
GPIO-4
GPIO-20
\EMU0
GND
\RST
LCD_
VIBDR
WS
I2S_
CSYNC
CDI
KBR2
KBR1
GND
SPKVDD
I2S_
SDX
I2S_
SCK
CSCLK
KBC3
KBC1
HSOVMID
SPKND
SPKNA
I2S_
SDR
CDO
UP
VBACK
ON_
\OFF
EARP
SPKPD
SPKPA
BIAS
HSMIC
SIMDTC
VRIO
ADCIN2
EARN
MICIP
MICIN
MIC
BIAS
HS
DETECT
LED
VRW
LED_B
HSOL
HSOR
ADCIN
VBUS
VBATS
ICTLAC2
BM_
PRECH
HSMIC
FML
DM
USB_
DP
USB_
VAC
ICTLAC1
ICTL
USB2
FMR
AUXI_
GND
ID_
USB
VCCS
USB
PCHG
PCHGAC
ICTL
USB1
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
GPIO-9
GPIO-12
SDA
I2C_2_
UART_
SCL
I2C_2_
GND
14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
GPIO-11
GPIO-10
RTS
TRSTN
GPIO-5
GPIO-8
DSR
UART_
CTS
UART_
DTR
UART_
GND
UART_
UART_
UART_
CLK32K_
GPIO-17
TX
DCD
UART_
RX
BUF
GND
GND
RING
GND
GPIO-2
GND
GND
GPIO-1
GND
VRSIM
GPIO-19
GND
KBR3
RST
SIM_
GND
KBR0
KBC0
_12
TSPACT
CLK
SIM_
IO
SIM_
KBC2
GND
GND
GND
GND
LED_C
GND
GND
GND
GND
LED_A
GND
GND
GND
GND
ADCIN3
GND
GND
GND
GND
VBAT
VBAT
VBAT
GND
GND
VBAT
VBAT
VBAT
GND
ANT
E
D
C
B
A
GSM0408IG001 Page 30 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 36

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.6. Circuit Protection
Other than very low level ESD protection within the module’s integrated circuits, the module does
not have any protection against ESD events or other excursions that exceed the specified
operating parameters.
Generally, ESD protection (typically TVS/Transzorb devices) should be added to all signals that
leave the host board. This includes V
Series resistors (typically 47 Ω) can also be added in series with data lines to limit the peak
current during a voltage excursion.
NOTE: DO NOT ADD SERIES RESISTANCE TO THE SIM ELECTRICAL LINES.
Minimum ESD Protection Levels ESD/Input Voltage
Pad #’s ESD Test Method Min Nom/
All I/O, other
than
VBUS/PWR
All VBUS/PWR)
RF Antenna, A1 IEC 61000-4-2 8000 V
Human Body Model
EIA/JEDEC22-A114-A
Charge Device Model
EIA/JEDEC22-C101-A
Human Body Model EIA/JEDEC22A114-A
Charge Device Model EIA/JEDEC22C101-A
/V .
BAT CC
High/
Avg
500 V
200 V
2000 V
500 V
Peak
Units
Caution – It is the Integrator’s responsibility to protect
the Enabler IIIG BGA module from electrical
disturbances and excursions that exceed the specified
operating parameters.
GSM0408IG001 Page 31 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 37

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7. Pad Signal Descriptions and Functions
Please note that the following descriptions are intended to
provide hardware-level definitions. In some cases, specific
lines will have no firmware functionality implemented.
Information for each hardware-specific feature will be noted
in the appropriate section.
5.7.1. Module Power (Pads C1, C2, D1, D2, E1, E2)
The module uses a single voltage source of VCC=+3.3V to 4.5V. (The exact values of the uplink
currents are shown in the tables in section
V
BAT
Main Battery Supply
Peak Current
Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Voltage In Regulation 3.3 4.5 Vdc
1000 μF on Host at module
interface
5.3.1.)
TBD mA
The uplink burst will cause strong ripple on the voltage
lines and should be effectively filtered. It is recommended
that 1000 to 2000 F of capacitance be placed as close to
the modem power input pads as possible.
It should be noted that the input voltage level should not
drop below the minimum voltage rating under any
circumstances, especially during the uplink burst period.
GSM0408IG001 Page 32 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 38

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.2. Antenna (Pad A1)
The module has one RF antenna pad on the module. The connection is for the GSM section of
the module.
5.7.3. Reset Signal (Pad F6, also known as ON_\OFF)
The Reset signal is used to force the modem to start at a known state. When the Reset is pulled
low the modem will immediately suspend any function and will not exit the reset state until the
Reset signal is released to be pulled high. Once the transition from low to high is complete, the
modem will boot. The Reset signal is falling edge triggered, so the reset function is set
immediately when the signal is pulled low.
When using Reset, it will immediately detach the connection from the GSM network, which is not
considered ideal. Typically during a normal shutdown, the modem will issue a detach request to
the network to indicate that it is being removed. Reset should be used during network operations
only when there is no response from the module.
Controlling the Reset signal
must only be preformed by an open collector/open drain device.
Driving the Reset signal high will interfere with the normal operation of the modem power on/off
sequences. Power sequencing cannot be guaranteed if Reset is being driven high by an external
device. If driving from an external microprocessor, the reset can be controlled by driving the
control pin low as an output, then change the pin control to be an input. This will satisfy the high
impedance requirement.
Parameter Parameter/Conditions MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
IL
V
IH
I
PU
I
IL
Reset Pulse
Input Voltage – Low or float 0.58 Vdc
Input Voltage – High 1.36 1.95 Vdc
Internal Pull-Up Resistor -40 -31 -15
μA
Current sink -2.0 mA
10 mS
Duration
GSM0408IG001 Page 33 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 39

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.4. Power Control (Pad K9) (PWR_CTL)
The input is equivalent to a “phone ON-button”. A falling-edge on this Active-Low input will
switch-ON the module or switch-OFF the module after a delay
resistor internal to the module. This input can be left grounded if the “RTC Sleep Function” is not
required. If RTC Sleep is required, then the PWR_CTL line must be floated to allow the internal
resistor to pull the line high. See section 6.6.9 for more info on the RTC.
Controlling the Power Control signal must only be performed by an open collector/open drain
device. Driving the Power Control signal high may interfere with the normal operation of the
modem. If driving from an external microprocessor, the Power Control can be controlled by
driving the control pin low as an output, then change the microprocessor’s pin control to be an
input (this will satisfy the high impedance requirement).
*. This input has a “weak pull-up”
*The OFF Delay is controlled by the AT$OFFDLY
command. A value of 0 disables the PWR_CTL line from
turning the module off. 0 is the default value.
To enable the module to switch-OFF via PWR_CTL you
must set AT$OFFDLY to a value other than 0. The valid
range is 100 to 1000 milliseconds.
Turning ON the Enabler IIIG BGA
Pulling the PWR_CTL line on the module LOW for at least 50mS (after Vbat is applied and
stabilized) is required to turn it ON. Section
Do not use a pull-up resistor on the PWR_CTL line since the line is pulled up internal to the
modem.
Turning OFF the Enabler IIIG BGA
The module can be turned off by either a low pulse on the PWR_CTL line, or by a software
command (AT$OFF, see AT guide for further details). Section
provide the signal.
0 describes various ways to provide the signal.
0 describes various ways to
GSM0408IG001 Page 34 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 40

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Using the Power Control Signal
Typical use powering module on/off with a switch:
Figure 13 – Power Control Switch
Modem
VBAT
PWR_CTL
Float
RESET
Figure 14 – Typical connection of PWR_CTL to modem:
Figure 15 – Typical use controlling PWR_CTL from microcontroller:
Figure 16 shows a typical connection to the module in a machine-to-machine application using the external
PWR_CTL signal, when there is not an external processor controlling the power on/off states. The RTC deep
sleep functions will
Sleep” mode. Either the RESET pad must be toggled (as described in section
NOT function since the PWR_CTL pad is tied low, the processor will never stay in a “RTC
5.7.3), or power (VBAT) must be
cycled to reset the module.
GSM0408IG001 Page 35 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 41

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Modem
VBAT
PWR_CTL
Float
RESET
Figure 16 - External Power Control Signal (no external processor)
Figure 17 shows a typical connection from an external processor to the module, using the external PWR_CTL
signal. The module can be powered on by using the PWR_CTL signal, and reset with the RESET signal.
When using PWR_CTL, the I/O or serial lines can be at any voltage state desired. It is recommended that the
I/O and serial lines be tri-stated or set low when the module is shutdown for an extended period of time to
prevent any leakage current from the processor to the modem.
CPU
Open drain, or Tri-State I/O
Open drain, or Tri-State I/O
VBAT
GPIO
SERIAL
PWR_CTL
RESET
Modem
Figure 17 - Power Control Signal (using external processor)
Parameter Parameter/Conditions MIN TYP MAX UNIT
V
IL
V
IH
I
PU
I
IL
Input Voltage – Low or float 0.3 x V
Input Voltage – High 0.7 x V
BAT
1.95 Vdc
Internal Pull-Up Resistor -40 -31 -15
BAT
Vdc
μA
Current sink -2.0 mA
ON Pulse Duration 10 50 mS
OFF Pulse Duration Minimum is programmable
10 100 5000 mS
(AT$OFFDLY)
Boot time Time to boot from power on
1.1 Sec
to command prompt
GSM0408IG001 Page 36 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 42

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.5. Level Translation Reference Power (Pad G5)
To be used as a voltage reference source ONLY. Do not connect current loads to this pad. This pad
must be decoupled to ground with at least a 0.1 μF capacitor at the output. Noise induced on this pad
will affect the performance of the baseband.
Low Power Mode is entered when RTCWAKE is used to power down the modem with just the RTC
running.
V I/O
R
Output voltage V
OUT
Rated output current I
Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
ON mode
LOW POWER mode
ON mode
OUT
LOW POWER mode
1.65
1.65
1.8
1.8
20
1.95
1.95
0.5
5.7.6. USB (Pads J2, J3, K1, K2)
Pad Name Pad
Number
Signal
Direction
Description
USB_VBUS J3 In 5 V tolerant power Supply VBUS line;
Used only as a USB sense, not for powering the
module. (optional connection)
USB_DP J2 I/O 5 V tolerant USB differential positive data pin
USB_DM K2 I/O 5 V tolerant USB differential negative data pin
ID_USB K1 I/O 5 V tolerant ID line, it defines the type of device
connected to the phone’s USB port;
And also the default state (host / device) at the
cable connection;
The transceiver senses the voltage of this pin to
determine if the pin is either floating (typical),
grounded or resistively connected to ground (102
kΩ, 200 kΩ, 440 kΩ);
This is for Enfora Debug only
Vdc
mA
5V Tolerant Transceiver
USB Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Input Voltage 4.4 4.65 5.25 V
High (Driven) 2.8 3.3 3.6 Vdc Output voltage
Low 0.0 0.1 0.3 Vdc
Transceiver D+/Leakage Current
5.7.7. General Purpose Input/Output Interface
Each general-purpose signal may be selected as inputs or outputs. The GPIOs can be used
independently as a user-specified function, or may be used to provide modem control and status
signals. Several examples of modem control signals are: power shutdown command,
GSM0408IG001 Page 37 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
-2 2 A
Page 43

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
register/deregister on network command, and transmitter disable. Several examples of modem
status signals are: registration status and ready-for-power-down status to be used with power
shutdown command signal.
GPIO
number
Pad number Secondary
Fuction
GPIO 1 C9
GPIO 2 A10
GPIO 3 F14
GPIO 4 J9
GPIO 5 A13
GPIO 6 G13
GPIO 7 F12
GPIO 8 E12
GPIO 9 E14 MCSI_CLK
GPIO 10 D13 MCSI_FSYNC
GPIO 11 E13 MCSI_TX
GPIO 12 D14 MCSI_RX
GPIO 13 G11
GPIO 14 F11
GPIO 15 H12
GPIO 16 H11
GPIO 17 E11
GPIO 18 G12
GPIO 19 E8
GPIO 20 H9
I/O Lines Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
VIL Input Voltage – Low 0 0.60 Vdc
VIH Input Voltage – High 1.11 1.8 Vdc
VOL Output Voltage – Low 0.45 Vdc
VOH Output Voltage – High 1.26 Vdc
IOL / I
OH
Rated Output Current 4 mA
GSM0408IG001 Page 38 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 44

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
The below table shows the factory default modem GPIO configuration:
I/O
No
PU/PD
Enabled
PU/DN I/O
setting
PU/PD
capability
PU
Value
KOhm
PD
Value
KOhm
1 1 PU IN PU/PD 18 90 4
2 X X IN - - 8 10k
3 1 PD IN PD - 18 8
4 1 PU IN PU/PD - 90 4
5 1 PU IN PU/PD - 90 8
6 1 PU IN PU/PD - 90 4
7 1 PU IN PU/PD - 90 4
8 1 PU IN PU/PD - 90 8
9 1 PU IN PU 18 - 8
10 1 PU IN PU 18 - 8
11 1 PU IN PU 18 - 8
12 1 PU IN PU 18 - 8
13 1 PD IN PD - 18 8
14 1 PD IN PD - 18 8
15 1 PD IN PD - 18 8
16 1 PU IN PU/PD 90 90 8
17 1 PU IN PU/PD 90 90 8
18 1 PU IN PU 18 - 8
19 1 PU IN PU/PD 18 90 8
20 1 PU IN PU/PD 90 90 8
Factory Default Settings for I/O Pads, PU/PD Capability and Value of PU/PD Resistors.
5.7.8. RTC Sleep
Iout Notes
Pulldown
on
Modem
In this mode, the modem is off except for its Real-Time-Clock. When put into this mode, the modem
can wake itself up at a designated time/interval. See Section 4.10 of the Enabler III AT command
manual for details
GSM0408IG001 Page 39 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 45

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.9. Serial Interface
The pad naming for TX/RX/RTS/CTS/DTR/DSR is referenced as a DCE .The DTE device should
match their input pads to the Enfora outputs and visa-versa. Additionally, there are AT
commands that may need to be executed in order to ensure proper operation. See the chart
below.
NOTE: The UART interface on the Enabler IIIG BGA, as well as other I/O, is 1.8V logic.
It should not be directly connected to a higher voltage interface. The table below is a
reference of D connector pin numbers only.
9 way D
Connector
Pin Number
Signal Signal
Direction
Enfora
Pad
Number
1 Carrier Detect (CD) from DCE C11 AT&C
2 Receive Data (RD) from DCE B11
3 Transmit Data (TD) from DTE D11
4 Data Terminal Ready (DTR) from DTE B12 AT&D
5 Signal Ground both
6 Data Set Ready (DSR) from DCE D12
7 Request To Send (RTS) from DTE C13 AT+IFC
8 Clear To Send (CTS) from DCE C12 AT+IFC
9 Ring Indicator (RI) from DCE C10
The key features of the UART in the modem mode are as follows:
• 16C750 compatibility
• Baud rate from 300 bits/s up to 921600 Kbits/s, autobaud
• Configurable data format:
• Data bit: 5, 6, 7, or 8 bits
• Parity bit: even, odd, none
• Stop bit: 1, 1.5, 2 bit(s)
• Hardware flow control RTS/CTS
Enfora AT
Command
• Software flow control using XON/XOFF characters
Default settings are 8 data, 1 stop, no parity, and autobaud. DTR may be used to force the
modem into AT command mode from online data mode (See AT Command Document, command
AT&D). RTS and CTS may be used for hardware handshaking. DSR is always active (asserted
low) while the modem is on. RING may be used to alert the host to a variety of incoming calls.
For a minimal implementation, connect RxData and TxData to the COM port serial data lines
(through level translation if the interface is not 1.8V). Connect DTR and RTS on the host side of
the interface to GND, while leaving the corresponding lines on the module floating.
Ring Indicate (Pad C10)
The module is capable of using the Ring line to discern the type of incoming call. The function of
the Ring line depends on the type of the call received.
When the module is receiving a voice call, the Ring line goes low for 1 second and high for
another 2 seconds. Every 3 seconds the ring string is generated and sent over the Receive (Data
Out) (Rx) line. If there is a call in progress and call waiting is activated for a connected handset
GSM0408IG001 Page 40 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 46

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
g
g
g
g
g
Modem Integration Guide
or hands free device, Ring switches to ground in order to generate acoustic signals that indicate
the waiting call.
Ring
When a Fax or data call is received, Ring goes low and will remain low. Every 3 seconds a ring
string is generated and sent over the Receive (Data Out) (Rx) line.
Ring
1 second
RING Strin
2 seconds
1 second
RING Strin
3 seconds
2 seconds
3 seconds
RING Strin
RING Strin
When an incoming SMS is received , Ring indicate goes low for 1 second, then returns to a high
state. See below logic diagram.
Ring
1 second
URC
Figure 18 - Ring Indicate Timing
Serial I/O & Control Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
V
V
OL
V
OH
IOL / I
IL
IH
OH
Input Voltage – Low 0.54 Vdc
Input Voltage – High 1.26 1.95 Vdc
Output Voltage – Low 0.54 Vdc
Output Voltage – High 1.26 1.95 Vdc
Rated Output Current 2.0 mA
5.7.10. MCSI – Multi-Channel Serial Interface (Pads D13, D14, E13, E14)
This port is only available in Master mode and to be used for PCM digital audio. Below are the
settings for configuring it operation and the interface specification:
RING Strin
Digital Audio Configuration
The default settings for the digital audio are:
Mode = Master
MCSI_CLK = 520KHz
Word Size = 16 Bits
Sync Pulse = 8KHz
Frame mode = burst
Clock edge Sync = rising edge
GSM0408IG001 Page 41 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 47

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Configuring the MCSI for Digital Audio
The following two commands are required to set the unit up in digital audio mode:
AT$voicepth=2 This configures the EIII module to use digital audio instead of analog audio.
at$ioblks=0,1 This configures the I/O pads of the module to be used as the secondary
Do not alter the settings for these 4 pads manually (direction, pull up or alternate configuration) as
this will stop the MCSI port working for digital audio.
Data Format
The 16-bit word is sent MSB first. Data received is also MSB first. No other data manipulation is
done within the module.
Pad Name Pad Number Signal Direction Description
MCSI_RX D14 I Serial Data Input
MCSI_TX E13 O Serial Data Output
MCSI_CLK E14 IO Serial Clock I/O
MCSI_FSYNC D13 IO Frame Synchronization I/O
5.7.11. VBACKUP Input (Pad G6)
function which is the MCSI port. It automatically configures the direction of
the pads.
The backup battery can be recharged from the main battery. A programmable voltage regulator
powered by the main battery allows recharging the backup battery. The backup battery charge
starts when the following conditions are met:
Backup battery charge is enabled by a control bit:
• Main Battery voltage > Backup Battery voltage
• Main battery > 2.8 Vdc
Note: If the backup battery is not present, the backup battery pad is connected to main battery
pad. V
is a power input for the Real-Time-Clock when using RTC-Sleep Function (Section
BACKUP
5.7.8)
V
BACKUP
Input Voltage
Range
Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
ON mode 2.5 VCC1 5.5
BACKUP mode, VBAT=0v 1.9 V
BACKUP
5.5
Vdc
BACKUP mode, VBACKUP=0v 1.9 VCC2 3.0
Input Current 10
μA
V is a backup voltage that can maintain the RTC clock and alarm functions. If V
BACKUP BACKUP
is
not present in the system (intentionally or not) the RTC clock may still be powered if leakage
voltage exists on VCC. Otherwise, the RTC clock will lose power and be reset when VCC is
restored.
GSM0408IG001 Page 42 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 48

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
PARAMETER Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Backup Voltage (Real-Time-Clock)
V
BACKUP
I
BACKUP
Backup Voltage for Real-Time-Clock
Input Current (V
= 3.2 V, V =
BACKUP
BAT
0 V, No Load on GPIO or Serial Port)
2.7 3.0 4.5 Vdc
3.0 6.0
μAdc
V
has been tested in the above scenarios and does not contribute to leakage. It will properly
BACKUP
provide backup power to the RTC clock.
5.7.12. 32 kHz output (Pad A11)
A 32.768 kHz signal is available as an output from the module. This signal should only be used
as an input to a high impedance device. Additional loads or capacitance on the line may cause
performance issues with the module. If the line is not used, leave floating.
32kHz Clock-Out Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
V
IH
V
IL
Maximum capacitor
Vdc
Vdc
tbd pF
load
Maximum resistive load
Frequency
± 30 ppm
32.768 kHz
Ω
5.7.13. Analog-To-Digital Input (Pad K3)
The monitoring ADC (MADC) consists of a successive approximation 10–bit analog–to–digital
converter (ADC).
Analog-To-Digital Input Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
ADC
BRES
ADC
REF
V
ADC
Integral/Differential Non-
ADC Binary Resolution 10 Bits
ADC Reference Voltage 1.75 Vdc
ADC Range 0 1.75 Vdc
-2 2 LSB
Linearity
Input Leakage tbd
μA
Retuning Frequency 1 MHz
5.7.14. Handset Microphone Input (Pads K4, L4)
The handset differential inputs MICIP and MICIN can be amplified by the differential handset
microphone amplifier. This amplifier has a gain of 25.6 dB and a bias generator MICBIAS
provides an external voltage of 2 V or 2.5 V to bias the microphone.
Handset Mic Input Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Maximum Input Range –
Mic(+) to Mic(-)
Inputs 3 dBm0 (Max. digital
sample amplitude when
32.5 mV
PGA gain set to 0 dB)
Nominal Ref. Level –
Mic(+) to Mic(-)
Differential MIC
-10 dBm0
GSM0408IG001 Page 43 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
RMS
Page 49

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Differential Input
Resistance –
Mic(+) to Mic(-)
Differential MIC, MICAMP
gain = 25.6 dB
(INMODE = 0001)
36
Microphone PreAmplifier Gain
Differential MIC
25.6 dB
5.7.15. Handset Microphone Bias Output (Pad J4)
Mic Bias Output Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Set to 2.0 V 1.9 2.1 Vdc Bias Voltage on Mic(+)
Set to 2.5 V 2.4 2.6 Vdc
Mic Bias Current
2.0 mA
Capability
5.7.16. Handset Speaker Output (Pads M4, M5)
Pad Name Pad Number Signal Direction Description
EARP 71 O Earphone positive output
EARN 73 O Earphone negative output
The earphone amplifier provides a full differential signal on the terminals EARP and EARN (Earphone).
Handset Spkr Output Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Maximum Differential
Resistive Load
Maximum Differential
Output Swing 3.9 V
Output Swing 1.5 V
PP
PP
100 pF
120
33
Capacitive Load
Common Mode
At Internal Speaker (+) or (-) 200
Minimum Resistive Load
Common Mode
At Internal Speaker (+) or (-) 50 pF
Maximum Capacitive
Load
Amplifier Gain EARG = 1
EARG = 0
1
-11
dB
Parameter Test Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Earphone output
swing at EARP-EARN
Distortion 2% and 120 , VSP input
level = +3 dBm0, amp gain = -11 dB
Distortion 2% and 33 , VSP input level
0.98
0.38
= -5.34 dBm0, amp gain = -11 dB
Distortion 2% and 120 , I2S input level
0.93
= +3 dBm0, amp gain = -11 dB
Distortion 2% and 120 , VSP input
3.1 3.92
level = +3 dBm0, amp gain = 1 dB
Distortion 2% and 33 , VSP input level
1.2 1.5
= -5.34 dBm0, amp gain = 1 dB
Distortion 2% and 120 , I2S input level
2.96 3.7
= +3 dBm0, amp gain = 1 dB
Earphone amplifier
gain
EARG = 1
EARG = 0
1
-11
Ω
Ω
kΩ
dB
kΩ
V
dB
dB
P-P
GSM0408IG001 Page 44 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 50

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Earphone amplifier
High Z
state in power down
Earphone amplifier
1 kHz, 100 mVp-p 50 dB
power supply rejection
An external audio amplifier should be used for loads of less than 16 Ω or if volume is inadequate.
5.7.17. Headset Microphone Input (Pad M2)
Mic Input Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
The headset differential
inputs HSMIC and
AUXI can be amplified
by the differential
handset microphone
amplifier. This amplifier
has two different gains
4.9 dB or 25.6 dB and a
bias generator
HSMICBIAS provides
an external voltage of 2
V or 2.5 V to bias the
microphone. Headset
Mic Input
Maximum Input Range Inputs 3 dBm0 (Maximum
78 mV
digital sample amplitude with
PGA gain set to 0 dB),
AUXAMP gain = 18 dB,
Single HSMIC
Nominal Ref. Level -10 dBm0
Microphone Pre-
18 dB
Amplifier Gain
Input resistance at
HSMIC
HSMIC single input,
AUXAMP
gain = 18 dB
40.5 k
5.7.18. Headset Microphone Bias Output (Pad J5)
RMS
Mic Bias Output Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Set to 2.0 V 1.9 2.1 Vdc Bias Voltage on Mic(+)
Set to 2.5 V 2.4 2.6 Vdc
Mic Bias Current
2.0 mA
Capability
GSM0408IG001 Page 45 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 51

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.19. Headset Speaker Output Left & Right (Pads M3, L3)
Pad Name Pad Number Signal Direction Description
HSOL 57 O
HSOR 59 O
Headset Out 32Ω Speaker Left
Headset Out 32Ω Speaker Right
HSOVMID 61 I Headset Out pseudo ground return
The left and right headset amplifiers provide the stereo signal on terminals HSOL and HSOR. A
pseudo ground is provided on terminal HSOVMID to eliminate external capacitors. The mono
audio signal can be provided on the Right or the Right and Left headset outputs. HSOVMID is
available to allow integrators to supply a bias or DC offset to increase the dynamic range of the
Headset.
Headset Spkr Output Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Distortion ≤ 2% and 32 Ω, VSP
1.6 1.96 Maximum Swing
input level = +3 dBm0
Distortion ≤ 2% and 32 Ω, I2S
1.48 1.85
input level = +3 dBm0
Maximum Capacitive
100 pF
Load
Minimum resistive load
32
at HSOL and HSOR:
Zload
Amplifier Gain
HSOL/R amplifier
Power supply rejection
1 kHz, 100 mVpp
-5 dB
50 dB
Amplifier State in
High Z
Power Down
The left and right channels of the headset speaker output are a single ended output. An external
audio amplifier should be used for loads of less than 32 Ω or if volume is inadequate.
V
P-P
Ω
5.7.20. Headset Output Common Mode (Pad M6)
The left and right headset amplifiers provide the stereo signal on terminals HSOL and HSOR. A
pseudo ground is provided on terminal HSOVMID to eliminate external capacitors.
NOTE: In the audio reference design outlined above, this pin is left unconnected. It is
recommended that a series zero ohm resistor be used if unsure of the levels required by the
application.
HSOVMID Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
Maximum
200 pF
Capacitor Load
DC Level 1.2 1.35 1.5 V
GSM0408IG001 Page 46 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 52

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
5.7.21. Headset Detect (Pad H4)
Headset Plug/Unplug detection. This pad is used to automatically switch to the headset audio
path when enabled with AT$VSELECT=3. The device will default to handset when no Headset is
detected.
• 2 modes:
Module already ON (Battery connected, VRIO ON) and plug event;
Module OFF and plug event: the plug detection will be effective once VRIO is set ON
• Plug and unplug detections are digitally debounced (debouncing time = 8 ms).
• The jack plug detection feature is addressed through the HSDET pad. The integrated pull up,
connected to the pad, forces a high level (VBAT) when the headset load is not connected. At
jack insertion headset load connection (32 Ω) imposes a low level on that node (Headset left
channel): as an example HSDET = 1 mV after jack plug for VBAT = 4 V.
• Input comparator threshold voltages are defined as VT
VBAT/2 + 100 mV, VBATmin = 3.2 V. The plug and unplug detection remains functional if
there is no signal from HSOL amplifier output (stereo path is OFF) or if there is a signal from
HSOL (stereo path is ON): maximum level on HSOL when the stereo path is ON is 1 Vp-p
which stays far enough from the comparator threshold levels VBATmin/2 – 100 mV and
VBATmin/2 + 100 mV.
• Jack plug detection is functional if a plug event occurs before the power up of the module or if
the plug event occurs after the power up of the module: analog detection part is always active
if the battery is connected. Detection interrupts will be generated once the VRIO regulator is
power up during the module power up sequence.
• A level change on HSDET pad is sensed by a Schmitt trigger to provide a jack detection
signal to the audio digital control. The audio digital control receives the detection signal and
proceeds to a digital debouncing (time: 8 ms = 256 * 32 kHz clock periods) before sensing
that a plug event happened on the jack connector.
= VBAT/2 – 100 mV and VT
low high
=
Headset Detect Parameter/Conditions MIN TYP MAX UNIT
Low level input voltage VIL
related to VBAT
0.3 *
VBAT
High level input voltage
VIH related to VBAT
0.7 *
VBAT
V
Current with pull-up -40 -31 -15 A
5.7.22. Remote Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) (Pads A7, A9, B7, B8, H5)
The SIM, an integral part of any GSM terminal device, is a “smart card” that is programmed with
subscriber information:
• The user information consists of an International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) number,
which is registered with the GSM provider, and an encryption Ki (pronounced "key"). This
information consists of a microprocessor and memory installed on a plastic card.
Note: The Enabler IIIG BGA module does not include an on-board SIM carrier, nor is a
SIM provided with the module. The SIM must be obtained from the GSM service provider
and must be provisioned by the operator for data and/or voice. Always take care to
protect the SIM - the module will not operate properly without an attached SIM.
V
GSM0408IG001 Page 47 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 53

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
The SIM provides the IMSI for authentication. To gain access to the GSM network, the network
must recognize the IMSI number, and the terminal must be able to properly decrypt the data sent
by the network. The SIM also serves as a buffer for SMS messages, storing the message for
transmission until a radio link is available and buffering received messages until retrieved.
The module supports the use of 1.8 V and 3 V SIM cards. All baud-rates defined in ISO 7816-3
standard are supported for high-speed transmission.
As noted above, the Enabler IIIG BGA requires a remote SIM carrier/connector. When using a
remote SIM, the following guidelines are provided:
• To utilize a remote SIM, the integrator must provide a suitable SIM connector.
• The maximum distance from the module to the remote SIM connector must not exceed 25.4
cm (10 inches).
• It is recommended to have Zero resistance between the SIM connector and the module.
• External ESD Protection is Required;
15 kV Air Discharge;
8 kV Contact Discharge;
The transzorb must have a low junction capacitance (typically < 10 pf) such as the following part:
Enfora PN: TRS-0000-5009
Enabler IIIG
module
SIM
Interface
<25.4 cm (10 in)
SIM_VDD
SIM_RST
SIM_CLK
SIM_DTC
SIM_I/O
Manufacturer: On Semi
Manufacturer PN: NSQA6V8AW5T2G
Remote SIM
Figure 19 - Remote SIM Interface
GSM0408IG001 Page 48 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 54

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Pad Name Pad Number Signal Direction Description
SIM_VDD A8 O SIM VDD
SIM_CLK B7 O Card Reference Clock
SIM_RST B8 O Card Reset
SIM_I/O A7 I/O Card I/O Data
SIMDTC H5 I Card detect
The module provides the regulated supply voltage for the SIM-card and the circuitry to detect the
insertion or extraction of the SIM-Card in or from the mobile.
The SIMDTC is disabled by default (see AT$SIMDTC in the EIII AT Command Manual for
settings). When enabled, the SIMDTC pad has an internal pull up to Vcc and can be configured
to detect a SIM insertion when the SIMDTC is either pulled to ground or left floating.
It can configured to detect either just a SIM removal or both removal and insertion.
When the module detects a SIM removal, it will de-register from the network. When the module
is configured to and detects a SIM insertion, it will reset the module and re-register on the
network.
The SIM-card presence detection logic is active even when the system is in idle mode.
USIM Parameter/Conditions Min Typ Max Units
VIH High level input voltage 1.15 V
VIL Low level input voltage 0.61 V
VOH High level output voltage, IO = 4 mA Vdd-0.45 V
VOL Low level output voltage, IO = 1 mA 0.4 V
II Input leakage current ±1 A
Iout Output current 4 mA
PU PU resistance 32 k
PD PD resistance 30 k
Iz Leakage current ± 30 A
Debouncing time (SIM-card insertion) 0.5 mS
Card
Detect
Debouncing time (SIM-card
extraction)
Pull-up resistor (resistor + resistive
switch)
5.7.22.1. Remote SIM Component Information
1.65 1.8 1.95 V VDD SIM VDD voltage
2.7 2.85 2.95 V
15 mS
475 k
Any compatible SIM carrier can be used in conjunction with the Enabler IIIG BGA module.
For example:
Lumberg P/N 8840_A_21.
or Suyin P/N: 254016MA006G103ZL
GSM0408IG001 Page 49 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 55

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
6. GSM/GPRS Modes of Operation
GSM/GPRS supports many optional services and modes. The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module
supports the following GSM/GPRS services:
• Circuit-switched data
• Short-Message Services (SMS)
• Class B GPRS Functionality
• Voice communication
6.1. Enabling the Transmission Modes for the GSM/GPRS Services
Each of the GSM/GPRS services has two modes that can be enabled separately:
• Mobile-originated (MO): allows the making of a service request (such as, making a telephone call
or sending an SMS)
• Mobile-terminated (MT): allows receiving a service request (such as receiving a telephone call or
an SMS)
Note: Contact your local GSM operator to ensure that the services and modes have been
provisioned for the SIM.
6.2. Voice Communication
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module has full voice capabilities, provided the necessary connections
have been made for the speaker and microphone pads. The Enfora Enabler-IIIG AT Command Set
Reference - GSM0308AT001 has the entire list of commands that can be used to control the voice
functionality. The quick start guide in this manual provides a basic command set that can be used to
initialize and test the voice functionality.
The module supports four vocoder compression algorithms for voice communication: Full-Rate (FR),
Enhanced Full-Rate (EFR), Half-rate (HR) and Adaptive Multi-rate (AMR).
6.3. Circuit-Switched Data
In this mode, the module supports both of the connection modes of transmission that are provided by
GSM:
• Non-Transparent mode delivers a constantly low error rate but with a non-guaranteed throughput
or delay. The Non-Transparent service provides a performance that is closest to using a modem
over a fixed Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) line.
Note: All GSM service providers may not support transparent mode. In those cases, the
module can be configured to switch automatically to Non-Transparent mode. This
capability depends on the settings in the AT+CBST command.
GSM0408IG001 Page 50 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 56

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
6.4. SMS: Short Message Services
Short Message Services (SMS) is a feature-rich GSM service. The Enabler IIIG BGA module can
perform the following tasks:
• Sending and receiving binary messages of up to 160 characters (7-bit characters)
• Sending and receiving text messages of up to 140 bytes (8-bit data)
• Submitting a SMS Protocol Data Unit (PDU) to a SMSC (Short Message Service Center) and
storing a copy of the PDU until either a report arrives from the network or a timer expires
• Receiving a SMS PDU from a SMSC
• Returning a delivery report to the network for a previously received message
• Receiving a report from the network
• Notifying the network when the module has sufficient memory capacity available to receive one or
more SMS messages (after the module had previously rejected a message because its memory
capacity was exceeded)
GSM0408IG001 Page 51 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 57

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
7. SIM Operation
7.1. Provisioning the SIM
The SIM can support optional features or services. Most operators typically configure the SIM to
send/receive voice calls and to receive SMS; however, some may require an additional tariff to
enable the SIM to send SMS. The transmission of circuit switched and GPRS data are also
additional services that may be required to allow the service:
• Mobile-originated (MO): allows making a service request (such as, making a call or sending an
SMS)
• Mobile-terminated (MT): allows receiving a service request (such as, receiving a phone call or an
SMS)
It is imperative for the Enabler IIIG BGA module that the SIM be configured for the optional services
that are required for the application.
7.2. GSM Services Supported by the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The module supports four GSM services (modes of operation) that must be enabled by the operator:
• Voice calls (MO and MT): requires a telephone number
• SMS (MO and MT): uses the telephone number for Voice
• Circuit-switched data calls (MO and MT): requires a telephone number
• The GSM SIM can have multiple telephone numbers.
7.3. GPRS Services Supported by the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The module supports the following GPRS (modes of operation) that must be enabled by the operator:
• GPRS Packet Connectivity (MO and MT) with Both Dynamic and Static IP option
• GPRS SMS (MO and MT): uses the IP (Dynamic or Static) set by the operator
• Multiple APN Setting
• Quality of Service Options
• Multi-slot 10 Class of Service
7.4. Selecting the GSM Modes of Operation
When provisioning the SIM for the module, enable the following modes of operation:
• Voice calls: configure the SIM for both MO and MT service (to send and receive)
• SMS: configure the SIM either for MT alone (to receive) or for both MO and MT (to send and
receive)
• Circuit Switched Data: configure the SIM either for MO alone (to send) or for both MO and MT (to
send and receive)
GSM0408IG001 Page 52 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 58

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Voice SMS CS Data GPRS Function
MO/MT MT MO Voice calls, receive SMS, make data calls
MO/MT MO/MT MO Voice calls, receive / send SMS, make data calls
MO/MT MO/MT MO/MT Voice calls, receive / send SMS, make / receive
data calls
(requires an additional data telephone number)
GSM0408IG001 Page 53 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 59

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8. Software Interface
8.1. Software Interface
The application sends commands to the module via the UART interface pads. These commands use
the Enfora AT Command Set and/or Enfora’s Packet API.
The Enabler IIIG BGA module operates in one of the following modes:
• Command mode: Used for configuring the module, for interrogating the GSM network, and for
placing and receiving calls. It uses the AT command set via the serial port for communication.
• On-line mode: Used after a circuit-switched data call has been established. Data is passed
between the Enabler IIIG BGA module and the controlling application without command
interpretation. The only AT command that is interpreted in On-line mode is the +++ command.
(This command places the module in Command mode but does not terminate the circuit-switched
data call.)
• IP Packet /API Mode: Used to read/write modem parameters, interrogate network information,
and place and receive calls in real-time, multi-tasking mode. The Packet API mode is facilitated
over a PPP connection and the packets can be constructed according to the information provided
in the Enfora GSM-GPRS Family API Reference GSM0308UG001.
The AT command driver of the module never exits the Command state, that is, it never enters the Online mode. Although the host interface may not be able to access the AT command interpreter, it is
always running and is available via the API Mode over a PPP connection and/or via the RF interface.
• In the Command state, characters that are received from the Customer Premise Equipment
(CPE) are treated as AT commands by the module.
• In response to the commands received from the CPE, the module sends characters (AT
commands) to the CPE.
• Various events can also trigger the module to send characters (AT commands) to the CPE.
Format for the AT Commands
The general format of the command line is: <prefix> <command> <CR>
<prefix>
<command>
AT
See AT Command
Manual
<CR>
0X0D
The prefix AT obtains synchronization, identifies the character parameters, and indicates that a
command may be in the following characters.
AT commands are not case sensitive: use either capital letters or lower-case letters for the AT
command.
Note: Some AT Command parameter values ARE case sensitive and are documented in the
Enfora Enabler-IIIG AT Command Set Reference – GSM0308AT001.
GSM0408IG001 Page 54 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 60

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8.2. Enfora AT Command Set
For a full description of the AT commands, refer to the Enfora GSM0308AT001 - Enabler-III AT
Command Set.
Note: A command description that includes an *asterisk denotes that the GSM service provider
must enable supplementary services functionality before the command is available.
8.3. Enfora Packet Application Programming Interface
8.3.1. API Architecture
For description and overview of the Enfora UDP and TCP-based API architecture please refer to
the GSM0308UG001 - Enfora GSM-GPRS Family -API Reference.
8.4. Setup and Initialization
8.4.1. General Setup
The GPRS modem is controlled through the Modem RS232 port on the development board.
Connect a 9-pin straight through serial cable from the Modem RS232 connector to the serial port
on the controlling computer.
Hook up power supply, connect antenna, and install SIM into modem.
8.4.2. HyperTerminal Configuration for the Enabler IIIG BGA module
The following provides an example for setting up a Windows HyperTerminal session that can be
used to experiment with various configurations on the module for controlling computer:
1. Select the connection interface, Direct to Com 1 (or whatever port is the serial port).
Figure 20 – Hyper Terminal Definition
GSM0408IG001 Page 55 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 61

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
2. Configure the COM port as displayed below.
Figure 21 - COM Port Settings
8.4.3. Initialization (AT Command Interface)
In the GSM vocabulary, a call from GSM mobile to the PSTN is called a "mobile-originated call" or
"outgoing call". A call from the fixed network to a GSM mobile is called a "mobile-terminated call"
or "incoming call."
In the following examples, “Entry” refers to the application. The following convention describes
the direction of the data exchange:
• The data exchange from the customer application to the module is designated as:
Entry
The data exchange from the module to the customer application is designated as:
Response
Note: With the exception of the +++ command (Online Escape Sequence), all commands
must be preceded by the AT attention code (or command prefix) and terminated by
pressing the <CR> character.
In the following examples, the <CR> and <CR><LF> are intentionally omitted for clarity and
space.
GSM0408IG001 Page 56 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 62

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8.4.4. Initial Response to the AT Command
After power is applied to the module, the module performs a power-up self-test. The self-test
completes within one (1) second. When queried with the AT command, the module responds
with one of the following result codes:
• OK signifies that the module is ready, that it correctly interprets the AT command, and that it
has executed the command.
• ERROR signifies that the module does not understand the command or that the command is
invalid.
Entry
Response
AT
OK
Command valid: module is ready
The module must be in AT Command mode (please refer to section
8.6 GPRS Packet Examples
for packet mode initialization and setup) when any command is entered (with the exception of the
online escape sequence). Commands entered when the module is in On-line mode are treated
as data, and are transmitted as such to the receiving module. i.e. If the module is in PPP or SLIP
mode, AT commands cannot be entered.
8.4.5. Sending an Initialization String to the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The following example provides the sample AT commands and responses for the following
initialization tasks:
• Reset the module to the factory defaults
• Disable character echo
• Transmit Result Codes
• Set the module to Verbose mode (to display result codes as words)
• Set the DCD to match the state of remote modem
• Ignore the DTR
Entry
Response
Entry
Response
AT&FE0Q0V1&C1&d0
OK
ATSO=1
OK
Initialization string
Command is valid
Auto answer on 1st ring
Command is valid
GSM0408IG001 Page 57 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 63

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8.4.6. Setting Up the Communication Mode for the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
The following example sequence provides the AT command and response for setting the Enabler
IIIG BGA module for full phone functionality, automated operator selection, 9600 baud, nontransparent mode.
Entry
Response
Entry
Response
Entry
Response
AT+CFUN=1
OK
AT+COPS=0
OK
AT+CBST=7,0,1
OK
FULL phone functionality
Command is valid
Automatic operator selection
Command is valid
9600 baud, non-transparent mode
Command is valid
8.4.7. Querying the Status of the Enabler IIIG BGA Module
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN006 – Enabler-G Module
Status Query.
8.4.8. Setting Module Reporting Parameters for GSM and GPRS
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN007 - Enabler-G Status
Reporting.
8.5. GSM/SMS Examples
8.5.1. Initialize the Enabler IIIG BGA Module to Send and Receive SMS Text Messages
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN004 - Enabler-G SMS
Configuration and Use.
8.5.2. Managing SMS Messages
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN004 - Enabler-G SMS
Configuration and Use.
8.5.3. Data Call Configuration
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN003 - Enabler-G Data Ci rcuit
Switched Call Configuration and Use.
8.5.4. Voice Call Configuration
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN003 - Enabler-G Data Ci rcuit
Switched Call Configuration and Use.
8.6. GPRS Packet Examples
8.6.1. GPRS ATTACH and ACTIVATE
This topic is addressed in the Enfora Application Note GSM0000AN005 - Enabler-G Automated
Network Connection Configuration and Use.
GSM0408IG001 Page 58 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 64

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
8.6.2. Windows PPP Setup
The Enabler IIIG BGA module can be used in a Windows operating system environment as a
standard serial modem device. The required setup and configuration process is contained in
Enfora Application Notes GSM0000AN001 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for Windows 98
and GSM0000AN002 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for Windows 2000.
GSM0408IG001 Page 59 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 65

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
9. Integration and Testing
The Enabler IIIG BGA module has been designed to minimize the amount of time required for integration
and testing the application. By being fully certified by the appropriate bodies, the module provides
seamless integration into the GSM network.
The integration issues for the application can be narrowed to the utilization of the AT commands and the
use of the GSM functionality. Coverage and signal quality may be evaluated by using the RSSI
commands. Additional network information can be determined by using AT commands.
Integration of the GPRS Packet capabilities is more complicated than using AT command sequences to
initiate the connection and begin transferring data. The following Application Notes should be used to
integrate the GPRS packet capabilities:
GSM0000AN001 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for Windows 98
GSM0000AN002 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for Windows 2000
GSM0000AN008 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for Windows XP
GSM0000AN010 - Enabler-G PPP Configuration for PocketPC 2002
GSM0000AN005 - Enabler-G Automated Network Connection Configuration and Use
9.1. Integrating the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA Module Note: Generally, all interfaces that are externally available to the end user need to be ESD-
conditioned and terminated in some way. Many of these interfaces should not be connected with
power applied.
At the highest level, this is done using some type of GSM test equipment (such as, Racal 6103E),
a computer, and a serial interface tester. The GSM test equipment must be able to simulate a
GSM call and measure the key parameters related to the module.
Additionally, the serial interfaces and some minimal SIM functionality can be verified by sending
AT commands to the module.
All of these conditions need to be verified at ambient as well as extreme conditions.
GSM0408IG001 Page 60 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 66

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
As part of integration, each of the following interfaces must be verified:
Information Recommendations
SIM
The maximum line length of the SIM interface is 25.4 cm (10 inches).
The module takes care of the signal conditioning
As a minimum, an external application with a remote SIM will require a
standard SIM carrier.
Filter the SIM VCC signal with a 10 uf / 10 V capacitor to help with the
line length.
Primary and
secondary serial
Interfaces
Reset Interface
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module uses a 1.8V digital interface.
The RS-232 signals must be level-shifted to get standard levels.
These signals must be ESD-protected.
Resets the module when tied low. The signal must be driven from an
open collector/drain source.
Audio/Microphone
Interface
Preliminary balancing on the module.
Maximum length TBD
Testing the following parameters verifies the RF parameters that may be affected by such things
as RF path loss, power supply noise, and external interference.
Functionality Parameters to be Tested
Transmitter
Frequency Error
Phase Error
PA Ramp
Modulation Spectrum
RF Power Steps
Timing Advance
Receiver
BER Based RX Tests (RXQUAL RXLEV)
BER Based Sensitivity
Testing the following GSM functionality verifies proper network communication.
Functionality Parameters to be Tested
Transmitter
Frequency Error
Phase Error
PA Ramp
Modulation Spectrum
RF Power Steps
Timing Advance
Receiver
BER Based RX Tests (RXQUAL RXLEV)
BER Based Sensitivity
Testing the following GSM functionality verifies proper network communication.
Functionality Parameters to be Tested
Network Function
Synchronization and registration
Call set-up and call termination (both MT and MO calls)
SMS and/or data calls
GSM0408IG001 Page 61 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 67

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
10. APPENDIX A - LIMITED WARRANTY
10.1. Scope
Enfora warrants to the original purchaser of the product that, for a period of one (1) year from the date
of product purchase, the product hardware, when used in conjunction with any associated software
(including any firmware and applications) supplied by Enfora, will be free from defects in material or
workmanship under normal operation. Enfora further warrants to such original purchaser that, for a
period of ninety (90) days from the date of product purchase, any software associated with the
product will perform substantially in accordance with the user documentation provided by Enfora, and
any software media provided with the product will be free from defects in material or workmanship
under normal operation. Enfora does not warrant that (a) the product hardware or any associated
software will meet the purchaser’s requirements, (b) that the operation of the product hardware or
software will be uninterrupted or error-free, or (c) the product, when integrated in, or combined with,
other products or software not supplied by Enfora, will continue to perform substantially in accordance
with the user documentation. This limited warranty is only for the benefit of the original purchaser and
is not transferable. No other party may act on behalf of such purchaser for the purpose of claiming or
exercising any rights or benefits under or in connection with this limited warranty except as may be
provided in a written agreement between Enfora and such other party.
10.2. Hardware
During the warranty period applicable to the product hardware, Enfora, at its expense and in its sole
discretion, will repair or replace the product if it is determined to have a covered hardware defect,
provided that the purchaser first notifies Enfora of any such defect, furnishes Enfora with a proof of
purchase, requests and obtains a return merchandize authorization (RMA) number from Enfora, and
returns the product, shipping charges prepaid, to Enfora under that RMA. If, upon reasonable
examination of the returned product, Enfora does not substantiate the defect claimed by purchaser, or
determines that the defect is not covered under this limited warranty, Enfora will not be required to
repair or replace the product, but may instead reship the product to the purchaser, in which case
purchaser shall be responsible for paying Enfora’s usual charges for unpacking, testing, and
repacking the product for reshipment to purchaser. Purchaser shall bear the risk of loss or damage in
transit to any product returned by purchaser to Enfora, or any returned product not found to be
defective or covered under this warranty and reshipped by Enfora to purchaser. In the event Enfora
repairs or replaces a defective product, the repaired or replacement product will be covered under
this limited warranty for the remainder of the original warranty period on the defective product. If
Enfora is unable to repair or replace a defective product, the purchaser’s exclusive remedy shall be a
refund of the original purchase price. Any returned and replaced product, or any product for which
Enfora has refunded the original purchase price, becomes the property of Enfora.
10.3. Software
During the warranty period applicable to the software or its media, Enfora, at its expense, will replace
any defective software or media if purchaser gives written notification of the defect to the technical
support department at Enfora during the applicable warranty period. Enfora will ship or otherwise
transmit the replacement software or media to purchaser, and purchaser shall be responsible for
incorporating any replacement software in the product. Enfora shall not have any obligation to
provide any software bug fixes, upgrades or new releases except as may be necessary to correct any
covered defect of which purchaser notifies Enfora in writing during the applicable warranty period.
Enfora, from time to time and in its sole discretion, may make available for download on its website
www.enfora.com) certain software bug fixes, upgrades or new releases for the product. The
(
purchaser should periodically visit such website to determine whether any such bug fixes, upgrades
or new releases have become available. Download and use of any such bug fixes, upgrades or new
GSM0408IG001 Page 62 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 68

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
releases is subject to all of the applicable terms and conditions of Enfora’s technical support policy as
posted and updated on its website.
Exceptions and Disclaimers
Enfora shall have no obligation under this limited warranty for (a) normal wear and tear, (b) the cost of
procurement of substitute products or (c) any defect that is (i) discovered by purchaser during the
warranty period but purchaser does not notify or request an RMA number from Enfora, as required above,
until after the end of the warranty period, (ii) caused by any accident, misuse, abuse, improper
installation, handling or testing, or unauthorized repair or modification of the product, (iii) caused by use of
any software other than any software supplied by Enfora, or by use of the product other than in
accordance with its documentation or (iv) the result of electrostatic discharge, electrical surge, fire, flood
or similar causes. Unless otherwise provided in a written agreement between the purchaser and Enfora,
the purchaser shall be solely responsible for the proper configuration, testing and verification of the
product prior to deployment in the field.
ENFORA’S SOLE RESPONSIBILITY AND PURCHASER’S SOLE REMEDY UNDER THIS
LIMITED WARRANTY SHALL BE TO REPAIR OR REPLACE THE PRODUCT HARDWARE,
SOFTWARE OR SOFTWARE MEDIA (OR IF REPAIR OR REPLACEMENT IS NOT
POSSIBLE, OBTAIN A REFUND OF THE PURCHASE PRICE) AS PROVIDED ABOVE.
ENFORA EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF NONINFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY PERFORMANCE AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL ENFORA BE LIABLE FOR ANY
INDIRECT, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES
(INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION LOSS OR INTERRUPTION OF USE, DATA, REVENUES
OR PROFITS) RESULTING FROM A BREACH OF THIS WARRANTY OR BASED ON ANY
OTHER LEGAL THEORY, EVEN IF ENFORA HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OR
LIKELIHOOD OF SUCH DAMAGES.
10.4. Other Considerations
Some jurisdictions may require a longer warranty period than specified above and, accordingly, for
products sold in those jurisdictions the applicable warranty period shall be extended as required under the
laws of those jurisdictions. Furthermore, some jurisdictions may not allow the disclaimer of implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above disclaimer,
limitation or exclusion may not apply to products sold in those jurisdictions. This limited warranty gives
the purchaser specific legal rights and the purchaser may have other legal rights that vary from
jurisdiction to jurisdiction.
In some instances, certain aspects of the product warranty may also be covered in a separate written
agreement between Enfora and the distributor or reseller, if any, from whom purchaser purchased the
product. That agreement may provide, for example, a different product return procedure that may also be
available to purchaser (e.g., the product may be returned to Enfora through that distributor or reseller).
Governing Law
This limited warranty shall be governed by the laws of the State of Texas, United States of
America, without regard to conflict of laws principles. This limited warranty shall not be governed
in any respect by the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of
Goods.
GSM0408IG001 Page 63 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 69

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
11. APPENDIX B - Regulations and Compliance
This section summarizes the responsibilities and actions required of manufacturers and integrators who
incorporate OEM versions of the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module into their products. In certain
situations and applications, these products will require additional FCC, CE, GCF, PTCRB or other
regulatory approvals prior to sale or operation. Appropriate instructions, documentation and labels are
required for all products. For more information concerning regulatory requirements, please contact
Enfora.
11.1. GCF/PTCRB Approval (Formerly FTA)
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module is type approved in accordance with the requirements of and
through the procedures set forth by the GSM industry association. The relevant conformance
specification is 3GPP TS 51010-1. Any OEM changes in the SIM interface, antenna port, software or
the physical makeup of the unit may require an incremental FTA to ensure continued compliance with
the above-mentioned standard. For more information concerning type approval, please contact
Enfora.
11.2. Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) and Safety Requirements
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module has been tested and approved for application in the United
States of America (US) and the European Union (EU). The compliance details for each of these
markets follow. For other markets, additional or alternative regulatory approvals may be required.
Always ensure that all rules and regulations are complied with in every country that the OEM
application is to be operated. Regardless of the country or market, the OEM must comply with all
applicable regulatory requirements.
11.3. EMC/Safety Requirements for the USA
Compliance to the US rules and regulations falls under two categories:
• Radio approvals: Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
• Transmitter: FCC Rules, Part 22 & 24
• Unintentional emission: FCC Rules, Part 15
Although the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module has been authorized by the FCC and listed as a
component by an NRTL, products and applications that incorporate the module will require final
verification of EM emission and product safety approval.
Note: Particular attention should be made to the following statements regarding RF Exposure:
GSM0408IG001 Page 64 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 70

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
11.4. Human Exposure Compliance Statement
GSM0408 GSM/GPRS Module
Enfora certifies that the Enabler IIIG BGA 850/900/1800/1900 MHz GSM Radio Module (FCC ID:
MIVGSM0408) complies with the RF hazard requirements applicable to broadband PCS equipment
operating under the authority of 47 CFR Part 24, Subpart E and Part 22 of the FCC Rules and
Regulations. This certification is contingent upon installation, operation and use of the Enfora
Enabler IIIG BGA module and its host product in accordance with all instructions provided to both the
OEM and end user. When installed and operated in a manner consistent with the instructions
provided, the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module meets the maximum permissible exposure (MPE)
limits for general population / uncontrolled exposure at defined in Section 1.1310 of the FCC Rules
and Regulations.
Note: Installation and operation of this equipment must comply with all applicable FCC Rules
and Regulations, including those that implement the National Environmental Policy Act of 1969
(Part 1, Subpart I), with specific regard to antenna sitting and human exposure to radio frequency
radiation. For further guidance, consult the FCC Rules, a certified FCC test house, or Enfora.
11.5. Compliance with FCC Regulations
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is the agency of the Federal Government that
oversees all non-governmental radio frequency transmitters that operate within the United States.
Unintentional emissions from digital devices are regulated by Part 15 of the FCC Rules and
Regulations, which distinguishes between the environments in which these devices may operate.
Intentional radiators operating as a GSM-1900 radio transmitter are regulated under Part 22 & 24,
Subpart E—Broadband PCS of the FCC Rules and Regulations.
11.6. Unintentional Radiators, Part 15
Equipment designated as Class A is intended for use in a commercial, industrial or business
environment. The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module has been tested and found to comply with the
limits for a Class A digital device and can be integrated into equipment or applications intended for
use in commercial, industrial or business environments.
The following statement must be included in the user manual for such products:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case
the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Equipment intended for use in a residential environment (not-withstanding use in commercial,
industrial or business environments) is designated as Class B. The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module
has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device and can be integrated
into equipment or applications intended for use in residential environments.
The following statement must be included in the user manual for such products:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
GSM0408IG001 Page 65 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 71

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
11.7. Intentional Radiators, Part 22 & 24
Products incorporating the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module operate as Personal Communications
Services (PCS) devices under the authority of Part 22 & Part 24, Subpart E—Broadband PCS, of the
FCC Rules and Regulations. All such transmitters must be authorized by the FCC through its
Certification process, as detailed in Part 2, Subpart J - Equipment Authorization Procedures.
Through the Certification process, the FCC verifies that the product complies with all applicable
regulatory and technical requirements, including those that address human exposure to radio
frequency radiation. In general, radio frequency transmitters cannot be sold or operated in the US
prior to FCC approval.
11.8. Instructions to the Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM)
To comply with the requirements of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) of 1969, operation
of an FCC-regulated transmitter may not result in human exposure to radio frequency radiation in
excess of the applicable health and safety guidelines established by the FCC. Further information on
RF exposure issues may be found in the FCC's Office of Engineering and Technology (OET) Bulletin
Number 65, "Evaluating Compliance with FCC Guidelines for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency
Electromagnetic Fields" and Supplement C, "Additional Information for Evaluating Compliance of
Mobile and Portable devices with FCC Limits for Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Emissions.”
Both of these documents are available via the Internet at the OET web site:
http://www.fcc.gov/oet
The Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA modules are GSM radio transceivers, which operate under the authority
of 47 CFR Part 24, Subpart E and Part 22 of the FCC Rules and Regulations. When installed and
operated in accordance with the instructions provided in this manual, these devices comply with
current FCC regulations regarding human exposure to radio frequency radiation.
The following installation and operation restrictions apply to all Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA devices:
• This device may only be used in fixed and mobile applications.
• Portable applications, as defined by the FCC, are prohibited.
• The use of this device for desktop and other applications where the antenna can easily
be relocated are considered by the FCC to be mobile applications.
• A separation distance of at least 20 cm (7.87 inches) between the antenna and the body
of the user and other persons must be maintained at all times
• In FIXED applications, antenna gain is limited to a maximum of 7 dBi, with a
corresponding Equivalent Isotropic Radiated Power (EIRP) of 37 dBm / 5 W.
• In MOBILE applications, antenna gain is limited to a maximum of 2 dBi, with a
corresponding EIRP of 33 dBm / 2 W.
GSM0408IG001 Page 66 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 72

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
• End products must provide instructions to ensure compliance with radio frequency
radiation exposure requirements.
• A warning label visible to all persons exposed to the antenna and identical to that
described in this manual must be displayed on or next to the antenna.
• Separate FCC approval for RF exposure compliance is required for end products that do
not meet these conditions.
Antenna gain is defined as gain in dBi (dB referenced to an isotropic radiator) minus cabling loss.
Note: Additional care must be taken by the installer and/or user of the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
module to ensure proper antenna selection and installation. Adherence to the above conditions is
necessary to comply with FCC requirements for safe operation regarding exposure to RF
radiation.
Depending upon the application and type of product into which the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
module has been incorporated, specific OEM actions and responsibilities required to meet these
conditions vary. However, in all cases the primary concern is to ensure compliance with current
FCC guidelines and regulations that limit human exposure to radio frequency radiation.
Definitions
For the purpose of determining compliance with current FCC rules addressing human
exposure to radio frequency radiation, the FCC has established the following three
categories of transmitting devices:
• Portable Devices – devices where the antenna is located within 20 cm (7.87
inches) of any person, including the user, if applicable. Portable devices
operating under the authority of Part 22 or 24 (broadband PCS) are limited to a
maximum of 2 W EIRP.
• Mobile Devices – devices designed to be used in other than fixed locations and
generally such that the antenna is located at a minimum of 20 cm (7.87 inches)
from any person, including the user, if applicable. Mobile devices operating
under the authority of Part 22 or 24 (broadband PCS) are limited to a maximum
of 2 W EIRP.
• Fixed devices – devices in which the antenna, either integral to the product or
remotely located, is physically secured at one location and is not able to be easily
moved to another location. The antenna for a fixed device is mounted on an
outdoor permanent structure with a minimum separation distance of 2 meters (79
inches)
11.8.1. OEM Responsibilities for All Products Containing the Enabler IIIG BGA module
In addition to any other regulatory requirements, OEMs and integrators must include or provide
the following information, instructions, warnings and labels with any device or product into which
the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA GSM1900 GSM transceiver has been incorporated:
GSM0408IG001 Page 67 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 73

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
Information Description
Detailed
Operating
Instructions for
ensuring
compliance with
current FCC
guidelines which
limit human
exposure to radio
frequency
radiation
The OEM must provide an operating/installation manual with the final product which clearly
indicates that these operating conditions and restrictions must be observed at all times to
ensure compliance with current FCC guidelines which limit human exposure to radio
frequency radiation.
20 cm (7.87 inch) separation distance between the antenna and all persons must be
maintained at all times for all fixed and mobile products and applications
Portable devices and applications are prohibited unless such devices and products are
specifically authorized by the FCC
Maximum antenna gain is limited to 2 dBi* in mobile products and applications
For fixed applications (2 meter separation) the antenna gain can be as much as 26 dBi.
Modifications and/or additions to the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA GSM transceiver, including
use of antennas with higher gain than those authorized by the FCC, are prohibited
*dBi = antenna gain in dB relative to an isotropic radiator
Antenna
Avoidance
Label
Attach the following warning label
directly to or displayed next to the
antenna. Furthermore, this label must
be visible to and easily readable by all
persons in the immediate vicinity of the
antenna
Human Exposure
Compliance
Include the following statement in the
instruction / operation manual.
Statement
WARNING
To comply with FCC RF exposure
requirements, a separation distance of 20 cm
(7.87”) or more must be maintained between
this antenna and all persons
Enfora certifies that the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
™ GSM Radio Module (FCC ID: MIVGSM0408)
complies with the RF hazard requirements
applicable to broadband PCS equipment
operating under the authority of 47 CFR Part 22 or
Part 24, Subpart E of the FCC Rules and
Regulations.
This certification is contingent upon installation,
operation and use of the
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module and its host
product in accordance with all instructions
provided to both the OEM and end used. When
installed and operated in a manner consistent with
the instructions provided, the Enfora Enabler IIIG
BGA module meets the maximum permissible
exposure (MPE) limits for general population /
uncontrolled exposure at defined in Section
1.1310 of the FCC Rules and Regulations.
GSM0408IG001 Page 68 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 74

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
11.8.2. Specific OEM Responsibilities for Portable Products and Applications
Each device or product into which the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA PCS-1900 GSM transceiver has
been incorporated, and which is intended to be used in an application that meets the definition of
"portable", MUST be separately authorized by the FCC for the purposes of determining
compliance with current FCC guidelines limiting human exposure to radio frequency radiation.
Portable devices must be evaluated for RF exposure based on Specific Absorption Rate (SAR)
limits; further information on such evaluations are available from the FCC via the Internet.
11.8.3. Specific OEM Responsibilities for Mobile Products and Applications
Separate or additional FCC approvals are NOT required for devices or products, into which the
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA PCS-1900 GSM transceiver has been incorporated, that are used in
applications that meet the definition of "mobile."
For all end products, the OEM or integrator must provide instructions, warnings and labels to
ensure that the product complies with current FCC guidelines limiting human exposure to radio
frequency radiation.
Current FCC regulations limit the EIRP of mobile devices to 2 W. Because the nominal RF output
power of the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA GSM1900 GSM transceiver is 1.0 W (31 dBm), antenna
gain for mobile products and applications cannot exceed 2 dBi.
11.8.4. Specific OEM Responsibilities for Fixed Products and Applications
Separate or additional FCC approvals are not required for devices or products, into which the
Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA GSM transceiver has been incorporated, that are used in applications
that meet the definition of "fixed.”
For all end products, the OEM or integrator must provide the instructions, warnings and labels to
ensure that the product complies with current FCC guidelines limiting human exposure to radio
frequency radiation.
Separate or additional FCC approvals are required for devices or end products used in fixed
applications where antenna gain in excess of 7dBi is desired.
GSM0408IG001 Page 69 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 75

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
11.9. EMC/Safety Requirements for the Countries of the European Union (EU)
The European Union (EU) is comprised of fifteen countries that follow a harmonized set of standards,
utilizing the CE mark as a uniform mark of acceptance. The member countries are:
• Austria
• Belgium
• Cyprus
• Czech Republic
• Denmark
• Estonia
• Finland
• France
• Germany
• Greece
• Hungary
• Ireland
• Italy
• Latvia
• Lithuania
• Luxembourg
• The Netherlands
• Poland
• Portugal
• Slovakia
• Slovenia
• Spain
• Sweden
• United Kingdom
11.10. EMC/Safety Requirements for Other Countries
In most other countries that have not been listed above there are similar rules and regulations that
must be met for importing the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA module. Each may require a different mark of
approval (for example, the CB Scheme) as an acceptance requirement. For each of these cases the
country should identified, and the appropriate steps should be taken to meet the requirements set
forth in the intended market.
GSM0408IG001 Page 70 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 76

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
12. APPENDIX C - Glossary and Acronyms
AMR
API
App Application
AT Command Set
BER
Bit Error Rate
CMUX
CPE
Customer Premise
Equipment
CSD
Circuit Switched Data
dBi
DCE
Data Communications
Equipment
DCS
Digital Cellular System
DTE
Data Terminal Equipment
EFR
Enhanced Full Rate
EIR
Equipment Identity Register
EIRP
Equivalent Isotropic
Radiated
Power
EMC
Electromagnetic
Compatibility
ESD
Electrostatic Discharge
EU
European Union
FTA
Full Type Approval
GPRS
General Packet Radio
Service
GSM
Global System for Mobile
Communications
Adaptive Multi-Rate
Application Programming Interface.
Refers to the Application which sends or receives
commands/responses from the Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA Module
Commands issued by intelligent device to a modem to perform
functions, such as to initiate call, to answer call, or to transmit
data.
Bit Error Rate
Multiplexer protocol that operates between an MS and a TE and
allows a number of simultaneous sessions over a normal serial
asynchronous interface
A terminal in fixed location on the customer’s premises.
Data link from a terminal through the network allowing real-time,
duplex connectivity at 9600 bytes/second.
Decibels referenced to an isotropic radiator
Data Communications Equipment
A collection of services and capabilities providing flexibility of
access and mobility through a combination of wireless and wire-
line networks, utilizing the 1800 MHz bandwidth.
Data Terminal Equipment
Voice (vocoder) compression algorithms which offer the highest
quality voice communication.
A database used to store International Mobile Equipment Identity
(IMEI) of a locally issued terminal.
In a given direction, the gain of a transmitting antenna multiplied
by the net power accepted by the antenna from the connected
transmitter.
The ability of a device to function satisfactorily in its
electromagnetic environment without inducing intolerable
disturbance to that environment (or to other devices)
Static electricity that can damage electronic equipment.
An organization of 15 European states whose purpose is to
organize relations between the Member States and between their
peoples.
GSM Full Type Approval
Standard for packet communications utilizing Global Standard for
Mobility (GSM) infrastructure.
Standard for digital communications. Allows consistent
communications in various parts of the world despite variations in
RF spectrum allocations. Transferring the SIM (see below)
permits users to roam by changing terminal equipment.
GSM0408IG001 Page 71 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 77

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
HLR
Home Location Register
IMEI
International Mobile
Equipment Identity
IMSI
International Mobile
Subscriber Identification
Ki
MO
Mobile Originated
MT
Mobile Terminated
MSC
Mobile Switching Center
Non-Transparent Mode
NRTL
Nationally Recognized Test
Laboratory
OEM
PA
Packet
PCS
PDA
PDU
PPP
SIM
SMS
SMSC
SUPL
UDP
Stores the identity and user data for all subscribers belonging to
the area of the related MSC.
A unique number for each GSM Terminal tracked by the GSM
operators in their Equipment Identity Register (EIR) database.
A unique number identifying the subscriber stored in the SIM card.
Number is used in conjunction with the network for call routing.
A secret code used in authentication and encryption by the
terminal.
Any GSM/GPRS service originated at the mobile terminal.
Any GSM/GPRS service originated from or routed through the
network and sent to the mobile terminal.
The central switch of the GSM network. Performs call routing,
collects call detail records for billing, and supervises system
operations.
Delivers a constantly low error rate but with a non-guaranteed
throughput or delay. The Non-Transparent service provides a
performance that is closest to using a modem over a fixed PSTN
line.
OSHA-approved Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory
Original Equipment Manufacturer.
Power Amplifier.
A collection of data transmitted over a digital network in a burst.
Personal Communication Services.
Personal Digital Assistant.
Packet Data Unit.
Point-To-Point Protocol.
Subscriber Identity Module.
Short Message Service.
Short Message Service Center.
Secure User Plane Location
User Datagram Protocol.
GSM0408IG001 Page 72 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 78

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
13. APPENDIX D – Tables and Figures
TABLES
.................................................................................................. 8 Table 1 - Enabler IIIG BGA Key Features
FIGURES
...................................................................................15 Figure 3 – Example of thermal relief and Vbat feed
.................................................................................................16 Figure 4 - Example of Vbat Voltage Droop
..............................................................................................17 Figure 5 – Example of layer 2 routing fanout
..............................................................................17 Figure 6 – Example of layer 3 UART and audio fanout
.........................................................................................18 Figure 7– Handset Audio Reference Schematic
........................................................................................19 Figure 8 – Headset Audio Reference Schematic
................................................................................................19 Figure 9 – Audio interface layout examples
................................................................................21 Figure 10 - Enabler IIIG BGA Module Block Diagram
..................................................................................................................24 Figure 11 - Module Dimensions
...................................................................................................................25 Figure 12 - Host PCB Footprint
..............................................................................................................35 Figure 13 – Power Control Switch
...........................................................................35 Figure 14 – Typical connection of PWR_CTL to modem:
.....................................................................36 Figure 17 - Power Control Signal (using external processor)
.................................................................................................................41 Figure 18 - Ring Indicate Timing
...............................................................................................................48 Figure 19 - Remote SIM Interface
........................................................................................................55 Figure 20 – Hyper Terminal Definition
....................................................................................................................56 Figure 21 - COM Port Settings
........................................14 Figure 1 – Example of placement and ground plane for the module host board
........................................................14 Figure 2 – Example of solid flooding on layer 4 with via interconnect
.........................................................35 Figure 15 – Typical use controlling PWR_CTL from microcontroller:
...........................................................36 Figure 16 - External Power Control Signal (no external processor)
GSM0408IG001 Page 73 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
Page 79

Enfora Enabler IIIG BGA
Modem Integration Guide
14. APPENDIX E - Contacting Enfora
For technical support and customer service dealing with the modem itself, contact the company where
you purchased the product. If you purchased the product directly from Enfora, visit the SUPPORT page
on the Enfora website:
http://www.enfora.com/support_newissue.asp
GSM0408IG001 Page 74 Rev. DRAFT – 03/10/2008
 Loading...
Loading...