Page 1

GB
BU 2100
EtherNet/IP Bus module
Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Page 2
EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Designation:
Part No.:
608 21 02
Series:
EtherNet/IP™ Bus System
Name
previous versions
Software
Version
Remarks
BU 2100 EN, May 2013
Part No. 608 21 02 / 2213
V. 1.1 R0
First issue
NOTICE
Supplementary operating manual
This supplementary operating manual is only valid in conjunction with the operating manual supplied for the
respective frequency inverter. This is an essential prerequisite for the availability of all the relevant information
required for the safe commissioning of the frequency inverter.
Documentation
Version list
Table 1: Version list
Publisher
Getriebebau NORD GmbH & Co. KG
Rudolf-Diesel-Str. 1 D-22941 Bargteheide http://www.nord.com/
Tel.: +49 (0) 45 32 / 289-0 Fax +49 (0) 45 32 / 289-2555
2 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 3

Publisher
BU 2100 GB-2213 3
Page 4

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Table of Contents
1. Introduction ................................................................................................................................................. 7
1.1 General .............................................................................................................................................. 7
1.2 Bus modules ...................................................................................................................................... 7
2. Bus Configuration ....................................................................................................................................... 8
2.1 Topology ............................................................................................................................................ 8
2.2 Cable layout and shielding (EMC measures) ..................................................................................... 8
3. Configuration in the Bus System ............................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Addressing ................................................................ ......................................................................... 9
3.2 Integration into the busmaster ............................................................................................................ 9
3.3 Remote Maintenance (in preparation) .............................................................................................. 10
4. Communication and Protocol .................................................................................................................. 11
4.1 Processing of Process Data in the Frequency Inverter .................................................................... 11
4.1.1 Control word (STW) ............................................................................................................ 12
4.1.2 Status word (ZSW) ............................................................................................................. 12
4.1.3 Frequency inverter status machine ..................................................................................... 13
4.1.4 Setpoint (SW) and Actual Value (IW) ................................................................................. 16
4.1.5 Example: "Switch on and off + setpoint" ............................................................................. 16
4.2 Transfer of Data in the Bus System (I/O connections) ..................................................................... 17
4.2.1 Assembly ............................................................................................................................ 17
4.3 Parameter Transfer (Explicit Messages) .......................................................................................... 18
4.4 Timeout monitoring .......................................................................................................................... 20
5. Parameter ................................................................................................................................................... 21
5.1 Bus - Module Parameters ................................................................................................................ 21
5.2 Frequency Inverter Parameters ....................................................................................................... 28
6. Additional information .............................................................................................................................. 31
6.1 Repair information ............................................................................................................................ 31
6.1.1 Repairs ............................................................................................................................... 31
6.1.2 Internet information ............................................................................................................. 31
6.2 Furhter Documentation and Software .............................................................................................. 32
4 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 5

List of illustrations
List of illustrations
Fig. 1: Installation and cable laying information ....................................................................................................... 8
Fig. 2: Status Machine of the Frequency Inverter .................................................................................................. 15
BU 2100 GB-2213 5
Page 6

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
List of tables
Table 1: Version list ................................................................................................................................................. 2
Table 2: Hardware Overview ................................................................................................................................... 7
Table 3: Control word (STW) ................................................................................................................................. 12
Table 4: Status word (ZSW) .................................................................................................................................. 13
Table 5: Depiction of 32Bit setpoint/actual values ................................................................................................. 16
Table 6: Example: "Switch FI on and off + setpoint" .............................................................................................. 17
Table 7: Assembly Instance................................................................................................................................... 17
Table 8: Input Structure in Assembly Instance 111 ............................................................................................... 18
Table 9: Output Structure in Assembly Instance 110 ............................................................................................. 18
Table 10: Assignent of Devices to an EtherNet/IP™ Class ................................................................................... 18
6 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 7

1 Introduction
Name
Part. No.
Remarks
Document
SK TU3-EIP
275 900 150
for NORD frequency inverters SK 5xxE
TI 275900150
SK TU4-EIP
275 281 119
for frequency inverters SK 180E … SK 2xxE (IP55)
TI 275281119
plus:
SK TI4-TU-BUS
275 280 000
Bus connection unit (IP 55)
TI 275280000
SK TU4-EIP-C
275 281 169
for frequency inverters SK 180E … SK 2xxE (IP66)
TI 275281169
plus:
SK TI4-TU-BUS-C
275 280 500
Bus connection unit (IP 66)
TI 275280500
1. Introduction
1.1 General
Modern field bus systems, microcontrollers and communication networks have had a great influence
on automation systems and have resulted in greater flexibility, availability, and ultimately, a reduction
in costs.
The widespread use of PC-based control only became possible with the availability of field bus
systems. With increasing control unit performance, the classic field bus ultimately became the limiting
criterion for the entire system. It was therefore an obvious step to adapt Ethernet technology, which
provides high rates of data transmission in IT applications, to the field of automation.
EtherNet/IP™ (Ethernet Industrial Protocol) is an Ethernet-based field bus. This is an open standard,
which is administered by the users' organisation ODVA.
1.2 Bus modules
Specific bus modules are available as interfaces between the field bus system and the NORD system
bus or the NORD frequency inverter. A document exists for each module (Technical Information / Data
Sheet), which includes the technical data, as well as installation and configuration information
(www.nord.com).
Table 2: Hardware Overview
BU 2100 GB-2213 7
Page 8

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Fixed cable
Freely laid cable
Bending radius of cable
Minimum radius
5 x cable diameter
Minimum radius
10 x cable diameter
Correct
Incorrect
NOTICE
Potential equalisation
If earthing potential values are different, transient current may flow through shielding which is connected on both
sides. This may be a danger to electronic components. Differences in potential must be reduced by means of
adequate potential equalisation.
2. Bus Configuration
2.1 Topology
Up to 255 NORD bus modules can be integrated into an EtherNet/IP™ network. The network can be
configured either with a ring topology or as a linear bus. Configuration in a star topology is also
possible, however only with the use of a corresponding switch.
The length of cable between two neighbouring devices must not exceed100m.
Detailed information about the bus modules is contained in the relevant Technical Information / Data
Sheets.
2.2 Cable layout and shielding (EMC measures)
If EMC measures are not in place, high-frequency interference which is mainly caused by switching
processes or lightning often causes electronic components in the bus subscribers to be faulty and
error-free operation can no longer be ensured.
Appropriate shielding of the bus cable reduces electrical interference which can arise in an industrial
environment.
The best shielding qualities can be achieved with the following measures:
• Do not make cable connections shorter than 1 m between bus participants
• Avoid long connections between bus participants
• Shield the bus cable at both ends with large-area connection to the plug housing
• Avoid spur lines
• Avoid extensions to bus cables via plug connectors
Bus lines should be laid with a minimum spacing of 20 cm to other lines which carry a voltage higher
than 60 V. This applies to lines laid inside and outside of control cabinets.
Special attention should be paid to bending radii:
Fig. 1: Installation and cable laying information
8 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 9
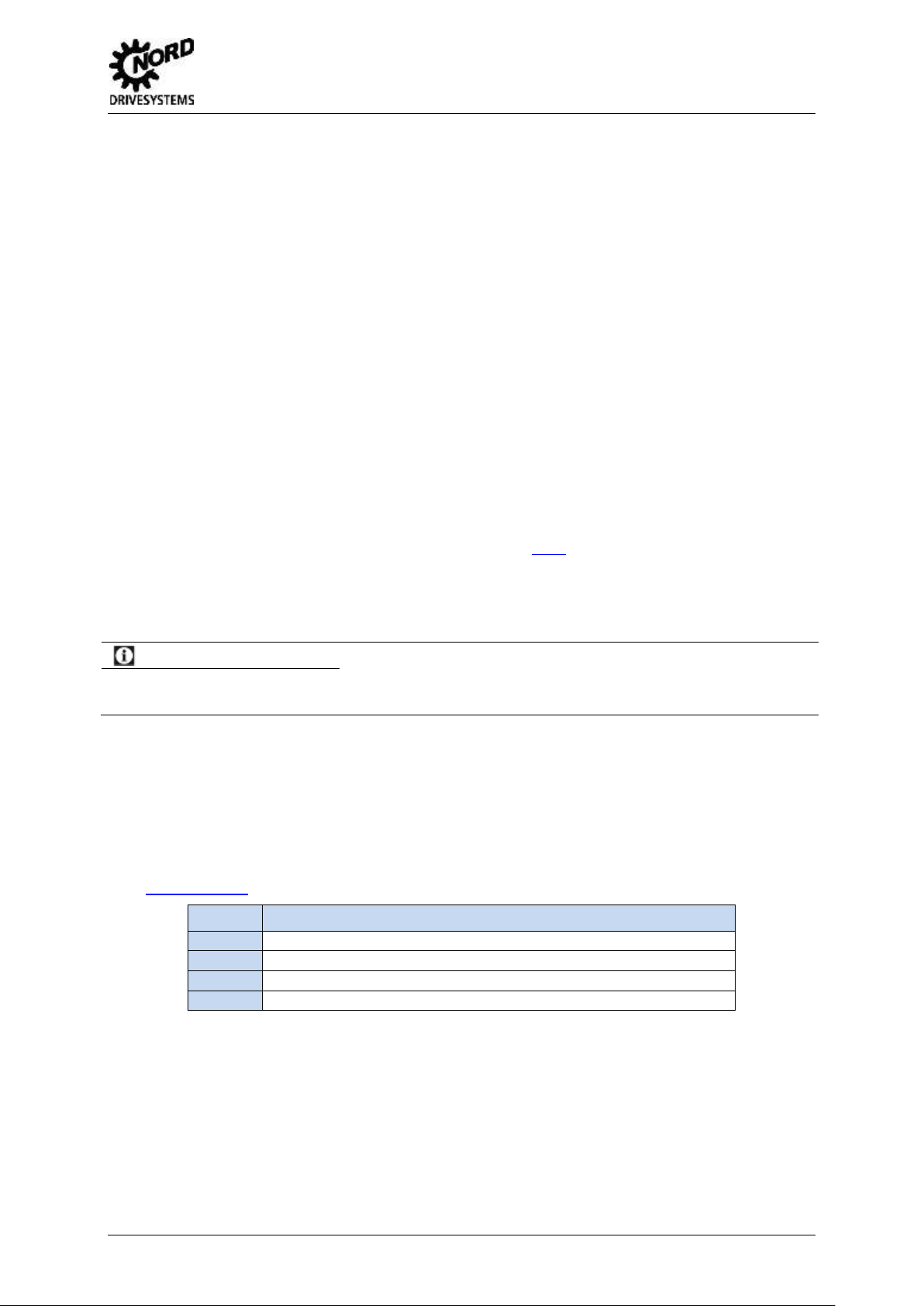
3 Configuration in the Bus System
1.
IP address via DHCP or BOOTUP mode
Select the addressing mode in the module parameter P165 and
then configure the module via Ethernet.
2.
IP address via module parameter
Carry out addressing via the module parameters P160, P161 and P164.
P165 must have the value "0" (default value).
3.
IP address via DIP switch
Alternatively:
The last byte of the IP address can be set via the DIP switches on the module. (refer to the
Technical Information or Data Sheet for the module ( LINK)
Information
Adoption of the address
All settings to the parameters P160 ... P165 and the DIP switches are only adopted after a bootup (restart of the
module).
Step
Action
1.
Install the eds file in the PLC interface
2.
Integrate the bus module from the PLC database into the project.
3.
Configure the assembly
4.
Configure the IP address
3. Configuration in the Bus System
3.1 Addressing
The addressing of the EtherNet/IP™ module (SK xUx-EIP-…) can be performed by three methods:
The resulting settings of the IP address and the sub-net mask can be read out in parameters P185
and P186.
3.2 Integration into the busmaster
In order to be able to use the devices in the bus system, they must be integrated into the PLC or the
project.
The necessary device data for the bus devices are saved in the electronic data sheets (eds files).
According to the module, various eds files are available. These can be downloaded free of charge
from www.nord.com.
BU 2100 GB-2213 9
Page 10

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Information
PLC Busmaster
By means of certification, NORD ensures that the bus system complies with the requirements which are made by
the bus interfaces.
Various planning tools or control systems are commercially available. NORD assumes that the user who
integrates the NORD bus module into the relevant control unit has the necessary knowledge of the bus system
and is sufficiently familiar with the use of the planning tool or PLC.
3.3 Remote Maintenance (in preparation)
With the aid of the NORD CON software it is possible to access the module via the Internet for
maintenance purposes. The data transfer is carried out with encryption via a secure connection.
Authentication is by means of a password, which can be saved in the module (Parameter P169).
The access rights for remote maintenance are assigned with DIP switch and range from "read only
parameter" (default) to "reading and writing access of parameters" and "remote control of the drive
unit".
(For details, please refer to the "Technical Information / Data Sheet for the bus module).
10 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 11

4 Communication and Protocol
4. Communication and Protocol
4.1 Processing of Process Data in the Frequency Inverter
In the process data area (PZD), control words and setpoints are transferred from the master to the
frequency inverter and in return, status words and actual values are sent from the frequency inverter
to the master. The structure of the PZD area is always the same in terms of the sequence of its
elements (words), however, dependent upon direction of data Master Slave / Slave Master, it is
described differently. Each word has a length of 16 Bit. To communicate 32 Bit values (e.g. position
values), 2 words are required (e.g setpoint 1 and setpoint 2).
BU 2100 GB-2213 11
Page 12

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Bit
Valu
e
Meaning
Remarks
0 0 Not ready for operation
Reverse with the brake ramp, with disconnection from supply at f=0Hz (OFF1)
1
Ready for operation
Frequency inverter ready for operation
1
0
Disable voltage
Cut off voltage; the inverter output voltage is switched off; the FI enters a state
where switching on is disabled. (OFF2)
1 Do not disable voltage
Operating condition OFF 2 is cancelled
2
0
Emergency Stop active
Quick stop with programmed quick stop time; with disconnection from supply at
f=0Hz; the FI switches to starting disabled condition (OFF3).
1 Emergency Stop not
active
Operating condition OFF 3 is cancelled
3 0 Disable operation
Cut off voltage; the inverter output voltage is switched off; the FI enters a state
where switching on is enabled.
1
Enable operation
The output voltage is enabled; ramp to the existing setpoint
4 0 Pulse not enabled
Ramp generator is set to zero; no disconnection from supply at f=0Hz; FI remains
in the operation enabled state.
1
Enable pulses
Enable ramp generator
5 0 Ramp not enabled
The setpoint currently provided by the ramp generator is "frozen" (frequency is
maintained).
1
Enable ramp
Enable setpoint on ramp generator
6 0 Setpoint not enabled
Selected setpoint value is set to zero on the ramp generator.
1
Enable setpoint
Selected ramp generator setpoint is activated.
7 0 No acknowledgement
With the switch from 0 to 1, errors which are no longer active are acknowledged.
1
Acknowledge error
(01)
Note: If a digital input has been programmed for the "ack.fault" function, this bit
must not permanently be set to 1 via the bus (otherwise, flank evaluation would
be prevented).
8 0
1
Start function 480, 11
Bus bit 8 from the control word is set. Only for SK 2xxE and SK 5xxE. For further
details of the function please refer to parameter P480.
9 0
1
Start function 480, 12
Bus bit 9 from the control word is set. Only for SK 2xxE and SK 5xxE. For further
details of the function please refer to parameter P480.
10 0 Control data invalid
The transmitted process data is invalid.
1
Control data valid
Valid process data is transferred from the master.
Note: In order for the transmitted setpoint to be valid, this bit must also be set
(setting: interface), even if only setpoint values are transmitted via the bus.
11 0
1
Rotation right is on
Rotational direction right (priority) ON*
12 0
1
Rotation left is on
Rotational direction left ON*
13
0/1
Reserved
Reserved
14
0/1
Parameter set Bit 0 ON
00 = Parameter set 1
01 = Parameter set 2
10 = Parameter set 3
11 = Parameter set 4
15
0/1
Parameter set Bit 1 ON
4.1.1 Control word (STW)
The control word (STW) is the first word transferred to the frequency inverter in the process data area
in an order telegram. For example, a control word "Ready for switch-on" corresponds to 047E
general the command "Standby" should be the first command which is transferred to the inverter.
(hex)
. In
* If Bit 12=0, then "Direction of rotation right ON" applies
Table 3: Control word (STW)
4.1.2 Status word (ZSW)
In the inverter response telegram, in the area of the process data the status word (ZSW) is transferred
as the first word. The meaning of the individual bits deviate for some types of devices.
12 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 13

4 Communication and Protocol
Bit
Valu
e
Meaning
Remarks
0 0 Not ready to start
1
Ready to start
Initialisation completed, charging relay ON, output voltage disabled
1 0 Not ready for operation
Causes: No command has been activated, fault is signaled, OFF2 or OFF3
activated, starting disabled state activated
1
Ready for operation
ON command activated, no faults present. The inverter can be started with the
command ENABLE OPERATION
2 0 Operation not enabled
1
Operation enabled
The output voltage is enabled; ramp to the existing setpoint
3 0 No error
1
Fault
Drive fault resulting in stoppage; this state is changed to starting disabled after
the fault has been successfully acknowledged
4 0 Voltage not enabled
OFF2 command applied
1
Voltage enabled
5 0
Emergency stop
OFF3 command applied
1 No emergency stop
6 0
Starting not disabled
1
Starting disabled
Switches first to OFF1, then to ready-to-start status
7 0 No warning
1
Warning active
Drive operation continues, no acknowledgement necessary
8 0 Setpoint not reached
Actual value does not match the setpoint (with posicon: failure to reach setpoint
position)
1
Setpoint reached
Actual value matches required setpoint (setpoint has been reached)
(with posicon: setpoint has been reached)
9 0 Bus control not active
Guidance on local device has been activated
1
Bus controller active
The master has been requested to assume guidance.
10 0
1
Start function 481.9
Bus bit 10 from the status word is set. For further details of function, please refer
to parameter P481.
11 0
1
Rotation right is on
Inverter output voltage is turning right
12 0
1
Rotation left is on
Inverter output voltage is turning left
13 0
1
Start function 481.10
Bus bit 13 from the status word is set. For further details of function, please refer
to parameter P481.
14
0/1
Parameter set Bit 0 ON
00 = Parameter set 1
01 = Parameter set 2
10 = Parameter set 3
11 = Parameter set 4
15
0/1
Parameter set Bit 1 ON
Table 4: Status word (ZSW)
4.1.3 Frequency inverter status machine
The frequency inverter passes through a status machine. The changes between various states are
triggered by the respective control commands in the process data control word. The actual status is
returned in the process data status word.
After switching on, the inverter is in switch-on disabled status. This status can only be ended by
transmitting the “Shut down (Off 1)” command.
The answer to a master telegram normally does not yet contain a reaction to the control command.
The controller must check the answers from the slaves as to whether the control command has been
carried out.
The following bits indicate the status of the frequency inverter:
BU 2100 GB-2213 13
Page 14

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Status
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Switch-on
disable
Emergency
stop
Disable
voltage
Fault
Operation
enabled
Standby
Ready for
switch-on
Not ready to start
0 X X 0 0 0 0
Starting disabled
1 X X 0 0 0 0
Ready to start
0 1 1 0 0 0 1
Activated
0 1 1 0 0 1 1
Operation enabled
0 1 1 0 1 1 1
Fault
0 X X 1 0 0 0
Error active
0 X X 1 1 1 1
Emergency stop
active
0 0 1 0 1 1 1
14 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 15

4 Communication and Protocol
Switch-on
disabled
Ready for
sw itch-on
Activated
Operation
enabled
Emergency stop
active
Error reaction
active
Error
From any device status
3 4 5 6 8
4 5
5
Not on standby
Switching on theinverter
Loading relay applied
Error
Error reaction complete
Bit0 = 0: Shut down
& Bit1 = 1: Enable voltage
& Bit2 = 1: Enable pulses
(xxxx x1xx xxxx x110)
Bit 3 = 0: Disable operation Bit0 = 1: Switch on
Bit3 = 1: Enable operation
Bit2 = 0: Emergency stop
Bit1 = 0: Disable voltage
v Bit2 = 0:Emergency stop
Priority of control commands:
1. Disable / enable voltage
2. Emergency stop
3. Shut down
4. Enable operation
5. Switch on
6. Disable operation
7. Reset error
Coding of status:
1: Bit 0 = 0
2: Bit 6 = 1
3: Bit 0 = 1
4: Bit 1 = 1
5: Bit 2 = 1
6: Bit 5 = 0
7: Bit 2 & Bit 3 = 1
8: Bit 3 = 1
3
5
2 3
3 64
2
2
1
2
3
7
8
f = 0 reached
(emergency stop complete)
Bit701
Error acknowledgement
Control bits
0. Standby / Shut down
1. Disable / enable voltage
2. Enable pulses / emergency stop
3. Disable / enable operation
4. Betriebsbedingung / HLGsperren
5. Enable / stop RUE
6. Enable / disable setpoint
7. Error acknowledgement (01)
10. Control data valid / invalid
11. Direction of rotation clockwise
12. Direction of rotation anticlockwise
14. Parameter set Bit 0
15. Parameter set Bit 1
4
5
6
Bit4 = 0: Move down emergency stop ramp and
remain in'Operation enabled'
Bit5 = 0: Hold frequency
Bit6 = 0: Setpoint = 0%
Bit0 = 0: Shut down
5
Bit3 = 1: Enable operation
& Bit0 = 1: Switch on
2
Internal status machine
2
Fig. 2: Status Machine of the Frequency Inverter
BU 2100 GB-2213 15
Page 16

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Type
Relevant parameter
Setpoint
P546 … P548
Actual value
P543 … P545
16384
105PValue
Frequency
16384
112PValue
Current
Direction of
transmission
Transmitted data (12 Byte)
1st word
2nd word
3rd word
4th word
5th word
6th word
Busmaster
bus module
Control word
32 bit setpoint
Setpoint 3
Setpoint 4
Setpoint 5
Busmaster
bus module
Status word
Actual value
1
32 bit actual value
Actual value
4
Actual value
5
4.1.4 Setpoint (SW) and Actual Value (IW)
The functions of the setpoint and the actual value are assigned via frequency inverter parameters:
The following three kinds of data transfer are possible:
Percentage transfer
The process value is transferred as an integer with a value range of -32768 to 32767 (8000 hex to
7FFF hex). The value 16384 (4000 HEX) corresponds to 100 %. The value -16384 (C000 hex) is
equal to -100 %.
For frequencies, the 100 % value corresponds to the FI parameter "Maximum Frequency" (P105) and
for currents, this is the FI parameter "Torque Current Limit" (P112) Frequencies and currents result
from the following formulae.
"Value" represents the 16Bit actual or setpoint value transmitted via the bus
Binary transmission
Inputs and outputs, as well as Digital In bits and Bus Out bits are processed bit-by-bit.
Transmission of positions
In the FI, positions have a value range of +/- 50000.000 rotations. A motor rotation can be divided into
a maximum of 1000 steps. This scaling is independent of the encoder which is used.
The 32 Bit value range is divided into a Low word and a High word, so that 2 setpoints or actual values
are required for the transfer. It does not matter which 2 words (except for the 1st word) are used for
this.
Table 5: Depiction of 32Bit setpoint/actual values
It is also possible to only transmit the Low component of the position. This results in a limited value
range from +32,767 to -32,768 rotations. This value range can be extended with the aid of the gear
ratio factor (P607 & P608). However, it must be noted that there is an according reduction in the
resolution.
4.1.5 Example: "Switch on and off + setpoint"
In this example, a frequency inverter is controlled with a setpoint (setpoint frequency). The frequency
inverter responds with an actual value (actual frequency). The "maximum frequency" is parameterised
to 50 Hz.
Relevant parameters:
16 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 17

4 Communication and Protocol
Parameter
Setting value
Meaning
Parameter number
SK 180E …
SK 2xxE,
SK 54xE
SK 500E …
SK 535E
Maximum frequency
50.0
50 Hz
P105
P105
Actual bus value 1
1
Actual frequency
P543[-01]
P543
Function Bus setpoint 1
1
Setpoint frequency
P546[-01]
P546
Order to FI
Response from FI
Control word
Setpoint 1
Status word
Actual value 1 Explanation
- - -
- - -
0000h
0000h
- - -
- - -
xx40h
0000h
Switch-on of the mains voltage to the FI
047Eh
0000h
xx31h
0000h
Sets the FI in the status "Standby"
047Fh
2000h
xx37h
2000h
Sets the FI to the status "Operation
enabled" with the setpoint 50%.
The FI is enabled, the motor is supplied with current and rotates with a frequency of 25 Hz.
0047Eh
2000h
xx31h
0000h
Sets the FI to "Standby" status. The
motor runs on its parameterised ramp up
to speed 0 and then the power is
switched off.
The FI is locked again and the motor is without current.
047Fh
1000h
xx37h
1000h
Sets the FI to the status "Operation
enabled" with the setpoint 25 %.
The FI is enabled, the motor is supplied with current and rotates with a frequency of 12.5 Hz.
Instance
Length
(Byte)
Meaning*
Device class
(SK ...)
Data length
100
12
STW + SW1 + SW2 + SW3 + SW4 + SW5
TU3-EIP,
TU4-EIP
Fixed
101
12
ZSW + IW1 + IW2 + IW3 + IW4 + IW5
TU3-EIP,
TU4-EIP
Fixed
110
50
Bus module outputs + four FIs
Structure for each FI:
STW + SW1 + SW2 + SW3 + SW4 + SW5
TU4-EIP
Variable
111
50
Module inputs + four FIs
Structure for each FI:
ZSW + IW1 + IW2 + IW3 + IW4 + IW5
TU4-EIP
Variable
* STW = Control word, ZSW = Status word, SW = Setpoint, IW = Actual value
Table 6: Example: "Switch FI on and off + setpoint"
4.2 Transfer of Data in the Bus System (I/O connections)
Process data is exchanged between the SK xUx-EIP bus module and the EtherNet/IP Master via I/O
connections. An "Exclusive Owner" connection can be opened, through which the setpoints and actual
values can be exchanged. In addition, two "Listen Only" connections can be opened, through which
the actual values of the FI can be read.
4.2.1 Assembly
Only process data, but no protocol information can be transmitted via the I/O Message Object.
Assignment of the relevant setpoints and actual values is performed via the Assembly Object. The
following table lists several pre-defined configurations (Instances).
Table 7: Assembly Instance
BU 2100 GB-2213 17
Page 18

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
• A frequency inverter with 3 setpoints + Bus I/O:
Length: 10 Bytes
• A frequency inverter with 5 setpoints + Bus I/O:
Length: 14 Bytes
• Two frequency inverters with 5 setpoints + Bus I/O:
Length: 26 Bytes
High byte
Low byte
Bit 15
Bit 14 to 8
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Valid Flag
Reserve
DIN8
DIN7
DIN6
DIN5
DIN4
DIN3
DIN2
DIN1
High byte
Low byte
Bit 15 to 8
Bit 7
Bit 6
Bit 5
Bit 4
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Reserve
Reserve
DO2
DO1
All parameters of the bus module and the
connected frequency inverter can be accessed
via EtherNet/IP™. For this, parameter data are
exchanged between the Master and the bus
module (SK xUx-EIP) via an Explicit Messaging
Connection.
The frequency inverters which are connected to
the bus module are accessed via various
classes.
EtherNet/IP™
Class
Accessed device
100
Bus module
101
FI 1
102
FI 2
103
FI 3
104
FI 4
For the instances 110 / 111 the transferred data length may be truncated in the PLC. The missing
bytes are also deducted from the end of the protocol
Digital IOs (only SK TU4-EIP)
The SK TU4-EIP is equipped with 8 digital inputs and 2 digital outputs. Both can be accessed via the
Assembly Instance 110 and 111.
Inputs (status value)
A 16 bit word is transferred. The 8 inputs are located in the Low byte and the High byte on Bit 15
contains the "Valid Flag" for the inputs. The transferred inputs are only valid if this flag is set to 1.
Table 8: Input Structure in Assembly Instance 111
Outputs (Setpoint)
The SK TU4-EIP is provided with 2 digital 24V outputs. The outputs can be set with a 16 bit word.
Table 9: Output Structure in Assembly Instance 110
4.3 Parameter Transfer (Explicit Messages)
18 BU 2100 GB-2213
Table 10: Assignent of Devices to an EtherNet/IP™ Class
Page 19

4 Communication and Protocol
FI parameter number to EtherNet/IP™
EtherNet/IP™ to FI parameter number
Class
= Table 10
Parameter number
= Attribute
Attribute
= FI parameter number
Sub-index
= Instance
Instance
= Sub-index
Parameter set
Bit 1
Bit 0
Instance
1
0 0 0
2
0 1 1
3
1 0 2
4
1 1 3
array
…
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Instance
[-01]
0 0 0 0 0 [-02]
0 0 0 1 1 [-03]
0 0 1 0 2 [-04]
0 0 1 1 3 [-05]
0 1 0 0 4 … …
array
Parameter set
array
Parameter set
…
Bit 3
Bit 2
Bit 1
Bit 0
Instance
[-01] 1 0 0 0 0 0 [-01] 2 0 0 0 1 1 [-01] 3 0 0 1 0
2
[-01] 4 0 0 1 1
3
[-02] 1 0 1 0 0 4 [-02] 2 0 1 0 1
5
… …
…
Device
Parameter
array
Parameter set
Class
Attribute
Instance
Inverter 1
P103
--
1
101
103
0
Inverter 4
P103
--
3
104
103
2
Inverter 3
P465
[-01]
--
103
465
0
Inverter 3
P465
[-02]
--
103
465
1
Inverter 2
P400
[-01]
3
102
400
2
Inverter 2
P400
[-03]
1
102
400
12
Inverter 2
P400
[-03]
3
102
400
14
Coding of the FI parameters into the EtherNet/IP™ format is performed as follows:
Formation of the instance
The formation of the instance depends on the structure of the relevant parameter.
The following applies for parameter set-dependent parameters without an array (e.g. P103):
The following applies for parameters which do not depend on a parameter set, but which have an
array (e.g.P465):
The following applies for parameters which depend on a parameter set and also have an array (e.g.
P400):
Examples
BU 2100 GB-2213 19
Page 20

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Module type
Parameter
SK TU3-EIP
P513
SK xU4-EIP-…
P151
4.4 Timeout monitoring
The Ethernet monitors the data traffic by means of the bus system watchdog. Monitoring by the
frequency inverter is also possible.
Monitoring by the inverter is is triggered if the process data contact is interrupted or the process data
is transferred with an invalid control word (Bit10 in control word = 0). This function is activated when
the first valid process data telegram is received.
20 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 21

5 Parameter
Information
Deviating Parameter Settings
According to the type or equipment of the frequency inverter, individual parameters may be different or restricted.
Information
Control terminal functions
When activated, the functions block voltage, quick stop, remote control and cancel error, are available at the
(local) control terminals. To operate the drive, a High signal must be present on the digital inputs being used
before the drive can be enabled.
Parameter
{Factory seting}
Setting value / Description / Note
Device
Type
P150
Set Relay
(Set relay)
SK EB…
SK TU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 4
{ 0 }
The switching statuses of the digital outputs can be modified.
0 =
Via Bus:
All digital outputs can be controlled via the system bus: the
fucntions are defined in the frequency inverter (P480).
1 =
Outputs Off:
All digital outputs are Off (Low = 0V).
2 =
Output 1 On (DO1):
The digital output DO1 is set to "High" (active); digital
output DO2 remains switched off.
3 =
Output 2 On (DO2):
The digital output DO2 is set to "High" (active); digital
output DO1 remains switched off.
4 =
Outputs 1 and 2 On:
All digital outputs are set to "High" (active)
P151
External Bus Timeout
(Timeout for external bus)
SK xU4-…
16 bit
0 ... 32767 ms
{ 0 }
Monitoring function of the active bus technology unit. Following receipt of a valid telegram, the
next one must arrive within the set period. Otherwise the technology unit or the connected
inverter reports an error and switches off with the error message E010 / E10.3 >Bus Time Out<.
0 =
Off:
Monitoring is switched off.
5. Parameter
In order to operate the frequency inverter on the bus system, some parameter settings must be made
on the bus interface and on the frequency inverter.
The frequency inverter can always be parameterised. The control source can be selected with
parameter P509 (control word) and parameter P510 (setpoint source). The telegram down time P513
can be selected depending on the bus system.
5.1 Bus - Module Parameters
Standard Bus Parameter (P15x)
BU 2100 GB-2213 21
Page 22

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
P152
Factory Setting
(Load factory settings)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 1
{ 0 }
With the selection of the relevant value anc confirmation with the OK key, the selected parameter
range is set to the factory setting. Once the setting has been made, the value of the parameter
automatically returns to 0.
0 =
No change: Does not change the parameterisation.
1 =
Loading the factory settings: The complete parameterisation of the FI reverts to the
factory setting. All originally parameterised data are lost.
P153 ... [-01]
... [-02]
Min. System Bus Cycle
(Minimum cycle time of system bus)
SK EB…
SK xU4-…
16 bit
0 ... 250.00 ms
{ [-01] = 10 }
{ [-02] = 5 }
In order to reduce the bus load on the system bus, the transmission cycle time of the Service
Data Objects and Process Data Objects can be extended.
[-01] = SDO Inhibit Time
[-02] = PDO Inhibit Time
P154 ... [-01]
... [-02]
TB-IO Access
(Access to technology unit IOs)
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 5
{ [-01] = 0 }
{ [-02] = 0 }
Assignment of the writing and reading rights of the connected frequency inverter to the inputs and
outputs of the technology unit.
[-01] = Inputs
[-02] = Outputs
0 =
OFF, no effect
1 =
Broadcast, all FIs read the inputs
2 =
FI 1, reads and writes to the IOs
3 =
FI 2, reads and writes to the IOs
4 =
FI 3, reads and writes to the IOs
5 =
FI 4, reads and writes to the IOs
Parameter
{Factory seting}
Setting value / Description / Note
Device
Type
P160 ... [-01]
…
... [-04]
IP Address
(IP Address)
SK TU3-EIP
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 255
{ [-01] = 192 }
{ [-02] = 168 }
{ [-03] = 1 }
{ [-04] = 0 }
Parameterised IP address consisting of four bytes.
The settings are only adopted after a restart of the module.
[-01] = IP High (NET-ID)
[-02] = IP (NET-ID)
[-03] = IP (NET-ID)
[-04] = IP Lo (Host)
Information
IP Lo (Host)
A value "0" in array [-04] means that the setting for this array has been made with the module
DIP switches.
Specific Bus Parameters (P16x)
22 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 23

5 Parameter
P161 ... [-01]
…
... [-04]
IP Sub-net Mask
(IP Sub-net mask)
SK TU3-EIP
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 255
{ [-01] = 255 }
{ [-02] = 255 }
{ [-03] = 255 }
{ [-04] = 0 }
Parameterised IP sub-net mask consisting of four bytes.
The settings are only adopted after a restart of the module.
[-01] = IP Sub 1
[-02] = IP SUB 2
[-03] = IP Sub 3
[-04] = IP SUB 4
P164 ... [-01]
…
... [-04]
IP Gateway
(IP Gateway)
SK TU3-EIP
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 255
{ [-01] = 192 }
{ [-02] = 168 }
{ [-03] = 1 }
{ [-04] = 100 }
Parameterised IP address of the gateway consisting of four bytes.
The setting is only adopted after a restart of the module.
[-01] = IP High (Net-ID)
[-02] = IP (Net-ID)
[-03] = IP (Net-ID)
[-04] = IP Lo (Host)
P165
Addressing Mode
(Addressing mode)
SK TU3-EIP
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 2
{ 0 }
Setting of the addressing mode of the module
0 =
Fixed (P160/DIP):
Addressing is performed via the parameters or DIP
switches of the module.
1 =
BOOTP:
Addressing is performed via the BOOTUP mode.
2 =
DHCP:
Addressing is performed via DHCP.
P166
PZD Transmission format
(Process data transmission format)
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 1
{ 0 }
Adjustment of the transmission format of the process data.
0 =
32 bit Header+Status:
PZD telegram with process and header data.
1 =
Modeless Format:
PZD telegram with process data only.
Information
Modeless Format
The Modeless format (setting "1") can only be used for the Assembly Instances 110 and 111
(variable data length). In all other instances (100 and 101) the data length is fixed and contains
the 32 bit header.
BU 2100 GB-2213 23
Page 24

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
P167 ... [-01]
…
... [-20]
Password
(Password)
SK TU3-EIP
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
45 ... 122 ASCii
{ 0 }
Setting of a password to protect access to the module via remote maintenance. Up to 20
characters (numbers, letters and special characters) Sonderzeichen) can be entered in ASCii
code in the range from 45
dec
– 122
dec
.
Information
The parameter has no function
Integration of the parameter into the system is being prepared. At present the parameter does
not have a function.
Parameter
Setting value / Description / Note
Device
Type
P170 ... [-01]
... [-02]
Present Error
(Present Error)
SK EB…
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 9999
Error present in the bus module. The error message is reset when the supply voltage is switched
off.
[-01] = Present module error
[-02] = Last error message from module
For a list of possible error messages, please refer to the section "Error Monitoring and
Error Messages".
P171 ... [-01]
…
... [-03]
Software Version
(Software Version/ Revision)
SK EB…
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
16 bit
0 ... 9999
This parameter shows the software and revision numbers in the module. Array [-03] provides
information about any special versions of the hardware or software. A zero stands for the
standard version.
[-01] = Software version 1:
"Version number": (E.g.: V1.0)
[-02] = Software version 2:
"Revision number": (E.g.: R1)
[-03] = Software version 3:
"Special version": (E.g.: 0)
General Bus InformationParameters (P17x)
24 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 25

5 Parameter
P172
Configuration level
(Configuration level)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
SK EB…
16 bit
0 ... 4
Indicates the module version which is used.
0 =
CU4 (internal):
Internal module for decentralised frequency inverters
1 =
TU4 (external):
External module (IP55 / IP66)
2 =
TU3:
Bus module for FI series SK 5xxE
3=
TU3 (with DIP):
Module with DIP switches for FI series SK 5xxE
4=
EBIOE-2:
Decentralised module IP20
BU 2100 GB-2213 25
Page 26

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
P173
Module Status
(Module status)
SK EB…
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
16 bit
0 ... 0xFFFF
Operating status of the module.
Bit 0 =
Module ready for operation*
Bit 1 =
Cyclic communication*
Bit 2 =
Timeout by Ethernet bus*
Bit 3 =
Timeout (P151/P513)*
Bit 4 =
No communication with ASIC*
Bit 5 =
General configuration error*
Bit 6 =
System bus "BUS Warning"**
Bit 7 =
System bus "BUS OFF"**
Bit 8 =
FI 1 status
Bit 9 =
FI 1 status
Bit 10 =
FI 2 status**
Bit 11 =
FI 2 status**
Bit 12 =
FI 3 status**
Bit 13 =
FI 3 status**
Bit 14 =
FI 4 status**
Bit 15 =
FI 4 status**
* Except for ...IOE modules
** Except for SK TU3 versions
THe status of the frequency inverter is determined from a High bit and a Low bit: e.g. FI
1: High bit: Bit 9; low Bit: Bit 8
High Bit
Low Bit
Meaning
0 0 FI is offline
0 1 FI is not supported
1 0 FI is online
1 1 Bus error (PDO or SDO monitoring)
P174
Status of digital input
(Status of the digital inputs)
SK EB…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 0xFF
Image of the switching status of the digital inputs of the module.
Bit 0 =
Digital input 1
Bit 1 =
Digital input 2
Bit 2 =
Digital input 3*
Bit 3 =
Digital input 4*
Bit 4 =
Digital input 5**
Bit 5 =
Digital input 6**
Bit 6 =
Digital input 7**
Bit 7 =
Digital input 8**
* Except for ... CU4- modules
** Only SK TU4-ECT, SK TU4-EIP, SK TU4-PNT and SK TU4-POL
P175
Relay Status
(Switching status of relay)
SK EB…
SK TU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 3
Image of the switching status of the relay outputs of the module.
Bit 0 =
Relay 1
Bit 1 =
Relay 2
26 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 27

5 Parameter
P176 ... [-01]
…
... [-25]
Process Data Bus In
(Process data Bus In)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
16 bit
-32768 ... 32767
Bus data received from Bus Master / controller
[-01] = Bus module outputs*
[-02] = Control word FI 1
[-03] = Setpoint 1 for FI 1
[-04] = Setpoint 2 for FI 1
[-05] = Setpoint 3 for FI 1
[-06] = Setpoint 4 for FI 1
[-07] = Setpoint 5 for FI 1
[-08] = Control word FI 2*
[-09] = Setpoint 1 for FI 2*
[-10] = Setpoint 2 for FI 2*
[-11] = Setpoint 3 for FI 2*
[-12] = Setpoint 4 for FI 2*
[-13] = Setpoint 5 for FI 2*
[-14] = Control word FI 3*
[-15] = Setpoint 1 for FI 3*
[-16] = Setpoint 2 for FI 3*
[-17] = Setpoint 3 for FI 3*
[-18] = Setpoint 4 for FI 3*
[-19] = Setpoint 5 for FI 3*
[-20] = Control word FI 4*
[-21] = Setpoint 1 for FI 4*
[-22] = Setpoint 2 for FI 4*
[-23] = Setpoint 3 for FI 4*
[-24] = Setpoint 4 for FI 4*
[-25] = Setpoint 5 for FI 4*
* Except for SK TU3 versions
Information
Control data via UDP or TCP/IP
Process data via UDP or TCP/IP are only displayed if there is no EtherNet/IP master.
P177 ... [-01]
…
... [-25]
Process Data Bus Out
(Process data Bus Out)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
16 bit
-32768 ... 32767
Bus data sent from Bus Master / Controller.
[-01] = Bus module inputs*
[-02] = Status word FI 1
[-03] = Actual value 1 from FI 1
[-04] = Actual value 2 from FI 1
[-05] = Actual value 3 from FI 1
[-06] = Actual value 4 from FI 1
[-07] = Actual value 5 from FI 1
[-08] = Status word FI 2*
[-09] = Actual value 1 from FI 2*
[-10] = Actual value 2 from FI 2*
[-11] = Actual value 3 from FI 2*
[-12] = Actual value 4 from FI 2*
[-13] = Actual value 5 from FI 2*
[-14] = Status word FI 3*
[-15] = Actual value 1 from FI 3*
[-16] = Actual value 2 from FI 3*
[-17] = Actual value 3 from FI 3*
[-18] = Actual value 4 from FI 3*
[-19] = Actual value 5 from FI 3*
[-20] = Status word FI 4*
[-21] = Actual value 1 for FI 4*
[-22] = Actual value 2 for FI 4*
[-23] = Actual value 3 for FI 4*
[-24] = Actual value 4 for FI 4*
[-25] = Actual value 5 for FI 4*
* Except for SK TU3 versions
BU 2100 GB-2213 27
Page 28

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Parameter
Setting value / Description / Note
Device
Type
P180 ... [-01]
... [-02]
Active Assembly
(Active Assembly)
SK xU4-EIP
8 bit
0 ... 255
Indicates the active assembly object
[-01] = Consumer Assembly
[-02] = Producer Assembly
P181 ... [-01]
…
... [-06]
MAC Adddress
(MAC Address)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 0xFF
Displays the Ethernet (MAC) address (unique identification of module)
[-01] … [-03] = NORD manufacturer ID
F0 . 5F . 5A
[-04] … [-06] = NORD free address range
xx . xx . xx
P185 ... [-01]
…
... [-04]
Present IP Address
(Present IP Address)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 255
Displays the present IP address
[-01] … [-04] = IP Address
xxx . xxx . xxx . xxx
P186 ... [-01]
…
... [-04]
Present IP Sub-net Mask
(Present IP Sub-net mask)
SK TU3-…
SK xU4-…
8 bit
0 ... 255
Displays the present IP sub-net mask.
[-01] … [-04] = IP Sub-net mask
xxx . xxx . xxx . xxx
Parameter
Parameter name
Recommended setting
Remarks
SK 5xxE
SK 180E … SK 2xxE
P120
Option monitoring
Not available, or
not relevant for
SK TU3 modules
{1} = Auto
P509
Source Control Word
{8} = Ethernet TU
{3} = System bus
P510
Setpoint source
{0} = Auto
{0} = Auto
P513
Telegram timeout
{0.5} = 0.5s
{0.0} = Off
Do not set this value too low
P543
Actual BUS value
According to the
function:
According to the
function:
SK 54xE and SK 180E …
SK 2xxE: up to 5 actual
values each
P544
Actual BUS value 2
According to the
function:
Not available
Only SK 500E … 535E
Bus-specific Information Parameters (P18x)
m
5.2 Frequency Inverter Parameters
Various parameters of the frequency inverter are relevant for the commissioning of the bus system or
the frequency inverter in the bus system and may need to be changed.
A detailed description of the inverter parameters can be found in the manual for the relevant frequency
inverter.
28 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 29

5 Parameter
Parameter
Parameter name
Recommended setting
Remarks
SK 5xxE
SK 180E … SK 2xxE
P545
Actual BUS value 3
According to the
function:
Not available
Only SK 500E … 535E
P546
Function Setpoint BUS
value
According to the
function:
According to the
function:
SK 54xE and SK 180E …
SK 2xxE: up to 5 setpoints
each
P547
Function BUS setpoint
2
According to the
function:
Not available
Only SK 500E … 535E
P548
Function BUS setpoint
3
According to the
function:
Not available
Only SK 500E … 535E
Info parameters
P700
Present Operating
status
Fault / Warnings / Reason for
starting disabled condition
P701
Last fault
P740
Process data BUS In
P741
Process data BUS Out
P742
Data base version
P744
Configuration
Not relevant
P745
Module version
Not available
P746
Module status
Not available
Possible values
Bit
Meaning
0
Module initialised
1
Cyclical communication
2
Vacant
3
Vacant
4
Error 1
5
Error 2
6
Error 3
7
Vacant
8-15
Module number
EtherNet/IP = 23
Table of Errors
Error
Meaning
3 2 1 0 0 0 No error
0 0 1
No communication
with ASIC
0 1 0
Bus Timeout
0 1 1
P513 timeout
1 0 0
IP already assigned
1 0 1
General config. error
1 1 0
No Ethernet cable
1 1 1
Communication error
P748
CANopen status
Not relevant for
SK TU3 modules
System bus status
Error messages
Error messages from the module - present errors or archived messages relating to the last error - can
be read out via the module parameter (P170). The error messages are lost if the module is switched
off.
BU 2100 GB-2213 29
Page 30

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Error
Meaning
Remarks
1000
EEPROM error
EMC fault, module defective
1020
Timeout
via P151/P513 monitoring
1030
System bus BUS OFF
No 24V supply to the bus, connections not correct
5501
DIP switch error
The DIP switches (IP address) could not be read correctly
5600 …
5609
Internal error
Module not ready
5610
General network error
5611
Ethernet Watchdog timeout
5612
Bus cable fault
Bus cable connection interrupted
5613
IP address error
IP address of the module has been doubly assigned
5640
MAC address error
Error
(E010)
Meaning
Remarks
10.0
Connection error
Contact to SK xU4 lost
10.1
ASIC errors
Communication to EtherNet/IP - ASIC lost
• Switch-off of the supply voltage
10.2
Ethernet/IP Watchdog timeout
Telegram transfer error
• Check the connections and links, program sequence and
Bus Master
10.3
Timeout by P151/P513
Telegram transfer error
• Check the connections and links
• Check the Watchdog time
10.4
IP address error
IP address of the module has been doubly assigned
10.5
Internal error
Module not ready
10.6
Bus cable fault
Bus cable connection interrupted
10.8
The connection between the inverter
and the module had a timeout
Only SK TU3 module
10.9
The connection between the inverter
and the module had a timeout
Only SK xU4 module
Errors which occur in relation to the module are depicted as follows in the error memory of the
frequency inverter (P700 / P701).
30 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 31

6 Additional information
Information
Reason for return
If possible, the reason for returning the component/device should be stated. If necessary, at least one contact for
queries should be stated.
This is important in order to keep repair times as short and efficient as possible.
On request you can also obtain a suitable return goods voucher from Getriebebau NORD.
Unless otherwise agreed, the device is reset to the factory settings after inspection or repair.
ATTENTION
Possible Consequential Damage
In order to rule out the possibility that the cause of a device fault is due to an optional module, the connected
optional modules should also be returned in case of a fault.
6. Additional information
6.1 Repair information
If you contact our technical support, please have the precise device type (rating plate/display),
accessories and/or options, the software version used (P707) and the series number (name plate) at
hand.
6.1.1 Repairs
The device must be sent to the following address if it needs repairing:
NORD Electronic DRIVESYSTEMS GmbH
Tjüchkampstraße 37
26605 Aurich, Germany
For queries about repairs, please contact:
Getriebebau NORD GmbH & Co. KG
Tel.: 04532 / 289-2515
Fax: 04532 / 289-2555
If a frequency inverter is sent in for repair, no liability can be accepted for any added components, e.g.
such as mains cables, potentiometer, external displays, etc.!
Please remove all non-original parts from the frequency inverter.
6.1.2 Internet information
You can also find the comprehensive manual in German and in English on our Internet site.
www.nord.com
BU 2100 GB-2213 31
Page 32

EtherNet/IP Bus module – Supplementary manual options for NORD - Frequency Inverters
Software
Name
Software
Name
EDS File
Electronic Data Sheet (Object data file)
NORD CON
Parameterisation and diagnostic software
Document
Name
Document
Name
BU 0000
Description of the NORD CON software
TI 275900150
Technical Information / Data Sheet SK TU3-EIP
BU 0040
ParameterBox manual
TI 275281119
Technical Information / Data Sheet SK TU4-EIP
BU 0500
SK 500E - SK 535E frequency inverter manual
TI 275281169
Technical Information / Data Sheet SK TU4-EIP-C
BU 0505
SK 54xE frequency inverter manual
BU 0180
SK 180E / SK 190E frequency inverter manual
BU 0200
SK 2xxE frequency inverter manual
6.2 Furhter Documentation and Software
(www.nord.com)
32 BU 2100 GB-2213
Page 33

Key word index
Key word index
A
Active assembly (P180) ...................................... 28
Address ............................................................... 31
Addressing Mode (P165) .................................... 23
Min.system bus cycle (P153) ............................. 22
Module IOs ......................................................... 18
Module status (P173) ......................................... 26
P
Assembly ............................................................ 17
B
Bus-specific Information Parameters (P18x) ...... 28
C
Configuration level (P172) .................................. 25
Control word ....................................................... 12
E
eds File ................................................................. 9
Electronic Data Sheet ........................................... 9
EMC ...................................................................... 8
F
Factory settings (P152)....................................... 22
G
General bus information parameters (P18x) ...... 24
I
I/O Connections .................................................. 17
Internet ................................................................ 31
IP address (P160) ............................................... 22
IP Gateway (P164) ............................................. 23
IP sub-net mask (P161) ...................................... 23
L
Load factory setting ............................................ 22
M
MAC address (P181) .......................................... 28
Maintenance ....................................................... 31
Parameter .......................................................... 21
Password (P167) ............................................... 24
Present error (P170) .......................................... 24
Present IP address (P185) ................................ 28
Present IP sub-net mask (P186) ........................ 28
Process data Bus In (P176) ............................... 27
Process data bus Out (P177) ............................ 27
PZD transmission format (P166) ....................... 23
Q
Queries .............................................................. 31
R
Relay status (P175) ........................................... 26
Repairs ............................................................... 31
S
Service ............................................................... 31
Set relay (P150) ................................................. 21
Shielding .............................................................. 8
Software version (P171) .................................... 24
Specific Bus Parameters (P16x) ........................ 22
Standard Bus Parameter (P15x) ........................ 21
Status of digital input (P174) .............................. 26
Status word ........................................................ 12
T
TB-IO access (P154) ......................................... 22
Timeout for external bus (P151) ........................ 21
BU 2100 GB-2213 33
Page 34

6082102 / 2213
 Loading...
Loading...