Page 1

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/
AAV-SD-DMUX(-R)
HD/SD analog / digital audio de-embedder
User manual
Rev. 7
P.O. Box 1020, 3204 Sandefjord, Norway – Tel: +47 33 48 99 99 – Fax: +47 33 48 99 98
Nevion Europe AS
www.nevion.com
Page 2
AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Rev.
Repl.
Date
Sign
Change description
7 6 2011-11-22
AJM
Updated the optical receiver specifications
6 5 2011-03-08
AA
Updated Declaration of Conformity.
5 4 2009-07-09
MDH
Removed references to inputs in examples. New DIP
switch routing table. 600 ohm backplane option.
4 3 2009-05-26
MDH
Changed table of signal sources P.12
3 2 2008-12-18
MDH
Changed Dip descriptions
2 1 2008-08-26
MDH
Video input manual mode described. Embedder
audio core diagram changed.
1 0 2008-07-10
NBS
Updated formats to company standard
0 - 2007-06-05
MDH
First revision derived from AV-HD-XMUX manual
rev3
Nevion Support
Nevion Europe
P.O. Box 1020
3204 Sandefjord, Norway
Support phone 1: +47 33 48 99 97
Support phone 2: +47 90 60 99 99
E-mail: support@nevion.com
See http://www.nevion.com/support/ for service hours for customer support globally.
Toll free North America: (866) 515-0811
Outside North America: +1 (805) 247-8560
Nevion USA
1600 Emerson Avenue
Oxnard, CA 93033, USA
Revision history
Current revision of this document is the uppermost in the table below.
nevion.com | 2
Page 3

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Contents
1 Product overview ..................................................................................................... 4
1.1 Audio signal flow ............................................................................................................. 5
1.2 Signal flow ....................................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Data signal ...................................................................................................................... 6
2 Specifications .......................................................................................................... 7
2.1 Measurement conditions.................................................................................................. 7
2.2 General ........................................................................................................................... 7
2.3 Processing....................................................................................................................... 7
2.4 Inputs .............................................................................................................................. 7
2.5 Outputs ............................................................................................................................ 8
3 Configuration ......................................................................................................... 10
3.1 DIP switch and routing ....................................................................................................10
3.2 Other DIP Switches ........................................................................................................12
3.3 GYDA Control .................................................................................................................13
3.4 Data transmission ...........................................................................................................15
4 Connections ........................................................................................................... 17
4.1 Audio connections DB25 ................................................................................................18
4.2 GPI/Data connections 8P8C Jack ...................................................................................18
5 Operation ................................................................................................ ............... 19
5.1 Front panel LEDs............................................................................................................19
5.2 GPI alarms .....................................................................................................................19
6 Laser safety precautions ........................................................................................ 20
General environmental requirements for Nevion equipment..................................... 21
Product Warranty ...................................................................................................... 22
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling information..................................... 23
EC Declaration of Conformity ................................................................................... 24
nevion.com | 3
Page 4
AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
1 Product overview
The only difference between the AAV-SD-DMUX and the AAV-HD-DMUX is that
the latter can also handle HD SDI video.
The rest of the manual will only refer to the AAV-HD-DMUX.
The AAV-HD-DMUX is a highly integrated audio embedding module in the Flashlink range,
offering simultaneous embedding and de-embedding of audio from a digital HD or SD serial
video signal.
The modules can:
AAV-HD-DMUX can handle SD and HD digital uncompressed video.
AAV-SD-DMUX can handle SD digital uncompressed video.
De-embed and embed all groups of audio.
Copy or move audio groups without additional delay.
De-embed 2 AES3 digital audio and non-audio signals.
De-embed 4 analog audio signals.
Apply extra audio delay.
Swap stereo channels.
Make mono or sum from stereo signals.
Have optical input.
Transport asynchronous serial data.
Generate video and audio signals.
De-glitch correctly synchronized switched video.
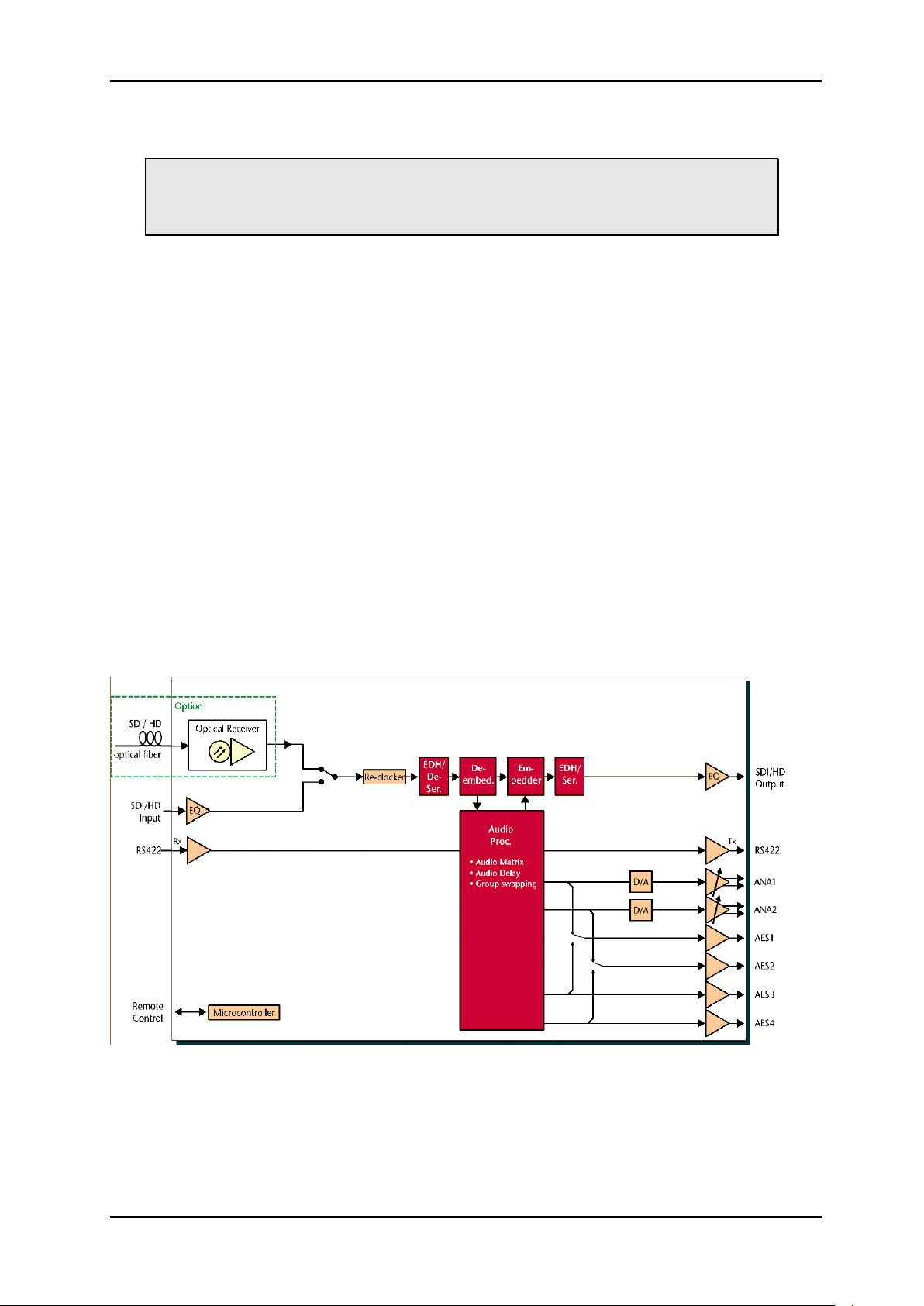
Figure 1: Module overview
The module has two main processing blocks. One processes the video stream and the
packet data, the other processes the audio. The packet processing core forms a group router
which can route embedded audio between groups without any extra delay.
nevion.com | 4
Page 5
AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
The AAV-HD-DMUX audio core is an AES3 stereo audio router. The received embedded
audios are the sources in the router. The embedded output groups and audio outputs are the
destinations. This feature may also be used to perform stereo channel swapping.
Four stereo delay lines are also available in the router with a total combined delay of 1.25s.
Audio processing is possible within each stereo output. The channels may be changed
allowing L/R swapping, mono assignment, summing, MS conversion and phase reversal of
one of the signals.
All embedding and de-embedding is performed with synchronous 48 kHz audio.
The unit may be ordered with optional optical receivers. The optical receiver may be either
the HD single mode PIN or the HD multi mode PIN. Both units will receive both HD and SD
data rates. The module has signal generators for audio and video for test and line up
applications. The internal video generator may be used as a fall-back source that is used if
the both the electrical and the optical input signals fail. This allows uninterrupted
transmission of embedded audio. The user may also configure the module to mute the
outputs if the input signal disappears.
1.1 Audio signal flow
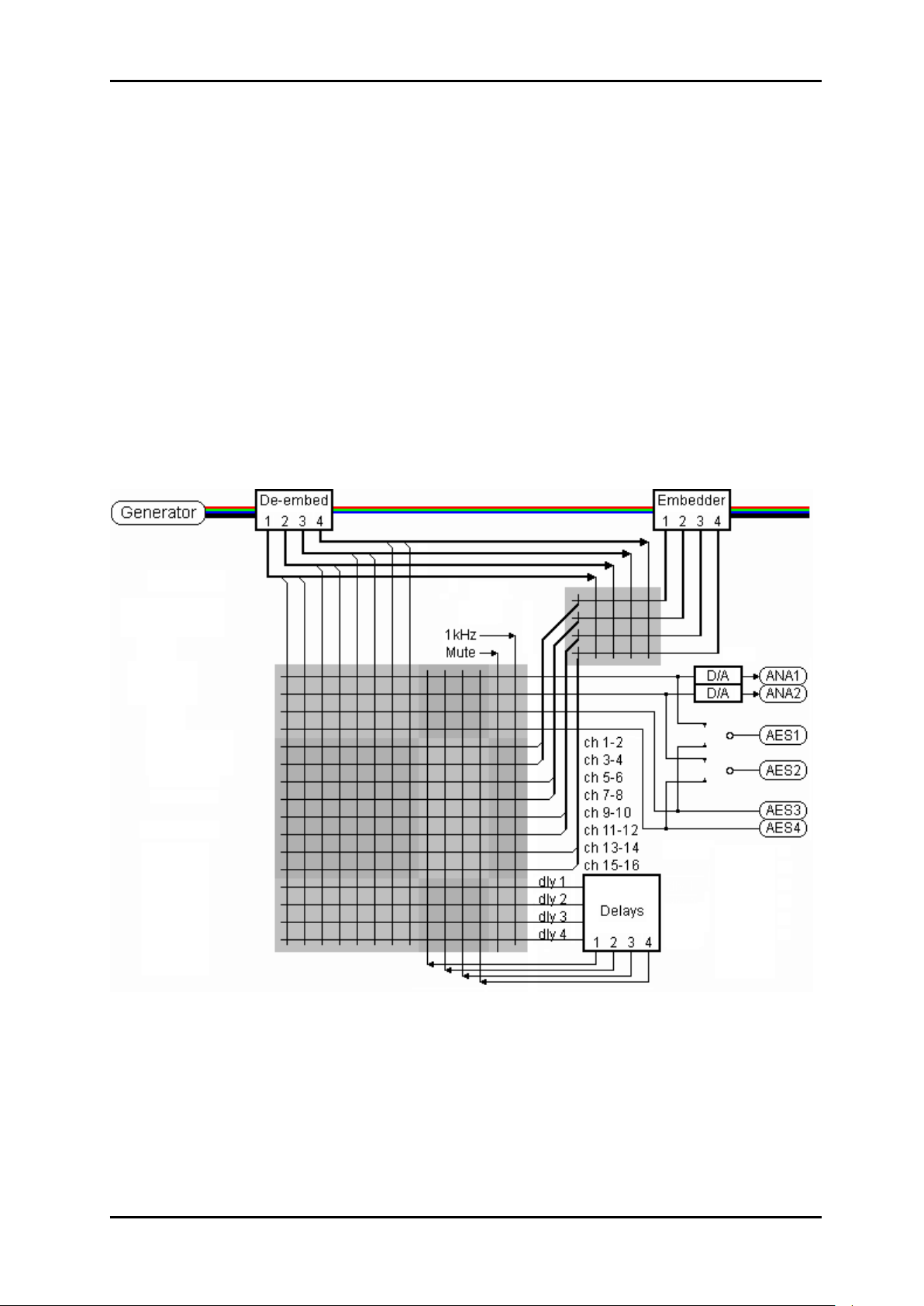
Figure 2: Processing core overview
1.2 Signal flow
Video may be presented on the optical or electrical inputs. The module will switch to the
other input if the module can not lock to a signal. The video is re-clocked and transformed to
parallel video. The parallel video goes into a line buffer which is used to de-glitch the video
when switched on the correct line. No errors are flagged or produced when the video is
switched on the appropriate switching line. All ancillary data, including embedded audio is
nevion.com | 5
Page 6

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
extracted from the video signal. All the packed data is sent to the group router. The deembedded audio is sent to the stereo audio cross-point router.
The audio processing is performed on the stereo router outputs.
Four of the router outputs are connected to the four stereo delay lines. The outputs of the
delay lines are connected to four inputs of the stereo audio router.
The audio signal is delayed by a few samples during de-embedding, re-packeting the audio
and audio processing. Signals that pass through the stereo audio router will be delayed by a
small number of samples. The group router outputs from the de-embedders do not introduce
any additional delay as the audio does not require unpacking and re-packing.
The embedder core embeds either re-packeted audio from the stereo router or the existing
de-embedded audio as configured in the group router.
The embedded audio packets are inserted into the video signal together with the control
packets and any other packets that were present in the original video signal. The video is
serialized and output through the cable and laser drivers.
The audio signals are taken from the outputs of the audio router. Outputs 1&2 are sent to the
audio DACs (digital to analog converters) while output 3&4 are sent to the AES outputs 3&4.
AES outputs 1&2 are extra AES outputs which may be fed with the audio data of either
outputs 1&2 or 3&4.
1.3 Data signal
The data signal is transported using the User bits in one of the embedded audio streams.
De- embedded data is output on the RS485 output and data received at the R422 input is
embedded into the output video. The configuration sets the audio source containing the data
signal to de-embed, the data format to be received on the backplane connector and which
output signal to embed data into.
nevion.com | 6
Page 7

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Audio Sampling rate
48 kHz
Analog audio output level setting
+18 dBu = 0dBFS
Ambient temperature
25ºC
Power:
+5V DC 0.72A 3.6W
+/-15V DC 0.02A 0.6W
Control:
DIP switches, GYDA system controller.
Monitoring:
Front panel LEDs, GYDA system controller and GPI.
EDH/CRC processing:
Full. Received flags are updated, new CRCs are
calculated.
Boot time:
1 second.
Digital audio outputs:
Conform to AES3-2003
Video inputs and outputs:
Conform to SMPTE 292M-1998
Data input and output:
Conform to EIA RS-485
Video:
des+4+350+256+2+ser video samples = 45.3us
Audio embedding:
2+1+16 audio samples = 19/48000 = 396us
Audio de-embedding:
4+16+1+29 audio samples = 50/48000 = 1.04ms
Embedding GPI mode:
8+4+32 96kHz samples = 44/96000 = 458us
Embedding UART mode:
32+128+17+16 96kHz samples = 193/96000 = 2.01ms
De-embedding GPI mode:
8+32+8 96kHz samples = 44/96000 = 458us
De-embedding UART mode:
8+32+8 96kHz samples = 48/96000 = 458us
Video:
des+8+1024+1024+3+ser video samples = 27.6us
Audio embedding:
2+1+8 = 11/48000 = 833us
Audio de-embedding:
2+8+1+29 = 40/48000 = 229us
Embedding GPI mode:
8+4+16 96kHz samples = 28/96000 = 292us
Embedding UART mode:
16+128+17+16 96kHz samples = 177/96000 = 1.84ms
De-embedding GPI mode:
4+16+8 96kHz samples = 28/96000 = 292us
De-embedding UART mode:
4+16+8 96kHz samples = 28/96000 = 292us
Video Data rate:
270Mbps or 1,485Gbps
Video frame rate:
24p, 25i, 30i, 50p or 60p and pull down rates
Video Data rate:
270Mbps
Video frame rate:
25i and pull down 30i rates
2 Specifications
2.1 Measurement conditions
2.2 General
2.3 Processing
Video latency is variable due to the de-glitcher but the values below apply when the video
signal is first applied.
Other latency values are maximum values.
2.3.1 SD latencies
2.3.2 HD latencies
2.4 Inputs
2.4.1 Electrical video input
AAV-HD-DMUX
AAV-SD-DMUX
nevion.com | 7
Page 8

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Equalization:
Automatic up to 35dB
Impedance:
75 ohm
Return loss:
>15dB up to 1,5GHz
Signal level:
Nom. 800mV
Connector:
BNC
Optical wavelength:
1200-1620nm ±40 nm
Maximum Optical power:
-3 dBm
Minimum Optical power
HD-SDI:
SD-SDI:
-22dBm
-25dBm
Return loss:
Better than 27 dB.
Maximum reflected power:
4%
Transmission circuit fiber:
Single mode, multi-mode option on request.
Connector:
SC/UPC
RS422:
1
Connector:
8P8C Jack
Packet mode:
Baud rates:
9600 to 115200
Data length:
7 or 8 bits
Parity:
None, odd or even
Stop bits:
1, 1.5 or 2 bits
GPI mode:
Raw data sampling frequency:
93750 Hz
Number of HD/SDI outputs:
1
Connector:
BNC
Impedance:
75 ohm
Return loss:
> 15 dB to1.5GHz
Signal level:
nom. 800mV.
Rise/fall time:
typically 650ps. @270Mbps. < 270ps @1.485Gbps
Number of outputs:
4.
Sampling frequency:
48 kHz.
Differential output impedance:
53 ohms.
Common mode output impedance:
20 kohm.
Connector (C1 backplane):
25 pin D-sub female.
Maximum signal level (0 dBFS):
+24dBu or lower in 0.5 dB steps.
Common mode voltage tolerance:
+50V, -0V
Frequency response:
20 Hz – 20 kHz +/-0.1 dB
Pass-band ripple:
+/- 0.002 dB
Stop band attenuation:
82 dB
Dynamic range1:
Min. 99 dB (A)2;
Typ. 105 dB(A) 0 dBFS = +18dBu
THD+N @ -1 dBFS:
Max. -85 dB, typical -96 dB.
1
2
2.4.2 Optical video input
2.4.3 Data inputs
2.5 Outputs
2.5.1 Electrical video output
2.5.2 Analog audio outputs
|THD+N of -60 dBFS 1 kHz signal| + 60
Dynamic range scales with output full scale level. Minimum result is obtained with 0dBFS = +12dBu
nevion.com | 8
Page 9

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Intermodulation distortion3:
Max. -90 dB
Crosstalk:
Max. -90 dB, typical -95 dB.
CMRR (1kHz BBC method):
Max. 46 dB, typical 65 dB.
Number of AES3 outputs:
4
Audio data rate:
48 kHz
Impedance (C1 backplanes):
110 ohm transformer balanced.
Connector (C1 backplanes):
25 pin D-sub female.
Number of RS485 outputs:
1
Connector:
8P8C Jack
Signals:
Power status good, no video input lock, laser failure.
Connector:
8P8C Jack
Signal type:
Open drain transistor with free-wheel diode.
Maximum voltage:
100 V
Maximum current:
150 mA
3
2.5.3 Digital Audio outputs
2.5.4 Data outputs
2.5.5 GPI outputs
Signal at -12 dBFS, SMPTE 4:1 60 Hz + 7 kHz
nevion.com | 9
Page 10

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
3 Configuration
The XMUX embedding core can be considered as a 14x16 stereo audio router and a 5x4
group router.
The group router is used to transport or shuffle groups without introducing any additional
delay.
The inputs or sources in the stereo router are from the de-embedded audio groups, the delay
line outputs and the two built in generators.
The stereo router outputs or destinations are the groups of embedded audio in the output
video, the audio outputs and the delay line inputs.
A normal de-embedder configuration would route the de-embedded audio to the audio
outputs.
The AAV-HD-DMUX module can de-embed and re-embed/ shuffle at the same time!
Many other configurations are possible and the module may be dynamically controlled as a
14x16 audio router via the system controller, GYDA.
Full control of the module is performed with the GYDA system controller. Controls only
possible with GYDA are:
The data transmission parameters and channel selection.
The output processing of each stereo signal (LR, RL, LL, RR, MS, Sum, ØLR, LØR).
The delay lines delays and routing.
Video and audio generator configuration.
3.1 DIP switch and routing
Full hardware control of all of the parameters in the module would require either, a
complicated menu type of control interface with a display and control buttons; or an
enormous number of switches. In many cases, most of the parameters will not be changed
from the default settings. It was decided to control only the most used parameters with
switches. This still requires the use of 24 switches.
The switches are only read if SW1.8 (DIP configuration mode) is in the on position (see
Chapter 3.2.2).
There are not enough switches on the module to allow full stereo routing configurations.
Groups of four channels are routed together as units, for example: AES input channels 1&2,
embedded audio group 1.
3.1.1 Destinations
The switches control the routing of signals to the outputs or destinations. There are four
embedded audio groups and two pairs of audio outputs. The configuration assigns sources
to output groups and pairs of stereo audio outputs. This allows the same input signals to be
routed to several outputs.
There is a group of three switches for each of the outputs. The combination of the three
switches set the input source or disables the output e.g.
Group 1 embedded output is controlled by switches on SW1 positions 1, 2 and 3.
The analog audio outputs are controlled by switches on SW3 positions 1, 2 and 3.
nevion.com | 10
Page 11

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Outputs to Embedders
External outputs
Group 1
Group 2
Group 3
Group 4
DAC1/2
AES3/4
Switch 1
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 2
Switch 3
Switch 3
1 2 3
4 5 6
1 2 3
4 5 6
1 2 3
4 5 6
From De-
embedders
Group 1
0 0 1
0 0 1
0 0 1
0 0 1
0 0 1
0 0 1
Group 2
0 1 0
0 1 0
0 1 0
0 1 0
0 1 0
0 1 0
Group 3
0 1 1
0 1 1
0 1 1
0 1 1
0 1 1
0 1 1
Group 4
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
1 0 0
Stereo Tone
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
No Output
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
3.1.2 Sources
There are eight possible permutations of the switches. Five of the permutations choose the
input sources. One of the settings (off, off, off) is used to disable the group embedding or set
the AES outputs to silence. Two of the permutations are not in use.
Table 1: Switch encoding
1 = on, 0 = off
3.1.3 Examples
Figure 3: Example 1
The module above (Figure 3) is set to the following:
Group1 output is embedded with signals from de-embedded group1
Group2 output is embedded with signals from de-embedded group2
Group3 output is embedded with signals from de-embedded group3
Group4 output is not embedded
Analog DAC outputs signals from de-embedded group1
AES 3&4 outputs signals from de-embedded group2
nevion.com | 11
Page 12

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
S2,S1,S0
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
Level
(dBu)
+12
+13.5
+15
+16.5
+18
+20
+21
+24
Figure 4: Example 2
The module above (Figure 4) is set to the following:
Group1 output is not embedded
Group2 output is embedded with a stereo tone from the internal generator
Group3 output is embedded with signals from de-embedded group 2
Group4 output is not embedded
Analog DAC outputs signals from de-embedded group1
AES 3&4 outputs signals from de-embedded group1
Users familiar with binary numbers may see that source numbers 1 to 4 (001 to 100)
correspond to groups 1 to 4. Binary numbers 5 (101) and 6 (110) are not used on this
module.
3.2 Other DIP Switches
3.2.1 DAC converter gain, SW1.7, SW2.7 and SW3.7
The DAC convert output levels may be set to one of the eight preset levels with the DIP
switches. The analog levels correspond to the maximum sine wave level, otherwise known
as 0 dBFS. The three switches are labeled S2, S1 and S0 on the board. The combinations of
the three switches set up the output level as shown in the table. 0 is off or down, 1 is on or
up.
All four input levels are set by the DIP switches in DIP configuration mode. GYDA can set the
levels for each channel individually.
3.2.2 DIP Configuration, SW1.8
SW1.8 on, forces the DIP switch configuration to be used. If there is a GYDA present, the
switch configuration on the module will be used and the configuration will be just be
monitored in the GYDA controller.
nevion.com | 12
Page 13

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
SW1.8 off will not use the DIP switches but will be configured from either the stored
configuration in the module or from GYDA if there is GYDA present. The configuration will be
stored when a GYDA configuration command is used. Therefore if a GYDA is present, the
internal configuration will be overwritten by the GYDA controller.
The switch settings are only read when the module is powered up.
The DIP switch settings control the routing and a couple of other important settings. Other
stored settings, such as data embedding and generator settings will always be used.
3.2.3 EDH insert, SW2.8
SD video output from the module will only contain an EDH packet if SW2.8 is on.
3.2.4 AES Output 1&2 SW3.8
AES outputs 1&2 are extra outputs fed either from the same signals as the DAC converters
or the AES outputs 3&4. AES outputs 1&2 are fed with the same signals as the DAC
converters if the switch is in the off position.
3.3 GYDA Control
Full control of the stereo audio router is possible with the GYDA system controller. The
module stores its routing configuration in non-volatile memory when a GYDA command is
given. This allows complex configurations to be restored after a power loss.
If a GYDA system controller is present, the last configuration of the module will
be only be restored by GYDA if SW1.8 is off. The intention is that SW1.8 is used
to show that the card is manually configured when switched on.
3.3.1 Audio delay lines
The unit has four stereo audio delay lines connected to the audio router. Audio to be delayed
is routed to one of the delay inputs and the output of that delay is routed to the intended
output. The length of each delay line is set up on the configuration page of GYDA. The
maximum delay for each of the four delays is 16384 audio samples, which is about 341ms.
The delay lines may be cascaded if longer delays are required.
3.3.2 Stereo audio processing
The output of each stereo signal may be manipulated (LL, RR, LR, RL ØLR, LØR, L+R/2,
MS) this is controlled with the GYDA controller.
The stereo signals may be output in one of the following ways:
LR, Left / Right No change.
RL, Right/ Left Channels are swapped.
LL, Left/ Left Left channel is copied into the right channel.
RR, Right/ Right Right channel is copied into the left channel.
ØLR, ØLeft/ Right The left channel is phase inverted.
LØR, Left/ ØRight The right channel is phase inverted.
L+R/2, Left + Right The left and right channels are summed.
MS, MS/AB The left and right channels are converted from AB stereo to MS
stereo.
The sum products (L+R/2 and MS) are reduced in level by 6 dB to avoid any possibility of
clipping.
nevion.com | 13
Page 14

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
3.3.3 RS422 Data port configuration
The RS422 data 8P8C Jack input must be configured with GYDA. The baud rate, data
length, parity and stop bits must be configured if UART mode is used.
The router destination where the data is to be embedded must be set up and the source
channel containing the received data that will be output on the 8P8C Jack must be also be
configured. See also Chapter 3.4 below.
3.3.4 Transport and shuffling of audio groups
The AAV-HD-DMUX stereo audio router involves de-embedding, buffering and re-embedding
which introduces a small delay relative to the video signal.
The group router is used to avoid this extra delay. Groups that only pass through the group
router are re-embedded in the same video line. This avoids any extra delay and means that
incompatible audio formats (asynchronous audio) may still be transported. The AAV-HDDMUX automatically uses the group router whenever possible when controlled with the DIP
switches.
“Shuffling” of groups is when existing embedded audio groups are re-assigned to different
groups. Copying of groups is also possible i.e. Group 1 may be transported to Group 1 and
duplicated to Group 2. This function also takes place in the group router which means that
there is no extra delay.
3.3.5 Audio generator
The stereo audio generator is available in the audio router as a source. It is a high purity 1
kHz sine wave with a 250ms interruption on the left channel every 3 seconds. The audio
level may be set to one of two standards. The two levels are -18 dBFS and -20 dBFS. These
two levels correspond to EBU R68 and SMPTE RP 155.
3.3.6 Video generator
The video generator has several different simple signals:
Color bar, 100% white, 75% colors, no set-up level.
Red, Green, Blue or Black full field.
The generator may be used as the video source if there is no video signal present at either of
the video inputs. The generator may also be switched on with GYDA. This will override video
input but the generator signal will be locked to the input.
The video standard of the generator may be set with GYDA but only if there is no video input
present.
3.3.7 Video input switching
The default mode of operation is auto-switch between the optical and electrical inputs. The
video output may be configured to either use the internal generator, or to switch off when no
video is detected on the inputs. The card will use the internal generator while it switches
between inputs until it finds a valid video signal.
There is also a manual input mode which disables the input automatic switching between
inputs. The video generator may be also selected to override the input video picture. The
input video will decide the timing of the output video and any embedded packets will still be
used by the module. Only the picture will be overwritten. If the video signal is removed
however, the input will not switch even if there is a valid signal at the other input.
3.3.8 De-glitching
Upstream video switching in a router causes glitches in the digital video. The module will
remove these glitches if the switch occurs on the correct video line for the standard in use.
nevion.com | 14
Page 15

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
The input buffer is two video lines of the longest standard and starts in the middle.
Subsequent switches will be transparent if the new signal is within a line from the original
video. There will be a glitch on the output if the new video phase is outside of this range and
the buffer will be re-aligned to the middle with the new signal phase.
3.4 Data transmission
The module can de-embed and embed asynchronous data. An AES3 audio signal is used as
a carrier. Both embedded audio and normal AES3 signals may be used to carry the RS422
data. The fiber connection usually only goes one direction so any desired return path must
be created by the user with another circuit. Return data may be sent over fiber via a link
comprising of AAV-HD-DMUX, D422 or D422-MG modules.
The 8P8C Jack data input works in one of two modes:
UART Mode: The data is checked for correct reception according to the configuration. The
data words are packaged and sent when present.
Raw sampling mode: The data input is sampled at 93.75 kHz and embedded as a data
stream. No checking is performed.
3.4.1 Data latencies
The data channel has a total latency of approximately 30us when using raw sampling.
Normal data rates of up to 9600 may be used with raw data sampling to have a low latency.
The latency is 500us when using the normal data encoding due to the block structure of the
AES User bits.
The configuration of the data channel is always stored in the module and used regardless of
the GYDA override switch.
3.4.2 Embedding
The AAV-HD-DMUX has a RS422 data input for the embedding of control data. The baud
rate and other parameters are configured with GYDA. The factory default is 115200 baud, no
parity, one stop bit.
The data channel is encoded in the User bits in an embedded audio stereo signal assigned
with GYDA. The factory default is Audio channels 1&2 in Group 1.
The data is sampled asynchronously at a constant bit rate. The range of baud rates is from
DC to 115,200 bps. The data bytes are either encoded as packets in the transmitted data or
transmitted as an asynchronous bit stream which may also be used to transmit a DC signal
such as GPI.
3.4.3 De-embedding
The audio channel with the data signal to be de-embedded must be configured by GYDA as
there may be several data channels available.
The AAV-HD-DMUX will automatically detect the data channel format when present and
output the data on the 8P8C Jack connector. The output driver will only be active when data
is output in UART mode. The means that the output is always active when raw data is used.
3.4.4 Limitations
1. There is one thing the user must do in order to receive embedded data. The audio
source where the data is embedded must be routed to a destination in the stereo
router. This is because the extraction of the data takes place on the output of the
router.
Example: Data is to be de-embedded from embedded audio channels 1&2.
Embedded audio channels 1&2 routed to output to Delay 4.
nevion.com | 15
Page 16

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
2. The normal UART mode checks the data when receiving and only embeds valid
bytes. The data format must be correct. This also means that a BREAK condition of
many spaces will not be detected or transmitted. Contact support if this is a
requirement.
nevion.com | 16
Page 17

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
4 Connections
Two backplanes are presently available for the AAV-HD-DMUX and AAV-SD-DMUX.
Figure 5: AAV-DMUX-C1 AAV-HD-DMUX-C6
The AAV-DMUX-C1 is the standard backplane/ connector module with BNC video electrical
inputs and outputs. A 25 pin d-sub type connector is provided for the analog and AES3 audio
inputs and outputs. The pin configuration used is the industry standard TASCAM DA-88 type
so that commercially available 'snakes' may be used.
The AAV-HD-DMUX-C6 is a backplane with series resistors for the analogue outputs to allow
the module to be used with 600 ohm lines. This module should only be used when there is
requirement for a matched impedance as it also introduces a 6 dB level reduction. The
module can not produce analogue audio signals higher than +18 dBu when the outputs are
correctly terminated in 600 ohm with this backplane.
The standard AAV-DMUX-C1 backplane is compatible with 600 ohm equipment, as the
module will drive a 600 ohm load without any problems. The standard backplane should be
used if there is not a requirement for matched impedance.
nevion.com | 17
Page 18

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Pin number
Description
1
Power present
2
No Video signal
3
Laser failure
4
RS485/422 output +
5
RS485/422 output -
6
RS422 input +
7
RS422 input -
8
Ground
4.1 Audio connections DB25
Figure 6: D-sub 25 audio connector wiring
4.2 GPI/Data connections 8P8C Jack
Figure 7: 8P8C connector layout
nevion.com | 18
Page 19

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Diode \ state
Red LED
Orange LED
Green LED
No light
Card status
PTC fuse has
been triggered or
FPGA
programming has
failed
Module has
not been
programmed
Module is OK
Module has no
power
SDI input
status
Video signal
absent.
Electrical
video signal
present
Optical video
signal Present
Module has not
been
programmed
Embedded
group 1&2
status:
Group 1 & 2 not
present
Either group 1
or 2 present
Both group 1 &
2 present
Module has not
been
programmed
Embedded
group 3&4
status:
Group 3 & 4 not
present
Either group 3
or 4 present
Both group 3 &
4 present
Module has not
been
programmed
Card status
Input status
Group 1&2
status
Group 3&4
status
AAV-HD-XMUX
5 Operation
Figure 8: LED overview
(Text not printed on the front panel). Each module has 4 LED’s. The colors of each of the
LED’s have different meanings as shown in the tables below.
5.1 Front panel LEDs
5.2 GPI alarms
Only three alarms are present on the 8P8C Jack connector as four of the pins are used for
the RS422 data port.
The three alarms are:
An active alarm condition means that the transistor is conducting.
The power present alarm should always be active during normal operation.
nevion.com | 19
Power present (negative logic)
Video signal lost
Laser failure
Page 20

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Maximum output power4: 5 mW
Operating wavelengths: > 1270 nm
4
6 Laser safety precautions
These are guidelines to limit hazards from laser exposure.
All the available EO and –T units in the Flashlink range include a laser.
Therefore this note on laser safety should be read thoroughly.
The lasers emit light at wavelengths from 1270nm up to 1610nm. This means that the human
eye cannot see the beam, and the blink reflex cannot protect the eye. (The human eye can
see light between 400 nm to 700 nm).
A laser beam can be harmful to the human eye (depending on laser power and exposure
time). Therefore:
Be careful when connecting / disconnecting fiber pigtails (ends).
Never look directly into the pigtail of the laser/fiber.
Never use microscopes, magnifying glasses or eye loupes to look into a fiber
end.
Use laser safety goggles blocking light at 1310 nm and at 1550 nm
Instruments exist to verify light output power: Power meters, IR-cards etc.
Flashlink features:
All the laser module cards in the Flashlink product range, are Class 1 laser products
according to IEC 825-1 1993, and class I according to 21 CFR 1040.10 when used in normal
operation.
More details can be found in the user manual for the FR-2RU-10-2 frame.
Max power is for safety analysis only and does not represent device performance.
nevion.com | 20
Page 21

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
1.
The equipment will meet the guaranteed performance specification under the following
environmental conditions:
-
Operating room temperature range:
0°C to 45 °C
-
Operating relative humidity range:
<90% (non-condensing)
2.
The equipment will operate without damage under the following environmental
conditions:
-
Temperature range:
-10°C to 55°C
-
Relative humidity range:
<95% (non-condensing)
General environmental requirements for Nevion equipment
nevion.com | 21
Page 22

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
Product Warranty
The warranty terms and conditions for the product(s) covered by this manual follow the
General Sales Conditions by Nevion, which are available on the company web site:
www.nevion.com
nevion.com | 22
Page 23

AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R) Rev. 7
組成名稱
Part Name
Toxic or hazardous substances and elements
鉛
Lead
(Pb)
汞
Mercury
(Hg)
镉
Cadmium
(Cd)
六价铬
Hexavalent
Chromium
(Cr(VI))
多溴联苯
Polybrominated
biphenyls
(PBB)
多溴二苯醚
Polybrominated
diphenyl ethers
(PBDE)
AAV-HD-DMUX(-/R)/
AAV-SD-DMUX(-R)
O O O O O
O
O: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in all of the homogeneous materials for this
part is below the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
X: Indicates that this toxic or hazardous substance contained in at least one of the homogeneous materials
used for this part is above the limit requirement in SJ/T11363-2006.
Appendix A Materials declaration and recycling information
A.1 Materials declaration
For product sold into China after 1st March 2007, we comply with the “Administrative
Measure on the Control of Pollution by Electronic Information Products”. In the first stage of
this legislation, content of six hazardous materials has to be declared. The table below
shows the required information.
This is indicated by the product marking:
A.2 Recycling information
Nevion provides assistance to customers and recyclers through our web site
http://www.nevion.com/. Please contact Nevion’s Customer Support for assistance with
recycling if this site does not show the information you require.
Where it is not possible to return the product to Nevion or its agents for recycling, the
following general information may be of assistance:
Before attempting disassembly, ensure the product is completely disconnected from
power and signal connections.
All major parts are marked or labeled to show their material content.
Depending on the date of manufacture, this product may contain lead in solder.
Some circuit boards may contain battery-backed memory devices.
nevion.com | 23
Page 24

EC Declaration of Conformity
MANUFACTURER
Nevion Europe AS
P.O. Box 1020, 3204 Sandefjord, Norway
AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE
(Established within the EEA)
Not applicable
MODEL NUMBER(S)
AAV-HD-DMUX(-R)/ AAV-SD-DMUX(-R)
DESCRIPTION
HD/SD analog / digital audio de-embedder
DIRECTIVES this equipment complies with
Low voltage (EU Directive 2006/95/EC)
EMC (EU Directive 2004/108/EC)
RoHS (EU Directive 2002/95/EC)
China RoHS5
WEEE (EU Directive 2002/96/EC)
REACH
HARMONISED STANDARDS applied in order
to verify compliance with Directive(s)
EN 55103-1:1996
EN 55103-2:1996
TEST REPORTS ISSUED BY
Notified/Competent Body
Report no:
Nemko
E11038.00
TECHNICAL CONSTRUCTION FILE NO
Not applicable
YEAR WHICH THE CE-MARK WAS AFFIXED
2008
TEST AUTHORIZED SIGNATORY
MANUFACTURER
AUTHORIZED
REPRESENTATIVE
(Established within EEA)
Date of Issue
2011-03-08
Place of Issue
Not applicable
Sandefjord, Norway
Name
Thomas Øhrbom
Position
VP of Quality, Nevion
(authorized signature)
5
Administration on the Control of Pollution Caused by Electronic Information Products
P.O. Box 1020, 3204 Sandefjord, Norway – Tel: +47 33 48 99 99 – Fax: +47 33 48 99 98
Nevion Europe AS
www.nevion.com
 Loading...
Loading...