Page 1
Test Equipment Depot - 800.517.8431 - 99 Washington Street Melrose, MA 02176 - TestEquipmentDepot.com
NETWORKSUPERVISION
key
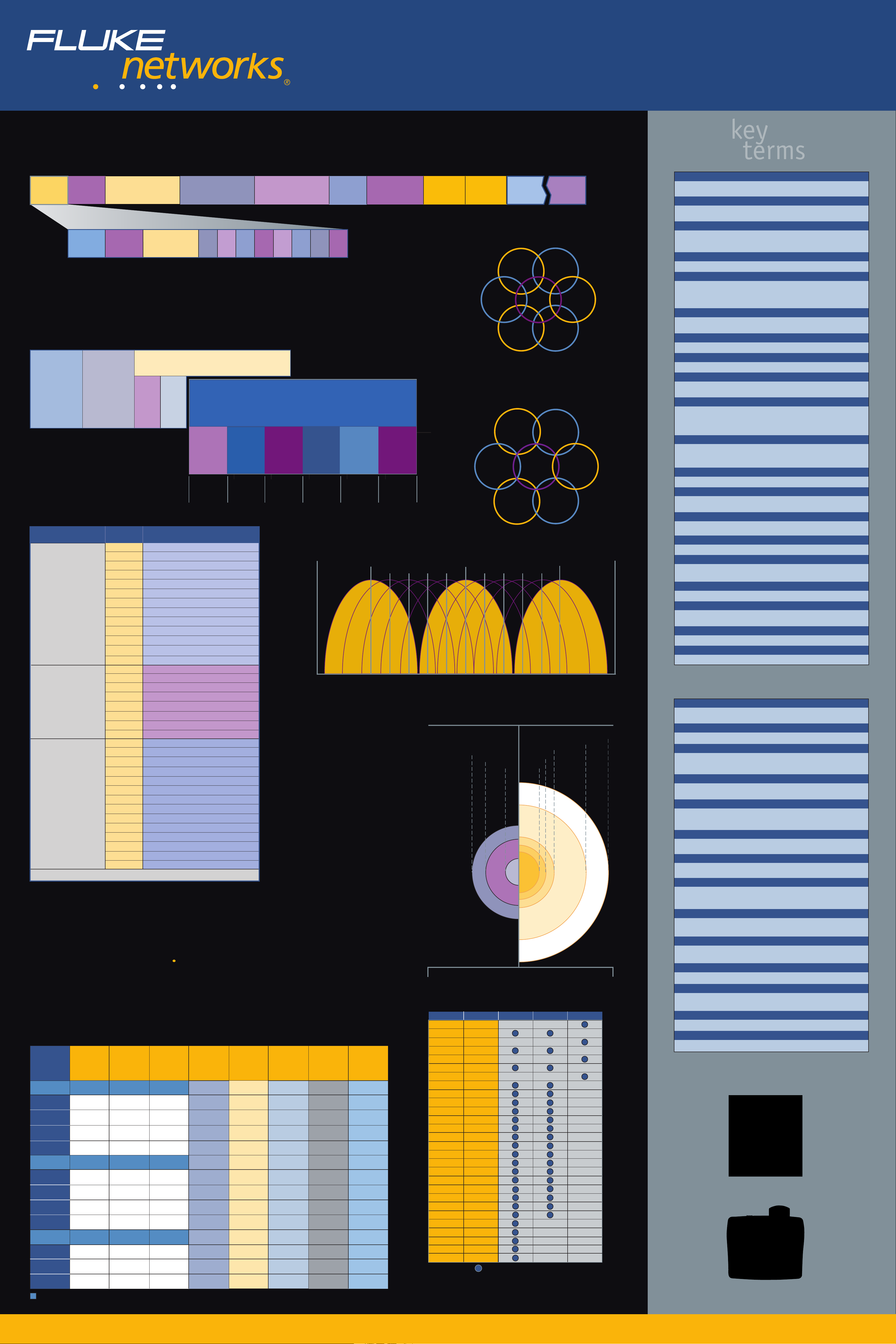
802.11 MAC Frame Formats
2 Octets 6 Octets 6 Octets 6 Octets 2 Octets
Frame
Control
2 Octets
Duration/
ID
Protocol
2
Address
Type=Data
2
Address
1
Subtype
4 1
2
ToDSFromDSMore
Frag
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Retry
Address
Pwr
Mgmt
3
More
Data
Sequence
Control
WEP Order
IEEE 802 Standards Family
6 Octets
Address
4
2 Octets
QoS Control HT Control
4 Octets
Typical 20 Mhz Channel Selections
802.11a/n – 5 GHz
52
0-7955
Octets
Frame
Body
56
44
64
4 Octets
60
40
FCS
36
terms
Wireless Terms
Access Point
Wireless LAN transceivers that connect WLAN clients to the wired LAN or bridge
to other access points.
Ad-Hoc mode
Wireless LAN clients that network together directly (peer-to-peer) as opposed to
using access points.
AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
NIST (National Information and Standards Institute), and FIPS (National Information
Processing Standard) supported encryption mechanism that uses a symmetric
encryption algorithm.
EAP
Extensible Authentication Protocol
EAP is a general protocol for authentication.
EAP-TLS
Enables authentication between WLAN devices using certificates. A client that
requests access to the WLAN is sent a certificate from an authentication server.
The client then validates the server certificate and responds with its own certificate.
Both certificates are used to create encryption keys.
Encryption Key
A series of numbers or letters that is referenced by a security method in order to
encrypt and decrypt data.
Infrastructure mode
The use of access points to allow and control wireless client access to the network.
Extensible Authentication Protocol with Transport Layer Security
802
Overview and
Architecture
802.1
Management
802.3
MAC
802.3
PHY
802.5
MAC
802.5
PHY
802.2
Logical Link Control (LLC)
802.11
FHSS
PHY
1 Mbps
2.4 GHz
802.11
2 Mbps
2.4 GHz
DSSS
PHY
802.11
802.11bg
HR/DSSS
PHY
11 Mbps
2.4 GHz
MAC
802.11a
OFDM
PHY
54 Mbps
5 GHz
802.11g
OFDM
PHY
54 Mbps
2.4 GHz
802.11n
HT-OFDM
PHY
248 Mbps
2.4 GHz
and 5GHz
Typical 20 Mhz Channel Selections
802.11b/g/n – 2.4 GHz
(minimize cell overlap)
6
1
11
1
6
1
6
Lightweight Access Point
Dynamically configured radio and antenna managed by a wireless controller.
Mesh networks
Wireless mesh routers communicate with each other forming a self-healing wireless
infrastructure (a mesh) over which edge devices can communicate.
MIMO
This base 802.11n technology is referred to as multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO),
or smart antenna systems. MIMO exploits the use of multiple signals transmitted into
the wireless medium and multiple signals received from the wireless medium to improve
wireless performance.
Multipath
Radio signals that are reflected off metal, concrete, and other materials resulting
in multiple duplicate signals being received at the access point or client at different
points in time.
RADIUS
IETF specification for authentication, traditionally used for dial-up access to ISPs.
Rogue Access Point
An unauthorized access point installed on a network that may provide an entry point
for unauthorized network access.
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
MAC Type and Subtype Decodes
Frame Type (bit 3, bit 2)
Management Type 0000 Association Request
00 0001 Association Response
0010 Reassociation Request
0011 Reassociation Response
0100 Probe Request
0101 Probe Response
1000 Beacon
1001 Announcement Traffic Indication (ATIM)
1010 Dissassociation
1011 Authentication
1100 Deauthentication
1101 Action
1110 Action no ACK
Subfield
(Bits 7,6,5,4)
Frame Function
Overlapping and Non-Overlapping Channels
2400 MHz 2483 MHz
CH1
CH2 CH3 CH4
CH6
CH5 CH7 CH8 CH9 CH10
CH11
RSSI
Relative Signal Strength Indicator
A measurement of radio signals at the point in which they are received
(measured in dBm).
SSID
Service Set Identification
Typically a unique name up to 32 characters in length.
WEP
Wire Equivalent Privacy
Wireless standard for security as required by Wi-Fi. Initially available only in
40 bit length keys, now available up to 128 bit.
Wireless bridging
Used to connect remote networks to each other.
Wireless controller
Wireless ‘switch’ that allows centralized management and configuration of light weight
(thin) access points. An overlay architecture.
WPA
Wi-Fi Protected Access
A pre-standard implementation of 802.11i based on TKIP and WEP.
WPA2
Implementation of 802.11i with AES for authentication and encryption.
Control Type 0111 Wrapper
01 1000 Block ACK Request
1001 Block ACK
1010 Power-Save (PS) Poll
1011 Request to Send (RTS)
1100 Acknowledgement (ACK)
1110 Contention Free (CF) End
1111 CF End + CF ACK
Data Type 0000 Data
10 0001 Data + CF ACK
0010 Data + CF Poll
0011 Data + CF ACK + CF Poll
0100 Null (no data)
0101 CF ACK
0110 CF Poll
0111 CF ACK + CF Poll
1000 QoS Data
1001 QoS Data + CF ACK
1010 QoS Data + CF Poll
1011 QoS Null
1110 QoS CF Poll
1111 QoS CF ACK + CF Poll
Reserved Type 11
Channels 1, 6 and 11 are non-overlapping channels
Typical Indoor Range
802.11a (5 GHz) 802.11g (2.4 GHz)
210 '
150'
60' 90'
618545418116 1
160'
120'
300'
410'
IEEE 802.11
802.11
Standard for RF technology used for local area networking (WLANs). It defines the network access
layer, media access control, and physical layer interfaces.
802.11a
Standard for WLAN in 5 GHz frequency range, with a maximum data transfer rate of 54 Mbps.
802.11b
WLAN standard for 2.4 GHz frequency range operating at a maximum data rate of 11 Mbps. Uses 11
channels, with channels 1, 6, and 11 being non-interfering. External interferrers include microwave
ovens and Bluetooth radios.
802.11d
802.11d adds support for "additional regulatory domains". This support includes the addition of
country information element to beacons, probe requests, and probe responses.
802.11e
802.11e defines a set of quality of service (QoS) enhancements for wireless LAN applications
through modifications to the MAC layer. The standard is considered of critical importance for
delay-sensitive applications, such as Voice over Wireless IP and Streaming Multimedia.
802.11h
802.11h adds spectrum and transmit power management. It solves problems like interference with
satellites and radar using the same 5 GHz frequency band.
802.11k
802.11k defines radio resource management for improving the way traffic is distributed within a
network – assisted roaming and load balancing.
802.11n draft 2.0
(as of 4/08)
wireless
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
)
LAN
)
)
IEEE 802.11 b/g/n 2.4 GHz Channels
Low Center High Canada/ Europe Spain France Japan
Channel Frequency Frequency Frequency N. America (ETSI)
(GHz) (FCC, IC)
1 2.401 2.412 2.423 • • •
2 2.406 2.417 2.428 • • •
3 2.411 2.422 2.433 • • •
4 2.416 2.427 2.438 • • •
5 2.421 2.432 2.443 • • •
6 2.426 2.437 2.448 • • •
7 2.431 2.442 2.453 • • •
8 2.436 2.447 2.458 • • •
9 2.441 2.452 2.463 • • •
10 2.446 2.457 2.468 • • • • •
11 2.451 2.462 2.473 • • • • •
12 2.456 2.467 2.478 • • •
(as of 03/08)
802.11n typical indoor range is 300Mpbs (max) at 230 feet
IEEE 802.11a 5 GHz Channels as of (03/08)
Channel Frequency Americas EMEA Japan
34 5.170
36 5.180
38 5.190
40 5.200
42 5.210
44 5.220
46 5.230
48 5.240
52 5.260
56 5.280
60 5.300
64 5.320
100 5.500
104 5.520
108 5.540
112 5.560
116 5.580
120 5.600
124 5.620
128 5.640
132 5.660
136 5.680
140 5.700
149 5.745
153 5.765
157 5.785
161 5.805
165 5.825
Draft wireless LAN standard enhancement for higher throughput. 802.11n brings higher data rates,
longer range and more reliable coverage than previous WiFi technology. Operates in both 2.4 and
5GHz bands.
802.11g
2.4 GHz wireless LAN standard for 54 Mbps transfer rate. A total of 14 channels with channels 1, 6,
and 11 being non-interfering.
802.11i
Standard for WLAN security using AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), and TKIP (temporal key
integrity protocol).
80211j
Standard for 4.9 GHz-5 GHz frequency use for WLAN systems that operate in Japan.
Task Group – r
Fast BSS transition (roaming). The standard is considered of critical importance for delay-sensitive
applications, such as Voice over Wireless IP.
Task Group – s
Mesh networking – using "radio-aware” metrics over self-configuring multi-hop topologies.
Task Group – w
Protection of management frames. Secure against network disruption caused by malicious systems.
Fluke Networks’ portable wireless
network analyzers
OptiView
Network Analyzer
TM
Integrated
13 2.461 2.472 2.483 • • •
14 2.473 2.484 2.495 •
Non-Overlapping Channels
Approved Channels
802.11n supports optional high throughput 40 MHz channels.
Two adjacent 20 MHz channels are combined to create a single
40 MHz channel which morethan doubles the effective data rate
under a given set of RF conditions.
EtherScopeTM
Network Assistant
© 2008 Fluke Corporation. All rights reserved
Printed in U.S.A. 4/2008 1999555 G-US-N Rev F
 Loading...
Loading...