Page 1
VSP SERIES
Installation, Operation and
Maintenance Manual
VARIABLE SPEED PERISTALTIC
METERING PUMPS
VSP-12 and VSP-20 Models
READ ALL WARNINGS CAREFULLY BEFORE
INSTALLING PUMP
Page 2
PUMP DATA/SPECIFICATIONS
Fill in information from pump data label
Series:
Serial #:
Model #:
Nominal output:
Maximum pressure:
Volts/Hz/Amps/Phase:
KOPkit® #:
Tubing material/size:
WARRANTY:
The manufacturer warrants its equipment of its manufacture to be free of defects in material or
workmanship. Liability under this policy extends to eighteen (18) months from the date of purchase
or one (1) year from date of installation or whichever comes first. The manufacturer’s liability is
limited to repair or replacement of any device or part, which is returned, prepaid, to the factory and
which is proven defective upon examination. This warranty does not include installation or repair
costs and in no event shall the manufacturer’s liability exceed the selling price of such part.
The manufacturer disclaims all liability for damage to its products through improper installation,
maintenance, use or attempts to operate such products beyond their functional capacity, intentionally
or otherwise, or any unauthorized repair. Replaceable elastomeric parts are expendable and are not
covered by any warranty either expressed or implied. The manufacturer is not responsible for
consequential or other damages, injuries or expense incurred through use of its products.
The above warranty is in lieu of any other warranty, either expressed or implied. The
manufacturer makes no warranty of fitness or merchantability. No agent of ours is authorized to
make any warranty other than the above
Page 2 of 8
Page 3

VSP SERIES
TABLE of CONTENTS
Safety Instructions ................................................................................................................................................3
Technical specifications........................................................................................................................................4
Material of Construction........................................................................................................................................4
Installation.............................................................................................................................................................4
Operation ..............................................................................................................................................................5
Maintenance .........................................................................................................................................................6
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS PRIOR TO USE
***
*** DO NOT PUMP FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS.
*** To reduce risk of electric shock before maintenance, repair, or moving pump, disconnect power cord and
de-pressurize system and drain chemical.
*** Do not cut the plug or ground lug off the electrical cord. Consult a licensed electrician for proper installation.
**
chemical metering pumps.
** Inspect tubing regularly for cracking or deterioration and replace as necessary. (Always wear protective
clothing and safety glasses when inspecting tubing.)
** Use CAUTION to keep fingers away from rotating parts.
** If pump is exposed to direct sunlight, use a UV resistant tubing.
** Follow directions and warnings provided from the chemical manufacturer. The user is responsible for
determining the chemical compatibility with the chemical feed pump.
** Make sure the voltage on the pump name tag matches the installation voltage. If pump fails to start, check
line voltage.
** Consult with local health officials and/or qualified water conditioning specialists when treating potable water.
** Always depressurize system prior to installation or disconnecting the metering pump tubing.
** If injection point is lower than the chemical tank and pump, install an anti-siphon valve.
** DO NOT MODIFY PUMP. This poses a potentially dangerous situation and will void the warranty.
*
pumped will react with water (i.e., sulfuric acid).
* Hand tighten plastic connections (Do not use wrench).
* Consult licensed plumber and electrician before installation to conform to local codes.
NOTE: For accurate volume output, pump must be calibrated under all operating conditions.
: Secure chemicals and metering pumps, making them inaccessible to children and pets.
: Always wear protective clothing, including gloves and safety glasses, when working on or near
: All pumps are factory tested with water. Remove tubing and thoroughly dry if the chemical being
Page 3 of 8
Page 4

TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Feed Rate: Refer to name plate.
* Model VSP-12: 1.6 to 12-gal/day (6 to 45.4-LPD).
Tube size: 38in. -O.D. x .19in. -I.D.
Model VSP-20: 2.6 to 20-gal/day (9.8 to 75.7-LPD.
Tube size: 44in. -O.D. x .25in. -I.D.
‘*’ Denotes approximate feed rates. Actual output
Must be measured at time of application,
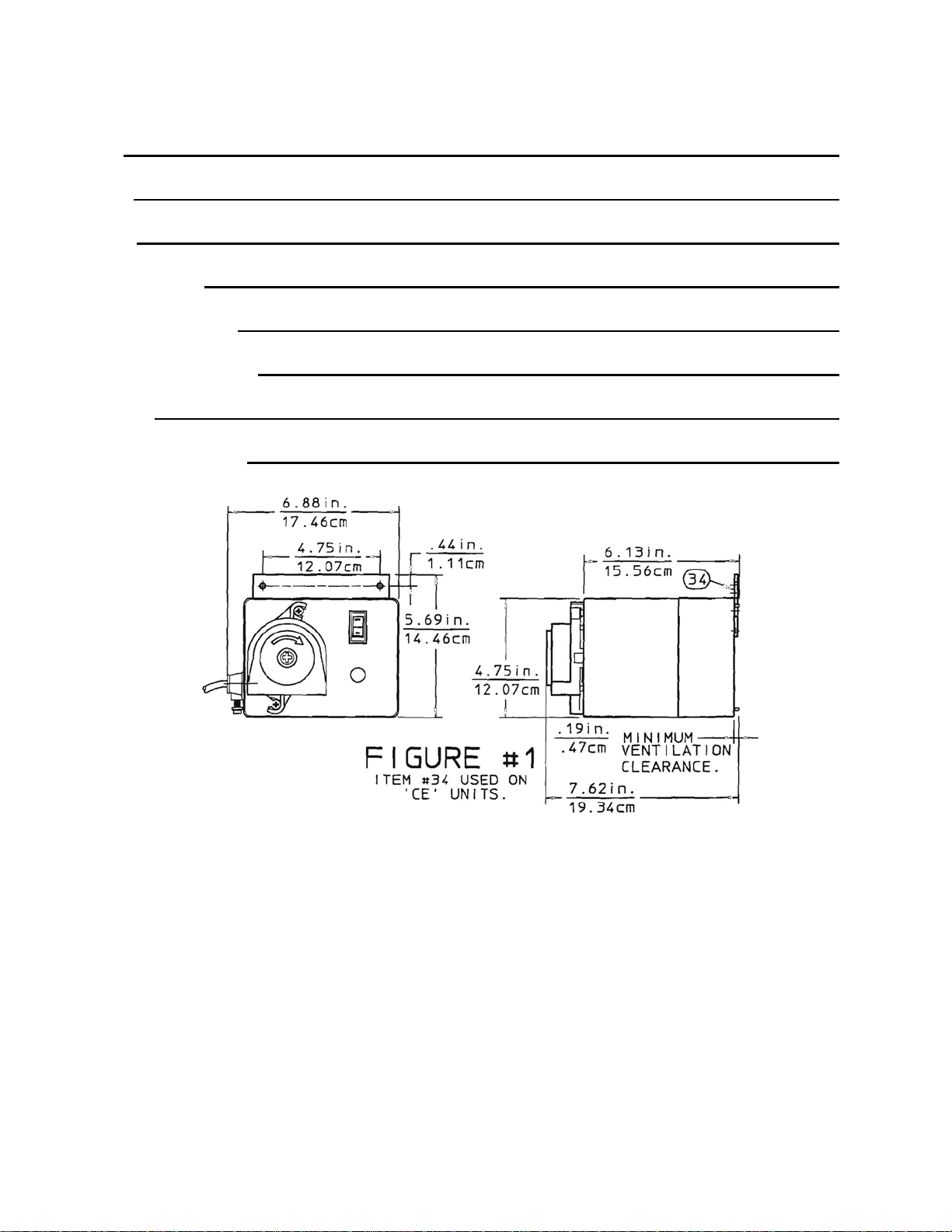
Dimensions: See Figure 1 on page 2.
Electrical rating: Refer to name plate.
Maximum Ambient Temperature: 104ºF (40ºC).
Maximum Pressure: 25psi (1.76-kPa).
MATERIAL OF CONSTRUCTION
Pump Head: Chemical Resistant Polycarbonate Resin.
Pump head Tubing: Norpreen (standard) or Viton or Silicon.
Injection fitting (standard w/check valve): PVC (standard).
Strainer: FPP (standard).
Suction/Discharge Tubing: Polyethylene (standard).
Pump Housing: Chemical Resistant Resin.
INSTALLATION
1. Mounting: Locate the feeder so there is
direct access to the power cord plug.
: DO NOT POSITION SO THAT
COOLING VENTS IN THE REAR OF THE
CASE ARE OBSTRUCTED, .19in. (4.7mm)
minimum ventilation clearance is required, see
Figure 1.
2. Alternate Mounting (not approved for ‘CE’): Set
the feeder on a flat level surface that will support its
weight. The feeder should be mounted on its 4(four)
rubber feet (or use keyholes on back for wall mounting
(4.75in. (12.07cm) typical spacing), see Figure 1.
Locate the feeder so there is direct access to the
power cord plug.
3. Electrical - Verify the electrical requirements for the pump as
listed on the pump data label and connect to an appropriate electrical
source in compliance with local codes for the specific application.
4. Injection Fitting - Relieve system pressure in the drain piping run where the injection fitting is to be
installed. See Figure 2. The injection fitting must not be installed in a dead end pipe or a deeply
recessed tee. It should be installed so as to place the tip at the center of the fluid stream. The
injection fitting has .25-18 NPT (female) threads. If necessary drill a .44in.-diameter hole and using care not
to tap to deeply, tap for .25-18 NPT. Apply Teflon tape to the injection fitting threads and install into piping
system. DO NOT REMOVE THE PLASTIC SLEEVE ON THE TIP OF THE FITTING. It is a functional part.
: Inspect piping system and eliminate piping cross-connections to prevent feeding
chemical to areas not needing treatment.
Page 4 of 8
Page 5
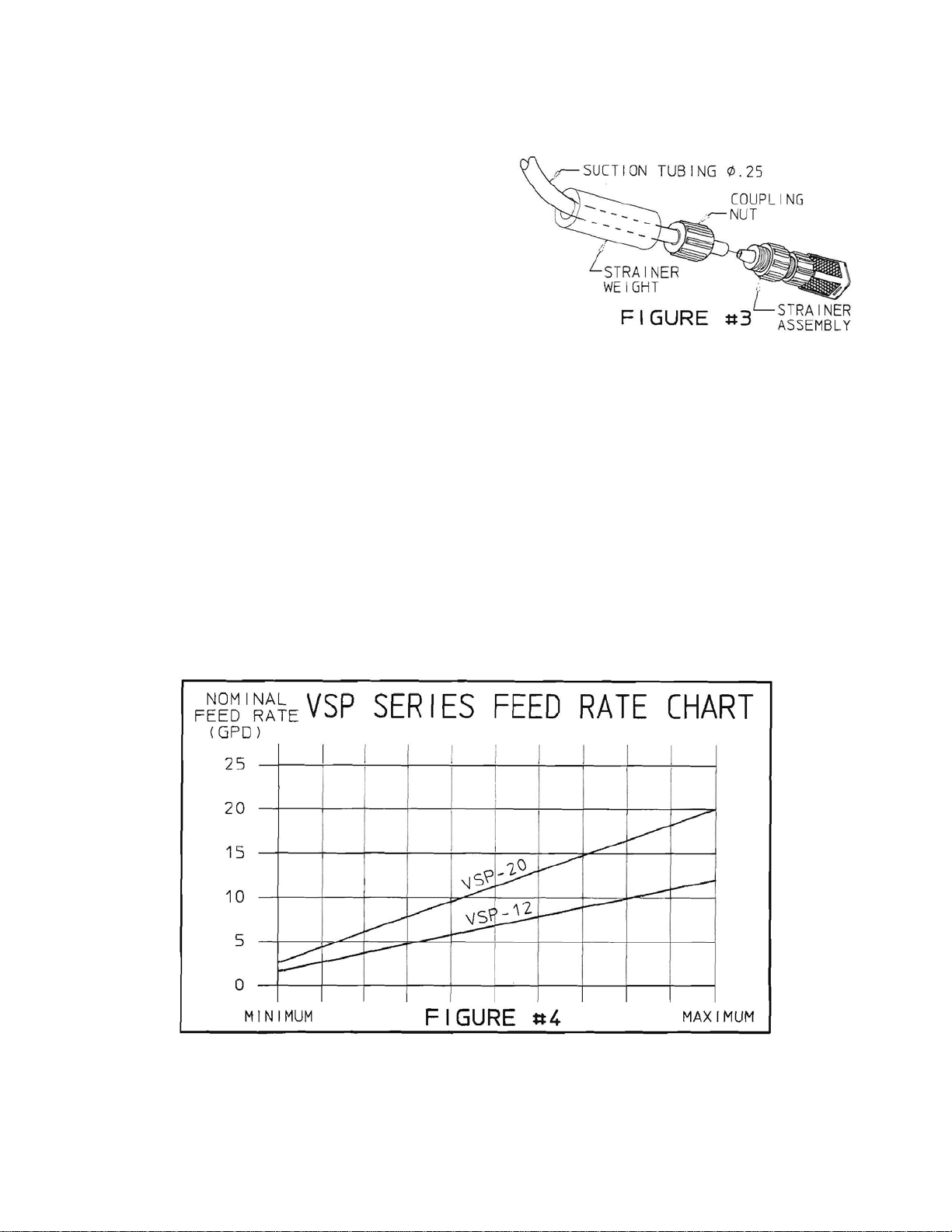
5. Suction and Discharge Tubing - Take the 15-ft (4.5m) length of .25in.-diameter tubing included, measure
and cut the lengths needed to run from the pump head to the injection fitting, and to the chemical tank
(Figure 2). Cut the tubing ends square
6. Refer to maintenance section to install the pump head
tubing.
7. Connect discharge tubing to the injection fitting.
Remove the injection fitting nut slide it over the end of
the tubing, see Figure 3. Push the end of the tubing
onto the injection fitting. Note: Immerse tubing in hot
water to soften prior to pushing on fitting. Turn on and
tighten the nut firmly, Hand tighten only do not use
wrenches.
8. Connect suction tubing to strainer - Install strainer so it is off the bottom of the chemical container 1-2
inches (2.5-5cm) see Figure 2. Measure suction tubing length required. Cut tubing end square and install
on suction fitting of the pump. Hand tighten only do not use wrenches.
OPERATION
1. Fill the chemical tank with the chemical you will feed.
2. Turn the feeder switch on to start the pump. It will begin to feed chemical into the system when all tubing
has filled.
3. Set the feed percentage adjustment knob - Remove hole cover (item 9) and turn the potentiometer shaft
to vary motor RPM to achieve the desired feed rate, reference feed rate chart shown in Figure 4. For
example, to feed approximately 6 gallons (22.7-liters) per day with the VSP-12, set the potentiometer shaft
approximately in the center of its range.
NOTE: To get actual feed rates for specific settings, actual output must be verified by measuring volume
output. Use the flow chart as a guide (Figure 4). To get actual feed rate for specific setting each pump must be
calibrated for its flow. As with any peristaltic pump output varies with pressure and tubing condition. It is
recommended that feed rate be verified at every tubing change and after every 250 hours. More critical
applications require more frequent verification.
Page 5 of 8
Page 6

MAINTENANCE
NOTE: NO USER SERVICEABLE COMPONENTS INSIDE ENCLOSURE. SHOULD THE POWER SUPPLY
CORD BECOME DAMAGED, IT MUST BE REPLACED BY PULSAFEEDER or ITS REPRESENTATIVES or A
SIMILARLY QUALIFIED PERSON IN ORDER TO AVOID A HAZARD.
: Do not attempt to feed chemicals without consulting your chemical feeder dealer or
chemical supplier.
Filling the chemical tank - To avoid running out of chemical, follow a regular schedule of monitoring chemical
supply. Also inspect and clean the strainer by flushing with a compatible liquid, as needed.
peristaltic tubing frequently and replace when deterioration becomes apparent. Peristaltic tubing will
eventually wear and break if neglected. This occurrence will cause chemical spillage and potential for
personal injury or damage to equipment. If a potential hazardous or corrosive chemical is handled, take
precautions to prevent personal injury and damage in the event of tubing failure. Refer to chemical
manufacturer’s recommendations with regard to safety and handling precautions. Always wear protective
clothing and safety glasses when working near chemical feed systems.
: Do not expose pump head tubing to pressure over 25-PSIG (1.76-kPa).
Tubing inspection: inspect all tubing regularly and replace it if deteriorating. Use the following instructions to
replace the pump head tubing.
Replacing pump head tubing:
: Wear protective gloves, goggles, and other adequate protection for the chemical hazard. Before
replacing the pump head, remove chemical from tubing as follows: Remove strainer from chemical tank, then
run feeder until all chemical is removed from the tubing.
1. Remove the hose clamps from the tubing at the pump head (twist clamp to disengage teeth).
2. Pull the suction and discharge tubing from the pump head tubing.
3. Rotate the pump head counter-clockwise (see arrows in Figure 5) to disengage from the collars on the
feeder cover. DO NOT REMOVE or LOOSEN COLLAR SCREWS.
4. Grasp the tabs on the back cover of the pump
head and pull straight out to remove, see Figure
7.
the center hole in the back cover. It’s not
necessary to remove the spider and bearing
from the housing.
5. Remove the old tubing and retaining tube
collars from the pump head (see Figure 6).
6. Position the spider about as shown in Figure 6.
Then put the retaining collar on the pump head
tubing as shown, and position the collar in the
pump head with the open end facing outward.
7. While rotating the spider counter-clockwise (←), push the tubing into the housing to center over the rollers
as shown in Figure 6.
: Do not lose the bearing from
: Inspect
Page 6 of 8
Page 7

MAINTENANCE (continued)
8. Replace the back cover on the pump head. Be sure it fits tightly against and flush with the housing
(Figure #7).
9. Slide the pump head onto the motor drive shaft and turn it clockwise to lock onto the 2 (two) locking collars.
10. Push the suction tubing and discharge tubing into the pump head tubing (Figures 5 and 11). Do not push
tubing past retaining collars. Install a hose clamp to hold the tubing together. Use pliers to squeeze the
clamp tightly.
.13in.-I.D. Norpreen tubing with barb fittings (no clamps).
: Hose clamps must be tightened securely to prevent leakage, except when using
Page 7 of 8
Page 8

Page 8 of 8
 Loading...
Loading...