Page 1
Nortel Contact Center
What’s New in Release 6.0
Product release 6.0 Standard 4.01 July 2007
297-2183-903
Page 2

Page 3

Nortel Contact Center
What’s New in Release 6.0
Publication number: 297-2183-903
Product release: 6.0
Document release: Standard 4.01
Date: July 2007
Copyright © 2007 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Information is subject to change without notice. Nortel Networks reserves the right to make changes
in design or components as progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant.
The process of transmitting data and call messaging between the Meridian 1 and Contact Center is
proprietary to Nortel Networks. Any other use of the data and the transmission process is a violation
of the user license unless specifically authorized in writing by Nortel Networks prior to such use.
Violations of the license by alternative usage of any portion of this process or the related hardware
constitutes grounds for an immediate termination of the license and Nortel Networks reserves the
right to seek all allowable remedies for such breach.
*Nortel, the Nortel Networks logo, the Globemark, CallPilot, Contivity, DMS, DMS-10, DMS-100,
DMS-200, DMS-250, DMS-300, DMS-500, DMS-MTX, DMS-STP, DPN, DPX, Dualmode,
Helmsman, ICN, IVR, MAP, Meridian, Meridian 1, Meridian Mail, Meridian SL, Norstar, Optera,
Optivity, Passport, Periphonics, SL, SL-1, Succession, Supernode, and Symposium are trademarks
of Nortel Networks.
CRYSTAL REPORTS is a trademark of Crystal Decisions, Inc.
ACTIVE DIRECTORY, INTERNET EXPLORER, MICROSOFT, MICROSOFT ACCESS, MS-DOS,
POWERPOINT, WINDOWS, WINDOWS NT, and WINDOWS XP are trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
REPLICATION SERVER and SYBASE are trademarks of Sybase, Inc.
PCANYWHERE and THE NORTON ANTIVIRUS are both trademarks of Symantec Corporation.
InterSystems Caché is a trademark of InterSystems Corporation.
Page 4

Page 5

What’s New in Release 6.0 v
Revision history
July 2007
The Standard 4.01 version of Nortel Contact Center What’s
New in Release 6.0 is released. This version is updated to
include support for CS 1000 Release 5.0.
September 2006
The Standard 4.0 version of Nortel Contact Center What’s
New in Release 6.0 is released.
May 2006
The Standard 3.0 version of Nortel Contact Center What’s
New in Release 6.0 is released.
December 2005
The Standard 2.0 version of Nortel Contact Center What’s
New in Release 6.0 is released.
November 2005
The Standard 1.0 version of Nortel Contact Center What’s
New in Release 6.0 is released.
Page 6

vi Contact Center
Revision history Standard 4.01
Page 7

What’s New in Release 6.0 vii
Contents
1 Introduction 9
What is a contact center? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
About this document. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2 About Contact Center 6.0 13
Overview. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Software delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Components in Release 6.0. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Installation configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
System operations and supported platforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Documentation suite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
How to get help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
3 New in this release 41
Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Contact Center portfolio rebranding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Upgrading from a previous release. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Product changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
A Acronyms in Contact Center 61
Acronyms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Glossary 67
Index 81
Page 8

viii Contact Center
Contents Standard 4.01
Page 9

What’s New in Release 6.0 9
Chapter 1
Introduction
In this chapter
What is a contact center? 10
About this document 11
Page 10

10 Contact Center
Introduction Standard 4.01
What is a contact center?
Contact centers are constantly evolving to meet existing needs. Once an
environment designed to process telephone calls, call centers have evolved to
become customer contact centers, processing all types of media transactions.
The contact center is now seen as the core of a business due to its critical role in
maximizing customer satisfaction, while at the same time realizing efficiency.
The integral parts of a contact center consist of
representatives who handle customer transactions (also called agents)
management personnel
technology to handle each customer contact, including routing to the best
qualified agent, treatment, and fulfillment of the contact
A contact center is often a department in a comp an y, or it can be the sole
business unit in a company. Frequently, the contact center is the only point of
contact between a company and its customers or suppliers. Regardless of the
size and complexity of a contact center, its objectives and goals remain
consistent:
to deliver customer satisfaction through prompt, professional contact
handling
to control costs by using resources and technology more efficiently
to help staff work more productively
to increase profitability
Contact centers are accessed globally with customer satisfaction support
becoming increasingly important. Cohesive contact center presence requires
multiple contact centers with different switch platforms.
Some contact centers use Session Initiated Protocol (SIP) technology to enhance
the capabilities of their agents. SIP is the latest development in contact center
technology , and enables conver ged voice and multimedia services such as voiceenriched e-commerce, W eb page click-to-dial, and instant messaging with buddy
lists, personalized music, forms, and customized video clips.
Page 11

What’s New in Release 6.0 11
July 2007 Introduction
About this document
Nortel has proven to be a world leader in contact center technology, with contact
centers in more than 100 countries. Nortel understands the needs of the contact
center environment, and creates lasting relationships with customers by
developing the solutions to address their ever-changing business needs.
What’s New in Release 6.0 describes the components of Nortel Contact Center
Release 6.0, highlights new features, and describes product changes for this
release. It is organized into the following sections:
Chapter 1, “Introduction,” includes
what is a contact center
information about this document
Chapter 2, “About Contact Center 6.0,” includes
how the software is delivered
the components of Contact Center Release 6.0
important contact center features
system operations and supported switch platforms
documentation released with the Contact Center Release 6.0 product
how to contact Nortel.
Chapter 3, “New in this release,” includes
Contact Center portfolio rebranding information for Release 6.0
information about upgrading from previous releases
an overview of new features and product improvements for Release 6.0
Appendix A, “Acronyms in Contact Center,” includes information about
acronyms commonly seen in contact center documentation.
“Glossary” on page 67 defines terms commonly seen in contact center
documentation.
Page 12

12 Contact Center
Introduction Standard 4.01
Page 13

What’s New in Release 6.0 13
Chapter 2
About Contact Center 6.0
In this chapter
Overview 14
Software delivery 15
Components in Release 6.0 16
Installation configurations 30
System operations and supported platforms 32
Documentation suite 34
How to get help 38
Page 14

14 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Overview
Nortel Contact Center 6.0 represents the next generation of contact center
software. Contact Center 6.0 is a set of software components that addresses the
business requirements of sophisticated contact center environments. Contact
Center 6.0 is sold as a single software media suite with a licensing mechanism
that offers custom functionality and features, either using corporate or nodal
licensing.
Nortel Contact Center 6.0 utilizes the latest in communications technologies to
deliver superior contact management capabilities. It offers a full range of
functionality covering inbound and outbound voice, multimedia (e-mail, text
chat, video), and Computer-Telephony Integration (CTI). It offers a
multimedia-ready agent desktop along with supervisor tools to manage the
multimedia contact center . It has extensive reporting tools that generate reports
that are meaningful and useful for businesses.
Contact Center 6.0 provides integrated outbound capability for the creation,
modification, and monitoring of outbound campaigns.
Contact Center 6.0 contains a rich scripting language that provides flexibility in
the way contacts are treated and routed. It employs advanced skill-based routing
to enable individual contact treatment and to connect customers with the agents
most qualified to serve them, locally or across a network.
Server software features ensure that your contact center is geographically
resilient, reducing contact center unplanned downtime and facilitating disaster
recovery strategies.
This chapter provides an overview of Contact Center 6.0—the components,
switch support, and documentation.
Page 15

What’s New in Release 6.0 15
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Software delivery
For Release 6.0, all Contact Center components, including the documentation,
are delivered on a single DVD. The DVD contains the following Nortel
applications:
Contact Center Manager Server (including the Contact Center Manager
Network Control Center)
License Manager
Contact Center Replication Server
Server Utility
Contact Center Manager Administration
Communication Control Toolkit
Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound
You are prompted to select the components you want to install. Your selection
invokes the individual component installation. Component applications are not
integrated—each application is stored as a separate entity.
Page 16

16 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Components in Release 6.0
The Contact Center 6.0 suite consists of a host of integrated applications
providing solutions for the very basic to the most complex contact center. The
following sections provide an overv iew of the dif ferent components and features
of Contact Center 6.0.
Contact Center Manager Server
Contact Center Manager Server is the core contact center component that
provides the intelligent routing capability for telephony calls and multimedia
contacts. Use Contact Center Manager Server to route calls and contacts to the
most qualified agent. The most qualified agent is the agent with the appropriate
capability for handling the type of call or contact and the appropriate skillset or
unique abilities. Rules for contact treatment (what happens while the customer is
waiting for a response) and routing (the contact response) can be simple or
complex.
Script elements are used to create call routing schemes and treatments. Some
examples of elements that you can use to create call scripts are:
Queue to Agent—Queues a call to a specific agent or group of agents.
Queue to Skillset—Queues a call to a specific skillset.
Give Music—Provides a caller with music from a defined source.
Give RAN—Provides a recorded announcement to a caller.
Give Broadcast Announcement—Broadcasts an announcement to
multiple callers at the same time (for example, to let the caller know the call
may be recorded).
Give IVR—Provides a caller with an automated method of entering and
retrieving information from a voice system while maintaining their place in
a queue.
Collect Digits—Collects information from the caller, such as the reason for
the call or an account number. The collected digits can then be used to route
or treat the call.
Page 17

What’s New in Release 6.0 17
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
The comprehensive reporting tools of Contact Center Manager Server help
managers and supervisors accurately track agent performance, resource
utilization, and trends. The system’s real-time and historical reporting can help
in adjusting staffing levels in peak periods and in forecasting business
requirements and human resource needs over the long term.
Contact Center Manager Server provides a number of open interfaces that third
party developers can use to build applications that interwork with Contact
Center Manager Server. Real Time Statistics Multicast (RSM) and Real-Time
Interface (RTI) provide real time information to applications such as wall
boards. The Host Data Exchange (HDX) provides an interface for applications
to communicate with the call processing script/workflow. This interface is
typically used to allow the workflow to access information in an external
database. With the Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) interface, an
application can extract information from the Contact Center Manager Server
database. The Meridian Link Service Manager (MLSM) interface provides
messaging and control of resources on the telephony switch. The MLSM
interface is typically used for implementing softphone features.
Contact Center Manager Server can manage multimedia contacts using the Open
Queue feature introduced in Contact Center 6.0. The Open Queue is a licensed
feature that provides seamless integration between Contact Center Manager
Server, Administrator, Multimedia, and Communication Control Toolkit
products. It provides true workflow, queuing, routing, reporting, and
management of voice, outbound, and e-mail contacts.
Contact Center Manager Server can also be used in a SIP-enabled contact center,
where communication sessions are established over Internet Protocol (IP)
networks for interactive communication between two or more entities. SIP
enables converged voice and multimedia services, such as voice-enriched ecommerce, Web page click-to-dial, instant messaging with buddy lists, and
video.
Contact Center Manager Server establishes the nodal and corporate licenses for
features such as universal networking and the standby server.
Page 18

18 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Network Control Center server
The Network Control Center server manages the Network Skill-Based Routing
(NSBR) configuration and communication between servers in a Contact Center
Manager network. The Network Control Center server is required when servers
in multiple Contact Center Manager Server sites are networked and operating as
a single distributed contact center. The Network Control Center server runs the
Network Control Center (NCC) software application, a feature of the Contact
Center Manager Server application software.
License Manager
Nortel uses a License Manager for the centralized licensing and control of all
Contact Center 6.0 components and features across the Contact Center suite
(Contact Center Manager, Contact Center Manager Administration,
Communication Control Toolkit, and Contact Center Multimedia).
You must install the License Manager on the Contact Center Manager Server or
on the primary Contact Center Manager Server in a networked cont act ce nt er. If
you are working in a Knowledge W orker environment, where there is no Contact
Center Manager Server, install the License Manager on the Communication
Control Toolkit server.
A Corporate License feature is available with Contact Center 6.0, where
licensing for the entire contact center network is administered on a centralized
License Manager server, thereby reducing administration overhead. With
Corporate Licensing, you can enable the concurrent agent licenses across a
contact center network. For example, if an agent logs off in California, the seat
(agent license) becomes available for use by an agent based in Texas, thereby
maximizing the corporate license investment.
You can install a backup License Manager server on another Contact Center
Manager Server to ensure business continuity if the primary License Manager
server fails.
Standby and Replication Server
The Replication Server is a third-party software server that replicates data and
distributes it to the standby server. If the active Contact Center Manager Server
fails, the standby server can be quickly deployed.
Page 19

What’s New in Release 6.0 19
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Server Utility
You can use the Server Utility to monitor and maintain Contact Center Manager
Server Release 6.0. The Server Utility provides functionality that is not available
through Contact Center Manager Administration.
With the Server Utility, you can
Monitor and maintain user accounts for the Server Utility, database
logons, access classes, serial ports, switch resources, the Voice Prompt
Editor, server settings, and connected sessions, backup scheduler, and
alarm monitor.
Use the Provider application to receive Contact Center script
information over the Host Data Exchange (HDX) interface.
Additionally, the Provider application can be configured to return
information to the Contact Center script.
Use the Service Monitor application to monitor the status of Contact
Center Manager Server 6.0 services from a stand-alone computer. The
information returned is similar to the information provided by SMONW.
Use PC Event Browser to view events that occur on the client PC where
the Server Utility is running.
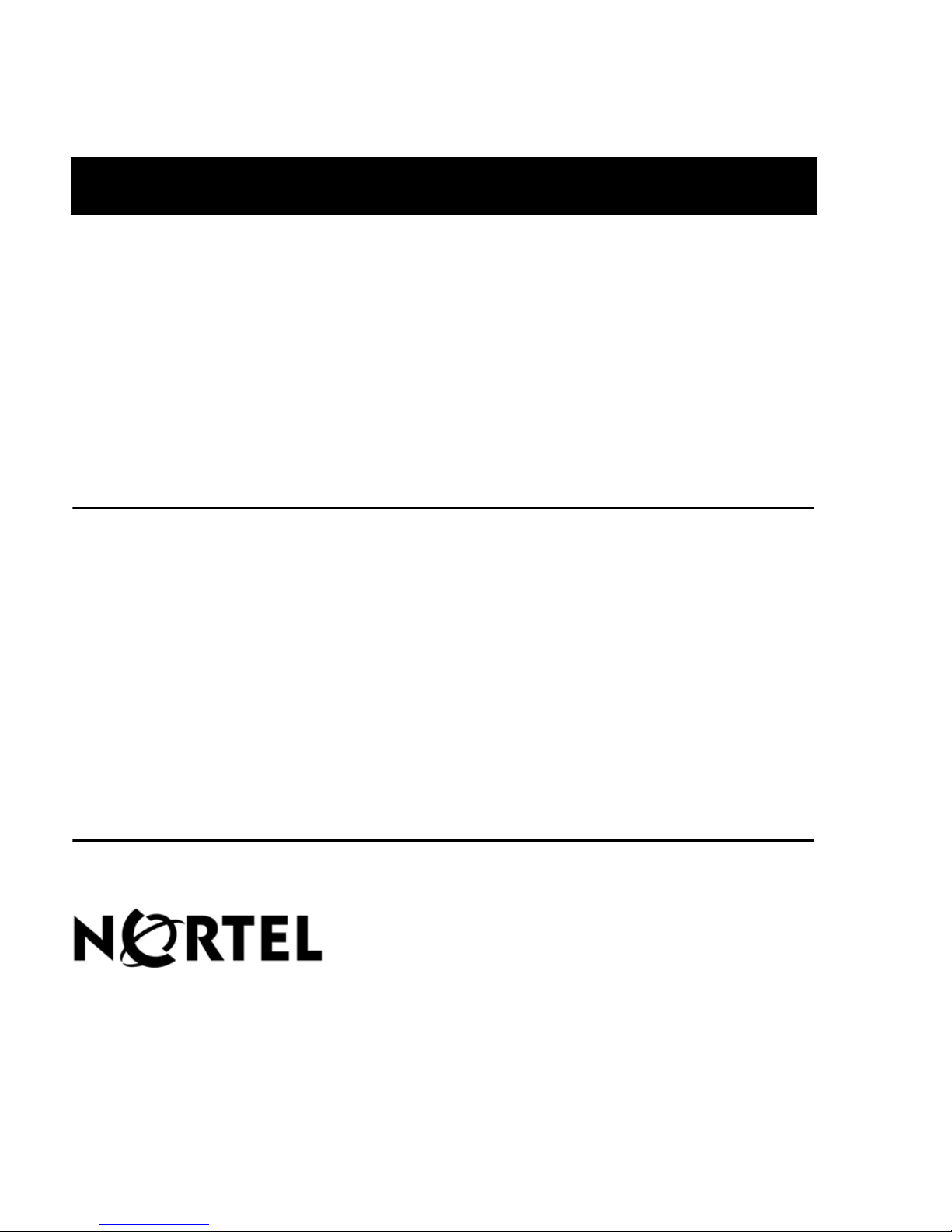
Contact Center Manager Administration
Contact Center Manager Administration is a browser-based tool for contact
center administrators and supervisors. You can use Contact Center Manager
Administration to manage and configure a contact center and it s users, define
access to data, and view real-time and historical reports. You can install the
Contact Center Manager Administration component on the same server as
Contact Center Manager Server, or on a separate networked server.
Page 20
20 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
With the Contact Center Manager Administration Web-based platform, you can
perform the following functions based on the CS 1000/Meridian 1, CS 2x00/
DMS, or SIP configuration of your contact center:
Contact Center Management—Configure access levels for agent to
skillset and agent to supervisor assignments, view the schedule of agent to
skillset and agent to supervisor assignments, choose priority/standby from a
drop-down menu in agent to skillset assignments, display the current status
of an agent, and change all agents in an agent to supervisor assignment to
one supervisor simultaneously. The database contains a new column in the
application and skillset views to hold the contact type.
Access and Partition Management—Create a Contact Center Manager
administrator and partitions and access classes for agents and supervisors.
Partitions define what a user can view and access classes define what the
user can create, change, or modify.
Configuration—Configure data such as users and skillsets for the contact
center. You can use templates in Microsoft Excel spreadsheets to upload
Contact Center Manager information.
Page 21

What’s New in Release 6.0 21
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Scripting—Create, modify , and validate contact routing in structions for the
contact center.
Real-Time Reporting—Display real-time skillset reports, include or
exclude non-staffed skillsets, select filters for real-time displays, and
configure colors for both networked and single-node contact centers.
Historical Reporting—View and print historical report schedules, modify
report templates on a network drive, and print access and partition
management information.
Report Creation Wizard—Create, maintain, and modify customized
reports through a user-friendly interface. You can view real-time reports on
a per-skillset basis (if outbound skillsets are defined) and standard
historical outbound reports through Contact Center Manager
Administration. Yo u can use the Report Creation Wizard to generate
custom outbound reports. For more information, see the Contact Center
Manager Supervisor’s Guide.
Emergency Help—View notifications of agent emergencies. Agents can
click an Emergency button on the Contact Center Agent Desktop to alert
supervisors of contact emergencies.
Audit Trail—View a record of all actions performed in the Contact Center
Manager Administration configuration.
Outbound—Configure outbound campaigns if the Multimedia/Outbound
server software is installed. For more information about the Multimedia/
Outbound server, see “Contact Center Multimedia” on page 23.
Agent Desktop Display
The Agent Desktop Display application is a separate application that can run
along with the Agent Desktop application to provide real-time skillset
monitoring on agent desktops.
Page 22

22 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Communication Control Toolkit
The Communication Control Toolkit server is a server/client application that
helps you implement Computer-Telephony Integration(CTI) for installed and
browser-based client integrations. For switches, the Communication Control
Toolkit facilitates the integration of contact center, Knowledge Worker , and selfservice solutions with your client applications. In the SIP-enabled contact center ,
the Communication Control Toolkit integrates the contact center users with the
SIP CTI on the CS 1000 Signaling Server.
The Communication Control Toolkit contains the following elements:
Communication Control Toolkit server—The component responsible for
managing client sessions consists of the following subcomponents:
Contact Management Framework—An infrastructure component that
manages the states of contacts, agents, terminals, and addresses.
Telephony Application Program Interface (TAPI) Connector—A
connecter that converts Communication Control Toolkit requests to
TAPI calls, and TAPI events to Communication Control Toolkit events.
The TAPI Connector sits between the Nortel TAPI Service Provider and
the Contact Management Framework. The TAPI Connector is not used
in SIP-enabled contact centers.
TAPI Service Provider—A Microsoft TAPI client responsible for CTI
operations of all lines controlled by the Communication Control Toolkit
platform that are initialized by TAPI. The TAPI Service Provider is not
used in SIP-enabled contact centers.
SIP Connector—A SIP-enabled contact center requires a
Communication Control Toolkit Connector to accommodate Contact
Center Manager Server agent logons from the Contact Center Agent
Desktop application. A SIP-enabled contact center also requires the
functionality of a Communication Control Toolkit Connector that is
built into the Contact Center Manager Server product as a SIP service.
Intelligent Call Manager (ICM) connector—The Communication
Control Toolkit now supports ICM on CS 2x00.
Communication Control Toolkit API—An application programming
interface (API) that controls voice resources. The API is published as
Microsoft .NET types and distributed as a Windows assembly, which is
referenced by application developers.
Page 23

What’s New in Release 6.0 23
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Client applications—Third-party components including software phones,
agent telephony toolbars, or call management applications. The Contact
Center Agent Desktop is a Nortel software application that provides the
agent telephony toolbar functionality.
Contact Center Multimedia
The Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound server contains contact center
applications that expand the contact center to allow agents to view, respond to,
and track requests over the Internet. E-mail and outbound contacts are directed
to the first available agent in the skillset who can handle the contact type. If
more than one agent is available, the contact is routed to the agent with the
highest priority for the skillset. Supervisors and administrators view real-time
displays and run historical reports to determine volume and completion
statistics.
The Contact Center Multimedia server contains the following components:
Multimedia/Outbound database—The server component includes the
Caché database, or multimedia database, that stores all incoming e-mail
contacts, outbound campaigns, and associated responses in a structured
format within the database.
Contact Center Standby server—You can optionally install a warm
standby server, or redundancy server, to shadow the Caché database and
provide a quick recovery if the primary Contact Center Multimedia server
fails. All multimedia services are disabled on the Standby server until it is
required to run as the primary server.
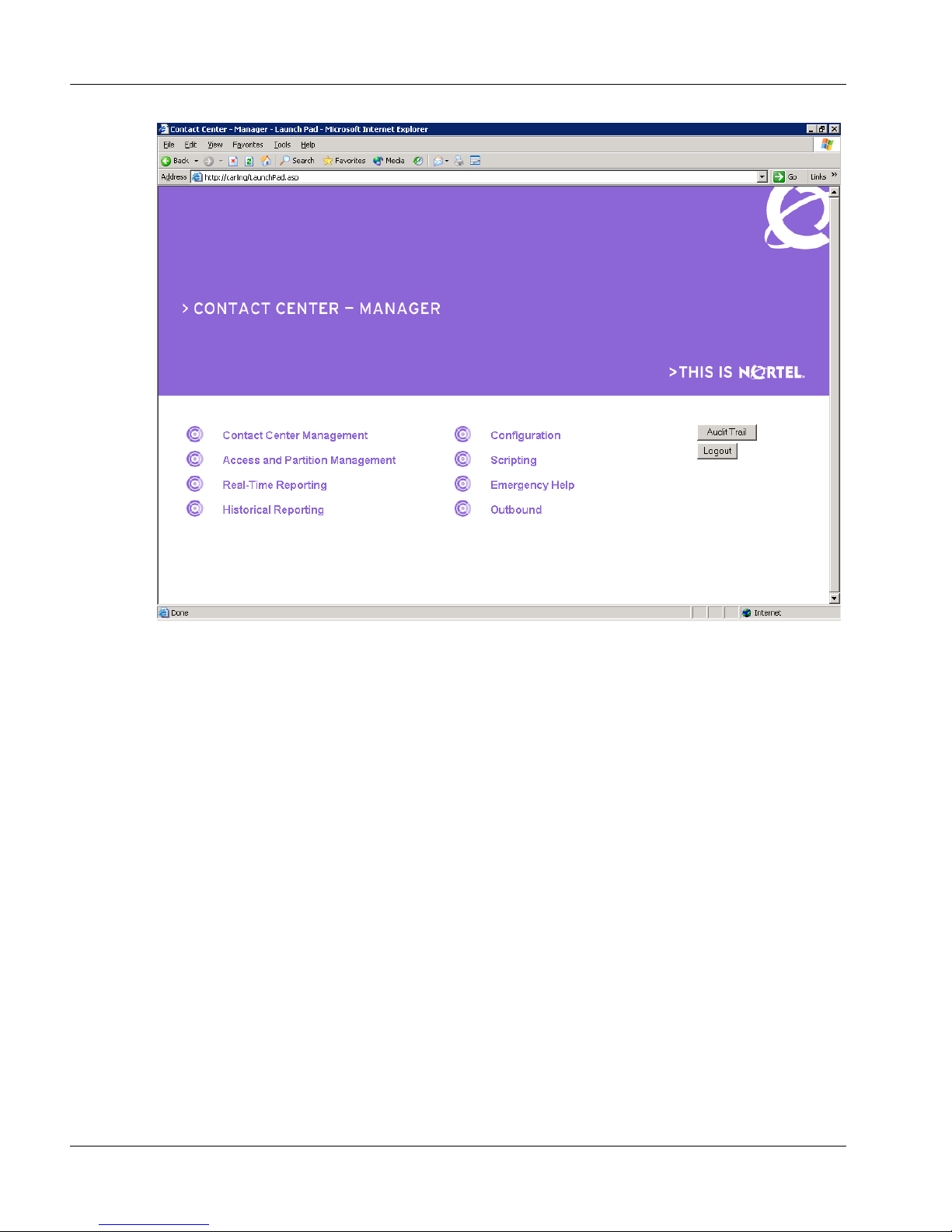
Contact Center Multimedia Administrator—Use the Multimedia
Administrator application to configure the properties required for routing
contacts. For outbound contacts, you must configure skillsets. For e-mail
messages, you must configure E-mail Manager settings such as recipient
mailboxes, rules for routing e-mail messages, and skillsets. For Web
communications text chats, you must configure the Web Communications
Manager settings, such as customer and agent labels and skillsets.You can
Page 24
24 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
use the Multimedia Administrator application for administration and data
management tasks such as backing up data in the database.
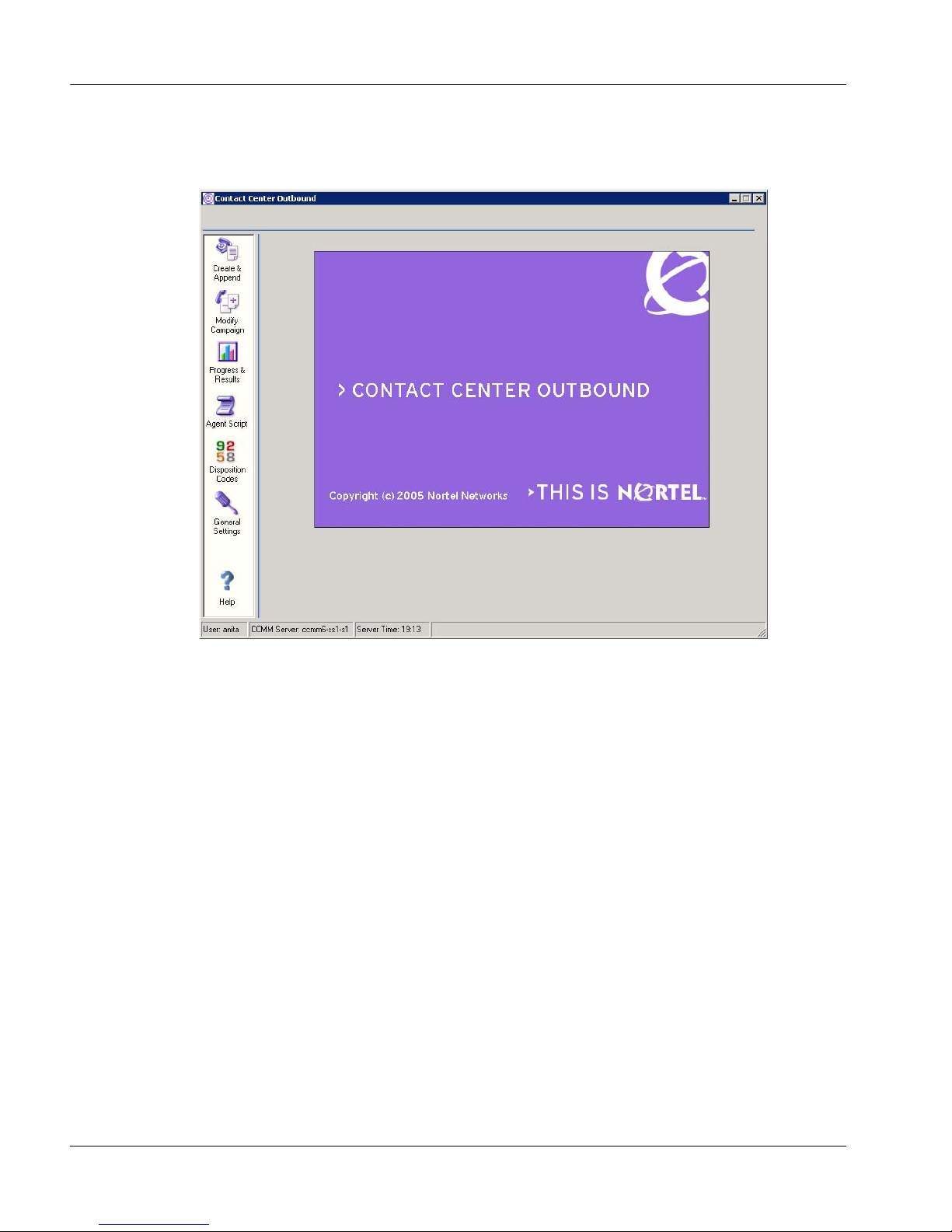
Outbound Campaign Management Tool—You access the Outbound
Campaign Management Tool from the Contact Center Manager
Administration application. Administrators use the integrated Outbound
Campaign Management Tool to create, modify, and monitor outbound
campaigns. An outbound campaign is a series of outbound calls to
customers for one specific purpose, for example, a customer survey or a
Page 25
What’s New in Release 6.0 25
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
sales promotion. For more information, see the Contact Center Manager
Administrator’s Guide.
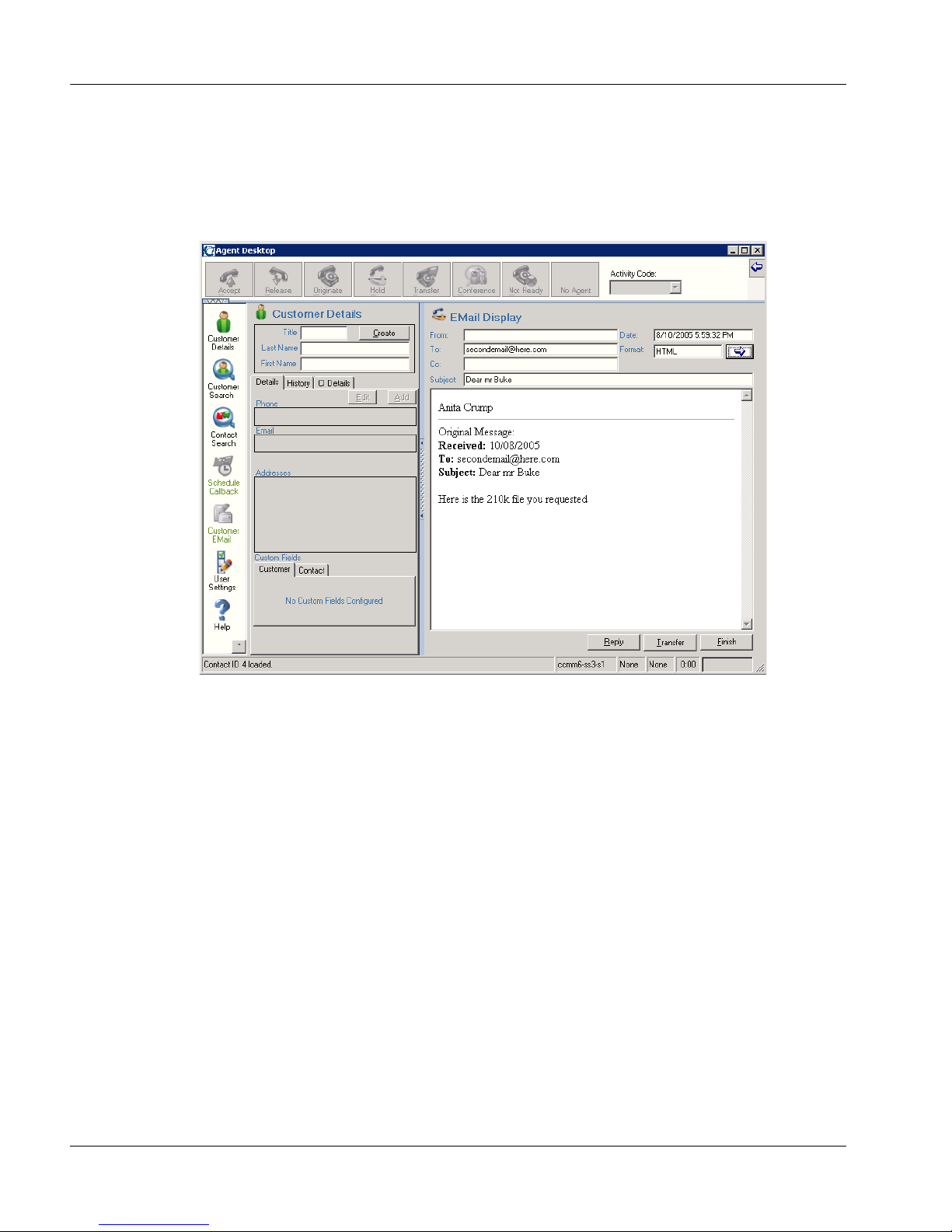
Contact Center Agent Desktop—Agents use Internet Explorer to connect
to a new W eb service-based unified Agent Desktop interface on the Contact
Center Multimedia server. The Communication Control Toolkit pushes
e-mail, Web requests, outbound contacts, and voice calls to the Agent
Desktop interface. Agents use the Agent Desktop interface to retrieve
e-mail and outbound campaign informati on, and customer details and
history from the Multimedia database. Agents also use the Agent Desktop
application to send e-mail replies and save outbound call details in the
multimedia database. The Agent Desktop is deployed using .NET smart
technology and accessed by the agent by entering a URL address in
Windows Explorer or Internet Explorer.
The Contact Center Agent Desktop provides the agent with customer
details, call scripting, preview with auto-dial capability, call rescheduling,
and storage of disposition codes and script results for each call. For more
information, see the Contact Center Agent Desktop User Guide.
Page 26
26 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
The Contact Center Multimedia server is not used in a SIP-enabled Contact
Center; however, you can install the Contact Center Agent Desktop on a
Communication Control Toolkit server or another server to facilitate
handling of voice contacts on the agent desktop.
Migration Utility—You can use this utility to migrate data from the
Symposium Web Center Portal database to the new Contact Center
Multimedia database.
Page 27
What’s New in Release 6.0 27
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
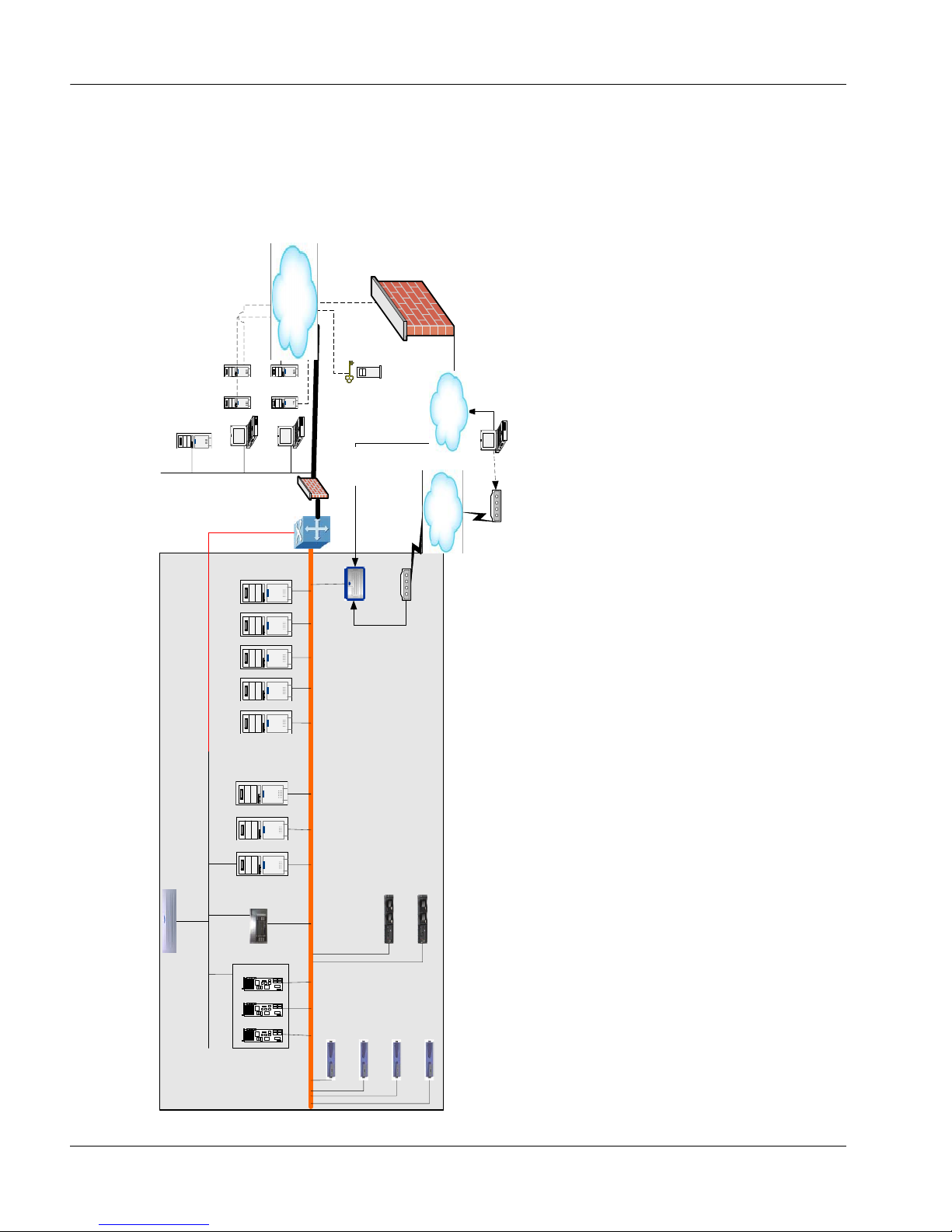
Network architecture
The following diagram shows the network architecture for Contact Center 6.0 in
a single-node configuration.
Customer LAN
CCMA
NCC CCTCCMM
VPN
Router
1100
DNS
DHCP
Server
CCMS
Modem
Firewall
Nortel server subnet
(Managed Ethernet Switch– for
example, BPS 2000, Baystack450,
and so on)
DMZ
(Optional)
Routing
Switch
ELAN subnet
HDX Application
Server
PSTN
Remote-Support
Remote-Agent
Modem
TACACS or
RADIUS
CallPilot
External
Web Server
POP3/SMTP
Mail Server
CallPilot
Web Server
Media
Gateway
VGMC
VGMC
VGMC
OTM
Call Server
Signaling
Server
Nortel Media
Application Servers
MCS Database
Server
MCS Application
Server (SIP
Proxy/Registrar)
MCS Mgmt/
Accnt Server
MCS IP/Web
Client Manager
Gateways
Firewall
(Optional)
Enterprise
LAN / WAN
Internet
Page 28

28 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
The network architecture of Contact Center Manager Server has three
requirements:
routed ELAN subnet
Nortel server subnet
single network interface card Contact Center Manager Server configuration
The ELAN subnet must be connected to the Nortel server subnet wit h one router
only.
Nortel Contact Center 6.0 works with the following switches: CS 1000/Meridian
1, CS 2x00/DMS, and MCS 5100. The switch determines the types of contacts
customers can use. For example, the CS 1000/Meridian 1 and CS 2x00/DMS
switches support inbound and outbound voice and e-mail contacts. The SIPenabled contact center interacts with two switches: CS 1000 and MCS 5100.
The SIP CTI control is delivered with the CS 1000 signaling server. A SIPenabled environment supports inbound voice contacts, video, sharing
documents, instant messaging, and buddy lists, which are used to enrich
customer interaction with the contact center.
Capacity Assessment Tool
The Capacity Assessment T ool (CapT o ol) helps you to assess the Contact Center
Manager Server impact on local area network (LAN) and wide area network
(WAN) bandwidth utilization, Contact Center Manager Server configuration
requirements, Contact Center Manager Administration server and client
configuration requirements, and switch-related configuration requirements for
your anticipated call volume.
Prior to purchasing the servers, run CapTool to determine the hardware required
for handling the call volume. You can obtain a copy of the CapTool through the
Partner Information Center (http://www.nortel.com/pic).
Page 29

What’s New in Release 6.0 29
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Media Application Server
The Media Application Server (MAS) acts as the termination and origination
point in SIP-enabled contact centers. Use the MAS to
support supervisor features such as Observe and Barge-In silently or with a
tone
transfer DTMF digits from the customer to the IVR service
provide announcements in audio or video
provide music in audio files
provide voice/XML dialogs for prompting to collect digits
Page 30

30 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Installation configurations
Contact Center 6.0 supports the following configurations:
single-node configuration on CS 1000/Meridian 1
direct-connect (Knowledge Worker) on CS 1000/Meridian 1
network configuration on CS 1000/Meridian 1
single-node configuration on CS 2x00/DMS
direct-connect (Knowledge Worker) configuration on CS 2x00/DMS
network configuration on CS 2x00/DMS
Contact Center Manager Server and Contact Center Manager
Administration configuration on CS 2x00/DMS
multiple node configuration on CS 2x00/DMS
universal networking
SIP configuration on MCS 5100
For more detailed information and diagrams, see the Nortel Contact Center
Planning and Engineering Guide.
Page 31

What’s New in Release 6.0 31
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Other software that works with Contact Center
You can install other software to work with the components of Contact Center:
Use Host Data Exchange (HDX) as an optional host computer to run a
third-party provider application that receives data from Contact Center
Manager Server and returns data (such as an account balance) to the
Contact Center Manager Server. Contact Center Manager Server supports
up to 10 open interface applications.
Use the CallPilot/Meridian Mail Client voice mail system (on CS 1000/
Meridian 1 only) as a front-end interactive voice response (IVR) or voice
service for Contact Center Manager Server.
Use IVR to allow telephone callers to interact with a host computer using
prerecorded messages and prompts. You can use Nortel IVR or third-party
IVR systems to provide front-end IVR to calls before they are handed over
to Contact Center Manager Server, or in a GIVE IVR command in the
scripts after Contact Center Manager Server takes control of the call.
Use LinkPlexer (on CS 2x00/DMS only) for accommodating multiple
applications connected to the Contact Center Manager Server. With
LinkPlexer, multiple applications can monitor and control devices on a
single link and an application can initiate an operation on a device that
impacts another application on the link.
Page 32

32 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
System operations and supported platforms
Introduction
This section provides an overview o f Contact Center Release 6.0 switch support
and system requirements.
Switch support
Contact Center Release 6.0 provides support for the following switches:
Nortel Meridian 1 PBX
Nortel Communication Server 1000 (CS 1000)
DMS
SL-100
Communication Server 2000 (CS 2000 or CS 2x00)
Communication Server 2100 (CS 2100 or CS 2x00)
Multimedia Communication Server 5100 (MCS 5100)
Supported switch software versions
The following table shows supported switch software versions for Contact
Center Release 6.0:
Switch Supported versions
Meridian 1 PBX 11C - Chassis R25.40b, 26
Meridian 1 PBX 11C - Cabinet R25.40b, 26
Meridian 1 PBX 61C R25.40b, 26
Meridian 1 PBX 51C R25.40b, 26
Communication Server 1000 3.0, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0
DMS CCM10/SCAI12 to CCM17/SCAI17
Page 33

What’s New in Release 6.0 33
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
System requirements
There are updates to the system requirements for Contact Center Release 6.0:
Platform requirements—Contact Center Release 6.0 requires an increase in
minimum requirements for the CPU, memory, and disk space. A DVD
drive is required.
Operating system requirements (servers)—The Contact Center Release 6.0
servers (Contact Center Manager Server, Contact Center Manager
Administration, Communication Control Toolkit, and Contact Center
Multimedia/Outbound) require Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition or
Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition operating system.
Operating system requirements (clients)—The Contact Center Release 6.0
client applications (Contact Center Manager Administration Client,
Contact Center Agent Desktop, and Contact Center Manager Server
Utility) require Windows XP Professional SP2, Windows 2000
Professional SP4, Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition, or Windows
Server 2003 Enterprise Edition operating system.
For complete details about platform and server requirements, see the Nortel
Contact Center Planning and Engineering Guide.
SL-100 CCM10/SCAI12 to CCM17/SCAI17
Communication Server 2000 SE06/SCAI17
Communication Server 2100 SE06/SCAI17
MCS 5100 Rls 3.0/3.5
Switch Supported versions
Page 34

34 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Documentation suite
Introduction
All Release 6.0 guides are available in PDF format on the Contact Center DVD.
Changes and updates to the guides are available from the Nortel Partner
Information Center (www.nortel.com/pic) or Helmsman (www.nortel.com/
helmsman). Online Help is also accessible through the Help menu within the
applications. You can obtain the third-party programmer’s guides through the
Developer Partner Program.
Guides
The following guides are available on the Contact Center DVD or on the Nortel
Web site (www.nortel.com).
For information about Refer to NTP number
Planning and
engineering guidelines,
and server requirements
Contact Center Planning and
Engineering Guide
297-2183-934
Nortel Contact Center Manager
CapTool User’s Guide
297-2183-935
Server Requirements Nortel Contact Center Server and
Operating System Requirements
Guide
297-2183-263
The Contact Center
portfolio
Contact Center What’s New in
Release 6.0
297-2183-903
Required installation
and server data
Contact Center Installer’s Roadmap
(see www.nortel.com/pic)
297-2183-226
Switch configuration Contact Center Communication
Server 1000/Meridian 1 and Voice
Processing Guide
297-2183-931
Page 35

What’s New in Release 6.0 35
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Contact Center Manager Switch
Guide for Communication Server
2X00/DMS
297-2183-937
SIP Contact Center Switch
Configuration Guide
297-2183-962
Server operating system
configuration and
requirements
Contact Center Manager Server
Technical Requirements and
Operating System Configuration
Guide
297-2183-212
Contact Center Manager Server
Technical Requirements and
Operating System Configuration
Guide for the co-resident server
297-2183-944
Contact Center Manager
Administration Technical
Requirements and Operating System
Configuration Guide
297-2183-213
Communication Control Toolkit
Server Technical Requirements and
Operating System Configuration
Guide
297-2183-215
Contact Center Multimedia Server
Technical Requirements and
Operating System Configuration
Guide
297-2183-214
Contact Center 6.0 Security Guide
Contact Center Portfolio Service
Packs Compatibility and Security
Hotfixes Applicability List
For information about Refer to NTP number
Page 36

36 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Installation, upgrades,
migration, and
maintenance
Contact Center Manager Server
Installation and Maintenance Guide
297-2183-925
Contact Center Manager Server
Installation and Maintenance Guide
for the Co-resident Server
297-2183-218
Contact Center Manager Server
Installation and Maintenance Guide
for the Standby Server
297-2183-219
Contact Center Manager
Administration Installation and
Maintenance Guide
297-2183-926
Communication Control Toolkit
Installation and Maintenance Guide
297-2183-946
Contact Center Multimedia
Installation and Maintenance Guide
297-2183-929
Nortel Media Application Server
Installation and Configuration Guide
for Contact Center 6.0
297-2183-227
Nortel LinkPlexer Installation and
Configuration Guide
297-2183-964
Scripting Contact Center Manager Scripting
Guide for Communication Server
1000/Meridian 1 PBX
297-2183-930
Contact Center Manager Scripting
Guide for Communication Server
2X00/DMS
297-2183-936
Contact Center Manager Database
Integration User Guide
297-2183-940
For information about Refer to NTP number
Page 37

What’s New in Release 6.0 37
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Application online Help
Each Contact Center application contains online Help that explains tasks and
describes the windows in the application.
Networked contact
center
Contact Center Manager Network
Control Center Administrator’s Guide
297-2183-932
Administering contact
centers
Contact Center Manager
Administrator’s Guide
297-2183-927
Supervising contact
centers
Contact Center Manager
Supervisor’s Guide
297-2183-928
Contact Center Historical Reporting
and Data Dictionary
297-2183-914
Handling contacts Contact Center Agent Desktop User
Guide
297-2183-945
For information about Refer to NTP number
Page 38

38 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
How to get help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Finding the latest updates on the Nortel Web site
The content of this documentation was current at the time the product was
released. To check for updates to the latest documentation and software for
Contact Center 6.0, click one of the following links:
Getting help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support Web site:
w
ww.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and tools
to address issues with Nortel products. From this site, you can:
download software and related tools
download technical documents, release notes, and product bulletins
sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation
search the Technical Support Web site and Nortel Knowledge Base for
answers to technical issues
open and manage technical support cases
Link to Takes you directly to the
Latest software Nortel page for Contact Center located at
www.nortel.com/espl.
Latest documentation
Nortel page for Contact Center documentation located
at www.nortel.com/helmsman.
Page 39

What’s New in Release 6.0 39
July 2007 About Contact Center 6.0
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you do not find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support
Web site, and you have a Nortel sup port co ntract, y ou can also get h elp over the
phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the phone
number for your region:
w
ww.nortel.com/callus
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some Nortel Technical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
w
ww.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor or
authorized reseller, you can contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
Page 40

40 Contact Center
About Contact Center 6.0 Standard 4.01
Page 41

What’s New in Release 6.0 41
Chapter 3
New in this release
In this chapter
Introduction 42
Contact Center portfolio rebranding 43
Upgrading from a previous release 44
Product changes 51
Page 42

42 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Introduction
This chapter contains information that is important to users who used previous
releases of the Nortel contact center software. It describes product rebranding,
upgrade paths from previous releases, and improvements to the Contact Center
portfolio.
Page 43

What’s New in Release 6.0 43
July 2007 New in this release
Contact Center portfolio rebranding
Introduction
For Release 6.0, the Symposium portfolio is rebranded as the Nortel Contact
Center portfolio. Many of the application names within the Contact Center
portfolio are updated to align with the overall portfolio. This section provides an
overview of the changes.
Identifying the new product names
The following table provides a list of new application and component names for
the Contact Center portfolio.
Former application or
component name Release 6.0 name
Symposium Call Center Server
(including Web Client)
Nortel Contact Center – Manager
Symposium Call Center Server
(server)
Contact Center Manager Server
Network Control Center Contact Center Network Control
Center
Symposium Web Client
(application server)
Contact Center Manager
Administration
Configuration Tool Contact Center Manager
Configuration Tool
Agent Desktop Display Agent Desktop Display
Symposium Web Center Portal Nortel Contact Center Multimedia/
Outbound
Nortel Networks Communications
Control Toolkit
Nortel Communication Control Toolkit
Page 44

44 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Upgrading from a previous release
Introduction
This section describes the supported software upgrade paths, operating system
migration paths, and enhancements for the Contact Center components.
Contact Center Manager Server
Upgrading your server
For upgrade planning considerations, see the Nortel Contact Center Planning
and Engineering Guide. For detailed installation and upgrade procedures, see
the Nortel Contact Center Manager Server Installation and Maintenance Guide.
Before you upgrade the Contact Center Manager Server software, you must
ensure your new hardware meets the required specifications. For detailed
information, see the Nortel Contact Center Planning and Engineering Guide or
the Contact Center Manager Server Technical Requirements and Operating
System Configuration Guide.
You can upgrade from the following releases of Symposium Call Center Server
to Contact Center Manager Server:
from Release 4.2 to Release 6.0
from Release 5.0 to Release 6.0
from Release 6.0 to Release 6.0
Upgrading from previous releases
Nortel recommends the following upgrade paths.
Release Action
1.5 Upgrade to Release 4.2, and then upgrade to Release 6.0.
3.0 Upgrade to Release 4.2, and then upgrade to Release 6.0.
Page 45

What’s New in Release 6.0 45
July 2007 New in this release
Installing and configuring the server
A preinstallation checker verifies that a DVD drive exists, the operating system
is Windows Server 2003 Standard or Enterprise Edition, the D: partition has
adequate space to install the additional new components, and the database size is
sufficient to perform a successful migration to Release 6.0. If an error occurs,
the installation stops.
The installation is an unattended automatic installation with all configuration
data entered up front in the Server Configuration Utility.
The installation includes:
Network interface card (NIC) solution—Changes to the Server
Configuration Utility allow administrators to select whether they want to
configure one network interface card (NIC) or two. If they select one, the
server subnet IP address is entered and no ELAN subnet IP address is
prompted. The single-NIC solution requires a routed ELAN subnet. Nortel
recommends the single-NIC configuration as future Contact Center
Manager Server releases and features (such as SIP Contact Center) do not
support the dual-NIC configuration.
New components installed—As part of the Contact Center Manager
Server installation, the following new components are installed: Java
Virtual Machine (JVM)/Java Runtime Environment (JRE) for Contact
Management Framework (CMF) and Session Initiation Protocol (SIP); the
MCS application, including SIP stack; Gigaspaces build; the CMF jar file;
and the Universal Networking Engine (UNE) component.
Flexible licensing—Release 6.0 uses a License Manager to provide access
to features and functions of the Contact Center portfolio in packages.
Database partition size—The maximum database size increases from
64 GB to 128 GB. The maximum partition size increases from 16 GB to
32 GB.
Dynamic port allocation—To control port usage for component
communication, use the Server Configuration Utility to configure the range
of ports within a specified range to be used for intercomponent messaging.
4.0 Upgrade to Release 5.0, and then upgrade to Release 6.0.
Release Action
Page 46

46 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Installing the standby server
Enhancements for Release 6.0 reduce the complexity of switching from the
active Contact Center Manager Server to the standby server and minimize the
amount of time required to activate the standby server:
The standby server retains its computer name and IP address after it is
activated (you do not need to manually change the name and IP address to
match the primary server, and then restart the server).
Both the active and standby servers can be added as distinct members of the
Windows domain to avoid the requirement for intervention by a domain
administrator when the standby server is activated.
The enhanced Replication Server utility enables users to initiate the entire
switchover process to the standby server by running a utility.
Release 6.0 introduces the ability to replicate the networked contact center.
Providing serviceability and support
Log files provide two new functions:
Enhancement to the Skillset Promote Utility provides an indication of
whether execution of the utility is successful by writing results to a new log
file.
An event log message is generated when a site comes back up after it was
filtered out.
The Server Configuration Utility is updated to enforce the correct binding order
of Nortel server subnet followed by ELAN subnet; if the ELAN su bn et network
interface card (NIC) is configured first, an error message appears. (This is only
applicable if the server is configured with dual NIC cards.)
Coresiding server applications
For Release 6.0, Contact Center Manager Server, License Manager, Contact
Center Manager Administration, Server Utility, and Communication Control
Toolkit can all co-reside on the same server. The Server Utility coresiding with
Contact Center Manager Administration alone is not supported. The Server
Utility can also be installed on a stand-alone client. In a network, the Server
Utility can co-reside with the Network Control Center server.
Page 47

What’s New in Release 6.0 47
July 2007 New in this release
Contact Center Server Utility
The Contact Center Server Utility is a new product. All installations are new
installations for this release. The Contact Center Server Utility can be installed
on a stand-alone computer, on the Contact Center Manager Server, or in a
networked contact center, co-resident with the Network Control Center server.
Contact Center Manager Administration can co-reside with the Release 6.0
Server Utility.
In an environment with Symposium Call Center Server Release 4.2 or 5.0 and
Contact Center Manager Server Release 6.0, if administrators want to continue
using the Classic Client to maintain the Release 4.2 or 5.0 server, they can keep
the Classic Client on the administrator’s computer temporarily while the data is
migrated from previous releases to Release 6.0. For more information about
administering network scenarios, refer to the Nortel Contact Center Planning
and Engineering Guide.
Contact Center Manager Administration
Upgrading your server
Contact Center Manager Administration supports upgrades from Symposium
Web Client Release 4.5 SUS0601v1 (or later).
Security
Security is enhanced on Contact Center Manager Administration with firewalls
that limit the range of ports used. Application and Meridian Mail passwords are
masked and a warning message is enabled. ActiveX controls are updated for
security.
Backing up and restoring data
For Contact Center Manager Administration, you can easily schedul e backups of
the data stored in Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM) and in data files
at the same time, whether Contact Center Manager Administration is
stand-alone or co-resident with Contact Center Manager Server, using a new
online backup procedure. You can the Microsoft Windows Backup Utility to
perform scheduled or manual backups and restores.
Page 48

48 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Installing and configuring Contact Center Manager Administration
For Release 6.0, the Scripting Manager component is a fully integrated Webbased component; Terminal Services is no longer a prerequisite for installation.
The preinstallation checker ensures that the operating system is Windows Server
2003 Standard or Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition.
As part of the Contact Center Manager Administration installation, the
following new components are installed: Report Creation Wizard, Crystal CE
Embedded 10, Crystal Report Viewer 10, SIP reports and Configuration Tool,
License Manager Interface, and Outbound report templates.
Installing the Replicating server
With Release 6.0, new features ensure that Contact Center Manager
Administration is geographically resilient so that you can replicate the Contact
Center Manager Administration database.
A new procedure provides backups for Contact Center Manager
Administration application-specific data that does not reside in ADAM.
Data in ADAM cannot be replicated.
Users can change the name or IP address of the Contact Center Manager
Server in the Contact Center Manager Administration tool. This feature lets
Contact Center Manager Administration to continue communicating with
the server, even though it has a different name.
There is now an automatic check and update of the server IP address, if a
server name change is made in the Configuration component.
Providing serviceability and support
Error messages presented to the end user are reviewed and updated to include a
description of the error and the action to be taken by the customer.
Additional troubleshooting scenarios are added to the Contact Center Manager
Administration Installation and Maintenance Guide to address the
stand-alone/co-residency solutions; sample scenarios of error codes are also
provided. The IceRTDTrace tool is packaged in a separate MSI file so it can be
installed on client computers for troubleshooting Real-Time Display (RTD)
issues.
Page 49

What’s New in Release 6.0 49
July 2007 New in this release
The complete list of Event Codes is included in the Contact Center Manager
Administration Installation and Maintenance Guide as well as events
recommended for trapping.
The CS 1000/M1 Data Extraction Tool is modified to allow the download of
trunk numbers without leading zeros (LD 20 and LD 81). For more information
about the M1 Data Extraction Tool, see the Contact Center Manager
Administrator’s Guide.
The Audit Trail in Contact Center Manager Administration tracks all changes t o
the configuration, including the Access and Partition Management, Historical
Reporting, Configuration Management, Report Creation Wizard, and
Configuration and Scripting.
Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound
Installing on a new server
Because the Multimedia server runs on Windows 2003, while Symposium Web
Center Portal Release 4.0 runs on Windows 2000, the Contact Center
Multimedia/Outbound server requires the introduction of a new server with a
fresh installation of Windows Server 2003. You can use a migration to ol to
upgrade the data from the previous release.
The installation process includes a preinstallation check, which ensures that the
system meets the product requirements and displays status messages. The
preinstallation check also determines whether any required third-party software
such as Java Run Environment (JRE) or Microsoft .NET Framework is installed;
if not, it installs the software.
Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound provides the facility to silently install the
software and the database on the target system.
Backing up and restoring data
For Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound, you can start a backup utility from
the Multimedia Administrator to back up the data in the Multimedia database.
You must back up the incoming and outgoing e-mail attachment folders
separately. You can also archive the Multimedia database using an archive
utility. In case of server failure, you can restore the database from the backup or
the archive. You must use the Microsoft Windows Backup Utility to back up the
server configuration.
Page 50

50 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Installing the Standby server
The Caché database offers database shadowing to provide a near real-time
replication of the database to a standby Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound
server. You can install the Redundancy server and configure the database
shadowing after you install the primary Multimedia server.
Providing serviceability and support
Log files can be created to track errors, warnings, and notices for each
application within the Multimedia server.
Coresiding client applications
Contact Center 6.0 Agent Desktop application and the Outbound Campaign
Management Tool can co-reside on the same server. These two applications can
co-reside with the Symposium Web Center Portal 4.0 Agent Interface
temporarily while the migration to Release 6.0 occurs.
Patching
For Contact Center Release 6.0 components, there are two types of patches—
Service Updates and Service Update Supplements:
Service Updates (SU) contain many fixes. You must remove any other
patches before installing an SU because all previous fixes are included in
the SU. Any subsequent SU always contains all fixes from previous SUs or
Service Update Supplements (SUS).
Service Update Supplements (SUS) are patches that contain a small number
of fixes and are installed on top of the last SU.
Page 51

What’s New in Release 6.0 51
July 2007 New in this release
Product changes
Introduction
This section provides an overview of product changes for the Contact Center
Manager Server, Contact Center Manager Administration, and Contact Center
Multimedia/Outbound server.
Classic Client not available
The Classic Client software is not part of Contact Center 6.0. Most of the
functionality from the Classic Client software is available in Contact Center
Manager Administration. For more information about Contact Center Manager
Administration, see “Contact Center Manager Administration” on page 19 . The
remaining server maintenance and monitoring utilities are part of the Contact
Center Server Utility. For more information about the Contact Center Server
Utility, see “Server Utility” on page 19.
Contact Center Manager Server product improvements
Contact Center Manager Server contains the following product improvements
for Release 6.0.
Open Queue
You can use the Open Queue feature in Contact Center 6.0 to route multimedia
contacts to agents using the scripting and skillset routing features traditionally
associated with telephony calls. The Open Queue feature provides a generic
mechanism that third-party software applications can use to provide access to
Contact Center workflow, queueing, routing, and reporting for their contacts in
an integrated manner.
The contact management programming interface is Java API. Third-party
applications are built with Java libraries supplied by Nortel. The Open Queue
specification for contacts supports create, read, and delete operations for
contacts. It also supports a set of mutable and immutable intrinsics associated
Page 52

52 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
with the contacts. The workflow script accesses the values in the intrinsics and
uses them to make routing decisions. The Contact Center Multimedia
applications use the Open Queue API for access to Contact Center Manager
Server, replacing the Dynamic Transaction Handler (DTH) mechanism.
The Open Queue feature works in conjunction with agent licensing to provide
agents with contact handling capability to match the type of contact. Contact
Center Multimedia provides a desktop that is integrated with Communication
Control Toolkit and that supports multiple contact types, including e-mail and
outbound. These contact types are configured in Contact Center Manager Server
and administered using Contact Center Manager Administration. For third-party
applications, the agent interaction with Open Queue contacts takes place through
the Communication Control Toolkit, which delivers events relating to Open
Queue contacts to desktop applications. Open Queue also delivers contactcontrol commands (such as answer and close actions), initiated by desktop
applications to Contact Center Manager Server contact processing components.
Default ACD Queue Management
A contact center administrator can assign a default Automatic Call Distribution
(ACD) Queue to an agent using Contact Center Manager Administration. This
default ACD Queue is delivered to the switch during the agent logon process.
The contact center administrator now has control over moving agents of similar
skillsets to the same ACD Queue so that during the default behavior of the
switch, agents of similar skillsets receive relevant calls. This feature is supported
only on the Meridian 1 PBX/Communication Server switch platform.
Universal networking
You can use Network Skill-Based Routing to route voice calls between
networked sites in a mixed switch environment. For more information abo ut the
supported switch environments, see “System operations and supported
platforms” on page 32.
Universal networking provides the ability to deploy virtual contact centers
across all Nortel switch platforms and Nortel Interactive Voice Response (IVR)
systems, increases deployment flexibility, and increases network-wide agent
utilization and productivity.
Page 53

What’s New in Release 6.0 53
July 2007 New in this release
Geographic redundancy
The Contact Center portfolio contributes to the high availability solution by
allowing alternative operational sites into geographically distributed
configurations. In the event of a disaster that causes a total outage at the primary
site, the alternative site can be started quickly. This is also applicable to local
redundancies, addressing the problem of a single component failure within a
site.
Note: The geographic resiliency enhancements are not applicable when the
Contact Center Manager Server is configured as a SIP contact center.
Increase in configured agents
The maximum number of configured agents increases from 6000 to 10000. The
number of active agents is 3350.
Increase in call variables
The maximum number of available call variables increases from 20 to 50.
Increase in skillsets per agent
The maximum number of skillsets assigned to an agent increases from 50 to
100.
Reporting
Contact Center Manager Server offers the following reporting improvements:
Virtual network skillset calls offered and calls abandoned statistics are
added to the Skillset view. These statistics provide a consistent view of
activity across a virtual skillset.
New application historical statistics include Talk Time, Post-Call
Processing Time, Wait Time, Dialed Number Out External Talk Time, and
Dialed Number Out Internal Talk Time.
New skillset historical statistics include Post-Call Processing Time, Talk
Time, Wait Time, Dialed Number Out External Talk Time, and Dialed
Number Out Internal Talk Time.
Application call answer delay and call abandoned delay pegging is more
accurate: statistics are calculated from the time the call enters the primary
application rather than from the Master script.
Page 54

54 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
New Agent By Skillset and Agent By Application statistics include Calls
Offered, Ring Time, Calls Returned To Queue, Calls Transferred, Calls
Returned To Queue Due Timeout, Calls Conferenced, Dialed Number Out
Internal Talk Time, and Dialed Number Out External Talk Time.
Additional network consolidated views are available for the networked
contact center, similar to the network consolidated Skillset view. The new
views are Application, Agent Performance, Agent By Application, and
Agent By Skillset.
Some of the statistics in existing historical reports require a new
interpretation due to the effect of multimedia pegging. For example, Calls
Answered statistics are updated to include multimedia contacts and are
reinterpreted as Contacts Accepted. Similarly, Talk Time statistics are
reinterpreted as Processing Time. For details about the statistics affected
and their new definitions, see the Historical Reporting and Data
Dictionary.
Note: The labels of these statistics as they appear in the reports and the
reporting open interface database views are not changed for Release 6.0.
Note: The new statistics added to the nodal Agent By Application and Agent By
Skillset and the networked contact center are available in the Report Creation
Wizard.
Contact Center Manager Administration improvements
The following improvements to the Contact Center Manager Administration
work on a Symposium Web Client server 5.0 that is connected to a Release 6.0
Contact Center Manager Server.
Contact Center Manager Administration Web client improvements
General improvements to the Contact Center Manager Administration include
the following.
Toolbar updates
view server time and connection status
access additional NTP titles
Page 55

What’s New in Release 6.0 55
July 2007 New in this release
Configuration improvements
synchronize data from the Network Control Center to a particular site in the
network
view routing table assignment schedules
use the Server Utility to check the license configuration
update icons for IP phoneset displays
Contact Center Management
General improvements to the Contact Center Management component of the
Contact Center Manager Administration include the following:
add or delete agents in bulk
display the current status of an agent (logged on or logged off) in all
Supervisor, Skillset, Agent Details, and Assignment views
assign a group of agents to a new supervisor
run user-defined assignments at any time
view the schedule of all agent to skillset and agent to supervisor
assignments
choose a priority for agent to skillset assignments
change skillset assignments for a group of agents all at once
limit the number of skillsets assigned to agent
apply assignment changes to multiple agents simultaneously
Access and Partition Management
General improvements to the Access and Partition Management component of
the Contact Center Manager Administration include the following:
use dynamic standard partitions that are easier to configure
use new access classes for real-time reporting and historical reporting
use access levels for agent to skillset assignments and agent to supervisor
assignments
Page 56

56 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Real-Time Displays
General improvements to the Real-Time Displays component of the Contact
Center Manager Administration for tabular reports include the following:
use a collection to arrange up to six tabular and graphical displays
configure colors for standard tabular displays where the threshold is below
level 1
choose filters
link from Standard Skillset report to Skillset view
link from Standard Supervisor report to Supervisor view
General improvements to the Real-Time Displays component of the Contact
Center Manager Administration for graphical reports include the following:
share graphical displays
use a collection to arrange up to six tabular and graphical displays
use a collection to display up to 25 individual billboards
show service level percentage on charts
chart labels (data element names on the y-axis or x-axis of bar charts)
view threshold timers on billboards
change background color on billboards
view non-staffed skillsets
improve agent maps:
show an agent’s personal dialed number (DN) in the title bar of the
agent map
exclude logged off agents from the agent map
resize the agent map
create threshold alerts (flashing text on the agent map) when a thres hold
is exceeded
provide more information about agents
show a linked display from the agent map
Page 57

What’s New in Release 6.0 57
July 2007 New in this release
Historical Reporting
General improvements to the Historical Reporting component of the Contact
Center Manager Administration include the following:
view and print all historical report schedules
modify report templates on the network drive
update remote site reports when the Contact Center Manager Server IP
address changes
Configuration Report for Default Queue Management
performance enhancements
For more information about reports, see “Reporting” on page 53.
Report Creation Wizard
Report Creation Wizard is a new reporting feature that runs in Contact Center
Manager Administration 6.0 and is accessible through the main Historical
Reporting interface. Use Report Creation Wizard to create, maintain, and
modify custom ad hoc reports through a user-friendly interface. You can then
import and schedule the reports in Historical Reporting. In previous releases of
Contact Center Manager Administration (formerly known as Symposium Web
Client), users had to be familiar with the Crystal Reports Designer and
Structured Query language (SQL) to modify certain aspects of user-created
reports, such as
the databases, table, and views to use within the report
the field and column data for the report
the title and subtitle, and other aspects of the report’s appearance
After you create reports through Report Creation Wizard, you can work with
them in the Historical Reporting component and use the same access
permissions, partitions, and filter sets as you can with any other report. You can
also use the Historical Reporting interface to schedule reports that you create
with the Report Creation Wizard.
Page 58

58 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Scripting improvements
The requirement for Terminal Services is replaced by the script manager as a
fully integrated Web-based solution. In addition to providing the functionality
previously available, the Web-based scripting manager also provides the ability
to
list all scripts
sort column headers
You can use the script editor to
edit, validate and activate scripts
view multiple scripts
import and export scripts
search for unused script variables
search and replace within a script
highlight the line in the script with an error
rename inactive scripts
Number of active and configured supervisors
The maximum number of active supervisors increases from 150 to 350.
The maximum number of configured supervisors increases from 300 to 600.
Agent ID digit support
Contact Center Manager Administration supports 10-digit agent IDs for DMS
and 16-digit agent IDs for Meridian 1 PBX/CS 1000. Administrators can
configure the system to use 4- to 10-digit IDs for DMS.
Page 59

What’s New in Release 6.0 59
July 2007 New in this release
Agent Desktop Display enhancements
The following functionality is added to the Agent Desktop Display:
An agent can run Agent Desktop Display without being logged on.
An agent can hide the title bar.
The space between columns is reduced.
The client can be configured with active and standby servers using a host
name, not just an IP address.
You can disable automatic downloads of upgrades to client PCs.
Contact Center Multimedia server improvements
Contact Center Multimedia provides the following improvements based on the
Symposium Web Center Portal server:
Simplified installation
Installation of the Caché database software is automated and, where possible,
third-party software is silently installed, greatly reducing installation time. In
addition, Release 6.0 incorporates individual components into one installation
package and provides a common look and feel using industry-standard dialog
boxes.
Contact Management Framework (CMF) integration
The mechanism for routing contacts was telephony-based for previous releases.
Routing and reporting for contacts, both for telephony and multimedia, is
software-based.
Unified reporting and administration
For Release 6.0, administrators run multimedia reports using the Report
Creation Wizard and view real-time display information about multimedia
contacts on the Contact Center Manager Administration real-time displays.
Administrators also configure user and skillset information and supervisor logon
functionality in Contact Center Manager Administration. The real-time
reporting component from Symposium Web Center Portal Release 4.0 is
removed. For more information, see “Report Creation Wizard” on page 57.
Page 60

60 Contact Center
New in this release Standard 4.01
Improved agent interaction
All agent interaction with the server occurs through firewall-friendly Secure
Web Services from the Multimedia/Outbound server, with the option to
configure the system to transmit all data between the client and the server in
encrypted form using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
Increase in number of contacts handled
The Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound server handles up to 5000 contacts
per hour. This maximum applies to all multimedia contact types.
Contact Center Manager Server support
The Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound server aligns with Contact Center
Manager Server to support a maximum of 9900 configured agents.
Increase in number of active agents
The Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound server supports a maximum of 600
active agents.
Storage capacity
The Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound database supports 12 months of
storage based on an average size of 2 million contacts.
Page 61

What’s New in Release 6.0 61
Appendix A
Acronyms in Contact Center
In this chapter
Acronyms 62
Page 62

62 Contact Center
Acronyms in Contact Center Standard 4.01
Acronyms
The following list defines commonly used acronyms in Contact Center.
Acronym Definition
ACD Automatic Call Distribution
API Application Programmer Interface
ASA Average Speed of Answer
ASE Sybase Adaptive Server Enterprise version
CC Contact Center
CCM Contact Center Manager
CCMA Contact Center Manager Administration
CCMM Contact Center Multimedia
CCMS Contact Center Manager Server
CCT Communication Control Toolkit
CLAN Customer Local Area Network (new name: Server Subnet)
CORBA Common Object Request Broker Architecture
CSE Call Server for Enterprise
CMF Contact Management Framework
CTI Computer-Telephony Integration
DHCP Dynamic Host Control Protocol
DMI Desktop Management Interface
DMS Digital Multiplex Switch
DN Directory Number
Page 63

What’s New in Release 6.0 63
July 2007 Acronyms in Contact Center
DSN Data Source Name
DTMF Dual Tone Multi Frequency
ELAN Embedded Local Area Network
GA General Availability
GRTD Graphical Real-Time Display
GUI Graphical User Interface
HDC Historical Data Collector
HDM Historical Data Manager
HDX Host Data Exchange
IDL Interface Definition Language
IP Internet Protocol
IPT Integrated Project Team
IVR Interactive Voice Response
LAN Local Area Network
LIA Longest Idle Agent
LM License Manager
LMIF License Manager Interface
MAS Media Application Server
MAT Meridian Administration Terminal
NACD Network ACD
NCC Network Control Center
NIC Network Interface Card
Acronym Definition
Page 64

64 Contact Center
Acronyms in Contact Center Standard 4.01
OC Open Client
OCMT Outbound Campaign Management Tool
ORB Object Request Broker
PBX Private Branch Exchange
PLM Product Line Management
PRD Product Requirements Document or Platform Recovery Disk
PVI Platform Vendor Independence
RCW Report Creation Wizard
RSM Real-time Statistics Multicast
RTD Real-time Data API
RTI Real-time Interface
SEI Symposium Event Interface
SCCS Symposium Call Center Server
SIP Session Initiated Protocol
SQL Structured Query Language
SWCP Symposium Web Center Portal
SU Service Update package
SUS Service Update Supplement
TAPI Telephony Application Program Interface
UNE Universal Networking Engine
USB Universal Serial Bus
VNS V irtual Network Services
Acronym Definition
Page 65

What’s New in Release 6.0 65
July 2007 Acronyms in Contact Center
VPN Virtual Private Network
Acronym Definition
Page 66

66 Contact Center
Acronyms in Contact Center Standard 4.01
Page 67

What’s New in Release 6.0 67
Glossary
A access class
A collection of access levels that defines the actions a member of the access
class can perform within the system. For example, a member of the
Administrator access class can be given a collection of Read/Write access levels.
access level
A level of access or permission given to a particular user for a particular
application or function. For example, a user can be given View Only acces s to
historical reports.
activated script
A script that is processing calls or is ready to process calls. Before you can
activate a script, you must first validate it.
Before you can activate a script, you must first validate it.
active server
In a system with a Replication Server, the server that is providing call processing
and administration services.
activity code
A number that agents enter on their phoneset during a call. Activity codes
provide a way of tracking the time agents spend on various types of incoming
calls. They are also known as Line of Business (LOB) codes. For example, the
activity code 720 can be used to track sales calls. Agents can then enter 720 on
their agent desktop applications during sales calls, and this information can be
generated in an Activity Code report.
adapter
Hardware required to support a particular device. For example, n etwork adapters
provide a port for the network wire. Adapters can be expansion boards o r part of
the computer’s main circuitry.
Page 68

68 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
administrator
A user who sets up and maintains Contact Center Manager and Contact Center
Multimedia.
agent
A user who handles inbound and outbound voice calls, e-mail messages, and
Web communications.
agent logon ID
A unique identification number assigned to a particular agent. The agent uses
this number when logging on. The agent ID is not associated with any particular
phoneset.
application
1. A logical entity that represents a Contact Center Manager script for reporting
purposes. The Master script and each primary script have an associated
application. The application has the same name as the script it represents. 2. A
program that runs on a computer.
application program interface
A set of routines, protocols, and tools that programmers use to develop software
applications. APIs simplify the development process by providing commonly
used programming procedures.
application server
The server on which the Contact Center Manager Administration software is
installed. This server acts as the middle layer that communicates with Contact
Center Manager Server and makes information available to the client PCs.
associated supervisor
A supervisor who is available for an agent if the agent’s reporting supervisor is
unavailable. See also reporting supervisor.
automatic call distribution
A means of automatically distributing an organization’s incoming calls among a
number of answering positions (ACD agents). Automatic call distribution is
useful in operations where callers want a service rather than a specific person.
Calls are serviced in the order they arrive and are distributed so that the
workload at each answering position is approximately equal.
Page 69

What’s New in Release 6.0 69
July 2007 Glossary
automatic call distribution call
A call to an ACD-DN. ACD calls are distributed to agents in an ACD group
based on the ACD routing table on the switch. See also automatic call
distribution directory number.
automatic call distribution directory number
A primary or supplementary DN associated with an ACD group. Calls made to
an automatic call distribution directory number are distributed to agents
belonging to the group, based on the ACD routing table on the switch.
automatic call distribution group
An entity defined on the switch for the purpose of call distribution. When a
customer dials an ACD group, the call is routed to any agent who is a member of
that group.
automatic call distribution routing table
A table configured on the switch that contains a list of ACD-DNs used to define
routes for incoming calls. This ensures that incoming calls not processed by
Contact Center Manager Server are queued to ACD groups and handled by
available agents.
automatic call distribution subgroup
An entity defined on the switch to assign supervisory responsibilities. Each
subgroup has one supervisor phoneset and a number of agent phonesets
associated with it. Agents can log on to any phoneset within their ACD
subgroup. The supervisor must log on to the supervisor phoneset to monitor
assigned agents.
Automatic Number Identification
A telephony feature that provides the originating local telephone number of the
caller.
C call priority
The priority given to a request for a skillset agent in a QUEUE TO SKILLSET
or QUEUE TO NETWORK SKILLSET script element. This priority is used
only in queuing a pending request in the pending request queue corresponding to
the required skillsets. This allows pending requests with greater priority in a
Page 70

70 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
skillset to be presented to agents before calls of lesser priority. Call priority has a
range of 1 to 6, with 1 having the greatest priority. Six priorities are used to fully
support the many queuing variations provided by existing NACD functionality.
Call priority is maintained at target nodes for network call requests.
call treatment
A script element that enables you to provide handling to a call while it is waiting
to be answered by a contact center agent. For example, a caller can hear a
recorded announcement or music while waiting for an agent.
call variable
A script variable that applies to a specific call. A call variable follows the call
through the system and is passed from one script to another with the call.
CallPilot
A multimedia messaging system you can use to manage many types of
information, including voice messages, fax messages, e-mail messages,
telephone calls (including conferencing), calendars, and directories.
central processing unit
The component of a computer that performs the instructions of computer
programs. Also known as a processor or microprocessor.
Classic Client
The Windows-based client component for Symposium Call Center Server.
client
The part of Contact Center Manager Server that runs on a personal computer or
workstation and relies on the server to perform some operations. Two types of
client are available: Server Utility and Contact Center Manager Administration.
See also server.
Communication Control Toolkit
A client/server application that integrates a telephone on a user’s desktop with
client- and server-based applications.
Computer-Telephony Integration
An application that enables a comp uter to control telephone calls.
Page 71

What’s New in Release 6.0 71
July 2007 Glossary
Contact Center Agent Desktop
An agent tool that enables contact center agents to provide intelligent and
personalized customer care. Agents use a personal computer to access the
telephony and multimedia functions.
Contact Center – Manager
A client/server contact center solution for varied and changing business
requirements. It offers a suite of applications that includes call processing and
agent handling, management and reporting, networking, and third-party
application interfaces.
Contact Center Manager Administration
A browser-based tool for contact center administrators and supervisors use for
managing and configuring a contact center and its users, defining access to data,
and viewing real-time and historical reports. The Contact Center Manager
Administration software is installed on an application server. See also Contact
Center Manager Administration server.
Contact Center Manager Administration server
The server on which the Contact Center Manager Administration software is
installed. This server acts as the middle layer that communicates with Contact
Center Manager Server and makes information available to the client PCs.
Contact Center Manager Server
This server is responsible for functions such as the logic for call processing, call
treatment, call handling, call presentation, and the accumulation of data into
historical and real-time databases.
Contact Center Multimedia server
A client/server contact center application that expands inbound telephony
capabilities to include outbound voice, e-mail, and Web communications.
Contact Center standby server
The server that contains an up-to-date backup version of the Contact Center
Manager Server database for use if the active server fails. The database is kept
up-to-date by the Replication Server.
Page 72

72 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
controlled directory number
A special directory number that allows calls arriving at the switch to be queued
when the CDN is controlled by an application such as Contact Center Manager
Server. When a call arrives at this number, the switch notifies the application
and waits for routing instructions, which are performed by scripts in Contact
Center Manager Server.
Customer Local Area Network
The LAN to which your corporate servers, third-party applications, and desktop
clients connect.
Customer Relationship Manager
An application that provides the tools and information that an organization
requires to manage its customer relationships.
D default skillset
The skillset to which calls are queued if they are not queued to a skillset or a
specific agent by the end of a script.
Dialed Number Identification Service
An optional service that allows Contact Center Manager Server to identify the
phone number dialed by the incoming caller. An agent can receive calls from
customers calling in on different DNISs and, if the DNIS is displayed on the
phoneset, can prepare a response according to the DNIS.
directory number
The number that identifies a phoneset on a switch. The directory number (DN)
can be a local extension (local DN), a public network telephone number, or an
automatic call distribution directory number (ACD-DN).
E Emergency key
A key on an agent’s phoneset that, when pressed by an agent, automatically calls
their supervisor to notify the supervisor of a problem with a caller.
Page 73

What’s New in Release 6.0 73
July 2007 Glossary
event
1. An occurrence or action on Contact Center Manager, such as the sending or
receiving of a message, the opening or closing of an application, or the reporting
of an error. Some events are for information only, while others can indicate a
problem. Events are categorized by severity: information, minor, major, and
critical. 2. An action generated by a script command, such as queuing a call to a
skillset or playing music.
F firewall
A set of programs that protects the resources of a private network from external
users.
H Host Data Exchange
A rich scripting language provided with Contact Center – Manager to control
treatment of calls.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
The set of rules for transferring data on the World Wide Web.
I Interactive Voice Response
An application that allows telephone callers to interact with a host computer
using prerecorded messages and prompts.
Internet Protocol address
An identifier for a computer or device on a TCP/IP network. Networks use TCP/
IP to route messages based on the IP address of the destination. For customers
using NSBR, site IP addresses must be unique and correct. The format of an IP
address is a 32-bit numeric address written as four values separated by periods.
Each value can be 0 to 255 (f or example, 1.160.10.240).address.
L local area network
A computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs connect
workstations and personal computers and are confined to a single building or
group of buildings.
Page 74

74 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
local call
A call that originates at the local site.
M M1
Meridian 1 switch
M1 IE
Meridian 1 Internet Enabled switch
Meridian Link Services
A communications facility that provides an interface between the switch and a
third-party host application.
Meridian Mail
A Nortel product that provides voice messaging and other voice and fax
services.
Multimedia database
A Caché database used to store customer information and contact details for
outbound, e-mail, and Web communication contacts.
MSL-100
Meridian Stored Logic 100 switch
N Network Control Center
The server on a Contact Center Manager system where Network Skill-Based
Routing is configured and where communication between servers is managed.
network interface card
An expansion board that enables a PC to connect to a local area network (LAN).
Network Skill-Based Routing
An optional feature with Contact Center Manager Server that provides skillbased routing to multiple networked sites.
Page 75

What’s New in Release 6.0 75
July 2007 Glossary
O outbound campaign
A group of outgoing calls from the contact center for a specific purpose, for
example, customer satisfaction surveys.
P pegging
The action of incrementing statistical counters to track and report on system
events.
personal directory number
A DN on which an agent can be reached directly, usually for private calls.
phoneset
The physical device, conn ected to the sw itch, to which calls are presented. Each
agent and supervisor must have a phoneset.
phoneset display
The display area on an ag ent’s phoneset where information about incoming calls
can be communicated.
private branch exchange
A telephone switch, typically used by a business to service its internal telephone
needs. A PBX usually offers more advanced features than are generally
available on the public network.
public switched telephone network
The international network of private and government-owned voice-oriented
public telephone networks.
R redundant server
A warm standby server used for shadowing the Multimedia database on the
Multimedia server and providing a quick recovery if the primary server fails.
Replication Server
A server that backs up the active Contact Center Manager Server to the standby
Contact Center Manager Server in real time.
Page 76

76 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
reporting supervisor
The supervisor who has primary responsibility for an agent. When an agent
presses the Emergency key on the phoneset, the emergency call is presented to
the agent’s reporting supervisor. See also associated supervisor.
route
A group of trunks. Each trunk carries either incoming or outgoing calls to the
switch.
router
A device that connects two LANs. Routers can also filter messages and forward
them to different places based on various criteria.
routing table
A table that defines how calls are routed to the sites on the network.
S script
A set of instructions that relates to a particular type of call, caller, or set of
conditions, such as time of day or day of week.
server
A computer or device on a network that manages network resources. Examples
of servers include file servers, print servers, network servers, and database
servers. Contact Center Manager Server is used to configure the operations of
the contact center. See also client.
server subnet
The subnet to which the Nortel servers, such as Contact Center Manager Server,
Network Control Center, Contact Center Manager Administration, Contact
Center Multimedia, and CallPilot are connected.
service level
The percentage of incoming calls answered within a configured number of
seconds.
Page 77

What’s New in Release 6.0 77
July 2007 Glossary
Service Update
A Contact Center supplementary software application that enhances the
functionality of previously released software by improving performance, adding
functionality, or correcting a problem discovered since the original release. All
previous Service Updates (SU) for the release are included in the latest Service
Update. For example, SU02 contains the contents of SU01 as well as the fixes
delivered in SU02. SU03 contains SU01, SU02 and the fixes deliv ered in SU03.
See also Service Update Supplementary.
Service Update Supplementary
A stand-alone Contact Center supplementary software application installed on
top of a specific Service Update (SU). It does not contain the contents of
previous SUs. The next SU includes SUSs built on top of previous SUs. For
example, SUS0301 is installed on top of SU03. SU04 contains SU03 and
SUS0301 (and any subsequent SUSs built on top of SU03). See also Service
Update.
Simple Network Management Protocol
A systematic way of monitoring and managing a computer network. The SNM P
model consists of four components:
managed nodes, which are any device, such as hosts, routers, and printers,
capable of communicating status to network-management systems through
an SNMP management process called an SNMP Agent
management stations, which are computers running special network
management software that interact with the agents for status
management information, which is conveyed through exact specifications
and format of status specified by the MIB
Management Protocol or SNMP, which sends messages called protocol
data units (PDUs)
site
1. A system using Contact Center Manager Server that can be accessed using
Server Utility. 2. A system using Contact Center Manager Server and
participating in Network Skill-Based Routing.
skillset
A group of capabilities or knowledge required to answer a specific type of call.
Page 78

78 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
standby server
A server that contains an up-to-date version of the database, for use when the
active server becomes unavailable.
supervisor
A user who manages a group of agents. See also associated supervisor and
reporting supervisor.
T telephony
The science of translating sound into electrical signals, transmitting them, and
then converting them back to sound. The term is used frequently to refer to
computer hardware and software that perform functions traditionally performed
by telephone equipment.
telephony switch
The hardware that processes calls and routes them to their destination.
Telephony Application Program Interface
An interface between the switch and an application that controls the telephone
on a user’s desktop.
threshold
A value for a statistic at which system handling of the statistic changes.
trunk
A communications link between a PBX and the public central office, or between
PBXs. Various trunk types provide services such as Direct Inward Dialing (DID
trunks), ISDN, and Central Office connectivity.
U utility
A program that performs a specific task, usually related to managing system
resources. Operating systems contain a number of utilities for managing disk
drives, printers, and other devices.
Page 79

What’s New in Release 6.0 79
July 2007 Glossary
V variable
A placeholder for values calculated within a script, such as CLID. Variables are
defined in the Script Variable Properties sheet and can be used in multiple scripts
to determine treatment and routing of calls entering Contact Center Manager
Server.
Virtual Private Network
A private network that is configured within a public network to take advantage
of the economies of scale and management facilities of large networks.
Voice over IP
Voice traffic that is transmitted in digital format using the IP protocol.
W wide area network
A computer network that spans a relatively large geographical area. Typically, a
WAN consists of two or more local area networks (LANs). The largest WAN in
existence is the Internet.
Page 80

80 Contact Center
Glossary Standard 4.01
Page 81

What’s New in Release 6.0 81
Index
A
ACD queue management 52
active agents 60
active supervisors 58
Agent Desktop application
See Contact Center Agent Desktop
application
agents
number supported
53
alternative operational sites 53
application Help 37
assessment of capacity 28
auditing 21
B
backup
Contact Center Manager Server
18
License Manager 18
Multimedia/Outbound 49
C
cache database 23
call variables 53
capacity assessment tool 28
Classic Client 51
client applications
Outbound Campaign Management Tool
24
client operating system requirements 33
Communication Control Toolkit server
overview
22
component failures 53
Computer-Telephony Integration (CTI) 22
configured supervisors 58
configuring
e-mail contacts
23
outbound contacts 23
contact center
access
20
core component 16
management 20
product names 43
scripting 21
software delivery 15
viewing real-time statistics 21
Contact Center Agent Desktop application
handling outbound contacts
25
in SIP 26
on Multimedia server 25
Contact Center Manager Administration
installation
48
overview of application 19
product improvements 54
tracking changes 21
upgrade and migration 47
Contact Center Manager Server
installation
45
product enhancements 51
product improvements 51
redundancy 18
SIP 17
upgrade and migration 44
Contact Center Multimedia server
installation
49
Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound server
administration
23
Agent Desktop 25
backup and restore 49
database 23
database capacity 60
migration 26
Outbound Campaign Management Tool 24
overview 23
server enhancements 59
simplified installatio n 59
Standby server 23, 50
upgrade and migration 49
contacts
Page 82

82 Contact Center
Index Standard 4.01
number handled 60
routing 16
treatments 16
co-resident applications 50
corporate licensing 18
D
database
migrating Multimedia/Outbound data
26
Multimedia contacts 23
default ACD queue 52
Default Queue Management 52
definitions
contact routing
16
contact treatment 16
outbound campaign 24
skillset 20
disaster recovery 53
documentation
format
34
duplication
Contact Center Manager Server
18
Multimedia/Outbound server 23
DVD 15
E
ESPL Web site 38
F
failure, recovering from 53
format of documentation 34
H
handling e-mail, outbound, voice 25
HDX application server 31
Help 37
historical reporting 21
I
installation
Contact Center Manager Administration
48
Contact Center Manager Server 45
Contact Center Multimedia server 49
Replication Server 46
Server Utility 47
interactive voice response (IVR) 31
L
latest updates to software 38
license manager 18
licensing corporate 18
M
managing components using a license 18
Media Application Server 29
migrating Multimedia/Outbound databases 26
migration paths 44
monitoring
the status of Contact Center Manager
Server
19
Multimedia Server 59
multimedia storage capacity 60
multiple switches in contact center 52
N
NET Framework 25
Network Control Center (NCC) software 18
network skill-based routing 52
new report statistics 53
number
active agents
60
active supervisors 58
agents 53
call variables supported 53
configured supervisors 58
contacts handled 60
skillsets per agent 53
Page 83

What’s New in Release 6.0 83
July 2007 Index
O
online Help 37
Open Queue 51
open queue 17
operating system requirements 33
operational sites 53
Outbound Campaign Management Tool 24
outbound contacts
reporting
21
P
patching 50
portfolio rebranding 43
product improvements
Contact Center Manager Administration
54
Contact Center Manager Server 51
Contact Center Multimedia 59
product names 43
Q
queueing contacts 17
R
real-time reports 21
rebranding 43
redundancy
Contact Center Manager Server
18
Multimedia/Outbound server 23
Replication Server
installation
46
Report Creation Wizard
accessing
21
reporting
Contact Center Manager Server
enhancements
53
historical 21
improvements 53
outbound contacts 21
real-time 21
requirements
operating system
33
server 33
restore
Contact Center Multimedia/Outbound
49
routing
contacts
16
S
saving outbound data 25
scripting
application
21
improvements 58
sending e-mail 25
server
hardware requirements
33
operating system requirements 33
upgrade and migration overview 44
Server Utility
installation
47
introduction 19
service updates 50
SIP
Contact Center Manager Server
17
Media Application Server 29
using Contact Center Agent Desktop 26
skill-based routing over networks 52
skillsets
definition
20
per agent 53
software
delivery
15
software phones 23
software-based queue 17
statistics in reports 53
switch
multiple switches
52
support 32
Symposium Web Portal Server 59
system recovery 53
system requirements 33
T
telephony integration 22
Page 84

84 Contact Center
Index Standard 4.01
third-party applications
agent telephony toolbars
23
call management applications 23
interactive voice response 31
other Nortel products 31
software phones 23
tracking changes in Administration 21
treatment of contacts 16
U
universal networking 52
upgrades
Contact Center Manager Administration
47
Contact Center Manager Server 44
overview 44
V
viewing real-time statistics 21
voice mail 31
voice responses 31
W
Web site addresses 38
Page 85

Reader Response Form
Contact Center
Product release 6.0
What’s New in Release 6.0
Tell us about yourself:
Name:
Company:
Address:
Occupation: Phone:
1. What is your level of experience with this product?
New user Intermediate Experienced Programmer
2. How do you use this book?
Learning Procedural Reference Problem solving
3. Did this book meet your needs?
Yes No
If you answered No to this question, please answer the following questions.
4. What chapters, sections, or procedures did you find hard to understand?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
5. What information (if any) was missing from this book?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
6. How could we improve this book?
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________________________
Please return your comments by fax to 353-91-756050, or mail your comments to
Contact Center Documentation Research and Development Prime, Nortel, Mervue Business Park,
Galway, Ireland.
Page 86

R
e
ader
Res
p
o
nse For
m
Read
er R
e
spo
nse Form
Page 87

Page 88

Nortel Contact Center
What’s New in Release 6.0
Nortel Networks
Mervue Business Park
Galway, Ireland
Copyright © 2007 Nortel Networks. All Rights Reserved.
Information is subject to change without notice. Nortel Networks reserves the right to make changes
in design or components as progress in engineering and manufacturing may warrant.
The process of transmitting data and call messaging between the Meridian 1 and Contact Center is
proprietary to Nortel Networks. Any other use of the data and the transmission process is a violation
of the user license unless specifically authorized in writing by Nortel Networks prior to such use.
Violations of the license by alternative usage of any portion of this process or the related hardware
constitutes grounds for an immediate termination of the license and Nortel Networks reserves the
right to seek all allowable remedies for such breach.
Publication number: 297-2183-903
Product release: 6.0
Document release: Standard 4.01
Date: July 2007
To provide feedback or report a problem in this document, go to www.nortel.com/documentfeedback
.
 Loading...
Loading...