Page 1

SPG-AVA-DMUX
SPG-AVA-DMUX-R
Sync-Pulse Generator/Replicator
with Linear Time Code and AES reference outputs
User manual
Rev. C
Nevion
Nordre Kullerød 1
3241 Sandefjord
Norway
Tel: +47 33 48 99 99
nevion.com
Page 2
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Nevion Europe
P.O. Box 1020
3204 Sandefjord, Norway
Support phone 1: +47 33 48 99 97
Support phone 2: +47 90 60 99 99
Nevion USA
1600 Emerson Avenue
Oxnard, CA 93033, USA
Toll free North America: (866) 515-0811
Outside North America: +1 (805) 247-8560
E-mail: support@nevion.com
See http://www.nevion.com/support/ for service hours for customer support globally.
Rev.
Repl.
Date
Sign
Change description
C B 2014-11-06
CC
Updated de-embedder latency
B A 2013-10-29
TB
Corrected bit depth for analog video
A 0 2013-06-13
TB /
JR
Replaced top view of the module, updated
description of the DIP switch groups; new
template
0 - 2012-09-03
TB
Initial version
Nevion Support
Revision history
Current revision of this document is the uppermost in the table below.
nevion.com | 2
Page 3

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Contents
Revision history ........................................................................................................ 2
1 Product overview ................................................................................................... 4
1.1 The core functionality .................................................................................................... 4
1.2 Secondary functionality ................................................................................................. 4
1.2.1 Audio sync output ....................................................................................................... 4
1.2.2 Linear time code output .............................................................................................. 4
1.2.3 Input change-over with fallback to internal generators ................................................ 4
1.3 Product variants and how they differ ............................................................................. 5
2 How to get started ................................................................................................. 6
2.1 Power requirements ...................................................................................................... 6
2.2 Physical connections ..................................................................................................... 6
2.2.1 Sync input .................................................................................................................. 7
2.3 What the LEDs mean .................................................................................................... 8
2.3.1 Exceptions/special conditions for the LEDS ............................................................... 8
2.4 Selecting between Gyda mode or Manual mode ........................................................... 8
2.5 A very brief guide to Gyda mode set-up ........................................................................ 9
2.6 How to get back to factory defaults? .............................................................................. 9
3 Detailed control.................................................................................................... 10
3.1 Detailed control in manual mode ..................................................................................10
3.1.1 Rotary switch and push buttons.................................................................................10
3.1.2 DIP switch functions ..................................................................................................10
3.1.3 Factory reset function ................................................................................................12
3.2 Detailed control in Gyda mode .....................................................................................13
3.2.1 Information page .......................................................................................................13
3.2.2 Configuration page ....................................................................................................14
3.2.3 Phase delay ..............................................................................................................14
3.2.4 Subcarrier delay ........................................................................................................15
3.2.5 Linear time code ........................................................................................................15
3.2.6 Video input ................................................................................................................15
3.2.7 Output switch ................................................................ ............................................17
3.2.8 Frequency lock mode ................................................................................................17
3.2.9 Analog sync mode .....................................................................................................17
3.2.10 Digital audio sync mode ..........................................................................................17
3.2.11 Tri-level standard ....................................................................................................18
3.2.12 Black-burst standard ...............................................................................................18
3.2.13 Signal integrity .........................................................................................................18
Appendix A Specifications ...................................................................................... 20
Appendix B General environmental requirements for Nevion equipment ............... 22
Product Warranty.................................................................................................... 23
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling information .................................. 24
A.1 Materials declaration ....................................................................................................24
A.2 Recycling information ...................................................................................................24
nevion.com | 3
Page 4
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
1 Product overview
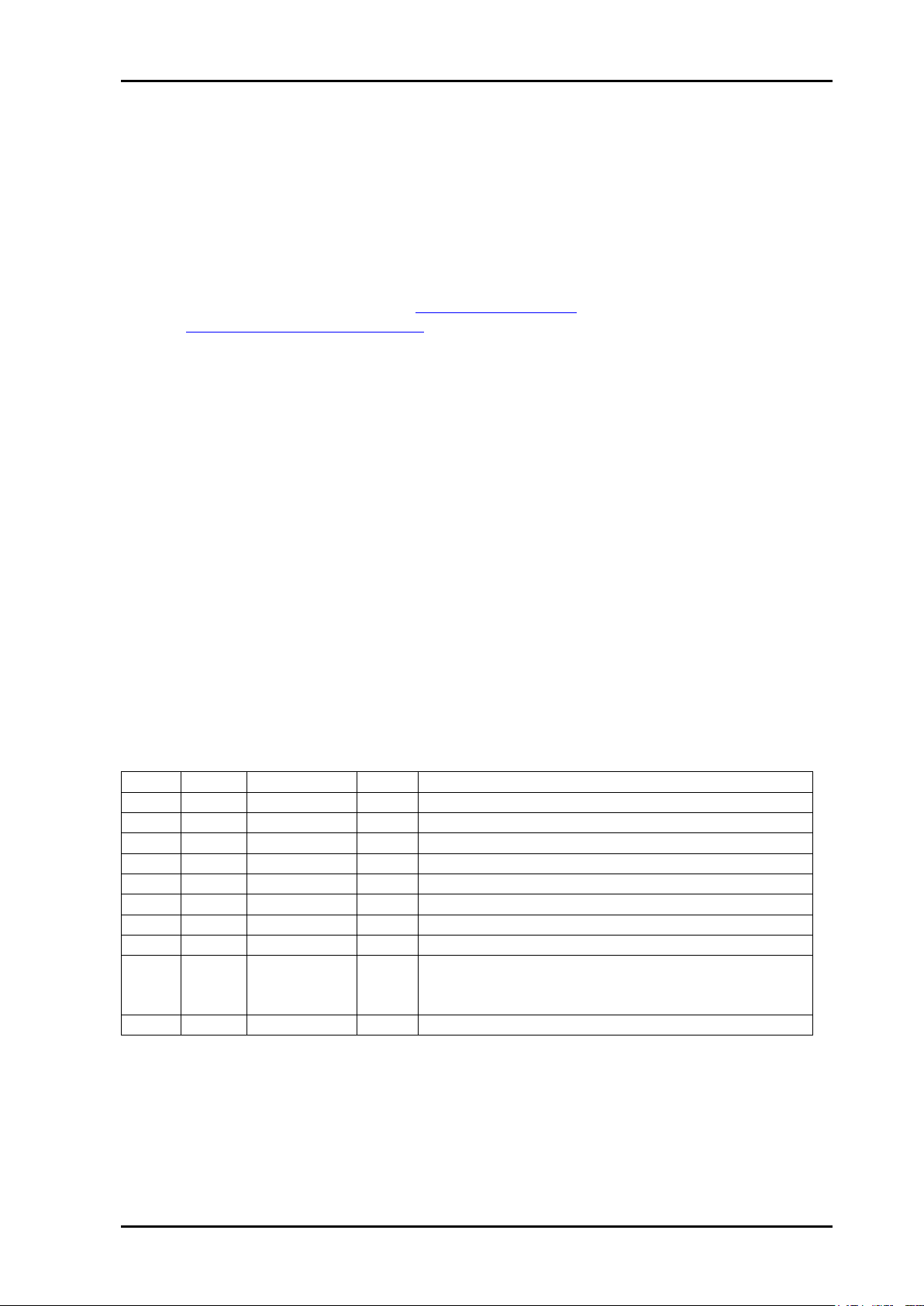
Figure 1: Simplified block diagram of the SPG-AVA-DMUX card
1.1 The core functionality
The SPG-AVA-DMUX takes an SDI input signal and uses this as a frequency reference to
generate an analog sync signal, either Black burst or Tri-level. The sync signal is also
available in digital SDI form on two BNC outputs, and these signals can then be fed to DACs
or distribution amplifiers. Alternatively, the signal on these BNC outputs can be taken directly
from the reclocked input.
A full frame synchronizer and de-glitcher handles interruptions on the input and ensures that
the signal to the frequency generating logic is kept stable. If the input should disappear, the
SPG-AVA-DMUX will still generate Black burst or Tri-level signal with the same frequency.
The frequency generating logic has two modes: One that will react instantly to input frequency
changes and try to follow it (slave mode), and one that will average out frequency variations
over a long time (master mode). If cascading several SPG-AVA-DMUX units, the first could
be put in master mode to average out frequency variations, while the down-stream units
should be put in slave mode to follow the frequency generated by the master as tightly as
possible.
1.2 Secondary functionality
1.2.1 Audio sync output
At the same time as producing the video sync signal, the SPG-AVA-DMUX also generates
an audio reference signal based on the same input frequency. This can be either AES11 or
Word clock, both intended to synchronize external audio equipment, and thereby prevent
unintentional and unnecessary use of sample rate converters. The audio sync output will still
be generated if the input signal is lost.
1.2.2 Linear time code output
Linear Time Code (LTC) is de-embedded and available on a separate output. Since this is
de-embedded from the input and not generated, the output will be missing if the input signal
disappears.
1.2.3 Input change-over with fallback to internal generators
The SPG-AVA-DMUX comes with an electrical SDI input and an additional (optional) optical
input. Sophisticated input selection logic can switch between the physical input when signals
are available, and/or switch to internal video generators in the event that no physical input is
present.
nevion.com | 4
Page 5

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
SPG-AVA-DMUX
Sync-pulse generator with one electrical input only.
Three analog video outputs (Black burst or Tri-level), one digital
audio sync output (AES11 or Word clock), and two SDI outputs (SDI
version of the Analog video output, or a reclocked version of the input
signal).
SPG-AVA-DMUX-R
Sync-pulse generator with one electrical input and one high
sensitivity 9/125µm single mode optical input.
Three analog video output (Black burst or Tri-level), one digital audio
sync output (AES11 or Word clock), and two SDI outputs (SDI
version of the Analog video output, or a reclocked version of the input
signal).
1.3 Product variants and how they differ
Only two variants of the SPG-AVA-DMUX exist: With and without optical input. The variant
with optical input is denoted with an -R appended to its name. Both variants have the electrical
input, and the variant with optical input can use one input as fallback for the other.
nevion.com | 5
Page 6
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
2 How to get started
2.1 Power requirements
The absolute maximum total power consumption for this module is 6.75 W, of which 4.2 W
are drawn from the +5 V supply, 2.3 W are drawn from the +15 V supply, and 0.25 W are
drawn from the -15 V supply. These numbers include 0.5 W from the +5 V supply for the
optional optical input module, and the calculation of how many modules can be powered by
a single power supply can thus be based on 3.7 W for the SPG-AVA-DMUX and 4.2 W for
the SPG-AVA-DMUX-R.
Note that the module will draw its power from multiple supply voltages. When
calculating the number of modules that can safely be used in one frame, it’s
important to consider each supply voltage separately for the power supply in
question. In general there will be no load-sharing between the supply voltages,
and the number of modules will be limited by the worst-case result from the
individual calculations.
2.2 Physical connections
Figure 2: The cable side of the backplane, SPG-AVA-DMUX-C1
The backplane for the SPG-AVA-DMUX is labeled SPG-AVA-DMUX/-R. It is designed to be
fitted in a Flashlink rack unit and to take up a single slot. The connection side will face outward
on the back side of the Flashlink rack when mounted correctly. The table below is an overview
of the connectors and their associated functions.
nevion.com | 6
Page 7
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
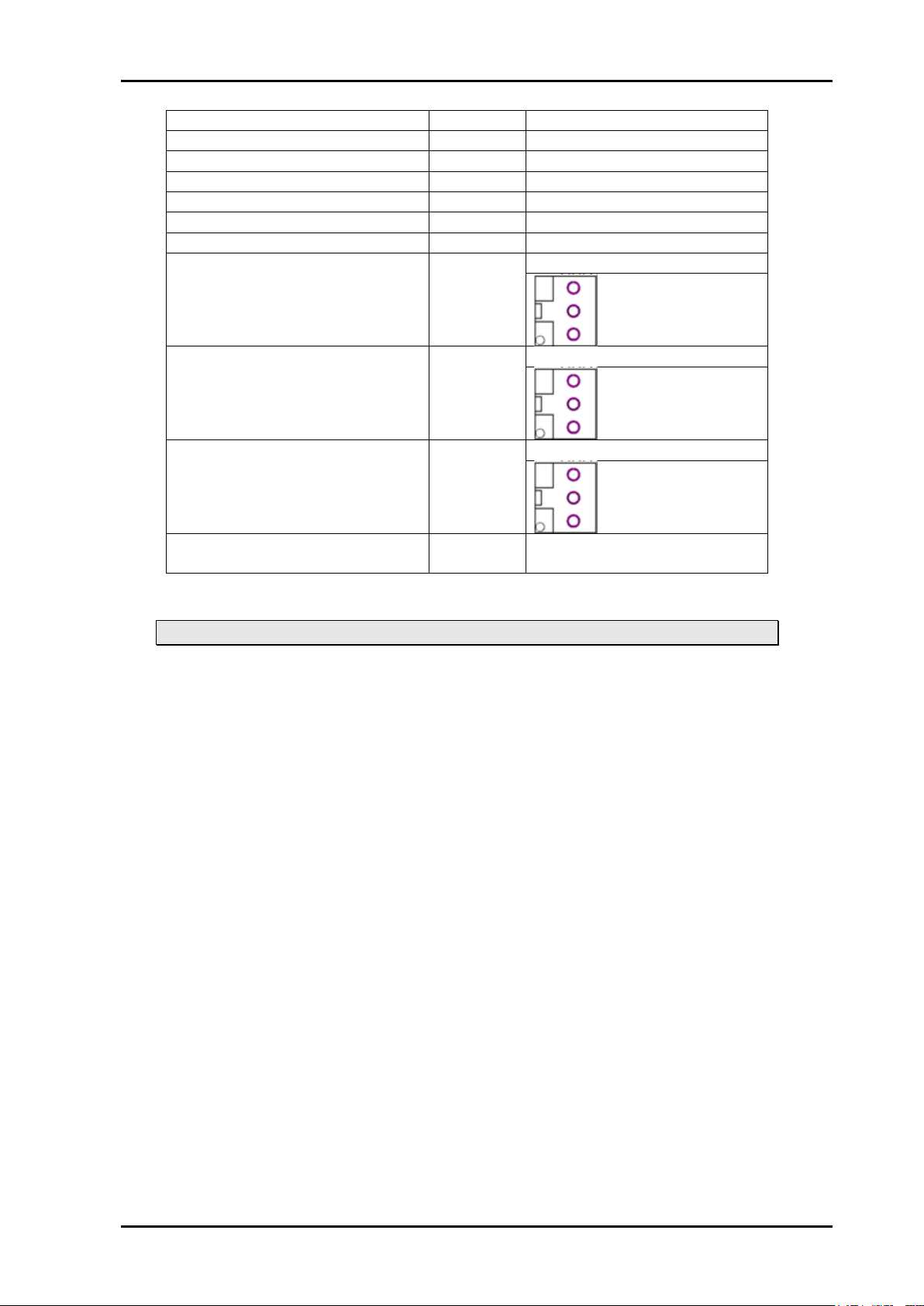
Function
Label
Connector type
HD/SD-SDI input
IN
BNC
HD/SD-SDI sync output 1
O1
BNC
HD/SD-SDI sync output 2
O2
BNC
Analog sync output, Y/G/CVBS
Y/G/CVBS
BNC
Analog sync output, Pb/B/Y
PB/B/Y
BNC
Analog sync output, Pr/R/C
PR/R/C
BNC
Linear time code output 1
AAL
WECO Audio connector
Positive
GND
Negative
Linear time code output 2
AAR
WECO Audio connector
Positive
GND
Negative
AES11 / Word clock output
AES
WECO Audio connector
Positive
GND
Negative
Optical input
No label
BSC-II (for SC input)
Sync input (Not in use)
SYNC
BNC
Table 1: Connector functions
Unused SDI inputs/outputs should be terminated with 75 Ohm.
2.2.1 Sync input
The sync connector is not in use for the SPG-AVA-DMUX(-R) and is therefore blocked by a
protective cap.
nevion.com | 7
Page 8
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Diode \ state
Red LED
Orange LED
Green LED
No light
Card status
PTC fuse has been
triggered or FPGA
loading has failed
FPGA
loading. If
more than a
few seconds:
DIPs 14+15
both set to the
‘On’ position,
or module not
programmed
FPGA loaded,
module OK
Module has no
power
SDI input
status
Video signal absent
Video signal
present but
card not able
to lock VCXO
Video input
signal in lock
Module not
programmed, or
DIPs 14+15 both
set to the ‘On’
position
Sync input
status
The SPG-AVA-DMUX does not use the sync input.
The Sync input LED always shows the same state as the SDI input LED.
Audio input
status
(Group 1 is
the LTC
source)
No audio
embedded in
Group 1
---
Audio
detected in
Group 1
Module not
programmed, or
DIPs 14+15 both
set to the ‘On’
position
2.3 What the LEDs mean
Table 2: LED states and what they mean
2.3.1 Exceptions/special conditions for the LEDS
The locate command will make all four LEDs blink on and off synchronously to quickly identify
the module in a larger installation. The operation of the card is not otherwise affected by the
command, only the appearance of the LEDs will change. The LEDs will return to their normal
states and functions after the special locate condition times out.
FPGA firmware upgrades will activate running lights after the firmware download has finished.
Do not remove power to the card when running lights are active, the card is unpacking and
installing the new firmware. The SPG-AVA-DMUX will automatically reboot after a successful
upgrade, and the LEDs will then also return to their normal functions.
2.4 Selecting between Gyda mode or Manual mode
The board can be configured either manually or via the system controller Multicon GYDA.
Since there’s a limited number of switches available compared to the total number of settings
available for the module, only a subset of the parameters can be adjusted when operating in
manual mode. Generally, the parameters that cannot be directly controlled by the DIP
switches will take their settings from the previous Multicon GYDA session. This means that
for a specific manual setup it may be necessary to configure the module with a Multicon
GYDA before switching to manual mode.
To reach manual mode, the lower DIP (labelled OVR) on the module must be switched to the
“On” position (to the right) and the board must be re-booted. This isolates the board from
Multicon GYDA control, but the module will still accept commands to retrieve its status, and
also the commands necessary to initiate and perform firmware upgrades.
In addition to the DIP switches, manual mode will also activate the rotary switch and the two
push-buttons at the front of the module. These are used to control the phase delay for the
sync-pulse generator.
nevion.com | 8
Page 9

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
2.5 A very brief guide to Gyda mode set-up
All of these settings are covered in much more detail in chapter 3.2. These are just the most
important settings to get started:
Arguably the most important setting is where to take the input from. If the module was
purchased with the electrical input only, this would be a good starting point:
What this means is that the electrical input will be chosen whenever a signal is present, and
if a signal is not present, the output will frame freeze for 500 ms before resorting to an internal
fallback generator. Here this generator is set to produce just black video frames.
If the module was purchased with the optical input option, the setup could either be like above,
or with the Optical input instead of the Electrical input, or one input could serve as a backup
for the other, with a final fallback to generator, as illustrated below:
Once the input source has been decided, it must be decided how this reference should be
handled by the card:
The “Soft (master)” setting ensures that the card will not track variations in the input frequency
instantly, but average them out.
The rest of the settings on the configuration page either deal with setup of the frame
synchronizer, or with the multiple choice selection of formats for the module outputs. See ch
3.2 for more detailed description of all the available options.
2.6 How to get back to factory defaults?
To access the function that will reset the module and reload the factory default settings, the
module must briefly be put into manual mode. The entire procedure is described in chapter
3.1.3.
nevion.com | 9
Page 10

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
3 Detailed control
3.1 Detailed control in manual mode
To reach manual mode, the lower DIP (labelled OVR) on the module must be switched to the
“On” position (to the right) and the board must be re-booted. This isolates the board from
Multicon GYDA control, but the module will still accept commands to retrieve its status, and
also commands related to initiate and perform firmware upgrades.
The Manual Mode configuration controls are all found on the front side of the board. There
are two sets of DIP switches, one rotary switch, and two push buttons.
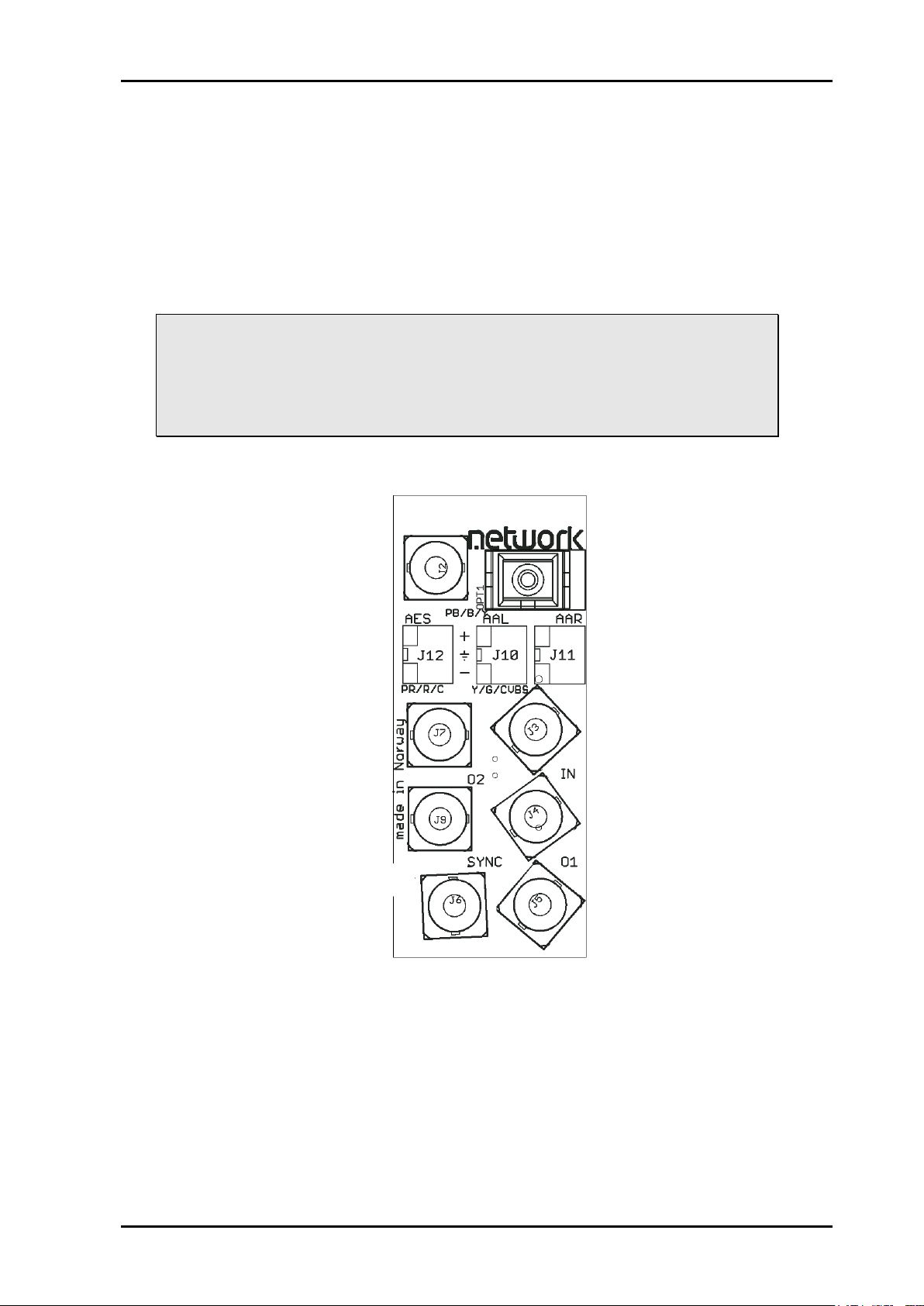
Figure 3: The figure shows a top view component printout of the board
3.1.1 Rotary switch and push buttons
The rotary switch and the push buttons are used to control the phase delay setting of the
frame-synchronizer. They are accessible from the front of the module and are meant to be
adjusted when the module is powered and active. No change will be seen in output video
unless a sync input (black & burst or tri-level) is present.
The rotary switch, labelled DLY, adjusts the phase delay from -5 to +4 video lines.
The push buttons, labelled INC and DEC, are used to fine adjust the phase delay one sample
at a time. They can adjust the additional samples setting within +/- ½ video lines for the
present video standard. Pressing both buttons simultaneously will reset the number of
additional samples to 0. Holding one of the buttons in will accelerate the increase/decrease
action until the button is released (or one of the limits -½ or +½ video lines is reached). When
the samples setting is reset or one of the limits reached, this will be acknowledged with a
series of short flashes on the LED(s) closest to the activated button(s).
3.1.2 DIP switch functions
The two horizontally mounted DIP switch packages are here denoted DIP1DIP16, counted from left to right. The vertically mounted DIP package is denoted
with DIP17-DIP24, counted from top to bottom.
nevion.com | 10
Page 11

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Switch
Function name
Function DIPs
Comment
1
Master/Slave
Off = Slave
On = Master
See ch 3.2.8
2
AES11/ Word
clock
Off = AES11
On = Word clock
See ch 3.2.10. Note that to
change between AES11 and
Word clock also involves two
slide switches.
3-4
Video sync
[3] [4]
0 0 Black burst
0 1 1080/25i (29i)
1 0 1080/25p (29p)
1 1 720/50p (59p)
0=Off, 1=On
See ch 3.2.9 and 3.2.12
5-6
RESERVED
Both DIP 5 and DIP 6 must be
kept in the Off position for Black
burst to work correctly.
7
Black burst
standard
Off = PAL B/G (NTSC)
On = PAL N (PAL M)
See ch 3.2.12
8
Pedestal
Off = Pedestal off
On = Pedestal on
See ch 3.2.12
9-11
Frame delay /
Subcarrier delay
[ 9 ] [10] [11]
0 0 0 0 frames
0 0 1 1 frames
0 1 0 2 frames
0 1 1 3 frames
1 0 0 4 frames
1 0 1 5 frames
1 1 0 6 frames
1 1 1 7 frames
0=Off, 1=On
See ch 3.2.4
12
SDI OUT 1
Off = Through mode
On = Processed mode
In through mode the video only
goes through a re-clocker. In
processed mode, the output will
be taken after the delay and
frequency adjustment circuits.
13
SDI OUT 2
Off = Through mode
On = Processed mode
In through mode the video only
goes through a re-clocker. In
processed mode, the output will
be taken after the delay and
frequency adjustment circuits.
14
OPT/EL
Off = Optical input is main
On = Electrical input is
main
Optical / Electrical input priority.
If the optical input is not
installed, this DIP will have no
effect.
F-RESET
F-RESET
Off: Use values preset by
MULTICON GYDA.
On: RESET to factory
defaults
This DIP is only read at power
up. See chapter 3.1.3.
OVR
OVR
Off: MULTICON GYDA
mode
On: Manual mode
This DIP is only read at power
up.
OVR is short term for
MULTICON GYDA override
nevion.com | 11
Table 3: DIP SWITCH FUNCTIONS
Page 12

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
3.1.3 Factory reset function
The factory reset puts the card back to its initial state, as it was delivered from the factory.
These settings are just a starting condition for the board, and new settings applied by the
user will still take effect and be stored.
If a Multicon GYDA is controlling the frame in which the factory reset operation is
performed, Multicon will see the re-insertion of the card in step 4 below as a hotswap event, and it will try to write the previously stored settings back to the card.
There are two ways to avoid this mechanism: The safest and easiest way is to
keep the Multicon GYDA pulled out during the factory reset procedure. The next
best thing is to select the Manual mode in step 3, which will effectively prevent
the card from acknowledging the commands sent from Multicon in step 4. After
~30 seconds the Multicon settings will instead have been updated from the card
settings (some of which may now have been overridden by the DIP
switches!), and then the card can be unplugged once more, and returned to
Gyda mode.
The factory reset is a four-step procedure:
1. Pull the main card out of the frame, and set the two DIPs labelled F-RESET and
OVR to their On positions.
2. Re-insert the card into the frame. The Status LED will now be a permanent orange
colour. No further waiting is needed after seeing the Status LED lit up orange.
3. Pull the card out of the frame again, and return the DIP F-RESET to its Off position,
and set the OVR to the desired mode of operation.
4. Re-insert the card into the frame, and it should now boot as normal again. It is only
at the end of this boot-up that the settings are actually reset, and to ensure that the
new settings are stored properly it is important that the card is now kept powered for
a few seconds after the Status LED has turned green. The card will start to operate
as normal with the new settings right away.
nevion.com | 12
Page 13

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
3.2 Detailed control in Gyda mode
All functions of the card can be controlled through the Multicon GYDA control system. The
Multicon GYDA has an information page and a configuration page.
3.2.1 Information page
Figure 4: Multicon GYDA information page
The information page shows a dynamic block-diagram of the board and some additional
informative text. The block diagram updates with the board status, showing input signal
selected and signals missing (by red crosses over signal lines
The information text below the dynamic block diagram lists information not easily conveyed
in a graphical manner.
Electrical input and Optical input will indicate either Signal detected or Loss of signal.
Reclocker will indicate either Locked or Loss of lock.
Phase delay denotes the time difference in samples between incoming sync source and
outgoing video signal.
Video in will indicate the currently selected input source.
Input frequency lock will indicate either Soft (master) or Hard (slave). This is a user setting,
see ch 3.2.8.
nevion.com | 13
Page 14
SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Tri-level standard will indicate either 720/50p(59p), 1080/25p(29p), or 1080/25i(29i). This is
a user setting, see ch 3.2.11.
Black Burst standard will indicate either PAL B/G or PAL N for 50 Hz, and either NTSC or
PAL M for 60 Hz. These are user settings, see ch 3.2.12.
Signal integrity shows the incoming video format and counts errors found on this signal. The
error mask is set up in the Signal integrity block on the configuration page. To reset the
counter to 0, press the Reset button.
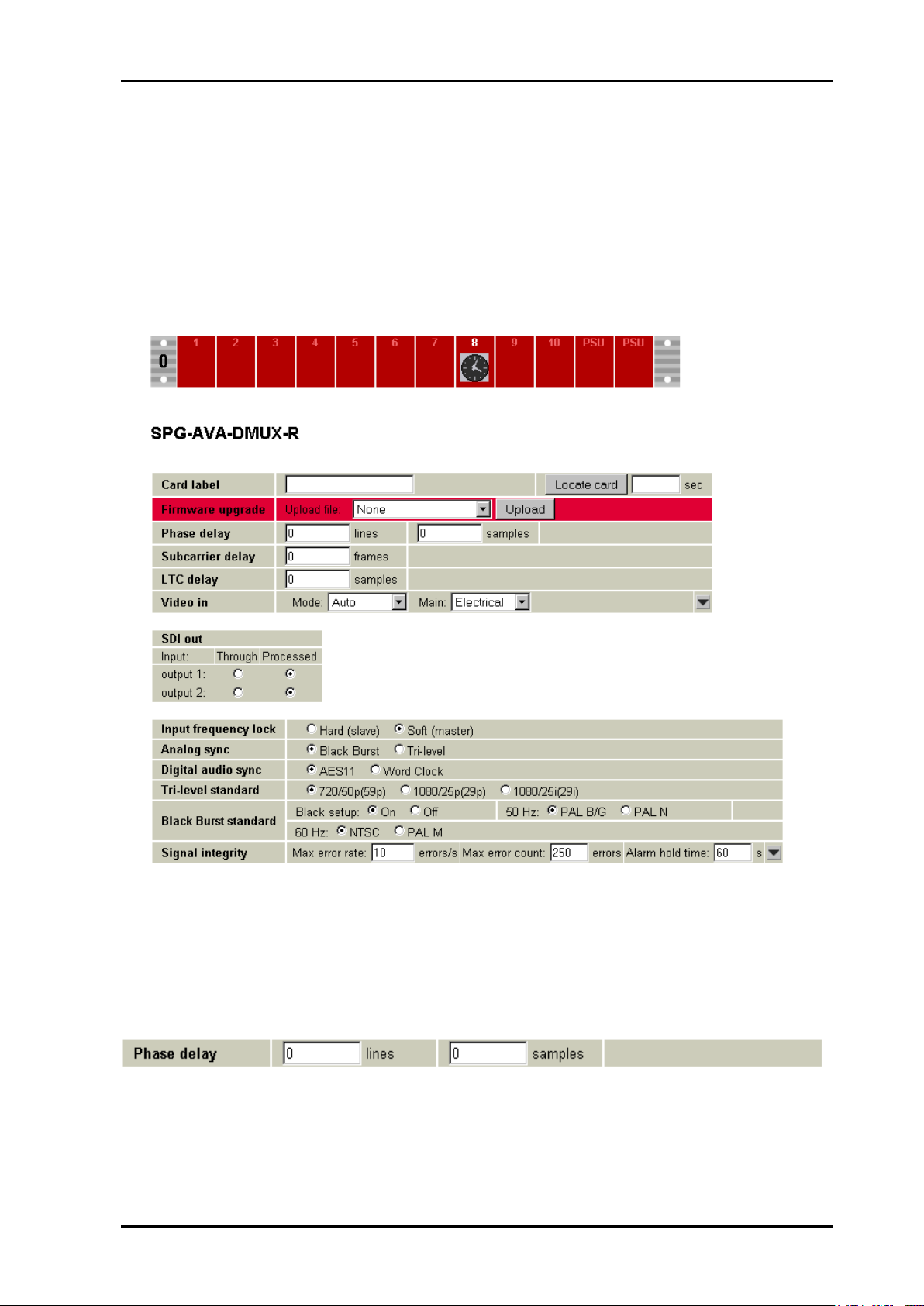
3.2.2 Configuration page
Figure 5: The whole Multicon Gyda configuration page
In the subsequent sections, each line/logical block of the user interface will be treated
individually, in the order they appear on the Multicon Gyda configuration page.
3.2.3 Phase delay
The Phase delay settings are used to adjust the phase of the video output from the module
relative to the input.
Figure 6: Multicon Gyda view of the Phase delay settings
A positive delay means that the output will be delayed relative to the input. Negative delays
are allowed, but the signal can of course never appear on the output before it has been
received at the input. Hence, in order to use negative phase delays, at least one frame delay
must be added to the output, see Subcarrier delay below.
nevion.com | 14
Page 15

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
3.2.4 Subcarrier delay
Figure 7: Multicon Gyda view of the Subcarrier delay setting
The Subcarrier delay setting will add entire frames to the delay through the module. The
range is 0-7 frames. For strictly periodic signals like Black burst and Tri-level, the delay is not
important as such. There are however two good reasons to care about this delay:
1. A subcarrier delay of at least one frame must be added in order to use negative
phase delays. (The exact same phase between input and output can be achieved by
using a positive phase delay instead, it is just a matter of how one likes to think
about it).
2. The subcarrier of the analog video sync outputs has eight different phases,
i.e. it takes eight frames to complete a full cycle. Most modern equipment, like digital
frame synchronizers, doesn’t need or use the subcarrier phase, but many video
DACs do. Matched subcarrier phases will be necessary to do seamless analog
switching between.
3.2.5 Linear time code
The linear time code (LTC) is de-embedded from the video input. When video delay/phase is
changed by adjusting the Phase delay and Subcarrier delay above, the LTC will automatically
be delayed the same amount as the video. It is possible to add an extra delay to the LTC,
relative to the video outputs. This delay can then be either positive or negative, given as a
number of 48 Hz audio samples. But once again, the negative LTC delay can not be larger
than the total positive video delay. Demanding otherwise would require the LTC to be
presented on the output before it had even been received in the incoming video.
Figure 8: Multicon Gyda view of the Linear Time Code delay setting
While the maximum negative relative LTC delay will be limited by the actual positive video
delay, the maximum positive LTC delay is limited by the fact that the sum of the video delay
and the relative audio delay cannot be larger than 32000 audio samples (approx. 0.67 ms
with 48 kHz audio). If the video delay is set to minimum, the full 32000 audio samples will be
available, but if the video delay is set to – say – 5 frames, the maximum relative audio delay
is reduced to 20000 audio samples (assuming 25 frames per second, 5 frames equals 0.2
seconds, which in turn equals 12000 audio samples, and 32000-12000=20000).
The LTC is de-embedded from channel 1 and 2 in group 1. The two channels now used are:
channel one for Left and channel two for Right. The default setting is set to LR, this has been
changed from LL when there was only one channel.
3.2.6 Video input
The SPG-AVA-DMUX has one electrical and one (optional) optical input. The input can be
chosen either by an automatic selection with priorities and a selected rule for switching, or by
direct manual selection. When the input selection is done manually by selecting one of the
inputs from the Mode menu, no fallback is available to other sources. Instead there will be a
frame freeze for as long as the input is gone.
If the Video in Mode choice is set to auto in Multicon GYDA, three input choices (priorities)
can be made. The available choices are electrical, optical, internal generator, muted, or ‘–‘
(none). When the signal is missing on the input selected as ‘Main’, the change-over logic will
nevion.com | 15
Page 16

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
switch to the next priority and look for a signal there, and so on. If the user doesn’t want to
use all three priority levels, the unused ones can be set to ‘–‘. Should the user specify a list
of priorities where it is actually impossible to reach one or both of the backup levels (because
the main input is selected to be an internal generator, and therefore always present), the card
will also display the unreachable levels as ‘–‘. The most typical setups will be as follows:
Electrical → Video gen. → ‘–‘ (Internal generator as fallback for the Electrical input)
Optical → Video gen. → ‘–‘ (Internal generator as fallback for the Optical input)
Electrical → Optical → Video gen. (Optical as fallback for the Electrical input, and internal
generator as final fallback)
Optical → Electrical → Video gen. (Electrical as fallback for the Optical input, and internal
generator as final fallback)
The generated video will be black. The internal video generator in the setups above can be
replaced with Mute, which will turn the output drivers off when the input diappear. If internal
video generator above is replaced with ‘–‘, no special action will be taken when the inputs(s)
disappear, the output will just frame-freeze forever/until a valid input is again detected.
The switching is always latching. This means that when both physical inputs are missing,
then the module will look for a valid input in the background. But if there is a signal on the
physical input selected as first fallback, then the module will not go back to the input selected
as main unless the fallback disappears. The user can however force the module back to main
by pressing the latch Reset button.
Hold time and lock time can also be adjusted. These specify how long a signal can be missing
before the next input in the prioritized list is attempted, and how long a lost signal has to be
present before it is considered OK again, respectively.
Figure 9: Multicon GYDA view of electrical input selected manually
Figure 10: Multicon GYDA view of the auto mode input selection
nevion.com | 16
Page 17

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
3.2.7 Output switch
The board has four SDI outputs organized as two pairs of inverting and non-inverting outputs.
Each pair can be routed either directly from the re-clocker (Through) or via the processing
unit (Processed). When Processed is selected, the output can also come from the internal
video generators. They can act as fallback when video input is missing, or the module can
be used as a standalone generator. This is controlled from the Video in block described I the
previous chapter. In Through mode the output will be muted (i.e. output drivers turned off)
when the video input is missing.
Figure 11: Multicon GYDA view of the SDI output selection block
3.2.8 Frequency lock mode
This setting determines how the module will handle variations in input frequency. If Soft
(master) is selected, then the module will continuously low-pass filter the input, meaning that
the output frequency will be a long-term average of the input frequency. If on the other hand
the Hard (slave) mode is selected, then the module will track the input frequency instantly
and as precisely as it can. Several modules may be daisy-chained (to get more outputs, or
tri-level and black burst at the same time, for instance), and a typical setup would then be to
use one SPG-AVA-DMUX module in master mode (to average out input variations) followed
by one or more modules in slave mode. The outputs from the slave module(s) would then be
in near perfect sync with each other and the outputs from the master module..
Figure 12: Multicon GYDA view of the frequency lock mode selector
3.2.9 Analog sync mode
This setting determines whether the three BNCs on the backplane will be used as three
separate Black burst outputs or as Tri-level outputs. See ch 3.2.11 for where to select the trilevel standard, and see ch 3.2.12 for where to specify the Black burst modulation and Black
setup (pedestal).
Figure 13: Multicon GYDA view of the analog sync mode selector
3.2.10 Digital audio sync mode
This selects the format of the audio sync outputs. While AES11 is probably the more common
format, the user should refer to the manual of the product that will use the audio sync signal.
Due to limitations in the current hardware, the process of changing between AES11 and Word
clock also involves operation of two slide switches on the backside of the module. They DC
couple the output signals when the module is in Word clock mode and AC couple the signal
when the module is in AES11 mode. For AES11, select AES11 in Multicon and move the
slide switches to their right-most positions. For Word clock, select Word clock in Multicon and
move the slide switches to their left-most position. Figure 15 shows where on the module the
slide switches can be found, along the top edge.
Figure 14: Multicon GYDA view of the audio sync mode selector
(The single slide switch on the left card edge is not used for this product).
nevion.com | 17
Page 18

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Figure 15: The figure shows the component layout of the bottom side of the board. The slide
switches are highlighted with a red color.
3.2.11 Tri-level standard
This selects the video standard for the Tri-level sync output. Note that there’s a separate
selector between Tri-level output and Black burst outputs, see ch 3.2.9.
Figure 16: Multicon GYDA view of the tri-level sync standard selector
3.2.12 Black-burst standard
This selects the video modulation for the Black burst sync outputs. The user must select the
modulation for 50 Hz input and 60 Hz input separately, and the module will use either based
on the detected frequency base of the input. The Black setup setting will only take effect for
NTSC output. Note that there’s a separate selector between Tri-level output and Black burst
outputs, see ch 3.2.9.
Figure 17: Multicon GYDA view of the black burst standard selector
3.2.13 Signal integrity
This is where the user can select which types of input errors will result in an increase the
error counter, and which types of errors will simply be ignored. An excessive amount of errors
(that are not being ignored) will trigger an alarm.
Figure 18: Multicon GYDA view of the signal integrity block
The names of the error fields should be read as follows:
NO_EDH: EDH package missing
VS: Video Standard error
FF-CRC: Full Frame CRC error (SD only)
AP-CRC: Active picture CRC error (SD only)
LOCK: Loss of lock
nevion.com | 18
Page 19

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
CCS: Chroma checksum error
YCS: Luma checksum error
CCRC: (Chroma CRC error (HD only)
YCRC: Luma CRC error (HD only)
LNUM: Line NUMbering error (HD only)
SAV: Start of Active Video error
EAV: End of Active Video error
Note that the error fields that are HD only are not selectable for the SPG-AVADMUX(-R), because the product accepts SD input only.
nevion.com | 19
Page 20

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Data rate optical:
270 Mbps
Sensitivity
Better than -20 dBm (short haul) / -30 dBm (long haul)
Detector overload threshold:
Min. -3 dBm (-8 dBm long haul version)
Detector damage threshold:
> +1 dBm
Optical wavelength:
1200 –1620 nm
Transmission circuit fiber:
9/125 µm Single Mode
Connector return loss:
> 40 dB w/ SM fiber
Connector:
SC/UPC
Connectors
75 Ohm BNC
Equalization
Automatic
> 275 m @270 Mbps w/Belden 8281, with BER < 10E-12
Input Return loss
> 15 dB, 5 MHz – 270 MHz
Jitter tolerance
10 Hz – 1 kHz: >1 UI
10 kHz – 5 MHz: >0.2 UI
Sync input not in use
Number of outputs
4 (2 pairs, each pair consists of 1 inverting + 1 non-inverting)
Connectors
75 Ohm BNC
Output Return loss
> 15 dB, 5 MHz –270 MHz
Output signal level
800 mV +/- 10%
Output signal rise / fall time
20% – 80%
[0.4 ns – 1.5 ns]; <0.5 ns rise/fall var.
Amplitude overshoot
< 10%
Output timing jitter
< 0.2 UI
Output alignment jitter
< 0.15 UI
Number of CVBS outputs
3
Connectors
3 x 75 R BNC
DC offset
< 0±15 mV
White level, NTSC
100±1 IRE
Sync level, NTSC
40±1 IRE
Return loss
> 35 dB @ 10 MHz, >40 dB @ 5MHz
White level, PAL
100±1 IRE
Sync level, PAL
40±1 IRE
Diff gain
< 0.5%
Diff phase
< 1 deg
AM noise
< -60 dB
PM noise
< -60 dB
S/N
< -60 dB
2T K-factor
(2T pulse distortion)
< 0.5%
Luma non-linearity
< 2%
Output resolution
12 bits
Appendix A Specifications
Optional optical SD-SDI input
Electrical SD-SDI input
Electrical Sync input
Electrical SD-SDI outputs
Black burst outputs, NTSC/PAL
nevion.com | 20
Page 21

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Number of outputs
3
Connectors
3 x 75 R BNC
DC offset
< 0±15 mV
White level
100±1 IRE
Return loss
> 30 dB @ 30 MHz
Output resolution
12 bits
Number of outputs
2
Connectors
2 x WECO audio connectors
Impedance
< 66 R
Dynamic range
> 100 dB(A)
Crosstalk
< -60 dB 20 Hz – 20 kHz
THD+N
-70dB
Frequency response
20 Hz – 20 kHz +/- 0.5 dB
Output level
24 dBu +/- 1 dB
Common mode DC
immunity
0 – 48V
Level adjustment range
0 – 24 dBu in 0.5 dB steps
Two tone intermodulation
< -80 dB
Output resolution
24 bits
Maximum delay line
32000 audio samples (48 kHz)
Number of outputs
2 (left and right)
Connectors
WECO
Output jitter
< 0.0025 UI peak
Impedance
110 R transformer balanced
Return loss
110 R +/-20% 0.1 MHz – 6.144 MHz
Output jitter
<0.0025 UI peak
SD, 270 Mbps
SMPTE 259M, SMPTE 272M-AC
Analog video
SMPTE 170m, SMPTE 274M, ITU-R. BT.470
AES
AES11-1996
Optical
SMPTE 297M
EDH
Compliant to SMPTE-RP165
+5 VDC
4.2 W 1
+15 VDC
2.3 W
-15 VDC
0.25 W
1
Tri-level Analog Video outputs
Linear Time Code output
AES11 / Word clock output
Supported standards
Maximum power consumption (at 50°C)
Deduct 0.5 W for modules without the optional optical module
nevion.com | 21
Page 22

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
1.
The equipment will meet the guaranteed performance specification under the
following environmental conditions:
-
Operating room temperature
range:
0°C to 45°C
-
Operating relative humidity range:
<90% (non-condensing)
2.
The equipment will operate without damage under the following environmental
conditions:
-
Temperature range:
-10°C to 55°C
-
Relative humidity range:
<95% (non-condensing)
Appendix B General environmental requirements for
Nevion equipment
nevion.com | 22
Page 23

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
Product Warranty
The warranty terms and conditions for the product(s) covered by this manual follow the
General Sales Conditions by Nevion, which are available on the company web site:
www.nevion.com
nevion.com | 23
Page 24

SPG-AVA-DMUX Rev. C
組成名稱
Part Name
Toxic or hazardous substances and elements
鉛
Lead
(Pb)
汞
Mercury
(Hg)
镉
Cadmium
(Cd)
六价铬
Hexavalent
Chromium
(Cr(VI))
多溴联苯
Polybrominated
biphenyls
(PBB)
多溴二苯醚
Polybrominated
diphenyl ethers
(PBDE)
SPG-AVA-DMUX
SPG-AVA-DMUX-R
O O O O O
O
O: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in all of the homogeneous materials for this part is
below the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
X: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in at least one of the homogeneous materials used
for this part is above the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling
information
A.1 Materials declaration
For product sold into China after 1st March 2007, we comply with the “Administrative Measure
on the Control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products”. In the first stage of this
legislation, content of six hazardous materials has to be declared. The table below shows
the required information.
This is indicated by the product marking:
A.2 Recycling information
Nevion provides assistance to customers and recyclers through our web site
http://www.nevion.com/. Please contact Nevion’s Customer Support for assistance with
recycling if this site does not show the information you require.
Where it is not possible to return the product to Nevion or its agents for recycling, the following
general information may be of assistance:
Before attempting disassembly, ensure the product is completely disconnected from
power and signal connections.
All major parts are marked or labeled to show their material content.
Depending on the date of manufacture, this product may contain lead in solder.
Some circuit boards may contain battery-backed memory devices.
nevion.com | 24
 Loading...
Loading...