Page 1
Secure Multimedia Controller
Command Reference
Document Number: NN10300-091
Document Release: Standard 1.00
Date: May 2006
Year Publish FCC TM
Copyright © 2006 Nortel Networks. All rights reserved.
Produced in Canada
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical
data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented
without express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products
specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Nortel, Nortel (Logo), the Globemark, SL-1, Meridian 1, and Succession are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Title page
Page 2

Page 3

Page 3 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
4
Revision history
May 2006
Standard 1.00. This document is a new NTP. It was created to support the
Secure Multimedia Controller 2450.
Page 4

Page 4 of 126 Revision history
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Page 5

Page 5 of 124
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
8
Contents
About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Subject .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Applicable systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Intended audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Conventions .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Related information .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
How to get help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting help from the Nortel web site .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel
Solutions Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . 14
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Main menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Information menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Info_host menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Information_net menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Route Information menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
VRRP Information menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Administration Information menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Statistics Information menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Page 6

Page 6 of 124 Contents
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Configuration menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
System menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Date and Time menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
DNS Servers menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Cluster menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Access List menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Administrative Applications menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Platform Logging menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
User menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Network Configuration menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Port menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Interface menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Routes menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
VRRP Settings menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Proxy ARP menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Multimedia Security menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Security Zone menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Inbound Access menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Flow Control menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Outbound Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
SMC Settings menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
UNIStim Security menu .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
SMC Network menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Service menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Boot menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Software Management menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Software Patches menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Maintenance menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Tech Support Dump menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
UNIStim Flow Maintenance menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
UNIStim Connection Rate menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
UNIStim Packet Rate menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
UNIStim Bandwidth Rate menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Page 7

Page 7 of 124
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Appendix A: Selected firewall attacks . . . . . . . . . . 121
SYN flooding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Source routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Mime flood . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
FTP bounce . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
IP unaligned timestamp .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Sequence number prediction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Sequence number out of range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
ICMP redirect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
IP spoofing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Ping of death . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Land attacks .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
IP reassembly . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Appendix B: Firewall limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Page 8

Page 8 of 124 Contents
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Page 9

Page 9 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
12
About this document
This document is a global document. Contact your system supplier or your
Nortel representative to verify that the hardware and software described are
supported in your area.
Subject
This document describes Secure Multimedia Controller (SMC) 2450 system
architecture, software and hardware requirements, components, and network
connections.
Note legacy products and releases
This Nortel Technical Publication (NTP) contains information about systems,
components, and features that are compatible with Nortel Communication
Server 1000 Release 4.5 and
Nortel Multimedia Communication Server 5100 software. For more
information about legacy products and releases, click the
Technical Documentation link under Support & Training on the Nortel
home page:
www.nortel.com
Applicable systems
This document applies to the following systems:
• Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
• Communication Server 1000S (CS 1000S)
• Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
Page 10

Page 10 of 126 About this document
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
• Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
• Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
• Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
• Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
• Multimedia Communication Server 5100 Server Micro System (V100)
• Multimedia Communication Server 5100 Server Simplex System (V100)
• Multimedia Communication Server 5100 Server Redundant System
(V100)
• Multimedia Communication Server 5100 Server Large System (N240)
For more information, see the following:
• Communication Server 1000S: Upgrade Procedures (553-3031-258)
• Communication Server 1000E: Upgrade Procedures (553-3041-258)
Intended audience
This document is intended for individuals responsible for installation,
configuration, administration, and maintenance of the SMC 2450.
Conventions
Terminology
In this document, the following systems are referred to generically as system:
• Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
• Communication Server 1000S (CS 1000S)
• Communication Server 1000M (CS 1000M)
•Meridian1
The following systems are referred to generically as Small System:
• Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
• Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
Page 11

About this document Page 11 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
The following systems are referred to generically as Large System:
• Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
• Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
• Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
• Meridian 1 PBX 51C
• Meridian 1 PBX 61C
• Meridian 1 PBX 61C CP PII
•Meridian1 PBX81
• Meridian 1 PBX 81C
• Meridian 1 PBX 81C CP PII
Related information
This section lists information sources that relate to this document.
NTPs
The following NTPs are referenced in this document:
• Secure Multimedia Controller: Implemention guide (553-3001-225)
• Secure Multimedia Controller: Planning and engineering guide
(NN42320-200)
Online
To access Nortel documentation online, click the Technical Documentation
link under Support & Training on the Nortel home page:
www.nortel.com
Page 12

Page 12 of 126 About this document
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
CD-ROM
To obtain Nortel documentation on CD-ROM, contact your Nortel customer
representative.
Page 13

Page 13 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
14
How to get help
This chapter explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting help from the Nortel web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support web site:
www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and
tools to address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for
Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting help over the telephone from a Nortel
Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical
Support web site, and you have a Nortel support contract, you can also get
help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Page 14

Page 14 of 126 How to get help
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Outside North America, go to the following web site to obtain the telephone
number for your region:
www.nortel.com/callus
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing
Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
www.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
Page 15
Page 15 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
18
Main menu
After you complete the initial Secure Multimedia Controller (SMC) system
setup and perform a successful connection and logon, the Main menu of the
command line interface (CLI) appears.
For more information about the CLI and how to use it, see Secure Multimedia
Controller: Implemention guide (553-3001-225).
Table 1 identifies and describes the Main menu commands.
Table 1
Main menu commands
Command Description
info Displays information about the current status of the SMCs. For menu
items, see “Information menu” on page 19.
cfg Displays the Configuration menu, which you can use to configure the
SMCs. Some commands in the Configuration menu are available for only
the administrator user account. For menu items, see “Configuration
menu” on page 29.
boot Displays the Boot menu, which you can use to upgrade the SMC
software and reboot, if necessary. Only the administrator user account
can access the Boot menu. For menu items, see “Boot menu” on
page 113.
maint Displays the Maintenance menu, which you can use to send dump files
and log details to the servers. For menu items, see “Maintenance menu”
on page 117.
Page 16
Page 16 of 126 Main menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
diff Displays the pending configuration changes. Only pending changes
made during your current administrator session are included. Pending
changes made by other CLI or browser-based interface (BBI)
administrator sessions are not included.
validate Validates pending configuration changes made during your current
administration session. This command does not include pending
changes made by other CLI or BBI administrator sessions.
When you enter the Validate command, your pending changes are
validated to ensure that they are complete and consistent. If problems
exist, warning or error messages are displayed.
• Warnings identify conditions that require special attention, but that do
not cause errors or prevent the configuration when you enter the
Apply command.
• Errors identify serious configuration problems that you must correct
before you apply the changes. Uncorrected errors cause the Apply
command to fail.
If the Validate command returns warning or error messages, heed the
messages and make any necessary configuration changes.
security Lists the status (enabled or disabled) for remote management features
such as Telnet, SSH, and BBI. The Security command also displays a list
of users still using default passwords that should be changed.
Table 1
Main menu commands
Command Description
Page 17
Main menu Page 17 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
apply Applies and saves configuration changes made during your current
administration session. Changes are considered pending and do not take
effect until you issue the Apply command. Pending changes made by
other CLI or BBI administrator sessions are not affected.
When issued, the Apply command first validates your session’s pending
changes. If problems exist, applicable warning and error messages are
displayed.
• Warnings identify conditions that require special attention, but that do
not cause errors or prevent the configuration when you enter the
Apply command.
• Errors identify serious configuration problems that you must correct
before you apply the changes. Uncorrected errors cause the Apply
command to fail.
If no errors exist, the changes are saved and put into effect.
If multiple CLI or BBI administrators apply changes to the same set of
parameters concurrently, the latest applied changes take precedence.
revert Cancels all pending configuration changes made during your current
administration session. The revert command does not affect:
• applied changes
• pending changes made by other CLI or BBI sessions
Table 1
Main menu commands
Command Description
Page 18
Page 18 of 126 Main menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
paste [<global key
import password>]
Restores a saved configuration dump file that includes encrypted private
keys.
When you create a configuration dump using the Dump command, you
create a password to decrypt the private keys. When you enter the Paste
command, you are prompted to supply the password. The password
phrase remains in effect until cleared.
Note: To clear the password phrase, enter the Paste command again.
You can then open the configuration dump file in your text editor, copy the
information, and paste it to the CLI window. After you paste the
information, the SMC batch processes the configuration content. The
pasted configuration enters as a pending configuration, and any included
private keys are decrypted. You can use the global Diff command to view
the pending configuration changes. To apply the pending configuration
changes, use the global Apply command.
help
[<menu command>]
Provides brief information about the specified command. When used
without a parameter, the Help command displays a list of global
commands.
exit Logs off the current session and exits the CLI. Pending changes made
during your current session are lost if not applied. This command does
not affect other open CLI or BBI sessions.
Table 1
Main menu commands
Command Description
Page 19
Page 19 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
28
Information menu
The Information menu (/info) provides access to information about the
current status of the SMC.
Table 2 identifies and describes the Information menu commands.
Table 2
Information menu (/info)
Command Description
summary Displays runtime information for the host SMC. The runtime information
includes the host IP address, the host type, whether the host owns the
cluster Management IP (MIP) address, CPU usage, memory usage, and
operational status.
clu Displays runtime information for all SMCs in the cluster. The runtime
information includes:
•CPU usage
• hard disk usage
• status of important applications such as Web server, SNMP, and
Internet server
• secure UNIStim proxy and firewall information
Page 20
Page 20 of 126 Information menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
host Displays runtime information for the specified SMC host. The runtime
information includes:
•CPU usage
• hard disk usage
• status of important applications such as Web server, SNMP, and
Internet server
• secure UNIStim proxy and firewall information
For menu items, see “Info_host menu” on page 22.
net Displays the current network configuration. This information is the same
information that the /cfg/net/cur command provides. For menu items, see
“Information_net menu” on page 23.
admin Provides access to administration menu items, such as accesslist, Telnet,
SSH, Web, and UPS configurations. For menu items, see “Administration
Information menu” on page 25.
log Displays configuration and UNIStim log archiving information, including
the e-mail address to which the SMC can send the log files upon log
rotation.
stats Displays the Statistics menu. For menu items, see “Statistics Information
menu” on page 26.
ethereal Displays the text-based interface of ethereal, which provides information
about the traffic log. It also can dump the output to the console, a USB
memory stick, or a remote device using the ftp/sftp/scp/tftp command.
sensor Displays the current status of hardware parameters such as temperature
and fan rotation per minute (RPM) status.
The sensor module generates alarm events when the fan RPM values
reach the critical level or when the temperature reaches the maximum
level.
Table 2
Information menu (/info)
Command Description
Page 21

Information menu Page 21 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
about Displays system information such as the product type and version of the
running build.
alarms Lists the alarms generated in the system.
dump Displays the current configuration information available in the Information
menu.
Table 2
Information menu (/info)
Command Description
Page 22
Page 22 of 126 Information menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Info_host menu
The Info_host menu (/info/host) provides configuration, status, and statistics
information about the host runtime, link, Ethernet, and syslog parameters.
Table 3 identifies and describes the Info_host menu commands.
Table 3
Info_host menu (/info/host)
Command Description
status
<Host number>
Displays the runtime and application status for the specified host.
link Displays the status information for all network interface ports. The
auto-negotiate status and link status (Up or Down) are always displayed. If
the link status is UP, the port speed and the duplex mode are also displayed.
ether Displays the statistics of all interfaces configured in the cluster. The statistics
are Rx Count, Tx Count, Rx Bytes, Tx Bytes, and so on.
syslog Displays the last 100 syslog messages. After each set of 10 syslog
messages is displayed, you are prompted to continue the display (y) or exit
(n).
fwlog Displays the last 100 fwlog messages. After each set of 10 fwlog messages
is displayed, you are prompted to continue the display (y) or exit (n).
usecplog Displays the last 100 usecplog messages. After each set of 10 usecplog
messages is displayed, you are prompted to continue the display (y) or exit
(n).
Page 23
Information menu Page 23 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Information_net menu
The Information_net menu (/info/net) shows the interface, route, and VRRP
details.
Table 4 identifies and describes the Info_net menu commands.
Route Information menu
The Route Information menu (/info/net/route) provides access to information
about static routes.
Table 5 identifies and describes the Route Information menu commands.
Table 4((
Info_net menu (/info/net)
Command Description
if Displays the interface details such as the ID, IP address and netmask, port
assignment, operational status, and Virtual LAN (VLAN) number.
arp Displays the ARP entries in the cluster.
gw Displays the default gateway configured in the cluster.
route Displays the Route Information menu. For menu items, see “Route
Information menu” on page 23.
vrrp Displays the VRRP Information menu, which displays Virtual Router
Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) configuration and status information. For
menu items, see “VRRP Information menu” on page 24.
Table 5
Route Information menu (/info/net/route)
Command Description
static Displays all static routes configured on the system.
Page 24
Page 24 of 126 Information menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
VRRP Information menu
The VRRP Information menu (/info/net/vrrp) provides access to information
about the status and configuration of VRRP.
Table 6 identifies and describes the VRRP Information menu commands.
Table 6
VRRP Information menu (/info/net/vrrp)
Command Description
status Displays the status for the VRRP Virtual Router ID (vrid).
cfg Displays the VRRP settings such as high availability (HA), VRRP
advertisement interval, gratuitous ARP (GARP) delay interval, GARP
broadcast interval, Advanced Failover Check (AFC), and Preferred Master
details.
Page 25
Information menu Page 25 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Administration Information menu
The Administration menu (/info/admin) provides access to information about
accesslist, Telnet, SSH, Web, and UPS configurations.
Table 7 identifies and describes the Administration Information menu
commands.
Table 7
Administration Information menu (/info/admin)
Command Description
accesslist Displays the access rights configured for the cluster and displays the list of
enabled networks accessing the SMC cluster from the remote sites.
telnet Displays the current Telnet configuration settings: enabled or disabled.
ssh Displays the current SSH configuration settings: enabled or disabled.
web Displays the current BBI configuration settings such as status (enabled or
disabled), service port number for HTTP and HTTPS, and certificate
information for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Page 26
Page 26 of 126 Information menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Statistics Information menu
The Statistics Information menu (/info/stats) provides access to information
about SMC statistics.
Table 8 identifies and describes the Statistics Information menu commands.
Table 8
Statistics Information menu (/info/stats)
Command Description
fwattack Displays historical statistics for approximately 130 firewall attacks against which
the SMC provides protection. Only attacks within the previous day are listed. For
each type of attack, this command displays a count of how many times it
occurred in the current hour, the past hour, and the past day. If no attacks
occurred, the list is empty.
fwsession Displays a list of current sessions in use on the SMC. The list entry for each
session contains the source IP, destination IP, the protocol, the destination port,
and the number of bytes transferred.
Page 27
Information menu Page 27 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
fwpolicy Lists the number of times a firewall policy was successfully matched for a stream
of traffic and the number of times a match was not made. The statistics for the
current hour, past hour, and day total are displayed.
unistim Displays relevant statistics for the UNIStim servers:
• server statistics: total number of servers configured on SMC
• client statistics:
— number of secure clients currently connected through the SMC
— number of non-secure clients currently connected through the SMC
— cumulative number of secure clients connected through SMC from when the SMC
was started until present
— cumulative non-secure clients connected through SMC from when the SMC was
started until present
• policy statistics:
— number of times the Allow Policy is triggered for the secure or non-secure clients
— number of times the Switch Policy is triggered for the clients to force non-secure
clients to reconnect in secure mode
— number of times the Deny Policy is triggered for the secure or non-secure clients
•errors:
— number of invalid or out of sequence packets arrived from the server causing the
SMC to send a NAK to the server
— number of errors on the Secure UNIStim proxy due to lack of resources
— number of invalid or out of sequence packets arrived from the client causing the
SMC to send a negative acknowledgement (NAK) to the client
— number of packets that are not in the expected state causing a bad transition in
the state machine of UsecProxy
— number of clients that come in as secure but have an invalid fingerprint of the
SMC Public Key
— Number of clients that are deleted as a result of too many server retransmissions
Table 8
Statistics Information menu (/info/stats)
Command Description
Page 28

Page 28 of 126 Information menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Page 29
Page 29 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
112
Configuration menu
Using the Configuration menu (/cfg), you can configure the SMC. Some
commands are available only from the administrator logon.
Table 9 identifies and describes the Configuration menu commands.
Table 9
Configuration menu (/cfg)
Command Description
sys Displays the System menu, which you can use to configure
system-wide parameters. For menu items, see “System
menu” on page 32.
net Displays the Network Configuration menu, which you can
use to configure the networks passing traffic through the
SMC. For menu items, see “Network Configuration menu” on
page 72.
smc Displays the Multimedia Security menu, which you can use
to configure multimedia security on the SMC. For menu
items, see “Multimedia Security menu” on page 81.
Page 30
Page 30 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
ptcfg <SCP/SFTP/TFTP/FTP
server> <server host name/IP
address> <file name>
Saves the current configuration, including private keys and
certificates, to a file on the selected server. The information
is saved in a plain-text file, and you can later restore the
configuration by using the gtcfg command.
The supported servers are:
•SCP
•SFTP
•TFTP
•FTP
The SCP and SFTP protocols are secure and encrypted.
TFTP and FTP are encrypted. When saving a configuration
to a secure server, you are prompted to specify a password.
Table 9
Configuration menu (/cfg)
Command Description
Page 31

Configuration menu Page 31 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
gtcfg <SCP/SFTP/TFTP/FTP
server> <file name>
Retrieves and applies the configuration file, including private
keys and certificates, from the selected server. If the server
is secure, such as the SCP and SFTP servers, you are
prompted to enter the same password phrase supplied when
the file was created using the ptcfg command.
You must reboot the SMC after restoring a configuration
using the gtcfg command.
dump Displays the current configuration parameters in CLI
compatible format. You can copy and save the configuration
information to a text editor file by performing a
copy-and-paste operation.
To view the pending configuration changes resulting from the
batch processing, use the Diff command. To apply the
configuration changes, use the Apply command.
If you choose to include private keys in the configuration
dump, you are required to specify a password phrase. The
password phrase enables encryption. When restoring a
configuration that includes secret information, use the global
Paste command. Before pasting the configuration, you are
prompted to reenter the password phrase.
Table 9
Configuration menu (/cfg)
Command Description
Page 32

Page 32 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
System menu
Using the System menu (/cfg/sys), you can configure system-wide
parameters.
Table 10 identifies and describes the System menu commands.
Table 10
System menu (/cfg/sys)
Command Description
time Configures the date, time, time zone, and Network Time Protocol
(NTP). For menu items, see “Date and Time menu” on page 33.
dns Changes Domain Name System (DNS) parameters. For menu items,
see “DNS Servers menu” on page 35.
cluster Displays the Host Information menu, which you can use to configure
the host IP address and cluster management IP (MIP) address for the
SMC host. You can also assign a physical port to the SMC host. For
menu items, see “Cluster menu” on page 36.
accesslist Displays the Access List menu, which you can use to restrict remote
access to SMC management features. You can add, delete, or list
trusted IP addresses that are allowed Telnet, Secure Shell (SSH), or
Browser-Based Interface (BBI) access to the SMC. For menu items,
see “Access List menu” on page 39.
adm Displays the Administrative Application menu, which you can use to
configure idle timeout and SMC remote management features such as
Telnet, SSH, SNMP, and BBI. For menu items, see “Administrative
Applications menu” on page 41.
Page 33

Configuration menu Page 33 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Date and Time menu
Using the Date and Time menu (/cfg/sys/time), you can configure the system
date, time, and time zone options.
Table 11 identifies and describes the Date and Time menu commands.
log Displays the Platform Logging menu, which you can use to configure
system message logging features. Messages can be logged to the
system console terminal and archived to a file for automatic e-mailing.
For menu items, see “Platform Logging menu” on page 60.
user Displays the User menu, which you can use to add, modify, delete, or
list SMC user accounts and change passwords. For menu items, see
“User menu” on page 68.
Table 11
Date and Time menu (/cfg/sys/time)
Command Description
date
<
YYYY-MM-DD>
Sets the system date according to the specified format.
time <HH:MM:SS> Sets the system time using a 24-hour clock format.
Nortel recommends that you reboot the SMC after entering a time
change that is greater than 1 minute.
tzone Sets the system time zone. When entered without a parameter, you are
prompted to select your time zone from a list of continents/oceans,
countries, and regions.
ntp Displays the NTP menu, which you can use to synchronize system time
with Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers. For menu items, see “NTP
menu” on page 34.
Table 10
System menu (/cfg/sys)
Command Description
Page 34

Page 34 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
NTP menu
Using the NTP menu (/cfg/sys/time/ntp), you can add or delete Network Time
Protocol (NTP) servers that synchronize system time.
Table 12 identifies and describes the NTP menu commands.
Table 12
NTP menu (/cfg/sys/time/ntp)
Command Description
list Lists all configured NTP servers by their index number and IP
address.
del <index number> Removes an NTP server from the configuration by specifying the
server index number. Use the List command to display the index
numbers and IP addresses of configured NTP servers.
add
<NTP server IP address>
Adds an NTP server to the list of NTP servers, which are used to
synchronize the SMC system clock. Add at least three NTP servers
to compensate for any discrepancies among the servers.
Page 35

Configuration menu Page 35 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
DNS Servers menu
Using the DNS Servers menu (/cfg/sys/dns), you can change Domain Name
System (DNS) parameters.
Table 13 identifies and describes the DNS Servers menu commands.
Table 13
DNS Servers menu (/cfg/sys/dns)
Command Description
list Displays all DNS servers by their index number and IP address.
del <index number> Removes a DNS server by index number. If required, use the List
command to display the index numbers and IP addresses of
added DNS servers.
add
<DNS server IP address>
Adds a new DNS server.
insert <index number>
<IP address>
Adds a new DNS server to the list at the specified index position.
All existing items at the specified index number and higher are
incremented by one position.
move <from index number>
<to index number>
Removes the DNS server from the specified index number and
inserts it at the specified index number.
Page 36

Page 36 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Cluster menu
Using the Cluster menu (/cfg/sys/cluster), you can configure the SMC host IP
address and cluster Management IP (MIP) address.
Table 14 identifies and describes the Cluster menu commands.
Table 14
Cluster menu (/cfg/sys/cluster)
Command Description
mip
<Management IP address>
Specifies the Cluster Management IP (MIP) address. The
cluster MIP address must be unique. Assign a cluster MIP
address that resides on the same subnet as the SMC host IP.
The cluster MIP address supports clustered SMCs in a high
availability (HA) configuration; however, you must configure the
cluster MIP address even if you do not have an HA
configuration.
host
<cluster host number>
Provides access to the Cluster Host menu for the specified
host. For menu items, see “Cluster Host menu” on page 37.
Page 37

Configuration menu Page 37 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Cluster Host menu
Using the Cluster Host menu (/cfg/sys/cluster/host), you can change
parameters for the SMC host. To identify the host number, use the
/cfg/sys/cluster/cur command.
Table 15 identifies and describes the Cluster Host menu commands.
Table 15
Cluster Host menu (/cfg/sys/cluster/host <cluster host number>)
Command Description
ip <host IP address> Specifies the IP address of the selected host. Changing this address
does not affect the cluster MIP address that defines the cluster. After
you apply the new IP address using the Apply command, the system
logs you off.
name Specifies a name for each SMC. When you log on as the
administrator, the name of the SMC appears as part of the banner.
licence Allows you to enter a Secure UNIStim license into the SMC cluster.
The license parameter determines how many Secure UNIStim users
are supported by the SMC. The license is associated with the MAC
address of port 1 on the SMC.
To enter a license, follow the prompts and paste the license string
directly into the CLI. When complete, press <Enter> to go to a new
line and then type three periods (...) to terminate the command
sequence. The license will be automatically stored on the particular
SMC.
In an HA cluster, two licenses are required to support secure UNIStim:
one on each SMC in the cluster.
Note 1: The license restriction applies only to secure UNIStim users.
Note 2: Ty p e cur within the Cluster Host screen to see the current
license for the SMC.
Page 38

Page 38 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
mac Displays the MAC address of port 1 on the SMC host. This MAC
address is used to generate the secure UNIStim license for that
particular device. To increase the number of secure UNIStim users in
an SMC cluster, you need to access the MAC address of each SMC
device using this command and send the MAC address back to Nortel
for license generation.
hwplatform Displays the hardware platform model number.
halt [y | n] Stops the selected host. Always use this command only before turning
off the device.
If the host is isolated from the cluster, you receive an error message
when performing the Halt command. You must log on log on to the
host using either its local serial port or through remote access to the
host IP address before you use the Halt command in the boot menu.
See “halt” on page 113.
Table 15
Cluster Host menu (/cfg/sys/cluster/host <cluster host number>)
Command Description
Page 39

Configuration menu Page 39 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Access List menu
Administrators can manage the SMC remotely using Telnet, SSH, or the BBI
and acquire various status parameters using SNMP. For security purposes,
access to these features is restricted to authorized clients through the access
list.
Using the access list menu (/cfg/sys/accesslist), you can specify IP addresses
or address ranges that are permitted remote access to the system. There is only
one access list, which applies to all remote management features. By default,
the management network is added to the access list.
reboot [y | n] Reboots the selected host. If the host is isolated from the cluster, you
receive an error message when performing the Reboot command. You
must log on log on to the host using either its local serial port or
through remote access to the host IP address before you use the
Reboot command in the boot menu. See “reboot” on page 113.
delete Removes the selected host from the cluster and resets the removed
host to its factory default configuration. The other host in the cluster is
unaffected.
To ensure that you removed the intended host, view the current
settings using the Cur command. To view the host number, type, and
IP address for both hosts in a cluster, use the /cfg/sys/cluster/cur
command string.
After you remove a host from the cluster using the Delete command,
you can access the device only through a console terminal connected
to its local serial port. You can log on using the administration account
(admin) and the default password (admin) to access the Setup menu.
When two hosts are present in a cluster, you cannot delete a particular
host if it is the only host with a health status of Up. In this case, you
receive an error message when performing the Delete command.
Table 15
Cluster Host menu (/cfg/sys/cluster/host <cluster host number>)
Command Description
Page 40

Page 40 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Requests for remote management access from any client whose IP address is
not on the access list are dropped. You can ping the SMC host from an IP
address not listed in the access list. When you add a client IP address to the
access list, that client can access all enabled remote management features.
Table 16 identifies and describes the Access List menu commands.
Table 16
Access List menu (/cfg/sys/accesslist)
Command Description
list Displays index and IP address information for the trusted clients
that can access enabled remote management features.
del <index number> Removes the specified access list entry by index number.
add <user network IP
address> <IP subnet
mask>
Adds the specified IP address or range of addresses to the access
list.
Page 41

Configuration menu Page 41 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Administrative Applications menu
Using the Administrative Applications menu (/cfg/sys/adm), you can enable
the SMC remote management features such as Telnet, SSH, SNMP, and the
BBI.
Table 17 identifies and describes the Administrative Application menu
commands.
Table 17
Administrative Application menu (/cfg/sys/adm)
Command Description
idle <CLI time-out period in
seconds (300-604800)>
Specifies the amount of time, in terms of seconds, that a CLI
or BBI session can remain inactive before automatically
logging off. The default value is 300 seconds, which equates
to 10 minutes. The maximum is 604800.
If a user makes changes to the SMC configuration and the
CLI or BBI times out before the user applies them, all
changes are lost.
telnet Enables or disables Telnet sessions for remote access to the
SMC management CLI. For menu items, see “Telnet
Administration menu” on page 42.
You need to add an entry into the access list for the client
before it can administer the SMC through Telnet. See
“Access List menu” on page 39.
ssh Enables or disables Secure Shell (SSH) for remote access to
the SMC management CLI. You can also generate SSH host
keys. For menu items, see “SSH Administration menu” on
page 43.
You need to add an entry into the access list for the client
before it can administer the SMC through SSH. See “Access
List menu” on page 39.
Page 42

Page 42 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Telnet Administration menu
Using the Telnet Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/telnet), you can enable
or disable remote Telnet access to the SMC CLI. By default, Telnet access is
disabled.
Note: Telnet is not a secure protocol. All data (including the password)
between a Telnet client and the SMC is unencrypted and
unauthenticated. Depending on the severity of your security policy, you
can enable Telnet access and restrict it to one or more trusted clients.
web Configures the Browser-Based Interface (BBI). The BBI
provides HTTP or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) access for
remote management of the SMC using a Web browser. For
menu items, see “Web Administration menu” on page 45.
You need to add an entry into the access list for the client
before it can administer the SMC through the BBI. See
“Access List menu” on page 39.
snmp Controls Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
read access and enables or disables SNMP event and alarm
messages for the SMC. You can also define SNMP
information, permission levels, and traps. For menu items,
see “SNMP Administration menu” on page 50.
You need to add an entry into the access list for the client
before it can issue requests to the SMC through SNMP. See
“Access List menu” on page 39.
audit Configures the servers to receive log messages on the
commands executed in the CLI and the Web user interface
(UI). For menu items, see “Audit menu” on page 56.
auth Configures RADIUS authentication. For menu items, see
“Authentication menu” on page 59.
Table 17
Administrative Application menu (/cfg/sys/adm)
Command Description
Page 43

Configuration menu Page 43 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 18 identifies and describes the Telnet Administration menu commands.
SSH Administration menu
Using the SSH Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh), you can enable or
disable Secure Shell (SSH) for remote access to the SMC management CLI.
You can also generate SSH host keys.
An SSH connection enables secure management of the SMC from any
workstation connected to the network. SSH access provides server host
authentication, encryption of management messages, and encryption of
passwords for user authentication. By default, SSH is disabled.
Table 18
Telnet Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/telnet)
Command Description
ena Enables the Telnet management feature. When enabled, trusted
clients on the access list can access the host IP address through
Te l ne t .
dis Disables the Telnet management feature. When disabled, all active
Telnet administration sessions are terminated, and all Telnet
requests sent to the host IP address are dropped.
The SMC uses iptables to implement access control to its
management interfaces (SSH, Telnet, HTTP, and HTTPS). Iptables
inspect packets above SMC-1 in the TCP/IP stack. The SMC can
limit external access to internal system management software that
uses sockets to communicate.
Page 44

Page 44 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 19 identifies and describes the SSH Administration menu commands.
SSH Host Keys menu
Using the SSH Host Keys menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh/sshkeys), you can generate
and manage SSH host keys.
Table 20 identifies and describes the SSH Administration menu commands.
Table 19
SSH Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh)
Command Description
ena Enables the SSH management feature. When enabled, trusted
clients on the access list can access the host IP address through
SSH.
dis Disables the SSH management feature. When disabled, all active
SSH administration sessions are terminated, and all SSH requests
sent to the host IP address are dropped.
sshkeys Configures and manages SSH host keys. For menu items, see “SSH
Host Keys menu” on page 44.
Table 20
SSH Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh/sshkeys)
Command Description
generate Generates new SSH host keys.
show Displays a list of current SSH host keys for the cluster.
knownhosts Manages SSH host keys of remote hosts. For menu items, see “SSH
Known Host Keys menu” on page 45.
Page 45
Configuration menu Page 45 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
SSH Known Host Keys menu
Using the SSH Known Host Keys menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh/sshkeys/
knownhosts), you can manage SSH host keys of remote hosts.
Table 21 identifies and describes the SSH Administration menu commands.
Web Administration menu
Using the Web Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web), you can configure
the Browser-Based Interface (BBI). The BBI is a remote management tool,
which you can use to access the SMC using a Web browser. You can
configure the BBI to use HTTP (non-secure), HTTPS with Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL), or both.
Table 22 identifies and describes the Web Administration menu commands.
Table 21
SSH Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/ssh/sshkeys/knownhosts)
Command Description
list Lists known SSH keys of remote hosts.
del Deletes SSH host key by index values.
add Adds a new SSH host key.
import Retrieves SSH keys of remote hosts.
Table 22
Web Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web)
Command Description
http Configures BBI access using HTTP (non-secure). For menu items,
see “HTTP Configuration menu” on page 46.
ssl Configures BBI access using HTTPS with Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL). For security reasons, Nortel recommends that you use SSL
with the BBI. For menu items, see “SSL Configuration menu” on
page 46.
Page 46

Page 46 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
HTTP Configuration menu
Using the HTTP Configuration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/http), you can
configure BBI access using HTTP. By default, HTTP access is enabled, but
restricted to trusted clients. Depending on the severity of your security policy,
you can disable HTTP access and refine the list of trusted clients.
Note: HTTP is not a secure protocol. All data (including passwords)
between an HTTP client and the SMC is unencrypted and
unauthenticated. If secure remote access is required, see the “SSL
Configuration menu” on page 46.
Table 23 identifies and describes the HTTP Configuration menu commands.
SSL Configuration menu
Using the SSL Configuration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl), you can
configure BBI access using HTTPS. HTTPS uses Secure Sockets Layer
(SSL) to provide server host authentication, encryption of management
messages, and encryption of passwords for user authentication. For security
reasons, Nortel recommends that you use SSL with the BBI. By default, SSL
is disabled.
Table 23
HTTP Configuration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/http)
Command Description
port <HTTP port number> Specifies the logical HTTP port used by the built-in BBI Web
server. By default, the Web server uses HTTP port 80. You can
specify any port number except ports used by other services.
ena Enables HTTP access to the BBI. When enabled, trusted clients
on the access list can access the host IP address through HTTP.
See “Access List menu” on page 39.
dis Disables HTTP access to the BBI. When disabled, HTTP requests
to the host IP address are dropped.
Page 47

Configuration menu Page 47 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
In addition to enabling and disabling the HTTPS feature, you can configure
the HTTPS port, SSL version, and access menus for generating SSL
certificates.
Table 24 identifies and describes the SSL Configuration menu commands.
Table 24
SSL Configuration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl)
Command Description
port <HTTPS port
number>
Specifies the logical HTTPS port for the built-in BBI Web server. By
default, the Web server uses HTTPS port 443. You can specify any
port number except ports used by other services.
ena Enables HTTPS access to the BBI. When enabled, trusted clients on
the access list can access the host IP address through HTTPS. See
“Access List menu” on page 39.
You must generate an SSL certificate using the Certificate
Management menu to use HTTPS functions. See “Certificate
Management menu” on page 48.
dis Disables HTTPS access to the BBI. When disabled, HTTPS requests
to the host IP address are dropped.
tls y | n Enables or disables Transport Level Security (TLS) for SSL.
sslv2 y | n Enables or disables SSL Version 2.
sslv3 y | n Enables or disables SSL Version 3.
certs Configures server certificates and external Certificate Authority
certificates required for SSL. See “Certificate Management menu” on
page 48 for menu items.
Page 48

Page 48 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Certificate Management menu
Using the Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs), you
can add or remove server certificates and external Certificate Authority (CA)
certificates required for SSL.
Table 25 identifies and describes the Certificate Management menu
commands.
Table 25
Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs)
Command Description
serv Generates a certificate request or creates a self-signed certificate.
For menu items, see “Server Certificate Management menu” on
page 49.
ca Provides management functions for intermediate CA certificates.
CA certificate management is a required task if server certificates
from external CAs are used. For menu items, see “CA Certificate
Management menu” on page 50.
Page 49

Configuration menu Page 49 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Server Certificate Management menu
Using the Server Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs/
serv), you can administer SSL server certificates.
Table 26 identifies and describes the Server Certificate Management menu
commands.
Table 26
Server Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs/serv)
Command Description
gen <Common Name>
<Country Code>
<Key Size>
Generates a certificate request or a self-signed certificates.
exp Exports certificate requests to an external Certificate Authority
(CA). This command produces output that you can copy and paste
into a text file and then send to the CA for authorization. Do not use
this command if to create a self-signed certificate. After the CA
responds with a Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM) certificate, use the
Add command to enter the certificate into the system.
list Displays a list of configured server certificates.
del Deletes a server certificate.
add Adds a signed server certificate. After you enter this command, the
system expects you to paste the PEM certificate into the CLI. When
you finish pasting the certificate, add three periods (...) and press
<Enter> to return to the CLI.
Page 50

Page 50 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
CA Certificate Management menu
Using the CA Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs/ca),
you can administer SSL external CA certificates.
Table 27 identifies and describes the CA Certificate Management menu
commands.
SNMP Administration menu
The SMC software supports elements of the Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP). If you are running an SNMP network management station
on your network, you can read SMC configuration information and statistics
using the following SNMP Managed Information Bases (MIBs):
• MIB II (RFC 1213)
• SMC private MIBs
You can access private MIBs using the cluster MIP address. The information
is the same regardless of which SMC device in a cluster is accessed. This is
not the case for the MIB-II information because the information is specific to
the accessed SMC.
Table 27
CA Certificate Management menu (/cfg/sys/adm/web/ssl/certs/ca)
Command Description
list Lists all configured CA certificates.
del Removes a CA certificate from the configuration.
add Adds an intermediate CA certificate. After you enter this command,
the system expects you to paste the PEM certificate into the CLI.
When you finish pasting the certificate, add three periods (...) and
press <Enter> to return to the CLI.
Page 51

Configuration menu Page 51 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 28 identifies and describes the SNMP Administration menu
commands.
Table 28
SNMP Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp)
Command Description
ena Enables SNMP features.
dis Disables SNMP features.
model v1 | v2c |
usm
Specifies the form of SNMP security:
• v1: SNMP version 1
• v2c: SNMP version 2C security model
• usm: SNMP version 3 User-based Security Model (USM)
level auth | priv Specifies the desired degree of SNMP USM security:
• none: no security.
• auth: Verify the SNMP user password before granting SNMP access.
SNMP information is transmitted in plain text.
• priv: Verify the SNMP user password before granting SNMP access and
encrypt all SNMP information with the user’s individual key.
Use this command when usm is selected using the Model command.
USM user names, along with their passwords and encryption keys, are
defined in the SNMP Users menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/users) on page 52.
access d | r Enables or disables access for the read community.
events y | n Enables or disables the automatic delivery of event messages to the SNMP
trap hosts. When enabled, messages regarding general occurrences, such
as detection of new components, are sent.
alarms y | n Enables or disables the automatic delivery of alarm messages to the SNMP
trap hosts. Alarm messages indicate serious conditions that can require
administrative action.
Page 52

Page 52 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
SNMP Users menu
Using the SNMP Users menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/users), you can list, add,
and remove USM users. When usm is selected as the security model (/cfg/sys/
adm/snmp/model), SNMP access is granted only for user/password
combinations defined both in this menu and in the Access List menu. See
“Access List menu” on page 39.
rcomm Displays the current read community value. You can change the value.
There is no restriction on the input string. The default read community value
is Public.
users Displays the SNMP Users menu, which you can use to list, add, and
remove USM users. When usm is selected as the security model, SNMP
access is granted only for the user/password combination that is defined in
both the SNMP Users menu and in the Access List menu. For menu items,
see “SNMP Users menu” on page 52.
hosts Displays the Trap Hosts menu, which you can use to add, remove, or list
hosts that receive event or alarm messages. For menu items, see “Trap
Hosts menu” on page 54.
system Displays the SNMP System Information menu, which you can use to
configure basic identification information such as support contact name,
system name, and system location. For menu items, see “SNMP System
Information menu” on page 55.
adv Displays the Advanced SNMP Settings menu, which you can use to
configure advanced SNMP options. For menu items, see “Advanced SNMP
Settings menu” on page 56.
Table 28
SNMP Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp)
Command Description
Page 53

Configuration menu Page 53 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 29 identifies and describes the SNMP Users menu commands.
Table 29
SNMP Users menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/users)
Command Description
list Lists all configured USM users.
del <user name> Removes a USM user from the configuration.
add <user name> Adds a USM user. You are prompted to enter the following:
• get and/or trap: Specify whether the user is authorized to perform
SNMP get requests, receive enabled trap event and alarm
messages, or both.
• authorization password (and confirmation): Specify the password
the user must enter for access.
• encryption string (and confirmation): If the level priv option is
selected on the SNMP Administration menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp),
you can encode SNMP traffic between the user and the SMC
using the encryption string.
Page 54

Page 54 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Trap Hosts menu
Using the Trap Hosts menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/hosts), you can add, remove,
or list hosts that receive SNMP event or alarm messages from the SMC
cluster.
Table 30 identifies and describes the Trap Hosts menu commands.
Table 30
Trap Hosts menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/hosts)
Command Description
list Lists all configured trap hosts that receive SNMP event or alarm
messages from the SMC cluster.
del <index number> Removes an SNMP trap host from the cluster configuration by
specifying the trap host index number. Use the List command to
display the index numbers and IP addresses of configured trap
hosts.
add <trap host IP address>
<port number>
<community string>
<trap user>
Adds an SNMP trap host. The trap host with the specified IP
address receives any enabled SNMP messages from the SMC.
You are prompted to enter a port number, community string, and
trap user information.
You can independently enable or disable event messages and
alarm messages in the SNMP Administration menu. See “SNMP
Administration menu” on page 50.
insert <index number>
<IP address>
Adds a new trap host IP address to the access list at the specified
index position. All existing items at the specified index number
and higher are incremented by one position.
move <from index number>
<to index number>
Removes the trap host IP address at the specified from index
number and inserts it at the specified to index number in the
access list.
Page 55

Configuration menu Page 55 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
SNMP System Information menu
Using the SNMP System Information menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/system),
you can configure basic identification information such as support contact
name, system name, and system location.
Table 31 identifies and describes the SNMP System Information menu
commands.
Table 31
SNMP System Information menu
Command Description
contact <new string,
maximum 64 characters>
Configures the name of the system contact. The contact can have
a maximum of 64 characters.
name <new string,
maximum 64 characters>
Configures the name for the system. The name can have a
maximum of 64 characters.
loc <new string, maximum
64 characters>
Configures the name of the system location. The location can
have a maximum of 64 characters.
Page 56

Page 56 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Advanced SNMP Settings menu
Using the Advanced SNMP Settings menu (/cfg/sys/adm/snmp/adv), you can
configure advanced SNMP options.
Table 32 identifies and describes the Advanced SNMP Settings menu
commands.
Audit menu
Using the Audit menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit), you can configure a RADIUS
server to receive log messages about commands executed in the CLI or the
BBI. If auditing is enabled but no RADIUS server is configured, events still
generate to the event log and any configured firewall logs. Auditing is
disabled by default.
An event is generated whenever a user logs on, logs off, or issues a command
from a CLI session. The event contains information about the user name, the
session ID, and the name of executed commands. This event is optionally sent
to a RADIUS server for audit trail logging according to RFC 2866 (RADIUS
Accounting).
Table 32
Advanced SNMP Settings menu
Command Description
trapsrcip
auto | unique | mip
Configures the source IP address for SNMP traps generated from the
SMC:
• auto: The IP address of the outgoing interface. This is the default IP
address.
• unique: The IP address of the individual SMC.
• mip: The IP address of the cluster MIP.
Note: The MIP setting is useful with applications that expect devices
to be limited to only one IP address.
Page 57

Configuration menu Page 57 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 33 identifies and describes the Audit menu commands.
Table 33
Audit menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit)
Command Description
servers Displays the RADIUS Audit Servers menu. For menu items, see
“RADIUS Audit Servers menu” on page 58.
vendorid Assigns the SMI Network Management Private Enterprise Code
(as defined by IANA in the file http://www.iana.org/assignments/
enterprise-number) to the following vendor specific attribute:
Vendor-Id.
The Vendor-Id (represented by the private enterprise number) is
one of the RADIUS vendor-specific attributes.
The default vendor-Id is 1872 (Nortel).
Note: If your RADIUS system uses another Vendor-ID, you can
use the Vendorid command to bring the RADIUS configuration in
line with the value used by the remote RADIUS system. Contact
your RADIUS system administrator for more information.
vendortype Assigns a number to the following vendor-specific attribute used in
RADIUS: Vendor type.
Used in combination with the Vendor-Id number, the vendor type
number identifies the audit attribute that contains the audit
information.
The default vendor type value is 2.
Note 3: To find audit entries in the RADIUS server log, define a
suitable string in the RADIUS server dictionary (for example,
Nortel-SMC-Audit-Trail) and map this string to the vendor type
value.
Note 4: If your RADIUS system uses another number for vendor
type, you can use the Vendortype command to bring the RADIUS
configuration in line with the value used by the remote RADIUS
system. Contact your RADIUS system administrator for more
information.
Page 58

Page 58 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
RADIUS Audit Servers menu
Using the RADIUS Audit Servers menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit/servers), you
can add, modify, and delete information about RADIUS audit servers.
Table 34 identifies and describes the Radius Audit Servers menu commands.
ena Enables the RADIUS server.
dis Disables the RADIUS server.
Table 34
Radius Audit Servers menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit/servers)
Command Description
list Lists the IP addresses and index numbers of configured
RADIUS audit servers.
del Removes the specified RADIUS audit server from the
configuration.
add <IP address>
<TCP port number> <shared
secret>
Adds a RADIUS audit server to the configuration. Specify the IP
address, a TCP port number, and the shared secret. The next
available index number is automatically assigned by the system.
For backup purposes, you can add several RADIUS audit
servers. The SMC contacts the server with the lowest index
number first. If the SMC cannot contact the server, the SMC
tries to contact the server with the next index number in
sequence, and so on.
Note: The default port number used for RADIUS audit is 1813.
Table 33
Audit menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit)
Command Description
Page 59

Configuration menu Page 59 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Authentication menu
Using the Authentication menu (/cfg/sys/adm/auth), you can configure
RADIUS authentication.
Table 35 identifies and describes the Authenticating menu commands.
RADIUS Authentication Servers menu
Using the RADIUS Authentication Servers menu (/cfg/sys/adm/auth/
servers), you can add, modify, and delete information about RADIUS
authentication servers.
insert
<index number to insert at>
<IP address of RADIUS
audit server to add>
Adds a RADIUS audit server and assigns the specified index
number to it. RADIUS audit servers have their current index
number incremented by one under the following condition: the
index number is higher than the one you specify. The shared
secret refers to the RADIUS server password.
move
<index number to move>
<destination index number>
Moves a RADIUS audit server up or down in the list of
configured servers. To view all servers currently added to the
configuration, use the List command.
Table 35
Authentication menu (/cfg/sys/adm/auth)
Command Description
servers Displays the RADIUS Authentication Servers menu. For menu items,
see “RADIUS Authentication Servers menu” on page 59.
timeout Specifies a timeout period for the RADIUS server.
fallback Enables the local password as fallback.
ena Enables RADIUS authentication.
dis Disables RADIUS authentication.
Table 34
Radius Audit Servers menu (/cfg/sys/adm/audit/servers)
Command Description
Page 60
Page 60 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 36 identifies and describes the Radius Authentication Servers menu
commands.
Platform Logging menu
Using the Platform Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log), you can configure system
message logging features. Messages can be logged to the system console
Table 36
Radius Authentication Servers menu (/cfg/sys/adm/auth/servers)
Command Description
list Lists the IP addresses and index numbers of configured
RADIUS authentication servers.
del Removes the specified RADIUS authentication server from
the configuration.
add <IP address>
<TCP port number>
<shared secret>
Adds a RADIUS authentication server to the configuration.
Specify the IP address, a TCP port number, and the shared
secret. The next available index number is automatically
assigned by the system.
For backup purposes, you can add several RADIUS
authentication servers. The SMC contacts the server with the
lowest index number first. If the SMC cannot contact the
server, the SMC tries to contact the server with the next index
number in sequence, and so on.
Note: The default port number used for RADIUS
authentication is 1813.
insert
<index number to insert at>
<IP address of RADIUS
authentication server to add>
Adds a RADIUS audit server and assigns the specified index
number to it. RADIUS audit servers have their current index
number incremented by one under the following condition:
the index number is higher than the one you specify. The
shared secret refers to the RADIUS server password.
move
<index number to move>
<destination index number>
Moves a RADIUS authentication server up or down in the list
of configured servers. To view all servers currently added to
the configuration, use the List command.
Page 61

Configuration menu Page 61 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
terminal and archived to a file that can be automatically e-mailed to an
administrator for debugging.
Table 37 identifies and describes the Platform Logging menu commands.
IMPORTANT!
Too many firewall logs can affect SMC performance. Nortel
recommends you update the firewall log configuration to prevent this
degradation in performance. For more information, see Secure
Multimedia Controller: Planning and engineering (NN42320-200).
Table 37
Platform Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log)
Command Description
syslog Displays the remote syslog menu, which you can use to configure the
system log (syslog) servers. After configuration, the SMC software can
send log messages to specified syslog hosts. For menu items, see
“System Logging menu” on page 62.
firewall Displays the Remote Firewall Log menu, which you can use to remotely
send firewall logs to an external system log server using the standard
remote syslog port.
Note: You can limit the logs by configuring firewall logging options in the
Message Logging menu. See “Message Logging menu” on page 90.
arch Displays the Log Archiving menu, which you can use to archive log files
after the file reaches a specific size or age. When log rotation occurs, the
current log file is stored or e-mailed to a specified address and a new log
file is created. For menu items, see “Log Archiving menu” on page 64.
Page 62

Page 62 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
System Logging menu
Using the System Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log/syslog), you can configure the
firewall logs. After configuration, the SMC software can send log messages
to specified syslog hosts.
Table 38 identifies and describes the System Logging menu commands.
debug y | n Enables or disables specialized debugging log messages. By default,
this setting is disabled. Enable it only as directed by Nortel technical
support.
sourceip
auto | uniqe | mip
Specifies the source IP address for logs generated from the SMC.
• auto: the IP address of the outgoing interface.
• unique: the IP address of the individual SMC.
• mip: the IP address of the cluster MIP.
The mip setting is useful with applications, such as HP OpenView, that
expect devices to be limited to only one IP address.
Table 38
System Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log/syslog)
Command Description
list Displays all configured firewall logs by their index number, IP
address, and facility number.
del <syslog index number> Removes the specified firewall log from the cluster configuration.
add <syslog server IP
address> <severity level>
Adds a new firewall log, including its IP address and local facility
number. The local facility number uniquely identifies syslog
entries.
Table 37
Platform Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log)
Command Description
Page 63

Configuration menu Page 63 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
insert <index number> <IP
address>
Adds a new firewall log to the list at the specified index position.
All existing items at the specified index number and higher are
incremented by one position.
move <from index number>
<to index number>
Removes the firewall log from the specified index number and
inserts it at the specified index number.
Table 38
System Logging menu (/cfg/sys/log/syslog)
Command Description
Page 64

Page 64 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Firewall Log menu
Using the Firewall Log menu (cfg/sys/log/firewall), you can remotely send
firewall logs to an external system log server using the standard remote syslog
port.
Table 39 identifies and describes the Firewall Log menu commands.
Log Archiving menu
Using the Log Archiving menu (/cfg/sys/log/arch), you can archive log files
when the files reach a specific size or age. When log rotation occurs, the
current log file is stored or e-mailed to a specified address and a new log file
is created.
If the rotate size is set above 0, log rotation occurs when the log surpasses the
rotate size, or when the log rotation interval is reached, whichever occurs
first. If the rotate size is set to 0, the file size is ignored and only the rotate
interval is used. If an e-mail address and SMTP server IP address are
configured, the log file is e-mailed when rotated.
Using the Log Archive menu, you can archive three primary types of logs
available in the SMC:
• syslog
• firewall
• UNIStim
Each of these are treated separately in the log archiving menu.
Table 39
Firewall Log menu
Command Description
addr Specifies the firewall log address.
del Removes the firewall log.
Page 65

Configuration menu Page 65 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 41 identifies and describes the Log Archiving menu commands.
Table 40
Log Archiving menu
Command Description
syslog Displays the System Log menu, which you can use to
configure system log parameters. For menu items, see
“System Log menu” on page 66.
firewall Displays the Firewall Log menu, which you can use to
configure firewall log parameters. For menu items, see
“Firewall Log menu” on page 66.
unistim Displays the UNIStim Log menu, which you can use to
configure UNIStim log parameters. For menu items, see
“UNIStim Log menu” on page 67.
Page 66

Page 66 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
System Log menu
Using the System Log menu (/cfg/sys/log/arch/syslog), you can configure
system log parameters. The system logs contain information and errors
generated during standard system operation.
Table 41 identifies and describes the System Log menu commands.
Firewall Log menu
Using the Firewall Log menu (/cfg/sys/log/arch/firewall), you can configure
firewall log parameters.
The firewall log contains all logging related to the firewall operation. The log
includes details on attacks and basic firewall operation, if configured. The
messages sent to the firewall logs are defined in the Platform Logging menu
(smc/settings/log/). You can also specify firewall logging for individual
packets that traverse the SMC by enabling logging in the security zone rules
(either inbound or outbound).
Table 41
System Log menu
Command Description
email <e-mail address> Specifies the e-mail address to which log files are sent
when the log interval or maximum log size is reached. Use
this command in conjunction with the SMTP command.
smtp <SMTP server IP address> Specifies the IP address of the SMTP mail server that
hosts the e-mail address specified in the Email command.
Specify the IP address in dotted decimal notation.
Note: Configure the specified SMTP server to accept
messages from the SMC.
int <days> <hours> Specifies the time interval for log rotation. The interval is
specified in number of days and number of hours.
size <max size (kb)> Specifies the maximum size a log file can reach before
triggering rotation. The size is specified in kilobytes.
Page 67

Configuration menu Page 67 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 42 identifies and describes the Firewall Log menu commands.
UNIStim Log menu
Using the UNIStim Log menu (/cfg/sys/log/arch/unistim), you can configure
UNIStim log parameters.
The secure UNIStim log contains all logging related to the secure UNIStim
proxy and includes general information about its operation. The log also
contains messages related to execution problems and security failures in the
secure UNIStim protocol.
Table 42
Firewall Log menu
Command Description
email <e-mail address> Specifies the e-mail address to which log files are sent
when the log interval or maximum log size is reached. Use
this command in conjunction with SMTP command.
smtp <SMTP server IP address> Specifies the IP address of the SMTP mail server that
hosts the e-mail address specified in the Email command.
Specify the IP address in dotted decimal notation.
Note: Configure the specified SMTP server to accept
messages from the SMC.
int <days> <hours> Specifies the time interval for log rotation. The interval is
specified in number of days and number of hours.
size <max size (kb)> Specifies the maximum size a log file can reach before
triggering rotation. The size is specified in kilobytes.
Page 68

Page 68 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 43 identifies and describes the UNIStim Log menu commands.
User menu
Using the User menu (/cfg/sys/user), you can add, modify, delete, or list SMC
user accounts, and change passwords.
The default user accounts are:
•admin
• oper
•root
Note: You cannot delete the default user accounts. Only the
Administrator can change the passwords.
Table 43
UNIStim Log menu
Command Description
email <e-mail address> Specifies the e-mail address to which log files are sent
when the log interval or maximum log size is reached. Use
this command in conjunction with SMTP command.
smtp <SMTP server IP address> Specifies the IP address of the SMTP mail server that
hosts the e-mail address specified in the Email command.
Specify the IP address in dotted decimal notation.
Note: Configure the specified SMTP server to accept
messages from the SMC.
int <days> <hours> Specifies the time interval for log rotation. The interval is
specified in number of days and number of hours.
size <max size (kb)> Specifies the maximum size a log file can reach before
triggering rotation. The size is specified in kilobytes.
Page 69

Configuration menu Page 69 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 44 identifies and describes the User menu commands.
Table 44
User menu (/cfg/sys/user)
Command Description
passwd <admin password>
<new admin password>
<confirm new admin
password>
Changes the administrator password. The password can
contain spaces and is case sensitive. There is no limitation on
the number of characters.
Only the admin user can perform this action. You are prompted
to enter the current administrator password. Then, you are
prompted to enter and confirm the new administrator password.
expire <# of seconds> Specifies password expiration time in seconds. If you set the
value to zero (the default), the password expiration is not
activated. After a password expires, the user is prompted at
logon to enter the old password once and the new password
twice.
Note: This command is visible only to users in the admin
group, and does not apply to the root user.
list Lists all editable user accounts.
del <user name> Deletes oper user accounts. Only the admin user can delete
user accounts.
add <user name> Adds a user account. Only the admin user can perform this
action. After adding a user account, you must also assign the
account to a group using the User Edit menu. See “User Edit
menu” on page 70.
edit <user name> Displays the User Oper menu, which you can use to edit the
user account passwords and group privileges for the specified
user. For menu items, see “User Edit menu” on page 70.
adv Displays the SSH User menu, which provides options for
administering SSH user access. For menu items, see “SSH
User Admin menu” on page 71.
Page 70

Page 70 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
User Edit menu
Using the User Edit menu (/cfg/sys/user/edit <user name>), you can change
passwords and assign group privileges for the user account specified by the
user name.
Table 45 identifies and describes the User Edit menu commands.
Table 45
User Edit menu (/cfg/sys/user/edit)
Command Description
password <admin password>
<new user password>
<confirm new user password>
Changes the password for the selected user. The password
can contain spaces and is case-sensitive. There is no
limitation on the number of characters.
Only the admin user can perform this action. You are
prompted to enter the current administrator password. Then,
you are prompted to enter and confirm the new user
password.
groups <group name> Adds or deletes the selected user to or from a group. The
three predefined groups are admin, oper, and root.
cur Displays the current user settings.
Page 71

Configuration menu Page 71 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
SSH User Admin menu
Using the SSH User Admin menu (/cfg/sys/user/adv/user <user name>), you
can create an SSH account on the SMC to provide a specified user with SSH
access to the SMC. You must specify a user name to open the menu.
Table 46 identifies and describes the SSH User Admin menu commands.
Groups menu
Using the Groups menu (/cfg/sys/user/edit <user name>/groups), you can list,
delete, or add groups.
Table 46
SSH User Admin menu (/cfg/sys/user/adv/user <user name>)
Command Description
name Specifies a descriptive name for the SSH account.
pubkey Specifies the RSA/DSA public key for the SSH account.
Note: The public key you enter must conform to OpenSSH v2 RSA or
DSA format.
ena Enables the SSH account for the specified user name.
dis Disables the SSH account for the specified user name.
del Deletes the SSH account.
Page 72

Page 72 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 47 identifies and describes the Groups menu commands.
Network Configuration menu
Using the Network Configuration menu (/cfg/net), you can configure ports,
gateways,
Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP), and Proxy ARP
(PARP)
.
Table 48 identifies and describes the Network Configuration menu
commands.
Table 47
Groups menu (/cfg/sys/user/edit/groups)
Command Description
list Lists all group members by index number and name; for
example:
1: admin
2: oper
del <Index number of entry to delete> Deletes a member from the selected group. Specify the
member by index number.
add <Index number of entry to add> Adds a member to the selected group. Specify the
member by index number.
Table 48
Network Configuration menu (/cfg/net)
Command Description
port <port > Displays the Port menu for the specified port, which you can use to
configure physical ports on the SMC. For menu items, see “Port menu”
on page 74.
if <interface> Displays the Interface menu for the specified interface. For menu items,
see “Interface menu” on page 74.
Page 73

Configuration menu Page 73 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
gateway <gateway IP
address>
Specifies the IP address of the SMC default gateway. Set the default
gateway to the IP address of the network router interface adjacent to
the SMC to allow remote administrative access through Telnet, SSH,
and the BBI.
routes Displays the Routes menu, which you can use to add, delete, or list
static routes. The SMC uses these routes to transmit packets within the
attached networks. For menu items, see “Routes menu” on page 77.
vrrp Displays the VRRP Settings menu. For menu items, see “VRRP
Settings menu” on page 77.
parp Displays the Proxy ARP menu, which you can use to access the proxy
ARP (PARP) list or enable PARP support in the SMC. For menu items,
see “Proxy ARP menu” on page 79.
Note: Use this command for testing the SMC in a lab environment; not
in production.
Table 48
Network Configuration menu (/cfg/net)
Command Description
Page 74

Page 74 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Port menu
Using the Port menu (/cfg/net/port <port_name>), you can configure the port
characteristics for a specified port.
Table 49 identifies and describes the Port menu commands.
Interface menu
Using the Interface menu (/cfg/net/if), you can configure IP address interfaces
for the SMC. Each IP address interface represents a network attached to the
SMC.
To ensure traffic flows through the SMC, configure the network device
attached to an SMC port to use an SMC IP address interface or SMC VRRP
interface as its default gateway.
The IP address interface naming conventions are as follows:
• ip1: Real IP Address of first host in a cluster
Table 49
Port menu (/cfg/net/port)
Command Description
autoneg on | off Enables or disables link auto-negotiation. If auto-negotiation is
disabled, the port operates at the speed set in the port speed
command.
Note: Enabling or disabling auto-negotiation can cause
temporary interruption to network traffic on all ports.
speed <port speed> Specifies the link speed of the port. Enter the port speed as an
integer representing megabytes per second (MB/s). For Fast
Ethernet ports, you can set the speed to 10 or 100. For Gigabit
Ethernet ports, the speed is fixed at 1000.
mode full | half Sets the port duplex mode to either full-duplex or half-duplex
mode. The default setting is full.
Page 75

Configuration menu Page 75 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
• ip2: Real IP Address of second host in a cluster
• vrrp/vip: Floating IP address shared between both hosts in a cluster but
owned by the VRRP master
Table 50 identifies and describes the Interface menu commands.
Table 50
Interface menu (/cfg/net/if)
Command Description
ip1 <interface IP address> IP address for the first host in a cluster on a particular
interface.
Note: In a standalone SMC configuration, each
interface has a single IP address (ip1) associated with it.
In a High Availability (HA) configuration, three IP
addresses are required to adequately configure an
interface. The first two IP addresses (ip1 and ip2) define
the real IP addresses of the two SMCs in the cluster; that
is, one SMC owns ip1 and the other SMC owns ip2. The
third IP address, the VRRP virtual IP, exists on the same
subnet as the other two IP addresses and is owned by
whichever SMC is the current HA master. If the current
HA master machine fails, the backup SMC becomes the
master and assumes responsibility for packets routed
through the VRRP IP address. For related information,
see “VRRP Settings menu” on page 77.
ip2 <interface IP address> IP address for the second host in a cluster on a particular
interface.
mask <IP subnet mask (such as
255.255.255.0)>
Configures the IP subnet address mask for the IP
address interface using dotted decimal notation.
vrrp Displays the Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
(VRRP) Interface menu, which you can use to configure
an interface for HA. VRRP ensures that if the active SMC
host fails, the redundant SMC host takes over. In an HA
configuration, configure each participating IP address
interface separately for VRRP. For menu items, see
“VRRP Interface menu” on page 76.
Page 76
Page 76 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
VRRP Interface menu
Using the VRRP Interface menu (/cfg/net/if <interface number>/vrrp), you
can configure redundant interfaces when two SMCs are present in a cluster.
VRRP ensures that if the active host fails, the backup host takes over. The
SMC interfaces (ip1 and ip2) form a virtual router. The virtual router IP
address becomes the real IP address for both hosts, though the virtual router
IP address is active only on the active master. Each subaddress must reside on
the same network as the virtual router IP address.
Note: Both hosts in the cluster must have the same configuration. The
host configurations are automatically synchronized.
Table 51 identifies and describes the VRRP Interface menu commands.
mgmt Enables management on this interface.
ena Enables this IP address interface.
dis Disables this IP address interface.
Table 51
VRRP Interface menu (/cfg/net/if/vrrp)
Command Description
vrid <virtual router ID
(1-255)>
Assigns an ID for the virtual router interface. Configure the virtual
router ID (VRID) on this interface the same for both the active
master and the backup. Separate interfaces must have unique
VRIDs.
vip <IP address> Defines the virtual IP address used to represent the SMC cluster in
the virtual router. The vip address must reside in the same subnet
as the interface IP address.
Table 50
Interface menu (/cfg/net/if)
Command Description
Page 77
Configuration menu Page 77 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Routes menu
Using the Routes menu (/cfg/net/route), you can add, delete, or list static
routes. The SMC uses these static routes to route transmit packets to
indirectly attached internal networks. You can configure up to 1000 static
routes.
Table 52 identifies and describes the Route menu commands.
VRRP Settings menu
Using the VRRP Settings menu (/cfg/net/vrrp), you can configure Virtual
Router Redundancy Protocol (VRRP) parameters for the SMC cluster.
Specify valid addresses for each SMC before you apply changes to the
Table 52
Route menu (/cfg/net/route)
Command Description
list Lists all configured routes by their index number and IP
address information.
del <index number> Removes a route from the configuration by specifying the
route index number.
add <destination IP address>
<destination mask>
<gateway IP address>
Adds a static route based on destination IP address,
destination subnet mask, and gateway IP address.
Note: The gateway IP address must be previously specified
and cannot be within the range specified by the destination
IP address and mask.
insert <index number>
<destination IP address>
<destination mask>
<gateway IP address>
Adds a new static route at a specific position (index number)
in the index.
move <index number>
<destination index number>
Moves a static route from one position in the index to
another.
Page 78

Page 78 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
parameter values. Both SMC hosts in the cluster must have the same
configuration.
Table 53 identifies and describes the VRRP Settings menu commands.
Table 53
VRRP Settings menu (/cfg/net/vrrp)
Command Description
ha y | n Enables or disables HA. Two hosts must be previously installed and
configured before you can enable HA.
adint <1-3600> Displays the current advertisement interval in seconds and provides the
option to change it. The active master sends a VRRP advertisement
message to the backup host at the specified advertisement interval.
Only the active master sends VRRP advertisement messages. If the
backup host does not receive a VRRP advertisement from the active
master within the advertisement interval, VRRP initiates VRRP failover.
The default value is 3, which is the lowest recommended value.
garp [1-600] Displays the current Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol (GARP)
value in seconds. You can change the GARP value. When the backup
host determines that the active master failed, it immediately flashes a
GARP message, which is an unsolicited ARP response, to all
end-hosts on the virtual router interface. Then the backup host delays a
period of time specified by the garp value before it begins sending
continuous GARP messages.
The GARP message forces end-hosts to update their ARP caches with
the MAC/IP address mapping for the newly active SMC instead of
waiting for end-hosts to acquire the MAC/IP address from periodic ARP
requests. The default value is 1.
Page 79

Configuration menu Page 79 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Proxy ARP menu
Using the Proxy ARP menu (/cfg/net/parp), you can configure IP addresses
to which the cluster sends ARP messages. The SMC can respond to ARP
requests intended for devices behind the SMC, including VLAN and VRRP
interfaces.
gbcast <2-100> Displays the present Gratuitous Broadcast (gbcast) value. You can
change the gbcast value. The gbcast value specifies the interval
between GARP messages sent by the active master to ensure that all
end-hosts have the correct MAC/IP address mapping. Increasing the
gbcast value cuts down on the gbcast traffic, but lengthens the interval
between end-host ARP cache updates.
The gbcast value is multiplied by the adint value to determine the
interval in seconds between GARP messages. For example, if your
adint value is 10 and your gbcast value is 3, the interval between GARP
messages is 30 (10 x 3) seconds. The default gbcast value is 2.
afc y | n Enables or disables Advanced Failover Checking (AFC). When AFC is
enabled, the system sends an ARP message before initiating a failover
caused by missed VRRP advertisements.
IMPORTANT!
Use Proxy ARP for testing the SMC in lab environments when IP
address allocation is an issue. Do not use Proxy ARP in production;
instead each interface should exist on its own subnet.
Table 53
VRRP Settings menu (/cfg/net/vrrp)
Command Description
Page 80

Page 80 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 54 identifies and describes the Proxy ARP menu commands.
Table 54
Proxy ARP menu (/cfg/net/parp)
Command Description
enable y | n Enables or disables Proxy ARP for the cluster. Proxy ARP is disabled by
default.
iface Specifies the interface to proxy ARP messages for a subnet on a different
interface. The subnet must contain the subnet address supported by the
proxy ARP interface. Specify the name of the interface, such as intranet,
management, or mcslan.
garp Sends gratuitous ARPs on behalf of clients that are subnets supported by
the proxy ARP interface. The gratuitous ARPs are sent from the proxy ARP
interface.
Page 81

Configuration menu Page 81 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Multimedia Security menu
Using the Multimedia Security menu (/cfg/smc), you can define the security
features of the SMC.
Table 55 identifies and describes the Multimedia Security menu commands.
Table 55
Multimedia Security menu (/cfg/smc)
Command Description
zone
[zone_name}
Displays the Security Zone menu, which you can use to configure the
secure multimedia zones. For menu commands, see “Security Zone menu”
on page 83.
settings Displays the Settings menu, which you can use to configure SMC settings.
See “SMC Settings menu” on page 89.
unistim Displays the UNIStim Security menu, which you can use to create a secure
UNIStim proxy server and specify the different policies to be applied to the
users when they connect to the server. For menu commands, see “UNIStim
Security menu” on page 100.
network Displays the SMC Network menu, which you can use to specify the different
networks used in configuring the SMC. The following networks are created
during installation:
• users networks: the subnets used by multimedia users
• administrators networks: the subnets used by administrators
Both users and administrators default to all networks. If required, you can
can add more networks. For menu items, see “SMC Network menu” on
page 110.
service Displays the Service menu, which you can use to specify the services and
protocols used for configuring the SMC firewall rules. Services map to a
protocol and a series of port ranges. You can consolidate frequently used
services into a single service specification and then use it repeatedly in
firewall rules. For menu items, see “Service menu” on page 112.
Page 82

Page 82 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
flow Displays the Flow Control menu, which you can use to specify the different
flow parameters for SMC firewall rules. For menu items, see “Flow Control
menu” on page 86.
addzone Initiates the Addzone Wizard, which guides you through the steps to add a
new security zone to the system. Each SMC can support a maximum of
four user-defined security zones. Each zone has a subnet and port
associated with it and a collection of firewall rules that are applied to all
traffic that flows into and out of the zone. After you add a zone, use the Auto
command to incorporate predefined rules.
Table 55
Multimedia Security menu (/cfg/smc)
Command Description
Page 83

Configuration menu Page 83 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Security Zone menu
Using the Security Zone menu (/cfg/smc/zone), you can define security
zones. Each zone represents a secure subnet, which contains the CS 1000 or
MCS servers. Each security zone is associated with a subnet and a port. Each
zone has a descriptive name.
Two types of access rules exist for each zone:
• inbound rules for traffic that flows into the zone
• outbound rules for traffic that flows out of the zone
If a packet does not match a rule, the packet is denied access.
In general, the traffic flowing into the zone is from the intranet and therefore
untrusted, such as SIP traffic from an IP phone to the signaling server. The
majority of access rules are applied for inbound calls. The default outbound
rules allow all traffic to exit the system.
When you add the first rule, a wizard guides you through a host of questions
to define the basic rule values. Subsequently, when you access any rule, the
CLI displays the Rules menu.
Each rule has a unique number, ranging from 1 through 1024. This number is
used to sequentially order the rules. Rules are applied to incoming traffic in
order according to the access number. A lower number means a higher
priority; therefore, rules with lower numbers are applied first. Each rule is
treated separately, and the first rule that matches a particular packet defines
how that packet is handled. For example, if a packet matches two rules in the
system, and the rule with the lower number allows the packet, and the rule
with the higher number denies the packet, the packet is allowed.
Page 84

Page 84 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Table 56 identifies and describes the Security Zone menu commands.
Table 56
Security Zone menu (/cfg/smc/)
Command Description
irule
[rule_number]
Displays the Inbound Access menu for the specified rule. For menu items,
see “Inbound Access menu” on page 85.
orule
[rule_number]
Displays the Outbound Access menu for the specified rule. For menu
items, see “Outbound Access” on page 87.
[zone <name>]
auto
Initiates automatic rule generation, which guides you through the following
steps:
1 Specify the multimedia users network, which is the collection of
subnets upon which the IP phones reside.
2 Specify the administrators network, which is the subnet upon which the
administrative clients reside.
3 [Optional] Delete existing rules.
Note: If you choose yes, all current rules are replaced with the
autogenerated rules. If you choose no, the autogenerated rules are
appended. Duplicate rules are not eliminated.
4 Select one or more rule groups to apply to a particular security zone.
Note: You can add numerous rule groups in a single wizard session.
5 Apply the rules.
cur Displays the current security zone settings.
del Deletes the security zone.
Page 85

Configuration menu Page 85 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Inbound Access menu
Using the Inbound Access menu (cfg/smc/irule<rule_number>), you can
specify inbound access rules.
Table 57 identifies and describes the Inbound Access menu commands.
Table 57
Inbound Access menu
Command Description
enable Enables or disables the rule. Disabled rules are ignored.
source Specifies the source network for the traffic. The source network is generally
located within the intranet and is untrusted. If the source value is an
asterisk (*), all source IP addresses match this rule.
dest Specifies the destination network for the traffic. For an inbound rule, this
represents the subnet of the security zone, or individual IP addresses
within the zone. If the dest value is an asterisk (*), all destination addresses
match this rule.
service Details the protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP) and ports for the traffic that matches
this rule. If the service value is an asterisk (*), all types of traffic match this
rule.
custom Displays the Custom Service menu, which you can use to define custom
services for individual rules. You can specify the minimum port, maximum
port, and protocol of the service. If you specify a custom service, it
overrides the normal service specification.
action Specifies whether to allow or deny traffic for this rule.
flow Displays the Flow Control menu, which you can use to specify flow control
for the specified rule. The flow control applies only to this individual rule
and the traffic that maps to it. For menu items, see “Flow Control menu” on
page 86.
Page 86

Page 86 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Flow Control menu
Using the Flow Control menu (/cfg/smc/flow/), you can specify the different
flow parameters for SMC firewall rules.
Table 58 identifies and describes the Flow Management menu commands.
log Defines whether matches to the rule are logged to file. You can view logs in
the CLI or BBI. The SMC firewall logs follow Webtrends Extended Log
Format (WELF). The location of the log file is /logs/firewall.log.
Note: Too many firewall logs can affect SMC performance. Nortel
recommends you update the firewall log configuration to prevent this
degradation in performance. For more information, see Secure Multimedia
Controller: Planning and engineering (NN42320-200).
comment Specifies a comment to identify what traffic the rule currently matches.
del Deletes this rule. When you delete a rule, its rule number becomes
reusable.
Table 58
Flow Management menu
Command Description
name Defines the name of the flow.
maxconn Defines the maximum number of connections for a given rule. For example,
a value of five (5) indicates a maximum of five concurrent connections.
conns Defines the rate at which the connections are created per unit of time
(defined in seconds) for a given firewall rule. For example, if the number of
connections is 5 and the interval is 1, it indicates that in 1 second a
maximum of five connections are created. The limit is applied
unidirectionally.
Table 57
Inbound Access menu
Command Description
Page 87

Configuration menu Page 87 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Outbound Access
Using the Outbound Access menu (/cfg/smc/zone <name>/orule), you can
configure outbound rule parameters.
Table 59 identifies and describes the Outbound Access menu commands.
packets Defines the number of packets that are transmitted per unit of time (defined
in seconds) for a given firewall rule. For example, if the number of packets
is set to five and the interval is one, it indicates in one second a maximum
of five packets can transmit for the policy. The limit is applied bidirectionally.
bandwidth Defines the amount of traffic (measured in kilobytes) that is transmitted per
unit of time (defined in seconds) for a given firewall rule. For example, if the
number specified is 10 KB and the interval set to one (1), it indicates that in
one second a maximum of 10 kilobytes of data is transmitted through for
this firewall rule. The limit is applied bidirectionally.
comment Specifies a comment for this flow.
del Removes the flow.
Table 59
Outbound Access menu
Command Description
enable Enables or disables the rule. Disabled rules are ignored.
source Specifies the source network for the traffic.
dest Specifies the destination network for the traffic.
service Details the protocol (TCP, UDP, ICMP) and ports for the traffic that matches
this rule. If the service value is an asterisk (*), all types of traffic match this
rule.
Table 58
Flow Management menu
Command Description
Page 88
Page 88 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
custom Display the Custom Service menu, which you can use to define custom
services for individual rules. You can specify the minimum port, maximum
port, and protocol of the service. If you specify a custom service, it
overrides the normal service specification.
action Specifies whether to allow or deny traffic for this rule.
flow Displays the Flow Control menu, which you can use to specify flow control
for the specified rule. The flow control applies only to this individual rule
and the traffic that maps to it. For menu items, see “Flow Control menu” on
page 86.
log Enables rule logging. The location of the log file is /logs/firewall.log.
Note: Too many firewall logs can affect SMC performance. Nortel
recommends you update the firewall log configuration to prevent this
degradation in performance. For more information, see Secure Multimedia
Controller: Planning and engineering (NN42320-200).
comment Defines a comment to identify what traffic the rule currently matches.
del Deletes this rule. When a rule is deleted, its rule number can is reusable.
Table 59
Outbound Access menu
Command Description
Page 89

Configuration menu Page 89 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
SMC Settings menu
Using the SMC Settings menu (/cfg/smc/settings), you can configure security
settings.
Table 60 identifies and describes the SMC Settings menu commands.
Table 60
SMC Settings menu
Command Description
attack Enables or disables the following advanced firewall attacks:
• SYN Flooding
• Source Routing
• WinNuke
•Mime Flood
• FTP Bounce
• IP Unaligned Timestamp
• Sequence Number Prediction
• Sequence Number Out Of Range
•ICMP Redirect
• ICMP Error Messages
For detailed descriptions of these firewall attacks, see Appendix A on
page 121.
log Displays the Message Logging menu, which you can use to customize the
types of messages sent to /logs/firewall.log. For menu items, see “Message
Logging menu” on page 90.
Note: Too many firewall logs can affect SMC performance. Nortel
recommends you update the firewall log configuration to prevent this
degradation in performance. For more information, see Secure Multimedia
Controller: Planning and engineering (NN42320-200).
Page 90

Page 90 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Message Logging menu
Using the Message Logging menu (
/cfg/smc/settings/log), you can customize
the types of messages sent to /logs/firewall.log. Doing so helps to limit the file
size of the firewall log.
The firewall log contains all logging messages that relate to firewall
operation, specific attacks, and basic packet logging due to the log settings in
the firewall inbound/outbound rules.
On the SMC, the firewall log files are stored in logs/firewall.log. Firewall
logs can also be:
alg Displays the ALG menu, which you can use to enable or disable application
layer gateway support for a variety of protocols. Without ALG support,
some of these protocols cannot traverse the SMC. For menu items, see
“ALG menu” on page 96.
maxconn/
<zone>/conn
Specifies the maximum connection limits for individual zones. The total
number of concurrent connections supported in the SMC across all zones
is 700 000. Traffic flowing between zones is counted as a concurrent
connection within the intranet zone, so Nortel recommends that the zone
have the highest maxconn value. The default value is 100000.
timeout Displays the Timeout menu, which you can use to specify inactivity timeout
values associated with network traffic. For menu items, see “Timeout
menu” on page 97.
portbypass Displays the Port Bypass menu, which you can use to bypass the SMC’s
stateful processing of packet to and from a given set of TCP ports. For
menu items, see “Port Bypass menu” on page 98.
multicast Displays the Multicast Bypass menu, which you can use to identify a
specific Multicast Groups for which you want the SMC to bypass the
processing and bridge the packets onto another network. For menu items,
see “Multicast Bypass menu” on page 99.
Table 60
SMC Settings menu
Command Description
Page 91

Configuration menu Page 91 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
• viewed in the BBI or the CLI.
• streamed in real-time to a firewall log using the /cfg/sys/log/firewall
command. See “Platform Logging menu” on page 60.
• e-mailed to an appropriate e-mail address.
Firewall logs can become quite large in high-traffic environments, slowing
down the SMC and filling up disk space. Nortel recommends that you modify
the firewall logging configuration appropriately if the log files are filling up
too quickly.
The SMC uses the industry standard Webtrends Extended Log Format
(WELF) for logging the network activity. The following text is a sample of a
log message in WELF generated by syslog.
Apr 18 04:25:52 172.16.1.247 id=firewall time="2002-04-18
16:15:34" fw=DEVICE1 pri=6 proto=6(tcp) src=172.16.7.246
dst=66.218.70.149 msg=Service access request successful
Src 3171 Dst 80 from EXT n/w agent=Firewall
Table 61 identifies and describes the Message Logging menu commands.
Table 61
Message Logging menu
Command Description
messages Enables and disables various logging message types. For menu
commands, see “Messages menu” on page 92.
threshold Sets the various thresholds for log messages sent to the remote firewall log
server as specified in the Platform Logging menu. See “Platform Logging
menu” on page 60. For menu commands, see “Thresholds menu” on
page 94.
rate Displays the Rate Limit menu for log messages sent to the remote firewall
log server as specified in the Platform Logging menu. See “Platform
Logging menu” on page 60. For menu commands, see “Rate Limit menu”
on page 95.
Page 92
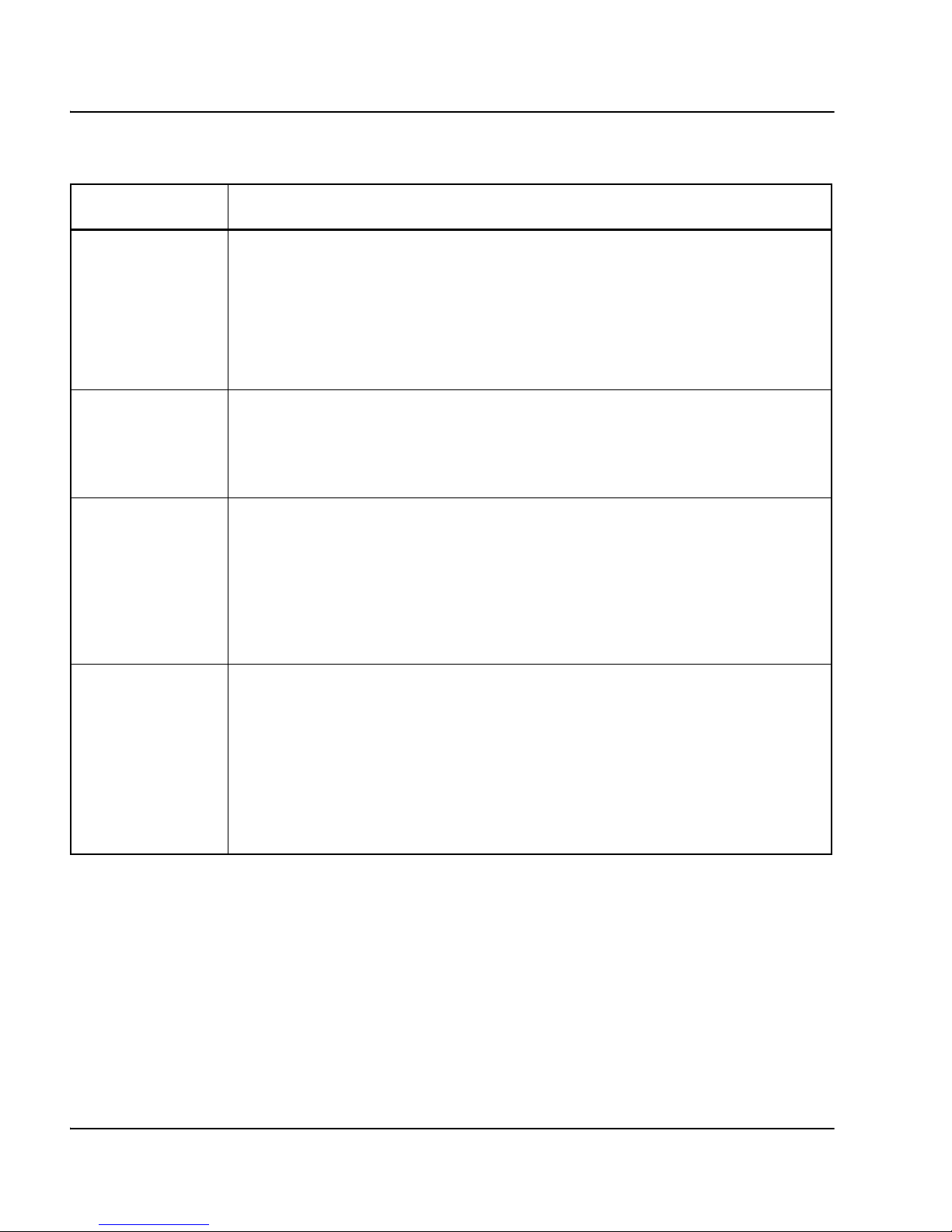
Page 92 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Messages menu
Using the Messages menu (/cfg/smc/settings/log/messages), you can enable
or disable specific types of firewall logs.
verbose Enables verbose generation of log messages. By default, this parameter is
disabled.
Note: Too many firewall logs can affect SMC performance. Nortel
recommends you update the firewall log configuration to prevent this
degradation in performance. For more information, see Secure Multimedia
Controller: Planning and engineering (NN42320-200).
queue Indicates the maximum number of log messages that are queued. This
value can be in the range of 1-75. A higher number increases performance
because the log messages are batched and sent at a single time; however,
it also increases the time it takes for a message to be logged.
attack Specifies a threshold for how many attack packets the firewall detects
before log messages are generated. Only one attack message is logged for
every nth attack packet. You can limit the total number of attack packets
that are logged. For example, if this number is set to 5, only one of every
five attacks are logged regardless of the type of attack.
Note: This can lead to message loss.
policy Specifies a threshold for how many attack packets the firewall cannot
match to a policy before log messages are generated. Only one attack
message is logged for every nth attack packet. You can limit the total
number of attack packets that are logged. For example, if this number is set
to 5, only one of every five attacks are logged regardless of whether of the
type of attack.
Note: This can lead to message loss.
Table 61
Message Logging menu
Command Description
Page 93

Configuration menu Page 93 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 62 identifies and describes the Messages menu commands.
Table 62
Messages menu
Command Description
synflood Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated as a result
of TCP SYN flooding.
ping Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated as a result
of a ping of death attack.
winnuke Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated every time a
WinNuke attack is detected.
syserror Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated by the SMC,
such as memory allocation failures.
deny Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated because of
deny access policies.
allow Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated at the end of
every connection in firewall.
unavail Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated as a result
of dropping packets due to non-availability of access policies.
attacks Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated when the
firewall treats invalid packets as an attack.
data Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated as a result
of dropping packets because of application command filtering.
ipspoof Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated as a result
of spoofed IP packets.
ipopt Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated when
attacks based on IP options occur.
access Enables and disables logging of messages that are generated when a
policy is accessed.
Page 94

Page 94 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Thresholds menu
Using the Threshold menu (/cfg/smc/settings/log/threshold), you can set the
message threshold to limit the number of repetitive messages sent to the
remote firewall log server (/cfg/sys/log/firewall). Messages are repetitive if
more than the one message contains the same message ID, protocol, source
IP address, destination IP address, source port, and destination port.
For example, the following parameters create a message queue for 200 issues:
• count = 10
• threshold time = 60 seconds
• scan time = 1 second
• max issues = 200
Repetitive messages create one issue entry in the message queue. Each
occurrence of the same message during 60 seconds increments the count of
the issue entry. The first message is always forwarded to the firewall log. The
tenth message within 60 seconds is also sent to the firewall log. If less than
10 instances of the same message arrive within 60 seconds, another message
with the current count is sent to the firewall log at the 60 second expiration.
The queue is scanned every scantime equals 1 second, and message issue
entries older than 60 seconds are sent to the firewall log if the count is any
number other than zero. If the count is zero, the message is not sent to the
firewall log.
Table 65 identifies and describes the Threshold menu commands.
Table 63
Threshold menu
Command Description
count Specifies the threshold count, which is the maximum number of repetitive
messages to accumulate in the queue before sending the issue to the
firewall log.
time Specifies the threshold time, which is the time interval over which the
number of messages are accumulated.
Page 95

Configuration menu Page 95 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Rate Limit menu
Using the Rate Limit menu (/cfg/smc/settings/rate), you can specify the limit
of log messages sent to the remote firewall log server. These messages are
averaged over a period of time and rate-limited accordingly.
For example, the following parameters rate-limit the messages sent to the
firewall log to 1 per millisecond:
• msgcount = 1000
• period = 1
Any message over this limit is dropped.
Table 65 identifies and describes the Rate Limit menu commands.
scan time Specifies the time interval at which the issues queue is scanned. For
example, if the scan time is 1 second, the issues queue is scanned every 1
second.
max issues Specifies the maximum size of the issues queue.
Table 64
Rate Limit menu
Command Description
msgcount Specifies the total message count allowed over the time period specified in
the Period command.
Note: Messages are counted; packets or bytes are not counted.
period Specifies the time period over which messages are allowed.
Table 63
Threshold menu
Command Description
Page 96

Page 96 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
ALG menu
Using the ALG menu (/cfg/smc/settings/alg), you can enable or disable
application layer gateway support for a variety of protocols. Without ALG
support, some of these protocols are unable to traverse the SMC.
Table 65 identifies and describes the ALG menu commands.
Timeout menu
Using the Timeout menu (/cfg/smc/settings/timeout), you can
configure
timeout values for TCP, UDP, ICMP protocols, TCP RESET, and services.
The following timeout values are configurable for the following connections:
• TCP-based (default is 600 seconds)
• UDP (default is 1200 seconds)
• ICMP (default is 60 seconds)
After the timeout value is reached, the firewall association database
maintained for a connection is removed.
The timeout value is also configurable for the TCP RESET command. The
default value for this timeout is 30 seconds.
You can also configure a timeout value for a particular service or application.
For example, if you configure a service timeout record of 100 for FTP service,
and the TCP used by an FTP application has a default timeout of 600, the FTP
connection still has a timeout of 100.
Table 65
ALG menu
Command Description
ftp Enables FTP. FTP is enabled by default.
tftp Enables TFTP. TFTP is disabled by default.
rpc Enables RPC. RPC is disabled by default.
pcanywhere Enables PCAnywhere. PCAnywhere is disabled by default.
Page 97

Configuration menu Page 97 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Table 66 identifies and describes the Timeout menu commands.
Custom Timeout menu
Using the Custom Timeout menu (/cfg/smc/settings/timeout/custom), you
can configure timeout parameters for specific TCP/UDP ports or protocols.
Table 67 identifies and describes the Custom Timeout menu commands.
Table 66
Timeout menu
Command Description
udp Specifies the inactivity timeout value after which the UDP connection is
removed. The default value is 1200 seconds.
icmp Specifies the inactivity timeout value after which the ICMP connection is
removed. The default is 60 seconds.
pre Specifies the timeout value after which a connection receiving a TCP
RESET is removed. The default is 30 seconds.
tcp Specifies the timeout value after which a TCP connection is removed. The
default is 600 seconds.
custom Displays the Custom Timeout menu, which you can use to configure
timeout parameters for a specific TCP/UDP ports or protocols. For menu
items, see “Custom Timeout menu” on page 97.
Table 67
Custom Timeout menu
Command Description
name Specifies a custom timeout name.
proto Specifies the allowed protocol.
port Specifies the service port number.
timeout Specifies the service timeout in terms of seconds.
delete Removes the custom timeout.
Page 98

Page 98 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Port Bypass menu
Using the Port Bypass menu (/cfg/smc/settings/portbypass), you can identify
a specific set of TCP ports for which you want the SMC’s stateful processing
to bypass. You can add, modify, and delete the IP addresses for the TCP ports
you want to bypass. When the Port Bypass feature is enabled, the SMC does
not process or check all packets matching the port list.
The default entry in the port list is the IP address, 0.0.0.0, which indicates
every TCP port is bypassed when the Port Bypass feature is enabled.
Alternatively, you can add IP addresses of the specific TCP ports you want
the SMC to bypass. You can configure up to a maximum of four sets of port
and IP addresses.
Table 68 identifies and describes the Port Bypass menu commands.
Table 68
Port Bypass menu
Command Description
enable Enables the Port Bypass feature.
disable Disables the Port Bypass feature.
portlist Displays the Port List menu, which you can use to add, modify, or delete IP
addresses to the list of port list. For menu commands, see “Port List menu”
on page 99.
Page 99

Configuration menu Page 99 of 126
Secure Multimedia Controller Command Reference
Port List menu
Using the Port List menu (/cfg/smc/settings/portbypass/portlist), you can add,
modify, and delete IP addresses from list of ports to bypass.
Table 69 identifies and describes the Port List menu commands.
Multicast Bypass menu
Using the Multicast Bypass menu (/cfg/smc/settings/multicast), you can
identify a specific multicast groups for which you want the SMC to bypass
the processing and bridge the packets onto another network. When the
Multicast Bypass feature is enabled, the SMC bridges all packets matching
the mcastlist from their source network to their destination network. You can
add, modify, and delete the multicast addresses, source network, and
destination network you want to bridge.
You can configure up to a maximum of eight multicast groups along with
their source and destination network.
Table 70 identifies and describes the Multicast Bypass menu commands.
Table 69
Port List menu
Command Description
add Adds the IP address you specify to the port list.
modify Modifies the IP address you specify.
delete Deletes the IP address you specify from the port list.
Table 70
Multicast Bypass menu
Command Description
enable Enables the Multicast Bypass feature.
Page 100

Page 100 of 126 Configuration menu
NN10300-091 Standard 1.00 May 2006
Multicast List menu
Using the Multicast menu (/cfg/smc/settings/multicast/mcastlist), you can
add, modify, and delete multicast groups, source network, and destination
network from the Multicast List to bypass.
Table 71 on page 100 identifies and describes the Multicast List menu
commands.
UNIStim Security menu
Using the UNIStim Security menu (cfg/smc/unistim/), you can define all
settings necessary to create a secure UNIStim proxy server and specify the
different policies that are applied to the users when they connect.
disable Disables the Multicast Bypass feature.
mcastlist Displays the Multicast List menu, which you can use to add, modify, or
delete multicast group info to the mcastlist to bypass. For menu
commands, see “Multicast List menu” on page 100.
Table 71
Multicast List menu
Command Description
add Adds the multicast group address, source network, and destination
network you specify to the mcastlist.
modify Modifies the multicast group address, source network, and destination
network you specify.
delete Deletes the multicast group address, source network, and destination
network you specify if already existing in the Mcastlist.
Table 70
Multicast Bypass menu
Command Description
 Loading...
Loading...