Net2Phone Max 410, Max 420, Max 430 User Manual



The specifications and information regarding the products in this manual
are subject to change without notice. All statements, information, and
recommendations in this manual are believed to be accurate but are
presented without warranty of any kind, express or implied. Users must
take full responsibility for their application of any products.
The software license and limited warranty for the accompanying product
are set forth in the information packet that shipped with the product and
are incorporated herein by this reference. If you are unable to locate the
software license or limited warranty, contact your Net2Phone
representative for a copy.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radiofrequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required
to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices:
The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate
radio-frequency energy. If it is not installed in accordance with 's
installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and
television reception. This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the
specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are
designed to provide reasonable protection against such interference in a
residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation.
Modifying the equipment without 's written authorization may result in
the equipment no longer complying with FCC requirements for Class A
or Class B digital devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment
may be limited by FCC regulations, and you may be required to correct
any interference to radio or television communications at your own
expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by
turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the
Net2Phone equipment or one of its peripheral devices. If the equipment
causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the
interference by using one or more of the following measures:

· Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
· Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
· Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
· Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the
television or radio. (That is, make certain the equipment and the
television or radio are on circuits controlled by different circuit breakers
or fuses.)
Modifications to this product not authorized by Net2Ph one c ould void
the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
Notwithstanding any other warranty herein, all document files and
software of these suppliers are provided "as is" with all faults. and the
above-named suppliers disclaim all warranties, expressed or implied,
including, without limitation, those of merchantability, fitness for a
particular purpose and non-infringement or arising from a course of
dealing, usage, or trade practice.
In no event shall Net2Phone or its suppliers be liable for any indirect,
special, consequential, or incidental damages, including, without
limitation, lost profits or loss or damage to data arising out of the use or
inability to use this manual, even if or its suppliers have been advised
of the possibility of such damages.
Max 410/420/430, Net2Phone, and the logo are registered trademarks
of , Inc. in the US and certain other countries. All other trademarks
mentioned in this document are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © 2002, Net2Phone, Inc. All rights reserved
The use, disclosure, modification, transfer, or transmittal of this work for
any purpose, in any form, or by any means, without the written
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide
Rev. 1.5.30 November 2003
permission of Net2Phone is strictly forbidden.
WARNING:
Handling the cord on this product will expose you to
lead, a chemical known to the State of California to
cause [cancer, and] birth defects or other
reproductive harm. Wash hands after handling.

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide
Table of Contents
1 WELCOME...................................................................................... 1
OVERVIEW.........................................................................................1
PRODUCT FEATURES..........................................................................1
NEW FEATURES AND FUNCTIONALITY ...................................................3
PACKAGE CONTENTS..........................................................................5
SYSTEM AND SERVICE REQUIREMENTS.................................................5
General Requirements.................................................................5
Hardware Requirements..............................................................6
ABOUT THIS GUIDE.............................................................................6
Symbols.......................................................................................8
2 GETTING STARTED.......................................................................9
OVERVIEW.........................................................................................9
LOCATING YOUR FXS AND/OR FXO PORTS .......................................10
Physical Port Numbering...........................................................10
INSTALLING THE MAX 410/420/430....................................................10
CONNECTING THE MAX TO A PBX......................................................12
Connecting the Max 410’s FXO Ports to a PBX.........................12
Connecting the Max 420’s FXS Ports to a PBX.........................13
Connecting the Max 430’s FXS/FXO Ports to a Telephone/PBX
...................................................................................................14
CONNECTING THE MAX 420/430’S FXS PORTS TO A FAX MACHINE...... 15
3 CONNECTING THE MAX 410/420/430 TO A LAN.......................17
CONNECTING THE MAX 410/420/430 TO A DHCP LAN......................17
Obtaining the Max 420/430’s DHCP IP Address via a Telephone
Keypad.......................................................................................18
Connecting to the Max 410 through a Serial Cable...................19
Using the HyperTerminal Emulation Program........................19
Obtaining the Max’s DHCP IP address via HyperTerminal ....21
CONNECTING TO A LAN WITH STATIC IP ADDRESSES ..........................21
Entering Static IP Addresses from a Telephone Keypad...........22
Disabling DHCP from a telephone keypad (Max 420/430).....22
Entering an IP Address from a Telephone Keypad (Max
420/430).................................................................................23
i

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide
Entering a Netmask Address from a Telephone Keypad (Max
420/430).................................................................................23
Re-enabling DHCP from a Telephone Keypad (Max 420/430)
...............................................................................................24
Entering Static IP Addresses via HyperTerminal (Max 410)...25
Turning DHCP On (or Off) from HyperTerminal.....................25
Entering an IP Address..........................................................25
4 LOGGING INTO THE MAX WEB MANAGER..............................29
OVERVIEW.......................................................................................29
LOGGING INTO THE WEB MANAGER....................................................29
5 USING THE MAX WEB MANAGER.............................................33
OVERVIEW.......................................................................................33
PORT CONFIGURATION .....................................................................34
NETWORK AND VOICE CONFIGURATION ..............................................34
Network Configuration Table.....................................................35
Voice Configuration Table..........................................................36
IP Configuration Table...............................................................36
CDR Configuration Table...........................................................37
Configuring Firewalls.................................................................38
ACCOUNT CONFIGURATION ...............................................................41
Single Account Management.....................................................42
Multiple Account Management...................................................43
The Login Button.......................................................................44
Announce Account Balance.......................................................44
ROUTING TABLE CONFIGURATION ......................................................44
Logical Port Numbering.............................................................45
Adding an Entry to the Current Routing Table...........................45
INTEGRATED VOICE RESPONSE (IVR) CONFIGURATION........................47
Remote IVR Configuration.........................................................47
Max-to-Max IVR Configuration...................................................51
Configuring Max-to-Max Calling.............................................52
Receiving Max-to-Max Calls...................................................54
INBOUND ALLOW LIST CONFIGURATION...............................................56
CLASS OF SERVICE CONFIGURATION..................................................58
PORT CLASS CONFIGURATION ...........................................................60
LOCAL DIALING SYSTEM....................................................................61
SYSTEM INFORMATION AND COMMANDS .............................................63
ii

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide
OTHER WEB MANAGER FUNCTIONS ...................................................64
Load Default Config...................................................................64
Show Log Messages .................................................................65
Restart System..........................................................................65
Upgrading the System Software................................................65
Preparing for the Upgrade......................................................66
Performing the Upgrade.........................................................67
Help with your Max 410/420/430 ...............................................68
6 PLACING CALLS .........................................................................69
OVERVIEW.......................................................................................69
THE POUND KEY..............................................................................69
PLACING CALLS TO THE PSTN..........................................................69
Placing Calls to Destinations within North America...................69
Placing International Calls .........................................................70
MAX-TO-MAX CALLING......................................................................70
Calling a Max 420’s FXS Port from Another Max.......................70
Calling a Max 410’s FXO Port from Another Max......................70
7 APPENDICES...............................................................................73
APPENDIX A – TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................................73
Installation Problems.................................................................73
Network Problems .....................................................................74
Configuration Problems.............................................................76
Calling Problems........................................................................76
Faxing Problems........................................................................77
APPENDIX B – TECHNICAL SUPPORT..................................................79
APPENDIX C – SYSTEM SPECIFICATIONS ............................................80
APPENDIX D – PHYSICAL AND LOGICAL PORT NUMBER TABLE..............82
APPENDIX E – APPROVALS AND LISTINGS...........................................83
For Max 410/ 430.......................................................................83
FCC Declaration of Conformity...............................................83
FCC Compliance Statement:..................................................83
For Max 420...............................................................................83
FCC Declaration of Conformity...............................................83
FCC Compliance Statement:..................................................83
Party responsible for product compliance: .............................84
APPENDIX F – END USER WARRANTY................................................85
8 INDEX ...........................................................................................87
iii


Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
1
1 Welcome
Overview
Congratulations on purchasing the Max 410/420/430!
The Max 410/420/430 is a Voice over Internet Protocol
(VoIP) device that allows you to make multiple outgoing
calls over the Internet using a single Ethernet Local Area
Network (LAN) connection. The Max 410/420/430 works
like a gateway to convert the analog signal from your
telephones to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP). It then
uses the LAN’s broadband connection to send calls over
the Internet via ’s service platform. Since Net2Phone calls
bypass most of the Public Switched Telephone Network
(PSTN), the result is significant savings on long-distance
communications services.
This chapter describes:
Product Features
New Features and Functionality
Package Contents
System and Service
Requirements
About this Guide
Product Features
The Max 410, 420, and 430 is a stand-alone device that
connects directly into an existing LAN through an RJ-45
port. The Max 410 contains four FXO ports, Max 420
contains four FXS ports and Max 430 contains 3 FXS
ports and 1 FXO port.
FXS (Foreign EXchange Station) interfaces are used to
connect standard analog devices such as corded and
cordless telephones or fax machines. Optionally, they may
be connected to the analog trunk card on a Public Branch
1

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
Exchange (PBX), Automatic Public Branch Exchange
(APBX), or Key Phone System (KPS) systems. They are
used to place outgoing calls over the Internet and to
receive incoming calls from other devices.
FXO (Foreign EXchange Office) ports connect to the
analog line card on a PBX, APBX, or KPS, or to an analog
phone jack, to provide connectivity to the Max from
phones both inside and outside of the PBX system.
In addition to the FXS functions, FXO ports provide limited
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) functionality, which
includes multiple options for caller greetings, passwords,
and Internet call forwarding. This allows the Max 410 to
assume many IVR functions when the PBX does not
provide them.
A separate port with its own telephone line connection to
the PBX, or to an analog telephone, is required for every
concurrent telephone call (or conversation). For example,
if capability for 3 concurrent calls is desired, then the Max
must have at least 3 ports connected to the PBX or to
analog telephones.
The Max 410, 420, and 430 feature several proprietary
QoS (Quality of Service) enhancements, including:
G.168 echo cancellation
Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
Comfort Noise Generation (CNG)
Dynamic jitter buffer control
More feature highlights include:
Improved Call Quality – The Max 410, 420,
and 430 are compatible with more state-of-theart gateways such as Nuera and Cisco (when
available), which greatly improves the quality of
calls with reduced latency.
Dropped Call Prevention – The Max 410,
420, and 430 are now more reliable in retaining
calls in progress by re-establishing connections
to call controllers if an IP stream is lost. This
feature will greatly improve dropped call
problems for ADSL or Cable modem users as
well as LAN network users.
2
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
Account Balance Announcement by Port –
The Max 410, 420, and 430 have a Web
configurable toggle switch that enables the IVR
to announce the account balance or minutes
remaining on the port that the call is going
over.
Greeting Message - A greeting message will
play prior to the dialed call being sent to the
call servers.
New Password Functionality - When a user
selects Password mode or Acc/Pin/Password
mode and the password field is empty, an error
message is displayed and the password value
is not saved in flash memory.
Call Detail Record (CDR) Generation –
Administrators can select to have CDRs
generated and sent to the Max Automated
Billing System (ABS).
TX/RX Silence Detection – The Max 410,
420, and 430 detects both TX/RX silence on an
FXO port and then disconnects the call based
on the duration of call silence.
Multiple Frames per Packet Support - The
Max 410, 420, and 430 supports multiple
frames per packet on the G.732 codec.
Upgraded Vocfiles – Updated vocfile included
with software upgrade.
New Features and Functionality
Version 1.5.30 provides the following new features:
T.38 Fax Protocol Supported – This version
features enhanced functionality of the industry
standard T.38 fax protocol, including automatic
fax detection, built-in redundancy, and higher
success rates.
IMPORTANT: Before upgrading to version
1.5.30 to take advantage of the enhanced
T.38 functionality, please refer to the
Upgrading the System Software section on
page 65 in this Guide.
3

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
Inbound Allow List – The Inbound Allow List
feature for FXO ports allows the user to specify
the allowable inbound numbers that can make
use of the port for outbound calls.
Class of Service – The new Class of Service
feature sets the call authorization classes for
restricting outbound calls. Users cannot make
a call to the restricted numbers that are in both
his/her own class and a higher class.
Local Dialing System – This version features
the addition of the Local Dialing System, which
enables users to dial phone numbers on the
Max 410, 420, and 430 products as they
normally do on their ordinary phones. That is,
users do not have to dial an international call
access number and country code number if the
call destination is the same country where user
lives. Similarly, the area code can be omitted
for calls made to the same area. Users can
configure a dialing pattern on the Max 410,
420, or 430 that is as close as possible to the
host country's dialing pattern.
FTP Block – The FTP Block feature enables
the Max to block an FTP connection. For
example, if you want to upgrade the Max via
FTP, you must start the FTP server daemon in
the Max unit. This is an important security
measure to help block unwanted connections .
HTTP Port Change – This version includes a
feature that allows the HTTP port number to be
changed from the standard port 80 using
HyperTerminal and telnet. Changing the port
number to a number other than 80 increases
the security for users accessing the Web
Manager.
If you have an older version of the Max 410, 420, or 430
software, and you want to take advantage of these new
features, you can download the software from:
http://web..com/partnersupport/ devicesoftware/
4
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
Package Contents
You should find the following contents in your Max 410,
420, or 430 package:
Max 410, 420, or 430 device
Power adapter
100-250V AC input 0.5A
+5V DC output 3.0A
One telephone cable (RJ-11)
User’s Guide (if not available in your package,
please contact your distributor)
Warranty card
System and Service Requirements
You will need the following items/services to use your Max
410, 420, and 430:
General Requirements
To configure and manage the unit, you will need:
A PC workstation with any recent Web
browser, connected to the LAN.
For the Max 410, which has FXO ports only
(for initial LAN configuration):
The HyperTerminal PC application
(included in all Microsoft operating
systems), or an equivalent terminalemulator application.
A standard serial cable
NOTE: On the Max 410, LAN settings must
be configured using a PC with a serial
cable connection. For details, refer to
Connecting to the Max 410 Through a
Serial Cable on page 17 of this Guide.
5

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
Hardware Requirements
To use the Max 410, 420, or 430, you will need:
A Max 410, 420, or 430 unit and power cord.
A Local Area Network (LAN) with a broadband
connection, which must not have proxy server
caching.
If your LAN uses static addresses you will also
need: an IP address, netmask, and gateway
address for the Max (all available from your
Network Administrator).
With FXS ports: a corded or cordless analog
telephone, and additional analog devices as
desired for each port. Optional: a PBX, APBX,
or KPS with an analog trunk card installed.
With FXO ports: a PBX, APBX, or KPS with an
analog line card installed.
A Net2Phone account number and PIN
(available from your reseller).
A separate port with its own telephone line
connection to the PBX, or to an analog
telephone, is required for each concurrent
telephone call desired. For example, if
capability for 3 concurrent calls is desired, then
the Max must have at least 3 ports, each
connected to the PBX or to an analog
telephone.
About this Guide
This User’s Guide, as well as the other instructional
literature that accompanies the Max 410, 420, and 430, is
intended for people who have a moderate degree of
experience installing networking equipment such as
routers, hubs, servers, and switches, and are familiar with
basic wiring and cabling practices.
In addition to this User’s Guide, the Max 410/420/430 is
shipped with a product manual containing four modules:
A Quick Start Guide describing hardware
installation, cabling, and configuration for a
basic, uncomplicated installat ion.
6

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
A Hardware Installation Guide describing
hardware installation, cabling, and safety related issues.
A User Guide outlining how to install,
configure, and use the Max.
NOTE: This Net2Phone User’s Guide,
marked with the latest version number,
supersedes the User Guide included in the
manual shipped with the device..
A Command Reference Guide describing
advanced configuration of the Max
410/420/430 through a serial connection.
The table below provides a brief overview of the main
topics covered in this Guide.
FOR INFORMATION ON… GO TO…
Product features
Hardware requirements
Installing the Max 410, 420,
or 430
Connecting the Max to a
PBX
Connecting the Max 420 or
430 to a Fax Machine
Connecting to a DHCP LAN
Connecting to a LAN with a
Static IP Address
Accessing the Max’s Web
Manager
Configuring Accounts
7
Chapter 1, Welcome
Chapter 1, Welcome
Chapter 2,
Getting Started
Chapter 2,
Getting Started
Chapter 2,
Getting Started
Chapter 3, Connecting
the Max 410, 420, and
430 to a LAN
Chapter 3, Connecting
the Max 410, 420, and
430 to a LAN
Chapter 4, Logging into
the Max Web Manager
Chapter 5, Using the
Max Web Manager
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 1
FOR INFORMATION ON… GO TO…
IVR Configuration
Upgrading the Firmware
Max-to-Max Calling
Troubleshooting
Technical Support
Chapter 5, Using the
Max Web Manager
Chapter 5, Using the
Max Web Manager
Chapter 6, Placing Calls
Chapter 7, Appendices
Chapter 7, Appendices
Symbols
Throughout the user’s guide, you will see information
highlighted for you with the following fun symbol icons:
SYMBOL REPRESENTS
Chapter Description
Note
Tip
Important
8

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
2
2 Getting Started
Overview
To start using your Max 410, 420, or 430, you simply have
to:
1. Install the Max 410/420/430 unit in its location
and connect the cabling.
2. Configure the LAN settings on the Max
410/420/430 so that it communicates with your
LAN.
3. Log in to the Max 410/420/430 Web Manager.
4. Finish configuring your FXS ports via the Web
Manager.
5. Test your installation by making an Internet
telephone call.
This chapter covers the first step in the process: installing
and connecting the Max 410/420/430 to a PBX or fax
.
This chapter describes:
Locating your FXS and FXO
ports
Installing the Max 410/420/430
Connecting the Max 410/420/430
to a PBX
Connecting the Max 410/420/430
to a fax machine
9

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
Locating Your FXS and/or FXO
Ports
You need to be able to identify the Max’s physical port
numbers before you can begin configuring its LAN
settings.
The RJ-11 sockets are visible on the Max’s rear panel.
Figure 1, below, shows the rear panel of a Max with 4
ports.
Physical Port Numbering
Figure 1 illustrates the physical port numbering on the Max
410/420/430’s rear panel for a unit with 4 ports installed.
These numbers are referenced by the Max Web Manager
when identifying ports, setting up the Max’s features and
configuring calling accounts.
Figure 1 – Physical Port Numbering
As the illustration shows, the ports are numbered from left
to right. The left-most port is port number 1 and the last
one on the right is number 4.
Ports also have logical numbers, used by the Routing
Table, which are different from their physical numbers.
Logical port numbering is where the FXS and FXO ports
are counted separately, and the count starts from zero
instead of one (See the Routing Table Configuration
section on page 42 in this Guide).
Installing the Max 410/420/430
Proceed with installation as follows:
1. Install the unit in a well-ventilated area. If it is to
be placed on a surface rather than in a rack, be
sure that all four rubber feet are in place to allow
10
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
for proper air circulation. Do not place objects in
excess of 20 pounds on top of the unit.
IMPORTANT: Please refer to the Max
410/420/430 Hardware Installation Guide
and observe the safety precautions listed.
2. Connect an analog telephone to any one of the
FXS ports. (Max-420).
NOTE: For the Max 410, initial LAN
configuration is done via a PC connected
to the Max through its serial port, using the
HyperTerminal terminal emulator
application (or equivalent), which is
included with all Microsoft™ operating
systems. This procedure is explained in
Using the HyperTerminal Emulation
Program on page 18 in this Guide.
3. Connect the RJ-45 LAN port to a hub or switch.
4. Connect your FXS and/or FXO ports to your PBX
as per the illustrations in Figures 2, 3, and 4,
below.
11

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
Connecting the Max to a PBX
The following images illustrate the connections necessary
when connecting the Max 410, 420, or 430 to a PBX.
Connecting the Max 410’s FXO Ports to a
PBX
Figure 2 – Max 410 Connections to a PBX
LEGEND:
COIC/COIB: Central Office Interface Card or Board
PBX: Private Branch Exchange
PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network
Trunk or CO Line: Line from Central Office switch
12
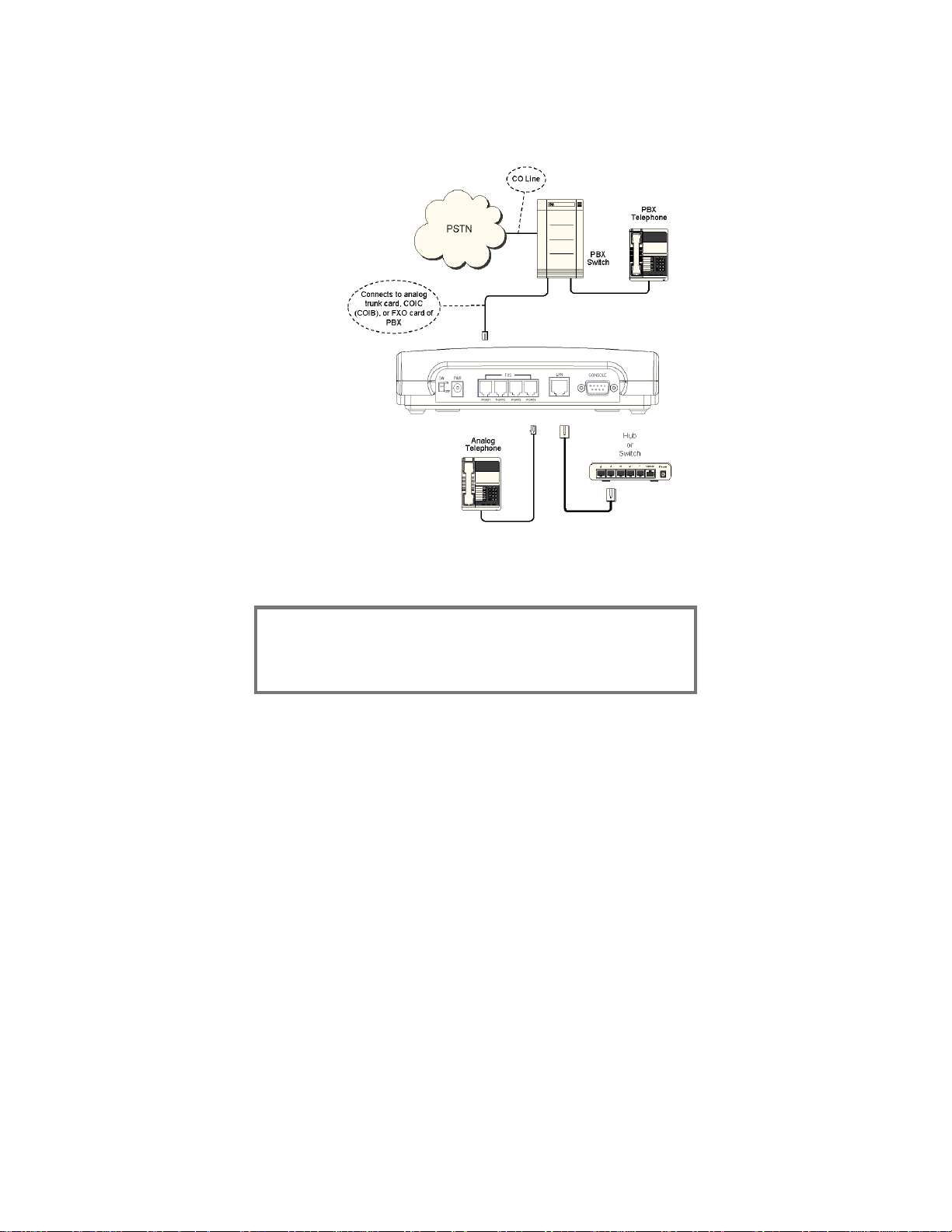
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
Connecting the Max 420’s FXS Ports to a
PBX
Figure 3 – Max 420 Connections to a PBX
LEGEND:
SLIC/SLIB: Subscriber Line Interface Card/Board
SLT: Single Line Terminal or Telephone (analog telephone)
Trunk or CO Line: Line from Central Office switch
13
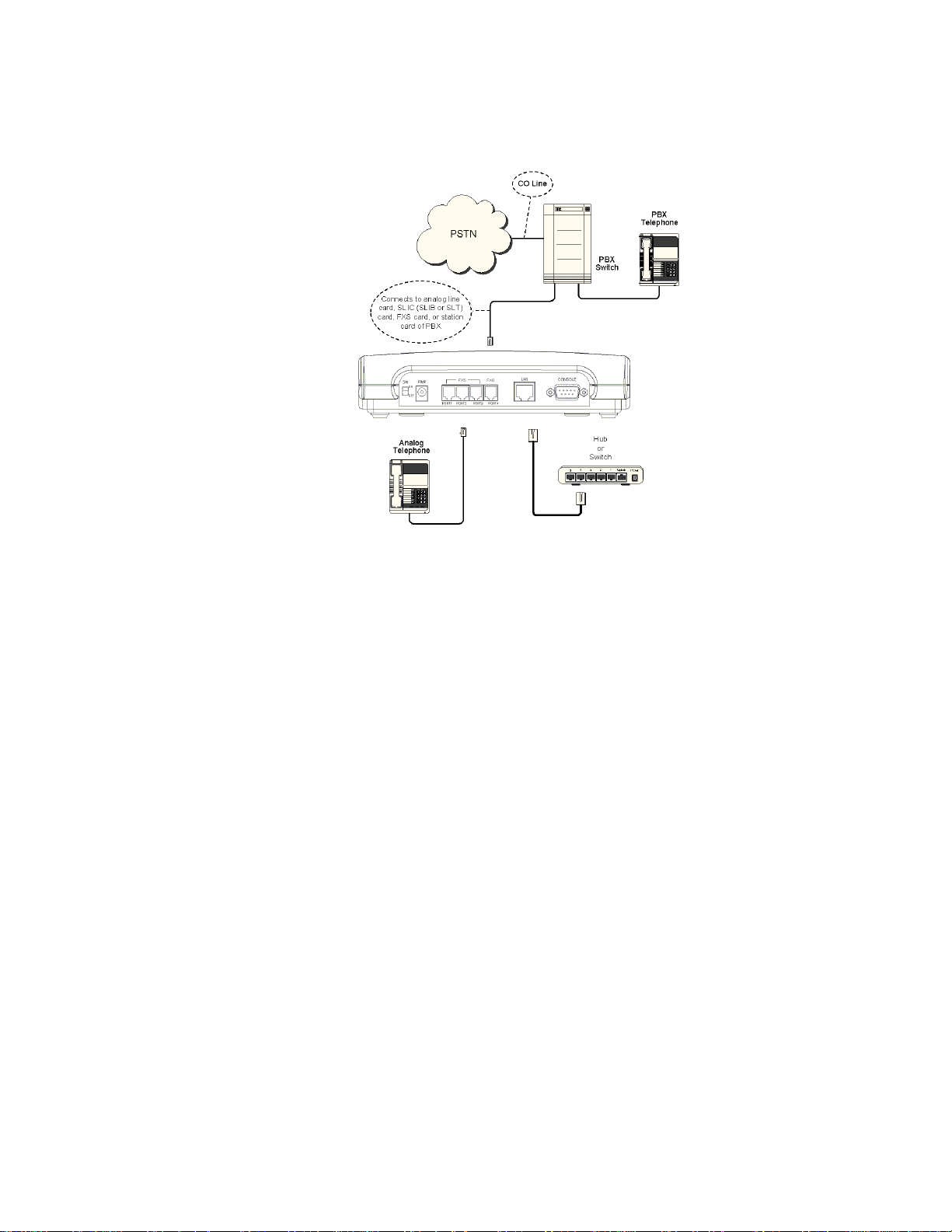
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
Connecting the Max 430’s FXS/FXO Ports to
a Telephone/PBX
Figure 4 – Max 430 Connections to a PBX
When you have finished connecting the Max’s FXS and
FXO ports as illustrated in one of the images above, plug
the unit into a power outlet and turn it on.
Your Max 410/420/430 hardware setup is now complete.
The next step is to configure the unit to communicate with
your LAN so that you can browse the Max Web Manager.
14

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
Connecting the Max 420/430’s FXS
Ports to a Fax Machine
Connecting your Max 420 or 430 to a fax machine is as
simple as connecting the fax mach ine’s RJ-1 1 cable to an
FXS port on the Max 420 or 430.
To place a fax call, just use the fax machine as usual: dial
the desired number and then send the fax.
NOTE: The Max 410 will not work with a fax
machine because it has no FXS ports, only
FXO ports.
15

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 2
16
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 3
3 Connecting the Max
3
410/420/430 to a LAN
Whether your LAN uses DHCP or static addresses, you
can set the Max 410/420/430’s LAN configuration in either
of two ways:
via a touch-tone keypad, or
through a serial connection via the
HyperTerminal terminal-emulator application.
This section explains how to set the Max 410/420/430’s
LAN configuration using either method.
This chapter describes:
Connecting the Max 410/420/430
to a DHCP LAN
Connecting to a LAN with static
IP addresses
NOTE: On a Max 410, LAN settings must
be configured using a PC with a serial
cable connection using the HyperTerminal
terminal emulator application, which is
included with all MS operating systems.
Connecting the Max 410/420/430 to
a DHCP LAN
This section explains how to connect your Web browser to
the Max 410, 420, or 430 if your LAN uses DHCP
addressing. If your LAN uses static IP addresses, skip to
Connecting to a LAN with Static IP Addresses, on page
20 in this Guide.
The default configuration for the Max 410, 420, and 430 is
for DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
17

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 3
Therefore, if your LAN uses DHCP, the Max
410/420/430’s IP address parameters were configured
automatically when you connected it to the LAN. In this
case, you only need to know the IP address that was
assigned to the unit by the LAN before you can browse the
Max Web Manager, Max 410/420/430’s Web-based
configuration system. If your LAN is using DHCP,
configuring the Max 410/420/430 will entail the following
steps:
1. Obtain the Max 410/420/430’s current IP address
(see Obtaining the Max 420/430’s DHCP IP
Address via a Telephone Keypad on page 17
in this Guide.).
2. Log in to the Max Web Manager.
3. Set the required configuration parameters in the
Max Web Manager.
Obtaining the Max 420/430’s DHCP IP
Address via a Telephone Keypad
The handiest way to query the Max 420’s current IP
address is usually from a telephone keypad (if an FXS port
is present). To use this procedure you will need a standard
analog corded or cordless touch-tone telephone. Get a
pencil and paper to write down the IP address.
1. Connect an analog telephone to any FXS port on
the Max 410/420/430.
2. Pick up the telephone handset and dial
(***1 on the keypad).
The voice prompt responds: “Your address is…”
and the IP address is announced.
3. Write down the address and hang up the
telephone. If you need to hear the address again,
hang up the telephone, then repeat step 2.
You are now ready to finish setting up the Max
410/420/430 using the Max Web Manager. Proceed to
Chapter 4, Logging In to the Max Web Manager.
18
***1
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 3
Connecting to the Max 410 through a Serial
Cable
This section explains how to connect to the Max and
obtain its DHCP IP address. The remaining configuration
tasks can then be completed more easily via the Max Web
Manager.
NOTE: For the Max 410 units, LAN settings
can only be configured using this method.
Using the HyperTerminal Emulation Program
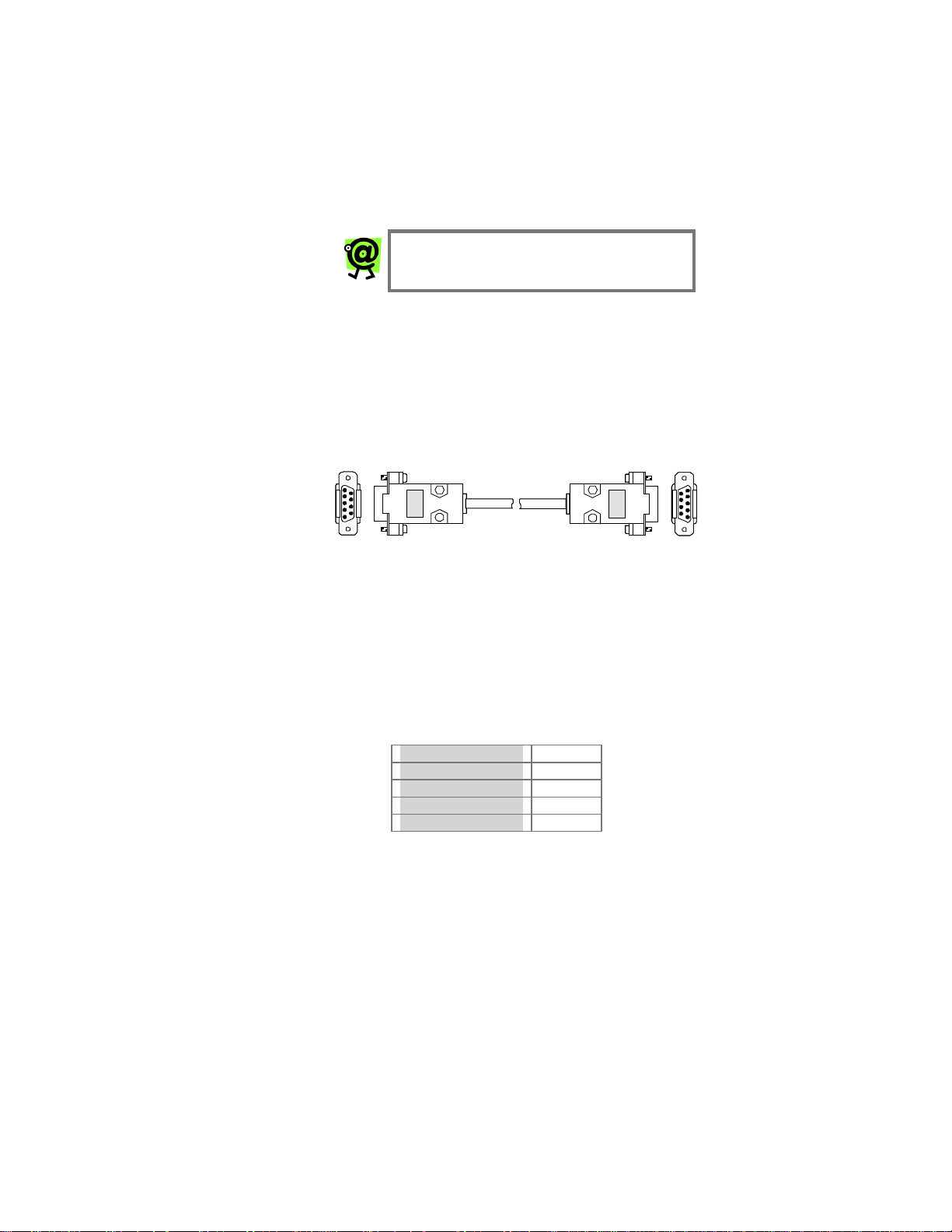
For this procedure you will need a standard serial cable
(D-sub 9-pin, male-to-female, straight-through connection)
as shown in Figure 5, and a PC running the
HyperTerminal terminal-emulator program (or an
equivalent), which is included with Microsoft operating
systems. It is usually found in the Programs menu, under
Accessories.
Figure 5 – Serial Cable Connection
1. With the power to the Max 410 turned OFF,
connect the cable from the unit’s serial port to
one of the PC’s serial ports. Note which of the
PC’s serial ports you are using.
2. Launch HyperTerminal and set up a new
connection.
3. In the dialog box, specify the appropriate serial
port, and set the serial communication
parameters as follows:
Baud rate
Parity
Character size
Stop Bit
Flow Control
19
19200
None
8
1
None

Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 3
4. Power-on the Max, then press the Enter key.
The boot messages are displayed, followed by
the command prompt n2p:>.
NOTE: n2p is the default system name with
which the unit is shipped. This can be
replaced by a system name you select, such
as MY_Max:>. To change the system name,
see System Information and Commands on
page 49 in this Guide.
5. Press the Enter key.
The Login: prompt is displayed.
6. Three default user IDs are provided:
root
manager
sysadm
Type one of these user IDs at the Login: prompt,
followed by the R key.
For example, type root, and then press the
Enter key.
The Password: prompt appears.
7. At the Password: prompt, type the default
password, n2p, and then press the Enter key.
The command line prompt n2p:> appears. You
are now logged in.
20
Max 410/420/430 User’s Guide – Chapter 3
NOTE:
• The Max 410/420/430 provides
three fixed user (or manager)
names. You can change any
manager’s password, but
managers cannot be created,
deleted, or renamed.
• Manager names and passwords are
case sensitive.
Obtaining the Max’s DHCP IP address via
HyperTerminal
If your LAN uses static addresses, refer to Entering
Static IP Addresses via HyperTerminal on page 21 in
this Guide.
1. Establish a serial connection from your computer
to the Max 410 (refer to Using the
HyperTerminal Emulatio n Program on page 18
in this Guide.)
2. After logging in to the Max 410, type
/config/ip at the command prompt.
The active directory changes to /config/ip
and the prompt becomes n2p:/config/ip>.
3. Type S followed by the Enter key.
The Max 410’s IP address and netmask are listed
on the screen. Write them down and keep them
for future reference.
If your LAN uses DHCP, you are now ready to finish
setting up the Max 410/420/430 using the Max Web
Manager. Proceed to Chapter 4, Logging Into the Max
Web Manager.
Connecting to a LAN with Static IP
Addresses
This section explains how to connect your Web browser to
the Max 410/420/430 if your LAN uses static IP
21
 Loading...
Loading...