Page 1

Page 2
Nokia M10
ADSL ROUTER
User’s Manual
C33539.20 B0
DRAFT
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
Page 3

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
COPYRIGHT Nokia Telecommunications Oy 1999
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be copied, distributed, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval
system, or translated into any human or computer language without the prior written permission
of Nokia Telecommunications Oy.
The manufacturer has made every effort to ensure that the instructions contained in the
documents are adequate and free of errors and omissions. The manufacturer will, if necessary,
explain issues which may not be covered by the documents. The manufacturer’s liability for any
errors in the documents is limited to the correction of errors and the aforementioned advisory
services.
The documents have been prepared to be used by professional and properly trained personnel,
and the customer assumes full responsibility when using them.The manufacturer welcomes
customer comments as part of the process of continual development and improvement of the
documentation in the best way possible from the user’s viewpoint. Please submit your comments
to the nearest Nokia sales representative.
NOKIA is a registered trademark of Nokia Corporation.
Any other trademarks mentioned in the documents are the property of their respective owners.
ii
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 4

Document History
Document Date Comment
C33539002SE_00 17 Dec 1998 First approved version
C33539002SE_A0
DRAFT
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
iii
Page 5

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
iv
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 6

Contents
Chapter 1
DRAFT
Introduction to Nokia M10 1-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 2
Applications and features 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1 Applications 2-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.1 Internet access using NAPT router 2-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.2 Remote work 2-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.1.3 LAN interconnection using M10 as a bridge 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . .
2.2 Functionality 2-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Routing 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bridging 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Network Address Port Translation 2-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dynamic Host Configuration 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ATM and ADSL 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Payload encapsulations 2-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2.3 Management 2-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 3
Interfaces and indicator lights 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.1 10Base-T Ethernet interface 3-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.2 ADSL line interface 3-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3.3 Front panel indicator lights 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
STA indicator 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DSL indicator (ADSL line status) 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LAN indicators 3-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
v
Page 7

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Chapter 4
Installation 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.1 Internet access (NAPT router) 4-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 1a: Connect cables (data services only) 4-3. . . . . . . . . .
Step 1b: Connect cables (data and telephone services) 4-3. .
Step 2: Switch power on 4-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 3: Turn on your PC 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 4a: Connect to M10 with a Web browser (password
disabled) 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 4b: Connect to M10 with a Web browser (password
enabled) 4-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 5a: Configure M10 (password disabled) 4-4. . . . . . . . .
Step 5b: Configure M10 (password enabled) 4-5. . . . . . . . .
Step 6: Surf 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.2 Remote work (Basic router) 4-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 1: Connect cables 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 2: Turn on your PC and start the terminal software 4-8.
Step 3: Configure the M10 4-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 4: Connect your M10 to the network 4-14. . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 5: Check that the connection works 4-14. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.3 LAN interconnection (Basic Ethernet bridge) 4-14. . . . . . . . .
Step 1: Connect cables 4-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 2: Turn on your PC and start the terminal software 4-15.
Step 3: Configure the M10 using CLI commands 4-15. . . . . .
Step 4: Connect your M10 to the network 4-20. . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 5: Check that the connection works 4-21. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.4 Default settings 4-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4.5 Troubleshooting 4-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Is the ADSL connection to the remote network working? 4-24
Is the Ethernet connection working? 4-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Is the ATM connection working? 4-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Is the PPP connection working? 4-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 5
Management 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1 Browser management 5-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.1 Opening a connection 5-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.2 QuickConfig page 5-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
QuickStart settings 5-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
vi
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 8

DRAFT
PAP and CHAP Setup settings 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PPP Connection Manager settings 5-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.3 Router page 5-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering router settings 5-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.4 Bridge page 5-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering bridge settings 5-11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.5 ATM page 5-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering ATM settings 5-12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuring ATM channels 5-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PPP over ATM (VC-muxed) 5-13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Other encapsulations 5-15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.6 NAT pinhole page 5-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pinhole configuration example 5-17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.7 SNMP page 5-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering SNMP settings 5-19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.1.8 Monitor page 5-20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2 Command line interface 5-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.1 Starting and ending a CLI session 5-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting from telnet 5-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting from the console port 5-21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Logging in 5-22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Entering commands in Nokia M10 CLI 5-22. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ending a CLI session 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Using the CLI help facility 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Saving settings 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.2 The Root command hierarchy 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Root prompt 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Root command shortcuts 5-24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Root commands 5-25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.2.3 Config command hierarchy 5-40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Config prompt 5-41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Navigating the Config hierarchy 5-41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Displaying current settings 5-43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stepping through M10 configuration 5-43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Validating your configuration 5-44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Config command reference 5-44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System settings 5-45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
CLI preferences 5-47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ATM settings 5-48. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TCP/IP settings 5-52. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Static route settings 5-68. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
vii
Page 9

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
BNCP setting 5-72. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DHCP settings 5-73. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Domain Name System settings 5-75. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Bridging settings 5-76. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DMT (ADSL) setting 5-78. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PPP settings 5-79. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SNMP settings 5-85. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pinhole settings 5-87. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Integrated server settings 5-89. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.3 SNMP 5-90. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5.4 Software download 5-91. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chapter 6
How your Nokia M10 works 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.1 ADSL 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.2 ATM and frames over ADSL 6-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3 Routing and bridging 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.1 TCP/IP routing 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.2 Static and dynamic routes 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.3.3 Bridging 6-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.4 Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) 6-3. . . . . . . . . .
6.4.1 Pinhole 6-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.5 IP address management 6-4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.6 Payload encapsulation 6-5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7 Point-to-point protocol (PPP) 6-6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7.1 Authentication 6-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.7.2 Network configuration 6-7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.8 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) 6-8. . . . . . .
6.8.1 DHCP for LAN clients 6-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.8.2 DHCP for WAN port configuration 6-8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6.9 Domain Name Service (DNS) relay 6-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Appendix A
Technical specifications A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A.1 Features A-1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A.2 Mechanical construction and power supply A-2. . . . . . . . . .
viii
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 10

DRAFT
A.3 Ambient conditions, EMC and safety A-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Installation environment A-2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EMC A-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Safety A-3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Glossary
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
ix
Page 11

Chapter 1
Introduction to Nokia M10
DRAFT
Introduction to Nokia M10
Nokia M10 is an ADSL modem which enables high-speed Internet
access and LAN interconnection. It increases the capacity of the
already installed telephone lines used traditionally for telephone
services. M10 enables high-speed connections for residential users,
small offices and telecommuters.
Figure 1-1 Nokia M10
Nokia M10 is a modem with an ADSL router and bridge. This allows a
PC equipped with a 10Base-T Ethernet interface to be connected to a
remote IP network via a Digital Subscriber Line Access Multiplexer
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
1-1
Page 12

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
(DSLAM) and an ATM access network. M10 can also act as a bridge
between the Ethernet LAN and ADSL/ATM network interfaces.
The ADSL transmission is based on a DMT line code and it provides
speeds up to 8 Mbit/s downstream (from the network) and 1 Mbit/s
upstream (to the network). M10 can adjust its speed to the line
conditions in steps of 32 kbit/s maximising the data throughput over
the given distance. M10 is compatible with Nokia Eksos B DSLAM.
M10 provides optimised access to high-speed data services. It can be
used to connect telecommuters to the corporate network or netsurfers
to the Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) network, for example.
As a default, M10 supports plug-and-play operation for an Internet
access application. The ADSL connection, data connection as well as
Internet network addresses are set up automatically.
M10 has an integrated W eb server which enables the configuration of
the most frequently used parameters with an ordinary W eb browser . It
can also be managed through a command line interface via telnet
protocol or via local console interface.
An external POTS filter enables the simultaneous use of the
conventional telephone service and the ADSL data services.
1-2
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 13
Chapter 2
Applications and features
DRAFT
Applications and features
This chapter introduces the most common applications, features and
management method options of M10.
2.1 Applications
M10 has three main applications:
D Internet access
D Remote work
D LAN interconnection
In these application examples M10 can act as a router, bridge or NAPT
router . The selected mode for every single application depends on the
access and service provider network architectures. T able 2-1 presents
the different application examples and the respective modes of M10.
The application examples described in this manual are marked with
bold ’X’s. See Chapter 6 for more information on routing, bridging and
Network Address Port Translation.
Application NAPT Router Bridge
Business Internet access X X X
Residential Internet access X X
Remote work X X X
LAN interconnection X X
Table 2-1 Applications and M10 modes
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
2-1
Page 14
DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
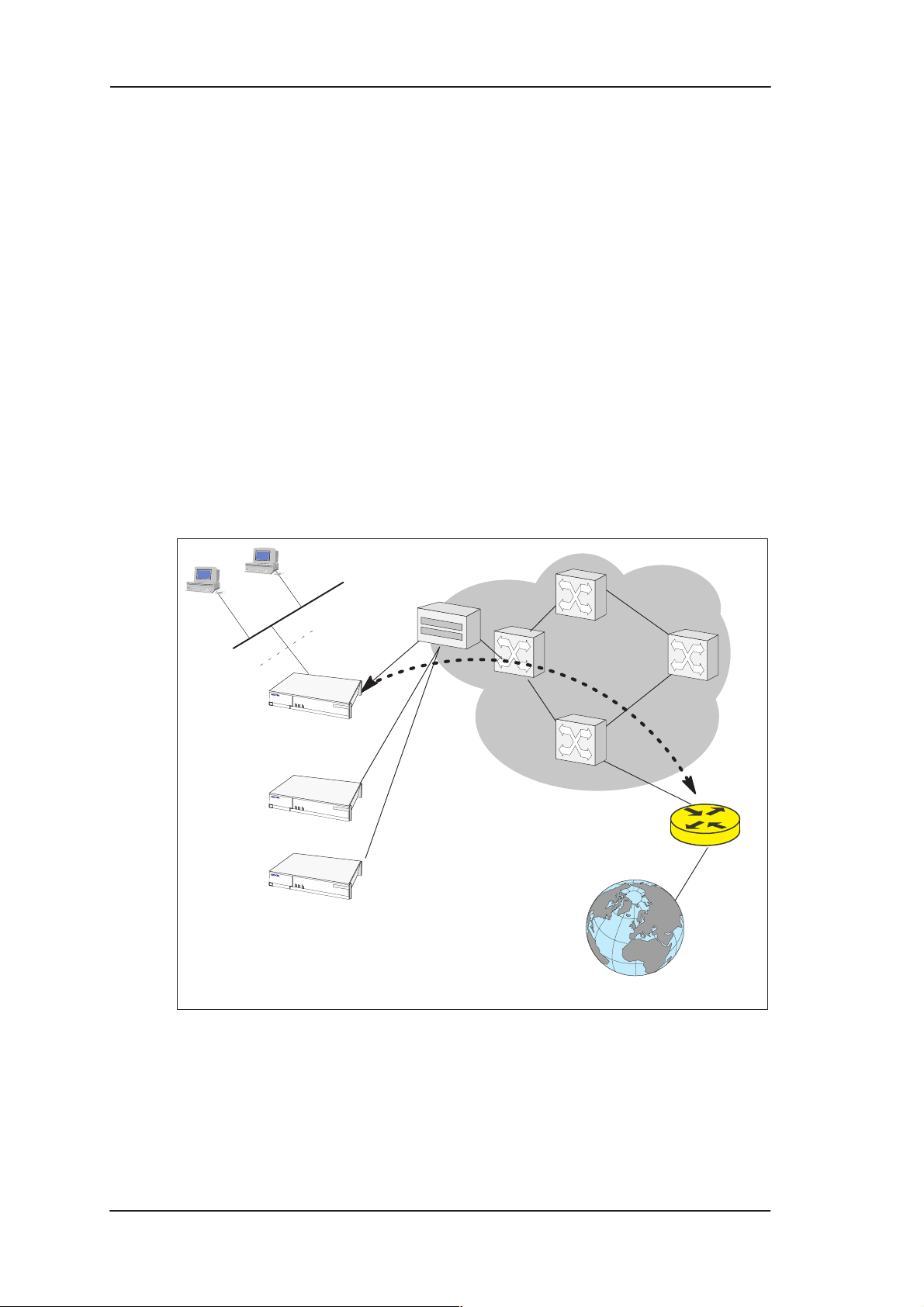
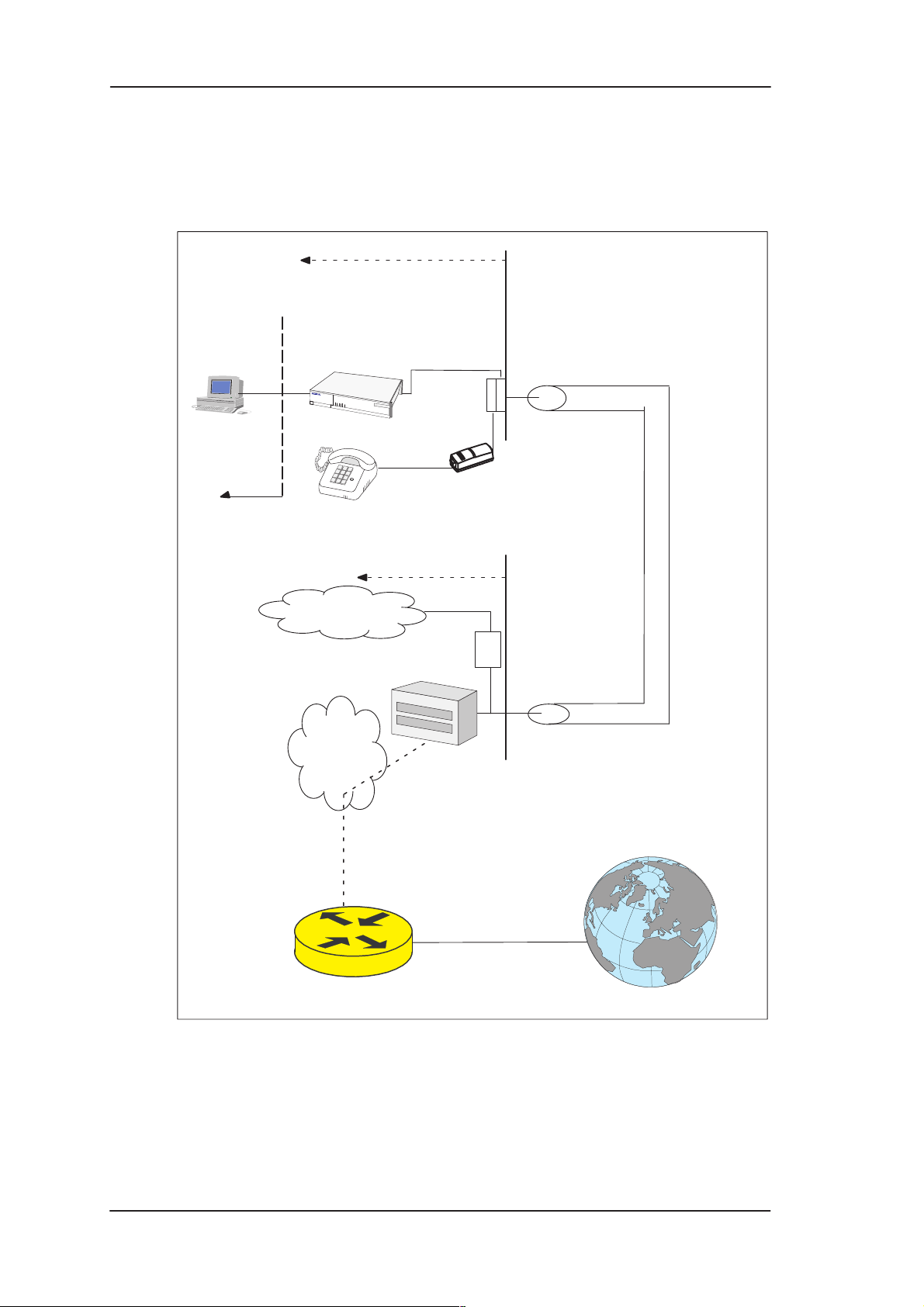
2.1.1 Internet access using NAPT router
M10 can connect your PC via your operator’s Digital Subscriber Line
Access Multiplexer (DSLAM) and ATM network to an Internet
service provider (ISP). If you are connected to a single ISP the network
addresses (IP addresses) in your home can be part of the ISP’s IP
address range. However, in many cases it is more practical that the
home network is an independent network utilising private IP addresses
which are not visible to outside and that M10 has only one external IP
address received from the ISP. The external Internet services are
accessed through this single IP address. This mode of operation is
called the Network Port Address Translation (NAPT).
The benefits of NAPT are the minimum coupling of the ISP and the
home network, the saving of public IP addresses, and in–built simple
firewall functionality.
Home
network
Home
network
Home
network
LAN
10Base-T
Nokia M10
DSLAM
ATM
network
ISP Router
Internet
2-2
Figure 2-1 Internet access using NAPT router
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 15
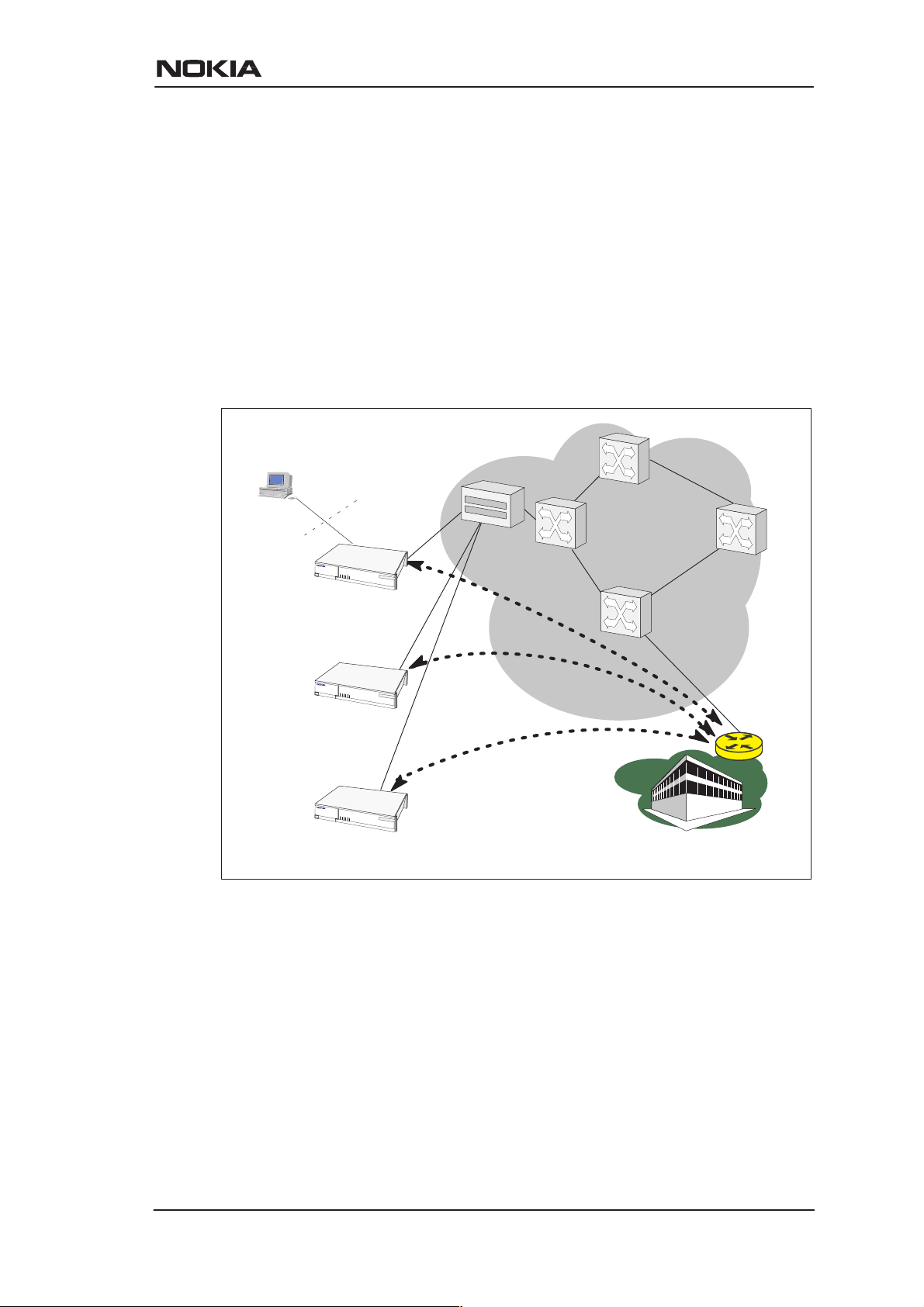
2.1.2 Remote work
In a typical remote work application M10 is used as an IP router to
provide access to corporate Intranet services. Using routing
functionality between the home and the corporate networks prevents
unnecessary broadcast traffic as well as non-IP protocol traffic from
loading the access connection still providing sufficient transparency
for Intranet applications. M10 routing table can be static or can be
updated dynamically using RIP version 1 and RIP version 2 routing
protocols.
DRAFT
Applications and features
DSLAM
10Base-T
ATM
network
Remote
worker
Nokia M10
Remote
worker
Remote
worker
...
Corporate
network
Company
router
Figure 2-2 Remote work using M10 as a standard router
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
2-3
Page 16
DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
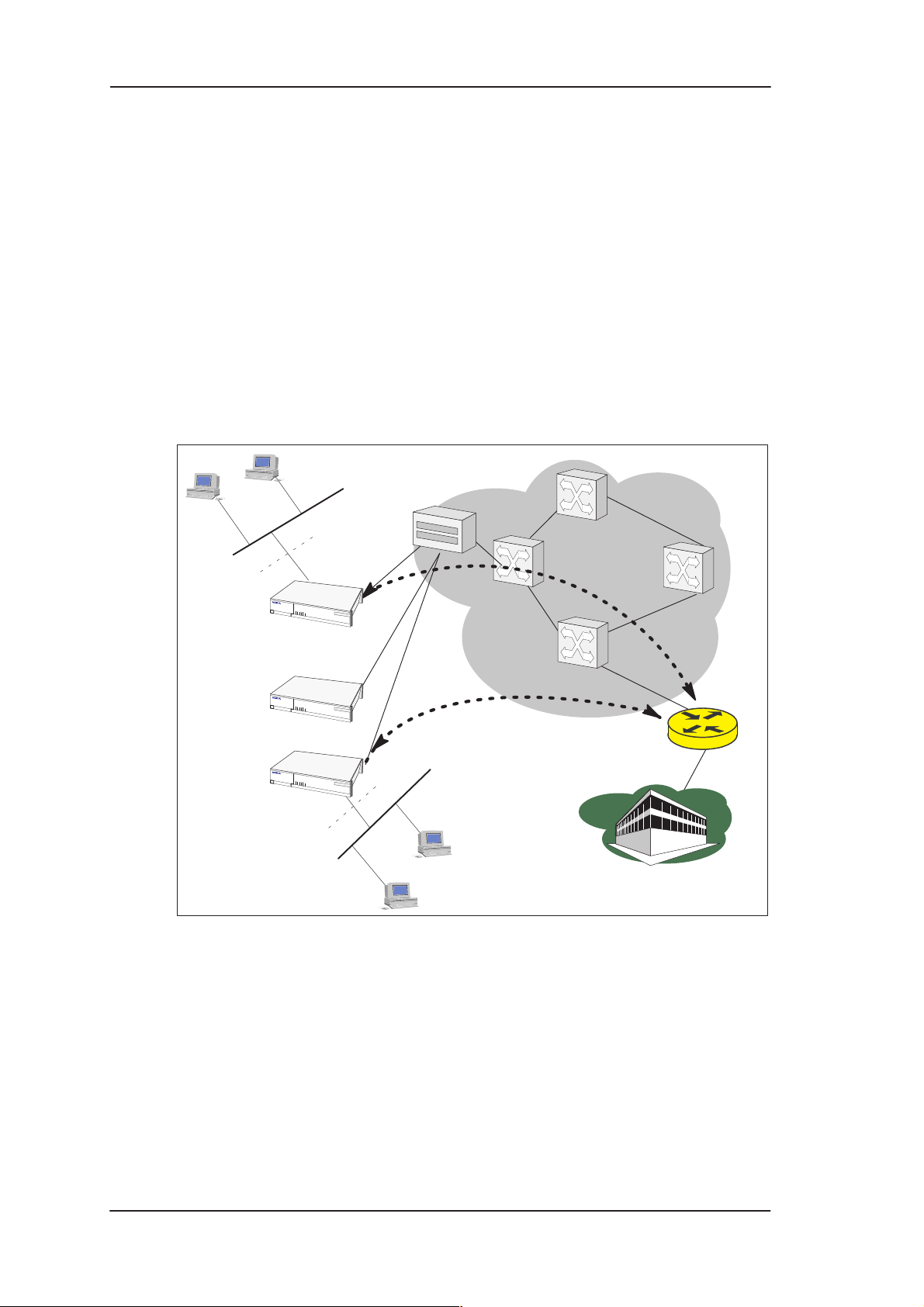
2.1.3 LAN interconnection using M10 as a bridge
LAN interconnection between a corporate headquarters and its remote
office is another typical application for M10. In the LAN
interconnection application M10 is typically used as an Ethernet
bridge which relays all non-local Ethernet traffic between the
corporate headquarters and remote sites through the ATM core
network.
The benefit of bridging in this application example is the transparency
for all network protocols in a multiprotocol data communications
corporate network.
Remote
office 1
Remote
office 2
10Base-T
LAN
10Base-T
Nokia M10
...
LAN
DSLAM
ATM
network
Company
bridge
Corporate
network
Figure 2-3 Internet access and LAN interconnection
2.2 Functionality
M10 can operate as an OSI layer 3 Internet Protocol (IP) router
between the Ethernet interface and the virtual channels of ADSL/A TM
interface. M10 supports both dynamic and static routing.
2-4
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 17
DRAFT
Applications and features
It can also operate as a self-learning bridge supporting up to 256 MAC
addresses.
Routing
Routing is based on routing entries in a routing table. Static routes are
added via the management interface and dynamic routing is done using
RIP and RIPv2. Routing is done between the Ethernet 10Base-T
interface and the virtual channel connection (VCC) of the A TM/ADSL
interface. Optionally, the routing between the VCCs can be disabled.
M10 supports up to 8 simultaneous VCCs.
Bridging
Bridging is supported if full protocol transparency is required.
Bridging can be used simultaneously with IP routing. M10 works as a
self-learning bridge supporting up to 256 MAC addresses. Bridging is
done between the Ethernet 10Base-T interface and each ATM VCC
interface. Optionally , the bridging between the VCCs can be disabled.
M10 supports up to 8 simultaneous VCCs.
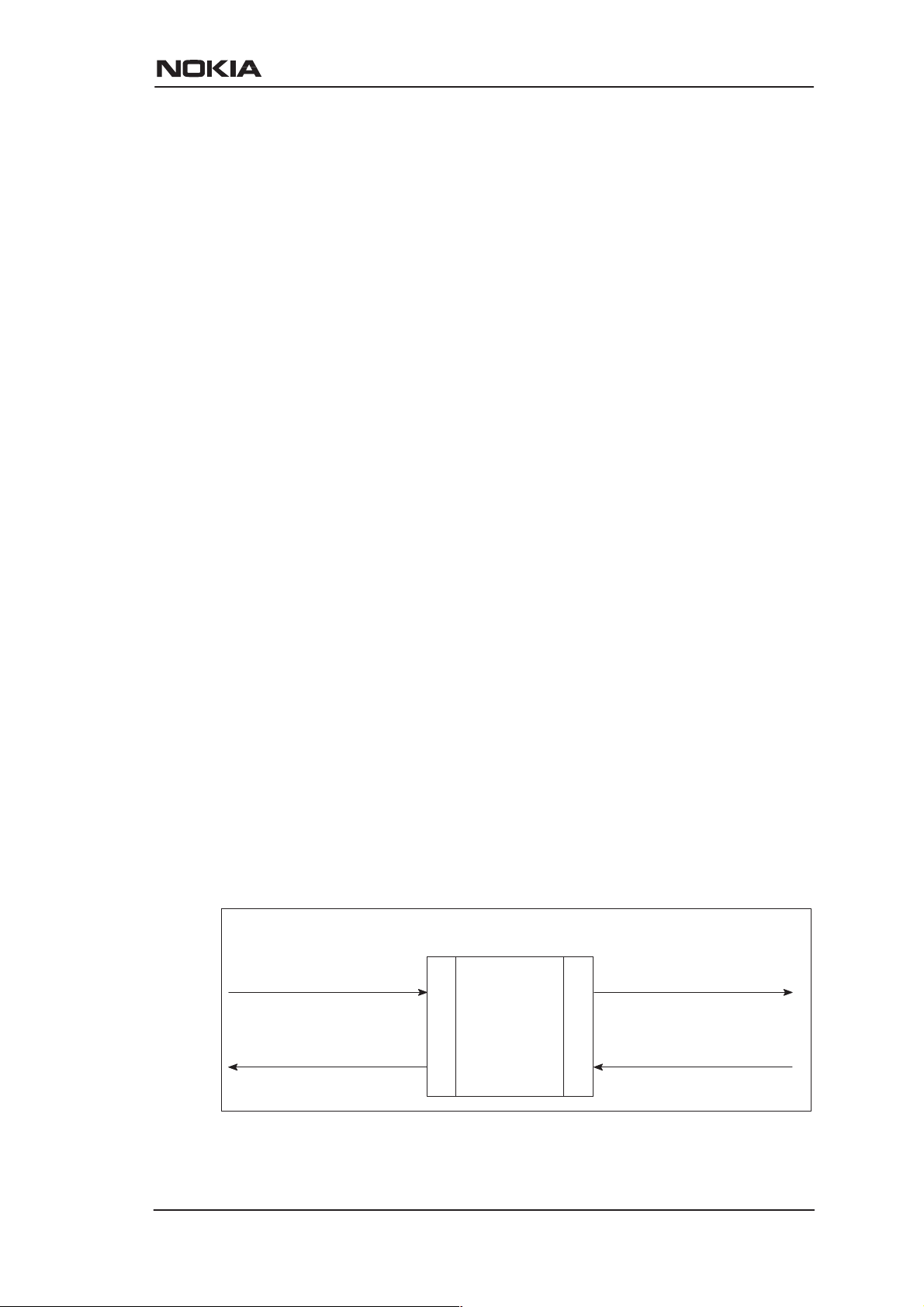
Network Address Port Translation
M10 supports Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) for TCP/IP
and UDP/IP protocols. When NAPT is used a single IP address is
allocated to a VCC to the public IP network. The Ethernet subnet has
private IP addressing and is not visible to the VCC. NAPT translates
the IP source address and source port number dynamically to the VCC
IP address and port number . Similarly packets coming from the VCC
are mapped back to the original destination addresses. NAPT allows
up to 253 hosts to share the single VCC IP address to the public
network. The Network Address Port Translation principle is presented
in Figure 2-4.
Home network (LAN) Internet (WAN)
src:192.168.1.112:1228
dst:194.112.11.111:80
NAPT router
src:194.112.11.111:80
src:195.112.12.161:1234
dst:194.112.11.111:80
src:194.112.11.111:80
dst:192.168.1.112:1228
Figure 2-4 Network Address Port Translation
NTC C33539002SE_A0
192.168.1.254
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
195.112.12.161
dst:195.112.12.161:1234
2-5
Page 18

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
NAPT may restrict the operation of some IP applications. NAPT also
operates as a simple IP firewall because translation is only allowed
when the first packet is transmitted from the LAN because the NAPT
table entry is created on when a packet is sent from the home network
to the Internet. With a pinhole capability the user can add static entries
to the NAPT table allowing the translation always in both directions.
This capability is used to add servers (HTTP, NNTP, and FTP), which
are visible from the public IP network via the VCC, in the LAN subnet
Dynamic Host Configuration
M10 can act as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
server for the PCs in the end-user LAN. In this mode M10 can assign
up to 253 IP addresses to the PCs in the home network.
ATM and ADSL
M10 supports up to 8 simultaneous VCCs and supports UBR
(Unspecified bit rate) traffic shaping on all VCCs. The maximum
transmit rate on each VCC is the ADSL upstream capability . If more
than one VCCs are transmitting simultaneously the ADSL upstream
capability is temporarily shared between these VCCs. When one VCC
is idle the bandwidth is used by another VCC.
The ADSL transmission is based on the DMT line code. M10 provides
a DMT line rate up to 8 Mbit/s downstream and up to 1 Mbit/s
upstream. The DMT transceiver is rate adaptive and capable of
providing faster rates over short distances or slower rates over long
distances. The transceiver adapts itself to the line conditions. The
ADSL interface of M10 functions completely automatically and all
configuration related to the ADSL connection is done at the access
multiplexer in the operator ’s premises.
The ATM over ADSL transmission is based on ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
recommendation.
Rate adaptation is done in steps of 32 kbit/s. The network operator can
set the data rates as a part of the network management functionality
provided by Nokia Eksos B DSLAM.
2-6
Payload encapsulations
Both routed and bridged protocols are encapsulated in the A TM link by
using either RFC 1483 LLC/SNAP encapsulation or VC multiplexing.
M10 also supports PPP over AAL5 encapsulation, in which both
bridged and routed protocols are first encapsulated in PPP (RFC 1661).
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 19

PPP is then encapsulated in ATM according to the IETF PPP over
AAL5 using RFC 2364 VC multiplexing.
Routed IP packets can also be encapsulated using LLC/SNAP or
VC-multiplexed Ethernet (bridged) encapsulations. See Chapter 6 for
more information on the payload encapsulations.
2.3 Management
There are four management methods in M10:
D Command line interface (CLI) over console serial port
D CLI via telnet
D SNMP
DRAFT
Applications and features
D Web browser management
The CLI allows complete configuration of the unit and the Web
browser management addresses the most frequently used
configuration parameters. SNMP can be used to read some equipment
identity information and to provide traps for authentication failures.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
2-7
Page 20

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
2-8
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 21
Interfaces and indicator lights
Chapter 3
Interfaces and indicator lights
DRAFT
M10 provides one Ethernet 10Base-T interface and one ADSL line
interface. The ADSL line interface is ANSI T1.413 Issue 2
compatible.
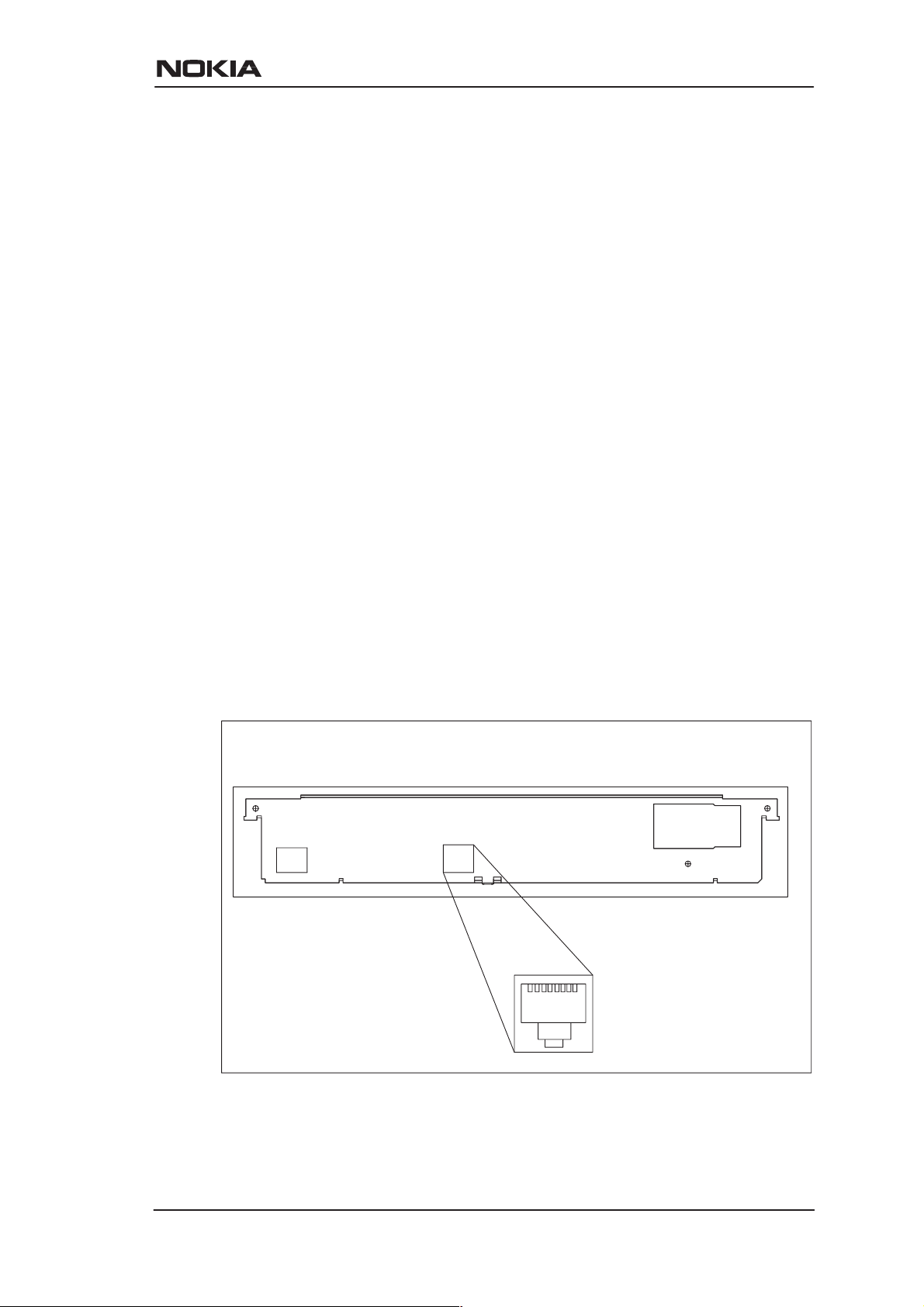
3.1 10Base-T Ethernet interface
The Ethernet interface is a standard 10 Mbit/s half-duplex 10Base-T
interface. The mechanical connector is an 8-pin RJ-45 connector.
ETH
18
Figure 3-1 Ethernet connector location
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
3-1
Page 22
DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
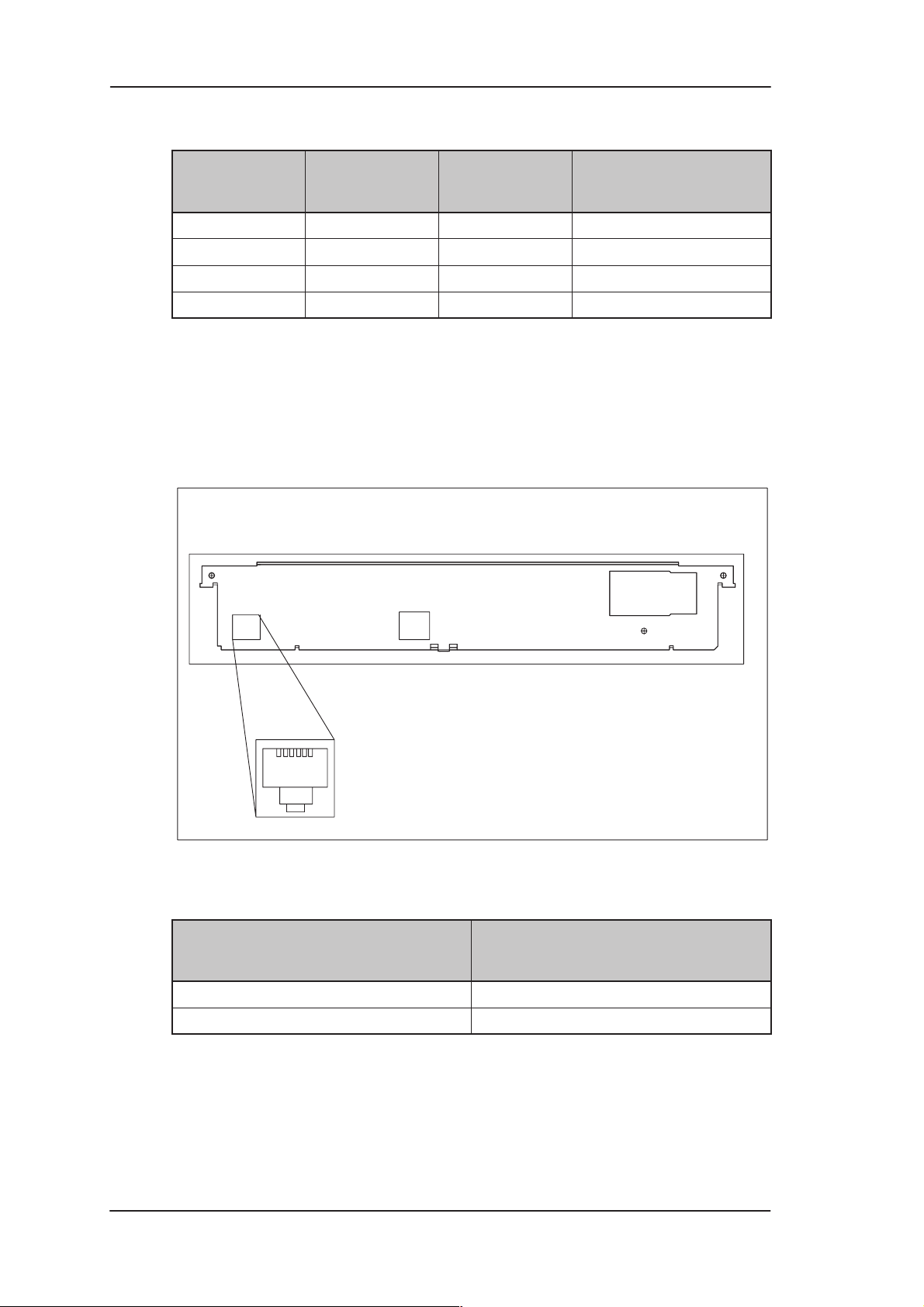
PIN Signal Direction
1 Tx+ –> Transmit data +
2 Tx– –> Transmit data –
3 Rx+ <– Receive data +
6 Rx– <– Receive data –
3.2 ADSL line interface
The ADSL line interface is ANSI T1.413 Issue 2 compatible. The
mechanical connector is a 6-pin RJ-11 connector.
MDI signal
M10-Ethernet
LINE
16
Figure 3-2 ADSL line connector location
PIN Signal
3 DSL1
4 DSL2
3-2
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 23
Interfaces and indicator lights
3.3 Front panel indicator lights
Six indicator lights have been grouped into three groups in the front
panel:
D STA
D DSL
D LAN
STA DSL LAN
ERR COLINA
DRAFT
OK LNK RX TXACT
Figure 3-3 Front panel indicator lights
STA indicator
D Err (red): There is a malfunction in the unit. Switch power off and
on again. If this does not help send the unit for repair.
D OK (green): Unit is functional
DSL indicator (ADSL line status)
D INA (red): ADSL line is inactive (no connection). Blinking light
indicates that the ADSL link is training.
D ACT (green): ADSL line is active (connection).
LAN indicators
D COL (red): Blinking light indicates collisions on the Ethernet.
D LNK (green): Lit if the Ethernet connection is OK.
D Rx (green): Blinking light indicates that M10 is receiving Ethernet
packets.
D Tx (green): Blinking light indicates that M10 is transmitting
Ethernet packets.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
3-3
Page 24

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
3-4
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 25

Chapter 4
Installation
DRAFT
Installation
This chapter presents a step-by-step installation example procedure
for three different application examples of Nokia M10:
D Internet access (NAPT router)
D Remote work (basic router)
D LAN interconnection (basic bridge)
These installation procedures are examples to guide you through some
of the typical use cases.
The installation examples assume that you have a new M10 with a
factory default configuration. The complete default configuration is
presented in the end of this chapter. The default settings are, briefly:
D Single ADSL/ATM channel (VPI = 0, VCI = 100)
D PPP over ATM/AAL5 encapsulation
D M10 retrieves IP address configuration from the IP network using
PPP-IPCP negotiation
D Network Address Port Translation activated
D Private IP addresses in use in LAN
D DHCP server for the LAN interface activated
Before starting the installation, unpack the unit and check that it is
physically undamaged.
4.1 Internet access (NAPT router)
This application is based on the default configuration of the Nokia
M10. By default, Nokia M10 is an Internet access device that uses
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-1
Page 26
DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Network Address Port T ranslation between the private home network
and the public Internet.
Customer premises
PC
uses
DHCP
Private IP
addresses
Nokia
M10/NAPT
Operator premises
Telephone
network
Filter
ATM
network
DSLAM
PPP
ATM
ADSL
low-pass filter
Telephone
cable
PPP
ATM
ADSL
4-2
single ATM
channel to
the ISP
ISP router
Figure 4-1 Internet access application
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
Internet
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 27

DRAFT
Installation
The Internet access application requires that your PC uses Dynamic
Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to get its network address (IP
address) from your Nokia M10.
The installation procedure depends on whether you want to use data
services only or data and simultaneous telephone services. If you want
data services only start from the Step 1a. Start from Step 1b if you want
both data and telephone services.
M10 has an optional three-level password (user, user-admin, and
admin) which also affects the installation procedure. By default, the
password is disabled but it can be enabled through the command line
interface (see Chapter 5 Management). Steps 4b and 5b describe the
actions when password is enabled.
Step 1a: Connect cables (data services only)
Connect the following cables:
D Connect the mains power cord first to the Nokia M10 and to a
power outlet.
D Connect the Ethernet cross cable to the Nokia M10 ETH connector
and the other end to your PC’s Ethernet port.
D Connect the ADSL cable to the telephone socket.
D Go to Step 2.
Step 1b: Connect cables (data and telephone services)
If you want to use your telephone line for both the high-speed ADSL
service and normal telephone service you must install a POTS filter.
You can use Nokia POTS filter T66130 or T66150. See separate
installation instructions for POTS filters.
Connect the following cables:
D Connect the mains power cord first to the Nokia M10 and to a
power outlet.
D Connect the Ethernet cross cable to the Nokia M10 ETH connector
and the other end to your PC’s Ethernet port.
D Connect the ADSL cable and the telephone according to the
separate POTS filter installation instructions.
Step 2: Switch power on
Turn the Nokia M10 on. The green STA indicator and red DSL
indicator light up. After a while the DSL light starts blinking indicating
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-3
Page 28

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
that the connection is being established. Green DSL light indicates that
the unit has a connection to the central office.
Step 3: Turn on your PC
Turn on your PC. The LAN/LNK indicator lights up in the Nokia M10
front panel. Note that you must activate the DHCP functionality in
your PC to make it retrieve an IP address from M10.
Step 4a: Connect to M10 with a W eb browser (password disabled)
Start the W eb browser in your PC, write the IP address (192.168.1.254)
or the name (”M10”) of the M10 to the HTTP address field and press
Enter. The M10 QuickConfig page is displayed. Note that the
QuickConfig page is displayed first only when M10 has its factory
default settings active. If M10 has been previously configured the first
page to appear is the M10 home page. Go to Step 5a.
Step 4b: Connect to M10 with a W eb browser (password enabled)
Start the W eb browser in your PC, write the IP address (192.168.1.254)
or the name (”M10”) of the M10 to the HTTP address field and press
Enter . Enter Network Password dialog is shown. Enter your M10 User
name and Password and click OK. Goto Step 5b.
Step 5a: Configure M10 (password disabled)
Click Internet Access-Single PPP button to set your username and
password for the Internet service.
4-4
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 29

DRAFT
Installation
Here it is assumed that the default settings of M10 are suitable for
accessing the Internet through your Internet Service Provider, i.e. the
connection from M10 to the ISP uses PPP over AAL5 protocol, the ISP
provides the required network address information to your M10
automatically, and the default connection channel (VPI and VCI
values) of M10 is correct. This means that you only have to enable the
needed authentication method (CHAP or P AP) by clicking the relevant
radio button and to type in your username and password related to the
authentication method. You will get the information which
authentication method to use and your corresponding username and
password from your Internet Service Provider. After entering the
information click Save and restart M10.
Step 5b: Configure M10 (password enabled)
Enable PAP or CHAP authentication and type in your corresponding
user name and password. You will get the information which
authentication method to use and your corresponding username and
password from your Internet Service Provider. After entering the
information click Save and restart M10.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-5
Page 30

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Step 6: Surf
After the ADSL connection has been established the installation is
complete and you can use your Web browser normally.
4.2 Remote work (Basic router)
In the remote work application example the Nokia M10 routes you to
your company’s LAN through an ATM network. It is assumed that
your PC belongs to your company’s IP network and has a fixed IP
address. It is also assumed that static IP routing is used. An example is
shown in Figure 4-2.
4-6
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 31

M10 IP address
DRAFT
Installation
192.168.1.1
255.255.255.0
PC’s IP address:
192.168.1.180
255.255.255.0
192.168.2.2
255.255.255.0
Nokia M10
RFC 1483
IP/A TM
ATM
ADSL
DSLAM
ATM
network
VCI/VPI connected
Company LAN
from DSLAM to
company router
Company
router
192.168.2.1
255.255.255.0
Gateway/firewall
192.168.3.4
255.255.255.0
Figure 4-2 Remote work application
Your server
192.168.3.3
Internet
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-7
Page 32

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Here the configuration is done using the command line interface (CLI)
through the console port of Nokia M10. A special cable is needed, type
designation E64320.01.
Step 1: Connect cables
D Connect the mains power cord to your M10 and the other end to the
power outlet.
D Connect the M10 console cable to the console port behind the
hatch in the front panel of your M10. Connect the other end of the
cable to the serial port of your PC/terminal.
! # !
$
"#
Figure 4-3 Location of the console port
D Turn on your Nokia M10. The green status indicator and the red
DSL indicator light up.
Step 2: Turn on your PC and start the terminal software
Set the following terminal software parameters: 9600, 8 bits, no parity ,
1 stop bit, no flow control.
Press enter in the terminal window . The Nokia command line interface
prompt will be displayed.
4-8
Step 3: Configure the M10
The configurations given here assume that the unit uses its default
configurations and the changes are done on top of the default
configuration.
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 33

DRAFT
Installation
The Nokia M10 command line interface includes a step mode to
automate the process of entering configuration settings. When you use
the Config step mode, the CLI prompts you for all required and
optional information. You can enter the configuration values
appropriate for your site without having to enter complete CLI
commands.
When you are in step mode, the CLI prompts you to enter required and
optional settings. If a setting has a default value or a current setting, the
command line interface displays the default value for the command in
parentheses. If a command has a limited number of acceptable values,
those values are presented in brackets, with each value separated by a
vertical line. For example, the following CLI step command indicates
that the default value is off and that valid entries are limited to on and
off.
option (off) [on|off]: on
You can accept the default value for a field by pressing the Enter key .
To use a different value, type it in and press Enter.
Enter the Config step mode by typing
set from the top node of the
Config hierarchy. See Chapter 5 section Stepping through M10
configuration for more information on the step mode.
In the following example the values changed by the user are in bold
type. The default values have been accepted by pressing Enter.
M10> config
Config Mode v1.0
(admin level privileges –– read/write
M10 (top)>>set
Stepping set mode (press Control–X <Return/Enter> to
exit)...
system
name (”M10”): <Enter>
Diagnostic Level List
low
medium
high
warnings
failures
diagnostic-level (high): <Enter>
dmt
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-9
Page 34

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
encap (CELL) [HDLC|PPP|CELL]: <Enter>
downRate (1536.0) [1536.0|3072.0|4608.0|
6144.0] CO Only: <Enter>
upRate (64.0) [64.0|160.0|384.0|576.0|640.0]
CO Only: <Enter>
margin (3) [–3 – 9] CO Only: <Enter>
atm
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
vcc 1
option (on): <Enter>
vpi (0) [0 – 255]: <Enter>
vci (100) [0 – 65535]: <Enter>
encap (ppp-vcmux)
ppp-vcmux : PPP over ATM,
ether-vcmux : RFC-1483, briged
ether-llc : RFC-1483, bridged
ip-vcmux : RFC-1483, routed IP,
ip-llc : RFC-1483, routed IP,
[ppp-vcmux|ether-vcmux|ether-llc|
ip-vcmux|ip-llc]: ip-llc
vcc 2
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 3
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 4
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 5
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 6
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 7
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 8
option (off): <Enter>
cell
ehead (0x00000001) [0x0 – 0xffffffff]:
<Enter>
epayload (0x6a6a6a6a) [0x0 – 0xffffffff]:
VC-muxed
Ethernet, VC-muxed
Ethernet, LLC-SNAP
VC-muxed
LLC-SNAP
4-10
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 35

<Enter>
hec_coset (on): <Enter>
payload_scrambling (on): <Enter>
bncp
option (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
ip
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
ethernet
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
address (192.168.1.254): 192.168.1.1
broadcast (192.168.1.255): <Enter>
netmask (255.255.255.0): <Enter>
proxy-arp (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
rip-send (v1) [off | v1 | v2 |
v1-compat]: <Enter>
rip-receive (v1) [off | v1 | v2 |
v1-compat]: <Enter>
dsl vcc1
option (off) [on|off]: on
address (0.0.0.0): 192.168.2.2
broadcast (0.0.0.255): 192.168.2.255
netmask (255.255.255.0): <Enter>
addr-mapping (on) [on|off]: off
proxy-arp (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
rip-send (v1) [off | v1 | v2 |
v1-compat]: <Enter>
rip-receive (v1) [off | v1 | v2 |
v1-compat]: <Enter>
admin-disable (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
gateway
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
interface () [ip-address]: ip-address
default (0.0.0.0): 192.168.2.1
interwan-routing (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
static routes
DRAFT
Installation
IP Static Route List
destination-network (0.0.0.0) [enter a
listed or new static route address]: <Enter>
location
Location names: <Enter>
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-11
Page 36

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
name (””) [enter a listed or new location name]:
<Enter>
dhcp
option (on) [on|off]: off
dns
domain-name (””): <Enter>
primary-address (0.0.0.0): <Enter>
secondary-address (0.0.0.0): <Enter>
bridge
option (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
interwan-bridging (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
snmp
Community Name List
“public”
community (””): <Enter>
traps
authentication-traps (off) [on|off]:
<Enter>
IP Trap List
ip-traps (0.0.0.0) [enter a listed or
new IP address]: <Enter>
sysgroup
contact (””): <Enter>
location (””): <Enter>
ppp
peer-database
Authentication User List
peer-name (””) [enter a listed or new
user name]: <Enter>
pinhole
4-12
Pinhole Table
item (0) [enter a listed or new
pinhole entry]:
servers
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 37

DRAFT
Installation
web-http (80) [0 – 32767]: <Enter>
telnet-tcp (23) [0 – 32767]: <Enter>
Stepping mode ended.
M10 (top)>> save
WARNING: ’dns domain-name’ is null, indicating no
domain name is available.
WARNING: ’dns primary-address [0.0.0.0]’ and ’dns
secondary-address [0.0.0.0]’ indicates no nameserver
is available.
Configuration data saved.
M10 (top)>> exit
M10> restart
REBOOT scheduled in 2 seconds
Goodbye.
The following changes were made in the above basic router example:
D Ip-llc encapsulation was selected for the ATM channel 1. This
encapsulation is used by your company’s main office router.
Alternatively vc-mux encapsulation could be used. See Chapter 6
for more information on the payload encapsulations.
D IP address was assigned to the Ethernet port of your M10.
D IP and broadcast addresses were assigned to the ATM/ADSL
interface of your M10.
D Address mapping was disabled because your PC and M10 belong
to your company network.
D Default gateway was enabled and its IP address defines the IP
gateway interface.
D IP address of the default gateway was given.
D DHCP was disabled.
The warnings in the end of the above example indicate that the
addresses have not been specified. 0.0.0.0 setting indicates that M10
retrieves the name server addresses from the network. W arning is not
fatal. If an error message occurs the configuration has not been
validated successfully and M10 does not save the configuration.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-13
Page 38

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Step 4: Connect your M10 to the network
Connect the ADSL cable to the telephone socket and the Ethernet
interface to your PC. The green LAN LNK indicator lights up when
you connect the Ethernet cable. After a while the DSL light starts
blinking indicating that the connection is being established. The green
DSL light indicates that the unit has a connection to the central office.
Step 5: Check that the connection works
Ping the company server or the gateway to check that the connection
works.
4.3 LAN interconnection (Basic Ethernet bridge)
In this application example Nokia M10 connects transparently to a
remote office or company headquarters.
Hub
PC
Nokia
M10/bridge
RFC 1483
Ethernet
over ATM
ADSL A TM
Headquarters
LAN
Virtual ATM channel
connected from DSLAM
to HQ access bridge
ATM
DSLAM
Headquarters
access bridge
network
4-14
Figure 4-4 LAN interconnection
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 39

DRAFT
Installation
Step 1: Connect cables
D Connect the mains power cord to your M10 and the other end to the
power outlet.
D Connect the M10 console cable to the console port behind the
hatch in the front panel of your M10. Connect the other end of the
cable to the serial port of your PC/terminal. A special cable is
needed, type designation E64320.01.
D Turn on your Nokia M10. The green status indicator and the red
DSL indicator light up.
! # !
$
"#
Figure 4-5 Location of the console port
Step 2: Turn on your PC and start the terminal software
Set the following terminal software parameters: 9600, 8, no parity , no
flow control.
Step 3: Configure the M10 using CLI commands
The configurations given here assume that the unit uses its default
configurations and the changes are done on top of the default
configuration.
The Nokia M10 command line interface includes a step mode to
automate the process of entering configuration settings. When you use
the Config step mode, the CLI prompts you for all required and
optional information. You can enter the configuration values
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-15
Page 40

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
appropriate for your site without having to enter complete CLI
commands.
When you are in step mode, the CLI prompts you to enter required and
optional settings. If a setting has a default value or a current setting, the
command line interface displays the default value for the command in
parentheses. If a command has a limited number of acceptable values,
those values are presented in brackets, with each value separated by a
vertical line. For example, the following CLI step command indicates
that the default value is off and that valid entries are limited to on and
off.
option (off) [on|off]: on
You can accept the default value for a field by pressing the Enter key .
To use a different value, type it in and press Enter.
Y ou can enter the Config step mode by typing
set from the top node of
the Config hierarchy.
In the following example the values changed by the user are in bold
type. The default values have been accepted by pressing Enter.
M10> config
Config Mode v1.0
(admin level privileges –– read/write
M10 (top)>>set
Stepping set mode (press Control–X <Return/Enter> to
exit)...
system
name (”M10”): <Enter>
Diagnostic Level List
low
medium
high
warnings
failures
diagnostic-level (high): <Enter>
dmt
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
encap (CELL) [HDLC|PPP|CELL]: <Enter>
downRate (1536.0) [1536.0|3072.0|4608.0|
6144.0] CO Only: <Enter>
upRate (64.0) [64.0|160.0|384.0|576.0|640.0]
CO Only: <Enter>
4-16
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 41

margin (3) [–3 – 9] CO Only: <Enter>
atm
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
vcc 1
option (on): <Enter>
vpi (0) [0 – 255]: <Enter>
vci (100) [0 – 65535]: <Enter>
encap (ppp-vcmux)
ppp-vcmux : PPP over ATM,
VC-muxed
ether-vcmux : RFC-1483, briged
Ethernet, VC-muxed
ether-llc : RFC-1483, bridged
Ethernet, LLC-SNAP
ip-vcmux : RFC-1483, routed IP,
VC-muxed
ip-llc : RFC-1483, routed IP,
LLC-SNAP
[ppp-vcmux|ether-vcmux|ether-llc|
ip-vcmux|ip-llc]: ether-llc
vcc 2
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 3
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 4
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 5
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 6
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 7
option (off): <Enter>
vcc 8
option (off): <Enter>
cell
ehead (0x00000001) [0x0 – 0xffffffff]:
<Enter>
epayload (0x6a6a6a6a) [0x0 – 0xffffffff]:
<Enter>
hec_coset (on): <Enter>
payload_scrambling (on): <Enter>
bncp
option (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
DRAFT
Installation
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-17
Page 42

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
ip
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
ethernet
option (on) [on|off]: off
dsl vcc1
option (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
gateway
option (on) [on|off]: off
interwan-routing (on) [on|off]: off<Enter>
static routes
IP Static Route List
destination-network (0.0.0.0) [enter a
listed or new static route address]: <Enter>
location
Location names: <Enter>
name (””) [enter a listed or new location name]:
<Enter>
dhcp
option (on) [on|off]: off
dns
domain-name (””): <Enter>
primary-address (0.0.0.0): <Enter>
secondary-address (0.0.0.0): <Enter>
bridge
option (off) [on|off]: on
ethernet
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
dsl vcc1
option (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
interwan-bridging (on) [on|off]: <Enter>
snmp
Community Name List
“public”
4-18
community (””): <Enter>
traps
authentication-traps (off) [on|off]:
<Enter>
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 43

IP Trap List
ip-traps (0.0.0.0) [enter a listed or
new IP address]: <Enter>
sysgroup
contact (””): <Enter>
location (””): <Enter>
ppp
peer-database
Authentication User List
peer-name (””) [enter a listed or new
user name]: <Enter>
pinhole
DRAFT
Installation
Pinhole Table
item (0) [enter a listed or new
pinhole entry]:
servers
web-http (80) [0 – 32767]: <Enter>
telnet-tcp (23) [0 – 32767]: <Enter>
Stepping mode ended.
M10 (top)>> ip
M10 (ip)>> set
Stepping set mode (press Control-X <Return/Enter> to
exit)...
ip
option (on) [on|off]: off
interwan-routing (off) [on|off]: <Enter>
static routes
IP Static Route List
Stepping mode ended.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
destination-network (0.0.0.0) [enter a
listed or new static route address]:
<Enter>
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-19
Page 44

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
M10 (top)>> save
WARNING: ’dns domain-name’ is null, indicating no
domain name is available.
WARNING: ’dns primary-address [0.0.0.0]’ and ’dns
secondary-address [0.0.0.0]’ indicates no nameserver
is available.
Configuration data saved.
M10 (ip)>> exit
M10> restart
REBOOT scheduled in 2 seconds
Goodbye.
The following changes were made in the above basic router example:
D Ether-llc encapsulation was selected for the ATM channel 1. This
encapsulation is used by your company’s main office bridge.
Alternatively ether-vcmux encapsulation could be used. See
Chapter 6 for more information on the payload encapsulations.
D IP functionality, default gateway and interwan routing were
disabled in the Ethernet. Note, that you have to go through the IP
option twice. First to disable Ethernet and gateway options and
then to disable the IP option.
D DHCP option was disabled.
D Bridge was enabled.
Warnings related to 0.0.0.0 settings of DNS servers are irrelevant in
this configuration because the M10 is now a transparent bridge.
W arnings are not fatal. If an error message occurs the configuration has
not been validated successfully and M10 does not save the
configuration.
Step 4: Connect your M10 to the network
4-20
Connect the ADSL cable to the telephone socket and the Ethernet
interface to your office hub. The green LAN LNK indicator lights up
when you connect the Ethernet cable. After a while the DSL indicator
starts blinking indicating that the connection is being established. The
green DSL light indicates that the unit has a connection to the central
office.
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 45

Step 5: Check that the connection works
Establish a connection to the office server to check that the connection
works.
4.4 Default settings
The table below indicates the default settings for Nokia M10. By
default, Nokia M10 works as a plug and play unit for Internet access
application. Node and Subnode refer to Config command hierarchy
nodes (see Chapter 5).
Node Subnode Parameter M10 default
System System name M10
DRAFT
Installation
System Diagnostic Level
System Name
Password/
User
System Name
Password/
Admin
CLI Verbose OFF
CLI Lines 16
ATM Option ON
Empty Cell
Header Value
Empty Cell
Payload Value
ATM HEC
Coset
Payload
Scrambling
3 (high)
<empty>
<empty>
0x00000001
0x6A6A6A6A
ON
ON
BNCP Option OFF
PPP Option ON
NTC C33539002SE_A0
ATM VCC Options (8)
VCI (VCC1) 100
VPI (VCCI1) 0
Encapsulation
(VCC1)
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
ON (VCC1), others
OFF
ppp-vcmux
4-21
Page 46

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
M10 defaultParameterSubnodeNode
PPP Maximum Receive
Unit
LCP Magic
Number Negotiation
Protocol Compression
Address Compression
LCP Echo Requests
Failures-max 10
Configure-
max
Terminate-
max
Restart Timer 3
Activity Time-
out
1500
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
10
2
0
Chap Option OFF
Chap Name “empty”
Chap Secret “empty”
PAP Option OFF
PAP Name “empty”
PAP Pass-
word
Chap Peer
Option
PAP Peer Option
Peer Host
Name(s)
Peer Host
CHAP Secrets
Peer Host
PAP Passwords
IP Option ON
“empty”
OFF
OFF
“empty”
“empty”
“empty”
4-22
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 47

DRAFT
Installation
M10 defaultParameterSubnodeNode
IP Gateway
Option
IP Ethernet
Option
IP Gateway
Interface
IP Gateway IP
Address
IP Ethernet
Address
IP Ethernet
Broadcast Address
IP Ethernet
Netmask
IP Ethernet
RIP send
IP Ethernet
RIP receive
ON
ppp (VCC1)
“empty”
ON
192.168.1.254
192.168.1.255
255.255.255.0
RIP V1
RIP V1
IP WAN Option
IP DSL Option OFF
IP-ppp Option ON (VCC1)
IP-PPP IP Address
IP-PPP Peer
IP Address
IP-PPP Address mapping
IP-PPP RIP
Send
IP-PPP RIP
Receive
IP-PPP Flush
Routes
Static Routes
Tbl
OFF
0.0.0.0 (VCC1)
0.0.0.0 (VCC1)
ON (VCC1)
OFF
OFF
OFF
Empty
DHCP Option ON
NTC C33539002SE_A0
DHCP Start IP
address
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
192.168.1.1
4-23
Page 48

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
M10 defaultParameterSubnodeNode
DNS Default Do-
main Name
Primary DNS
Server Address
Secondary
DNS Server
Address
Bridge Option OFF
SNMP List of
communities
(table)
SNMP Auth-
entication
Traps
Trap IP Ad-
dress
Trap Com-
munity Name
SysGroup
Contact Info
<empty>
0.0.0.0 (The address
will be retrieved from
through the PPP link)
0.0.0.0 (The address
will be retrieved
through the PPP link)
Public
None
Empty
Public
Empty
Table 4-1 Nokia M10 default settings
4.5 Troubleshooting
In case the data transmission does not work you can check the
following things:
Is the ADSL connection to the remote network working?
The front panel DSL indicator should be green if the ADSL link is
functioning. You can also view the ADSL link status by giving the
show dsl command line interface command. In case the ADSL link is
not functioning, check that the cables connecting the unit to the
telephone line/splitter are properly attached and then turn on the M10
again. If the ADSL link still does not work contact your service
provider.
4-24
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 49

DRAFT
Installation
Is the Ethernet connection working?
The front panel LAN LNK indicator is green if the Ethernet cable is
properly attached. If not, check that the cables are properly connected.
Check also that you are using a right kind of Ethernet cable. If you
connect your M10 directly to a PC, you should use a cross-connect
cable. If you connect your M10 to a HUB, you should use a direct
cable.
Is the ATM connection working?
You can check if the ATM connection is working by giving the
atm
CLI command. For the ATM connection to be functioning, the
show
ADSL connection must be working first. In case the ADSL connection
is OK but the ATM connection is not contact your service provider.
Is the PPP connection working?
If you are using PPP to connect to your service provider, you can also
check that your PPP connection is working. Y ou can do this by giving
show ppp CLI command. If the ADSL link and ATM link are
the
working but the PPP link is not you should first check that the
username and password you are using on the PPP link are correct. Y ou
can also try to restart the M10 (power-off and power -on) and check if
the connection is established. If these do not work contact your service
provider for help.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
4-25
Page 50

Chapter 5
Management
DRAFT
Management
M10 can be managed with a Web browser or command line interface
(CLI). The Web configuration pages of M10 can be accessed through
the Ethernet port or through the ADSL/A TM channels of M10. In order
to access the Web management feature, the IP functionality must be
activated and the IP address must be given to the interface.
The command line interface (CLI) can be accessed through the console
port on the M10 front panel. The console interface is an asynchronous
V.24/V.28 character -based interface with 9600 bps, 8 bits, no parity , 1
stop bit and no flow control. A special cable for connecting PC’ s serial
port to this interface is available from Nokia, type designation
E64320.01. The CLI contains an in-built step procedure which helps
you to configure you M10 through the CLI. This procedure is
presented in section Stepping through M10 configuration in this
chapter.
The command line interface can also be accessed through the Ethernet
port of M10 or through the ADSL/A TM channels of M10 on top of the
telnet protocol. In order to use the CLI through telnet, IP functionality
must be activated and IP address must be given to the interface.
5.1 Browser management
You can use your PC’s Web browser software to access the Web
configuration pages in M10. T o access the W eb pages you must know
the IP address of your M10 or, alternatively , the “name” that your M10
recognises.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-1
Page 51

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
5.1.1 Opening a connection
To open a connection to the Nokia M10 follow the next steps:
1. Start your Web browser.
2. Enter the name or IP address of your Nokia M10 in the browser’s
Open Location field and press enter.
For example, you would enter http://192.168.1.254 if your Nokia
M10 is using its default IP address. The default name is M10.
Note If a password has been assigned to your Nokia M10,
enter your username and password and click OK. Now
PAP and CHAP Setup page appears, see Figure 5-4.
3. The Nokia M10 home page appears. If you connect to your M10
for the first time the QuickConfig page appears.
5-2
Figure 5-1 M10 home page
4. Use the links on the Nokia M10 home page to issue a command or
open a window.
D QuickConfig link opens the QuickConfig window which lets you
enter basic Internet access application settings for your Nokia
M10.
D Monitor link opens the Monitor window which displays operating
statistics for your Nokia M10.
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 52

DRAFT
Management
D Router link is used to configure some generic routing/IP address
management parameters and Ethernet interface IP parameters if
M10 is used as a router.
D Bridge link is used to enable bridging and attach interfaces to the
bridge function.
D ATM link is used to activate ATM channels, select payload
encapsulations to ATM and configure important ATM channel
parameters.
D DSL link opens the DSL Port Configuration window which lets
you configure the DSL port settings of M10 when the unit is
working in frame (not ATM) mode on the ADSL line.
D Restart M10 link restarts your M10 causing it to activate any
updated configuration information.
D SNMP link is used to configure the SNMP parameters of M10.
5.1.2 QuickConfig page
The QuickConfig page lets you enter basic configuration information
for your Nokia M10. To display the QuickConfig page, click
QuickConfig on the M10 homepage.
Figure 5-2 QuickConfig page
By clicking the Internet Access-Single PPP button you can enter basic
Nokia M10 settings for an Internet access application. Normally you
only need to enter your username and password for the Internet
service.
If you have configured multiple PPP channels into use, you can
manage them through the PPP Connection Manager.
If a password has been assigned to you M10 the P AP and CHAP Setup
page will be displayed instead of the QuickConfig page.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-3
Page 53

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
QuickStart settings
Figure 5-3 QuickStart page
1. Change virtual path and channel identifiers if needed.
VPI and VCI are used to select the connection channel that is used
between M10 and the Internet service provider (ISP). Normally
you do not have to change these values.
2. Enable PAP or CHAP if needed. Enter the respective username
and password.
3. Enter local LAN Domain Name if required.
4. Enter Domain Name Server addresses if required. Normally these
are assigned automatically and the user should not fill these fields.
5. Save the configuration and restart M10.
You must save the new configuration and restart your M10 for
your changes to take effect.
5-4
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 54

DRAFT
Management
PAP and CHAP Setup settings
If a password has been assigned to your M10 PAP and CHAP Setup
page will appear when you enter your M10 username and password
and click OK.
On this page you can enable/disable PAP/CHAP and enter the
corresponding usernames and passwords. By clicking the Pinhole link
you can go to the NAT Pinhole page and configure pinhole settings.
Monitor link takes you to the Monitor page where you can monitor the
performance of your M10.
Figure 5-4 PAP and CHAP Setup page
PPP Connection Manager settings
You can set the username and password for each PPP connection you
have configured. Select the PPP connection you want to modify from
the option menu. Press Get values to modify username and password
of the connection. Press Reload to restart the PPP connection of the
selected channel. The PPP connection will be restarted and new CHAP
or PAP values will be used.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-5
Page 55

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Figure 5-5 PPP Connection manager pages
5-6
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 56

5.1.3 Router page
Router page is used to configure ’global’ parameters of the IP routing
functionality of M10, as well as IP parameters of the Ethernet
interface.
DRAFT
Management
Figure 5-6 Router page
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-7
Page 57

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Entering router settings
1. Enter the name of your M10 in the System Name field.
Each M10 is assigned a name as a part of its factory initialisation.
The default name is M10. A device name can be 1-16 characters
long and cannot include spaces or special characters. The name
can be later used to access the M10 through a telnet connection or a
Web page from the Ethernet interface.
2. Enter the IP address of your M10.
Local address is the IP address of your M10’ s Ethernet interface.
3. Enter the subnet mask.
Subnet mask is used to identify the network portion of an IP
address. The subnet mask specifies which bits of the 32-bit binary
IP address represent network information. Most sites should use
255.255.255.0 for their subnet mask.
4. Enter the broadcast address.
Broadcast address is used to send messages to all computers on
your network. Most sites should use xxx.yyy.zzz.255 as their
broadcast address, where xxx.yyy.zzz is the network portion of the
IP address.
5. Enter RIP settings for the Ethernet interface.
Rip-send and Rip-receive radio buttons are used to enable
dynamic routing using Routing Information Protocol (RIP). RIP
and RIP version 2 can be used. RIP-send with V1-compat option
enables the sending of RIPv2 packets using multicast. RIP-receive
with V1-compat option accepts both RIPv1 and RIPv2 packets.
6. Enable/disable routing between ATM VCCs (Routing Policy).
5-8
IP forwarding and dynamic route distribution between A TM VCC
routing can be disabled when multiple VCCs are used.
7. Enable/disable default gateway.
The default gateway is the host to which your M10 will send a
packet when it does not know how to reach the packet’s
destination host.
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 58

DRAFT
Management
8. Select the default gateway port from the Interface option menu.
The default gateway port can be one of the active PPP channels or a
specified IP address defined in Default Address field (see step 9.).
9. Enter IP address for your default gateway if you selected
’ip-address’ in step 8.
10. Enter domain name server settings.
A domain name server is a network computer responsible for
matching host names to numeric IP addresses so that network
traffic can be routed correctly. These fields are set if DNS
addresses are not allocated dynamically. Consult your service
provider for further assistance.
Domain names identify organisations on the Internet. The domain
name is usually the domain name of your company or your ISP.
If secondary name server address is configured the M10 relays the
name service request to that server if the primary name server is
unavailable.
11. Enable/disable DHCP server.
As a Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) server your M10
can assign IP addresses to other devices on your LAN. If you want
your M10 to assign IP addresses, enter the first number of the IP
address range in the Start Address field and the last number of the
IP address range to the End Address field. Lease Time indicates
how often the PC will renew the DHCP lease.
If you want your M10 to relay the DHCP request to an external
server you can do this by enabling relay-agent and entering the
server’s IP address to the Server Address field.
Note If you use M10 as a DHCP server, you should assign IP
addresses outside the M10’s DHCP address range to
devices requiring static IP addresses. Before M10
assigns an IP address to a DHCP client, it verifies that
no other device is using that address. However,
network conflicts can result when the M10 assigns an
address in its DHCP range to one device and the
another device configured to use that address is turned
on.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-9
Page 59

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
12. Change M10 Web-HTTP port number if needed.
You can change M10 internal Web server port number default
value 80 if the same number is used for pinhole functionality.
13. Change M10 telnet port number if needed.
You can change M10 internal telnet server port number default
value 23 if the same number is used for pinhole functionality.
14. Click Go to NAT Setup to configure the pinhole functionality, if
needed.
15. Enter static routes
Static route identifies a manually configured route to a remote
network. Unlike dynamic routes, which are acquired and
confirmed periodically from other routers, static routes do not time
out.
You can enter static routes by entering the remote router’s
destination address, net mask and gateway address. After you
have entered the required information click Add.
16. Save the configuration.
Y ou must save the new configuration. Save command takes you to
the M10 home page.
17. Restart your M10.
You must restart your M10 by clicking Restart M10 for your
changes to take effect.
5-10
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 60

5.1.4 Bridge page
Bridge page is used to enable/disable bridging. When bridging is
enabled the page is used to select the interfaces which are included in
the bridging function.
DRAFT
Management
Figure 5-7 Bridge page
Only those A TM interfaces which support ’ether-llc’ or ’ether -vcmux’
encapsulation or ’ppp-vcmux’ encapsulation with BNCP support can
be used in bridging operation.
Entering bridge settings
1. Turn on bridge
2. Click ATM to configure ATM channels, if needed (see Section
5.1.5).
3. Select the interfaces you want to use for bridging.
Ethernet indicates the Ethernet interface of M10. DSL VCC [N]
radio buttons indicate ATM channels using ’ether-llc’ or
’ether-vcmux’ encapsulation. WAN VCC [N] radio buttons
indicate ATM channels using ’ppp-vcmux’ encapsulation with
BNCP support.
4. Enable/disable bridging between ATM VCCs.
This option can be used when multiple M10s are connected
together using bridged connection. Disabling the bridging
between the VCCs eliminates the loops from the bridged network.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-11
Page 61

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
5. Save the configuration.
Y ou must save the new configuration. Save command takes you to
the M10 home page.
6. Restart your M10.
You must restart your M10 by clicking Restart M10 for your
changes to take effect.
5.1.5 ATM page
ATM page is used to enable/disable ATM channels and select the
payload encapsulation method for the particular channel. After
enabling an A TM channel you can configure the channel in more detail
through the ATM-channel-specific Config buttons.
5-12
Figure 5-8 ATM page
Entering ATM settings
1. Enable a channel by selecting the encapsulation from the option
menu. Up to eight ATM channels can be used.
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 62

Management
2. Configure the ATM channels.
Click Config button for the channel you want to configure.
Configuring ATM channels
PPP over ATM (VC-muxed)
DRAFT
Figure 5-9 ATM channel configuration page (VC–muxed)
1. Set the virtual path and virtual channel identifications.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-13
Page 63

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
2. Enable/disable IP.
IP Settings allows you to activate the IP layer function of the A TM
channel. Local address and peer address specify the basic IP
address parameters of the ATM channel interface (PPP over
ATM). If you enter 0.0.0.0 to these fields the M10 will try to get
them from the network either using IPCP protocol (ATM channel
using PPP) or DHCP (ATM channel not using PPP).
Address mapping radio button activates/deactivates the Network
Address Port Translation (NAPT).
3. Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP) settings.
Enable/disable dynamic routing for the active IP interface on the
ATM channel by selecting the corresponding radio buttons. If
RIP-send is selected the M10 sends RIP messages (version 1, 2 or
both) to the network. If RIP-receive is selected the M10 listens to
RIP messages from the network. RIP-send with V1-compat option
enables the sending of RIPv2 packets using multicast. RIP-receive
with V1-compat option accepts both RIPv1 and RIPv2 packets. If
you enable Flush Routes the learned routes are deleted when the
PPP connection is disconnected.
4. Add static routes to the routing table of the interface.
Enter destination address, net mask and gateway and click Add.
5. Save the configuration.
Y ou must save the new configuration. Save command takes you to
the M10 home page.
6. Restart your M10.
You must restart your M10 by clicking Restart M10 for your
changes to take effect.
5-14
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 64

Other encapsulations
DRAFT
Management
Figure 5-10 ATM channel configuration page (other encaps.)
1. Set the virtual path and virtual channel identifications.
2. Enable/disable IP.
IP settings allows you to activate the IP layer function of the A TM
channel. Local address, netmask and broadcast address specify
the basic IP address parameters of the ATM channel interface (IP
over RFC1483). If you enter 0.0.0.0 to these fields the M10 will try
to get them from the network either using IPCP protocol (ATM
channel using PPP) or DHCP (ATM channel not using PPP).
Address mapping radio button activates/deactivates the Network
Address Port Translation (NAPT).
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-15
Page 65

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
3. Configure Routing Information Protocol (RIP) settings.
Enable/disable dynamic routing for the active IP interface on the
ATM channel by selecting the corresponding radio buttons. If
RIP-send is selected the M10 sends RIP messages (version 1, 2 or
both) to the network. If RIP-receive is selected the M10 listens to
RIP messages from the network. RIP-send with V1-compat option
enables the sending of RIPv2 packets using multicast. RIP-receive
with V1-compat option accepts both RIPv1 and RIPv2 packets.
4. Add static routes to the routing table of the interface.
Enter destination address, net mask and gateway and press Add.
5. Save the configuration.
Y ou must save the new configuration. Save command takes you to
the M10 home page.
6. Restart your M10.
You must restart your M10 by clicking Restart M10 for your
changes to take effect.
5-16
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 66

5.1.6 NAT pinhole page
NAT pinhole page is used to make servers located in LAN visible to
WAN through a VCC. It allows fixed NAPT mapping between
WAN/VCC IP address/port number and internal LAN IP address/port
number. Separate entries are created for TCP and UDP ports.
The standard port numbers for the most common protocols are:
D HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is TCP port 80
D FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is TCP port 21
D SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is TCP port 25
D NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is TCP port 119
DRAFT
Management
Figure 5-11 NAT pinhole page
1. Enter the External Port Start and External Port End number . These
define the available range of allowed external ports (port number
in WAN interface). Select the protocol. Enter Internal IP address
(server IP address in LAN) and Internal Port number (server port
number in LAN).
2. Click Add.
3. Repeat until each server’s information is filled.
4. To remove entry just press delete.
Pinhole configuration example
The pinhole configuration example in Figure 5-12 can be used to allow
access from W AN to a W eb server in LAN. The example configuration
relays the traffic coming to the M10 WAN TCP port 80 to the LAN IP
address 192.168.1.1 port 80. Port 80 is a standard TCP port for HTTP .
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-17
Page 67

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Note M10’s integral Web server used for monitoring and
configuration uses also port 80 by default. You must
change the Server Port Setup through the Router page
or else the TCP traffic to this port is directed to the M10
Web server instead of the Web server in LAN.
Figure 5-12 Pinhole configuration example
5-18
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 68

5.1.7 SNMP page
SNMP page is used to configure the SNMP-related parameters of
M10. In M10, the SNMP can be used only for writing/reading system
contact information and trap addresses. Trap address is an address to
which a trap is sent in case of an authentication violation.
DRAFT
Management
Figure 5-13 SNMP page
Entering SNMP settings
1. Enter contact information and system location information in the
corresponding fields.
2. Enable/disable authentication traps.
3. Add/delete user communities, if needed.
Enter the name of the new user community into the field.
4. Enter trap destination addresses.
Enter the IP addresses of the hosts to which the traps are sent. Enter
also the community string related to this address.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-19
Page 69

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
5. Save the configuration.
Y ou must save the new configuration. Save command takes you to
the M10 home page.
6. Restart your M10.
You must restart your M10 by clicking Restart M10 for your
changes to take effect.
5.1.8 Monitor page
You can get information about the status and statistics of the M10
through the Monitor page. The following links are available on the
Monitor page.
D Overview displays the basic identification information of M10.
D Memory displays the memory usage of M10.
D Show displays the Diagnostic log of M10.
D Reset scrolls the Diagnostic log window back to the first message.
D PPP displays status information about the IP/PPP interfaces.
D Ethernet displays status information of the Ethernet interface.
D ATM displays status information of the ATM channels.
D Interfaces displays status information of the active interfaces.
D Routes displays the routing table.
D ARP displays the ARP cache table.
D DHCP Server displays the DHCP server lease table.
D DHCP Client displays the IP address settings M10 has received
from the network.
D DSL displays the the status of the ADSL connection and statistics
about the connection.
D Table displays the bridge table
D Home returns to home page.
5-20
Figure 5-14 Monitor page
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 70

5.2 Command line interface
The Nokia M10 operating software includes a command line interface
(CLI) that lets you monitor and configure your M10 over a telnet or a
local serial console connection. You can use the CLI to enter and
update a Nokia M10’s configuration settings, monitor its performance,
and restart it. Some CLI commands are not available until certain
conditions are met. For example, you must turn a function on before
you can enter settings for that function.
The commands of the CLI are divided into two hierarchies: Root and
Config. The Root command hierarchy lets you monitor the
performance of your M10, display and reset M10 statistics, and issue
administrative commands to restart M10 functions. The Config
command hierarchy lets you configure the settings of your M10.
DRAFT
Management
5.2.1 Starting and ending a CLI session
You can open a command line interface session by opening a telnet
connection from a workstation on your network to an M10 Ethernet or
ADSL port or by connecting a terminal to the console port on the Nokia
M10.
Connecting from telnet
You initiate a telnet connection by issuing the following command
from an IP host that supports telnet (or a personal computer running a
telnet application such as Microsoft or NCSA Telnet).
telnet ADSL_ip_address
You must know the IP address of the Nokia M10 before you can
connect to is via a telnet connection to it. Y ou can use a W eb browser or
the serial console to configure the M10’s IP address.
Connecting from the console port
You can connect a terminal or a terminal emulator to the console port
on the Nokia M10 front panel to configure, administer, and monitor
your Nokia M10. To use the Nokia M10 console, you need a serial
cable and either a terminal or a terminal emulator (such as a personal
computer with a terminal emulation application that supports
9600-baud communication).
To connect your Nokia M10 to a terminal or terminal emulators:
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-21
Page 71

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
1. Plug the serial cable E64320.01 into the console port behind the
hatch on the Nokia M10 front panel.
2. Connect the other end of the serial cable to the serial port on your
terminal (or terminal emulator) or the serial port of your computer.
3. T urn on the terminal or run the terminal emulator program on your
computer.
Use the following settings to configure your terminal emulation
session:
Setting Value
Speed 9600
Parity None
Data bits 8
Stop bits 1
Duplex Full
Flow control None
The console interface uses the same command line interface as the
telnet interface.
Logging in
The command line interface login process emulates the login process
for a Unix host. If your Nokia M10 has been assigned an administrator
password, you must enter a username (up to 32 characters) and your
administrator or user password.
Entering your username lets the Nokia M10 record your access; your
username is not used to validate your authorisation. Entering the
administrator password lets you display and update Nokia M10
settings. Entering a user password lets you display (but not update)
Nokia M10 settings.
5-22
When you have logged in successfully, the command line interface
lists the username and the security level (admin or user) associated
with the password you entered in the diagnostic log.
Entering commands in Nokia M10 CLI
CLI commands consist of keywords and arguments. Keywords in a
Config command specify the action you want to take or the entity on
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 72

DRAFT
Management
which you want to act. Arguments in a Config command specify the
values appropriate to your site. For example, the Config command
ip ip-ppp address
ip-ppp, and address) and one argument (
ip_address
consists of three keywords (ip,
ip_address
). When you
configure your M10, you replace command arguments with values
appropriate to your site. For example,
192.31.222.57
set ip ip-ppp address
The optional arguments are marked with braces {argument} and the
mandatory arguments with square brackets [argument].
The Table 5-1 provides guidelines for formatting CLI commands.
set
Command component
Command word CLI commands must start with a command
Keywords Keywords are not case-sensitive. You can
Argument text Text strings can be as many as 32 characters
Rules for entering CLI commands
word (set, show, delete). You can truncate
CLI commands to three characters (set,
sho, del). CLI commands are not casesensitive. You can enter “SET“, “Set“ or set.
enter “system, “System“ or “SYSTEM“ as a
keyword without changing its meaning. Keywords can be abbreviated to the length that
they are differentiated from other keywords.
For example, you can reduce the command
“set ip ip-ppp option on“ to “set i i
o on“.
long, unless otherwise specified. Special
characters are represented using backslash
notation. Text strings may be enclosed in
double (”) or single (’) quote marks. If the text
string includes an embedded space, it must
be enclosed in quotes.
Numbers Enter numbers as integers.
IP addresses Enter IP addresses in dotted decimal notation
Table 5-1 CLI syntax
If a command is ambiguous or miskeyed, the Nokia CLI prompts you
to enter additional information.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
(nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn, where nnn = 0 to 255).
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-23
Page 73

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Ending a CLI session
You end a command line interface session by typing
mode. Entering
quit in the Config mode switches the session into the
Root mode.
Using the CLI help facility
The help command lets you display on-line help for Root and Config
commands. To display a list of the commands available to you from
your current location in the command line interface hierarchy, type
help. To display help related to a particular command type the
command followed by a question mark, e.g.
Saving settings
The
save command saves the working copy of the settings to restart
values. You can save the changes you have entered for a specific
function or for all functions in the Nokia M10. The Nokia M10
automatically validates its settings when you save and displays a
warning message if the configuration is not correct.
5.2.2 The Root command hierarchy
quit in the Root
show ?.
Y ou begin in Root mode when you start a CLI session. The Root mode
lets you monitor the performance of your M10, display and reset M10
statistics, and issue administrative commands to restart M10
functions.
Root prompt
When you are in Root mode, the CLI prompt is the name of the M10
followed by a right angle bracket (>). For example, if you open a
command line interface to the M10 named “Kilo” you would see
Kilo> as your CLI prompt.
Root command shortcuts
You can truncate most commands in the command line interface to
their shortest unique string. For example, you can use the truncated
command q in place of the full quit command to exit the command
line interface. However, you would need to enter
command, since the first characters of
restart command.
reset are common to the
rese for the reset
5-24
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 74

DRAFT
Management
The only command you cannot truncate is restart. To prevent
accidental interruption of communications, you must enter the
restart command in its entirety.
Y o u can use the
!! command to repeat the last command you entered.
You can press the Ctrl-P or Esc-k key sequences to obtain the same
result.
Root commands
You can get a list of the Root commands by typing
? in the Root
prompt.
D help command to get help
D configure command to configure unit’s options
D ping command to send ICMP Echo request
D atmping command to send ATM OAM loopback
D arp command to send ARP request
D quit command to quit shell
D reset command to reset subsystems
D restart command to restart unit
D show command to show system information
D telnet command to telnet to a remote host
D who command to show who is using the shell
D log command to add a message to the diagnostic log
D loglevel command to report or change diagnostic log level
D install command to download and program an image
into flash
D download command to download a config file
D upload command to upload a config file
D clear command to erase all stored configuration
information
The following tables present the Root commands, their detailed
descriptions, syntax and usage examples.
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-25
Page 75

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Send ARP request
Description Sends an Address resolution protocol request to match
the nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn IP address to an Ethernet hard-
ware address.
Syntax arp [nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn]
Arguments The argument is an IP string which consists of four
decimal numbers with values between 0 and 255 sep-
arated by dots.
Example M10> arp 192.221.11.11
Command Clear configuration settings
Description Clears the configuration settings of your M10. Issuing
the restart command after the clear command re-
stores the default configuration. clear command alone
clears the configuration and brings M10 into an unde-
fined state.
Syntax clear {yes}
Arguments If you do not use the optional yes argument CLI
prompts you to confirm the clear command.
Example M10> clear yes
5-26
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 76

DRAFT
Management
Command Download software update
Description Downloads a new version of the Nokia M10 operating
software from a TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol)
server, validates the software image, and programs the
image into the Nokia M10 memory. After you install new
operating software, you must restart the Nokia M10.
Syntax install [server_address] [filename] {confirm}
Arguments The TFTP server must be accessible on your Ethernet
network or through one of the active ATM virtual chan-
nels and a route to the server must exist. The server
address argument identifies the IP address of the
TFTP server on which your Nokia M10 operating soft-
ware is stored. The filename argument identifies the
path and name of the operating software file on the
TFTP server. If you include the optional confirm key-
word, you will not be prompted to identify a TFTP
server or file name. Your Nokia M10 begins the soft-
ware installation using its default boot settings.
Example M10> install 192.168.1.1 m10c_500.d39
*** WARNING *** YOU ARE ABOUT TO ERASE
AND REPROGRAM THE NOKIA M10’S PERMANENT
SOFTWARE STORAGE WITH A NEW SOFTWARE VER-
SION OBTAINED VIA THE TFTP PROTOCOL.
About to install new Flash EPROM software
image:
server: 192.168.1.1
file: “m10c_500.d39”
Do you wish to proceed? (type ’yes’ to
confirm): yes
Installing
M10>
Command Add message to log
Description Adds the message in the
to the Nokia M10 diagnostic log.
Syntax log [message_string]
Arguments message_string argument is the message you want
to add to the log.
message_string
argument
Example M10> log 05/05/99
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-27
Page 77

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Define log level
Description Displays or modifies the types of log messages you
want the Nokia M10 to record. You can enter the loglevel command with the level argument to specify the
types of diagnostic messages you want to record. All
messages with a level number equal to or greater than
the level you specify are recorded.
Syntax loglevel {level}
Arguments If you enter the loglevel command without the op-
tional
rent log level setting. The values for the argument are:
1 or low Trivial status messages.
2 or medium Messages that can help
3 or high Status messages that may be
4 or warning Recoverable error conditions
5 or failure Messages describing error
level
argument, the Nokia CLI displays the cur-
monitor the network traffic.
significant but do not
constitute errors.
and useful operator
information
conditions that may not be
recoverable
Example M10> loglevel 3
Command Ping
Description Causes the Nokia M10 to issue a series of ICMP Echo
requests for the device with the specified IP address.
You can use the ping command to determine whether
an IP address is already in use on your network. You
cannot use the ping command to ping the Nokia M10’s
own IP address. If a host using the specified IP address
is active, it returns one or more ICMP Echo replies,
confirming that it is accessible from your network.
Syntax ping [ip_address]
Arguments ip_address argument is the IP address, in dotted
decimal notation, of the device you want to locate.
Example M10> ping 192.122.12.11
5-28
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 78

DRAFT
Management
Command ATM ping
Description Sends 5 OAM F5 loopback cells to the specified VPI/
VCI destination with a 5 second total timeout interval.
Syntax atmping [vpi] [vci] [segment | end-to-end]
Arguments vpi and vci specify the channel and the third argu-
ment specifies segment or end-to-end loopback.
Example m10> atmping 0 100 segment
Command Exit
Description Exits the Nokia M10 command line interface.
Syntax quit
Arguments None.
Example M10> quit
Command Reset ATM statistics
Description Resets ATM statistics to zero.
Syntax reset atm
Arguments None
Example M10> reset atm
Command Clear crash information
Description Clears crash-dump information which identifies the con-
tents of M10 registers at the point of system malfunc-
tion.
Syntax reset crash
Arguments None.
Example M10> reset crash
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-29
Page 79

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Reset DHCP server leases
Description Resets DHCP server leases.
Syntax reset dhcp server
Arguments None
Example M10> reset dhcp server
Command Release DHCP client lease
Description Resets DHCP client lease of the WAN port.
Syntax reset dhcp client lease
Arguments None
Example M10> reset dhcp client lease
Command Retrieve DHCP client configuration
Description Retrieves the DHCP client configuration for the WAN
port.
Syntax reset dhcp client retrieve
Arguments None
Example M10> reset dhcp client retrieve
Command Reset ADSL connection
Description Resets the ADSL connection.
Syntax reset dsl
Arguments None.
Example M10> reset dsl
Command Reset Ethernet statistics
5-30
Description Resets the Ethernet statistics to zero.
Syntax reset enet
Arguments None.
Example M10> reset enet
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 80

DRAFT
Management
Command Rewind log
Description Rewinds the diagnostic log display to the top of the ex-
isting M10 diagnostic log. The reset log command
does not clear the diagnostic log. The next show log
command will display information from the beginning of
the log file.
Syntax reset log
Arguments None.
Example M10> reset log
Command Reset PPP connection
Description Resets and restarts the PPP connection of the speci-
fied ATM logical channel. When you issue the reset
ppp command the Nokia M10 closes the PPP session
on the specified ATM channel and restarts the connec-
tion.
Syntax reset ppp [vccx]
Arguments vccx indicates the ATM channel, x = 1 – 8.
Example M10> reset ppp vcc1
Command Reset packet statistics
Description Resets packet statistics to zero.
Syntax reset xdsl
Arguments None
Example M10> reset xdsl
Command Restart M10
Description Restarts M10. You must enter the the complete restart
command to initiate a restart.
Syntax restart {seconds}
Arguments If you include the optional seconds arguments your
Example M10> restart 5
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Nokia M10 will restart when the specified number of
seconds has elapsed.
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-31
Page 81

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Show crash information
Description Displays the most recent crash information.
Syntax show crash
Arguments None.
Example M10> show crash
Command Show DHCP server leases in RAM
Description Displays the DHCP leases stored in RAM.
Syntax show dhcp server leases
Arguments None.
Example M10> show dhcp server leases
Command Show DHCP server leases in NVRAM
Description Displays the DHCP leases stored in NVRAM
Syntax show dhcp server store
Arguments None.
Example M10> show dhcp server store
Command Show DHCP client parameters
Description Displays the DHCP client parameters of the WAN port.
Syntax show dhcp client
Arguments None.
Example M10> show dhcp client
5-32
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 82

DRAFT
Management
Command Show Ethernet statistics
Description Displays the Ethernet statistics of your M10.
Syntax show enet {all}
Arguments Optional argument all displays more detailed informa-
tion.
Example M10> show enet
Ethernet driver statistics, device 0:
Packets out: 16578
Packets in: 11
Xmit errors: 0
Recv errors: 0
CRC errors: 0
Frame errors: 0
No buffers: 0
No handler: 0
No message: 0
M10>
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-33
Page 83

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Show ADSL information
Description Displays the current status and some statistics about
the ADSL connection, e.g. upstream and downstream
data rates.
Syntax show dsl
Arguments None.
Example M10> show dsl
DSL Statistics:
Type: ADI DMT
Datapump HW Rev: 0
Datapump FW Rev: 2220ca05
Current Status: Operational
Init Status: Initialization successful
Last Init Status: Initialization success-
ful
Current rate 7968000 bps 640000 bps
Maximum rate 10336000 bps 832000 bps
Fast parity bytes 0 0
Fast Codeword Size 1 1
Int Parity Bytes 10 8
Int Codeword Size 136 184
Interleve Depth 8 0
Downstream Upstream
Near end
Error seconds 0
Noise Margin 7 db
Attenuation 17 db
Transmitted blocks 34814571
Received Blocks 34814433
Corrected Blocks 0
Uncorrected Blocks 0
M10>
5-34
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 84

DRAFT
Management
Command Show ATM information
Description Displays the current status and some statistics of the
active ATM channels.
Syntax show atm {all}
Arguments Optional argument all displays more detailed informa-
tion.
Example M10> show atm
ATM port status: Cell delineation
achieved
Serial Rx relay: 4
Rx data rate (bps): 7968000
Tx data rate (bps): 640000
VCC# Type VPI VCI Bound Encapsulation
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
1 PVC 0 100 Yes PPP over ATM (VC-
muxed)
M10>
Command Show ARP table
Description Displays the Ethernet address resolution table stored in
M10.
Syntax show ip arp
Arguments None.
Example M10> show ip arp
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-35
Page 85

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Show IP interfaces
Description Displays the IP interfaces of your M10.
Syntax show ip interfaces
Arguments None.
Example M10> show ip interfaces
IP Interfaces:
ENET (lan): (up broadcast default ripsend v1 rip-receive v1)
inet 192.168.1.254
netmask ffffff00
broadcast 192.168.1.255
physical address 00.40.43.08.ff.ff
mtu 1500
PPP (vcc1): (up point-to-point rip-send
v2 rip-receive v2)
inet 10.98.20.21
netmask 0
peer address 10.98.20.1
physical address
00.00.00.00.00.00
mtu 1500
M10>
Command Show IP routes
Description Displays the IP routes stored in your M10.
Syntax show ip routes
Arguments None.
Example M10> show ip routes
IP gateway (route) table:
0. Default Gateway –> PPP (vcc1), D 2, T
0, (configured) UP DEFAULT
IP route cache
Net 192.168.1.1, gateway 192.168.1.1,
metric 0, timeout 0, via ENET (lan)
Net 192.168.1.255, broadcast, via ENET
(lan)
M10>
5-36
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 86

DRAFT
Management
Command Show diagnostic log
Description Displays blocks of information from the Nokia M10
diagnostic log.
Syntax show log {all}
Arguments to see the entire log you can repeat the show log com-
mand or you can use the argument all and scroll
through the complete log.
Example M10> show log all
Command Show memory usage
Description Displays the memory usage of your M10.
Syntax show memory {all}
Arguments Optional argument all displays more detailed informa-
tion.
Example M10> show memory all
Command Show PPP information
Description Displays information about open PPP links.
Syntax show ppp {stats | lcp | ipcp | bncp | lastconnect}
Arguments You can display a subset of the PPP statistics by in-
cluding optional stats, lcp, ipcp, bncp, or last-
connect argument.
Example M10> show ppp
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-37
Page 87

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Show M10 information
Description Displays current status of a Nokia M10, the device’s
hardware and software revision levels, a summary of
errors encountered, and the length of time the Nokia
M10 has been running since it was last restarted.
Syntax show status
Arguments None.
Example M10> show status
Terminal shell v1.0
M10 multiport ADSL router/bridge
Running Nokia M10 software version 5.0.0
(build D35)
Software built by alan on Fri Nov 13
14:02:16 EST 1998
(completed login: admin level)
Serial number J984001344, CPU MPC860,
firmware 2.2
Product ID T66160.09 0
Error logger message counts:
Low 0, Medium 0, High 61, Warning 26,
Lost 0, Total 87
Boot state: running in dram
Uptime 00:00:12:25
M10>
5-38
Command Open telnet session
Description Opens a telnet session to a remote host
Syntax telnet [host] {port}
Arguments host is the IP address of the remote host. Optional
argument indicates the port of the remote host.
Example M10> telnet 1.12.123.123
Command Show users
Description Displays the names and hostnames of the current shell
users.
Syntax who
Arguments None
Example M10> who
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 88

DRAFT
Management
Command Download configuration file
Description Downloads a configuration file from a TFTP server.
Syntax download [server-ipaddress] [filename] {confirm}
Arguments server-ipaddress is the IP address of the TFTP
server. filename is the name of the configuration file.
If invoked as download with no arguments, you will be
prompted for information. If the optional confirm keyword is added, the transfer will proceed without further
questions.
Example M10> download 1.12.123.123 config1.cfg
***WARNING*** YOU ARE ABOUT TO DOWNLOAD A
CONFIGURATION FILE.
About to download configuration file:
server: 1.12.123.123
file: config1.cfg
Do you wish to proceed? (type ’yes’ to
confirm):yes
Downloading
Downloading file into RAM
File Download was successful
Replace existing configuration with downloaded configuration? (type ’yes’ to confirm):yes
172.16.0.0 has been added to the
list
Configuration data saved.
M10>
Command Upload configuration file
Description Uploads a configration file to a TFTP server.
Syntax upload [server-ipaddress] [filename] {confirm}
Arguments server-ipaddress is the IP address of the TFTP
server. filename is the name of the configuration file.
If invoked as upload with no arguments, you will be
prompted for information. If the optional confirm keyword is added, the transfer will proceed without further
questions.
Example M10> upload 1.12.123.123 config2.cfg con-
NTC C33539002SE_A0
firm
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-39
Page 89

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
5.2.3 Config command hierarchy
The Config mode lets you configure the parameters of your M10. The
command hierarchy consists of nodes and subnodes. Each node
contains the configurable parameters of that particular function.
top
system
dmt
atm
bncp
ip
location
dhcp
vcc
cell
ethernet
dsl
wan
gateway
ip–ppp
static_routes
vcc:1
vcc:2
vcc:3
vcc:4
vcc:5
vcc:6
vcc:7
vcc:8
vcc:N
vcc:N
vcc:N
dns
bridge
snmp
ip trap list
ppp
pinhole
servers
ethernet
dsl
wan
sysgroup
module
peer_database
vcc:N
vcc:N
vcc:N
port authentication
peer authentication
vcc:N
vcc:N
vcc:N
5-40
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 90

Config prompt
DRAFT
Management
Y ou reach the configuration mode of the M10 CLI by typing
config at
the Root prompt. When you are in Config mode, the CLI prompt
consists of the name of your M10 followed by your current node in the
hierarchy and two angle brackets (>>). For example, when you enter
Config mode (by typing
(top)>>
prompt reminds you that you are at the top of the Config
hierarchy. If you move to the
typing
ip at the Config prompt), the prompt changes to M10 (ip)>> to
config at the Root prompt), the M10
ip node in the Config hierarchy (by
identify your current location.
Navigating the Config hierarchy
You start at the top when you enter Config mode. The command line
interface reminds you of your location by showing your current node
after the M10 name:
M10 (top)>>
D
Moving from Config to Root
You can navigate from anywhere in the Config hierarchy back to
the Root level by entering the
quit command at the Config
command prompt and pressing Enter.
M10 (top)>> quit
M10>
Moving from top to a subnode
D
You can navigate from the top node to a subnode by entering the
node name (or the significant letters of the node name) at the
Config prompt and pressing Enter . For example, you move to the
ip subnode by entering
M10 (top)>> ip
M10 (ip)>>
ip and pressing Enter.
As a shortcut, you can enter the significant letters of the node in
place of the full node name at the Config prompt. The significant
characters of a node name are the letters that uniquely identify the
node. For example, only the
atm Config node starts with a, you
could enter one letter (”a”) to move to the atm node.
M10 (top)>> a
M10 (atm)>>
NTC C33539002SE_A0
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-41
Page 91

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Y ou would have to enter two or more letters (”ppp”) to move to the
PPP node, since its node name shares the first letter with the
preferences node.
D Jumping down several nodes at once
You can jump down several levels in the Config hierarchy by
entering the complete path to a node.
M10 (top)>> ip ip-ppp
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>>
Moving up one node
D
Y ou can move through the Config hierarchy one node at a time by
entering the
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>> up
M10 (ip)>>
up command.
Jumping to the top node
D
You can jump to the top level from anywhere in the Config
hierarchy by entering the
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>> top
M10 (top)>>
Moving from one subnode to another
D
top command.
You can move from one subnode to another by entering a partial
path that identifies how far back to climb.
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>> ppp module
M10 (ppp module)>>
Moving from any subnode to any other subnode
D
Y ou can move from any subnode to any other subnode by entering
a partial path that starts with a top-level Config command.
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>> ip gateway
M10 (ip gateway)>>
5-42
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 92

DRAFT
Management
D Entering commands without changing nodes
You can enter a complete Config command from anywhere in the
hierarchy without changing your current node.
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>> set system diag high
M10 (ip ip-ppp)>>
Here diagnostic level is set high in the system without jumping to
the node first.
Displaying current settings
Y ou can use the
your M10. When you are in Config mode, you use the
to display the current Config settings. If you enter the
show command to display the current Root settings of
show command
show command
at the top level of the Config hierarchy, the command line interface
displays the settings for all enabled functions in the M10. If you enter
show command at an intermediate node, you see all settings for that
the
node and its subnodes.
Stepping through M10 configuration
The Nokia M10 command line interface includes a step mode to
automate the process of entering configuration settings. When you use
the Config step mode, the CLI prompts you for all required and
optional information. You can enter the configuration values
appropriate for your site without having to enter complete CLI
commands.
When you are in step mode, the CLI prompts you to enter required and
optional settings. If a setting has a default value or a current setting, the
command line interface displays the default value for the command in
parentheses. If a command has a limited number of acceptable values,
those values are presented in brackets, with each value separated by a
vertical line. For example, the following CLI step command indicates
that the default value is off and that valid entries are limited to on and
off.
option (off) [on|off]: on
You can accept the default value for a field by pressing the Enter key .
To use a different value, type it in and press Enter.
Y ou can enter the Config step mode by typing
the Config hierarchy . Y ou can enter step mode for a particular node by
typing
NTC C33539002SE_A0
set
node_name
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
. For example:
set from the top node of
5-43
Page 93

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
M10 (top)>> set system
Stepping set mode (press Control-X <Enter> to exit)
system
name (”M10”): Kutoja
Diagnostic Level (High): medium
Stepping mode ended
See Chapter 4 for step mode installation examples.
Validating your configuration
You can use the
validate command to make sure that your
configuration settings have been entered correctly. If you use the
validate command M10 verifies that all required settings are present
and that the settings are consistent.
M10 (top)>> validate
Error: Subnet mask is incorrect
Global Validation did not pass inspection!
You can use the validate command to verify your configuration
settings at any time. Your M10 automatically validates your
configuration any time you save a modified configuration.
Config command reference
The top level configuration command nodes are listed below:
D system Unit system options
D preference CLI preferences
D atm ATM options
D bncp BNCP options
D ip TCP/IP options
D location Location Manager options
D dhcp DHCP options
D dns DNS options
D bridge Bridge options
D dmt DMT ADSL options
D snmp SNMP options
D ppp PPP options
D pinhole NAT/NAPT server configuration
D servers Local integrated server configuration
5-44
The sections below explain the commands under each top level
configuration node.
E Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 94

DRAFT
Management
System settings
Y ou can configure system settings to assign a name to your Nokia M10
and to specify what types of messages you want the diagnostic log to
record.
Command Set system name
Description Specifies the name of your Nokia M10. Each Nokia
M10 is assigned a name as a part of its factory initialisation. The default name for Nokia M10 is “M10”.
Once you have assigned a name to your Nokia M10,
you can enter that name in the Open Location text field
of your browser to open a connection to your Nokia
M10.
Syntax set system name [name]
Arguments name is an alphanumeric string of 16 characters.
Example m10> set system name M10
Command Set diagnostic level
Description Specifies the types of log messages you want the M10
to record. All messages with a level number equal to or
greater than the level you specify are recorded.
Syntax set system diagnostic-level {level}
Arguments If you enter the command without the optional level
argument, the Nokia CLI displays the current diagnostic
level setting. The values for the level argument are:
1 or low Trivial status messages.
2 or medium Messages that can help
monitor the network traffic.
3 or high Status messages that may be
significant but do not
constitute errors.
4 or warning Recoverable error conditions
and useful operator
information.
5 or failure Messages describing error
conditions that may not be
recoverable.
Example m10> set system diagnostic-level 3
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-45
Page 95

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Set password
Description Specifies the administrator, user-administrator, or user
password for a Nokia M10. When you enter the
system password
repeat the new password to verify that you entered it
correctly the first time. To prevent anyone from observing the password you enter, characters in the old and
new passwords are not displayed as you type them. A
password can be as many as eight alphanumeric characters. Passwords are case-sensitive and cannot include special characters or leading, trailing, or embedded spaces. For example, if you assign a password
of “NokiA” to an M10, you could not enter “NOKIA”,
“nokia”, “Nokia”, or “Nokia “ (with a trailing space) as an
acceptable password.
set
command, you are prompted to
Syntax set system password [admin | user-admin | user]
Arguments Arguments admin, user-admin and user specify
whether administrator, user-administrator or user password will be set. User password gives only viewing
rights. User-admin password gives rights to change
PAP and CHAP usernames and passwords and configure pinhole settings. You must set an admin password
before you can set user or user-admin passwords.
Example m10> set system password admin *****
Note An administrator or user password goes into effect
immediately . Y ou do not have to restart the M10 for the
password to take effect. Assigning an administrator or
user password to M10 does not affect communications
through the device.
5-46
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 96

DRAFT
Management
CLI preferences
You can set the CLI preferences to customize your environment.
Command Set CLI help mode
Description Specifies whether you want command help and
prompting information displayed. By default, the CLI
verbose preference is turned off. If you turn it on, the
CLI displays help for a node when you navigate to that
node.
Syntax set preference verbose [on | off]
Arguments The argument enables/disables verbose mode.
Example m10> set preference verbose off
Command Set display length
Description Specifies how many lines of information you want the
CLI to display at one time.
Syntax set preference more [lines]
Arguments
Example m10> set preference more 20
The lines argument specifies the number of lines you
want to see at one time. By default, the command line
interface shows you 16 lines of text before displaying
the prompt
lines argument the CLI displays information as an
uninterrupted stream (which is useful for capturing in-
formation to a text file).
More ... [y|n]?. If you enter 0 as the
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-47
Page 97

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
ATM settings
You can enable ATM over ADSL operation and configure up to eight
ATM channels into use. Y ou can select between five dif ferent ways to
encapsulate your payload in an ATM channel. You can also fine tune
the physical layer parameters of the ATM channel. See also DMT
(ADSL) settings on page 5-78.
Command Enable/disable ATM
Description Enables/disables the use of ATM on the ADSL link. Dis-
abling ATM forces M10 to work in a frame mode on the
ADSL link.
Syntax set atm option [on | off]
Arguments The argument enables/disables ATM.
Example m10> set atm option on
Command Set ATM cell header of an empty cell
Description Defines the ATM cell header of an empty (idle) ATM cell
as an 8-bit variable. This command affects the low-level
functionality of the ATM physical layer link and usually
you do not have to change this setting.
Syntax set atm cell ehead [0xbbbbbbbb]
Arguments ADSL standard value is 0x00000001 or 0x00000000
depending on the DSLAM. Nokia B20 requires the
value 0x00000001.
Example m10> set atm cell ehead 0x00000001
Command Set payload content of an empty cell
Description Defines the payload content of an empty (idle) ATM cell
as an 8-bit variable. This command affects the low-level
functionality of the ATM physical layer link and usually
you do not have to change this setting.
5-48
Syntax set atm cell epayload [0xbbbbbbbb]
Arguments ADSL standard value is 0x6A6A6A6A.
Example m10> set atm cell epayload 0x6A6A6A6A
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 98

DRAFT
Management
Command Enable/disable header error correction coset func-
tion
Description Enables/disables ATM header error correction coset
function in the ATM link. This command affects the lowlevel functionality of the ATM physical layer link and
usually you do not have to change this setting.
Syntax set atm cell hec_coset [on | off]
Arguments ADSL standard value is ON.
Example m10> set atm cell hec_coset off
Command Enable/disable ATM payload scrambling
Description Enables/disables the scrambling of the ATM payload on
the ADSL/ATM link. This command affects the low-level
functionality of the ATM physical layer link and usually
you do not have to change this setting.
Syntax set atm cell payload_scrambling [on | off]
Arguments ADSL standard value is ON.
Example m10> set atm cell payload_scrambling off
Command Enable/disable specific ATM channel
Description Enables/disables the specific logical ATM virtual chan-
nels. M10 supports up to eight ATM virtual channels.
Syntax set atm vcc [1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8] option [on | off]
Arguments The first argument 1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8 specifies the
channel and the second argument enables/disables it.
Example m10> set atm vcc 1 option off
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-49
Page 99

DRAFT
Nokia M10 User’s Manual
Command Set virtual path identifier for ATM channel
Description Sets the virtual path identifier for the specific logical
ATM channel. M10 is delivered to you with a default virtual circuit identifier so usually you do not have to
change this setting.
Syntax set atm vcc [1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8] vpi [0–255]
Arguments The first argument 1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8 specifies the
channel and the second argument sets the virtual path
identifier.
Example m10> set atm vcc 2 vpi 30
Command Set virtual channel identifier for ATM channel
Description Sets the virtual channel identifier for the specified logi-
cal ATM channel. M10 is delivered to you with a default
circuit identifier and usually you do not have to change
this setting.
Syntax set atm vcc [1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8] vci [0–65535]
Arguments The first argument 1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8 specifies the
channel and the second argument sets the virtual chan-
nel identifier.
Example m10> set atm vcc 2 vci 1221
5-50
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Page 100

DRAFT
Management
Command Set payload encapsulation for specific ATM chan-
nel
Description Defines how the payload is capsulated to the specified
logical ATM channel.
Syntax set atm vcc [1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8] encap [ip-llc | ip-
vcmux | ether-llc | ether-vcmux | ppp-vcmux]
Arguments The first argument 1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8 specifies the
channel and the second argument sets the encapsulation. The ip-llc and ether-llc encapsulations are according to RFC 1483 with LLC/SNAP encapsulation for ip
and Ethernet frames, respectively. The ip-vcmux and
ether-vcmux encapsulation are vc-multiplexed according to RFC 1483 for IP and Ethernet frames, respectively. In ppp-vcmux encapsulation both bridged and
routed protocols are first encapsulated to point-to-point
protocol (PPP) which is, in turn, encapsulated to ATM
according to RFC 1483 vc-multiplexing.
Example m10> set atm vcc 2 encap ip-llc
NTC C33539002SE_A0
Copyright Nokia Telecommunications Oy
5-51
 Loading...
Loading...