Page 1

Page 2

Contents
1. Introduction ...........................................................................................................................................4
Product Overview ...................................................................................................................................4
Items that you will need and things you will need to know .........................................................................5
NetComm SmartVoice Gateway Features .................................................................................................6
SmartVoice Gateway Hardware Description ..............................................................................................9
Front Panel (all models) ..........................................................................................................................9
Rear Panel (all models) .........................................................................................................................10
Restore the Gateway .............................................................................................................................10
2. Installation and Applications ..................................................................................................................11
Connecting your SmartVoice Gateway(s) ................................................................................................11
Network Connections ............................................................................................................................12
Telephone Connection ..........................................................................................................................16
3. Configuring the Gateway via WEB Browser .............................................................................................19
Network Settings ..................................................................................................................................20
QoS Settings ........................................................................................................................................24
NAT/DDNS (NAT Traversal) .................................................................................................................25
Telephony Settings ...............................................................................................................................27
SIP Settings .........................................................................................................................................30
Private Network ................................................................................................................................... 34
Calling Features ...................................................................................................................................36
Advanced Options ...............................................................................................................................37
Digit Map .............................................................................................................................................43
Phone Book ........................................................................................................................................44
Speed Dial ..........................................................................................................................................45
Caller Filter ..........................................................................................................................................46
Transit Call Control ...............................................................................................................................47
Long-Distance Control Table .................................................................................................................49
Long Distance Exception Table ..............................................................................................................49
CPT/Cadence Settings ..........................................................................................................................50
Current Status and System Information .................................................................................................. 57
RTP Packet Summary ...........................................................................................................................58
STUN Inquiry ........................................................................................................................................59
Ping Test ..............................................................................................................................................60
Port Filtering ........................................................................................................................................61
IP Filtering ...........................................................................................................................................62
MAC Filtering .......................................................................................................................................63
Virtual Server .......................................................................................................................................64
DMZ ....................................................................................................................................................65
URL Filter .............................................................................................................................................66
Special Applications .............................................................................................................................. 67
2 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 3

NTP (Network Time Protocol) .................................................................................................................70
System Operations (Save Settings) ........................................................................................................72
Software Upgrade .................................................................................................................................73
Logout .................................................................................................................................................74
4. Configuring the Gateway via IVR ............................................................................................................75
IVR (Interactive Voice Response) ............................................................................................................76
5. Dialing and dialed number routing principle ...........................................................................................82
Instruction ...........................................................................................................................................82
Dialed Number Processing Flow ............................................................................................................82
Appendix A: Glossary ................................................................................................................................... 84
Appendix B: Cable Information .....................................................................................................................90
RJ-45 Network Ports ...........................................................................................................................90
Straight and crossover cable configuration ............................................................................................91
Straight-Through Cabling ......................................................................................................................91
Cross-Over Cabling ..............................................................................................................................91
Appendix C: Registration and Warranty Information ......................................................................................92
IMPORTANT NOTE
To ensure your Gateway complies with Australian Standards:
1) The symbol shall be marked next to the protective earthing terminal (not
GND) and the terminal shall be permanently connected via building wire.
2) The colour of the protective earth conductor insulation shall be green-and-yellow.
3) The protective earthing conductor shall be permanently connected first prior to
other connections (eg. telephone cables) and removed last after all other cables
have been disconnected.
4) The protective earthing shall not rely on telecommunications network or a cable
distribution system.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 3
YML832 Rev1
Page 4

1. Introduction
Product Overview
The NetComm SmartVoice series of stand-alone VoIP Gateways carry both voice and facsimile over
an IP network. They support the SIP industry standard call control protocol to be compatible with free
registration services or VoIP service providers’ systems and they work in two different modes: UA (User
Agent) or Server. As a standard user agent, the gateways are compatible with all well-known Soft
Switches and SIP proxy servers. With optional server software, the gateways can also be configured to
establish a private VoIP network over the Internet without a 3
Each of the SmartVoice series VoIP gateways have a different combination of FXS and FXO ports; FXS
ports are used to connect directly to a telephone set and FXO ports are used to connect directly to PSTN
lines. There are a number of SmartVoice Gateway models available with 4 ports, 8 ports, 16 ports and
32 ports combinations. The gateways can be seamlessly integrated into existing networks by connecting
to a phone set, PBX, key telephone system, fax machine or PSTN line. With only a broadband connection
such as an ADSL bridge/router, Cable Modem or leased line router, the gateways allow you to gain
access to voice and fax services over an IP network thereby reducing the cost of international and long
distance calls.
In addition, each gateway includes an in-built 4 port Ethernet switch which supports comprehensive
Internet gateway functions to accommodate other PCs or IP devices to share the same broadband
stream. The QoS function allows voice and data traffic to flow through at the highest priority. and with
TOS/DiffServ bit enabled, it guarantees that voice packets will have the first priority to pass through a
TOS/DiffServ enabled router.
With the support of DDNS, the gateways are reachable by a domain name where the IP address is
dynamically assigned by the ISP, thereby allowing users to host a web site or mail server in a PPPoE or
DHCP network.
Each gateway can be assigned with a fixed IP address or by DHCP, PPPoE, adopting the G.711, G.726,
G.729A or G.723.1 voice compression format to save the network bandwidth while providing real-time
and toll quality voice. In addition, in the event that the power supply fails or the Internet connection is
lost, each gateway can divert the FXS lines to the PSTN network on the FXO ports so that users can still
use their conventional PSTN line to make calls.
rd
party SIP Proxy Server.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
• When using your telephone equipment, basic safety precautions should always be followed
to reduce the risk of fire, electric shock and injury to persons, including the following:
• Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There
may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do not use the telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
• Use only the power cord indicated in this manual.
4 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 5

Items that you will need and things you will need to know
To correctly install and set up your VoIP Gateway you will need to ensure that the required broadband
hardware and services are setup and configured in the appropriate way to integrate this equipment.
Broadband Service
• You will need access to a high speed broadband service via a RJ 45 (Ethernet) connection to a
broadband modem.
VoIP Service
• You will need a VoIP account from your VoIP service provider. The quality of your voice service will
depend on your service provider’s network. (Note: With the SmartVoice gateway(s), you will be able
to build your private VoIP network but with limited voice call reachablity.)
Computer/Network
• You will need a PC or laptop with a network card and Web browsing application (for configuration
only).
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 5
YML832 Rev1
Page 6

NetComm SmartVoice Gateway Features
WAN
• One 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation, auto-crossover RJ-45 Ethernet port
• Support static IP, PPPoE, Bigpond Cable and DHCP address assignment and dynamic DNS (DDNS)
• QoS: IP TOS (Type of Services) and DiffServ (Differentiated Services) for both SIP signaling and RTP
• NAT Traversal : Port Forwarding, STUN, UPnP and Outbound Proxy
• NTP: (Network Time Protocol RFC 1305), Accepts up to 3 Time Server
• Time Zone Support
• MAC Address Clone
• RTP Packet Summary : packet sent, packet received, packet loss for voice quality analysis
LAN
• Four 10/100Mbps auto-negotiation, auto-crossover RJ 45 Ethernet ports
• Supports router and bridge mode (NAT mode and Non-NAT mode)
• DHCP server
Advance Firewall and DoS Protection
• NAT (Network Address Translation) and PAT (Port Address Translation)
• DMZ, Virtual Server
• Traffic Filtering based on MAC address, IP address, TCP/UDP Port number and URL string pattern
• Prevents attacks based on TCP, UDP, IP and ICMP protocols
• Prevents attacks such as SYN Flood, IP Spoofing, Ping of Death, Tear Drop, etc.
Voice Features
• SIP (RFC3261) compatible
• Voice codecs : G.711 a /ulaw, G.726, G.729A, G.723.1
• CNG (Comfort Noise Generation)
• VAD (Voice Activity Detection)
• Silence suppression/detection
• G.165/G.168 echo cancellation
• Adjustable Jitter Buffer and programmable Gain Control
• In-Band DTMF, Out-Of-Band DTMF relay (RFC2833, SIP INFO)
• Multiple SIP Proxy server entries with failover mechanism
• Polarity reversal detection (FXO/PSTN) and generation (FXS)
• T.30 (G.III) / Real time T.38 / Secured T.38 FAX relay
• DTMF, FSK (Bellcore & ETSI) Caller ID detection and generation.
• Support Caller ID Restriction (CLIR)
• FXO hang up detection : Busy Tone cadence auto learning/detection*
• Support VoIP-to-PSTN (transit out) / PSTN-to-VoIP (transit in) applications*
• Digit Map for dial plan
6 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 7

• Speed Dial
• Local phone book for peer-to-peer calling
• E.164 Numbering & ENUM support
• Hot-Line, Warm-Line support
• Single Number / Account (reprehensive number) for multiple ports
• Group Hunting function
• Recordable greeting message
• Proprietary server and protocol enables small businesses to build private VoIP network; and use
standard SIP network as same time – for dual network support
• Supplementary call features**:
o Call Hold, Call Waiting, Call Pickup
o Call Forward - Unconditional, Busy, No Answer
o Call Transfer - Unattended, Attended
o Three Way Calling (Media Server required)
• Failsafe mechanism :
o Network failure
o Service unavailable
o Power loss
• Analogue interface
o Connector : RJ-11
o Signaling protocol : Loop Start
Configuration & Maintenance
• Configuration methods:
o Web
o IVR
o Telnet
• Status reports:
o Port status
o Registration status
o Ping tests
o STUN/UPnP status
o Hardware / software information
• Firmware Upgrade through TFTP, FTP and proprietary image server
• Configuration Backup/Restore
• Reset button (with restore factory default function)
• Front Panel LED : voice ports, WAN, LAN1~4, Run, Power, Alarm
• Optional Auto Provisioning Server (APS) for mass deployment
• SNMP V1 / V2c (optional)
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 7
YML832 Rev1
Page 8

General Specifications
• Power Adaptor : AC 100V~240V 50/60Hz input, DC 12V output
• Temperature : Operation 0 °C ~ 45 °C
• Storage -25 °C ~ 75 °C
• Humidity : up to 90% RH, non-condensing
• 4-port Model Dimension (W/D/H) 4-port: 202 x 172 x 35 mm
• 8-port Model Dimension (W/D/H) 4-port: 287 x 161 x 38 mm
• 16-port Model Dimension (W/D/H) 4-port: 442 x 325 x 43 mm
• 32-port Model Dimension (W/D/H) 4-port: 442 x 325 x 43 mm
• 4-port Model Weight: 0.43Kg
• 8-port Model Weight: 1.34Kg
• 16-port Model Weight: 4.13Kg
• 32-port Model Weight: 4.13Kg
Note*: Features are only available in models which have FXO ports.
Note**: The availability of these features may depend on your VoIP service provider’s
network
8 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 9

SmartVoice Gateway Hardware Description
Front Panel (all models)
• Power Indicator: Green light indicates a normal power supply.
• Run Indicator: Blinking green light indicates normal operation.
• Alarm Indicator: When the system starts up, the red light will blink. It also indicates abnormal
gateway behaviour.
• P1 – PX stands for Port 1 – Port X (or Line 1 – Line X)
• WAN stands for the WAN Port Indicator.
• L1 – LX stands for the LAN Port Indicator.
When starting up the system, the Alarm, Run, and Power indicators will light
up. After approximately 15 seconds, the Alarm indicator will go off, the Run
indicator will blink green, and the Power indicator will stay green under operational
conditions. If the Alarm indicator continues to blink, it means the system is
currently communicating with the ISP and has yet to obtain an IP address.
When the WAN is connected, the WAN indicator will light up green and if data is
being transmitted over the Internet, the indicator blinks green and orange.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 9
YML832 Rev1
Page 10

Rear Panel (all models)
Phone ports are telephone ports (FXS) to be connected to telephone sets or PBX CO ports. Line ports
(FXO) are to be connected to PSTN lines (telephone lines from a PSTN network).
NOTE: Do not connect FXS ports to each other. Also, do not connect any FXS port
directly to a PSTN line or internal PBX. Doing so may damage VoIP gateway.
Restore the Gateway
To restore the gateway to its factory default setings (IP address, Username and Password only):
(1) Disconnect the power plug.
(2) Press reset (do not let go of the reset button).
(3) Connect the power plug back into the socket (do not let go of the reset button).
(4) Let go of the reset button after 6 seconds. The default IP address and username/password for web
login will be restored.
NOTE: This reset action only resets the gateway IP and username/password
settings. Other settings still remain in the gateway’s flash memory. A complete
hardware reset can be done through the gateway’s IVR system and Web
configuration interface.
10 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 11

2. Installation and Applications
Connecting your SmartVoice Gateway(s)
1. Connect the WAN port of your SmartVoice Gateway to your Broadband Modem using an ethernet
cable.
2. Connect the power adapter to your SmartVoice Gateway and plug it into a powerpoint.
Please use the power adapter that comes with VoIP gateway. Using an adapter
other than the one supplied with the VoIP gateway, may cause problems and will
affect the warranty of the product.
3. Connect the Phone or PSTN lines as required to setup your SmartVoice Gateway. The way you setup
the lines will depend on the model you have purchased. Refer to the following sections on both
Network Connections and Telephone Connections for more information on the possible applications
of your SmartVoice Gateway.
Once you have connected your gateway you can configure it using one of the two configuration options
provided:
1) Web Interface
2) Telephone IVR (Interactive Voice Response)
The IVR provides basic query and configuration, while the Web interface provides a full configuration.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 11
YML832 Rev1
Page 12
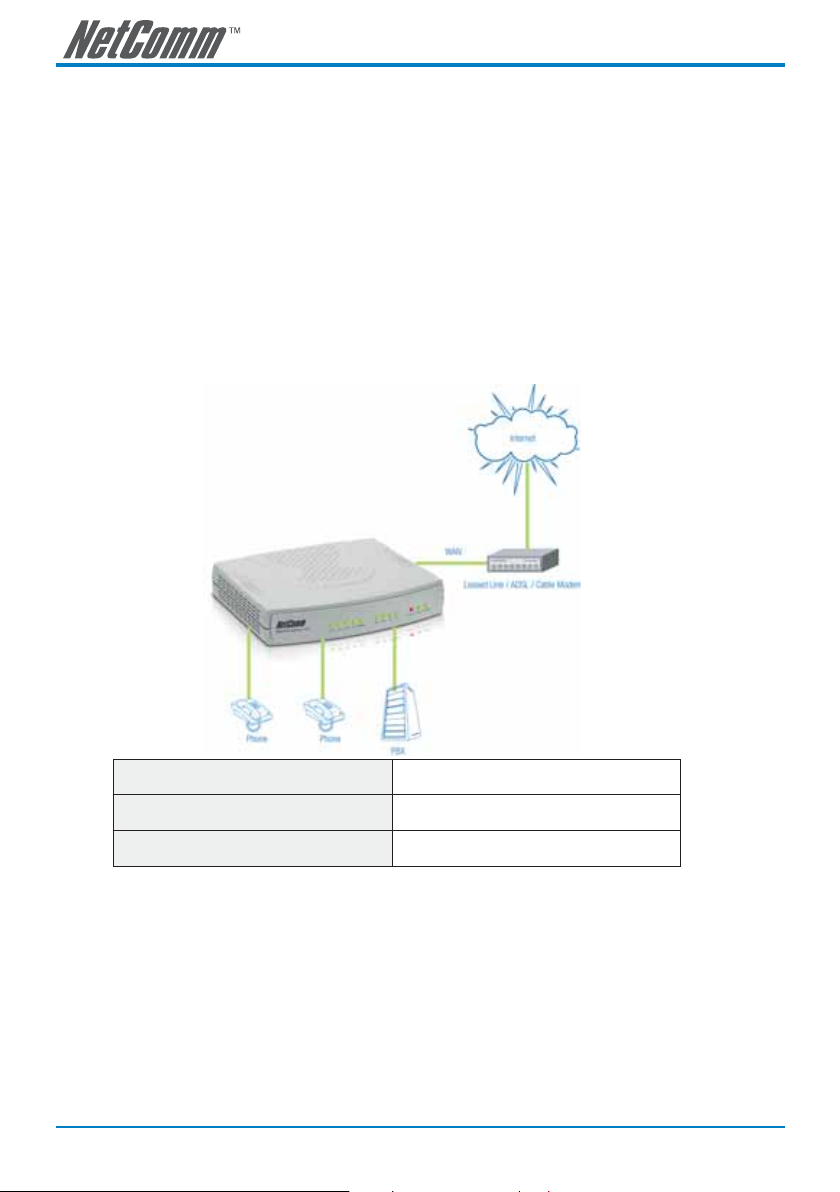
Network Connections
Possible network connections are divided into 3 basic modes as described below:
• Gateway can be assigned with a Public IP Address
• Gateway can be installed under the existing NAT
• Gateway can be assigned with a Public IP address and serve as an IP sharing router.
Gateway Assigned with a Public IP Address
The VoIP gateway will have a Public IP address for its Internet connection regardless of whether it is a
static IP address, DHCP (using a Cable Modem), or PPPoE (Dialup / ADSL).
The following diagram shows a typical network connection in which broadband devices, such as an ADSL
router or Cable modem, need to work in bridged mode so that the gateway is able to obtain a public IP
address either through PPPoE, DHCP or static IP.
Gateway IP Settings Need to be set up as static IP, DHCP, or PPPoE
NAT/STUN Settings Unnecessary (Disabled)
DDNS Settings Unnecessary (Disabled)
Note: The above diagram shows a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
12 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 13
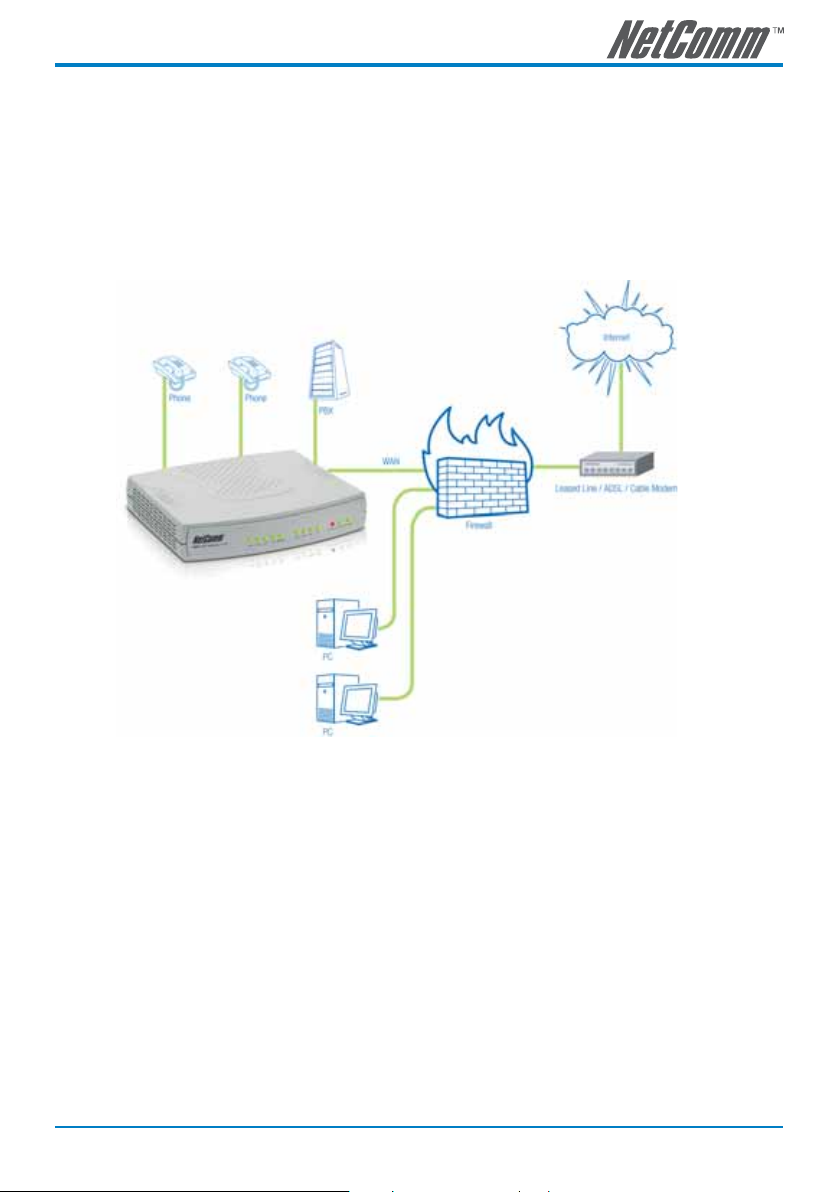
Gateway behind a NAT/Firewall Network
The VoIP gateway uses a private IP address and the Internet sharing function of other systems to connect
to the Internet.
The following diagram shows a typical network connection in which broadband devices such as an
ADSL router work in router (NAT) mode so that the gateway is behind a NAT/Firewall. In this case, the
broadband router (NAT/Firewall) and the gateway need to be configured correctly in order to allow the
gateway to communicate with the Internet and VoIP network properly, using different techniques to
traverse the NAT/Firewall.
Note: The above diagram shows a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 13
YML832 Rev1
Page 14
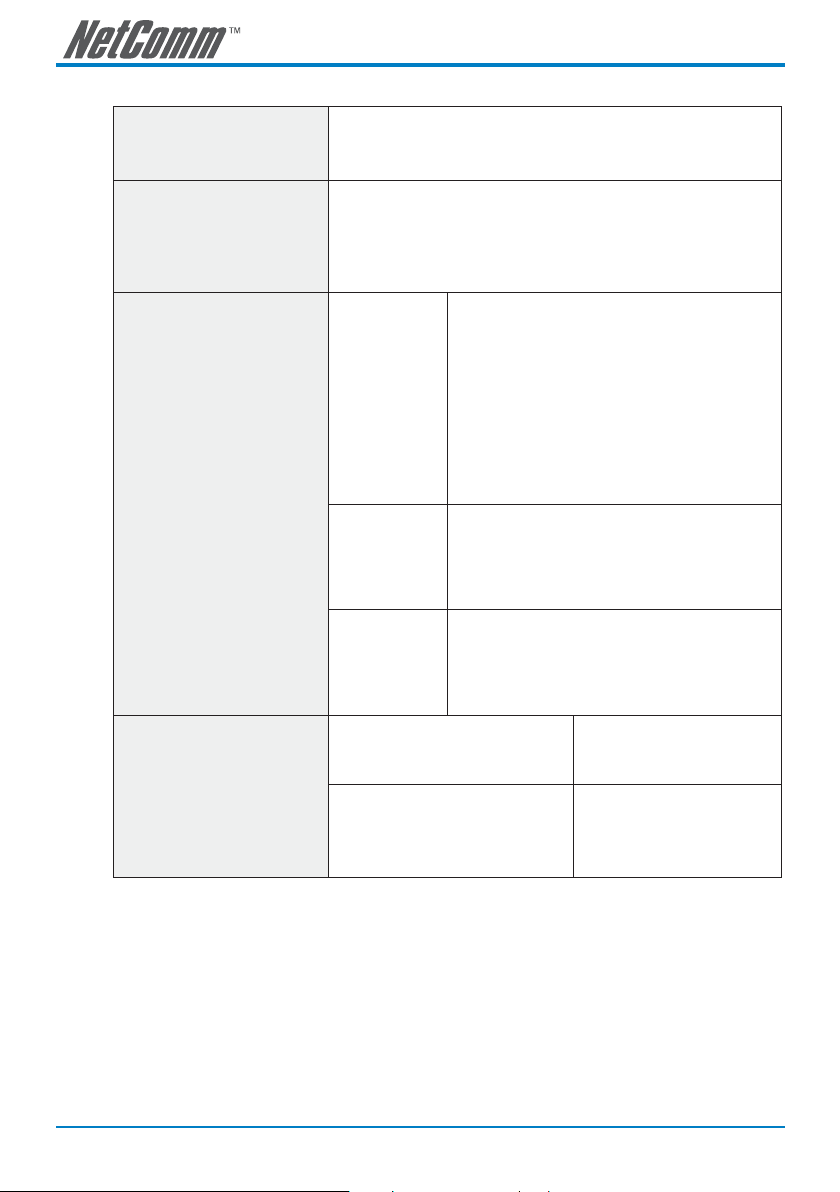
The table shown below lists possible solutions for different network scenarios.
LAN IP address of Internet sharing Please avoid IP address 192.168.8.1-192.168.8.254 (You may need to
WAN IP of SmartVoice gateway Set as a static private IP address or DHCP; when the WAN port is set as a
NAT Traversal
There are three ways to configure
a SmartVoice gateway to traversing
NAT in Internet sharing devices. For
details, please refer to page 26.
change the settings of Internet sharing device or change the SmartVoice
gateway LAN Port IP address)
static private IP, assign the LAN IP address of the Internet sharing to as default
gateway IP of SmartVoice gateway; When the WAN IP is set as DHCP, please
make sure you have DHCP server running in network to issue an IP to the
SmartVoice gateway.
NAT Public IP If the WAN of the IP sharing device has a static public IP
STUN client
UPnP Control
point
address, then the “NAT IP/Domain” address is set as the
Public IP address of the Internet sharing devices.
If the WAN of the Internet sharing device uses a dynamic
public IP address and you specify a domain name in “NAT
IP/Domain” field, which has to comply with the DDNS
settings.
Note: you also need to forward specific ports on the NAT
router to the WAN port of the SmartVoice gateway.
Enable STUN client will avoid problems of configuring port
forwarding in the Internet sharing device, but some NAT
routers do not support STUN.
Using UPnP to enable the SmartVoice gateway to pass
through NAT of Internet sharing device. This function only
works when the Internet sharing devices support UPnP
and has it enabled.
DDNS Settings
For details, please refer to page 27
for the DDNS Settings
14 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
The WAN of the Internet sharing device
has a static public IP address.
The WAN of the Internet sharing device
has a dynamic IP address.
(Unnecessary) Disabled
Enabled: enter the registered
URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
and DDNS server info into
corresponding areas.
Page 15
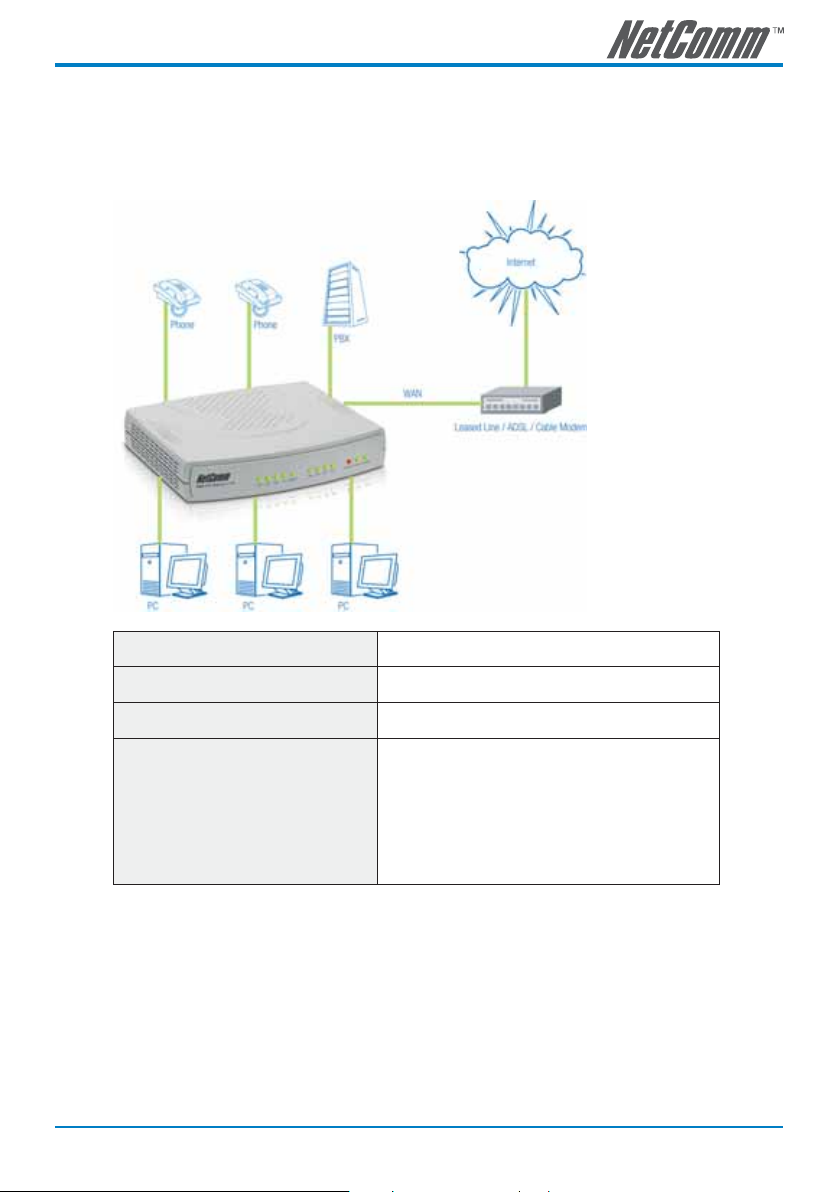
Gateway Assigned with a Public IP Address and Serving as an Internet Sharing Device
The SmartVoice gateway will have a Public IP address, regardless of whether it is the public IP from a
static setting, DHCP (using a Cable Modem), or PPPoE (to connect to your ADSL account), and can use
the built-in Internet sharing functions to allow other PCs attached to SmartVoice gateway LAN ports to
share the Internet connection. The network connection is shown in following diagram.
Gateway IP Settings Needs to be set up as either in static IP, DHCP, or PPPoE
NAT/STUN Settings Unnecessary (Disabled)
DDNS Settings Unnecessary (Disabled)
DHCP service for PCs, please refer to page
24 for the gateway DHCP server settings
Default private IP addresses of the gateway LAN ranging
from: 192.168.8.1-192.168.8.253
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway: 192.168.8.254
PC can be set either in DHCP or static IP mode
Note: The above diagram shows a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 15
YML832 Rev1
Page 16
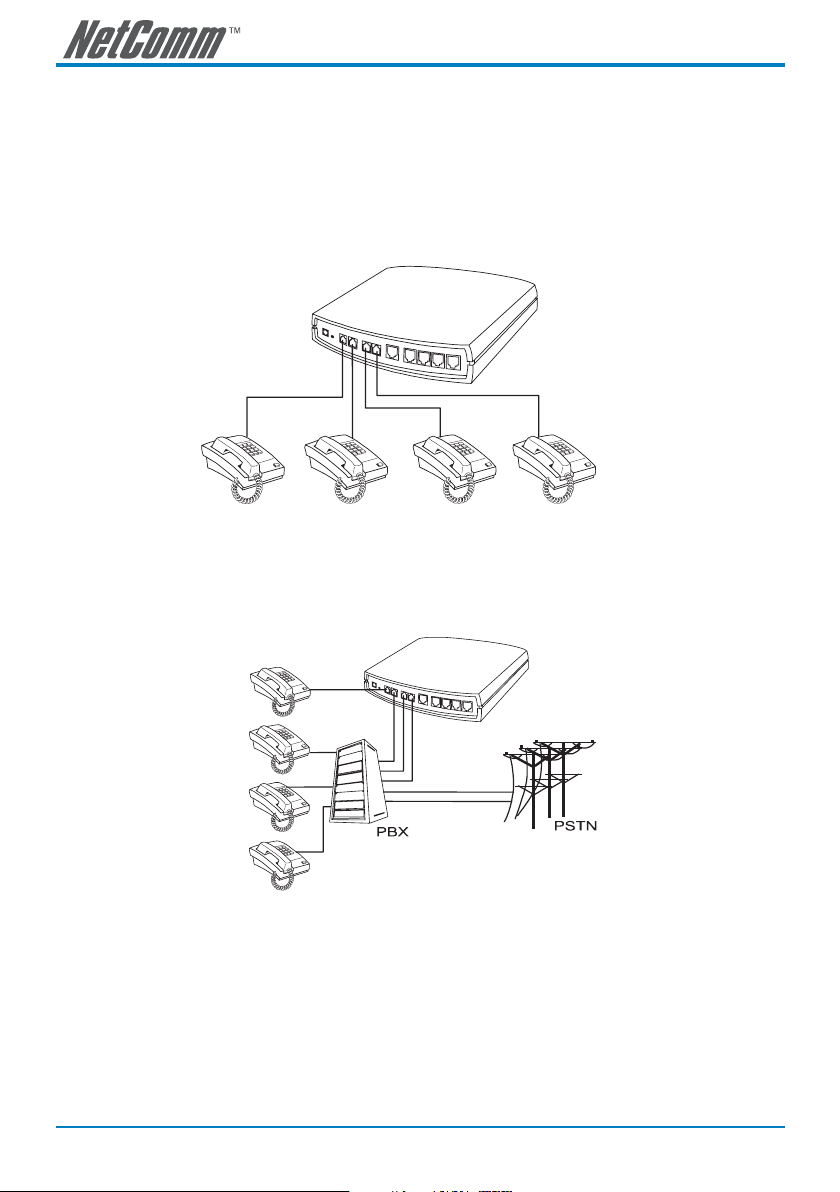
Telephone Connection
Example of SmartVoice Gateway using FXS interfaces
SmartVoice Gateway connecting directly to phone sets
After connecting telephone sets to Phone1-Phone4, users can make direct calls (Phone1-Phone4 are
FXS interfaces). Each set acts as an independent extension line.
Integrating the SmartVoice Gateway with PBX
Phone1-Phone4 are FXS interfaces, and some of them can be connected to telephone sets for direct
calls. Others can be connected to the PBX CO lines so that other extension lines can make VoIP calls.
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
16 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 17
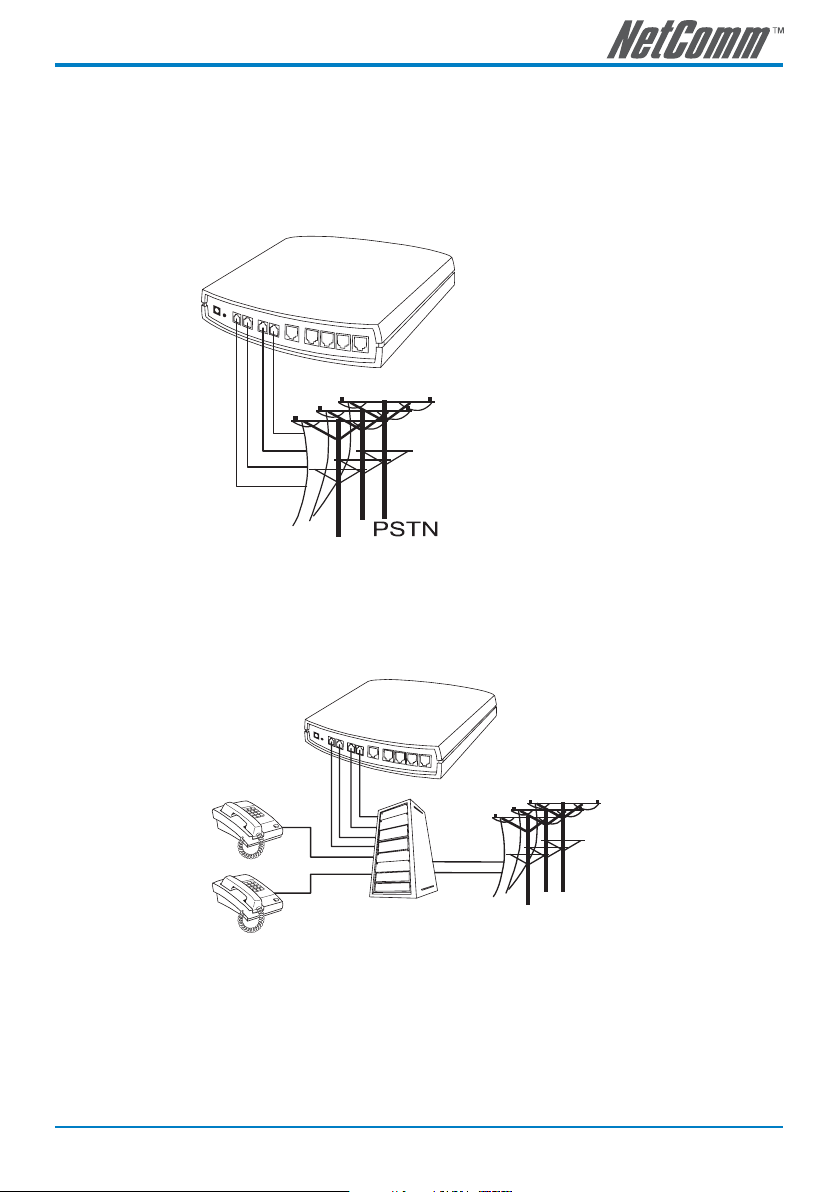
Example of SmartVoice Gateway using FXO interfaces
SmartVoice Gateway connecting directly to the Telephone Line of a PSTN
Line1-Line4 are FXO interfaces and can all be connected to a PSTN to serve as a bridge between the
PSTN and VoIP network.
Integrating the SmartVoice Gateway with PBX
Line1-Line4 are FXO interfaces and can be connected with PBX extension lines (this is exclusively for an
analog interface, and is not applicable for a digital interface).
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 17
YML832 Rev1
Page 18
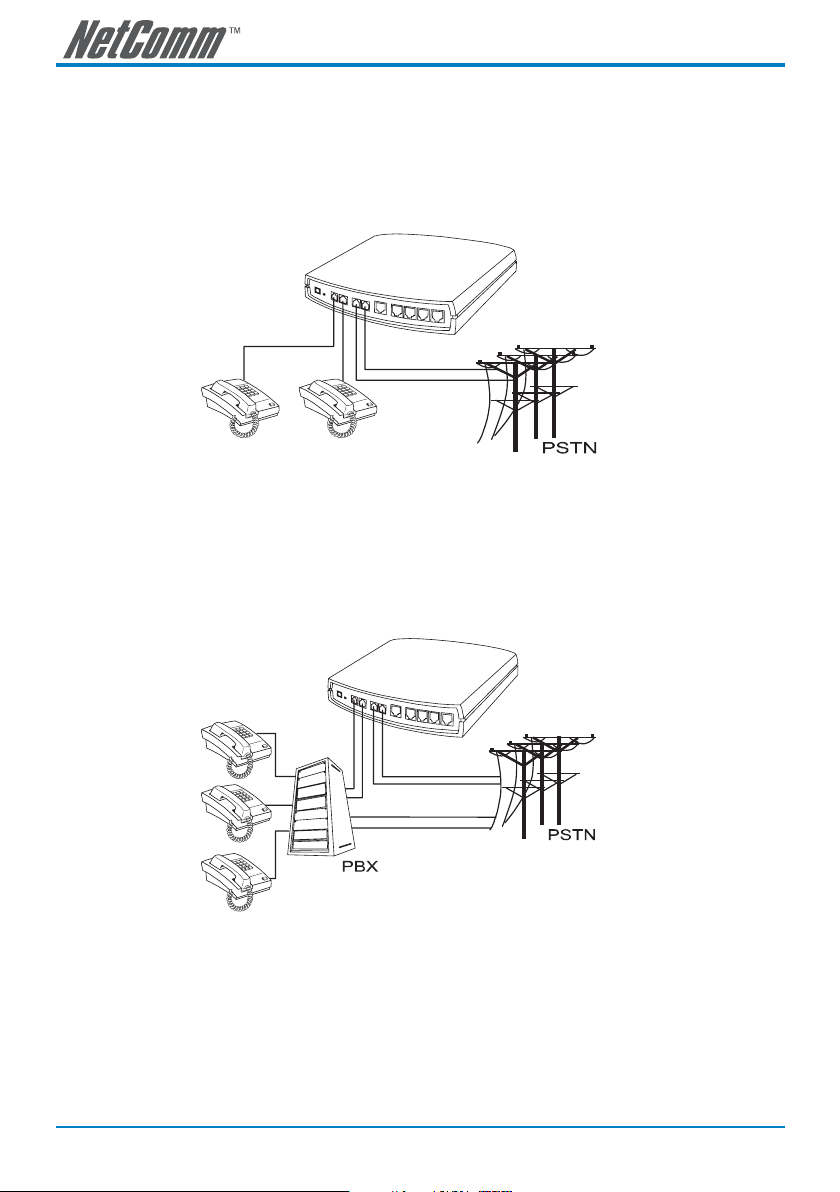
Example of SmartVoice Gateway using a combination of FXS and FXO ports
Phone1-Phone2 are FXS interfaces and can be directly connected to telephone sets for direct calls.
Line1-Line2 are FXO interfaces and can be connected to PSTN lines to serve as a bridge between the
PSTN and other VoIP telephones. The system also allows a call to be made from a traditional telephone
line to connect with a user behind the SmartVoice Gateway.
Integrating the SmartVoice Gateway with PBX
Phone1-Phone2 are FXS interfaces and can be connected to PBX CO lines; Line1-Line2 are FXO
interfaces and can be connected to a PSTN to act as a bridge between the PSTN and other VoIP
telephones. The system also allows a call to be made from a traditional telephone line to connect with a
user behind the SmartVoice Gateway.
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
18 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 19

3. Configuring the Gateway via WEB Browser
The gateway also allows users to change gateway settings using a web browser. After opening a browser
window, enter the gateway’s IP address as the website address in order to enter the Web configuration
screen as shown in the following diagram. (IE Browser used for example: Enter http://192.168.1.2.)
The factory default WAN IP address for Gateway is 192. 168. 1. 2. You can also enter ”101” from the handset
to inquire about the current WAN Port IP address. The factory default LAN Port IP address is 192.168.8.254.
Instructions
• Open an Internet browser window.
• Enter the gateway’s WAN Port IP address in the website address area (If the PC is connected to the
LAN Port, enter the LAN Port IP address. The default is 192.168.8.254)
• The following registration screen will appear (The factory default settings for both Login ID and
Password are set to ‘admin’).
• After completing and confirming the settings, some of the settings will take effect immediately, but
some settings e.g. network related settings will only take effect after the gateway is restarted. Please
go to System Operation to save the settings before restarting the system.
The gateway doesn’t allow multiple users to configure the gateway at same time. Once a user logs into
the gateway, other users from different IP addresses cannot login at the same time. Please remember to
logout or restart the system if you are not using the web configuration function.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 19
YML832 Rev1
Page 20
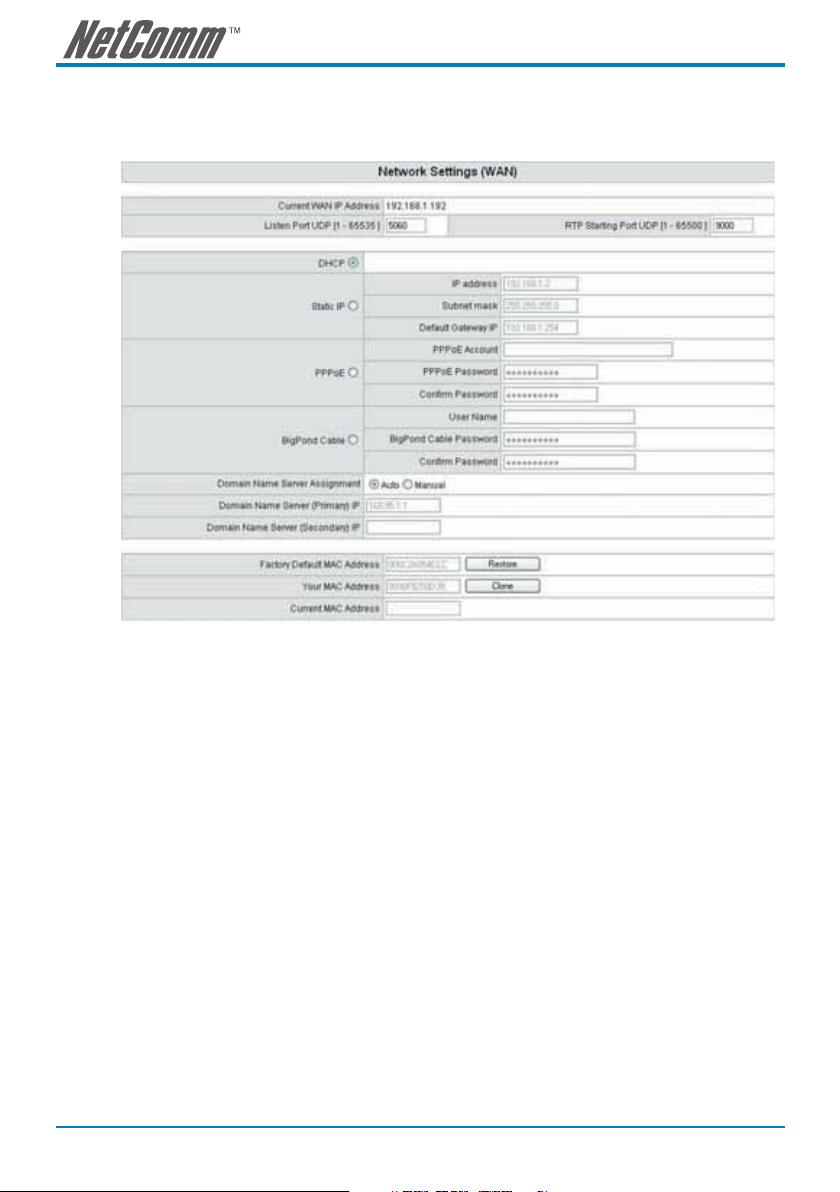
Network Settings
The network settings are used to set the gateway’s communication ports, IP configurations, DNS and
DHCP server etc.
• Current WAN IP Address: The IP address of the WAN port.
• Listen Port UDP: It is not necessary to change the protocol of the communication port used by the
gateway, unless it conflicts with ports used by another device in your network.
• RTP Starting Port UDP: The initial value of the port number for transmitting voice data among
gateway(s). Each line requires 2 ports. For example, the 400 series gateway requires 8 UDP ports
and the 800 series gateway requires 16 UDP ports. It is not necessary to change these, unless it
conflicts with ports used by another device in your network.
For example, if the starting port is 9000, then Line 1 is using ports 9000 and 9001, and Line 2 is using
ports 9002 and 9003, and so forth.
IP Configuration (Setting WAN Port)
There are three methods of obtaining a WAN IP address:
1. Static IP
2. DHCP, means a Dynamic IP (Cable Modem)
3. PPPoE (Dialup ADSL)
Using the DHCP and PPPoE for obtaining an IP address may vary. If you are not familiar with the network
connection, please contact your local ISP.
20 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 21

Setting Dynamic IP (DHCP)
Click “DHCP” to obtain a Dynamic IP address, and then click the “Accept” button at the bottom of the
screen.
To save the settings click System Operation to select “Save Settings”, “Restart”, and then click the
”Accept” button. Wait for a while (about 40 seconds), and the system will obtain the related IP value from
the DHCP Server.
NOTE: After the system has obtained a new IP address, if using WAN Port to enter
the Web Configuration Screen, a new IP address has to be used. The same applies
to the following two settings.
Setting Static IP
Select “Static IP” and enter the IP address, Subnet Mask and Default Gateway values. Then click the
“Accept” button at the bottom of the screen.
Save the settings, and then restart the system. Wait for about 40 seconds for the system to restart.
ADSL PPPoE Settings
Select “PPPoE” and enter the Account Number, Password and re-enter Password to confirm. Then click
the “Accept” button at the bottom.
Save the settings, and then restart the system. The system will take about 40 seconds to restart.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 21
YML832 Rev1
Page 22

BigPond
Click “BigPond Cable”. Enter User Name and Password and then click the “Accept” button at the bottom.
DNS Settings
Domain Name Server (DNS): While a gateway is accessing another gateway or computer with a
hostname, it will look up the IP address from the DNS provided by the ISP. The ISP whilst negotiating
with PPPoE or DHCP usually assigns the DNS information. In the case that the DNS is not assigned
automatically or WAN port is assigned with a static IP address, the DNS information must be assigned
manually.
Auto Gateway uses primary & secondary DNS addresses from
ISP’s DHCP server or PPPoE server.
Manual Enter the primary & secondary DNS addresses manually.
Please be sure the IP addresses are correct otherwise the
gateway will not be able to access any hosts with their
hostname.
Clone MAC
Some Internet Service Providers (ISP) assign the bandwidth via the MAC (Media Access Control) address.
You can click the “Clone” button to type in a MAC address which is recognized by ISP. It is only necessary
to fill in the field if required by your ISP.
The “Your MAC Address” will be blank as you log in through WAN port.
22 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 23

LAN interface mode
• Router: The system serves as a router.
• Bridge: The system serves as a bridge between WAN port and LAN port. (LAN default gateway will
still be accessible for configuration).
Network Settings (LAN)
• Network Settings (LAN): The gateway’s LAN IP address and subnet mask value. Please note that
the gateway is built under NAT: The gateway’s LAN IP address cannot be in the same section as
the Internet sharing devices, or else it is unable to make or receive calls. For example, if the LAN IP
address of the Internet sharing device is 192.168.8.1, then the gateway’s LAN IP address cannot be
in the range between 192.168.8.1 ~ 192.168.8.254. If it is, please change the LAN IP address of
the gateway (e.g. set the IP address to 192.168.99.254 instead).
• Enable DHCP Server: Enable or Disable DHCP server service of gateway.
• IP Pool Starting Address: The first IP address to be assigned to DHCP clients.
• IP Pool ending Address: The last IP address to be assigned to DHCP clients.
• Lease Time: The valid period of an assigned IP address.
• Domain Name Server Assignment: The DNS information to be assigned to DHCP clients.
Auto : Assigns the same DNS information of WAN port to the DHCP clients.
Manual : Manually assign the DNS information for DHCP clients.
• Port of Web Access from WAN: Http port for WAN. To make this setting, the web configuration
must be performed via the gateway’s LAN port. The gateway always uses port 80 for Http
connections via LAN ports of the gateway.
NOTE: For network security concern, Web Access for WAN port is disabled by
default (port number “0” in this option means disable the Web Access). To enable
it simply type in a valid port number in this field.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 23
YML832 Rev1
Page 24

QoS Settings
WAN QoS
• QoS (Quality of Service): Sets true bandwidth of your Internet connection to ensure sound quality
during transmission. (When this function is enabled, the voice packet has the highest priority to
ensure telecommunication quality while less bandwidth is assigned for data transmission). Some
models of the VoIP gateway without this function can adjust the bandwidth automatically.
NOTE: The WAN QoS function only works as expected when you connect/configure
the gateway as described on Page 13. If the gateway is behind an Internet sharing
device as described in Page 14, QoS for VoIP traffic should be guaranteed by your
network routers and not the VoIP gateway.
• ToS/DiffServ (Type of Service/DSCP): The voice packet has the highest priority to
ensure telecommunication quality; the larger the value you set, the higher priority
you will get.
NOTE: Please contact your ISP when you configure these values.
24 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 25

NAT/DDNS (NAT Traversal)
If a gateway is set up behind an Internet sharing device, you can select either the NAT or STUN protocol.
• NAT Public IP: The IP address used by the gateway should be a private address. Furthermore,
users must set the Virtual Server Mapping in the Internet sharing device (For example, a virtual
server is usually defined as a Service Port, and all requests to this port will be redirected to this
specified server’s private IP address).
The default ports of the gateway are listed below:
• Listen Port (UDP): 5060
• RTP Starting Port (UDP): 9000~9015 (Listen Port used for telephone communication).
• Port of Web Access from WAN (TCP): the number you specified in this option in Network
Settings page.
NOTE: You need to configure your Internet sharing device to forward the above
ports to the WAN IP address of the gateway.
• NAT IP/Domain: Enter the NAT Server IP address (real public IP address of the Internet sharing
device); or fill in a true URL (Uniform Resource Locator) when DDNS is used. Please refer to the
DDNS settings.
NOTE: If setting a public IP in this field, it has to be a static public IP, otherwise
VoIP communication may not be established properly. Please contact your ISP to
check whether your Internet connection has static public IP addresses.
• Enable STUN Client: Using the STUN protocol prevents problems with setting the IP sharing
function, but some NAT does not support this protocol.
NOTE: You can use the “Status - STUN Inquiry” page to detect type of NAT of your
Internet sharing device. If the NAT type is “Symmetric NAT”, then the gateway is
not able to traverse the NAT. It is not a flaw of the gateway design, but limitations
of the STUN protocol.
• STUN Server IP/Domain and Port: Enter the STUN server IP address and Listen Port number. You
can set 2 STUN servers separated by a semicolon.
• Enable UPnP Control Point: To enable the gateway’s IP traffic to pass through an Internet sharing
device. This function only works when the Internet sharing device supports UPnP and has it enabled.
NOTE: The “Status - Current Status” page will show the status of UPnP.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 25
YML832 Rev1
Page 26
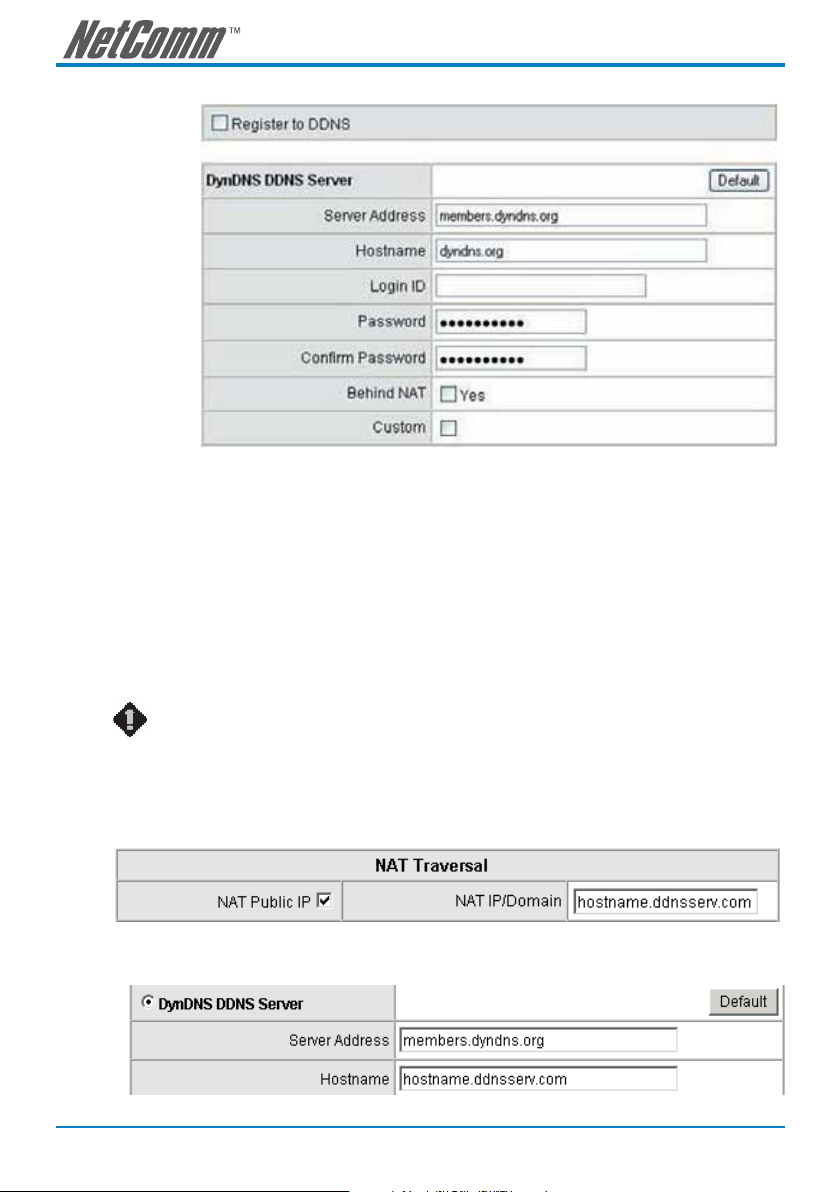
DDNS
These settings are only necessary when the gateway is set up behind an Internet sharing device that
uses a dynamic IP address and does not support DDNS.
You need to apply for an account with a DDNS service from www.dyndns.org before you type in the
following information.
• Server address: Sets up the IP address or URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the DDNS Server.
• Hostname: The URL of the system (or NAT) – apply from domain name registration providers (e.g.
www.dyndns.org).
• Login ID and Password: The ID and password are used to log into the DDNS server.
• Behind NAT: Select only when the system is set up behind a NAT device.
NOTE: If the gateway is set up under NAT, then enter the hostname into the NAT
IP/Domain that is the same with Hostname of DDNS.
Example:
NAT
DDNS
26 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 27

Telephony Settings
Prefix Number Rules
• Trunk Dial Out Verify/ Trunk Dial Out Replace: The system will transfer the number for all transit
out calls through the FXO port. For example: If you transit out with 01907123456, the system will
replace it with 190601 907123456. If you transit out with 008621123456 the system will replace it
with 190200 8621123456.
• Trunk Dial Out Deny: The system will deny the call with the leading number filled in this column.
NOTE: This rule only applies to transit out calls of gateway FXO ports.
• FXS Caller ID Generation: Select this option to enable the caller ID display function on FXS ports.
FSK is used for Australian caller ID standards.
• FXO Caller ID Detection: Used to detect the Caller ID delivered from the PSTN to the FXO port.
When enabled, the Caller ID detected on the FXO port will be sent to the SIP Proxy Server on transit
in (dialing out) calls.
• Detection Level: If FXO can’t detect Caller ID, try to adjust it until it can.
NOTE: You have to enable “Wait for Caller ID before FXO / Trunk pick up” to ensure
Caller ID is detected correctly.
• FSK Caller ID Type: Bellcore is used in Australia caller ID standards.
• Anonymous Caller ID (CLIR): When enabled, the gateway will use “anonymous” as caller
identification to place calls.
• Anonymous Transit in W/O Caller ID: When enabled, if the FXO can detect caller ID in calls
from PSTN, the gateway will use the detected caller ID as caller identification for transit in calls; if
FXO cannot detect caller ID, the gateway will use “anonymous” as caller identification for transit in
calls. When it not checked, if the FXO can detect caller ID in calls from PSTN, the gateway will use
the detected caller ID as caller identification for transit in calls; if FXO cannot detect caller ID, the
gateway will use its port phone number as caller identification for transit in calls.
• Trunk Incoming Prompt Voice: Select the greeting (must use the IVR 132 function to record a
voice file) when FXO receives an inbound call (transit in).
• FXO Hunting VoIP call in option:
Caller Indicate Dial-Out: When users make calls to FXO ports from Internet, they will be required to
dial a PSTN number after the calls connects to FXO port.
Default Dial-Out: When users make calls to FXO ports from Internet, the gateway will dial to PSTN
with the number filled in “FXO Hunting Default Dial-Out”.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 27
YML832 Rev1
Page 28

• FXO Hunting Default Dial-Out:
This will take effect as FXO Hunting VoIP call in option is set to Default Dial-Out.
• FXO Line VoIP call in options:
The usage of this option is as same as FXO Hunting VoIP call in option. The Default Dial-Out
refers to individual lines rather than a hunting group. The individual FXO line default dial out
number can be set in Line configuration section as below.
• Enable: To enable a line; if some lines are not used, disable them (Pause Function) to avoid
unnecessary waiting when an incoming call is diverting to this line.
Hotline Functions
• FXS port: When the user picks up the phone, the gateway automatically dials your assigned hotline
number. When in hotline mode, other phone numbers cannot be dialed.
• FXO port: When receiving a call from an outside line, the gateway will divert the call to the assigned
hotline number.
• Hot Line No.: Enter the hot line number for automatic dialing function.
• Warm Line: When the Warm Line function is in use, user can dial a number. Otherwise the system
will divert incoming calls from an outside line to the Hot Line Number after a set wait time.
Example:
Assume the assigned hotline for the SmartVoice Gateway line 3 is 701 and the Warm Line (Hot Line
Delay) is 5 seconds. If no extension number is dialed within 5 seconds, the call will be automatically
diverted to the assigned hotline (ext 701). The system allows users to record a voice prompt (e.g. “Please
enter an extension number or wait for the operator to connect you”) to use in this situation.
Assume the assigned hotline for the SmartVoice Gateway line 4 is 702 and the wait time is 0 second.
When P4 receives a call from an outside line, it will be automatically diverted to extension 702.
• Dial-out Prefix: It is the number dialed automatically by the system when the FXO interface diverts
a call to the PSTN by VoIP.
• FXO Line Default Dial-Out: Default number that FXO will dial out when it receive an incoming call
from VoIP.
Example:
If PBX extension needs to dial “0” to make a PSTN call, and the FXO ports are connected to PBX
extension. In this case, the Dial-out prefix should be set to “0”. If the PBX requires some delay time
before capturing a line, then the trunk prefix should be set as “0,” so that after dialing a 0, it will pause
for 1 second before dialing the destination number. Each comma represents a 1 second delay. If more
delay time is required, simply add more commas. Please note that if a Dial-out prefix is set, the line won’t
be able to dial any PBX extension line (the FXS interface does not have a trunk prefix function).
28 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 29
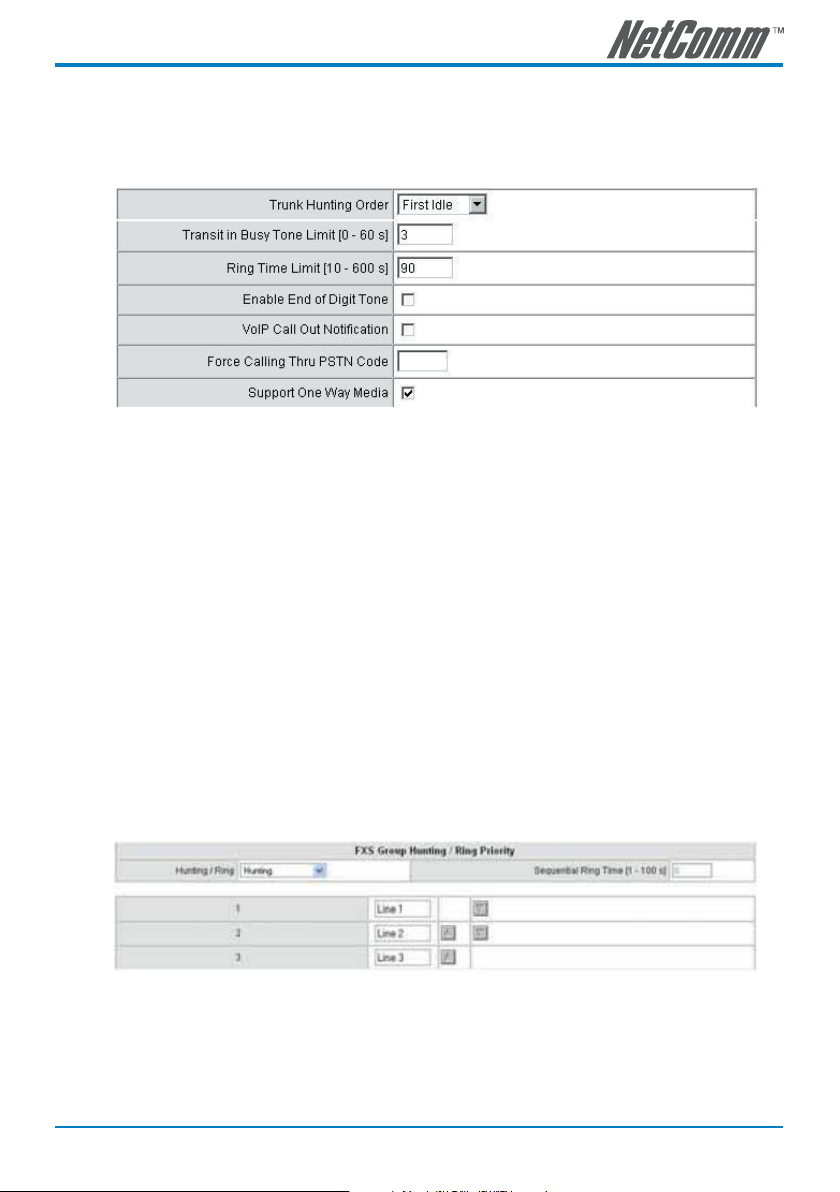
• Group Hunting: Select group hunting when there is an incoming call and the gateway will
automatically assign an unassigned call according to the Hunting Priority. If Line 2 does not want to
be set as an assigned line to receive any inbound calls, the function can be disabled. Users can also
use the Up or Down key to adjust hunting priority (No setting is required for the FXO interface).
• Enable FAX: Enable this line to detect if there is a FAX tone to transfer the codec.
Description:
• Trunk Hunting Order: To set FXO dial-out mode when there is an incoming call dialed FXO
representative number. (This option only appears in the gateway which has more one FXO ports)
First Idle: The gateway will assign each unassigned call from first FXO line.
Sequential: The gateway will automatically assign the first unassigned call to the first FXO line. The
second FXO line will dial the second unassigned call out. Each line will be used.
• Transit in Busy Tone Limit: The duration the VoIP gateway plays a busy tone before FXO port goes
on-hook. Used to notify the caller from PSTN that this call is finished.
• Ring Time Limit (10 - 600secs): The timeout to cancel a call when no one answers.
• Enable End of Digit Tone: The VoIP gateway will play a “Beep-Beep” tone to notify that the call is
in progress.
• VoIP Calling Notification: The gateway will play a tone to notify the call is through VoIP.
• Force Calling Thru PSTN code: Dial the code to get a PSTN line for dial out. For example: If you
specify “33” in this option and would like dial “23456789” through PSTN, just dial “33 23456789”
• Support One Way Media: If it is disabled, the system will send RTP immediately when the
connection with Proxy is set up. The default is enabled. If communicating with other Gateway has
problem, please disable this function.
• Hunting/Ring: It is able to set FXS group hunting using simultaneous ring or sequential ring.
• Sequential Ring Time: To set the ring time of each port, when sequential ring is chosen.
• Hunting Priority: it can be adjusted using the Up or Down arrows.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 29
YML832 Rev1
Page 30

SIP Settings
• All Call through OutBound Proxy: An outbound proxy server handles SIP call signaling as a
standard SIP proxy server would. Furthermore, it receives and transmits phone conversation traffic
(media) in between two communication parties. This option tells the gateway to send and receive all
SIP packets to the destined outbound proxy server rather than the remote gateway. This helps VoIP
calls to pass through any NAT protected network without additional settings or techniques. Please
make sure your VoIP service provider supports outbound proxy services before you enable it.
• Session Expiration: It is to avoid the billing of abnormal dropping the call because of Internet.
The default is disabled.
• Session Refresh Request: to send the packet of UPDATE or re-INVITE to
• Session Refresher: It is the gateway’s role in Session Timer. UAS is an originator, and UAC is a
replier.
30 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 31

E.164
• International Call Prefix Digit: Enter the International call prefix.
• Country Code: Select the desired country code.
• Long Distance Call Prefix Digit: The long-distance prefix digit for making a long-distance call.
• Area Code: Please enter the area code.
• E.164 Numbering: To invite Proxy to follow the E.164 rule. It depends on the Proxy.
NOTE: All settings in this section are specific to your VoIP network. Please ask your
VoIP service provider whether they require these settings.
• Enable Support of SIP Proxy Server / Soft Switch: Enable the functions to inter-work with Proxy
Server / Soft Switch. When SIP Proxy 1 and 2 are enabled, the system will register to SIP Proxy 2
after all lines are failed to register to SIP Proxy 1. SIP Proxy 2 is a backup system.
• Proxy Server IP/Domain: Enter the Proxy Server IP address or URL (Uniform Resource Locator).
You can set 3 redundant Proxy spread by semicolon.
EX: 61.123.231.1;12.34.56.78;proxy.sip.sip
• Proxy Server Port: Enter the Proxy Server listen port number. (The default value is 5060)
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 31
YML832 Rev1
Page 32

• Proxy Server Realm: This is used for gateway SIP account authentication in a SIP server. In most
cases, the gateway can automatically detect your SIP server realm. So you can leave this option as
blank. However, if your SIP server requires you to use a specific realm you can manually type it in
here. If you fail to make a call, please contact your VoIP service provider.
• TTL: Enter the desired time interval at which the gateway will report to your Proxy Server.
• SIP Domain/Use Domain to Register: Enter the correct SIP domain to avoid registration failure (it
is not necessary to set this with some Proxy Servers). If you enable “Uses Domain to Register” the
VoIP Gateway will register to Proxy with the domain name you filed. Alternatively, the VoIP Gateway
will register to a Proxy with the IP it resolves. If you fail to make a call, please contact your VoIP
service provider.
• Bind Proxy Interval for NAT: This function is able to keep the binding is existed when VoIP
Gateway is behind NAT and SIP Proxy is not able to keep the binding.
• Initial Unregister: After rebooting, it is unregistered first and then do the general register process.
32 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 33

FXS/ FXO Representative number registers to Proxy:
Assuming that your registered ID and password are individual, the settings should be as above:
• FXS Representative Number: Register all FXS ports as a hunting group.
• FXO Representative Number: Register all FXO ports as a hunting group.
All the grouped FXO ports will be hunted automatically. It is available when FXO registers to Proxy.
• Register: Register to Proxy if ticked.
Hunting pattern of grouped FXS/FXO ports will be based on the hunting policy you specified on page 33.
NOTE: Please contact your VoIP provider about whether they can provide
reprehensive numbers to allow you to use them for more than one FXS and FXO
ports. FXS and FXO reprehensive numbers should be different.
Each line registers to Proxy independently:
• Number: VoIP phone number
• User ID/Account: VoIP account Authentication ID or account name
• Password: password for VoIP account authentication
• Invite with ID / Account: VoIP gateway can be invited to a VoIP trunk gateway w/o registering with
a Proxy. Please contact your VoIP provider.
As there are various Proxy Server providers, NetComm has designed the gateway to be compatible with
as many SIP VoIP networks as possible, and according to RFC standards. If any registration problem
occurs, please consult your VoIP provider.
NOTE: When you register with a Proxy Server, dialing principles may vary with
different Proxy Servers, especially when dialing through a FXO port. Please consult
your VoIP Service Provider for details.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 33
YML832 Rev1
Page 34

Private Network
Users can establish a private network by using the Phone Book Manager Service. The Phone Book
Manager Service is different from using the Proxy. The gateway is able to register with the Phone Book
Manager Service and the SIP Proxy at the same time.
Server Settings
• Enable Phone Book Manager Server: It allows other Gateway users to register the IP address
and Gateway Number in this Phone book manager server. It is recommended to use a static IP for
the Phone Book Manager Server.
• Share Local Phone Book to clients: While this option is enabled and the gateway is performing
as a Phone Book Manager Server, this gateway will append its local Phone Book entries to the
Server for other clients to lookup.
• TTL (Time to Live): If a Gateway system that is controlled by the Phone Book Manager Server does
not report back within the deadline set by TTL, the system will be excluded from the user’s list. Each
Gateway should report to the Phone Book Manager Server once every 30 seconds.
Client Settings
• Register to Phone Book Manager: Used to register to the Phone Book Manager. If the gateway is
the Phone Manager Server, it has to enable this function to communicate with other clients.
• Gateway Name for Phone Book Manager: The alias registered with the Phone Book Manager
Server.
• Phone Book Manager IP/Domain: Enter the IP address for the Phone Book Manager Server. It
supports URL (Uniform Resource Locator).
• Phone Book Manager Server Listen Port: The protocol communication port for transmitting
signals between the Phone Book Manager and other Gateway systems.
• Phone Book Manager Login Password: Enter the password for Phone Book Manager Service.
If the gateway works as a Phone Book Manager client, the Login password is the one which is used
to register in a Phone Book Manager server.
If the gateway works as Phone Book Manager server, the Login password is the one which is used
for checking against Phone Book Manager clients when they registering in the server.
34 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 35

NOTE: When the gateway is configured as Phone Book Manager server, it can also
be configured as a client at the same time by enabling Register to Phone Book
Manager option. This means the gateway also shares its Private Gateway Number
to other clients which register on it.
Private Network Numbers
• Gateway Number: A self-defined phone number for the gateway that the gateway will use as its
phone number to register on a Phone Book Manager server.
• Line: A self-defined extension number which allows remote gateways to reach a specific extension
line.
Example:
Assume a gateway uses “5700” as its gateway number and registers on a Phone Book Manager server
which your gateway registers on. To make a call to the gateway, simply dial 5700 which will cause one
of the FXS ports of the gateway to ring (the ringing port depends on hunting policy of the gateway). If the
gateway has configured its line extensions as “901”~“904”, then to reach the extension line “902” of
the gateway you just simply dial 5700902.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 35
YML832 Rev1
Page 36

Calling Features
• Do Not Disturb: It will only be able to call out when it is enabled. All incoming calls will be
restricted.
• Unconditional Forward: All incoming calls will be forwarded to the “Forwarding Number”
automatically. If it forwards to FXO, it only make FXO hook off, not make FXO dial out.
• Busy Forward: Forward the incoming call to “Forwarding Number” when the port is busy.
• No Answer Forward: Forward the incoming call to “Forwarding Number” after ring timeout expires
without answer.
• Call Hold: Enable the call hold feature on the specific FXS port.
NOTE: Call Hold must be checked; Call Transfer or Call Waiting is active.
• Call Transfer: Enable the call transfer feature on the specific FXS port.
• Call Waiting: Enable the call waiting feature on the specific FXS port.
Calling Feature Instructions:
• Call Hold: Call will be put on hold after FLASH button pressed on the phone set. The gateway will
play on-hold music, which is provided by your VoIP network, to the remote end.
• Call Transfer: Call will be put on hold after FLASH button pressed on local phone set (gateway
plays on-hold music to the remote end). Meanwhile, the local user can dial out to another number
after dial tone is observed. After the handset is replaced back on-hook, the call on hold will then be
transferred to the new call regardless of the status of the new call. If the wrong number is dialed
for the new call, just press the FLASH button to get back the call on hold. In another case, if the
local user doesn’t hang up the phone after the new call is set up, press the FLASH button to switch
between the first call and the new call. Please be informed that the PBX between phone sets and
the gateway must support FLASH features in order to use this function. If a phone set is connecting
directly to the FXS port of the gateway and not functioning to FLASH, please adjust the settings in
“Flash Detect Time” in “Advanced Options” section.
NOTE: The availability of the above features also depends on your VoIP network.
Please also check with your service provider on these services.
36 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 37

Advanced Options
NOTE: There are two levels to enter Web. Administrator is able to change all
settings. Web UI only changes some settings.
• Administrator’s name and Password: Enter administrator name and password, which has the
highest level of control of the gateway.
• Web UI Login ID and Web UI/IVR Password: Enter login ID and password when you log into the
Web interface/IVR of the gateway as a normal user.
• Web UI auto log out: If a user does not act within the effective time range when logging into the
web interface, the user will be disconnected from the web page to allow others to login.
• Dial Wait Timeout: Use it to set the waiting time for the user’s first key pressing when dialing a
number. The user will hear a busy tone if he/she does not press the first key within the set time
frame.
• Inter Digits Timeout: Set the waiting time between each key pressing. The entered numbers will
be dialed after the timeout.
• Minimum DTMF ON Length (Dial on)/ Minimum DTMF OFF Length (Dial off - between
tones): Used to set dial tone when a call is being diverted to another extension.
• DTMF Detection Sensitivity: Used to adjust the sensitivity of the telephone keys.
• Enable Out-of-Band DTMF: To send DTMF keys (0~9, *, #,) follow the RFC2833 rules or via SIP
Info.
NOTE: Out-of-Band DTMF transport method may vary with different VoIP networks,
please contact your VoIP provider for their preferred method.
NOTE: The 800 series gateway has three extra options compared to the 400
series gateway: FXO Dial Type, FXO Impendance and FX Impedance. Use the
default settings for these options as they have been configured for the Australian
telephone network.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 37
YML832 Rev1
Page 38

• Payload Type: payload type of RFC2833.
• Uses Second CPT for VoIP Call: This function is usually applied when the user selects VoIP as
the primary path for outgoing calls and PSTN as the backup. By enabling this function, the gateway
will generate a different set of tones to inform the user that VoIP is in service. Should VoIP fail and
fallback to PSTN, the user will hear PSTN tones instead of the second set CPT. (for CPT related
settings, please refer to Trunk Management -> CPT/Cadence Settings).
38 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 39

Line Settings
• Listening Volume: Adjusts the hearing volume.
• Speaking Volume: Adjusts the speaking volume.
• Tone Volume: This setting will be applied to all tones generated by the VoIP gateway including Dial
Tone, Busy Tone, and so on.
• Flash Time:
FXS: Used to adjust the detection period of flash signal from the phone set connected to the FXS
port. For example, if pressing the FLASH key disconnects a call, increase the “Flash Detect
Time” to fix this issue.
FXO: Used to set the time frame that FXO generates a FLASH signal.
• Enable Polarity Reversal:
FXS: As the remote site answers this call or goes on hook the FXS port will reverse the polarity.
FXO: This option forces the gateway to detect the reversal of polarity on FXO port as the primary
signal to drop a call. Some telephone switches or PBX systems reverse the line polarity to inform
the remote end to drop an ongoing call. Please consult with the telephone service provider for
availability of this feature.
• PSTN Answer Detection: This is only used with specific VoIP providers.
• PSTN Ring Off Length: This is for PSTN making out if the call rings off before picking up.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 39
YML832 Rev1
Page 40

Codec Settings
• Preferred Codec Type: Since different voice codecs have different compression ratios, so the
sound quality and occupied bandwidths will also be different. It is recommended that you use the
default provided (G.729) because it is popular and will provide better sound quality.
• Jitter Buffer: Adjusts the jitter to receive a packet. If the jitter range is too wide, it will delay voice
transmission.
• Silence Detection/Suppression: If one side of a connection is not speaking, the system will stop
sending voice data (packet) to decrease bandwidth usage.
• Echo Cancellation: Prevents voice quality caused by echo interference.
• Packet Interval: Defines how long the VoIP gateway sends a RTP packet to the other party of a
VoIP conversation. The smaller the value, the more bandwidth usage. The larger the value, the more
voice delay.
• Approximate Bandwidth Require: The bandwidth required varies with codec format and packet
time.
40 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 41

Fax Settings
• T.38: The T.38 protocol is used for better and faster facsimile transmission. So it is recommended
to enable this function to gain better fax quality. When this function is enabled, please select UDP or
TCP. If selecting TCP and some gateways cannot use the Fax function, please select UDP instead.
NOTE: When a FAX tone is detected in a call, the gateway will automatically switch
from voice mode to fax mode. So fax settings will be temporarily applied to a
specific port which detects fax tones, instead of its voice settings.
• Enable High Quality: The system sends the same FAX frame twice to get a high quality of the FAX.
It requires more bandwidth.
• T.30: The system uses T.30 as the protocol for fax transmission. The parameter settings are the
same as for voice transmission. However, enabling the T.30 will consume more network resources
and will affect transmission quality.
• FAX Detect sensitivity: Used to adjust the sensitivity of detection as to whether a phone call is a
FAX or not.
NOTE: When you send fax over an IP network it needs your network to support
fax over IP function (either T.38 or T.30). Please consult your VoIP provider for this
setting.
This is used as a standard to determine whether or not to hang up the phone. The system will hang up
the phone automatically to avoid keeping the line engaged if the detected volume is below the Silence
Detection Threshold and the time exceeds the Drop Silent Call Timeout.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 41
YML832 Rev1
Page 42

Drop Inactive Call
• Silence Detection Threshold: The volume below the threshold is used as a standard to determine
whether or not to hang up the phone.
• Drop Silent Call Timeout: If the detected volume is below the threshold and the time exceeds the
silence detection interval, the system will hang up the phone automatically to avoid keeping the line
engaged.
NOTE: Please be careful with these setting. Improper values might cause
unexpected automatic disconnection of a call. Default values are recommended.
42 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 43

Digit Map
There are 50 sets of leading digit entries to choose voice routing interface – Auto select, PSTN or VoIP.
• Default Call Route: The default call route can be Auto, VoIP, PSTN and Deny.
Auto (VoIP first): The call route is VoIP first, and the next is PSTN.
VoIP: The call route is VoIP only.
PSTN: The call route is PSTN only.
Deny: The call will be deny if the dial-out number is not in the table.
• Enable: Enable detection of this entry.
• Leading Digits: The leading digits for the VoIP gateway to scan while the user is dialing.
• Total Digit Count: Total number of digits that VoIP gateway should accept. 0 means that the VoIP
gateway scans leading digits only and disregards total digit count.
• Route: The interface that calls should go through if above conditions are satisfied.
Example:
For the above setting, if a user dialed 0394978867, which matches Digit Map rule 1, then the gateway
will route this call through VoIP. If 0294278766 is dialed, then the gateway will route this call through
PSTN.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 43
YML832 Rev1
Page 44

Phone Book
The system can set up and store 100 phone numbers in the phone book and provide an IP address
query when calling other Gateway(s). If no Phone book manager is set within a Gateway group, then all
Gateway systems have to set up phone data for each VoIP gateway to communicate with each other.
• Gateway Name: Enter the Gateway’s code or an easy-to-remember name.
• Gateway Number: Enter the desired Gateway number.
• IP/Domain Name: Enter the IP address or URL (Uniform Resource Locator) of the Gateway.
• Port: Enter the Gateway’s port.
44 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 45

Speed Dial
This system can set up 100 numbers for speed dialing. Setting methods are as follows:
Method 1- Single mapping: Fill a short code into the “Speed Dial Code” column, and enter the desired
phone number into the “Number To Dial” column.
For example, pick up the handset and dial 55# and the system will dial 32568791.
Method 2- Multi mapping: Fill the prefix code into the “Speed Dial Code” column and the format to
transfer into the “Number To Dial” column.
For example, pick up the handset and dial 301#, and the system will dial 521301.
If the user dials 00 1657987456321#, the system will DIAL 856 1657987456321
NOTE: The gateway uses the “#” key as a delimiter to detect end of dialed number
input.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 45
YML832 Rev1
Page 46

Caller Filter
This function is used to allow or deny the SIP Invite message from the Proxy list ONLY.
• Filter IP Address: Enter the IP address that you would like to allow/deny.
• Subnet mask: Enter the subnet mask that is applied to the IP that entered in the Filter IP address
field.
46 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 47

Transit Call Control
If you wish to restrict a general user (one who is not required to enter the PIN code) to local calls only
and prohibit him/her from making long-distance calls started with a prefix “0”, do the following steps:
1. Enable the Outbound Call Control function,
2. Set the PIN code for Outbound Level 5 to blank,
3. Set the Long-Distance Control Table to correspond with the Outbound Level 5 to prohibit making any
call with the prefix “0”.
NOTE: Transit Call Control is effective when it cooperate with Long-Distance
Control Table.
• Inbound Call Control: Determines when users make a phone call from a PSTN to Gateway FXO
whether or not they check the inbound PIN code while placing the phone call to VoIP network only
effective for incoming calls calling from a PSTN trunk.
• Outbound Call Control: Determines when users utilize the Gateway FXO interface to divert to PSTN
network whether or not they check the outbound PIN code only effective for outgoing calls being
diverted to a PSTN Trunk.
• PIN Code: Enter the PIN code (4-6 digits or leave blank. A blank indicates no PIN code is required at
this level. Generally, the PIN at level 5 can remain blank to simplify the phone number.)
• Enable: Enables the PIN code at each level.
• Privileges: The level is divided into 0~5 (The levels are in descending order; 0 stands for the
highest authority and 5 stands for the lowest.)
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 47
YML832 Rev1
Page 48

Dialing principle to enable PIN code
*Inbound Call Control PIN Code * Outbound Call Control PIN Code * Phone number
Using * to the separate PIN code and the phone number based on actual settings. The PIN can also be
omitted.
The actual operation is shown below:
• If making a call from Gateway A to Gateway B, and diverting to PSTN (local call) when Gateway A
and Gateway B both have Outbound Call Control disabled, dial as follows:
Gateway B Number + Local Phone Number
For example: 5168 35020311#
• When Gateway A disables Inbound Call Control and Gateway B enables Outbound Call Control, then
dial as follows:
* Gateway B PIN Code * Gateway B Number Local Phone Number
For example:*123456* 5168 35020311# (Gateway B PIN Code: 123456)
• When Gateway A enables Inbound Call Control and Gateway B disables Outbound Call Control, then:
If using an extension line at Gateway A to make a local call to a remote end (at Gateway B site)
through Gateway B, then dial
Gateway B Number + Local Phone Number
For example: 5168 35020311#
• If using a trunk line to dial to Gateway A, and then making a local call to a remote end (at Gateway B
site) through Gateway B, then dial
* Gateway A PIN Code * Gateway B Number + Local Phone Number
• When the instruction “Enter phone number” is given, then dial
For example:*111111* 5168 35020311# (Gateway A PIN Code: 111111)
• If using a trunk line to dial to Gateway A and then to the extension line of Gateway B, dial
* Gateway A PIN Code * Gateway B Number
When the instruction “Enter phone number” is given.
For example:*111111* 5168#
• When Gateway A has Inbound Call Control enabled and Gateway B has Outbound Call Control
enabled, then if using an extension line at Gateway A to make a phone call to a remote end through
Gateway B, dial:
* Gateway B PIN Code * Gateway B Number Local Phone Number
For example: *123456* 5168 35020311# (Gateway B PIN Code: 123456)
• If using a trunk line to dial to Gateway A, and then dialing a local call to a remote site through
Gateway B, please dial
* Gateway A PIN Code * Gateway B PIN Code * Gateway B Number Local Phone Number
For example:*111111* 123456* 5168 35020311# (Gateway A PIN Code 111111 Gateway B PIN
Code 123456)
48 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 49

Long-Distance Control Table
This table controls the level of authority of an outgoing (transit out) call that is dialed through FXO and
diverted to PSTN, as below:
Descriptions:
• Digit strings in this table are prefixes that the gateway will check on dialed numbers in transit out
calls.
• This table is used to prohibit dialing any numbers started with specified prefixes.
• If Level 0 (the highest level) is set to prohibit dialing any number started with prefix 0204, then any
level below 0 (including Levels 1 to 5) are also prohibited.
• If Level 1 is set to prohibit dialing any number with prefix 0, then any level below 1 (including Levels
2 to 5) are also prohibited. Since Level 0 is not restricted to any prefix, therefore at level 0 users can
dial a number with the prefix 0.
Principle: Downward Restriction —If users at a higher level cannot dial a number with a
certain prefix, then users at lower levels also cannot dial a number with the same prefix.
Long Distance Exception Table
This table handles any exceptions to the long-distance call table.
Instruction:
• According to the Long Distance Control Table, users at Level 0 are prohibited from dialing a number
with the prefix 0204. But, if the number 020488988 is set in the Exception Table as above, then
users can dial this number.
Principle: Upward Opening — If the users at a lower level can dial a number with a certain
prefix, then the users at higher levels can also dial a number with the same prefix.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 49
YML832 Rev1
Page 50

CPT/Cadence Settings
CPT/Cadence setting parameters serve as the basis of an FXO interface to determine whether or not a
PSTN-call receiving party has hung up the phone. If the following parameters differ from the parameters
of the actual assigned lines, it could cause the FXO to continue to engage a line.
Busy Tone Cadence Measurement
• Busy Tone Cadence Measurement and auto learning: Provides a solution of FXO integrated
with PSTN or PBX. FXO will learn the busy tone automatically.
• BTC Detection Sensitivity: The more sensitivity, the more quickly the system will cut off the call. If
the system often cuts off an un-finished call, select less sensitivity.
CPT parameters Table
The CPT has 3 sets of parameter tables. You can adjust it based on local PSTN or PBX.
Moreover, users can use CPT Auto Detect to detect CPT parameters. Instructions are shown in the
following section. The method to detect CPT is as follows:
50 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 51

NOTE: To cope with different local PSTN and different PBX models, the system
provides auto busy tone cadence learning to prevent the FXO from engaging a
line. However, if the line of the receiving party is engaged and his/her PSTN uses
a voice prompt to replace the traditional beep sound, then the system would not
be able to detect a busy tone. Silence detection should then be used to determine
whether or not to end the call.
CPT Auto Detect
• 2 PSTN phone numbers or 2 PBX extension lines are needed.
• Connect one of the phone sets to a FXO port.
• The line of “Dial Number” must be on-hook. Set the outgoing phone number the same as the phone
line that is in use as above, and click the “Accept” button to start detection.
• If detection is successful, the parameters obtained will automatically be inserted into the CPT
parameter.
• Save settings and restart the system.
Detailed description is given below:
Click “CPT auto detect” at the bottom of Trunk CPT Settings.
If CPT auto detect is used, the function would halt every operation of the Gateway. Select “I am sure of it”,
and then click the “Accept” button. Wait for 15 seconds, and then you will enter CPT auto detect window.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 51
YML832 Rev1
Page 52

Direct Connection to PSTN
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
• Connect one of the trunk lines to the Gateway FXO Port.
• The line of “Dial Number” (36008913) must be on-hook.
• Detect Channel: Enter 3 (if the trunk line is connected to P3, and uses P3 for outgoing detection).
• Phone Number: Enter the number of the FXO line.
• Dial Number: Enter the number of the end to be tested—36008913.
• CPT group: Enter the group to save your settings to once the test has been completed.
• Finally, click the “Accept” button.
Detection in Progress: during detection, the following windows will appear.
52 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 53

Once detection of a busy tone is in progress, the system will dial the number to be tested (in this case
36008913). After it rings pick up the phone and enter”#”, then hang up. The system will then detect a
busy tone automatically.
After detecting it will be as below:
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 53
YML832 Rev1
Page 54

Connected to a PBX Extension Line
If the gateway is connected to a PBX extension line, then the busy tone of both the PBX and the PSTN
must be detected.
Connecting to a PBX extension line and detecting the busy tone of the PBX
36008913
307
301
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
• Connect one of the PBX extension lines to the Gateway FXO Port.
• Detect Channel: Enter 4 (if the trunk line is connected to P4, and uses P4 for outgoing detection).
• Phone Number: Set the number of the FXO line –to detect Reorder Tone.
• Dial Number: Enter the number of the end to be tested—307.
• CPT group: Enter the group to save your settings to once the test has been completed.
• Finally, click the “Accept” button.
54 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 55

Connected to a PBX extension line to detect the busy tone of PSTN
36008913
36008914
307
301
Note: The above diagrams show a 4-port SmartVoice gateway for illustration purposes.
An 8, 16 or 32 port SmartVoice gateway could also be used depending upon your
network requirements.
• Connect one of the PBX extension lines to the gateway’s FXO Port.
• Detect Channel: Enter 3 (if the trunk line is connected to P3, and uses P3 for outgoing detection).
• Phone Number: Set the number of FXO line –to detect Reorder Tone.
• Dial Number: Enter the trunk prefix of a PBX, comma, and the number of the end to be tested
-- 0,36008913. (Assuming that an extension line is set to dial 0 to make outgoing calls).
• CPT group: Enter the group to save your settings to once the test has been completed. If
connecting the gateway to a PBX extension line, please do not set the detected busy tone of the PBX
and the PSTN in the same set, otherwise the value detected the first time will be overwritten.
• Finally, click the “Accept” button.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 55
YML832 Rev1
Page 56

Filling in the CPT Table
Fill in the table after the detection is completed as below, where the values are the frequency and Onand-Off ratio detected. Please click the “Accept” button. If connecting the Gateway to a PBX extension
line, please do not set the detected busy tone of the PBX and the PSTN in the same set, otherwise the
value detected the first time will be overwritten.
Save Settings
Save the settings and restart the system after the test is completed. Then click the “Accept” button. The
Gateway will use the new parameter to detect whether a call has ended.
56 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 57

Current Status and System Information
These two pages show that the status of VoIP Gateway. There are Port Status, Server Registration Status,
WAN Port Information, LAN Port Information and Hardware.
• Port Status: It includes if each port registers to Proxy successfully, the lasted dialed number, how
many calls each port had since the system is start, etc.
• Server Registration Status: It shows the registration status of DDNS, Phone Book Manager, STUN
and UPnP.
• WAN Port Information: It shows IP address, subnet mask, default gateway and DNS server. If you
use PPPoE to obtain IP, you can know if the IP is obtained through this.
• LAN Port Information: It shows LAN port IP, subnet mask, and the status of DHCP server.
• Hardware: It shows the hardware platform.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 57
YML832 Rev1
Page 58

RTP Packet Summary
Displays the information of the last finished call. It contains peer IP, peer port, packets sent, packet
received and packet lost. Press the Refresh button to get the latest RTP Packet Summary. Voice quality
can be degraded significantly if packet lost exceeds 5%. To avoid high packet loss, you need either to
increase your broadband bandwidth or configure your QoS in your broadband router.
58 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 59

STUN Inquiry
Using “STUN Inquiry” to detect your IP sharing device’s NAT type and communication between STUN
server and client (built-in SmartVoice gateway).
NOTE: If detected NAT type is “Symmetric NAT”, then the gateway is not able
to traverse the NAT of your Internet sharing devices. This is not a flaw of the
gateway’s design, but nature of STUN protocol design.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 59
YML832 Rev1
Page 60

Ping Test
Use “ping” to identify if the remote peer is reachable. Fill in remote IP address and click “Test” will start
the test.
60 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 61

Port Filtering
Port filtering enables you to control all data that can be transmitted in routers; principles of filtering-
--When the port used at the source end is within the limited scope, it will be filtered without
transmission.
• Enable port filtering: whether to enable this function or not.
• Port Range: Set the range of port to be filtered, suppose it is 80 and when use protocol is Both or
TCP, all computers will be unable to use the services of http (port 80)— will be unable to browse
normal Web pages.
NOTE: If you filter port 80, it will also block you from web access to the gateway.
So be careful with these settings.
• TCP/UDP: Choose to either filter TCP or UDP, or choose to filter both.
• Remark: Remark field, you can write comments by yourself.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 61
YML832 Rev1
Page 62

IP Filtering
IP Filtering is to limit internal users from accessing the Internet.
• IP: Input the IP address that you want to filter; the limited IP address will be unable to transmit the
data to the Internet.
• TCP/UDP: Choose to either filter TCP or UDP, or choose to filter both.
• Remark: Remark filed, you can write comments by yourself.
62 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 63

MAC Filtering
MAC (Media Access Control) address filtering is to filter the transmission of data by network card
physical address.
MAC: input MAC that will be limited to accessing Internet.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 63
YML832 Rev1
Page 64

Virtual Server
Enabling the users on Internet to access the WWW, FTP and other services under your NAT. When remote
user are accessing Web or FTP servers through WAN end IP address, it will be routed to the server at the
internal LAN end and be routed to the server at the internal LAN end as appropriate in accordance with
the externally required services.
• WAN Port Range: Input the port on the WAN side.
• TCP/UDP: Select the communication protocols used by the server—TCP or UDP.
• LAN Host IP Address: Input IP address that provides various services servers.
• Server Port Range: Input the port used by the LAN host.
64 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 65

DMZ
Lets the server on the LAN to be directly exposed to the Internet for accessing data. Either this function
or the virtual server can be selected for use.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 65
YML832 Rev1
Page 66

URL Filter
URL filter is used to deny device from LAN accessing specific web sites. The system will
block the URL that contains the string.
66 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 67

Special Applications
Provide multiple connections for special applications.
• Name: The name of the special application.
• Incoming Type: The protocol used by the special application.
• Incoming Port range: Port range on the WAN side that will be used to access the application.
• Trigger Type: The protocol used to trigger the application.
• Trigger Port Range: Port range used to trigger the application.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 67
YML832 Rev1
Page 68

DoS Prevention Settings
• Enable DoS Prevention: To prevent DoS from WAN.
• Enable DoS Prevention on LAN: To prevent DoS from LAN.
• Packet/Second: If the same type of packets received in one second is more than the specified value,
then it will be treated as attacks. And VoIP gateway will block the IP if you checked “Enable Source
IP Blocking”.
68 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 69

• Enable Source IP Blocking: Block the IP.
• Blocking Time: The time to block the IP.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 69
YML832 Rev1
Page 70

NTP (Network Time Protocol)
Time Zone: Set the Time Zone where VoIP gateway resides.
Time Server #1~#3: Set the Time Server where VoIP gateway should sync up during start up. (NTP
protocol)
Backup and Restore (Configuration)
You can backup settings to a file and restore settings from that file. You also can restore all settings back
to default by selecting Restore Default Configurations and click Restore.
NOTE: It needs to Save Settings and Restart, and all settings will back up default
settings or have new setting that you upload.
• Configuration File: Backup the all settings.
• Configuration Template File: Backup the settings as template file for editing.
70 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 71

Provision Settings
Options in this section are only required for VoIP networks in which provisioning system has
implemented.
Fill in the parameters needed of Provision Server from your service provider.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 71
YML832 Rev1
Page 72

System Operations (Save Settings)
Some settings are effective by Restart. Remember to save all settings by Save Settings before to
restart.
• Save Settings: Save settings after completing. The new settings will take effect after the system is
restarted. Please select “Save Settings”.
• Restart: If it is necessary to restart the system, please select “Restart” and click the
“Accept” button.
72 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 73

Software Upgrade
Gateway provides software upgrade function from a remote end. Please consult your service provider for
all following details.
• Upgrade Server: Choose the server type.
• Software Upgrade Server IP: Enter the software server IP address.
• Software Upgrade Server Port: Enter the port that server uses. TFTP is 69, FTP is 21 and
SmartVoice gateway upgrade server is 6001.
• User Name/ Password: The account to access FTP server.
• Directory: The path of TFTP or FTP.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 73
YML832 Rev1
Page 74

Logout
Gateway only allows one user to login at a time, so whenever a change is made, please save the
settings, restart the system, or logout to avoid the situation where other users cannot login to change
settings.
74 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 75

4. Configuring the Gateway via IVR
Preparation
• Install the Gateway according to the instructions as described in Chapter 2.
• If a static IP is used, confirm the desired IP settings of the WAN Port (IP address, Subnet Mask, and
Default gateway). Please contact your local Internet Service Provider (ISP) if you have any questions.
• If using dialup ADSL (PPPoE) for network connection, confirm your broadband account name and
password.
• If users wish to build a Gateway under the NAT, Gateway WAN Port IP address and LAN Port should
not use the same range. This is to avoid phone failures.
Configuration Methods
The gateway provides two configuration options:
1) Web Interface
2) Telephone IVR (Interactive Voice Response)
The IVR provides basic query and configuration, while the Web interface provides a full configuration.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 75
YML832 Rev1
Page 76

IVR (Interactive Voice Response)
The gateway provides a convenient IVR function. Users only need to pick up a handset and enter the
function code for the query and setting. A PC is not required.
NOTE: After finishing the settings, make sure the new settings are saved. This is
so that the new settings will take effect after the system is restarted.
Instructions
FXS Port:
1. Connected the Gateway to the telephones as required.
2. To access the gateway via IVR, pick up the handset and press ***[password]#. Convert your
password to a numerical sequence.The character to number conversion can be acquired from
PPPoE Character Conversion Table on page 86.
3. After entering a correct IVR password, you will hear a indication tone which is beep tones about
approximate 1 second apart, now the system is in IVR mode. Enter function codes to check or set
the gateway configurations.
For example: The factory default IVR access password is “admin”. Enter ***4144534954#, you are
now in IVR setting mode, enter a function code to check or configure the gateway. If your password
is “1234”, then enter **1234# to enter IVR setting mode.
FXO Port:
1. Connect the Gateway to the PSTN line as required.
2. To access the gateway via IVR, dial the phone number of the FXO Port using an external line. You will
hear the instruction “enter value”.
3. Enter the IVR password. The factory default code is “admin”. Enter ***4144534954# as above. You
are now in the IVR setting mode. Refer to the IVR Function Table over the page for the query codes.
4. Once the first setting or query has been completed, you will hear the tone indication again . Then
use the same procedure to make a second query or setting.
5. Dial 509 to save the settings and wait for about 3 seconds for the confirmation tone. To exit IVR
mode, simply hang up the phone.
Example:
enter the password ***4144534954# (You are now in IVR mode)
enter 101 (to query IP address of the gateway’s WAN port)
the system responds with an IP address
you can continue with more settings or queries: enter 111 (to set IP address)
enter 192*168*1*2 (IP number).
Inquire Current Gateway’s WAN Port IP address
After entering IVR mode, dial 101. The system will repeat the current WAN Port IP address. If the system
does not repeat the IP address, it indicates that the Gateway fails to get an IP from DHCP or PPPoE.
Please check that the cable connection, account number, and password are correct.
Save Settings
After entering IVR mode, dial 509 (Save Settings). Wait for about 3 seconds and after hearing a
confirmation tone “1”, hang up the phone. Please reboot the Gateway to enable the new settings.
76 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 77

IVR Functions Table
Function Code Description Example
111/101 WAN Port IP address Set/Query Use in conjunction with function code 114, select
112/102 WAN Port Subnet Mask Set/Query
113/103 WAN Port Default Gateway Set/Query
114/104 Current Network IP Access Set/Query (1:
Static IP, 2.DHCP, 3.PPPoE)
115/105 DNS IP address Set/Query
116/106 Phone book manager IP address Set/Query Must use 116/106, 117/107 in conjunction with
117/107 Set/Query whether or not to use Public
Telephone Book (0: Disable 1:Enable)
199/099 Set/Query whether or not this Gateway acts
as the phone book manager (0: Disable 1:
Enable)
066 Query the connection to Phone book manager
118 Restart
121 Setting PPPoE Account Use in conjunction with function code 114, select
122 Setting PPPoE Password
123 Setting NAT router public IP address Must use 123 and 124 in conjunction with each
124 Uses NAT router port forwarding (0: Disable
1: Enable)
151/141 Register to Proxy Server Set/Query (0: Disable
1: Enable)
152/142 Proxy Server IP address Set/Query
153/143 Proxy Server Port Set/Query
125 Set Proxy Server account
126 Set Proxy Server password
154/144 Uses STUN Set/Query (0: Disable 1: Enable)
155/145 STUN IP address Set/Query
156/146 STUN Port Set/Query
311/301 LAN Port IP address Set/Query
312/302 LAN Port Subnet Mask Set/Query
131/132 Play/Record greeting message
133 Saving greeting message
211/201 Set/Query International Prefix code Prefix dialed before making an international call
212/202 Set/Query Country Code Setting country code, e.g. 61
213/203 Set/Query Area Prefix Code (Long-Distance
Prefix Code)
214/204 Set/Query Area Code eg. “02” for NSW.
1 for a Static IP function.
each other.
3 for a PPPoE function
other.
e.g. 0011.
Prefix dialed before making a long-distance call
e.g. 0.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 77
YML832 Rev1
Page 78

Function Code Description Example
215/205 Set/Query Gateway Telephone Number
216/206 Set/Query the extension number of Line 1.
217/207 Set/Query the gateway web configuration interface
109 Restoring factory default IP address configuration A static IP address for WAN Port
409 Restoring factory default settings
509 Save settings
209 Soft Upgrade
(Representative Number)
port number
IP: 192.168.1.2
Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.1.254
78 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 79

IP Configuration Settings (WAN port)
Static IP Settings
NOTE: Complete static public/private IP settings should include a static IP (Option
1 under 114), IP address (111), Subnet Mask (112), and Default Gateway (113).
Please contact your local Internet Service Provider (ISP) if you have any questions.
Function Command
Select a Static IP • After entering IVR mode, dial 114.
• After hearing “Enter value”, dial 1 (to select static IP)
IP address Settings • After entering IVR mode, dial 111. After hearing “Enter value”, enter
Subnet Mask Settings • After entering IVR mode, dial 112. After hearing “Enter value”, enter
Default Gateway Settings • After entering IVR mode, dial 113. After hearing “Enter value”, enter
Save Settings and Restart • To save settings, dial 509 (Save Settings). The system will save the
your IP address, followed by “#”.
Example: If the IP address is 192.168.1.200, dial 192*168*1*200#.
your subnet mask, followed by “#”.
Example: If the mask value is 255.255.255.0, dial 255*255*255*0#.
your default gateway’s IP address, followed by “#”.
Example: If the Default Gateway is 192.168.1.254, dial 192*168*1*254#.
settings. Please restart the system. Wait for about 40 seconds for the
system to restart, and then enter 101 to check if the IP address is
retained. If the IP address is not repeated, it indicates that Gateway has
not been properly connected; please check if the cable connection is
correct.
Dynamic IP (DHCP) Settings
After entering IVR mode, dial 114.
After hearing “Enter value”, dial 2 (to select DHCP).
Saving settings –press 509 (Save Settings). Please restart the system. After the system is restarted,
press 101 to check if the IP address is retained.
NOTE: If the system does not repeat the IP address, it indicates that the Gateway
failed to communicate with a DHCP server. Please check your DHCP server or
consult your ISP if they issue an IP address to you via DHCP protocol.
ADSL PPPoE Settings
NOTE: Complete PPPoE settings should include: Select PPPoE (Option 3 of 114),
PPPoE account (121) and PPPoE password (122).
Please contact your local Internet Service Provider (ISP) if you have any questions.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 79
YML832 Rev1
Page 80

Select PPPoE
• After entering IVR mode, dial 114.
• After hearing “Enter value”, dial 3 (to select PPPoE).
PPPoE Account Settings
• After entering IVR mode, dial 121.
• After hearing “Enter value”, enter the account number, followed by ”#”.
Example: If the account is “0284943122@isp.com.au”, please enter 0 208 04 09 04 03 01 02 02 71 49 59 56
72 43 55 53 #.
Please note that it is necessary to enter two digits for each character/number; for example, enter “01”
for “1” and “11” for “A”.
It is recommended that you use the Web Interface to configure your PPPoE account details to make your
life easier. Refer to the PPPoE Character Conversion table on the following page for key mappings.
PPPoE Password Setting
• After entering IVR mode, dial 122 after hearing “enter value” followed by “#”.
Example: If the password is “3ttixike”, please enter “03 60 60 49 64 49 51 45#”.
Save Settings and Restart
To save settings, dial 509 (Save Settings). The system will save the settings. Please restart the system.
Wait for about 40 seconds for the system to restart, and then enter 101 to check if the IP address is
retained. If the IP address is not repeated, it indicates that the Gateway has not been properly connected.
Please check that the cable connection, account, or password are correct.
Recorded Voice File
• The gateway allows users to record their incoming call greeting message, when calling via FXO
(transit-in calls).
• After entering IVR mode, dial 132. After hearing “Enter value”, record the incoming call greeting
message. To end recording, simply hang up.
• To listen to the recorded message, press 131. Press 133 to save the message.
• To use (activate) recorded greeting voice for transit-in calls, choose “Recorded voice file” option in
“Trunk Incoming Prompt Voice”.
80 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 81

PPPoE Character Conversion Table
Number Input Key Upper Case
000A11A41@71
101B12B42•72
202C13C43 ! 73
303D14D44 “74
404E15E45$75
505F16F46%76
606G17G47&77
707H18H48 ‘ 78
808I19I49(79
909J20J50 ) 80
Letter
K21K51+81
L22L52,82
M23M53 - 83
N24N54 / 84
O25O55 : 85
P26P56 ; 86
Q27Q57<87
R28R58=88
S29S59>89
T30T60?90
U31U61 [ 91
V32V62 \92
W33W63 ] 93
X34X64^94
Y35Y65_95
Z36Z66 { 96
Input Key Lower Case
Letter
Input Key Symbol Input Key
|97
}98
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 81
YML832 Rev1
Page 82

5. Dialing and dialed number routing principle
g
y
Instruction
• After a phone number is entered, dial # to call out immediately or, wait until the “Inter DTMF
Timeout” expires (defined in “Advanced Options”, default=4 seconds).
• If the phone number fits the setting of Digit Map, the gateway dials out the phone number through
the assigned interface automatically.
• The phone number should have at least 2 digits (not including * and #).
Dialed Number Processing Flow
To maintain maximum flexibility, the number dialed will be looked up from several tables defined in the
gateway. Once no match can be found, it will look up again from the registered SIP Proxy Server. The
look up flow is shown below:
Speed Dial
Table
Extension
Number
A complete flow chart is on the next page.
Local Phone
Book
Phone Book
Mana
er
SIP
Prox
82 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 83

p
Start
Enter a phone
number (D#)
Dial the number
defined in
SpeedDial table
Dial (D#) through
the first available
FXO port to PSTN
Yes
Yes
Is (D#)
defined in Speed
Dial table?
No
Is (D#)
defined in Extension
table?
No
Is (D#)
defined in Phonebook
defined in Phonebook
defined in SIP proxy
table?
No
Is (D#)
Manager?
No
Is (D#)
server?
No
Does this
gateway has an
FXO
ort?
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Dial out as defined
in the first matc h
case through the
gateway
No
End
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 83
YML832 Rev1
Page 84

Appendix A: Glossary
10BASE-T A designation for the type of wiring used by Ethernet networks with a data rate of
100BASE-T A designation for the type of wiring used by Ethernet networks with a data rate of
ADSL Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line. The most commonly deployed type of
analog Of data, having a form is analogous to the data’s original waveform. The voice
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode A standard for high-speed transmission of data, text,
authenticate To verify a user’s identity, such as by prompting for a password.
binary The “base two” system of numbers, that uses only two digits, 0 and 1, to represent
bit Short for “binary digit,” a bit is a number that can have two values, 0 or 1. See also
bps bits per second
bridging Passing data from your network to your ISP and vice versa using the hardware
broadband A telecommunications technology that can send different types of data over the
Broadcast To send data to all computers on a network.
CO Central Office A circuit switch that terminates all the local access lines in a
DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP automates address assignment and
10 Mbps. Also known as Category 3 (CAT 3) wiring. See also data rate, Ethernet.
100 Mbps. Also known as Category 5 (CAT 5) wiring. See also data rate, Ethernet.
DSL for home users. The term asymmetrical refers to its unequal data rates for
downloading and uploading (the download rate is higher than the upload rate).
The asymmetri cal rates benefit home users because they typically download much
more data from the Internet than they upload.
component in DSL is an analog signal. See also digital.
voice, and video, widely used within the Internet. ATM data rates range from 45
Mbps to 2.5 Gbps. See also data rate.
all numbers. In binary, the number 1 is written as 1, 2 as 10, 3 as 11, 4 as 100,
etc. Although expressed as decimal numbers for convenience, IP addresses in
actual use are binary numbers; e.g., the IP address 209.191.4.240 is 1101000
1.10111111.00000100.11110000 in binary. See also bit, IP address, network
mask.
binary.
addresses of the devices at each location. Bridging contrasts with routing, which
can add more intelligence to data transfers by using network addresses instead.
The My ADSL Modem can perform both routing and bridging. Typically, when both
functions are enabled, the device routes IP data and bridges all other types of data.
See also routing.
same medium. DSL is a broadband technology.
particular geographic serving area; a physical building where the local switching
equipment is found. xDSL lines running from a subscriber’s home connect at their
serving central office.
management. When a computer connects to the LAN, DHCP assigns it an IP address from a shared pool of IP addresses; after a specified time limit, DHCP returns
the address to the pool.
84 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 85

DHCP relay Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol relay. A DHCP relay is a computer that
DHCP server Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server. A DHCP server is a computer that is
digital Of data, having a form based on discrete values expressed as binary numbers (0’s
DNS Domain Name System. The DNS maps domain names into IP addresses. DNS
domain name A domain name is a user-friendly name used in place of its associated IP address.
download To transfer data in the downstream direction, i.e., from the Internet to the user.
DSL Digital Subscriber Line A technology that allows both digital data and analog voice
Ethernet Local area network traffic will be carried by standard Category 5 cable referred to
Filtering To screen out selected types of data, based on filtering rules. Filtering can be ap-
filtering rule A rule that specifies what kinds of data a routing device will accept and/or reject.
Firewall Any method of protecting a computer or LAN connected to the Internet from intru-
FTP File Transfer Protocol - A program used to transfer files between computers con-
GGP Gateway to Gateway Protocol. An Internet protocol that specifies how gateway rout-
Gbps Abbreviation for Gigabits (GIG-uh-bits) per second, or one billion bits per second.
GRE Generic Routing Encapsulation. TCP/IP protocol suite, transport layer encapsulation
forwards DHCP data between computers that request IP addresses and the DHCP
server that assigns the addresses. Each of the My ADSL Modem’s interfaces can
be configured as a DHCP relay. See DHCP.
responsible for assigning IP addresses to the computers on a LAN. See DHCP.
and 1’s). The data component in DSL is a digital signal. See also analog.
information is distributed hierarchically throughout the Internet among computers
called DNS servers. When you start to access a web site, a DNS server looks up
the requested domain name to find its corresponding IP address. If the DNS server
cannot find the IP address, it communicates with higher-level DNS servers to
determine the IP address. See also domain name.
For example, www.globespan.net is the domain name associated with IP address
209.191.4.240. Domain names must be unique; their assignment is controlled
by the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN). Domain
names are a key element of URLs, which identify a specific file at a web site, e.g.,
http://www.netcomm.com.au. See also DNS.
signals to travel over existing copper telephone lines.
as Ethernet. The most commonly installed computer network technology, usually
using twisted pair wiring. Ethernet data rates are 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps. See also
BASE-T,100BASE-T, twisted pair.
plied in one direction (upstream or down stream), or in both directions.
Filtering rules are defined to operate on an interface (or multiple interfaces) and in
a particular direction (upstream, downstream, or both).
sion or attack from the outside. Some firewall protection can be provided by packet
filtering and Network Address Translation services.
nected to the Internet. Common uses include uploading new or updated files to a
web server, and downloading files from a web server.
ers communicate with each other.
Internet data rates are often expressed in Gbps.
protocol.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 85
YML832 Rev1
Page 86

hop When you send data through the Internet, it is sent first from your computer to a
hop count The number of hops that data has taken on its route to its destination. Alterna-
host A device (usually a computer) connected to a network.
HTTP Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol HTTP is the main protocol used to transfer data from
ICMP Internet Control Message Protocol An Internet protocol used to report errors and
IGMP Internet Group Management Protocol An Internet protocol that enables a computer
in-line filter See Microfilter
Internet The global collection of interconnected networks used for both private and busi-
intranet A private, company-internal network that looks like part of the Internet (users ac-
IP See TCP/IP.
IP address Internet Protocol address The address of a host (computer) on the Internet,
ISP Internet Service Provider A company that provides Internet access to its customers,
LAN Local Area Network A network limited to a small geographic area, such as a home,
LED Light Emitting Diode An electronic light-emitting device. The indicator lights on the
MAC address Media Access Control address The permanent hardware address of a device,
mask See network mask.
Mbps Abbreviation for Megabits per second, or one million bits per second. Network data
router, and then from one router to another until it finally reaches a router that is
directly connected to the recipient. Each individual “leg” of the data’s journey is
called a hop.
tively, the maximum number of hops that a packet is allowed to take before being
discarded , See also TTL.
web sites so that it can be displayed by web browsers. See also web browser
other network-related information. The ping command makes use of ICMP.
to share information about its membership in multicast groups with adjacent
routers. A multicast group of computers is one whose members have designated
as interested in receiving specific content from the others. Multicasting to an IGMP
group can be used to simultaneously update the address books of a group of
mobile computer users or to send company newsletters to a distribution list.
ness communications.
cess information using web browsers), but is accessible only by employees.
consisting of four numbers, each from 0 to 255, separated by periods, e.g.,
209.191.4.240. An IP address consists of a network ID that identifies the particular
network the host belongs to, and a host ID uniquely identifying the host itself on
that network. A network mask is used to define the network ID and the host ID.
Because IP addresses are difficult to remember, they usually have an associated
domain name that can be specified instead. See also domain name, network mask.
usually for a fee.
office, or small building.
front of the My ADSL Modem are LEDs.
assigned by its manufacturer. MAC addresses are expressed as six pairs of characters.
rates are often expressed in Mbps.
86 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 87

Microfilter In splitterless deployments, a microfilter is a device that removes the data frequen-
NAT Network Address Translation A service performed by many routers that translates
NAT rule A defined method for translating between public and private IP addresses on your
network A group of computers that are connected together, allowing them to communicate
network mask A network mask is a sequence of bits applied to an IP address to select the
NIC Network Interface Card An adapter card that plugs into your computer and provides
Pass-through Line The line that connects the NB9/NB9W to a POTS line may be referred to as a pass-
packet Data transmitted on a network consists of units called packets. Each packet con-
ping Packet Internet (or Inter-Network) Groper A program used to verify whether the host
port A physical access point to a device such as a computer or router, through which
POTS Plain Old Telephone Service Traditional analog telephone service using copper
POTS splitter See splitter.
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol A protocol for serial data transmission that is used to
PPPoA Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM One of the two types of PPP interfaces you can
PPPoE Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet One of the two types of PPP interfaces you
cies in the DSL signal, so that telephone users do not experience interference
(noise) from the data signals. Microfilter types include in-line (installs between
phone and jack) and wall-mount (telephone jack with built-in microfilter). See also
splitterless.
your network’s publicly known IP address into a Private IP address for each
computer on your LAN. Only your router and your LAN know these addresses; the
outside world sees only the public IP address when talking to a computer on your
LAN.
LAN.
with each other and share resources, such as software, files, etc.A network can be
small, such as a LAN, or very large, such as the Internet.
network ID while ignoring the host ID. Bits set to 1 mean “select this bit” while bits
set to 0 mean “ignore this bit.” For example, if the network mask 255.255.255.0 is
applied to the IP address 100.10.50.1, the network ID is 100.10.50, and the host
ID is 1. See also binary, IP address, subnet
the physical interface to your network cabling, which for Ethernet NICs is typically
an RJ-45 connector. See Ethernet, RJ-45.
through line
tains a payload (the data), plus overhead information such as where it came from
(source address) and where it should go (destination address).
associated with an IP address is online. It can also be used to reveal the IP address
for a given domain name.
data flows into and out of the device.
telephone lines. Pronounced pots. See also PSTN.
carry IP (and other protocol) data between your ISP and your computer. The WAN
interface on the My ADSL Modem uses two forms of PPP called PPPoA and PPPoE.
See also PPPoA, PPPoE.
define for a Virtual Circuit (VC), the other type being PPPoE. You can define only
one PPPoA interface per VC.
can define for a Virtual Circuit (VC),the other type being PPPoA. You can define one
or more PPPoE interfaces per VC.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 87
YML832 Rev1
Page 88

protocol A set of rules governing the transmission of data. In order for a data transmission
remote In a physically separate location. For example, an employee away on travel who
RIP Routing Information Protocol The original TCP/IP routing protocol. There are two
RJ-11 Registered Jack Standard-11 The standard plug used to connect telephones,
RJ-45 Registered Jack Standard-45 The 8-pin plug used in transmitting data over phone
routing Forwarding data between your network and the Internet on the most efficient
rule See filtering rule, NAT rule.
SDNS Secondary Domain Name System (server) A DNS server that can be used if the
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol The TCP/IP protocol used for network
splitter A device that splits off the voice component of the DSL signal to a separate line, so
splitterless A type of DSL installation where no splitter is installed, saving the cost of a service
subnet A subnet is a portion of a network. The subnet is distinguished from the larger net-
subnet mask A mask that defines a subnet. See also network mask.
TCP See TCP/IP.
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol The basic protocols used on the
Telnet An interactive, character-based program used to access a remote computer. While
to work, both ends of the connection have to follow the rules of the protocol.
logs in to the company’s intranet is a remote user.
versions of RIP: version and version II.
fax machines, modems, etc. to a telephone jack. It is a 6-pin connector usually
containing four wires.
lines. Ethernet cabling usually uses this type of connector.
route, based on the data’s destination IP address and current network conditions. A
device that performs routing is called a router.
primary DSN server is not available. See DNS.
management.
that data and telephone service each have their own wiring and jacks. The splitter
is installed by your telephone company where the DSL line enters your home. The
CO also contains splitters that separate the voice and data signals, sending voice
to the PSTN and data on high-speed lines to the Internet. See also CO, PSTN,
splitterless, microfilter.
call by the telephone company. Instead, each jack in the home carries both voice
and data, requiring a microfilter for each telephone to prevent interference from the
data signal. ADSL is usually splitterless; if you are unsure if your installation has a
splitter, ask your DSL provider. See also splitter, microfilter.
work by a subnet mask which selects some of the computers of the network and
excludes all others. The subnet’s computers remain physically connected to the
rest of the parent network, but they are treated as though they were on a separate
network. See also network mask.
Internet. TCP is responsible for dividing data up into packets for delivery and reassembling them at the destination, while IP is responsible for delivering the packets
from source to destination. When TCP and IP are bundled with higher-level applications such as HTTP, FTP, Telnet, etc., TCP/IP refers to this whole suite of protocols.
HTTP (the web protocol) and FTP only allow you to download files from a remote
computer, Telnet allows you to log into and use a computer from a remote location.
88 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 89

TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol. A protocol for file transfers, TFTP is easier to use than
TTL Time To Live A field in an IP packet that limits the life span of that packet. Originally
twisted pair The ordinary copper telephone wiring long used by telephone companies. It con-
upstream The direction of data transmission from the user to the Internet.
USB Universal Serial Bus A serial interface that lets you connect devices such as print-
VC Virtual Circuit A connection from your ADSL router to your ISP.
VCI Virtual Circuit Identifier Together with the Virtual Path Identifier (VPI), the VCI
VPI Virtual Path Identifier Together with the Virtual Circuit Identifier (VCI), the VPI
VSP VoIP Service provider
WAN Wide Area Network Any network spread over a large geo graphical area, such as
Web browser A software program that uses Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to download
Web page A web site file typically containing text, graphics and hyperlinks (cross-references)
Web site A computer on the Internet that distributes information to (and gets information
WLAN Wireless Local Area Network
WWW World Wide Web Also called (the) Web. Collective term for all web sites anywhere in
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) but not as capable or secure.
meant as a time duration, the TTL is usually represented instead as a maximum
hop count; each router that receives a packet decrements this field by one. When
the TTL reaches zero, the packet is discarded.
tains one or more wire pairs twisted together to reduce inductance and noise. Each
telephone line uses one pair. In homes, it is most often installed with two pairs. For
Ethernet LANs, a higher grade called Category 3 (CAT 3) is used for 10BASE-T networks, and an even higher grade called Category 5 (CAT 5) is used for 100BASE-T
networks. See also 10BASE-T, 100BASE-T, Ethernet.
ers, scanners, etc. to your computer by simply plugging them in. The My ADSL
Modem is equipped with a USB interface for connecting to a stand-alone PC.
uniquely identifies a VC. Your ISP will tell you the VCI for each VC they provide. See
also VC.
uniquely identifies a VC. Your ISP will tell you the VPI for each VC they provide. See
also VC.
a country or continent. With respect to the My ADSL Modem, WAN refers to the
Internet.
information from (and upload to) web sites, and displays the information, which
may consist of text, graphic images, audio, or video, to the user. Web browsers
use Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Popular web browsers include Netscape
Navigator and Microsoft Internet Explorer. See also HTTP, web site, WWW.
to the other pages on that web site, as well as to pages on other web sites. When a
user accesses a web site, the first page that is displayed is called the Home page.
See also hyperlink, web site.
from) remote users through web browsers. A web site typically consists of web
pages that contain text, graphics, and hyperlinks. See also hyperlink, web page.
the world that can be accessed via the Internet.POTS A telephone line used
for a standard phone-line and service will be referred to as POTS (=Plain Old
Telephone Service)
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 89
YML832 Rev1
Page 90

Appendix B: Cable Information
This cable information is provided for your reference only. Please ensure you only connect the appropriate cable
into the correct socket on either this product or your computer.
If you are unsure about which cable to use or which socket to connect it to, please refer to the hardware
installation section in this manual. If you are still not sure about cable connections, please contact a professional
computer technician or NetComm for further advice.
RJ-45 Network Ports
RJ-45 Network Ports can connect any networking devices that use a standard LAN interface, such as a
Hub/Switch Hub or Router. Use unshielded twisted-pair (UTP) or shield twisted-pair (STP) cable to connect the
networking device to the RJ-45 Ethernet port. Depending on the type of connection, 10Mbps or 100Mbps, use
the following Ethernet cable, as prescribed.
10Mbps: Use EIA/TIA-568-100-Category 3, 4 or 5 cable.
100Mbps: Use EIA/TIA-568-100-Category 5 cable.
Note: To prevent loss of signal, make sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection
does not exceed 100 metres.
RJ-45 Connector
Pin Assignment Normal Assignment
1 Input Receive Data +
2 Input Receive Data -
3 Output Transmit Data +
6 Output Transmit Data -
4,5,7,8 Not used
Figure 1
RJ-45 plug attached
to cable
Figure 2
90 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 91

Straight and crossover cable configuration
There are two types of the wiring: Straight-Through Cables and Crossover Cables. Category 5 UTP/STP cable has
eight wires inside the sheath. The wires form four pairs. Straight-Through Cables has same pinouts at both ends
while Crossover Cables has a different pin arrangement at each end.
In a straight-through cable, wires 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 and 8 at one end of the cable are still wires 1~8 at the other end.
In a crossover cable, the wires of 1,2,3,6 are reversed so that wire 1 become 3 at the other end of the cable, 2
becomes 6, and so forth.
To determine which wire is wire 1, hold the RJ-45 cable tip with the spring clip facing towards the ground and the
end pointing away from you. The copper wires exposed upwards to your view. The first wire on the far left is wire
1. You can also refer to the illustrations and charts of the internal wiring on the following page.
Straight-Through Cabling
Figure 3
Wire Becomes
1 1
2 2
3 3
6 6
Cross-Over Cabling
Figure 4
Wire Becomes
1 3
2 6
3 1
6 2
Note: To prevent loss of signal, make sure that the length of any twisted-pair connection
does not exceed 100 metres.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 91
YML832 Rev1
Page 92

Appendix C: Registration and Warranty Information
All NetComm Limited (“NetComm”) products have a standard 12 month warranty from date of purchase against defects in manufacturing and that
the products will operate in accordance with the specifications outlined in the User Guide. However some products have an extended warranty
option (please refer to your packaging). To be eligible for the extended warranty you must supply the requested warranty information to NetComm
within 30 days of the original purchase by registering on-line via the NetComm web site at:
www.netcomm.com.au
Contact Information
If you have any technical difficulties with your product, please do not hesitate to contact NetComm’s Customer Support Department.
Email: support@netcomm.com.au
Fax: (+612) 9424-2010
Web: www.netcomm.com.au
Copyright Information
This manual is copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purposes of private study, research, criticism or review, as permitted under the
Copyright Act, no part may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form, by any means, be it electronic, mechanical,
recording or otherwise, without the prior written permission of NetComm Limited. NetComm Limited accepts no liability or responsibility, for
consequences arising from the use of this product. Please note that the images used in this document may vary slightly from those of the actual
product. Specifications are accurate at the time of the preparation of this document but are subject to change without notice.
NetComm Limited reserves the right to change the specifications and operating details of this product without notice. NetComm is a registered
trademark of NetComm Limited. All other trademarks are acknowledged the property of their respective owners.
92 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 93

Customer Information
ACA (Australian Communications Authority) requires you to be aware of the following information and warnings:
(1) This unit shall be connected to the Tel ecommu ni cation Network through a line cord which meets the requirements of the ACA
TS008 Standard.
(2) This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the Standards for C-Tick and or A-Tick as set by the ACA. These
standards are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio noise and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions detailed within this
manual, may cause interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur with the
installation of this product in your home or office. If this equipment does cause some degree of interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, we encourage the user to try to correct the interference
by one or more of the following measures:
• Change the direction or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between this equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an alternate power outlet on a different power circuit from that to which the receiver/TV is connected.
• Consult an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
(3) The power supply that is provided with this unit is only intended for use with this product. Do not use this power supply with any
other product or do not use any other power supply that is not approved for use with this product by NetComm. Failure to do so
may cause damage to this product, fire or result in personal injury.
SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide 93
YML832 Rev1
Page 94

Product Warranty
The warranty is granted on the following conditions:
1. This warranty extends to the original purchaser (you) and is not transferable;
2. This warranty shall not apply to software programs, batteries, power supplies, cables or other accessories supplied in or with the
product;
3. The customer complies with all of the terms of any relevant agreement with NetComm and any other reasonable requirements of
NetComm including producing such evidence of purchase as NetComm may require;
4. The cost of transporting product to and from NetComm’s nominated premises is your responsibility; and,
5. NetComm does not have any liability or responsibility under this warranty where any cost, loss, injury or damage of any kind,
whether direct, indirect, consequential, in ci den tal or otherwise arises out of events beyond NetComm’s reasonable control. This
includes but is not limited to: acts of God, war, riot, embargoes, acts of civil or military authorities, fire, floods, electricity outages,
lightning, power surges, or shortages of materials or labour.
6. The customer is responsible for the security of their computer and network at all times. Security features may be disabled within
the factory default settings. NetComm rec ommends that you enable these features to enhance your security.
The warranty is automatically voided if:
1. You, or someone else, use the product, or attempts to use it, other than as specified by NetComm;
2. The fault or defect in your product is the result of a voltage surge subjected to the product either by the way of power supply or
communication line, whether caused by thunderstorm activity or any other cause(s);
3. The fault is the result of accidental damage or damage in transit, including but not limited to liquid spillage;
4. Your product has been used for any purposes other than that for which it is sold, or in any way other than in strict accordance
with the user manual supplied;
5. Your product has been repaired or modified or attempted to be repaired or modified, other than by a qualified person at a service
centre authorised by NetComm; and,
6. The serial number has been defaced or altered in any way or if the serial number plate has been removed.
Limitations of Warranty
The Trade Practices Act 1974 and corresponding State and Territory Fair Trading Acts or legalisation of another Government (“the relevant acts”) in
certain circumstances imply mandatory conditions and warranties which cannot be excluded. This warranty is in addition to and not in replacement
for such conditions and warranties.
To the extent permitted by the Relevant Acts, in relation to your product and any other materials provided with the product (“the Goods”) the liability
of NetComm under the Relevant Acts is limited at the option of NetComm to:
• Replacement of the Goods; or
• Repair of the Goods; or
• Payment of the cost of replacing the Goods; or
• Payment of the cost of having the Goods repaired.
94 SmartVoice Gateway(s) User Guide
YML832 Rev1
Page 95

 Loading...
Loading...