Page 1

Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and
Diagnostics
NN44200-701
.
Page 2

Document status: Standard
Document version: 01.02
Document date: 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks
All Rights Reserved.
Sourced in Canada
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical
data, and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without
express or implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications of any products specified in this
document. The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks.
The process of transmitting data and call messaging between the CallPilot server and the switch or system is
proprietary to Nortel Networks. Any other use of the data and the transmission process is a violation of the user
license unless specifically authorized in writing by Nortel Networks prior to such use. Violations of the license by
alternative usage of any portion of this process or the related hardware constitutes grounds for an immediate
termination of the license and Nortel Networks reserves the right to seek all allowable remedies for such breach.
Trademarks
*Nortel Networks, the Nortel Networks logo, the Globemark, and Unified Networks, BNR, CallPilot, DMS, DMS-100,
DMS-250, DMS-MTX, DMS-SCP, DPN, Dualmode, Helmsman, IVR, MAP, Meridian, Meridian 1, Meridian Link,
Meridian Mail, Norstar, SL-1, SL-100, Communication Server 1000, Supernode, Contact Center, Telesis, and
Unity are trademarks of Nortel Networks.
3COM is a trademark of 3Com Corporation.
ADOBE is a trademark of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
ATLAS is a trademark of Quantum Corporation.
BLACKBERRY is a trademark of Research in Motion Limited.
CRYSTAL REPORTS is a trademark of Seagate Software Inc.
EUDORA is a trademark of Qualcomm.
eTrust and InoculateIT are trademarks of Computer Associates Think Inc.
DIRECTX, EXCHANGE.NET, FRONTPAGE, INTERNET EXPLORER, LINKEXCHANGE, MICROSOFT,
MICROSOFT EXCHANGE SERVER, MS-DOS, NETMEETING, OUTLOOK, POWERPOINT, VISUAL STUDIO,
WINDOWS, WINDOWS MEDIA, and WINDOWS NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
GROUPWISE and NOVELL are trademarks of Novell Inc.
LOGITECH is a trademark of Logitech, Inc.
MCAFEE and NETSHIELD are trademarks of McAfee Associates, Inc.
MYLEX is a trademark of Mylex Corporation.
NETSCAPE COMMUNICATOR is a trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation.
NOTES is a trademark of Lotus Development Corporation.
NORTON ANTIVIRUS and PCANYWHERE are trademarks of Symantec Corporation.
QUICKTIME is a trademark of Apple Computer, In.
Page 3

RADISYS is a trademark of Radisys Corporation.
SLR4, SLR5, and TANDBERG are trademarks of Tandberg Data ASA.
SYBASE is a trademark of Sybase, Inc.
TEAC is a trademark of TEAC Corporation
US ROBOTICS, the US ROBOTICS logo, and SPORTSTER are trademarks of US Robotics.
WINZIP is a trademark of Nico Mark Computing, Inc.
XEON is a trademark of Intel, Inc.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Information for Japan
Japan Denan Statement
The following applies to server models 1005r, 703t, and 1002rp:
Japan VCCI statement
The following applies to server models 1005r, 703t, 201i, and 1002rp:
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Information
Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this equipment is used in a domestic environment, radio disturbance may occur, in
which case, the user may be required to take corrective action.
Page 4

Page 5

5
Publication History
April 2007
CallPilot 5.0 Standard 01.02 of the 1002rp Server Maintenance and
Diagnostics is issued for general release. Added a precaution note on
replacement hard drive size.
February 2007
CallPilot 5.0 Standard 01.01 of the 1002rp Server Maintenance and
Diagnostics is issued for general release.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 6

6 Publication History
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 7

7
Contents
Chapter 1 How to get help 11
Chapter 2 About this guide 13
Maintenance and diagnostics overview 13
Chapter 3 Troubleshooting your CallPilot system 17
Startup diagnostics overview 17
Basic hardware check 17
Power-On Self-Test diagnostics 18
Interpreting POST diagnostics 19
Interpreting startup diagnostics from SCSI BIOS 20
What to do when the server fails to boot into service 21
Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools 23
Overview 23
Viewing event logs 23
Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools 27
Using the chkdsk utility 34
Chapter 5 Using serial port diagnostic tools 37
Overview 37
Shutting down services 37
Conducting TSTSERIO tests 40
Conducting TSTSERIO tests with the loopback plug 42
Restarting services 43
Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware 45
Understanding fault management 45
Alarm Monitor 47
Event Browser 48
Channel and Multimedia Monitors 50
The Maintenance screen 50
Viewing component states 53
Starting and stopping components 55
Running integrated diagnostics 58
Viewing the last diagnostic results 60
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 8

8 Contents
Working with the Multimedia Monitor 61
Working with the Channel Monitor 63
Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities 67
Overview 67
Diagnostics Tool 68
PEP Maintenance utility 69
Session Trace 69
System Monitor 71
Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components 77
Removing the front bezel and server cover 77
Replacing air filters 80
Replacing the power supply 81
Replacing the SCA SCSI drive cage and fused power cable 84
Replacing the cooling fan 88
Replacing the fuse (AC system only) 91
Replacing the alarm board 93
Setting jumpers on the alarm board 94
Replacing the status display panel 96
Chapter 9 Replacing media drives 99
Replacing a faulty hard drive 99
About the media drive bay 103
Removing the media drive carrier from the chassis 103
Replacing a tape, CD-ROM or floppy drive 106
Installing a tape drive 108
Chapter 10 RAID operations 113
Outlining RAID functions 113
Configuring RAID firmware, driver, and power console 113
Replacing the LSI1600 card with LSI320-2 114
Configuring the RAID controller after a hardware change 116
Splitting the RAID drives 119
Synchronizing RAID drives 121
Chapter 11 Configuring MPB96 boards 125
Determining board and card configuration 125
Identifying hardware components 126
Installing valid configurations 128
Chapter 12 Replacing or adding voice processing boards 131
DSP numbering and location 131
Replacing an MPB96 board 132
Chapter 13 Replacing the D/480JCT-2T1 T1 interface card 135
TD/480JCT-2T1 card function 135
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 9
Contents 9
Chapter 14 Maintaining the Pentium III SBC card 141
Overview 141
Replacing the Pentium III SBC card 142
Configuring the 1002rp Pentium III BIOS 144
Replacing or adding dual inline memory modules 147
Maintaining the onboard video and network cards 149
Index 150
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 10

10 Contents
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 11

11
Chapter 1
How to get help
This section explains how to get help for Nortel products and services.
Getting help from the Nortel Web site
The best way to get technical support for Nortel products is from the Nortel
Technical Support Web site:
h
ttp://www.nortel.com/support
This site provides quick access to software, documentation, bulletins, and
tools to address issues with Nortel products. More specifically, the site
enables you to:
• download software, documentation, and product bulletins
•
search the Technical Support Web site and the Nortel Knowledge Base
for answers to technical issues
•
sign up for automatic notification of new software and documentation
for Nortel equipment
•
open and manage technical support cases
Getting help over the phone from a Nortel Solutions Center
If you don’t find the information you require on the Nortel Technical Support
Web site, and have a Nortel support contract, you can also get help over the
phone from a Nortel Solutions Center.
In North America, call 1-800-4NORTEL (1-800-466-7835).
Outside North America, go to the following Web site to obtain the phone
number for your region:
h
ttp://www.nortel.com/callus
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 12

12 Chapter 1 How to get help
Getting help from a specialist by using an Express Routing Code
To access some NortelTechnical Solutions Centers, you can use an Express
Routing Code (ERC) to quickly route your call to a specialist in your Nortel
product or service. To locate the ERC for your product or service, go to:
h
ttp://www.nortel.com/erc
Getting help through a Nortel distributor or reseller
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel product from a distributor
or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that distributor
or reseller.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 13

13
Chapter 2
About this guide
In this chapter
"Maintenance and diagnostics overview" (page 13)
Maintenance and diagnostics overview
The maintenance and diagnostic activities discussed in this guide are
divided into two groups of activities:
•
troubleshooting and diagnostics (identifying the cause of system
problems and resolving them)
•
performing hardware maintenance
This guide is for administrators, technicians, and engineers responsible for
maintaining a CallPilot server. This guide assumes that you have basic
computing skills, and are familiar with necessary safety procedures.
If you are not able to resolve your system problem with the resources
described in this guide, you can also refer to the following document:
•
Troubleshooting Guide (NN44200-700)
Note: Nortel continually updates the Troubleshooting Guide,
which is available from the Partner Information Center (PIC) at
h
ttp://www.nortel.com/pic.
The "Starting up and shutting down the CallPilot server" chapter in the
Installation and Configuration Task List (NN44200-306) explains how to
restart, shut down, and power up the CallPilot server. You may be asked to
perform one or more of these tasks while maintaining your server.
When you purchased your CallPilot server, it came preinstalled with the
Windows operating system and CallPilot server software. If your CallPilot
server no longer functions because of a software problem, you may need to
reinstall the CallPilot software or rebuild the system.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 14

14 Chapter 2 About this guide
Replacement parts
Before replacing any parts on your server, refer to the Nortel product
catalog for the part codes.
CAUTION
Risk of system damage
The use of parts that are not supplied by Nortel can cause serious
system problems or void your Nortel warranty.
Preparing for maintenance activities
Before you proceed with hardware maintenance activities, review the
1002rp Server Hardware Installation (NN44200-300) guide for the following
information:
•
required tools and equipment
•
recommended safety precautions for electrostatic discharge, handling
cards, and handling your server
•
instructions for shutting down your 1002rp server or for taking it out of
service
Reference documents
For a list of all CallPilot documents, see the following Customer
Documentation Map.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 15

Maintenance and diagnostics overview 15
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 16

16 Chapter 2 About this guide
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 17

17
Chapter 3
Troubleshooting your CallPilot system
In this chapter
"Startup diagnostics overview" (page 17)
"Basic hardware check" (page 17)
"Power-On Self-Test diagnostics" (page 18)
"Interpreting POST diagnostics" (page 19)
"Interpreting startup diagnostics from SCSI BIOS" (page 20)
"What to do when the server fails to boot into service" (page 21)
Startup diagnostics overview
This section contains procedures for interpreting the startup diagnostics
on the 1002rp server.
Types of startup diagnostics
The following types of startup diagnostics are available on the server:
•
basic hardware check (for example LEDs)
•
Power-On Self-Test (POST) diagnostics
•
SCSI controller diagnostics or RAID controller diagnostics
These diagnostics are available at initial system startup, or after any 1002rp
server reset.
Basic hardware check
This section describes some basic checks that you can do when you start
up the server.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 18

18 Chapter 3 Troubleshooting your CallPilot system
To run the startup test
Step Action
1
Power on the server and observe the front panel display.
Result: All LEDs on the panel illuminate for a few seconds. The
green power LED remains illuminated.
2
Observe the following server actions:
• Cooling fans on the front panel start up, and the red fault LED
next to each fan extinguishes.
•
Drives spin up, and the amber hard drive activity LEDs over the
front panel display extinguish, and then flash with activity.
•
LEDs illuminate temporarily as the system checks the floppy
drive, tape drive, and CD-ROM drive.
•
The LED on each power supply lights up red as supply fans spin
up and components charge. LEDs turn green when the attached
power supply is fully operational.
3
Check the monitor for any error messages as the server counts RAM
and completes a POST.
See "Power-On Self-Test diagnostics" (page 18) for more details on
POST.
—End—
Power-On Self-Test diagnostics
The Power-On Self-Test (POST) is a system diagnostic program (stored in
the BIOS) that runs each time the 1002rp server is started. The function of
the POST is to test system components and then display status messages.
To run the POST
Step Action
1
Power up the CallPilot server and monitor.
Result: After a few seconds, POST begins to run.
After the memory test, various screen prompts and messages
appear. The screen prompts may be accompanied by a single beep.
2
Observe the screen for any error messages and listen for POST
beep codes. When POST completes, the server beeps once.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 19

Interpreting POST diagnostics 19
If the server halts before POST is finished, the server emits a
beep code indicating that a fatal system error requires immediate
attention. See "Interpreting POST diagnostics" (page 19) for details.
If POST can display a message on the monitor, the server emits two
beeps as the message appears.
Record the message that appears on the monitor and the beep code
that you hear. This information is useful if you need assistance from
your technical support representative.
—End—
Interpreting POST diagnostics
This section provides an explanation of the POST diagnostic codes.
POST beep codes
If an error occurs before video initialization, POST emits beep codes that
indicate errors in hardware, software, or firmware.
A beep code is a series of separate tones, each equal in length. Record the
beep code sequence before calling Nortel technical support.
ATTENTION
Some POST beep codes are fatal and may require that you replace the Single
Board Card (SBC). See the table below for more information about beep codes.
POST beep codes
Beep
count Error message Description
1
Refresh Failure The memory refresh circuitry of the processor
board is faulty.
2
Parity Error A parity error was detected in the base memory
(the first block of 64 kbytes) of the system.
3
Base 64KB
Memory Failure
A memory failure occurred within the first 64
kbytes of memory.
4
Timer Not
Operational
A memory failure occurred within the first
64 kbytes of memory, or Timer #1 on the
processor board failed to function properly.
5
Processor Error The Central Processing Unit (CPU) on the
processor board failed to function properly.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 20

20 Chapter 3 Troubleshooting your CallPilot system
Beep
count Error message Description
6
8042 - Gate A20
Failure
The keyboard controller (8042) contains
the Gate A20 switch, which allows the CPU
to operate in protected mode. This error
message means that the BIOS cannot switch
the CPU into protected mode.
7
Processor
Exception
Interrupt Error
The CPU on the processor board generated
an exception interrupt.
8
Display Memory
Read/Write Error
The system video adapter is either missing or
its memory is faulty.
Note: This is not a fatal error.
9
ROM Checksum
Error
The ROM checksum value does not match the
value encoded in the BIOS.
10
CMOS Shutdown
Register
Read/Write Error
The shutdown register for the CMOS RAM
failed.
11
Cache Memory
Bad: Do Note
Enable Cache
The cache memory test failed. Cache memory
is disabled.
Note: Do not press Ctrl+Alt+Shift<+> to enable
cache memory.
Interpreting startup diagnostics from SCSI BIOS
The results from the SCSI controller diagnostics appear after the POST
results.
Applicable cards
Results of the startup diagnostics appear only if you have the following
cards installed on your system:
•
Adaptec SCSI controller
The adapter is integrated in the SBC and can be disabled.
•
LSI Elite 1600 controller
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 21
What to do when the server fails to boot into service 21
What to do when the server fails to boot into service
This section suggests tasks you can perform to determine why the server
fails the bootup cycle.
To determine why the server failed to boot to Windows
Step Action
1 Make a note of any diagnostic codes.
2
Try restarting the server by pressing the power button on the server.
3
During the boot sequence, view the diagnostic codes on the monitor
for failures.
4
Refer to the Troubleshooting Guide (NN44200-700) for other
suggestions. If you still cannot determine the cause of the startup
failure, call your Nortel technical support representative.
—End—
To determine why the server failed to boot into CallPilot
If the system-ready indicator indicates that the system is not booting into
CallPilot, follow these steps:
Step Action
1
Make a note of any diagnostic codes.
2
Try restarting the server by pressing the power button on the server.
3
During the boot sequence, view the diagnostic codes on the monitor
for failures.
4 View the event logs. For instructions, see "Viewing event logs" (page
23).
5
Refer to the Troubleshooting Guide (NN44200-700) for other
suggestions. If you still cannot determine the cause of the startup
failure, call your Nortel technical support representative.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 22

22 Chapter 3 Troubleshooting your CallPilot system
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 23

23
Chapter 4
Using Windows online diagnostic tools
In this chapter
"Overview" (page 23)
"Viewing event logs" (page 23)
"Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools" (page 27)
"Using the chkdsk utility" (page 34)
Overview
This section describes how to access the run-time online diagnostic tools
provided by the Windows server software. Use the following tools when a
serious problem prevents the use of the CallPilot diagnostic tools that are
available in CallPilot Manager.
•
Windows Event Viewer
•
TCP/IP diagnostics
•
chkdsk utility
CAUTION
Risk of software corruption
Do not run any utilities that are not documented in this guide.
Viewing event logs
When the server startup cycle is complete, and if the CallPilot server has
been configured, messages in dialog boxes on the monitor indicate that
CallPilot is ready to accept calls.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 24

24 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
If one or more messages appear on the monitor, the message may contain
information about an event, or a fault may have occurred. To determine
what happened, you can use the following diagnostic tools:
•
Windows Event Viewer on the 1002rp server
•
CallPilot Event Browser or Alarm Monitor in CallPilot Manager
Note: The Event Browser and Alarm Monitor include online Help for
events, which may help you to resolve the problem. If you cannot log
on to the CallPilot system using a web browser due to server problems,
then use the Windows Event Viewer.
Types of event logs
Three types of event logs are available from the Windows Event Viewer, as
follows:
Log type Description
System Logs events by Windows components, including RRAS
or other Windows services.
Security Logs security events, such as logons, logoffs, and
illegal access. This option is available only to users
with Administrative access.
Applications Logs events by application, such as database file
errors.
To use the operating system Event Viewer
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Administrative Tools → Event Viewer.
Result: The Event Viewer window appears.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 25
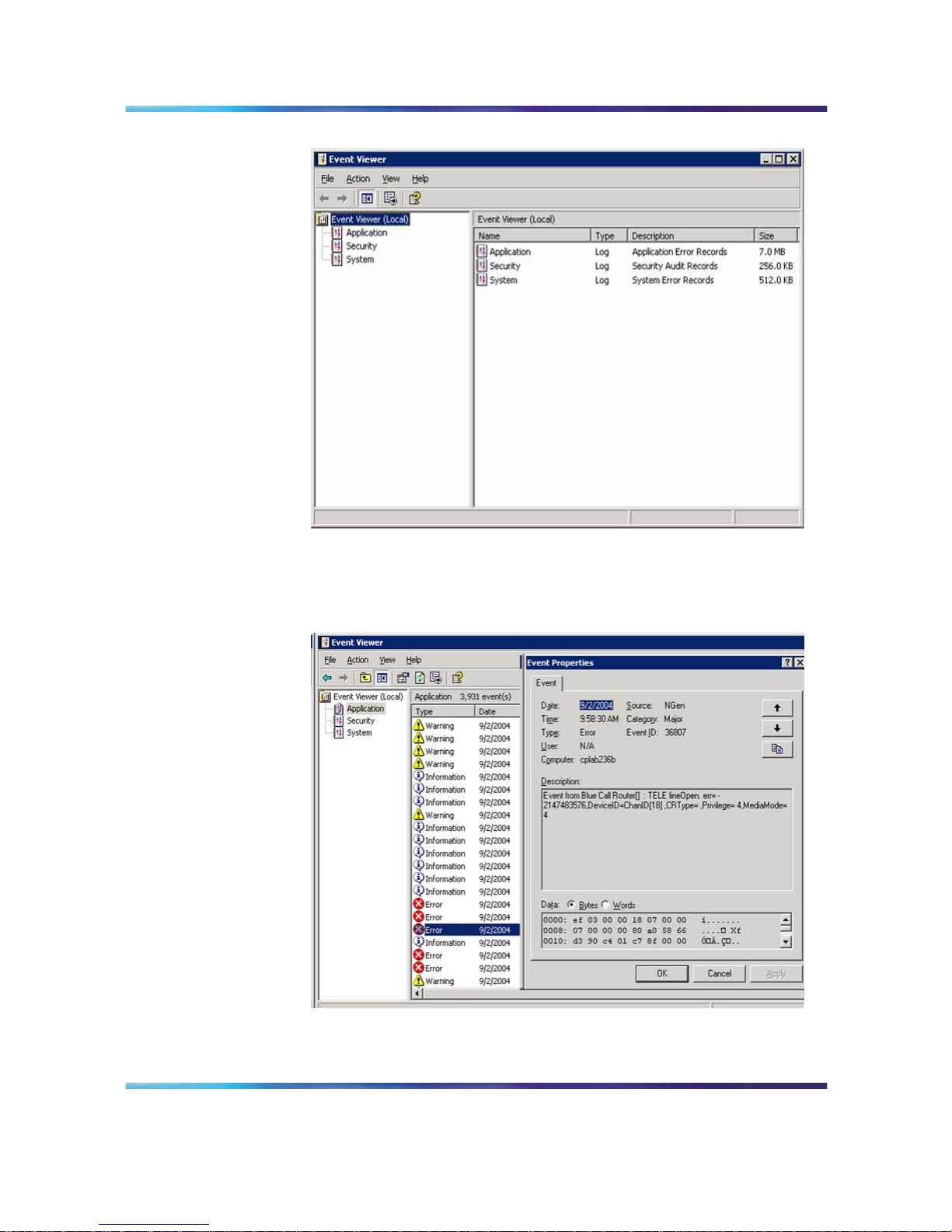
Viewing event logs 25
Event Viewer
2
To view a log, click the name of the log in the left pane of the window.
The following illustration shows an example of the Application Log.
Application log
The following illustration shows an example of a System log.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 26
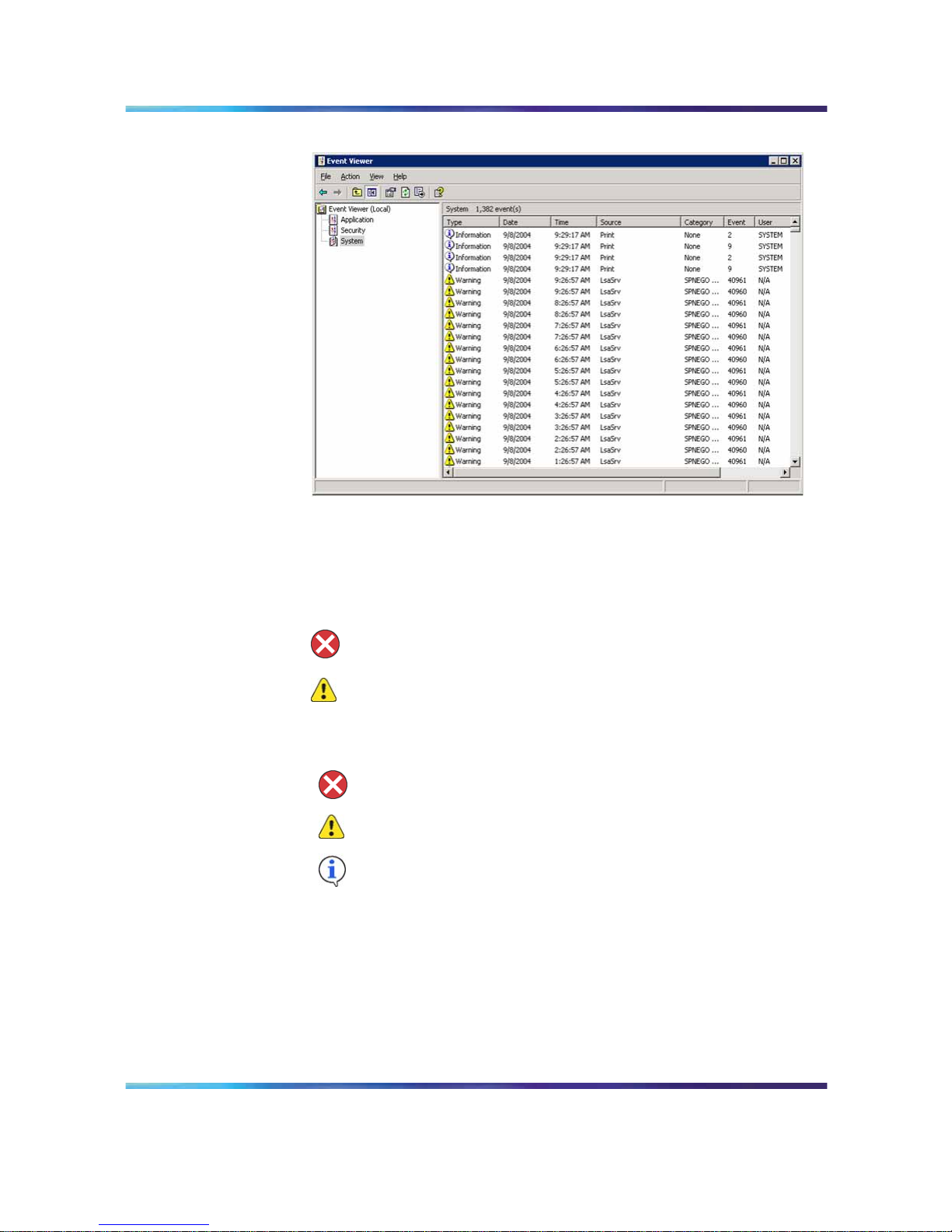
26 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
System log
Note: The Security log, which is available only to administrators,
is not shown.
3
Look for error codes that have occurred since the last startup. Error
codes are flagged with the following symbols.
Note: Each error is date- and time-stamped.
indicates major or critical errors
indicates minor errors
indicates information
4 To determine the cause of the error, select and then double-click
the error.
Result: A description of the error appears in an Event detail dialog
box. Use the description to help determine how to resolve errors.
Note: If the error persists or the error description does not
suggest a solution, contact your Nortel support representative.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 27

Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools 27
5
Click Close.
Result: The event log reappears.
6
Click Log → Exit.
Result: The Event Viewer closes.
—End—
Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools
This section describes the following TCP/IP diagnostic tools which are
available for the network adapter:
•
ipconfig
•
ping
•
tracert
•
arp
•
nbtstat
•
netstat
These utilities help you to verify network connectivity, test the network
interface, and isolate any configuration problems.
The ipconfig command
The ipconfig command displays IP configuration information.
ipconfig default
If you run the command without flags, it displays the IP address, subnet
mask, and default gateway for each adapter bound to TCP/IP.
ipconfig command syntax
The ipconfig command uses the following syntax:
ipconfig /[ ]
The following flags are available for the ipconfig command.
ipconfig command extensions
Flag Description
/? Displays Help information.
/all Displays full configuration information.
/release Releases the IP address for the specified adapter.
/renew Renews the IP address for the specified adapter.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 28

28 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
To run the ipconfig command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type ipconfig <parameters>.
Example: ipconfig /all
3 Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the ipconfig utility.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
The ping command
The ping command sends an echo request to a specified host. Use this
command to verify network connectivity to the remote device.
Ping command syntax
The ping command uses the following syntax:
ping [-t] [-a] [-n count] [-l size] [-f] [-i TTL]
[-v TOS] [-r count] [-s count]
[[-j host-list] | [-k host-list]]
[-w timeout] destination-list
ping command extensions
Parameter Description
-t
Pings the specified host until interrupted.
-a
Resolves addresses to host names.
-n count
Specifies the number of echo requests to send.
-l size Sends buffer size.
-f Sets Don’t Fragment flag in packet.
-i TTL Specifies the Time To Live
-v TOS Specifies the Type Of Service
-r count
Specifies the number of Record route for count hops
-s count
Specifies the number of Time stamp for count hops
-j host-list Specifies the Loose source route along host list
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 29

Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools 29
Parameter Description
-k host-list Specifies the Strict source route along host list
-w timeout Specifies the Timeout in milliseconds to wait for each
reply
To run the ping command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type ping <destination IP
address> (for example, ping 200.286.32.0), or ping <computer
name>.
3
Press Enter.
Result: The system displays the ping results.
4 Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
The tracert command
This utility determines the route taken to a destination.
How tracert works
The tracert utility follows several steps to complete its task:
•
Tracert sends Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) echo packets
with varying Time-To-Live (TTL) values to the destination.
•
Each router along the path must decrement the TTL on a packet by at
least 1 before forwarding it, so the TTL is effectively a hop count.
•
When the TTL on a packet reaches 0, the router sends back an ICMP
Time Exceeded message to the source system.
•
Tracert determines the route by sending the first echo packet with a TTL
of 1, and incrementing the TTL by 1 on each subsequent transmission
until the target responds, or the maximum TTL is reached.
•
Tracert then examines the ICMP Time Exceeded messages sent back
by intermediate routers.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 30

30 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
Tracert syntax
The tracert command uses the following syntax:
tracert [-d] [-h maximum_hops] [-j host_list]
[-w timeout] [target_name]
Tracert parameters
the following table shows the tracert parameters.
Tracert parameters
Parameter Description
-d Specifies not to resolve addresses to hostnames.
-h maximum_hops Specifies the maximum number of hops to search for
the target.
-j host-list Specifies a loose source route along the host list.
-w timeout Waits the number of milliseconds specified by the
timeout for each reply.
target_name
Specifies the name of the target host.
To run the tracert command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type the following command:
tracert [-d] [-h maximum_hops] [-j host_list] [-w
timeout] [target_name]
Example: tracert 200.286.0.32
3
Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the tracert utility.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
The arp command
The arp command displays and modifies the IP-to-physical address
translation tables used by Address Resolution Protocol (ARP).
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 31

Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools 31
ARP command syntax
The ARP command uses the following syntax:
arp -s inet_addr eth_addr [if_addr]
arp -d inet_addr [if_addr]
arp -a [inet_addr] [-N if_addr]
ARP command parameters
ARP command parameters
Parameter Description
-a
Displays current arp entries by interrogating the current protocol
data. If inet_addr is specified, the IP and physical addresses for
only the specified computer appear. If more than one network
interface uses arp, entries for each arp table appear.
-g
Same as -a.
inet_addr Specifies an Internet address.
if_addr Specifies the Internet address of the interface where the
address translation table should be modified. If not present, the
first applicable interface is used.
eth_addr Specifies a physical address.
-N if_addr Displays the arp entries for the network interface specified by
if_addr.
-d Deletes the host specified by inet_addr.
-s
Adds the host and associates the Internet address inet_addr
with the physical address eth_addr. The physical address is
given as six hexadecimal bytes separated by hyphens. The
entry is permanent.
To run the arp command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type arp with the required parameters (for
example, arp -g 200.286.0.32).
3 Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the arp command.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 32

32 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
—End—
The nbtstat command
The nbtstat command displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP
connections using NBT.
Nbtstat command syntax
The nbtstat command uses the following syntax:
nbtstat [-a remotename] [-A IP address] [-c] [-n]
[-R] [-r] [-S] [-s] [interval]
nbstat command parameters
nbstat command parameters
Parameter Description
-a remotename
Lists the remote computer name table using its name.
-A IP address Lists the remote computer name table using its IP
address.
-c
Lists the contents of the NetBIOS name cache giving
the IP address of each name.
-n
Lists local NetBIOS names. Registered indicates that
the name is registered by broadcast (Bnode) or WINS
(other node types).
-R Reloads the LMHOSTS file after purging all names
from the NetBIOS name cache.
-r
Lists name resolution statistics for Windows networking
name resolution. On a Windows computer configured
to use WINS, this option returns the number of names
resolved and registered through broadcast or through
WINS.
-S Displays both client and server sessions, listing the
remote hosts by IP address only.
-s
Displays both client and server sessions and attempts
to convert the remote host IP address to a name using
the HOSTS file.
interval Displays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds
between each display. Press Ctrl+C to stop displaying
statistics. Without this parameter, nbtstat prints the
current configuration information once.
To run the nbtstat command from Windows
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 33

Using TCP/IP diagnostic tools 33
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2 At the Command prompt, type nbtstat with the required
parameters.
3
Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the nbtstat utility.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
The netstat command
The netstat command displays current TCP/IP network connections and
protocol statistics.
Netstat command syntax
The netstat command uses the following syntax:
netstat [-a] [-e] [-n] [-s] [-p proto] [-r] [interval]
netstat command parameters
netstat command parameters
Parameter Description
-a
Displays all connections and listening ports.
-e
Displays Ethernet statistics. This can be combined with the
-s option.
-n
Displays addresses and port numbers in numeric form.
-s
Displays statistics for each protocol.
-p proto
Shows connections for the protocol specified by proto. Proto
can be tcp or udp. If used with the -s option, proto can be tcp,
udp, or ip.
-r
Displays the contents of the routing table.
interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing between each display.
Press Ctrl+C to stop redisplaying.
To run the netstat command from Windows
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 34

34 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2 At the Command prompt, type netstat with the required
parameters.
3
Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the netstat utility.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
Using the chkdsk utility
The chkdsk utility checks a specified disk on the server and displays a
status report. You can run the utility on drives C, D, E, or F. It is an online
utility, but it reduces system performance while it is running.
The chkdsk utility checks for errors at the Windows file system level. CallPilot
can be affected by errors at both the Windows and CallPilot file system
levels. The chkdsk utility will not detect CallPilot file system level errors.
Note: A version of this utility, called autocheck, automatically runs
during Windows startup. Output from this utility appears on the blue
startup screen.
Chkdsk utility syntax
The chkdsk utility uses the following syntax:
chkdsk [drive:][path]filename] [/F] [/V] [/R]
Chksdsk utility parameters
Chksdsk utility parameters
Parameter Description
drive: Drive letter of the drive that you want to check.
filename Names of files to check for fragmentation.
/F Optional parameter to fix errors on the disk.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 35

Using the chkdsk utility 35
Parameter Description
/V Optional parameter to display the full pathname of
every file on the disk.
/R Optional parameter to locate bad sectors and to
recover readable information.
To run the chkdsk utility from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type chkdsk <drive letter:> (for
example, chkdsk c:).
3
Press Enter.
Result: The system runs the chkdsk utility.
4
Type Exit to exit the Command Prompt window and return to
Windows.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 36

36 Chapter 4 Using Windows online diagnostic tools
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 37

37
Chapter 5
Using serial port diagnostic tools
In this chapter
"Overview" (page 37)
"Shutting down services" (page 37)
"Conducting TSTSERIO tests" (page 40)
"Conducting TSTSERIO tests with the loopback plug" (page 42)
"Restarting services" (page 43)
Overview
You may want to test the serial ports when remote access does not work.
This chapter describes how to run serial port diagnostics on the CallPilot
server using the TSTSERIO command. Direct the TSTSERIO command
to serial ports on the server after services on these ports have been shut
down manually, as described in this chapter.
Shutting down services
This section describes how to shut down a service using a specific serial
port. Use the following procedures before you invoke the TSTSERIO local
loopback tests.
CAUTION
Risk of communications loss
By stopping the services on COM1 or COM2, you lose the support
access feature.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 38

38 Chapter 5 Using serial port diagnostic tools
CAUTION
Risk of stopping call processing
By stopping the services on COM2, you stop call processing on
CallPilot.
Services to stop for COM1 testing
•
Routing and Remote Access Service
Services to stop for COM2 testing
• CallPilot SLEE Service
•
CallPilot MWI Service
•
CallPilot Access Protocol Emulator
• CallPilot Blue Call Router
•
CallPilot Call Channel Router
•
CallPilot Time Service
•
Routing and Remote Access Service
Net Stop command
Use the Net Stop command to stop a specified service on a serial port.
Net stop command syntax
The Net Stop command uses the following syntax:
net stop <service_name>
ATTENTION
You must restart the services that you shut down through the Net Start command
after you run the diagnostic. For details, see "Restarting services" (page 43).
To invoke the Net Stop command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type net stop "service_name", and
then press Enter.
Example: Type net stop "Remote Access Server", and then
press Enter.
Note: The quotation marks are required, as in the example
above.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 39

Shutting down services 39
Result: The system runs the Net Stop command utility.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
—End—
Service Control (SC) command
Use the Service Control command to stop a specified service on a serial
port.
Service Control command syntax
The Service Control command uses the following syntax:
sc <service_name>
ATTENTION
You must restart the services that you shut down through the Service Control
command after you run the diagnostic. For details, see "Restarting services"
(page 43).
To invoke the Service Control command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type sc stop "service_name", and
then press Enter.
Example: Type sc stop "Remote Access Server", and then
press Enter.
Note: The quotation marks are required, as in the example
above.
Result: The system runs the Service Control command utility.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 40

40 Chapter 5 Using serial port diagnostic tools
Conducting TSTSERIO tests
The TSTSERIO command performs local loopback tests of the serial
communication ports from the server run-time environment.
Note: Before conducting these tests, shut down the appropriate
services. See "Shutting down services" (page 37).
CAUTION
Risk of communications loss
By stopping the services on COM1 or COM2, you lose the support
access feature.
CAUTION
Risk of stopping call processing
By stopping the services on COM2, you stop call processing on
CallPilot.
TSTSERIO command syntax
The syntax for the TSTSERIO command is as follows:
TSTSERIO [/?] /P:comport [/S:subtstname] [/L:loops]
TSTSERIO command parameters
TSTSERIO command parameters
Flag Requirement Description
? n/a Displays Help.
/P:comport Required Specifies the symbolic
port name assigned to
the port you want to test.
/S:subtstname Optional Specifies a TSTSERIO
subtest. See the following
table for a description of
the available subtests.
/L:loops Optional Specifies the number of
times (up to a maximum
of 65 535) to execute
the requested test. The
default number of tests is
1. A value of 0 infinitely
loops until you enter
Ctrl+C.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 41

Conducting TSTSERIO tests 41
TSTSERIO internal loopback diagnostic subtests
The following internal loopback subtests are available for the TSTSERIO
command. For each of these tests, the communications resource must
be available.
TSTSERIO internal loopback subtests
Subtest name
Description
idata Internal data bus loopback
imsr Internal modem status register
baud Internal data bus loopback at various baud rates
word Test 5-, 6-, 7-, and 8-bit data lengths
stop
Test 1, 1.5, and 2 stop bits
pari Test odd/even parity
fifo Test that device can operate in fifo mode
To invoke the TSTSERIO /P command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type tstserio with the required
parameters, and then press Enter.
For example, type TSTSERIO /P com1 or TSTSERIO /P com
2, and then press Enter.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 42

42 Chapter 5 Using serial port diagnostic tools
TSTSERIO external loopback plug subtests
The following external loopback subtests are available for the TSTSERIO
command. For each of these tests, an external loopback connector must
be used. For more information, see "Conducting TSTSERIO tests with
the loopback plug" (page 42)
TSTSERIO external loopback plug subtests.
Subtest
name
Description
edata External data bus loopback. This test requires an external
loopback connector.
emsr
External modem status register. This test requires an external
loopback connector.
eint Test ability of device to generate interrupts. This test requires
an external loopback connector.
To invoke the TSTSERIO /S command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result:The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type tstserio with the required
parameters, and then press Enter.
For example, type TSTSERIO /P com1 /S extr, and then press
Enter.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
—End—
Conducting TSTSERIO tests with the loopback plug
The TSTSERIO command requires an external loopback connector plug for
its edata, emsr, and eint subtests.
9-pin connector plug
The standard serial loopback connector is a female 9-pin D-sub connector.
This connector has the following pins wired together:
•
CTS (pin 8) wired to RTS (pin 7)
•
SIN (pin 2) wired to SOUT (pin 3)
•
DTR (pin 4) wired to DSR (pin 6)
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 43

Restarting services 43
Once the plug is installed on the serial port, TSTSERIO can be invoked
according to the procedure outlined in the previous section.
Restarting services
This section describes how to restart the services for COM1 or COM2 after
invoking the TSTSERIO local loopback tests.
Services to restart after COM1 testing
•
Routing and Remote Access Service
Services to restart after COM2 testing
•
CallPilot SLEE Service
•
CallPilot MWI Service
•
CallPilot Access Protocol Emulator
•
CallPilot Blue Call Router
•
CallPilot Call Channel Router
• CallPilot Time Service
•
Routing and Remote Access Service
Net Start command
Use the Net Start command to restart a specified service on a serial port.
The syntax for the Net Start command is as follows:
net start <service name>
To invoke the Net Start command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type net start "service_name",
and then press Enter.
For example, type net start "Remote Access Server", and
then press Enter.
Note: The quotation marks are required, as in the example
above.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 44

44 Chapter 5 Using serial port diagnostic tools
—End—
Service Control Start command
Use the Service Control Start command to restart a specified service on a
serial port. The syntax for the Service Control Start command is as follows:
sc <service name>
To invoke the Service Control Start command from Windows
Step Action
1
Click Start → Programs → Accessories → Command Prompt.
Result: The Command Prompt window appears.
2
At the Command prompt, type sc start "service_name", and
then press Enter.
For example, type sc start "Remote Access Server", and
then press Enter.
Note: The quotation marks are required, as in the example
above.
3
Type Exit, and then press Enter to exit the Command Prompt
window.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 45

45
Chapter 6
Using CallPilot Manager to monitor
hardware
In this chapter
"Understanding fault management" (page 45)
"Alarm Monitor" (page 47)
"Event Browser" (page 48)
"Channel and Multimedia Monitors" (page 50)
"The Maintenance screen" (page 50)
"Viewing component states" (page 53)
"Starting and stopping components" (page 55)
"Running integrated diagnostics" (page 58)
"Viewing the last diagnostic results" (page 60)
"Working with the Multimedia Monitor" (page 61)
"Working with the Channel Monitor" (page 63)
Understanding fault management
Fault management is a term that describes how the CallPilot server detects
and notifies you of potential or real hardware problems (faults). The server
processes events to detect hardware problems and raises alarms to notify
you when these problems occur.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 46

46 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Event processing
An event is any change in system configuration or operational state. An
event is also any action taken by the system that requires user notification.
Events can be as insignificant as a user logon attempt or as serious as a
faulty MPB96 card switching to disabled status.
All events are reported to the fault management server, a subsystem within
the CallPilot server. The fault management server enables the CallPilot
server to listen and respond to its clients. The interaction is called event
processing and is the means by which the server detects hardware faults.
Alarm notification
Alarms are warnings generated by events. Alarms communicate the same
information as events. However, alarms are reported in the Alarm Monitor
instead of the Event Browser, and are managed differently than events.
When an alarm appears in the Alarm Monitor, you must investigate the
problem, isolate it, and then fix the cause of the problem. When you fix the
problem, the alarm is cleared from the Alarm Monitor.
Component dependencies
The status of some components are dependent on the operational status
of other components. If a component fails or is stopped, the dependent
components go out of service.
Note: Based on the CallPilot server type, and the type of switch
connected to CallPilot, some of these components may not appear on
your system.
Component
Dependent components
Media Bus All MPBs, all multimedia channels, and all call channels.
MPB board All multimedia and call channels associated with the MPB
board.
Time Switch All multimedia and call channels associated with the same
MPB as the time switch.
MPB96 All multimedia channels on the MPB96 card.
DS30X All DS30X channels associated with the DS30X link.
T1 board Telephony Interface. All DS0 (zero) channels associated with
the telephony interface.
Detecting hardware problems
Typically, you first become aware of a hardware problem when an alarm is
raised. All hardware faults produce an alarm (or series of alarms, depending
on the problem) in the Alarm Monitor.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 47

Alarm Monitor 47
Other indications of a hardware problem include the following:
•
user complaints
•
call processing difficulties, such as busy signals, static, dropped calls,
connection problems, and cross talk (hearing other conversations)
•
system administrator logon difficulties
•
alert icons on the Maintenance screen
Alarm Monitor
Use the Alarm Monitor to investigate one or more raised alarms.
About alarms
Alarms are warnings generated by events. Alarms communicate the same
information as events. However, alarms are reported in the Alarm Monitor
instead of the Event Browser, and are managed differently than events:
•
Alarms appear in the Alarm Monitor only for Minor, Major, and Critical
events (not Information events). All events can be reported in the Event
Browser (depending on filtering criteria defined in the Event Browser).
•
The first time an event occurs, it generates an alarm that appears in
the Alarm Monitor. If the same event continues to occur, a new alarm
is not generated. Instead, the time and date assigned to the original
generated alarm is updated.
•
Alarms can be cleared from the Alarm Monitor, but the event that
generated the alarm is not cleared from the event log or the Event
Browser.
Each alarm in the Alarm Monitor has Help text that often provides a solution
to the problem. If the solution is not apparent, use the Event Browser or the
Maintenance screen to further investigate the problem.
To investigate using the Alarm Monitor
Step Action
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click System→Alarm Monitor.
Result: The Alarm Monitor screen appears.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 48

48 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Alarm monitor screen
3
Click the Event Code for the first Critical or Major alarm.
Result: A description of the event appears in a new web browser
window.
4
Review the description and recovery action.
5
Repeat steps 3 and 4 for more alarms, if necessary.
6
If the solution to the problem is not apparent, obtain the return code
of the first event and continue the investigation by using the Event
Browser (see "Event Browser" (page 48)).
—End—
Event Browser
Use the Event Browser to investigate a series of events that occurred
around the time an alarm was raised. The event listing can help you
determine the root cause of a problem.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 49

Event Browser 49
About events
The Event Browser displays events that have been recorded in the server
log. Each event identifies the time the event occurred, the object that
generated the event, and the cause of the event.
Events are classified as Information, Minor, Major, or Critical. By default, the
Event Browser displays only the latest 100 critical events.
To investigate using the Event Browser
Step Action
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2 In CallPilot Manager, click System→Event Browser.
Result: The Event Browser screen appears.
Event browser screen
3
Click an event that appears to be related to the problem, or an event
that occurred near the time the alarm was raised.
Result: A description of the event appears in a new web browser
window.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 50

50 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
4
View the description and recovery action.
5
Repeat steps 3 and 4 for more events, if necessary.
6 If the solution to the problem is not apparent, contact your Nortel
technical support representative.
—End—
Note: For information on how to use the Event Browser refer to the
CallPilot Manager online Help.
Channel and Multimedia Monitors
The Channel Monitor shows the status of call channels. The call channels
are the connections between the server and the switch that carry the call
signals to CallPilot.
The Multimedia Monitor shows the status of multimedia channels. The
multimedia channels are the DSP ports that process the calls. They are the
voice, fax, and speech recognition channels.
Disabling call channels
If you must take the CallPilot system out of service to perform software
or hardware maintenance, Nortel recommends that you disable all call
channels first. There are two ways to disable the call channels:
•
Courtesy stop the channels (preferred method).
When you courtesy stop call channels, CallPilot waits until the channels
are no longer active before disabling them, instead of suddenly
terminating active calls.
•
Stop the channels.
When you stop channels, you suddenly disable them and terminate
all active calls.
The Maintenance screen
Use the Maintenance screen in CallPilot Manager to do the following:
•
Obtain general information about components.
•
View component states.
•
Start and stop components.
•
Run integrated diagnostic tests.
•
View the results of the last diagnostic test run against a component.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 51

The Maintenance screen 51
What the Maintenance screen provides
The Maintenance screen identifies the server platform and switch
connectivity type. It also provides a tree that, when expanded, lists the
physical and logical hardware components down the left side of the screen.
To list the server hardware components, click the plus sign (+) at the top of
the tree. To list the subcomponents for each component, click the plus sign
(+) beside the component.
Note: The components that are listed on the Maintenance screen are
based on the CallPilot server type and the switch that is connected to
CallPilot. The examples in this chapter are for illustration purposes and
may not appear exactly the same on your system.
"Partially expanded tree for 1002rp" (page 51) shows a partially expanded
tree for the 1002rp server.
Partially expanded tree for 1002rp
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 52

52 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
When you click a component, the screen refreshes to show the details
about that component. Details are divided into the sections described
in the following table.
Component sections
Section
Description
General This section shows general technical information about
the selected component. This typically includes the
following details:
•
the name, class, type, series, or version of a
component
• various capabilities of a component (for example,
whether a component is removable)
Note: This section does not appear for all components.
Maintenance This section shows the state of the selected
component. Use this section to start and stop a
component before running a diagnostic test.
This section appears only for components on which you
are allowed to perform maintenance administration.
For more information about working with component
states, see the following sections:
• "Viewing component states" (page 53)
•
"Starting and stopping components" (page 55)
Diagnostics Use the Diagnostics section to run one or more
diagnostic tests, or to view the results of the last
diagnostic tests that were run on the selected
component.
This section appears only for components on which
you are allowed to run diagnostics.
For more information about running diagnostics, see
the following sections:
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 53

Viewing component states 53
Section
Description
•
"Running integrated diagnostics" (page 58)
•
"Viewing the last diagnostic results" (page 60)
Maintenance activities for each component
The following table identifies the maintenance activities you can perform for
each component that is listed in the component tree.
Maintenance activities
Component
Start,
stop?
Courtesy
stop?
Diagnostics
available? Replaceable?
Media Bus Yes No Yes No
MPB96 board Yes No Yes Yes
Time Switch No No No No
MPCs (embedded on MPB
boards)
Yes No Yes embedded:
No
Multimedia channels Yes Yes Yes No
Call channels Yes Yes No No
DS30X link Yes No No No
Note: The MGate card and DS30X cable are replaceable. If you are having problems with the
DS30X link, determine if either one or both of these items are causing the problem and need to be
replaced.
Viewing component states
View a component state to determine the general condition of the
component, including whether the component is disabled or off duty. The
component state is shown in the Maintenance section of the Maintenance
screen.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 54

54 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Component states
You can determine the state of a component by looking at the State box
in the Maintenance section.
State
Description
Active The component is working and currently involved in
processing a call.
Disabled The diagnostic failed.
Idle The component is working but not currently involved
in processing a call.
InTest A diagnostic is running on the resource or device.
Loading The component has been started, which takes it out
of the Off Duty state.
This state occurs quickly and is immediately followed
by Idle.
Local (Red) Alarm A Receive Loss of Synchronization error occurred on
incoming data over a T1 link and lasted more than 2.5
seconds. This condition will exist until synchronization
is recovered and remains recovered for 12 seconds.
No resources The hardware required for the component to operate is
not installed or is not operating properly.
Not Configured The device is not configured in CallPilot.
For example, a DSP is not being used because it was
not allocated in the Configuration Wizard.
Off Duty The component has been stopped.
Remote Off Duty The component has been taken out of service at the
switch.
Remote (Yellow)
Alarm
A red alarm exists at the receiving device. This alarm
is sent by the receiving T1 device to CallPilot, and it
remains in effect until the red alarm is cleared at the
receiving device.
Shutting Down The component is in the process of stopping.
This state occurs quickly and is immediately followed
by Off Duty.
Uninitiated The call processing component has not initialized the
resource.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 55

Starting and stopping components 55
Alert icons
If one of the following icons appears next to a component in the tree, then
the component or one of its subcomponents is experiencing a problem.:
Icon Description
A problem exists with a subcomponent of the selected
component. Expand the tree to locate the subcomponent with
the problem.
A problem exists with the selected component.
To view the state of a hardware component
Step Action
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Maintenance Admin.
Result: The Maintenance screen appears.
3
Click the plus sign (+) beside the CallPilot server to expand the
component tree.
4
Continue clicking the plus sign (+) until the component with which
you want to work is visible.
5
Click the hardware component with which you want to work.
Result: The Maintenance screen refreshes to show details about
the component.
6
Scroll down to the Maintenance section.
7
View the state of the selected component in the State box.
—End—
Starting and stopping components
When you stop a component, you take it out of service and prevent it from
operating. You must stop a component before you can replace it (if the
component is replaceable) or run a diagnostic test on it.
To bring an out-of-service component back into service, you must start it.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 56

56 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Start and stop components from the Maintenance section on the
Maintenance screen.
ATTENTION
Nortel recommends that, if possible, you courtesy stop a component. Courtesy
stop is available only at the individual channel level.
To courtesy stop CallPilot, use the following:
•
Multimedia Monitor - to courtesy stop a range of multimedia channels
•
Channel Monitor - to courtesy stop a range of call (DS30X, also known
as DS0) channels
Stop versus courtesy stop
The following two methods of taking a component out of service allow you to
choose how active calls are affected.
Courtesy stop
A courtesy stop takes the component out of service only after the
component has finished processing the active call.
•
If the component is currently processing a call, the call is not dropped;
the component remains active until the call is finished.
•
If the component is not currently in use, it is taken out of service
immediately.
Courtesy stop is the preferred method for taking a component out of service.
Stop
A stop takes the component out of service immediately, regardless of
whether the component is currently processing calls. All active calls are
dropped. Typically, you perform a stop only when severe problems that
are affecting a large number of incoming calls occur or if your organization
determines a special need for it.
Components that can be started and stopped
Only the following components can be started and stopped.
Note: If you want to start or stop more than one or two multimedia
(DSP) or call (DS30X) channels, use the Multimedia Monitor or Channel
Monitor.
Component
Effect of stopping
Media Bus Takes all call processing resources out of service.
MPB board Takes all call processing resources on the selected board
out of service.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 57

Starting and stopping components 57
Component
Effect of stopping
Time Switch You cannot perform maintenance administration on the
time switch.
Multimedia Channel Takes the selected Multimedia Channel out of service.
Channels Takes the selected DS30X channel out of service.
DS30X link Takes the selected DS30X link out of service.
To start or stop a component
Step Action
1 Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Maintenance Admin.
Result: The Maintenance screen appears.
3
Click the plus sign (+) beside the CallPilot server to expand the
component tree.
4
Continue clicking the plus sign (+) until the component with which
you want to work is visible.
5
Click the hardware component that you want to start or stop.
Result: The Maintenance screen refreshes to show details about
the component.
6
Scroll down to the Maintenance section.
7
Click Courtesy Stop, or Start as required.
Button Description
Start If the selected component is out of service, click this
button to put it into service.
Courtesy
Stop
Click this button to take the selected component out
of service. CallPilot waits for calls to be completed
before disabling the component.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 58

58 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Button Description
ATTENTION
If you are courtesy stopping all components (that is,
you are taking the entire system down), ensure that
you inform all administrators, desktop messaging
users, and web messaging users so that they can
log off their sessions before you proceed.
The system asks you to confirm the courtesy stop.
If you click OK, the component is put out of service
after all calls are finished.
Stop
Click this button to take the selected component out
of service immediately. All calls that are in progress
are disconnected immediately.
ATTENTION
If you are stopping all components (that is, you are
taking the entire system down), ensure that you
inform all administrators, desktop messaging users,
and web messaging users so that they can log off
their sessions before you proceed.
—End—
Running integrated diagnostics
Run diagnostic tests from the Diagnostics section on the Maintenance
screen in the following circumstances:
•
You want to ensure that a component is operating properly after
installing or reinstalling it.
•
The CallPilot server is having trouble processing incoming calls and you
are hoping that diagnostic results can tell you why.
Problems include static, dropped calls, and cross talk (hearing another
conversation).
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 59

Running integrated diagnostics 59
Before you begin
ATTENTION
Take the component out of service before you run the diagnostic test. See
"Starting and stopping components" (page 55).
Components that have diagnostic tests available
The following table identifies the components on which you can run
diagnostics.
Component
Diagnostics available? Replaceable?
Media Bus No No
MPB96
board
Yes Yes
Time Switch No No
Multimedia
Channels
Yes No
Channels No No
DS30X link
(cable)
Yes Yes
Diagnostic tests available for each component
The diagnostic tests that are available for each component are listed in the
Diagnostic section of the Maintenance screen. To view the list of diagnostic
tests for a particular component, click the component in the component tree.
If a diagnostic test fails or cannot be run
If a warning message appears, the diagnostic test cannot be run because a
prerequisite condition has not been met. If a diagnostic test fails, a message
appears in a new browser window (see the example on screen step 8).
In both cases, check the Alarm Monitor to determine the reason and the
appropriate action to take.
If the Alarm Monitor and Event Browser do not provide a solution to a
hardware problem, you may need to replace or service a component. If
the problem is with a component that is not replaceable because it is not
a physical entity (such as the Time Switch), you must either replace its
parent component or contact your Nortel technical support representative,
depending on the component.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 60

60 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
To run a diagnostic test
Step Action
ATTENTION
Nortel recommends that you courtesy stop rather than stop a component if
possible. For instructions, see "Starting and stopping components" (page 55).
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Maintenance Admin.
Result: The Maintenance screen appears.
3
Click the plus sign (+) beside the CallPilot server to expand the
component tree.
4
Continue clicking the plus sign (+) until the component with which
you want to work is visible.
5
Click the hardware component for which you want to run diagnostics.
Result: The Maintenance screen refreshes to show details about
the component.
6
Scroll down to the Maintenance section, and ensure that the
component is out of service.
7
Scroll down to the Diagnostics section.
8
Select the check box for each diagnostic that you want to run.
Note: If you want to run all of the diagnostics, select the
Diagnostic Description check box at the top of the list.
9
Click Run.
Result: A new web browser window opens to display the progress
and results of the diagnostics.
Note: The Diagnostic Results box in the Diagnostics section
displays diagnostic results when you click Get Last Result.
—End—
Viewing the last diagnostic results
You can review the results of diagnostics by clicking the Get Last Results
button for a component.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 61

Working with the Multimedia Monitor 61
To view the last diagnostics result
Step Action
ATTENTION
Nortel recommends that you courtesy stop rather than stop a component if
possible. For instructions, see "Starting and stopping components" (page 55).
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Maintenance Admin.
Result: The Maintenance screen appears.
3
Click the plus sign (+) beside the CallPilot server to expand the
component tree.
4
Continue clicking the plus sign (+) until the component with which
you want to work is visible.
5
Click the hardware component for which you want to run diagnostics.
Result: The Maintenance screen refreshes to show details about
the component.
6
Scroll down to the Diagnostics section.
7
Select the check box for each diagnostic for which you want to
review results.
8
Click Get Last Result.
Result: The results appear in the Diagnostic Results box with the
following information:
•
diagnostic title
•
diagnostic result: pass or fail
•
the date and time the test was completed
—End—
Working with the Multimedia Monitor
The Multimedia Monitor shows the status of multimedia channels. The
multimedia channels are the DSP ports that process the calls. They are the
voice, fax, and speech recognition channels.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 62

62 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
To view or work with multimedia channel states
Step Action
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Multimedia Monitor.
Result: The Multimedia Monitor screen appears, showing the
channels associated with each DSP.
Multimedia monitor screen
Note: For an explanation of the channel states, refer to the
CallPilot Manager online Help.
3
Do one of the following:
IF you want to stop or start THEN
all of the channels associated with
a DSP
select the check box to the left of
the DSP that you want to stop or
start.
Repeat this step for each DSP.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 63

Working with the Channel Monitor 63
IF you want to stop or start THEN
only one or several channels that
are associated with a DSP
select the check box for each
channel that you want to stop or
start.
4
Click Courtesy Stop, Stop, or Start as required.
Result: If you clicked Courtesy Stop or Stop, you are asked to
confirm the Courtesy Stop or Stop. Click OK.
The selected channels change to off-duty or on-duty status,
according to the action you chose.
Note: If the buttons are not available, wait a few seconds for the
screen to refresh.
—End—
Working with the Channel Monitor
The Channel Monitor shows the status of call channels. The call channels
are the connections between the server and the switch that carry the call
signals to CallPilot.
To view or work with call channel states
Step Action
1
Run CallPilot Manager and log in.
2
In CallPilot Manager, click Maintenance→Channel Monitor.
Result: The Channel Monitor screen appears, showing the DS30X
(also known as DS0) channels associated with each DS30X link.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 64

64 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Channel monitor screen
Note: For an explanation of the channel states, refer to the
CallPilot Manager online Help.
3
Do one of the following:
IF you want to stop or start THEN
all of the channels associated with
a DS30X link
select the check box to the left of
the DS30X link that you want to
stop or start.
Repeat this step for each DS30X
link.
only one or several channels that
are associated with a DS30X link
select the check box for each
channel that you want to stop or
start.
4
Click Courtesy Stop, Stop, or Start as required.
Result: If you clicked Courtesy Stop or Stop, you are asked to
confirm the Courtesy Stop or Stop. Click OK.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 65

Working with the Channel Monitor 65
The selected channels change to off-duty or on-duty status,
according to the action you chose.
Note: If the buttons are not available, wait a few seconds for the
screen to refresh.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 66

66 Chapter 6 Using CallPilot Manager to monitor hardware
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 67

67
Chapter 7
Using CallPilot system utilities
In this chapter
"Overview" (page 67)
"Diagnostics Tool" (page 68)
"PEP Maintenance utility" (page 69)
"Session Trace" (page 69)
"System Monitor" (page 71)
Overview
The following table lists the CallPilot system utilities.
Utility Description
Diagnostics Tool Allows CallPilot startup diagnostics to be enabled or
disabled (turned on or off).
PEP Maintenance Displays a list of installed PEPs and enables PEP
removal.
Session Trace Displays detailed information about the activity in a
user’s mailbox and the state of the message waiting
indicator (MWI).
System Monitor Displays the following information:
•
the status of all CallPilot channels
•
the status of all CallPilot services
Note: This status is more accurate than the status that
Windows provides in the Services Control Panel.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 68

68 Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities
Utility Description
•
particulars about the CallPilot System, such as
names, keycodes, serial numbers, IP addresses,
and system numbers
Accessing the system utilities
All CallPilot utilities are accessible from the CallPilot server in the Start →
Programs → CallPilot → System Utilities menu.
Diagnostics Tool
The Diagnostics Tool allows you to enable or disable CallPilot startup
diagnostics. CallPilot startup diagnostics automatically identify hardware
problems that may exist when the system and its services are started.
When you disable startup diagnostics, you can save time during system
maintenance operations where restarts or call processing services restarts
are required. There are three recommended steps:
•
Use the Diagnostics Tool to turn off CallPilot startup diagnostics.
•
Perform system maintenance.
•
Use the Diagnostics Tool to turn on CallPilot startup diagnostics.
To access the Diagnostics Tool
On the Windows desktop, click Start → Programs → CallPilot → System
Utilities → Diagnostic Tool.
Result: The Diagnostics Tool window appears.
To enable startup diagnostics
From the Diagnostics Tool window, select Configuration → Maintenance
Startup Diag → Enable.
To disable startup diagnostics
ATTENTION
Nortel recommends that you leave the startup diagnostics turned on. When you
disable CallPilot startup diagnostics, you prevent CallPilot from automatically
identifying hardware problems that may exist when the system and its services
are started (for example, DSP, TimeSwitch, or MediaBus).
On the Diagnostics Tool window, select Configuration → Maintenance
Startup Diag → Disable.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 69

Session Trace 69
PEP Maintenance utility
The PEP Maintenance utility displays a list of all installed PEPs on the
server and enables you to uninstall PEPs. For information on installing
or uninstalling PEPs, refer to the Installation and Configuration Task List
(NN44200-306).
To access the PEP Maintenance utility
From the Windows desktop, click Start → Programs → CallPilot → System
Utilities → PEP Maintenance Utility.
Result: The DMI Viewer window appears.
To view a list of all installed PEPs
Step Action
1
Click the component for which you want to display the PEP list.
2
Click Show PEPs.
Result: A list of all installed PEPs appears in the left pane.
3
If you want to review the readme file associated with a PEP, click the
PEP, and then click Read.
Result: The readme file opens in Notepad.
—End—
Session Trace
The Session Trace tool displays detailed information about the activity in a
user’s mailbox and the state of the message waiting indicator (MWI). The
session information includes
•
voice messaging
•
call answering
•
express messaging activity (messages composed and sent, or left in
a mailbox)
•
the number of messages played or unplayed at the beginning, middle,
and end of a session
•
messages and personal distribution lists restored into a mailbox
•
the last change to the MWI (turned on or off, or untouched)
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 70

70 Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities
This session information allows an administrator or technician to study
the state of a user’s mailbox and the MWI, and to use that information to
follow up on any user complaints. For example, a user may complain that
the MWI was on, but no voice messages were in the mailbox when the
user logged on. The session information can tell the administrator why the
MWI was turned on.
To access the session trace tool
From the Windows desktop, click Start → Programs → CallPilot → System
Utilities → Session Trace Tool.
Result: The MCE Session Trace window appears.
To find a session
Step Action
1
Fromthe Session Type drop-down menu, choose the type of session.
To display a list of all session types, select All Session Types.
2
Enter as much information in the search criteria boxes to identify
the session you want to view. To display a list of all users for the
selected Session Type, leave the search criteria boxes blank.
3
Click Search to initiate the search.
a. If you did not enter any user information, a list of users matching
the Session Type appears at the bottom of the window. To select
a user from the list, double-click the user name to display session
type information.
b. If you selected All Session Types for a user, the session type
information appears to the right of the window.
4
Double-click the session type to display the session information.
Result: The Session Type information appears at the bottom of
the window. The following example shows Call Answering session
type information.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 71

System Monitor 71
Call answering session
—End—
System Monitor
The System Monitor consists of three tabs, as described in the following
table.
System Monitor tabs
Tab Description
Channel Monitor Shows the status of all CallPilot services, multimedia
channels, and call channels (DS30X channels).
System Info Displays details about the CallPilot System, such as
features purchased, keycode, serial number, and
CallPilot server IP addresses.
Legend/Help Provides a description of icons and terminology
displayed in the System Monitor window.
System Monitor is a nondestructive tool that does not alter the behavior of
any CallPilot components.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 72

72 Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities
To access the System Monitor
On the Windows desktop, click Start → Programs → CallPilot → System
Utilities → System Monitor.
Result: The CallPilot System Monitor window appears. By default, the
Channel Monitor tab appears on top. Click the other tabs to view the
information on those tabs.
Channel Monitor tab
The following is an example of the Channel Monitor tab when connected
to an Meridian 1*
Channel Monitor with M1.
The following is an example of the Channel Monitor tab when connected to
a T1/SMDI.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 73

System Monitor 73
channel Monitor with T1/SMDI
CallPilot services
The Service Name pane shows the status of services from a CallPilot
perspective. The status shown in the Windows Services Control Panel
may state that a service is running, but it may not actually be fully running
or in service from a CallPilot perspective. Refer to the System Monitor tool
Channel Monitor tab for the true status.
The services listed under Service Name should be either running or in full
service when CallPilot is functioning optimally. If any CallPilot services are
stopped, investigate the cause of this. Call Nortel technical support for
assistance.
Note: While any stopped services should be investigated, some
services are not critical. CallPilot may continue to handle call processing
even with some services stopped.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 74

74 Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities
The critical services that are required for basic CallPilot call answering are
listed in the following table. For your reference, the equivalent names as
they appear in the Windows Control Panel are also listed.
CallPilot
System Monitor
Windows Control Panel
equivalent
CTMS Service CTMS Server
Telephony (TAPI) Telephony Service
MCE SLEE CallPilot SLEE Service
MCE Notification CallPilot MWI Service
MAS Notification CallPilot Notification Service
MAS CCR CallPilot Call Channel Router
MAS BCR CallPilot Blue Call Router
SQL Anywhere Adaptive Server Anywhere -
%ComputerName%_SQLANY
MAS MltmediaCache CallPilot Multimedia Cache
MAS MltmediaVol1 CallPilot Multimedia Volume 1
MAS MltmediaVol102 (TRP only) CallPilot Multimedia Volume 102 (TRP
only)
MAS MltmediaVol103 (TRP only) CallPilot Multimedia Volume 103 (TRP
only)
MAS Rsrc. Pckg. 1 CallPilot Resource Package1
DSPs
In the DSP pane, each DSP is represented in a separate row. Each box in
the row is one DSP channel or multimedia channel. Click the Legend/Help
tab to view descriptions of the multimedia channel icons.
For tower and rackmount CallPilot servers, DSPs reside in MPB96 and
MPB16-4 boards and MPC-8 cards. For 1002rp servers, DSPs are
distributed as follows:
•
MPB96 board has 12 DSP sections embedded on board
•
One MPB16-4 board consists of two embedded DSPs and up to four
MPC-8 cards.
•
Each MPC-8 card contains a single DSP.
DS30X links
In the DS30X link pane, each DS30 row represents a separate DS30X
link (also referred to as a DS30 link). Each box in the row represents one
DS30X channel.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 75

System Monitor 75
The DS30X links connect the CallPilot server to the MGate card
(NTRB18CA) in the Meridian 1 switch or Communication Server 1000*
system.
For the 1002rp server, the DS30X link to the switch is supported by the
connection of the server to the switch backplane.
T1 Links
In the T1 link pane, each row represents a T1 link. Each box in the row
represents one DS0 channel.
The T1 links connect the Callpilot Server to a Line Side T1 card on the
SL100 or to a Channel Bank on the DMS-100* switch.
System Info tab
"System info tab" (page 75) shows an example of the System Info tab.
System info tab
The numbered items provide information about the features purchased.
Information about the underlying operating system is provided in the top
right corner, including the server IP addresses.
PEP information and configured Service DNs are listed in the bottom part of
the window.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 76

76 Chapter 7 Using CallPilot system utilities
Legend/Help tab
"Legend/Help tab" (page 76) shows an example of the Legend/Help tab.
Consult this window for descriptions of the icons found in the Channel
Monitor tab.
Legend/Help tab
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 77

77
Chapter 8
Replacing basic chassis components
In this chapter
"Removing the front bezel and server cover" (page 77)
"Replacing air filters" (page 80)
"Replacing the power supply" (page 81)
"Replacing the SCA SCSI drive cage and fused power cable" (page 84)
"Replacing the cooling fan" (page 88)
"Replacing the fuse (AC system only)" (page 91)
"Replacing the alarm board" (page 93)
"Setting jumpers on the alarm board" (page 94)
"Replacing the status display panel" (page 96)
Removing the front bezel and server cover
If the maintenance task requires replacing front panel components, you
must remove the front bezel. The exception is the hard drives, which can be
accessed by simply unlocking and opening the front bezel doors.
If you require access to the server interior, remove both the front bezel
and the server cover.
Requirements
Before you remove the front bezel and server cover, gather the following
tools:
•
the customer’s chassis keys for the front bezel doors
• a flat-blade screwdriver
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 78

78 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
•
an antistatic wrist strap
About the front bezel doors
Two locked doors on the front of the server cover the front panel, including
the CD-ROM drive and tape drive.
These doors are part of the front bezel. You must unlock the front panel
doors before you can remove the front bezel.
To remove the front bezel
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage
Do not attempt to move or lift the server before you have removed
the front bezel. If the front bezel is attached, the server can
disengage from the front bezel and fall.
Front bezel removed
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 79

Removing the front bezel and server cover 79
Step Action
1
Unlock and open the double doors of the front bezel. See A in "Front
bezel removed" (page 78).
2
Firmly grasp the front bezel by the hand-holds on either side of the
chassis, and pull the front bezel from the chassis. See B in "Front
bezel removed" (page 78).
—End—
To remove the server cover
Step Action
DANGER
Risk of electric shock
High current inside the chassis can cause severe injury.
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage
Take precautions to protect internal components. Electrostatic
discharge (ESD) can damage boards and make them unusable.
Wear an ESD wrist strap.
1
Remove the front bezel.
2
Power down the server and disconnect all power cords.
3
Loosen the three thumbscrews at the rear of the top cover.
4
Remove the server cover by pulling the cover toward the rear of the
chassis, and then lifting it up and off.
5
Clip the lead from your ESD wrist strap to an unpainted metal section
of the chassis.
—End—
To replace the front bezel after maintenance is complete
When the CallPilot server maintenance is complete, replace the front bezel.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 80

80 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Front bezel replaced
Step Action
1
Align the front bezel with the ball studs located at each faceplate
corner.
2
Apply pressure evenly until the bezel snaps onto each ball stud.
3
Close and lock the double doors of the front bezel.
—End—
Replacing air filters
To ensure your server cools and functions properly, remove and clean air
filters every six months in clean environments and every three months in
industrial or dirty environments. If they appear to be damaged or become
inefficient, replace the filters. There are four air filters on the 1002rp
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 81

Replacing the power supply 81
server—one inside each of the two doors of the front bezel, and two on the
top half of the front bezel. They are made of polyester foam material and
are flame retardant.
Requirements
You require the customer’s chassis keys for the front bezel.
To replace the front bezel air filter
Step Action
1
Remove the front bezel from the chassis. See "To remove the front
bezel" (page 78).
2
Pull the filters away from the Velcro strips that secure them to the
bezel.
3
Replace the filter by seating the new filter pads evenly over the
Velcro strips and securing them.
4
Install and lock the front bezel on the chassis.
—End—
To replace the door air filter
Step Action
1
Unlock and open the front doors.
2
The air filter is trapped between the inside of the door and the wire.
The wire pivots near the key lock. Pull the wire away from the key
lock to free the air filter.
3
Remove and replace the air filter.
4
Pivot the wire to trap the filter, ensuring that the ends of the wires
are pinched inside the door.
5
Close and lock the doors.
—End—
Replacing the power supply
The power supply is hot-swappable. This means that you can replace the
power supply without powering down the server.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 82

82 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Requirements
Before you hot-swap a power supply, gather the following tools:
•
one flat-blade screwdriver
•
one Phillips screwdriver
•
one antistatic wrist strap
•
the replacement power supply
When to hot-swap the power supply
A green LED indicates that the power supply is working properly. If the
green LED on the power supply module is unlit or red, the module is failing
or has failed. Other indicators of failure are the alarm that sounds and the
power supply module LED on the status display that turns red.
To hot-swap a power supply
Step Action
DANGER
Risk of electric shock
High current inside the chassis can cause severe injury.
1
Loosen the thumbscrews at the top right and left of the failed power
supply module (see A in the following diagram).
If needed, use a flat-blade screwdriver. The thumbscrew must rotate
freely and not contact the chassis threads.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 83

Replacing the power supply 83
2
Grasp the molded horizontal handles on the power supply module
and pull the power supply module free from the chassis (see B in
the preceding diagram).
3
Align the replacement module with the empty chassis bay.
4
Slide the replacement power supply module into the bay until the
module is secured by its connector. Use some force, if necessary.
5
Secure the power supply module to the chassis with two
thumbscrews at the corners of the power supply faceplate.
Result: The power supply LED illuminates green.
Note: If the LED does not illuminate, remove and reinstall the
power supply with more force. If this does not work, contact your
Nortel customer support representative.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 84

84 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Replacing the SCA SCSI drive cage and fused power cable
Due to the potential of an over-current condition, Nortel provides a retrofit
SCSI power cable kit for the N0029330 power cable. The kit comprises an
improved SCSI power cable, product label, and retrofit procedure.
The cable kit part number for all locations, except EMEA, is FR029367.At
EMEA locations, use part number N0029367.
•
Only qualified field technicians who are familiar with CallPilot and RAID
should attempt this procedure.
•
A full-system backup and RAID drive consistency check must be
performed prior to replacing the SCSI power cable. These can both be
performed while the server is online.
•
If at any step in the procedure, the result is not as indicated, stop and
contact your next level of support for assistance before continuing.
To replace the SCSI power cable
Step Action
1
Log into the CallPilot server.
2
Launch the MegaRAID client to check the status of the RAID
sub-system:
a. Click Start → Programs → MegaRAID Client.
b. Open the Server Selection window.
c. Select Access Mode → Full Access and click OK.
Result: The MegaRAID Power Console Plus window appears.
MegaRAID Power Console Plus
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 85

Replacing the SCA SCSI drive cage and fused power cable 85
3
Open the Physical Devices window and check the drive pair settings.
The table below shows the correct settings.
Drive pair settings
LED
No
ID
Channel-1
LED
No
ID
Channel-2
00
ONLIN A01-01
30
ONLIN A01-02
11
ONLIN A02-01
41
ONLIN A02-02
22
ONLIN A03-01
52
ONLIN A03-02
Note: If your settings do not match those in the table, stop
and contact your next level of support for assistance before
continuing.
4
Check that all drives are marked in green and Online.
Note: If they are not all online, stop and contact your next level
of support for assistance before continuing.
5
Check the RAID drive consistency:
a. Select Check Consistency.
Result: The Logical Drives Configured dialog box appears.
b. Use the arrow key to highlight the first drive to be checked.
c. Press the space key to select the drive.
d. Press F10 to check consistency.
Result: The Do you wish to continue? dialog box appears.
e. Click Ok.
Result: The consistency check begins and a status dialog box
appears.
f. Repeat steps c to e for each drive until all three drives have
been checked for consistency. This may take up to 2 hours to
complete. If any data consistency errors are detected, they are
corrected automatically.
6
Perform a full-system backup of the CallPilot server (either to tape
or file server).
7
Review the backup logs to verify success.
8
Perform a controlled shutdown of the CallPilot software:
a. Click Ctrl+Alt+Delete and select Shutdown from the Windows
Security window.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 86

86 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Result: The Shutdown Computer dialog box appears.
b. Select Shutdown.
Result: The CallPilot server turns off.
9 Remove power from the system by disconnecting the AC or DC
mains.
10
Remove the bezel cover from the front of the chassis using the four
snaps located at each corner.
Bezel cover on chassis front
11
Remove the 4 Phillips-head screws from each corner of the SCSI
disk-drive cage
Chassis front with bezel removed.
12 Carefully remove the SCSI drive cage from the chassis to provide
access to the internal cable assemblies.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 87

Replacing the SCA SCSI drive cage and fused power cable 87
SCSI drive cage attached to chassis
Note: An arrow points to the SCSI power cable in the picture
above.
13
Unplug the original power cable from the SCA backplane and from
the T board inside the chassis. The power cable is schematically
shown in "SCSI power cable attached to T board" (page 87).
SCSI power cable attached to T board
Note: Leave all other cable assemblies connected. Do not
damage or disconnect other components on the SCA backplane.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 88

88 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
14
Replace the original SCSI power cable with the new cable. Securely
attach it to both the SCA backplane and the T board inside the
chassis.
15
Reinstall the SCSI drive cage into the bay and screw it into place.
Torque the screws at 6 to 8 inch lbs.
16
Affix a revised product label above the existing labels on the left
rear of the chassis.
Product label location on chassis
17 Replace the bezel cover on the front of the chassis.
18
Reconnect the AC or DC mains power.
19
Reboot the CallPilot server and bring it into full service.
—End—
Replacing the cooling fan
The cooling fan is hot-swappable, so you can replace the cooling fan without
powering down the server.
When to hot-swap the cooling fan
When the LED associated with a cooling fan turns red, the fan requires
replacement.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 89

Replacing the cooling fan 89
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage
Use an ESD wrist strap to protect static-sensitive components.
To hot-swap a cooling fan
Step Action
1
Remove the front bezel.
2
Use the front panel display LED to locate the defective fan.
3
Loosen the thumbscrew located on the outside of the failed cooling
fan module (see A "Cooling fan thumbscrew" (page 90)).
If needed, use a flat-blade screwdriver. The thumbscrew must rotate
freely and not contact the chassis threads.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 90

90 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Cooling fan thumbscrew
4
Unseat the cooling fan module by sliding the module horizontally
away from the display and toward the rack rail (see B in the diagram).
Result: The module power connector unseats from the power
connector located behind the display and LEDs.
5
Slide the failed cooling fan module out of the chassis (see C in the
diagram).
6
Align the replacement cooling fan module tabs with the four support
slots on the chassis.
Ensure that the module is oriented with the thumbscrew, and insert
the tabs into the supporting slots of the chassis.
7
Slide the cooling fan module toward the front panel display and into
position.
Result: The fan module connects with slight resistance. The fans
rotate and pull air into the chassis. The cooling fan LED goes out.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 91

Replacing the fuse (AC system only) 91
8
Tighten the module thumbscrew and replace the front bezel.
—End—
Replacing the fuse (AC system only)
The fuse is located below the power input socket on the rear panel. When
the server fuse blows, the server stops operating.
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage and personal injury
Disconnect power from the server before replacing a fuse.
Requirements
You require the following:
•
an approved fuse for replacement
Two different types of fuses exist: one for North America, and one for
international use. Ensure that the fuse you are replacing has been
approved by Nortel for your region.
•
a flat-blade screwdriver
To replace the fuse
Step Action
1
Power off the server.
2
Unplug the power cable from the wall outlet.
3
Unplug the power cable from the power input socket on the server.
4
Unscrew the fuse receptacle (see A in "Fuse receptacle" (page 92)).
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 92

92 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Fuse receptacle
5
Slide the fuse receptacle out of the fuse chamber.
Note: Observe how the blown fuse is positioned in the
receptacle.
6
Remove the blown fuse from the fuse receptacle.
7 Install the approved replacement fuse. Use a flat-blade screwdriver
to screw in the fuse receptacle with a push and 1/4 clockwise turn.
8
Slide the fuse receptacle back into its chamber.
9
Fasten the fuse receptacle with a flat-blade screwdriver.
10
Plug the power cable back into the power input socket on the server.
11
Plug the power cable into the wall outlet.
12
Power on the server.
—End—
ATTENTION
If the fuse blows after replacement, swap one power supply module with the other.
If this does not work, call your Nortel customer support representative.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 93

Replacing the alarm board 93
Replacing the alarm board
The 1002rp server alarm board and status panel are used to monitor and
indicate the server status. The basic hardware check on page "Basic
hardware check" (page 17) fails if the board is defective or damaged. When
these units are damaged, replace them immediately.
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage
Take precautions to protect computer boards. ESD can damage
boards and make them unusable. Wear an ESD wrist strap.
Requirements
Before replacing the alarm board or panel display, gather the following tools:
•
a Phillips screwdriver
•
an antistatic wrist strap
•
the replacement components
To replace the alarm board
Step Action
1
Power off the server.
2
Loosen the two thumbscrews securing the faceplate to the left of
the 1002rp server power supply modules (see A in "Alarm board
carrier" (page 94)).
If needed, use a flat-blade screwdriver. The thumbscrew must rotate
freely and not contact the chassis threads.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 94

94 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Alarm board carrier
3
Pull the carrier free from the chassis (see B in "Alarm board carrier"
(page 94)).
4
The alarm board is secured to the carrier by two Phillips-head
screws. Remove the defective alarm board from the carrier.
5
Secure the replacement alarm board to the carrier using two
Phillips-head screws.
6
Align the carrier with the chassis and slide the board into the chassis.
Note: The card encounters some resistance as it meets the
connector.
7
Tighten the thumbscrews to secure the faceplate to the chassis.
—End—
Setting jumpers on the alarm board
The jumpers on the alarm board enable or disable sensing and display
functions. This section describes the features that are enabled or disabled
by setting jumpers on the alarm board.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 95

Setting jumpers on the alarm board 95
The default and recommended setting is to have only JP3 jumpered (see
"Jumpers on alarm board" (page 95)). This setting enables normal sensing
and LED display.
Jumpers on alarm board
Jumper descriptions
JP6 - do not change
Leave the jumper installed on JP6.
JP5 - Disarming no power in the bottom bay
If you are operating with one power supply, you can disable sensing of no
power from the bottom power supply. To do this, install a jumper on jumper
block 1, JP5.
Ensure that the functioning power supply is installed in the upper power bay.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 96

96 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
JP4
Not used.
JP3 - LED display
Install a jumper on jumper block 1, JP3, to configure the alarm board to
send alarm signals to the full array of LEDs. This is the default setting and
the required setting for normal server operation.
If this jumper is not installed over both pins, the alarm board does not send
the correct format of signals to the front panel display.
Replacing the status display panel
The display is located at the front of the chassis and is cabled to the rear
of the chassis and the alarm board.
To replace the status display panel
Step Action
CAUTION
Risk of equipment damage
Use an ESD wrist strap to protect static-sensitive components.
1
Power off the server.
2
Remove the top cover and the front bezel from the chassis.
3
Removethe cooling fans (see "Replacing the cooling fan" (page 88)).
The cooling fans block the access to the status panel.
4 Loosen the four Phillips-head screws that secure the status display
panel to the front of the chassis (see A in "Status display panel."
(page 97))
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 97

Replacing the status display panel 97
Status display panel.
5
Label and remove the 40-pin flat cable from the back of the status
display panel.
6
Move the defective status display panel towards the back of the
chassis, and then lift it out of the chassis (see B and C in the
diagram).
7
Set the replacement status display panel into position, and secure it
to the chassis by replacing the Phillips-head screws.
8 Reconnect the cable.
9
Replace the top cover and front bezel.
—End—
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 98

98 Chapter 8 Replacing basic chassis components
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 99

99
Chapter 9
Replacing media drives
In this chapter
"Replacing a faulty hard drive" (page 99)
"About the media drive bay" (page 103)
"Removing the media drive carrier from the chassis" (page 103)
"Replacing a tape, CD-ROM or floppy drive" (page 106)
"Installing a tape drive" (page 108)
Replacing a faulty hard drive
The hard drives are hot-swappable. This means that you can replace a
faulty hard drive without powering down the server.
ATTENTION
Replacement hard drives must be the same size or larger than the hard drives
being replaced
When to hot-swap hard drives
With a RAID controller, hot-swap device drivers, and operating system
support, faulty SCA SCSI hard drives can be hot-swapped on the 1002rp
server.
Note: Identify which hard drive to remove using the Windows Event
Viewer (see "Viewing event logs" (page 23)). The appearance of event
codes such as 40211(disk access error) or 40218 (error reading or
writing multimedia volume) may be an indication of a failing disk drive.
Use the RAID management software to check if any drives are in a failed
state.
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
Page 100

100 Chapter 9 Replacing media drives
The following image shows a failed drive highlighted in red with the
corresponding logical drive highlighted in yellow (degraded mode)
Failed hard drive displayed in red
RAID SCSI hard drive configuration
"RAID SCSI hard drive configurations" (page 100) shows proper SCSI drive
bay, channel, and ID configurations in the hot-swappable drive bay. The
SCSI backplane assigns the SCSI IDs as shown.
RAID SCSI hard drive configurations
Hard drive bay
SCSI
channel SCSI ID Logical drive label
a
1 (far left)
00
A01-01 (primary hard drive)
201
A02-01 (primary hard drive)
302
A03-01 (primary hard drive)
410
A01-02 (secondary hard drive)
a. RAID pairs (logical drives) consist of the following pairs: hard drives 1 and
4,2 and 5, and 3 and 6. these pairs are represented in the software with the
lables A01-01 and A01-02, A02-01 and A02-02, and A03-02, A03-02 where the
first number is the logical drive number (for example, A03) and the second
number indicates if it is the primary or secondary hard drive (01 for primary
and 02 for secondary)
Nortel CallPilot
1002rp Server Maintenance and Diagnostics
NN44200-701 01.02 Standard
5.0 4 April 2007
Copyright © 2007, Nortel Networks Nortel Networks Confidential
.
 Loading...
Loading...