Page 1

Title page
Nortel Communication Server 1000
Nortel Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5
IP Phones
Description, Installation, and Operation
Document Number: 553-3001-368
Document Release: Standard 20.00
Date: December 2006
Year Publish FCC TM
Copyright © 2006 Nortel Networks. All rights reserved.
Produced in Canada
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical
data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented
without express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products
specified in this document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
Nortel, Nortel (Logo), the Globemark, SL-1, Meridian 1, and Succession are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
Page 2

Page 3

6
Page 3 of 600
Revision history
December 2006
Standard 20.00. This document is up-issued to support CS 1000 Release 4.5
and the addition of the Expansion Module for IP Phone 1100 Series.
October 2006
Standard 19.00. This document is up-issued to include updated content due to
CR Q01462514.
October 2006
Standard 18.00. This document is up-issued to support the addition of the
IP Phone 1150E.
August 2006
July 2006
June 2006
April 2006
April 2006
Standard 17.00. This document is up-issued to include updated technical
content due to CR Q01434634.
Standard 16.00. This document is up-issued to include updated technical
content for CR Q01337301.
Standard 15.00. This document is up-issued to include UNIStim firmware upversion.
Standard 14.00. This document is up-issued to include content for the
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 Release 2.
Standard 13.00. Not issued.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 4

Page 4 of 600 Revision history
March 2006
Standard 12.00. This document is up-issued to include updated content for the
IP Softphone 2050 V2.
January 2006
Standard 11.00. This document is up-issued to include updated content for the
IP Phone 1120E and IP Phone 1140E.
January 2006
Standard 10.00. This document is up-issued to include updated content for the
IP Phone1140E, on pages 405-412, and 509-530.
January 2006
Standard 9.00. This document is up-issued to reflect change in technical
content on page 456 due to CR Q01233903.
November 2005
Standard 8.00. This document is up-issued to support the addition of
IP Phone 1140E.
August 2005
Standard 7.00. This document is up-issued to support CS 1000 Release 4.5.
April 2005
Standard 6.00. This document is up-issued to support the addition of the
IP Phone 2007.
April 2005
Standard 5.00. This document is up-issued to support the addition of the
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033.
February 2005
Standard 4.00. This document is up-issued to support the 8.x Firmware
Upgrade for IP Phones.
September 2004
Standard 3.00. This document is up-issued to support Communication Server
1000 Release 4.0.
June 2004
Standard 2.00. This document is up-issued to include the Nortel Networks
Mobile Voice Client 2050.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 5

October 2003
Revision history Page 5 of 600
Standard 1.00. This document is a new NTP for Succession 3.0 Software. It
was created to support a restructuring of the Documentation Library. This
document contains information previously contained in the following legacy
document, now retired: Internet Terminals Description (553-3001-217).
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 6

Page 6 of 600 Revision history
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 7

18
Page 7 of 600
Contents
List of procedures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
How to get Help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Getting help from the Nortel web site .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center . . . . . . . . 31
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code . . . . 32
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
About this document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Subject .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Applicable systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Intended audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Conventions .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Related information .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Nortel IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Supported features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Display characteristics .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 8

Page 8 of 600 Contents
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Replacing an IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Nortel IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Supported features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Features not currently supported .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Replacing an IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Removing an IP Phone 2002 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Nortel IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 9

Contents Page 9 of 600
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Supported features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Central Answering Postion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Display characteristics .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Package components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Replacing an IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Removing an IP Phone 2004 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Nortel IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Supported features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Touch panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Dialpad entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Display characteristics .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Local Tools menu password protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 10

Page 10 of 600 Contents
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Installation and Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Replacing an IP Phone 2007 .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Removing an IP Phone 2007 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
IP Phone
Key Expansion Module (KEM) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
IP Phone KEM startup initialization .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
Operating parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Nortel IP Softphone 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 204
Supported features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 11

Contents Page 11 of 600
Operating parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 219
System components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 220
Before you begin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 221
First-time installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Installing or upgrading the IP Softphone 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 224
Running the IP Softphone 2050 for the first time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Changing the TN of an existing IP Softphone 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
Removing an IP Softphone 2050 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
Nortel WLAN Handset 2210,
WLAN Handset 2211, and
WLAN Handset 2212 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Nortel Mobile Voice Client 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
System components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 235
Application software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
MVC 2050 Call Handling screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Operating parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 257
Operation .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
MVC 2050 installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
MVC 2050 removal .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 262
MVC 2050 and WLAN .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 279
Nortel IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . . . 281
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 281
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 282
Extension microphones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 12

Page 12 of 600 Contents
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 284
Supported features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 287
Features not currently supported .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 289
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 292
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 293
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 296
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 313
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
Reinstalling an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
Replacing an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
Removing an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 from service . . . . . . . 317
Connecting an extension microphone .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
Nortel IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 319
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 320
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 321
Supported features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 327
Features not currently supported .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 330
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Local Tools menu password protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 333
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 335
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 336
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 337
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 354
TFTP firmware upgrade .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 13

Contents Page 13 of 600
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Reinstalling an IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 357
Replacing an IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Removing an IP Phone 1120E from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Nortel IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 361
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 362
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 363
Supported features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 369
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 372
Display characteristics .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 373
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
Local Tools menu password protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 375
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 377
Package components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 378
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 379
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 397
TFTP firmware upgrade .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 399
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 399
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 399
Bluetooth wireless technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 399
Reinstalling an IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
Replacing an IP Phone 1140E .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
Removing an IP Phone 1140E from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
Nortel IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 403
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 404
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 14

Page 14 of 600 Contents
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 406
Supported features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 413
Features not currently supported .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 417
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 417
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
Headset support .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
Local Tools menu password protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 420
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 423
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 425
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 426
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 444
TFTP firmware upgrade .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 446
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Bluetooth wireless technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Reinstalling an IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 447
Replacing an IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
Removing an IP Phone 1150E from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
Expansion Module for IP Phone 1100 Series . . . . 451
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 451
Features .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 453
Display characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
Package components .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 454
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 455
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 456
Expansion Module startup initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 460
Operating parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 462
Services key operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 463
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 15

Contents Page 15 of 600
Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 465
Features overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 467
Corporate Directory .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
Personal Directory .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 468
Redial List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
Callers List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
Password Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
IP Call Recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 469
Virtual Office . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
Emergency Services for Virtual Office .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
Active Call Failover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 470
Enhanced UNIStim Firmware download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 471
SRTP media encryption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 472
Regulatory and safety information . . . . . . . . . . . . 475
Warnings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 476
Other compliancies . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 477
DenAn regulatory information for Japan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 478
Appendix A: Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 479
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 479
Environmental specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 482
Appendix B: 802.1Q VLAN description . . . . . . . . . 483
Contents .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 483
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 484
IP Phone support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 485
Three-port switch support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 486
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 16

Page 16 of 600 Contents
VLAN IDs .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 487
Enhanced DATA VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 489
Appendix C: 802.1x Port-based network access
control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 493
Extensible Authentication Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 494
Appendix D: 802.1ab Link
Layer Discovery Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 495
Appendix E: IP Phone diagnostic utilities . . . . . . 497
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 497
Text-based diagnostic utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 498
Graphic-based diagnostics utilities . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 531
Appendix F: Configuring the
Local Tools menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
Configuring the Local Tools options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 551
Appendix G: Bluetooth wireless
technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
Introduction .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 557
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 17

Contents Page 17 of 600
Appendix H: TFTP Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 571
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 571
TFTP Server planning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 571
Updating IP Phones firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
Appendix I: IP Phone context-sensitive soft keys 587
Appendix J: Call features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 589
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 593
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 18

Page 18 of 600 Contents
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 19

30
Page 19 of 600
List of procedures
Procedure 1
Configuring the IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Procedure 2
Installing the IP Phone 2001 for the
first time using manual configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Procedure 3
Installing an IP Phone 2001 for the first time
using DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Procedure 4
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Procedure 5
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Procedure 6
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . 70
Procedure 7
Replacing an IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Procedure 8
Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service . . . . . . . . . . 71
Procedure 9
Configuring the IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 20

Page 20 of 600 List of procedures
Procedure 10
Installing the IP Phone 2002 for the
first time using manual configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Procedure 11
Installing an IP Phone 2002 for the first time
using DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Procedure 12
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Procedure 13
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Procedure 14
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . 107
Procedure 15
Replacing an IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Procedure 16
Removing an IP Phone 2002 from service . . . . . . . . . . 109
Procedure 17
Configuring the IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Procedure 18
Installing the IP Phone 2004 for the
first time using manual configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Procedure 19
Installing an IP Phone 2004 for the first time
using DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Procedure 20
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Procedure 21
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 21

List of procedures Page 21 of 600
Procedure 22
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . 146
Procedure 23
Replacing an IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Procedure 24
Removing an IP Phone 2004 from service . . . . . . . . . . 148
Procedure 25
Configuring the IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Procedure 26
Installing the IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Procedure 27
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Procedure 28
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Procedure 29
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . 186
Procedure 30
Replacing an IP Phone 2007 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Procedure 31
Removing an IP Phone 2007 from service . . . . . . . . . . 187
Procedure 32
Connecting the IP Phone KEM to an IP Phone 2002 or
IP Phone 2004 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Procedure 33
Preinstallation checklist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
Procedure 34
Installing an IP Softphone 2050 for the first time . . . . . 223
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 22

Page 22 of 600 List of procedures
Procedure 35
Installing the IP Softphone 2050 on the PC
(new installation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 225
Procedure 36
Upgrading the IP Softphone 2050 on your PC . . . . . . . 225
Procedure 37
Uninstalling the IP Softphone 2050 (Version 1) . . . . . . 226
Procedure 38
Uninstalling the IP Softphone 2050 (Version 2) . . . . . . 226
Procedure 39
Installing the Accessibility Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 226
Procedure 40
Installing the Windows QoS Packet Scheduler . . . . . . 227
Procedure 41
Changing the TN of an existing IP Softphone 2050 . . . 229
Procedure 42
Removing an IP Softphone 2050 from service . . . . . . . 229
Procedure 43
Starting MVC 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 258
Procedure 44
Synchronizing a PDA with a desktop PC
using ActiveSync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 259
Procedure 45
Installing MVC 2050 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 260
Procedure 46
Removing MVC 2050 from your PDA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 261
Procedure 47
Enable Auto-Create . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 267
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 23

List of procedures Page 23 of 600
Procedure 48
Disabling Automatic Gain Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 273
Procedure 49
Configuring the IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . 297
Procedure 50
Installing the IP Audio Conference Phone 2033
for the first time using manual configuration . . . . . . . . 301
Procedure 51
Installing an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033
for the first time using DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 307
Procedure 52
Enable Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 314
Procedure 53
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 315
Procedure 54
Changing the TN of an existing
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 316
Procedure 55
Replacing an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . 317
Procedure 56
Removing an IP Audio Conference Phone 2033
from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 317
Procedure 57
Connecting an extension microphone to the
IP Audio Conference Phone 2033 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 318
Procedure 58
Configuring the IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .339
Procedure 59
Installing the IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 347
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 24

Page 24 of 600 List of procedures
Procedure 60
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 355
Procedure 61
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 356
Procedure 62
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 1120E . . . . . 358
Procedure 63
Replacing an IP Phone 1120E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 359
Procedure 64
Removing an IP Phone 1120E from service . . . . . . . . . 359
Procedure 65
Configuring the IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 381
Procedure 66
Installing the IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 389
Procedure 67
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 397
Procedure 68
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 398
Procedure 69
Changing the TN of an existing
IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 400
Procedure 70
Replacing an IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 401
Procedure 71
Removing an IP Phone 1140E from service . . . . . . . . . 401
Procedure 72
Configuring an IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 428
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 25

List of procedures Page 25 of 600
Procedure 73
Installing the IP Phone 1150E for the first time
using manual configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 436
Procedure 74
Enabling Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 445
Procedure 75
Checking Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 446
Procedure 76
Changing the TN of an existing
IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .448
Procedure 77
Replacing an IP Phone 1150E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 449
Procedure 78
Removing an IP Phone 1150E from service . . . . . . . . . 449
Procedure 79
Connecting the Expansion Module to the IP Phone . . 457
Procedure 80
Accessing the Network Diagnostic Tools
menu in Local mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 502
Procedure 81
Executing Ping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 502
Procedure 82
Executing TraceRoute . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
Procedure 83
Accessing Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 503
Procedure 84
Accessing IP Network Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .503
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 26

Page 26 of 600 List of procedures
Procedure 85
Accessing IP Set & DHCP Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
Procedure 86
Accessing the Diagnostics submenu
in Remote Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 504
Procedure 87
Accessing Diagnostic Tools in Remote mode . . . . . . . 505
Procedure 88
Entering an IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
Procedure 89
Changing the number of Pings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 506
Procedure 90
Pinging an IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
Procedure 91
Reviewing the results of the Ping: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
Procedure 92
Entering an IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 507
Procedure 93
Changing the number of Hops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 508
Procedure 94
Tracing a route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 508
Procedure 95
Reviewing the results of the trace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
Procedure 96
Browsing Ethernet Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
Procedure 97
Checking 802.1x Supplicant status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 509
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 27

List of procedures Page 27 of 600
Procedure 98
Checking 802.1x Supplicant Authentication state . . . . 510
Procedure 99
Checking Device ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .510
Procedure 100
Checking Authenticator ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
Procedure 101
Browsing IP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 511
Procedure 102
Browsing RUDP Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .512
Procedure 103
Browsing Quality of Service Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . 512
Procedure 104
Using Network Diagnostic Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 532
Procedure 105
Using Ethernet Statistics tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 534
Procedure 106
Using the IP Network Statistics tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 535
Procedure 107
Using the IPSet&DHCP Information tool . . . . . . . . . . . . 537
Procedure 108
Using the IP Set&DHCP Information tool . . . . . . . . . . . 539
Procedure 109
Using Network Diagnostic Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 541
Procedure 110
Using Ethernet Statistics tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 543
Procedure 111
Using the IP Network Statistics tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 546
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 28

Page 28 of 600 List of procedures
Procedure 112
Using the USB Devices tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 549
Procedure 113
Locking the Tools menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 555
Procedure 114
Unlocking the Tools menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 556
Procedure 115
Configure the Bluetooth wireless technology
administration setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 559
Procedure 116
Enabling Bluetooth wireless technology
on the IP Phone 1140E . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 560
Procedure 117
Pairing the Bluetooth wireless technology headset
with your IP Phone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 565
Procedure 118
Switching between a wired headset
and wireless headset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 569
Procedure 119
Unpairing a wireless headset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 570
Procedure 120
Updating the IP Phones firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 573
Procedure 121
Downloading the firmware for the IP Phone 2007 . . . . 575
Procedure 122
Upgrading the firmware for IP Phone 1120E,
IP Phone 1140E, and IP Phone 1150E
using automatic TFTP download at bootup . . . . . . . . . 581
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 29

List of procedures Page 29 of 600
Procedure 123
Upgrading the firmware for IP Phone 1120E,
IP Phone 1140E, and IP Phone 1150E using BootC . . . 582
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 30

Page 30 of 600 List of procedures
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 31

32
Page 31 of 600
How to get Help
This chapter explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting help from the Nortel web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support web site:
www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and
tools to address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
• search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
• sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation for
Nortel equipment
• open and manage technical support cases
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical
Support web site, and you have a Nortel support contract, you can also get
help over the telephone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 32

Page 32 of 600 How to get Help
Outside North America, go to the following web site to obtain the telephone
number for your region:
www.nortel.com/callus
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
www.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 33

38
Page 33 of 600
About this document
This document is a global document. Contact your system supplier or your
Nortel representative to verify that the hardware and software described is
supported in your area.
Subject
This document contains description, installation, and administration
information for the following:
• Nortel IP Audio Conference Phone 2033
• Nortel IP Phone 2001, IP Phone 2002, IP Phone 2004, and IP Phone 2007
• Nortel IP Phone Key Expansion Module (KEM)
• Nortel IP Softphone 2050
• Nortel Mobile Voice Client 2050 for Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs)
• Nortel IP Phone 1120E
• Nortel IP Phone 1140E
• Nortel IP Phone 1150E
• Expansion Module for IP Phone 1100 Series
Note on legacy products and releases
This NTP contains information about systems, components, and features that
are compatible with Nortel Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5
software. For more information on legacy products and releases, click the
Technical Documentation link under Support on the Nortel home page:
http://www.nortel.com
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 34

Page 34 of 600 About this document
Applicable systems
This document applies to the following systems:
• Communication Server 1000S (CS 1000S)
• Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
• Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
• Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
• Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
• Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
• Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
• Meridian 1 PBX 51C
• Meridian 1 PBX 61C
•Meridian1 PBX81
• Meridian 1 PBX 81C
Note: When upgrading software, memory upgrades may be required on
the Signaling Server, the Call Server, or both.
System migration
When particular Meridian 1 systems are upgraded to run CS 1000
Release 4.5 software and configured to include a Signaling Server, they
become CS 1000M systems. Table 1 lists each Meridian 1 system that
supports an upgrade path to a CS 1000M system.
Table 1
Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems (Part 1 of 2)
This Meridian 1 system... Maps to this CS 1000M system
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis CS 1000M Chassis
Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet CS 1000M Cabinet
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 35

Table 1
Meridian 1 systems to CS 1000M systems (Part 2 of 2)
This Meridian 1 system... Maps to this CS 1000M system
Meridian 1 PBX 51C CS 1000M Half Group
Meridian 1 PBX 61C CS 1000M Single Group
Meridian 1 PBX 81 CS 1000M Multi Group
Meridian 1 PBX 81C CS 1000M Multi Group
For more information, see one or more of the following NTPs:
• Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Small System Upgrade
Procedures (553-3011-258)
• Communication Server 1000M and Meridian 1: Large System Upgrade
Procedures (553-3021-258)
• Communication Server 1000S: Upgrade Procedures (553-3031-258)
Intended audience
About this document Page 35 of 600
Conventions
This document is intended for individuals responsible for maintaining
Internet Enabled systems.
Terminology
In this document, the following systems are referred to generically as
“system”:
• Communication Server 1000S (CS 1000S)
• Communication Server 1000M (CS 1000M)
• Communication Server 1000E (CS 1000E)
•Meridian1
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 36

Page 36 of 600 About this document
The following systems are referred to generically as “Small System”:
• Communication Server 1000M Chassis (CS 1000M Chassis)
• Communication Server 1000M Cabinet (CS 1000M Cabinet)
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Chassis
• Meridian 1 PBX 11C Cabinet
The following systems are referred to generically as “Large System”:
• Communication Server 1000M Half Group (CS 1000M HG)
• Communication Server 1000M Single Group (CS 1000M SG)
• Communication Server 1000M Multi Group (CS 1000M MG)
• Meridian 1 PBX 51C
• Meridian 1 PBX 61C
•Meridian1 PBX81
• Meridian 1 PBX 81C
Related information
This section lists information sources that relate to this document.
NTPs
The following NTPs and documents are referenced in this document:
• IP Phone 2001 User Guide (NN43115-102)
• IP Phone 2002 User Guide (NN43116-104)
• IP Phone 2004 User Guide (NN43117-102)
• IP Phone 2007 User Guide (NN43118-100)
• IP Phone Audio Conference Phone 2033 User Guide (NN43111-100)
• IP Phone 1120E User Guide (NN43112-103)
• IP Phone 1140E User Guide (NN43113-106)
• IP Phone Key Expansion Module User Guide (NN43119-102)
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 37

About this document Page 37 of 600
• Expansion Module for IP Phones 1100 Series User Guide
(NN43130-101)
• WLAN IP Telephony: Installation and Configuration (NN43001-504)
• Mobile Voice Client 2050 User Guide (NN43119-103)
• Converging the Data Network with VoIP (NN43001-260)
• Signaling Server: Installation and Configuration (NN43001-312)
• IP Peer Networking: Installation and Configuration (NN43001-313)
• Secure Multimedia Controller (NN43001-325)
• System Security Management (NN43001-604)
• Features and Services (NN43001-106)
• Software Input/Output: Administration (NN43001-611)
• IP Line: Description, Installation, and Operation (NN43001-500)
• Software Input/Output: Maintenance (NN43001-711)
Online
To access Nortel documentation online, click the Technical Documentation
link under Support on the Nortel home page:
http://www.nortel.com
CD-ROM
To obtain Nortel documentation on CD-ROM, contact your Nortel customer
representative.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 38

Page 38 of 600 About this document
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 39

72
Page 39 of 600
Nortel IP Phone 2001
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Supported features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Display characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Package components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Extensible Authentication Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Replacing an IP Phone 2001 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Introduction
This section explains how to install and maintain the IP Phone 2001. For
information on using the IP Phone 2001, see the IP Phone 2001 User Guide.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 40

Page 40 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
This section contains the following procedures:
• Procedure 1, “Configuring the IP Phone 2001” on page 52.
• Procedure 2, “Installing the IP Phone 2001 for the first time using
manual configuration” on page 55.
• Procedure 3, “Installing an IP Phone 2001 for the first time using DHCP”
on page 61.
• Procedure 4, “Enabling Full Duplex mode” on page 68.
• Procedure 5, “Checking Ethernet Statistics” on page 68.
• Procedure 6, “Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2001” on
page 70.
• Procedure 7, “Replacing an IP Phone 2001” on page 71.
• Procedure 8, “Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service” on page 71.
Note: After an IP Phone has been installed and configured, if power to
the phone is interrupted, re-entry of the IP parameters, Node Number,
TN, or re-acquisition of firmware is not required.
Description
The IP Phone 2001 uses the customer IP data network to communicate with
the Communication Server 1000. The IP Phone 2001 translates voice into
data packets for transport using Internet Protocol. A Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server can be used to provide information
that enables the IP Phone 2001 network connection, and connection to the
Communication Server 1000.
Figure 1 on page 41 shows the IP Phone 2001.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 41

Figure 1
IP Phone 2001
Components and functions
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 41 of 600
This section describes the following components and functions of the
IP Phone 2001:
• Keys and functions
•Services menu
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 42

Page 42 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Keys and functions
Table 2 describes the IP Phone 2001 keys and functions.
Table 2
IP Phone 2001 keys and functions
Key Function
Speaker Press the Line key to activate the speaker for on-hook dialing and
listening.
Message waiting/
Incoming call indicator
Volume control bar Use the volume control bar to adjust the volume of the Handset,
Navigation keys Use the navigation keys to scroll through menus and lists in the
Line key Use the Line key to access the single line and activate on-hook
Hold key Press the Hold key to put an active call on hold. Press the Dial/Line
Soft keys
(self-labeled)
Message key Press the Message key to access your voicemail box.
Goodbye key Press the Goodbye key to terminate an active call.
The Message waiting lamp turns ON to indicate that a message has
been left for the user. This lamp also flashes when the set ringer is
ON.
Ringer, and On-hook Dialing/Listen tones.
Press the right side of the rocker bar to increase volume; press the
left side to decrease volume.
display area.
dialing. No status icon or LED is provided.
key to return to the caller on hold.
Soft keys (self-labeled) are located below the display area. The LCD
label above the key changes, based on the active feature.
Note: A triangle before a key label indicates that the key is active.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 43

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 43 of 600
Services menu
Table 3 shows the Services menu.
Table 3
Services menu (Part 1 of 2)
Services key Press the Services key to access the following items:
• Telephone Options (see Notes 1 and 2):
— Volume adjustment
— Contrast adjustment
— Language
— Date/Time
— Local DialPad Tone
—Set Info
— Diagnostics
— Ring type
—Call Timer
• Password Admin:
— Station Control Password
• Virtual Office Login and Virtual Office Logout (if Virtual Office is
configured)
• Test Local Mode and Resume Local Mode (if Branch Office is configured)
Press the Services key to exit from any menu or menu item.
Double-press the Services key to access Network diagnostic utilities. For
more information on Network diagnostic utilities, see Appendix E “IP Phone
diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 44

Page 44 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Table 3
Services menu (Part 2 of 2)
Note 1: If a call is presented while the user is manipulating information, the phone rings.
However, the screen display is not updated with Caller ID and the programming text is not
disturbed.
Note 2: The user can originate a call using Autodial or Last Number Redial while manipulating
an option. However, the display is not updated with the dialed digits or Caller ID, and Autodial
and Last Number Redial intercept the dialpad.
Supported features
The IP Phone 2001 supports the following telephony features:
• four soft keys providing access to a maximum of nine features
Note: Functions for the soft keys are configured in LD 11.
• volume control bar for adjusting ringer, speaker, handset, and headset
volume
• two specialized feature keys:
— Message/Inbox
— Services
• two call-processing keys
— Goodbye
— Hold
• Virtual Office
•Branch Office
• Active Call Failover
• Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download
The IP Phone 2001 supports the following data network features:
• 10/100 Mbps Full Duplex mode
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 45

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 45 of 600
• automatic network configuration through DHCP
For more information about automatic network configuration, see
Table 5 on page 54.
• 802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
For more information about LLDP, see Appendix D “802.1ab Link Layer
Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
• Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) media encryption
For more information about SRTP media encryption, see “Features
overview” on page 467.
• 802.1Q VLAN and 802.1p priority support, industry standards for
managing bandwidth usage
— VLAN filtering which allows the IP Phone to only see Voice VLAN
traffic. The integrated switch will pass DATA VLAN traffic to the
PC Ethernet port. This prevents the Data VLAN broadcast traffic
from reaching the IP Phone. For more information, see Appendix B
“802.1Q VLAN description” on page 483 and Converging the Data
Network with VoIP (553-3001-160).
• 802.1x Port-based network access control, industry standard for passing
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) over a LAN
For more information about 802.1x port-based network access control,
see Appendix C “802.1x Port-based network access control” on
page 493.
• integrated hardware to support Power over Ethernet (PoE) for IEEE
802.3af Power Classification 2
• Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol (GARP) Protection
The IP Phone 2001 supports the following languages:
English, French, Swedish, Danish, Norwegian, German, Dutch,
Portuguese, Czech, Finnish, Hungarian, Italian, Polish, Spanish,
Japanese, Russian, Latvian, Turkish
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 46

Page 46 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Features not currently supported
The following features are not supported on the IP Phone 2001:
• External three-port switch to support sharing LAN access with a PC or
other data device is not provided. However, the IP Phone 2001 does
provide 100 Mbps full-duplex support.
• Integrated switch
• Personal Directory, Call Log and Redial List are not supported.
However, if the primary DN on an IP Phone 2001 is an MADN of an IP
Phone 2002, IP Phone 2004, or IP Softphone 2050, Preferred Name
Match and Idle Set Display (new call indication) are supported.
• Corporate Directory
• Automatic Call Distribution
• IP Key Expansion Modules
• Support of accessory modules
• Live Dialpad
• Group Listening
• Set-to-Set messaging
• Context-sensitive soft keys
• Handsfree operation
• Headset support
Display characteristics
An IP Phone 2001 has two display areas:
• information line display
• soft key label display
Figure 2 on page 47 shows these two display areas.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 47

Figure 2
IP Phone 2001 display areas
Information line display
An IP Phone 2001 has a one-line information display area with the following
information:
• Caller Number
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 47 of 600
•Caller Name
• Feature prompt strings
• User-entered digits
• Date and time information (if the IP Phone is in an idle state) or Call
Timer (if provisioned in the Telephone options menu)
• Set information
The information area changes, according to call processing state and active
features.
Soft key label display
The soft key label has a maximum six characters. Each soft key includes the
soft key label and an icon. When a soft key is in use, a triangle icon displays
at the beginning of the soft key label, and the label shifts one character to the
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 48

Page 48 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
right. (If the label is six characters long, the last or rightmost character is
truncated.) If a feature is enabled, the icon state turns to On. It remains in the
on state until the feature key is pressed again. This cancels the enabled feature
and turns the icon off, returning the soft key label to its original state.
Use the More soft key to navigate through the layers of functions. If there are
only four functions assigned to the soft keys, the More key does not appear
and all four functions are displayed.
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen
Gently wipe the IP Phone display screen with a soft, dry cloth.
CAUTION
Do not use any liquids or powders on the IP Phone 2001.
Using anything other than a soft, dry cloth can
contaminate IP Phone components and cause premature
failure.
Key number assignments
A maximum of nine functions can be assigned to the four soft-labeled,
pre-defined soft keys. Because they are pre-defined, the user cannot change
the key number assignment. Functions are assigned to the soft keys in layers
in LD 11.
The Message key is numbered 16. Key numbers 17 to 31 are the four soft key
labels below the display area. See Figure 1 on page 41.
Key numbers 17 to 31 support the features A03, A06, CFW, CHG, CPN,
PRK, PRS, RGA, RNP, SCC, SCU, SSC, SSU, and TRN. See Appendix I “IP
Phone context-sensitive soft keys” on page 587 for a description of these
features.
Key number assignments at the Call Server are aligned with that of the
IP Phone 2002. The mappings between IP Phone 2001 soft key numbers and
PBX CPU key numbers are the same as on the IP Phone 2002 and IP Phone
2004.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 49

Package components
The following information applies to Phase II IP Phones. Product codes for
Phase II IP Phones are different from previous sets.
See the product code on the back of the phone to confirm whether it is a Phase
II IP Phone. The product code for Phase II IP Phones appears as IP Phone
200x. The product code for previous versions of the IP Phones appears with
an “i” in front of the model number; example, i200x.
The AC power adapter must be ordered separately if local power using the
AC adapter is required, because Phase II IP Phones include integrated support
for a number of power over LAN options, including support for IEEE 802.3af
standard power.
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 49 of 600
Table 4 lists the IP Phone 2001 package components and product codes.
Table 4
IP Phone 2001 components list (Part 1 of 2)
IP Phone 2001 package contents include:
• IP Phone 2001
• handset
• handset cord
• footstand
• 7 ft. Cat5 Ethernet cable
• Getting Started card
IP Phone 2001(Ethergray) with Icon keycaps NTDU90AA16/A0533387
IP Phone 2001 (Ethergray) with English text label keycaps NTDU90BA16/A0533388
IP Phone 2001 (Charcoal) with Icon keycaps NTDU90AA70/A0053389
IP Phone 2001 (Charcoal) with English text label keycaps NTDU90BA70/A0533390
Replacement parts
7 ft. Cat5 Ethernet Cable A0648375
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 50

Page 50 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Table 4
IP Phone 2001 components list (Part 2 of 2)
Handset, Ethergray A0788874
Handset, Charcoal A0758634
Handset cord, Ethergray; for IP Phone 2004 and IP Phone 2001 A088682
Handset cord, Charcoal; for IP Phone 2004 and IP Phone 2001 N0000764
IP Phone 2001/2002/2004 Power Adapters
Power transformer (117/120 VAC 50/60 Hz) (North America) A0619627
Power transformer 3-prong AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 240
VAC, 50Hz to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Ireland and UK)
Power transformer AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 230 VAC, 50/
60 Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Europe)
Power transformer 2-prong wall plug direct plug-in AC to AC,
8W, 240 VAC, 50 Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Australia and New
Zealand)
Power transformer AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 100 VAC, 50
Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA
For more information, and for information about previous versions of the
IP Phone, contact your Nortel representative.
Installation and configuration
The following sections provide a step-by-step guide through the
IP Phone 2001 installation and configuration process:
• Before you begin
• First-time installation
• Configuring the IP Phone 2001
A0656598
A0619635
A0647042
A0828858
• Startup sequence
• Installing the IP Phone 2001
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 51

Before you begin
Before installing the IP Phone 2001, complete the following pre-installation
checklist:
• Ensure there is one IP Phone 2001 boxed package for each
IP Phone 2001 being installed. The package contains:
— IP Phone 2001
—handset
— handset cord
— 2.3 m (7 ft) CAT5 Ethernet cable
— Getting Started Card
• Ensure the host Call Server is equipped with the Voice Gateway Media
Card, or a Signaling Server with the Line TPS application.
• If an AC power adapter is required, ensure the correct AC power
transformer is used. The voltage rating of the transformer must match the
wall outlet voltage. Refer to Table 4 on page 49.
First time installation
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 51 of 600
You must first install an IP Telephony Node with the Communication Server.
For information about installing an IP Telephony Node, see Signaling Server:
Installation and Configuration (553-3001-212), or IP Line: Description,
Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365) .
CAUTION
Do not plug your IP Phone 2001 into an ISDN
connection. Severe damage can result.
Configuring the IP Phone 2001
Use Procedure 1 on page 52 to configure the IP Phone 2001 for the first time.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 52

Page 52 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Procedure 1
Configuring the IP Phone 2001
1 Configure a virtual loop on the Call Server using LD 97.
For more information about configuring a virtual loop, see IP Line:
Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365), and Software
Input/Output: Administration (553-3001-311).
2 Configure the IP Phone 2001 on the Call Server using LD 11.
For more information, see Software Input/Output: Administration
(553-3001-311).
3 Connect the IP Phone 2001 components:
a. Connect one end of the handset cord to the handset jack on the back
of the IP Phone identified with a handset icon.
b. Connect the other end of the handset cord to the handset.
4 Connect one end of the CAT5 Ethernet cable to the network interface
located on the back of the IP Phone (identified with a LAN icon, see
Figure 3). The other end of the CAT5 Ethernet cable plugs into the IP
network.
5 Connect the AC power adapter (optional). Leaving the AC adapter
unplugged from the power outlet, connect the adapter to the AC adapter
jack in the bottom of the phone. Form a small bend in the cable and then
thread the adapter cord through the channels in the stand.
6 Secure the IP Phone footstand to the base of the IP Phone. Use the angle
adjustment grip on the top back of the IP Phone to adjust the position.
CAUTION
Damage to Equipment
Do not plug any device into your IP Phone 2001
Ethernet port other than one PC.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 53

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 53 of 600
Figure 3
IP Phone 2001 Ethernet network interface connections
7 Power the IP Phone 2001 using either the Power over Ethernet or an AC
power transformer (local power). If you are using local power, plug the AC
power transformer into the nearest power outlet. Make sure you use the
correct AC power transformer is used. The voltage rating of the
transformer must match the wall outlet voltage. Refer to Table 4 on
page 49.
Note: The IP Phone 2001 supports both AC power and Power over LAN
options, including IEEE 802.3af Power Classification 2. To use Power
over Ethernet, where power is delivered over the CAT5 cable, the LAN
must support Power over Ethernet, and an AC adapter is not required. To
use local AC power, the optional AC adapter can be ordered separately.
8 Use Procedure 2 on page 55 to install the IP Phone 2001 for the first time
using manual configuration, or use Procedure 3 on page 61 to install the
IP Phone 2001 for the first time using DHCP.
End of Procedure
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 54

Page 54 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Startup sequence
When an IP Phone 2001 is connected to the network, it must perform a startup
sequence. The elements of the startup sequence include:
• obtaining VLAN ID (if supported by the network infrastructure)
• obtaining the IP parameters
• connecting to the Call Server
• obtaining a User ID
See Table 5 for a summary of the IP parameters and how they are obtained.
Table 5
IP Phone 2001 IP parameters
Parameter Method of Acquisition
VLAN ID Manually entered or automatically obtained through
DHCP, and LLDP.
IP Address Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
Net Mask Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
Default Gateway Address Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
Connect Server (IP address, port,
action and retry count — primary
and secondary)
User ID (Node ID, Node Password
and TN)
Manually entered or automatically retrieved through Full
DHCP.
Manually entered for first-time configuration. Retrieved
from local storage on subsequent power cycles.
Installing the IP Phone 2001
To install the IP Phone 2001 for the first time using manual configuration, use
Procedure 2. To install the IP Phone 2001 for the first time using DHCP, use
Procedure 3 on page 61.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 55

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 55 of 600
Procedure 2
Installing the IP Phone 2001 for the
first time using manual configuration
IMPORTANT!
Timing information
There are only 4 second(s) between plugging in the IP Phone 2001
power transformer and the appearance of the Nortel logo in the middle
of the display. When you see the logo, you have 1 s to respond by
pressing the four soft keys at the bottom of the display in sequence from
left to right, one at a time. If you miss the 1-s response time, the
IP Phone 2001 attempts to locate the connect server. You can begin the
power-up sequence again, or you can double-press the Services key to
open the network diagnostic utilities to access the IP Phone settings.
See Appendix E “IP Phone diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
To edit network configuration the following soft keys are available:
• OK—accept current settings and proceed to the next configuration
option. If all configuration options are presented, the configuration is
saved and the IP Phone reboots with the saved changes.
• BkSpace—backspace a configuration entry to change it
• Clear—clear an entire configuration entry
• Cancel—cancels out of network configuration. The IP Phone reboots
without saving changes.
1 At the prompt EAP Enable?, enter 1-Yes (1 for Yes) if the network
infrastructure supports 802.1x port-based network access control. Enter
DeviceID and Password.
If you select 0-No (0 for No), you will not be prompted to enter Device ID
and Password.
For more information about EAP, refer to Appendix C “802.1x Port-based
network access control” on page 493.
2 At the prompt, LLDP Enable?, enter 1-Y (1 for Yes, default), or 0-N (0 for
No).
For more information about LLDP, see Appendix D “802.1ab Link Layer
Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 56

Page 56 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
3 At the prompt DHCP Yes/No?, enter 0-N (0 for No). You are prompted to
enter all parameters.
By default, Full DHCP is configured on the IP Phone 2001. Depending on
the configuration requirements, you can change the IP Phone 2001
configuration to allow the following IP address assignments:
• Static—enter all parameters
• Partial DHCP—IP Phone address, subnet mask, and default
Gateway are obtained from the DHCP server
• Full DHCP— (default) all parameters are obtained from the DHCP
server
Note: A DHCP server and DHCP relay agents must also be installed,
configured, and running if you choose Partial DHCP, or Full DHCP
configuration.
For more information on how to set up DHCP servers for use with the
IP Phones, refer to Converging the Data Network with VoIP
(553-3001-160).
4 Enter the following information:
Screen prompt Description
set IP A valid IP Phone 2001 IP address.
net msk A subnet mask.
def gw The default Gateway for the IP Phone 2001 on the
LAN segment to which the IP Phone 2001 is
connected.
5 Enter the information for the primary Connect Server (S1) and the
secondary Connect Server (S2):
S1 IP The primary CS 1000 node IP
S1 Port This is a fixed value: 4100
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
address for the IP Phone 2001.
Page 57

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 57 of 600
S1 action Choose one of the following:
• for TPS only, enter 1
• for TPS and Secure Media
Controller, enter 6 or 1
For more information about Secure
Media Controller, see Secure
Media Controller: Implementation
Guide (553-3001-225).
Note: You are not prompted for
S1 PK if S1 Action is set to 1.
S1 retry count The number of times the IP Phone
2001attempts to connect to the
server. Enter 10.
S1 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
The Private key of the Secure
Media Controller to which the IP
Phone is connected.
If you are using a Secure Media
Controller, do the following:
• Set S1 PK to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal
number.
S2 IP The secondary CS 1000 node IP
address for the IP Phone 2001.
S2 Port Same as S1
S2 action Same as S1
Note: You are not prompted for
S2 PK if S2 Action is set to 1.
S2 retry count Same as S1
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 58

Page 58 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
S2 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
Cfg XAS? (0-No,1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
XAS IP: Enter the IP address of the XAS
VLAN Cfg? (0-No, 1-Yes)
The Private key of the alternate
Secure Media Controller to which
the IP Phone is connected.
If you are using a Secure Media
Controller, do the following:
• Set to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal
number.
Note: If there is no External
Application Server (XAS), enter 0
(for No). You are not prompted to
enter the XAS IP address.
server.
VLAN Cfg? 0-Auto, 1-Man: 1-Man
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Enter the VLAN ID manually. This
is a number between 1 and 4094.
0-Auto
Automatically obtains VLAN ID
using DHCP or the 802.1ab data
switch.
Page 59

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 59 of 600
LLDP-MED? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID
is configured automatically to the
value received in the Network
Policy TLV.
You are not prompted for
LLDP-MED if VLAN is not set to
Auto (2-Auto,) or if LLDP is not
enabled.
LLDP VLAN? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID
is configured automatically to the
value received in the VLAN NAME
TLV.
You are not prompted for LLDP
VLAN if VLAN is not set to Auto (2Auto), or if LLDP is not enabled.
DHCP (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1-Y (1 for Yes), the
VLAN ID is configured
automatically to a value received
from the DHCP server.
You are not prompted for DHCP if
VLAN is not set to Auto (2-Au), or if
DHCP is not enabled.
VLANFILTER (0-No, 1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
You will not be prompted for
VLANFILTER if VLAN is not
enabled.
Duplex? (0-Auto, 1-Full) Default 0 (for Auto)
PSK SRTP? (0 for No, 1 for Yes) Default 0 (for No)
GARP Ignore? (0-No,1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)\
Note: You are prompted to enter the TFTP Server IP address if you are
using a TFTP Server to download the current firmware. For CS 1000
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 60

Page 60 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Release 4.5, accept the default value of 0.0.0.0. For Succession Release
3.0 or CS 1000 Release 4.0, enter the TFTP Server IP address. The
IP Phone searches for the TFTP Server for firmware upgrade. If the file
name specified in configuration file is not the same as the current
firmware, the IP Phone downloads the file and upgrades the firmware.
This takes several minutes. When the upgrade is complete, the IP Phone
reboots. For further information about TFTP Server configuration, see
Appendix H “TFTP Server” on page 571.
The IP Phone 2001 can support primary (S1) and secondary (S2) connect
server. If you require IP Phones to register on multiple nodes, refer to
“Enhanced Redundancy for IP Line Nodes” in IP Line: Description,
Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
The IP Phone 2001 saves the configuration and then reboots. The IP
Phone 2001 searches for the connect server. When the connection is
complete, proceed with step 6.
6 Enter the following information:
Screen prompt Description
Password IP Phone Installer Password
Node The node ID.
TN The TN or VTN.
You are not prompted to enter the IP Phone
Installer Password if it has not been configured
in your system.
The IP Phone 2001 registers with the Terminal Proxy Server (TPS) and,
if needed, begins the firmware download. This takes several minutes.
When the download is complete, the IP Phone 2001 resets.
Note: The Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download feature for IP Phones
provides an improved method of delivering new firmware to IP Phones.
For further information on Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download, refer
to IP Line: Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
The current system date and time appear on the top line of the display
when the configuration is complete. Self-labeling keys also appear.
7 Check for dial tone and the correct DN above the display.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 61

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 61 of 600
8 (Optional) Customize the feature keys as required. For more information,
see IP Phone 2001 User Guide.
End of Procedure
Procedure 3
Installing an IP Phone 2001 for the first time
using DHCP
IMPORTANT!
Timing information
There are only 4 second(s) between plugging in the IP Phone 2001
power transformer and the appearance of the Nortel logo in the middle
of the display. When you see the logo, you have 1 s to respond by
pressing the four soft keys at the bottom of the display in sequence from
left to right, one at a time. If you miss the 1-s response time, the
IP Phone 2001 attempts to locate the connect server. You can begin the
power-up sequence again, or you can double-press the Services key to
open the network diagnostic utilities to access the IP Phone settings.
See Appendix E “IP Phone diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
To edit network configuration the following soft keys are available:
• OK—accept current settings and proceed to the next configuration
option. If all configuration options are presented, the configuration is
saved and the IP Phone reboots with the saved changes.
• BkSpace—backspace a configuration entry to change it
• Clear—clear an entire configuration entry
• Cancel—cancels out of network configuration. The IP Phone reboots
without saving changes.
1 At the prompt EAP Enable?, enter 1-Yes (1 for Yes) if the network
infrastructure supports 802.1x port-based network access control. Enter
DeviceID and Password.
If you select 0-No (0 for No), you will not be prompted to enter Device ID
and Password.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 62

Page 62 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
For more information about EAP, refer to Appendix C “802.1x Port-based
network access control” on page 493.
2 At the prompt, LLDP Enable?, enter 1-Y (1 for Yes, default), or 0-N (0 for
No).
For more information about LLDP, refer to Appendix D “802.1ab Link
Layer Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
3 At the prompt DHCP Yes/No?, select 1-Y (1 for Yes).
By default, Full DHCP is configured on the IP Phone 2001. Depending on
the configuration requirements, you can change the IP Phone 2001
configuration to allow the following IP address assignments:
• Static—enter all parameters
• Partial DHCP—IP Phone address, subnet mask, and default
Gateway are obtained from the DHCP server
• Full DHCP— (default) all parameters are obtained from the DHCP
server
A DHCP server and DHCP relay agents must also be installed,
configured, and running if you choose Partial DHCP, or Full DHCP
configuration.
For more information on how to set up DHCP servers for use with the
IP Phones, refer to Converging the Data Network with VoIP
(553-3001-160).
4 At the prompt, Cached IP?, select 0 (0-No, default) to conform to the
DHCP standard and to obtain an IP address from the DHCP server. Only
select 1 (1 for Yes) to force the IP Phone to start with a cached IP address
in the event that the IP Phone cannot connect to the DHCP server and
obtain an IP address.
5 Select Partial or Full DHCP.
a. If you select Full DHCP, then the following parameters are retrieved
from the DHCP server:
— a valid IP Phone 2001 IP address
— a subnet mask
— the default Gateway for the IP Phone 2001 on the LAN segment
to which it is connected
— the S1 IP. The primary CS 1000 node IP address of the IP
Phone.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 63

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 63 of 600
— the S1 action
— the S1 retry count. This is the number of times the
IP Phone 2001 attempts to connect to the server
— the S2 IP. The secondary CS 1000 node IP address of the IP
Phone.
— the S2 action
— the S2 retry count
b. If you select Partial DHCP, then you must enter the following
parameters:
Screen prompt Description
S1 IP The primary CS 1000 node IP address for the IP
Phone 2001.
S1 Port This is a fixed value: 4100
S1 action Choose one of the following:
• for TPS only, enter 1
• for TPS and Secure Media Controller, enter 6 or
1
For more information about Secure Media
Controller, see Secure Media Controller:
Implementation Guide (553-3001-225).
Note: You are not prompted for S1 PK if the S1
action is set to 1.
S1 retry count The number of times the IP Phone 2001attempts
to connect to the server. Enter 10.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 64

Page 64 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
S1 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
S2 IP The secondary CS 1000 node IP address for the
S2 Port Same as S1
S2 action Same as S1.
S2 retry count Same as S1
S2 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
The Private key of the Secure Media Controller to
which the IP Phone is connected.
If you are using a Secure Media Controller, do the
following:
• Set to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal number.
IP Phone 2001.
Note: You are not prompted for S2 PK if the S2
action is set to 1.
The Private key of the alternate Secure Media
Controller to which the IP Phone is connected.
If you are using a Secure Media Controller, do the
following:
• Set to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal number.
Cfg XAS?
(0-No,1-Yes)
XAS IP: Enter the IP address of the XAS server.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Default 0 (for No)
Note: If there is no External Application Server
(XAS), enter 0 (for No). You are not prompted to
enter the XAS IP address.
Page 65

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 65 of 600
6 Enter the following parameters:
VLAN Cfg? (0-No, 1-Yes)
VLAN Cfg? 0-Auto, 1-Man: 1-Man
Enter the VLAN ID manually. This
is a number between 1 and 4094.
0-Auto
Automatically obtains VLAN ID
using DHCP, or the 802.1ab data
switch.
LLDP-MED? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID
is configured automatically to the
value received in the Network
Policy TLV.
You are not prompted for
LLDP-MED if VLAN is not set to
Auto (2-Auto,) or if LLDP is not
enabled.
LLDP VLAN? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID
is configured automatically to the
value received in the VLAN NAME
TLV.
You are not prompted for LLDP
VLAN if VLAN is not set to Auto (2Auto), or if LLDP is not enabled.
DHCP (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), the
VLAN ID is configured
automatically to a value received
from the DHCP server.
You are not prompted for DHCP if
VLAN is not set to Auto (2-Au), or if
DHCP is not enabled.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 66

Page 66 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
VLANFILTER (0-No, 1-Yes) Default 0 (0 for No)
Duplex? (0-Auto, 1-Full) Default 0 (for Auto)
PSK SRTP? (0 for No, 1 for Yes) Default 0 (for No)
GARP Ignore? (0-No,1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
Note: You are prompted to enter the TFTP Server IP address if you are
using a TFTP Server to download the current firmware. For CS 1000
Release 4.5, accept the default value of 0.0.0.0. For Succession Release
3.0 or CS 1000 Release 4.0, enter the TFTP Server IP address. The
IP Phone searches for the TFTP Server for firmware upgrade. If the file
name specified in configuration file is not the same as the current
firmware, the IP Phone downloads the file and upgrades the firmware.
This takes several minutes. When the upgrade is complete, the IP Phone
reboots. For further information about TFTP Server configuration, see
Appendix H “TFTP Server” on page 571.
The IP Phone 2001 can support a primary (S1) and secondary (S2)
connect server. If you require IP Phones to register on multiple nodes,
refer to “Enhanced Redundancy for IP Line Nodes” in IP Line:
Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
You will not be prompted for
VLANFILTER if VLAN is not
enabled.
The IP Phone 2001 saves the configuration and then reboots. The
IP Phone 2001 searches for the connect server. When the connection is
complete, proceed to step 7.
7 Enter the following information:
Screen prompt Description
Password IP Phone Installer Password
You are not prompted to enter the IP Phone
Installer Password if it has not been
configured in your system.
Node The node ID
TN The TN or VTN
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 67

The IP Phone 2001 registers with the TPS and, if needed, begins the
firmware download. This takes several minutes. When the download is
complete, the IP Phone 2001 resets.
Note: The Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download feature for IP Phones
provides an improved method of delivering new firmware to IP Phones.
For further information on Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download, refer
to IP Line: Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
The current system date and time appear on the top line of the display
when the configuration is complete. Self-labeling keys also appear.
8 Check for dial tone and the correct DN above the display.
9 (Optional) Customize the feature keys as required. For more information,
see IP Phone 2001 User Guide.
Full Duplex mode
In the Configuration menu, Auto Negotiate mode is the default setting for
initial startup. Typically, the IP Phone is connected to a network that supports
Auto Negotiate, and it selects the best speed and duplex mode available.
There is no intervention required under normal operation.
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 67 of 600
End of Procedure
Note: Changing the speed and/or duplex mode on the phone changes
both the LAN Ethernet port and PC Ethernet Port interfaces.
IMPORTANT!
It is recommended that Auto Negotiate mode is used on the network
and the IP Phone. Use Full Duplex mode only when the network is
forced Full Duplex for 100BT Full Duplex mode, otherwise a duplex
mismatch will result.
If the IP Phone is connected to a network configured for Full Duplex mode
only, the IP Phone cannot automatically negotiate the proper configuration.
Therefore, in this instance, to allow the IP Phone to work at the optimum
speed and duplex mode, Full Duplex mode must be enabled.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 68

Page 68 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Use Procedure 4 on page 68 to enable Full Duplex mode.
Procedure 4
Enabling Full Duplex mode
1 Reset the phone by disconnecting and re-connecting power.
2 When the Nortel logo appears, press each of the soft keys in sequence.
See Procedure 3 on page 61.
3 If no other configuration changes are required, press OK repeatedly until
the Duplex network option appears.
4 Select 1 to enable Full Duplex mode.
5 When the Speed option appears, select one of the following:
• 0 for 10 Mbps
• 1 for 100 Mbps (default)
6 Select OK to confirm the change.
7 Restart the IP Phone 2001. The firmware settings are read and are
applied to UPLINK and the PC Ethernet Port.
End of Procedure
When the IP Phone is restarted, the firmware reads the setting for Full Duplex
mode and sets the LAN Ethernet port, PC Ethernet port, duplex, and speed
accordingly.
Use Procedure 5 to confirm activation of Full Duplex mode.
Procedure 5
Checking Ethernet Statistics
1 Double-click the Services key. The Network Diagnostics menu appears.
2 Select Ethernet Statistics.
• If Full Duplex mode is active, the following is displayed:
— Link: UP
— Duplex: Full
— Speed: 10 (Mb) or 100(Mb)
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 69

Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 69 of 600
— Auto-Negotiate Capability: N
— Auto-Negotiate Completed: N
End of Procedure
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol (GARP) Protection prevents the
IP Phone 2001 from GARP Spoof attacks on the network. In a GARP Spoof
attack, a malicious device on the network takes over an IP address (usually
the default gateway) by sending unsolicited (or Gratuitous) ARP messages,
thus manipulating the ARP table of the victim’s machine. The malicious
device launches a variety of attacks on the network, resulting in undesired
traffic routing. For example, a GARP attack can convince the victim machine
that the malicious device is the default gateway. In this scenario, all traffic
from the victim’s machine flows through the malicious device.
To enable GARP Protection during configuration, refer to Procedure 1,
“Configuring the IP Phone 2001” on page 52 or Procedure 1, “Installing an
IP Phone 2001 for the first time using DHCP” on page 61.
Extensible Authentication Protocol
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is a general protocol that fulfills
the protocol requirements defined by 802.1x. For further information on
802.1x, refer to Appendix C “802.1x Port-based network access control” on
page 493.
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2001
You can reinstall an existing previously configured IP Phone 2001 on the
same system. For example, the IP Phone 2001 can be assigned to a new user
(new TN) or to an existing user who moved to a new subnet by changing the
TN of the IP Phone 2001.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 70

Page 70 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
Procedure 6
Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2001
1 Repower the IP Phone 2001.
Note: During the reboot sequence of a previously configured IP Phone,
the IP Phone 2001 displays the existing node number for approximately
five seconds.
2 If the node password is enabled and NULL, choose one of the following:
a. Disable the password.
b. Set the password as non-NULL.
3 Press OK when the node number displays.
If Then
the node password is enabled and
is not NULL
the node password is disabled a TN screen displays. Go to
4 Enter password at the password screen, and press OK.
A TN screen displays.
Note: To obtain the password, enter the nodePwdShow command in
Element Manager. For further information, see Element Manager:
System Administration (553-3001-332).
5 Select the Clear soft key to clear the existing TN.
6 Enter the new TN.
End of Procedure
a password screen displays. Go to
step 4.
step 5.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 71

Replacing an IP Phone 2001
Two IP Phones cannot share the same TN. You must remove the
IP Phone 2001 that is currently using the TN.
Procedure 7
Replacing an IP Phone 2001
1 Obtain the node and TN information of the phone you want to replace.
2 Disconnect the IP Phone 2001 that you want to replace.
3 Follow Procedure 1 on page 52 and Procedure 2 on page 55 or
Procedure 3 on page 61 to install and configure the IP Phone 2001.
4 Enter the same TN and Node Number as the IP Phone 2001 you
replaced. The system associates the new IP Phone 2001 with the
existing TN.
Nortel IP Phone 2001 Page 71 of 600
IMPORTANT!
End of Procedure
Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service
Procedure 8
Removing an IP Phone 2001 from service
1 Disconnect the IP Phone 2001 from the network or turn off the power.
If the IP Phone 2001 was automatically configured, the DHCP lease
expires and the IP address returns to the available pool.
2 In LD 11, enter OUT at the TN prompt.
End of Procedure
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 72

Page 72 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2001
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 73

110
Page 73 of 600
Nortel IP Phone 2002
Contents
This section contains information on the following topics:
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Components and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Supported features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Features not currently supported . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Display characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Key number assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Package components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Installation and configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Full Duplex mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Extensible Authentication Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Reinstalling an IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Replacing an IP Phone 2002 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Removing an IP Phone 2002 from service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 74

Page 74 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Introduction
This section explains how to install and maintain the IP Phone 2002. For
information on using the IP Phone 2002, see the IP Phone 2002 User Guide.
This section contains the following procedures:
• Procedure 9, “Configuring the IP Phone 2002” on page 87.
• Procedure 10, “Installing the IP Phone 2002 for the first time using
manual configuration” on page 91.
• Procedure 11, “Installing an IP Phone 2002 for the first time using
DHCP” on page 98.
• Procedure 12, “Enabling Full Duplex mode” on page 105.
• Procedure 13, “Checking Ethernet Statistics” on page 106.
• Procedure 14, “Changing the TN of an existing IP Phone 2002” on
page 107.
• Procedure 15, “Replacing an IP Phone 2002” on page 108.
• Procedure 16, “Removing an IP Phone 2002 from service” on page 109.
Note: After an IP Phone has been installed and configured, if power is to
the phone is interrupted, re-entry of the IP parameters, Node Number,
TN, or re-acquisition of firmware is not required.
Description
The IP Phone 2002 uses the customer IP data network to communicate with
the Communication Server 1000. The IP Phone 2002 translates voice into
data packets for transport using Internet Protocol. A Dynamic Host
Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server can be used to provide information
that enables the IP Phone 2002 network connection, and connection to the
Communication Server 1000.
Figure 4 on page 75 shows the IP Phone.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 75

Figure 4
IP Phone 2002
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 75 of 600
Components and functions
This section describes the following components and functions of the
IP Phone 2002:
• Keys and functions
•Services menu
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 76

Page 76 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Keys and functions
Table 6 describes the IP Phone 2002 keys and functions.
Table 6
IP Phone 2002 keys and functions (Part 1 of 2)
Key Function
Speaker Press the In LD 11, enter OUT at the TN prompt. key to activate the
speaker.
User-defined feature
keys (self-labeled)
Message waiting light/
Incoming call indicator
Soft keys (self-labeled) Soft keys (self-labeled) are located below the display area. The LCD
Navigation keys Use the navigation keys to scroll through menus and lists in the
Inbox (Message) Press the Message (Inbox) key to access your voicemail box.
Outbox/Shift The Outbox/Shift key is a fixed key that is reserved for future feature
Directory Press the Directory key to access Directory services.
Quit Press the Quit key to end an active application.
User-defined feature keys (self-labeled) are configured for various
features on the IP Phone. One must be the prime DN key.
A steady LCD light beside a line (DN) key indicates the feature or
line is active. A flashing LCD indicates the line is on hold or the
feature is being programmed.
The Message waiting light turns ON to indicate that a message has
been left for the user. This light also flashes when the set ringer is
ON.
label above the key changes, based on the active feature.
Note: A triangle before a key label indicates that the key is active.
display area.
development.
Pressing the Quit key does not affect the status of the calls currently
on your IP Phone.
Expand to PC The Expand to PC key is used to access external server
applications such as External Application Server (XAS).
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 77

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 77 of 600
Table 6
IP Phone 2002 keys and functions (Part 2 of 2)
Key Function
Goodbye Press the Goodbye key to terminate an active call.
Hold Press the Hold key to put an active call on hold. Press the line (DN)
key beside the flashing LCD to return to the caller on hold.
Headset Press the Headset key to answer a call using the headset or to
switch a call from the handset or Handsfree to the headset.
Mute Press the Mute key to listen to the receiving party without
transmitting.
Press the Mute key again to return to a two-way conversation.
The Mute key applies to Handsfree, Handset, and Headset
microphones.
The Mute LED flashes when the Mute option is in use.
Volume control bar Use the volume control bar to adjust the volume of the handset,
headset, speaker, ringer, and, Handsfree feature.
Press the right side of the rocker bar to increase volume; press the
left side to decrease volume.
Handsfree key Press the Handsfree key to activate the Handsfree feature.
The LED lights to indicate when handsfree is active.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 78

Page 78 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Services menu
Table 7 shows the Services menu.
Table 7
Services menu
Services key Press the Services key to access the following items:
• Telephone Options:
— Volume Adjustment
— Contrast Adjustment
— Language
— Date/Time Format
— Display diagnostics
— Local Dialpad Tone
—Set Info
— Ring type
— OnHook Default Path
— Change Feature key label
—Call Timer
• Password Administration
• Virtual Office Login and Virtual Office Logout (if Virtual Office is configured)
• Test Local Mode and Resume Local Mode (if Branch Office is configured)
Double-press the Services key to access Network diagnostic utilities. For more information on
Network diagnostic utilities, see Appendix E “IP Phone diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
Note 1: If a call is presented while the user is manipulating an option, the IP Phone 2002 rings
and the DN key flashes. However, the screen display is not updated with Caller ID information
and programming text is not disturbed.
Note 2: The user can originate a call using Autodial or Last Number Redial while manipulating
an option. However, the display is not updated with the dialed digits or the Caller ID information,
and Autodial and Last Number Redial intercept the dialpad.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 79

Supported features
The IP Phone 2002 supports the following telephony features:
• four feature keys
• four soft keys (self-labeled) providing access to a maximum of nine
features
Note: Functions for the soft keys are configured in LD 11.
• volume control bar for adjusting ringer, speaker, handset, and headset
volume
• six specialized feature keys:
— Quit
— Directory
— Message/Inbox
— Shift/Outbox
— Services
— Copy
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 79 of 600
• six call-processing fixed keys:
— Mute
— Handsfree
— Goodbye
— Expand to PC
— Headset
— Hold
• Call Duration Timer
• ability to change the user-defined feature key labels
• Corporate Directory
• Personal Directory
• Redial List
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 80

Page 80 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
•Callers List
• Password Administration
• Virtual Office
•Branch Office
• Active Call Failover
• Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download
The IP Phone 2002 supports the following data network features:
• integrated switch for shared PC access
— LAN Ethernet port supports 10/100BT Mbps Full Duplex mode
— PC Ethernet port supports 10/100BT Mbps Full Duplex mode
• automatic network configuration through DHCP
For more information about automatic network configuration, see
Table 9 on page 90.
• 802.1ab Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP)
For more information about LLDP, refer to Appendix D “802.1ab Link
Layer Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
• Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) media encryption
For more information about SRTP media encryption, see “Features
overview” on page 467.
• 802.1Q VLAN and 802.1p priority support, industry standards for
managing bandwidth usage
— full VLAN capability, including a manageable integrated switch in
the IP Phone; allows VLAN and priority tagging for the IP Phone
traffic and VLAN tagging for PC traffic
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 81

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 81 of 600
— VLAN filtering which allows the IP Phone to only see Voice VLAN
traffic. The integrated switch will pass DATA VLAN traffic to the
PC Ethernet port. This prevents the Data VLAN broadcast traffic
from reaching the IP Phone. For more information, see Appendix B
“802.1Q VLAN description” on page 483 and Converging the Data
Network with VoIP (553-3001-160).
• 802.1x Port-based network access control, industry standard for passing
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) over a LAN
For more information about 802.1x port-based network access control,
see Appendix C “802.1x Port-based network access control” on
page 493.
• integrated hardware to support Power over Ethernet (PoE) for IEEE
802.3af Power Classification 2
• Gratuitous Address Resolution Protocol Protection (GARP)
The IP Phone 2002 supports the following user interface features:
• External Application Server (XAS)
• language support: English, French, Swedish, Danish, Norwegian,
German, Dutch, Portuguese, Czech, Finnish, Hungarian, Italian, Polish,
Spanish, Japanese, Russian, Latvian, and Turkish
• IP Key Expansion modules
Features not currently supported
The following features are not supported on the IP Phone 2002:
• Live Dialpad
• Group Listening
• Set-to-Set messaging
• Context-sensitive soft keys
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 82

Page 82 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Display characteristics
An IP Phone 2002 has three major display areas:
• user defined feature key label
• information line
• soft key label
Figure 5 on page 82 shows these three display areas.
Figure 5
IP Phone 2002 display areas
User defined feature key label display
The feature key label area displays a ten-character string for each of the four
feature keys. Each feature key includes the key label and an icon. The icon
state can be on, off, or flashing. A telephone icon displays the status of the
configured DN. Key labels are left-aligned for keys on the left side of the
screen, and right-aligned for keys on the right side of the screen.
Note: If a label is longer than ten characters, the last ten characters are
displayed and the excess characters are deleted from the beginning of the
string.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 83

Information line display
An IP Phone 2002 has a one-line information display area with the following
information:
• Caller number
•Caller name
• Feature prompt strings
• User-entered digits
• Date and time information (if the IP Phone is in an idle state) or Call
Timer (if provisioned in the Telephone options menu)
The information in the display area changes, according to the call processing
state and active features.
Soft key label display
The soft key label has a maximum six characters. Each soft key includes the
soft key label and an icon. When a soft key is in use, a triangle icon displays
at the beginning of the soft key label, and the label shifts one character to the
right. (If the label is six characters long, the last or rightmost character is
truncated.) If a feature is enabled, the icon state turns to On. It remains in the
on state until the feature key is pressed again. This cancels the enabled feature
and turns the icon off, returning the soft key label to its original state.
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 83 of 600
Use the More soft key to navigate through the layers of functions. If there are
only four functions assigned to the soft keys, the More key does not appear
and all four functions are displayed.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 84

Page 84 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Cleaning the IP Phone display screen
Gently wipe the IP Phone display screen with a soft, dry cloth.
CAUTION
Do not use any liquids or powders on the IP Phone.
Using anything other than a soft, dry cloth can
contaminate IP Phone components and cause premature
failure.
Key number assignments
A maximum of nine functions can be assigned to the four soft-labeled,
predefined soft keys. Because they are pre-defined, the user cannot change
the key number assignment. Functions are assigned to the soft keys in layers
in LD 11.
The Message key is numbered 16. Key numbers 17 to 31 are the four soft key
labels below the display area. See Figure 5 on page 82.
Key numbers 17 to 31 support the features A03, A06, CFW, CHG, CPN,
PRK, PRS, RGA, RNP, SCC, SCU, SSC, SSU, and TRN. See Appendix I “IP
Phone context-sensitive soft keys” on page 587 for a description of these
features.
Key number assignments at the Call Server are aligned with that of the
IP Phone 2004. The mappings between IP Phone 2002 soft key numbers and
PBX CPU key numbers are the same as on the IP Phone 2004.
Package components
The following information applies to Phase II IP Phones. Product codes for
Phase II IP Phones are different from previous sets.
See the product code on the back of the phone to confirm whether it is a Phase
II IP Phone. The product code for Phase II IP Phones appears as
IP Phone 200x. The product code for previous versions of the IP Phone
appears with an i in front of the model number (for example, i200x).
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 85
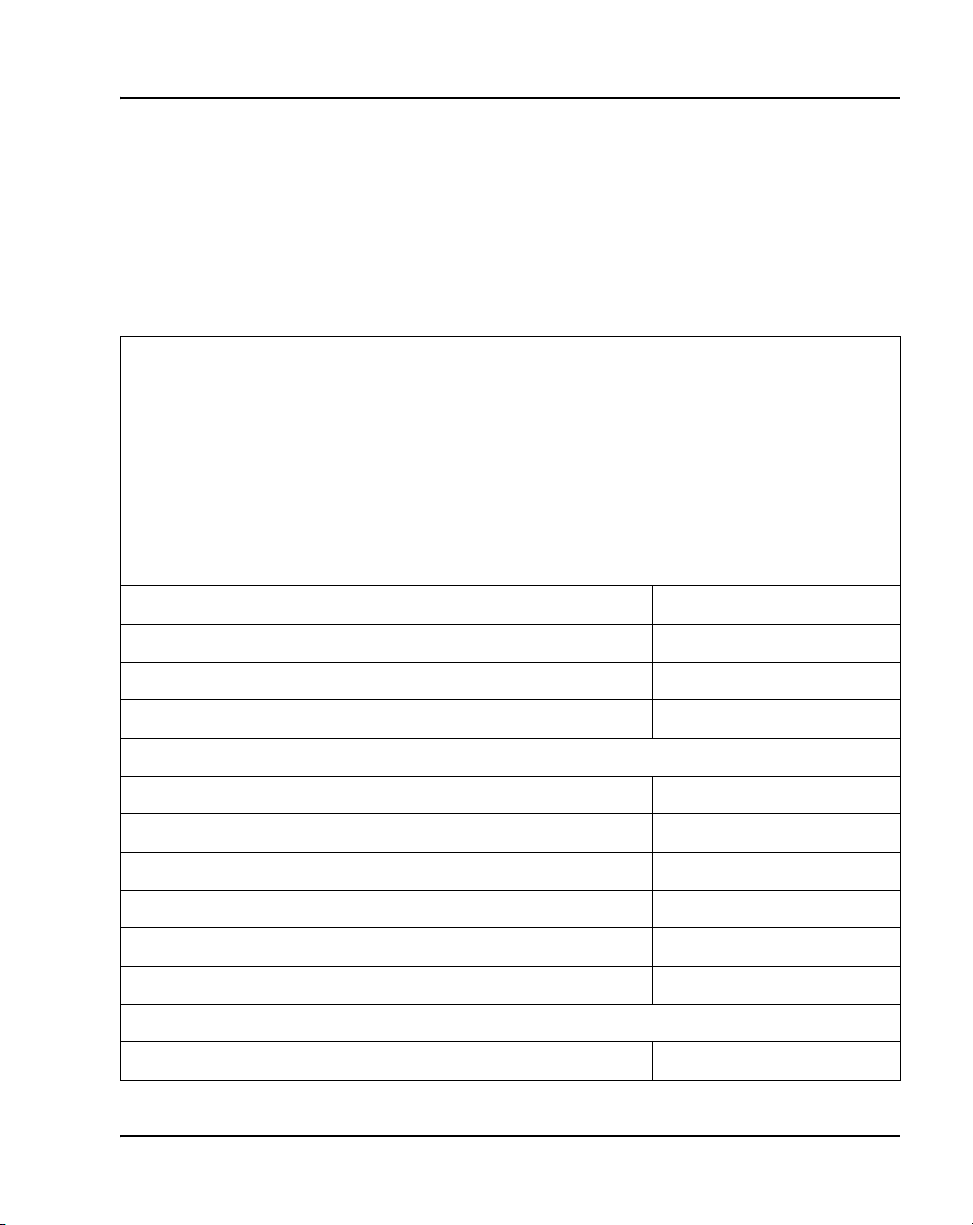
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 85 of 600
The AC power adapter must be ordered separately if local power using the
AC adapter is required, because Phase II IP Phones include integrated support
for a number of power over LAN options, including support for IEEE 802.3af
standard power.
Table 8 lists the IP Phone 2002 package components and product codes.
Table 8
IP Phone 2002 components list (Part 1 of 2)
IP Phone 2002 package contents include:
• IP Phone 2002
• Handset
• Handset cord
• Footstand
• 7ft Cat5 Ethernet cable
• Getting Started card
IP Phone 2002 (Ethergray) with Icon keycaps NTDU91AA16/A0533404
IP Phone 2002 (Ethergray) with English text label keycaps NTDU91BA16/A0533405
IP Phone 2002 (Charcoal) with Icon keycaps NTDU91AA70/A0533406
IP Phone 2002 (Charcoal) with English text label keycaps NTDU91BA70/A0533407
Replacement parts
7 ft. Cat5 Ethernet cable A0648375
Handset, Ethergray A0788874
Handset, Charcoal A0758634
Handset cord, Ethergray A0897725
Handset cord, Charcoal N0000763
Footstand, Charcoal (used for Ethergray and Charcoal models) A0891619
IP Phone 2001/2002/2004 Power Adaptors
Power transformer (117/120 VAC 50/60 Hz) (North America) A0619627
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 86

Page 86 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Table 8
IP Phone 2002 components list (Part 2 of 2)
Power transformer 3-prong AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 240
VAC, 50Hz to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Ireland and UK)
Power transformer AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 230 VAC, 50/60
Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Europe)
Power transformer 2-prong wall plug direct plug-in AC to AC,
8W, 240 VAC, 50 Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA (Australia and New
Zealand)
Power transformer AC to AC, direct plug-in, 8W, 100 VAC, 50
Hz, to 16 VAC at 500 mA
For more information, and for information about previous versions of the IP
Phone, contact Nortel.
Installation and configuration
The following sections provide a step-by-step guide through the
IP Phone 2002 installation and configuration process:
• Before you begin
• First-time installation
• Configuring the IP Phone 2002
A0656598
A0619635
A0647042
A0828858
• Startup sequence
• Installing the IP Phone 2002
Before you begin
Before installing the IP Phone 2002, complete the following pre-installation
checklist:
• Ensure there is one IP Phone 2002 boxed package for each
IP Phone 2002 being installed. The package contains:
— IP Phone 2002
— handset
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 87

— handset cord
— 2.3 m (7 ft) CAT5 Ethernet cable
— Getting Started Card
• Ensure the host Call Server is equipped with the Voice Gateway Media
Card, or a Signaling Server with the Line TPS application.
• If an AC power adapter is required, ensure the correct AC power
transformer is used. The voltage rating of the transformer must match the
wall outlet voltage. Refer to Table 8 on page 85.
First-time installation
You must first install an IP Telephony Node with the Communication Server.
For information about installing an IP Telephony Node, see Signaling Server:
Installation and Configuration (553-3001-212), or IP Line: Description,
Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365) .
CAUTION
Do not plug your IP Phone 2002 into an ISDN
connection. Severe damage can result.
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 87 of 600
Configuring the IP Phone 2002
Use Procedure 9 to configure the IP Phone 2002 for the first time.
Procedure 9
Configuring the IP Phone 2002
1 Configure a virtual loop on the Call Server using LD 97.
For more information about configuring a virtual loop, see IP Line:
Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365), and Software
Input/Output: Administration (553-3001-311).
2 Configure the IP Phone 2002 on the Call Server using LD 11.
For more information, see Software Input/Output: Administration
(553-3001-311).
3 Connect the IP Phone 2002 components:
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 88

Page 88 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
a. Connect one end of the handset cord to the handset jack on the back
of the IP Phone (identified with a handset icon).
b. Connect the other end of the handset cord to the handset.
4 Choose one of the following connections:
• For an IP Phone not sharing LAN access with a PC:
Connect one end of the CAT5 Ethernet cable to the network interface
located on the back of the IP Phone (identified with a LAN icon, see
Figure 6 on page 89). The other end of the CAT5 Ethernet cable
plugs into the IP network.
• For an IP Phone sharing LAN access with a PC:
Connect one end of the CAT5 Ethernet cable to the network interface
located on the back of the IP Phone (identified with a LAN icon, see
Figure 6 on page 89) and the other end to the IP network. Insert on
end of a second CAT5 Ethernet cable into the PC network interface
located on the back of the IP Phone (identified with a PC icon, see
Figure 6 on page 89) and the other end into the computer.
CAUTION
Damage to Equipment
Do not plug any device into your IP Phone 2002
Ethernet port other than one PC. The IP Phone 2002
does not support multiple devices connected through
the PC Ethernet port.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 89

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 89 of 600
Figure 6
IP Phone 2002 Ethernet network interface connections
Network
Ethernet
PC
Ethernet
5 Connect the AC power adapter (optional). Leaving the AC adapter
unplugged from the power outlet, connect the adapter to the AC adapter
jack in the bottom of the phone. Form a small bend in the cable and then
thread the adapter cord through the channels in the stand.
6 Secure the IP Phone footstand to the base of the IP Phone. Use the angle
adjustment grip on the top back of the IP Phone to adjust the position.
7 Power the IP Phone 2002 using either the Power over Ethernet or an AC
power transformer (local power). If you are using local power, plug the AC
power transformer into the nearest power outlet. Make sure you use the
correct AC power transformer is used. The voltage rating of the
transformer must match the wall outlet voltage. Refer to Table 8 on
page 85.
Note: The IP Phone 2004 supports both AC power and Power over LAN
options, including IEEE 802.3af Power Classification 2. To use Power
over Ethernet, where power is delivered over the CAT5 cable, the LAN
must support Power over Ethernet, and an AC adapter is not required. To
use local AC power, the optional AC adapter can be ordered separately.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 90

Page 90 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
8 Use Procedure 10 on page 91 to install the IP Phone 2002 for the first
time using manual configuration, or use Procedure 11 on page 98 to
install the IP Phone 2002 for the first time using DHCP.
Startup sequence
When an IP Phone 2002 is connected to the network, it must perform a startup
sequence. The elements of the startup sequence include:
• obtaining VLAN ID (if supported by the network infrastructure)
• obtaining the IP parameters
• connecting to the Call Server
• obtaining a User ID
See Table 9 for a summary of the IP parameters and how they are obtained.
Table 9
IP Phone 2002 IP parameters
Parameter Method of Acquisition
VLAN ID Manually entered or automatically obtained through
DHCP, and LLDP.
IP Address Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
Net Mask Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
DefaultGateway Address Manually entered or automatically retrieved through
Partial or Full DHCP.
Connect Server (IP address, port,
action and retry count — primary
and secondary)
User ID (Node ID, Node Password
and TN)
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Manually entered or automatically retrieved through Full
DHCP.
Manually entered for first-time configuration. Retrieved
from local storage on subsequent power cycles.
Page 91

Installing the IP Phone 2002
To install the IP Phone 2002 for the first time using manual configuration, use
Procedure 10 on page 91. To install the IP Phone 2002 for the first time using
DHCP, see Procedure 11 on page 98.
Procedure 10
Installing the IP Phone 2002 for the
first time using manual configuration
Timing information
There are only 4 s between plugging in the IP Phone 2002 power
transformer and the appearance of the Nortel logo in the middle of the
display. When you see the logo, you have 1 s to respond by pressing the
four soft keys at the bottom of the display in sequence from left to right,
one at a time. If you miss the 1-s response time, the IP Phone 2002
attempts to locate the connect server. You can begin the power-up
sequence again, or you can double-press the Services key to open the
network diagnostic utilities to access the IP Phone settings. See
Appendix E “IP Phone diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 91 of 600
IMPORTANT!
To edit network configuration the following soft keys are available:
• OK—accept current settings and proceed to the next configuration
option. If all configuration options are presented, the configuration is
saved and the IP Phone reboots with the saved changes.
• BkSpace—backspace a configuration entry to change it
• Clear—clear an entire configuration entry
• Cancel—cancels out of network configuration. The IP Phone reboots
without saving changes.
1 At the prompt EAP Enable?, enter 1-Yes (1 for Yes) if the network
infrastructure supports 802.1x port-based network access control. Enter
DeviceID and Password.
If you select No, you are not prompted to enter Device ID and Password.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 92

Page 92 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
For more information on EAP, refer to Appendix C “802.1x Port-based
network access control” on page 493.
2 At the prompt, LLDP Enable?, enter 1-Y (1 for Yes, default), or 0-N (0 for
No).
For more information about LLDP, refer to Appendix D “802.1ab Link
Layer Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
3 At the prompt DHCP Yes/No?, enter 0-N (0 for No).
By default, Full DHCP is configured on the IP Phone 2002. Depending on
the configuration requirements, you can change the IP Phone 2002
configuration to allow the following IP address assignments:
• Static—enter all parameters
• Partial DHCP—IP Phone address, subnet mask, and default
Gateway are obtained from the DHCP server
• Full DHCP— (default) all parameters are obtained from the DHCP
server
Note: A DHCP server and DHCP relay agents must also be installed,
configured, and running if you choose Partial DHCP, or Full DHCP
configuration.
For more information on how to set up DHCP servers for use with the
IP Phones, refer to Converging the Data Network with VoIP
(553-3001-160).
4 Enter the following information:
Screen prompt Description
set IP A valid IP Phone 2002 IP address.
net msk A subnet mask.
def gw The default Gateway for the IP Phone 2002 on
the LAN segment to which it is connected.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 93

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 93 of 600
5 Enter the information for the primary Connect Server (S1) and the
secondary Connect Server (S2):
Screen prompt Description
S1 IP The primary CS 1000 node IP
address for the IP Phone 2002.
S1 Port This is a fixed value: 4100
S1 action Choose one of the following:
• for TPS only, enter 1
• for TPS and Secure Media
Controller, enter 6 or 1
For more information about Secure
Media Controller, see Secure Media
Controller: Implementation Guide
(553-3001-225).
Note: You are not prompted for S1
PK if S1 Action is set to 1.
S1 retry count The number of times the IP Phone
2002
attempts to connect to the
server. Enter 10.
S1 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
The Private key of the Secure Media
Controller to which the IP Phone is
connected.
If you are using a Secure Media
Controller, do the following:
• Set to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal
number.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 94

Page 94 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
S2 IP The secondary CS 1000 node IP
S2 Port Same as S1
S2 action Same as S1
S2 retry count Same as S1
S2 PK Default is ffffffffffffffff.
address for the IP Phone 2002.
Note: You are not prompted for S2
PK if S2 Action is set to 1.
The Private key of the alternate
Secure Media Controller to which the
IP Phone is connected.
If you are using a Secure Media
Controller, do the following:
• Set to 6 or 1.
• Enter a 16-digit hexadecimal
number.
Cfg XAS? (0-No,1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
XAS IP: Enter the IP address of the XAS
VLAN Cfg? (0-No, 1-Yes)
VLAN Cfg? 0-Auto, 1-Man: 1-Man
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Note: If there is no External
Application Server (XAS), enter 0 (for
No). You are not prompted to enter
the XAS IP address.
server.
Enter the VLAN ID manually. This is a
number between 1 and 4094.
Page 95

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 95 of 600
0-Auto
Automatically obtains VLAN ID using
DHCP or the 802.1ab data switch.
LLDP-MED? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID is
configured automatically to the value
received in the Network Policy TLV.
You are not prompted for LLDP-MED
if VLAN is not set to Auto (2-Auto,) or
if LLDP is not enabled.
LLDP VLAN? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1 (1 for Yes), VLAN ID is
configured automatically to the value
received in the VLAN NAME TLV.
You are not prompted for LLDP VLAN
if VLAN is not set to Auto (2- Auto), or
if LLDP is not enabled.
DHCP (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1-Y (1 for Yes), the VLAN
ID is configured automatically to a
value received from the DHCP
server.
You are not prompted for DHCP if
VLAN is not set to Auto (2-Au), or if
DHCP is not enabled.
VLANFILTER (0-No, 1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
You will not be prompted for
VLANFILTER if VLAN is not enabled.
PC Port? (1-On, 0-Off) Default 1 (for On).
Select 0 (for Off) to disable the PC
port.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 96

Page 96 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Data VLAN? (0-No, 1-Yes) If you select 1-Y (1 for Yes), and if
Data VLAN Cfg? (0-A, 1-M) If you select 0 (0 for A), VLAN ID is
Data VLAN ID: This prompt is displayed if Data
Duplex? (0-Auto, 1-Full) Default 0 (for Auto)
PSK SRTP? (0-No, 1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
GARP Ignore? (0-No,1-Yes) Default 0 (for No)
LLDP is enabled, the Data VLAN Cfg
prompt appears on the display.
This prompt is not displayed if the PC
port prompt is set to OFF.
configured automatically to the value
received in the VLAN NAME TLV.
This prompt is not displayed if Data
VLAN, or LLDP is not enabled.
VLAN is enabled but LLDP is not
enabled.
Note: You are prompted to enter the TFTP Server IP address if you are
using a TFTP Server to download the current firmware. For CS 1000
Release 4.5, accept the default value of 0.0.0.0. For Succession Release
3.0 or CS 1000 Release 4.0, enter the TFTP Server IP address. The
IP Phone searches for the TFTP Server for firmware upgrade. If the file
name specified in configuration file is not the same as the current
firmware, the IP Phone downloads the file and upgrades the firmware.
This takes several minutes. When the upgrade is complete, the IP Phone
reboots. For further information about TFTP Server configuration, see
Appendix H “TFTP Server” on page 571.
The IP Phone 2002 can support a primary (S1) and secondary (S2)
connect server. If you require IP Phones to register on multiple nodes,
refer to “Enhanced Redundancy for IP Line Nodes” in IP Line:
Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
The IP Phone 2002 searches for the connect server. When the
connection is complete, proceed with step 6.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 97

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 97 of 600
6 Enter the following information:
Screen prompt Description
Password IP Phone Installer Password
You are not prompted to enter the IP Phone
Installer Password if it has not been configured
in your Call Server.
Node The node ID.
TN The TN or VTN.
The IP Phone 2002 registers with the Terminal Proxy Server (TPS) and,
if needed, begins the firmware download. This takes several minutes.
When download is complete, the IP Phone 2002 resets.
Note: The Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download feature for IP Phones
provides an improved method of delivering new firmware to IP Phones.
For further information on Enhanced UNIStim Firmware Download, refer
to IP Line: Description, Installation, and Operation (553-3001-365).
The current Call Server date and time appear on the top line of the display
when the configuration is complete. Self-labeling keys also appear.
7 Check for dial tone and the correct DN above the display.
8 (Optional) Customize the feature keys as required. For more information,
see IP Phone 2002 User Guide.
End of Procedure
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 98

Page 98 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
Procedure 11
Installing an IP Phone 2002 for the first time
using DHCP
Timing information
There are only 4 s between plugging in the IP Phone 2002 power
transformer and the appearance of the Nortel logo in the middle of the
display. When you see the logo, you have 1 s to respond by pressing the
four soft keys at the bottom of the display in sequence from left to right,
one at a time. If you miss the 1-s response time, the IP Phone 2002
attempts to locate the connect server. You can begin the power-up
sequence again, or you can double-press the Services key to open the
network diagnostic utilities to access the IP Phone settings. See
Appendix E “IP Phone diagnostic utilities” on page 497.
To edit network configuration the following soft keys are available:
• OK—accept current settings and proceed to the next configuration
option. If all configuration options are presented, the configuration is
saved and the IP Phone reboots with the saved changes.
IMPORTANT!
• BkSpace—backspace a configuration entry to change it
• Clear—clear an entire configuration entry
• Cancel—cancels out of network configuration. The IP Phone reboots
without saving changes.
1 At the prompt EAP Enable?, enter 1-Yes (1 for Yes) if the network
infrastructure supports 802.1x port-based network access control. Enter
DeviceID and Password.
If you select No, you will not be prompted to enter Device ID and
Password.
For more information on EAP, refer to Appendix C “802.1x Port-based
network access control” on page 493.
2 At the prompt, LLDP Enable?, enter 1-Y (1 for Yes, default), or 0-N (0 for
No).
For more information about LLDP, refer to Appendix D “802.1ab Link
Layer Discovery Protocol” on page 495.
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Page 99

Nortel IP Phone 2002 Page 99 of 600
3 At the prompt DHCP Yes/No?, enter 1-Y (1 for Yes).
By default, Full DHCP is configured on the IP Phone 2002. Depending on
the configuration requirements, you can change the IP Phone 2002
configuration to allow the following IP address assignments:
• Static—enter all parameters
• Partial DHCP—IP Phone address, subnet mask, and default
Gateway are obtained from the DHCP server
• Full DHCP— (default) all parameters are obtained from the DHCP
server
A DHCP server and DHCP relay agents must also be installed,
configured, and running if you choose Partial DHCP, or Full DHCP
configuration.
For more information on how to set up DHCP servers for use with the
IP Phones, refer to Converging the Data Network with VoIP
(553-3001-160).
4 At the prompt, Cached IP?, select 0 (0-No, default) to conform to the
DHCP standard and to obtain an IP address from the DHCP server. Only
select 1 (1 for Yes) to force the IP Phone to start with a cached IP address
in the event that the IP Phone cannot connect to the DHCP server and
obtain an IP address.
5 Select Partial or Full DHCP.
a. If you select Full DHCP, then the following parameters are retrieved
from the DHCP server:
— a valid IP Phone 2002 IP address
— a subnet mask
— the default Gateway for the IP Phone 2002 on the LAN segment
to which it is connected
— the S1 IP. The primary CS 1000 node IP address of the IP
Phone.
— the S1 action
— the S1 retry count. This is the number of times the IP Phone
attempts to connect to the server.
— the S2 IP. The secondary CS 1000 node IP address of the IP
Phone.
IP Phones Description, Installation, and Operation
Page 100

Page 100 of 600 Nortel IP Phone 2002
— the S2 action
— the S2 retry count
— the External Application Server (XAS) IP address
b. If you select Partial DHCP, then you must enter the following
parameters:
Screen prompt Description
S1 IP The primary CS 1000 node IP
S1 Port This is a fixed value: 4100
S1 action Choose one of the following:
address for the IP Phone 2002.
• for TPS only, enter 1
• for TPS and Secure Media
Controller, enter 6 or 1
For more information about Secure
Media Controller, see Secure Media
Controller: Implementation Guide
(553-3001-225).
S1 retry count The number of times the IP Phone
553-3001-368 Standard 20.00 December 2006
Note: You are not prompted for S1
PK if S1 Action is set to 1.
2002 attempts to connect to the
server. Enter 10.
 Loading...
Loading...