
Nokia and Nokia Connecting People are registered trademarks of Nokia Corporation

Nokia E61
Configuring connection settings
Nokia E61 Configuring connection settings
Legal Notice
Copyright © Nokia 2006. All rights reserved.
Reproduction, transfer, distribution or storage of part or all of the contents in this
document in any form without the prior written permission of Nokia is prohibited.
Nokia and Nokia Connecting People are registered trademarks of Nokia Corporation.
Other product and company names mentioned herein may be trademarks or trade
names of their respective owners.
Nokia operates a policy of continuous development. Nokia reserves the right to make
changes and improvements to any of the products described in this document
without prior notice.
Under no circumstances shall Nokia be responsible for any loss of data or income or
any special, incidental, consequential or indirect damages howsoever caused.
The contents of this document are provided "as is". Except as required by applicable
law, no warranties of any kind, either express or implied, including, but not limited
to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, are
made in relation to the accuracy, reliability or contents of this document. Nokia
reserves the right to revise this document or withdraw it at any time without prior
notice.
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.

Introduction
This document is a support guide for the configuration of
Internet settings needed to use the Nokia E61 for data
connections.
To access the Internet (in order to use WWW or mail), the
following conditions must exist:
• The cellular network (GSM 850/900/1800/1900) you
use must support data calls.
• The data service (also the high-speed HSCSD service if
used) must be activated for your SIM card.
• You must have obtained an Internet access point (IAP)
from an Internet service provider.
• Proper Internet settings must have been configured in
your device.
If you are using a wireless LAN (WLAN) connection, you do
not need SIM data service and GSM data call support.
For information about the correct settings, contact your
Internet service provider or system administrator. The
service provider may be able to configure the access point
for you using a special SMS message or WWW page, which
sets up all the necessary Internet access settings. Please
contact your Internet service provider (ISP) for details.
The necessary settings for Internet configuration are
provided by your Internet Service Provider. If your Internet
settings are incomplete or incorrect, please contact your
service provider. Depending on your ISP or network
operator, you may not need to fill in all of the settings.
When you insert a SIM card, the device will read the
necessary GPRS, MMS, and SMSC settings from the SIM
card if they are available, and no manual configuration is
necessary. Note that this may not work with all operators
and SIM cards.
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Introduction
3
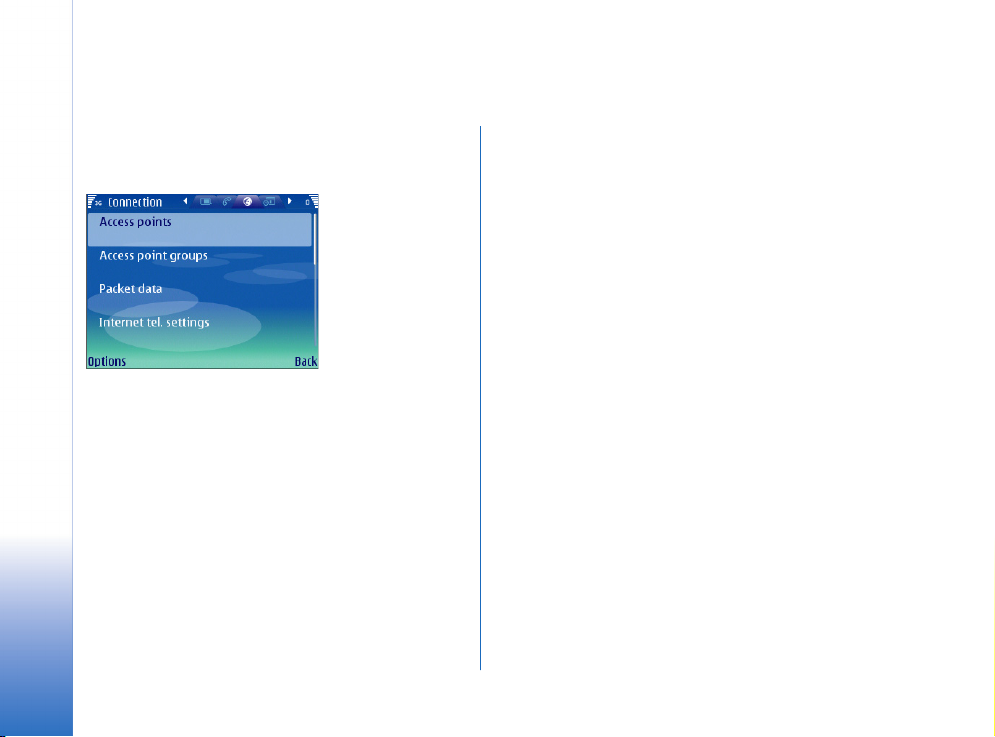
Creating Internet connections
Creating an Internet access point for data calls
Creating Internet connections
1 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→
Access points.
2 The list of existing access points is shown. Press
→ New access point to create a new Internet
Options
access point.
To use an existing access point as a basis for the new
one, select Use existing settings. To start with an empty
access point, select Use default settings.
3 Define the following settings:
• Connection name — Type a descriptive name for the
Internet access point, such as My Data Call
Internet.
• Data bearer — Select Data call or High speed data (GSM
only).
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
4
• Dial-up number — Enter the modem telephone
number of the acess point. Remember to type +
before international numbers.
• User name — Enter your user name if required by the
service provider. User names are often case-sensitive
and provided by your service provider.
• Prompt password — Select Yes to enter your password
each time you log into a server or No to save the
password in your device memory and automate the
login.
• Password — Enter your password if required by the
service provider. The password is often casesensitive and provided by the service provider.
• Authentication — Select Secure to always send your
password encrypted or Normal to send your password
encrypted when possible.
• Homepage — Enter the Web address of the page you
want to display as a home page when you use this
access point.
• Data call type — Select Analogue or ISDN. This setting
depends on both your GSM network operator and
Internet service provider, because some GSM
networks do not support certain types of ISDN
connections. For details, contact your Internet
service provider. If ISDN connections are available,
they establish connections more quickly than analog
methods.
• Max. data speed — Select the limit to apply to the
transfer speed. The speed represents the maximum
speed at which your connection will operate. During
the connection, the operating speed may be less,
depending on network conditions. If you select
Automatic, the data transfer rate is determined by
the network and may be affected by network traffic.
Some service providers may charge more for higher
data rates.
4 After setting up a basic Internet access point for Data
call or High speed data (GSM only), select Back to save the
settings and exit, or Options
define the following advanced settings:
→ Advanced settings to
• IPv4 settings — Enter the device IP and name server
addresses for IPv4 Internet protocol.
• IPv6 settings — Enter the device IP and name server
addresses for IPv6 Internet protocol.
• Proxy serv. address — Enter the IP address or the
domain name of the proxy server. For example,
domain names are company.com and
organisation.org
• Proxy port number — Enter the proxy server port
number. The port number is related to the protocol.
Common values are 8000 and 8080, but vary with
every proxy server.
Proxy servers are intermediate servers between a
browsing service and its users, which are used by
some service providers. These servers may provide
additional security and speed up access to the
service.
• Use callback — Select Yes if you have a service that
dials back to your device when you establish an
Internet connection.
• Callback type — Select Use server no. or Use other no.,
according to instructions from your service
provider.
• Callback number — Enter your data call phone
number of your device, which the callback server
uses.
• Use PPP compress. — Select Yes to speed up the data
transfer, if it is supported by the remote PPP server.
• Use login script — Select Yes, if your Internet service
provider requires a login script, or if you want to
automate your login. A login script is a sequence of
instructions that the system follows during the
login process.
• Login script — Enter the login script. This setting is
available only if you have selected Use login script
Yes.
→
• Modem initialisation — Enter a command string for
the connection setup, if required by your service
provider.
Creating Internet connections
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
5

Creating an Internet access point for packet data (GPRS)
1 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→
Access points.
Creating Internet connections
2 The list of existing access points is shown. Press
→ New access point to create a new Internet
Options
access point.
To use an existing access point as a basis for the new
one, select Use existing settings. To start with an empty
access point, select Use default settings.
3 Define the following settings:
• Connection name — Type a descriptive name for the
Internet access point, such as My GPRS Internet.
• Data bearer — Select Packet data.
• Access point name — Enter the name for the access
point. The name is usually provided by your service
provider or network operator.
• User name — Enter your user name if required by the
service provider. User names are often casesensitive and provided by your service provider.
• Prompt password — Select Yes to enter your password
each time you log into a server or No to save the
password in your device memory and automate the
login.
• Password — Enter your password if required by the
service provider. The password is often casesensitive and provided by the service provider.
• Authentication — Select Secure to always send your
password encrypted or Normal to send your
password encrypted when possible.
• Homepage — Enter the Web address of the page you
want to display as a home page when you use this
access point.
4 After setting up a basic Internet access point for Packet
data (GPRS), select Back to save the settings and exit,
or Options
advanced settings:
• Network type — Select IPv4 or IPv6 as the Internet
• Phone IP address — Enter the IP address of your
• DNS address — Enter the IP addresses of the Primary
→ Advanced settings to define the following
protocol type. The Internet protocol defines how
data is transferred to and from your device.
device. Select Automatic to have the network
provide the device IP address. This setting is
available only if you have selected Network type→
IPv4.
DNS address and Secondary DNS addr. if required by
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
6

your service provider or network operator.
Otherwise, the name server addresses are provided
automatically.
• Proxy serv. address — Enter the address of the proxy
server. Proxy servers are intermediate servers
between a browsing service and its users, which are
used by some service providers. These servers may
provide additional security and speed up access to
the service.
Creating an Internet access point for WLAN
1 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→ Access
points.
2 The list of existing access points is shown. Press
→ New access point to create a new Internet
Options
access point.
To use an existing access point as a basis for the new
one, select Use existing settings. To start with an empty
access point, select Use default settings.
3 Define the following settings:
• Connection name — Type a descriptive name for the
Internet access point, such as My WLAN Internet.
• Data bearer — Select Wireless LAN.
• WLAN netw. name — To enter the service set identifier
(SSID), that is, the name that identifies the specific
wireless LAN, select Enter manually. To select the
network from the wireless LANs in range, select
Search for netw..
• Network status — Select Hidden if the network you
are connecting to is hidden, or Public if it is not
hidden.
• WLAN netw. mode — If you select Infrastructure,
devices can communicate with each other and with
wired LAN devices through a wireless LAN access
point. If you select Ad-hoc, devices can send and
receive data directly with each other, and no
wireless LAN access point is needed.
• WLAN security mode — You must select the same
security mode that is used in the wireless LAN
access point. If you select WEP (wired equivalent
privacy), 802.1x, or WPA/WPA2 (Wi-Fi protected
access), you must also configure the relevant
additional settings as described in step 4.
• Homepage — Enter the Web address of the page you
want to display as a home page when you use this
access point.
Note: The settings available for editing
may vary.
4 If you selected WPA/WPA2 as the WLAN security mode,
define the following in WLAN security sett.:
• WPA mode — Select EAP if you want to use an EAP
module for authentication. If you select Pre-shared
key, type the password (also called a master key) in
the field. Note that the same key must be entered in
the wireless LAN access point.
• EAP plug-in settings — If you selected EAP, you must
also define these settings. See page 9 for more
information.
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Creating Internet connections
7

• TKIP encryption — To enable TKIP encryption, based
on transient keys changed often enough to prevent
misuse, select Allowed. All devices in the wireless
LAN must either allow or prevent the use of TKIP
encryption.
If you selected 802.1x as the WLAN security mode,
define the following in WLAN security sett.:
• WPA mode — Select EAP if you want to use an EAP
module for authentication. If you select Pre-shared
key, type the password (also called a master key) in
the field. Note that the same key must be entered in
the wireless LAN access point.
Creating Internet connections
• EAP plug-in settings — If you selected EAP, you must
also define these settings. See page 9 for more
information.
Note: 802.1x authenticates and
authorizes devices to access a wireless
network, and prevents access if the
authorization process fails.
If you selected WEP as the WLAN security mode, define
the following in WLAN security sett.:
• WEP key in use — Select which WEP key is used (#1-
#4).
• Authentication type — Select Open or Shared.
• WEP key settings — The remaining settings are
defined here:
WEP encryption — Select the desired WEP encryption
key length. Supported options are 64, 128, and 256
bits. The more bits there are in the key, the higher
the level of security. WEP keys consist of a secret key
and a 24-bit initialization vector. For example, some
manufacturers refer to the 104-bit key as a 128-bit
key (104+24). Both keys offer the same level of
encryption and are therefore interoperable.
WEP key format — Select whether you want to enter
the WEP key data in Hexadecimal format or in text
format (ASCII).
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
8

WEP key — Enter the WEP key data. The number of
characters you can enter depends on the key length
you have chosen.
Note: Wired equivalent privacy (WEP)
encryption method encrypts data before it
is transmitted. Access to the network is
denied to users who do not have the
required WEP keys. When WEP security
mode is in use, if your device receives a data
packet not encrypted with the WEP keys,
the data is discarded. In an Ad-hoc
network, all devices must use the same
WEP key.
5 After setting up a basic Internet access point for
Wireless LAN, select Back to save the settings and exit,
or Options
advanced settings:
→ Advanced settings to define the following
• IPv4 settings — Enter the device IP and name server
addresses for IPv4 Internet protocol.
• IPv6 settings — Select or enter the name server
addresses for IPv6 Internet protocol.
• Ad-hoc channel — If the selected network mode is
ad-hoc, select User defined to manually enter a
channel number (1-11).
• Proxy serv. address — Enter the proxy server address.
• Proxy port number — Enter the proxy server port
number. Proxy servers are intermediate servers
between a browsing service and its users, which are
used by some service providers. These servers may
provide additional security and speed up access to
the service.
Note: The settings availabe for editing
may vary. Contact your service provider for
more information.
Modifying EAP settings
The extensible authentication protocol (EAP) plug-ins are
used in wireless networks to authenticate wireless devices
and authentication servers, and the different EAP plug-ins
make possible the use of various EAP methods (network
service).
To use an EAP plug-in when you connect to a WLAN using
the access point, select the desired plug-in and Options
Enable. The EAP plug-ins enabled for use with this access
→
Creating Internet connections
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
9

point have a check mark next to them. To not use a plugin, select Options
To edit the EAP plug-in settings, select Options
Configure.
Creating Internet connections
To change the priority of the EAP plug-in settings, select
→ Raise priority to attempt to use the plug-in
Options
before other plug-ins when connecting to the network
with the access point, or Options
this plug-in for network authentication after attempting
to use other plug-ins.
The available options may vary.
→ Disable.
→ Lower priority to use
Creating an Internet access point for IP passthrough
1 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→
Access points.
→
2 The list of existing access points is shown. Select
→ New access point→ Use default settings to
Options
create a new access point.
3 Define the following settings:
• Connection name — Type a descriptive name for the
Internet access point, such as My IP Passthrough.
• Data bearer — Select IP passthrough.
4 After configuring the basic settings for IP passthrough,
select Back to save the settings and exit, or Options
Advanced settings to define the following advanced
settings:
→
• IPv4 settings — Enter the Phone IP address and DNS
address for the IPv4 Internet protocol.
• IPv6 settings — Enter the DNS address for the IPv6
Internet protocol.
• Proxy serv. address — Enter the address of the proxy
server. Proxy servers are intermediate servers
between a browsing service and its users, which are
used by some service providers. These servers may
provide additional security and speed up access to
the service.
• Proxy port number — Enter the proxy server port
number.
Note: DNS is an Internet service that
translates domain names such as
www.nokia.com into IPv4 addresses such
as 192.100.124.195, or IPv6 addresses like
3ffe:2650:a640:1c2:341:c39:14.
10
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.

Activating IP passthrough
Note: Use the USB data cable driver to
establish a cable connection between your
device and a compatible Windows-based PC.
For Windows 2000 and Windows XP users:
the drivers for the Nokia DKU-2 and CA-53
cables are integrated into Nokia PC Suite
version 6.7 and onwards. Instead of
downloading the cable driver separately, it is
recommended that you download the
Nokia PC Suite.
Select Menu
passthrough to use the data cable for the IP passthrough
Internet access point.
Nokia Network Bridge (which can be downloaded from
forum.nokia.com) is the IP passthrough application that
allows you to obtain a network connection on your device
from a compatible PC through a USB data cable. Connect
the USB data cable to the bottom of the device. Connect
the other end of the data cable to a compatible PC, and
wait for the PC to recognize your device.
Use IP passthrough as you use any Internet access point to
browse or synchronize remotely. If a wireless network
connection is unavailable, use IP passthrough to access the
Internet or a LAN. You cannot use IP passthrough at the
same time as Nokia PC Suite. You cannot activate the
→ Connect.→ Data cable→ Options→ IP
modem if you select IP passthrough in cable connection
settings.
Selecting an Internet access point
When you establish an Internet connection, you are asked
to select the Internet access point you want to use for
that connection. Select an Internet access point from the
list of available access points, and press Select.
Tip: The Select access point dialog opens only if
you have selected Always ask in the Access
point field in the Web settings. Otherwise, the
selected default Internet access point is used.
To check the status of the setting, select
→ Web→ Options→ Settings.
Menu
Access point groups
Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→ Access
point groups.
An access point group is used for grouping and prioritizing
access points. An application can use a group as a
connection method instead of a single access point. In
that case the best available access point inside a group is
used for making connection and in case of email, also for
roaming.
Creating Internet connections
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
11

To create an access point group, select Access point
→ Options→ New groups. In the Group name field,
groups
enter a name for the group. Define in the Conn. switching
field whether to show the connection switching process
on the display of your device. Choose and edit the access
points that belong to this group in the Access points
section.
To remove an access point in an access point group, select
the access point and Options
→ Remove.
Creating Internet connections
12
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.

Configuring wireless LAN
1 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→
Wireless LAN to access WLAN settings:
• To have an indicator displayed when there is a
wireless LAN available in your current location,
select Show availability
• To select the time in terval fo r your dev ice to s can for
available wireless LANs and update the indicator,
select Scan for networks. This setting is not visible
unless you select Show availability→ Yes.
2 Select Menu→ Tools→ Settings→ Connection→
Wireless LAN→ Options→ Advanced settings to access
advanced WLAN settings. The wireless LAN advanced
settings are normally defined automatically, and
changing them is not recommended. To edit the
settings manually, select Automatic config.
and define the following:
• Long retry limit — Enter the maximum number of
transmission attempts if the device does not receive
a receiving acknowledgement signal from the
network.
• Short retry limit — Enter the maximum number of
transmission attempts if the device does not receive
a clear-to-send signal from the network.
• RTS threshold — Select the data packet size at which
the wireless LAN access point device issues a request
to send before sending the packet.
→ Yes.
→ Disabled,
• TX power level — Select the power level of your device
when sending data.
• Radio measurements — Enable or disable the radio
measurements.
• Power saving — Enable or disable power saving.
To restore all settings to their original values, select
Options
→ Restore defaults.
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
Configuring wireless LAN
13

Configuring text messages (SMS)
Note: Before you can send and receive text
messages, the following conditions must
exist:
•The phone must be turned on.
•The network you are using must support the
text message service.
•The text message service must be activated
for your SIM card.
Configuring text messages (SMS)
• The text message settings must be defined.
Configuring text message center settings
Select Menu→ Messag.→ Options→ Settings→ Text
→ Message centres to access the message center
message
settings.
To edit message centers, select the message center, and
→ Edit.
Options
To add new message centers, select Options
centre.
14
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
→ New msg.
To delete message centers, select the message center, and
→ Delete.
Options
Configuring text message settings
Select Menu→ Messag.→ Options→ Settings→ Text
message to access the following text message settings.
• Msg. centre in use — Select the message center you want
to deliver your text messages.
• Character encoding — Select Reduced support to use
automatic character conversion to another encoding
system when available.
• Receive report — Select Yes if you want that the network
sends you delivery reports on your messages (network
service).
• Message validity — Select how long the message center
resends your message if the first attempt fails (network
service). If the recipient cannot be reached within the
validity period, the message is deleted from the
message center.
• Message sent as — Convert the message to another
format, such as Text, Fax, Paging or E-mail. Change this

option only if you are sure that your message center is
able to convert text messages into these other formats.
Contact your network operator.
• Preferred conn. — Select the preferred method of
connection when sending text messages from your
device.
• Reply via same ctr. — Select whether you want the reply
message to be sent using the same text message center
number (network service).
Configuring text messages (SMS)
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
15

Configuring multimedia messages (MMS)
16
Note: Only devices that have compatible
features can receive and display multimedia
messages. The appearance of a message may
vary depending on the receiving device.
Before you can send or receive multimedia
messages on your device, you must define the
multimedia message settings. Your device may
have recognized the SIM card provider and
automatically configured the multimedia
message settings. If not, contact your service
provider.
Select Menu
Multimedia message to access the multimedia message
settings.
Configuring multimedia messages (MMS)
• Image size — Select Small or Large to scale images in
multimedia messages. Select Original to maintain the
original image size of multimedia messages.
• MMS creation mode — Select Restricted to have your
device prevent you from including content in
multimedia messages that may not be supported by
the network or the receiving device. To receive
warnings about including such content, select Guided.
To create a multimedia message with no restrictions
on attachment type, select Free. If you select Restricted,
creating multimedia presentations is not possible.
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
→ Messag.→ Options→ Settings→
• Access point in use — Select the default access point to
connect to the multimedia message center. You may
not be able to change the default access point if it is
preset in your device by your service provider.
• Multimedia retrieval — Select Always automatic to
always receive multimedia messages automatically,
Aut. in home network to receive notification of a new
multimedia message that you can retrieve from the
message center (for example, when you are traveling
abroad and are outside your home network), Manual to
retrieve multimedia messages from the message center
manually, or Off to prevent receipt of any multimedia
messages.
• Allow anon. msgs. — Select whether you want to receive
messages from unknown senders.
• Receive adverts — Select whether you want to receive
messages defined as advertisements.
• Receive report — Select Yes to have the status of the
sent message to be shown in the log (network service).
Receiving a delivery report of a multimedia message
that has been sent to an e-mail address may not be
possible.
• Deny report sending — Select Yes to not send delivery
reports from your device for received multimedia
messages.

• Message validity — Select how long the message center
resends your message if the first attempt fails (network
service). If the recipient cannot be reached within the
validity period, the message is deleted from the
message center. Maximum time is the maximum
amount of time allowed by the network.
Configuring multimedia messages (MMS)
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
17

Configuring voice mailbox (network service)
To configure your voice mailbox settings, select Menu→
Organiser→ Voic.mail.
When you open the voice mailbox application for the first
time, you are asked to enter the number of your voice
Configuring voice mailbox (network service)
mailbox. To change the number, select Options
number. To call the number, select Options
mailbox.
Tip: To call your voice mailbox (network
service) in standby mode, press and hold 1, or
press 1 then the call key.
→ Change
→ Call voice
18
Copyright © 2006 Nokia. All rights reserved.
 Loading...
Loading...