Page 1

Nortel Communication Server 1000
Communication Server 1000 to
MCS 5100 Converged Desktop
Type 2 Configuration Guide
NN43001-321
.
Page 2

Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.05
Document date: 15 February 2008
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada
LEGAL NOTICE
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly agreed
to in writing NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY
KIND,EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are subject to
change without notice.
Nortel, the Nortel Logo, the Globemark, SL-1, Meridian 1, and Succession are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 3

Revision history
February 2008
Standard 01.05. This document is up-issued to update the instructions for
Configuring Meet Me Audio Conferencing in the NRS for CDS.
January 2008
Standard 01.04. This document is up-issued to add instructions for
Configuring Meet Me Audio Conferencing in the NRS for CDS.
December 2007
Standard 01.03. This document is up-issued to update the Converged
Desktop Feature installation.
June 2007
Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued to remove the Nortel Networks
Confidential statement.
May 2007
Standard 01.01. This document is up-issued to support Communication
Server (CS) 1000 Release 5.0. This document contains information
previously contained in the following legacy document, now retired: CS
1000 to MCS 5100 Converted Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
(553-3001-521). No new content has been added for Communication
Server 1000 Release 5.0. All references to Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5 are applicable to Communication Server Release 5.0.
3
In addition, changes for the following CRs are included:
CR Q01473312, in the section "Feature implementation" (page 30), a note
is added regarding call forwarding on a converged telephone.
CR Q01377222, a note is added regarding the default configuration on-hook
Handsfree.
CR Q01492694, a sentence is added regarding a virtual trunk call queued
on a CDN, explaining why a DSP resource is used.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 4

4 Revision history
CR Q01478214, two options are added to "Configuring MCS 5100 in the
NRS for CDS" (page 90). MCS 5100 is configured as a Gateway Endpoint
in the first option and as a Collaborative Server in the second.
October 2006
Standard 3.00. This document is up-issued for CR Q01412328-01, to add
prompt and response to LD-17 Configuration of Value Added Server (VSID)
table, to set the VSID security for the SIP CD AML link to No. This prompts
the Signaling Serverto send a Cancel message to convergeddesktop so that
the PC Client does not continue to ring after call is answered by Call Pilot.
April 2006
Standard 2.00. This document is up-issued for CR Q01291954, updating
the available MCS 5100 documentation.
September 2005
Standard 1.00. This document is a new document issued to support
Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5, and Multimedia Communication
Server 5100 Release 3.5.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 5

Contents
How to get help 7
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site 7
Getting help from the Nortel Web site 7
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center 7
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code 8
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller 8
Introduction 9
Subject 9
Applicable systems 9
Intended audience 10
Conventions 10
Related information 10
Converged Desktop Services 13
Contents 13
Introduction 13
How Converged Desktop Services works 14
Operating parameters and feature interactions 26
Call walk-throughs 27
Feature requirements 29
Feature implementation 30
Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network 30
5
Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed
networks 37
Contents 37
Introduction 37
Mixed network example: UDP 37
Mixed network example: CDP 42
CDS configuration: overview 47
Contents 47
Introduction 47
Configuration notes 47
Description of the network configured in this document 48
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 6

6 Contents
Configuring CS 1000 49
Contents 49
Before you begin 49
CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 49
Configuring the Converged Desktop User 66
Configuring MCS 5100 67
Contents 67
Before you begin 67
Implementation summary 68
Implementation details 68
Configuring a Converged Desktop user 81
CS 1000 NRS operation 87
Contents 87
Introduction 87
Operation 88
Operational logic 96
Maintenance 99
Contents 99
Introduction 99
CS 1000 CLI commands 99
MCS 5100 tools 101
Appendix A Parameter configuration for a SIP URI 103
Contents 103
Introduction 103
Example 103
Phone-context strings 104
Appendix B PC Client windows 107
Procedures
Procedure 1 Configuring SIP CDS on the Signaling Server 57
Procedure 2 Adding the IP Address of the IP Telephony node as an
Authenticated Server 68
Procedure 3 Configuring the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group 69
Procedure 4 Configuring number qualifiers 74
Procedure 5 Configuring a route list 75
Procedure 6 Configuring routes for each dialing plan entry 78
Procedure 7 Configuring a Service Package 82
Procedure 8 Configuring a Converged Desktop User in MCS 5100 83
Procedure 9 Configure Meet Me Audio Conferencing 94
Procedure 10 Using the MCS 5100 Translation Verification tool 101
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 7
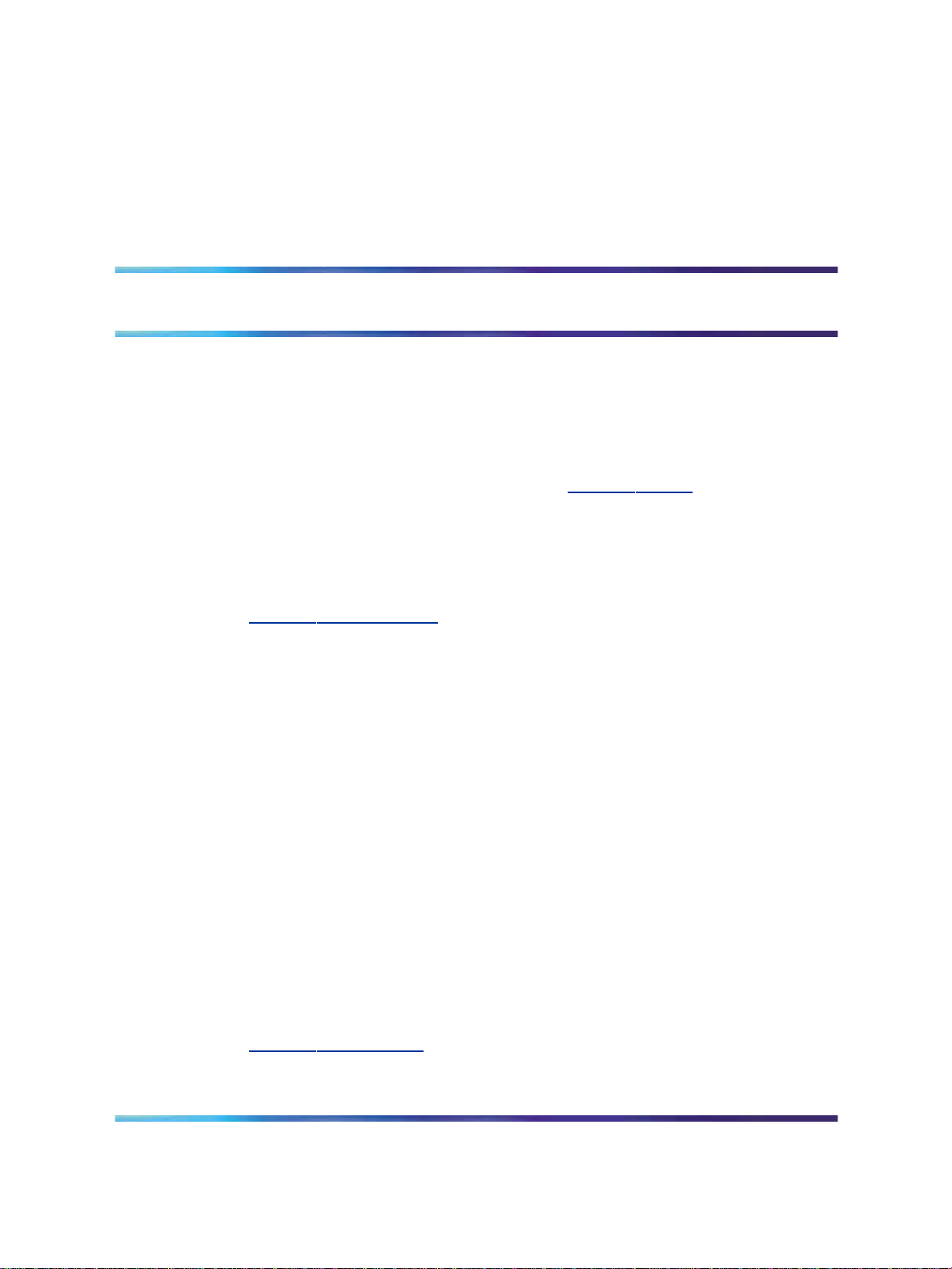
How to get help
This chapter explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site
The content of this documentation is current at the time the product
is released. To check for updates to the latest documentation for
Communication Server (CS) 1000, go to w
the Technical Documentation page for CS 1000.
Getting help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support web site:
ww.nortel.com/support
w
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and
tools to address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
•
download software, documentation, and product bulletins
ww.nortel.com
7
and navigate to
•
search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation
for Nortel equipment
•
open and manage technical support cases
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support
web site, and you have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help over
the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835). Outside North
America, go to the following web site to obtain the telephone number for
your region:
w
ww.nortel.com/callus
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 8

8 How to get help
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
w
ww.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 9

Introduction
This document is a global document. Contact your system supplier or your
Nortel representative to verify that the hardware and software described
are supported in your area.
Subject
This document describes Session Internet Protocol Converged Desktop
System (SIP CDS) and its configuration on Communication Server 1000
(CS 1000) and Multimedia Communication Server 5100 (MCS 5100)
systems. It also provides examples of the configuration of a dialing plan and
numbering plan for a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network.
This document is describes the design and configuration of a Converged
Desktop environment between CS 1000 and MCS 5100 systems. The
examples provided in this document represent only one example of design
and configuration. "Description of the network configured in this document"
(page 48) provides the outline of the network used as an example only.
9
Note on legacy products and releases
This technical document contains information about systems, components,
and features that are compatible with Nortel CS 1000 Release 3.5 and
MCS 5100 Release 4.0 software. For more information on legacy products
and releases, click the Technical Documentation link under Support &
Training on the Nortel home page:
ww.nortel.com
w
Applicable systems
This document applies to the following systems:
•
Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E) CP PII, CP PIV and CP PM.
•
Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG) CP PII,
CP PIV
•
Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG) CP PII,
CP PIV
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 10

10 Introduction
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
•
Meridian 1 PBX 61C CP PII, CP PIV
•
Meridian 1 PBX 81C CP PII, CP PIV
Note: When upgrading software, memory upgrades may be required on
the Signaling Server, the Call Server, or both.
Intended audience
This document is intended for individuals responsible for administering CS
1000 and Meridian 1 systems.
Conventions
Terminology
In this document, the following systems are referred to generically as
"system":
•
Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
•
Communication Server 1000M (CS 1000M)
•
Meridian 1
The following systems are referred to generically as "Small System":
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
•
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
The following systems are referred to generically as "Large System":
•
Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
•
Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
•
Meridian 1 PBX 61C CP PII, CP PIV
• Meridian 1 PBX 81C CP PII, CP PIV
Related information
This section lists information sources that relate to this document.
Technical Documents
The following technical documents referenced in this document:
•
IP Peer Networking Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-313)
Refer to the following MCS 5100 documentation for additional information
about CDS:
•
Provisioning Client User Guide (NN42020-105)
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 11

Related information 11
•
Feature Description Guide (NN42020-125)
•
Interworking Fundamentals (NN42020-127)
Online
To access Nortel documentation online, click the Technical Documentation
link under Support & Training on the Nortel home page:
w
ww.nortel.com
CD-ROM
To obtain Nortel documentation on CD-ROM, contact your Nortel customer
representative.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 12

12 Introduction
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 13

Converged Desktop Services
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 13)
"Scope of this document" (page 14)
"How Converged Desktop Services works" (page 14)
"Users in a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network" (page 18)
"Converged Mode and Unconverged Mode" (page 19)
"CDS originating and terminating call handling" (page 19)
"AML ELAN numbers and VAS numbers" (page 25)
"Click-to-Call" (page 25)
"Operating parameters and feature interactions" (page 26)
"Call walk-throughs" (page 27)
13
"Feature requirements" (page 29)
"Feature implementation" (page 30)
"Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network" (page 30)
"Digit-based addresses and alphanumeric addresses" (page 30)
"Dialing plan issues" (page 31)
"DNs as MCS aliases versus DNs as MCS usernames" (page 32)
"Directory Number qualification" (page 32)
"Converged Desktop implications" (page 34)
Introduction
This section provides an overview of Converged Desktop Services (CDS)
to give the user a perspective on what CDS is, how it works, and what
it requires. This section also provides an overview of dialing plan and
numbering plan issues for mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 networks.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 14
14 Converged Desktop Services
Scope of this document
This document is intended to assist technical administrators in designing
and configuring a Converged Desktop environment between CS 1000 and
MCS 5100 systems. The examples provided in this document represent
only one example of design and configuration. "Description of the network
configured in this document" (page 48) provides the outline of the network
used as an example only.
How Converged Desktop Services works
Session Initiation Protocol Converged Desktop Service (SIP CDS) is a CS
1000 and MCS 5100 feature. SIP CDS allows users to have simultaneous
access to multimedia features on MCS 5100, and to business grade
telephony features on CS 1000 systems. The Converged Desktop feature
gives users access to business grade telephony features not supported
by the SIP standard, while also allowing users to take advantage of the
multimedia functionality of MCS 5100. The user’s existing telephone is
used for telephony functionality while the PC Client delivers the multimedia
features.
A Converged Desktop consists of a telephone and multimedia PC Client
(PCC) software (see Figure 1 "Converged Desktop" (page 14)). The
supported telephones include analog (500 or 2500-type) telephones, digital
telephones, and IP Phones. A SIP Phone cannot be configured as a
Converged Desktop. A SIP telephone can be configured on the MCS 5100
as a stand-alone device or be tied to a PC Client. In both instances, the SIP
telephone receives only features associated with the MCS 5100.
Figure 1 Converged Desktop
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 15

How Converged Desktop Services works 15
In Converged Mode, both the CS 1000 telephone and the MCS 5100 PC
Client are integrated to provide both feature sets. In Converged Mode, the
CS 1000 telephone effectively becomes the audio device for the MCS 5100
PC Client, so that any audio requirement from the MCS 5100 user (for
example, Click-to-Call) is directed to the CS 1000 telephone.
A user may selectively deactivate Converged Mode, so both the MCS 5100
client and the CS 1000 telephone become stand-alone devices. This allows
remote users to utilize the MCS 5100 client for both multimedia and voice
functionality (for example, using a USB headset with the MCS 5100 PC
Client). The voice functionality on a MCS 5100 client in Unconverged Mode
is limited to the voice features supported on the MCS 5100. The CS 1000
telephone maintains its full feature set as programmed.
The Converged Desktop feature utilizes the CDS software on the Signaling
Server and the SIP Trunking Application to integrate the two systems.
These functions became available in CS 1000 Release 4.0.
CDS is enabled between CS 1000 and MCS 5100 using several
components, including:
•
SIP Trunking Application — SIP Gateway and Virtual Trunk Route
•
CDS on the Signaling Server
•
Application Module Link (AML) and Value Added Server (VAS) assigned
to the CDS application over the common ELAN subnet
•
Control Directory Number (CDN) (Converged Services Directory
Number [CSDN]) to trigger messaging over the AML/VASlink associated
with CDS
•
Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) queue with agents — used for the
Personal Call Assistant (PCA) application associated with CDS
•
telephone Class of Service — used to enable Converged Desktop
messaging
•
telephone option for CSDN — redirects inbound calls directed to the
telephone to CSDN to enable Converged Desktop signaling
•
optional Recorded Announcement (RAN) route — used to play progress
or delay indication to caller while waiting for PCA agent
•
Converged Desktop as a part of the Service Package for the MCS
Client user
•
dialing plan for CS 1000 and MCS 5100
In general, when a CS 1000 user is designated as a Converged Desktop
user, they receive a CS 1000 telephone and an MCS 5100 PC Client. The
telephone is programmed with a Class of Service to allow CDS messaging
(the options described in "CDS configuration: overview" (page 47)).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 16

16 Converged Desktop Services
When a call terminates to the CS 1000 telephone, the CDMV or CDMO
Class of Service redirects the call to the CSDN defined on the telephone,
before ringing the CS 1000 telephone. The CSDN is a CDN used for CDS.
This CDN number is also configured on the Signaling Server so that it can
be acquired by the CDS application when the Signaling Server starts.
When the call terminates to the CDN a message is sent over AML/VAS to
the CDS as notification of the incoming call. If the call is a virtual trunk
call, and queued on a CDN, a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) resource is
used to play the ringback to the caller because CDN is a TDM resource. (A
DSP resource is required to handle media between a TDM resource and
an IP resource.) The CDS cannot determine where the call terminates,
either on the CS 1000 telephone or in the SIP network; the termination
location is based on the user’s Advanced Screening options in the MCS
5100 Client. Therefore, the CDS instructs the Call Server to make a Virtual
Trunk call to a predetermined number, as defined on the Signaling Server
(the Service DN used for making a VTRK call from an Agent) and the CS
1000 dialing plan. This call reserves a Virtual Trunk in case it is required to
terminate the call to a SIP device (if so configured in the user’s Advanced
Screening options). After the Virtual Trunk call is established, CDS sends a
SIP INVITE message to the MCS 5100 using the SIP Gateway Application.
The MCS 5100 receives the INVITE message and processes it on the
user’s PC Client. The user’s Advanced Screening options are checked for
any rules that determine the destination. If no rules exist and the user is
in Converged Mode, the MCS 5100 notifies the CDS application to notify
the converged telephone. The CDS bridges the call and the Virtual Trunk is
dropped. An MCS 5100 call notification screen-pop appears, and the CS
1000 telephone rings. The call is answered on the CS 1000 telephone and
call logs are generated on the MCS 5100 PC Client. If the caller is another
SIP device or Converged Desktop user, all MCS 5100 features become
available for the call.
For outbound calls, the user may use their MCS client in a Click-to-Call
scenario or use the keypad of their CS 1000 telephone. When using the
MCS 5100 Client, the user has access to all directories available and can
process a call. When the user selects a directory entry or dials a telephone
number, the MCS 5100 sends an INVITE message to the CS 1000, and
CDS processes the call to the CS 1000 telephone. The telephone must be
answered before CDS can process the second leg of the call. When the call
is answered at the CS 1000 telephone, the destination called and the two
calls are bridged together. The PCA application is used for making these
calls. The MCS 5100 Client activates call logs. If the destination is another
SIP device, the MCS 5100 Client allows multimedia features.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 17

How Converged Desktop Services works 17
In Converged Mode, incoming and outgoing calls to and from a converged
telephone notify the MCS 5100. Upon notification, the MCS 5100 then
provides different SIP services and features to the user. The features
include the following, depending on where the call is destined, or from
where it originated.
All calls to or from a Converged Desktop user receive:
•
Call log — Allows a user to see who has called and when the call
occurred.
•
Real-time call state update — Provides the presence (status) of a user.
For example, "active on the phone" or "active available".
•
Presence update — Displays the status of other users if the user is
added in the Friends list. The Friends list is a list of friends/users that
were added (by the user) from the Personal Directory Book, Global
Directory Book, or from the call logs. This feature is provided by the
MCS 5100 to all PC Clients (including the Converged PCC). Activity on
the telephone can update the presence on the PC Client. For example,
establishing a voice call to the telephone can update your presence for
all registered MCS 5100 users to a presence update such as "Active on
the phone". Other presence updates include "Available", "Unavailable",
or "Offline".
•
Popup window on the converged PC Client — Opens a window when
receiving a call. The user sees the caller’s name and picture ID (if a
picture is available). A popup window also opens when the user calls
another Converged Desktop user or calls a stand-alone SIP user.
•
Click-to-Call — Allows a user to click a contact from their PC Client and
make a call. The call is initiated from the PC Client but the call is placed
from the telephone. For more information, see "Click-to-Call" (page 25).
The following features are available if the call if originated on, or destined
for, a SIP client:
• Application sharing — Allows users to share applications such as
whiteboard functionality, clipboard transfers, instant messaging, and
file transfers.
•
Video — Allows users to have a video conversation. The voice portion
of the conversation is provided by the telephone and the video portion
is provided by the PC Client. It is possible to add video to an already
initiated telephone conversation. If in Converged Mode, the video
can be started manually from the PC Client. The Converged Desktop
application knows from where to pick up the video because the
requested video session is bound with the voice conversation. If the
voice conversation is dropped, then the video session is automatically
closed.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 18
18 Converged Desktop Services
•
Web co-browsing — Allows users to share a web browser. If both users
have the web co-browsing feature, then one user can automatically
control (or drive) the other user’s web browser.
All of these features are achieved by sending originating and terminating
call notifications to the MCS 5100.
Users in a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network
CS 1000 and MCS 5100 systems can interoperate directly using SIP. Both
systems can be deployed in a single mixed customer network. Table 1
"Types of users in a mixed CS 1000 and MCS 5100 customer network"
(page 18) shows the three types of users in this mixed CS 1000 and MCS
5100 customer network.
Table 1 Types of users in a mixed CS 1000 and MCS 5100 customer network
User Description
CS 1000 user A CS 1000 user has an account created on the CS 1000 system. The only
client available to the CS 1000 user is a client under CS 1000 control.
This user does not have an account on the MCS 5100 system and the user
cannot use clients under MCS 5100 control.
MCS 5100 user An MCS 5100 user has an account created on the MCS 5100 system. The
only client available to the MCS 5100 user is a client under MCS 5100
control.
This user does not have an account on the CS 1000 system. The user
cannot use clients under CS 1000 control.
Converged Desktop
(CD) user
A Converged Desktop user has two accounts:
•
a CS 1000 account
•
an MCS 5100 account
The Converged Desktop user also has two available clients:
• a client under CS 1000 control (for example, an IP Phone 2004)
•
a client under MCS 5100 control (the Multimedia PC Client)
A Converged PC Client always uses the CS 1000 client as an endpoint
for audio streams (in this configuration, the Multimedia PC Client cannot
terminate/originate audio streams). A call itself can be initiated on the CS
1000 client or on the Multimedia PC Client. The Multimedia PC Client uses
the "Click-to-Call" mechanism to engage the CS 1000 client in the call.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 19

How Converged Desktop Services works 19
Note: When a Converged Desktop user is not in a converged state, the
user effectively becomes an MCS 5100 user and the CS 1000 device
becomes a stand-alone voice device.
Converged Mode and Unconverged Mode
An MCS 5100 client can be in one of the two following modes:
•
Converged Mode — The MCS 5100 client uses the CS 1000 voice path.
It also uses the AML link for CDS signaling.
• Unconverged Mode — The MCS 5100 client uses the MCS 5100 voice
path. It does not use the AML link for CDS signaling.
The mode is defined when each Client is configured.
Note: Thisdocument assumes that the MCS 5100 client is in Converged
Mode. Exceptions for Unconverged Mode are noted.
CDS originating and terminating call handling
The implementation of the Converged Desktop Service includes two parts:
•
outgoing call (or a telephone-originated call) notification to the MCS 5100
•
incoming call (or a call terminated on a converged telephone) notification
to the MCS 5100
Users in Converged Mode can be defined with two Classes of Services for
Converged Desktop:
•
CDMO = Converged Desktop Multimedia Only — The user has an MCS
5100 PC Client and a CS 1000 desktop telephone. The user has access
to all MCS 5100 multimedia features (such as video), except Personal
(PA) routing.
•
CDMV = Converged Desktop Multimedia and Voice — The user has an
MCS 5100 PC Client and a CS 1000 desktop telephone. The user has
access to all MCS 5100 multimedia features (such as video), including
PA routing.
Making a call
Users can make an outgoing Converged Desktop call in two ways:
•
Dial from a CS 1000 telephone.
•
"Dial" from an MCS 5100 PC Client (Click-to-Call) in one of the following
ways:
— Press the Make a call button.
— Select from a Call Log.
A call from the inbox to the PSTN is not supported.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 20
20 Converged Desktop Services
— Select from a Friends list or Directory book.
In both instances the following functionality is automatically provided:
•
The Call Log is updated after the call.
•
A pop-up window is generated if another CD user or SIP user was called.
•
The users’ Presences are updated after the call is answered.
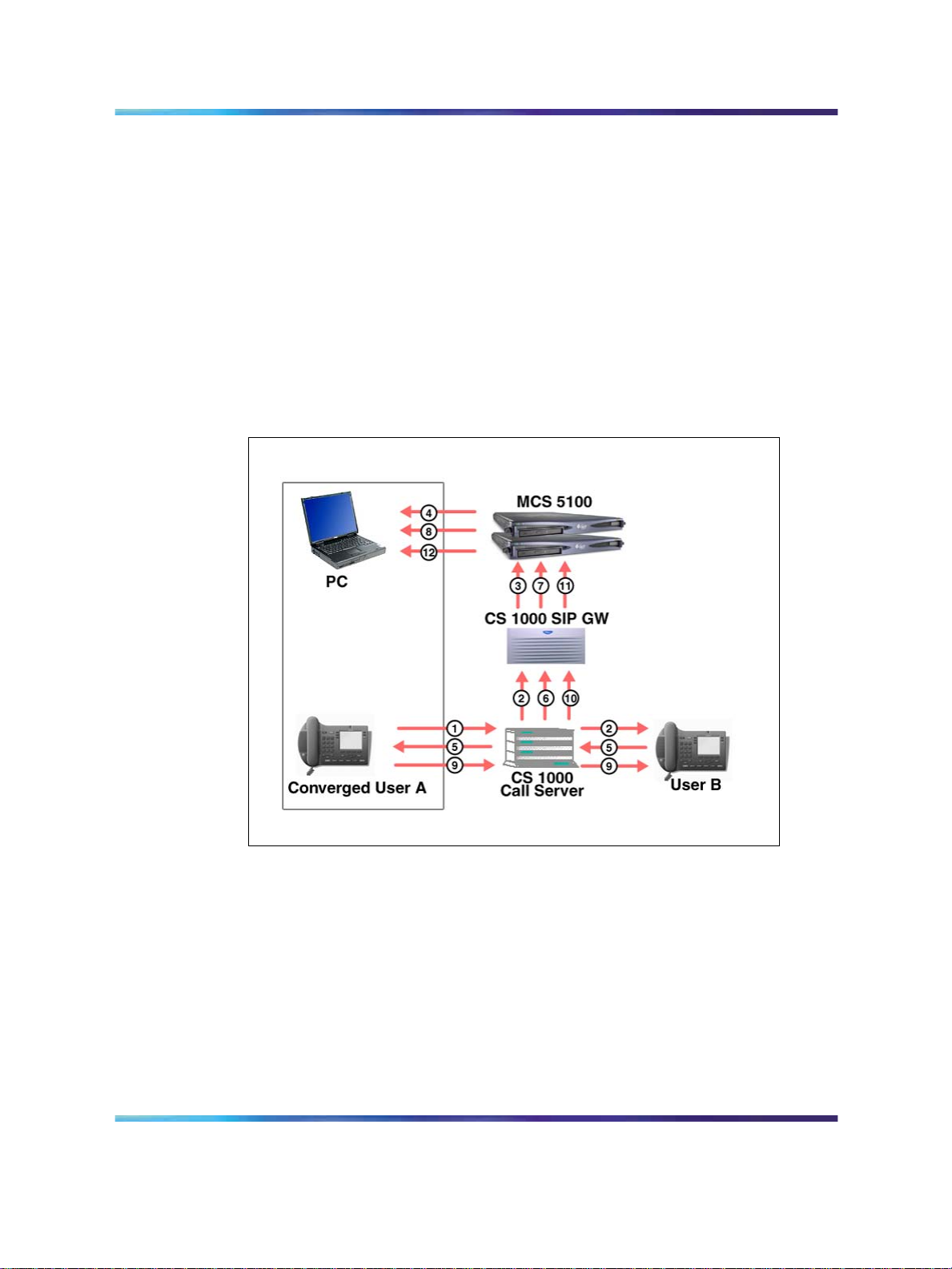
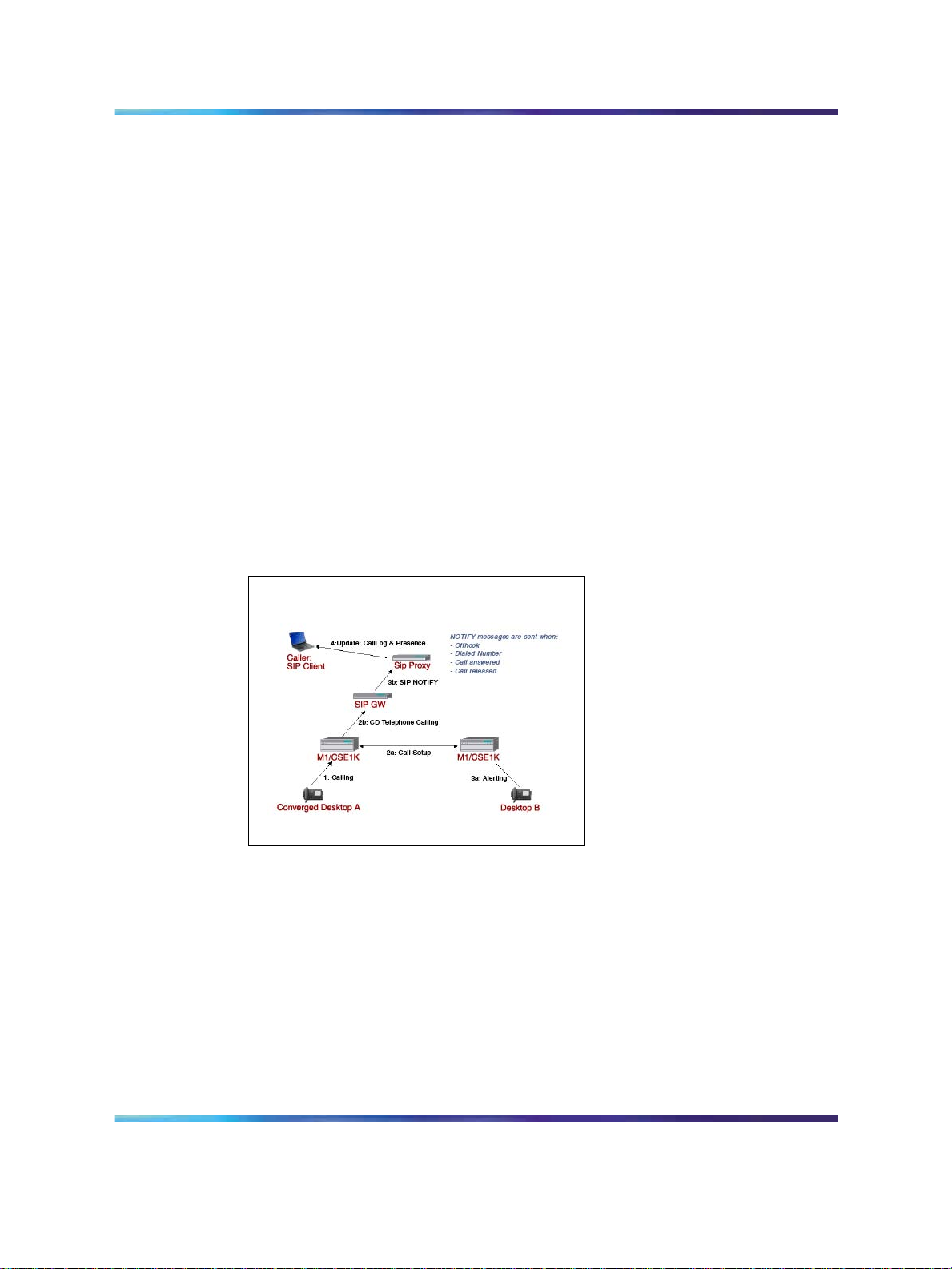
Figure 2 "Call flow: making a call from a CS 1000 desktop telephone" (page
20) shows the call flow and messaging that occurs when a call is made
from a CS 1000 desktop telephone.
Figure 2
Call flow: making a call from a CS 1000 desktop telephone
Legend:
1 Converged user A dials user B.
2
User B rings; Off-hook message sent.
3
Calling message sent.
4 PCC Call Log updated.
5
User B answers call.
6
Active message sent.
7
Active message sent.
8
Call timer started.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 21
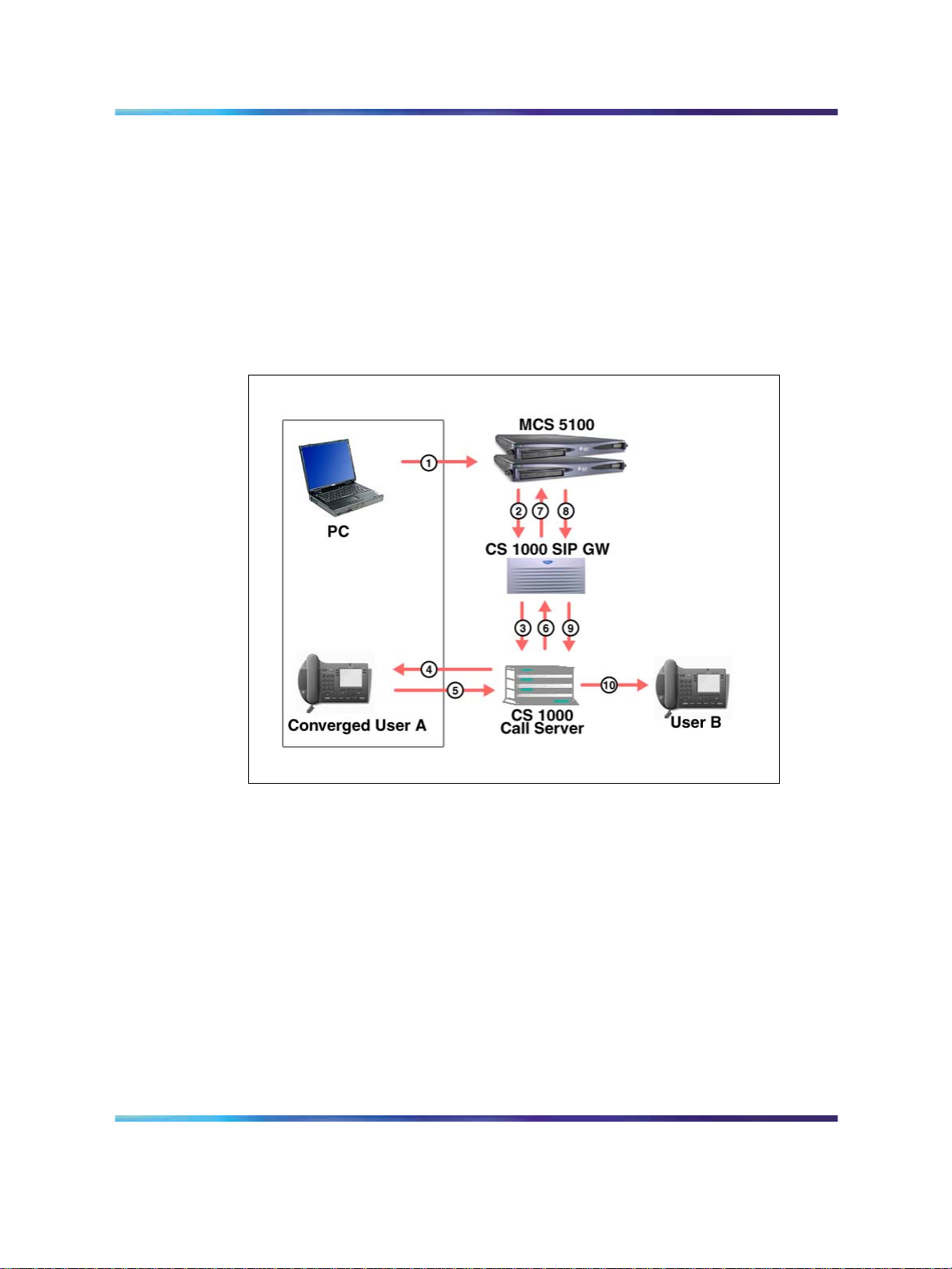
How Converged Desktop Services works 21
9
Converged user A releases.
10
Call disconnected; Disconnect message sent.
11
Release message sent.
12 Call timer stopped, Call Log updated.
Figure 3 "Call flow: Click-to-Call" (page 21) shows the call flow and
messaging that occurs during a Click-to-Call session.
Figure 3
Call flow: Click-to-Call
Legend:
1
Click-to-Call action initiated.
2
Click-to-Call Invite message sent.
3
One idle PCA selected to call own phone.
4 Converged user A rings.
5
User A answers.
6
Initial call is answered.
7
Call is answered.
8
Call made to user B.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 22
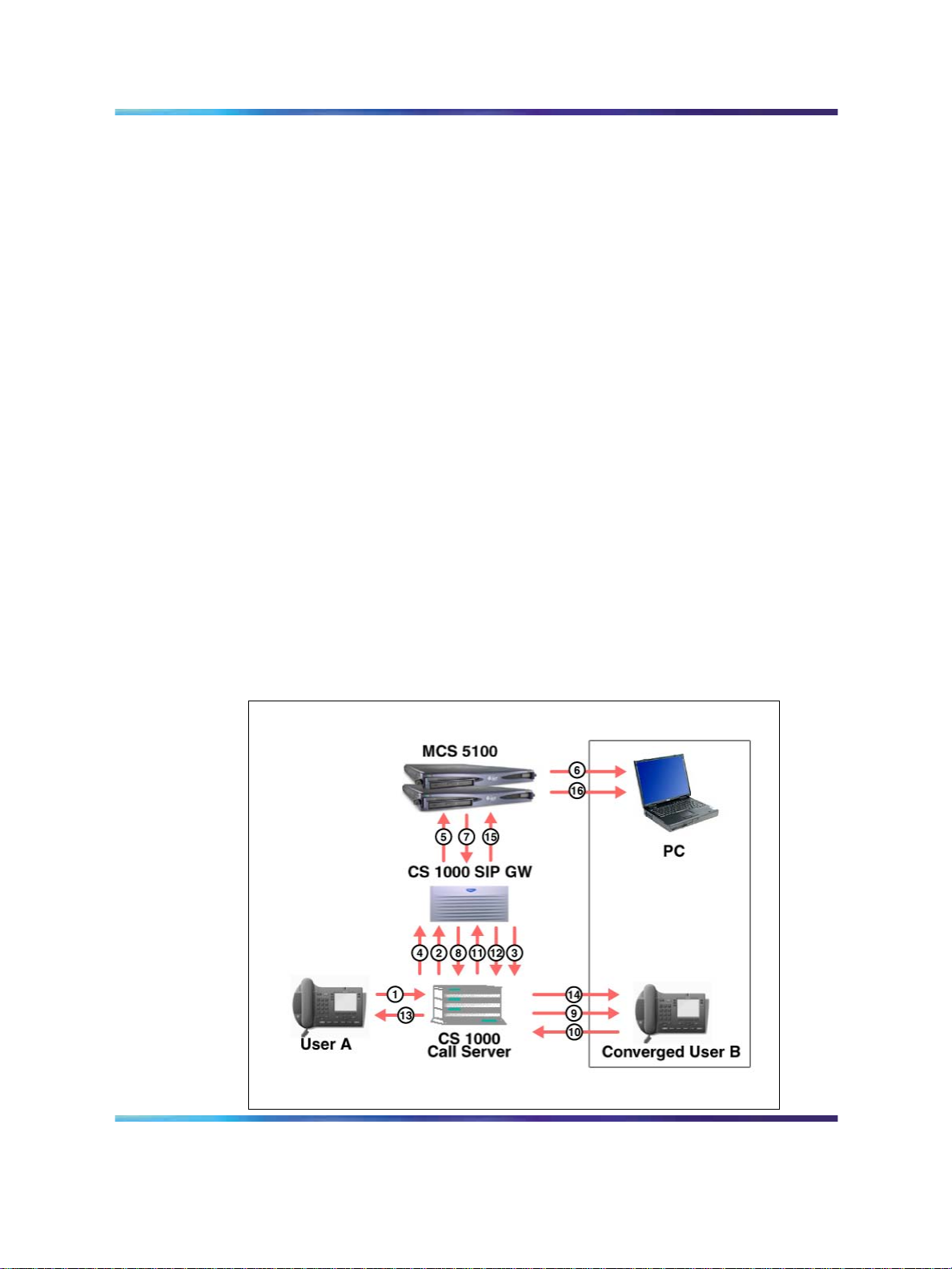
22 Converged Desktop Services
9
Call between PCA and converged user A disconnected; call made from
converged user A to user B.
10
Call placed to user B.
Receiving a call
Depending on the Class of Service (CDMV or CDMO) of the converged
user, the call flow will differ slightly. To receive a call, note the following:
•
A CD user in CS 1000 can be defined as Multimedia Only user or
Multimedia and Voice user.
•
All calls to CD users are sent first to a predefined CDN queue.
•
The MCS 5100 forks the call based on the user’s PA setting.
•
The new Class of Service (CDMO or CDMV) distinguishes the CD user
from other users.
•
The CSDN prompt in LD10/11 defines the CDN queue.
•
A group of PCAs are defined to serve as the agents servicing CDN.
• Use AML messages for call notification and call control.
Figure 4 "Call flow: call terminating to a user with a CDMV Class of
Service" (page 22) shows the call flow and messaging that occurs for a call
terminating to a user with a CDMV Class of Service.
Figure 4
Call flow: call terminating to a user with a CDMV Class of Service
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 23

How Converged Desktop Services works 23
Legend:
1
User A dials user B; call is forwarded to CDN.
2
Incoming call to CDMV user sent to CDS.
3
PCA selected; call made to Service DN to select a Virtual Trunk.
4
Virtual Trunk reserved.
5
INVITE message sent to CDS URL.
6 INVITE PC Client
•
Call Forking based on PA route
•
Call Log updated
•
Pop-up window generated
If PA settings allow a call to converged user B, then:
7
INVITE message sent to converged user B.
8
Select one idle PCA to call converged user B.
9
Calling converged user B.
10 Converged user B answers.
11
Call Answered message sent to CDS.
12
Message sent to Call Server to release Virtual Trunk and to connect user A
and converged user B.
13,14 Call is established between user A and converged user B.
15
User B is active.
16
Call Log updated; call timer started.
Figure 5 "Call flow: call terminating to a user with a CDMO Class of
Service" (page 24) shows the call flow and messaging that occurs for a call
terminating to a user with a CDMO Class of Service.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 24
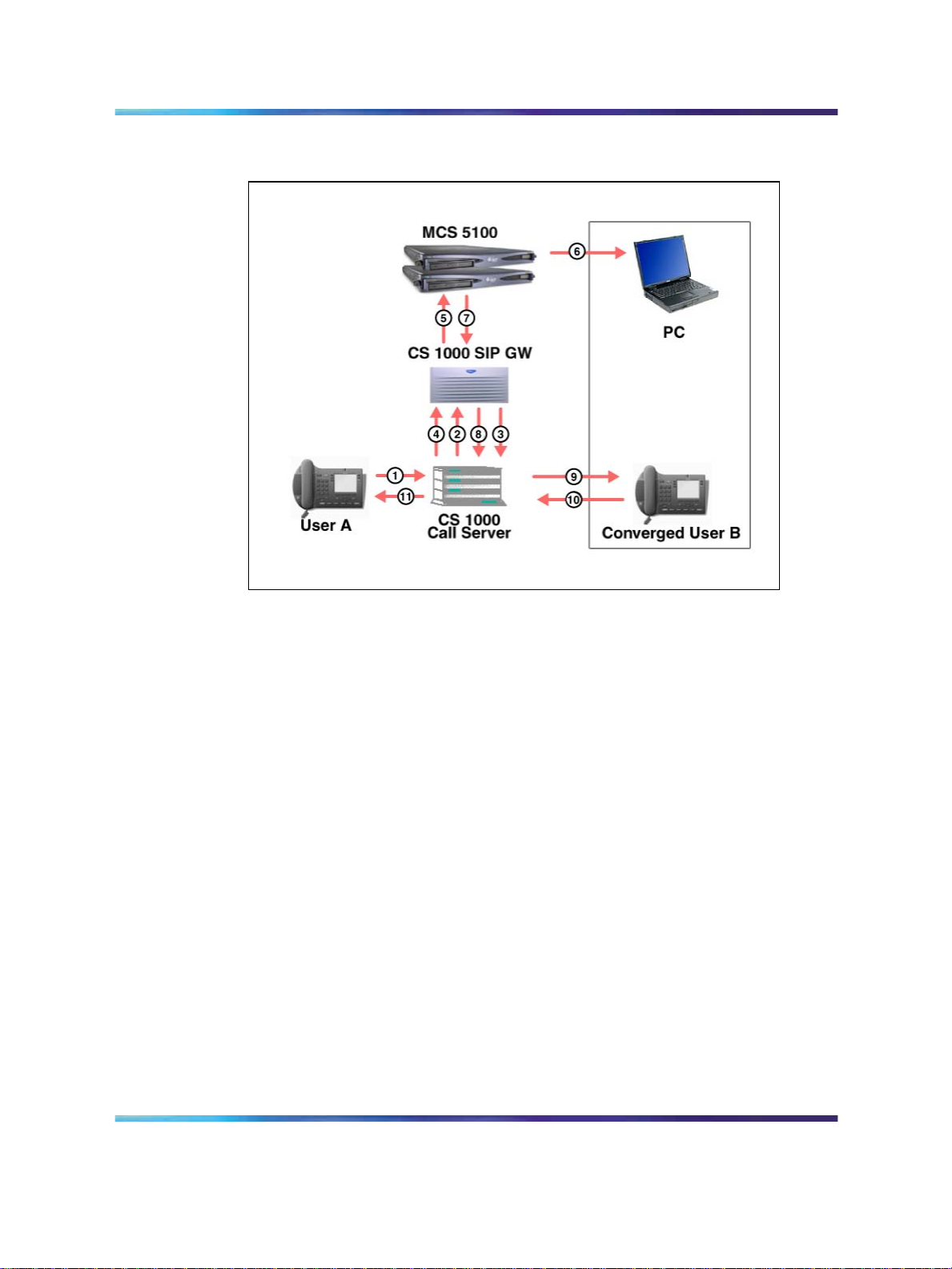
24 Converged Desktop Services
Figure 5
Call flow: call terminating to a user with a CDMO Class of Service
Legend:
1 User A dials user B; call is forwarded to CDN.
2
Incoming call to CDMO user sent to CDS.
3
PCA selected; call made to Service DN to select a Virtual Trunk.
4
Virtual Trunk reserved.
5
INVITE message sent to CDS URL.
6
INVITE PC Client
•
No Call Forking
•
Call Log updated
•
Pop-up window generated
7
302 Moved Temporarily message sent to CDS.
8
Message sent to Call Server to release Virtual Trunk and to connect user A
and converged user B.
9
Converged user B called.
10Converged user B answers call.
1
Call is established between user A and converged user B.
1
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 25

How Converged Desktop Services works 25
When receiving a call, the functionality of the PC Client is different from that
when making a call. With CDMO, a call to a converged telephone always
rings the converged telephone. It does not invoke PA routing. But with
CDMV, a call to a converged telephone on MCS 5100 invokes PA routing to
determine if it is to ring the converged telephone or another telephone.
AML ELAN numbers and VAS numbers
The messaging required for CDS to operate between the CS 1000 Call
Server and the Signaling Server is achieved by defining two functions:
•
Application Module Link (AML) — AML is the definition of a link to
provide connectivity between two applications.
•
Value Added Server (VAS) — VAS is the Application Layer link carried
through the AML link.
A new range of AML/VAS IDs has been created for CDS. To distinguish
this AML link from existing AML ELAN links, the AML ELAN link numbers
and VAS numbers are:
•
a range of 32–47 (inclusive) on Small Systems
• a range of 32–127 (inclusive) on Large Systems
with numbers greater than 32 reserved for the "logical" AML ELAN link.
These numbers enable multiple CDS gateways and multiple MCS 5100
systems to be supported on CS 1000 systems in addition to other Meridian
Link products (such as Symposium, CallPilot, or IP Call Recording), which
also use ELAN link numbers.
The 16 existing AML links are used for physical connections to other
applications.
Click-to-Call
The Click-to-Call feature enables users to originate voice calls from their PC
Client when in Converged Mode. This feature is not available to CS 1000
telephones not configured for CDS.
Note: Click-to-Call operation for MCS 5100 Clients in Unconverged
Mode may differ from that described.
When the call is established, a voice path is set up between the telephone
of the originating converged user and the terminating side. The PC Client is
not used to establish the voice path.
The user originates a Click-to-Call call by clicking on a number or address
from such things as an address book, a call log, a buddies list, an inbox, an
outbox, or by entering an address in an address field on the PC Client.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 26

26 Converged Desktop Services
The following steps must be performed when using Click-to-Call:
•
The caller makes a call from the PC Client software and the caller’s
telephone rings.
•
The caller must answer their telephone when it rings if the desktop
telephone is an analog (500/2500-type) telephone or is part of a Multiple
Appearance DN (MADN) group. Answering the telephone then directs
the call to the called party. However, the call is automatically answered
if the desktop telephone is a digital telephone or an IP Phone and is
a Single Appearance DN.
Note: If the caller is in an MADN group, and the answered phone is
configured with the default on-hook path Handsfree, the answered
phone rings the called party using handsfree, even if the call is answered
using a headset. This occurs because the answered phone makes the
new call to the called party using the default on-hook path.
Operating parameters and feature interactions
The following items apply to all Converged Desktop users (including both
incoming and outgoing Converged Desktop calls):
•
When a Converged Desktop user is a member of a Multiple Appearance
Directory Number (MADN) group, the user must be Multiple Appearance
Redirection Prime (MARP) to receive the Converged Desktop Service.
Or,all users in the same MADN group must be configured with the same
Class of Service, so that they receive the same Converged Desktop
Service.
• The CDS feature applies only to a primary DN key. Calls made or
received on any other keys do not receive the Converged Desktop
Service.
•
If a call is answered by any non-Converged Desktop telephone, then the
popup window, call log, and presence of the Converged Desktop user
are removed after a few seconds. The timeout value for this setting is
configurable (default value is 2 seconds).
•
A ConvergedDesktop user does not receive a popup window if the caller
is an attendant and is using the Attendant Monitor feature. An attendant
call terminating to the Converged Desktop does not notify the MCS 5100.
•
Group Call does not apply to a Converged Desktop caller. Initiating
Group Call from a Converged Desktop user does not notify the MCS
5100.
•
MCS 5100 clients can be in Converged Mode or Unconverged Mode.
The selected mode determines which functionality is available, as
described throughout this document.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 27
•
In the Converged Desktop Environment, voice mail is supported only on
the CS 1000 telephone, not the MCS 5100 Client.
Call walk-throughs
The figures in this section show messages exchanged between a CS 1000
system and an MCS 5100 system with different configurations. Although
two CS 1000 systems appear in the figures, they collapse into one if the
call is internal.
The different configurations are:
• Figure 6 "Outgoing Converged Desktop call" (page 27)
•
Figure 7 "Incoming call to CDMV user with forking" (page 28)
•
Figure 8 "Incoming call to CDMV user with NO forking" (page 28)
•
Figure 9 "Incoming call to CDMO user" (page 28)
•
Figure 10 "Combined incoming and outgoing Converged Desktop call"
(page 29)
Figure 6 Outgoing Converged Desktop call
Call walk-throughs 27
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 28
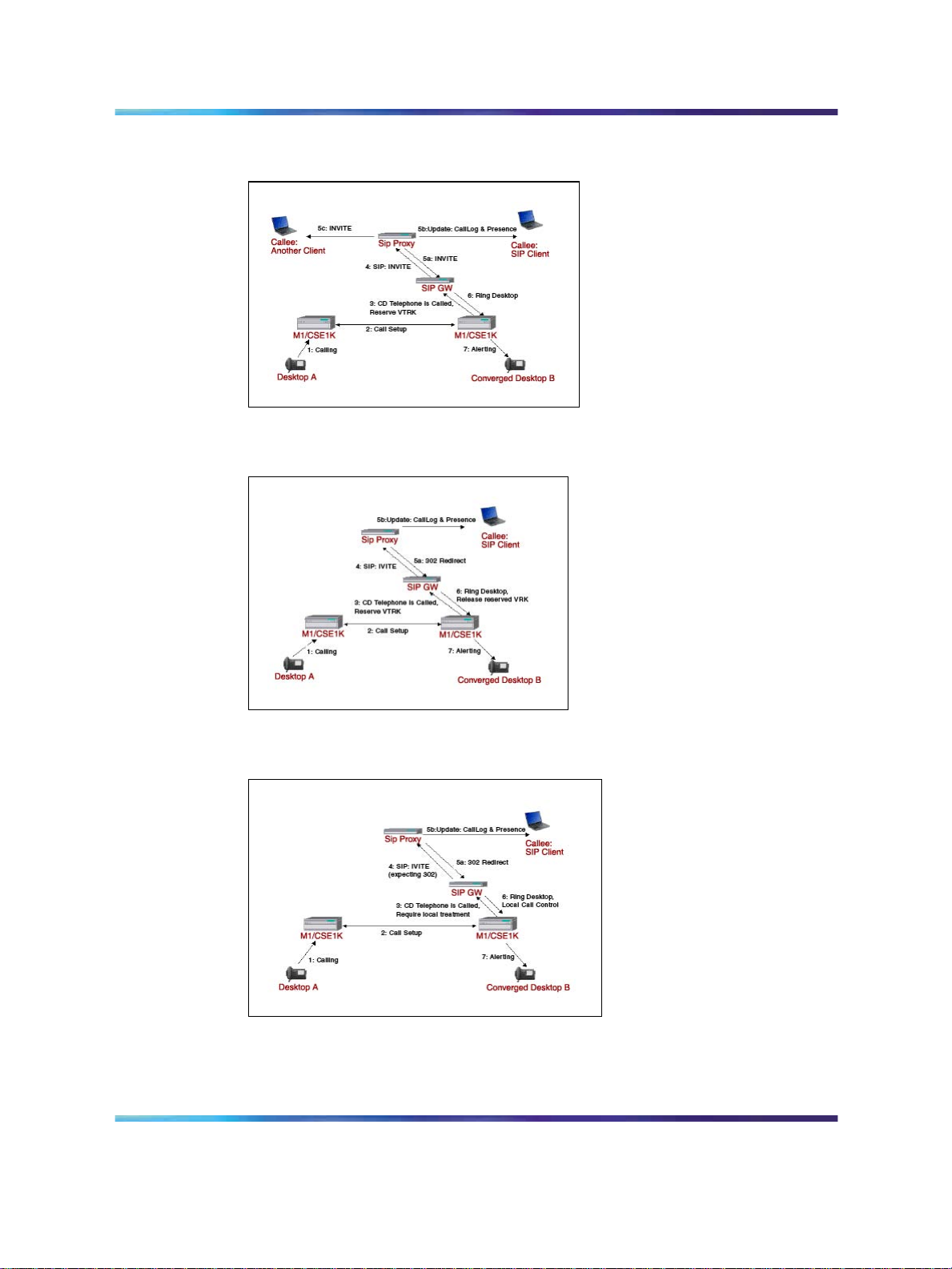
28 Converged Desktop Services
Figure 7 Incoming call to CDMV user with forking
Figure 8 Incoming call to CDMV user with NO forking
Figure 9 Incoming call to CDMO user
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 29

Figure 10 Combined incoming and outgoing Converged Desktop call
Feature requirements
CS 1000 systems
CS 1000 systems require:
Feature requirements 29
•
CS 1000 Release 4.0 or later software
•
Nortel Symposium Call Center (NGCC) (also referred to as Next
Generation Call Center) package 311 (Level 2 or 3b)
•
SIP Gateway and Converged Desktop Package (SIP) package 406
(Level 2)
•
ACD and PCA licenses for PCA Agents
•
SIP Access Ports for the CDS application; may also need other SIP
Access Ports for MCS 5100 users calling in Unconverged Mode,
depending on traffic requirements
•
Signaling Server with CDS and SIP Trunk applications enabled
MCS 5100 systems
MCS 5100 systems require MCS 5100 Release 3.5 or later software.
Product Enhancement Packages and Patches
In addition, you must ensure that all required Product Enhancement
Packages (PEP) and patches are installed. For a list of the required PEPs
and patches, refer to the Nortel web site at:
ww.nortel.com
w
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 30

30 Converged Desktop Services
Feature implementation
For CDS to operate, you must have the following conditions in place:
•
MCS 5100 clients must assume the location identifier (LOC) of a CS
1000 system. This enables one MCS 5100 system to provide CDS to
many CS 1000 systems, having the MCS 5100 clients assume the
location identifier (LOC) of each CS 1000 system.
•
The dialing plan and numbering plan between the CS 1000 systems and
the MCS 5100 system must be compatible. See "Dialing and numbering
plan issues for the mixed network" (page 30), and "Examples of dialing
and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks" (page 37).
Note: If the original converged phone is call forwarded to another
number, the forwarded phone is used as the terminator, however the
Converged Multimedia PC Client call window for the original Converged
phone continues to appear.
Implementation summary
In order to use SIP Converged Desktop Services, the SIP Trunk Gateway
must first be configured. See IP Peer Networking Installation and
Commissioning (NN43001-313).
Configuration of the SIP CDS requires configuration on both the CS 1000
system and the MCS 5100 system. For CS 1000 configuration, refer to
"Configuring CS 1000" (page 49). For MCS 5100 configuration, refer to
"Configuring MCS 5100" (page 67).
Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network
In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network, special attention must be placed
on addressing.
If a call is originated by a CS 1000 user and the call must terminate at an
MCS 5100 user, the destination address given to the MCS 5100 system
must make sense for the MCS translation engine. The same requirement
applies to the call in the opposite direction — a destination address passed
to the CS 1000 system by the MCS 5100 must make sense to the CS 1000
translation engine.
Digit-based addresses and alphanumeric addresses
The CS 1000 translation engine supports only digit-based addresses. An
example is 5573.
The MCS 5100 translation engine supports both digit-based and
alphanumeric addresses. Examples are 3435573 and asmith.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 31

Rule 1: All users in a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network must be accessible by
all systems through a digit-based address.
On the MCS 5100 system, each username must have an alias that is all digits,
or each username must be all digits.
Dialing plan issues
The term "dialing plan" is used in a very broad sense in this context. It
includes all the arrangements that determine an exact digit sequence that
the user must dial to access a destination. To access a destination, a user
must know an appropriate access code (for the type of destination being
called) and the unique address of the destination (within a certain address
space).
In most cases, a set of the following access codes may be needed:
•
access code for private/UDP numbers (for example, 6)
•
access code for public/local numbers (for example, 9 used for the NXX in
North America and for local exchange Special Numbers (SPN) outside
North America)
Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network 31
ATTENTION
•
access code for public/national numbers (for example, 61)
• access code for public/international numbers (for example, 6011)
No access code is needed for private/CDP numbers.
Special numbers used to access a service (for example, 911 and 411)
are a special case. Depending on which system is providing the special
number service (CS 1000, MCS 5100, or PSTN), the special number can be
accessed as follows:
•
without dialing an access code (for example, with an emergency service
the user dials 911)
•
with an access code (for example, with the PSTN directory service the
user may be required to dial 9411).
ATTENTION
Rule 2: In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network, both systems must have the
dialing plan set up in the same manner. MCS 5100 clients in Converged Mode
must share the UDP LOC of the CS 1000 client with which it is converged.
For example, at a certain location, a user must be able to make a call to a UDP
number by dialing the same digit string on a CS 1000 client as on an MCS 5100
client.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 32

32 Converged Desktop Services
Rule 2 is important for a CD user. Although a CD user can enter a
destination number on the Multimedia PC Client, the call itself is originated
under CS 1000 control.
DNs as MCS aliases versus DNs as MCS usernames
This section describes how to assign a digit-based address (that is, directory
number [DN]) to an MCS 5100 user.
The following options are available to associate a DN with an MCS user:
•
Provision the user’s username in the form of a DN.
• Provision the user’s alias in the form of a DN.
You must also do the following as part of the setup:
•
Provision the user’s CD alias in the form of a DN.
•
Provision the user’s public and private charge ID in the form of a DN.
The existing MCS practice is to provision a user with an alias in the DN
form. This works for non-converged MCS 5100 users but presents problems
to CD users when they initiate calls from the converged Multimedia PC
Client in the Click-to-Call mode, specifically from the following locations:
•
Call Logs – Inbox window
•
Friends Online window
•
Directory window
In the cases, if the item represents an MCS 5100 user, the call is initiated
towards the destination identified by the MCS username. In the case of a
CD user, the call is actually handled by the CS 1000 Call Server that can
route based on DN addresses only. To ensure that the CS 1000 Call Server
receives a DN-based address, the MCS 5100 replaces the username with
the user’s private charge ID.
Rule 3: In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network with Converged Desktop users,
MCS 5100 private charge IDs must be in the form of a UDP number (LOC + DN).
Directory Number qualification
An additional aspect of using digit-based addressing is the directory number
qualification.
Existing telephony systems support multiple address spaces. The address
spaces include the following:
ATTENTION
•
Public address space — which is subdivided into the following
categories:
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 33

Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network 33
— Local numbers
— National numbers
— International numbers
— Special numbers
•
Private address space — which is subdivided into the following
categories:
— Level 0 regional numbers (in CS 1000, these are known as
Coordinated Dialing Plan [CDP] numbers)
— Level 1 regional numbers (in CS 1000, these are known as Universal
Dialing Plan [UDP] numbers)
To be useful, a DN must be scoped within an appropriate address space.
One way of achieving this is by qualifying DNs.
Both CS 1000 and MCS 5100 systems have implemented a phone-context
parameter of the userinfo-field of the telephony-based SIP URI as a means
to fully qualify a DN.
•
A SIP URI with the user=phone-context parameter is known as
a telephony-based SIP URI. For more information, see Appendix
"Parameter configuration for a SIP URI" (page 103).
•
A SIP URI without the user=phone-context parameter is known as a
non-telephony-based SIP URI or a regular SIP URI.
The format of a telephony-based SIP URI is as follows:
sip:[directorynumber];phone-context=[phonecontext]@[domainame];
user=phone
sip:+[directorynumber]@[domainname];user=phone (for international
PSTN numbers)
The format of a regular SIP URI is as follows:
sip:[username]@[domainame]
ATTENTION
Rule 4: In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network, all DNs passed between the two
systems must be in the form of a telephony-based SIP URI.
If Rule 4 is not followed, a CDP DN may be incorrectly interpreted as a UDP
number or a public/local number as a UDP number.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 34

34 Converged Desktop Services
Non-telephony-based SIP URIs
In accordance with the preceding Rule 4, non-telephony-based, or regular,
SIP URIs must not be passed between systems in a mixed CS 1000/MCS
5100 network.
There is one exception to this rule — regular SIP URIs can be passed
between systems in the Refer-to header.
Rule 5: In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network, for routing purposes, regular
SIP URIs can be passed between the two systems only within a Refer-to header.
The refer operation is not initiated by CS 1000 SIP Gateways. It is used by
the MCS 5100 in the following scenarios:
•
Call redirection (for example, a call transfer) initiated by the MCS 5100
— The SIP URI in the Refer-to header is analyzed only by the MCS
5100 system and has no impact on the CS 1000 system.
•
Click-to-Call operation of a CD user — The SIP URI in the Refer-to
header is analyzed by the CS 1000 system and has to be understood
by the system. Therefore, the Username field of the SIP URI must be
in the form of a DN.
ATTENTION
Rule 6: In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network with Converged Desktop users,
the CS 1000 SIP Gateway must support regular SIP URIs within the Refer-to
header.
If the Username field of the SIP URI is not in the form of a DN, the CS
1000 SIP Gateway handles the refer operation according to normal SIP
processing. In other words, it lets the MCS system route the call to the
destination indicated in the Refer-to header.
If the Username field of the SIP URI is in the form of a DN, the CS 1000
SIP Gateway configures NPI = Private and TON = CDP (the default settings;
the latter having the same effect as TON = Unknown). The CS 1000 SIP
Gateway then passes the processing of the refer operation to the CS 1000
Call Server.
Converged Desktop implications
The biggest impact of the adopted addressing scheme on the Converged
Desktop feature in a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network is on Click-to-Call.
With Click-to-Call, Converged Desktop users initiate a call using their
converged Multimedia PC Client user interface, but use their CS 1000 client
to conduct the voice conversation when in Converged Mode.
ATTENTION
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 35

Dialing and numbering plan issues for the mixed network 35
The converged Multimedia PC Client provides several ways for a user to
initiate Click-to-Call, including:
•
using the Directory window
•
using the Friends Online window
•
using the Call Logs window (Outbox and Inbox tabs)
•
using the Make a Call window (Dialpad, Recent, and Directory tabs)
These four user interfaces retrieve an address. The retrieved address has
several origins, including:
•
The address is an MCS 5100 username (as defined by an MCS 5100
administrator).
•
The address was delivered by an incoming call over a route.
•
The address was entered directly by the user (personal directory).
•
The address was entered by an MCS 5100 administrator or retrieved
from a directory (global directory).
It is very difficult for the CS 1000 system to route calls based on the
retrieved address alone. The address must be either:
•
explicitly qualified (in terms of phone-context) by the MCS 5100 system,
or
•
implicitly qualified (using a proper prefix) by the MCS 5100 system
Problematic Click-to-Call scenarios
Scenario 1:
Click-to-Call using an incoming call log when the call has come from a
route In this scenario, the calling party number stored in the call log must
be explicitly or implicitly qualified. The MCS 5100 system must store the
original phone-context in the call log.
Scenario 2:
Click-to-Call using a directory entry (Call at...) In this scenario, the
number stored in the directory entry must include the proper prefix.
The problem arises because directory entries are created by users
themselves (PA, Contact Info), MCS 5100 system administrators, or an
external Directory Service (such as the Nortel Global Directory). Directory
entries may not include the required access codes.
Users must be warned to ensure that all directory entries they intend to use
include correct access codes. An MCS 5100 or CD user may edit their
personal directory through the PA.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 36

36 Converged Desktop Services
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 37

Examples of dialing and numbering
plan configuration for mixed networks
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 37)
"Mixed network example: UDP" (page 37)
"Sample network" (page 38)
"CS 1000 setup" (page 39)
"MCS 5100 setup" (page 40)
"Mixed network example: CDP" (page 42)
"Sample network" (page 42)
"CS 1000 setup" (page 43)
"MCS 5100 setup" (page 40)
37
Introduction
This section provides examples of a dialing plan setup for a mixed CS
1000/MCS 5100 network. The following examples are provided:
•
Uniform Dialing Plan (UDP)
• Coordinated Dialing Plan (CDP)
The values given in the following examples are examples only. Actual values
may differ between applications.
Mixed network example: UDP
The following is an example of a dialing plan setup for a mixed CS
1000/MCS 5100 network. UDP numbers are used to dial among sites.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
ATTENTION
Page 38

38 Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks
Sample network
The sample network has the following characteristics:
•
The network includes several sites.
•
Each site has a mixture of CS 1000 users, MCS 5100 users, and
Converged Desktop users.
•
Dialing within a site is done using CDP numbers (no access code,
4-digit numbers).
•
Dialing among the sites is done by dialing 6 + 7-digit UDP number.
• Local PSTN hop-off is done by dialing 9 + local number.
•
AC1 = 9 is used for calls on the public network; AC2 = 6 is used for
calls on the private network.
— National dialing is done by dialing 9 + 1 + national number.
— International dialing is done by dialing 9 + 011 + international
number.
Figure 11 "Network diagram: mixed UDP" (page 38) shows this network.
Figure 11 Network diagram: mixed UDP
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 39

CS 1000 setup
The CS 1000 setup includes both a user setup and translation setup.
User setup
The CS 1000 user setup involves both the general user setup and the
Converged Desktop user setup.
General user setup The general user setup applies to both stand-alone
and Converged Desktop users. The general user setup involves the
following:
• Configure the user’s extension as a 4-digit number.
For example: extension = 5573
•
Configure the 3-digit HLOC codes for user groups (that is, customers).
For example: HLOC = 334
•
The HLOC and user’s extension creates the user’s UDP number. The
number is unique within an Enterprise: HLOC + Extension.
For example: UDP Number = 3345573
•
Configure the Private Network Identifier (PNI) for user groups (that is,
customers).
For example: PNI = 00002
Mixed network example: UDP 39
•
PNI, HLOC, and the user’s extension create the Global user ID that is
globally unique: PNI + HLOC + Extension.
For example: Global ID: 000023345573
Converged Desktop user setup The Converged Desktop user setup
involves the following:
•
Configure the user’s Class of Service (CLS) to include CDMO or CDMV.
•
Configure the Converged Desktop Service (CDS) parameters.
•
CS 1000 SIP Services use the user’s global ID within CD-related
signaling (for example: INVITE and NOTIFY).
Translation setup
The translation setup involves the following:
•
Configure CDP routing (Distant Steering Codes [DSC] and Local
Steering Codes [LSC]) (based on the 4-digit CDP numbers).
•
Configure UDP routing (AC2, HLOCs, and LOCs) (based on the 6 +
7-digit UDP number).
•
Configure PSTN routing (AC1, NXX, NPA,SPN, and so on) according to
the preceding access codes.
•
Configure the CS 1000 SIP Trunk Gateways at each site with appropriate
phone-context strings:
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 40

40 Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks
— UDP phone-context
For example: phone-context="udp"
— CDP phone-context
For example: phone-context="cdp.udp"
— Public/Local phone-context
For example: phone-context="+1613"
— Public/National phone-context
For example: phone-context="+1"
MCS 5100 setup
The MCS 5100 setup involves includes both a user setup and translation
setup.
User setup
The MCS 5100 user setup involvesboth the general user setup, stand-alone
user setup, and the Converged Desktop user setup.
General user setup The general user setup applies to both stand-alone
and Converged Desktop users. The general user setup involves the
following:
•
Configure the user’s username as an alphanumeric address.
For example: Username = asmith
•
Configure the user’s private charge ID as the UDP number.
For example: Private Charge ID = 3345573
Standalone user setup The stand-alone user setup involvesthe following:
•
Do not include the CDS in the service package.
•
Configure the user’s alias as the Global ID.
For example: Alias = 000023345573
Note: The alias for a stand-alone user is unique to the Network Routing
Service (NRS) of the CS 1000 system. It cannot be a DN within any DN
range used in the CS 1000 NRS Level0 or Level1 Domain configuration.
Converged Desktop user setup The Converged Desktop user setup
involves the following:
•
Include the CDS in the service package.
•
There is no need to define the user’s "regular" alias.
•
Configure the user’s CD alias as the Global ID:
For example: CD Alias = 000023345573
•
Configure the user’s Preferred Audio Device (PAD) as: 6 + UDP
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 41

Mixed network example: UDP 41
number.
For example: PAD = 63345573
The number 6 is the access code configured for UDP calls as configured
on CS 1000. The configured values must match in both configurations.
Translation setup
The MCS 5100 translation setup includes pretranslation setup, private
telephony routes setup, and gateway telephony routes setup.
Pretranslation setup Configure pretranslations to support CS
1000-to-MCS 5100 calls to do the following:
•
If the UDP number qualifier is received, insert 6.
For example, if number qualifier="udp", insert 6.
•
If the CDP number qualifier is received, insert 6 + HLOC.
For example, if number qualifier="cdp.udp", insert 6334.
•
If the Public/Local number qualifier is received, insert 9.
For example, if number qualifier="+1613", insert 9.
•
If the Public/National number qualifier is received, insert 91.
For example, if number qualifier="+1", insert 91.
• If the Public/International number is received, insert 9011.
For example, DN starts with a plus sign (+), insert 9011.
Private telephony routes Configure private telephony routes to support
CS 1000-to-MCS 5100 calls and MCS 5100-to-MCS 5100 calls as follows:
•
Local termination using UDP dialing
(to/from digits 6 + HLOC, length 8, remove 1, prefix PNI)
For example: to/from digits 6334, length 8, remove 1, prefix 00002
•
Local termination for CDP dialing
(to/from digits LSC, length 4, remove 0, prefix PNI + HLOC)
For example: to/from digits 5, length 4, remove 0, prefix 00002334
Gateway telephony routes Configure gateway telephony routes to
support MCS 5100-to-CS 1000 calls as follows:
•
Outgoing routes using UDP dialing
(to/from digits 6 + LOC, length 8, remove 1, use UDP number qualifier)
For example: to/from digits 6334, length 8, remove 1,
number qualifier="udp", Gateway Route Type = private
•
Outgoing routes using CDP dialing
(to/from digits DSC, length 4, remove 0, use CDP number qualifier)
For example: to/from digits 2 to 7, length 4, remove 0,
number qualifier="cdp.udp", Gateway Route Type = private
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 42

42 Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks
Mixed network example: CDP
The following is an example of a dialing plan setup for a mixed CS
1000/MCS 5100 network. CDP numbers are used to dial among sites.
Sample network
The sample network has the following characteristics:
•
The network includes several sites.
•
Each site has a mixture of CS 1000 users, MCS 5100 users, and
Converged Desktop users.
•
Dialing within a site and between sites is done using CDP numbers
(no access code, 5-digit numbers).
•
Local PSTN hop-off is done by dialing 9 + local number.
•
AC1 = 9 is used for calls on the public network; AC2 = 6 is used for
calls on the private network.
— National dialing is done by dialing 9 + 1 + national number.
— International dialing is done by dialing 9 + 011 + international
number.
Figure 12 "Network diagram: mixed CDP" (page 43) shows this network.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 43

Figure 12 Network diagram: mixed CDP
Mixed network example: CDP 43
CS 1000 setup
The CS 1000 setup includes both a user setup and translation setup.
User setup
The CS 1000 user setup involves both the general user setup and the
Converged Desktop user setup.
General user setup The general user setup applies to both stand-alone
and Converged Desktop users. The general user setup involves the
following:
•
Configure the user’s extension as a 5-digit number.
For example: extension = 35573
•
The user’s extension creates the user’s CDP number. The number is
unique within an Enterprise.
For example: CDP Number = 35573
• Configure the HLOC codes for user groups (that is, customers).
For example: HLOC = 34
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 44

44 Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks
Note: Although the network is CDP-only, some UDP configuration is
necessary to support MCS 5100 private charge ID, which is always
presented as a UDP number.
•
Configure the Private Network Identifier (PNI) for user groups (that is,
customers).
For example: PNI = 00002
•
PNI, HLOC, and the user’s extension create the Global user ID that is
globally unique: PNI + HLOC + Extension.
For example: Global ID: 000023435573
Converged Desktop user setup The Converged Desktop user setup
involves the following:
•
Configure the user’s Class of Service (CLS) to include CDMO or CDMV.
•
Configure the Converged Desktop Service (CDS) parameters.
•
CS 1000 SIP Services use the user’s global ID within CD-related
signaling (for example: INVITE and NOTIFY).
Translation setup
The translation setup involves the following:
•
Configure CDP routing (Distant Steering Codes [DSC] and Local
Steering Codes [LSC]) based on the 5-digit CDP numbers.
•
Configure minimal UDP routing (AC2, HLOCs, and so on) to support
incoming calls using UDP numbers.
•
Configure PSTN routing (AC1, NXX, NPA,SPN, and so on) according to
the preceding access codes.
•
Configure the CS 1000 SIP Trunk Gateways at each site with appropriate
phone-context strings:
— CDP phone-context
For example: phone-context="cdp.udp"
— UDP phone-context
For example: phone-context="udp"
— Public/Local phone-context
For example: phone-context="+1613"
— Public/National phone-context
For example: phone-context="+1"
MCS 5100 setup
The MCS 5100 setup includes both a user setup and translation setup.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 45

Mixed network example: CDP 45
User setup
The MCS 5100 user setup involvesboth the general user setup, stand-alone
user setup, and the Converged Desktop user setup.
General user setup The general user setup applies to both stand-alone
and Converged Desktop users. The general user setup involves the
following:
•
Configure the user’s username as an alphanumeric address.
For example: Username = asmith
•
Configure the user’s private charge ID as the UDP number.
For example: Private Charge ID = 3435573
Standalone user setup The stand-alone user setup involvesthe following:
•
Do not include the CDS in the service package.
•
Configure the user’s alias as the Global ID.
For example: Alias = 000023435573
Converged Desktop user setup The Converged Desktop user setup
involves the following:
•
Include the CDS in the service package.
•
There is no need to define the user’s "regular" alias.
•
Configure the user’s CD alias as the Global ID: PNI + HLOC +
CDP number.
For example: CD Alias = 000023435573
•
Configure the user’s Preferred Audio Device (PAD) as: CDP number.
For example: PAD = 35573
Translation setup
The MCS 5100 translation setup includes pretranslation setup, private
telephony routes setup, and gateway telephony routes setup.
Pretranslation setup Configure pretranslations to support CS
1000-to-MCS 5100 calls to do the following:
•
If the CDP number qualifier is received, ignore the phone-context.
For example, if number qualifier="cdp.udp", leave the digits as is.
•
If the UDP number qualifier is received, insert 6.
For example, if number qualifier="udp", insert 6.
•
If the Public/Local number qualifier is received, insert 9.
For example, if number qualifier="+1613", insert 9.
•
If the Public/National number qualifier is received, insert 91.
For example, if number qualifier="+1", insert 91.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 46

46 Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed networks
•
If the Public/International number is received, insert 9011.
For example, DN starts with a plus sign (+), insert 9011.
Private telephony routes setup Configure private telephony routes to
support CS 1000-to-MCS 5100 calls and MCS 5100-to-MCS 5100 calls as
follows:
•
Local termination for CDP dialing
(to/from digits LSC, length 5, remove 0, prefix PNI + HLOC)
For example: to/from digits 3, length 5, remove 0, prefix 0000234
Gateway telephony routes setup Configure gateway telephony routes to
support MCS 5100-to-CS 1000 calls as follows:
•
Outgoing routes using CDP dialing
(to/from digits DSC, length 5, remove 0, use CDP number qualifier)
For example: to/from digits 2, length 5, remove 0,
number qualifier="cdp.udp", Gateway Route Type = private
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 47

CDS configuration: overview
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 47)
"Configuration notes" (page 47)
"Description of the network configured in this document" (page 48)
Introduction
In order to use SIP Converged Desktop Services, the SIP Trunk Gateway
must first be configured. See IP Peer Networking Installation and
Commissioning (NN43001-313) for detailed instructions.
Configuration of SIP CDS on CS 1000 requires configuration on both the
Call Server and the Signaling Server. See "Configuring CS 1000" (page
49) for detailed instructions on configuring these elements.
47
SIP CDS must also be configured on MCS 5100. Refer to "Configuring
MCS 5100" (page 67) for detailed instructions.
Configuration notes
You must configure UDP/Home Location (HLOC) codes using an Access
Code (either AC 1 or AC2) and the ESN Data Block with Local Termination
Feature (LTER). You must also configure a Route List Block entry (RLI) to
delete the HLOC when the CS 1000 recognizes a user has dialed within
its own customer (Home Location) or when a converged MCS 5100 user is
dialing within the CS 1000 Home Location. This feature is needed for the
MCS 5100 PC Clients in a Click-to-Call call from a Friends list or call log.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 48

48 CDS configuration: overview
Description of the network configured in this document
The user will encounter one of many CDS configuration situations. This
section describes the basic characteristics of the network to which the
configuration described in the rest of this document applies. The intent is
to provide a configuration example which the user can then adapt to their
particular situation.
The network configured in this document has the following characteristics:
•
The CS 1000 system is a CS 1000M system.
•
The NRS is used to route all Converged Desktop calls.
• The network supports both pure UDP and CDP calls dialing plans, as
seen from the users’ perspective.
•
The dialing range of MCS overlaps that of CS 1000 in a "split-range"
manner — half of the overlap is directed to the MCS side and the other
half is directed to the CS 1000 side. DSCs are used to direct the calls
accordingly.
The following entities are used in this network:
•
SIP Domains:
— Service Domain — mydomain.com
— Level 1 Domain — udp
— Level 0 Domain — cdp
•
SIP Gateway route — myGWRoute
•
SIP Gateway route list — my RouteList
•
SIP Trunk group — my TrkGroup
•
CDS Class of Service — cdCOS
•
MCS Application Server — MyMCSAppSrv
The sample configuration uses the following IP addresses:
• IP Telephony node — 12.123.1.123
•
MCS Application server — 12.234.3.234
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 49

Configuring CS 1000
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Before you begin" (page 49)
"CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing" (page 49)
"Configuring the Call Server" (page 49)
"Configure the Signaling Server usingCS 1000 Element Manager" (page 57)
"Verifying configuration" (page 64)
"Configuring the Converged Desktop User" (page 66)
Before you begin
Some values in these instructions are taken from the values in "Description of the
network configured in this document" (page 48), and from example numbering
plans described in "Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration
for mixed networks" (page 37). Note that actual values may differ between
applications.
49
ATTENTION
Before you begin configuring CDS on the CS 1000, you must have a
SIP Trunk Gateway configured. The SIP Trunk must have Insert ESN
Access Code (INAC) configured for incoming LOC calls. Refer to IP Peer
Networking Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-313) for details.
Ensure that CDS calls are routed over the SIP Trunk Gateway that is
associated with the CDS application.
CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing
Configuring the Call Server
The following is a summary of the tasks in this section:
1. "LD 15 Configure CLID and HLOC." (page 50).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 50

50 Configuring CS 1000
2. "LD 17 Configure the Application Module Link (AML)." (page 51).
3. "LD 17 Configure Value Added Server (VAS)." (page 51).
4. "LD 23 Configure Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Directory Number
(DN)." (page 52).
5. "LD 23 Configure Control Directory Number (CDN)." (page 52).
6. "LD 86 Configure ESN Data Block with AC1 and AC2 (if not already
defined)." (page 52).
7. "LD 90 Configure Home Location Code (HLOC)." (page 53).
8. "LD 86 Configure Access Code (AC1 or AC2)." (page 53).
9. "LD 86 Configure Digit Manipulation." (page 54).
10. "LD 86 Configure Home Location Code." (page 54).
11. One of the following:
•
•
"LD 90 Configure Service DN for Converged Desktop." (page 54).
"LD 87 Configure Steering Code to be used as the Service DN for
making Virtual Trunk call from Agent." (page 55).
In the case where the customer has used all Special Numbers (SPN),
a CDP Distance Steering Code (DSC) can be used as a Service DN.
12. "LD 11 Configure Personal Call Assistant (PCA)." (page 56).
LD 15 Configure CLID and HLOC.
Prompt Response Description
REQ CHG Change existing data block.
CUST Customer number
0-99
0-31
TYPE NET Networking
AC2 LOC Access Code 2
ISDN YES Integrated Services Digital Network allowed.
-PNI
-HLOC
-CLID Yes Allow Calling Line Identification option.
--ENTRY
---HLOC
2
334
0
334
Range for Large Systems and CS 1000E system
Range for Small Systems and Media Gateway 1000B
Private Network Identifier
PNI cannot be zero (0).
Home Location Code (ESN) (1-7 digits)
This must be the same HLOC as configured under CLID.
CLID entry to be configured (Table 0 for CLID)
Home Location Code (ESN)
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 51

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 51
Prompt Response Description
-PFX1
613
Prefix 1
-PFX2
962
Prefix 2
DITI Yes DID to TIE connections allowed.
To connect external DID and internal network TIE trunks
for the customer (which allows an external trunk to be
transferred across an internal network TIE trunk), set
DITI=YES.
LD 17 Configure the Application Module Link (AML).
Prompt Response Description
REQ CHG Change existing data.
TYPE ADAN Action Device And Number
- ADAN NEW ELAN x Action Device And Number
Where x is the ELAN Link number:
x = 32 to 47 (inclusive) for Small Systems
x = 32 to 127 (inclusive) for Large Systems
AML link number within the preceding range implies that
the transport is over TCP/RUDP link.
CTYP ELAN AML over Ethernet card type
LD 17 Configure Value Added Server (VAS).
Prompt Response Description
REQ CHG Change existing data.
TYPE VAS Value Added Server configuration
VAS NEW New Value Added Server data block
- VSID
32-500
VAS Identifier
= 32 to 47 for Small Systems
= 32 to 127 for Large Systems
Nortel recommends that the VAS Identifier match the
ELAN Link number configured in the last step (LD 17 —
Configuring AML).
- ELAN
x
Associate Value Added Server ID (VSID) x with Application
Module Link over Ethernet (ELAN) x
Note: The AML ELAN link number must match the number
provisioned in the last step (LD 17 — Configuring AML).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 52

52 Configuring CS 1000
LD 23 Configure Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) Directory Number (DN).
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW Add new data.
TYPE ACD Automatic Call Distribution data block
CUST
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
(Customer number associated with this data block.)
ACDN
5300
ACD Directory Number
LD 23 Configure Control Directory Number (CDN).
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW Add new data.
TYPE CDN Control Directory Number data block
This is a special DN created to specify a destination ACD
DN to which incoming calls are directed. Multiple CDNs
can direct calls to the same ACD DN providing different
treatments based on the CDN parameters.
CUST
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
(Customer number associated with this data block.)
CDN
5200
Control DN
CDSQ YES CDN queue is used for Converged Desktop Service.
DFDN
x...x
Local Default ACD DN
IMPORTANT: The Local Default ACD DN must match
ACDN configured in the previous step (LD 23 – Configuring
ACD DN).
Up to 4 digits; up to 7 digits with Directory Number
Expansion (DNXP) package 150.
CNTL YES Control DN is in control.
VSID
<cr>
Value Added Service ID
LD 86 Configure ESN Data Block with AC1 and AC2 (if not already defined).
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW
CHG
CUST
xx
Add new data.
Change existing data.
Customer number
FEAT ESN Electronic Switched Network
AC1
AC2
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
9
6
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
NARS/BARS Access Code 1
NARS/BARS Access Code 2
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 53

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 53
Configuring HLOC is necessary to properly handle a UDP number sent
by the MCS 5100 based on the Private Charge ID of the MCS 5100 user
profile. The MCS 5100 always qualifies this number as a UDP number.
HLOC will already have been configured if UDP is used. Even if only CDP is
used, you must still configure HLOC.
LD 90 Configure Home Location Code (HLOC).
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW Add new data.
CUST
FEAT NET Network translation tables
TRAN AC1 or AC2 Translator
TYPE HLOC Home Location Code.
HLOC
xx
334
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
Note: HLOC must match what MCS 5100 is sending.
Home Location code.
DMI
1-255
Digit Manipulation Index numbers
Note: DMI range is dependent on which Package is used.
(0) No digit manipulation required
(0)-31CDP
(0)-255 NARS and BARS
(0)-999 NARS and BARS with FNP
DMI is only prompted when the Directory Number
Expansion (DNXP) package 150 is equipped and SDRR =
LDID.
The maximum number of Digit Manipulation tables is
defined by prompt MXDM.
Configuring AC1 or AC2 is necessary to properly handle a UDP number
sent by the MCS 5100 based on the Private Charge ID of the MCS 5100
user profile. The MCS 5100 always qualifies this number as a UDP number.
AC1 or AC2 will already have been configured if UDP is used. Even if only
CDP is used, you must still configure AC1 or AC2.
LD 86 Configure Access Code (AC1 or AC2).
Prompt Response Description
REQ CHG Change existing data block.
CUST
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
FEAT ESN Electronic switched network
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 54

54 Configuring CS 1000
Prompt Response Description
...
AC1
xxxx
1-4 digit Flexible Numbering Plan Access Code 1.
or
The access code cannot conflict with the numbering plan.
AC2
Removal of the HLOC digits is necessary so that local termination is
possible. Configuring digit manipulation is necessary to properly handle a
UDP number sent by the MCS 5100 based on the Private Charge ID of the
MCS 5100 user profile. The MCS 5100 always qualifies this number as a
UDP number. Digit manipulation will already have been configured if UDP is
used. Even if only CDP is used, you must still configure digit manipulation.
LD 86 Configure Digit Manipulation.
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW Add new data.
CUST
FEAT DGT Digit manipulation data block
DMI
DEL
LD 86 Configure Home Location Code.
xx
3
3
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
Digit Manipulation Index numbers
Number of leading digits to be Deleted (HLOC)
Prompt Response Description
REQ CHG Change existing data.
CUST
xx
Customer number
FEAT NET Feature
HLOC
-DMI
334
3
Home Location Code
Digit Manipulation Index
LD 90 Configure Service DN for Converged Desktop.
Prompt Response Description
REQ NEW Add new data.
CUST
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
(Customer number associated with this telephone.)
FEAT NET Network translation tables
TRAN AC1 or AC2 Access code, where:
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 55

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 55
Prompt Response Description
AC1 = NARS/BARS
AC2 = NARS
TYPE: SPN Special Number translation (Special code translation block)
Configure the CDS Service DN as an SPN, and point it
to the SIP trunk. This number is only internal between
the Call Server and the Signaling Server for reserving the
Virtual Trunk when routing the terminating CD call out to
the MCS 5100.
SPN
5100
Special Number.
The same DN must be used in the config.ini file in the
Service DN field on the Signaling Server.
- FLEN
xx
Flexible length number of digits
Flexible length is the exact number of digits the system
expects to receive before accessing a trunk and outpulsing
those digits.
-RLI
xxx
Route List Index for Converged Desktop Service Class of
Service (CLS)
The RLI number must point to the SIP Virtual Trunk on the
desired Signaling Server. For example, if the CDN and
SPN are configured on Signaling Server 1, then this RLI
must use the route configured on Signaling Server 1.
In the case where the customer has used all Special Numbers (SPN), a
CDP Distant Steering Code (DSC) can be used as a Service DN.
ATTENTION
Do this only if the Service DN has not already been configured as a Special
Number in LD 90 on "LD 90 Configure Service DN for Converged Desktop." (page
54).
LD 87 Configure Steering Code to be used as the Service DN for making Virtual Trunk call
from Agent.
Prompt Response Description
REQ: NEW Add new data block.
CUST
FEAT: CDP Coordinated Dialing Plan
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
(Customer number associated with this telephone.)
TYPE DSC Distant Steering Code
DSC
x...x
Service DN
-FLEN (0)-24 Flexible length number of digits
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 56

56 Configuring CS 1000
Prompt Response Description
Flexible length is the exact number of digits the system
expects to receive before accessing a trunk and outpulsing
those digits.
-DSP
aaa
Display, where aaa = LSC, LOC, DN.
-RRPA (NO) YES Remote Radio Paging Access
-RLI
xxx
Route List to be accessed for Distant Steering Code.
Virtual Route RLI with no DMI changes.
-CCBA (NO) YES Collect Call Blocking
-NPA
-NXX
xxxxxxx
xxxxxxx
NPA code, maximum 7 digits
NXX code, maximum 7 digits
LD 11 Configure Personal Call Assistant (PCA).
Prompt Response Description
REQ: NEW Add new data block to the system.
TYPE: PCA Personal Call Assistant
TN Terminal Number
l s c u Format for Large System and CS 1000E system,
where l = loop, s = shelf, c = card, u = unit
cu
Format for Small System, Media Gateway 1000B, and
Media Gateway 1000T where c = card and u = unit
CUST
xx
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
(Customer number associated with this telephone.)
TGAR
xx
Trunk Group Access Restriction
Make sure this value is non-blocking.
NCOS (0)-99 Network Class of Service Group.
IMPORTANT: Ensure this value is high enough to allow
calls on SIP trunks.
CLS UNR Unrestricted Class of Service.
KEY Telephone function key assignments
0 ACD 5308 cccc zzzz Automatic Call Distribution (ACD) key
Where:
•
yyyy = ACD DN configured in LD 23 for Converged
Desktop use
•
cccc = CLID table entry of (0)-N, where N = the value
entered at the SIZE prompt in LD 15 minus 1
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 57

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 57
Prompt Response Description
zzzz = agent’s position ID (zzzz can be up to 4 digits; up to
7 digits with Directory Number Expansion [DNXP] package
150).
2 MCN 3604 Multiple Call Non-Ringing key
Where yyyy = DN
The DN can be up to 4 digits; up to 7 digits with Directory
Number Expansion (DNXP) package 150. Once the MCN
key has been defined, the MARP prompt appears.
Since MCN and DN are used by the feature to originate
calls, the same DN can be applied to all PCAs.
Configure the Signaling Server using
CS 1000 Element Manager
To configure SIP Converged Desktop Services using CS 1000 Element
Manager, follow the steps in Procedure 1 "Configuring SIP CDS on the
Signaling Server" (page 57).
Note: The SIP Trunk Gateway must be configured for SIP CDS. Refer
to IP Peer Networking Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-313)
for detailed instructions.
Procedure 1
Configuring SIP CDS on the Signaling Server
Step Action
1 Log in to Element Manager.
2
Select IP Telephony > Nodes: Servers, Media Cards >
Configuration from the navigator.
The Node Configuration web page opens, as shown in Figure 13
"Node configuration web page" (page 57).
Figure 13
Node configuration web page
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 58

58 Configuring CS 1000
3
Click Edit next to the node for which SIP CDS is to be configured.
The Edit web page opens, as shown in Figure 14 "Edit web page"
(page 58).
Figure 14 Edit web page
4
Select SIP CD Services to expand the section, as shown in Figure
15 "SIP CD Services" (page 59).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 59

Figure 15 SIP CD Services
CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 59
5
Enter the necessary information in the following fields:
a. Service Enabled: Select whether the Converged Desktop
Service application is enabled or disabled for this node. CDS is
enabled by default (the check box is selected).
Note: If CDS is not enabled, no calls are sent to the MCS
5100, including both originating and terminating calls either
to or from the Converged Desktop telephone.
b. Service DN used for making VTRK call from Agent: Enter the
Service DN. The Service DN is a number for CS 1000 to call the
Signaling Server CDS application over a SIP Virtual Trunk. This
number can be composed of:
•
LOC + extension
•
Extension
•
SPN
As described in "How Converged Desktop Services works"
(page 14), upon receipt of an incoming call notification over
the AML/VAS links, the CDS application must reserve a Virtual
Trunk until the destination of the call is determined. The CDS
application instructs the Call Server to make a call to this Service
DN. The Call Server’s numbering plan directs the call to the
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 60

60 Configuring CS 1000
Virtual Trunk route based on translations. The CDS answers
and reserves the Virtual Trunk in case it is needed to terminate
the incoming call.
The example shown uses an SPN and is defined as follows:
Service DN = AC1 (from LD 86) + SPN (from LD 90)
For example, the value entered for the Service DN is 65100,
where 6 is Access Code 1 (AC1) (configured in LD 86 on "LD 86
Configure Access Code (AC1 or AC2)." (page 53)) and 5100
is the Special Number (SPN) (configured in LD 90 on "LD 90
Configure Service DN for Converged Desktop." (page 54)).
c. Converged Telephone Call Forward DN: This field is required if
the SIP Trunk Gateway application is enabled and the Converged
Desktop Service will be used. The Converged Telephone Call
Forward DN is the CDN defined in LD 23 for the CDS application.
This entry designates the CDN that CDS will acquire to obtain
messaging for call activity. CS 1000 telephones with CDMO
or CDMV Class of Service redirect all calls to the CDN. The
acquisition of the CDN identified in this field allows messaging
for call activity to be processed to the CDS Application on the
Signaling Server.
For example, the value entered is 5100, which is the Control
DN (CDN) configured in LD 23 on "LD 23 Configure Control
Directory Number (CDN)." (page 52).
User Info. field for Invite message on the Converged
d.
Desktop MO Set: Verify the field against the following string:
sip:convergeddesktop@SIPdomainname;nortelconverged=
continueforce
Ensure that the SIPdomainname is part of the string. The SIP
Domain name should have been configured during the SIP Trunk
Gateway configuration.
If the string is missing the SIP Domain name (that is, the string
is sip:convergeddesktop@;nortelconverged=continueforce),
then the SIP Domain name was not configured during the SIP
Trunk Gateway configuration. The SIP Domain nameis found
under Signaling Server > Signaling Server xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Properties on the Edit web page (Figure 14 "Edit web page"
(page 58)).
This field is used in the INVITE message of Converged Desktop
terminating call handling if the telephone is a multimedia-only
telephone.
e. User Info. field for Invite message on the Converged
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Desktop MV Set: Verify the field against the following string:
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 61

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 61
sip:convergeddesktop@SIPdomainname;nortelconverged=
conditionalfork
Ensure that the SIPdomainname is part of the string. The SIP
Domain name should have been configured during the SIP Trunk
Gateway configuration.
If the string is missing the SIP Domain name (that is, the string
is sip:convergeddesktop@;nortelconverged=conditionalfork),
then the SIP Domain name was not configured during the SIP
Trunk Gateway configuration. The SIP Domain name is found
under Signaling Server > Signaling Server xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Properties on the Edit web page (Figure 14 "Edit web page"
(page 58)).
This field is used in the INVITE message for Converged Desktop
terminating call handling if the telephone is both a multimedia
and a voice telephone.
User Info. field in the notify message for Converged
f.
Desktop: Verify the field against the following string:
sip:convergeddesktop@SIPdomainname
Ensure that the SIPdomainname is part of the string. The SIP
Domain name should have been configured during the SIP Trunk
Gateway configuration.
If the string is missing the SIP Domain name (that is, the string is
sip:convergeddesktop@), then the SIP Domain name was not
configured during the SIP Trunk Gateway configuration. The SIP
Domain name is found under Signaling Server > Signaling
Server xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx Properties on the Edit web page
(Figure 14 "Edit web page" (page 58)).
This field is used in the NOTIFY message for Converged
Desktop.
g. RAN route for Announce: Enter the Recorded Announcement
(RAN) route number for call announce. The route was configured
in LD 16. The range is 0 to 127 for Small Systems. The range
is 0 to 511 for Large Systems.
The RAN definition in this field can be used in two distinct ways:
•
Call progress – A customer may want to announce to a caller
that their call is proceeding and to please wait. RAN can be
used when delays may be longer than expected, as PCA
makes calls to other devices. If RAN is not used, callers will
hear only ringback tone.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
•
PCA busy – If PCA agents are busy processing a call and the
caller must wait for a PCA so CDS can process the call, the
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 62

62 Configuring CS 1000
user can be directed to RAN. The RAN typically will say, for
example, "Your call is proceeding, please wait..."
h. Wait time before a caller is sent to RAN Queue: Enter the time
(in seconds) that the caller waits before the called is directed to
the RAN queue. The range is -1 to +32767 seconds, where:
Value Meaning
-1
0
+1 to
+32767
Never send to RAN queue. This is the default.
Immediately send to RAN queue.
Wait n seconds before sending to RAN queue.
i. Timeout for Ringing indication of the CD set: Enter the time to
wait for ringing indication on the Converged Desktop telephone.
If a timeout occurs, the system considers the telephone as busy
or call-forwarded to other devices. As a result, the Converged
Desktop call is canceled. The timeout range is 5 to 60 seconds
(default is 10 seconds).
j. Timeout for CD Server: Enter a timeout value. This value is
used when the MCS 5100 is not available or there are network
problems. An incoming Converged Desktop call is terminated
directly to Converged Desktop telephone without waiting for the
MCS 5100. The timeout range is 1 to 30 seconds (default is 5
seconds).
Note: Nortel recommends that the timeout value not be
configured as a small value. If the time is too short, then a
delayed packet can eventually reach the MCS 5100. This
can cause a "race condition" between the MCS 5100 routing
the call and the CS 1000 routing the call. If the administrator
knows of a persistent network problem, or if the MCS 5100 is
out-of-service for a period of time, then Nortel recommends
that the Converged Desktop Service be disabled instead of
having a small timeout value.
k. Timeout for call answered by other than CD phone set: Enter
6
Select SIP URI Map to expand the section, as shown in Figure 16
"CS 1000 SIP URI Map" (page 63).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
a timeout value. If a call is answered on any telephone (within
the CS 1000 network) other than Converged Desktop telephone
itself, then the SIP session is torn down automatically after this
timeout. The purpose is to remove"lone" screen pop-ups on the
Converged Desktop PC Client (PCC). The timeout range is 2 to
60 seconds (default is 2 seconds).
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 63

CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 63
Note: The fields require a character string that is less than 128
characters in length. The valid characters include: alphanumeric
(a-z, 0-9), period (.), dash (-), underscore (_), and plus sign
(+). These fields must be completed if the SIP Trunk Gateway
application is enabled.
Figure 16 CS 1000 SIP URI Map
7
Fill in the fields as follows:
a. Type +1 in the Public E.164/National domain name text box.
b. Type +1613 in the Public E.164/Subscriber domain name text
box.
c. Type publicUnknown in the Public E.164/Unknown domain
name text box.
d. Type publicSpecial in the Public E.164/Special Number
domain name text box.
e. Type udp in the Private/UDP domain name text box.
f. Type cdp.udp in the Private/CDP domain name text box.
g. Type special.udp in the Private/Special Number domain
name text box.
h. Type privateUnknown in the Private/Unknown (vacant
number routing) domain name text box.
i. Type unknown.unknown in the Unknown/Unknown domain
name text box.
Note: The values entered in these fields must agree with values
entered in MCS 5100. See "Configure number qualifiers" (page
72).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 64

64 Configuring CS 1000
8
Click Save and Transfer.
Verifying configuration
After configuring the Virtual IP D-channel, SIP Route, Converged Desktop
AML, and the other elements, log in to the Leader Signaling Server of the
node. At the Command Line Interface (CLI), use the commands cdsShow
and cdsAgentShow to verify the configuration. Output of the commands
will be similar to that shown inFigure 17 "Verifying configuration: cdsShow"
(page 65) and Figure 18 "Verifying configuration: cdsAgentShow" (page 65).
The two diagrams show that the AML link is Up and your PCA agents have
been acquired by the ACD queue you configured for CD2.
Note: InFigure 17 "Verifying configuration: cdsShow" (page 65) and
Figure 18 "Verifying configuration: cdsAgentShow" (page 65), CDN is
the Converged Telephone Call Forward DN.
—End—
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 65

Figure 17
Verifying configuration: cdsShow
CS 1000 SIP configuration and UDP location dialing 65
Figure 18
Verifying configuration: cdsAgentShow
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 66

66 Configuring CS 1000
Note: If your Agents do not show Up, you may not have Nortel
Symposium Call Center (NGCC) package 311 equipped. You need
CS 1000 PEP MPLR19786 if the package is not equipped and you are
using CS 1000 Release 4.0 software. This PEP is not required on CS
1000 Release 4.5 or later software.
Configuring the Converged Desktop User
The Converged Desktop user is configured in LD 10 for analog
(500/2500-type) telephones or LD 11 for digital telephones.
LD 10/11 Configure Converged Desktop User.
Prompt Response Description
REQ: NEW
CHG
TYPE:
TN Terminal Number
CUST
CLS Converged Desktop Service Class of Service (CLS)
CSDN
a..a
l s c u Format for Large System and CS 1000E system,
cu
xx
(CDMR)
CDMV
CDMO
5200
Add new data.
Change existing data.
Type of data block
where l = loop, s = shelf, c = card, u = unit
Format for Small System, CS 1000S system,
Media Gateway 1000B, and Media Gateway 1000T,
where c = card and u = unit
Customer number as defined in LD 15.
Converged Desktop Multimedia Restricted (default)
Converged Desktop Multimedia and Voice
Converged Desktop Multimedia Only
Note: Nortel recommends CDMV to give users all features.
Converged Service Directory Number
Converged Desktop Service Control Directory Number
(CDN) configured in LD 23.
CSDN is only prompted if CLS is defined as CDMV or
CDMO.
KEY Telephone function key assignments
0 SCR yyyy Single Call Ringing key
Where yyyy = DN
The DN can be up to 4 digits; up to 7 digits with Directory
Number Expansion (DNXP) package 150. Use a single
appearance DN to terminate Voice Call (VCC) or Signaling
(SIG) calls. Once the SCR key has been defined, the
MARP prompt appears.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 67

Configuring MCS 5100
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Before you begin" (page 67)
"Implementation summary" (page 68)
"Implementation details" (page 68)
"Add IP address of IP Telephony node as an Authenticated Server" (page 68)
"Configure the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group" (page 69)
"Configure number qualifiers" (page 72)
"Configure a route list" (page 75)
"Configure routes for each dialing plan entry" (page 77)
"Configuring a Converged Desktop user" (page 81)
"Configure a Service Package" (page 81)
67
"Configuring the Converged User on the MCS 5100" (page 83)
Before you begin
Some values in these instructions are taken from the example numbering plans
described in "Description of the network configured in this document" (page
48) and "Examples of dialing and numbering plan configuration for mixed
networks" (page 37). Note that actual values may differ between applications.
Before you begin configuring CDS on the MCS 5100, you must have a
Service Domain configured in MCS with the same name as in CS 1000. For
this example, the domain name is mydomain.com.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
ATTENTION
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 68

68 Configuring MCS 5100
Implementation summary
The following is a summary of the tasks in this section:
•
"Add IP address of IP Telephony node as an Authenticated Server"
(page 68).
•
"Configure the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group" (page 69).
•
"Configure number qualifiers" (page 72).
•
"Configure a route list" (page 75).
•
"Configure routes for each dialing plan entry" (page 77).
Implementation details
Add IP address of IP Telephony node as an Authenticated Server
Use Procedure 2 "Adding the IP Address of the IP Telephony node as an
Authenticated Server" (page 68) to add the IP address of the IP Telephony
node to the Application Server as an Authenticated Server.
Procedure 2 Adding the IP Address of the IP Telephony node as an Authenticated Server
Step Action
1
Access the MCS 5100 Management Console on the MCS Client:
a. Choose MCP from the Start menu.
b. Click Start console.
c. Log in using your username and password.
d. Select Sites.
e. Select Servers.
f. Select Application Server.
g. Select Components.
h. Select the application server.
2
Right-click on Authentication (or Authent...).
3 Select Modify.
4
Enter 12.123.1.123, the IP address of the IP Telephony node, in
the Authorized Node IP Address field.
5
Click Add.
6
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Click Apply.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 69

Implementation details 69
7
Verify the address appears in the list under the Authentication tab,
as shown in Figure 19 "IP address of IP Telephony node added as
an Authenticated Server" (page 69):
a. Right-click on the application server.
b. Select Query.
Figure 19 IP address of IP Telephony node added as an Authenticated Server
—End—
Configure the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group
Use Procedure 3 "Configuring the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group"
(page 69) to configure the CS 1000 Node IP address as a SIP Gateway, and
configure the corresponding trunk and trunk group.
Procedure 3
Configuring the SIP Gateway, trunk, and trunk group
Step Action
1
Enter the IP address of the MCS Provisioning Client in a web
browser.
The Provisioning Client Login web page opens, as shown in
Figure 20 "Provisioning Client Login" (page 70).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 70

70 Configuring MCS 5100
2 Enter your Username and Password.
Figure 20 Provisioning Client Login
The Provisioning Client web page opens, as shown in Figure 21
"Provisioning Client" (page 70). The Provisioning Client navigator
is in the section on the left of the web page.
Figure 21 Provisioning Client
3
Add a new gateway, as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Gateways > Add Gateway in the
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Provisioning Client navigator.
The Add a new gateway web page opens, as shown in Figure
22 "Provisioning Client: Add a new gateway" (page 71).
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 71

Implementation details 71
Figure 22 Provisioning Client: Add a new gateway
b. Enter mydomain.com:maddr=12.123.1.123 in the Gateway
host text box.
c. Select CS 1000 in the Gateway type drop-down list.
d. Select Other from the Location drop-down list.
e. Select TRUE for Trusted Node.
f. Select TRUE for Is Gateway.
g. Click Submit.
4
Add a new route, as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Gateways > Add Route in the
Provisioning Client navigator.
The Create new gateway route web page opens, as shown
in Figure 23 "Provisioning Client: Create new gateway route"
(page 71).
Figure 23 Provisioning Client: Create new gateway route
b. Enter myGWRoute in the Route Name text box.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 72

72 Configuring MCS 5100
c. Select mydomain.com in the Domain drop-down list.
d. Click Save.
5
Add a trunk group directed to the gateway and route just created,
as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Gateways > Add TrunkGroup in the
Provisioning Client navigator.
The Trunkgroup Provisioning web page opens, as shown in
Figure 24 "Provisioning Client: Trunkgroup Provisioning" (page
72).
Figure 24 Provisioning Client: Trunkgroup Provisioning
b. Select mydomain.com:maddr=12.123.1.123 from the Gateway
drop-down list.
c. Select myGWRoute from the Route drop-down list.
d. Enter myTrkGroup in the Trunk Group edit box.
e. Click Save.
Configure number qualifiers
Use Procedure 4 "Configuring number qualifiers" (page 74) to configure
number qualifiers in MCS 5100 so they match the values configured in the
CS 1000 NRS SIP URI phone-context Level 1 and Level 0 Domains, and
the CS 1000 SIP URI Map.
The following three sets of provisioned information must match:
•
CS 1000 SIP URI Map (see Figure 25 "CS 1000 SIP URI Map" (page
73)) as configured in Procedure 1 "Configuring SIP CDS on the
Signaling Server" (page 57).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
—End—
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 73

Implementation details 73
•
CS 1000 NRS SIP URI phone-context in the Endpoint Routes (see
Figure 26 "CS 1000 NRS Endpoint Routing Entries" (page 73)).
•
MCS 5100 Telephony Routes Number Qualifiers (see Figure 27 "MCS
5100 Number Qualifiers" (page 74)).
where:
•
cdp.udp is the CDP/Level 0 Domain, with NPI = private and TON =
Level0
•
udp is the UDP Level 1 Domain, with NPI = private and TON = Level1
Figure 25 CS 1000 SIP URI Map
Figure 26 CS 1000 NRS Endpoint Routing Entries
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 74

74 Configuring MCS 5100
Figure 27
MCS 5100 Number Qualifiers
Procedure 4
Configuring number qualifiers
Step Action
1
Enter the IP address of the MCS Provisioning Client in a web
browser.
The Provisioning Client Login web page opens, as shown in
Figure 20 "Provisioning Client Login" (page 70).
2
Enter your Username and Password.
The Provisioning Client web page opens, as shown in Figure 21
"Provisioning Client" (page 70).
3
Add a new gateway, as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com >
Telephony Routes > Number Qualifiers in the Provisioning
Client navigator.
The Number Qualifiers web page opens, as shown in Figure
28 "Provisioning Client: Number Qualifiers" (page 75). The
Current Number Qualifiers section shows the number qualifiers
configured so far. Those listed in Figure 28 "Provisioning Client:
Number Qualifiers" (page 75) are configured by default. You can
use or Delete any of all of them as you prefer.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 75

Implementation details 75
4
Add a number qualifier for each entry in the SIP URI map (shown in
Figure 25 "CS 1000 SIP URI Map" (page 73)) as follows:
a. Enter the name in the Name text box, for example cdp.udp.
b. Enter a description in the Description text box, for example My
CDP phone context.
c. Click Add.
Figure 28
Provisioning Client: Number Qualifiers
Configure a route list
Use Procedure 5 "Configuring a route list" (page 75) to add a route list.
Procedure 5
Configuring a route list
Step Action
1
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Enter the IP address of the MCS Provisioning Client in a web
browser.
—End—
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 76

76 Configuring MCS 5100
The Provisioning Client Login web page opens, as shown in
Figure 20 "Provisioning Client Login" (page 70).
2
Enter your Username and Password.
The Provisioning Client web page opens, as shown in Figure 21
"Provisioning Client" (page 70).
3
Configure the Class of Service, as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com > Telephony
Routes > Routing COS in the Provisioning Client navigator.
The Class of Service Information web page opens, as shown
in Figure 29 "Provisioning Client: Class of Service Information"
(page 76).
Figure 29
Provisioning Client: Class of Service Information
b. Enter a name for the Class of Service, such as cdCOS, in the
c. Enter a description for the Class of Service, such as CD COS,in
d. Click Save.
4
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Add a new route list, as follows:
Name text box.
the Description text box.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 77

Implementation details 77
a. Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com > Telephony
Routes > Add RouteList in the Provisioning Client navigator.
The Create a New Route List web page opens, as shown in
Figure 30 "Provisioning Client: Create a New Route List" (page
77).
Figure 30
Provisioning Client: Create a New Route List
b. Enter a list name, such as myRouteList, in the Name text box.
c. Enter a list description, such as myRouteList, in the Description
text box.
d. Select ALLOW from the Incoming Other Domain Tree Call
Routing drop-down list.
e. Select ALLOW from the Incoming Same Domain Tree Call
Routing drop-down list.
f. Select cdCOS from the Class of Service drop-down list.
5 Click Save.
—End—
Configure routes for each dialing plan entry
For each dialing plan entry, you must configure the following routes:
•
private CDP route
•
private UDP route
•
Gateway CDP route
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 78

78 Configuring MCS 5100
•
Gateway UDP route
•
private PSTN route
•
route for local Dial-9 National (NPA) dialing using the Gateway CS 1000
PSTN
•
route for national Dial-9 National (NPA) dialing using the Gateway CS
1000 PSTN
Use Procedure 6 "Configuring routes for each dialing plan entry" (page
78) to configure these routes.
Procedure 6
Configuring routes for each dialing plan entry
Step Action
1
Enter the IP address of the MCS Provisioning Client in a web
browser.
The Provisioning Client Login web page opens, as shown in
Figure 20 "Provisioning Client Login" (page 70).
2
Enter your Username and Password.
The Provisioning Client web page opens, as shown in Figure 21
"Provisioning Client" (page 70).
3
Add the new routes, as follows:
a. Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com > Telephony
Routes > Add Telephony Route in the Provisioning Client
navigator.
The Create New Telephony Route web page opens, as shown
in Figure 31 "Provisioning Client: Create New Telephony Route"
(page 79).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 79

Implementation details 79
Figure 31
Provisioning Client: Create New Telephony Route
b. Configure each new route, as follows:
Table 2
Values for configuring Routes
Entry Field
Name
Description
Private
CDP
myCDP
Route
Private
myCDP
Route
Private
Private
UDP
myUDP
Route
Private
myUDP
Route
Private
1. Enter the values for the appropriate fields, as listed in Table 2
"Values for configuring Routes" (page 79).
Do not use blank spaces in text fields.
Note: In the Name field, only the following characters are
valid: A-Z, a-z, 0-9, comma (,), period (.), hyphen (-), and
underscore (_). Any other character in the route Name
causes an error message.
2. Click Save.
Route Type
Private
PSTN
myPST
NRoute
Private
myPST
NRoute
Private
Gateway
CDP
myCDP
RouteGW
myCDP
Route GW
Gateway
UDP
myUDP
RouteGW
myUDP
RouteGW
Public
Local
myLocal
Route
Public
myLocal
Route
Public
Public
National
my National
Route
Public
my National
Route
Public
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 80

80 Configuring MCS 5100
Route Type
Entry Field
From Digits
To Digits
Min Numbe
r of Digits
Max Numb
er of Digits
Private
CDP
7100 6334 9 7100 6334 9 9961
7199 6334 9 7199 6334 9 9969
48 84 8 118
4 8 22 4 8 22 8
Private
UDP
Private
PSTN
Gateway
CDP
Gateway
UDP
Public
Local
Public
National
Route Type Private Private Private Gateway Gateway Gateway Gateway
Remove
Prefix
01 10 1 1 1
0000233
4
00002
Not applicable
Recursive No No Not applicable
Gateway
Route
Gateway
Route Type
Number
Qualifier
Not applicable myGWRoute
Not applicable Private Private Public Public
Not applicable cdp.udp udp
+1 +1613
Route List myRouteList
4
Configure the Pretranslation table:
a. Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com >
Telephony Routes > Pretranslation Table in the Provisioning
Client navigator.
The Pre translations web page opens, as shown in Figure 32
"Provisioning Client: Pre translations" (page 81). The Current
Pretranslations section shows any pretranslations currently
configured.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 81

Configuring a Converged Desktop user 81
Figure 32 Provisioning Client: Pre translations
b. Configure pretranslations for each of the number qualifiers in the
Add New Pretranslations section, as follows:
1. Select the appropriate number qualifier from the Number
Qualifier drop-down list.
2. Enter a number in the Length text box.
3. Enter a prefix in the Prefix text box.
4. Click Add.
—End—
Configuring a Converged Desktop user
Configure a Service Package
Before you configure any Converged Desktop user in MCS, you must
configure a Service Package for the Domain which includes the SIP CDS
feature. Use Procedure 7 "Configuring a Service Package" (page 82) to
configure a Service Package.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 82

82 Configuring MCS 5100
Procedure 7
Configuring a Service Package
Step Action
1
Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com > Service
Package > Create Package in the Provisioning Client navigator.
The Create new package web page opens, as shown in Figure 33
"Provisioning Client: Create new package" (page 82).
2
3
Enter a package name in the Name of the Packages text box.
Select services and their appropriate parameters as appropriate,
including the following:
a. Select Converged Desktop.
b. Select Converged Desktop from the Setup drop-down list.
c. Select Yes from the Converged Desktop Enabled drop-down
list.
4
Click Save.
Figure 33 Provisioning Client: Create new package
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 83

Configuring a Converged Desktop user 83
—End—
Configuring the Converged User on the MCS 5100
Use Procedure 8 "Configuring a Converged Desktop User in MCS 5100"
(page 83) to configure each Converged Desktop user in MCS 5100.
Procedure 8
Configuring a Converged Desktop User in MCS 5100
Step Action
1
Select Provisioning > Domains > mydomain.com > Users > Add
Users in the Provisioning Client navigator.
The Add a new user web page opens, the upper portion of which is
shown in Figure 34 "Provisioning Client: Add a new user" (page 83).
Figure 34 Provisioning Client: Add a new user
2
Enter appropriate values in the fields, including the following:
a. Enter 3345573 in the Private Charge ID text box.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 84

84 Configuring MCS 5100
This is the HLOC + DN of the converged telephone. This number
is used for Click-to-Call in Converged Mode, and must be a UDP
number.
b. Enter 6139625573 in the Public Charge ID text box.
This is the NPA + NXX + DN of the converged telephone. It is the
caller identification information sent on a publiccall. This value is
required, and may be need even in Unconverged Mode.
c. Select cdCOS from the Class of Service drop-down list.
This is the same Class of Service configured in Procedure 5
"Configuring a route list" (page 75).
Note: You do not have to configure an alias, but if you do,
ensure that it does not conflict with the alias properties
configured in Step 3.
d. Click Save.
3
Set up the converged properties, as follows:
a. Click Converged Desktop properties.
The Converged Desktop Data web page opens, as shown in
Figure 35 "Provisioning Client: Converged Desktop Data" (page
84).
Figure 35 Provisioning Client: Converged Desktop Data
b. Enter 000023345573 in the Converged Desktop Alias text box.
c. Enter one of the following values in the Converged Desktop
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
This is the PNI + HLOC + DN of the converged telephone.
Preferred Audio Device text box:
•
If you are configuring UDP, enter the Access Code (AC1 or
AC2) + HLOC + DN of the converged telephone.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 85

Configuring a Converged Desktop user 85
•
If you are configuring CDP, enter the CDP number.
d. Select Enterprise Converged User from the Converged
Desktop User Type drop-down list.
—End—
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 86

86 Configuring MCS 5100
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 87

CS 1000 NRS operation
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 87)
"Operation" (page 88)
"Domains" (page 88)
"Gateway Endpoints" (page 89)
"Routing entries" (page 90)
"Configuring MCS 5100 in the NRS for CDS" (page 90)
"Configuring Meet Me Audio Conferencing in the NRS for CDS" (page 94)
"Operational logic" (page 96)
Introduction
In a mixed CS 1000/MCS 5100 network, the following is expected to occur:
87
•
The CS 1000 SIP Redirect Server routes calls to SIP endpoints
(gateways and SIP lines) under CS 1000 control.
•
The MCS 5100 routes calls to SIP endpoints (gateways and SIP clients)
under MCS 5100 control.
Note: In the context of SIP, the usage of the phrase "endpoint under
XXX control" indicates that entity XXX is the only entity that knows the
contact information for the endpoint.
Provisioning is impacted in the following manner:
• The CS 1000 SIP Redirect Server represents all CS 1000 endpoints in
the MCS 5100 provisioning.
•
The MCS 5100 Session Manager represents all MCS 5100 endpoints in
the CS 1000 provisioning.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 88

88 CS 1000 NRS operation
This network configuration requires the CS 1000 SIP Redirect Server and
MCS 5100 to interwork seamlessly. Therefore, this section describes the
basics of the redirect server logic.
Operation
Note: Some values in these instructions are taken from the example
numbering plans described "Examples of dialing and numbering plan
configuration for mixed networks" (page 37). Note that actual values
may differ between applications.
Domains
The following domains are created in the CS 1000 NRS.
• Service Domain = mydomain.com (see Figure 36 "Service Domain"
(page 88))
•
L1 Domain (UDP) = udp (see Figure 37 "Level1 Domain" (page 88))
•
L0 Domain (CDP) = cdp (see Figure 38 "Level0 Domain" (page 89))
These domains must match in both CS 1000 and in MCS 5100.
Figure 36 Service Domain
Figure 37 Level1 Domain
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 89

Figure 38 Level0 Domain
Gateway Endpoints
The Gateway endpoint is configured with the following properties:
•
ID — Node134Loc334
This matches the SIP Endpoint name configured in CS 1000.
•
Call Signaling IP address — 12.123.1.123
Operation 89
This is the IP address of the CS 1000 IP Telephony node.
• SIP Support — Dynamic SIP endpoint
•
SIP Transport Protocol — UDP
•
SIP port — 5060
This effectively configures the CS 1000 as an NRS endpoint. See Figure
39 "Gateway Endpoints" (page 89).
Figure 39 Gateway Endpoints
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 90

90 CS 1000 NRS operation
Routing entries
The routing entries configured in CS 1000 NRS for Gateway Endpoint
Node134Loc334 are shown in Figure 40 "Routing Entries" (page 90).
Note: SIP URI phone-contexts are configured in CS 1000 NRS as part
of the Level1 Domain (udp).
Figure 40 Routing Entries
Configuring MCS 5100 in the NRS for CDS
To implement CDS in the NRS, configure the MCS 5100 system in one
of two ways:
•
Configure the MCS 5100 as a Gateway Endpoint.
This is the preferred option and is the only option when multiple
Collaborative Servers are required in the system. When configuring
the MCS 5100 as a Gateway Endpoint in the NRS, note the following
requirements:
— endpoint name = convergeddesktop
— call signaling IP address = 12.234.3.234
This is the application server logical IP address on the MCS 5100.
— SIP support = static SIP endpoint
— SIP transport = UDP
SIP transport protocol must always be UDP.
— SIP port = 5060
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 91

Configure at least two routing entries against this Gateway Endpoint,
so the Gateway Endpoint can be added to the lookup table.
•
Configure the MCS 5100 as a Collaborative Server. See Figure 41
"MCS 5100 configured as a Collaborative Server" (page 92).
Note: This option is not recommended and can only be used when
no other Collaborative Servers exist in the system.
When you configure the MCS 5100 system in the NRS, note the
following requirements:
— domain = 12.234.3.234
— alias name = MyMCSAppSrv
— domain type = L1
— SIP support = yes
Indicate yes for SIP support with a check mark.
— SIP transport = UDP
SIP transport protocol must always be UDP.
Operation 91
— SIP port = 5060
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 92

92 CS 1000 NRS operation
Figure 41
MCS 5100 configured as a Collaborative Server
To route calls from MCS 5100 to CS 1000 when MCS is configured as a
Collaborative Server, choose one of two configuration options:
1. Configure MCS 5100 as a Gateway Endpoint for the NRS without routing
entries for calls from CS 1000 to MCS 5100. See Figure 42 "MCS 5100
configured as a Gateway Endpoint without routing entries" (page 93).
When configuring MCS 5100 in NRS without routing entries, use the
following entries:
•
endpoint name = Converged Desktop
•
call signaling IP address = 12.234.3.234
This is the application server logical IP address on the MCS 5100.
•
SIP support = static SIP endpoint
•
SIP transport = UDP
SIP transport protocol must be UDP.
•
SIP port = 5060
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 93

Operation 93
Figure 42
MCS 5100 configured as a Gateway Endpoint without routing entries
2. Configure telephony routes on MCS 5100 to contact the CS 1000 SIP
Gateway directly (not through NRS). See Figure 43 "Configure telephony
routes on MCS 5100" (page 94). For more information about configuring
MCS 5100, see "Configuring MCS 5100" (page 67).
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 94

94 CS 1000 NRS operation
Figure 43
Configure telephony routes on MCS 5100
Configuring Meet Me Audio Conferencing in the NRS for CDS
To configure Meet Me Audio Conferencing for CDS, you must point the
meetme DID to the convergeddesktop gateway end point as a CDP entry.
Note: You must create the convergeddesktopendpoint before beginning
this procedure. For more information, see "Gateway Endpoints" (page
89).
Procedure 9
Configure Meet Me Audio Conferencing
Step Action
1
2
3
4
Log into the Network Routing Service Manager as admin.
Select Configuration > Routing Entries.
In the top toolbar, select the set Standby DB view radio button.
In the Routing Entries section, from the pulldown lists, select the
<Domain name>, the <L1 level>, and the <L0 level>.
5 In the Gateway Endpoint field, select convergeddesktop.
6
In the With DN Type field, select the DN Type and click Show.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 95

Operation 95
7
8
9
10
11
Click Add.
Enter the DN Type, DN Prefix, and Route Cost.
Click Save.
Navigate to Tools > Database Actions.
Under Select database action, choose Cut over & Commit.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 96

96 CS 1000 NRS operation
12
Operational logic
The following items describe the operational logic of the CS 1000 SIP
Redirect Server:
•
When an INVITE is received, the Public Address is extracted from the
request URI.
For example:
INVITE <sip:dn;phone-context=pc@domain;user=phone> SIP/2.0
•
When the SIP Redirect Server searches the location database, it tries to
find all the endpoints that meet the following requirements:
— The endpoint belongs to the specified domain.
— The endpoint has associated routing entries (with both of the
Click Submit.
—End—
following) :
– exact phone-context as the one received
– longest DN-prefix that prefixes the received DN
Table 3 "Search results of location database" (page 97) shows the
possible outcomes of the location database search.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 97

Table 3 Search results of location database
If... Then...
The resolution fails (that is, no
endpoints are found), the SIP Redirect
Server redirects to a collaborating
• Send the 302 response (Moved Temporarily)
•
server.
Operational logic 97
Build the Contact Address of the 302 response to
include the collaborating servers IP address
Note: For the purpose of this
discussion, the collaborating server can
be an MCS 5100 Session Manager.
A single endpoint is found.
Multiple endpoints are found.
For example:
<sip:dn;phone-context=pc@domain:5060; maddr=47.11.1
60.010;transport=TCP;user=phone>
•
Send the 302 response (Moved Temporarily)
•
Build the Contact Address of the 302 response to
include the IP address of the endpoint. (This can be IP
address of the MCS 5100 Session Manager, for the
purposes of this discussion)
For example:
<sip:dn;phone-context=pc@domain:5060; maddr=47.11.1
82.170;transport=TCP;user=phone>
•
Send the 300 response (Multiple Choices)
•
Include multiple Contact-headers in the 300 response
• Individual Contact-header URIs are built
•
Contact-headers are ordered according to route costs
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 98

98 CS 1000 NRS operation
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 99

Maintenance
Contents
This section contains information about the following topics:
"Introduction" (page 99)
"CS 1000 CLI commands" (page 99)
"MCS 5100 tools" (page 101)
"Translation Verification tool" (page 101)
Introduction
This section contains CS 1000 Command Line Interface (CLI) commands
that can be used with CDS. The CS 1000 CLI commands are used from the
Signaling Server CLI.
This section also contains a diagnostic tool available on MCS 5100 for
verifying translations.
99
CS 1000 CLI commands
The CS 1000 Signaling Server provides a Command Line Interface (CLI)
through a serial port or a Telnet session. This section contains the CLI
commands available at that interface that are applicable to CDS.
Signaling Server CLI commands are available at three levels:
•
Level One — Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)
shell for basic technician support and general status system checking
(oam>prompt)
• LevelTwo — ProblemDetermination Tool (PDT) shell for expert support;
also includes all Level One (OAM) commands (pdt>prompt)
•
Level Three — Nortel proprietary vxWorksª shell for advanced
debugging and design support (prompt)
Note: This section describes the Level One (OAM) and Level Two
(PDT) CLI commands. Level Three commands are considered expert
support and design level commands, and are not documented here.
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
Page 100

100 Maintenance
You must log in to the Signaling Server to use the CLI commands. Refer
to Signaling Server Installation and Commissioning (NN43001-312) for
this procedure.
Table 4 "CDS OAM commands" (page 100) shows the Converged Desktop
CLI commands available on the Signaling Server from the OAM shell.
Table 4 CDS OAM commands
Command
Description
cdsShow Displays the current Converged Desktop configuration.
The command is used to check the basic Converged
Desktop application status.
cdsAgentShow Displays the Personal Call Assistance (PCS) agent’s
information and status.
Table 5 "CDS PDT commands" (page 100) shows the Converged Desktop
CLI commands available on the Signaling Server from the PDT shell.
Table 5 CDS PDT commands
Command
cdsAmlTrace <level> Sets the Application Module Link (AML) trace level for the
Description
CDS application. Turns tracing on/off for troubleshooting
message flows between the Call Server and the Signaling
Server.
Where <level> is:
0 – turns off trace
1 – prints all input/output AML data buffer
2 – prints all input/output AML data buffer except POLLING
message
3 – prints all input/output AML data buffer except POLLING
message, with Information Element (IE)-type decoding
4 – prints all input/output AML data buffer except POLLING
message, with IE type and data decoding
Communication Server 1000 to MCS 5100 Converged Desktop Type 2 Configuration Guide
Copyright © 2005-2008, Nortel Networks
.
Note: This command prints the AML messages to/from the
Call Server at the transport layer. Because sending and
receiving AML messages is based on each AML link instead
of each DN or TN, no good solution exists for filtering on
this AML trace tool. Nortel recommends that tracing not be
turned on in a busy system. Instead, Nortel recommends
the use of the cdsCallTrace tool or vtrkCallTrace tool.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-321 01.05 Standard
Release 5.0 15 February 2008
 Loading...
Loading...