NELFC AZ10E111, AZ100E111 Datasheet
DATA SHEET
AZ10E111
ARIZONA MICROTEK, INC.
AZ100E111
1:9 Differential Clock Driver
FEATURES
• Low Skew
• Guaranteed Skew Spec
• Differential Design
• Enable
• V
• Extended 100E V
BB
Output
Range of -4.2V to -5.46V
EE
• 75kΩ Internal Input Pulldown Resistors
• Direct Replacement for Motorola MC10EL111 & MC100EL111
• Manufactured Under License By Lucent Technologies
DESCRIPTION
The AZ10E/100E111 is a low skew 1-to-9 differential driver, designed with clock distribution in mind. It
accepts one signal input, which can be either differential or single-ended if the VBB output is used. The signal is
fanned-out to 9 identical differential outputs. An Enable input is also provided. A HIGH disables the device by
forcing all Q outputs LOW and all QN outputs HIGH.
The device is specifically designed, modeled and produced with low skew as the key goal. Optimal design
and layout serve to minimize gate-to-gate skew within-device, and empirical modeling is used to determine process
control limits that ensure consistent tpd distributions from lot-to-lot. The net result is a dependable, guaranteed low
skew device.
To ensure that the tight skew specification is met, both sides of the differential output must be terminated
into 50Ω, even if only one side is used. In most applications all nine differential pairs will be used and therefore
terminated. In the case where fewer than nine pairs are used, it is necessary to terminate at least the output pairs
on the same package side (i.e. sharing the same V
minimum skew. Failure to do this will result in small degradations of propagation delay (on the order of 10-20ps)
of the output(s) being used which, while not being catastrophic to most designs, will mean a loss of skew margin.
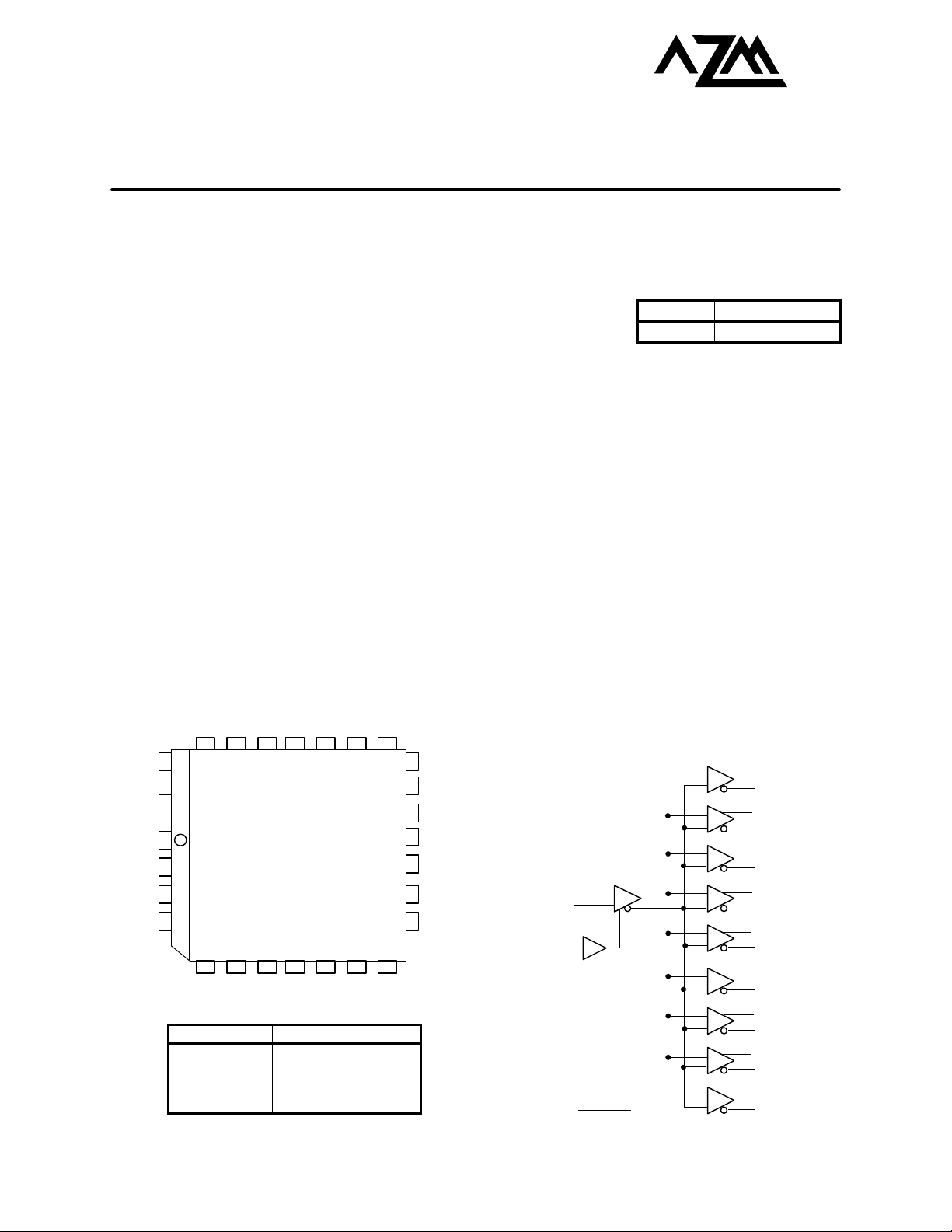
Q0 Q0N Q1 Q2VCCO Q1N Q2N
25 24 23 22 21 20 19
26
V
EE
27
ENN
28
IN
1
V
CC
2
INN
V
3
BB
4
NC
Pinout: 28-Lead PLCC
(Top View)
Q7N
Q7VCCOQ8Q8N
Q6N
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
111098765
Q6
PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN FUNCTION
IN, INN
ENN
Q0, Q0N-Q8N,
Q
8
Differential Input Pair
Enable
Differential Outputs
VBB Output
) as the pair(s) being used on that side, in order to maintain
CCO
LOGIC SYMBOL
Q3
Q3N
Q4
VCCO
Q4N
Q5
Q5N
IN
INN
ENN
V
BB
PACKAGE AVAILABILITY
SUFFIX DESCRIPTION
FN Plastic 28 PLCC
Q0
QON
Q1
Q1N
Q2
Q2N
Q3
Q3N
Q4
Q4N
Q5
Q5N
Q6
Q6N
Q7
Q7N
Q8
Q8N
6/99
AZ10E111
AZ100E111
DC Characteristics (VEE = 10E(-4.94V to -5.46V),100E(-4.2V to -5.46V); VCC = V
= GND)
CCO
-40°C 0°C 25°C 85°C
Symbol Characteristic Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit Cond
V
BB
I
IH
I
EE
Reference Voltage 10E
100E
Input HIGH Current 150 150 150 150
Power Supply 10E
Current 100E
-1.43
-1.38
-1.30
-1.26
484860
60
-1.38
-1.38
-1.27
-1.26
484860
60
-1.35
-1.38
-1.25
-1.26
484860
60
-1.31
-1.38
-1.19
-1.26
485560
69
V
µA
mA
VPP (DC) Input Sensitivity 50 50 50 50 mV 1
V
CMR
Common Mode Range -1.6 -0.4 -1.6 -0.4 -1.6 -0.4 -1.6 -0.4 V 2
1. Differential input voltage required to obtain a full ECL swing on the outputs.
2. V
is defined as the range within which the VIH level may vary, with the device still meeting the propagation delay specification. The VIL level must
CMR
be such that the peak-to-peak voltage is less than 1.0V and greater than or equal to VPP(min).
AC Characteristics (VEE = 10E(-4.94V to -5.46V),100E(-4.2V to -5.46V); VCC = V
= GND)
CCO
-40°C 0°C 25°C 85°C
Symbol Characteristic Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit Cond
Propagation Delay
t
PLH
t
PHL
t
S
t
h
t
R
t
skew
V
tr / t
PP
to Output IN (Diff)
IN (SE)
Enable
Disable
380
280
400
400
680
780
900
900
460
410
450
450
560
610
850
850
480
430
450
450
580
630
850
850
510
460
450
450
610
660
850
850
ps
Setup Time ENN to IN 250 0 200 0 200 0 200 0 ps 5
Hold Time IN to ENN 50 -200 0 -200 0 -200 0 -200 ps 6
Release Time ENN to IN 350 100 300 100 300 100 300 100 ps 7
Within-Device Skew 25 75 25 50 25 50 25 50 ps 4
(AC) Minimum Input Swing 250 250 250 250 mV 8
Rise/Fall Time 250 450 650 275 375 600 275 375 600 275 375 600 ps
f
1. The differential propagation delay is defined as the delay from the crossing points of the differential input signals to the crossing point of the
differential output signals.
2. The single-ended propagation delay is defined as the delay from the 50% point of the input signal to the 50% point of the output signal.
3. Enable is defined as the propagation delay from the 50% point of a negative transition on ENN to the 50% point of a positive transition on Q (or a
negative transition on QN). Disable is defined as the propagation delay from the 50% point of a positive transition on ENN to the 50% point of a
negative transition on Q (or a positive transition on QN).
4. The within-device skew is defined as the worst case difference between any two similar delay paths within a single device.
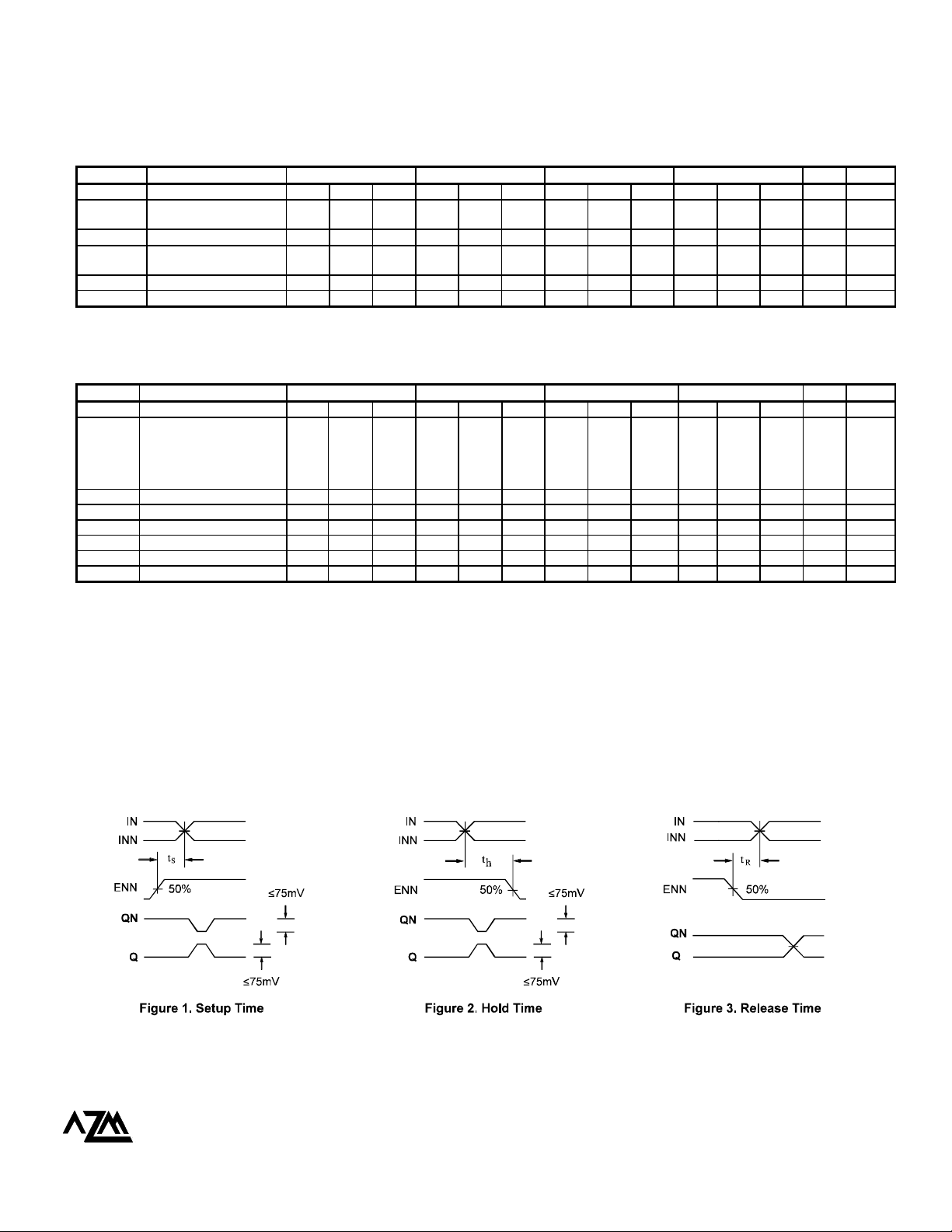
5. The setup time is the minimum time that ENN must be asserted prior to the next transition of IN/INN to prevent an output response greater than ±75
mV to that IN/INN transition (see Figure 1).
6. The hold time is the minimum time that ENN must remain asserted after a negative going IN or a positive going INN to prevent an output response
greater than ±75 mV to that IN/INN transition (see Figure 2).
7. The release time is the minimum time that ENN must be deasserted prior to the next IN/INN transition to ensure an output response that meets the
specified IN to Q propagation delay and output transition times (see Figure 3).
8. VPP(min) is defined as the minimum input differential voltage which will cause no increase in the propagation delay. The VPP(min) is AC limited for
the E111, as a differential input as low as 50 mV will still produce full ECL levels at the output.
1
2
3
3
ARIZONA MICROTEK, INC. 225 E. FIRST ST., SUITE 107 • MESA, AZ 85201-6700 • (480) 962-5881 • FAX (480) 890-2541
http://www.azmicrotek.com
 Loading...
Loading...