Nortel Networks NN43001-504 User Manual

Nortel Communication Server 1000
WLAN IP Telephony Installation
and Commissioning
NN43001-504
.

Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.02
Document date: 15 June 2007
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical
data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without
express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this
document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Nortel, the Nortel logo and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

Revision history
June 2007
Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued to reflect a change in the
revision history.
May 2007
Standard 01.01. This document is issued to support Nortel Communication
Server 1000 Release 5.0. This document contains information previously
contained in the following legacy document, now retired: WLAN IP
Telephony Installation and Configuration (553-3001-304).
August 2005
Standard 4.00. This document is up-issued to support Nortel
Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5.
September 2004
Standard 3.00. This document is up-issued to support Nortel Networks
Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0.
3
June 2004
Standard 2.00. This document is up-issued to reflect changes in technical
content.
May 2004
Standard 1.00. This document is issued to support the Nortel Networks
WLAN system, including the Nortel Networks WLAN IP Telephony Manager
2245, Nortel Networks WLAN Application Gateway 2246, Nortel Networks
WLAN Handset 2210, and Nortel Networks WLAN Handset 2211.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

4 Revision history
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Contents
New in this release 13
Feature description 13
Other changes 13
How to get help 17
Getting help from the Nortel Web site 17
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center 17
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code 17
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller 18
5
Multicast 14
Zones for wireless handsets 14
Open and use the Admin menu on the handset 14
Admin menu options for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 14
Download the software 14
Feature programming for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 14
Test the wireless handsets 14
Run Site Survey for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 14
Diagnostics mode 14
Push-to-talk 14
Wireless handset status messages 15
Overview 19
Subject 19
Applicable systems 20
Conventions 21
Resources 21
Declaration of conformity 22
Shielded cable 22
Wireless telephone network description 22
Call Server 24
DHCP Server 25
DHCP options 25
TFTP Server 25
Firewall 25
WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140 25
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

6 Contents
Components 26
Language 27
Licenses 27
Wi-Fi Multimedia 27
Wired Equivalent Privacy 28
Wi-Fi Protected Access 28
Wi-Fi Protected Access2 28
Virtual Private Network 28
Push-to-talk feature 28
Text-messaging feature 28
Loud noise environments 29
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 29
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 30
Access Points 30
Handset switchover 31
Handset switchover 31
Loss of signal 31
Planning 33
Challenges of integrating voice applications 33
High overhead of 802.11 34
Rate scaling and variable capacity 34
Power adjustments and variable capacity 35
Quality of Service 35
DHCP server planning 36
TFTP Server planning 38
Syslog Server planning 40
Access point planning 40
Site survey 41
Effective site survey 43
Example of AP placement 44
Solving coverage issues 45
Solving overlap issues 45
Network planning 46
Network recommendation 46
Sample Access Control List 47
Network management 47
Assessment through a WLAN site survey 48
Assessment using NetIQ Vivinet Assessor 49
Monitoring and reporting with Enterprise Network Monitoring System 50
Monitoring and reporting with Communication Server 1000 Telephony
Manager 52
Monitoring and reporting with NetiQ Vivinet Assessor, Vivinet AppManager, and
Vivinet Diagnostics 53
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Contents 7
Communication Server 1000 Telephony Manager 54
Zones 54
Other network design considerations 55
Access Point interference 56
SSID options and limitations 57
Layer 3 implementation 58
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 planning 59
Installation requirements 59
Capacities 59
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 groups 60
Gateway and timing function 64
Roaming and handover 64
Multicast 65
Placement guidelines for the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 65
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 planning 73
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 and WLAN Application Gateway 2246
installation requirements 74
IP address planning 74
IP addressing with DHCP 75
Planning worksheets 75
System information 77
Bandwidth management 77
Zones 77
Zones for wireless handsets 78
Call blocking 79
Codecs 79
Jitter buffer 80
RLR and SLR 80
RTCP 80
Gain adjustment 81
Programmable rings and tones 81
In/Out of Service tones 81
Virtual Office 81
Branch Office 81
Local mode display 81
Survivable Remote Gateway 82
External Applications Server 83
End-to-end QoS 83
NAT 83
NAT Traversal feature 84
Network configurations 84
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 in a NAT environment 88
DHCP Server location in a NAT environment 88
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

8 Contents
TFTP Server location in a NAT environment 89
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 in a NAT environment 89
CS 1000 features 90
IP Phone 2004 features 91
Installation 93
Required materials 93
Supplied equipment 94
Preinstallation checklist 94
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 installation tasks 94
About the front panel 94
Wall-mount 95
Rack-mount 96
LAN connection 97
Power connection 97
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 installation 97
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 configuration 99
Introduction 99
Functional description 99
Configuration tasks 101
Connect to the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 101
Serial port connection 101
Telnet connection 102
Configure the network 103
Save the configuration 105
Changing the master IP address 106
Configure the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 106
Change the password 108
Administration and maintenance 111
Adding a WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 to the system 111
Checking in to the Gateway 111
Replacing a WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 112
Failed master WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 112
Replacing the failed WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 112
Removing a WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 from the system 113
Wireless handset scenarios 113
Changing the master WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 113
View software version 113
For the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 114
For the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 114
For a wireless handset 114
Software updates 114
Update software on the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 115
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Contents 9
Update software on the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 115
Update software on a wireless handset 115
Software update (version 97.070) for the WLAN Handsets 2210/2211/2212 116
Displays 117
Wireless handset download messages 117
Normal download messages 117
Download failure or recovery messages 118
Troubleshooting 119
Troubleshooting the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 119
Error Status screen 119
Network Status screen 120
Software Version Numbers screen 121
Speed or duplex mismatch 122
Troubleshooting the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 122
Troubleshooting the handset 122
Context 122
Access Point problems 123
Configuration problems 123
Duplex mismatch 124
No ring 124
Far-end echo 124
Dropped calls 124
Wireless handset status messages 125
Using Call Server overlay commands 139
TPS CLI commands 141
Determining alias IP addresses 144
Troubleshooting coverage issues 144
Before calling Nortel Technical Support 144
Appendix A WLAN Application Gateway 2246 147
Introduction 147
System overview 148
Front panel 149
Third-party applications 150
Nurse-call systems 151
Installation 151
Configuring the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 IP address 152
Configuration 153
Administration console navigation 154
Task summary list 154
Configuring the OAI Box 155
Configuring network parameters 155
Connecting to the LAN 157
Connecting to the Application Server 158
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

10 Contents
Continuing configuration through Telnet 160
Connecting through Telnet 160
Configuring the Telephone Line 161
Deleting a handset 162
Searching for a handset 162
Feature programming 163
Setting or changing a password 164
System status 164
Network status 165
Software versions 166
Telephone line status 167
Certification testing 167
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 certification 167
Wireless handset certification 167
Software 168
Software updates 168
TFTP software updates Systems 170
Planning Worksheet for Handsets 171
Free the serial port for administrative purposes 172
Appendix B Troubleshooting WLAN IP Telephony
installations 173
Site data-gathering tables 173
Product-specific configuration 176
Terminal proxy server 176
Handsets 177
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 177
Quality of Service 177
WLAN specific configuration 177
Nortel switches 178
Cisco access points and switches 178
General WLAN configuration 183
DHCP server options 184
DHCP options 184
DHCP support for handsets that emulate the IP Phone 2004 187
Format of the IP Phone 2004 Terminal DHCP Class Identifier field 187
Format of the IP Phone 2004 Terminal DHCP Encapsulated Vendor Specific
option 188
Format of the IP Phone 2004 Terminal DHCP Site Specific option 189
Quality of Service checklist for voice over WLAN applications 191
RF basics and AP configuration 193
Troubleshooting 196
Diagnosis flows 196
Handset error messages 198
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Contents 11
Timing information 199
Diagnostic Tools 200
Run Site Survey for the WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 200
Run Site Survey for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 201
Diagnostics Mode 204
Syslog Mode 207
Data capture 213
Questions 213
Data checklist 213
Site-data required for the capture analysis 214
Syslog capture configuration 215
Signaling Server log capture 216
General data capture 217
Capture assert error messages with the Configuration Cradle 218
Network speech levels 219
Reference documents 220
Appendix C Compatible Access Points 223
Index 224
Procedures
Procedure 1 Measuring jitter, delay, and packet loss 71
Procedure 2 Wall-mounting the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 96
Procedure 3 Rack-mounting the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 96
Procedure 4 Connecting the power 97
Procedure 5 Connecting to the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 through
a serial port 102
Procedure 6 Connecting to the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 through
Telnet 103
Procedure 7 Saving the configuration 105
Procedure 8 Changing the password 108
Procedure 9 Changing a forgotten password 109
Procedure 10 Replacing a WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 112
Procedure 11 Viewing the software version 114
Procedure 12 Updating software (v97.070) for the WLAN Handsets 2210/
2211/ 2212 116
Procedure 13 Installing the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 152
Procedure 14 Connecting to the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 through a
serial port 152
Procedure 15 Configure the system type from the OAI Box Configuration
option 155
Procedure 16 Configuring the network 156
Procedure 17 Connecting the WLAN Application Gateway 2246 to the
LAN 157
Procedure 18 Connecting to a WLAN Application Gateway 2246 through
Telnet 160
Procedure 19 Configuring a telephone line 161
Procedure 20 Deleting a handset 162
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

12 Contents
Procedure 21 Searching for a handset 162
Procedure 22 Programming a feature 163
Procedure 23 Setting or changing a password 164
Procedure 24 Viewing system status 165
Procedure 25 Certifying wireless handsets on an existing system 168
Procedure 26 Transferring the software using FTP 169
Procedure 27 Loading software updates 170
Procedure 28 Using the serial port as the Application Server communication
link 172
Procedure 29 Using the CLI to capture a Signaling Server log 216
Procedure 30 Obtaining the wired and wireless captures 217
Procedure 31 Recording an assert error message 218
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

New in this release
The following sections detail what is new in WLAN IP Telephony Installation
and Commissioning (NN43001-504) for CS 1000, Release 5.0.
Feature description
Support is provided for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 through the addition
of the Nortel WLAN Handset 6100 Series Administration Tool Software.
For more information about this tool for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140,
including personal computer requirements, how to install the USB driver,
and how to install and use the software, see WLAN Handsets Fundamentals
(NN43001-505).
Other changes
This document is renamed and renumbered from WLAN IP Telephony:
Installation and Configuration (553-3001-304) to WLAN IP Telephony
Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-504). WLAN Handset
configuration information is moved to WLAN Handsets Fundamentals
(NN43001-505).
13
For information about changes that are not feature-related,see the following
sections:
•
"Multicast" (page 14)
•
"Zones for wireless handsets" (page 14)
•
"Open and use the Admin menu on the handset" (page 14)
•
"Admin menu options for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140" (page 14)
•
"Download the software" (page 14)
•
"Feature programming for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140" (page 14)
•
"Test the wireless handsets" (page 14)
•
"Run Site Survey for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140" (page 14)
•
"Diagnostics mode" (page 14)
•
"Push-to-talk" (page 14)
•
"Wireless handset status messages" (page 15)
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

14 New in this release
Multicast
The WLAN Handset 6140 uses IP multicast addresses.
Zones for wireless handsets
The WLAN Handset 6120/6140 is added to the designated wireless handset
types.
Open and use the Admin menu on the handset
The procedures for opening and using the Admin menu on the WLAN
Handset 6120/6140 and how to make an alphanumeric string entry are
added.
Admin menu options for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140
A full description of all the options available from the Admin menu is given
for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140.
Download the software
The procedure for downloading the software for the WLAN Handset
6120/6140 is described.
Feature programming for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140
A full description of the feature programming available for the WLAN
Handset 6120/6140 is provided. This section includes soft key assignment,
feature assignment, programming memory keys, accessing features, and
programming the keys on the WLAN Handset 6120/6140.
Test the wireless handsets
The procedure for testing the WLAN IP 6120 handset is provided.
Run Site Survey for the WLAN Handset 6120/6140
Site Survey is used to evaluate the facility coverage before certifying that
an installation is complete.
Diagnostics mode
Diagnostics screen 2 shows the GatewayType for all handsets.
Push-to-talk
With the Push-to-talk (PTT) feature, the WLAN Handset 6120/6140 can
operate in a PTT group-broadcast mode like a two-way radio, in addition
to the standard telephone operation. This section describes how to initiate
and receive a PTT call.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Wireless handset status messages
The new messages are:
•
Error!
•
Server Unavailable. Restarting...
Other changes 15
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

16 New in this release
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

How to get help
This chapter explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support Web site:
ww.nortel.com/support
w
This site provides access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools to
address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
•
download software, documentation, and product bulletins
•
search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
•
arrange for automatic notification of new software and documentation
for Nortel equipment
•
open and manage technical support cases
17
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support
Web site, and you have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help
over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the telephone
number for your region:
w
ww.nortel.com/callus
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an
Express Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in
your Nortel product or service. To locate the current ERC for your product
or service, go to:
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

18 How to get help
www.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Overview
This chapter contains information about the following topics:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
19
"Subject" (page 19)
"Applicable systems" (page 20)
"Conventions" (page 21)
"Related information" (page 21)
"Declaration of conformity" (page 22)
"Shielded cable" (page 22)
"Wireless telephone network description" (page 22)
"Call Server" (page 24)
"DHCP Server" (page 25)
"TFTP Server" (page 25)
"Firewall" (page 25)
•
"WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140"
(page 25)
•
"WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245" (page 29)
•
"WLAN Application Gateway 2246" (page 30)
•
"Access Points" (page 30)
•
"Handset switchover" (page 31)
Subject
This document describes the planning, installation, configuration,
maintenance, and troubleshooting for the Nortel WLAN system, including
the following elements:
•
Nortel WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245
•
Nortel WLAN Application Gateway 2246 (optional)
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2210
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007
20 Overview
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2211
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2212
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 6120
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 6140
Note about legacy products and releases
This NTP contains information about systems, components, and features
that are compatible with Nortel Communication Server 1000 Release 5.0
software. For more information about legacy products and releases, click
the Technical Documentation link under Support & Training on the
Nortel home page:
w
ww.nortel.com
Applicable systems
This document applies to the following systems:
•
Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
•
Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
Note: When upgrading software, memory upgrades can be required on
the Signaling Server, the Call Server, or both.
System migration
When particular Meridian 1 systems are upgraded to run CS 1000 Release
5.0 software and configured to include a Signaling Server, they become
CS 1000M systems. Table 1 "Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems"
(page 20) lists each Meridian 1 system that supports an upgrade path to
a CS 1000M system.
Table 1 Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems
This Meridian 1 system
Meridian 1 PBX 51C CS 1000M Half Group
Meridian 1 PBX 61C CS 1000M Single Group
Meridian 1 PBX 81C CS 1000M Multi Group
Maps to this CS 1000M system
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Conventions
Resources
Resources 21
In this document, the following systems are referred to generically as
system:
• Communication Server 1000M (CS 1000M)
•
Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
The following systems are referred to generically as large systems:
•
Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
This section lists information sources that relate to this document.
NTPs
The following NTPs are referenced in this document:
•
WLAN Handset 2210 User Guide (NN10300-077)
•
WLAN Handset 2211 User Guide (NN10300-078)
•
WLAN Handset 2212 User Guide (NN10300-071)
•
WLAN Handset 6120 User Guide (NN43150-100)
•
Features and Services Fundamentals (NN43001-106)
•
Main Office Configuration Guide for Survivable Remote Gateway 50
(NN43001-307)
•
Branch Office Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-314)
•
IP Line Fundamentals (NN43001-500)
•
WLAN Handsets Fundamentals (NN43001-505)
Online
To access Nortel documentation online, click the Technical Documentation
link under Support & Training on the Nortel home page:
w
ww.nortel.com
CD-ROM
To obtain Nortel documentation on CD-ROM, contact your Nortel customer
representative.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

22 Overview
Declaration of conformity
The WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 and WLAN Application Gateway
2246 have been found to comply with the following:
•
FCC Part 15 Class A - Radiate and Conducted Emissions requirements
•
CISPR 22 Class A - Radiate and Conducted Emissions requirements
•
ICES 003 Class A - Radiate and Conducted Emissions requirements
•
EN 55022 Class A - Radiated and Conducted Emissions requirements
•
EN 55024 Immunity Requirements
•
EN 61000-3-2 Harmonic Current Emissions
•
EN 61000-3-3 Flicker Emissions
WARNING
Changes or modifications to this equipment not approved by
Nortel can cause this equipment to not comply with part 15 of the
FCC rules and void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
WARNING
This equipment contains no user-serviceable parts inside. Refer
servicing to qualified service personnel.
Shielded cable
Nortel recommends the use of shielded cable for all external signal
connections in order to maintain FCC Part 15 emissions requirements.
Wireless telephone network description
The Nortel WLAN wireless telephone network consists of the following
components:
•
Call Server
•
DHCP server
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Wireless telephone network description 23
•
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server
•
Firewall
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212, and Nortel WLAN Handset
6120/6140
•
Nortel WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245
•
Nortel WLAN Application Gateway 2246 (optional)
•
Access Point (AP)—one or more as required by the site
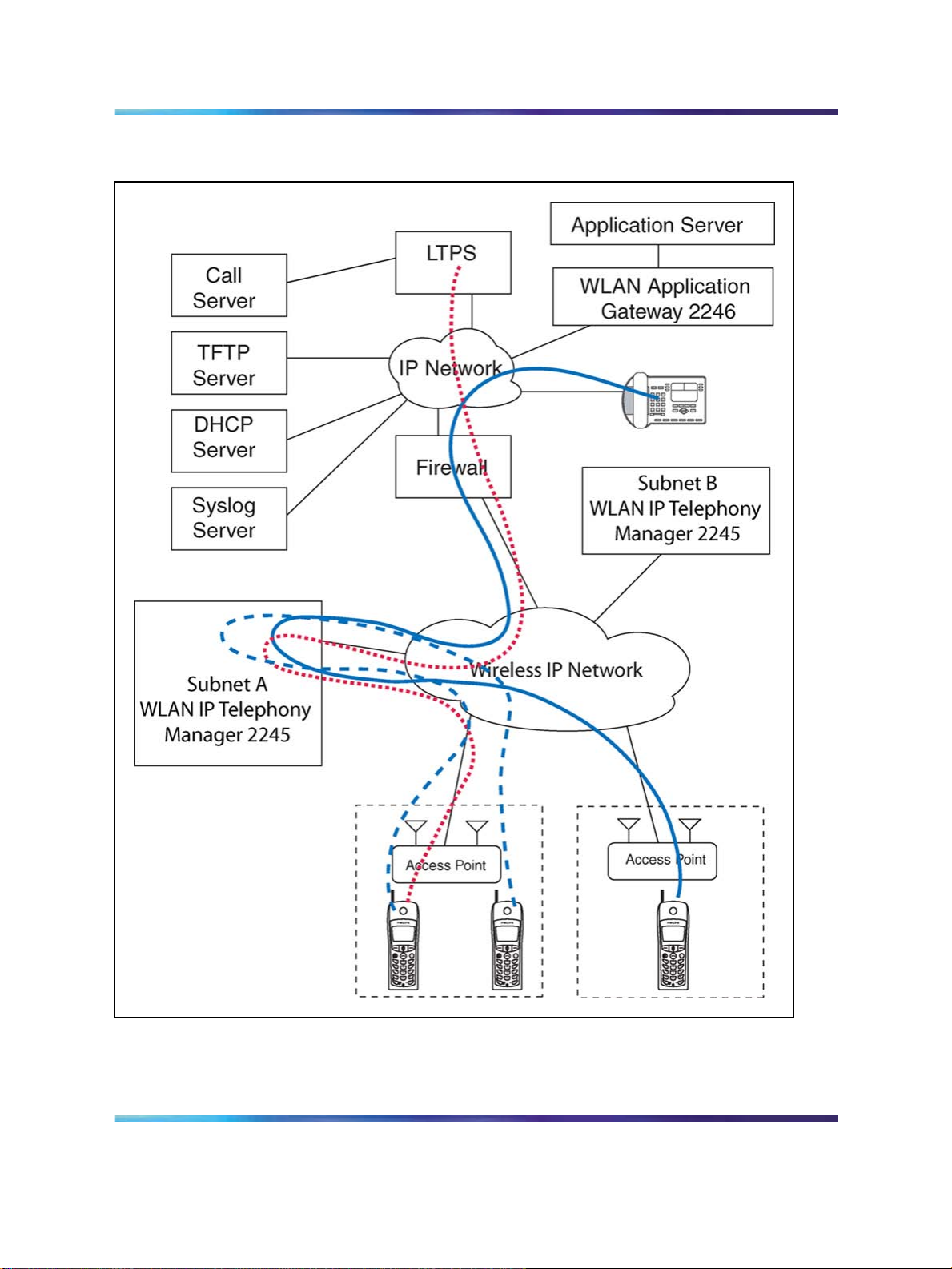
Figure 1 "Typical wireless telephone network configuration" (page 24) shows
a typical wireless telephone network configuration. The three different lines
indicate the following:
•
Red—signalling
•
Blue dashed—wireless to wireless audio
•
Blue solid—wireless to wired audio
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007
24 Overview
Figure 1
Typical wireless telephone network configuration
Call Server
The Call Server can be the Call Server of any Nortel Communication Server
(CS) 1000 system running CS 1000 Release 5.0 software.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

DHCP Server
DHCP options
WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140 25
The existing DHCP Server can be on either side of the firewall, according
to the site administrator’s preference. The DHCP server is optional if the
wireless handsets and WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 are statically
configured.
If you use a DHCP Server, configure the following options:
•
DHCP Option 3—the Default Gateway
•
DHCP Option 7—the Syslog Server
•
DHCP Option 42—the Time Server
•
DHCP Option 60—the Class Identifier
•
DHCP Option 66—the IP address of the TFTP Server
•
DHCP Option 151—the IP address of the WLAN IP Telephony Manager
2245
• DHCP Option 152—the IP address for the optional WLAN Application
Gateway 2246
For more information, see "DHCP server options" (page 184).
TFTP Server
A TFTP Server is required in an IP Telephony system to distribute software
to the wireless handsets and WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245. It can
reside on a different subnet than the Call Server and APs. The TFTP Server
can be located on either side of the firewall.
Firewall
The firewall is an optional element that is often used to separate the wireless
and wired domains.
WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140
The WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140 uses
Voice over IP (VoIP) technology on IEEE 802.11-compliant Wireless Local
Area Networks (WLANs). Access points (AP) use radio frequencies to
transmit signals to and from the wireless handsets.
ATTENTION
In this document, handsets means the WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and
WLAN Handset 6120/6140. Where the feature refers only to a specific handset,
the full handset name is used.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

26 Overview
Employees carry wireless handsets to make and receive calls as they move
throughout the building. The handsets are used only on the premises; they
are not cellular phones. The handsets communicate with the CS 1000 and
with the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245. Just like wired telephones, the
wireless handsets receive calls directly, receive transferred calls, transfer
calls to other extensions, and make outside and long-distance calls (subject
to corporate restrictions).
The handsets interoperate with other IP Line and IP Trunk features and
devices, such as IP Peer, and the IP Phone 20xx and IP Softphone 2050
series of IP Phones, with the exception of some media-related constraints
described in "Codecs" (page 79).
The frequencies that are allocated are governed by IEEE guidelines for
WLANs and are part of the free spectrum. The WLAN Handset 6120/6140
uses a, b, and g frequencies, and the WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212
uses the b frequency.
The handsets work only in a Nortel Succession 3.0 (and later) environment
coordinated with a Communication Server (CS) 1000 or Business
Communications Server (BCM). These handsets communicate with the
Nortel call server through the Unified Network IP Stimulus (UNIStim)
protocol. The media path of the voice call goes from the handset directly to
the destination device (through the WLAN Telephony Manager 2245). In
addition, the handset encapsulates all traffic in the SpectraLink VoicePriority
(SVP) protocol. The WLAN Telephony Manager 2245 deencapsulates the
VoIP traffic from SVP and passes it onto the network—it does not translate
between UNIStim and SVP. Therefore, the Telephony Manager 2245 is in
the path of all communication to and from the handset. Likewise, signaling
goes from the handset to the Telephony Manager 2245 to the call server.
The WLAN Handset 2211 and the WLAN Handset 6140 are the most
durable and they are the only handsets that support Push-to-talk (PTT).
For more information about the handsets, see the following publications:
•
WLAN Handset 2210 User Guide (NN10300-077)
•
WLAN Handset 2211 User Guide (NN10300-078)
•
WLAN Handset 2212 User Guide (NN10300-071)
•
WLAN Handset 6120 User Guide (NN43150-100)
•
WLAN Handsets Fundamentals (NN43001-505)
Components
The WLAN Handset Series 2200 offers the following components for local
configuration:
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2200 Series Configuration Cradle
Software—software only
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007
WLAN Handset 2210/2211/2212 and WLAN Handset 6120/6140 27
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 2200 Series Configuration Cradle—required
hardware (serial cable included)
The WLAN Handset 6100 Series offers the following components for local
configuration:
•
Nortel WLAN Handset 6100 Series Administration Tool
Software—software only
•
Nortel WLAN Handset6100 Series Dual Slot Handset Charger—required
hardware (USB cable not included)
•
USB Cable for the Nortel WLAN Handset 6100 Series Dual Slot Handset
Charger
ATTENTION
For the purposes of this document
•
Configuration Cradle refers to the Nortel WLAN Handset 2200 Series
Configuration Cradle.
•
Handset Administration Tool refers to the Nortel WLAN Handset 6100
Series Administration Tool Software.
•
Dual Slot Handset Charger or Handset Charger refers to the Nortel
WLAN Handset 6100 Series Dual Slot Handset Charger.
Language
The handset menus and screens that originate from the Call Server
are displayed in the languages supported on the Call Server. The
administration and configuration menus, and all other local handset prompts
are English-only.
Licenses
The handset appears to the Call Server as a standard IP Phone 2004.
Therefore, each wireless handset requires one IP User License and is
subject to the same feature packaging requirements as the existing IP
Phone 2004.
Wi-Fi Multimedia
The handsets support basic Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) to improve Quality
of Service (QoS), as defined in the 802.11e specification. WMM provides
prioritized QoS capability when concurrent applications, each with unique
latency requirements, are competing for network resources.
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

28 Overview
Wired Equivalent Privacy
Wi-Fi Protected Access
Wi-Fi Protected Access2
When WMM is used, all voice traffic originating from the wireless handset is
assigned the WMM Voice Access Category, making it the highest priority
application. If the wireless network supports WMM, the handsets enable
WMM support automatically; otherwise, SpectraLink Voice Prioritization
(SVP) is used.
The handsets support Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) as defined by the
802.11a, b, and g specification. Nortel offers the product with both 40-bit
and 128-bit encryption. WEP increases the security of the wireless LAN to a
level similar to a wired Ethernet LAN.
The handsets support Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) using preshared key
(PSK), as defined by the 802.11i specification. WPA increases the security
of the wireless LAN, using key encryption, key rotation, authentication and
message integrity checking.
The handsets support Wi-Fi Protected Access2 (WPA2) using preshared
key (PSK) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), as defined by the
802.11i specification. WPA2 increases the security of the wireless LAN,
using key encryption, key rotation, data encryption, authentication, and
message integrity checking.
Virtual Private Network
The WLAN Handset 2212 supports Virtual Private Network (VPN) security.
VPN security provides a secure tunnel for the transfer of unencrypted
information. A two-phase approach is used to negotiate the tunnel, with
Phase 1 protecting Phase 2. Phase 1 uses preshared keys, Diffie-Hellman
group, hashing, and encryption. Phase 2 uses hashing and encryption.
Both phases have limited, configurable lifetimes.
Push-to-talk feature
With the Push-to-talk (PTT) feature, the WLAN Handset 2211 and the
WLAN Handset 6140 can operate in a PTT group-broadcast mode like a
two-way radio, in addition to the standard telephone operation.
For more information, see WLAN Handsets Fundamentals (NN43001-505).
Text-messaging feature
All WLAN handsets support text messaging applications through the WLAN
Application Gateway 2246. The application server communicates to the
WLAN Application Gateway 2246 through a proprietary Open Application
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007

Interface (OAI) messaging protocol. The WLAN Application Gateway
2246 forwards the messages to the WLAN IP Telephony Manager, which
encapsulates the message for delivery to the handset.
If text-messaging functions are programmed, the handset can receive text
messages. While you access text messages, the handset is in messaging
mode. Incoming calls ring with the second call-ringing sound.
Loud noise environments
The handsets are designed to provide optimal voice quality. However, when
used in extremely loud noise environments, (for example, close to working
heavy machinery), degradation in call quality can be experienced due to
echo. Avoid using the handsets in loud noise environments.
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245
The WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 is a device that manages IP
telephony network traffic on the WLAN system. It is required to utilize the
11Mbs maximum transmission speed available in the handsets. The WLAN
IP Telephony Manager 2245 acts as a proxy for the wireless handsets. It
provides a number of services including a QoS mechanism, AP bandwidth
management, and efficient RF link utilization.
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 29
The WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245 works with the APs to provide
Quality of Service (QoS) on the WLAN. All voice packets are encapsulated
by the wireless handsets. The encapsulated voice packets to and from the
wireless handsets are handled by the WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245
and routed to and from a Call Server.
SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP) is the QoS mechanism implemented on
the wireless handsets and APs to enhance voice quality over the wireless
network. SVP gives preference to voice packets over data packets on
the wireless medium, increasing the probability that all voice packets are
transmitted and with minimum delay. SVP is fully compliant with the IEEE
802.11 and 802.11a, b, and g standards.
Each subnet, where the wireless handsets operate, requires at least one
WLAN IP Telephony Manager 2245. One standalone unit can process up to
80 simultaneous calls depending on the model, as listed in Table 2 "WLAN
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007
30 Overview
Telephony Manager 2245 model numbers and capacities" (page 30).If
greater capacity is required, multiple units can be used in a master-slave
arrangement.
Table 2 WLAN Telephony Manager 2245 model numbers and capacities
Model number Maximum
NTTQ60BA 10 simultaneous users
NTTQ60CA 20 simultaneous users
NTTQ60AA 80 simultaneous users (standard)
WLAN Application Gateway 2246
The WLAN Application Gateway 2246 is an optional device that enables
third-party applications to communicate directly with up to 10 000 wireless
handsets. The WLAN Application Gateway 2246 is connected to the LAN
Ethernet switch through an RJ-45CAT5 cable.
For more information about the WLAN Application Gateway 2246, see
Appendix "WLAN Application Gateway 2246" (page 147).
number users
A WLAN Application Gateway 2246 supports 64 to 10 000 wireless
handsets, depending on the model of Gateway, as listed in Table 3 "WLAN
Application Gateway 2246 models and capacities" (page 30).
Table 3 WLAN Application Gateway 2246 models and capacities
Access Points
802.11a, b, and g APs provide the connection between the wired Ethernet
LAN and the wireless (802.11) LAN. APs must be positioned in all areas
where the wireless handsets are used. The number and placement of APs
Model number
NTTQ65AA
NTTQ65BA
NTTQ65CA
NTTQ65DA
NTTQ65EA
NTTQ65FA
Maximum
number of users
64
128
256
512
1024
10 000
WLAN IP Telephony Installation and Commissioning
Copyright © 2004-2007, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-504 01.02 Standard
Release 5.0 15 June 2007
 Loading...
Loading...