Page 1

Technical Documentation
Programs After Market Services (PAMS)
Copyright E 1997. Nokia Mobile Phones. All Rights Reserved.
SERVICE
MANUAL
[NMP Part No.0275385]
NSE–6 SERIES
CELLULAR
PHONES
NSE–6 last update: 08/98
Page 2
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
Foreword
Original 08/98
Page 2
AMENDMENT RECORD SHEET
Amendment
Number
Date Inserted By Comments
Page 3

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
Foreword
Original 08/98
Page 3
NSE–6 SERIES CELLULAR PHONES
SERVICE MANUAL – OVERALL CONTENTS
Service Manual comprising
NSE–6 Series Transceiver booklet comprising
Chapter 1: Foreword
Chapter 2: General Information
Chapter 3: System Module US8
Appendices to Transceiver booklet covering a specific variant
Appendix 1: Transceiver NSE–6NX
Booklets comprising
Service Software Instructions
Tuning Instructions
Service Tools
Disassembly/Troubleshooting Instructions
Non–serviceable Accessories
Page 4

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
Foreword
Original 08/98
Page 4
IMPORTANT
This document is intended for use by qualified service personnel only.
Company Policy
Our policy is of continuous development; details of all technical modifications will
be included with service bulletins.
While every endeavour has been made to ensure the accuracy of this document,
some errors may exist. If any errors are found by the reader, NOKIA MOBILE
PHONES Ltd should be notified in writing.
Please state:
Title of the Document + Issue Number/Date of publication
Latest Amendment Number (if applicable)
Page(s) and/or Figure(s) in error
Please send to: Nokia Mobile Phones Ltd
PAMS Technical Documentation
PO Box 86
24101 SALO
Finland
Page 5

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
Foreword
Original 08/98
Page 5
Warnings and Cautions
Please refer to the phone’s user guide for instructions relating to operation,
care and maintenance including important safety information. Note also the
following:
Warnings:
1. CARE MUST BE TAKEN ON INSTALLATION IN VEHICLES
FITTED WITH ELECTRONIC ENGINE MANAGEMENT
SYSTEMS AND ANTI–SKID BRAKING SYSTEMS. UNDER
CERTAIN FAULT CONDITIONS, EMITTED RF ENERGY CAN
AFFECT THEIR OPERATION. IF NECESSARY, CONSULT THE
VEHICLE DEALER/MANUFACTURER TO DETERMINE THE
IMMUNITY OF VEHICLE ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS TO RF
ENERGY.
2. THE HANDPORTABLE TELEPHONE MUST NOT BE OPERATED
IN AREAS LIKELY TO CONTAIN POTENTIALLY EXPLOSIVE
ATMOSPHERES EG PETROL STATIONS (SERVICE STATIONS),
BLASTING AREAS ETC.
3. OPERATION OF ANY RADIO TRANSMITTING EQUIPMENT,
INCLUDING CELLULAR TELEPHONES, MAY INTERFERE WITH
THE FUNCTIONALITY OF INADEQUATELY PROTECTED
MEDICAL DEVICES. CONSULT A PHYSICIAN OR THE
MANUFACTURER OF THE MEDICAL DEVICE IF YOU HAVE
ANY QUESTIONS. OTHER ELECTRONIC EQUIPMENT MAY
ALSO BE SUBJECT TO INTERFERENCE.
Cautions:
1. Servicing and alignment must be undertaken by qualified
personnel only.
2. Ensure all work is carried out at an anti–static workstation and that
an anti–static wrist strap is worn.
3. Ensure solder, wire, or foreign matter does not enter the telephone
as damage may result.
4. Use only approved components as specified in the parts list.
5. Ensure all components, modules screws and insulators are
correctly re–fitted after servicing and alignment. Ensure all cables
and wires are repositioned correctly.
6. All PC’s used with NMP Service Software for this produce must be
bios and operating system ”Year 2000 Compliant”.
Page 6

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
Foreword
Original 08/98
Page 6
This page intentionally left blank.
Page 7

PAMS Technical Documentation
NSE–6 Series Transceivers
Original 08/98
Chapter 2
General Information
Page 8

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
General Information
Page 2 – 2
Original 08/98
CONTENTS
Product Selection 2 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Handportables 2 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Desktop Option 2 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Product and Module List 2 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Specifications 2 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Specifications of Transceiver NSE–6 2 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 9
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
General Information
Page 2 – 3
Original 08/98
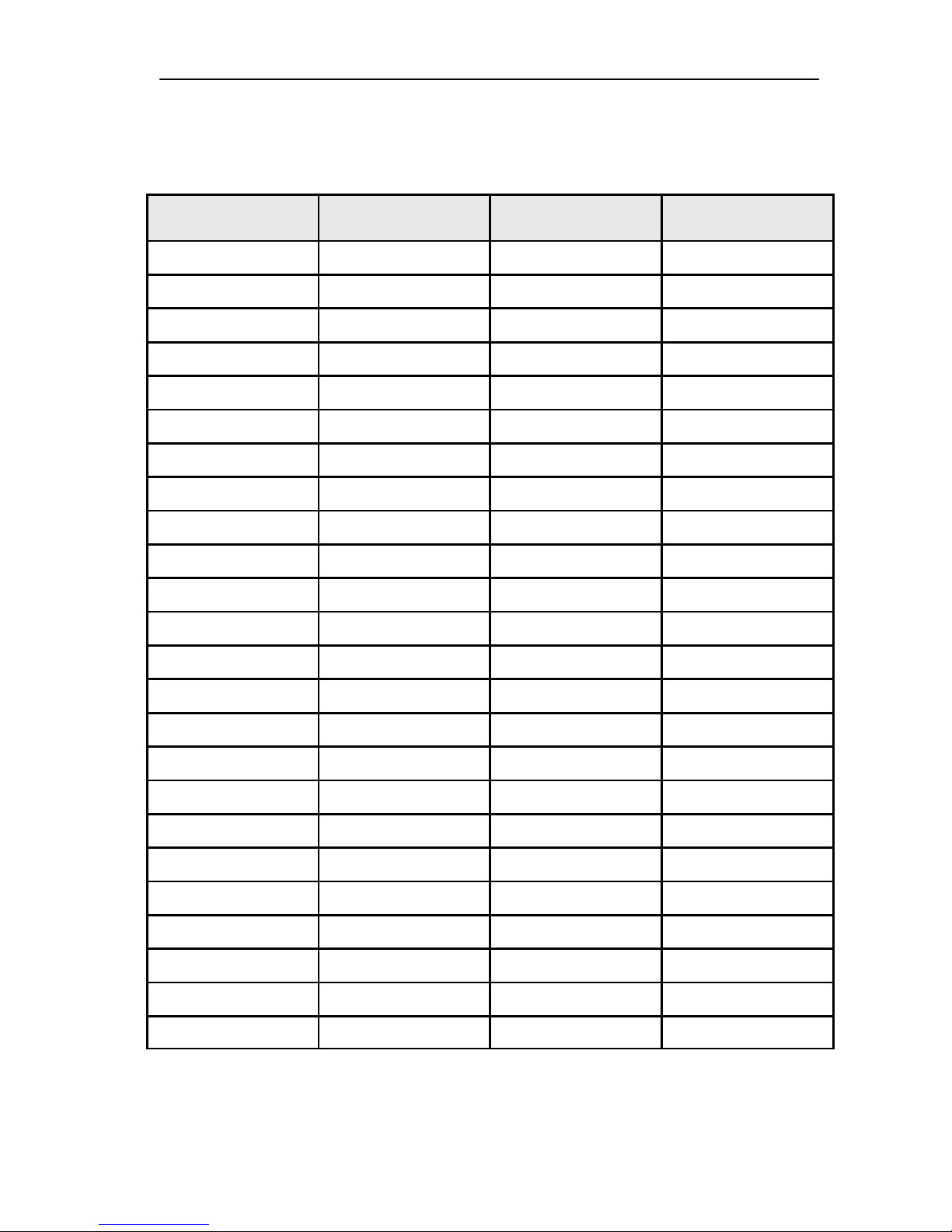
Product Selection
Handportables
The NSE–6 is a handportable mobile telephone for the GSM network.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
ACP–7E
ACP–7U
ACP–7C
ACP–7X
ACP–7H
ACP–7A
Item Name: Type code: Material code:
1. Transceiver See variant Appendices
2. Standard battery (NiMH 600 mAh) BMP–1D 0670240
3. AC Travel Charger
(Euro plug) 207–253 Vac ACP–7E 0675144
4. AC Travel Charger
(US plug) 108–132 V ac ACP–7U 0675143
AC Travel Charger
(US plug) 198–242 V ac ACP–7C 0675158
5. AC Travel Charger
(UK plug) 207–253 V ac ACP–7X 0675145
AC Travel Charger
(UK plug) 180–220 V ac ACP–7H 0675146
6. AC Travel Charger
(Australia) 216–264 Vac ACP–7A 0675148
Page 10
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
General Information
Page 2 – 4
Original 08/98
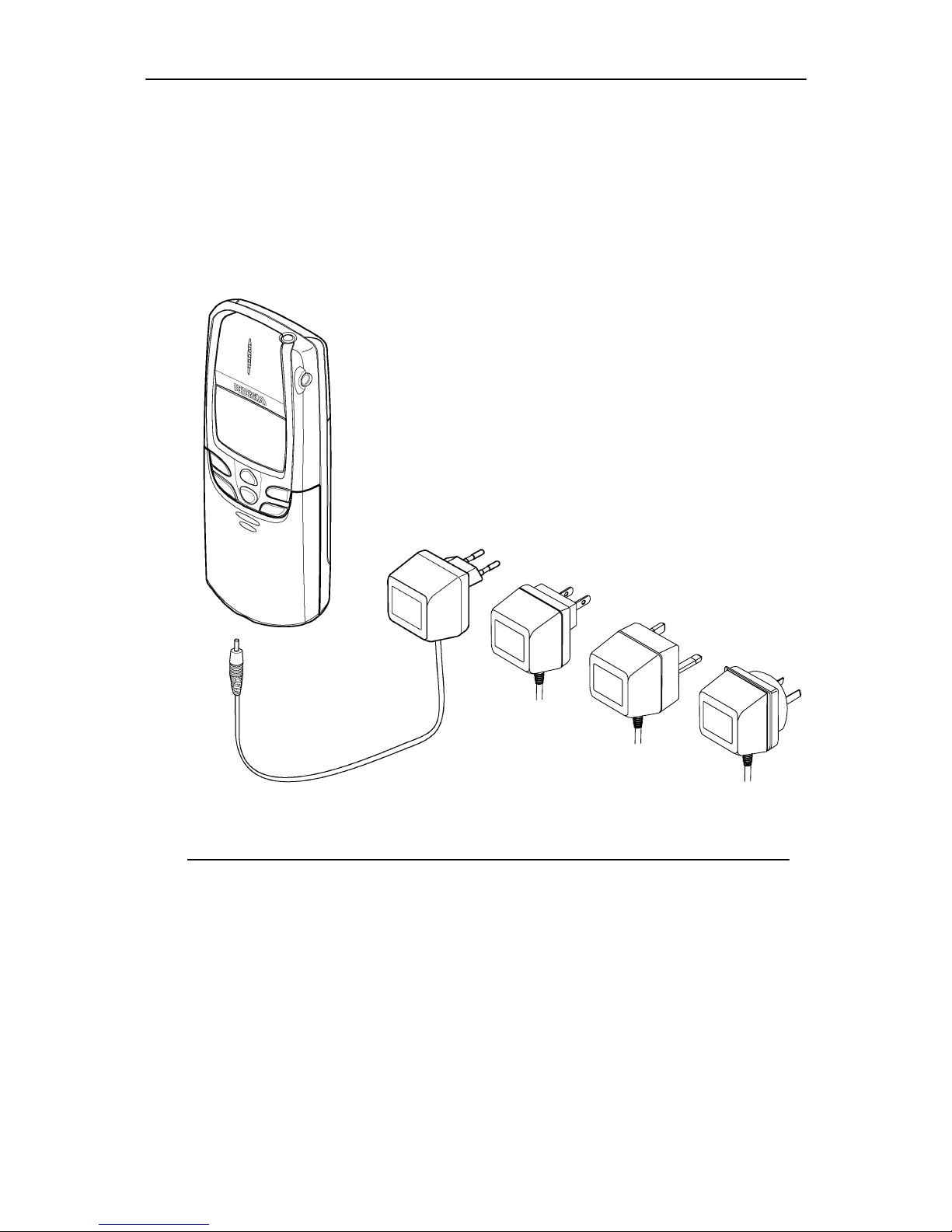
Desktop Option
The desktop option allows the user to charge the handportable and spare
battery from mains.
1.
3.
4.
5.
2.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Item Name: Type code: Material code:
1. Desktop stand CGE–1 0675180
2. AC Travel Charger
(Euro plug) 207–253 Vac ACP–7E 0675144
3. AC Travel Charger
(US plug) 108–132 V ac ACP–7U 0675143
AC Travel Charger
(US plug) 198–242 V ac ACP–7C 0675158
4. AC Travel Charger
(UK plug) 207–253 V ac ACP–7X 0675145
AC Travel Charger
(UK plug) 180–220 V ac ACP–7H 0675146
5. AC Travel Charger
(Australia) 216–264 Vac ACP–7A 0675148
6. Performance Travel Chg.
(Euro plug) 90–264 Vac ACT–1E 0675183
7. Performance Travel Chg.
(US plug) 90–264 V ac ACT–1U 0675184
8. Performance Travel Chg.
(UK plug) 90–264 V ac ACT–1X 0675185
9. Performance Travel Chg
.(Australia) 90–264 Vac ACT–1A 0675186
Page 11
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
General Information
Page 2 – 5
Original 08/98
Product and Module List
Unit/type: Product code:
Transceiver NSE–6 See variant
Appendixes
Standard Battery BMP–1D 600 mAh NiMH, black 0670240
Glossy Chrome Battery BMP–1A 600 mAh NiMH 0670230
AC Travel Charger ACP–7E (EUR) 207–253 Vac 0675144
AC Travel Charger ACP–7U (US) 108–132 Vac 0675143
AC Travel Charger ACP–7C (US) 198–242 Vac 0675158
AC Travel Charger ACP–7X (UK) 207–253 Vac 0675145
AC Travel Charger ACP–7H (UK) 180–220 Vac 0675146
AC Travel Charger ACP–7X (AUS) 216–264 Vac 0675148
Performance Travel Charger ACT–1E (EUR)
90–264 Vac
0675183
Performance Travel Charger ACT–1U (US)
90–264 Vac
0675184
Performance Travel Charger ACT–1X (UK)
90–264 Vac
0675185
Performance Travel Charger ACT–1A (AUS)
90–264 Vac
0675186
Cigarette Lighter Charger LCH–9 0675120
Desktop Stand CGE–1 0675180
Headset HDC–9 0694053
Page 12
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
General Information
Page 2 – 6
Original 08/98
Technical Specifications
General Specifications of Transceiver NSE–6
Parameter Unit
Cellular system GSM
RX frequency band 935 ... 960 MHz
TX frequency band 890 ... 915 MHz
Output power +5 ...+33 dBm / 3.2 mW ... 2 W
Duplex spacing 45 MHz
Number of RF channels 124
Channel spacing 200 kHz
Number of TX power levels 15
Sensitivity , static channel –102 dBm/ BER < 2.439 %
Frequency error, static channel < 0.1 ppm
RMS phase error < 5.0
o
Peak phase error < 20.0
o
Page 13

NSE–6 Series Transceivers
PAMS Technical Documentation
Original 08/98
Chapter 3
System Module
Page 14

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 2
CONTENTS
Transceiver NSE–6 3 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Introduction 3 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Operation Modes 3 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Interconnection Diagram 3 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Module 3 – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External and Internal Connectors 3 – 7. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contacts Description 3 – 8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Baseband Module 3 – 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Block Diagram 3 – 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Technical Summary 3 – 9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charging Connector 3 – 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Headset Connector 3 – 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service connections 3 – 12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Connector 3 – 13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SIM Card Connector 3 – 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Microphone in Slide 3 – 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RTC Backup Battery 3 – 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Buzzer 3 – 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description 3 – 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution 3 – 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery charging 3 – 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Startup Charging 3 – 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Overvoltage Protection 3 – 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Removal During Charging 3 – 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Different PWM Frequencies ( 1Hz and 32 Hz) 3 – 20. . . . . . .
Battery Identification 3 – 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Temperature 3 – 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Supply Voltage Regulators 3 – 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switched Mode Supply VSIM 3 – 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Up 3 – 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power up with a charger 3 – 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Up With The Power Switch (PWRONX) 3 – 25. . . . . . .
Power Up by RTC 3 – 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Up by IBI 3 – 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Acting Dead 3 – 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Active Mode 3 – 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sleep Mode 3 – 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Charging 3 – 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Off 3 – 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Watchdog 3 – 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Audio control 3 – 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
External Audio Connections 3 – 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Analog Audio Accessory Detection 3 – 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 15

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 3
Original 08/98
Headset Detection 3 – 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Internal Audio Connections 3 – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4–wire PCM Serial Interface 3 – 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Alert Signal Generation 3 – 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Digital Control 3 – 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MAD2 3 – 32. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Memories 3 – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Program Memory 3 – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SRAM Memory 3 – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EEPROM Memory 3 – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
MCU Memory Map 3 – 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flash Programming 3 – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
COBBA–GJ 3 – 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Real Time Clock 3 – 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RTC backup battery charging 3 – 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vibra Alerting Device 3 – 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IBI Accessories 3 – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Phone Power–on by IBI 3 – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IBI power–on by phone 3 – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF Module 3 – 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Maximum Ratings 3 – 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF Frequency Plan 3 – 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Distribution Diagram 3 – 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Characteristics 3 – 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Regulators 3 – 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Control Signals 3 – 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description 3 – 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Frequency synthesizers 3 – 49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver 3 – 51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter 3 – 52. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AGC strategy 3 – 54. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
AFC function 3 – 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Receiver blocks 3 – 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RX interstage filter 3 – 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1st mixer in CRFU_1a 3 – 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1st IF–filter 3 – 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter Blocks 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
TX interstage filter 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power amplifier module 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Synthesizer blocks 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
VHF VCO and low pass filter 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UHF PLL 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UHF PLL block in SUMMA 3 – 56. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UHF VCO module 3 – 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
UHF local signal input in CRFU_1a 3 – 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 16

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 4
Connections 3 – 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
RF baseband signals 3 – 57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Timings 3 – 60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Synthesizer control timing 3 – 60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmitter power switching timing diagram 3 – 62. . . . . . . . . . .
Synthesizer clocking 3 – 62. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Parts list of US8 (EDMS Issue 7.13) Code: 0201187 3 – 63. . . . . . . . .
Schematic Diagrams: US8
Block Diagram of UIF 3/A3–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram of UIF (Version 7.0 Edit 218) for layout version 07 3/A3–2
Block Diagram of Baseband 3/A3–3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram of Baseband (Version 7.0 Edit 105) for layout 07 3/A3–4
Circuit Diagram of Power Supply (Version 7.0 Edit 257) for layout 07 3/A3–5
Circuit Diagram of SIM Connectors (Version 7.0 Edit 71) for layout 07 3/A3–6
Circuit Diagram of CPU Block (Version 7.0 Edit 208) for layout 07 3/A3–7
Circuit Diagram of Audio (Version 7.0 Edit 126) for layout 07 3/A3–8
Circuit Diagram of IR Module (Version 7.0 Edit 96) for layout 07 3/A3–9
RF Block Diagram 3/A3–10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Diagram of RF Block (Version 1.0 Edit 244) for layout 07 3/A3–11
Layout Diagram of US8 – Top (Version 07) 3/A3–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Layout Diagram of US8 – Bottom (Version 07) 3/A3–12. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Testpoints of US8 – Top (Version 07) 3/A3–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Testpoints of US8 – Bottom (Version 07) 3/A3–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Testpoint references (Version 07) 3/A3–14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 17

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 5
Original 08/98
Transceiver NSE–6
Introduction
The NSE–6 is a radio transceiver unit designed for the GSM network. It is a
GSM phase 2 power class 4 transceiver providing 15 power levels with a
maximum output power of 2 W. The transceiver is a true 3 V transceiver.
The transceiver consists of System/RF module (US8), Keyboard module
(UK8) and assembly parts.
The transceiver has full graphic display and two soft key based user interface. The antenna is internal. External antenna connection is not available. The transceiver has leakage tolerant earpiece and noise cancelling
microphone. Integrated IR link provide connection for two NSE–6 transceivers or NSE–6 transceiver and PC.
The plug–in SIM ( Subscriber Identity Module ) card is located inside the
phone, slot for inserting is in the left side of the phone, accessable when
battery is removed and slide is open.
Operation Modes
There are six different operation modes:
– power off mode
– idle mode
– NSPS mode
– active mode
– charge mode
– local mode
In the power off mode only the circuits needed for power up are supplied.
In the idle mode circuits are powered down and only sleep clock is run-
ning.
In the No Serve Power Save mode circuits are powered down, and only
sleep clock is running if no carrier is found during the scanning period.
The purpose of this mode is to reduce power consumption in the non–
network area.
In the active mode all the circuits are supplied with power although some
parts might be in the idle state part of the time.
The charge mode is effective in parallel with all previous modes. The
charge mode itself consists of two different states, i.e. the charge and the
maintenance mode.
The local mode is used for alignment and testing.
Page 18
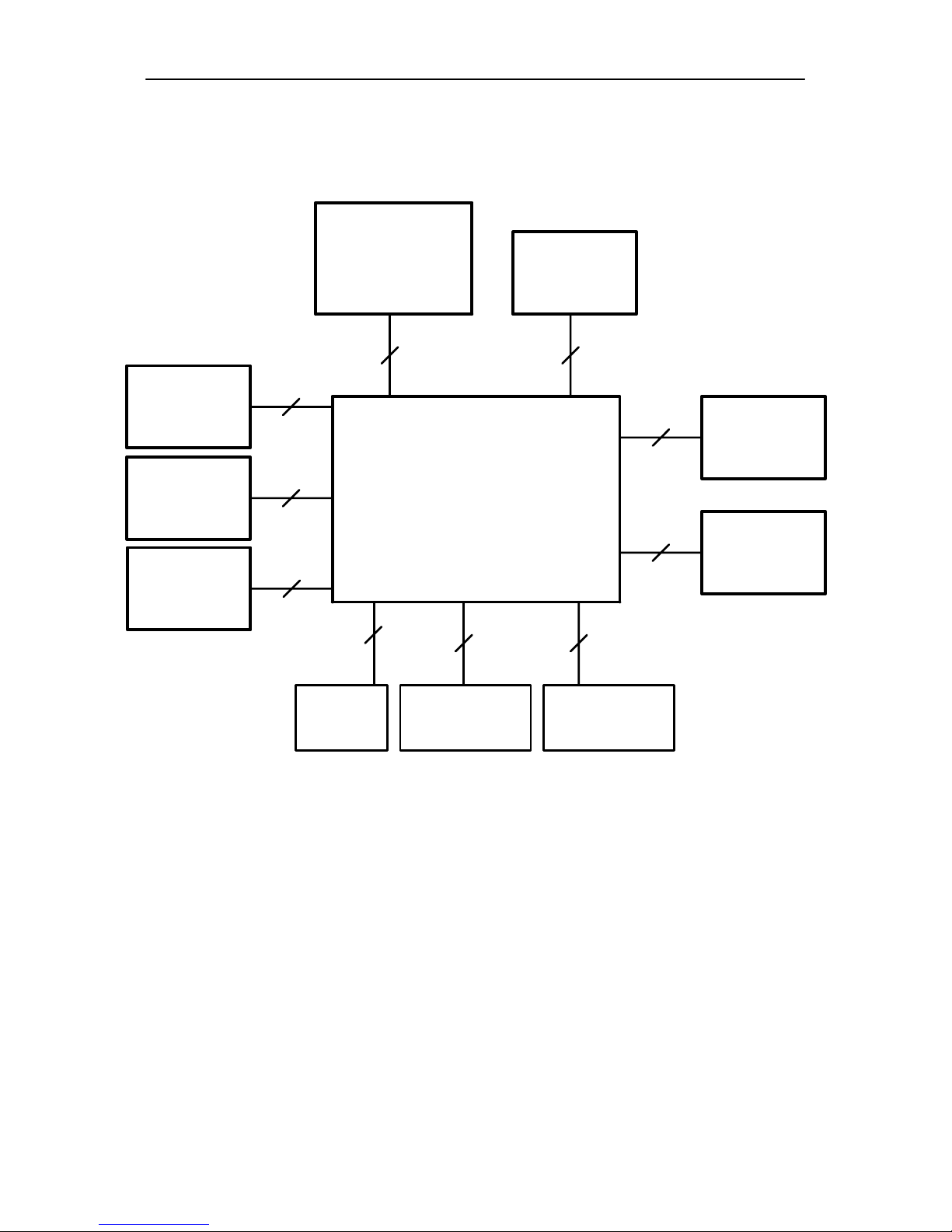
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 6
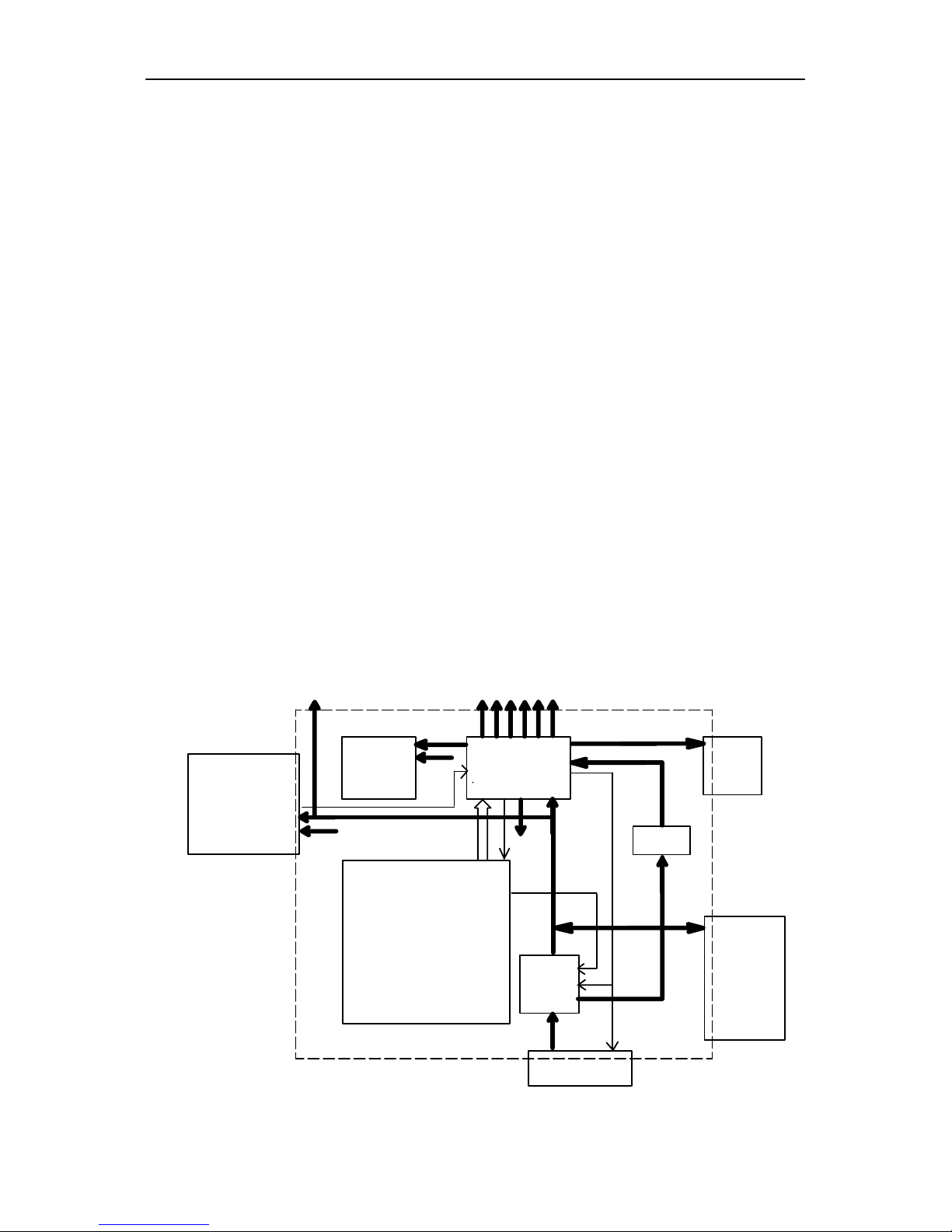
Interconnection Diagram
Module
System/RF
US8
Display
SIM
Battery
Charger
Antenna
3 + 3
Earpiece
IR Module
6
4
2
Mic
2
14
2
9
Keyboard
module
UK8
6
Vibra
2
Page 19
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 7
Original 08/98
System Module
External and Internal Connectors
Suppply Voltages and Power Consumption
Connector Line Symbol Minimum Typical /
Nominal
Maximum/
Peak
Unit / Notes
Charging VIN 7.1 8.4 9.3 V/ Travel charger,
ACT–1
Charging VIN 7.25 7.6 7.95 V/ Travel charger.
ACP–7
Charging I / VIN 720 800 850 mA/ Travel char-
ger, ACT–1
Charging I / VIN 320 370 420 mA/ Travel char-
ger, ACP–7
Battery contact signals
Pin Line
Symbol
Parameter Mini-
mum
Typical
/ Nomi-
nal
Maxi-
mum
Unit / Notes
1 BVOLT Battery voltage 3.0 3.6 5.3 V/ Maximum voltage in idle
mode with a charger connected
2 BSI
Input voltage 0 2.85 V/ Battery size indication
Phone has 100k pull up resistor
SIM Card removal detection
Battery indication
18"1% kohm/ Ni battery
resistor
20 22 24 kohm/ service battery
27 51 kohm/ 4.1V Li battery
68 91 kohm/ 4.2V Li battery
3 BTEMP Input voltage
Input voltage
Output voltage
0
2.1
1.9
1.4
3
2.8
V/ Battery temperature indication
V/ Phone power up (pulse)
V/ Battery power up (pulse)
4 BGND 0 0 V
Page 20

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 8
Contacts Description
The transceiver electronics consist of the Radio Module ie. RF + System
blocks, the keyboard PCB, the display module and audio components.
The keypad and the display module are connected to the Radio Module
with connectors. System blocks and RF blocks are interconnected with
PCB wiring. The Transceiver is connected to accessories via charger connector (includes jack and plates), headset connector and IR–link.
The System blocks provide the MCU, DSP and Logic control functions in
MAD ASIC, external memories, audio processing and RF control hardware in COBBA ASIC. Power supply circuitry CCONT ASIC delivers operating voltages both for the System and the RF blocks.
The RF block is designed for a handportable phone which operates in the
GSM system. The purpose of the RF block is to receive and demodulate
the radio frequency signal from the base station and to transmit a modulated RF signal to the base station. The SUMMA ASIC is used for VHF
and PLL functions. The CRFU ASIC is used at the front end.
Page 21
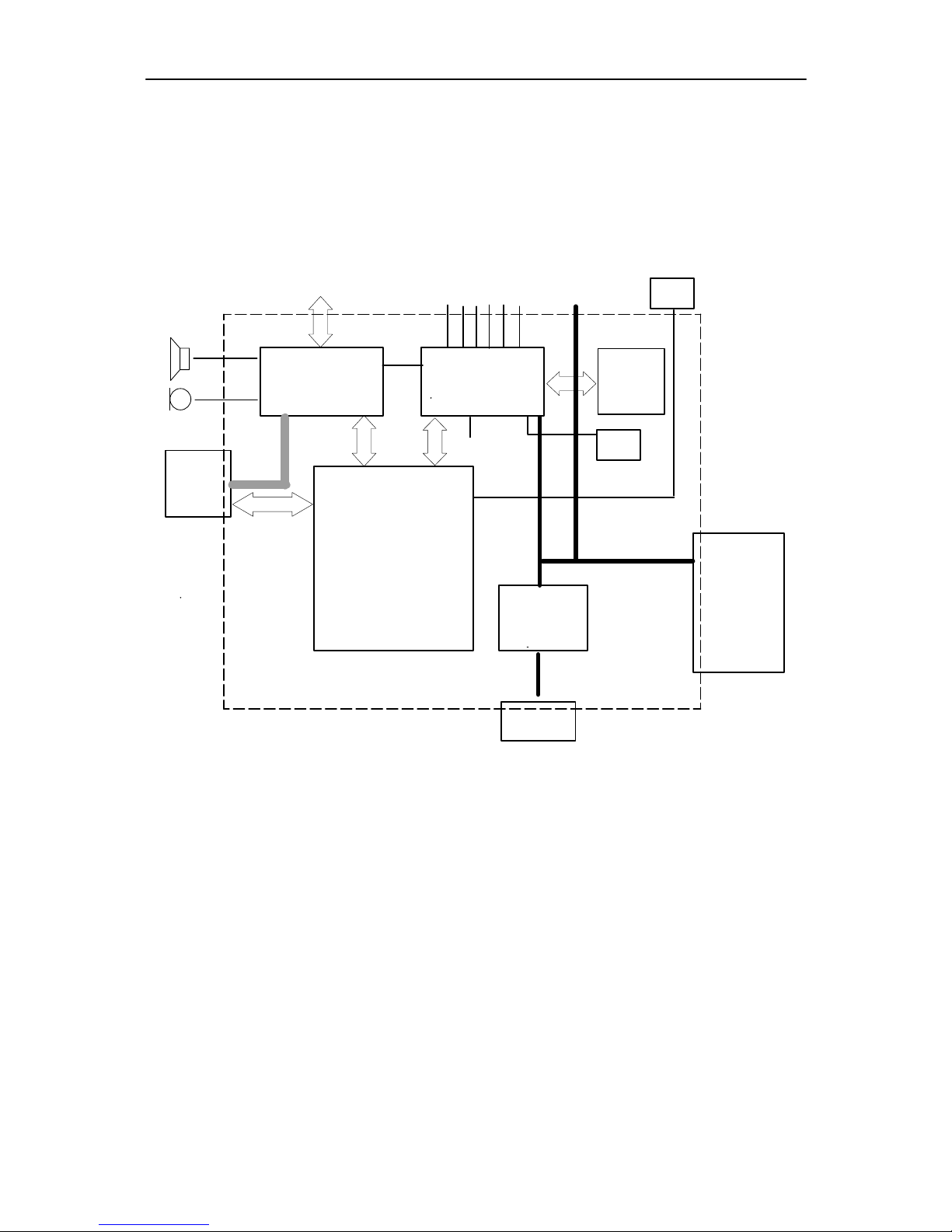
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 9
Original 08/98
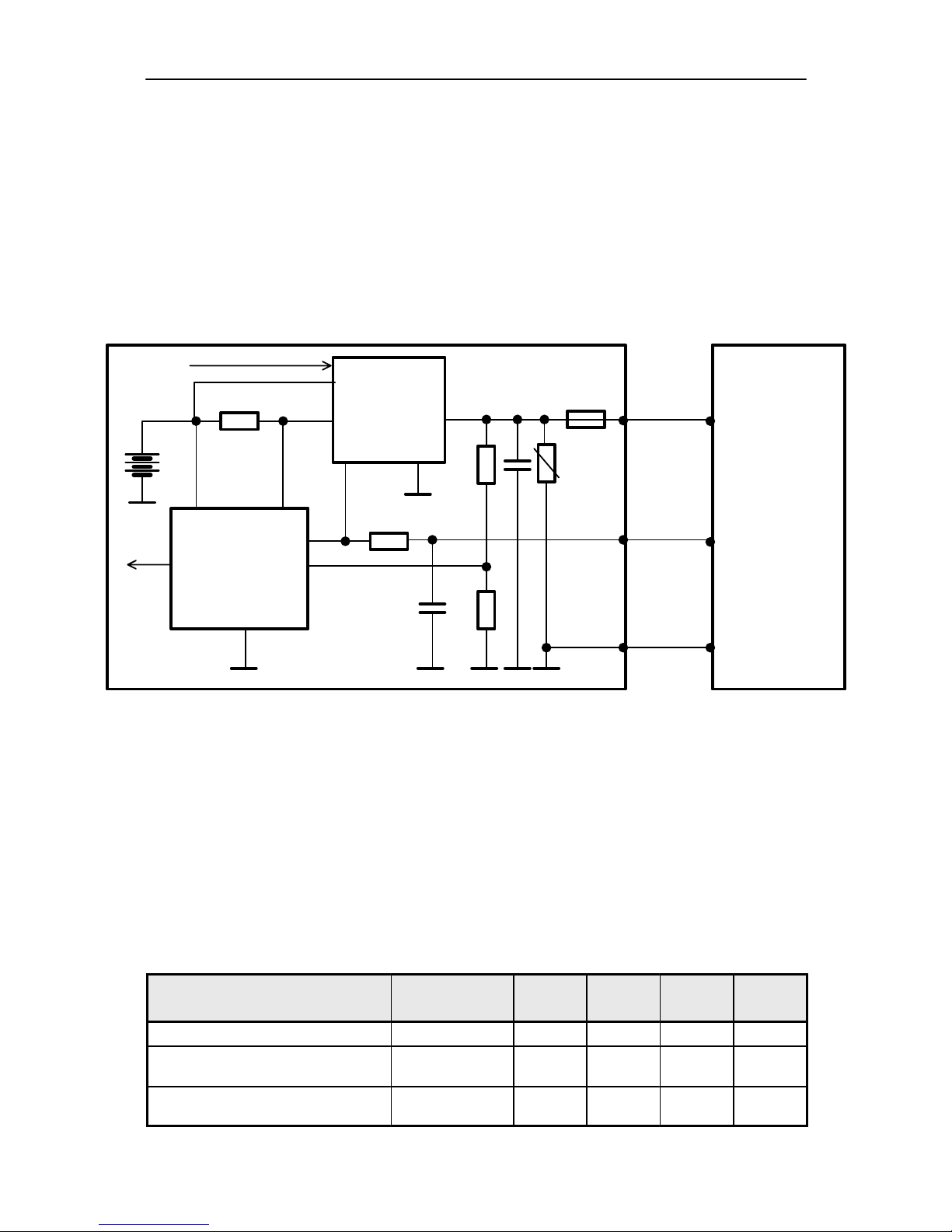
Baseband Module
Block Diagram
CCONT
UI
SIM
MAD
DC–jack
CHAPS
COBBA
BATTERY
PA SUPPLY
RF SUPPLIES
BB SUPPLY
TX/RX SIGNALS
BASEBAND
VBAT
+
MEMORIES
COBBA SUPPLY
32kHz
CLK
13MHz
CLK
SLEEP CLOCK
SYSTEM CLOCK
Technical Summary
The baseband module consists of four asics, CHAPS, CCONT, COBBA–
GJ and MAD2, which take care of the baseband functions of NSE–6.
The baseband is running from a 2.8V power rail, which is supplied by a
power controlling asic. In the CCONT asic there are 6 individually controlled regulator outputs for RF–section and two outputs for the baseband. In addition there is one +5V power supply output VCP for RF–part.
The CCONT contains also a SIM interface, which supports both 3V and
5V SIM–cards. A real time clock function is integrated into the CCONT,
which utilizes the same 32kHz clock supply as the sleep clock. A backup
power supply is provided for the RTC, which keeps the real time clock
running when the main battery is removed. The backup power supply is a
rechargable polyacene battery. The backup time with this battery is minimum of ten minutes.
Page 22

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 10
The interface between the baseband and the RF section is handled by a
specific asic. The COBBA asic provides A/D and D/A conversion of the
in–phase and quadrature receive and transmit signal paths and also A/D
and D/A conversions of received and transmitted audio signals to and
from the UI section. The COBBA supplies the analog TXC and AFC signals to rf section according to the MAD DSP digital control and converts
analog AGC into digital signal for the DSP. Data transmission between the
COBBA and the MAD is implemented using a parallel connection for high
speed signalling and a serial connection for PCM coded audio signals.
Digital speech processing is handled by the MAD asic. The COBBA asic
is a dual voltage circuit, the digital parts are running from the baseband
supply VBB and the analog parts are running from the analog supply
VCOBBA.
The baseband supports two external microphone inputs and two external
earphone outputs. The inputs can be taken from an internal microphone,
a headset microphone or from an signal source. The microphone signals
from different sources are connected to separate inputs at the COBBA
asic.
The output for the internal earphone is a dual ended type output capable
of driving a dynamic type speaker. Input and output signal source selection and gain control is performed inside the COBBA asic according to
control messages from the MAD. Keypad tones, DTMF, and other audio
tones are generated and encoded by the MAD and transmitted to the
COBBA for decoding. A buzzer alert and vibra control signals are generated by the MAD via UI–Switch.
Page 23

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 11
Original 08/98
Charging Connector
Contact Line Symbol Function
DC–jack
side contact
(DC–plug ring)
L_GND Charger ground
DC–jack
center pin
VIN Charger input voltage
DC–jack
side contact
(DC–plug jacket)
CHRG_CTRL Charger control output (from phone)
Pin Name Min Typ Max Unit Notes
2, b VIN
7.25
3.25
320
7.6
3.6
370
7.95
16.9
3.95
420
V
V
V
mA
Unloaded ACP–7 Charger (5kohms
load)
Peak output voltage (5kohms load)
Loaded output voltage (10ohms load)
Supply current
7.1
3.25
720
8.4
3.6
800
9.3
3.95
850
V
V
mA
Unloaded ACP–9 Charger
Loaded output voltage (10ohms load)
Supply current
3, a L_GND 0 0 V Supply ground
4, c CHRG_
0 0.5 V Charger control PWM low
CTRL
2.0 2.85 V Charger control PWM high
32 Hz PWM frequency for a fast charger
1 99 % PWM duty cycle
Headset Connector
Contact Line Symbol Function
2 XMIC Accessory microphone signal input (to phone)
1 SGND Accessory signal ground
3 XEAR Accessory earphone signal output (from phone)
Pin Name Min Typ Max Unit Notes
2 XMIC
2.0 2.2 kΩ Input AC impedance
1 Vpp Maximum signal level
100 600 µA Bias current
58 490 mV Maximum signal level
1 SGND
10 µF Series output capacitance
0 Ω Resistance to phone ground
Page 24
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 12
NotesUnitMaxTypMinNamePin
3 XEAR
47 Ω Output AC impedance (ref. SGND)
10 µF Series output capacitance
16 150 300 Ω Load AC impedance to SGND (Head-
set)
1.0 Vpp Maximum output level (no load)
22 626 mV Output signal level
16 1500 Ω Load DC resistance to SGND (Head-
set)
2.8 V DC voltage (47k pull–up to VBB)
Service connections
Pin Name Min Typ Max Unit Notes
J124 MBUS 0 logic low 0.8 V Serial bidirectional control bus.
2.0 logic high 2.85
Baud rate 9600 Bit/s
Phone has a 4k7 pullup resistor
J255 FBUS_RX 0 logic low 0.8 V Fbus receive. Serial Data
2.0 logic high 2.85
Baud rate 9.6k–230.4kBit/s
Phone has a 220k pulldown resistor
J256 FBUS_TX 0 logic low 0.5 V Fbus transmit. Serial Data
2.0 logic high 2.85
Baud rate 9.6k–230.4kBit/s
Phone has a 47k pullup resistor
J123 GND 0 0.3 V Supply ground
MBUS
FBUS RX
FBUS TX
GND
Battery pack lay
Battery connector
Phone from back sid
TOP
Page 25
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 13
Original 08/98
Battery Connector
The electrical specifications for the battery connector is shown in
NO TAG. The BSI contact on the battery connector is used to detect when
the battery is to be removed to be able to shut down the operations of the
SIM card before the power is lost if the battery is removed with power on.
The BSI contact in the battery pack is 0.7mm shorter than the supply
power contacts to give enough time for the SIM shut down.
Pin Name Min Typ Max Unit Notes
4 BVOLT 3.0 3.6 4.5 V Battery voltage
5.0
5.3
Maximum voltage in call state with charger
Maximum voltage in idle state with charger
3 BSI
0 2.85 V Battery size indication
Phone has 100kohm pull up resistor.
SIM Card removal detection
(Threshold is 2.4V@VBB=2.8V)
18"1% kohm Battery indication resistor (Ni battery)
20 22 24 kohm Battery indication resistor (service battery)
27 51 kohm Battery indication resistor (4.1V Lithium bat-
tery)
68 91 kohm Battery indication resistor (4.2V Lithium bat-
tery)
2 BTEMP
0 1.4 V Battery temperature indication
Phone has a 100k (+–5%) pullup resistor,
Battery package has a NTC pulldown resistor:
47k+–5%@+25C , B=4050+–3%
2.1
1 10
3
20
V
ms
Phone power up by battery (input)
Power up pulse width
1.9
90 100
2.85
200
V
ms
Battery power up by phone (output)
Power up pulse width
0 1 kohm Local mode initialization (in production)
1 BGND 0 0 V Battery ground
Page 26
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 14
SIM Card Connector
Pin Name Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
4 GND GND 0 0 V Ground
3, 5 VSIM 5V SIM Card
3V SIM Card
4.8
2.8
5.0
3.0
5.2
3.2
V Supply voltage
6 DATA 5V Vin/Vout
3V Vin/Vout
4.0
0
2.8
0
”1”
”0”
”1”
”0”
VSIM
0.5
VSIM
0.5
V SIM data
Trise/Tfall max 1us
2 SIMRST 5V SIM Card
3V SIM Card
4.0
2.8
”1”
”1”
VSIM
VSIM
V SIM reset
1 SIMCLK Frequency
Trise/Tfall
3.25
25
MHz
ns
SIM clock
Internal Microphone in Slide
Pin Name Min Typ Max Unit Notes
6 MICP 0.55 4.1 mV Connected to COBBA MIC2N input. The
maximum value corresponds to1 kHz, 0
dBmO network level with input amplifier
gain set to 32 dB. typical value is maximum value – 16 dB.
7 MICN 0.55 4.1 mV Connected to COBBA MIC2P input. The
maximum value corresponds to1 kHz, 0
dBmO network level with input amplifier
gain set to 32 dB. typical value is maximum value – 16 dB.
RTC Backup Battery
The RTC block in CCONT needs a power backup to keep the clock running when the phone battery is disconnected. The backup power is supplied from a rechargable polyacene battery that can keep the clock running minimum of 10 minutes. The backup battery is charged from the
main battery through CHAPS.
Signal Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
VBACK
Backup battery charging from CHAPS
3.02 3.15 3.28 V
Backup battery charging from CHAPS
100 200 500 uA Vout@VBAT–0.2V
VBACK
Backup battery supply
to CCONT
2 3.28 V Battery capacity
65uAh
Backup battery supply
to CCONT
80 uA
Page 27
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 15
Original 08/98
Buzzer
Signal Maximum
output cur-
rent
Input
high level
Input
low level
Level (PWM)
range, %
Frequency
range, Hz
BuzzPWM /
BUZZER
2mA 2.5V 0.2V 0...50 (128 lin-
ear steps)
440...4700
Page 28
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 16
Functional Description
Power Distribution
In normal operation the baseband is powered from the phone‘s battery.
The battery consists of three Nickel Metal Hydride cells. There is also a
possibility to use batteries consisting of one Lithium–Ion cell. An external
charger can be used for recharging the battery and supplying power to
the phone. The charger can be either a standard charger that can deliver
around 400 mA or so called performance charger, which can deliver supply current up to 850 mA.
The baseband contains components that control power distribution to
whole phone excluding those parts that use continuous battery supply.
The battery feeds power directly to following parts of the system: CCONT,
power amplifier, and UI (buzzer, display, keyboard lights, IR and vibra).
Figure below shows a block diagram of the power distribution.
The power management circuit CHAPS provides protection agains overvoltages, charger failures and pirate chargers etc. that would otherwise
cause damage to the phone.
CCONT
SIM
+
DC–jack
CHAPS
COBBA
BATTERY
PA SUPPLY
RF SUPPLIES
VBB
BASEBAND
VBAT
VCOBBA
VSIM
VBB
CNTVR
PWM
VBAT
PWRONX
PURX
VIN
UI
BACKUP
RTC
MEMORIES
MAD
LIM
VBB
Page 29
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 17
Original 08/98
Battery charging
The electrical specifications give the idle voltages produced by the acceptable chargers at the DC connector input. The absolute maximum input voltage is 30V due to the transient suppressor that is protecting the
charger input. At phone end there is no difference between a plug–in
charger or a desktop charger. The DC–jack pins and bottom connector
charging pads are connected together inside the phone.
VIN
CHAPS
4k7
1n
PWM
VBAT
GND
CCONT
CHRG_CTRL
L_GND
CHARGER
PWM_OUT
TRANSCEIVER
0R22
VCHAR
ICHAR
47k
22k
1u
1.5A
30V
VCH
VOUT
RSENSE
GND
NOT IN
ACP–7
CCONTINT
MAD
LIM
MAD
Startup Charging
When a charger is connected, the CHAPS is supplying a startup current
minimum of 130mA to the phone. The startup current provides initial
charging to a phone with an empty battery. Startup circuit charges the
battery until the battery voltage level is reaches 3.0V (+/– 0.1V) and the
CCONT releases the PURX reset signal and program execution starts.
Charging mode is changed from startup charging to PWM charging that is
controlled by the MCU software. If the battery voltage reaches 3.55V
(3.75V maximum) before the program has taken control over the charging, the startup current is switched off. The startup current is switched on
again when the battery voltage is sunken 100mV (nominal).
Parameter Symbol Min Typ Max Unit
VOUT Start– up mode cutoff limit Vstart 3.45 3.55 3.75 V
VOUT Start– up mode hysteresis
NOTE: Cout = 4.7 uF
Vstarthys 80 100 200 mV
Start–up regulator output current
VOUT = 0V ... Vstart
Istart 130 165 200 mA
Page 30
PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 18
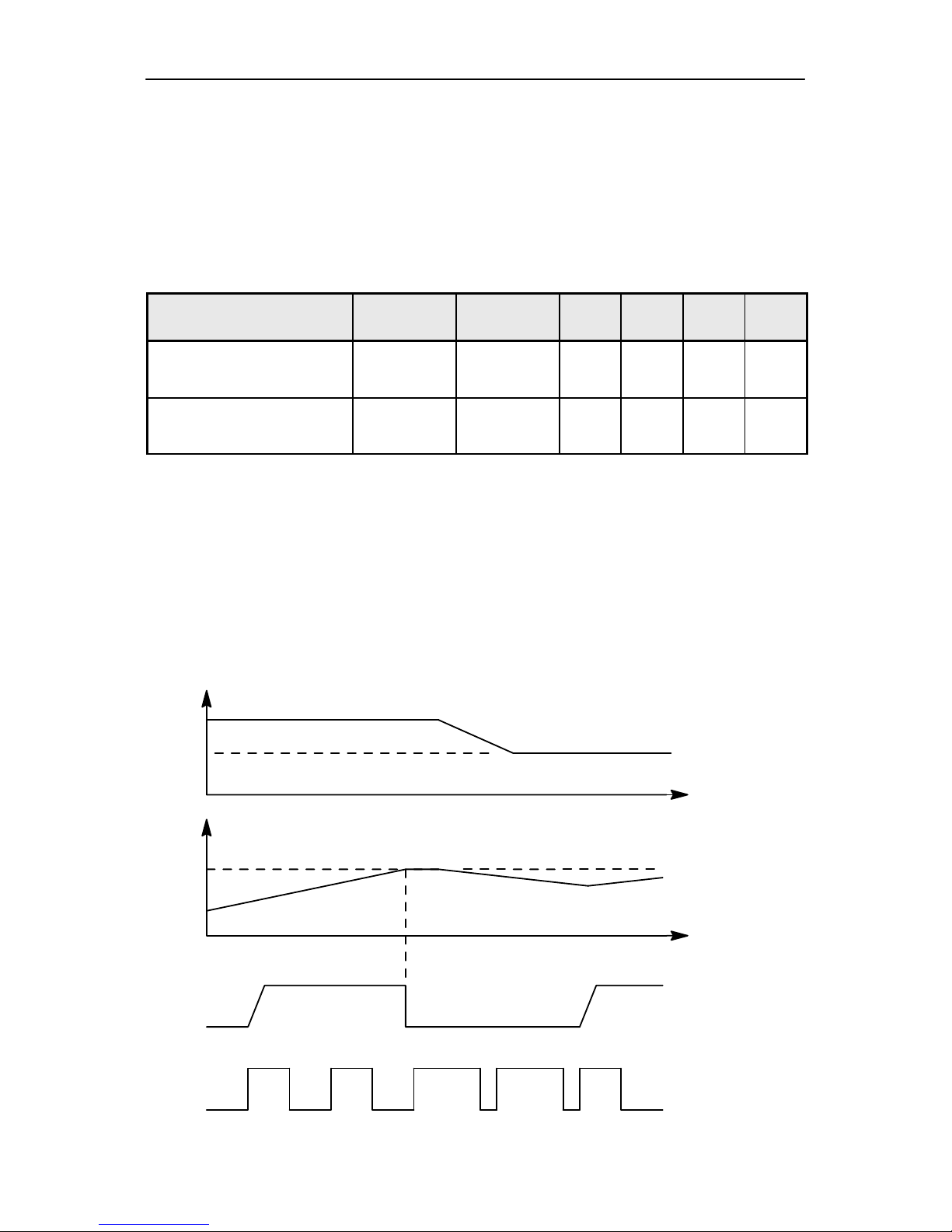
Battery Overvoltage Protection
Output overvoltage protection is used to protect phone from damage.
This function is also used to define the protection cutoff voltage for different battery types (Li or Ni). The power switch is immediately turned OFF if
the voltage in VOUT rises above the selected limit VLIM1 or VLIM2.
Parameter Symbol LIM input Min Typ Max Unit
Output voltage cutoff limit
(during transmission or Li–
battery)
VLIM1 LOW 4.4 4.6 4.8 V
Output voltage cutoff limit
(no transmission or Ni–bat-
tery)
VLIM2 HIGH 4.8 5.0 5.2 V
The voltage limit (VLIM1 or VLIM2) is selected by logic LOW or logic
HIGH on the CHAPS (N101) LIM– input pin. Default value is lower limit
VLIM1.
When the switch in output overvoltage situation has once turned OFF, it
stays OFF until the the battery voltage falls below VLIM1 (or VLIM2) and
PWM = LOW is detected. The switch can be turned on again by setting
PWM = HIGH.
PWM (32Hz)
VOUT
VLIM1 or VLIM2
t
SWITCH
ON OFF
VCH
t
VCH<VOUT
ON
Page 31

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 19
Original 08/98
Battery Removal During Charging
Output overvoltage protection is also needed in case the main battery is
removed when charger connected or charger is connected before the battery is connected to the phone.
With a charger connected, if VOUT exceeds VLIM1 (or VLIM2), CHAPS
turns switch OFF until the charger input has sunken below Vpor (nominal
3.0V, maximum 3.4V). MCU software will stop the charging (turn off
PWM) when it detects that battery has been removed. The CHAPS remains in protection state as long as PWM stays HIGH after the output
overvoltage situation has occured.
PWM
t
VOUT
t
4V
VLIM
”1”
”0”
SWITCH
t
ON
OFF
2
1.1Battery removed, (standard) charger connected, VOUT rises (follows charger voltage)
2. VOUT exceeds limit VLIM(X), switch is turned immediately OFF
3.3VOUT falls (because no battery) , also VCH<Vpor (standard chargers full–rectified
output). When VCH > Vpor and VOUT < VLIM(X) –> switch turned on again (also PWM
is still HIGH) and VOUT again exceeds VLIM(X).
4
4. Software sets PWM = LOW –> CHAPS does not enter PWM mode
Vstart
5
5. PWM low –> Startup mode, startup current flows until Vstart limit reached
VCH
(Standard
Charger)
Vpor
Vstarthys
Drop depends on load
Istart off due to VCH<Vpor
& C in phone
6
6. VOUT exceeds limit Vstart, Istart is turned off
7. VCH falls below Vpor
7
Page 32

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 20
Different PWM Frequencies ( 1Hz and 32 Hz)
When a travel charger (2– wire charger) is used, the power switch is
turned ON and OFF by the PWM input when the PWM rate is 1Hz. When
PWM is HIGH, the switch is ON and the output current Iout = charger current – CHAPS supply current. When PWM is LOW, the switch is OFF and
the output current Iout = 0. To prevent the switching transients inducing
noise in audio circuitry of the phone soft switching is used.
The performance travel charger (3– wire charger) is controlled with PWM
at a frequency of 32Hz. When the PWM rate is 32Hz CHAPS keeps the
power switch continuously in the ON state.
SWITCH
PWM (1Hz)
SWITCH
PWM (32Hz)
ON
ON ONON OFF OFF
Page 33

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 21
Original 08/98
Battery Identification
Different battery types are identified by a pulldown resistor inside the battery pack. The BSI line inside transceiver has a 100k pullup to VBB. The
MCU can identify the battery by reading the BSI line DC–voltage level
with a CCONT (N100) A/D–converter.
SIMCardDetX
MAD
BSI
CCONT
VBB
2.8V
TRANSCEIVER
R
s
BATTERY
BSI
BGND
BTEMP
BVOLT
10k
10n
100k
The battery identification line is used also for battery removal detection.
The BSI line is connected to a SIMCardDetX line of MAD2 (D200). SIMCardDetX is a threshold detector with a nominal input switching level
0.85xVcc for a rising edge and 0.55xVcc for a falling edge. The battery
removal detection is used as a trigger to power down the SIM card before
the power is lost. The BSI contact in the battery pack is made 0.7mm
shorter than the supply voltage contacts so that there is a delay between
battery removal detection and supply power off.
0.550.05 Vcc
0.850.05 Vcc
Vcc
GND
S
IGOUT
SIMCARDDETX
Page 34

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 22
Battery Temperature
The battery temperature is measured with a NTC inside the battery pack.
The BTEMP line inside transceiver has a 100k pullup to VREF. The MCU
can calculate the battery temperature by reading the BTEMP line DC–
voltage level with a CCONT (N100) A/D–converter.
100k
VREF
1.5V
TRANSCEIVER
R
T
BATTERY
BTEMP
BGND
BSI
BVOLT
10n
NTC
1k
MAD
BTEMP
CCONT
VibraPWM
10k
1k
MCUGenIO4
Supply Voltage Regulators
The heart of the power distrubution is the CCONT. It includes all the voltage regulators and feeds the power to the whole system. The baseband
digital parts are powered from the VBB regulator which provides 2.8V
baseband supply. The baseband regulator is active always when the
phone is powered on. The VBB baseband regulator feeds MAD and memories, COBBA digital parts and the LCD driver in the UI section. There is
a separate regulator for a SIM card. The regulator is selectable between
3V and 5V and controlled by the SIMPwr line from MAD to CCONT. The
COBBA analog parts are powered from a dedicated 2.8V supply VCOBBA. The CCONT supplies also 5V for RF. The CCONT contains a real
time clock function, which is powered from a RTC backup when the main
battery is disconnected.
Page 35

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 23
Original 08/98
The RTC backup is rechargable polyacene battery, which has a capacity
of 50uAh (@3V/2V) The battery is charged from the main battery voltage
by the CHAPS when the main battery voltage is over 3.2V. The charging
current is 200uA (nominal).
Operating mode Vref RF REG VCOB-
BA
VBB VSIM SIMIF
Power off Off Off Off Off Off Pull
down
Power on On On/Off On On On On/Off
Reset On Off
VR1 On
On On Off Pull
down
Sleep On Off Off On On On/Off
NOTE:
CCONT includes also five additional 2.8V regulators providing power to
the RF section. These regulators can be controlled either by the direct
control signals from MAD or by the RF regulator control register in
CCONT which MAD can update. Below are the listed the MAD control
lines and the regulators they are controlling.
– TxPwr controls VTX regulator (VR5)
– RxPwr controls VRX regulator (VR2)
– SynthPwr controls VSYN_1 and VSYN_2 regulators (VR4 and VR3)
– VCXOPwr controls VXO regulator (VR1)
CCONT generates also a 1.5 V reference voltage VREF to COBBA,
SUMMA and CRFU. The VREF voltage is also used as a reference to
some of the CCONT A/D converters.
In additon to the above mentioned signals MAD includes also TXP control
signal which goes to SUMMA power control block and to the power amplifier. The transmitter power control TXC is led from COBBA to SUMMA.
Page 36

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 24
Switched Mode Supply VSIM
There is a switched mode supply for SIM–interface and 5V regulator,
which supplies to RF section. SIM voltage is selected via serial IO. The
5V SMR can be switched on independently of the SIM voltage selection,
but can’t be switched off when VSIM voltage value is set to 5V.
NOTE: VSIM and V5V can give together a total of 30mA.
In the next figure the principle of the SMR / VSIM–functions is shown.
V5V
CCONT External
V5V_3
V5V_4
V5V_2
VBAT
5V
5V reg
VSIM
5/3V
Power Up
The baseband is powered up by:
1. Pressing the power key, that generates a PWRONX interrupt
signal from the power key to the CCONT, which starts the power up procedure.
2. Connecting a charger to the phone. The CCONT recognizes
the charger from the VCHAR voltage and starts the power up
procedure.
3. A RTC interrupt. If the real time clock is set to alarm and the
phone is switched off, the RTC generates an interrupt signal,
when the alarm is gone off. The RTC interrupt signal is connected to the PWRONX line to give a power on signal to the
CCONT just like the power key.
4. A battery interrupt. Intelligent battery packs have a possibility
to power up the phone. When the battery gives a short (10ms)
voltage pulse through the BTEMP pin, the CCONT wakes up
and starts the power on procedure.
Page 37

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 25
Original 08/98
Power up with a charger
When the charger is connected CCONT will switch on the CCONT digital
voltage as soon as the battery voltage exeeds 3.0V. The reset for
CCONT’s digital parts is released when the operating voltage is stabilized
( 50 us from switching on the voltages). Operating voltage for VCXO is
also switched on. The counter in CCONT digital section will keep MAD in
reset for 62 ms (PURX) to make sure that the clock provided by VCXO is
stable. After this delay MAD reset is relased, and VCXO –control
(SLEEPX) is given to MAD. The diagram assumes empty battery, but the
situation would be the same with full battery:
When the phone is powered up with an empty battery pack using the
standard charger, the charger may not supply enough current for standard powerup procedure and the powerup must be delayed.
Power Up With The Power Switch (PWRONX)
When the power on switch is pressed the PWRONX signal will go low.
CCONT will switch on the CCONT digital section and VCXO as was the
case with the charger driven power up. If PWRONX is low when the 64
ms delay expires, PURX is released and SLEEPX control goes to MAD. If
PWRONX is not low when 64 ms expires, PURX will not be released, and
CCONT will go to power off ( digital section will send power off signal to
analog parts)
VBB (2.8V)
CCPURX
PURX
Vchar
12 3
1:Power switch pressed ==> Digital voltages on in CCONT (VBB)
2: CCONT digital reset released. VCXO turned on
3: 62 ms delay to see if power switch is still pressed.
VR1,VR6
SLEEPX
PWRONX
Power Up by RTC
RTC ( internal in CCONT) can power the phone up by changing RTCPwr to
logical ”1”. RTCPwr is an internal signal from the CCONT digital section.
Page 38

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 26
Power Up by IBI
IBI can power CCONT up by sending a short pulse to logical ”1”. RTCPwr is
an internal signal from the CCONT digital section.
Acting Dead
If the phone is off when the charger is connected, the phone is powered
on but enters a state called ”acting dead”. To the user the phone acts as if
it was switched off. A battery charging alert is given and/or a battery
charging indication on the display is shown to acknowledge the user that
the battery is being charged.
Active Mode
In the active mode the phone is in normal operation, scanning for channels, listening to a base station, transmitting and processing information.
All the CCONT regulators are operating. There are several substates in
the active mode depending on if the phone is in burst reception, burst
transmission, if DSP is working etc..
Sleep Mode
In the sleep mode, all the regulators except the baseband VBB and the
SIM card VSIM regulators are off. Sleep mode is activated by the MAD
after MCU and DSP clocks have been switched off. The voltage regulators for the RF section are switched off and the VCXO power control,
VCXOPwr is set low. In this state only the 32 kHz sleep clock oscillator in
CCONT is running. The flash memory power down input is connected to
the ExtSysResetX signal, and the flash is deep powered down during the
sleep mode.
The sleep mode is exited either by the expiration of a sleep clock counter
in the MAD or by some external interrupt, generated by a charger connection, key press, headset connection etc. The MAD starts the wake up
sequence and sets the VCXOPwr and ExtSysResetX control high. After
VCXO settling time other regulators and clocks are enabled for active
mode.
If the battery pack is disconnect during the sleep mode, the CCONT pulls
the SIM interface lines low as there is no time to wake up the MCU.
Charging
Charging can be performed in any operating mode. The charging algorithm is dependent on the used battery technology. The battery type is indicated by a resistor inside the battery pack. The resistor value corresponds to a specific battery capacity. This capacity value is related to the
battery technology as different capacity values are achieved by using different battery technology.
Page 39

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 27
Original 08/98
The battery voltage, temperature, size and current are measured by the
CCONT controlled by the charging software running in the MAD.
The power management circuitry controls the charging current delivered
from the charger to the battery. Charging is controlled with a PWM input signal, generated by the CCONT. The PWM pulse width is controlled by the
MAD and sent to the CCONT through a serial data bus. The battery voltage
rise is limited by turning the CHAPS switch off when the battery voltage has
reached 4.2V (LiIon) or 5.2V (NiMH, 5V in call mode). Charging current is
monitored by measuring the voltage drop across a 220mohm resistor.
Power Off
The baseband is powered down by:
1. Pressing the power key, that is monitored by the MAD via keyboard line (row 4), which starts the power down procedure.
2. If the battery voltage is dropped below the operation limit, either by not charging it or by removing the battery.
3. Letting the CCONT watchdog expire, which switches off all
CCONT regulators and the phone is powered down.
4. Setting the real time clock to power off the phone by a timer.
The RTC generates an interrupt signal, when the alarm is gone
off. The RTC interrupt signal is connected to the PWRONX line
to give a power off signal to the CCONT just like the power key.
The power down is controlled by the MAD. When the power key has been
pressed long enough or the battery voltage is dropped below the limit the
MCU initiates a power down procedure and disconnects the SIM power.
Then the MCU outputs a system reset signal and resets the DSP. If there is
no charger connected the MCU writes a short delay to CCONT watchdog
and resets itself. After the set delay the CCONT watchdog expires, which
activates the PURX and all regulators are switched off and the phone is
powered down by the CCONT.
If a charger is connected when the power key is pressed the phone enters into the acting dead mode.
Watchdog
The Watchdog block inside CCONT contains a watchdog counter and
some additional logic which are used for controlling the power on and
power off procedures of CCONT. Watchdog output is disabled when
WDDisX pin is tied low. The WD-counter runs during that time, though.
Watchdog counter is reset internally to 32s at power up. Normally it is reset by MAD writing a control word to the WDReg. Watchdog counter can
be disabled b grounding J111.
Page 40

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 28
Audio control
The audio control and processing is taken care by the COBBA–GJ, which
contains the audio and RF codecs, and the MAD2, which contains the
MCU, ASIC and DSP blocks handling and processing the audio signals. A
detailed audio specification can be found from document
Slide
Headset connector
Pre
& LP
D
MIC3
LP
A
D
MIC3
MIC2
EAR
HF
AuxOut
MCU
Buzzer
DSP
UI
Switch
MAD
Bias +
EMC
XMIC
XEAR
SGND
MICP/N
EMC + Acc.
Interf.
EMC
Preamp
Multipl.Premult.
Amp Multipl.
COBBA
A
The baseband supports three microphone inputs and two earphone outputs. The inputs can be taken from an internal microphone, a headset microphone or from an external microphone signal source. The microphone
signals from different sources are connected to separate inputs at the
COBBA–GJ asic. Inputs for the microphone signals are differential type.
The MIC3 inputs are used for a headset microphone that can be connected directly to the headset connector. The internal microphone is connected to MIC2 inputs. In COBBA there are also three audio signal outputs of which dual ended EAR lines are used for internal earpiece and HF
line for accessory audio output. The third audio output AUXOUT is used
only for bias supply to the headset microphone. As a difference to DCT2
generation the SGND does not supply audio signal (only common mode).
Therefore there are no electrical loopback echo from downlink to uplink.
The output for the internal earphone is a dual ended type output capable
of driving a dynamic type speaker. The output for the headset is single
ended with a dedicated signal ground SGND. Input and output signal
source selection and gain control is performed inside the COBBA–GJ asic
according to control messages from the MAD2. Keypad tones, DTMF, and
other audio tones are generated and encoded by the MAD2 and transmitted to the COBBA–GJ for decoding.
Page 41

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 29
Original 08/98
External Audio Connections
The external audio connections are presented in figure below. A headset
can be connected directly to the system connector. The headset microphone bias is supplied from COBBA AUXOUT output and fed to microphone through XMIC line. The 330ohm resistor from SGND line to AGND
provides a return path for the bias current.
XEAR
SGN
D
47R
10m
HeadDet
H
F
HFC
M
47k
2.8 V
MIC1
N
MIC1
P
33n
33n
MIC3
N
MIC3
P
XMI
C
100n
22k
MAD
1u
22k
1m
AUXOUT
EAD
CCONT
2k2
2.8 V
47k
4k7
4k7
Baseband
47R
COBBA
HookDet
1M
1M
Page 42

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 30
Analog Audio Accessory Detection
In XEAR signal there is a 47 kW pullup in the transceiver and 6.8 kW
pull–down to SGND in accessory. The XEAR is pulled down when an
accessory is connected, and pulled up when disconnected. The XEAR is
connected to the HookDet line (in MAD), an interrupt is given due to both
connection and disconnection. There is filtering between XEAR and
HookDet to prevent audio signal giving unwanted interrupts.
External accessory notices powered–up phone by detecting voltage in
XMIC line. In Table 23 there is a truth table for detection signals.
Accessory connected HookDet HeadDet Notes
No accessory connected High High Pullups in the transceiver
Headset HDC–9 with a button switch
pressed
Low Low XEAR and XMIC loaded (dc)
Headset HDC–9 with a button switch released
High Low *) XEAR unloaded (dc)
Headset Detection
The external headset device is connected to the system connector, from
which the signals are routed to COBBA headset microphone inputs and
earphone outputs. In the XMIC line there is a (47 + 2.2) kW pullup in the
transceiver. The microphone is a low resistancepulldown compared to
the transceiver pullup.
In the XEAR line there is a 47 kW pullup in the transceiver. The earphone
is a low resistance pulldown compared to the transceiver pullup. When a
remote control switch is open, there is a capacitor in series with the earphone, so the XEAR (and HookDet) is pulled up by the phone. When the
switch is closed, the XEAR (and HookDet) is pulled down via the earphone. So both press and release of the button gives an interrupt.
During a call there is a bias voltage (1.5 V) in the AUXOUT, and the
HeadDet cannot be used. The headset interrupts should to be disabled
during a call and the EAD line (AD converter in CCONT) should be polled
to see if the headset is disconnected.
Page 43

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 31
Original 08/98
Internal Audio Connections
The speech coding functions are performed by the DSP in the MAD2 and
the coded speech blocks are transferred to the COBBA–GJ for digital to
analog conversion, down link direction. In the up link direction the PCM
coded speech blocks are read from the COBBA–GJ by the DSP.
There are two separate interfaces between MAD2 and COBBA–GJ: a
parallel bus and a serial bus. The parallel bus has 12 data bits, 4 address
bits, read and write strobes and a data available strobe. The parallel interface is used to transfer all the COBBA–GJ control information (both the
RFI part and the audio part) and the transmit and receive samples. The
serial interface between MAD2 and COBBA–GJ includes transmit and receive data, clock and frame synchronisation signals. It is used to transfer
the PCM samples. The frame synchronisation frequency is 8 kHz which
indicates the rate of the PCM samples and the clock frequency is 1 MHz.
COBBA is generating both clocks.
4–wire PCM Serial Interface
The interface consists of following signals: a PCM codec master clock
(PCMDClk), a frame synchronization signal to DSP (PCMSClk), a codec
transmit data line (PCMTX) and a codec receive data line (PCMRX). The
COBBA–GJ generates the PCMDClk clock, which is supplied to DSP SIO.
The COBBA–GJ also generates the PCMSClk signal to DSP by dividing
the PCMDClk. The PCMDClk frequency is 1.000 MHz and is generated
by dividing the RFIClk 13 MHz by 13. The COBBA–GJ further divides the
PCMDClk by 125 to get a PCMSClk signal, 8.0 kHz.
LSB
LSB
PCMDClk
PCMSClk
PCMTxData
PCMRxData
MSB
MSB
15 14 13 12 011 10
sign extended
sign extended
Page 44

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 32
Alert Signal Generation
A buzzer is used for giving alerting tones and/or melodies as a signal of
an incoming call. Also keypress and user function response beeps are
generated with the buzzer. The buzzer is controlled with a BuzzerPWM
output signal from the MAD. A dynamic type of buzzer must be used
since the supply voltage available can not produce the required sound
pressure for a piezo type buzzer. The low impedance buzzer is connected
to an output transistor that gets drive current from the PWM output. The
alert volume can be adjusted either by changing the pulse width causing
the level to change or by changing the frequency to utilize the resonance
frequency range of the buzzer.
A vibra alerting device is used for giving silent signal to the user of an incoming call. The device is controlled with a VibraPWM output signal from
the MAD2. The vibra alert can be adjusted either by changing the pulse
width or by changing the pulse frequency.
Digital Control
The baseband functions are controlled by the MAD asic, which consists of
a MCU, a system ASIC and a DSP.
MAD2
MAD2 contains following building blocks:
– ARM RISC processor with both 16–bit instruction set (THUMB mode)
and 32–bit instruction set (ARM mode)
– TI Lead DSP core with peripherials:
– API (Arm Port Interface memory) for MCU–DSP commu-
nication, DSP code download, MCU interrupt handling vec-
tors (in DSP RAM) and DSP booting
– Serial port (connection to PCM)
– Timer
– DSP memory
– BUSC (BusController for controlling accesses from ARM to API, Sys-
tem Logic and MCU external memories, both 8– and 16–bit memories)
– System Logic
– CTSI (Clock, Timing, Sleep and Interrupt control)
– MCUIF (Interface to ARM via B
USC). Contains MCU Boo-
tROM
– DSPIF (Interface to DSP)
– MFI (Interface to COBBA AD/DA Converters)
– CODER (Block encoding/decoding and A51&A52 ciphering)
Page 45

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 33
Original 08/98
– AccIF(Accessory Interface)
– SCU (Synthesizer Control Unit for controlling 2 separate
synthesizer)
– UIF (Keyboard interface, serial control interface for COBBA
PCM Codec, LCD Driver and CCONT)
– SIMI (SimCard interface with enhanched features)
– PUP (Parallel IO, USART and PWM control unit for vibra
and buzzer)
The MAD2 operates from a 13 MHz system clock, which is generated
from the 13Mhz VCXO frequency. The MAD2 supplies a 6,5MHz or a
13MHz internal clock for the MCU and system logic blocks and a 13MHz
clock for the DSP, where it is multiplied to 52 MHz DSP clock. The system
clock can be stopped for a system sleep mode by disabling the VCXO
supply power from the CCONT regulator output. The CCONT provides a
32kHz sleep clock for internal use and to the MAD2, which is used for the
sleep mode timing. The sleep clock is active when there is a battery voltage available i.e. always when the battery is connected.
Pin
N:o
Pin Name Pin
Type
Connected
to/from
Drive
req.
mA
Reset
State
Note Explanation
B1 MCUGenOut5 O Audio 2 0 MCU General
purpose output
port
C2 MCUGenOut4 O N101 2 0 MCU General
purpose output
port
C1
LEADGND
Lead Ground
D3 MCUGenOut3 O 2 0 MCU General
purpose output
port
D2 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
D1 MCUGenOut2 O 2 0 MCU General
purpose output
port
E3 MCUGenOut1 O MCU
memory
2 0 MCU General
purpose output
port
E2 MCUGenOut0 O 2 1 LoByteSelX
in 16–bit
mode
MCU General
purpose output
port
E1 Col4 I/O UIF 2 Input program-
mable pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board column 4
Page 46

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 34
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
F3 Col3 I/O UIF 2 Input program-
mable pullup
PR0201
I/O line for keyboard column 3
F2 GND Ground
F1 Col2 I/O UIF 2 Input program-
mable pullup
PR0201
I/O line for keyboard column 2
G4 Col1 I/O UIF 2 Input program-
mable pullup
PR0201
I/O line for keyboard column 1
G3 Col0 I/O UIF 2 Input program-
mable pullup
PR0201
I/O line for keyboard column 0
G2 LCDCSX I/O UIF 2 Input external
pullup/down
serial LCD driver
chip select, par-
allel LCD driver
enable
G1
LEADVCC
Lead Power
H1 Row5LCDCD I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
Keyboard row5
data I/O , serial
LCD driver com-
mand/data indi-
cator, parallel
LCD driver read/
write select
H4 VCC Core VCC in
3325c10
Power
H3 Row4 I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board row 4, par-
allel LCD driver
register selection
control
H2 Row3 I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board row 3, par-
allel LCD driver
data
J1 Row2 I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board row 2, par-
allel LCD driver
data
J4 Row1 I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board row 1, par-
allel LCD driver
data
J3 Row0 I/O UIF 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
I/O line for key-
board row 0, par-
allel LCD driver
data
Page 47

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 35
Original 08/98
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
J2 JTDO O 2 Tri–
state
JT AG data out
K1 GND Ground
K2 JTRst I Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD0201
JT AG reset
K4 JTClk I Input pulldown
PD0201
JT AG Clock
K3 JTDI I Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
JT AG data in
L1 JTMS I Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
JT AG mode se-
lect
L2 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
L3 CoEmu0 I/O 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
DSP/MCU
emulation port 0
L4 CoEmu1 I/O 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
DSP/MCU
emulation port 1
M1 MCUGenIO7 I/O 2 Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD1001
General purpose
I/O port
M2 MCUGenIO6 I/O UI 2 Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD1001
Lights
M3
LEADGND
Lead Ground
N1 MCUGenIO5 I/O UI 2 Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD1001
LCD reset
N2
ARMGND
ARM Ground
N3 MCUAd0 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
P1
ARMVCC
ARM Power
P2 MCUAd1 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
P3 MCUAd2 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
R1 GND Ground
R2 MCUAd3 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T1 MCUAd4 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U2 MCUAd5 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
Page 48

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 36
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
T3 MCUAd6 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U3 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
R4 MCUAd7 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T4 MCUAd8 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U4 MCUAd9 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
R5 MCUAd10 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T5 GND Ground
U5 MCUAd11 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
R6 MCUAd12 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T6 MCUAd13 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U6 MCUAd14 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
P7 MCUAd15 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
R7 MCUAd16 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T7 VCC Core VCC in
3325c10
Power
U7 MCUAd17 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U8 MCUAd18 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
P8 MCUAd19 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
R8 MCUAd20 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
T8 MCUAd21 O MCU
MEMORY
2 0 MCU address
bus
U9 ExtMCUDa0 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Input MCU data bus
P9 GND Ground
R9 ExtMCUDa1 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
T9 ExtMCUDa2 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
Page 49

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 37
Original 08/98
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
U10 ExtMCUDa3 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
T10 ExtMCUDa4 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
P10 ExtMCUDa5 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
R10 ExtMCUDa6 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
U11 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
T11 ExtMCUDa7 I/O MCU
MEMORY
2 Output MCU data bus
R11 MCUGenIO8 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
P11 MCUGenIO9 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
U12 MCUGenIO10 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
T12 MCUGenIO11 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
R12 GND Ground
U13 MCUGenIO12 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
T13 MCUGenIO13 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
R13 MCUGenIO14 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
U14 MCUGenIO15 I/O 2 Input MCU Data in
16–bit mode
General purpose
I/O port
T14 MCURdX O MCU
MEMORY
2 1 MCU Read
strobe
R14 VCC Core VCC in
3325c10
Power
U15 MCUWrX O MCU
MEMORY
2 1 MCU write
strobe
T15 ROM1SelX O MCU ROM 2 1 ROM chip select
U16 RAMSelX O MCU RAM 2 1 RAM chip select
T17 ROM2SelX O MCU ROM2 2 1 Extra chip select,
can be used as
MCU general
output
R16 MCUGenIO1 I/O 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
General purpose
I/O port
R17 DSPXF O 2 1 External flag
Page 50

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 38
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
P15
SCVCC
Special cell Pow-
er
P16 RFClk I VCXO Input System clock
from VCTCXO
P17 RFClkGnd Input System clock
reference ground
input
N15 SIMCardDetX I Input SIM card detec-
tion
N16
SCGND
Special cell
Ground
N17 BuzzPWM O BUZZER 2 0 Buzzer PWM
control
M15
LEADVCC
LEAD Power
M16 VibraPWM O VIBRA 2 0 Vibra PWM con-
trol
M17 GND Ground
L14 MCUGenIO3 I/O EEPROM 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR1001
WP
L15 MCUGenIO2 I/O EEPROM 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR1001
SCL
L16 EEPROMSelX O MCU EE-
PROM
2 1 Not used, can be
used as MCU
general output
L17 AccTxData I/O 4 Tri–
State
external
pullup
Accessory TX
data, Flash_TX
K17 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
K14 GenDet I Input General purpose
interrupt
K15 HookDet I Input Non–MBUS ac-
cessory connec-
tion detector
K16 HeadDet I Input Headset detec-
tion interrupt
J17 AccRxData I Input Accessory RX
data, Flash_RX
J14 GND Ground
J15 MCUGenIO4 I/O 2 Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD1001
General purpose
I/O port, BA TTI/
O
J16 MBUS I/O 2 Input,
exter-
nal
pullup
external
pullup
MBUS, Flash
clock
Page 51

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 39
Original 08/98
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
H17 VCXOPwr O CCONT 2 1 VCXO regulator
control
H16 SynthPwr O CCONT 2 0 Synthesizer reg-
ulator control
H14 VCC Core VCC in
3325c10
Power
H15 GenCCONTCSX O CCONT 2 1 Chip select to
CCONT
G17
LEADGND
LEAD Ground
G16 GenSDIO I/O CCONT, UIF 2 Input,
exter-
nal
pullup/
down
external
pullup/down
depending
on how to
boot
Serial data in/out
G15 GenSClk O CCONT, UIF 2 0 Serial clock
G14 SIMCardData I/O CCONT 2 0 SIM data
F17 GND Ground
F16 PURX I CCONT Input Power Up Reset
F15 CCONTInt I CCONT Input CCONT interrupt
E17 Clk32k I CCONT Input Sleep clock os-
cillator input
E16 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
E15 SIMCardClk O CCONT 2 0 SIM clock
D17 SIMCardRstX O CCONT 2 0 SIM reset
D16 SIMCardIOC O CCONT 2 0 SIM data in/out
control
D15 SIMCardPwr O CCONT 2 0 SIM power con-
trol
C17
LEADVCC
LEAD Power
C16 RxPwr O CCONT 2 0 RX regulator
control
B17 TxPwr O CCONT 2 0 TX regulator
control
A16 TestMode I Input,
pull-
down
pulldown
PD0201
Test mode select
B15 ExtSysResetX O 2 0 System Reset
A15 PCMTxData O COBBA 2 0 Transmit data,
DX
C14 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
Page 52

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 40
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
B14 PCMRxData I COBBA Input Receive data,
RX
A14 PCMDClk I COBBA Input Transmit clock,
CLKX
C13 PCMSClk I COBBA Input Transmitframe
sync, FSX
B13 COBBADAX I COBBA Input Data available
acknowledge
A13 GND Ground
C12 COBBAWrX O COBBA 2 1 COBBA write
strobe
B12 COBBARdX O COBBA 2 1 COBBA read
strobe
A12 COBBAClk O COBBA 4 1 COBBA clock,
13 MHz
D11 COBBAAd3 O COBBA 2 0 COBBA address
bit
C11 COBBAAd2 O COBBA 2 0 COBBA address
bit
B11 COBBAAd1 O COBBA 2 0 COBBA address
bit
A11 COBBAAd0 O COBBA 2 0 COBBA address
bit
A10 COBBADa11 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
D10 VCC Core VCC in
3325c10
Power
C10 COBBADa10 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
B10 COBBADa9 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
A9 COBBADa8 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
D9 COBBADa7 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
C9 COBBADa6 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
B9 GND Ground
A8 COBBADa5 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
B8 COBBADa4 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
D8 COBBADa3 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
C8 COBBADa2 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
A7 COBBADa1 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
B7 COBBADa0 I/O COBBA 2 0 COBBA data bit
C7 DSPGenOut5 O RF 2 0 DSP general
purpose output,
COBBA reset
Page 53

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 41
Original 08/98
ExplanationNoteReset
State
Drive
req.
mA
Connected
to/from
Pin
Type
Pin NamePin
N:o
D7 VCC IO VCC in
3325c10
Power
A6 DSPGenOut4 O 2 0 DSP general
purpose output
B6 DSPGenOut3 O IR 2 0 IR ON
C6 DSPGenOut2 O 2 0 DSP general
purpose output
A5 DSPGenOut1 O 2 0 DSP general
purpose output
B5 DSPGenOut0 O 2 0 DSP general
purpose output
C5 MCUGenIO0 I/O EEPROM 2 Input,
pullup
pullup
PR0201
EEPROM serial
data SDA
A4 FrACtrl O RF 2 0 SDATX0
B4 GND Ground
C4 SynthEna O SUMMA 2 0 Synthesizer data
enable
A3 SynthClk O SUMMA 2 0 Synthesizer
clock
B3 SynthData O SUMMA 2 0 Synthesizer data
A2 TxPA O SUMMA,
power ampli-
fier
2 0 Power amplifier
control
Page 54

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 42
Memories
The MCU program code resides in an external flash program memory,
which size is 16 Mbits (1024kx16bit). The MCU work (data) memory size
is 2Mbits (128kx16bit). A serial EEPROM is used for storing the system
and tuning parameters, user settings and selections, a scratch pad and a
short code memory. The EEPROM size is 256kbits (32kx8bit).
The BusController (BUSC) section in the MAD decodes the chip select
signals for the external memory devices and the system logic. BUSC controls internal and external bus drivers and multiplexers connected to the
MCU data bus. The MCU address space is divided into access areas with
separate chip select signals. BUSC supports a programmable number of
wait states for each memory range.
Program Memory
The program memory size is 16 Mbits (1024kx16bit).
The flash memory has a power down pin that should be kept low, during
the power up phase of the flash to ensure that the device is powered up
in the correct state, read only. The power down pin is utilized in the system sleep mode by connecting the ExtSysResetX to the flash power down
pin to minimize the flash power consumption during the sleep.
SRAM Memory
The work memory is a static ram of size 2Mbits (128kx16bit) in a shrink
MBGA48 package. The work memory is supplied from the common baseband VBB voltage and the memory contents are lost when the baseband
voltage is switched off. All retainable data should be stored into the EEPROM (or flash) when the phone is powered down.
EEPROM Memory
An EEPROM is used for a nonvolatile data memory to store the tuning
parameters and phone setup information. The short code memory for
storing user defined information is also implemented in the EEPROM.
The EEPROM size is 256kbits (32kx8bit). The memory is accessed
through a serial bus and the default package is SO8.
MCU Memory Map
MAD2 supports maximum of 4GB internal and 4MB external address
space. External memories use address lines MCUAd0 to MCUAd21 and
16–bit databus. The BUSC bus controller supports 8– and 16–bit access
for byte, double byte, word and double word data. Access wait state 2
and used databus width can be selected separately for each memory
block.
Page 55

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 43
Original 08/98
Flash Programming
The preprogrammable phone has to be connected to the flash loading
adapter (FLA–5) via modular cable (XCM–5). When FLA–5 switches supply voltage to the service box (JBU–5), a short pulse (IBI pulse) is generated to the power supply circuit via BTEMP line.
The power supply circuit (N100) switches power on and releases MCU
(MAD2) from reset state (power up reset, PURX rises up to 1 (2.8 V).
The program execution starts from the internal boot ROM of MAD2 and
MCU investigates the status of the MBUS line. Normally this line is high
(2.8 V) because of pull up resistor R115, but when the flash program
adapter is connected, the MBUS line is forced low. When MCU has recognized the flash loading adapter (MBUS line is low), it gives program start
(MCU boot) information to the flash loading adapter by forcing flash_tx
(FBUS_TX) line low.
The flash prommer sends all needed data for flash programming to phone
via flash_rx (FBUS_RX) line. The phone (MCU) sends all programming
acknowlegment signals for flash prommer via flash_tx (FBUS_TX) line.
The acknowlegment information (rising and falling edge of flash_tx line)
signal is sent to flash prommer when each step of flash programming is
passed. Flash_tx line is also used to send hardware configuration information (flash type etc.) to the flash prommer. Flash_tx and flash_rx
data is synchronized to flash clock signal, which is sent from the flash
prommer to phone via flash clock line (MBUS).
The flash programming voltage (VPP) is generated internally. Switchable
voltage regulator N201 (or N202) is used to generate flash programming
voltage for the program memory (D220). The regulator is controlled by
MCU (MAD2) via MCUGenOutput pin 1. The input voltage for the flash
programming voltage regulator is taken from output of charger pump
(J224) of power supply circuit CCONT (N100). The programming voltage
(3 V +/– 10 %) is supplied via UI connector X303 (pins 1,3) to the program memory D220. Thus the flash programming voltage (VPP) is
switched on only during the flash erasing and programming states.
COBBA–GJ
The COBBA–GJ provides an interface between the baseband and the
RF–circuitry. COBBA–GJ performs analogue to digital conversion of the
receive signal. For transmit path COBBA_GJ performs digital to analogue
conversion of the transmit amplifier power control ramp and the in–phase
and quadrature signals. A slow speed digital to analogue converter will
provide automatic frequency control (AFC).
The COBBA asic is at any time connected to MAD asic with two interfaces, one for transferring tx and rx data between MAD and COBBA and
one for transferring codec rx/tx samples.
Page 56

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 44
Real Time Clock
Requirements for a real time clock implementation are a basic clock
(hours and minutes), a calender and a timer with alarm and power on/off
–function and miscellaneous calls. The RTC will contain only the time
base and the alarm timer but all other functions will be implemented with
the MCU software. The RTC needs a power backup to keep the clock
running when the phone battery is disconnected. The backup power is
supplied from a rechargable polyacene battery that can keep the clock
running some ten minutes. If the backup has expired, the RTC clock restarts after the main battery is connected. The CCONT keeps MCU in reset until the 32kHz source is settled (1s max).
The CCONT is an ideal place for an integrated real time clock as the asic
already contains the power up/down functions and a sleep control with
the 32kHz sleep clock, which is running always when the phone battery is
connected. This sleep clock is used for a time source to a RTC block.
RTC backup battery charging
CHAPS has a current limited voltage regulator for charging a backup battery. The regulator derives its power from VOUT so that charging can take
place without the need to connect a charger. The backup battery is only
used to provide power to a real time clock when VOUT is not present so it
is important that power to the charging circuitry is derived from VOUT and
that the charging circuitry does not present a load to the backup battery
when VOUT is not present.
It should not be possible for charging current to flow from the backup battery into VOUT if VOUT happens to be lower than VBACK. Charging current will gradually diminish as the backup battery voltage reaches that of
the regulation voltage.
Vibra Alerting Device
A vibra alerting device is used for giving silent signal to the user of an incoming call. The device is placed in the phone. The vibra is controlled by
the MAD via the UI–switch asic.
Page 57

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 45
Original 08/98
IBI Accessories
All accessories which can be connected between the transceiver and the
battery or which itself contain the battery, are called IBI accessories.
Either the phone or the IBI accessory can turn the other on, but both possibilities are not allowed in the same accessory.
Phone Power–on by IBI
IBI accessory can power the phone on by pulling the BTEMP line up to 3
V.
IBI power–on by phone
Phone can power the IBI accessory on by pulling the BTEMP line up by
MCUGenIO4 of MAD2. BTEMP measurement is not possible during this
time.
The accessory is commanded back to power–off by MBUS message.
BATTERY
100k
VREF
TRANSCEIVER
BTEMP
GND
BSI
VBAT
1k
MAD
BTEMP
CCONT
VIBRAPWM
Accessory
power on
10k
R
T
NTC
–
+
+1.5 V
100ms
220k
33n 10n
MCUGenIO4
Page 58

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 46
RF Module
This RF module takes care of all RF functions of the engine. RF circuitry
is located on one side (B–side) of the 6 layer PCB. PCB area for the RF
circuitry is about 40 x 50 mm.
EMC leakage is prevented by using a metal B–shield, which screens the
whole engine. The metal gasket is used between the PCB and the
shield. The baseband circuitry is located on the A–side of the board,
which is shielded with a metallized frame and ground plane on UI–board.
Maximum Ratings
Parameter Rating
Battery voltage, idle mode 6.0 V
Battery voltage during call, highest power level 5.0 V
Regulated supply voltage 2.8 +/– 3% V
Voltage reference 1.5 +/– 1.5% V
Operating temperature range –10...+55 deg. C
RF Frequency Plan
SUMMACRFU_1
UHF
PLL
VHF
PLL
13 MHz
VCTCXO
232
MHz
f
f/2f/2
f
f
f/2
1006–
1031
MHz
LO–
buffers
935–960
MHz
890–915
MHz
1st IF 71 MHz 2nd IF 13 MHz
TX IF 116 MHz
2nd LO
58 MHz
Page 59

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 47
Original 08/98
Power Distribution Diagram
The power supply is based on the ASIC circuit CCONT. The chip consists
of regulators and control circuits providing functions like power up, reset
and watchdog. External buffering is required to provide more current on
some blocks.
The MCU and the CCONT circuits control charging together, detection
being carried out by the CCONT and higher level intelligent control by the
MCU. The MCU measures battery voltage by means of the COBBA via
DSP. Charger voltage and the temperature and size of the battery are followed via the MCU internal ADC.
Detailed power distribution diagrams are given in Baseband blocks and
RF blocks documents.
Page 60

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 48
VR
4
COBBA
ANAL.
TXP
SYNPWR
RXPWR
TXPWR
VXOENA
VBATT
VR
1
VR
2
VR
3
VR
5
VR
6
VR
7
VREF V5V
BATTERY
VCTCXO
CRFU,
PLLs
VCOs
PLUSSA
CRFU
BUFFERS
CHARGE
PUMPs
PA
VCP
VREF_1
SUMMA
VTX
VSYN_1
VSYN_2
VRX
VXO
2.3 mA
51 mA
18 mA
19.5 mA
84 mA
0.1 mA
1 mA
1.35 A
3.6 V
BUFFER
SUMMA
CRFU,
NOT USED
VREF_2
Page 61

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 49
Original 08/98
DC Characteristics
Regulators
Transceiver has got a multi function power management IC, which contains among other functions, also 7 pcs of 2.8 V regulators. All regulators
can be controlled individually with 2.8 V logic directly or through control
register. In GSM direct controls are used to get fast switching, because
regulators are used to enable RF–functions.
Use of the regulators can be seen in the power distribution diagram.
CCONT also provides 1.5 V reference voltage for SUMMA and CRFU1a
( and for DACs and ADCs in COBBA too ).
Control Signals
All control signals are coming from MAD and they are 2.8 V logic signals.
Functional Description
RF architecture has a conventional dual conversion receiver and in transmitter there is a upconversion mixer for the final TX–frequency.
The architecture contains three ICs. Most of the functions are horizontally
and vertically integrated. UHF functions except power amplifier and VCO
are integrated into CRFU_1a, which is a BiCMOS–circuit suitable for
LNA– and mixer–function. Most of the functions are in SUMMA, which
also is a BiCMOS–circuit. SUMMA is a IF–circuit including IQ–modulator
and PLLs for VHF– and UHF–
synthesizers.
Power amplifier is a MOSFET (hybrid) module. It contains three amplifier
stages including input, interstage matchings and output matching network. Also TX gain control circuitis integrated into the module.
Frequency synthesizers
Both VCOs are locked with PLLs into stable frequency source ( see figure
3 ), which is a VCTCXO–module ( voltage controlled temperature compensated crystal oscillator ). VCTCXO is running at 13 MHz. Temperature
effect is controlled with AFC ( automatic frequency control ) voltage,
VCTCXO is locked into frequency of the base station. AFC is generated
by baseband with a 11 bit conventional DAC in COBBA.
UHF PLL is located into SUMMA. There is 64/65 (P/P+1) prescaler, N–
and A–divider, reference divider, phase detector and charge pump for the
external loop filter. UHF local signal is generated by a VCO–module (
VCO = voltage controlled oscillator ) and sample of frequency of VCO is
fed to prescaler. Prescaler is a dual modulus divider. Output of the prescaler is fed to N– and A–divider, which produce the input to phase detec-
Page 62

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 50
tor. Phase detector compares this signal to reference signal, which is divided with reference divider from VCTCXO output. Output of the phase
detector is connected into charge pump, which charges or discharges integrator capacitor in the loop filter depending on the phase of the measured frequency compared to reference frequency.
Loop filter filters out the pulses and generates DC to control the frequency
of UHF–VCO. Loop filter defines step response of the PLL ( settling time )
and effects to stability of the loop, that’s why integrator capacitor has got
a resistor for phase compensation. Other filter components are for sideband rejection. Dividers are controlled via serial bus. SDATA is for data,
SCLK is serial clock for the bus and SENA1 is a latch enable, which
stores new data into dividers. UHF–synthesizer is the channel synthesizer, so the channel spacing is 200 kHz. 200 kHz is reference frequency
for the phase detector.
VCO
CHARGE
PUMP
PHASE
DET.
M
R
f_out
LP
Kvco
Kd
M = A(P+1) + (N–A)P=
f
ref
f_out /
M
freq.
reference
= NP+A
AFC–controlled VCTCXO
VHF PLL is also located into SUMMA. There is 16/17 ( P/P+1 ) dual modulus prescaler, N– and A–dividers, reference divider, phase detector and
charge pump for the loop filter. VHF local signal is generated with a discrete VCO–circuit. VHF PLL works in the same way as UHF–PLL. VHF–
PLL is locked on fixed frequency, so higher reference frequency is used
to decrease phase noise.
Page 63

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 51
Original 08/98
Receiver
Receiver is a dual conversion linear receiver. Received RF–signal from
the antenna is fed via the duplex filter to LNA (low noise amplifier ) in
CRFU_1a. Active parts ( RF–transistor and biasing and AGC–step circuitry ) are integrated into this chip. Input and output matching networks are
external. Gain selection is done with PDATA0 control. Gain step in LNA is
activated when RF–level in antenna is about –45 dBm.
After the LNA amplified signal ( with low noise level ) is fed to bandpass
filter, which is a SAW–filter ( SAW, surface acoustic wave ). Duplex filter
and RX interstage bandpass filters together define, how good are the
blocking characteristics against spurious signals outside receive band
and the protection against spurious responses, mainly the image of the
first mixer.
This bandpass filtered signal is then mixed down to 71 MHz, which is first
intermediate frequency. 1st mixer is located into CRFU_1a ASIC. This integrated mixer is a double balanced Gilbert cell. All active parts and biasing are integrated and matching components are external. Because this is
an axtive mixer it also amplifies IF–frequency. Also local signal buffering
is integrated and upper side injection is used. First local signal is generated with UHF–synthesizer.
First IF–signal is then bandpass filtered with a selective SAW–filter. From
the mixer output to IF–circuit input signal path is balanced. IF–filter provides selectivity for channels greater than +/–200 kHz. Also it attenuates
image frequency of the second mixer and intermodulating signals. Selectivity is required in this place, because of needed linearity and adjacent
channel interferers will be on too high signal level for the stages following.
Next stage in the receiver chain is AGC–amplifier. It is integrated into
SUMMA–ASIC. AGC has got analog gain control. Control voltage for the
AGC is generated with DA–converter in COBBA in baseband. AGC–stage
provides accurate gain control range ( min. 60 dB ) for the receiver.
After the AGC there is second mixer, which generates second intermediate frequency, 13 MHz. Local signal is generated in SUMMA by dividing
VHF–synthesizer output ( 232 MHz ) by four, so the 2nd LO–frequency is
58 MHz.
2nd IF–filter is a ceramic bandpass filter at 13 MHz. It attenuates adjacent
channels, except for +/– 200 kHz there is not much attenuation. Those
+/– 200 kHz interferers are filtered digitally by the baseband . So RX
DACs are so good, that there is enough dynamic range for the faded 200
kHz interferer. Also the whole RX has to be able to handle signal levels in
a linear way.
After the 13 MHz filter there is a buffer for the IF–signal, which also converts and amplifies single ended signal from filter to balanced signal for
the buffer and AD–converters in COBBA. Buffer in SUMMA has got voltage gain of 36 dB and buffer gain setting in COBBA is 0 dB. It is possible
to set gain step (9.5 dB) into COBBA via control bus, if needed.
Page 64

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 52
Transmitter
Transmitter chain consists of IQ–modulator, upconversion mixer, power
amplifier and there is a power control loop.
I– and Q–signals are generated by baseband also in COBBA–ASIC. After
post filtering ( RC–network ) they go into IQ–modulator in SUMMA. It generates modulated TX IF–frequency, which is VHF–synthesizer output divided by two, meaning 116 MHz. There is also an AGC–amplifier in SUMMA, but it is not used in GSM. Output is set to maximum with a 5–bit message in control register. AGC–amplifier is used in other digital systems,
because SUMMA is a core IC. After SUMMA signal is attenuated and filtered for upconversion into final TX–frequency in CRFU_1a.
Upconversion mixer in CRFU_1a is a so called image reject mixer. It is
able to attenuate unwanted sideband in the upconverter output. Mixer itself is a double balanced Gilbert cell. Phase shifters required for image
rejection are also integrated. Local signal needed in upconversion is generated by the UHF–synthesizer, but buffers for the mixer are integrated
into CRFU_1a. Output of the upconverter is buffered and matching network makes a single ended 50 ohm impedance.
Next stage is TX interstage filter, which attenuates unwanted signals from
the upconverter, mainly LO–leakage and image frequency from the upconverter. Also it attenuates wideband noise. This bandpass filter is a
SAW–filter.
The final amplification is realized with apower amplifier module. The
module contains three amplifier stages with matching circuits. Also there
is a gain control, which is controlled with a power control loop. PA has got
over 35 dB power gain and it is able to produce 2.5 W into output with 0
dBm input level. Gain control range is over 35 dB to get desired power
levels and power ramping up and down.
Harmonics generated by the nonlinear PA ( class AB ) are filtered out with
the lowpass/bandstop filtering in the duplexer. Bandstop is required because of wideband noise located on RX–band.
Power control circuitry consists of power detector in the PA output and error amplifier in SUMMA. There is a directional coupler connected between
PA output and duplex filter. It takes a sample from the forward going power with certain ratio. This signal is rectified in a schottky–diode and it produces a DC–signal signal after filtering. This peak–detector is linear on
absolute scale, except it saturates on very low and high power levels – it
produces a S–shape curve.
This detected voltage is compared in the error–amplifier in SUMMA to
TXC– voltage, which is generated by DA–converter in COBBA. Because
also gain control characteristics in PA are linear in absolute scale, control
loop defines a voltage loop, when closed. Closed loop tracks the TXC–
voltage quite linearilly. TXC has got a raised cosine form ( cos
4
– function
), which reduces switching transients, when pulsing power up and down.
Page 65

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 53
Original 08/98
Because dynamic range of the detector is not wide enough to control the
power ( actually RF output voltage ) over the whole range, there is a control named TXP to work under detected levels. Burst is enabled and set to
rise with TXP until the output level is high enough, that feedback loop
works. Loop controls the output via the control pin in PA MMIC to the desired output level and burst has got the waveform of TXC–ramps. Because feedback loops could be unstable, this loop is compensated with a
dominating pole. This pole decreases gain on higher frequencies to get
phase margins high enough.
PADIR.COUPLER
DETECTOR
ERROR
AMPLIFIER
RF_OUT
RF_IN
TXC
R1
R2
DOMINATING
POLE
K
K
K
K
det
cp
PA
= –R1/R2
C
2.8 VO
R
Page 66

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 54
AGC strategy
AGC–amplifier is used to maintain output level of the receiver almost
constant. AGC has to be set before each received burst, this is called
pre–monitoring. Receiver is switched on roughly xxx us before the burst
begins, DSP measures received signal level and adjusts RXC, which controls RX AGC–amplifier or it switches off the LNA with PDATA0 control
line. This pre–monitoring is done in three phases and this sets the settling
times for RX AGC. Pre–monitoring is required because of linear receiver,
received signal must be in full swing, no clipping is allowed and because
DSP doesn’t know, what is the level going to be in next burst.
There is at least 60 dB accurate gain control ( continous, analog ) and
one digital step in LNA. It is typically about 30...35 dB.
RSSI must be measured on range –48...–110 dBm. After –48 dBm level
MS reports to base station the same reading.
Because of RSSI–requirements, gain step in LNA is used roughly on –45
dBm RF–level and up to –10 dBm input RF–level accurate AGC is used
to set RX output level. LNA is ON ( PDATA0 = ”0” ) below –45 dBm. from
–45 dBm down to –95 dBm this accurate AGC in SUMMA is used to adjust the gain to desired value. RSSI–function is in DSP, but it works out
received signal level by measuring RX IQ–level after all selectivity filtering
( meaning IF–filters, Σ∆±converter and FIR–filter in DSP). So 50 dB accurate AGC dynamic range is required. Remaining 10 dB is for gain variations in RX–chain ( for calibration ). Below –95 dBm RF–levels, output
level of the receiver drops dB by dB. At –95 dBm level output of the receiver gives 50 mVpp. This is the target value for DSP. Below this it
drops down to ca. 9 mVpp @ –110 dBm RF–level.
This strategy is chosen because we have to roll off the AGC in SUMMA
early enough, that it won’t saturate in selectivity tests. Also we can’t start
too early, then we will sacrifice the signal to noise ratio and it would require more accurate AGC dynamic range. 50 mVpp target level is set,
because RX–DAC will saturate at 1.4 Vpp. This over 28 dB headroom is
required to have margin for +/– 200 kHz faded adjacent channel ( ca. 19
dB ) and extra 9 dB for pre–monitoring.
Production calibration is done with two RF–levels, LNA gain step is not
calibrated. Gain changes in the receiver are taken off from the dynamic
range of accurate AGC. Variable gain stage in SUMMA is designed in a
way, that it is capable of compensating itself, there is good enough margin in AGC.
Page 67

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 55
Original 08/98
AFC function
AFC is used to lock the transceivers clock to frequency of the base station. AFC–voltage is generated in COBBA with 11 bit AD–converter.
There is a RC–filter in AFC control line to reduce the noise from the converter. Settling time requirement for the RC–network comes from signalling, how often PSW ( pure sine wave ) slots occur. They are repeated after 10 frames , meaning that there is PSW in every 46 ms. AFC tracks
base station frequency continously, so transceiver has got a stable frequency, because changes in VCTCXO–output don’t occur so fast ( temperature ).
Settling time requirement comes also from the start up–time allowed.
When transceiver is in sleep mode and ”wakes” up to receive mode ,
there is only about 5 ms for the AFC–voltage to settle. When the first
burst comes in system clock has to be settled into +/– 0.1 ppm frequency
accuracy. The VCTCXO–module requires also 5 ms to settle into final
frequency. Amplitude rises into full swing in 1 ... 2 ms, but frequency settling time is higher so this oscillator must be powered up early enough.
Receiver blocks
RX interstage filter
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Passband 935 – 960 MHz
Insertion loss 3.3 dB
Maximum drive level +15 dBm
1st mixer in CRFU_1a
Parameter Min. Typ./
Nom.
Max. Unit/Notes
Supply voltage 2.7 2.8 2.85 V
RX frequency range 935 960 MHz
LO frequency range 1006 1031 MHz
IF frequency 71 MHz
Output resistance (balanced) 10 k ohm
1st IF–filter
Parameter min. typ. max. unit
Operating temperature range –20 +75 deg.C
Center frequency , fo 71 MHz
Maximum ins. loss at 1dBBW 8.5 dB
Page 68

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 56
Transmitter Blocks
TX interstage filter
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Passband 890 – 915 MHz
Insertion loss 3.3 dB
Power amplifier module
Parameter Symbol Test condition Min Typ Max Unit
Operating freq. range 880 915 MHz
Supply voltage Vcc 3.0 3.5 5.0 V
Gain control range
( overall dynamic
range)
Vpc= 0.5 ... 2.2 V 45 dB
Synthesizer blocks
VHF VCO and low pass filter
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit/Notes
Supply voltage range 2.7 2.8 2.58 V
Current consumption 4 7 mA
Control voltage 0.5 4.0 V
Operation frequency 232 MHz
Output level –13 –10 dBm ( output after
the lowpass filter )
UHF PLL
UHF PLL block in SUMMA
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit/notes
Input frequency range 650 1300 MHz
Reference input level 100 mVpp
Reference input frequency 30 MHz
Reference input impedance tbd.
Page 69

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 57
Original 08/98
UHF VCO module
Parameter Conditions Rating Unit/
Notes
Supply voltage, Vcc 2.8 +/– 0.1 V
Supply current, Icc Vcc = 2.8 V,
Vc= 2.25 V
< 10 mA
Control voltage, Vc Vcc = 2.8 V 0.8... 3.7 V
Oscillation frequency Vcc = 2.8 V
Vc = 0.8 V
Vc = 3.7 V
< 1006
> 1031
MHz
MHz
Tuning voltage in center frequency f = 1018.5 MHz 2.25 +/– 0.25 V
Tuning voltage sensitivity in operating
frequency range on each spot freq.
Vcc = 2.8 V
f=1006...1031
MHz
14 +/– 2 MHz/V
Output power level Vcc=2.7 V
f=1006...1031
MHz
–6.0 min. dBm
UHF local signal input in CRFU_1a
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit/Notes
Input frequency range 990 1040 MHz
Input level 200 700 mVpp
Connections
RF baseband signals
Signal
name
From To Parameter Mini-
mum
Typi-
cal
Maximum
Unit Function
VBATT Battery RF Voltage 3.0 3.6 5.0/6.0 V Supply voltage for
RF
VXO
ENA
MAD CCONT
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V VR1, VR6 in
CCONT ON
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V VR1, VR6 in
CCONT OFF
SYN
PWR
MAD CCONT
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V VR3, VR4 in
CCONT ON
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V VR3,VR4 in
CCONT OFF
RX
PWR
MAD CCONT
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V VR2, VR5 in
CCONT ON
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V VR2, VR5 in
CCONT OFF
Page 70

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 58
FunctionUnitMaxi-
mum
Typi-
cal
Minimum
ParameterToFromSignal
name
TX
PWR
MAD CCONT
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V VR7 in CCONT
ON
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V VR7 in CCONT
OFF
VREF CCONTSUMMA Voltage 1.478 1.5 1.523 V Reference voltage
for SUMMA and
CRFU1a
PDATA0
MAD CRFU_1
a
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V Nominal gain in
LNA
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V Reduced gain in
LNA
SENA1 MAD SUMMA
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V
PLL enable
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V
SDATA MAD SUMMA
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V
Synthesizer data
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V
SCLK MAD SUMMA
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V
Synthesizer clock
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V
AFC COB-BAVCTCXOVoltage 0.046 2.254 V Automatic fre-
quency control
signal for
VC(TC)XO
RFC VCTCX MAD
Frequency 13 MHz
High stability clock
O
Signal amplitude 0.5 1.0 2.0 Vpp
signal for the logic
circuits
RXIP/
RXIN
SUM-MACOBBA Output level 50 1344 mVppDifferential RX 13
MHz signal to
baseband
TXIP/
TXIN
COB-BASUMMA
Differential voltage
swing
0.75
x
1.022
0.75 x
1.1
0.75 x
1.18
Vpp
Differential in–
phase TX baseband signal for the
DC level 0.784 0.8 0.816 V
RF modulator
TXQP/
TXQN
COB-BASUMMA
Differential voltage
swing
0.75
x
1.022
0.75 x
1.1
0.75 x
1.18
Vpp
Differential quadrature phase TX
baseband signal
DC level 0.784 0.8 0.816 V
for the RF modulator
TXP MAD SUMMA
Logic high ”1” 2.0 2.85 V
Transmitter power
Logic low ”0” 0 0.8 V
control enable
Page 71

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 59
Original 08/98
FunctionUnitMaxi-
mum
Typi-
cal
Minimum
ParameterToFromSignal
name
TXC COB- SUMMA
Voltage Min 0.12 0.18 V
Transmitter power
BA
Voltage Max 2.27 2.33 V
control
RXC COB-BASUMMA
Voltage Min 0.12 0.18 V
Receiver gain
control
Voltage Max 2.27 2.33 V
Page 72

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 60
Timings
Synthesizer control timing
SDATA/
SENA
SYNTHPWR
RXPWR
#bits 23 23 23 23 23
MODE VHF R VHF N/A UHF R UHF N/A
10 us 10 us
10 us
10 us
8 us
6.9 ms ( 1.5 x 4.6 ms ( frame )
100 us
2us min
SCLK
min.
min. min. min. min.
Synthesizer Start–up Timing / clocking
SDATA/
SENA
SYNTHPWR
RXPWR
SCLK
RXC
VXOENA
MON MON MON MONRX RX RX RX
4.6 ms
0.5–2 sec.
20 ms
150 us 150 us
6.9 ms
Synthesizer Timing / IDLE,
one monitoring / frame,
frame can start also from RX–burst
Page 73

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 61
Original 08/98
In case of long list of adjacent channels, there might be two monitoring–
bursts/frame. Extra monitoring ”replaces” TX–burst.
SDATA/
SENA
SYNTHPWR
RXPWR
SCLK
RXC
VXOENA
MON MON MON MONRX RX RX RX
4.6 ms
0.5–2 sec.
20 ms
150 us 150 us
6.9 ms
MON MON MON
Synthesizer Timing / IDLE, 2 monitorings / frame
Frame can start from RX–burst
SDATA/
SENA
SYNTHPWR
RXPWR
SCLK
RXC
MON MON MON MONRX RX RX RX
150 us 150 us
TX TX TX
TXPWR
TXP
TXC
150 us
Sunthesizer Timing / traffic channel
Page 74

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 62
Transmitter power switching timing diagram
Pout
TXC
TXP
542.8 us
8.3..56.7 us
0...56.7 us
0...58 us
TXPWR
150 us 50 us
Transmitter power switching timing diagram for normal bursts
Synthesizer clocking
Synthesizers are controlled via serial control bus, which consists of
SDATA, SCLK and SENA1 signals. These lines form a synchronous data
transfer line. SDATA is for the data bits, SCLK is 3.25 MHz clock and
SENA1 is latch enable, which stores the data into counters or registers.
Page 75

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 63
Original 08/98
Parts list of US8 (EDMS Issue 7.13) Code: 0201187
ITEM CODE DESCRIPTION VALUE TYPE
R100 1430826 Chip resistor 680 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R102 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R103 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R104 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R109 1620017 Res network 0w06 2x100r j 0404 0404
R112 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R113 1430726 Chip resistor 100 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R115 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R116 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R118 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R120 1620025 Res network 0w06 2x100k j 0404 0404
R122 1620019 Res network 0w06 2x10k j 0404 0404
R123 1620025 Res network 0w06 2x100k j 0404 0404
R124 1620027 Res network 0w06 2x47r j 0404 0404
R125 1430808 Chip resistor 150 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R126 1620027 Res network 0w06 2x47r j 0404 0404
R127 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R129 1430853 Chip resistor 2.2 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R130 1430853 Chip resistor 2.2 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R131 1419003 Chip resistor 0.22 5 % 1210
R132 1825003 Chip varistor vwm5.5v vc15.5 0805 0805
R136 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R140 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R141 1430830 Chip resistor 1.0 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R154 1430834 Chip resistor 3.3 M 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R201 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R202 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R211 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R213 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R215 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R217 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R221 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R251 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R253 1430804 Chip resistor 100 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R255 1430718 Chip resistor 47 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R256 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R257 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R259 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R260 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R261 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R263 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R265 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R267 1430808 Chip resistor 150 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Page 76

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 64
R268 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R271 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R272 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R274 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R275 1430770 Chip resistor 4.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R281 1430792 Chip resistor 33 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R282 1430798 Chip resistor 56 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R301 1825009 Varistor network 4xvwm18v 1206 1206
R302 1825009 Varistor network 4xvwm18v 1206 1206
R303 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R304 1825003 Chip varistor vwm5.5v vc15.5 0805 0805
R305 1825003 Chip varistor vwm5.5v vc15.5 0805 0805
R310 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R311 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R331 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404 0404
R332 1430754 Chip resistor 1.0 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R333 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404 0404
R335 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404 0404
R337 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404 0404
R339 1620031 Res network 0w06 2x1k0 j 0404 0404
R341 1430690 Chip jumper 0402
R350 1413829 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.1 W 0805
R351 1413829 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.1 W 0805
R352 1413829 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.1 W 0805
R401 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R450 1825009 Varistor network 4xvwm18v 1206 1206
R500 1430778 Chip resistor 10 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R501 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R502 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R503 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R505 1430760 Chip resistor 1.8 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R506 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R507 1430776 Chip resistor 8.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R540 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R541 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R542 1430730 Chip resistor 150 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R543 1430784 Chip resistor 15 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R544 1620029 Res network 0w06 2x4k7 j 0404 0404
R545 1820031 NTC resistor 330 10 % 0.12 W 0805
R600 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R601 1430730 Chip resistor 150 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R602 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R603 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R604 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R605 1430796 Chip resistor 47 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R620 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R622 1430774 Chip resistor 6.8 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
Page 77

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 65
Original 08/98
R623 1430832 Chip resistor 2.7 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R624 1430738 Chip resistor 270 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R625 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R627 1430710 Chip resistor 22 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R628 1430744 Chip resistor 470 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R629 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R640 1430700 Chip resistor 10 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R641 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R660 1430788 Chip resistor 22 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R661 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R662 1430812 Chip resistor 220 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R663 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R700 1430748 Chip resistor 680 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R703 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R704 1430758 Chip resistor 1.5 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R705 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R706 1430740 Chip resistor 330 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R707 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R708 1430764 Chip resistor 3.3 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R709 1430722 Chip resistor 68 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R740 1430758 Chip resistor 1.5 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R742 1430762 Chip resistor 2.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R743 1430776 Chip resistor 8.2 k 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R745 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R746 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R748 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R749 1430848 Chip resistor 12 k 1 % 0.063 W 0402
R760 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R761 1430714 Chip resistor 33 5 % 0.063 W 0402
R762 1825009 Varistor network 4xvwm18v 1206 1206
R780 1430734 Chip resistor 220 5 % 0.063 W 0402
C100 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C101 2320548 Ceramic cap. 33 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C102 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C103 2604127 Tantalum cap. 1.0 u 20 % 35 V 3.5x2.8x1.9
C104 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C105 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C106 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C107 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C108 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C109 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C110 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C111 2320728 Ceramic cap. 220 p 10 % 50 V 0402
C112 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C113 2320508 Ceramic cap. 1.0 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C117 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C120 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
Page 78

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 66
C121 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C123 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C124 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C125 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C128 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C129 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C130 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C131 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C132 2312405 Ceramic cap. 2.2 u 10 % 10 V 1206
C133 2610003 Tantalum cap. 10 u 20 % 10 V 3.2x1.6x1.6
C140 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C141 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C143 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C144 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C145 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C148 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C149 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C151 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C152 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C200 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C201 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C202 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C203 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C212 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C213 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C220 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C230 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C240 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C241 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C251 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C252 2312295 Ceramic cap. Y5 V 1206
C254 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C255 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C257 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C260 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C261 2310784 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 25 V 0805
C262 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C263 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C266 2610100 Tantalum cap. 1 u 20 % 10 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C268 2610100 Tantalum cap. 1 u 20 % 10 V 2.0x1.3x1.2
C269 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C270 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C271 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C272 2320131 Ceramic cap. 33 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C274 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C275 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C280 2610023 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V 3.5x2.8x1.2
Page 79

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 67
Original 08/98
C281 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C282 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C283 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C291 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C292 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C301 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C302 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C303 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C304 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C305 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C306 2320576 Ceramic cap. 470 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C307 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C308 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C310 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C330 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C331 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C332 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C333 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C334 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C335 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C336 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C337 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C338 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C339 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C340 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C341 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C342 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C343 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C344 2320779 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 16 V 0603
C405 2310784 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 25 V 0805
C500 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C501 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C502 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C503 2320526 Ceramic cap. 3.9 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C504 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C505 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C506 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C507 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C508 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C509 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C510 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C511 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C512 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C513 2320514 Ceramic cap. 1.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C514 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C515 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C517 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
Page 80

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 68
C518 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C541 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C542 2320752 Ceramic cap. 2.2 n 10 % 50 V 0402
C543 2310784 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 25 V 0805
C600 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C601 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C602 2310181 Ceramic cap. 1.5 n 5 % 50 V 1206
C603 2320554 Ceramic cap. 56 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C604 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C610 2611677 Tantalum cap. 220 u 10 % 10 V 7.3x4.3x2.9
C620 2310248 Ceramic cap. 4.7 n 5 % 50 V 1206
C621 2320560 Ceramic cap. 100 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C622 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C623 2320544 Ceramic cap. 22 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C624 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C625 2320540 Ceramic cap. 15 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C626 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C627 2610023 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V 3.5x2.8x1.2
C640 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C641 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C642 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C660 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C661 2312401 Ceramic cap. 1.0 u 10 % 10 V 0805
C662 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C663 2320540 Ceramic cap. 15 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C664 2320584 Ceramic cap. 1.0 n 5 % 50 V 0402
C700 2320524 Ceramic cap. 3.3 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C701 2320107 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 50 V 0603
C702 2320620 Ceramic cap. 10 n 5 % 16 V 0402
C704 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C705 2610023 Tantalum cap. 4.7 u 20 % 10 V 3.5x2.8x1.2
C706 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C707 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C708 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C709 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C711 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C720 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C742 2320738 Ceramic cap. 470 p 10 % 50 V 0402
C743 2320530 Ceramic cap. 5.6 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C744 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C745 2320550 Ceramic cap. 39 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C746 2310784 Ceramic cap. 100 n 10 % 25 V 0805
C760 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C761 2320536 Ceramic cap. 10 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C763 2320522 Ceramic cap. 2.7 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C780 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C781 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
Page 81

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Page 3 – 69
Original 08/98
C782 2320534 Ceramic cap. 8.2 p 0.25 % 50 V 0402
C783 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
C784 2320546 Ceramic cap. 27 p 5 % 50 V 0402
L103 3203701 Ferrite bead 33r/100mhz 0805 0805
L104 3203701 Ferrite bead 33r/100mhz 0805 0805
L105 3203701 Ferrite bead 33r/100mhz 0805 0805
L307 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402 0402
L308 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402 0402
L500 3645123 Chip coil 10 n 5 % Q=31/800M 0603
L501 3645131 Chip coil 8 n 5 % Q=8/100M 0603
L502 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L503 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L504 3608326 Chip coil 330 n 5 % Q=33/50 MHz 1206
L505 3645017 Chip coil 5 n 10 % Q=10/100 MHz 0603
L620 3645183 Chip coil 56 n 5 % Q=12/100 MHz 0603
L621 3645161 Chip coil 150 n 5 % Q=14/100 MHz 0603
L660 3648808 Chip coil 10 % Q=50 1206
L700 3645121 Chip coil 6 n 5 % Q=32/800M 0603
L701 3203705 Ferrite bead 0.015r 42r/100m 0805 0805
L760 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L761 3641622 Chip coil 220 n 5 % Q=30/100 MHz 0805
L780 3203709 Ferrite bead 0.5r 120r/100m 0402 0402
B101 4510219 Crystal 32.768 k +–30PPM 9PF
B301 5140087 Buzzer 85db 2600hz 3.6v 10x10x3. 10x10x3.5
G600 4350143 Vco 1006–1031mhz 2.8v 10ma gsm
G660 4510217 VCTCXO 13.000 M +–5PPM 2.8V
F100 5119019 SM, fuse f 1.5a 32v 0603
Z300 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
Z301 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
Z303 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
Z304 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
Z305 1430005 Chip resistor 150 5 % 0.063 W 0603
Z306 1430005 Chip resistor 150 5 % 0.063 W 0603
Z400 3640035 Filt z>450r/100m 0r7max 0.2a 0603 0603
Z500 4512075 Dupl 890–915/935–960mhz 15.0x8.2 15.0x8.2
Z501 4511049 Saw filter 947.5+–12.5 M 3.1x3.1
Z502 4511059 Saw filter 71+–0.09 M 13.5X6.7 13.5x6.7
Z540 4510009 Cer.filt 13+–0.09mhz 7.2x3.2 7.2x3.2
Z700 4511051 Saw filter 902.5+/–12.5 M 3.1x3.1
V100 1825005 Chip varistor vwm14v vc30v 0805 0805
V116 4110067 Schottky diode MBR0520L 20 V 0.5 A SOD123
V120 4219904 Transistor x 2 UMX1 npn 40 V SOT363
V250 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V301 4113601 Emi filter emif01–5250sc5 sot23–5 SOT23–5
V320 4860005 Led Green 0603
V321 4860005 Led Green 0603
V322 4860005 Led Green 0603
Page 82

PAMS
Technical Documentation
NSE–6
System Module
Original 08/98
Page 3 – 70
V323 4860005 Led Green 0603
V324 4860005 Led Green 0603
V325 4860005 Led Green 0603
V336 4110089 Diode x 2 BAV70W 70 V .5 A 4 ns SOT323
V343 4100278 Diode x 2 BAV70 70 V 200 mA COM
CAT.SOT23
V620 4110062 Cap. diode BB535 30 V 2.1/18.7PFSOD323
V621 4210066 Transistor BFR93AW npn 12 V 35 mA SOT323
V660 4210100 Transistor BC848W npn 30 V SOT323
V700 4110014 Sch. diode x 2 BAS70–07 70 V 15 mA SOT143
V780 4112464 Pindix2 bar64–04 200v 0.1a sot23 SOT23
D200 4370383 Mad2 rom4 f711512 c12 ubga176 UBGA176
D220 4340295 IC, flash mem. UBGA
D230 4346015 IC, SRAM CSP48
D240 4340527 IC, EEPROM CHIP
D402 4340369 IC, dual bus buffer ssoTC7W126FU SSOP8
N100 4370393 Ccont2h dct3 bb asic lbga8x8
N101 4370165 Chaps charger control so16 SO16
N202 4340435 R1120n301b reg 3v/150ma sot23–5 SOT23–5
N250 4370371 Cobba gj b09 bb asic ubga UBGA
N310 4370433 Uiswitch asic tssop20 TSSOP20
N500 4370253 Crfu1a rx+tx uhf gsm v5 sot401–1 SOT401–1
N540 4370351 Summa v2 rx,tx,pll,pcontr. tqfp48 TQFP48
N700 435X106 IC, pow.amp. 3.5 V
N701 4551001 Dir.coupler 0.8–1ghz 3.5x1.8x1.2 3.5x1.8x1.2
S100 520Y015 SM, sw push button spst 5v s.key
S330 5219005 IC, SWsp–no 30vdc 50ma smSW TACT SMD
S331 5219005 IC, SWsp–no 30vdc 50ma smSW TACT SMD
S332 5219005 IC, SWsp–no 30vdc 50ma smSW TACT SMD
X303 5469081 SM, conn 2x7m p0.5 spr.50v pcb/p PCB/PCB
X452 5409073 SM, sim card conn 2x3pol p2.54 h H<2
9854297 PCB US8 100X42.4X0.75 M6 4/PA
0201225 Us8r ir–link module
Page 83

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–1
Block Diagram of UIF
UI–Switch
VIBRA
PWR
FLIP
MIC
EAR
Buzzer cntrl
Blight cntl
Vibra cntl
PWR
Slide detect
Headset conn.
XMIC
MICP
MICN
SGND
XEAR
EARP
EARN
Page 84

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–2
Circuit Diagram of UIF (Version 7.0 Edit 218) for layout version 07
Page 85

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–3
Block Diagram of Baseband
16M2M
Page 86

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–4
Circuit Diagram of Baseband (Version 7.0 Edit 105) for layout version 07
Page 87

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–5
Circuit Diagram of Power Supply (Version 7.0 Edit 257) for layout version 07
Page 88

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–6
Circuit Diagram of SIM Connectors (Version 7.0 Edit 71) for layout version 07
Page 89

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–7
Circuit Diagram of CPU Block (Version 7.0 Edit 208) for layout version 07
Page 90

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–8
Circuit Diagram of Audio (Version 7.0 Edit 126) for layout version 07
Page 91

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–9
Circuit Diagram of IR Module (Version 7.0 Edit 96) for layout version 07
Page 92

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–10
RF Block Diagram
TQFP–48
SUMMA
PA–module
TQFP–32
Page 93

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–11
Circuit Diagram of RF Block (Version 1.0 Edit 244) for layout version 07
Page 94

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–12
Layout Diagram of US8 – Top (Version 07)
Layout Diagram of US8 – Bottom (Version 07)
Page 95

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–13
Testpoints of US8 – Top (Version 07)
Testpoints of US8 – Bottom (Version 07)
Page 96

NSE–6
System Module US8
Original 08/98
3/A3–14
testpoint ref name condition dc–level ac–level
J101 FBUS_TX active state pulsed DC (0V72.8V)
J104 CCONTCSX (CCONT chip select) active state pulse active 0V, non–active 2.8V
J108 CHRG_CTRL charger connected pulsed DC (0V/2.8V)
J220 V5V active state nominal 5.0V (min 4.8V, max 5.2V)
J223 CCONTINT (charger, RTC interrupt) interrupt pulse active 2.8V, non–active 0V
J225 EXTSYSRESETX power on reset state 0V, normal state 2.8V
J226 VCXOPWR power on active state 2.8V, non–active 0V
J227 PURX (power on reset) power up/down reset state 0V, normal state 2.8V
J228 SLEEPCLK (32kHz clock) power on pulsed DC (0V/2.8V)
J235 ROM1SELX active state pulse active 0V, non–active 2.8V
J251 AGND pcb ground 0V
J256 COBBADAX active state pulse active 0V, non–active 2.8V
J500 Control voltage for UHF VCO module G600 channel 60
channel 1
channel 124
2.25 +/– 0.25 V
> 0.8 V
< 3.7 V
J504 Control voltage for VHF VCO circuit typ. 2.0 –2.2 V min 0.5 / max 4.0 V
J508 VSYN_2 ( regulated supply for PLLS ) 2.8 V min 2.7 / max 2.85 V
J534&J536 13 MHz IF output to N250 –95 dBm @ X540
(ext. RF connector )
RXC at level of full
calibrated gain
typ ca. 1.0 – 1.1 V pulsed
min. 0.7 / max. 1.4 V
typ. 50 mVpp balanced voltage at 13 MHz
J538 13 MHz output from Z620 to N620 –95 dBm @ X540
(ext. RF connector )
RXC at level of full
calibrated gain
typ. ca. 1.5 V pulsed typ. ca 600 uVrms
J542 VHF VCO output ( 232 MHz ) – typ. 400 mVpp.
> 100 mVpp required
J554 TXC ( TX power control voltage ) @level 19 typ. ca. 0.6 V pulse
@level 5 typ ca. 1.8 V pulse
J556 TXP ( TX enable ) 2.8 V logic level pulse,
( max. 0.8 V ”0” / min 2.0 V ”1” )
J558 TXQP ( other half of balanced Q–signal ) 0.8 V pulsed 400 mVpp
J560 TXIP ( other half of balanced I–signal ) 0.8 V pulsed 400 mVpp
Page 97

PAMS Technical Documentation
Original 08/98
Appendix 1
TRANSCEIVER NSE–6NX
Page 98

PAMS
Technical Documentation
Appendix 1
NSE–6NX
Page 1 – 2
Original 08/98
CONTENTS
Page No
Foreword 1 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transceiver NSE–6NX 1 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Functional Description 1 – 3. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Modules 1 – 4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Exploded View of Transceiver NSE–6NX 1 – 5. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Assembly Parts of NSE–6NX 1 – 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 99

PAMS
Technical Documentation
Appendix 1
NSE–6NX
Page 1 – 3
Original 08/98
Appendix 1
Foreword
This section of the service manual (Appendix) contains specific details for
the NSE–6NX handportable telephone.
The appendix comprises chapters as follows: Chapter 1, Foreword (this
chapter); Chapter 2, Transceiver NSE–6NX, containing an exploded view
of the NSE–6NX variant (including a list of assembly parts) plus
component parts lists covering the system module and the display
module.
NOTE: The Service Manual is intended for use by qualified
service personnel only.
NOTE: When assembling cover screws, use 17 Ncm torque.
Transceiver NSE–6NX
Functional Description
The NSE–6 is a radio transceiver unit designed for the GSM network. It is
a GSM phase 2, power class 4 transceiver providing 15 power levels with
a maximum output power of 2 W. The transceiver a is true 3 V transceiver.
The transceiver consists of System/RF module (US8), Keyboard module
(UK8) and assembly parts.
The plug–in SIM ( Subscriber Identity Module ) card is located inside the
phone, slot for inserting is in the left side of the phone, accessable when
battery is removed and slide is open.
Page 100

PAMS
Technical Documentation
Appendix 1
NSE–6NX
Page 1 – 4
Original 08/98
Modules
Transceiver NSE–6NX Nokia Euro–A 0501581
• system module US8 0201187
• mechanics MNSE6 0261795
 Loading...
Loading...