Page 1

MH110/MH120
IP Wireless Telephone
Setup and Administration Guide
NEC Business Solutions Ltd.
Doc. No: NEC-9123
Revision 1
July, 2005
Page 2

Page 3

Contents
i
Introduction 1-1
Using this Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
How this Guide is Organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Document Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide 2-1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Quick Start Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
System Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
System Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets 3-1
Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Display. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Alphanumeric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Voice mail Icon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Ringing and Tones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Audio Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Line Indicators. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Mobile Handset Configuration 4-1
The Admin Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 4

ii Contents
Opening the Admin Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Entering and Editing Admin Menu options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Alphanumeric String Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
ESSID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
License Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Restore Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Site Survey Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Regulatory Domain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
NEC Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
OAI On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Set Admin P.W.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
User-defined Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
License Management 5-1
Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Configuration Process. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
NEC VoIP Integration Factors 6-1
Voice Messaging Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
CODECs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
DHCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
TFTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
DNS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Feature Programming 7-1
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Feature Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
Feature Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
Line Appearances . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 5

Contents iii
Menu Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Feature List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Testing a Mobile Handset 8-1
Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets 9-1
Site Certification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
Site Survey Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Detect dBm coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Detect Overlap or Conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
Confirm Supported Data Rates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Solving Coverage Issues. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
Software Maintenance 10-1
Upgrade Mobile Handsets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
Normal Download Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-1
Download Failure or Recovery Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems 11-1
Access Point Problems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-1
Configuration Problems. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-2
Mobile Handset Status Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-2
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 6
iv Contents
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 7

Figures
Figure Title Page
v
2-1 NEC IP telephony server architecture example. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
3-1 MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
3-2 The Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
7-1 Programmable Line or Feature Keys. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
7-2 Feature Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
9-1 Detect dBm coverage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
9-2 Detect Overlap or Conflicts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
9-3 Confirm signal strength and data rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-4
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 8
vi Figures
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 9

Tables
vii
Table Title Page
1-1 Document Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
2-1 MH110/MH120 Wireless Telephones Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
3-1 Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
4-1 Admin menu options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4-2 Special Characters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
4-3 Admin menu commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
4-4 Wireless Telephone Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
4-5 Wireless Telephone Configuration Components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4-6 Optionally configured components . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
4-7 Navigation keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
4-8 Standby menu items . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
4-9 User-defined preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
6-1 DHCP options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
7-1 Function key displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7-2 Line key displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
7-3 Menu key displays . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
10-1 Normal Download Messages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
10-2 Download Failure and Recovery Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-2
11-1 Mobile Handset Status Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-2
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 10
viii Tables
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 11

1
Introduction
Welcome to the MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and
Administration Guide. This document explains how to configure and
maintain the MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone within the NEC Platform.
Chapter Topics • Using this Guide
• Document Conventions
1-1
Using this Guide
Chapter 1
Introduction
Chapter 2
MH110/MH120
IP Quick Start
Guide
Chapter 3
MH110/MH120
Mobile Handsets
Chapter 4
Mobile Handset
Configuration
This guide is designed to make MH110 and MH120 Wireless Telephones
easy to configure and maintain. There are step-by-step instructio ns for
the procedures you need to perform.
How this Guide is Organized
This chapter outlines how to use the manual, including the organization,
chapter layout, and conventions used in the MH110/MH120 Wireless
Telephone Setup and Administration Guide.
This chapter contains a Quick Start Guide and descriptions for MH110/
MH120 IP UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets, which are mobile handsets
for workplace IP telephone systems.
This chapter discusses the requirements for the MH110/MH120 Mobile
Handsets and the items on their display.
This chapter describes how to configure the Mobile Handset.
Chapter 5
License
Management
Chapter 6
NEC VoIP Integration Factors
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
This chapter details the process to properly configure MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets and download software via over-the-air
file transfer.
This chapter describes the mapping between the emulated NEC
DtermIP-16LD and the MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
Page 12

1-2 Introduction
Chapter 7
Feature Programming
Chapter 8
Testing a Mobile Handset
Chapter 9
Certifying MH110/MH120
Mobile Handsets
Chapter 10
Software Maintenance
Chapter 11
Troubleshooting Mobile
Handset Problems
This chapter describes feature programming for the MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
This chapter describes tests that can be performed in an active wireless
area to verify proper registration and operation of each Mobile Handset.
This chapter explains how to conduct a preliminary Site Survey Mode
test.
This chapter describes how to upgrade and maintain software for the
MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
This chapter discusses problem sources that determine the best method
of approaching any specific situation when using and troubleshooting
Mobile Handsets.
Document Conventions
This guide uses the conventions listed in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1 Document Conventions
When you see: It means: Example
Boldfaced
Capitalized
Menu > Submenu
(boldfaced font)
Field names
Button names
Drop-down list names
Commands, keywords, or other
user input
Menu names
Window names
Dialog box names
Menu paths Select Edit > Modify.
Enter the ID in the Name field.
Click Save.
Select the names from the
Employees drop-down list.
Enter login admin at the command
prompt.
From the File menu, choose Save.
From the Directory window, select
Edit > Modify.
Click OK to save and close the
Account Properties dialog box.
CTRL+S
CTRL+Shift+S
(boldfaced font)
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Shortcut keys Press CTRL+S to save your changes.
Page 13

Introduction 1-3
When you see: It means: Example
F1 Function keys Press F1 to access the online help.
Click
Right-click
Click the left mouse button
Click the right mouse button
Click OK to save your changes.
Right-click and select Delete from the
shortcut menu.
Used to warn against possible human
Warning
injury or risk of death from an action or
event.
Caution
Used when equipment or data could
be damaged by an action or event.
Important Emphasizes a MUST read statement.
Used to point out special details that
Note
you must know or actions that you
must take relevant to your current
actions.
Describes time-saving ideas and
Tip
other useful information for
completing procedures.
Reference
Step-by-step instructions are numbered. If more than one option is
available to complete a task in a procedure, the options may appear as
follows:
Step 1 Do one of the following to add a field to the Employee directory.
—Select the desired field from the Employee field and click Add.
—Double-click the desired field from the Employee field.
Step 2 To select all of the available fields, click Add all.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Indicates a reference to another
related document.
Page 14
1-4 Introduction
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 15

2
MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide
MH110/MH120 IP UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets are mobile handsets
for workplace IP telephone systems. This chapter contains a Quick Start
Guide, system diagram, and descriptions for MH110/MH120 IP
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
Chapter Topics • Overview
• Quick Start Guide
• System Diagram
• System Components
2-1
Overview
The Wireless T elephone oper ates over an 802.11b wireless Ethernet LAN
providing users a wireless voice over IP (V oIP) extension. By seamlessly
integrating with the NEC IP telephony system, Wireless Telephone users
are provided with high-quality mobile voice communi cations throughout
the workplace. The Wireless Telephone gives users the freedom to roam
throughout the workplace while providing all the features and
functionality of an IP desk phone.
The MH110/MH120 Wireless Telephone provides a wireless extension to
the NEC VoIP solutions. The Wireless Telephone supports the Protims
protocol, a proprietary protocol developed by NEC for communication
between a NEC DtermIP-16LD and a NEC PBX.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 16
2-2 MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide
The Wireless Telephones reside on the wireless LAN with other wireless
devices using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) radio
technology. The handset radio transmits and receives packets at up to
11Mb/s. The MH110/MH120 Wireless Telephone supports Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) as defined by the 802.11b specification. NEC
offers the product with both 40-bit and 128-bit encryption. WEP
increases the security of the wireless LAN to a level similar to a wired
Ethernet LAN.
• IP multicast addresses are used by the MH120 Wireless T elephone system. This requires
that multicasting be enabled on the subnet used for the MH110/MH120 Wireless
Telephones, SVP Server, and Telephony Gateways.
NOTE
• Routers are typically configured with filters to prevent multicast traffic from flowing outside
of specific domains. The wireless LAN can be placed on a separate VLAN or subnet to
reduce the effects of broadcast and multicast traffic from devices in other network
segments.
Quick Start Guide
Table 2-1 MH110/MH120 Wireless Telephones Requirements
Table 2-1 describes five conditions that must be met for MH110/MH120
Wireless Telephones.
Requirements Descriptions
Wireless LAN A wireless LAN must be properly configured and
operational through the use of 802.11b wireless
access points (APs) listed on the Access Point
Compatibility matrix.
TFTP Server A TFTP Server must be available on the network
in order to load the appropriate software into the
Wireless Telephones.
Refer to Chapter 5, “License Management” for
detailed instructions for loading software on
Wireless Telephones.
NEC VoIP The supported NEC VoIP solution must be
connected to your network and completely
operational.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 17
MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide 2-3
Requirements Descriptions
NEC SVP Serve The NEC SVP Server, which facilitates
the QoS on the wireless LAN for the Wireless
Telephones, must be on the same subnet as
the Wireless T elephones and have the proper
versions of software.
Note: Ensure you have the following versions:
• 173.xxx svp100.toc
• 174.xxx zvmlinux
• 175.xxx flashfs
Wireless Telephone Configure your Wireless Telephone to ensure
that it is associated with the Wireless LAN, has
the appropriate software, and has the correct IP
address for the supported NEC IP telephony
system.
Refer to Chapter 5, “License Management” for
detailed instructions about loading software on
Wireless Telephones.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 18
2-4 MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide
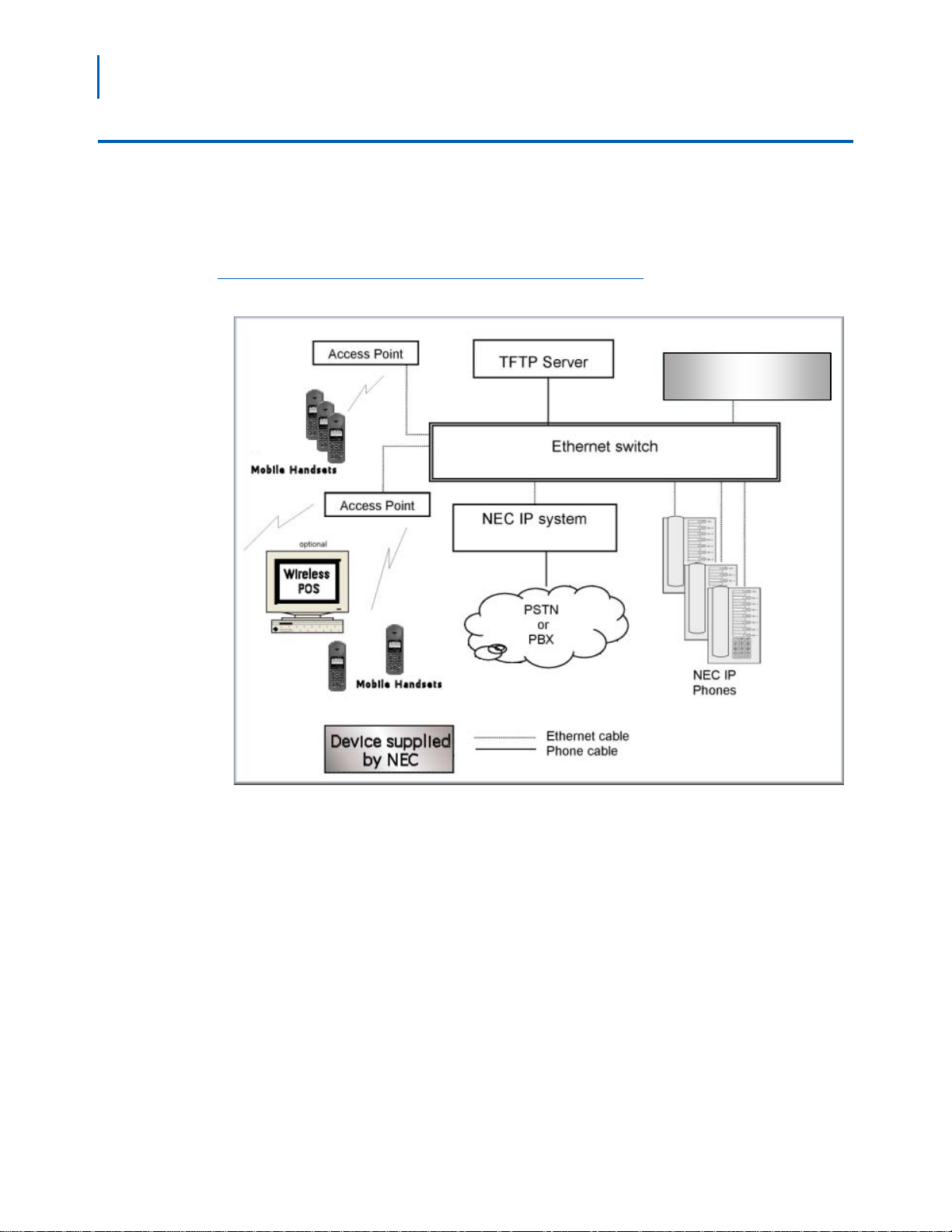
System Diagram
Figure 2-1 shows the NEC components residing on a network with the
NEC IP telephony system, access points (APs), and wireless LAN
Ethernet Switched Hub.
Figure 2-1
NEC IP telephony server architecture example
SVP SERVER
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 19

System Components
•The MH110 is a lightweight, dura ble handset specifically designed for
•The MH120 offers a durable design with push-to-talk functionality.
• SVP Server - SVP Server is the NEC quality of service (QoS)
• NEC IP System - NEC VoIP solution.
• Access Points - supplied by third party vendors, access points
MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide 2-5
mobile workplace use within a facility using the supported NEC IP
telephony system and 802.11b APs in a wireless LAN.
The MH110/MH120 functionality is provided by emulating the NEC
DtermIP-16LD. Among other features, the Mobile Handset can receiv e
calls directly, receive transferred calls, transfer calls to other
extensions, and make outside and long distance calls (subject to the
restrictions applied in your facility.) The Mobile Handsets are to be
used on-premises; they are not cellular or satellite phones.
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets use Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
radio technology (DSSS) to transmit audio packets over wireless LAN
APs that support SVP Server.
mechanism that is implemented in the Mobile Handset and AP to
enhance voice quality over the wireless network. SVP Server gives
preference to voice packets over data packets on the wireless medium,
increasing the probability that all voice packets are transmitted
efficiently and with minimum or no delay. SVP Server is fully
compatible with the IEEE 802.11b standards.
The SVP Server is an Ethernet LAN appliance that works
with the AP to provide QoS on the wireless LAN. All Protims packets to
and from the MH110/MH120 pass through the SVP Server and are
encapsulated for prioritization as they are routed to and from the
supported NEC VoIP solution or other Mobile Handset.
SVP Server is required for QoS because the current IEEE 802.11b
wireless LAN standard provides no mechanism for differentiating
audio packets from data packets. This standard is undergoing revision
to version 802.11e to provide all the functionality of SVP Server in an
industry standard, thus ensuring high-quality voice in a mixed client
environment. Once 802.11e is ratified, NEC and its 802.11b
technology partners will adopt the new specification.
provide the connection between the wired Ethernet LAN and the
wireless (802.11b) LAN. Access points must be positioned i n all areas
where Mobile Handsets will be used. The number and placement of
access points will affect the coverage area and capacity of the wireless
system. Typically, the requirements for use of MH110/MH120 are
similar to that of wireless data devices.
Access points must utilize SVP Server. Contact NEC, or a certified
NEC distributor, for information about APs that support SVP Server.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 20

2-6 MH110/MH120 IP Quick Start Guide
• Ethernet Switch - interconnects multiple network devices, including
the SVP Server, the supported NEC IP telephony system, NEC
DtermIP-16LDs and the access points. Ethernet switches provide
the highest performance networks, which can handle combined voice
and data traffic, and are required when using the MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
Although a single Ethernet switch network is recommended, the
Mobile Handsets and the SVP Server can operate in larger, more
complex networks, including networks with multiple Ethernet
switches, routers, VLANs, and/or multiple subnets, as long as the
SVP Server and access points are on the same subnet.
However, in such networks, it is possible for the quality of service
(QoS) features of the SVP Server to be compromised, and voice
quality may suffer. Any network that consists of more than a single
Ethernet switch should be thoroughly tested to ensure any quality
issues are detected.
The MH110/MH120 cannot “roam” from one subnet to another. If routers and multiple
subnets are in use, the Mobile Handsets must only use access points attached to a
NOTE
single subnet, or be powered off and back on to switch to a different subnet.
• NEC DtermIP-16LD - The wired LAN desksets provided by NEC for
use with the supported NEC IP telephony system.
• TFTP Server - Required in the system to distribute software to the
Mobile Handsets. May be on a different subnet than the supported
NEC IP telephony device(s) and APs.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 21

3
MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
This chapter discusses the requirements for the MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets and the items on their display.
Chapter Topics • Requirements
• Display
3-1
Line indicators
Left arrow
Low battery
icon
Up
Select
Down
Softkey A
Softkey B
Power On
Start Call
Function
Figure 3-1
MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
Earpiece
Right arrow
Voicemail icon
Shortcut menu &
Main display area
Softkey Function
display area
Softkey D
Softkey C
Power Off
End Call
Menu
Line
Microphone
Headset jackCharging contacts
Line indicators
Left arrow
Low battery
icon
Up
Select
Down
Softkey A
Softkey B
Power On
Star t Ca ll
Battery release
Function
Headset jackCharging contacts
Earpiece
Right arrow
Voicemail icon
Shortcut menu &
Main display area
Push-to-talk
Push-to-talk
radio control
radio control
Softkey Function
display area
Softkey D
Softkey C
Power Off
End Call
Menu
Battery release
Line
Microphone
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 22

3-2 MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
Requirements
In order for the MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets to
operate properly, your operating environment must meet the following
requirements.
Table 3-1 Requirements
Requirements Specificaitons
Radio frequency 2.400 - 24835 GHz
Transmission type Direct-Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Transmit data rate Up to 11 Mb/s
Radio QoS SVP Server
Wireless security Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), 40-bit and 128-bit
FCC certification Part 15.247
Display
Management DHCP, TFTP
Voice encoding G.711, G.729a/ab
VoIP Protocols Protims
Transmit power 100mW peak, < 10 mW average
Display Pixel-based (up to 4-line x 18-character) alphanumeric, plus
line and status indicators
SNP Dimensions 5.5” x 2.0” x 0.9” (14.0 x 5.1 x 2.3 cm)
RNP Dimensions 5.9” x 2.2” x 1.0” (15.0 x 5.6 x 2.5 cm)
SNP Weight 4.2 ounces (119.0 g)
RNP Weight 6.0 ounces (170.1 g)
Battery capacity 4 hours talk time, 80 hours standby
The Display section is broken in to the f o ll owi ng subsections:
• Alphanumeric
• Voice mail Icon
• Ringing and Tones
• Audio Features
• Line Indicators
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 23

MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets 3-3
Figure 3-2
The Display
Alphanumeric
Display information provided by the supported NEC VoIP solution when
the Mobile Handset is off-hook will be passed directly to the Mobile
Handset display. The Mobile Handset will display up to 18 characters of
each line. Certain characters may be used by the supported NEC VoIP
solution that are not implemented in the Mobile Handset such as
definable and special characters. Press the FCN key while off hook to
scroll through features and emulated keys. P ress the LINE key while off
hook to scroll through the line/memory keys.
Voice mail Icon
The Voicemail icon is controlled only by the OAI application.
Ringing and Tones
The ringing types are programmed by the Mobile Handset user into the
Mobile Handset and are not accessible or changeable by the supported
NEC VoIP solution. Whenever possible the audible and vibrating ringer
on the Mobile Handset will follow the Protims cadence commands
provided by the supported NEC VoIP solution.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 24

3-4 MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
Audio Features
Speakerphone features such as paging, hands-free mode and voice
announce are not available on the Mobile Handset. The te lephony switch
should not be programmed to support such features on the Mobile
Handset.
Line Indicators
The line indicators on the Mobile Handset will convert to a solid or
flashing number to mimic the icons next to Line keys on the NEC
DtermIP-16LD. The text that appears next to the line keys on the IP
Phone is accessed on the Mobile Handset by pressing the LINE key.
Line keys must be programmed on Lines 1-4 while features are programmed on
keys 5-16.
NOTE
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 25

4
Mobile Handset Configuration
The MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets (Mobile Handsets)
should be provisioned in the supported NEC VoIP solution in the same
manner as the NEC DtermIP-16LDs. Each Mobile Handset may be
configured for site-specific requirements by opening the Admin menu
and selecting options or entering specific information. Any settings
entered in the Admin menu must conform to system settings. Only the
Mobile Handset being configured is affected by the Admin menu
settings.
4-1
Chapter Topics • The Admin Menu
The Admin Menu
The Mobile Handset user may select several usability options from the
Standby menu, described in the
10. This information is also provided in the end user manual.
• User-defined Preferences
The Admin Menu contains configuration options that are stored locally
(on each Mobile Handset). Every Mobile Handset is independent and if
the default settings are not desired, the admin options must be set in
each Mobile Handset requiring different settings.
Opening the Admin Menu
Step 1 With the Mobile Handset powered OFF, simultaneously press and hold
the Power ON and Power OFF keys.
Step 2 Release the Power On key, wait for a single beep, then release the
Power Off key. The Admin Menu displays.
“User-defined Preferences” on page 4-
If an admin password has been set, the display will require its entry before opening
the Admin Menu. If no password is set, the display will proceed directly into the
NOTE
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Admin Menu.
Page 26

4-2 Mobile Handset Configuration
Entering and Editing Admin Menu options
An asterisk (*) next to an option in the display indicates that it is
selected. The default settings are shown in
Down, and Select side buttons and the softkeys to navigate and select
options.
Table 4-1 Admin menu options
Buttons & Softkeys Descriptions
Up/Down buttons Display previous/next menu item.
Select button Selects the menu item or option.
OK softkey Selects the menu item or option.
Save softkey Saves the entry.
Bksp softkey Backspaces to allow editing of entry.
Cncl softkey Cancels edit and returns to previous menu level.
Table 4-1. Use the Up,
Up softkey Returns to previous menu level.
Exit softkey Exits the menu (at the top level).
End Call key Exits to standby state (from any level)
Alphanumeric String Entry
Step 1 Press the first digit/letter. The digit displays. Press the key again to scroll
through the letters associated with that key.
Example: Press 2 repeatedly and you will see 2, A, B, and C, a, b, and c.
Table 4-2 describes keys which allow you to enter non-numeric
characters or other characters not represented on the keypad.
Table 4-2 Special Characters
. - _! # $% & ‘(),:; / \ = @ ~ 1
To Enter Press
Space 0
Q,q 7
Z,z 9
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 27

Mobile Handset Configuration 4-3
Step 2 When the correct entry displays, press the RIGHT ARROW to move on
to the next character. Repeat for each digit/letter of the entry. To erase,
press the LEFT ARROW or BACKSPACE softkey to erase the previous
character.
Step 3 Press the SAVE softkey to save the entry and return to the menu. Press
the Cncl softkey to abort and return to the menu without saving any
changes.
Table 4-3 lists the Admin Menu commands. Detailed descriptions of each
command appear in the following sections:
• “IP Address” on page 4-4
• “ESSID” on page 4-6
• “License Management” on page 4-6
• “Restore Defaults” on page 4-7
• “Site Survey Mode” on page 4-7
• “Regulatory Domain” on page 4-7
• “Security” on page 4-8
• “NEC Options” on page 4-9
• “OAI On/Off” on page 4-9
• “Set Admin P.W.” on page 4-10
Table 4-3 Admin menu commands
Admin Menu Items 2nd Level 3rd Level 4th Level
IP Address *Use DHCP
Static IP Phone IP
TFTP Server IP
Default Gateway
Subnet Mask
NEC PBX IP
DRS Self Port
SVPII IP
OAI Server IP
ESSID Static Entry
*Learn Once
Learn Always
License Management Set Current
Restore Defaults
Site Survey Mode
Regulatory Domain
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 28

4-4 Mobile Handset Configuration
Admin Menu Items 2nd Level 3rd Level 4th Level
Security *None
Extension number
OAI on/off Enable OAI
Admin PW
IP Address
Table 4-4 describes two modes in which Wireless Telephones can
operate:
WEP Authentication Open System
Shared Key
WEP On/Off
Key Information Default Key
Key Length
Key 1-4
Rotation Secret
Cisco FSR Username
Password
Disable OAI
•DHCP enabled
• Static IP
Select the mode for operation from the IP Address menu.
Table 4-4 Wireless Telephone Modes
Modes Descriptions
Use DHCP Will use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol to assign an IP
Static IP Allows you to manually set a fixed IP address. If selected, the Mobile
Table 4-5 describes components that must be configured, regardless of
the mode in which the Wireless Telephone is operating.
address each time the Mobile Handset is turned on. If DHCP is
enabled, the Mobile Handset also receives all other IP address
configurations from the DHCP server. *
Handset will prompt for the IP addresses of each configurable
network component. When entering addresses, enter the digits only,
including leading zeroes. No periods are required.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 29

Table 4-5 Wireless Telephone Configuration Components
Modes Descriptions
Mobile Handset Configuration 4-5
Phone IP The IP address of the Mobile Handset. This is automatically
assigned if DHCP is used. If using Static IP configuration, you must
obtain a unique IP address for each phone from your network
administrator.
NEC PBX IP The IP address of the NEC PBX call server. If using static IP
configuration, this is simply the IP address of the device.
DRS Self Port The UDP port of the Mobile Handset used to communicate with the
DRS in the NEC PBX. (Leave at default value 3455.)
SVP II IP The IP address of the SVP Server. If using Static IP
configuration, this is simply the IP address of the SVP Server.
Note that the SVP Server must be statically configured to have
a permanent IP address. If DHCP is being used, the Mobile
Handset will try the following, in order: the DHCP option 151, then
a DNS lookup of “SLNKSVP2” if the DHCP options 6 (DNS Server)
and 15 (Domain Name) are configured.
Table 4-6 describes components that may be configured optionally.
Table 4-6 Optionally configured components
Components Descriptions
TFTP Server IP The IP address of a TF TP server on your network which holds software
images for updating the Mobile Handsets. If this feature is configured
(not set to 0.0.0.0 or 255.255.255.255) either via Static IP configuration
or using DHCP option 66 (TFTP Server), or the Boot server/next server
(siaddr) field, the Mobile Handset will check for newer software each
time it is powered on or comes back into range of your network. This
check takes only a second and ensures that all Mobile Handsets in your
network are kept up-to-date with the same version of software.
OAI Server IP The IP address of the NEC OAI Gateway (if applicable). If using Static
IP configuration, this is simply the IP address of the NEC OAI Gateway.
If DHCP is being used, the Mobile Handset will try the DHCP option
152.
Default Gateway and
Subnet Mask
Used to identify subnets, when using a complex network which includes
routers. Both of these must be configured (not set to 0.0.0.0 or
255.255.255.255) for the Mobile Handset to contact any network
components on a different subnet. They can be set using either Static
IP configuration or via DHCP options 3 (Default Gateway) and 1
(Subnet Mask) respectively. Contact your network administrator for the
proper settings for your network. Note that the Mobile Handsets cannot
“roam” across subnets, since they cannot change their IP address while
operational. Ensure that all your access points are attached to the same
subnet for proper operation. The Mobile Handset can change subnets
if DHCP is enabled, and the Mobile Handset is powered off then back
on when within range of access points on the new subnet.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 30

4-6 Mobile Handset Configuration
ESSID
Select the option that will enable the Mobile Handset to acquire APs with
the correct ESSID (Extended Service Set ID, aka SSID) each time it is
turned on.
Note about Automatic Learn options:
Broadcast ESSID must be enabled in the access points for ESSID
learning to function.
Refer to the “Configuration Note” for your access point or call your access point
vendor for specifics.
REFERENCE
Overlapping wireless systems complicate the use of ESSID learning as
the Mobile Handset in an overlapping area could receive conflicting
signals. If this is the situation at your site, use Static Entry or Learn
Once in an area without overlapping ESSIDs.
• Learn Once: allows the Mobile Handset to scan all ESSIDs for a DHCP
server and/or TFTP server. Once either is found, the Mobile Handset
retains the ESSID from whichever access point it associates with at
that point. When overlapping wireless systems exist, the Learn Once
feature allows the Mobile Handset to use only the ESSID established
at first learn at all subsequent power ons. This ESSID is retained by
the Mobile Handset until the ESSID option is reselected.
• Learn Always: allows the Mobile Handset to auto m a ti c al ly learn the
ESSID at each power on or loss of contact with the wireless LAN (out
of range). This may be useful if the Mobile Handset will be used at
more than one site.
• Static Entry: If your access points do not accept broadcast ESSID or
if there are overlapping wireless systems in use at the site, enter the
correct ESSID manually.
License Management
License Management lets you select the VoIP protocol that your site is
licensed to download and run. The Protims protocol to use for the
MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets is 013. Any other
protocol will cause the Mobile Handset to malfunction. After selecting
the correct protocol for your site, you should upgrade the software for
the Mobile Handsets.
REFERENCE
Refer to “Upgrade Mobile Handsets” on page 10-1 for more information.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 31

REFERENCE
Mobile Handset Configuration 4-7
Restore Defaults
The Restore Defaults option will set all user and administrative
parameters to their factory defaults.
Site Survey Mode
Site Survey Mode is used to check the signal strength from access
points. When you select Site Survey Mode, the Mobile Handset will
remain in this mode until it is powered off.
Refer to Chapter 9, “Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets” for more
information on this mode.
NOTE
Regulatory Domain
The Regulatory Domain will default to North Americ a on the Mobile
Handset display. FCC requirements dictate that the menu for changing
the domain be available by password, which in our case is the LINE k ey.
To change the domain, press LINE and then enter the digits that
represent the site’s domain. Note that both digits must be entered.
01 - North America
02 - Europe (except Spain and France); Japan (channels 1-13)
04 - Spain
05 – France
As of this writing, Spain and France are adopting the general European Regulatory
rules. Check with your wireless LAN administrator or supplier for which domain to
enter in these countries.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 32

4-8 Mobile Handset Configuration
Security
*NONE disables any 802.11 encryption or security authentication
mechanisms.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a wireless encryption protocol that
encrypts data frames on the wireless medium allowing for greater
security in the wireless network. If WEP/Encryption is required at this
site, you must configure each Mobile Handset to correspond with the
encryption protocol set up in the access points. Select the entries from
the options below to enable the Mobile Handset to acquire the system.
• Set each of these options to match exactly the settings in your APs.
• Encryption codes display as they are entered. For security reasons codes will not display
NOTE
when a user returns to the Admin menu, Encryption options.
• Note that WEP may be set to “optional” at the AP if there are wireless devices in use that
do not have WEP capability. All wireless devices must be upgraded to WEP capability for
a fully secured WEP environment.
Authentication
Select either Open System or Shared Key.
WEP On/Off
Select either WEP Off or WEP On.
Key Information
Press the Right Arrow key to scroll through the options:
Default Key: Enter the key # specified for use by the Mobile
Handsets. This will be 1 through 4.
Key Length: Select either 40-bit or 128-bit depending on the key
length specified for use at this location.
Key 1-4: Scroll to the key option that corresponds to the Default Key
that was entered above. Enter the encryption key as a sequence of
hexadecimal characters. (Use the 2 and 3 keys to access hexadecimal
digits A-F, use the Right Arrow key to advance to the next digit, and
the Left Arrow key to backspace.) For 40-bit keys you will need to
enter 10 digits, for 128-bit keys you will need to enter 26 digits. The
display will scroll as needed.
Rotation Secret
This is used for proprietary WEP key rotation. Refer to your custom
document if this feature is supported in your system.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 33

Mobile Handset Configuration 4-9
Cisco FSR (Fast Secure Roaming)
In order to provide the highest level of security without compromising
voice quality on Cisco Aironet wireless LAN access points, NEC and Cisco
Systems have cooperated to implement the Fast Secure Roaming
mechanism. FSR is designed to minimize call interruptions for Mobile
Handset users as they roam throughout a facility. Existing Aironet 350,
1100, and 1200 APs may require a firmware upgrade to support FSR.
Cisco FSR requires advanced configuration of the Cisco access points in
your site. See your Cisco representative for detailed documentation on
configuring your access points and other required security services on
your wired network. To configure Cisco FSR in your Mobile Handset, you
must enter a Radius Server username and password into each phone.
Username: Enter a username that matches an entry on your Radius
server. Usernames are alphanumeric strings, and can be entered
using the alphanumeric string entry technique.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds to this Username.
NEC Options
The NEC Options menu includes the following sub-menus: NEC PBX IP,
DRS Self Port, DRS Far Port, PROTIMS Port, RTP Port, NGT Port, and
Listen Port.
The administrator enters the NEC Telephony Servers IP Address in the
NEC PBX IP menu. All other parameters should remain at the default
value.
OAI On/Off
NEC’s Open Application Interface (OAI) enables third-party computer
applications to display alphanumeric messages on the Mobile Handset
display and take input from the Mobile Handset keypad. Refer to the
Open Application Interface (OAI) Specification (Version 1.2)
documentation for information about administering the OAI Gateway
and the services it can provide.
If you have an O AI Gateway installed in your system, OAI may be
optionally enabled in each Mobile Handset. Y o u may select whether the
Mobile Handset should attempt to connect to the NEC OAI Gateway by
choosing either the ENABLE or DISABLE commands on this menu.
If OAI is enabled, and an OAI IP address is available to the telephone
(either via DHCP or Static IP conf i gu ration) , the telephone will
communicate with the OAI Server at power on, and periodically while it
is powered on. If you don’t have a NEC OAI Gateway installed at your
site, you should disable the OAI feature to preserve network bandwidth
and battery life.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 34

4-10 Mobile Handset Configuration
Set Admin P.W.
The Admin PW (password) controls access to the administration
functions in the Admin Menu. The password must be se t in each Mobile
Handset for which controlled access is desired. Mobile Handsets are
shipped without any Admin Menu pa ss word.
If you exit with no entry, the password is erased and the display will not require it
before displaying the Admin Menu.
NOTE
User-defined Preferences
Table 4-7 lists navigation keys used to display and select options.
User-defined preferences are also covered in the MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL
Mobile Handsets User Guide. The system administrator can refer to this list for more
REFERENCE
information about customizing Mobile Handset settings.
To configure the following options, the Mobile Handset must acquire the
system (no error message may display) and be at the extension display.
This is the standby state. While in the standby state, press and hold
FCN briefly to open the user options menu.
Table 4-7 Navigation keys
Key Names Descriptions
Up/Down buttons Displays previous/next menu item.
Select button Selects the menu item or option.
OK softkey Selects the menu item or option.
Save softkey Saves the entry.
Bksp softkey Backspaces to allow editing of entry.
Cncl softkey Cancels edit and returns to previous menu level.
Up softkey Returns to previous menu level.
Exit softkey Exits the menu (at the top level).
End Call key Exits to standby state (from any level).
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 35

Table 4-8 Standby menu items
Standby menu items 2nd Level 3rd Level
Mobile Handset Configuration 4-11
Ring Type Telephone ring Normal Ring
Noise Mode Normal
Alias IP Addr
Current IP Addr
Extension
Push-to-talk Channel 1-8
Table 4-9 User-defined preferences
Vibrate Ring
Vib/Norm Ring
Auxiliary ring 1 “
Auxiliary ring 2 “
High
Severe
Enable/Disable Enable
Disable
Preferences Descriptions
Ring Type Select Ring Type then Telephone Ring to change the
standard ring used for normal operation. Select one of the
following from the Telephone Ring menu:
• Normal Ring (an audible alert)
• Vibrate Ring
• Vib/Norm Ring (vibrate for five seconds and then audible
alert for subsequent rings).
Note: The Auxiliary Ring modes are reserved for future use.
The ring type currently in use displays with an asterisk
(*).
Noise Mode Provides options that describe the noise level in your
environment. Selecting the correct option will adjust the
Mobile Handset to account for background noise. Select one
of the following:
• Normal: for most office environments
• High: for moderate background noise
• Severe: for extremely noisy conditions.
Use of the non-Normal modes is not recommended unless
you are in a loud environment or you may find it difficult to be
heard on your Mobile Handset.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 36

4-12 Mobile Handset Configuration
Preferences Descriptions
Alias IP Addr Displays the IP address currently assigned to this Mobile
Handset by the SVP Server.
Current IP Addr Displays the IP address currently assigned to the Mobile
Handset. The IP address is not set here, it is merely displayed
and may not be changed.
Extension Allows you to enter the user extension for this Mobile
Handset. This number is for display purposes only, entering it
does not assign the extension in the host telephone system.
Push-to-talk Displays the menu for the two way radio feature in the
MH120.
• The Channel option allows you to select a channel 1-8 to
send and receive radio messages.
• The Enable/Disable option allows you to enable or disable
the radio feature.
Refer to the MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets end
user document for more information about push-to-talk.
Additional options may be present. Contact your system administrator
for information.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 37

5
License Management
The MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handset system supports a
number of different IP protocol integrations. All MH110/MH120 Handsets
are shipped from NEC with a generic software load that allows them to
associate to a wireless LAN and download their functional softw are from
a TFTP server. Th e Mob i le Han d sets will not function properly without
downloading appropriate software. This chapter details the process to
properly configure MH110/MH120 Handsets and download software via
over-the-air file transfer.
5-1
Chapter Topics • Requirements
• Configuration Process
Requirements
• A wireless LAN must be properly configured and operational through
the use of 802.11b wireless access points.
• The supported NEC IP telephony system must also be connected to
your network and completely operational.
• A TFTP Server must be available on the network in order to load the
appropriate software into the Mobile Handsets.
• Finally, ensure that the Battery Pack on the Mobile Handset is fully
charged.
Configuration Process
Step 1 Download the latest MH110/MH120 Handsets IP software.
Step 2 Load the latest version of the MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile
Handsets Protims code and place it on the TFTP Server and ensure the
TFTP Server is started. The three files that are needed must be named
—slnk_cfg.cfg
—pd11nec.bin
—pi110001.bin
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 38

5-2 License Management
Step 3 If statically assigning IP addresses, ensure that the Phone IP address,
REFERENCE
Step 4 Ensure the Mobile Handset has properly configured ESSID and
REFERENCE
Step 5 Using the Admin Menu on the Mobile Handset, ensure the License
TFTP Server IP, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway information are
accurate in the Admin Menu. If using a DHCP Server, ensure that the
DHCP options are set.
Refer to Table 4-3 on page 4-3 and to “IP Address” on page 4-4 for more
information about configuring the IP address through the Admin menu.
Regulatory Domain information within the Admin Menu. If you are
accepting broadcast ESSIDs at your access points, the handset will
automatically learn the ESSID information when powering on.
Refer to “ESSID” on page 4-6 and “Regulatory Domain” on page 4-7 in Chapter 4
for detailed configuration instructions.
Management menu option is set to 013. This ensures the handset will
check for the proper Protims files each time it powers on.
REFERENCE
NOTE
Refer to “License Management” on page 4-6 in Chapter 4 for more information
about configuring the License Management command on the Admin menu.
Step 6 Power cycle the Mobile Handset.
Step 7 The Protims code will now download to the handset. The status bar will
increment fully across the display for each function that is being
performed in the download process. Upon completion of the update
process, the handset will re-boot with the new firmware.
Step 8 If the Mobile Handset is statically configured, you may now enter the
SVP IP address and RTC address as detailed in
Step 9 Register the Mobile Handset with the supported NEC VoIP solution as if
Step 3.
it were a NEC DtermIP-16LD and properly label the handset with the
appropriate extension.
If using normal login procedures, the extension
does not need to be programmed, the proper number will appear after
login.
For future software upgrades, update the files that are stored on the TFTP Server.
Each time the Mobile Handset is powered on, it will check with the TFTP Server to
ensure it has the proper software version.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 39

6
NEC VoIP Integration Factors
This chapter describes the mapping between the emulated NEC
DtermIP-16LD and the MH110/MH120 Handsets.
Chapter Topics • Voice Messaging Access
• CODECs
• DHCP
• DNS
6-1
Voice Messaging Access
Voicemail access is obtained through the Message key whi ch is assigned
on the Mobile Handset to FCN + 3.
CODECs
The MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets is compatible with
the G.711 and G.729a/ab CODECs. There is no setting required on the
Mobile Handset.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a standardized protocol
that enables clients to be dynamically assigned with various
configuration parameters, such as an IP address, subnet mask, default
gateway, and other critical network configuration information. DHCP
servers centrally manage such configurat ion data, and are configured by
network administrators with settings that are appropriate for a given
network environment. The Mobile Handset will search for NEC server
configuration in the vendor specific and site-specific options listed in
Table 6-1. The Mobile Handset will use the following DHCP options if
DHCP use is enabled.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 40

6-2 NEC VoIP Integration Factors
Table 6-1 DHCP options
Options Descriptions
1 Subnet Mask
3 Default Gateway
6 DNS Server
15 Domain Name
66 TFTP Server
151 SVP Server
152 OAI Gateway
128 Mitel TFTP Server address (not currently used by Mobile Handset)
129 Mitel PBX RTC IP address
130 String containing “NEC DTERMIP-16LD”
TFTP
DNS
160 NEC PBX Registration IP
siaddr Boot server or next server
The Mobile Handset uses TFTP to update the Handset software over the
802.11b wireless LAN.
Domain Name System (DNS), an industry-standard protocol, locates
computers on an IP-based network. IP networks rely on number-based
addresses to move information on the network. However, users are
better at remembering friendly names than number-based addresses,
so, it is necessary to translate user-friendly names into addresses that
the network can recognize. The Mobile Handset will use DNS to
automatically translate names into IP addresses for these components:
TFTP Server and the SVP Server.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 41

7
Feature Programming
This chapter describes feature programming for the MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets.
Chapter Topics • Overview
• Feature Assignment
• Feature Access
7-1
Overview
The button mapping from the NEC DtermIP-16LD to the MH110/MH120
UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets is designed to preserve nearly all o f the
functionality of the IP Phone within a small, mobile device. All t elephone
functions and messaging features are supported if possible.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 42

7-2 Feature Programming
Figure 7-1
Programmable Line or Feature Keys
Programmable
Line or Feature
Keys
Speakerphone functions are not supported. Softkeys on the Wireless
Telephone emulate the softkeys on the DtermIP-16LD. Available lines
and features are displayed on three different lists. These are accessed
by pressing the LINE or FCN key in the active off-hook mode or the
MENU key while in the active on-hook mode. Lines and features may be
selected in two ways – either by using the shortcut key that is displ ayed
next to the label on the list of options or by using the Up, Down, and
Select side buttons to scroll through and select an option.
Feature Assignment
Table 7-1 through Table 7-3 show how the Wireless Telephone displays
the features of the DtermIP-16LD and the key sequences (shortcuts)
used to activate the corresponding feature.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 43

Table 7-1 Function key displays
Feature Programming 7-3
Function key displays
1 Hold Hold FCN + 1
2 Transfer Transfer FCN + 2
3 Conf Conference FCN + 3
4 Recall Recall FCN + 4
5 Redial Redial FCN + 5
7 Directory Directory FCN + 7
8 Message Message FCN + 8
9 Mute Mic FCN + 9
Table 7-2 Line key displays
Line key display Emulates lines programmed + number label
1-4 shortcut plus the label in
sequence as received from
PBX.
Emulates fixed
operation keys
Unlabeled keys will not be
displayed.
Mobile Handset
key sequences
Line + 1 - 4
Table 7-3 Menu key displays
Menu key display s Emulates programmed features
1-9, *, 0, # shortcut plus label in
sequence as received from
PBX.
If an Open Application Interface (OAI) is operational, a function key sequence will be
assigned in the OAI configuration and will override any function sequence
NOTE
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
established in the PBX. The OAI label will appear on the Function key display. Note
that FCN *, 0, # are not assigned and may be used by OAI without overriding any
assigned sequence.
Unlabeled keys will not be
displayed.
Menu + 1 to 9, *, 0, #
If no shortcut is available, the
feature must be activated
through the side buttons.
Page 44

7-4 Feature Programming
Feature Access
In its standby state, the Mobile Handset displays the extension assigned
to the handset or the extension the user entered at login. The acti ve
state is initiated by pressing the Start Call key.
When the active state is initiated, the Mobile Handset contacts the PBX
and displays the data provided – the time, date, default line icon, any
voice mail icon, softkey and feature key labels. The Mobile Handset is
off-hook and there is a dial tone. While in the active state, you may
switch to any display – Line, Feature, or Menu – by pressing its
corresponding key . Pressing a softkey will activ ate the feature displayed.
Figure 7-2
Feature Access
Line indicators
Left arrow
Low battery
icon
Up
Select
Select
Down
Softkey A
Softkey B
Power On
Star t Call
Earpiece
Right arrow
Voicemail icon
Shortcut Menu &
Main display area
Softkey Function
display area
Softkey D
Softkey C
Power Off
End Call
Menu
Function
Charging contacts
Headset jack
Line
Microphone
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 45

Feature Programming 7-5
Line Appearances
While off hook, press the LINE key to view the shortcut keys and
assigned extensions for line appearances. There are nine possible line
appearances which correspond to the nine indicators at the top of the
Mobile Handset display. Only the first four of the nine line keys are used
for line appearances.
When a line is in use, the indicator converts to the line nu m ber and a
PLUS SIGN (+) will appear after the shortcut key on the list, emulating a
lit LED. There are four possible line appearances which correspond to
the indicators at the top of the Handset display. To use an extension,
press the corresponding shortcut key. You ma y also use the Up, Down,
and Select buttons to scroll through the displays and activate the line
appearances on this list. Press the End Call key to exit the Line
Appearance list.
Menu Display
While off hook, press the MENU key to view the shortcut keys and
assigned extensions for features programmed to the programmable line
and feature keys. Press the MENU key again to display the second page
of the list if more than four line keys have been programmed.
To activate a feature, press the corresponding shortcut key. You may
also use the Up, Down, and Select buttons to scroll through the
displays and activate features on this list.
Note that there are 12 possible shortcuts and programmable keys. If
fewer than four lines have been progr ammed and the remaining keys
have been programmed to features, the last features on the list will not
have shortcut keys. Activate these by using the side buttons. Press the
End Call key to exit the Menu Display list.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 46

7-6 Feature Programming
Feature List
The IP Phone has several fixed feature keys. The NEC implementation
supports five fixed features that are suitable to a mobile user through
the Function (FCN) key on the Mobile Handset. When FCN is pressed,
the display lists the first four fixed features and the assigned shortcut
key . Pressing FCN repeatedly will display the remaining items on the list
as shown in the preceding table. OAI options appear at the end of the
list. All OAI keys will preempt shortcuts assigned to other keys.
Activate the fixed features on the off-hook Mobile Handset by pressing
FCN + the shortcut key. You may also use the Up, Down and Select
buttons to scroll through and activate the f eatures on this li st. Press the
End Call key to exit the list.
1 Hold
2 Transfer
3 Conf
4 Recall
5 Redial
7 Directory
8 Message
9 Mute
First Screen
Second Screen
* (OAI)
0 (OAI)
# (OAI)
Third Screen
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 47

8
Testing a Mobile Handset
This chapter describes tests that can be performed in an active wireless
area to verify proper registration and operation of each Mobile Handset.
Use the following steps to test a Mobile Handset.
Step 1 Power on the Mobile Handset by pressing Power On. You will see a
series of messages displayed as the Mobile Handset acquires the
system. The Mobile Handset should display the user extension or the
login screen.
8-1
Step 2 Login using the proper login id and password. Any error messages
should clear.
Step 3 Press the Start Call key. The extension number should be replaced by
information from the supported NEC VoIP solution and you should hear
dial tone.
Step 4 Place a call and listen to the audio quality. End the call by pressing the
End Call key.
Step 5 Place a call to the Mobile Handset and verify ring, answer, clear
transmit, and clear receive audio.
Step 6 Go off-hook and use the FCN key to verify the Features list.
Step 7 Go off-hook and use the LINE key to verify the Line appearances/Line
features list.
Step 8 Press the End Call key. Any line indicators should turn off and the
extension number display should return.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 48

8-2 Testing a Mobile Handset
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 49

9
Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile
Handsets
This chapter explains how to conduct a preliminary Site Survey Mode
test. Areas where coverage is conflicting, inadequate, or where there
are system difficulties should be noted and discussed with your wireless
LAN and/or LAN system administrator to determine the cause and
possible remedy. Refer to
Problems” for clues to possible sources of difficulties.
Chapter 11, “Troubleshooting Mobile Handset
9-1
Chapter Topics • Site Certi fication
Site Certification
IMPORTANT
• Site Survey Mode
• Solving Coverage Issues
The installer should not leave the site before performing
installation verification.
These tests must be performed in typical operating conditions,
especially if heavy loads occur. Testing sequence and procedure is
different for every installation. Generally, you should organize the test
according to area and volume, placing numerous calls to others who can
listen while you perform coverage tests. Note any areas with excessive
static or clarity problems and report it to Customer Service.
The coverage test will also require you to put t he Mobile Handset in Site
Survey Mode and walk the entire coverage area to verify all access
points.
The installation is not complete until these certification steps have
been performed. Do not hand out Mobile Handsets at a site that has
not been certified.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 50

9-2 Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
Site Survey Mode
Signal strength in the covered area is tested by performing a Site
Survey. Put a Mobile Handset in Site Survey Mode
Refer to “Configuration Process” on page 5-1 for more information.
REFERENCE
Walk the entire coverage area while viewing the display. The FCN key
toggles between the three coverage modes:
• Detect dBm coverage
• Detect Overlap or Conflicts
• Confirm Supported Data Rates
The Mobile Handset will remain in Site Survey mode until it is powered
off. When testing is complete, press Power Off to turn off the Mobile
Handset. Numbers racing across the Mobile Handset display indicate AP
information is being obtained. A Waiting messa g e i n d i ca t e s the system
is not configured properly and the Mobile Handset cannot find any APs.
Figure 9-1
Detect dBm coverage
As you walk the perimeter, the two-line display will show the top four
access points that the Mobile Handset can contact in a code as
illustrated below.
Detect dBm coverage
• XXX1 through XXX4 are the last four digits of the access points’ MAC
address. The primary access point (the access point which had the
strongest signal to this Mobile Handset) displays first, followed by the
three access points with the next strongest signals.
• YY is the power level in dBm at which this Mobile Handset heard the
associated access point. Although shown as a positive number, YY
represents negative dBm and lower numbers represent stronger
signals.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 51

NOTE
Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets 9-3
Example: A displayed value of 40 indicates -40dBm, and is therefore a
stronger signal than a display of 50 (which indicates
-50dBm). At least one access point’s reading should be
stronger than -70 dBm in all areas.
Note any areas that have inadequate dBm readings.
Detect Overlap or Conflicts
Press FCN to toggle to the Site Survey function that shows the channel
number of the access points. Use this information to detect overlaps or
conflicts in access point si gnaling.
Figure 9-2
NOTE
Detect Overlap or Conflicts
• XXX1 through XXX4 are the last four digits of the access points’ MAC
address.
• ZZ is the channel number that the access point is using.
Note any areas that have access points that are in contention for the same channel.
It is preferable that no overlaps exist anywhere in your facility. If the
site survey mode indicates two APs using the same channel, then at
least one other AP must be indicated at 10 dBm stronger than those APs
to avoid channel conflicts.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 52

9-4 Certifying MH110/MH120 Mobile Handsets
Confirm Supported Data Rates
Press FCN to toggle to the Detail function. Use this information to
confirm signal strength and supported data rates.
Figure 9-3
Confirm signal strength and data rates
• # is the number (1-4) of the AP
• Full MAC is the MAC address of the AP
• dB is the signal strength of the AP
• Ch is the channel of the AP
• 1b2b5b11b is an example of the data rate that may be displayed
Walk around the site to determine supported data rates, one AP at a
time. In any location you may click the RIGHT ARROW key to display
the second best AP, click the RIGHT ARROW again to display the third
best, and so on to the fourth best.
The LEFT ARROW key steps you back to the first best. Each data rate
(1,2,5.5, or 11Mb/s) that is supported by the AP is shown. Those rates
that are in the Basic Rate set (sometimes referred to as “required”
rates) are indicated by a ‘b’ following the rate number. The Supported
and Basic data rate(s) should be the same on all APs as is appropriate
for your environment.
Solving Coverage Issues
Coverage issues are best resolved by adding and/or relocating access
points.
Overlap issues may be resolved by reassigning channels to the access
points or by relocating the access points.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 53

10
Software Maintenance
This chapter describes how to upgrade and maintain software for the
The MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets. The MH110/MH120
Handsets use proprietary software programs written and maintained by
NEC. The software versions that are running on the Mobile Handsets can
be displayed during power on by holding down the Power On key.
NEC or its authorized dealer will provide information about software
updates and how to obtain the software (for example, downloading from
a web site).
10-1
Chapter Topics • Upgrade Mobile Handsets
• Download Failure or Recovery Messages
Upgrade Mobile Handsets
After software updates are obtained from NEC, they must be transferred
to the appropriate location in the LAN to update the code used by the
Mobile Handsets.
MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets allow over-the-air
transfer of software updates from the designated TFTP server to the
Mobile Handsets. The downloader function in the Mobile Handset checks
its software version every time the Mobile Handset is powered on. If
there is any discrepancy, the Mobile Handset immediately begins to
download the update.
Normal Download Messages
When the Mobile Handset is powered on, it displays a series of
messages indicating that it is searching for new software, checking the
versions, and downloading. The normal message progression is shown
in
Table 10-1.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 54

10-2 Software Maintenance
Table 10-1 Normal Download Messages
Messages Descriptions
Checking Code
Erasing Memory
Updating Code
When the update is complete, the Mobile Handset displays the login
screen or extension number, and is ready for use.
Mobile Handset is contacting the TF TP Server to determine if it has a newer
version of software that should be downloaded.
Mobile Handset has determined that a download should occur and is erasing
the current software from memory. This message also displays a progress
bar. When the progress bar fills the display line the erase operation is
complete.
Mobile Handset is downloading new software into memory. This message
also displays a progress bar. When the progress bar fills the display line the
update operation is complete on that file.
Download Failure or Recovery Messages
The following display messages indicate a failure or recovery situation
during the download process.
Table 10-2 Download Failure and Recovery Messages
Messages Descriptions
Server Busy
TFTP ERROR(x):yy
Erase Failed
Waiting
Mobile Handset is attempting to download from a TFTP Server that is busy
downloading other phones and refusing additional downloads. The Mobile
Handset will automatically retry the download every few seconds.
A failure has occurred during the TFTP download of one of the files. (x) = The
file number which was being downloaded; yy is an error code describing the
particular failure. Possible error codes are:
01 = TFTP server did not find the requested file.
02 = Access violation (reported from TFTP server).
07 = TFTP server reported “No such user” error. Check the TFTP server
configuration.
81 = File put into memory did not CRC. The Mobile Handset will attempt to
download the file again.
FF = Time-out error. TFTP server did not respond within a specified period
of time.
Download process failed to erase the memory in the Mobile Handset. This
operation will retry.
Mobile Handset has attempted some operation several times and failed, and
is now waiting for a period of time before attempting that operation again.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 55

11
Troubleshooting Mobile Handset
Problems
MH110/MH120 UNIVERGE WL Mobile Handsets can exhibit transmission
problems in several ways. They can cease fun c ti oning properly, display
error messages, or display incorrect data. This chapter discusses
problem sources that determine the best method of approaching any
specific situation when using and troubleshooting Mobile Handsets.
Chapter Topics • Access Point Problems
• Configuration Problems
• Mobile Handset Status Messages
11-1
Access Point Problems
Most, but not all, Mobile Handset audio problems have to do with access
point range, positioning and capacity. Performing a Site Survey as
described in
these types of problems. If the Mobile Handset itself is suspected,
conduct a parallel Site Survey with a Mobile Handset that is known to be
properly functioning.
In range/Out of range – service will be disrupted if a user moves
outside the area covered by the wireless LAN access points. Service is
restored if the user moves back within range. If a call drops because a
user moves out of range, the Mobile Handset will recover the call if the
user moves back into range within a few seconds.
Capacity – in areas of heavy use, the call capacity of a particular AP
may be filled. If this happens, the user wi ll hear three chirps from the
Mobile Handset. The user can wait until another user terminates a call,
or move within range of another AP and try the call again. If a user is on
a call and moves into an area where capacity is full, the system
attempts to find another AP. Due to range limitations, this may be the
same as moving out of range.
“Site Survey Mode” on page 9-2 can isolate the AP causing
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 56

11-2 Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems
Transmission Obstructions – prior to system installation, the best
location for APs for optimum transmiss ion coverage was determined.
However, small pockets of obstruction may still be present, or
obstructions may be introduced into the facility after system installation.
This loss of service can be restored by moving out of the obstructed
area, or by adding APs.
Configuration Problems
Certain problems are associated with improper configuration of either
the supported NEC VoIP solution or the Mobile Handset.
Configuration problems are generally corrected by changing the
configuration at the supported NEC VoIP solution or on the Mobile
Handset. There may also be incorrect programming of the AP.
Refer to the Configuration Note for the AP in use at the site.
REFERENCE
Mobile Handset Status Messages
Mobile Handset status messages provide information about the MH110/
MH120 Handset's communication with the AP and host telephone
system. The following table summarizes the status messages, in
alphabetical order.
Table 11-1 Mobile Handset Status Messages
Messages Descriptions Actions
3 chirps Mobile Handset is not able to
communicate with the best AP,
probably because that AP has no
bandwidth available.
Bad Config Some needed configuration
parameter has not been set.
Bad ESSID The Mobile Handset is configured for
“static ESSID” (as opposed to “Learn
once” or “Learn always” and no
ESSID has been entered.
None. This is only a warning, the call will handoff to the best AP
once it becomes available.
Check all required Mobile Handset configuration parameters for
valid settings.
Enter an ESSID in the configuration settings or change to one of
the “Learn” modes.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 57

Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems 11-3
Messages Descriptions Actions
(battery icon), Low
Low battery In call: the battery icon displays and a soft beep will be heard when
Battery and beep
Can’t Renew DHCP The functional code is not able to get
a lease renewal.
Charging … The Mobile Handset is charging in
the Desktop Charger.
Charge Complete The Mobile Handset is now fully
charged.
Checking Code Mobile Handset is contacting the
TFTP Server to determine if it has a
newer version of software that should
be downloaded.
Checking DHCP IP The Mobile Handset is retrieving
DHCP information from the DHCP
server.
CRC Code Error The software which has been TFTP
downloaded has a bad redundancy
code check.
the user is on the Mobile Handset and the battery charge is low.
User has 15–30 minutes of battery life left.
Not in call: The battery icon displays whenever the battery charge
is low The message Low Battery and a beep indicate a critically
low battery charge when user is not on the Mobile Handset. The
Mobile Handset will not work until the Battery Pack is charged.
Configuration problem. Check the gateway address in the DHCP
server.
No action needed.
No action needed.
None, this message should only last for approximately one
second. If message remains displayed, power off and contact
NEC customer support.
None. This is informational only.
Try the download again, it is possible the software was corrupted
during download. If the error repeats, check that the download
image on the TFTP server is not corrupted.
Code Mismatch! The software loaded into the Mobile
Handset is incorrect for this model
Replace the software image on the TF TP server with software that
is correct for the phone model.
phone.
DHCP Error (1-4) DHCP Error 1 The Mobile Handset cannot locate a DHCP server. It will try every
4 seconds until a server is located.
DHCP Error 2 The Mobile Handset has not received a response from the server
for a request to an IP address. It will retry until a server is found.
DHCP Error 3 The server refuses to lease the Mobile Handset an IP address. It
will keep trying.
DHCP Error 4 The server offered the Mobile Handset a lease that is too short.
The minimum lease time is 10 minutes but NEC engineers
recommend at least one hour minimum lease time. The Mobile
Handset will not retry. Reconfigure the server and power cycle the
Mobile Handset.
DHCP Lease Exp The Mobile Handset’s DHCP lease
has expired, and the call (if any)
cannot continue.
The Mobile Handset failed to renew its DHCP lease, either
because the DHCP server is not running, or because the
configuration has been changed by the administrator. The Mobile
Handset will attempt to negotiate a new lease, which will either
work, or change to one of the above DHCP errors (1-4)
DHCP NACK error A NACK (Negative ACKnowledge)
was received from the DHCP server.
The DHCP lease currently in use by the Mobile Handset is no
longer valid, which forces the Mobile Handset to restart. This
problem should resolve itself on the restart. If it does not, the
problem is in the DHCP server.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 58

11-4 Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems
Messages Descriptions Actions
DO NOT
POWER OFF
The Mobile Handset is in a critical
section of the software update.
None. Do not remove the battery or attempt to power off the phone
while this is displayed. Doing so may require the phone to be
returned to NEC to be recovered.
Duplicate IP The Mobile Handset has detected
another device with its same IP
address.
If using DHCP , check that the DHCP server is properly configured
to avoid duplicate addresses.
If using Static IP, check that the Mobile Handset was assigned a
unique address.
Erase Failed Download process failed to erase the
memory in the Mobile Handset.
Erasing Memory Mobile Handset has determined that
a download should occur and is
Operation will retry but may eventually report the error “int. error:
0F” Power cycle the phone.
None. When the progress bar fills the display line the erase
operation is complete.
erasing the current software from
memory.
Initializing … The is performing power on
None. This is informational only.
initialization.
Internal Err. # # The Mobile Handset has detected a
fault from which it cannot recover.
Record the error code so it can be reported.
Turn the Mobile Handset off then on again. If error persists, try
registering a different Mobile Handset to this telephone port. If
error still persists, contact NEC Technical Support and report the
error.
Network Busy All APs are full or busy. Try call again later.
No Host IP The Mobile Handset is configured for
“static IP” (as opposed to “use
Enter a valid IP address in the configuration settings or change to
“use DHCP”.
DHCP”) and no valid host IP address
(the Mobile Handset’s IP address)
has been entered.
No IP address Invalid IP. Check the IP address of the Mobile Handset and re-configure if
required.
No PBX Response The Mobile Handset tried to send a
message to the supported NEC VoIP
Verify the supported NEC VoIP solution is operational and
connected to the network.
solution and failed to get a response.
No SVP IP The Mobile Handset is configured for
“static IP” (as opposed to “use
Enter a valid SVP Server IP address in the configuration
setting or change to “use DHCP.”
DHCP”) and no valid SVP Server
address has been entered.
No SVP Response The SVP Server is not responding
to requests from the Mobile
Handset.
This may be caused by bad radio reception or a problem with the
SVP Server. The Mobile Handset will keep trying to fix the
problem for 20 seconds, and the message may clear by itself.
If it does not, the Mobile Handset will restart. Report this problem
to the system administrator if it keeps happening.
No SVPServer Mobile Handset can’t locate SVP
Server.
IP address configuration of SVP Server is wrong or missing.
SVP Server is not working. Check error status screen on SVP Server.
No LAN connection at the SVP
Verify SVP Server connection to LAN.
Server.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 59

Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems 11-5
Messages Descriptions Actions
No Net Access Cannot authenticate / associate with APVerify the AP configuration.
No Net Found This indicates any of the following:
No radio link
No ESSID – Autolearn not supported
Verify that the AP is turned on.
Verify the ESSID of the wireless LAN and enter or Autolearn it
again if required.
(or)
incorrect ESSID
Out of range Try getting closer to an AP . Check to see if other Mobile Handsets
are working within the same range of an AP. If so, check the
ESSID of this Mobile Handset.
Incorrect WEP settings Verify that all the WEP settings in the Mobile Handset match those
in the APs.
No Reg Domain Regulatory Domain not set. Configure the Regulatory Domain of the Mobile Handset
Not Installed! A required software component is
missing.
Check that all required software files are on the TFTP server, if
over-the-air downloading is being used. If the error repeats,
contact NEC Technical Support.
Press End Call If your call has ended. Press the Power Off / End Call key
to return to standby mode.
Restart
Command
The Mobile Handset received a
restart command from the supported
None. The Mobile Handset will automatically
restart in a few seconds.
NEC VoIP solution.
Select License The correct protocol has not
been selected from the license
set.
Using the administrative menus, select one license
from the set to allow the phone to download the
appropriate software.
Server Busy Mobile Handset is attempting to
download from a TFTP Server that is
None, the Mobile Handset will automatically retry the download
every few seconds.
busy downloading other devices and
refusing additional downloads.
SVP Service Rej. The SVP Server has rejected a
request from the Mobile Handset.
System Locked
SVP Server is locked. Try call again later, system has been locked for maintenance.
The Mobile Handset will restart and attempt to re-register with the
SVP Server, which should fix the problem. Report to your
administrator if it keeps happening.
(with Busy Tone)
System Busy
(with Busy Tone)
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
SVP Server is busy or out of
resources.
All call paths are in use, try call again in a few minutes.
Page 60

11-6 Troubleshooting Mobile Handset Problems
Messages Descriptions Actions
TFT P ERROR(x):yy A failure has occurred during a TFTP
software download. (x) = The file
number which was being
downloaded; yy, is an error code
describing the particular failure.
Possible error codes are:
• 01 = TFTP server did not find the
requested file.
• 02 = Access violation (reported
from TFTP server).
• 07 = TFTP server reported “No
such user” error.
• 81 = File put into memory did not
CRC.
• FF = Timeout error. TFTP server
did not respond within a specified
period of time.
Updating Code… Mobile Handset is downloading new
software into memory.
Updating … The Mobile Handset is internally
updating its software images.
Waiting… Mobile Handset has attempted some
operation several times and failed.
Error code 01, 02 or 07 - check the TFTP server configuration.
Error code 81, the Mobile Handset will attempt to download the file
again.
For other messages, power off the Mobile Handset, then turn it on
again to retry the download. If the error repeats, note it and
contact NEC Technical Support.
None. When the progress bar fills the display line the update
operation is complete on that file.
None. The Mobile Handset may do this briefly after a download.
This is informational only.
None. The Mobile Handset is waiting for a specified period of time
before attempting that operation again.
Watchdog Timeout The Mobile Handset failed to hear
from the supported NEC VoIP
solution within the watchdog timeout
interval.
Verify the supported NEC VoIP solution is operational and
connected to the network.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide - Revision 1
Page 61

For additional information or support on this NEC Business Solutions
product, contact your NEC Business Solutions representative.
Page 62

NEC Business Solutions Ltd.
MH110/MH120 IP Wireless Telephone Setup and Administration Guide
NEC-9123, Revision 1
 Loading...
Loading...