
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Nortel Converged Office
Fundamentals — Microsoft
Office Communications Server
2007
NN43001-121
.

Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.03
Document date: 30 April 2008
Copyright © 2005–2008, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
LEGAL NOTICE
While the information in this document is believed to be accurate and reliable, except as otherwise expressly agreed
to in writing. NORTEL PROVIDES THIS DOCUMENT "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF ANY
KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. The information and/or products described in this document are subject
to change without notice.
Nortel, the Nortel logo, the Globemark, Meridian 1, and Succession are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Sourced in Canada

Contents
New in this release 9
Office Communications Server 2007 features 9
Other changes 9
How to get help 11
Getting help from the Nortel web site 11
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center 11
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code 11
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller 12
Introduction 13
Converged Office component overview 15
Converged Office 15
Enterprise Voice 17
OCS 2007 Voice components 18
Media Gateways 19
Mediation Server 20
Remote Call Control with SIP CTI (TR/87) 22
Telephony Gateway and Services 23
Personal Call Assistant 25
Access Edge Server 27
OCS 2007 snap-in 27
Multimedia Convergence Manager 28
CDR data collection 28
SIP CTI (TR/87) Protocol 29
Hardware Load Balancer 31
Office Communicator 2007 32
Documentation References 32
3
Revision History 10
Planning and engineering 35
Planning process 35
Network configuration 36
Multiple customer network 40
Multiple location network 42
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

4 Contents
Load Balancer planning 43
Load Balancer requirements 44
Redundancy with Load Balancers 45
Nortel Application Switch 46
Capacity planning 46
OC 2007 client requirements 47
Load Balancer capacity requirements 47
SIP CTI (TR/87) services requirements 47
Mediation server requirements 49
Signaling Server requirements 49
Call Server requirements 50
OCS Proxy and MCM capacity requirements 50
General requirements 51
Server topology 52
Operating System Requirements 52
Hardware Requirements 53
Virtual Server 2005 54
Storage 55
Trunks 55
Basic Client Configuration 58
Port use 58
Security 59
Dial Plan considerations 61
Number formats supported by Office Communicator 63
E.164 international format numbers for SIP Gateway and SIP CTI 66
Telephony Gateway and Services planning 66
Systems, platforms, and applications 66
Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 73
LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence 82
Client considerations 82
Converged Office functionality 82
MCM 2.0 to MCM 3.0 84
Load balancer considerations 84
Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007 84
Determine your deployment options 86
Migration process 86
Description of Migration Phases 88
Unified Messaging 90
OCS 2007 users using CallPilot 90
OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—integrated 92
OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—non-integrated 95
Signaling with integrated Voice Mail 97
Signaling with non-integrated Voice Mail 98
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Contents 5
Installation 101
OCS 2007 installation preparation and deployment 103
CS 1000 and Signaling Server installation 105
OCS 2007 component installation 105
OCS Proxy server installation 107
Load Balancer installation 108
MCM installation 109
Configuration 111
Active Directory configuration 112
Office Communications Server configuration 119
Load Balancer configuration 120
Voice Properties configuration 120
OCS configuration procedures 122
Configuration of Static Routes 122
Host Authorization and Routing configuration 122
Mediation Server configuration 133
MCM 3.0 configuration 134
MCM architecture 135
MCM Direct configuration 137
MCM management console 137
Telephony Gateway and Services configuration 150
Call Server configuration 151
Configuring the Codec 151
Loss Plan configuration 152
Dialing Plan configuration to route to MCM 153
Configuring the Personal Call Assistant 154
Caller ID table configuration 157
Home LOC and Home NPA configuration 159
DNS Server configuration 159
SIP Trunk configuration 160
Domain naming 163
URI Mapping 165
SIP Gateway CLID Parameters configuration 167
SPS configuration 168
NRS configuration 169
CDR configuration 170
E.164 International Format Numbers from Office Communicator - Computer
Calls (SIP Gateway) 170
Phone number normalization 171
Remote Call Control configuration 171
Remote Call Control and PBX integration 171
RCC and PBX integration on OC client 172
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

6 Contents
CS 1000 configuration 173
Signaling Server configuration 177
SIP CTI Services configuration settings 181
SIP CTI CLID configuration parameters 185
Configuring the SIP URI Map 189
Configuring CDR 190
Dialing E.164 International Format Numbers from Office Communicator - Phone
Calls (SIP CTI) 190
Normalizing phone numbers 192
SIP Routing and Redundancy configuration 198
OCS 2007 users using UM 2007 in integrated mode 198
Option 1 adding user Alias as Exchange UM 198
Option 2 adding CS 1000 DN as Exchange UM 203
Maintenance 209
Introduction 209
Communication Server 1000 209
MCM 3.0 209
Remote Call Control 210
Operational Measurements for SIP CTI 212
Troubleshooting 215
Checking Telephony Gateway (SIP Gateway) configuration 215
Checking Remote Call Control (SIP CTI) configuration 216
Lack of memory on Signaling Server 216
SIP CTI services does not come up 217
SIP Dialog not established 217
Solution 1: Check configuration parameters in AD 218
Solution 2: Confirm FQDN and the IP address are correct 218
SIP CTI service is down 218
MCM not synchronizing new users in AD Cache mode 220
Solution 1: Check the Global Catalog content manually 220
Solution 2: Access permissions for the AD object properties 221
Solution 3: Enable propagation of the AD to the Global Catalog 222
OC client not registered 223
Pop-up not displayed 223
Two pop-ups are displayed 224
Delay for a SIP Gateway call 224
Call Forward is cancelled by Office Communicator 224
Office Communicator disconnecting from the network 225
Capturing traces and logs 225
Communication Server 1000 traces 225
AML traces on the Call Server (SIP CTI only) 226
SIP CTI traces on the Signaling Server 226
SIP Gateway traces on the Signaling Server 227
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Contents 7
MCM logs 228
Activating MCM logging 229
OCS logs 231
Case checklists 234
Appendix A Call Flow and protocol details 237
Contents 237
Overview 237
Message sequence 238
Call flow 239
Telephony Gateway and Services call flow 239
Supported features 246
Appendix B Configuration Examples 249
Contents 249
Introduction 249
Standard Edition 249
Setting up the lab 250
Collecting required data 251
Configuring the Call Server 252
Signaling Server checklist 262
Active Directory user configuration 269
Checking the MCM installation and configuration 272
Enterprise Edition 275
Overview of general lab set-up 275
OCS Management Console 278
Security/Certificates 282
Host Authorization 283
Routing 284
Configuring DNS 286
Active Directory configuration 288
Installing and configuring MCM 289
Signaling Server checklist 292
Configuring NRS 293
Normalizing Phone Numbers 295
Appendix C Abbreviations 297
Procedures
Procedure Migrating users from LCS to OCS 89
Procedure Installing the OCS Proxy server 108
Procedure Installing the Load Balancer 108
Procedure Installing MCM 3.0 109
Procedure Defining users 114
Procedure Configuring the Host Authorization and Routing for the OCS
Procedure Configuring host authorization for the OCS Proxy 126
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Front End server 123
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

8 Contents
Procedure Configuring a Mediation Server 133
Procedure Enabling replication to the Global Catalog 146
Procedure Configuring the SIP Trunk Domain name 164
Procedure Enabling Remote Call Control and PBX integration 171
Procedure Adding a new normalization rule 195
Procedure Configuring a basic mailbox for the UM user 199
Procedure Adding user Alias as Exchange UM 199
Procedure Configuring a basic mailbox for the UM user 203
Procedure Adding Exchange UM 204
Procedure Checking Telephony Gateway configuration 215
Procedure Checking Remote Call Control configuration 216
Procedure Reconfigure SIP CTI service 219
Procedure Checking the Global Catalog content manually 221
Procedure Accessing permissions for the AD object properties 222
Procedure Enabling propagation of the Active Directory field to the Global
Catalog 223
Procedure Resetting MCM debug trace 231
Procedure Activating OCS logs 232
Procedure Enabling OC logs 232
Procedure Setting up the lab 250
Procedure Checking the Call Server configuration 252
Procedure Checking the configuration of the Signaling Server 262
Procedure Checking NRS configuration 266
Procedure Checking the settings of Active Directory user
configuration 269
Procedure Checking the MCM installation and configuration 273
Procedure Identifying the active default applications 280
Procedure Checking the configuration of Certificates 282
Procedure Checking the configuration of Host Authorization 283
Procedure Checking that Routing is correctly configured 284
Procedure Checking that DNS is correctly configured 286
Procedure Checking that MCM is correctly installed and configured. 290
Procedure Checking that the Signaling Server is correctly configured 293
Procedure Checking that NRS is correctly configured 293
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

New in this release
Office Communications Server 2007 features
Signaling traffic between Communication Server 1000 and Office
Communications Server 2007 is supported by Multimedia Convergence
Manager (MCM) 3.0 . Media traffic is supported through the Mediation
Server.
The following list shows new Office Communicator 2007 client features for
Voice over IP (VoIP) mode:
•
Conference Call
•
Announced (Consulted) Call Transfer
•
Call Forward
•
Call Redirect (Deflect)
•
Dual Forking
•
DoNotDisturb (DND)
9
•
Federated calls
Other changes
•
The Mediation Server is introduced in OCS 2007 as a new component.
For more information about the Mediation Server, see"Mediation Server"
(page 20). Due to the introduction of the Mediation Server, the following
changes occur:
— Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Real-Time Transport
Protocol (SRTP) are not supported.
— OCS 2007 can talk to the Communication Server 1000 over a
Transport Control Protocol (TCP) or Transport Layer Security (TLS)
link. TLS transport is supported between MCM/OCS Proxy and CS
1000/SPS.
— Video support for Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) gateway calls is
not supported. Direct VOIP to VOIP and RCC to RCC calls can use
video. For more information, see "Feature Interactions" (page 68).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

10 New in this release
•
•
• The 8540 OCS desk phone can register as an OC 2007 client, however,
— SIP UPDATE method is not supported by Mediation Server. This
method enables SIP Gateways and Endpoints to update the call
information during a call. Because the OCS 2007 Mediation Server
does not support UPDATE, re-INVITE’s need to be sent to the
Mediation Server for every change in the call information during
a call. This has not changed since LCS 2005. There were no
interoperability issues.
— G.711 codec for the short leg (Mediation Server to Communication
Server 1000) and RT audio for the long leg of a call (Mediation
Server to OCS) is supported.
The NortelMultimedia Convergence Manager (MCM) 3.0 is introduced in
Converged Office. For more information, see "Multimedia Convergence
Manager (MCM)" (page 28).
OCS 2007 snap-in for MMC. For more information, see "OCS 2007
snap-in" (page 27).
Microsoft does not support using a CS 1000 twin phone with them.
Revision History
April 2008 Standard 01.03. This document is up-issued to correct the
syntax in the Installing the OCS Proxy section.
January 2008
Standard 01.02. This document is up-issued for new content to address
CRs, Unified Messaging, and LCS to OCS migration.
December 2007
Standard 01.01. This is a new document for Converged Office with Microsoft
Office Communications Server 2007.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
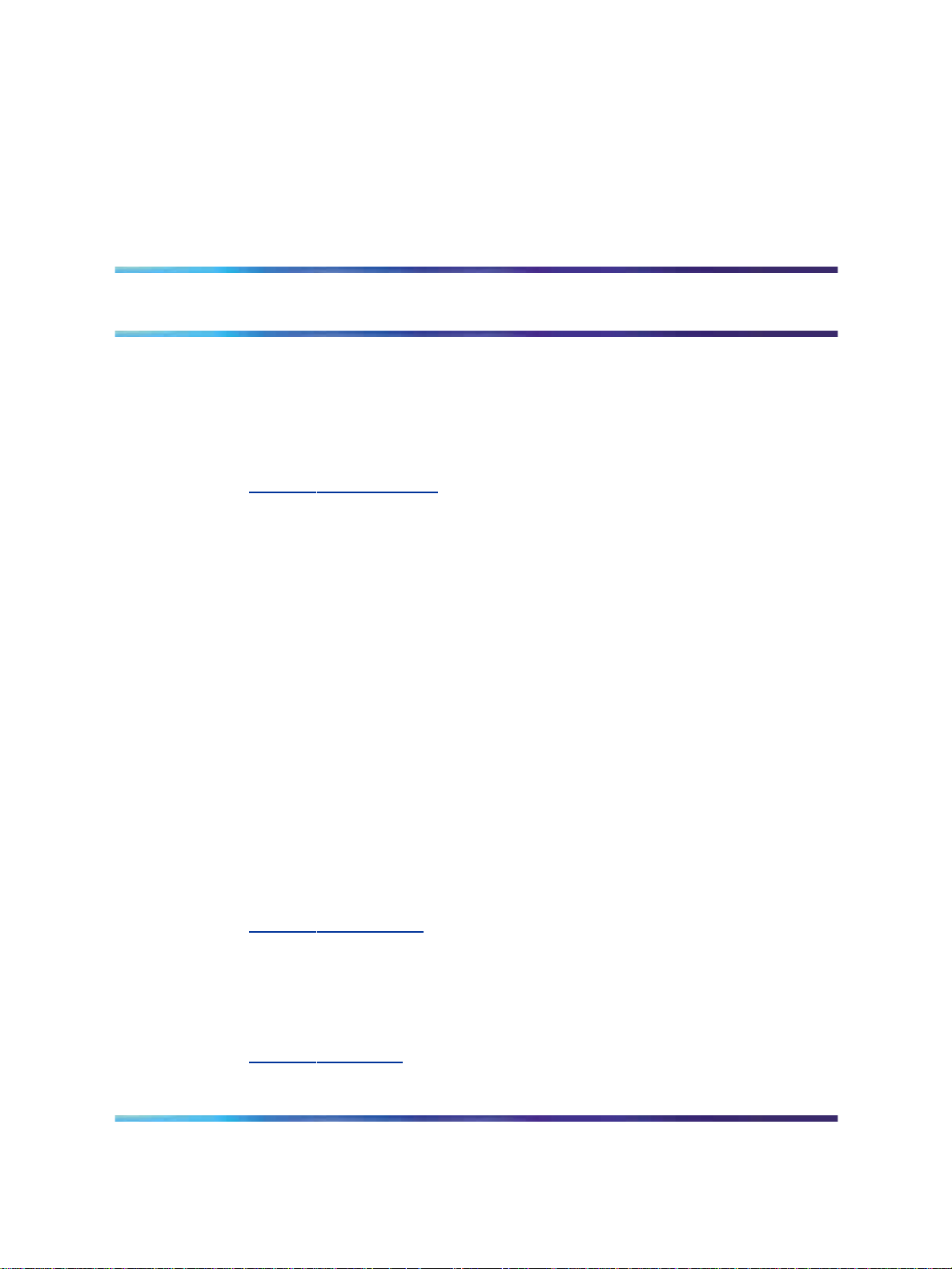
How to get help
This chapter explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting help from the Nortel web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support web site:
ww.nortel.com/support
w
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and
tools to address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
•
download software, documentation, and product bulletins
•
search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
•
sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation
for Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
11
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the NortelTechnical Support
web site, and you have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help over
the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following web site to obtain the telephone
number for your region:
w
ww.nortel.com/callus
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some NortelTechnicalSolutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
ww.nortel.com/erc
w
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

12 How to get help
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Introduction
This document describes the elements and processes necessary to
integrate Nortel Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000) with the Office
Communications Server 2007 (OCS 2007) in the Nortel Converged Office.
Prerequisites
•
Ensure CS 1000 Release 5.0 and the Product Enhancement Package
is installed.
•
Microsoft supportsthe coexistenceof LCS 2005 SP1 Standard Edition or
Enterprise Edition with OCS 2007 Standard Edition or Enterprise pools.
For more information, see "LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence"
(page 82).
Introduction navigation
•
"Converged Office component overview" (page 15)
•
"Planning and Engineering" (page 35)
13
• "Installation " (page 111)
•
"Configuration" (page 119)
•
"Maintenance" (page 209)
•
"Troubleshooting" (page 215)
•
Appendix "Call Flow and protocol details" (page 237)
•
Appendix "Configuration Examples" (page 249)
•
Appendix "Abbreviations" (page 297)
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

14 Introduction
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Converged Office component overview
This chapter provides a brief technical description of all the components
associated with Nortel Converged Office.
Component overview navigation
•
"Converged Office " (page 15)
•
"Enterprise Voice " (page 17)
•
"OCS 2007 Voice components" (page 18)
•
"Media Gateways" (page 19)
•
"Mediation Server" (page 20)
•
"Remote Call Control with SIP CTI (TR/87)" (page 22)
•
"Telephony Gateway and Services" (page 23)
• "Personal Call Assistant (PCA)" (page 25)
15
•
"Access Edge Server" (page 27)
•
"OCS 2007 snap-in" (page 27)
• "Multimedia Convergence Manager (MCM)" (page 28)
•
"CDR data collection" (page 28)
•
"SIP CTI (TR/87) Protocol" (page 29)
• "Hardware Load Balancer" (page 31)
•
"Office Communicator 2007" (page 32)
•
"Documentation References" (page 32)
Converged Office
Many Nortel CS 1000 customers base their multimedia strategy on
deploying Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007 and the Office
Communicator (OC) 2007 soft clients.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

16 Converged Office component overview
The Nortel Converged Office feature combines the business-grade
telephony of the CS 1000 with the OCS 2007 Enterprise Voice solution
to offer a powerful converged office solution set that improves worker
productivity. Telepresence and Multimodal (business set Voice over Internet
Protocol (VoIP), Instant Messaging (IM), and e-mail) communications
bundles, with applications such as Click-to-call and Access mobility, allow
workers to stay connected when not at their desks.
Nortel Converged Office comprises the following components:
•
Remote Call Control (RCC) with Session Initiation Protocol Computer
Telephony Integration (SIP CTI) (TR/87) provides full Microsoft Office
telephony integration to control business-grade telephony phones
from within Microsoft Office applications, as well as support for a
standards-based CTI interface defined by the TR/87 protocol.
•
Telephony Gateway and Services provides a basic SIP Telephony
Gateway to connect between Private and Public Telephony networks
and OC 2007 clients.
Nortel offers unique value with the two components that provide its
telephony services to OC 2007 clients and connectivity between the
Office Communications Server 2007 and the Nortel telephony network.
Nortel Converged Office provides the following benefits:
•
federated IM with industry name instant messaging
•
Microsoft application integration
•
click-to-call commands and missed call log
•
easy-to-use single soft client for IM, telepresence, and VoIP telephony
presence integration with Microsoft desktop and applications
•
a powerful suite of Nortel applications which include:
— Nortel Unified Messaging
— Contact Center
— Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
— conferencing
— click-to-call
Leveraging the CS 1000 and Microsoft desktop software allows end
users to access business-grade telephony services on the Nortel CS
1000 from the Microsoft Office Communicator desktop client. End users
can:
•
originate and receive telephone calls over existing CS 1000 phones from
an Office Communicator (OC) 2007 desktop client.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
•
•
Enterprise Voice
This section describes the Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007
Enterprise Voice solution. The Nortel Converged Office feature integrates
the OCS 2007 with the CS 1000. For a description of the integrated network
from the CS 1000 perspective, see "Network configuration" (page 36).
Enterprise Voiceis Microsoft’s software-powered VoIPsolution, a SIP-based
implementation of IP telephony for the enterprise that does not rely on
proprietary hardware investments. Enterprise Voice is a full-featured VoIP
solution that includes connectivity to the PSTN gateways and interoperation
with the CS 1000. Enterprise Voice, IM, group IM, enhanced presence,
and audio-video conferencing together constitute the Microsoft Unified
Communications solution.
The following figure shows the OCS 2007 Enterprise Voice components
extracted from the overall OCS 2007 architecture. COMO refers to
Communicator Mobile.
Enterprise Voice 17
originate and receive Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) calls
from the Office Communicator (OC) 2007 soft client when away from
the office.
take advantage of existing business telephony features on the CS 1000.
Figure 1 Enterprise Voice components - OCS 2007
When a user calls from an Enterprise Voice client by dialing or clicking on a
contact name or number in OC 2007 or Outlook:
•
the OCS Front End server normalizes the number to the E.164 format,
and invokes routing rules based on the location profile and user policy,
and directs the call to the appropriate Mediation Server
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

18 Converged Office component overview
•
the Mediation Server performs all necessary media transcoding and
routes the call to the IP-PSTN gateway.
•
the IP-PSTN gateway, based on topology, applies local or PBX dialing
rules and passes the call to the PSTN or PBX
Enterprise Voice uses Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) for media. Like
SIP, RTP is an InternetEngineering Task Force (IETF) standard. It defines a
packet format to carry audio and video over IP networks.
Enterprise Voice uses SIP for signaling and RTP for media. In the OCS,
SIP is used for IM, conferencing, presence subscriptions, video, and voice
enabling Enterprise Voice clients to provide a common user experience
across the communication modes.
Enterprise Voice is the Microsoft SIP–based implementation of IP telephony
for the Enterprise.
SIP sessions can include the sharing of real-time media. However, SIP
itself does not handle the actual media data, such as audio, video, and
application sharing. This separation means that SIP and various media
protocols can evolve independently.
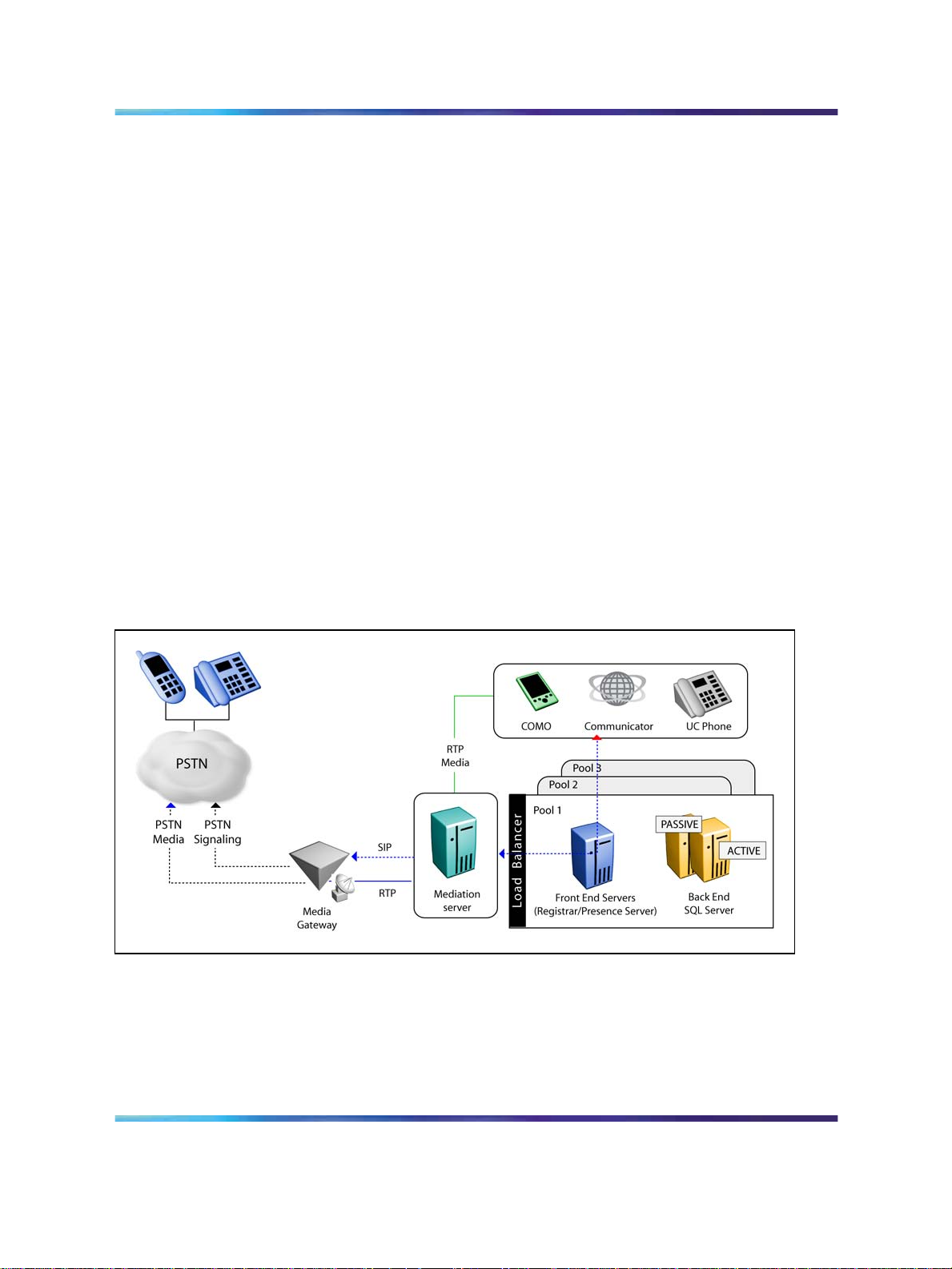
OCS 2007 Voice components
The core routing components for Enterprise Voice reside on the following:
•
Standard Edition Server (in the role of Front End Server or Director)
•
Enterprise Edition Front End Server
Other core routing server components include
• Translation Service—translates a dialed number into E.164 format
based on the normalization rules defined by the administrator.
•
Inbound Router—handles incoming calls according to user-specified
preferences.
•
Outbound Router—routes calls to CS 1000 or PSTN destinations after it
applies authorization rules to callers and determines the optimal media
gateway to route each call.
OCS 2007 Front End or Director components essential for voice support,
but are not voice components include
•
User Services—performs Reverse Number Look-up on the target phone
number for incoming phone calls.
• User Replicator—extractsuser phone numbers from the Active Directory
for use by User Services and the Address Book Service.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
•
Address Book Service—normalizes enterprise user phone numbers to
E.164 format to provision user Contacts in Office Communicator.
The following figure shows the components essential for voice support.
Figure 2 Core routing server components
Media Gateways 19
Media Gateways
Media gateways are third-party hardware components that provide a
common interface between the Enterprise Voice infrastructure and the
PSTN. Media gateways translate signaling and media between the PSTN
and Enterprise Voice infrastructure.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
20 Converged Office component overview
Media gateways translate the following protocols between the
circuit-switched PSTN network and the packet-switched Enterprise Voice
infrastructure:
•
Signaling protocol—SS7 and other protocols on the PSTN translate
to SIP for Enterprise Voice
•
Transport protocol—T-Carrier or E-Carrier on the PSTN convert to RTP
or Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) for Enterprise Voice
From the Nortel perspective, the CS 1000 functions as a media gateway for
the clients of the OCS 2007 server.
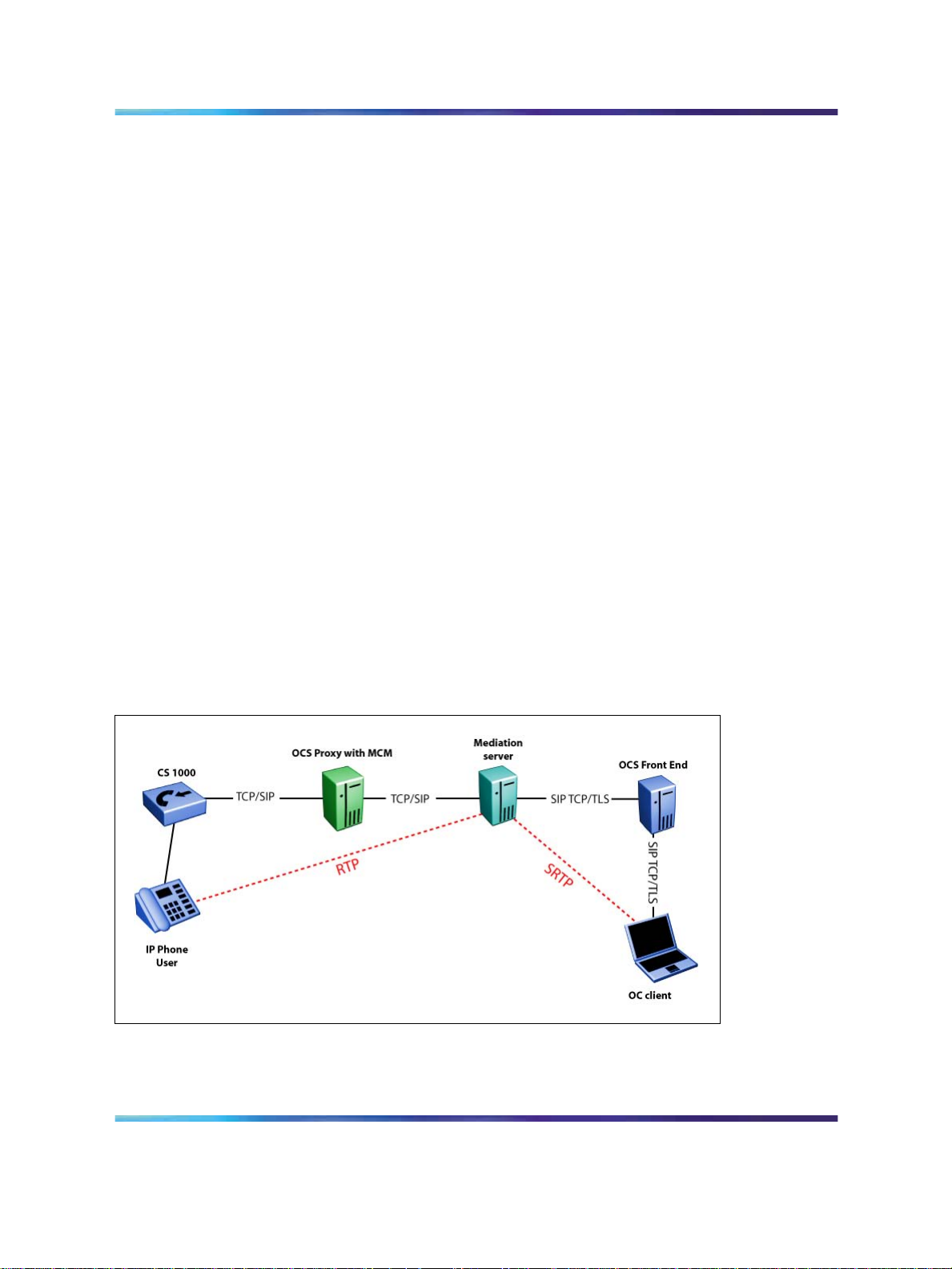
Mediation Server
The Mediation Server provides signaling and media translation between the
Enterprise Voice infrastructure and a CS 1000 gateway.
Figure 3 CS 1000 and OCS 2007 logical network elements
The Mediation Server provides the following functions:
•
translates SIP over Transport Control Protocol (TCP) (on the CS 1000
gateway side) to SIP over mutual Transport Layer Security (TLS) on the
Office Communications Server side
•
encrypts and decrypts SRTP on the Office Communications Server side
•
translates media streams (G.711) on the CS 1000 gateway side and RT
Audio on the Office Communication Server side
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
Mediation Server 21
•
connects clients outside the network to internal Interactive Connectivity
Establishment (ICE) components, to enable media traversal of NAT and
firewalls
•
acts as an intermediary for call flows that a gateway does not support
(such as calls from remote workers on an Enterprise Voice client)
The Mediation Server uses the following types of signaling:
•
For an inbound call from the CS 1000, the ms-call-source:non-ms-rtc
SIP header is inserted by the Mediation Server.
•
For an inbound call from the CS 1000, the Mediation Server Back 2
Back User Agent (B2BUA) generates a Session Description Protocol
(SDP) offer based on its capabilities in the OCS 2007.
•
For an inbound call from the CS 1000, the Mediation Server adds a
phone-context attribute to a number that is not in E.164 format.
•
For an outbound call from an OC 2007 client, the Mediation Server Back
2 Back (B2B) terminates the dialog and originates a new dialog with the
CS 1000. The From header is replaced with a phone number derived
from the p-asserted-identity header.
•
OC 2007 single step transfer. The Mediation Server terminates the
REFER message and returns the response code 202. The Mediation
server sends an INVITE message. The Mediation Server does not
forward the REFER message to the CS 1000.
Figure 4 Signaling and Media path between the OC client and CS 1000
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

22 Converged Office component overview
Remote Call Control with SIP CTI (TR/87)
The CS 1000 and OCS 2007 integration feature allows clients of the two
systems (Microsoft OCS 2007 and Nortel CS 1000) to communicate with
each other. You can associate an OC Client, which connects to the OCS,
with a CS 1000 line. You can perform operations on the CS 1000 line
through the OC Client using Remote Call Control (RCC) often referred to
as Phone-Mode. This feature allows for consistent access to RCC, service
control and configuration and telepresence functions across different
endpoints supported by the CS 1000.
The Nortel Converged Office Solution is implemented through an open
interface to ensure that any CS 1000 feature supported through OC 2007
is also accessible to applications from other vendors and application
developers who support these interfaces.
The SIP CTI (TR/87) protocol is on the CS 1000 Signaling Server. OC 2007
uses the TR/87 specification to implement phone integration throughout the
suite of Microsoft Office applications. You cannot use Office Communicator
to invoke a feature that is not supported by the phone.
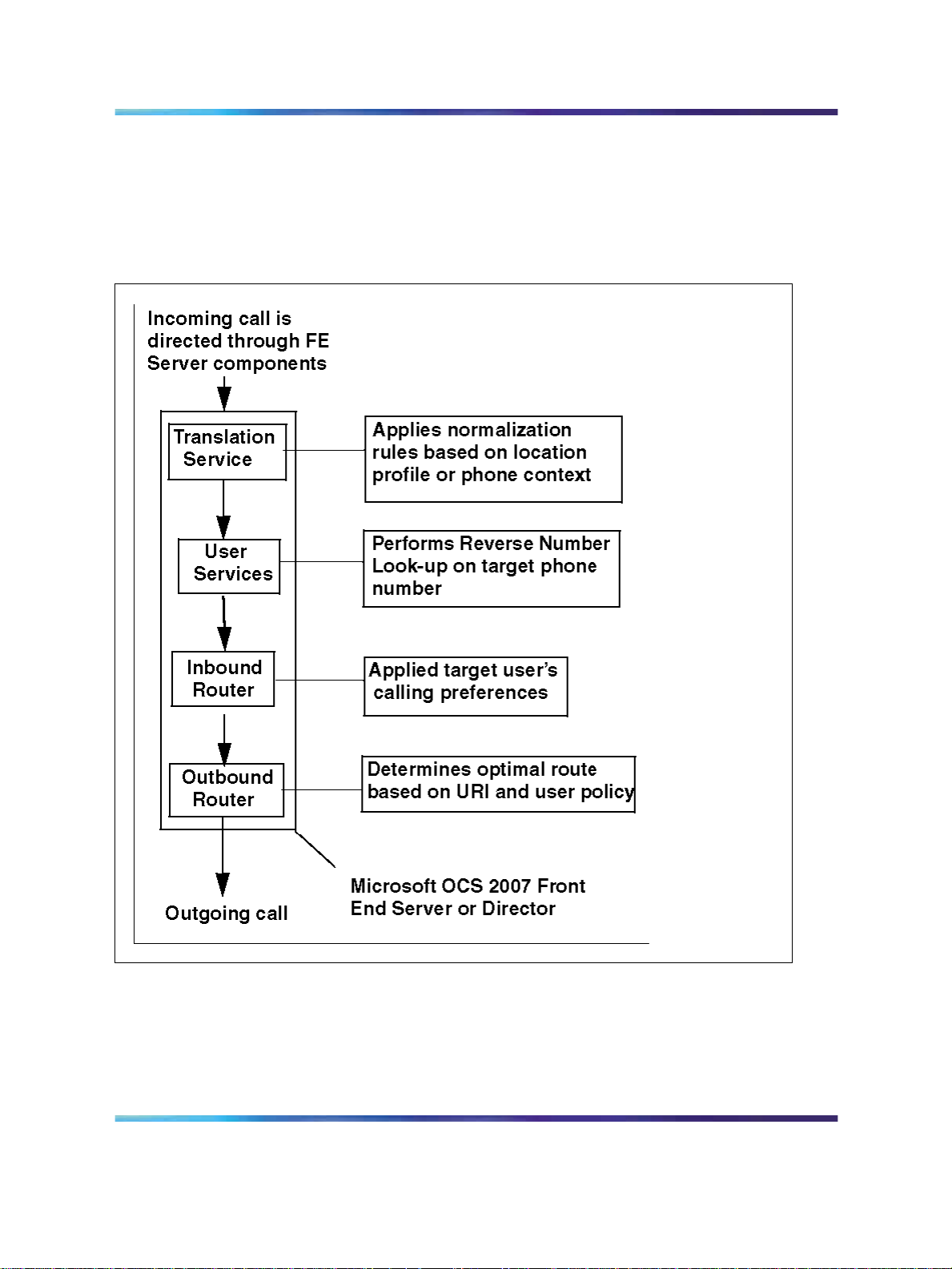
Example of RCC with SIP CTI (TR/87)
Figure 5 "Remote Call Control with SIP CTI (TR/87)" (page 23) shows
an example of a CS 1000 call to a mobile client. The following steps
correspond to the numbers in the figure:
1. A user selects Call to Chris’ mobile phone number from the CS 1000
telephone.
2. The Office Communications Server 2007 sends a call request to
the CS 1000.
3. The CS 1000 sets up a call from the user’s phone to Chris’ mobile
phone number.
4. Chris answers his mobile phone and a media path is established
between the two phones.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
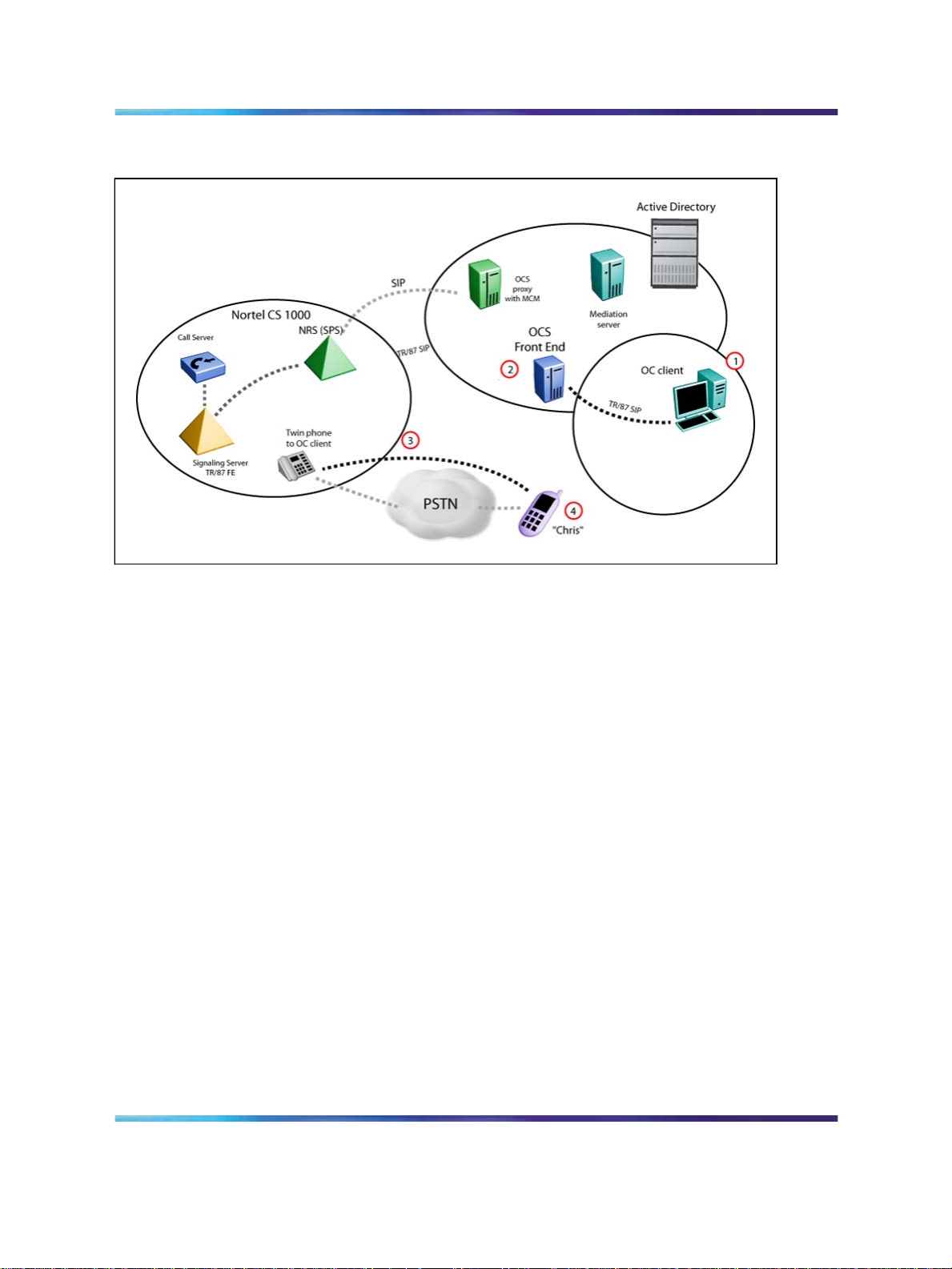
Figure 5 Remote Call Control
Telephony Gateway and Services 23
The full set of business-grade telephony features available with CS
1000 telephones is integrated with the OC 2007 client and can also be
operated from a CS 1000 IP Phone, even when the client is unavailable.
This integration ensures that telephony service reliability is preserved
during interruptions in soft client operation.
With the convergence of the CS 1000 with the OCS 2007, the OC 2007
client compliments the voice communications between two users by
allowing other media types, such as IM, file, and application sharing
to an existing voice call without the need to establish an independent
session between the users.
Telephony Gateway and Services
With the Telephony Gateway and Services component, users can choose
how to make and receive calls. For outgoing calls, users can make a
call from their Office Communicator soft client instead of their CS 1000
phone. You can handle incoming calls in one of two ways: through the
computer with OC 2007 or through a phone. This feature provides users
with computer-to-phone and phone-to-computer connectivity, leveraging the
Nortel provided dial plan, telephony infrastructure, and telephony features
to make and receive calls using Office Communicator (OC) 2007 Client
as a soft client.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

24 Converged Office component overview
With this solution, you can configure Personal Call Assistant (PCA) on the
CS 1000 for each user with this functionality. The CS 1000 configured with
the PCA provides number plan translations, Call Detail Recording (CDR)
for outgoing calls, and enables telephony features, such as Call forward
No Answer to Voice Mail, Attendant Recall, and participation as a client
in a Group Call for incoming calls.
With the Telephony Gateway and Services component, you can configure
the OC 2007 as a Multiple Appearance Directory Number (MADN) member
for users with PCA on the CS 1000. With PCA , calls to a user’s phone
number can be presented to both the desktop phone and to the OC 2007
client simultaneously. The user can then choose to answer on the most
convenient device.
The ability to connect between computers and phones is not natively
provided by Office Communications Server 2007; however, the Telephony
Gateway and Services component enables this functionality using the SIP
Gateway and Multimedia Convergence Manager (MCM) application. MCM
directs calls from an Office Communicator user to the CS 1000 connected
to their twinned telephone. Telephony Gateway and Services allows you
to originate and receive SIP calls (for example, VoIP and Computer calls)
from Office Communicator.
In Figure 6 "Dual forking example" (page 25), OCS Front End (FE) forks
the call to the CS 1000. The twin phone rings once and does not send
another invite. The same scenario applies to calls originating from the
CS 1000, the OCS does not get informed to perform another fork. A new
setting is introduced on OCS 2007 server that enables or disables dual
forking for each user. Remote Call Control (SIP CTI) is available when dual
forking is enabled.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
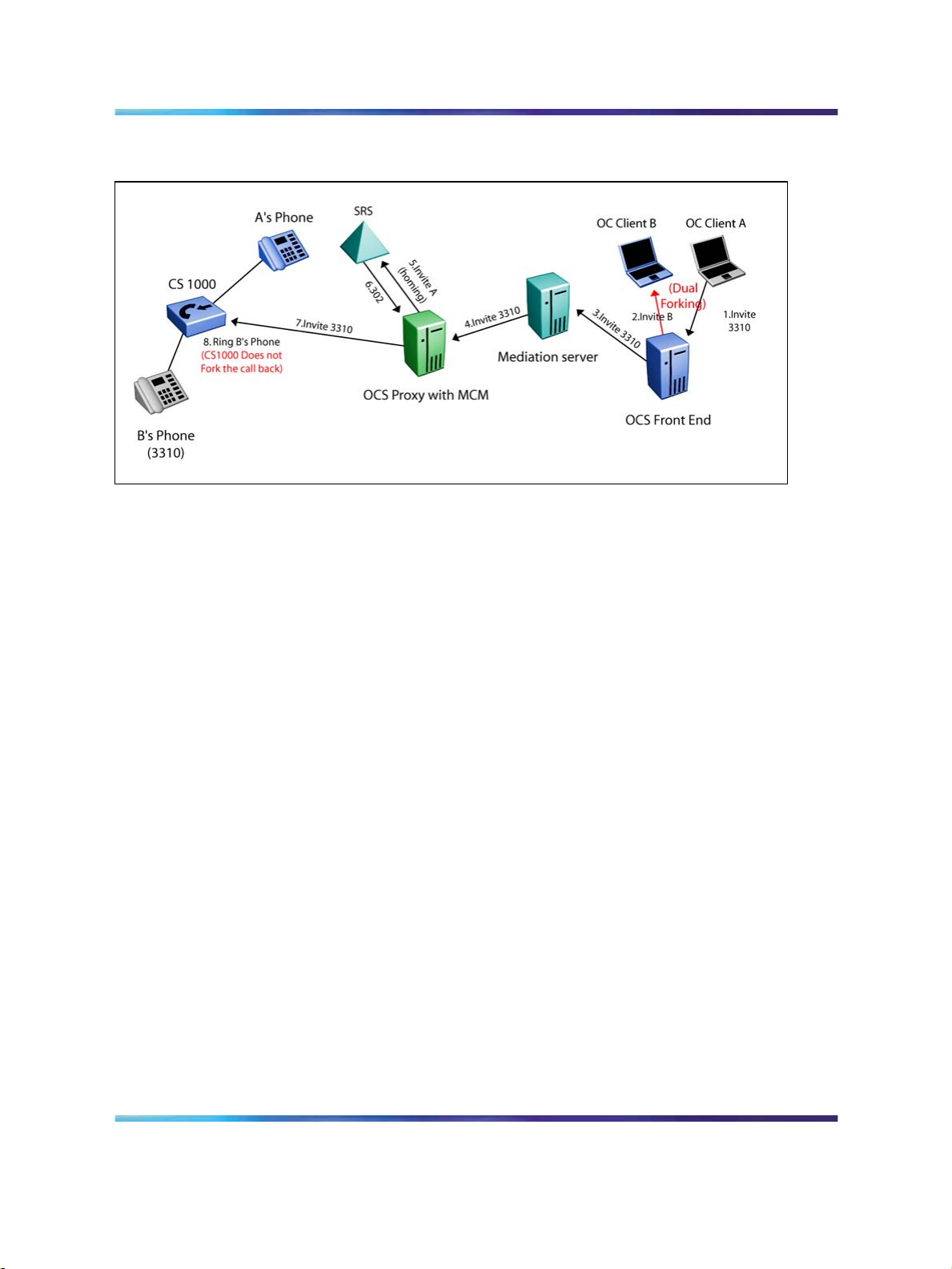
Figure 6 Dual forking example
Personal Call Assistant
Many of the features provided by CS 1000 to traditional telephones are
extended to Office Communicator clients configured with the Personal
Call Assistant (PCA). For example, calls that remain unanswered can be
forwarded using the Call Forward No Answer feature.
Personal Call Assistant 25
To use the Office Communicator soft client for voice calls using the
Telephony Gateway and Services, a PCA must be configured with the same
DN as the user in a MADN arrangement. This offers incoming voice calls
to the user’s DN on their Office Communicator, as well as any phones that
they have been configured with the same DN.
For incoming calls to be extended to the "twinned" Office Communicator
client, a PCA Terminal Number (TN) must be defined for that DN. A new
PCAM Class of Service prompt has been introduced so a distinction
is made between PCA associated with the OCS 2007 client and PCA
associated with other types of clients. Class is configured using BCC. For
more information on BCC, see Basic Client Configuration (BCC). PCA
associated with the OCS 2007 client, the class is set to PCAM . Other types
of clients use the default class PCAG. During call processing, the class
is checked to determine whether an incoming call should be extended to
the PCA target DN or not. For more information on configuring PCA , see
Features and Services (NN43001-106).
For outgoing calls from the Office Communicator, the user must have at
least one TN configured on the CS 1000 Call Server. The MCM locates the
Call Server associated with a user by their numbering plan entry in the
NRS. This generates calls from Office Communicator clients on Telephony
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
26 Converged Office component overview
Gateway and Services to always tandem through the user’s active Call
Server. Note that with Geographic Redundancy features, a user’s active
Call Server may change during failure scenarios.
The Network Class of Service (NCOS) setting for outgoing calls from Office
Communicator clients is determined by the configuration of the MARP TN
when in a MADN group, or by the configuration of the PCA when it is the
only TN for the user.
With PCA and Remote Call Control configured, users receive one pop-up
window for the incoming call to the phone or computer. Users can choose
the most convenient way to answer an incoming call.
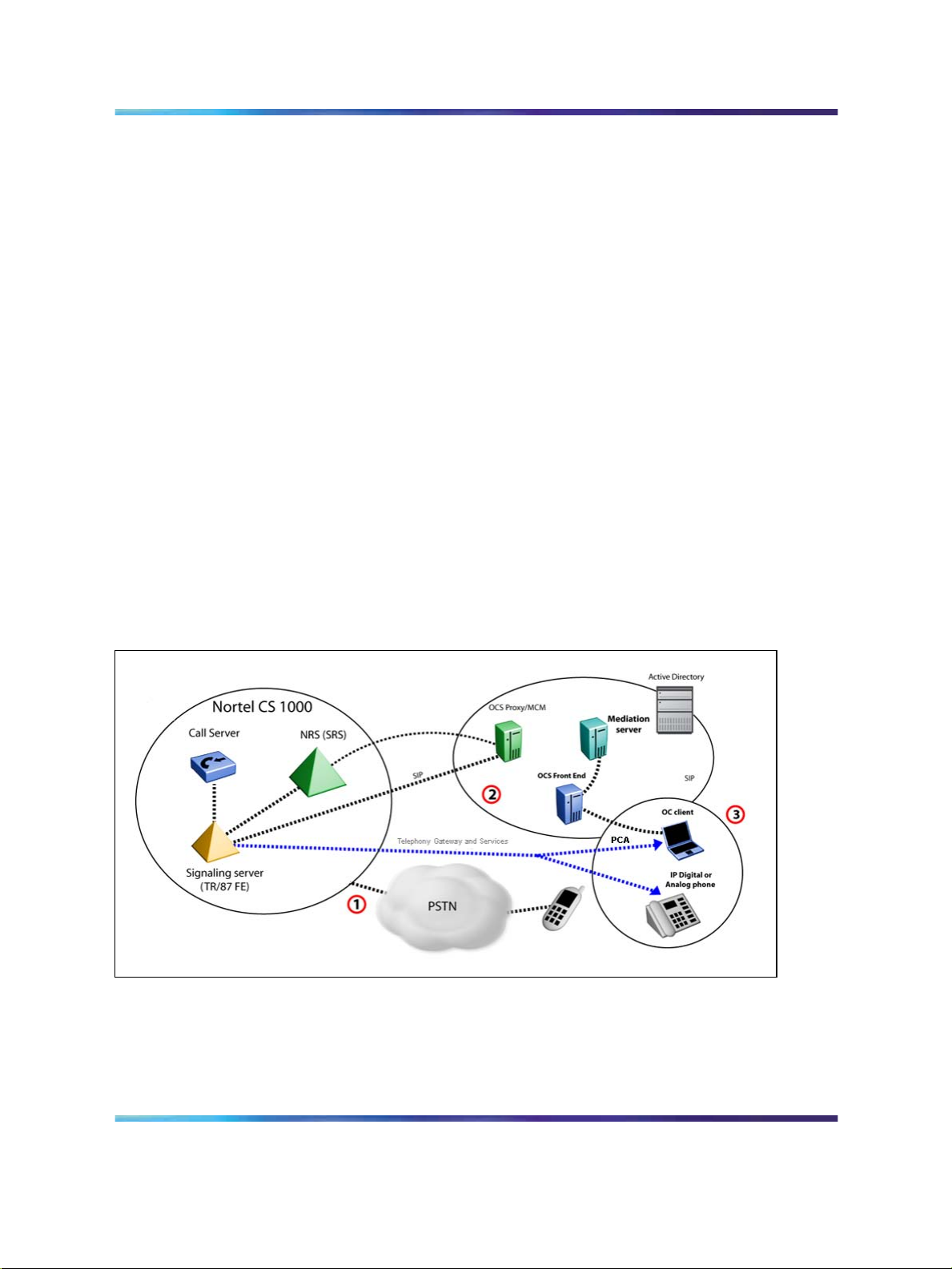
Personal Call Assistant (PCA) service
While at the office, a user may decide to use a desktop phone to answer
calls. However, the user can still accept calls through the OC 2007 while
they travel to locations that have network connectivity (for example,
at hotels).
The following steps correspond to the numbers in the figure:
1. The CS 1000 system receives a PSTN call to the user’s phone
number.
2. The CS 1000 uses the PCA feature to provide simultaneous ringing
to both the user’s phone and the Office Communicator voice client.
3. The user can answer the call through the CS 1000 phone or the
Office Communicator voice client.
Users can be reached anywhere on the network and significant cost
savings are incurred by using IP telephony through Virtual Private
Network (VPN) access to their private network.
As part of the telephony services, many incoming call features are
available even when using the OC 2007 as a telephony device or more
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

specifically in Computer mode. Features such as Call Forward No
Answer, Unified Messaging, Call Detail Recording, and Attendant Recall
are maintained within the CS 1000 system for calls presented to the
OC 2007.
Telephony Gateway and Services can access all of the telephony
network resources using the OC 2007 client. Calls can originate from the
OC 2007 client to the PSTN, phones, or services within the telephony
network. Users can access all of their telephony network resources
as long as they have the soft client and a high-quality connection to
their private network. Telephony Gateway and Services is enabled by
the interworking of the CS 1000 SIP Gateway with the OCS 2007 SIP
gateway software.
Access Edge Server
Access Edge Servers allow internal and external users to communicate
across corporate firewalls. Access Edge Servers enable IM and presence,
as well as Web conferencing and audio/video (A/V) collaboration between
internal and external users.
Access Edge Servers include the following server roles deployed on one or
more computers in the perimeter network:
OCS 2007 snap-in 27
•
The Access Edge Server handles the SIP traffic necessary to establish
and validate connections between internal and external users.
•
The Web Conferencing Edge Server enables external users to
participate in internal conference meetings. The Web Conferencing
Edge Server handles the exchange of meeting content between internal
and external users.
•
The Audio/Video (A/V) Edge Server enables A/V conferencing between
internal and external users to allow for the sharing of audio and video
with external users.
Microsoft recommends that you use the OCS 2007 Director, although it
is not required.
Office Communicator video is supported only for Remote Call Control between
two Office Communicator clients. Office Communicator video is not supported
if one of the clients goes through the SIP Gateway.
OCS 2007 snap-in
The Office Communications Server 2007 snap-in for MMC is redesigned.
The Status pane of the Office Communications Server 2007 snap-in
provides configuration settings at-a-glance for your forest, domains, pools,
ATTENTION
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

28 Converged Office component overview
servers, and users. The Status pane also features a new Database tab,
which can be used to query a pool’s back-end databases. Each query is
displayed as an expandable item in a list.
Microsoft Management Console (MMC) is automatically installed on each
server in the domain that is running Office Communications Server 2007 or
any computer on which Office Communications Server 2007 administrative
tools are installed. It is not used to administer Edge Servers or Proxy
Servers.
Enhanced presence must be enabled prior to Converged Office telephony
integration. You can enable enhanced presence from the Office Communications
Server Users Wizard in the Configure Users Settings window.
Multimedia Convergence Manager
MCM 3.0 is a software component that ensures interoperability between the
Nortel CS 1000 and the Microsoft Office Communicator Server (OCS) 2007.
The MCM ensures CS 1000 and OCS interoperability of protocols, users,
and phone numbers are managed within the Microsoft Active Directory. It
also allows the system to block calls where the client is not in the Active
Directory (AD). The MCM performs a number of functions that include:
ATTENTION
•
translation between telephony phone numbers and user IDs within the
Active Directory
•
authentication of user phone numbers for RCC
•
Numbering Plan normalization
• protocol interworking
•
redundant connections to the CS 1000 network components (SIP
Redirect Service (SRS), Sip Proxy Server (SPS), and redundant
Signaling Servers)
CDR data collection
OCS 2007 supports CDR capability. OCS 2007 CDRs collect different
kinds of data that include user logon and logoff, IM and audio call details,
Conferencing start and join. You must install the Archiving and CDR Server
to support these features. The outgoing calls from the OC 2007 to CS
1000 telephone are captured by this server, as well as OC to OC calls.
Thus a call accountant can retrieve CDRs from both the CS 1000 and
Archiving server to obtain a consolidated report. In RCC mode, CDRs are
captured only on the CS 1000 side. For more information, see Microsoft
Office Communications Server 2007 Archiving and CDR Server Deployment
Guide Download Microsoft technical documentation from the Download
Center at w
ww.microsoft.com.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
SIP CTI (TR/87) Protocol
The SIP CTI (TR/87) FE application introduced with this package is not
limited to Microsoft applications. Through support of the ECMA TR/87
standard, Nortel partners can use this interface to develop SIP CTI
capabilities for use with any specification-compliant application.
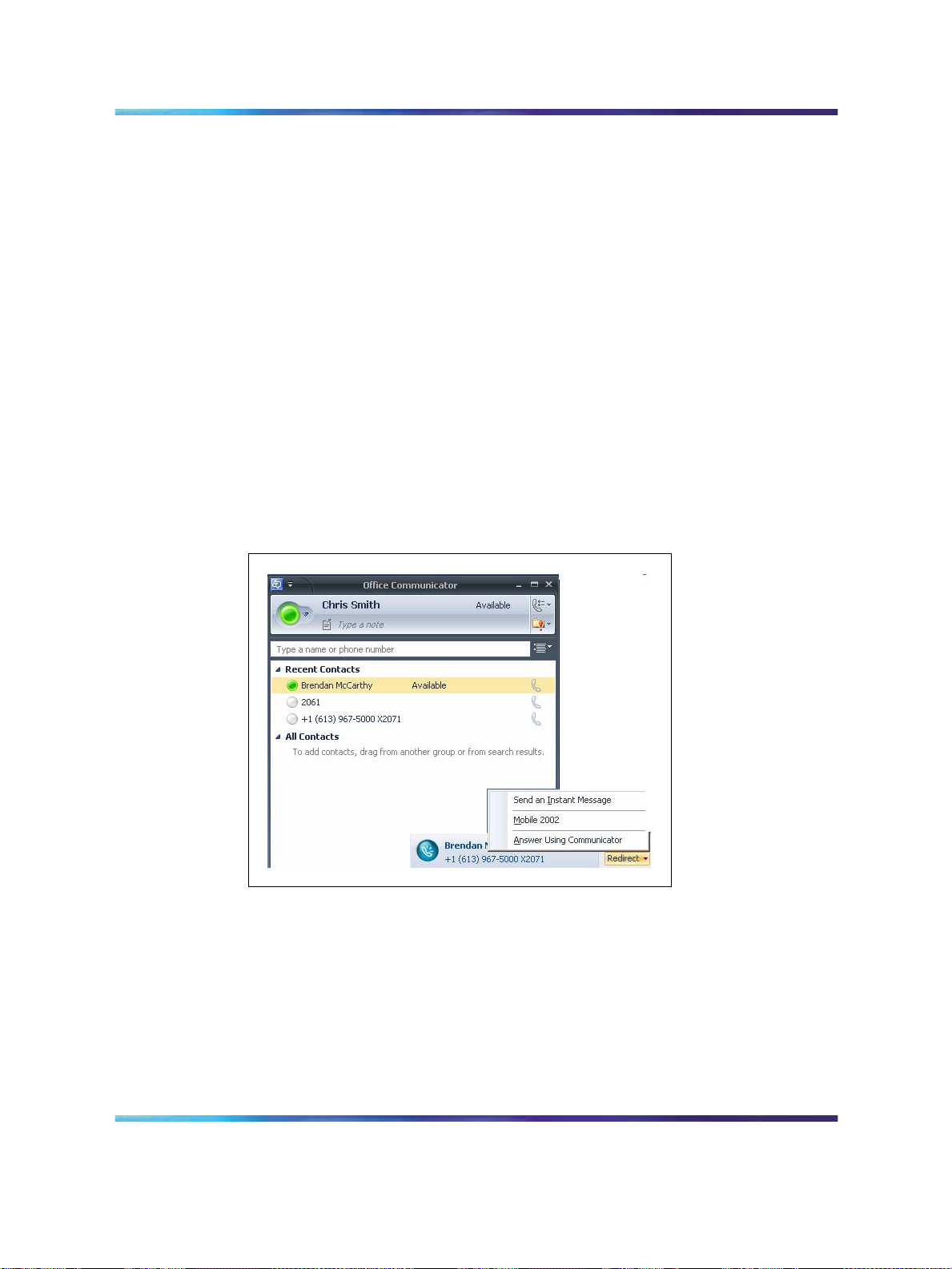
If Preferred Calling Device is configured as Phone, a user receives one
pop-up notification with an incoming call, as depicted in Figure 7 "Call
Appearance pop-up window" (page 29). The OC user can click Redirect to
choose the client as the answering device.
Certain portions of the protocol are not supported at this time. Additional
information about the SIP CTI (TR/87) protocol is available to Nortel
partners upon request.
Figure 7 "Call Appearance pop-up window" (page 29) shows an example
of an incoming call pop-up window.
Figure 7
Call Appearance pop-up window
SIP CTI (TR/87) Protocol 29
Figure 8 "SIP diagram" (page 30) depicts the SIP protocol information.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
30 Converged Office component overview
Figure 8
SIP diagram
Figure 9 "IP diagram" (page 31) depicts the IP protocol information.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 9
IP diagram
Hardware Load Balancer 31
Customers must not use their Office Communicator client to call Emergency
numbers (for example, 911). To ensure that emergency service organizations can
accurately trace the source of the call, always use a desktop phone to place
an emergency call.
Hardware Load Balancer
Hardware IP Load Balancers (for example, Nortel Application Switches) are
required for multiple Office Communications Server 2007 Enterprise Edition
deployment. The Load Balancer presents a single virtual IP (VIP) address
to clients to prevent direct access to individual OCS 2007 Enterprise
Edition servers. The Load Balancer uses an algorithm (for example,
round-robin, or fewest connections) to route new client requests to the
Office Communications Servers.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
ATTENTION
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

32 Converged Office component overview
Hardware Load Balancers deliver load distribution to avoid a single point
of failure. Other benefits include increased performance and added
redundancy. The CS 1000 uses Load Balancers for the signaling path of
VoIP calls and Remote Call Control.
A Load Balancer is not required if you deploy:
•
a Standard Edition server
•
a single Enterprise Edition Front End server
A load balancer is required if you deploy:
•
multiple OCS 2007 Enterprise Edition Front End servers
•
an Array of Edge Servers
•
an Array of Directors in OCS 2007
Microsoft recommends deploying a hardware load balancer for arrays of
Office Communications Server 2007, Edge Servers, and Directors but it is
not a requirement. Office Communications Server 2007 does not support
the use of Windows Server 2003 Network Load Balancer in production or
lab deployments. The CS 1000 is only concerned with the load balancers
for the signaling path for VoIP and Remote Call Control (RCC).
Office Communicator 2007
For detailed information about using Office Communicator 2007 and
its components, see Converged Office User Guide — Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 (NN43001-123).
Documentation References
A list of Nortel and Microsoft documentation is available for reference from
the following Web sites.
•
You can download Nortel documentation from the Nortel technical
documentation Web site at w
•
Download Microsoft technical documentation from the Download Center
ww.microsoft.com.
at w
The following Nortel technical documents are relevant to Nortel Converged
Office.
ww.nortel.com.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Table 1 Nortel technical documentation
Documentation References 33
Technical document
Converged Office User
Guide — Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007
(NN43001-123)
Communication Server 1000E
Planning and Engineering
(NN43041-220)
Features and Services
(NN43001-106)
CallPilot Network Planning
Guide (NN44200-201 )
Communication Server 1000M
and Meridian 1 Small System
Installation and Commissioning
(NN43011-310)
Content
Contains information about
using the OC client.
Contains instructions about
calculating the anticipated call
traffic for the CS 1000.
Contains information about the
Multiple Customer environment,
Multiple Appearance DN ,
Call Forward On feature, and
defining and configuring a PCA
TN.
Contains information about
configuring CallPilot for
Telephony Gateway (Computer
mode) calls.
Contains information about
CS 1000 Installation and
Commissioning
Primary audience
General users
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Communication Server 1000M
and Meridian 1 Large System
Installation and Commissioning
(NN43021-310)
Communication Server 1000E
Installation and Commissioning
(NN43041-310)
SignalingServer Installation and
Commissioning (NN43001-312)
IP Peer Networking
Installation and Commissioning
(NN43001-313)
Contains information about
CS 1000 Installation and
Commissioning
Contains information about
CS 1000 Installation and
Commissioning
Contains information about
CS 1000 Installation and
Commissioning
Contains information about
creating the required
components on a Call Server,
dialing plans, configuring
codecs, configuring HLOC and
HNPA, configuring SIP trunks,
configuring NRS, and alternate
routing logic (for Geographic
Redundancy).
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

34 Converged Office component overview
Technical document
Transmission Parameters
(NN43001-282)
Content
Contains information about
configuring the loss plan and
DTI Data Bock.
Element Manager System
Administration (NN43001-632)
Contains information about
how to access Operational
Measurementsthrough Element
Manager.
NRS Installation and
Commissioning (NN43001-564)
Communication Server 1000
with Microsoft Exchange
Server 2007 Unified Messaging
Contains procedural
information.
Contains information about how
to setup Unified Messaging on
Microsoft Exchange.
Fundamentals NN43001-122
Table 2 Microsoft OCS 2007 and OC 2007 documentation
Guide Contents
Microsoft Office
Communications Server
Guide to the contents and uses
of the documentation.
2007 Documentation Roadmap
Primary audience
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Administrators
Primary audience
Administrators
Office Communications Server
2007 Technical Overview
Microsoft Office
Communications Server
2007 Planning Guide
Microsoft Office
Communications Server
2007 Enterprise Voice Planning
and Deployment Guide
Microsoft Office Communicator
2007 Getting Started Guide
Office Communicator 2007
Quick Reference Cards
Migrating to Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007
Contains a high-level survey
and summary of the features,
architecture, and protocols of
Office Communications Server
2007.
Contains step-by-step
information about planning
your deployment.
Contains information on
how to plan, deploy, and
manage the new Enterprise
Voice capabilities in Office
Communications Server 2007.
Contains information on how
to get started with Office
Communicator 2007.
Contains a summary of
information for Office
Communicator 2007.
Contains information on
migrating from LCS 2005 to
OCS 2007.
Administrators
Senior Administrators
responsible for planning
deployment
Administrators and Telephony
Engineers responsible for
planning an IP telephony
infrastructure and deploying
Enterprise Voice
End-users and Administrators
End-users and Administrators
Administrators
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Planning and engineering
This chapter contains information about topics you must consider before
you implement Converged Office.
Planning and engineering navigation
•
"Introduction" (page 35)
•
"Network Design" (page 36)
— "Small network" (page 37)
— "Medium network" (page 38)
— "Large network" (page 39)
— "Multiple customer network" (page 40)
— Figure 14 "Multiple location network" (page 42)
•
"Load Balancer planning information" (page 43)
35
•
"Capacity Planning" (page 46)
•
"General Requirements" (page 51)
•
"Telephony Gateway and Services planning" (page 66)
•
"Remote Call Control with SIP CTI" (page 73)
•
"LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence" (page 82)
•
"Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007" (page 84)
Planning process
Before you install and configure Nortel Converged Office, you must consider
the network size and its impact on the type of software and hardware
required.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

36 Planning and engineering
Nortel recommends that you implement the Telephony Gateway and
Services component to provide basic connectivity (which you can more
readily debug), followed by the Remote Call Control (RCC) for more complex
feature operation. Configure both Telephony Gateway and Services and
RCC only in situations where both components are required.
Consider the following during the planning process.
•
Consider the size of your network. See "Network Design" (page 36) for
detailed information about determining your network architecture.
•
Determine the type of users (internal and external users) and
anticipated call traffic. For more information about type of users,
see Table 5 "Maximum supported users for each topology" (page
52). For information about calculating the anticipated call traffic for
the Communication Server 1000, see Communication Server 1000E
Planning and Engineering (NN43041-220).
•
Determine that the software and hardware components required for the
CS 1000 are installed and have the latest software versions. For more
information, see "CS 1000 and Signaling Server installation" (page 105).
•
Determine that the software and hardware components required for
Office Communications Server (OCS) 2007 have the latest software
versions. For more information, see "OCS 2007 component installation"
(page 105).
•
Determine the system requirements for the OC 2007 client. For more
information, see "OC 2007 client requirements" (page 47).
•
Determine capacity requirements for all components. For more
information, see "Capacity Planning" (page 46).
•
Prepare your infrastructure.
•
Plan for external user setup. For more information, see "Access Edge
Server" (page 27).
•
Plan your implementation strategy.
For more information on deploying OCS 2007, see the Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 Planning Guide . Download Microsoft
documentation from the Download Center at w
Network configuration
The main consideration when you plan and engineer the Converged
Office desktop is the size of the network. Networks are divided into three
main categories: small, medium, and large. Each type requires specific
configuration.
The following sections describe typical network topologies to assist in
determining capacity and robustness requirements.
ww.microsoft.com.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Note: The descriptions and graphical representations of the three
network types are for illustration only, and are not actual configurations.
The number of CS 1000 systems and Office Communications Server
2007 servers will be based on the engineering guidelines found in this
document and those provided by Microsoft.
Small network
If you have a small network that requires ease of management, you
can choose a basic configuration. Microsoft recommends the following
configuration for small organizations that do not require high availability for
OCS 2007.
A small network can include the following components:
•
a CS 1000 system with Media Gateway and Signaling Server
•
support for IM and conferencing for internal users and can include
external users
• up to 5000 users
You will need:
Network configuration 37
•
An Office Communications Server 2007 Standard Edition server
•
a single Edge Server deployed in the perimeter network for external
user access
•
An OCS Proxy server that runs MCM 3.0
•
a Mediation server
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

38 Planning and engineering
Figure 10
Small network configuration
Medium network
A medium network can include the following components:
•
one or multiple CS 1000 systems with Media Gateway and Signaling
Server
•
a Primary NRS with an Alternate Network Routing Service (NRS) that
co-reside on one of the Signaling Servers
•
up to 5000 users
•
high availability with system redundancy for OCS 2007
You will need:
• an Office Communications Server 2007 Enterprise Edition
•
an OCS Proxy server that runs MCM 3.0
•
a Mediation Server
If you install only one OCS 2007 Enterprise Edition server, a Load Balancer
is not required. SPS (Linux-based NRS) does not support co-residency.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 11
Medium network configuration
Network configuration 39
Large network
A large network can include the following components:
•
multiple CS 1000 systems with Media Gateway and Signaling Server
•
configured collaborative NRS
•
redundant Primary and Alternate NRS
•
more than 5000 users
•
high availability with system redundancy for OCS 2007
You will need:
•
an OCS 2007 Enterprise Edition server with Load Balancers to Front
End the pool of Enterprise Edition servers
•
a redundant OCS Proxy servers that run MCM 3.0 (the recommended
deployment requires that MCM reside on a separate OCS Proxy server)
•
Mediation servers
•
Load Balancers
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

40 Planning and engineering
The redundant, primary, and alternate NRS can be either the VxWorks NRS
or the Linux-based NRS (SPS/SRS). For the OCS 2007 Enterprise Edition
server, a SQL back end database server is a requirement.
If you set up more than one server that runs the Enterprise Edition of Microsoft
Office Communications Server 2007, you must use a Load Balancer in
accordance with the Unified Communications Engineering Rules and Guidelines.
The Load Balancer ensures that the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the
pool is not equal to the FQDN of any Front End server in the pool.
Figure 12
Large network configuration
ATTENTION
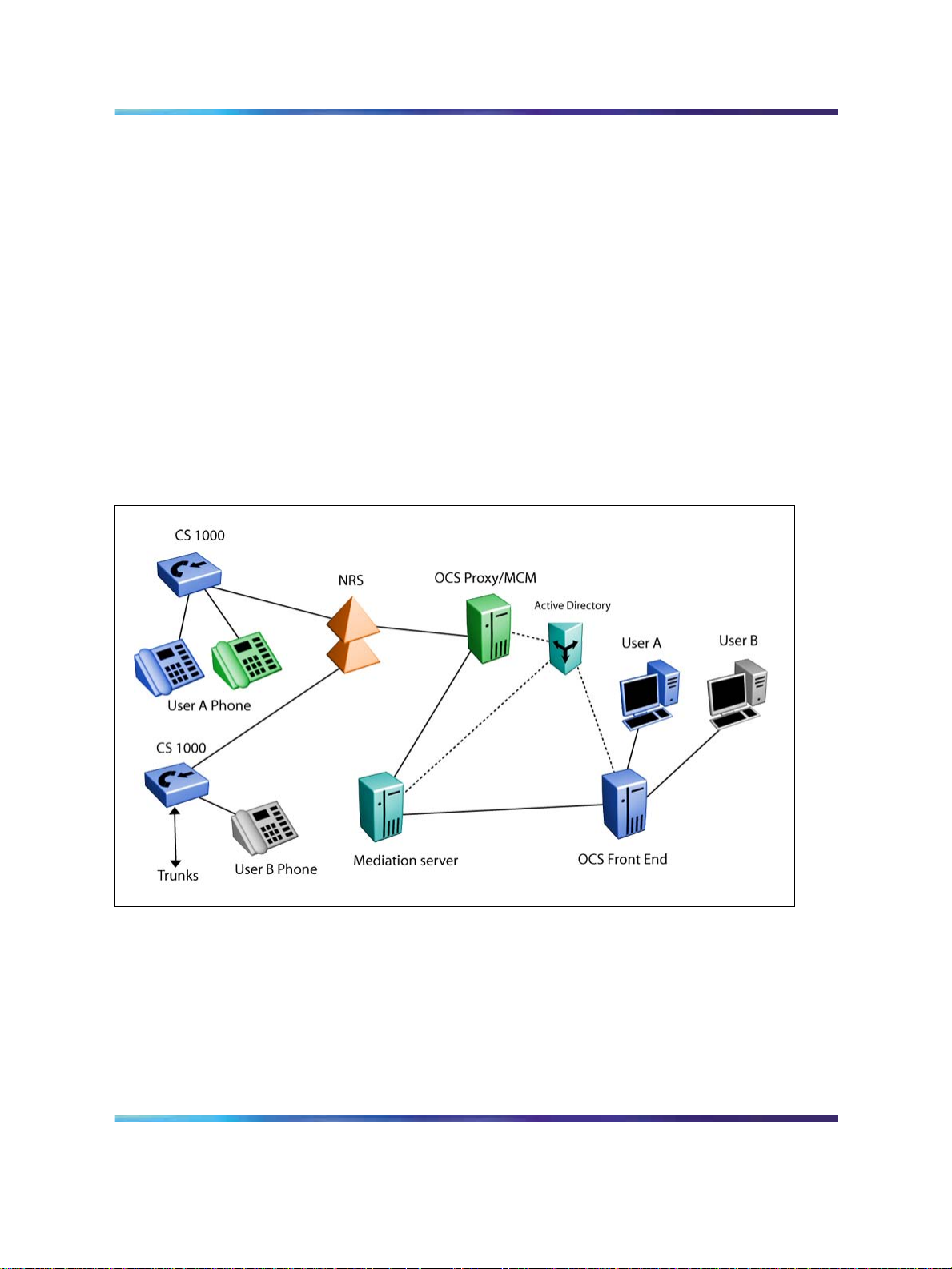
Multiple customer network
You can configure the CS 1000 with a number of customers that have
their own set of telephones, trunks, features, restrictions, and numbering
plans. In the Converged Office environment, each customer is treated as a
separate machine. Each customer shares one OCS deployment, but has
their own Node Number, MCM, Signalling Server, and SIP domain in the
forest. For more information about the Multiple Customer environment, see
Features and Services (NN43001-106).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 13 "Multiple customer network" (page 41) provides an example of a
multiple customer network. The figure shows two customers: Customer 1
(Ottawa) and Customer 2 (Belleville), each with their own set of associated
phones and Signalling Servers. This type of configuration is required for any
deployment that uses the Telephony Gateway and Services functionality,
or in scenarios where both Telephony Gateway and Services and Remote
Call Control functionality is deployed.
Figure 13
Multiple customer network
Network configuration 41
The Signaling Server for Customer 1 is in the domainOne.com domain.
For each customer, you must configure a separate Office Communications
Server domain. The Office Communications Server domain used by
Customer 1 is in the same domain as the Signaling Server domainOne.com.
Each OCS domain requires a separate Active Directory.
The only equipment that Customer 1 and Customer 2 share is the CS 1000
and the NRS. The NRS can only be shared by the two customers if it is
configured with both domainOne.com and domainTwo.com.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

42 Planning and engineering
The Signaling Server, OCS Proxy server (which runs MCM), OCS 2007
Front End server, and Active Directory are separate. The number of
Signalling Server(s), OCS 2007 Proxies, and OCS 2007 Front End servers
required for each customer are the same as if each customer were part of a
single system. However, the total number of users allowed for the CS 1000
is the total number of users for all customers.
Multiple location network
The following diagram shows the path of an inbound and outbound call in a
multiple location network configuration in a single forest deployment. The
MCM routes inbound calls from the Signaling Server to the appropriate
Mediation Server within the Mediation Server pool. When the current
Mediation Server does not answer, MCM jumps to the next Mediation Server.
Figure 14
Multiple location network
For regional or multiple location deployments, it is required to install
SPS/SRS. Two Primary/Secondary SPS/SRS may co-exist within one
configuration to improve the system’s robustness. In the previous versions
of the program, the MCM performs polling by sending SIP OPTION request
to determine which SPS/SRS is active. The active SPS/SRS becomes the
last one to send an OK response. The SIP Proxy Server (SPS) sits between
MCM and the TR\87 FE application that reside on CS 1000. This SIP
proxy allows communication between the CS 1000 and OCS when different
transport protocols (TLS and TCP) are used. An OCS configuration with
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Mediation servers supports only TCP. However, it can interact with TLS
gateway through SPS. SPS can act as a redirect server for SIP messages
so the link between CS 1000 and the SPS can be TLS.
Load Balancer planning
This section provide information on the Load Balancer requirements.
Load balancer navigation
•
"Load Balancer prerequisites" (page 43)
•
"Load Balancer requirements" (page 44)
•
"Redundancy with Load Balancers" (page 45)
•
"High scale and high availability configuration" (page 45)
•
"Nortel Application Switch (NAS)" (page 46)
Load Balancer prerequisites
•
Before you configure a Load Balancer to connect to the Office
Communications Server Enterprise pool, ensure you configure the
following:
Load Balancer planning 43
— The Load Balancer must meet the Microsoft criteria for a Load
Balancer. See "Load Balancer requirements" (page 44)
— Configure a static IP address for servers within your pool.
— For each server within the pool a certificate, include for both user
and server authentication issued by a certification authority in the
pool’s local domain.
— Configure a VIP address and a DNS record for the load balancer.
— Test users created and SIP-enabled in the pool.
— Install root certificate from CA in the domain (or trusted CA) on client
computers.
— Log on to all servers in the pool using TLS to ensure server and
client certificates work.
— Configure Port 135 on Load Balancers to enable server-side
block and allow functionality for users and move user scenarios to
pools through DCOM. For example, perform remote DCOM-based
database operations. Nortel recommends the minimum
configuration.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

44 Planning and engineering
Table 3
Load balancer minimum configuration
Service
TLS pool TCP
DCOM TCP
Protocol Port (range) Description
Load Balancer requirements
A Load Balancer for the Office Communications Server (OCS) Enterprise
pool must meet the following requirements:
• The Load Balancer must expose a VIP Address through Address
•
•
•
•
5061
135
The client listens over the same connection that is
open to the server. By default, the server listens
on port 5061 (TCP). The server sends packets to
the client only over the client TLS session.
Installation and management.
— Optionally,configure the TCP pool on port 5060 for clients to connect
to the Load balancer through TCP.
Resolution Protocol (ARP).
The VIP must have a single DNS entry, called the pool FQDN.
The VIP must be a static IP address.
The Load Balancer must allow multiple open ports on the same VIP.
Specifically, it must expose the ports5060, 5061, 135, 80, 443, and 444.
The Load Balancer must provide TCP-level affinity. This means that the
Load Balancer must ensure that it can establish TCP connections with
one Office Communications Server in the pool and all traffic on that
connection is destined for that same Office Communications Server.
•
The Load Balancer must provide a configurable TCP idle-timeout
interval with a maximum value greater than or equal to the minimum of
the REGISTER refresh or SIP Keep-Alive interval.
•
The Load Balancer must support a rich set of metrics (round robin,
least connections, and weighted). Nortel recommends a weighted least
connections-based load balancing mechanism for the Load Balancer.
This means that the load balancer ranks all Office Communications
Servers based on the weight assigned to them and the number of
outstanding connections. The Load Balancer use the rank to pick the
Office Communications Server to use for the next connection request.
•
The Load Balancer must detect Office Communications Server
availability by establishing TCP connections to ports 5060, 5061, or
both (often called a heartbeat or monitor). The polling interval must
be a configurable value with a minimum value of at least five seconds.
The load balancer must not select an Office Communications Server
that shuts down until it can establish a successful TCP connection
(heartbeat) again.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

•
Every Office Communications Server must have exactly one network
adapter. Multihoming an Office Communications Server is not
supported. If a 10/100 network adapter does not meet the required
bandwidth constraints, a gigabit network adapter must be used.
•
The network adapter must have at least one static IP address. This IP
address will be used for the incoming load-balanced traffic.
•
The computer must have a registered FQDN. The IP address registered
for this FQDN must be publicly accessible from within the enterprise.
•
The Load Balancer must include less than one gigabit capacity for up to
50 000 concurrent client connections. One gigabit of capacity is required
to support more than 50 000 concurrent client connections.
For more information about Load Balancer requirements, see Microsoft
Office Communications Server 2007 Document: Planning Guide.
Download Microsoft technical documentation from the Download Center at
ww.microsoft.com.
w
Redundancy with Load Balancers
You can add redundancy to your network by placing Load Balancers, such
as a Nortel Application Switch, between the OCS 2007 Front End servers
and Mediation Servers, and between the Mediation Servers and the OCS
2007 Proxy Servers.
Load Balancer planning 45
The outgoing Load Balancer balances SIP invites from the Mediation Server
to the OCS Proxy server. The Mediation Server sends all SIP Invites to
the Virtual IP (VIP) of the outgoing Load Balancer. The Load Balancer
then sends the SIP Invite to the least busy Office Communications Server
2007 OCS Proxy.
The incoming Load Balancer balances SIP invites from the Mediation Server
to the least busy Front End server. This is the same load balancer that is
used when the Office Communicator addresses the pool for registration.
The OCS Proxy sends all SIP invites to the Virtual IP (VIP) of the incoming
Load Balancer.
Redundancy is also ensured for calls to an Office Communicator user by
having each OCS Proxy server register to the MCM and the Mediation
Server to the NRS with a unique registration ID and different cost factor.
Therefore, if one of the OCS Proxy servers is unavailable, the next one
is selected.
High-scale and high availability configuration
The pool of Front End servers processes inbound and outbound traffic. In
this example, the Load Balancer routes incoming SIP messages to the
less busy server based on a configured algorithm. The Load Balancer VIP
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

46 Planning and engineering
address is used by clients as a single point of connection to the pool. This
address is listed in DNS and has an FQDN. Internal OCS clients require the
DNS server to establish a connection with the Enterprise Edition Pool.
Figure 15
Incoming Load Balancer
Nortel Application Switch
Nortel recommends that you use the Nortel Application Switch (NAS) for
Load Balancing.
Capacity planning
This section provides the capacity requirements for the various components.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Capacity planning navigation
•
"OC 2007 client requirements" (page 47)
•
"Load Balancer capacity requirements" (page 47)
•
"SIP CTI (TR/87) services requirements" (page 47)
•
"Mediation server requirements" (page 49)
•
"Signaling Server requirements" (page 49)
•
"Call Server requirements" (page 50)
•
"OCS Proxy and MCM capacity requirements" (page 50)
OC 2007 client requirements
The PC that runs the OC 2007 must be registered to the domain in which the
OCS 2007 server runs. The OC 2007 client can be installed on a PC that
runs most versions of Microsoft Windows with the hardware device driver
API DirectX 9 or later. For more information on the OC client requirements,
see Table 11 "Office Communicator client requirements" (page 54).
For more information about deploying the OC client, see Microsoft Office
Communicator 2007 Deployment Guide . Download Microsoft technical
documentation from the Download Center at w
Capacity planning 47
ww.microsoft.com.
Load Balancer capacity requirements
Capacity planning for OCS 2007 is measured in terms of the number
of clients. However, this becomes difficult to measure because of the
enhanced capabilities and services for a pool and the variety of components
that can be enabled in OCS 2007. Components can reside on separate
servers, which adds to the complexity of capacity planning. A single client
user can have multiple connection instances that depend on the features
enabled. Each feature has different bandwidth requirements that can differ
from one enterprise to another.
For more information on capacity guidelines, see Table 5 "Maximum
supported users for each topology" (page 52).
For more information about capacity planning, see the Microsoft Office
Communications Server 2007 Planning Guide. Download Microsoft
technical documentation from the Download Center at w
SIP CTI (TR/87) services requirements
When you plan for capacity with Session Initiation Protocol Computer
Telephony Integration (SIP CTI) services, observe the following restriction:
For a single CS 1000 that supports multiple nodes, (each with SIP CTI
services enabled), you can establish multiple SIP CTI (TR/87) sessions for
a DN through the same node—but not through different nodes.
ww.microsoft.com.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

48 Planning and engineering
To illustrate this, consider the following high-level example:
Client A sends a TR/87 SIP INVITE to Node 1 to monitor DN 1000. The
TR/87 association is established. Client B then sends a TR/87 SIP INVITE
to Node 1 (the same node) to monitor DN 1000. Both sessions are
established successfully. As a result of this sequence, two TR/87 sessions
exist for DN 1000 through Node 1.
However, if Client B attempts to send a TR/87 SIP INVITE to Node 2 (which
has an AML link to the same call server as Node 1), the attempt to establish
the TR/87 session fails because the DN is already in use by Client A’s
session through Node 1.
To solve this issue when you plan for capacity, SIP routing must ensure that
all TR/87 sessions for a DN always terminate on the same node when there
are multiple nodes for a single CS 1000 call server, as depicted in Figure 16
"SIP CTI (TR/87) example" (page 49).
This issue can arise in cases where a single user has multiple clients logged
on simultaneously (for example, a client at home, a client in the office, and a
mobile client; each with TR/87 capability).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 16
SIP CTI (TR/87) example
Capacity planning 49
Mediation server requirements
The CS 1000 can process up to 13 000 simultaneous calls. Therefore, you
may require several Mediation servers for one CS 1000. To correctly deploy
OCS 2007 to interwork with the CS 1000, you must correctly engineer the
network to handle the anticipated call traffic. Calculate the anticipated call
traffic for the CS 1000 using the instructions in
1000E Planning and Engineering (NN43041-220). For more information
on hardware requirements, see Table 7 "Mediation Server hardware
requirements" (page 53).
Signaling Server requirements
The maximum number of SIP CTI (TR/87) users on a single Signaling Server
is 5000. One Signaling server can support up to 1800 SIP trunks; therefore,
you require up to two Mediation servers for a single Signaling Server. To
increase the system capacity, associate a pool of Mediation Servers with
each Call Server. MCM routes inbound calls from the Signaling Server to
the appropriate Mediation Server within the Mediation Server pool.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Communication Server
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

50 Planning and engineering
For example, MCM works as a software load balancer in addition to a router.
MCM uses a round-robin algorithm for load balancing. When the current
Mediation Server does not answer, MCM jumps to the next Mediation
Server. You can use load balancing for direct mode and with SPS or SRS.
For Release 5.0, 1 GB of memory is required for a standard Signaling
Server. All signaling servers must run the latest software version. For
information on geographic redundancy, see "Geographic redundancy" (page
78).
Call Server requirements
The CS 1000 must run Release 5.0 with the Product Enhancement Package
or later.
For different CPUs, the number of supported users are:
•
CP PII: 7000 users
•
CP PIV: 13 000 users
•
CP PM: 13 000 users
OCS Proxy and MCM capacity requirements
The MCM is required to reside on a separate OCS Proxy server and the
capacity of the OCS Proxy server with MCM depends on the hardware
platform and the usage. For example, VoIP calls only, SIP CTI calls only
or a combination of both. Because capacity characterization cannot be
conducted on all server platforms, Nortel recommends using standardized
sets of relevant benchmarks available from the Standard Performance
Evaluation Corporation (SPEC). SPEC is a non-profit corporation formed
to establish, maintain, and endorse benchmarks that can be applied to the
newest generation of high-performance computers. A compressive list of
benchmarks is available at w
The server used for capacity characterization had a SPECint_rate2000
value of 18.6. See Table 4 "Maximum call rate" (page 50) for the maximum
call rate of this server for the three different configurations.
Table 4 Maximum call rate
Usage Maximum call rate
VoIP calls
SIP CTI (TR/87) calls
Combined 12 500*
ww.spec.org.
15 000
10 000
* Depends on the ratio of either call scenarios assumed 50% of each.
For example: Worst case–all SIP CTI calls, Best case–all VoIP calls.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

General requirements 51
The number of users the OCS Proxy server with MCM can handle depends
on the usage and the number of calls per hour per user. For example,
assuming 5 cph/user for VoIP calls would give 3000 users (15 000 cph/5
cph/user = 3000 users).
The following are the formulas (based on SPECint_rate2000) to calculate
the maximum call rate for different platforms:
•
VoIP calls only. Number of calls per hour supported = (15 000 x SPECint
of HW) / 29.8.
•
SIP CTI (TR/87) RCC calls only. Number of calls per hour supported =
(10000 x SPECint of HW) / 29.8.
•
Both VoIP and SIP CTI (TR/87) RCC calls combined. Number of calls
per hour supported = [(15 000 x SPECint of HW) x (VoIP_call%) + (10
000 x SPECint of HW) x (SIPCTI_call%)]/ 29.8.
ATTENTION
VoIP_call% or SIPCTI_call% must be less then 100%.
An OCS Proxy is not an Access Proxy. For more information on OCS proxy
hardware requirements, see Table 8 "OCS Proxy server hardware requirements"
(page 53).
General requirements
This section provides general guidelines and requirements to follow when
you deploy the Office Communications Server 2007.
General requirements navigation
•
"Server topology" (page 52)
•
"Operating System Requirements" (page 52)
•
"Hardware Requirements" (page 53)
•
"Virtual Server 2005" (page 54)
•
"Storage" (page 55)
•
"Trunks" (page 55)
•
"SIP access port " (page 55)
•
"Basic Client Configuration" (page 58)
ATTENTION
•
"Port use" (page 58)
•
"Security " (page 59)
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

52 Planning and engineering
•
"OC client authentication" (page 59)
•
"Authorization of TR/87 (Remote Call Control) Service Requests" (page
59)
•
"Signaling and Media Encryption" (page 59)
•
"Dial Plan considerations" (page 61)
•
"Computer (SIP) Calls" (page 61)
•
"Phone (RCC or TR/87) Calls" (page 62)
•
"Number formats supported by Office Communicator" (page 63)
•
"E.164 international format numbers for SIP Gateway and SIP CTI"
(page 66)
Server topology
Use the following table to determine the maximum supported users for your
topology.
Table 5 Maximum supported users for each topology
Topology
Standard Edition Server 1 Standard Edition server,
Enterprise pool: Consolidated
Configuration
Enterprise pool: Expanded
configuration with Mid-Range
Performance SQL back end
Enterprise pool: Expanded
configuration With High
Performance SQL back end
Servers required
(Optional) Archiving Server
collocated
4 Enterprise Edition Front
End servers running all server
roles, 1 back end SQL server
(Optional), 1 Archiving server
4 Front End servers, 2 Web
Conferencing servers, 2 A/V
Conferencing servers, 2 IIS
servers, 1 back end SQL server
(Optional), 1 Archiving server
8 Front End servers, 4 Web
Conferencing servers, 4 A/V
Conferencing servers, 2 IIS
servers, 1 back end SQL server
(Optional), 2 Archiving servers
Operating System Requirements
The operating system platform requirements for all Office Communications
Server 2007 server roles are:
Maximum clients
5000
4 servers X 5000 users per
server = 25 000 maximum
clients
10 000 users per access edge
server and 50 000 maximum
clients
125 000
•
Minimum: Microsoft Windows Server 2003 SP1.
•
Recommended: Windows Server 2003 R2 with SP2.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

General requirements 53
Hardware Requirements
Use the following table to determine hardware requirements for the OCS
2007 Standard and Enterprise Edition server.
Table 6
Office Communications Server 2007 Standard and Enterprise Edition hardware requirements
Hardware Requirements
CPU Dual processor, dual core 2.6 GHz +
Disk 2 x 18 GB
For collocated Standard Edition Server, add:
2 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0, for database log files
2 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0, for database data
Cache 1 MB L2 per core
Memory 2 GB (4 GB for Standard Edition server or Consolidated Enterprise Edition server)
Network Gbit NIC
Table 7 Mediation Server hardware requirements
Hardware
Single processor, dual core, 2 GHz, Memory: 2GB RAM 2 x 1 Gbit NIC
Single processor, dual core, 3 GHz Memory: 2GB RAM 2 x 1 Gbit NIC
Dual processor, dual core, 3 GHz Memory: 2GB RAM 2 x 1 Gbit NIC
Dual processor, quad core, 2.66 GHz, Memory: 2GB RAM 2 x 1 Gbit NIC
Table 8 OCS Proxy server hardware requirements
CPU Dual processor 3.2 GHz or equivalent for up to 120 concurrent calls
Dual processor, dual core 3.0 GHz or equivalent for more than 120 concurrent
calls
Disk 1 x 30 GB, 15K rpm SCSI
Cache 1 MB
Memory 2 GB
Network 1 x Gbit NIC
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

54 Planning and engineering
Table 9 Back end database for a small to medium Enterprise pool
CPU Dual processor, dual-core 2.6 GHz +
Disk Drive 1 (2 × 18 GB) for OS and Page File
Drive 2 (36 GB, 15K RPM) for database log file
Drive 3 (36 GB, 15K RPM) for database log file
Drive 4 (8 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0+1) for database files
Cache 2 MB L2 per core
Memory 8 GB
Network Gbit NIC
Table 10 Back end database for a large Enterprise pool
CPU Quad processor, dual-core 2.6 GHz +
Disk Drive 1 (2 × 18 GB) for OS and Page File
Drive 2 (4 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0+1) for database log file
Drive 3 (4 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0+1) for database log file
Drive 4 (8 x 36 GB, 15K RPM, RAID 0+1) for database files
Cache 2 MB L2 per core
Memory 16 GB
Network Gbit NIC
Table 11
Office Communicator client requirements
•
Operating System
Windows Vista 32-bit (RTM) operating system
•
Microsoft Windows XP Professional with Service Pack 2
•
Windows 2000 Professional with Service Pack 4 (requires Microsoft
Windows Media technologies player, version 9, and Microsoft Windows
Installer, version 3.0 or later)
Hardware device driver must be API DirectX 9 or higher.
•
Computer/Processor
Data and Voice: 500-megahertz (MHz) or higher processor. Intel
Pentium-compatible
•
For video: 1 GHz or higher
Memory 512 megabytes (MB) of RAM
Install Space 1.5 MB
Virtual Server 2005
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 is not supported as part of the Nortel
Converged Office feature. The Nortel software component Multimedia
Convergence Manager (MCM) must not be installed on Office
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Storage
General requirements 55
Communications Server that runs Microsoft Virtual Server 2005. For
additional information about Virtual Server 2005, see the Virtual Server Web
site at www.microsoft.com/windowsserversystem/virtualserver/default.mspx.
Store internal hard disks used for operating system and executable
software, data, and transaction files separately. The following lists shows
storage options:
•
Direct access storage device (DASD)
•
Storage Area Network (SAN)
•
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID)
Onboard storage:
•
2 SCSI Channels (split backplane)
• Five 18-GB hard disks, 15 000 rpm SCSI disk drives
Optional SAN:
Trunks
•
One Fibre Channel Host Bus Adapter (HBA)
•
SAN unit
To handle the traffic between the CS 1000 and the Office Communications
Server 2007, you must configure sufficient SIP trunks and PCAs . The
number of additional SIP trunks needed is determined by:
Determine the number of SIP trunks required by multiplying the number of
OC 2007 clients that use the SIP Gateway feature by the percentage of
users you expect on the phone at any time.
For example, 100 Office Communicator SIP Gateway users x 10% on the
phone at a time = 10 additional SIP trunks.
The percentage of users on the phone is decided by standard practice and
the environment involved (For example, Call Center or Normal Office).
PCA trunks are required for each Office Communicator user that uses the
Twinning (for SIP Gateway) feature.
SIP access port
Table 12 "Inputs" (page 56) defines the inputs used to calculate SIP access
ports and PCA requirements.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

56 Planning and engineering
Table 12 Inputs
Input Description
TN_MO_Users Total number of Office Communicator users that use the SIP Access Ports
for voice services.
PCA_MO_Users Number of Office Communicator users that use Personal Call Assistant (PCA).
The PCAs required here are additional to the number of PCAs provided in the
Enterprise Configurator (EC) tool Software screen.
P_PCA_SIP Percentage of PCA calls that use the soft client to answer a call.
Calculations Use the following formulas to calculate traffic requirements
(MO indicates Microsoft Office Communicator):
•
Traffic for PCAs = (PCA_MO_Users) x (CCS per user) x (1 P_PCA_SIP) x 10%
• Traffic for SIP ports = (TN_MO_Users - PCA_MO_Users) x (CCS per
user) + (PCA_MO_Users x P_PCA_SIP) x (CCS per user)
•
Total SIP Traffic = (Traffic for PCAs) + (Traffic for SIP ports)
•
Number of MO SIP ports = Poisson (Total SIP Traffic) at P.01 Grade of
Service
Table 13 "Traffic figures" (page 56) shows traffic in CCS and number of ports
calculated based on the Poisson formula at P.01 Grade of Service.
Table 13
Traffic figures
Traffic (CCS)
5
10 0.28 3
15 0.42 3
20 0.56 4
25 0.69 4
30 0.83 4
35 0.97
40 1.11
45 1.25
50 1.39 6
55
60 1.67 6
Traffic (Erlang) Number of ports
0.14 2
5
5
5
1.53 6
65 1.81 6
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

General requirements 57
Traffic (CCS)
70 1.94
75
80 2.22
85 2.36
Traffic (Erlang) Number of ports
7
2.08
7
7
7
90 2.5 8
95 2.64 8
100 2.78 8
125 3.47 9
150 4.17 10
175 4.86 12
200 5.56 13
225 6.25 14
250 6.94 15
275 7.64 16
300 8.33 17
325 9.03 18
350 9.72 19
375 10.42 19
400 11.11 20
425 11.81 21
450 12.5 22
475 13.19 23
500 13.89 24
550 15.28 26
600 16.67 28
650 18.06 29
700 19.44 31
750 20.83 33
800 22.22 35
850 23.61 36
900 25 38
950 26.39 40
1000 27.78 42
1500 41.67 58
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

58 Planning and engineering
Traffic (CCS)
2000 55.56 74
2500 69.44 90
3000 83.33 106
3500 97.22 121
4000 111.11 137
4500 125 152
5000 138.89 168
6000 166.67 198
7000 194.44 228
8000 222.22 258
9000 250 288
10 000 277.78 318
20 000 555.56 611
30 000 833.33 908
40 000 1111.11 1205
50 000 1388.89 1502
60 000 1666.67 1799
Traffic (Erlang) Number of ports
70 000 1944.44 2096
Basic Client Configuration
The PCAG and PCAM Class of Service (CLS) have been introduced. Basic
Client Configuration (BCC) can program the new Class of Service (CLS)
parameters PCAG or PCAM for PCA TNs. The CLS parameter PCAG will
be the default for all PCA TNs and PCAM will be the required value for all
PCAs associated with OCS 2007.
LD 11 supports the administration of telephones. BCC uses REQ
commands, such as NEW, CHG, and OUT. In LD 20, BCC uses the PRT
command to retrieve phones from the Call Server.
Port use
The CS 1000 uses the following ports related to TCP and TLS.
•
5060: TCP
• 5061: TLS
The dynamic port range used by Office Communicator for SIP/RTP is 1024
- 65535.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Security
General requirements 59
The port range can be controlled (restricted) to a smaller range using
the group policy settings as described on the Microsoft Web site:
support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=KB;EN-US;903056
Port ranges must not overlap.
When you consider a Converged Office deployment, ensure youunderstand
the following security concepts and integrate them into your deployment
planning.
OC client authentication
Authentication of Office Communicator clients is provided by the Office
Communications Server. For more information about authentication, see
Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007 Planning Guide . Download
Microsoft documentation from the Download Center at w
ww.microsoft.com.
Authorization of TR/87 (Remote Call Control) service requests
Authorization of TR/87 (Remote Call Control) service requests within a
Converged Office deployment is handled by the Nortel MCM. The main
requirement for authorization of service requests arises from Office
Communicator users who can manually override the Phone Integration
settings in Active Directory provisioned by an administrator. To ensure
that each Office Communications Server user is restricted to the Active
Directory configuration provisioned by an administrator for Remote Call
Control, MCM provides an option to enable or disable authorization of
TR/87 service requests. For details about the authorization process and
MCM configuration requirements, see "Configuring MCM for Remote Call
Control" (page 149) .
Signaling and media encryption
IP connectivity between the Office Communications Server and the CS
1000 is provided by TCP and TLS. Similarly, Office Communications Server
server-to-server traffic can also be TCP or TLS. The MCM 3.0 supportsTCP
only, therefore, the connections between the Mediation Server and the OCS
Proxy server and the Proxy server and the NRS/SIP Gateway are TCP.
To provide signaling security between the Office Communications Server
and the CS 1000 (see Figure 17 "Signaling Security" (page 60)), Nortel
Contivity VPN routers can be used to tunnel SIP signaling between the
Office Communications Server and the CS 1000. A single VPN router that
supports the Office Communications Server can service multiple individual
VPN routers from multiple CS 1000 deployments.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

60 Planning and engineering
Figure 17
Signaling security
•
Secure Management Zone (SMZ) provides management access to local
and remote devices over a secure connection. SMZ documents the LAN
and WAN configurations required for secure management.
•
Virtual Private Network (VPN) enables secure communications through
Secure Internet Protocol (IPSec) encryption.
•
Transport Layer Security (TLS) ensures that third-parties cannot
eavesdrop or tamper with messages when a server and client
communicate. MCM 3.0 does not support TLS.
Secure end-to-end policy is not supported with this application.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 18
Signaling security with TLS
Dial Plan considerations
Nortel Converged Office is comprised of the following two components:
General requirements 61
•
SIP CTI Services provides CS 1000 native TR/87 support to enable the
Remote Call Control functionality available with Office Communicator.
•
Telephony Gateway and Services allows you to originate and receive SIP
calls (for example, VoIP and Computer calls) from Office Communicator.
Whether you choose one or both components for deployment, an Office
Communicator is essential. This allows the existing dial plan (that users
have become accustomed to with their existing telephony interfaces) to
extend seamlessly to the Office Communicator client for either call type.
This includes all existing CS 1000 dial plan features such as Coordinated
Dial Plan (CDP) and Uniform Dial Plan (UDP), and Group Dial Plan.
The following lists summarize the features that contribute to the dial plan
configuration for the Converged Office feature from the perspective of calls
originated and received from Office Communicator.
Computer (SIP) Calls
•
Number format entered in Active Directory or Office Communicator
•
Office Communications Server Address Book Service Normalization
rules
•
Network Redirect Service (NRS)
• CS 1000 SIP Gateway configuration
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

62 Planning and engineering
•
CS 1000 Call Server configuration relating to the SIP Gateway
•
OCS Location Profile, Policy, Phone Usage, and Route configuration.
•
OC client configuration in the Active Directory
Phone (RCC or TR/87) Calls
•
The format of the number itself entered in Active Directory or entered in
Office Communicator
•
Office Communications Server Address Book Service Normalization
rules
•
CS 1000 SIP CTI Services Configuration
•
CS 1000 Call Server Configuration relating to PBX telephones
•
OC Client configuration in the Active Directory
The number format and normalization support provided by Office
Communications Server is used to format numbers for both Remote
Call Control and computer calls. However, the interface from which they
originate and receive calls from the CS 1000 is the TR/87 Front End and
SIP Gateway respectively (as illustrated in Figure 19 "Signaling and media
paths" (page 63)).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 19
Signaling and media paths
General requirements 63
Number formats supported by Office Communicator
Dialstrings and E.164 International number format are the two types of
numbers used by Office Communicator. Both number formats apply to
computer and phone calls with Office Communicator.
Dialstrings
By default, digits dialed from Office Communicator that are not fully
qualified are sent as dialstrings. The sequence of digits entered in Office
Communicator are sent directly to the Call Server to be dialed. This allows
a user to dial all numbers that you would typically expect to dial from a
phone local to the CS 1000. Normalization rules should be defined in the
Location Profile to convert the dialstrings to the E.164 International format
for all types of PSTN calls. For example, NXX, NPA and International.
E.164 International Format Numbers
The recommended format of numbers stored in Microsoft applications is the
E.164 International number format. This is a variable length number that
consists of a plus sign (+) followed by a 1 to 3 digit country code and a
national number 15-n digits long—where n is the length of the country code.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

64 Planning and engineering
All E.164 numbers presented to the CS 1000, computer, or phone are
expected in the following format:
+<country code><national number>
For example, in North America, the Office Communicator Phone Number
configuration input dialog box would have an entry similar to Figure 20
"North American format" (page 64).
Figure 20
North American format
Outside North America, the Office Communicator Phone Number
configuration input dialog box would have an entry similar to Figure 21
"Outside North America format" (page 64).
Figure 21
Outside North America format
The Normalization feature, provided by the Office Communications Server
Address Book Service, can be used to ensure that formats used within a
local deployment that do not conform to the convention can be converted
without changes to the original numbers.
For example, in the Netherlands, numbers in Active Directory can be
entered in the following format: +31(0)123456789
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

General requirements 65
A normalization rule can be used to strip the digit in brackets to conform to
the expected format for E.164 numbers when using the Converged Office
feature: +31123456789
Formore information about Normalizationrules, see "Creating Normalization
rules" (page 193).
Handling numbers called from Office Communicator in E.164 format
requires that the Call Server be configured to ensure that the number
requested is within the defined dial plans:
Within North America
Various types of numbers can be recognized, including international,
national, local (for example, NPA, NXX, and Free Calling Area Screening), or
private, that use one or two access codes and number translators (AC1 and
AC2). The E.164 number that enters the Call Server for Converged Office
calls must be recognizable by the Call Server so that the call can be routed
appropriately. The number is interpreted based upon the access code used
within the called number as it enters the Call Server (AC1 or AC2).
If calls that enter the Call Server are identified as international and outside
of North America (for example, the country code is not 1), the translator
must contain entries that recognize the international numbers and route the
call to the appropriate route list. These entries are generally within the
existing AC1/AC2 translator, as they are used to route internationalcalls that
are dialed directly from telephones.
If calls that enter the Call Server are national or local, the translation used
must recognize numbers with the national dialing prefix (for example,
Converged Office calls) and numbers without the national prefix (for
example, local calls dialed by users). To enable this recognition without
duplication of number plan entries, a Home NPA (HNPA) entrycan be added
to the AC1 translator to recognize calls within the local NPA that include
the North American national dialing prefix (for example, 1613 within NPA
613). After matching the HNPA entry within AC1, the translation software
automatically uses the AC2 translator to recognize the rest of the digits
received.
Outside North America
Various types of numbers are recognized, including international, national,
local, or private that use one of two access codes and number translators
(For example, AC1 and AC2) and SPN entries. The E.164 number that
enters the Call Server for Converged Office calls must be recognizable so
that the call can be routed appropriately. The number is interpreted based
upon the access code used within the called number as it enters the Call
Server (AC1 or AC2).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

66 Planning and engineering
If calls that enter the Call Server are international and outside of the
country of the caller, the translator must contain entries that recognize the
international numbers and route the call to the appropriate route list. These
entries are generally within the existing AC1/AC2 translator, as they are
used to route international calls that are dialed directly from telephones.
E.164 international format numbers for SIP Gateway and SIP CTI
For information about E.164 international format numbers for SIP Gateway
(Computer) calls, see "E.164 International Format Numbers from Office
Communicator - Computer Calls (SIP Gateway)" (page 170).
For information about E.164 international format numbers for SIP CTI
(Phone) calls, see "Dialing E.164 International Format Numbers from Office
Communicator - Phone Calls (SIP CTI)" (page 190).
Telephony Gateway and Services planning
This section describes the planning and engineering issues associated with
the Telephony Gateway and Services component.
Table 14 "Systems, platforms, and applications" (page 66) identifies the
systems, platforms, and applications supported by the Telephony Gateway
and Services component.
Telephony Gateway and Services navigation
•
"Systems, platforms, and applications" (page 66)
•
"Capacity" (page 67)
•
"Redundancy" (page 67)
•
"SIP routing" (page 67)
•
"Feature Interactions" (page 68)
Systems, platforms, and applications
Table 14 Systems, platforms, and applications
System, platform, or application Supported
M1/CS 1000 Systems
CS 1000M Cabinet Yes
CS 1000M Chassis Yes
CS 1000M Small Yes
CS 1000M HG Yes
CS 1000M SG (CP3/4) Yes
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Telephony Gateway and Services planning 67
System, platform, or application Supported
M1/CS 1000 Systems
CS 1000M SG (CP PIV) Yes
CS 1000M MG (CP3/4) Yes
CS 1000M MG (CP PIV) Yes
CS 1000E Yes
MG 1000B Yes
Capacity
For more information relating to the Telephony Gateway and Services and
Remote Call Control components, see "Capacity planning" (page 46).
Redundancy
Office Communications Server 2007 redundancy model is supported, with
limitations, using Load Balancers.
NRS redundancy NRS redundancy is similar to Converged Office
redundancy; a heartbeat mechanism between MCM 3.0 and NRS servers
is implemented. When a heartbeat failure from the primary NRS server is
detected, all messages are redirected to the secondary NRS server.
SIP routing
MCM directs calls from an Office Communicator user to the CS 1000
connected to their twinned telephone. A user can have a telephone number
in Active Directory associated with their account as depicted in Figure 22
"SIP Routing" (page 68), the number is 231-3052. Calls made from a user
to any endpoint (Public or Private) are directed to their CS 1000. The CS
1000 tandems the call to the other CS 1000 (if necessary).
SIP routing ensures the following:
•
Outgoing Office Communicator calls made by a twinned client can be
tracked by Call Detail Recordings (CDR).
•
Calls from an Office Communicator to incompatible systems can be
made.
In Figure 22 "SIP Routing" (page 68) the user david@ocsserver.com calls
6-441-5431 (AC1-LOC-DN). The From header in the INVITE has David’s
Line URI in the format of E.164;ext=2313051. The MCM gets the extension
number 2313051 and uses the NRS to find the CS 1000 associated with the
number 231-3052 and directs the call. This CS 1000 directs the call to the
CS 1000 that has the destination number of 441-5431, which then directs
the call to the appropriate end user device.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

68 Planning and engineering
Figure 22
SIP routing
Calls made to a CS 1000 that is different from the twinned telephone base
uses two SIP trunks: one incoming and one outgoing.
Additional SIP trunks are needed, if users commonly call between CS 1000
systems.
For more information about the number of required SIP trunks, see the
calculations described in "Trunking" (page 55) and the platform-specific
Planning and Engineering document.
Feature Interactions
This section describes the interactions of the Telephony Gateway (VoIP)
component.
Call transfers for Office Communicator direct PC-to-PC call If an
Office Communicator user sets up a call in Computer mode to another
Office Communicator user directly, the call is sent to a Computer instead of
a telephone number as depicted in Figure 23 "Computer call" (page 69).As
a result, the CS 1000 is not involved in the call and cannot transfer it to a
telephone number.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Telephony Gateway and Services planning 69
Figure 23
Computer call
LG-Nortel IP Phone 8540 OCS desk phone An Enterprise Voice only
client (no PBX integration enabled) that is configured for an OC 2007 client
or 8540 OCS desk phone, will be able to make PSTN calls using the CS
1000 as the gateway. You are required to configure a TN and twinned PCA
on the CS 1000 even if there is no actual phone present for this client. This
is because the MCM will perform homing on each OC client that makes an
outgoing call before allowing it to proceed with the call.
Mixed network with SPS and SRS servers On a mixed network where
both SPS and SRS servers are present, MCM must be configured in SRS
mode for collaboration server routing to work properly.
RCC only mode Nortel recommends you do not define users with RCC
only mode since certain restrictions apply to this functionality. For example,
a PCAM class of service should not be defined for these users.
Bandwidth usage direct OC-to-OC audio call The bandwidth usage of
a Mediation Server direct OC-to-OC audio call is not calculated on the CS
1000. This portion of the required bandwidth should be calculated with
Microsoft consultation and added to the Nortel bandwidth recommendations
for Converged Office users. Failure to do so might impact the quality of the
ConvergedOffice calls in case bandwidth usage exceeds the planned limits.
Microsoft CFAC Microsoft does not support Call Forward All Calls (CFAC)
to voice mail on the OC client when users have Call Forward No Answer
(CFNA) configured to voice mail and not Office Communicator. In order to
have this functionality for an Enterprise Voice user with PBX integration,
voice mail should be configured on the user’s phone. If the user is in
VoIP only mode (no phone) then the only option is for the administrator to
configure the PCA with Call Forward No Answer (CFNA). In this case, the
calls will ring 4 times before being redirected to voice mail.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

70 Planning and engineering
Office Communicator-initiated Call Transfer in Computer and PBX
Integration Enabled If the Office Communicator transfers a call, the SIP
stack of the CS 1000 must handle the request to transfer the call. As such,
the number a user is transferred to is not subject to the Class of Service
associated with either user (the transferred party or the party performing
the transfer). The Class of Service and Call Restriction that control the
transfer is that of the SIP trunk itself.
Multiple customer operation Multiple customer operation is not
supported within a single Signaling Server; a separate Signaling Server is
required for each customer. Each customer configured on the Call Server
requires a separate node number and domain. For more information about
how to configure a multiple customer environment, see "Multiple customer
network" (page 40).
Deployment You can find all of the information required to support
Office Communications Server 2007 and Microsoft Office Communicator
deployment on the Microsoft Web site. Download Microsoft technical
documentation from the Download Center at w
ww.microsoft.com.
MCM 3.0 uses LDAP queries to the Active Directory server for some OC
user’s attributes. You must engineer the Active Directory server properly
to provide the expected performance for the LDAP queries (less than 25
milliseconds). Office Communications Server and Active Directory APIs
are used for queries and mapping.
Office Communications Server 2007 availability The Office
Communications Server 2007 delivers an availability of up to 99.99%
as described on the Microsoft Web site at w
ww.microsoft.com. This is
a Microsoft limitation.
Office Communications Server 2007 redundancy The Office
Communications Server 2007 redundancy model is supported, with
limitations, using Load Balancers. For more information, see Load Balancer.
Office Communicator Web Access Converged Office requires the
client support SIP Gateway functionality. The Web version of Office
Communicator, called Office Communicator Web Access, does not support
SIP Gateway. Therefore, Office Communicator Web Access does not work
with Converged Office.
Office Communicator Mobile Converged Office requires the client to
support Telephony Gateway. The Mobile version of Office Communicator,
called Office Communicator Mobile (COMO), has limited support for
Telephony Gateway. Telephony Gateway is only supported when the device
runs Windows Mobile 5.0. VoIP calls work for incoming calls, but outgoing
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Telephony Gateway and Services planning 71
VoIP calls can only be placed to other Office Communicator users (computer
to computer calls). Outgoing VoIP calls to telephone numbers for Microsoft
Office Communicator Mobile are not supported.
Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 Microsoft Virtual Server 2005 is not
supported as part of Nortel Converged Office.
DTMF CS 1000 supports in-band DTMF digits and out-of-band DTMF
digits for SIP calls through RFC2833. RFC2833 is an out-of-band
mechanism for DTMF signaling. DTMF digit handling using RFC2833
enables Nortel CS 1000 products to work with other SIP products that
support out-of-band DTMF signaling.
With RFC2833, a key press on a telephone translates to a signaling packet
(or packets) that flow with the VoIP stream to the far end. These signaling
packets are RFC packets which contain the DTMF key that was pressed.
The same principle applies to TDM devices that are involved in a VoIP call.
The Voice Gateway (VGW) TN that converts the TDM stream to VoIP also
detects a tone on the TDM side and translates it to RFC2833 packets on the
VoIP side. The VGW TN can receive an RFC2833 packet on the VoIP side
and generates a tone on the TDM side.
Configure the correct Loss Values for in-band DTMF. For more information
about configuring the CS 1000 to support in-band DTMF tones, see
"Configuring the Call Server" (page 151).
2050 Soft phones Due to RFC2833 not being supported, 2050 soft
phones are not recommended to be deployed in a network with OCS 2007
components.
ITG-Pentium cards ITG-Pentium cards are not supported (regardless of
load) due to RFC2833 not being supported.
Multimedia Communicator Server MeetMe Conference support In
Release 5.0, there are no limitations for Office Communicator calls to the
Multimedia Communicator Server (MCS) MeetMe bridge provided that all
tandem nodes run Release 5.0 software.
Codecs G.711 A/MU law is supported for the Mediation Server. The
G.711 codec must use a 20-ms payload at this time, due to the Microsoft
Office limitation. The Mediation Server does not support G.723 and G.729.
Video support Office Communicator video is supported for Remote Call
Control between two Office Communicator clients and VoIP calls directly
between two OC clients without going through the Mediation Server. Office
Communicator video is not supported if one of the clients goes through
the Mediation Server.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

72 Planning and engineering
Video Call Transfer Office Communicator calls made in Computer mode
that have established video can transfer to another Office Communicator
user in Computer mode—although the new call is audio only. The
transferred Office Communicator user experiences the call becoming audio
only. After the transferred call is answered by the new endpoint, video can
be established. As with all Call Transfers in Computer mode, it is a Blind
Call Transfer, where the call is immediately transferred to the new party.
Local Tones Office Communicator supports the generation of local
tones (for example, Ringback), but the tones that the Office Communicator
generates are unique tones that are not specific to any country. Ringback is
generated only for a configured number of cycles; after which the other end
continues to ring, but there is no audible ringback.
Quality of Service Office Communicator does not support Quality of
Service (QoS) (L2: 802.1p/q or L3: diffserv).
Voice mail Voice mail is not supported for direct Office Communicator
calls. Voice mail is supported only with PCA , SimRing, and CD1 Call
Forward No Answer and MCS 5100 Advanced Screening calls.
Long distance/overseas control Long distance or overseas calls from
Office Communicator are allowed based on the Network Class of Service
(NCOS) for the MARP TN of the number and extension associated with
the Office Communicator user. For example, if user david@ocsuser.com
has a number and extension of 3052, david@ocsuser.com can call the
same long distance and overseas numbers that the number and extension
3052 can on the CS 1000. For more information, see "Configuring the Call
Server" (page 151).
MCS 5100 MCS 5100 interoperability and federation with Office
Communications Server requires that a CS 1000 reside between the two
servers, and is limited to voice.
SIP Trunks TCP or TLS-based SIP trunks are supported. SIP trunks and
gateways must be enabled with enough trunks to handle the traffic between
the CS 1000 and Office Communications Server. For more information, see
"Trunking" (page 55).
Phone mode Office Communicator supports phone mode where it
controls the desktop telephone to originate or answer calls and the VoIP
mode where voice calls can originate or be answered from the client.
Hold and Transfer Office Communicator supports Hold and Transfer in
stand-alone or VoIP mode.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 73
ipDialog Ethernet Phone Office Communicator clients can work with the
ipDialog Ethernet Phone only if it is tandemed through a CS 1000.
Country or region tone configuration Country or region tone
configuration is not supported by Office Communications Server or Office
Communicator.
Conference Incorrect participants are displayed on the conference
conversation window in the following scenario. For example, User A makes
a call by SIP alias in Office Communicator–Computer mode to User B in
Office Communicator–VoIP mode. User B answers the call and conferences
in User C in Office Communicator–VoIP mode. User C is invited to the
conference by phone number. User C joins the conference. This results
in four participants being displayed in the conversation window instead
of three. This is a Microsoft limitation and can be reproduced when the
CS 1000 system, Mediation Server outbound routing, and static Front End
routes are disabled.
Active Directory configuration A record in the Active Directory must be
created for all CS 1000 phones whether there is an Office Communicator
client associated with it or not. If a CS 1000 phone is not in the Active
Directory, an OC client user will notice the following:
•
Cannot add the telephone number to the Office Communicator Contact
List.
•
Will receive two toasts when calls are made from these telephones.
DTMF detection In order to handle DTMF detection properly with OCS
2007, all network components must support RFC 2833 which means all
Branch or Main offices need to be running a Release. 5.0 software as
a minimum. Otherwise there will be problems interacting with Interactive
Voice Response (IVR) systems, collect calls, using meet-me conference
bridges, and so on.
Remote Call Control with SIP CTI
The Remote Call Control component works in all configurations that include
a Signaling Server and is supported for IP, digital, and analog telephone
types.
Office Communicator client uses the ECMA TR/87 specification. Figure 24
"Simple network diagram" (page 74) shows a sample customer network
that deploys Active Directory, the OCS 2007 Front End, OCS proxy server
with MCM, and CS 1000.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

74 Planning and engineering
Figure 24
Simple network diagram
The TR/87 FE is the application that resides on the CS 1000 Signaling
Server to support the telephony control requests and responses received
from the Office Communicator 2007 client within an Office Communications
Server 2007 deployment.
CS 1000 is supported in both the Office Communications Server 2007
Standard Edition and Enterprise Edition network configurations. For more
information about restrictions, see "Capacity planning" (page 46).
Table 15 "Supported systems, platforms, and applications" (page
74) identifies the systems, platforms, or applications that are interoperable
or supported by the Remote Call Control component. Interoperable
means that this feature will not negatively impact any existing functionality
(regardless of whether this feature actually interacts with the system,
platform, or application).
Table 15 Supported systems, platforms, and applications
Systems, platforms, and applications
M1/CS 1000 systems
Option 11C Cabinet Y N
Option 11C Chassis Y N
Interoperable
Supported
Option 61C (CP-PII and -PIV) Y N
Option 81C (CP-PII and -PIV) Y N
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 75
Systems, platforms, and applications
Interoperable
Supported
CS 1000M SG (CP-PII and -PIV) Y Y
CS 1000M SG (CP PIV) Y Y
CS 1000M MG (CP-PII and -PIV) Y Y
CS 1000E SA/HA (CP-PII, -PIV, and -PM) Y Y
MG 1000T (SSC) Y N
MG 1000B (MGC and CP-PM) Y Y*
MG 1000E (MGC) Y Y*
* Digital and analog telephones in Branch Offices are supported when access to the proxy/redirect
server and OCS 2007 is available.
Other systems, call servers and
gateways
CS 2000 Y Y
CS 2100 Y Y
MCS 5100/CD Y N
SRG 1.0 Y Partial*
SRG 50 Y Partial*
BCM 50 Y Partial*
BCM 200/400 Y Partial**
Norstar VoIP Gateway (NT9B10AA) Y N
NetRIO Service Management Center
YN
(SMC)
* Telephones in normal mode (network connection to the main office up) are supported. No RFC
2833 support. Tandem calls out of a BCM/SRG from OCS with DTMF do not work.
Nortel applications
IP Phone 2001 Y Y
IP Phone 2002 Phase I Y Y
IP Phone 2002 Phase II Y Y
IP Phone 2004 Phase 0/I Y Y
IP Phone 2006 Y Y
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 Y Y
IP Softphone 2050 Y N
Mobile Voice Client 2050 Y N
WLAN Handset 2210 Y Y
WLAN Handset 2211 Y Y
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

76 Planning and engineering
Systems, platforms, and applications
Interoperable
WLAN Handset 2212 Y Y
IP Phone 1110 Y Y
IP Phone 2007 Y Y
IP Phone 1120E Y Y
IP Phone 1140E Y Y
IP Phone 1150E Y Y
TDM Phones M3900 series Y Y
M3000 Y Y
M2317 Y Y
M2006 Y Y
M2008 Y Y
M2316 Y Y
M2016S Y Y
PC Console Interface Unit Y Y
CDR Y N
Telephony Manager (TM) Y Y
Supported
Element Manager (EM) Y Y
Element Subscriber Manager (ESM) Y N
Call Pilot Y N
Call Pilot Mini Y N
Meridian Mail Y N
Meridian Mail Card Option Y N
Meridian/Succession Companion DECT
YN
(DMC8 version)
VoIP-802.11 Wireless IP Gateway Y N
Remote Gateway 9150 Y N
Meridian Home Office MHO-II – MD’ed Y N
Remote Office 9115/ IP Adaptor Y N
Carrier Remote Y N
Fiber I and Fiber II Y N
Symposium Desktop TAPI Service
YN
Provider for MCA
Meridian Link Services [MLS] Y N
Symposium TAPI Service Provider Y N
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 77
Systems, platforms, and applications
Interoperable
Symposium Agent Y N
Symposium Agent Greeting Y N
Symposium Express Call Center (SECC) Y N
Symposium Call Center Server [SCCS] Y N
Symposium Web Centre Portal (SWCP) Y N
Periphonics Open IVR (VPS/is) Y N
Periphonics Integrated Package for
YN
Meridian Link (IPML) – VPS
Periphonics Multimedia Processing
YN
Server (MPS) 100
Periphonics Multimedia Processing
YN
Server (MPS) 500
Integrated Call Assistant Y N
Integrated Conference Bridge Y N
Integrated Recorded Announcer Y N
Integrated Call Director Y N
Hospitality Integrated Voice Services
YN
(HIVS)
Supported
Enterprise Data Networking Y N
UM2000 Y N
Multimedia Application Server MAS Y N
Nortel Multimedia Conference Y N
Third party applications
Application gateway 1000 Y N
Microsoft Office Communication Server Y N
MS Exchange Server Y N
MS Virtual Server 2005 Y N
Audio Code Mediant 2000 SIP-PRI
YN
Gateway
Competitors
Cisco H.323 GW Y N
Avaya H.323 GW Y N
Cisco SIP GW Y N
Avaya SIP GW Y N
Verizon SIP Trunk Y N
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

78 Planning and engineering
Systems, platforms, and applications
AT&T SIP trunk Y N
Broadsoft Y N
ACME SBC Y N
3100 Mobile Communication Gateway Y N
Interoperable
Redundancy
Remote Call Control (RCC) services are supported (with limitations) in the
following scenarios:
•
Single node redundancy
•
Campus redundancy
•
Geographic redundancy
Single node Redundancy
The same master and follower mechanism used for Virtual Trunk (VTRK)
and TPS applications is used to support redundancy within a node for RCC.
After the master of the node fails, one of the followers takes over the node
IP and continues to deliver service. VoIP mode session state is preserved
when a new master is elected.
Supported
Redundancy across multiple nodes is possible using the Least Cost Routing
feature of NRS. When considering a multinode redundant configuration, see
the restrictions on establishing TR/87 sessions from multiple nodes that
have AML links to a single Call Server. For more information, see "Capacity
planning" (page 46) .
Campus redundancy
Campus Redundancy increases the distance between the two CPU cores of
CS 1000E.
The CS 1000E is the only large system that supports this feature.
Geographic redundancy
Geographic Redundancy can be supported with the limitations that currently
exist for SIP gateway SIP traffic. The main impacts are.
•
During transition periods, situations can arise where IP phones are
registered to a Call Server that is different from the call server that
provides support for the TR/87 FE. In this situation, TR/87 support is
undefined. TR/87 clients can register successfully; however, the status
of the IP Phone is impacted by any actions performed on the telephone
or the TR/87 client, as the FE and IP Phone interface different Call
Servers. NRS is required to support redundancy.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

•
After an event occurs that causes the IP Phones to register to a server
other than the Front End server (and then to return to the Front End
server), the Office Communicator 2007 client does not automatically
follow the IP Phone registration. To direct the TR/87 sessions back
to the TR/87 FE that corresponds to the home TPS, take one of the
following actions:
— Users must log out and log back onto the TR/87 client (for example,
— An administrator issues the SIPCTIStop all command on the
Table 16 SIPCTIStop all command
Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 79
Office Communicator 2007) to force the previous SIP dialog to
terminate so that a new dialog can be established, which NRS
redirects to the correct TR/87 FE.
Signaling Server on which the TR/87 sessions currently reside
to terminate the SIP dialogs. This forces the clients to send
another association request (for example, SIP INVITE), which the
NRS redirects to the correct TR/87 FE, as depicted in Table 16
"SIPCTIStop all command" (page 79).
Command
SIPCTIStop all De-acquire all AST DNs and terminate all TR/87 SIP sessions.
Description
Branch Office redundancy (MG 1000B/SRG)
Branch Office scenarios can be supported; however, SIP CTI support and
Telephony Gateway and Services are available for Branch User IP Phones
in Local mode (registered in the Branch Office) only when the following
conditions are met:
•
The Branch Office has SIP CTI and Telephony Gateway and Services
enabled and has a Signaling Server dedicated to each branch.
•
The network dialing plan is a Coordinated Dialing Plan (CDP).
•
The IP Phone (Branch User) has the same domain name configured in
both the Main Office and Branch Office.
• The Branch Office has access to the NRS and Office Communications
Server (OCS). If access is disrupted, failure cases may not be supported
if the NRS and OCS are located in close proximity to the Main Office,
which is no longer available. For example, when the WAN link to the
Main Office is down, the NRS and OCS are out-of-service.
•
The SIP Gateway in the Main Office is out -of-service (in which case the
SIP Gateway in the Branch Office is used).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

80 Planning and engineering
The Microsoft Office Communicator client has no automated mechanism
to register to the branch. Users must wait for the existing dialog to time
out (30 minutes) or manually log out and log on again after the IP phones
change to local mode.
Digital and analog telephones in the Branch Office can have Remote Call
Control (RCC) and PBX Integration Enabled support when the Branch
Office has access to the NRS and OCS.
Feature Interactions
This section describes the interactions of the Remote Call Control with
SIP CTI component.
Table 17 Feature Interactions of RCC
Feature Operation
Call Forwarding
Analog telephone
usage
Description
Office Communicator does not reflect call forward state changes made to
the CS 1000 telephone itself.
WARNING
Call Forward state changes
Office Communicator does not reflect Call Forward
state changes made to the CS 1000 telephone.
When Office Communicator is active and controls
a DN, make Call Forward changes through Office
Communicator to ensure that it is in the correct state.
When a user logs on to the OCS 2007 from their Office
Communicator client, the forwarding status saved
within Office Communicator overrides the forwarding
status configured from the telephone. For example,
if forwarding is off within Office Communicator, it is
turned off following log on, regardless of the phone
forwarding status at the time.
As a general rule, Office Communicator in phone mode can only control
and invoke telephony features supported by the telephone. If a feature
is not supported or configured on a particular telephone (either Analog,
IP, or Digital), it is not supported by Office Communicator. An Office
Communicator in phone mode that supervises an analog phone (2500)
has the following limitations:
•
Make Call - cannot be made through Office Communicator if the analog
phone (2500) phone does not go off-hook prior to placing the call.
•
Answer Call - cannot be performed through Office Communicator.
Answer Call must be performed through the analog phone (2500).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Remote Call Control with SIP CTI 81
Feature Operation
Description
•
Conference Call - cannot be performed through Office Communicator .
•
Call Hold - can be performed through Office Communicator.
•
Call Transfer - Analog telephones do not support the Conference
and Transfer key features. As a result, Call Conference and Call
Transfer (Announced and Blind) cannot be performed through Office
Communicator. Flexible Feature Code (FFC) is not supported by
AML and RCC.
•
Send DTMF digits - DTMF digits work with both Voice Mail and
Conferencing.
Multiple Customer
operation
Multiiple Customer operation is not supported within a single Signaling
Server; a separate Signaling Server is required for each customer.
Multi-customer support is a consideration for future releases. For more
information about how to configure a Multi-Customer environment, see
"Multiple customer network" (page 40).
TR/87 Front End
application
The TR/87 FE application on a Signaling Server can support only a single
Call Server.
UDP Location Code Only one UDP Location Code can be associated with each Signaling
Server TR/87 interface.
AML interaction CS 1000 has an Application Module Link (AML) limitation where only one
application can acquire a DN or TN at any time. For example, the TR/87
FE application and IP Call Recording feature cannot coexist on the same
DN or TN. This also applies to the interaction between Symposium and
Office Communicator Remote Call Control. Symposium uses the AML to
acquire and control telephones on the CS 1000 Call Server.
Office Communicator
Web Access
Converged Office requires that the client support RCC. The Web version
of Office Communicator, called Office Communicator Web Access, does
not support RCC.
Office Communicator
Mobile (COMO)
Converged Office requires the client to support Remote Call Control, but
the Mobile version of Office Communicator, called Office Communicator
Mobile, has limited support for Remote Call Control.
Outgoing VoIP calls to telephone numbers for Office Communicator Mobile
are not supported. Remote Call Control only permits telephone status
updates (for example, on a call or not) when you use Office Communicator
Mobile. Remote Call Control supports Call Forward with COMO.
Virtual Server 2005 Virtual Server 2005 is not supported as part of Nortel Converged Office.
Office Communicator
2007 Call Forward All
Calls
When the CS 1000 Call Forward All Calls feature is enabled, only calls
to the Prime DN or any single-appearance DN on the telephone are
forwarded. Therefore, if an Office Communicator 2007 acquires a MADN,
and it is not the Multiple Appearance Redirection Prime (MARP), the call
is not forwarded even if the Call Forward feature is enabled. For more
information, see Features and Services (NN43001-106).
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

82 Planning and engineering
Feature Operation
Office Communications
Server and MCS
coexistence
CallPilot
configuration
Conference Call and
Do Not Disturb (DND)
features
Description
ATTENTION
All Converged Office users must have their extension configured as
CLS CDMR.
A user cannot have both Office Communications Server and MCS
enabled for their extension (all TN’s that have a particular number
and extension). If any of the TN’s have CLS CDMV or CLS CDMO
configured, the extension is treated as having MCS enabled. When
MCS (SIP CD) is enabled on an extension, Office Communications
Server Converged Office is not supported for that extension in Release
4.5B and 5.0.
For PBX Integration Enabled (Computer Mode) calls to access the
CallPilot mailbox, the Pound key (#) is pressed. Every mailbox must
have the optional messaging network configured. In a normal CS 1000
- CallPilot scenario, this configuration is optional. For PBX Integration
Enabled (Computer Mode) calls to CallPilot to work properly, this extra
configuration is required. For more information about the configuration of
CallPilot, see
Conference Call and DND features in RCC mode are not supported by
Microsoft.
CallPilot Network Planning Guide (NN44200-201).
LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence
This section describes the coexistence limitations of LCS 2005 and OCS
2007.
Client considerations
Features hosted on Office Communications Server 2007 are not supported
by the OC 2005 client. After a user is configured for enhanced presence, the
account can no longer use previous versions of OC 2005 , Communicator
Web Access 2005, or Communicator Mobile 2005. Microsoft recommends
that you upgrade all client computers for a particular user at the same time.
Communicator 2007 clients cannot log on to Live Communications Server
2005. Verify that any user whose client is upgraded to Communicator 2007
is already provisioned on an Office Communications Server.
Converged Office functionality
An upgrade from the LCS Application Proxy to the OCS Proxy Server and
MCS 2.0 to MCM 3.0 is required to manage CS 1000 telephones by the
OC 2007 client in either VOIP or RCC mode. Inter-working of MCM 2.0
with OCS Proxy Server or MCM 3.0 with LCS Application Proxy is not a
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence 83
supported configuration because of incompatible underlying libraries. The
same CS 1000 can be connected to two or more different communication
servers (LCS 2005 or OCS 2007).
The following must be considered for coexistence of LCS 2005 and OCS
2007:
•
The CS 1000 must be upgraded to Release 5.0 with the required
Product Enhancement Packages (PEPs) .
•
OCS 2007 patches from Microsoft must be in service. For more
information, see the Attention box under "OCS 2007 component
installation" (page 105).
•
NRS is required to appropriately route a call to the Communication
Server.
•
Different server DNs (Hot Ps) are assigned for each Communications
Server (LCS or OCS). The PCA for each user is configured with the
corresponding server DN as a target DN
•
LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 can share the same Active Directory but
you can only have one OC client user account on either LCS 2005 or
OCS 2007.
•
For Remote Call Control (RCC) support , a single Signaling Server
cannot be used for both LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 as the configuration
of the SIP CTI FE is different for both. In this case, the following options
can be considered:
— RCC supported for both LCS 2005 and OCS 2007. Upgrade the
existing Communication Server 1000 to support OCS 2007 RCC
users. Configure an additional SIP CTI FE Signaling Server for
LCS 2005 RCC users. An additional AML ELANs is defined on the
Call Server. Change the static routing rule on the LCS 2005 Home
server to route RCC traffic directly to the SIP CTI FE for LCS 2005.
Geographic Redundancy is not supported for LCS 2005 RCC users
in this case.
— RCC supported for only LCS 2005 users. Enable RCC only for
LCS users in the Active Directory, on the OC clients, or both. The
SIP CTI FE should be configured according to the document Nortel
Converged Office Fundamentals (NN43001-525) for LCS 2005.
For example, the Phone context=dialstring configuration on the
Signaling Server is used.
— RCC supported only for OCS 2007 users. Enable RCC only for OCS
users in the Active Directory, on the OC clients, or both. The SIP CTI
FE should be configured according to this document. For example,
the Phone-context=<SIP URI Map Entries> configuration on the
Signaling Server is used.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

84 Planning and engineering
MCM 2.0 to MCM 3.0
There is no direct upgrade path from MCM 1.0 or 2.0 to MCM 3.0 . MCM
3.0 must be installed on the OCS Proxy server. The OCS Proxy install is
done from command line and not from the install wizard. It is still possible
to preserve the configuration data from a previous installation by first
performing a backup operation on MCM 2.0 and restore the data to MCM
3.0 on the OCS Proxy server. However, this will cause the new configuration
parameters to be set to default values as follows:
Table 18
Default configuration parameters
Parameter Default value
Call Server CS1000
MediationServer enabled
RoutingTable
DialPlan CDP
AccessCode
empty
empty
For more information on MCM 3.0 configuration, see "MCM configuration"
(page 134)
Load balancer considerations
You cannot use a single logical load balancer for LCS 2005 and OCS 2007.
For example, if you have an LCS 2005 application proxy with MCM 2.0
attached to a logical load balancer, you cannot simultaneously attach an
OCS Proxy server with MCM 3.0 to the same one. This same restriction
applies to all other server roles.
Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007
Live Communications Server 2005 with SP1 can only be upgraded to
Office Communications Server 2007 by using a side-by-side migration.
This involves deploying an Office Communications Server 2007 Standard
Edition or Enterprise pool alongside existing Live Communications Server
2005 with SP1 Standard Edition or Enterprise pool thus allowing the two
environments to coexist with minimal service disruption.
When migrating servers, Office Communications Server 2007 servers
should be deployed using a phased, outside-in approach. This involves
replacing the Access Proxies with Office Communications Server 2007
Access Edge Servers before you migrate to Office Communications Server
2007 in your internal environment. Upgrading all the servers of a particular
type at one time will help to minimize service disruptions.
The following flow chart depicts the migration phases:
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007 85
Prerequisites
Upgrading to Office Communications Server 2007 assumes the following:
•
An understanding of the basic migration process.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

86 Planning and engineering
•
An understanding of the coexistence interactions. For more information,
see "LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence" (page 82).
•
An understanding of CS 1000, Signaling Server, and networks.
•
An understanding of the user migration process.
Determine your deployment options
There are two deployment options depending on whether you are migrating
a small or large client base.
For a small client base, Office Communicator client users can be migrated
from LCS to OCS inside a set maintenance window. No extra servers are
required.
For a large client base, Office Communicator client users need to be
migrated over multiple maintenance windows using a phased approach.
The following choices must be made:
1. If using one SIP CTI FE Signaling Server
•
Only LCS users have RCC
OR
•
OCS users have RCC
2. If deploying an additional SIP CTI FE Signaling Server
•
RCC is supported for both LCS and OCS. One Signaling Server for
LCS RCC and the other for OCS RCC
ATTENTION
Before migrating to Office Communications Server 2007, existing Live
Communications Servers must have Live Communications Server 2005 SP1
installed.
Migration process
The following table breaks down the migration process using a phased,
outside-in approach and defines the impact for the user at each phase.
Table 19 User experience
Phase Description User experience
1. Upgrade your perimeter
network.
Introduce a new Office
Communications Server (OCS)
2007 Access Edge Servers
and Directors into your Live
Communications Server (LCS)
2005 SP1 environment.
No changes. Users continue
to use the Microsoft Office
Communicator (OC) 2005 client
and have the same IM and
presence functionality.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007 87
Phase Description User experience
2. Deploy OCS 2007 and begin
moving users to the new server
or pool.
3. Upgrade CS 1000 and if
determined for your migration,
add an additional Signaling
Server as the SIP CTI FE.
4. Deploy OCS 2007 Mediation
Server.
Deploy a new Office
Communications Server 2007
Enterprise pool or Standard
Edition server. If required,
deploy an Archiving and CDR
Server. Users are moved to
the new server or pool but will
continue to use OC 2005 .
Upgrade Call Sever and
Signaling Server. The feature
is provided as a Product
Enhancement Package (PEP)
for Release 5.0 Call Server and
Signaling Server.
If you have a large client base,
add an additional Signaling
Server as the SIP CTI FE so
both LCS 2005 and OCS 2007
can have RCC.
Deploy OCS 2007 Mediation
Servers.
No changes. OC 2007 client
is not rolled out at this phase
so users continue to use OC
2005 and have the same IM
and presence functionality.
No changes. Users continue
to use OC 2005 and have
the same IM and presence
functionality.
No changes. Users continue
to use OC 2005 and have
the same IM and presence
functionality
5. Deploy OCS Proxy server
with MCM 3.0 .
6. Enable enhanced presence,
roll out OC 2007 client, and
continue migrating users
7. Configure PCA routing for
new OC 2007 client users on
the CS 1000.
Deploy OCS Proxy Server with
MCM 3.0 .
Enable users for enhanced
presence, roll out the OC 2007
client, and the Live Meeting
2007 client to the users.
Configure PCA on the CS 1000.
Change NRS and SPS routing.
No changes. Users continue
to use OC 2005 and have
the same IM and presence
functionality
•
The migrated users can use
the full functionality of OC
2007 when communicating
with other migrated users.
•
Once enabled for enhanced
presence, these users can
no longer sign in to a OC
2005 client or previous
Communicator Web Access
or Communicator Mobile
Access clients.
Migrated users are able to
use Telephony Gateway and
Services functionality (VoIP)
and RCC.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

88 Planning and engineering
Phase Description User experience
•
8. Continue migrating users. Migrate remaining users.
Enable users for enhanced
presence. Roll out the OC 2007
client and the Live Meeting
2007 client to the users.
OC 2007 users can use the
full functionality of OC 2007
when communicating with
other OC 2007 users.
•
When OC 2007 client users
are communicating with OC
2005 users, they cannot
use the new features in OC
2007.
•
After Live Meeting 2007
is rolled out to your users,
they can participate in
on-premise conferences
internally and connect
to these conferences
remotely by using the Web
Conferencing Edge Server.
•
RCC is only available to
either OCS 2007 or LCS
2005 users when one
SIP CTI FE Signaling
Server is deployed.
For more information,
see "Converged Office
functionality" (page 82).
9. Decommission all Live
Communications 2005 servers
and MCM 2.0 after all users
have been migrated to OCS
2007
10. Decommission the SIP CTI
FE for LCS (if installed)
Description of Migration Phases
To deploy OCS 2007 in an existing Live Communications Server 2005
topology, Nortel recommends the following phases:
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Remove Live Communications
Server 2005 and MCM 2.0 from
your environment.
Remove the SIP CTI FE for
LCS (if an additional Signaling
Server was deployed).
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
All users are on OC 2007,
enabled for enhanced presence
and have full functionality of
OC 2007. If Live Meeting is
deployed, users can participate
in on-premise conferences
internally and connect to these
conferences remotely by using
the Web Conferencing Edge
Server.
None.

Migration planning from LCS 2005 to OCS 2007 89
Migrating users from LCS to OCS
Step Action
1
Upgrade your perimeter network by deploying an Access Edge
Server that communicates with Live Communications Server
2005 Director. When Director is not deployed, the edge server
communicates directly with your internal Live Communications
Server 2005 Standard Edition servers or Enterprise pool and the
new Access Edge Server is configured as the next hop server to
which existing pools and Standard Edition Servers will route external
traffic. Next, an Office Communications Server 2007 Director is
deployed to replace Live Communications Server 2005 Director.
Incoming and outgoing traffic is configured to go through the new
Director (if a Director was previously not used and you do not want
to use one now, this step can be skipped). For more information,
download Microsoft technical documentation from the Download
Center at w
2
In this phase, an internal Office Communications Server 2007
ww.microsoft.com.
Standard Edition Server or Enterprise pool is deployed. Move an
initial group of users to the new server or pool but they will continue
to use OC 2005 as their client. If required, deploy an Archiving and
CDR Server. DNS update is required next. For more details, see
"LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence" (page 82).
3 Upgrade CS 1000 and if determined for your migration, add an
additional Signaling Server as the SIP CTI FE. Upgrading Call Sever
and Signaling Server according to standard procedures. For more
information, see "LCS 2005 and OCS 2007 coexistence" (page 82).
4
Deploy OCS 2007 Mediation Server. For more information
on deploying Mediation Server, download Microsoft technical
documentation from the Download Center at w
5
Deploy OCS Proxy server with MCM 3.0 . For more information, see
"OCS Proxy server installation" (page 107) and "MCM installation"
(page 109).
6
Enable enhanced presence and continue migrating users. Start
to move users from Live Communications Server 2005 to Office
Communications Server 2007. By enabling enhanced presence,
users are allowed to use Office Communicator 2007 and the new
functionality that it provides. After enabling the users for enhanced
presence, roll out OC 2007 client to each computer for these users.
Once a user is enabled for enhanced presence, they can no longer
use any previous client versions. For more information on enhanced
presence, download Microsoft technical documentation from the
Download Center at w
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
ww.microsoft.com.
ww.microsoft.com.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

90 Planning and engineering
7
8
9
10
Unified Messaging
This section describes the interactions and inter-workings of Unified
Messaging (UM) with Converged Office. Office Communications Server
(OCS) 2007 users can access Unified Messaging capabilities using CallPilot
or Exchange Server 2007. Features that are accessible to the OCS
2007 users from CallPilot or Exchange depend on how the deployment is
performed. The following sections describe the user experience based
on deployments when using CallPilot, Exchange integrated with OCS,
and Exchange non-integrated with OCS. For more information on the
signaling that takes place in an integrated or non-integrated configuration,
see "Signaling with integrated Voice Mail" (page 97) and "Signaling with
non-integrated Voice Mail" (page 98).
Configure PCA routing for new OC client users on the CS 1000.
After configuration of PCA routing, users will be allowed to use
Telephony Gateway and Services (VoIP) and RCC functionality. A
Server URI field should be changed for migrated users to enable SIP
CTI functionality. Change NRS and SPS routing.
Continue migrating users. Enable users for enhanced presence.
Roll out the OC 2007 client and the Live Meeting 2007 client to
the users. For more information on enhanced presence, download
Microsoft technical documentation from the Download Center at
w
ww.microsoft.com.
Decommission all Live Communications 2005 servers and MCM 2.0
after all users have been migrated to OCS 2007.
Decommission the SIP CTI FE for LCS (if installed).
—End—
Unified Messaging navigation
•
"OCS 2007 users using CallPilot" (page 90)
•
"OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—integrated" (page 92)
•
"OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—non-integrated" (page 95)
•
"Signaling with integrated Voice Mail" (page 97)
•
"Signaling with non-integrated Voice Mail" (page 98)
OCS 2007 users using CallPilot
The table depicts Voice Mail access for OCS 2007 users using CallPilot in
the following configurations.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Table 20
CallPilot configurations
Unified Messaging 91
CS 1000
OC User
(VoIP) with
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
PCA + SIP CTI PCA PCA PCA SIP CTI
OC User
(VoIP) with no
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
OC User
(VoIP) with
no RCC and
no CS 1000
Phone
LG-Nortel
8540 (VoIP)
with no RCC
and no CS
1000 Phone
OC User RCC
only, with CS
1000 Phone
configuration
VM access
Dial CP DN Dial CP DN N/A N/A Dial CP DN
from phone
Login from
p/w only p/w only N/A N/A p/w only
phone
MWI on phone Yes Yes N/A N/A Yes
VM access
Dial CP DN Dial CP DN Dial CP DN Dial CP DN N/A
from OC
Login from OC p/w only p/w only p/w only p/w only N/A
MWI on OC No No No No No
Outlook New msg on
CP Mailbox
New msg on
CP Mailbox
New msg on
CP Mailbox
New msg on
CP Mailbox
New msg on
CP Mailbox
Phone CFNA CP DN CP DN PCA CFNA PCA CFNA CP DN
Phone CFB CP DN CP DN PCA CFB PCA CFB CP DN
Phone CFAC CP DN CP DN N/A N/A CP DN
OC client FC On Phone
(RCC to CP
CP DN Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
DN)
OC client
Re-direct
OC client
sim-ring
N/A Not
recommended
N/A Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
N/A
N/A
OC fwd to UM N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users using a Nortel telephone
Deploying Converged Office without configuring Remote Call Control (RCC) is not
recommended. If RCC is not deployed for these users, the Office Communicator
(OC) 2007 client provides call forwarding and call redirection options that can
result in undesirable behaviors. For example, calls forwarded or redirected to the
CallPilot DN, will be answered by the CallPilot logon prompt of "CallPilot from
Nortel Networks. Mailbox ?", instead of receiving the user’s mailbox greeting.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

92 Planning and engineering
For Converged Office users not using a Nortel telephone
For Converged Office users who use voice communications through the OC client
or from an LG-Nortel 8540 telephone (or both) and are configured with a Personal
Call Assistant (PCA) , the following cautions apply:
• Ensure that the Call Forward No Answer and Call Forward Busy
settings for the PCA are properly set to the CallPilot DN.
•
Advise users not to use the Office Communicator 2007 settings
for forwarding or redirecting calls to Voice Mail. For example, calls
forwarded or redirected to the CallPilot DN, will be answered by the
CallPilot logon prompt of "CallPilot from Nortel Networks. Mailbox ?",
instead of receiving the user’s mailbox greeting.
• Callers experience different call-answering behavior depending upon
the state of the user’s PCA . If the PCA is in a ringing state such
as a call waiting to be answered by the user, a second caller will be
forwarded immediately to the user’s Voice Mail. If the user has already
answered a call, a second caller will be forwarded to the user’s Voice
Mail only after the number of rings specified by the PCA’s Call Forward
No Answer setting.
ATTENTION
OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—integrated
The following tables depict Voice Mail access for OCS 2007 users using UM
2007 in integrated mode for Option 1 and 2.
Table 21
Unified Messaging 2007 integrated Option 1
OC User
(VoIP) with
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
CS 1000
configuration
VM access
from phone
Logon from
phone
MWI on phone No No N/A N/A No
VM access
from OC
PCA + SIP CTI PCA PCA PCA SIP CTI
Dial SA DN Dial SA DN N/A N/A Dial SA DN
Logon and
password
Dial SA DN Use Voice Mail
OC User
(VoIP) with no
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
Logon and
password
option
OC User
(VoIP) with
no RCC and
no CS 1000
Phone
N/A N/A Logon and
Use Voice Mail
option
LG-Nortel
8540 (VoIP)
with no RCC
and no CS
1000 Phone
UseVoice Mail
option
OC User RCC
only, with CS
1000 Phone
password
N/A
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Unified Messaging 93
Logon from
OC
Logon and
password
direct direct direct N/A
MWI on OC Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Outlook New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
Phone CFNA SA DN SA DN Not Required Not Required SA DN
Phone CFB SA DN SA DN Not Required Not Required SA DN
Phone CFAC SA DN SA DN N/A N/A SA DN
OC client FC On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
OC client
N/A No No No N/A
No No No On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
Re-direct
OC client
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
sim-ring
OC fwd to UM N/A Yes Yes Yes N/A
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users using a Nortel telephone
Deploying Converged Office without configuring Remote Call Control (RCC) is not
supported. If RCC is not deployed for these users, the Office Communicator (OC)
2007 client provides call forwarding and call redirection options that if selected
by the end user, will result in forward or redirected calls being answered by the
Exchange logon prompt instead of the user’s mailbox greeting. For example,
using Call Forward or redirect to the Exchange Unified Messaging System Access
number, will result in calls being answered by the Exchange logon prompt,
"Welcome, you are connected to Microsoft Exchange", instead of receiving the
user’s mailbox greeting.
For Converged Office users not using a Nortel telephone
For Converged Office users who use voice communications through the OC client,
an 8540 telephone, or both and are configured with a Personal Call Assistant
(PCA) , the following cautions apply:
The Voice Mail option is not available. Users cannot use the Office Communicator
2007 Voice Mail setting for forwarding or redirecting calls to Voice Mail. Calls
Forwarded or redirected to the Exchange Unified Messaging System by the OC
client are answered by the Exchange Unified Messaging logon prompt instead of
the user’s mailbox greeting. For example, using Call Forward or redirect to the
Exchange Unified Messaging, results in calls being answered by the Exchange
Unified Messaging logon prompt, "What is the prompt?", instead of receiving the
user’s mailbox greeting. The Exchange UM Call Sender feature will not work
properly.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
ATTENTION
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

94 Planning and engineering
Table 22
Unified Messaging 2007 integrated Option 2
CS 1000
OC User
(VoIP) with
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
PCA + SIP CTI PCA PCA PCA SIP CTI
OC User
(VoIP) with no
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
OC User
(VoIP) with
no RCC and
no CS 1000
Phone
LG-Nortel
8540 (VoIP)
with no RCC
and no CS
1000 Phone
OC User RCC
only, with CS
1000 Phone
configuration
VM access
Dial SA DN Dial SA DN N/A N/A Dial SA DN
from phone
Login from
p/w p/w N/A N/A p/w
phone
MWI on phone No No N/A N/A No
VM access
from OC
Dial SA DN User Voice
Mail option
Use Voice Mail
option
UseVoice Mail
option
N/A
Login from OC p/w direct direct direct N/A
MWI on OC Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Outlook New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
Phone CFNA SA DN SA DN Not required Not required SA DN
Phone CFB SA DN SA DN Not required Not required SA DN
Phone CFAC SA DN SA DN N/A N/A SA DN
OC client FC On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
OC client
N/A Voice Mail
Re-direct
OC client
N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
Voice Mail
option only
DN not
recommended
option only
DN not
recommended
Voice Mail
option only
DN not
recommended
Voice Mail
option only
DN not
recommended
Voice Mail
option only
DN not
recommended
By default
set to Voice
Mail after 20
seconds
On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
N/A
sim-ring
OC fwd to UM N/A Yes Yes Yes N/A
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users using a Nortel telephone
Converged Office users who internally access the Exchange Unified Messaging
Auto Attendant or use the Call Sender feature, are unable to use the Auto
Attendant to call other users. Any attempts to call another user will result in the
caller being disconnected.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Unified Messaging 95
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users not using a Nortel telephone
For Converged Office users who use voice communications through the OC client,
an 8540 telephone, or both and are configured with a Personal Call Assistant
(PCA) , the following cautions apply:
• Ensure users only use the OC 2007 client Voice Mail settings for
forwarding or redirecting calls to Voice Mail. For example, calls
forwarded or redirected to the Voice Mail option are answered with the
user’s personal greeting.
•
Calls should not be forwarded or redirected to the Unified Messaging
System Access number. Calls forward or redirected to the Exchange
Unified Messaging by the OC client 2007 are answered by the
Exchange Unified Messaging logon prompt instead of the user’s
mailbox greeting. For example, using Call Forward or redirect to the
Exchange Unified Messaging System Access number, results in calls
being answered by the Exchange Unified Messaging logon prompt,
"What is the prompt?", instead of receiving the user’s mailbox greeting.
•
Users using the Play on Phone feature are required to update the Play
on Phone destination with their telephone number for the first time they
use the Play on Phone option. The default SIP URI will not work.
OCS 2007 users using UM 2007—non-integrated
The table depicts Voice Mail access for OCS 2007 users using UM 2007 in
non-integrated mode for the following configurations.
Table 23
Unified Messaging 2007 non-integrated
CS 1000
configuration
VM access
from phone
Login from
phone
OC User
(VoIP) with
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
PCA + SIP CTI PCA PCA PCA SIP CTI
Dial SA DN Dial SA DN N/A N/A Dial SA DN
p/w only p/w only N/A N/A p/w only
OC User
(VoIP) with no
RCC and CS
1000 Phone
OC User
(VoIP) with
no RCC and
no CS 1000
Phone
LG-Nortel
8540 (VoIP)
with no RCC
and no CS
1000 Phone
OC User RCC
only, with CS
1000 Phone
MWI on phone Yes Yes N/A N/A Yes
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

96 Planning and engineering
VM access
Dial SA DN Dial SA DN Dial SA DN Dial SA DN N/A
from OC
Login from OC p/w only p/w only p/w only p/w only N/A
MWI on OC Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Outlook New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
New msg in
inbox
Phone CFNA SA DN SA DN PCA CFNA PCA CFNA SA DN
Phone CFB SA DN SA DN PCA CFB PCA CFB SA DN
Phone CFAC SA DN SA DN N/A N/A SA DN
OC client FC On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
OC client
N/A Not
Re-direct
OC client
N/A Not
sim-ring
Not
recommended
recommended
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
Not
recommended
On Phone
(RCC to SA
DN)
N/A
N/A
OC fwd to UM N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users using a Nortel telephone
Deploying Converged Office without configuring Remote Call Control (RCC) is not
recommended. If RCC is not deployed for these users, the Office Communicator
(OC) 2007 client provides call forwarding and call redirection options that can
result in undesirable behaviors. For example, using Call Forward or redirect to the
Exchange Unified Messaging System Access number, will result in calls being
answered by the Exchange logon prompt, "Welcome, you are connected to
Microsoft Exchange", instead of receiving the user’s mailbox greeting.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Unified Messaging 97
ATTENTION
For Converged Office users not using a Nortel telephone
For Converged Office users who use voice communications through the OC
client, an 8540 telephone, or both and are configured with a , the following
cautions apply:
• Ensure that the Call Forward No Answer and Call Forward Busy
settings for the PCA are properly set to the Exchange Unified
Messaging System Access number.
•
Ensure users do not use the Office Communicator 2007 settings
for forwarding or redirecting calls to Voice Mail. For example, using
Call Forward or redirect to the Exchange Unified Messaging System
Access number, results in calls being answered by the Exchange
Unified Messaging logon prompt, "What is the prompt?", instead of
receiving the user’s mailbox greeting.
•
Callers can experience different call-answering behavior depending
upon the state of the user’s PCA . If the PCA is in a ringing state such
as a call waiting to be answered by the user, a second caller will be
forwarded immediately to the user’s Voice Mail. If the user has already
answered a call, a second caller will be forwarded to the user’s Voice
Mail only after the number of rings specified by the PCA’s Call Forward
No Answer setting.
For more information on configuring Voice Mail access for OCS 2007 users using
UM 2007, see "OCS 2007 users using UM 2007" (page 198).
Signaling with integrated Voice Mail
In an integrated configuration, the Office Communicator (OC) client has the
capability of selecting a Voice Mail option and the dialing plan is TLS secure.
The following diagram depicts the signaling between OCS 2007, Exchange,
and the CS 1000 components in an integrated configuration.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

98 Planning and engineering
Figure 25
Signaling integrated
Signaling with non-integrated Voice Mail
In a non-integrated configuration, the Office Communicator (OC) client
does not have the capability of selecting a Voice Mail option, the signaling
between Exchange and the OC client is not defined. The following diagram
depicts the signaling between OCS 2007, Exchange, and the CS 1000
components in a non-integrated configuration.
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

Figure 26
Signaling non-integrated
Unified Messaging 99
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008

100 Planning and engineering
Nortel Converged Office Fundamentals — Microsoft Office Communications Server 2007
Copyright © 2005–2008, NortelNetworks
.
Nortel Communication Server 1000
NN43001-121 01.03 Standard
Release 5.0 30 April 2008
 Loading...
Loading...