Page 1

Page 2

2 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Contents
5
1.3 Initial set up for management .................................................................................................... 6
1.4 LED indicators information ........................................................................................................ 9
2. Web Management Function ...........................................................................................................10
2.1. Web Management Home Overview ...................................................................................... 10
2.2. Port status ............................................................................................................................. 11
2.3. Port Statistics ........................................................................................................................ 13
2.4. Show MAC Table ....................................................................................................................15
2.5. Administrator ......................................................................................................................... 16
2.6. TFTP Update Firmware ..........................................................................................................54
2.7. Configuration Backup ............................................................................................................ 55
2.8. Reset System ........................................................................................................................ 56
2.9. Reboot ...� 56
2.10. Event Logging ...................................................................................................................... 56
3. Console – Boot Loader .................................................................................................................. 57
3.1 1K X modem Firmware update ..............................................................................................58
3.2 TFTP Firmware update .......................................................................................................... 59
3.3 Set IP Address ....................................................................................................................... 59
3.4 Diagnose Sdram ....................................................................................................................60
4. Out-of-band Terminal mode management ...................................................................................... 61
4.1 Main Menu .............................................................................................................................62
4.2 Switch Static Configuration .................................................................................................... 63
4.3. Protocol Related Configuration ............................................................................................. 89
4.4. Status and Counters ...........................................................................................................104
4.5. Reboot Switch .................................................................................................................... 107
4.6. TFTP Update Firmware .......................................................................................................108
5. Application Examples .................................................................................................................... 110
5.1. VLAN application used with switch ...................................................................................... 110
5.2. Trunking Application used with switch ................................................................................. 112
5.3. “Single IP – Agent mode” application used with switch ........................................................ 112
5.4. “Single IP - Stacking mode” application used with switch ................................................... 117
5.5 Compatibility on Virtual Server and “Single IP” .................................................................... 122
Appendix A: Glossary of Terms ......................................................................................................... 124
Appendix B: Cable Information .......................................................................................................... 130
Appendix C: Registration and Warranty Information ........................................................................ 132
1. Introduction ....................................................................................................................................... 3
1.1 Unpacking ................................................................................................................................ 4
1.2 Installation .................................................................................................................................�
Page 3

NP2624M User Guide 3
YML827 Rev1
1. Introduction
The NP2624M switch is a high performance web-managed SNMP Layer 2 switch that provides
users with 24 x 10/100Mbps Ethernet and 2 x 1000Mbps Gigabit ports. This Switch has SNMP
management and remote control capabilities such as “Web Cluster”. The Gigabit module, which can
be copper or fibre media, supports 1000BASE-SX, 1000BASE-LX or 1000BASE-T, allowing users
to increase their network response time at gigabit speeds and with great flexibility. An RS-232 serial
port provides an easy way for to install and set-up the Switch.
Non-blocking and maximum wire speed performances are designed on all ports. The Switch not
only supports Auto-Negotiation, but also Auto-MDIX function on all switched 24 x 10/100Mbps RJ45 ports and two Gigabit Copper ports in both half or full duplex mode. The Auto-MDIX function
makes it convenient for the user, because it eliminates cabling on straight-line or cross-line issues.
The NP2624M switch provides a convenient way to operate layer 2 management through a web
browser. The User-friendly drop-down menus allow the user to easily learn, control and monitor the
Switch. It supports not only traditional SNMP function, but also RMON 1,2,3,9 groups for advanced
network analysis. A new management tool called “Single IP” provides the administrator an access
right to enter the private IP domain through a single real IP. Using this management tool, a network
manager can remotely control far-side servers in a private IP domain.
The Switch also supports both Port-based and Tag-based VLANs. To increase bandwidth
application, it supports 7 groups with up to 4 ports Trunk, and moreover, these trunk ports offer a
fail-over function and provide back up when one or more ports malfunction. A stacking mode is
introduced here to enhance the ability of VLAN. An integrated UI not only displays the link status
of the stacking sets, but also provides an easy way to set up the VLAN.
Total front access design with full LED status display provide easy installation, inspection and
maintenance in rack mount environments. An additional LED display of the fan status allows for
quick diagnosis of any over-heating.
Page 4

4 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
1.1 Unpacking
Open the shipping carton of the Switch and carefully unpack its contents, the carton should contain
the following items:
• One NP2624M port Fast Ethernet Layer 2 Switch.
• One Mounting Kit including 2 mounting brackets and screws.
• Four rubber feet with adhesive backing.
• One AC power cord.
• One RS-232 cable.
• One CD containing this User Guide.
Page 5

NP2624M User Guide 5
YML827 Rev1
1.2 Installation
You can use the following guidelines when choosing a place to install the Switch.
• The surface must support at least 3 kg. Do not place heavy objects on the Switch.
• You must be able to visually inspect the power cord and AC power connector.
• Ensure proper heat dissipation by making sure there is adequate ventilation around the
Switch.
Desktop or Shelf Installation:
When installing the Switch on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet included with the device should
attached first. Attach these cushioning feet on the bottom at each corner of the device. Allow
adequate space for ventilation between the device and the objects around it.
Rack Installation:
The NP2624M switch can be mounted in an ELA standard-sized, 19-inch rack, which can be placed
in a wiring closet with other equipment. To install, attach the mounting brackets on the switch side
panels (one on each side) and secure them with the screws provided. Then, use the screws provided
with the equipment rack to mount the switch on the rack.
Power on:
The NP2624M switch can be used with an AC power supply 100-240V AC, 50-60Hz. The AC
power connector is located at the rear of the unit. The switch’s power supply will adjust to the local
power source automatically and may be turned on with all or none of the LAN segment cables
connected.
After the power switch is turned on, the LED indicators should respond as follows:
• All LED indicators will momentarily blink. This blinking of the LED indicators
represents a reset of the system.
• The power LED indicator will blink while the Switch loads onboard software and
performs a self-test. After approximately 20 seconds, the LED will light again to
indicate the switch is in a ready state.
• The Speed, Link/Activity LED indicator may remain ON or OFF depending on every
port’s situation.
• The fan LED will switch off if the fan is working normally. The LED goes RED if the
fan has stopped or failed.
Page 6
6 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
1.3 Initial set up for management
There are two methods of management; one is out-of-band management, where you connect your
PC to the switch through an RS232 cable. The other method is in-band-management, where you also
connect your PC to the switch, but do so through an Ethernet network either locally or remotely,
or simply directly connect your PC and the switch with an Ethernet cable. Before you activate the
management function in the Switch, you should read the instructions below carefully to ensure you
can access the switch through your PC.
1.3.1 Out-of-band Terminal Mode Management through RS-232
Step 1: Set Hyper Terminal parameters on your PC
Firstly, turn on your PC and execute a terminal mode program. For example, if you are in a
Microsoft Window environment, you may choose “Hyper Terminal” from programs that are
listed for communication.
Open a New Connection using COM1 (or the port on your computer that you are going to
connect the Switch to) and select the following port settings:
Bits Rate per second = 57600
Data Bits = 8
Parity = None
Stop Bit = 1
Flow Control = None
Step 2: Access your Switch
After setting the above parameters on your PC, connect your switch device with the RS-232
cable provided and turn the switch on. After the switch runs its self-test, the device should
respond and ask you to enter the username and password. If the switch had already booted,
press the enter key to display the login screen. Type the default value for the username and
password to proceed, the default username is “admin” and default password “admin”. To
learn more about the operation of the Switch in this mode, refer the instructions in chapter 4
of this manual.
Page 7
NP2624M User Guide 7
YML827 Rev1
1.3.2 In-band Management through Ethernet
In addition to terminal mode operation, the NP2624M switch also supports in-band management
through a web browser. This function is much more user-friendly than terminal mode and can be
performed either locally or remotely through Ethernet.
Before you can access the switch:
1. You have to know the IP Address and Subnet Mask of both your switch and your PC.
The default value of the IP Address and Subnet Mask within the switch can be retrieved
through terminal mode operation described in chapter 4 and the IP Address and Subnet
Mask of your PC can be found in your PC operating system.
2. In general, within a network, the members in the same network domain must have the
same Subnet IP unless there are routers between them or members in the same network
domain can’t talk to each other. Ensure that all users in the same domain have different
IP Addresses on the same Subnet Mask.
3. If there is a DHCP server in the network domain, ensure that the DHCP function is
enabled in both your PC and the switch, then save the setting and reboot the switch
(power-off-and–on once). The DHCP server and its protocol will automatically assign
an IP address and related IP Subnet Mask and Default gateway. This allows you to
execute your web browser in your PC and simply type “http:// IP-Address-of-switch” to
access the switch through Ethernet or over the Internet. If there is no DHCP server in
the network, you must follow the steps instructed below:
4. Webpage login will prevent attacks from hackers. If a user fails to correctly login 3
times, http authentication will reject any http request for 3 minutes.
Connecting without a DHCP server
When there is no DHCP server in your network domain, you must ensure that the PC or switch have
different IP Addresses and same Subnet Mask. Below, are the steps to modify the IP configuration of
the switch to match the domain requirement of the PC:
Step 1: Get the IP configuration information in your PC.
Step 2: Get IP configuration value used for switch from your network manager.
Get an IP Address for your switch, the IP Subnet Mask, and the default gateway IP address (if
needed) from your network manager.
Step 3: Modify the IP configuration value within the
switch to match the rule
In the step 3, you must use the data from step 2 to modify
the default values within the switch. To achieve this, use
terminal mode operation mentioned as described in 1.3.1
above. After modifying the IP address, Subnet Mask, and
Default Gateway in the switch, save the setting and execute
the browser program with “http:// IP_Address_ of_ switch”.
The login dialog box will be displayed. Type in the user
name and password to proceed. Refer to the instructions in
chapter 3 for more information.
Page 8
8 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
1.3.3 Telnet management
In addition to local terminal mode operation, the NP2624M switch supports remote management
through Telnet over a network or the internet without a web browser. In this mode, the user has to
enter the same settings as required in in-band management to the IP Configuration before executing
the Telnet program. Again, after properly setting the switch, save the settings and connect your
Ethernet cable from your PC to any port of the Switch. Then you simply type the following at the
command line to access the switch:
Telnet IP_Address_of_Switch
The following window appears. Follow the prompts and type in the “username” and “password” to
proceed. Refer to the instructions in chapter 3 of this manual for more information.
Page 9
NP2624M User Guide 9
YML827 Rev1
1.4 LED indicators information
There are many LEDs on the front panel of switch. After the initial power on, these LEDs will
reflect the current status within the switch as explained below:
There is one power LED on the left side of the front panel. When power is applied, it turns green.
Below it is a Diagnostic LED which will blink whilst conducting power-on diagnostics. There are
two more FAN status LEDs beside the power LEDs. The upper one indicates the left fan status
and the lower one indicates the right fan status. These will turn RED if a fan has stopped or is
malfunctioning. Otherwise these LEDs will switch off when the fans are working normally.
Each of the RJ-45 10/100Mbps connectors has two LEDs built-in to its upper corners. The left one
indicates the link status and activity, while the right one indicates the speed.
The LEDs for the optional Gigabit module are somewhat different. The upper yellow LED indicates
a 10Mbps LINK, the middle green LED indicates a 100Mbps LINK, but for 1000Mbps, or Gigabit,
both upper and middle LEDs are lit (i.e. when a Gigabit port is linked with another Gigabit port).
LED Color Status
Solid Blinking
Power
Green Turn solid green when
power is applied to
this device.
N/A
DIAG
Green Successful diagnostic. During power on
diagnostics
FAN
Red Left or Right side fan
fail.
N/A
LINK/ACT
Green Successful connection
with Fast Ethernet.
Sending, receiving or
collision packets
10/100M
Green Successful connection
with 100Mbps Fast
Ethernet.
N/A
Vanish Successful connection
with 10Mbps Fast
Ethernet.
N/A
Page 10
10 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2. Web Management Function
2.1. Web Management Home Overview
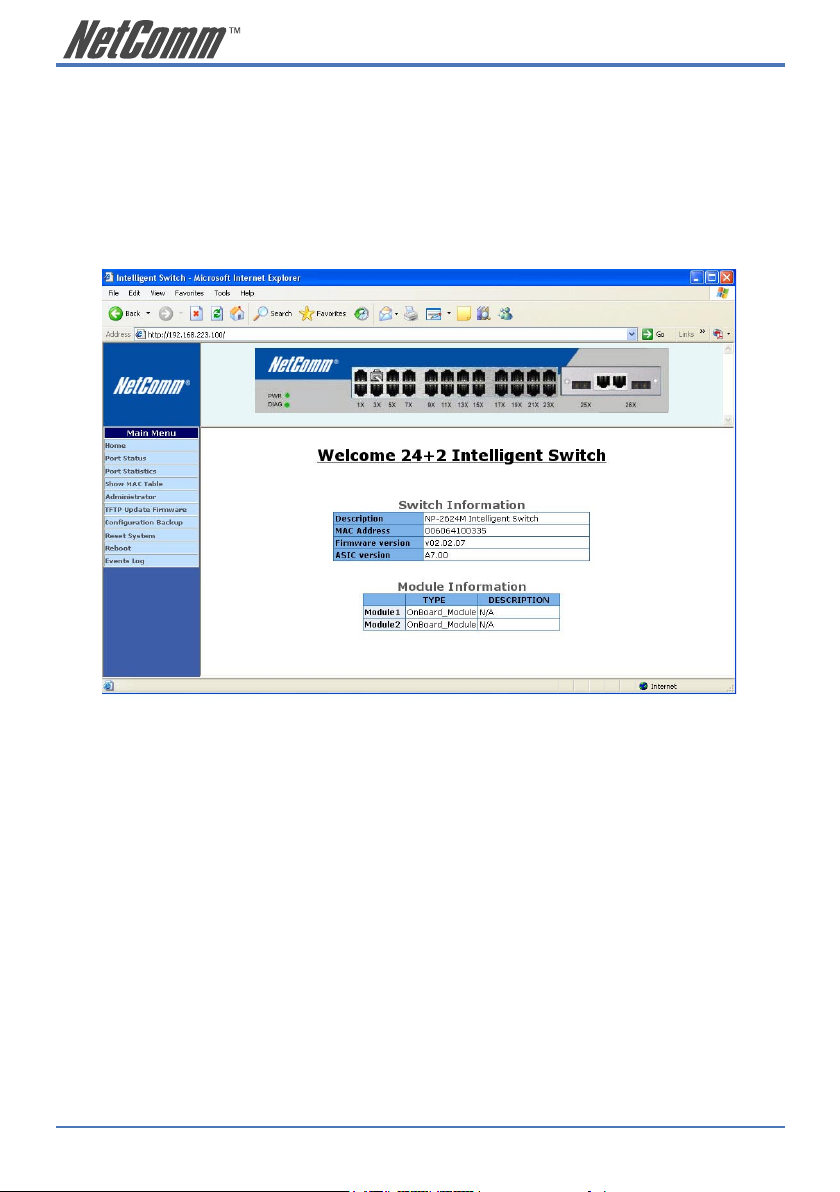
The first page you will see after login to the switch via a web browser is the Web Management page.
This page will display the basic switch and module information. All information displayed in
these fields is read-only. That is, the user cannot modify the contents of the fields. The fields are
described below:
Switch Information
Description: Displays the name of device type.
MAC Address: The unique hardware address assigned by
manufacturer (default).
Firmware Version: Displays the switch’s firmware version.
ASIC Version: Displays the switch’s ASIC version.
The image of the switch at the top of the page indicates the whether the port is connected. Click on
the menu items on the left of the screen to display more information.
The following sections give an explanation of each function.
Page 11
NP2624M User Guide 11
YML827 Rev1
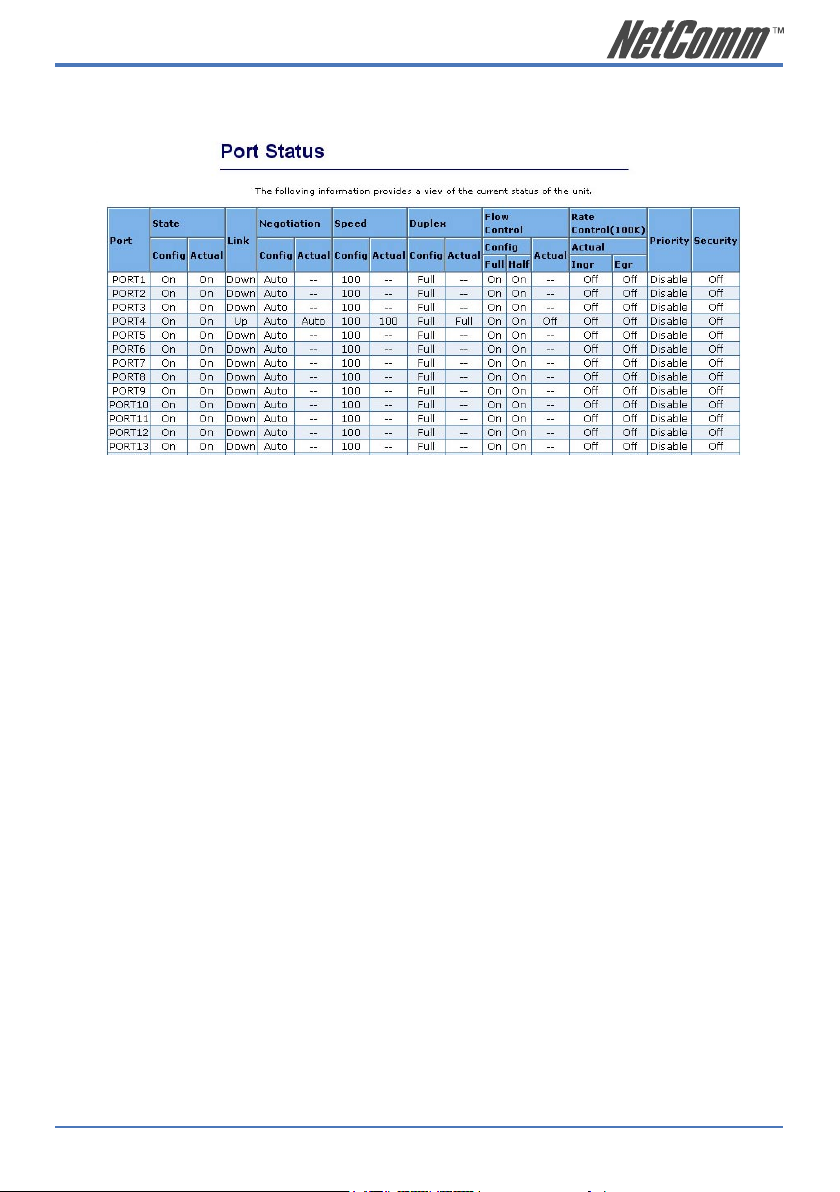
2.2. Port status
This page provides current status of every port and the negotiation result.
State: Displays the port status: On or Down. “Unlink” will
be treated as “off”.
Link Status: Displays the link status. Down means “No Link”, Up
means “Link”.
Auto Negotiation: Displays the auto negotiation mode: auto/force/
Nway-force.
Speed status: Displays the speed, port 1- 24 are 10/100Mbps, Port
25-26 are 10/100/1000Mbps.
Duplex status: Displays full-duplex or half-duplex mode.
Flow Control: Full: Displays the flow control is enabled or disabled
in full mode.
Half: Displays the backpressure is enabled or
disabled in half mode.
Rate Control: Displays the rate control setting.
Ingr: Displays the port effective ingress rate of user
setting.
Egr: Displays the port effective egress rate of user
setting.
Port Security: Displays the port security is enabled or disabled.
Config: Displays the state of user setting.
Actual: Displays the negotiation result.
Page 12
12 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
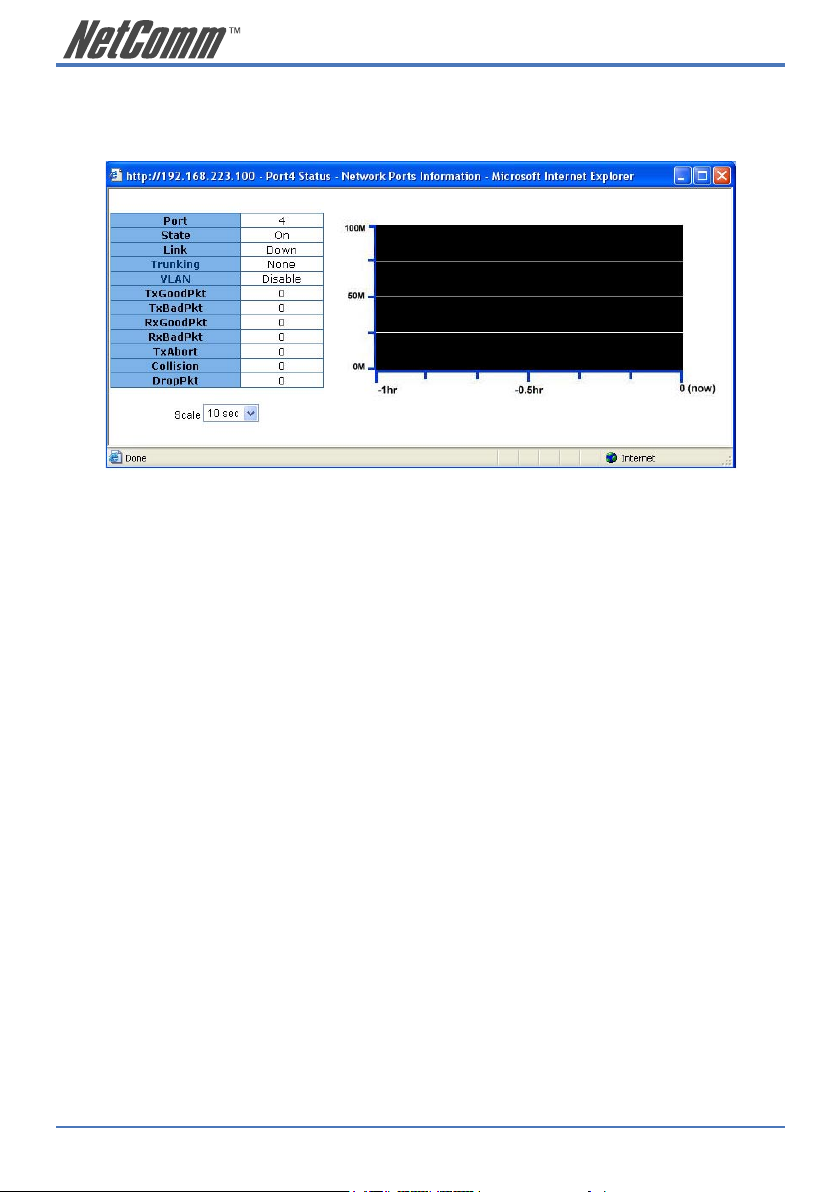
2.2.1 Single port counter and status
The user can also click any port directly on the front panel of the Home Page to get single port status
which is shown below.
There is a flow rate historical chart on the right. The user can track the flow rate of this port for the
last 60 hours. Changing the scale will re-calculate the chart.
Page 13
NP2624M User Guide 13
YML827 Rev1
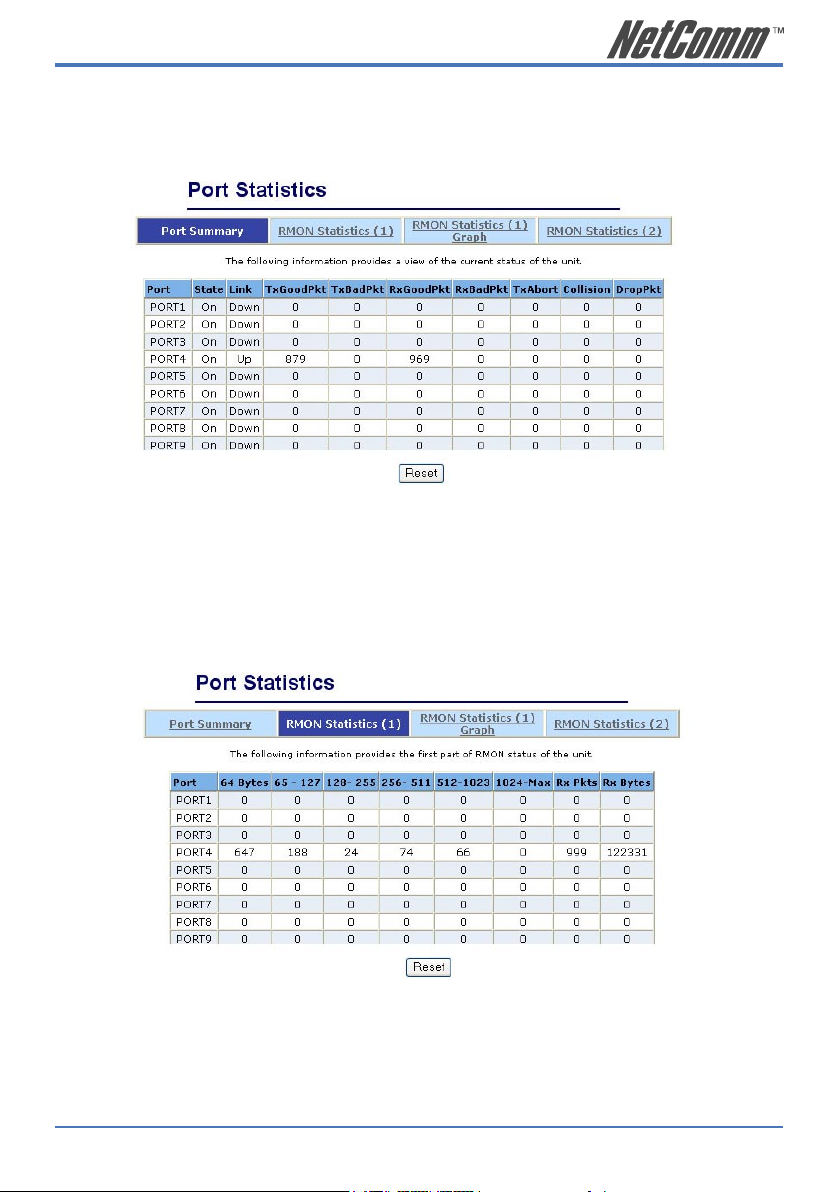
2.3. Port Statistics
Statistics pages are provided to monitor network traffic. They are: Port Summary, RMON
Statistics(1), RMON Statistics(1) Graph, RMON Statistics(2).
The above information provides a summary of the switch’s current status, including on/off state, link
status, good or bad packets of transmitting and receiving, packets of transmitting abort, packets of
collision and drop packets.
The following pages provide the statistics of RMON 1,2,3,9 groups. The first part collects the
information about packets and frame size within the ranges of 64, 65-127, 128-255, 256-511, 5121023, and 1024-1518 bytes, the total received packets and the total receives bytes.
Page 14
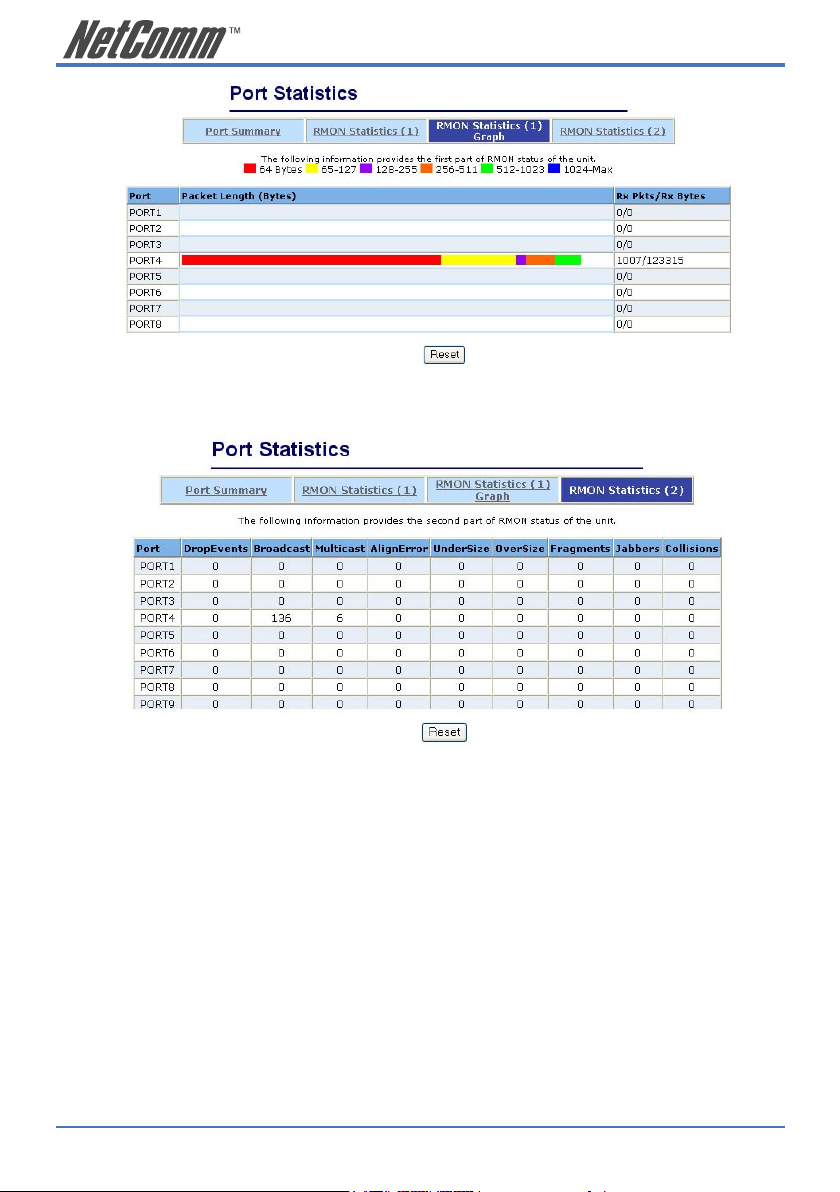
14 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
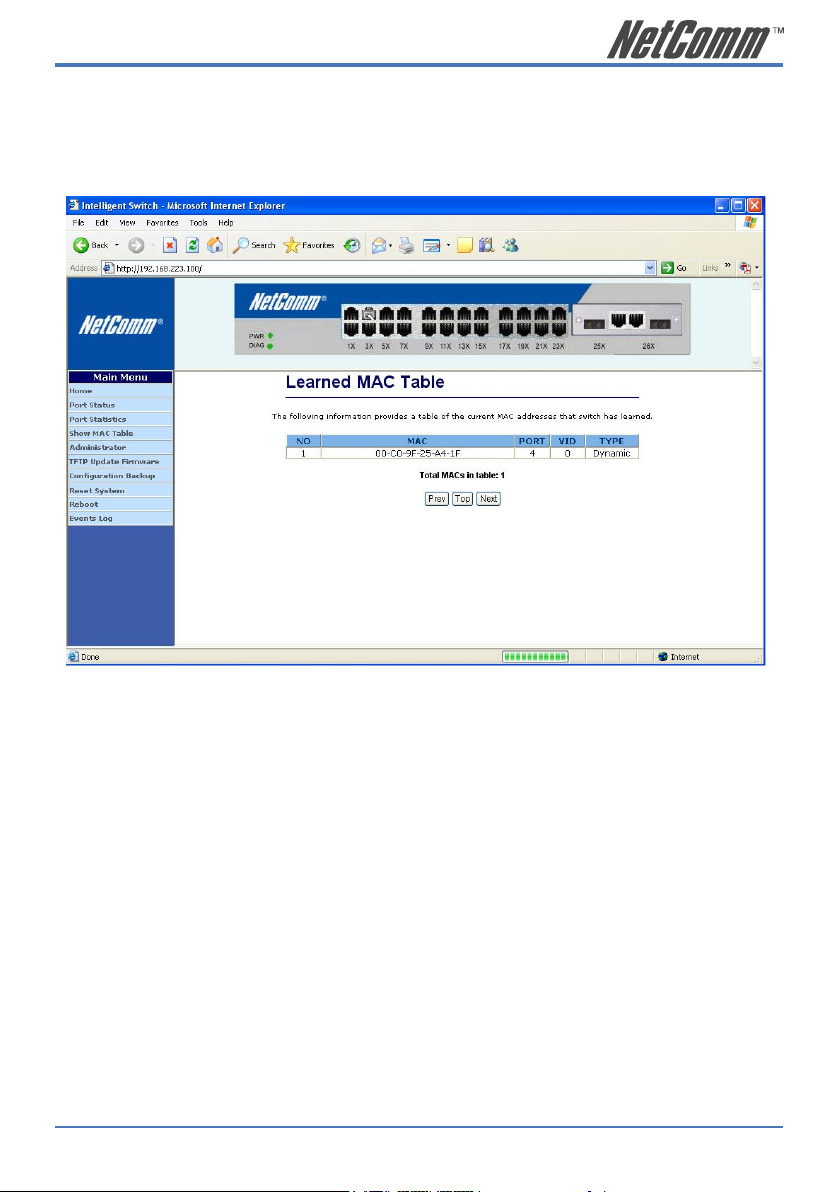
The second part collects the information about drop events, broadcast packets, multicast packets,
alignment errors, undersize packets, oversize packets, fragments, jabbers and collisions.
Press “Reset” button to clear the counter.
Page 15
NP2624M User Guide 15
YML827 Rev1
2.4. Show MAC Table
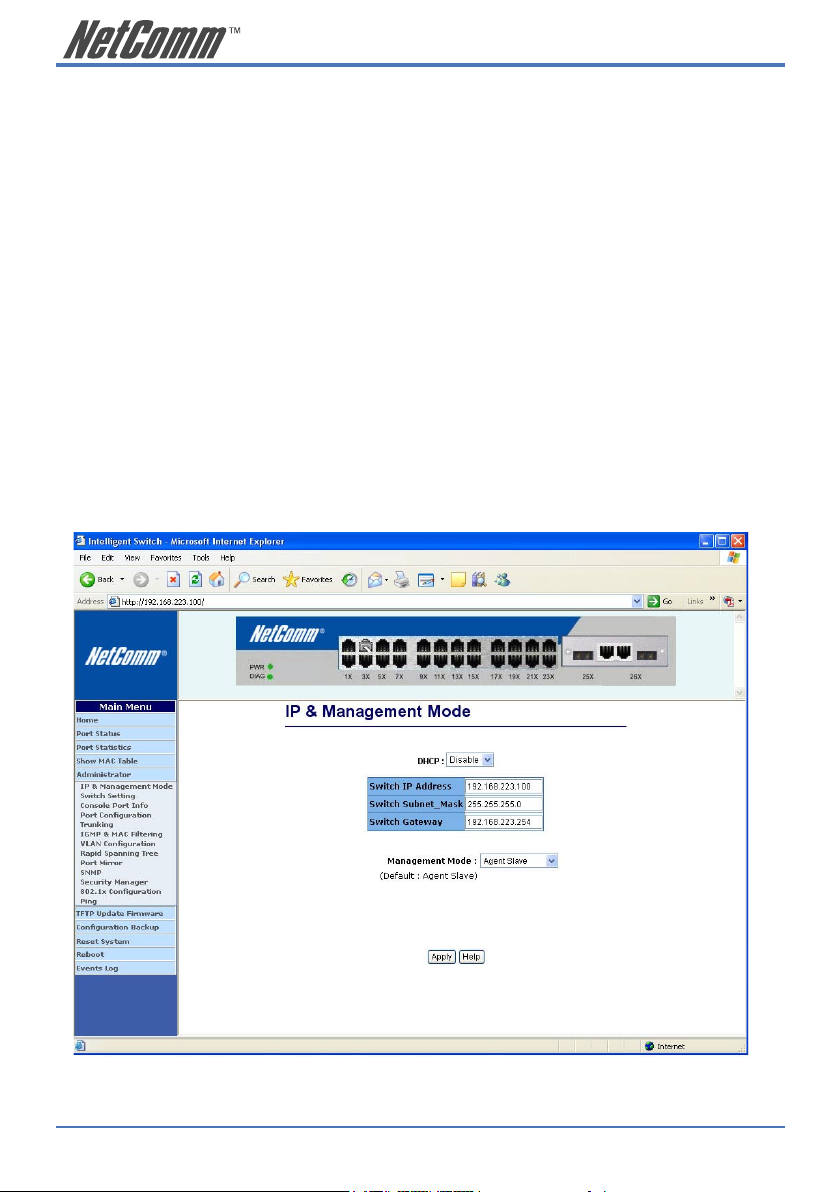
The following information provides a table of the current MAC address that the switch has learned.
Press “Prev” or “Next” button to browse previous 50 or next 50 items. The “Top” button will re-list
the table from the first MAC.
The table can be sorted by each of the headings by clicking the header on the top of table. For
instance, clicking the “MAC” on the top of table will refresh the table by the index of “MAC”.
Page 16
16 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5. Administrator
There are many management functions that can be set or performed if you click on Administrator
on Home Page, including:
• IP and Management mode
• Switch settings
• Console port information
• Port configuration
• Trunking
• IGMP and MAC Filter
• VLAN configuration
• Rapid Spanning tree
• Port Mirror
• SNMP
• Security Manager
• 802.1x Configuration
• Ping
Page 17

NP2624M User Guide 17
YML827 Rev1
2.5.1. IP and Management mode
The user can modify the switch IP Settings by entering the new values and clicking the “apply”
button to confirm (save) these settings. Then reboot the switch and the new IP configuration values
will be activated.
The Management mode indicates which role this switch is currently playing. “Agent Slave” means
it is treated as a normal switch. “Agent Master” means the “Single IP” is activated and the switch is
treated as agent manager. “Stacking Slave” is used only when this switch is going to be a member
of stacking set. This setting will force the switch to activate spanning tree protocol and some VLAN
settings in preparation for stacking switches. “Stacking Master” also does the same tasks but it
plays the role of manager of the stack. Only the “Stacking Slave” can be added into the members of
a stacking set under one “Stacking master”. The default management mode is “Agent Slave”.
The extra “Agent IP” setting is necessary for the “Single IP” management. It defines the IP and the
subnet mask the master switch will be assigned, which are in the same IP domain as the managed
hosts’ one.
The user can confine the “Single IP” function to local management by assigning the agent IP to the
same one as the switch’s IP. Different from original IP forwarding method, it will not increase the
loading of switch.
“Agent IP” setting and “Agent management” in the main menu will not show up if the agent mode
is set as “Slave”.
NOTE: If any of the values are changed in this screen, reboot is necessary.
Page 18

18 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.2 Switch Setting
2.5.2.1 Advanced
MAC Address Age-out Time: Type the number of seconds that an inactive MAC
address remains in the switch’s address table. The
valid range is 300~765 seconds. Default is 300
seconds.
Max bridge transit
delay bound control: Limits the packets queuing time in switch. If
enabled, the excess packets will be dropped. These
valid values are 1 sec, 2 sec, and 4 sec and off.
Default is 1 seconds.
NOTE: Make sure “Max bridge transit delay bound control” is enabled
before “Enable Delay Bound”, because “Enable Delay Bound” only
works under “Max bridge transit delay bound control”.
Enable Delay Bound: Limit the low priority packets queuing time in
switch. Default Max Delay Time is 255ms. If the
amount of time a low priority packet stays in the
switch exceeds the Max Delay Time, it will be sent.
The valid range is 1-255ms.
Broadcast Storm Filter: To configure broadcast storm control, enable it
and set the upper threshold for individual ports.
The threshold is the percentage of the port’s total
bandwidth used by broadcast traffic. When broadcast
traffic for a port rises above the threshold you set,
broadcast storm control becomes active. The valid
threshold value is 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and off.
Page 19
NP2624M User Guide 19
YML827 Rev1
Priority Queue Service settings:
First Come, First Serve: The sequence of packets sent is depending on the
arrival order.
All High before Low: The high priority packets are sent before the low
priority packets.
WRR: (Weighted Round Robin) Select the preference given
to packets in the switch’s high-priority queue. These
options represent the number of high priority packets
sent before one low priority packet is sent. For
example, 5 High:2 Low means that the switch sends
5 high-priority packets before sending 2 low- priority
packets.
QOS Policy: High Priority Levels: 0~7 priority level can be
mapped to a high or low queue.
2.5.2.2 Miscellaneous Configuration
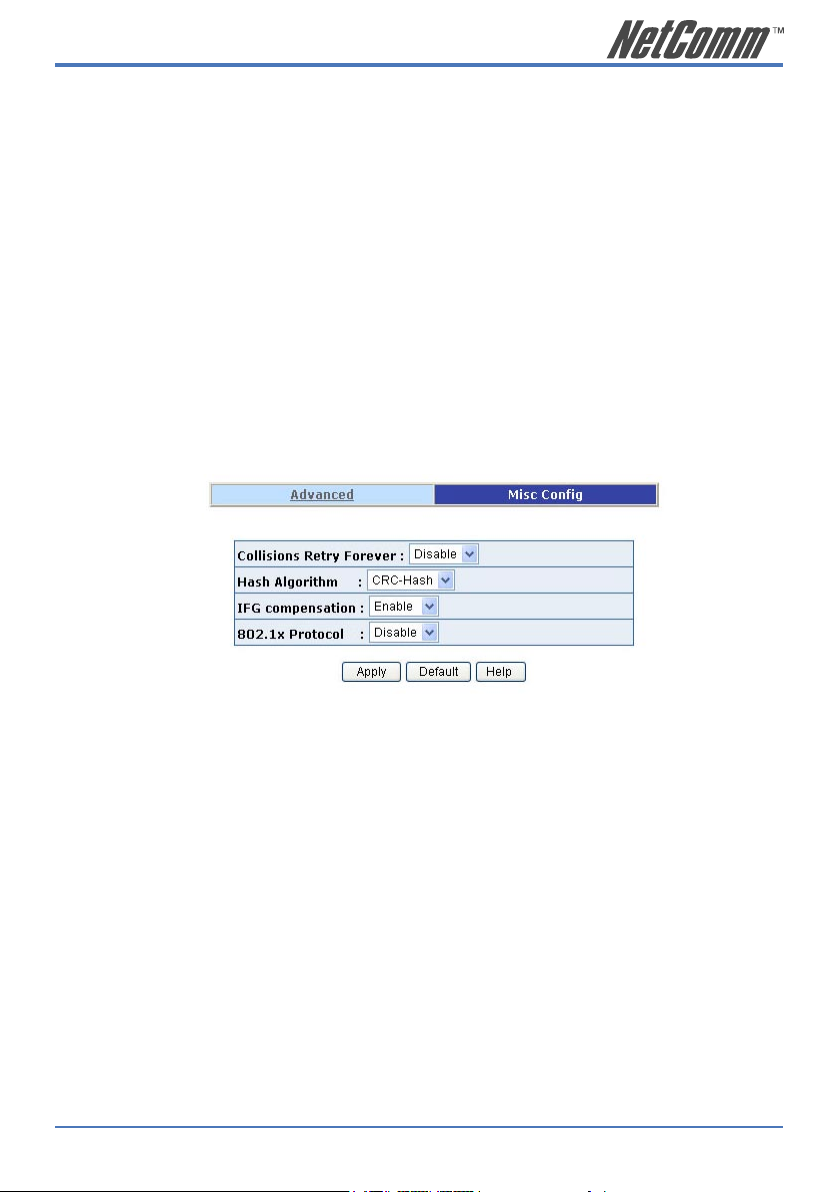
Collisions Retry Forever: Disable – In half duplex, the collision-retry
maximum is 48 times and packet will be dropped if
collisions still happen.
Enable – In half duplex, there is no collision-retry
limit. Retry will be attempted indefinitely.
Hash Algorithm: Choose algorithms, CRC-Hash or DirectMap, to
maintain MAC address table.
IFG Compensation: Enable or disable inter-frame gap (IFG)
compensation.
802.1x Protocol: Enable or disable 802.1x protocol.
Page 20
20 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
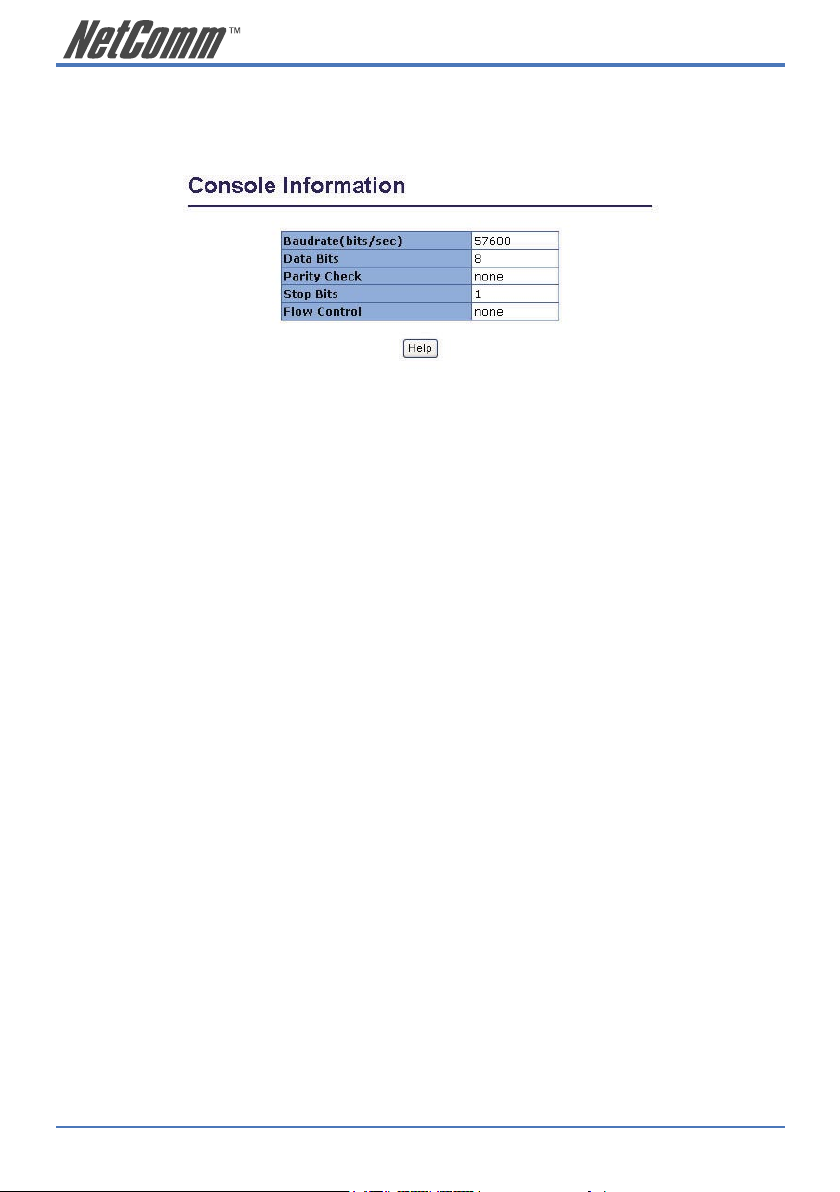
2.5.3 Console Port Information
The Console is a standard UART interface which allows you to communicate with the Switch via a
Serial Port. The user can use windows HyperTerminal program to link the switch.
Bits per seconds: 57600
Data bits: 8
Parity: none
Stop Bits: 1
Flow control: none
Page 21

NP2624M User Guide 21
YML827 Rev1
2.5.4 Port Controls
The user may modify or change mode operation in this page.
Port: Select a port.
State: User can disable or enable this port control.
Negotiation: User can set auto negotiation mode to Auto, Nway
(specify the speed/duplex on this port and enable
auto-negotiation), Force of per port.
Speed: User can set 100Mbps or 10Mbps speed on
Port1~Port24.
User can set 1000Mbps, 100Mbps or 10Mbps speed
on Port25~Port26 (depends on module card mode).
Duplex: User can set full-duplex or half-duplex mode per
port.
Flow Control: Full: User can set flow control function to enable or
disable in full mode.
Half: User can set backpressure to enable or disable
in half mode.
Rate Control: Port1 ~ port 24, supports by-port ingress and egress
rate control. For example, assume port 1 is 10Mbps,
users can set its effective egress rate at 1Mbps and
ingress rate at 500Kbps. The device will perform
flow control or backpressure to confine the ingress
rate to meet the specified rate.
Ingress: Type the port effective ingress rate. The valid range
is 0 ~ 1000. The unit is 100K.
0: disable rate control.
1 ~ 1000: valid rate value
Page 22

22 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Egress: Type the port effective egress rate. The valid range is
0~1000. The unit is 100K.
0: disable rate control.
1 ~ 1000: valid rate value.
Priority: Enable or disable the port priority function. There
are two priorities (high or low) provided if port
priority is enabled.
Security: A port in security mode will be “locked” without
permission of address learning. Only the incoming
packets with SMAC already existing in the address
table can be forwarded normally. Users can disable
the port from learning any new MAC addresses, then
use the static MAC addresses screen to define a list
of MAC addresses that can use the secure port.
Enter the settings, then click Apply button to change on this page.
Page 23
NP2624M User Guide 23
YML827 Rev1
2.5.5 Trunking
The Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) provides a standardized means for exchanging
information between Partner Systems on a link to allow their Link Aggregation Control instances
to reach agreement on the identity of the Link Aggregation Group to which the link belongs, move
the link to that Link Aggregation Group, and enable its transmission and reception functions in an
orderly manner. In conclusion, Link aggregation lets you group up to eight consecutive ports into a
single dedicated connection. This feature can expand bandwidth to a device on the network. LACP
operation requires full-duplex mode, more detail information refers to IEEE 802.3ad
2.5.5.1 Aggregator setting
System Priority: A value used to identify the active LACP. The switch
with the lowest value has the highest priority and is
selected as the active LACP. Valid value is 1~65535.
Group ID: There are seven trunk groups to provide configure.
Choose the “group id” and click “Get”.
LACP: If enabled, the group is LACP static trunking group.
If disabled, the group is local static trunking group.
All ports support LACP dynamic trunking group. If
connecting to the device that also supports LACP,
the LACP dynamic trunking group will be created
automatically.
Work ports: Allows for a maximum of four ports to be aggregated
at the same time. If LACP static trunking group,
exceeds ports is standby and able to aggregate if
work ports fail. If local static trunking group, the
number must be as same as the group member ports.
Page 24
24 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Select the ports to join the trunking group. Allow a maximum of four ports to be aggregated
at the same time.
If LACP is enabled, you can configure LACP Active/Passive status in each port on State
Activity page.
Click Apply.
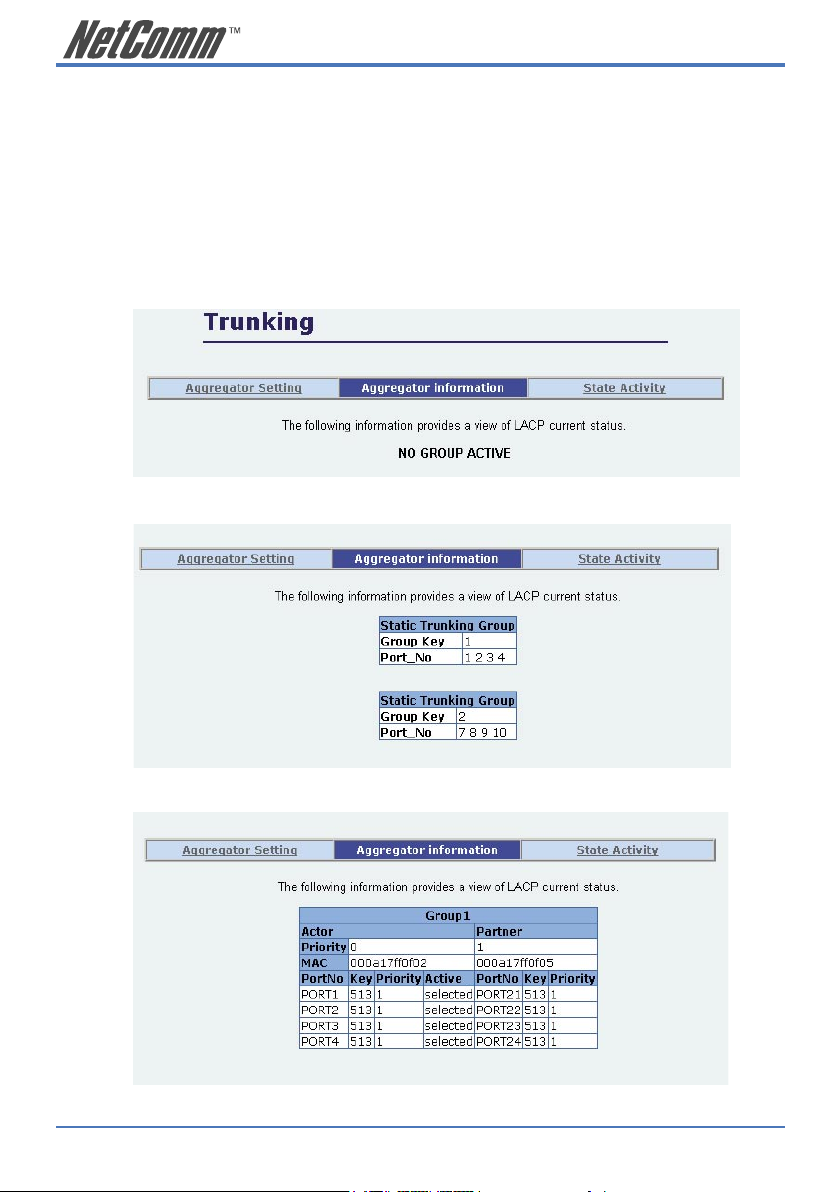
2.5.5.2 Aggregator Information
When you are setting LACP aggregator, related information will be displayed.
1. This page displays no group active. LACP is not working.
2. This page displays Static Trunking groups.
3. This page displays Actor and Partner trunking in one group.
Page 25
NP2624M User Guide 25
YML827 Rev1
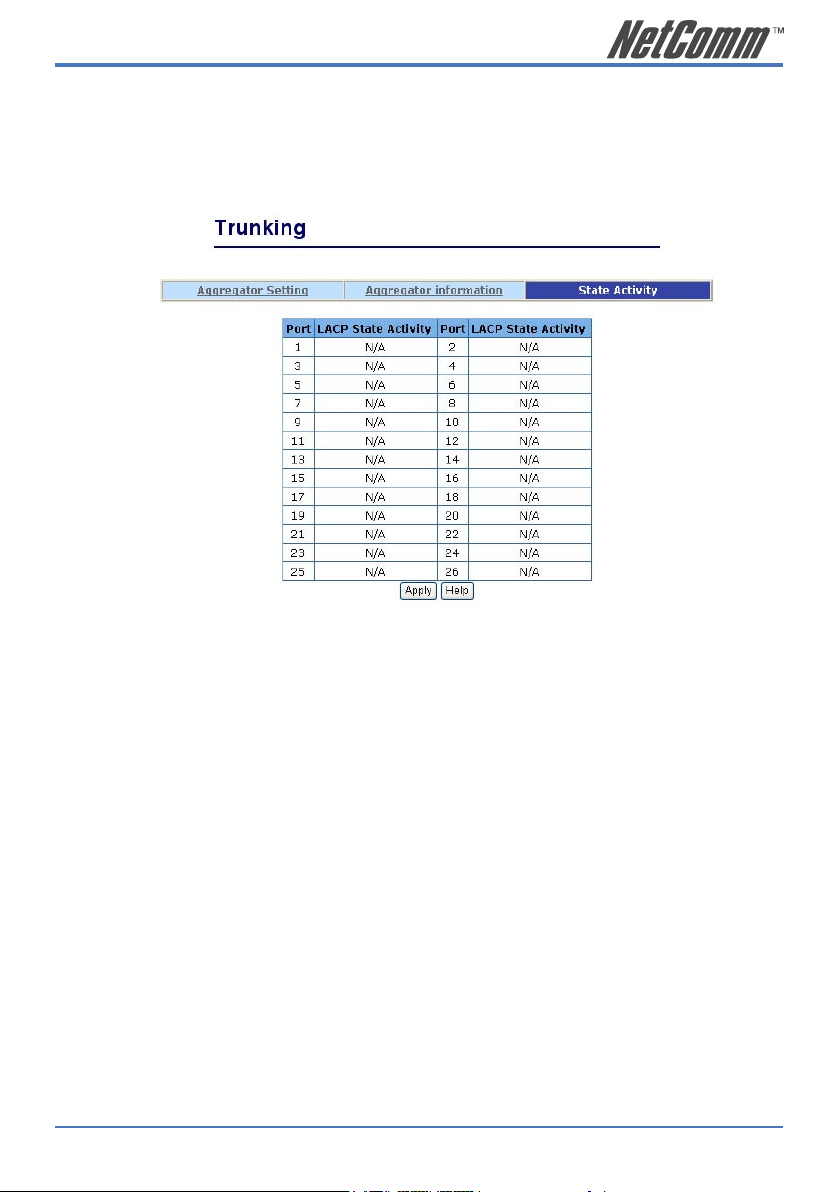
2.5.5.3 State Activity
Active (select): The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
N/A (no select): The port does not automatically send LACP protocol
packets, and responds only if it receives LACP
protocol packets from the opposite device.
1. A link that has either two active LACP ports or one active port can perform dynamic
LACP trunking. A link has two N/A LACP ports will not perform dynamic LACP
trunking because both ports are waiting for an LACP protocol packet from the opposite
device.
2. If you are active LACP’s actor, when you select trunking port, the active status will be
created automatically.
Page 26

26 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.6 Filter Database
2.5.6.1. IGMP Snooping
The NP2624M switch supports multicast IP. IGMP protocol can be enabled on this web page,
and IGMP snooping information is displayed on this page. All multicast groups, VIDs and
member ports are displayed in the list. IP multicast addresses range from 224.0.0.0 through
239.255.255.255.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of the Internet Protocol
(IP) suite.
IGMP can manage the multicast traffic if the members (switches, router or other network devices)
of groups support IGMP. With IGMP enabled, the member ports will detect IGMP queries, report
packets and manage the IP multicast traffic through the switch.
IGMP have three fundamental types of message as follows:
Message Description
Query A message is sent from the queries (IGMP router
or switch) asking for a response from each host
belonging multicast group.
Report A message is sent by a host to the queries to indicate
that the host wants to be or is a member of a given
group indicated in the report message.
Leave Group A message is sent by a host to the queries to indicate
that the host has quit being a member of a specific
multicast group.
Page 27
NP2624M User Guide 27
YML827 Rev1
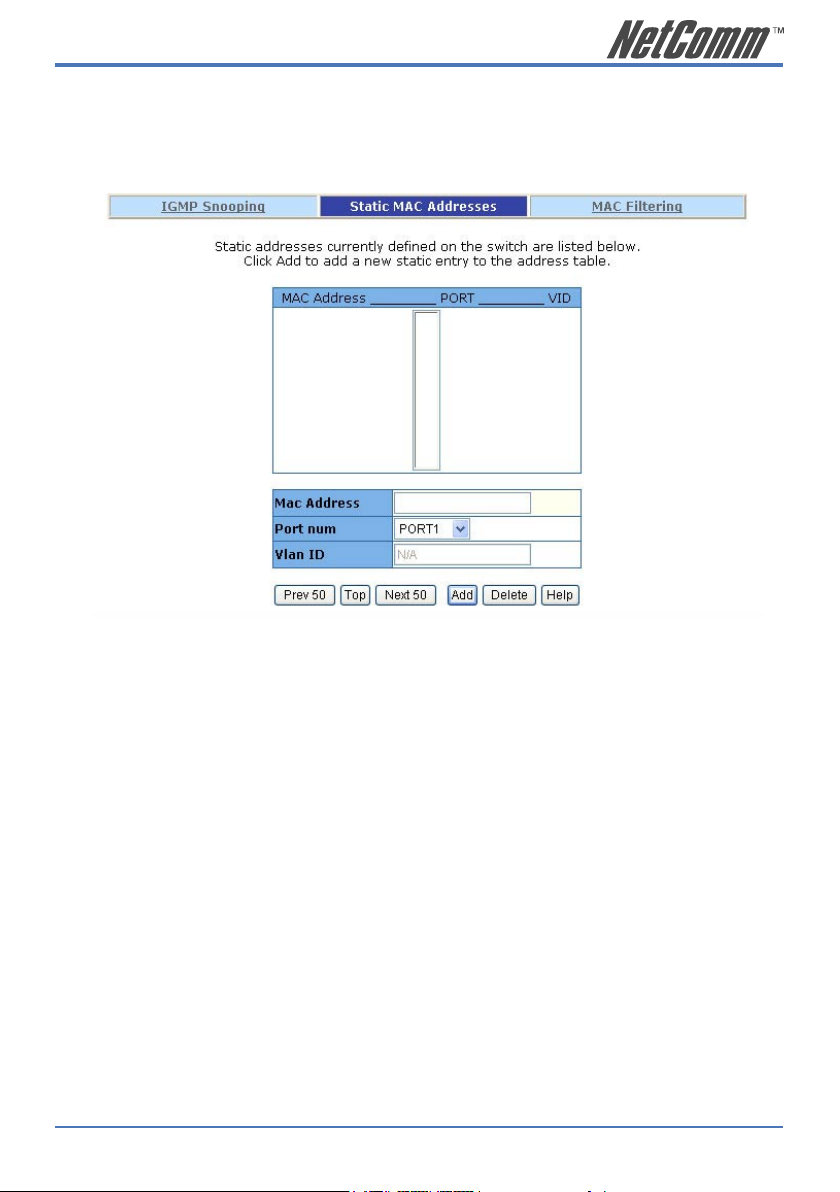
2.5.6.2. Static MAC Address
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch’s address table, regardless of whether
the device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the switch from having to re-learn a
device’s MAC address when the disconnected or powered-off device is active on the network again.
1. At the main menu, click Administrator >Filter Database >Static MAC Address.
2. In the MAC address box, enter the MAC address.
3. In the Port Number box, enter a port number.
4. If tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLANs are set up on the switch, static addresses are
associated with individual VLANs. Type the VID (tag-based VLANs) to associate with
the MAC address.
5. Click the Add.
6. Click the “Prev 50” will list the previous 50 MAC addresses.
7. Click the “Top” will refresh the list from the first entry.
8. Click the “Next 50” will list the next 50 MAC addresses.
Page 28
28 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
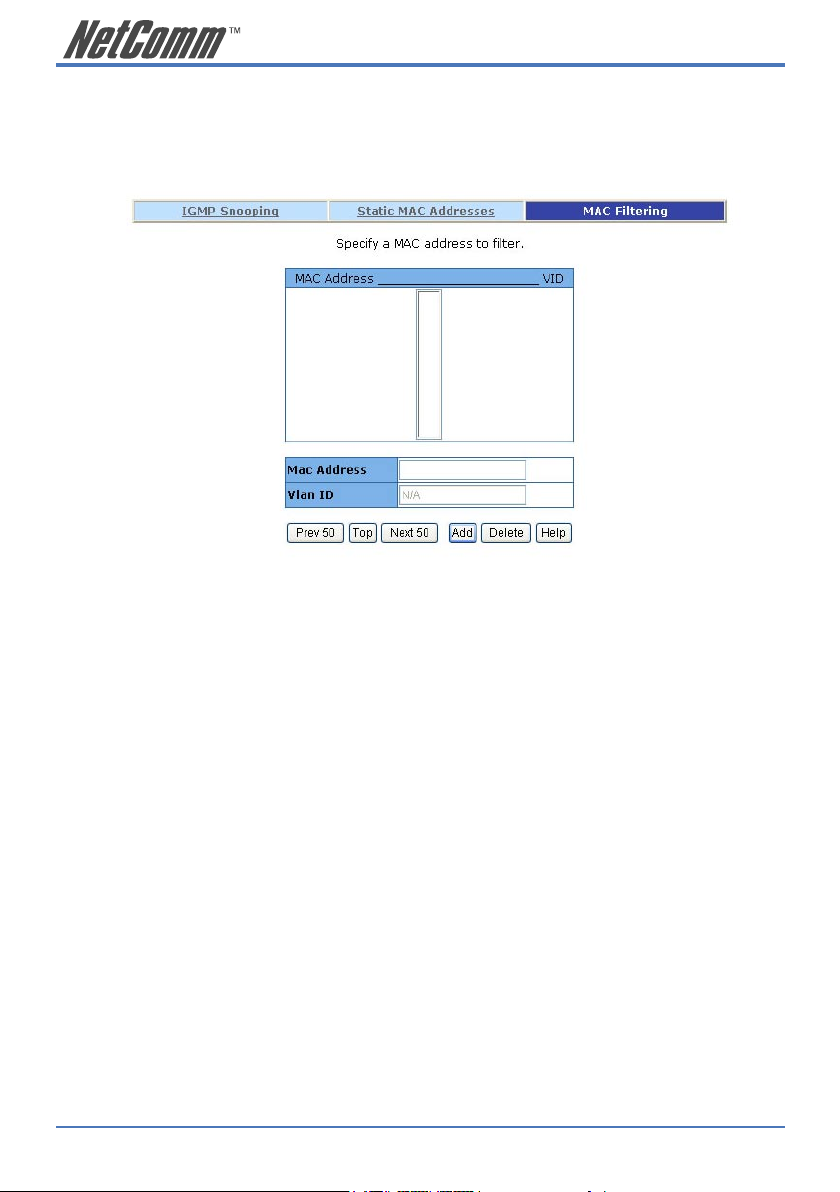
2.5.6.3 MAC filtering
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered based on the
destination addresses.
1. In the MAC Address box, enter the MAC address that you want to filter.
2. If tag-based (802.1Q) VLAN are set up on the switch, in the VLAN ID box, type the
VID to associate with the MAC address.
3. Click the Add.
4. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then click the Delete.
Page 29
NP2624M User Guide 29
YML827 Rev1
2.5.7. VLAN configuration
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical network grouping that limits the broadcast domain. It allows
you to isolate network traffic so only members of the VLAN receive traffic from the same VLAN
members. Basically, creating a VLAN from a switch is logically equivalent to reconnecting a group
of network devices to another Layer 2 switch. However, all the network devices are still plugged
into the same switch physically.
The NP2624M switch supports port-based, 802.1Q (tagged-based) and protocol-base VLAN in web
management page. In the default configuration, VLAN support is disabled.
Support Port-based VLAN
Packets can only be broadcast among members of the same VLAN group. Note all unselected ports
are treated as belonging to another single VLAN. If the port-based VLAN is enabled, the VLANtagging is ignored.
Page 30

30 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Support Tag-based VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q VLAN)
Tagged-based VLAN is an IEEE 802.1Q specification standard. Therefore, it is possible to create a
VLAN across devices from different switch venders. IEEE 802.1Q VLAN uses a technique to insert
a “tag” into the Ethernet frames. Tag contains a VLAN Identifier (VID) that indicates the VLAN
numbers.
Support Protocol-based VLAN
In order for an end station to send packets to different VLANs, it has to be either capable of tagging
packets it sends with VLAN tags or attached to a VLAN-aware bridge that is capable of classifying
and tagging the packets with a different VLAN ID based not only on the default PVID but also other
information about the packet, such as the protocol.
The NP2624M switch will support protocol-based VLAN classification by means of built-in
knowledge of layer 2 packet formats used by selected popular protocols, such as Novell IPX and
AppleTalk’s Ether Talk, and some degree of programmable protocol matching capability.
Page 31

NP2624M User Guide 31
YML827 Rev1
2.5.7.1. Port Based VLAN
1. Click Add to create a new VLAN group.
2. Enter the VLAN name, group ID and select the members for the new VLAN.
3. Click Apply.
4. If there are many groups that over the limit of one page, you can click the “Next Page”
to view other VLAN groups.
NOTE: If trunk groups exist, they will be displayed (eg: TRK1, TRK2…) in
select menu of ports. These can also be configured on the VLAN.
Page 32

32 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.7.2. 802.1Q VLAN
In this page, the user can create a Tag-based VLAN.
256 VLAN groups can be configured. If 802.1Q VLAN is enabled, then all ports on the switch will
belong to the default VLAN (VID is 1). The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
Basic
Create a VLAN and add tagged member ports to it.
1. From the main menu, click Administrator >VLAN configuration, click Add and the
following page will be displayed.
2. Type a name for the new VLAN.
Page 33

NP2624M User Guide 33
YML827 Rev1
3. Type a VID (between 2-4094). The default is 1.
4. Choose the protocol type.
The NP2624M supports 802.1v with the implementation of Port-and-Protocol-based
VLAN classification. Users can combine the field “Protocol VLAN” and the field of the
port number to form a new VLAN group.
NOTE: IEEE 802.1v allows a user to classify the packets through an untagged
port. There are two possible strategies of the 802.1v support: Portbased VLAN and Port-and-Protocol-based VLAN. Both are supported
in the NP2624M. Users set the VID to mark the packet from the
untagged port and then the packet can be scheduled by the way of
the IEEE 802.1q.
5. From the Available ports box, select ports to add to the switch and click “Add >>”. If
the trunk groups exist, they will be displayed here (eg: TRK1, TRK2…) and you can
configure it as a member of the VLAN if necessary.
6. Click Next. The following page will be displayed.
Page 34

34 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
7. Use this page to set whether the outgoing frames are VLAN-Tagged frames or not. Then
click Apply.
Tag: outgoing frames with VLAN-Tagged.
Untag: outgoing frames without VLAN-Tagged.
Port VID
From the main Tag-based (IEEE 802.1Q) VLAN page, click Port VID Settings to configure port
VID settings.
Port VID (PVID) Set the port VLAN ID that will be assigned to
untagged traffic on a given port. This feature is
useful for accommodating devices that you want to
participate in the VLAN but do not support tagging.
The NP2624M switch allows each port to set one
PVID, the range is 1~255, default PVID is 1. The
PVID must as same as the VLAN ID that the port
belong to VLAN group, or the untagged traffic will
be dropped.
Ingress Filtering Ingress filtering lets frames belonging to a specific
VLAN to be forwarded if the port belongs to that
VLAN. The NP2624M switch has two ingress
filtering rules as follows:
Ingress Filtering Rule 1: A forward only packet with
VID matching this port’s configured VID.
Ingress Filtering Rule 2: Drop Untagged Frame.
Page 35

NP2624M User Guide 35
YML827 Rev1
2.5.8. Rapid Spanning Tree
We provide Both Rapid-Spanning-Tree-Protocol (RSTP) and Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP).
The Spanning-Tree Protocol (STP) is a standardized method (IEEE 802.1D) for avoiding loops in
switched networks. Enable STP to ensure that only one path at a time is active between any two
nodes on the network.
The Rapid-Spanning-Tree-Protocol (RSTP) is a more advanced Protocol than STP. RSTP can
shorten spanning tree convergent time if your network topology changes. For the default, the switch
will use RSTP. If the switch receives a STP’s BPDU, the switch will degrade to STP.
You can enable STP (Spanning-Tree Protocol) using the web management’s switch setting advanced
item, select enable Spanning-Tree Protocol. We recommend that you enable STP on all switches to
ensure a single active path on the network.
1. You can view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge on the following screen:
2. You can view spanning tree status about the switch on the following screen:
Page 36

36 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
3. You can also set new values for RSTP parameters, then click the Apply button to modify
Parameter Description
Priority You can change the priority value. A value is used
to identify the root bridge. The bridge with lowest
value has the highest priority and is selected as the
root. Enter a number 1 through 65535.
Max Age You can change the Max Age value. The number of
second bridge waits without receiving Spanning-Tree
Protocol configuration messages before attempting a
reconfiguration. Enter a number 6 through 40.
Hello Time You can change the Hello time value. The number
of seconds among the transmission of Spanning-Tree
Protocol configuration messages. Enter a number 1
through 10.
Forward Delay Time You can change the forward delay time. The number
of seconds a port waits before changing from its
Spanning-Tree Protocol learning and listening states
to the forwarding state. Enter a number 4 through 30.
Page 37

NP2624M User Guide 37
YML827 Rev1
4. The following parameters can be configured on each port , click the Apply button to modify
Parameter Description
Port Number Select the port number.
Path Cost Specifies the path cost of the port that the switch uses
to determine which ports are the forwarding ports.
The lowest number is forwarding ports, the range is
1-65535 and default value base on IEEE802.1D
10Mb/s = 50-600 100Mb/s = 10-60 1000Mb/s = 3-10
Port Priority You can make it more or less likely to become the
root port, the range is 0-255, and default setting is
128.
The lowest number has the highest priority.
Edge Port Edge Port is a port connected to a device that knows
nothing about STP or RSTP. Usually, the connected
device is an end station. Edge Ports will keep in
forwarding state and skip the listening and learning
state. When the link on the edge port is changed, the
RSTP topology is not affected.
Page 38

38 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.9. Port Mirror
The Port Mirror is a method for monitoring traffic in switched networks. Traffic through ports can
be monitored by one specific port. That is, traffic going in or out monitored ports will be duplicated
into an Analysis port.
Roving Analysis Mode: Press Space key to set mirror mode: Disable \Rx \Tx
\Both.
Analysis Port: This port can be used to see all monitored ports’
traffic. You can connect analysis port to LAN
analyser or netxray.
Monitored Port: The ports you want to monitor. All monitored port
traffic will be copied to the analysis port. You can
select a maximum of 25 monitor ports in the switch.
Users can choose which port that they want to
monitor in only one mirror mode.
If you want to disable the function, you must deselect monitor port.
Page 39

NP2624M User Guide 39
YML827 Rev1
2.5.10. SNMP/Trap Manager
Any Network Management platform running the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
can manage the switch, provided the Management Information Base (MIB) is installed correctly on
the management station. The SNMP is a Protocol that governs the transfer of information between
management station and agent.
1. System Options:
Use this page to define management stations as trap managers and to enter SNMP
community strings. Users can also define a name, location, and contact person for the
switch. Fill in the system options data, and then click Apply to update the changes on
this page.
Name: Enter a name to be used for the switch.
Location: Enter the location of the switch.
Contact: Enter the name of a person or organisation.
2. Community Strings
Community Strings serve as passwords and can be entered as one of the following:
RO: Read only. Enables requests accompanied by this
string to display MIB-object information.
RW: Read write. Enables requests accompanied by this
string to display MIB-object information and to set
MIB objects.
3. Trap Manager
A trap manager is a management station that receives traps, the system alerts generated
by the switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps are issued. Create a trap manager
by entering the IP address of the station and a community string.
Page 40

40 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.11 Security Manager
On this page, users can change username and password with following steps.
1. In User Name: Type the new username.
2. In Assign/Change password: Type the new password.
3. In Reconfirm password: Retype the new password.
4. Click Apply.
Page 41

NP2624M User Guide 41
YML827 Rev1
2.5.12 802.1x Configuration
System Configuration
802.1x makes use of the physical access characteristics of IEEE802 LAN infrastructures in order to
provide a means of authenticating and authorizing devices attached to a LAN port that has point-topoint connection characteristics, and prevent access to that port in cases where the authentication
and authorization process fails.
To enable 802.1x, from Administrator \Switch setting \Advanced then fill in the authentication
server information:
Radius Server IP Address: The IP address of the authentication server.
Server Port: The UDP port number used by the authentication
server to authenticate.
Accounting Port: The UDP port number used by the authentication
server to retrieve accounting information.
Shared Key: A key shared between this switch and authentication
server.
NAS, Identifier: A string used to identify this switch.
Perport Configuration
In this page, users can select the specific port and configure the Authorisation State.
Each port can select four kinds of Authorisation State:
Page 42

42 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Fu: Force the specific port to be unauthorised.
Fa: Force the specific port to be authorised.
Au: The state of the specific port was determined by the
outcome of the authentication.
No: The specific port didn’t support 802.1x function.
Miscellaneous Configuration
In this page, users can change the default configuration for the 802.1x standard:
Quiet Period: Used to define periods of time during which it will
not attempt to acquire a supplicant (Default time is
60 seconds).
Tx Period: Used to determine when an EAPOL PDU is to be
transmitted (Default value is 30 seconds).
Supplicant Timeout: Used to determine timeout conditions in the
exchanges between the supplicant and authentication
server (Default value is 30 seconds).
Server Timeout: Used to determine timeout conditions in the
exchanges between the authenticator and
authentication server (Default value is 30 seconds).
Max requests: Used to determine the number of re-authentication
attempts that are permitted before the specific port
becomes unauthorized (Default value is 2 times).
Reauth Period: Used to determine a nonzero number of seconds
between periodic re-authentication off the
supplications (Default value is 3600 seconds).
Page 43

NP2624M User Guide 43
YML827 Rev1
2.5.13 Ping
The NP2624M switch provides a simplified ping function for users to check whether an IP is online
or not.
Enter the IP Address and number of counts for the ping packet to send. Press “Apply” to continue
next page.
This page will display the result of the pinging IP. It continues updating the “Reply Counts” to the
ping packets that are sent. Users can interrupt the progress by clicking the “Stop” button.
If the reply counts remain zero after the webpage reload stops, it could mean that the pinged host of
this IP does not exist.
Page 44

44 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.5.14 Single IP
The NP2624M switch provides a new management tool for a user to manage a group of LAN
switches by an IP agent method. “Single IP” is the name, meaning that the administrator can access
other network devices through one single IP device. There are two management modes: “Agent
mode” and “Stacking mode”.
Unlike a router’s NAT (from virtual IP domain to real IP domain), single IP provides a reverse
access (from real IP domain to virtual IP domain) using an IP-forwarding technology. With this IPagent method, the network administrator can remotely control his far-side hosts without being there,
accessing the private domain hosts through the agency of one real IP switch with a “Single IP”.
A maximum of 32 sets of information of network devices can be stored in the single IP switch and
16 sets in a stacking switch. Basically these network devices should provide http:// or telnet service
for the single IP switch to forward those protocol packets; meanwhile SNMP protocol can be also
passed through if they support SNMP service.
Moreover, this single IP switch has no exclusiveness, meaning that administrator can group
up network devices of any type (router, switch, server...) or brand without worrying their
incompatibility.
However, for stacking switch, only the switches of the same model can detect each other and
transfer information to their partner, so it won’t support other network devices in this instance. This
is the major difference between single IP agent mode and stacking mode. Please read Chapter 5 for
more information.
Web UIs of “Agent Management” and “Stacking Management” look similar. In these pages, users
can add or delete managed network devices. If the user disables the IP agent function, that is, sets
the management mode to “Agent Slave” or “Stacking Slave” in the IP setting webpage, this item
will not show up in the main menu.
2.5.14.1 Agent Management
Page 45

NP2624M User Guide 45
YML827 Rev1
Agent Control Port: The control port defines the specific TCP/UDP port
the single IP switch is listening, which the agent
manager sends its command to. Agent manager use
this specific port to tell the single IP switch to change
the current forwarding target host. The range of
available port number is 28000 ~ 30000. Ignore the
default settings of the “Agent Control Port” unless
the user has a special need for this protocol port, such
as virtual server. The default port number is 28019.
Add/Edit/Delete : To add a member, enter the IP and name in “IP
address” and “Host Name”, then press “Add/Edit”.
The new member will be listed on the left. To edit
a member’s host name, select the member in the list
and the IP and name will be shown on the right. Edit
the name and then press “Add/Edit” to update the list.
To remove a member, just select the member and
press “Delete”
Launch Manager : This button launches the Stacking manager.
2.5.14.2 Agent Manager
A floating menu be displayed after clicking “Launch Agent Manager” in the agent management
menu.
The agent manager holds 32+1 slots in the floating menu. The top slot (zero slot) displays the
master switch IP and its relative location. “Remote Agent” means that the user comes from another
IP domain than the managed ones, while “Local Agent” means that the user comes from the same
IP domain as the managed ones.
Page 46

46 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
There are differences between “Remote Agent” and “Local Agent”. The “Local Agent”, referred to
as “Local Single IP”, uses URL link method and the main browser window will directly jump to the
target host. Since the URL of the web browser has changed, authentication will be requested once
again when the new host is selected.
Due to switch loading, only one remote user can access the agent manager at a time. Other users
will be rejected if someone has launched the agent manager first. The switch will release the control
of single IP access in 25 seconds after the previous user closes his agent manager. For “Local Single
IP”, there is no restriction, but if a remote user has launched the agent manager in the same time, the
local user is also denied.
NOTE: Commands from agent manager cannot pass over current
management level, meaning that, in cases where a slave host is a
single IP switch with its agent function enabled, a user launching the
slave host’s agent manager will find the agent manager is replaced
by the slave’s one. Worse still, commands to pick the slave hosts
will cause an unexpected forwarding error here.
We strongly recommend that a single IP switch should not activate the IP agent manager when it is a
slave host of active master switch.
2.5.14.3 Stacking Management
Agent Control Port: The specific TCP/UDP port the single IP switch
is listening. See 2.5.14.1 Agent Management for
details.
There are two ways to add the members: “Auto-discover” and “Manual”.
Page 47

NP2624M User Guide 47
YML827 Rev1
Auto-discover method: Press “Find >>” and the found stackable switches
will be gathered in “Auto Discover List”. Select
these found members and press “ << Add” to add the
selected hosts to the list.
The searching range bases on Class C IP domain
within Agent IP. Changing the “Agent IP” in
“Administrator/IP & Management Mode” will alter
the search range. For example, if the Agent IP is
set to 192.168.223.100, and then the auto-discover
function will search for available switches in the
range from 192.168.223.1 to 192.168.223.255.
Manual method: Users can add members manually. Fill up the “IP
Address” and “Host Name”, then press “Apply” to
complete the addition of a new member.
Editing an existing member is also easy to do.
Simply select the host which needs to edited, the “IP
address” and “Host Name” will appear. Then modify
the “Host Name” for reference. For any IP that is not
within the member list, the modification will assume
to add a new member. Press “Apply” to confirm the
modification.
To delete an existing member, choose the host and
press “Delete”. Then the host will be removed from
the list.
Page 48

48 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Launch Manager: This button launches the Stacking manager.
For “Stacking mode”, there is an extra option
“VLAN Mode” for user to choose which type of
VLAN the stacking switch will carry on. There are
“802.1Q” and “Port-base” VLAN .
NOTE: In the case of the http:// authentication mechanism, the web
browser will always ask the administrator to input username and
password when agent manager changes a new host. Typically, the
web browser will keep the authentication key of the successful login
host and pass it to the other WebPages. The single IP switch remains
the URL of the master switch IP no matter how the agent manager
has changed the forwarding host, the new host will still receive the
same authentication key as the master switch when it requests the
login authentication. If the new host has a different username and
password from the master switch, authentication failure and hence
reentry will be required.
It is strongly recommended that the administrator change the usernames and passwords of the
managed hosts to the same ones as the master switch.
Page 49

NP2624M User Guide 49
YML827 Rev1
2.5.14.4 Stacking Manager
This web UI provides not only the integrated VLAN management, but also a handy IP agent. The
administrator can easily access other detail configurations in one individual switch of stacking set by
clicking the hostname on the right side of this panel and jumping to its configuration webpage.
Link Status
The first page shows the current link status of all stacking members. Link-up port numbers will
be highlighted. An off-line switch will dim to gray if it does not respond to the information
request from the stacking master in a period of time. This characteristic provides an easy method
of network diagnosis. The network administrator can check backbone connections of stacking
switches at a glance from this panel.
VLAN SETUP
To configure the VLAN setting of the stacking switch, click “VLAN” to bring up the VLAN
configuration panel.
There are two default VLANs existing in stacking switches.
Page 50

50 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
As seen above, the VLAN name “ DEFAULT” and VID “ 1” is standard setting for general Tag
VLAN , and all ports are added as untagged ports; The other VLAN “ 4091”, also called a “Stacking
Tag VLAN”, is a unique setting for this type of stacking. All Giga ports are set to tag members to
form a VLAN connection channel.
WARNING: Stacking Tag VLAN is highly restricted. Incorrect operation can ruin
the connection of stacking switches. Correct use of the Stacking Tag
VLAN will be discussed in the next section.
Add a VLAN
To Add a new VLAN, press “ Add” in the VLAN Panel. Two prompts will ask the user to input
VLAN name and VLAN ID.
After input, users can choose the VLAN member in the Stacking Manager panel by clicking the
designated port. Colour cycling from blue, yellow to black means that the port is set to untagged
port, tagged port or no member. When finished, press “ Apply” to submit the changes.
It is always wise to remember that the Giga ports of each member switch are set to tagged port and
keep at least one member port in the master switch.
Page 51

NP2624M User Guide 51
YML827 Rev1
The stacking switches interchange VLAN information through the Giga ports which are set to
tagged members by “Stacking Tag VLAN”. New VLANs should keep their Giga ports tagged.
Since the master switch holds all VLAN group information, the master switch should have the right
to access the new VLAN by adding at least one Giga port to its tagged member. An exclusion of
all master switch ports leads to unmanageability on this VLAN, for the master switch has no such
VLAN in its internal table.
Page 52

52 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Edit or Delete a VLAN
To edit an existing VLAN, just select the VLAN from the VLAN panel and modify the members in
the Stacking Manager panel. Once done, press “ Apply” to submit the setting.
To delete a VLAN is also an easy task. Select the unwanted VLAN and press “Delete” to remove it.
NOTE: The “DEFAULT VLAN” and “Stacking Tag VLAN” are undeletable! A
error message will pop up to cancel the task. The Stack VLAN also
cannot be edited.
Page 53

NP2624M User Guide 53
YML827 Rev1
PVID SETUP
The default PVID value of all ports of 802.1Q VLAN is 1. Hence only the default VLAN ( PVID =
1 ) has all of its ports as members in the beginning.
The available PVIDs are based on the VLANs that the user created in the previous “VLAN” page.
1. Select the PVID to be modified and choose the ports for this PVID value.
2. Click “Apply” button to submit and a message ”Please wait” will be displayed.
3. When a message advising “Current setting is on …” is displayed, the task is completed.
Page 54

54 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.6. TFTP Update Firmware
The following menu options provide some system control functions to allow a user to update
firmware and remotely boot the switch system:
1. Install TFTP program (such as Turbo98, or Cisco TFTP) and then execute.
2. Copy the updated firmware image.bin into TFTP server’s directory.
3. In web management select administrator—TFTP update firmware.
4. Download the new image.bin file by pressing <update firmware>.
5. After the update has completed, press <reboot> to restart the switch.
Page 55

NP2624M User Guide 55
YML827 Rev1
2.7. Configuration Backup
2.7.1. TFTP Restore Configuration
Use this page to set the ftp server address. You can restore the EEPROM value from here, but you
must restore the image in the ftp server, the switch will then download the flash image back.
2.7.2. TFTP Backup Configuration
Use this page to set TFTP server IP address. You can save current EEPROM value from here, then
go to the TFTP restore configuration page to restore the EEPROM value.
Page 56

56 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
2.8. Reset System
To Reset the Switch to its default configuration, click on the Reset button.
2.9. Reboot
To Reboot the Switch System, click on the Reboot button.
2.10. Event Logging
A history log is provided here to keep track of events occurring on the switch. This logs up to 100
events and then the latest event will overwrite the oldest one.
All records will be kept in flash memory even after writing default, unless user clears the event log.
Press “Prev” or “Next” button will browse previous 25 or next 25 sequences. The “Top” button will
re-list the table from the latest event. “Clear” button will clear all history.
Event logger displays the real time according to the time zone set by the user.
Page 57

NP2624M User Guide 57
YML827 Rev1
3. Console – Boot Loader
Each time the switch restarts, the user can get some basic information from console (use Hyper
terminal 57600 baud rate).
After switch tests are done, a 5-seconds countdown timer will prompt the user to press any key to
enter the “User Menu”.
There are five functions in the menu:
1. start kernel: Back to switch system initiation and enter login.
2. kernel update from xmodem : Use 1k X modem to update firmware.
3. kernel update from tftp: Use TFTP to update firmware.
4. set ip address: A shortcut to setup switch IP and gateway.
5. diagnose sdram: A basic SDRAM diagnosis.
Page 58

58 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
3.1 1K X modem Firmware update
We provide the 1k X modem to update firmware from RS232. 1K X modem only works in
57600bps mode. So you must change baud rate to 57600bps to download firmware.
1. Select “2” to start 1K X modem firmware update.
2. When “CCCC…” is displaying on console, select Transfer /Send File.
3. Select the 1K Xmodem in the Protocol item, and browse for the image for updating.
Press the Send button.
4. Start downloading the image file.
5. After the firmware has been downloaded, the switch will then automatically update it
and then the switch will reboot.
Page 59

NP2624M User Guide 59
YML827 Rev1
3.2 TFTP Firmware update
We provide the TFTP client to update firmware from Ethernet. The user has to first install TFTP
server on their PC and place the image in the download folder.
1. Press “3” to start TFTP update firmware.
2. Enter the Switch IP address and press “Enter” to accept default value.
3. Enter the TFTP Server IP address and press “Enter” to accept default value.
4. Enter the File name to download. Press “Enter” to accept default value and the TFTP
download will begin and the firmware will be updated.
3.3 Set IP Address
A shortcut to set switch IP address and gateway before switch system initialization has also been
provided. This saves time as the switch IP can be changed without the need to wait for the system to
boot up and reconfigure.
1. Press “4” to start IP setup.
2. Enter the Switch IP address. Press “Enter” to accept the default value.
3. Enter the Mask. Press “Enter” to accept the default value.
4. Enter the Gateway IP address. Press “Enter” to accept the default value.
Page 60

60 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
3.4 Diagnose Sdram
We provide a basic diagnosis for a SDRAM test. It is important to verify hardware faults when a
switch becomes unstable.
When the test is done, it will display the status and prompt the user to reset the switch.
Page 61

NP2624M User Guide 61
YML827 Rev1
4. Out-of-band Terminal mode management
The NP2624M switch also provides a serial interface to manage and monitor the switch. Users can
follow the Console Port Information provided online to use Windows HyperTerminal program to
link to the switch.
Type the username and press enter and then type the password and press enter to login.
The default username is “admin”; the default password is “admin ”.
Page 62

62 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.1 Main Menu
There are six items which can be selected:
Switch Static Configuration: Configure the switch.
Protocol Related Configuration: Configure the protocol function.
Status and Counters: Show the status of the switch.
Reboot Switch: Restart the system or reset switch to default
configuration.
TFTP Update Firmware: Use TFTP to download a firmware image.
Logout: Exit the menu line program.
Control Keys
The following control keys are provided for this mode operation:
Tab: Move the cursor to next item.
Backspace: Move the cursor to previous item.
Enter: Select item.
Space: Toggle selected item to next configure.
Page 63

NP2624M User Guide 63
YML827 Rev1
4.2 Switch Static Configuration
Control Keys
You can press the Tab or Backspace keys to choose an item, and press the Enter key to select an
item.
Action Menu Line
<Quit>: Exit the configuration page and return to the previous
menu.
<Edit>: Configure all items. When you have finished
configuring the item, press Ctrl+A to return back to
the action menu line.
<Save>: Save all configured values.
<Previous Page>: Return to previous page to configure.
<Next page>: Go to the next page to configure it.
Page 64

64 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.1. Port Configuration
This page allows you to change the status of every port.
Press the Space key to change the configuration of each item.
InRate (100K/unit): User can set input rate control, which is 100K per
unit. The valid range is 0~1000.
0: disable rate control.
1~1000: valid rate value.
OutRate (100K/unit): User can set output rate control, which is 100K per
unit. The valid range is 0~1000.
0: disable rate control.
1~1000: valid rate value.
Enabled: User can disable or enable this port control.
“Yes” that mean the port is enabled.
“No” that mean the port is disabled.
Auto: User can set auto negotiation mode to “Auto”,
“Nway_Force”, or “Force” per port.
Spd/Dpx: User can set “100Mbps” or “10Mbps” speed on port
1~port 24.
Set “1000Mbps”, “100Mbps” or “10Mbps” speed
on port25~port26 (dependant on optional Gigabit
module card), and set “full-duplex” or “half-duplex”
mode.
Flow Control: Full: User can enable or disable full flow control
function (pause).
Half: User can enable or disable half flow control
function (backpressure).
Page 65

NP2624M User Guide 65
YML827 Rev1
NOTE: Pressing “Save” will only save one page of configuration. If static
trunk groups exist, they will be displayed (eg: TRK1, TRK2…) after
port 26, and you can configure them as above.
4.2.2. Trunk Configuration
This page allows the user to create a maximum of seven trunk groups. Users can arbitrarily select
up to four ports from port 1~port 26 to build a trunk group.
1. Select <Edit> on the actions menu
2. Press space key to configure the member port of trunk group. You also have to set
“Static” or “LACP” for the corresponding trunk group of TRK1~TRK7 item.
“Static” – the normal trunk.
“LACP” – this trunk group has link aggregation control protocol.
3. Press Ctrl+A to go back action menu line
4. Select <Save> to save all configure value.
5. If the TRK1~TRK7 are “Disabled”, the trunk group is deleted.
6. All ports in the same static trunk group will be treated as a single port. So when setting
VLAN members and Port configuration they will be toggled on or off simultaneously.
NOTE: If a VLAN group exists, all of the members of static trunk group must
be in the same VLAN group.
Page 66

66 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.3. VLAN Configuration
4.2.3.1. VLAN Configure
This page allows the user to set VLAN mode to port-based VLAN or 802.1Q VLAN or disable
VLAN function.
NOTE: Changing the VLAN mode requires the switch to be restarted.
If the switch is set to 802.1Q VLAN, this page will allow the user to set PVID, ingress filtering 1
and ingress filtering 2.
Page 67

NP2624M User Guide 67
YML827 Rev1
1. PVID (Port VID: 1~255): Type the PVID.
2. Ingress Filter 1 NonMember Pkt:
NonMember Pkt works the same as Ingress Filtering Rule 1 on the web interface.
Forwarding only packets with VID matching this port’s configured VID.
Press Space key to choose “forward” or to “drop” the frame not matching this port’s
configured VID.
3. Ingress Filter 2 UnTagged Pkt:
UnTagged Pkt works the same as Ingress Filtering Rule 2 on the web interface.
Drop untagged frame.
Press Space key to choose “drop” or “forward” the untagged frame.
Page 68

68 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.3.2. Create a VLAN Group
Create Port-Based VLAN
Create a port-based VLAN and add member/nonmember ports to it.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. VLAN Name: Type a name for the new VLAN.
3. Grp ID: Type the VLAN group ID. The group ID range is 1~4094.
4. Member: Press <Space> key to choose VLAN member. There are two types to select:
a. Member: the port is member port.
b. No: the port is NOT member port.
5. Press Ctrl+A go back action menu line.
6. Select <Save> to save all configure value.
NOTE: If trunk groups exist, they will be displayed (eg: TRK1, TRK2…) after
port26, and you can configure if necessary.
Page 69

NP2624M User Guide 69
YML827 Rev1
Create 802.1Q VLAN
Create an 802.1Q VLAN and add tagged /untagged member ports to it.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. VLAN Name: Type a name for the new VLAN.
3. VLAN ID: Type a VID (between 1~4094). The default is 1. There are 256 VLAN
groups available.
4. Protocol VLAN: Press the Space key to choose the protocol type.
5. Member: Press the Space key to choose a VLAN member. There are three types to
select:
a. UnTagged: This is the member port of the VLAN group and outgoing frames are
NO VLAN-Tagged frames.
b. Tagged: This is the member port of the VLAN group and outgoing frames are
VLAN-Tagged frames.
c. NO: The port is NOT member of the VLAN group.
6. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line.
7. Select <Save> to save all configured values.
NOTE: If the trunk groups exist, they will be displayed (ex: TRK1, TRK2…)
after port 26, and you can configure them if necessary.
Page 70

70 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.3.3. Edit / Delete a VLAN Group
In this page, users can edit or delete a VLAN group.
1. Press <Edit> or <Delete> item.
2. Choose the VLAN group that you want to edit or delete and then press enter.
3. Users can modify the protocol VLAN item and the member ports are tagged or untagged and remove some member ports from this VLAN group.
4. After editing the VLAN, press the <Save> key to save all configuration values.
NOTE:
1. Pressing “Enter” once will complete the deletion when in delete mode.
2. The VLAN Name and VLAN ID cannot be modified.
3. The default VLAN cannot be deleted.
Page 71

NP2624M User Guide 71
YML827 Rev1
4.2.3.4. Groups Sorted Mode
In this page, users can select VLAN groups sorted mode:
(1) Sorted by Name
(2) Sorted by VID.
The Edit/Delete a VLAN group page will display the result.
In the Edit/Delete a VLAN Group page, the result of sorted by name.
Page 72

72 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
In the Edit/Delete a VLAN Group page, the result of sorted by VID.
Page 73

NP2624M User Guide 73
YML827 Rev1
4.2.4. Miscellaneous Configuration
4.2.4.1. Ping
Type the Host IP and the counts for pinging, then go back to action menu and press “Save”. “Reply
Counts” will display the result of pinging.
Page 74

74 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.4.2. MAC Age Interval
Type the number of seconds that an inactive MAC address remains in the switch’s address table.
The valid range is 300~765 seconds. Default is 300 seconds.
4.2.4.3. Broadcast Storm Filtering
This page configures the broadcast storm control.
1. Press <Edit> to configure the broadcast storm filter mode.
2. Press Space key to choose the threshold value.
The valid threshold value is 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and NO. Default is 5%.
Page 75

NP2624M User Guide 75
YML827 Rev1
4.2.4.4. Maximum bridge transmit delay bound
1. Max bridge transmit delay bound: Limits the packets queuing time in switch. If
enabled, when the amount of time the packets queued exceeding the maximum they will
be dropped. Press the Space key to set the time. Those valid values are 1sec, 2sec, and
4sec and off. Default is off.
2. Low Queue Delay Bound: Limits the low priority packets queuing time in switch. If
enabled, when the amount of time the low priority packet stays in the switch exceeds
Low Queue Max Delay Time, it will be sent. Press the Space key to enable or disable
this function. Default is disable.
3. Low Queue Max Delay Time: To set the amount of time that low priority packets
queuing in switch will be delayed. The valid range is 1~255ms. Default Max Delay
Time is 255ms.
NOTE: Make sure “Max bridge transmit delay bound control” is enabled
before enabling Low Queue Delay Bound, because Low Queue
Delay Bound must be work under “Max bridge transmit delay bound
control” is enabled situation.
Page 76

76 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.4.5. Port Security
A port in security mode will be “locked” without permission of address learning. Only the incoming
packets with SMAC already existing in the address table can be forwarded normally. The user can
disable the port from learning any new MAC addresses, then use the static MAC addresses screen to
define a list of MAC addresses that can use the secure port.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. Press Space key to choose enable / disable item.
3. Press Ctrl+A to go back action menu line.
4. Select <Save> to save all configure value.
5. You can press <Next Page> to configure port9 ~ port26, press <Previous Page> return to
last page.
4.2.4.5. Collisions Retry Forever
Collisions Retry Forever: Disable – In half duplex, in the event of a collision it
will retry up to 48 times before dropping the frame.
Enable – In half duplex, in the event of a collision it
will continue retrying forever (Default).
Page 77

NP2624M User Guide 77
YML827 Rev1
4.2.4.6. Hash Algorithm
Select CRC-Hash(default) or DirectMap for Hash algorithm.
4.2.4.7. IFG Compensation
Enable or disable the inter-frame gap (IFG) compensation function.
Page 78

78 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.5. Administration Configuration
4.2.5.1. Change Username
This page allows the user to change the web management username.
Type the new username, and then press <Save> item.
Page 79

NP2624M User Guide 79
YML827 Rev1
4.2.5.2. Change Password
This page allows the user to change the web management login password.
4.2.5.3. Device Information
This page allows the user to configure the device information.
Page 80

80 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.5.4. IP Configuration
This page allows the user to configure the IP settings and fill in the new values.
Page 81

NP2624M User Guide 81
YML827 Rev1
4.2.6. Port Mirror Configuration
Port mirroring is a method for monitoring traffic in switched networks. Traffic through ports can be
monitored by one specific port. That is, traffic going in or out of monitored ports will be duplicated
into the monitoring port.
Press the Space key to change configure of per item.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. Sniffer Mode: Press the Space key to set the sniffer mode to Disable,Rx,Tx or Both.
3. Monitoring Port: The sniffer port can be used to see all monitored ports traffic. Press the
Space key to choose it.
4. Monitored Port: The ports you want to monitor. All monitored ports traffic will be
copied to the sniffer port. You can select a maximum of 25 ports to monitor in the
switch. Users can choose which port to monitor in the sniffer mode. Press Space key to
choose member port, “V” – denotes a member, “—” – is not a member.
5. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line
6. Select <Save> to save all configured values.
7. On the action menu line you can press <Next Page> to configure port9 ~ port26, press
<Previous Page> return to last page.
NOTE: Only one sniffer mode is active in the switch at a time.
Page 82

82 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.7. Priority Configuration
4.2.7.1. Port Static Priority
This static priority based on the port, if you set the port to high priority, incoming frames from this
port will always be considered to be high priority frames.
Page 83

NP2624M User Guide 83
YML827 Rev1
4.2.7.2. 802.1P Priority Configuration
There are 0~7-priority levels that can be mapped to a high or low queue.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. Press Space key to select the priority level mapping to high or low queue.
3. High/Low Queue Service Ration H/L: User can select the ratio of high priority packets
and low priority packets.
4. Press Ctrl+A to go back action menu line.
5. Select <Save> to save all configured values.
Page 84

84 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.2.8. MAC Address Configuration
4.2.8.1. Static MAC Address
When you add a static MAC address, it remains in the switch’s address table, regardless of whether
the device is physically connected to the switch. This saves the switch from having to re-learn a
device’s MAC address when disconnected or powered-off.
In this page users can add / modify / delete a static MAC address.
Page 85

NP2624M User Guide 85
YML827 Rev1
Add static MAC address
1. Press <Add> > <Edit> key to add static MAC address.
2. MAC Address: Enter the MAC address which the port should permanently forward
traffic, regardless of the device’s network activity.
Page 86

86 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
3. Port num: Press the <Space> key to select the port number.
4. Vlan ID: If tag-based (802.1Q) VLAN are set up on the switch, static addresses are
associated with individual VLANs. Type the VID to associate with the MAC address.
5. Press Ctrl+A to go back action menu line.
6. Then select <Save> to save all configure value.
Edit static MAC address
1. Press <Edit> key.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to modify and then press enter.
3. Press <Edit> key to modify all the items.
4. Press Ctrl +A to go back to the action menu line, and then select <Save> to save all
configured values.
Delete static MAC address
1. Press <Delete> key.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then press enter.
3. Pressing <Enter> once will complete deletion in delete mode.
Page 87

NP2624M User Guide 87
YML827 Rev1
4.2.8.2. Filtering MAC Address
MAC address filtering allows the switch to drop unwanted traffic. Traffic is filtered based on the
destination addresses.
In this page users can add /modify /delete a MAC address filter.
Add filter MAC address
1. Press <Add> > <Edit> key to add a MAC address filter.
2. MAC Address: Type the MAC address to filter.
3. Vlan ID: If tag-based (802.1Q) VLAN are set up on the switch, type the VID to
associate with the MAC address.
4. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line, and then select <Save> to save all
configured values.
Page 88

88 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Edit filter MAC address
1. Press <Edit> key.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to modify and then press enter.
3. Press <Edit> key to modify all the items.
4. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line, and then select <Save> to save all
configured values.
Delete filter MAC address
1. Press <Delete> key to delete a filter MAC address.
2. Choose the MAC address that you want to delete and then press enter.
3. Pressing <Enter> once will complete the deletion when in delete mode.
Page 89

NP2624M User Guide 89
YML827 Rev1
4.3. Protocol Related Configuration
Page 90

90 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.3.1. RSTP
The Rapid-Spanning-Tree Protocol (RSTP) is a standardized method (IEEE 802.1w) for avoiding
loops in switched networks. RSTP is enabled, to ensure that only one path at a time is active
between any two nodes on the network.
4.3.1.1. Enable/Disable RSTP
This page allows the user to enable or disable the Spanning Tree function. Press the Space key to
select enable or disable.
4.3.1.2. RSTP System Configuration
1. You can view spanning tree information about the Root Bridge on the left.
2. On the right, users can set new values for the RSTP parameter.
NOTE: For more information on parameter descriptions please see section
2-4-8.
Page 91

NP2624M User Guide 91
YML827 Rev1
4.3.1.3. Per port Configuration
1. PortState: Displays spanning tree status about the switch which per port is forwarding or
blocking.
2. Select <Edit>.
3. PathCost: Specifies the path cost of the port that the switch uses to determine which
ports are the forwarding ports.
4. Priority: The Priority Port allows you to make it more or less likely to become the root
port.
5. EdgePort: If the port connected to a device does not understand STP or RSTP, you can
set as “No”. This means the switch will stay in the forwarding state.
6. Press Ctrl +A to go back to the action menu line.
7. Select <Save> to save all configured values.
8. On the action menu line you can press <Next Page> to configure port9 ~ port26, press
<Previous Page> return to last page.
NOTE: For more information on parameter descriptions please see section
2-4-8.
Page 92

92 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.3.2. SNMP
Any Network Management running the simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) can be
managed by the switch.
Use this page to define management stations as trap managers and to enter SNMP community
strings. Users can also define a name, location, and contact person for the switch.
4.3.2.1. System Options
1. Press <Edit>.
2. System Name: Type a name to be used for the switch.
3. System Contact: Type the name of contact person or organization.
4. System Location: Type the location of the switch.
5. System Description: Type the description of the switch.
6. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line.
7. Press <Save> to save the configured values.
Page 93

NP2624M User Guide 93
YML827 Rev1
4.3.2.2. Community Strings
Use this page to Add/ Edit/ Delete SNMP community strings.
1. Community Name: The name of current strings.
2. Write Access: Enable the rights as read only or read-write.
Restricted: Read only, enables requests accompanied by this
string to display MIB-object information.
Unrestricted: Read write, enables requests accompanied by this
string to display MIB-object information and to set
MIB objects.
Add Community Name
1. Press <Add> > <Edit> key.
2. Community Name: Type the community name.
3. Write Access: Press the Space key to toggle between restricted or unrestricted.
Page 94

94 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Edit Community Name
1. Press the <Edit> key, choose the item that you want to modify and then press Enter.
2. Community Name: Type the new name.
3. Write Access: Press the <Space> key to toggle between restricted or unrestricted.
Delete Community Name
1. Press the <Delete> key.
2. Choose the community name that you want to delete and then press enter.
3. Pressing <Enter> once will complete the deletion when in delete mode.
Page 95

NP2624M User Guide 95
YML827 Rev1
4.3.2.3. Trap Managers
A Trap Manager is a management station that receives traps; the system alerts generated by the
switch. If no trap manager is defined, no traps are issued. Create a trap manager by entering the IP
address of the station and a community string.
Add SNMP trap manager
1. Press <Add> > <Edit> to add the trap manager.
2. IP: Type the IP address.
3. Community Name: Type the community name.
4. Press Ctrl +A to go back to the action line menu and press <Save> key to save the
configuration.
Page 96

96 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
Edit trap managers
1. Press the <Edit> key, and then choose the item that you want to modify.
2. IP: Type the new IP address
3. Community Name: Type the community name.
4. Press Ctrl +A to go back to the action line menu and press <Save> key to save
configuration.
Delete trap manager
1. Press the <Delete> key.
2. Choose the trap manager that you want to delete and then press enter.
3. Pressing <Enter> once will complete deletion when in delete mode.
Page 97

NP2624M User Guide 97
YML827 Rev1
4.3.3. IGMP
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) is an internal protocol of the Internet Protocol
(IP) suite.
This page allows you to enable / disable the IGMP support.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. IGMP Protocol: Press Space key to choose Enable / Disable.
3. IGMP Query Mode: Press Space key to choose Auto / Enable /Disable.
4. Press Ctrl+A to go back to the action menu line.
5. Select <Save> to save configured values.
Page 98

98 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.3.4. LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol)
This page allows you to configure and view the LACP status.
NOTE: All ports support LACP dynamic trunk group. If connecting to the
device that also supports LACP, the LACP dynamic trunk group will be
created automatically.
4.3.4.1. Working Port Setting
This page allows you to set work ports in trunk groups.
1. Select <Edit>.
2. Group: Displays the trunk group ID.
3. LACP: Displays the trunk group’s LACP status.
Page 99

NP2624M User Guide 99
YML827 Rev1
4. LACP Work Port Num: Defines the maximum number of ports that can be aggregated
at the same time. If local static trunk group, the number must be the same as group
member ports.
NOTE: Before changing settings on this page, you have to set trunk group
on the page of Trunk Configuration first.
4.3.4.2. State Activity
1. Select <Edit>.
2. Press the Space key to choose the item.
Active: The port automatically sends LACP protocol packets.
Passive: The port does not automatically send LACP protocol packets, and responds
only if it receives LACP protocol packets from the opposite device.
3. Press Ctrl+A go back action menu line.
4. Select <Save> to save configured values.
NOTE: If a user sets LACP mode in the trunk group, all of the member ports
of this trunk group will set “Active” automatic.
Page 100

100 NP2624M User Guide
YML827 Rev1
4.3.4.3. LACP Status
Relational Information for trunk groups can be found on this page.
Static trunk group
LACP trunk group
<Quit>: Exit this page and return to previous menu.
<Previous Page>: Return to previous page to view.
<Next page>: Go to the next page to view.
 Loading...
Loading...