Navico RBU Italia SRTLAN25X, SRTLAN30S User Manual
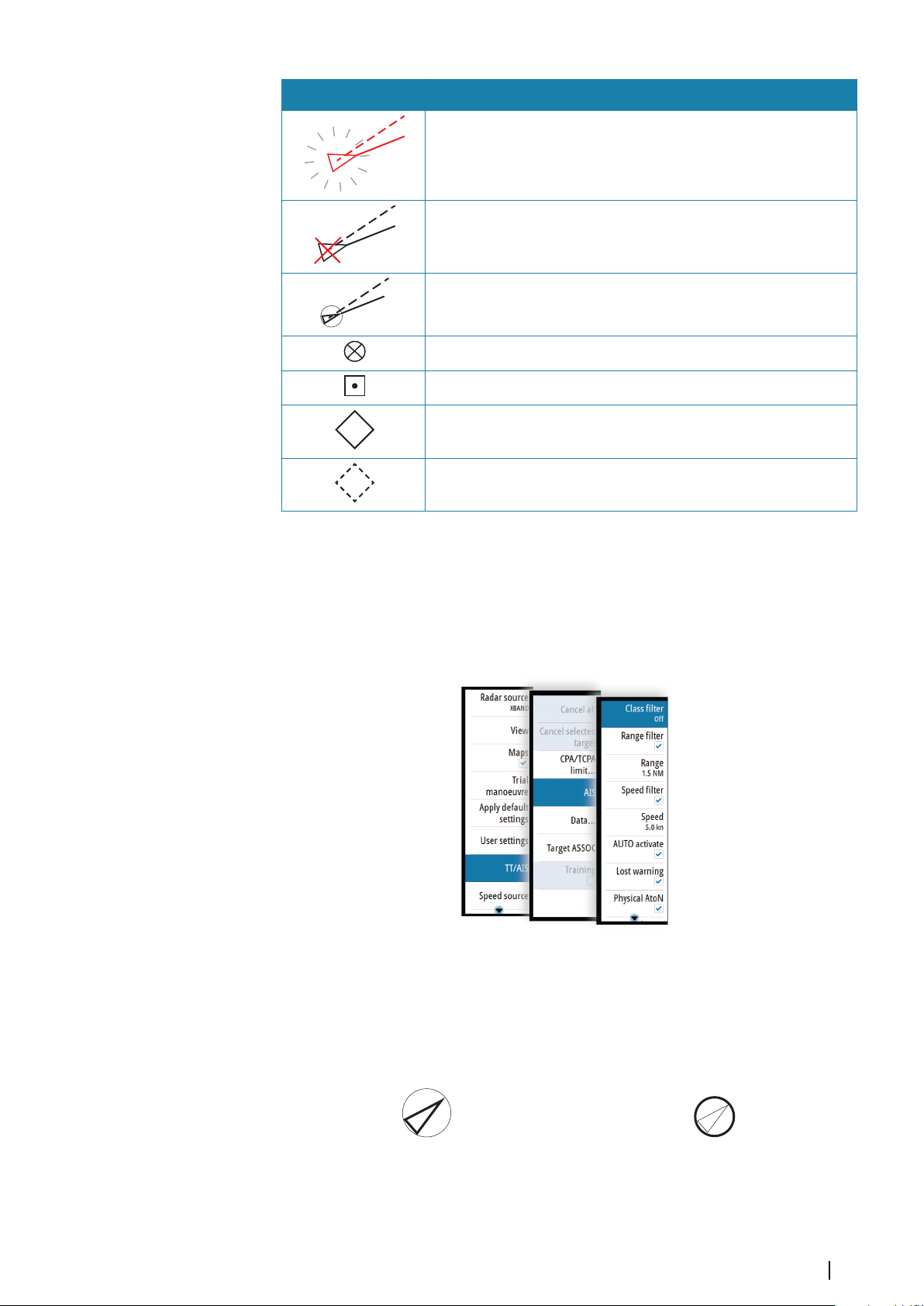
Symbol Description
+
Dangerous AIS target indicated with bold line and with red color.
The symbol flashes until the target alarm is acknowledged by the
operator
Lost AIS target, indicated with crossed lines centered on the target
symbol. The symbol is located at the last received position from the
target
Associated target - using AIS data
AIS SART (AIS Search And Rescue Transmitter)
AIS Base station
Real AtoN (Aids To Navigation)
Virtual AtoN
For a complete list of AIS and AtoN symbols, refer to "Target symbols" on page 70.
Note: A symbol is drawn with a dashed line if the collision avoidance cannot be
Ú
calculated.
AIS target filters
You can select to filter the icons based on AIS class, range and target speed.
AIS and radar target association
When an echo with its AIS symbol on top is being acquired for tracking, the system can
detect that the two symbols represent the same target with the target association function.
When the function is activated, the radar target and the AIS target are associated. You select
whether to use source data from the AIS target or from the tracked radar target.
Associated targets - using AIS data Associated targets - using radar data
This function is useful for reducing the number of AIS symbols and radar targets on the PPI.
Too many targets could clutter the screen and result in dangerous situations. The function
Targets | R5000 Operator manual
41
also compensates for a possible failure in one of the two targets, e.g. if the radar tracked
target is positioned behind an island, the system keeps tracking and visualizing the AIS
target.
Note: The tracked radar target continues to be analyzed by the system when the target
Ú
association is active.
Displaying target information
The vessels dialog
The vessels dialog displays a list of all AIS and MARPA targets.
By default, the dialog lists targets, arranged by distance to own vessel. You can select to
change the sort order, and to display only a selected target type.
The vessels dialog also lists received AIS messages.
To display the vessels dialog:
• select the data option in the menu
• press and hold the AIS key
AIS vessel details
Detailed information about an AIS target is available from the AIS vessels details dialog.
To display the dialog:
• select the AIS additional information option in the target menu
• select an AIS target in the vessels dialog
42
Targets | R5000 Operator manual
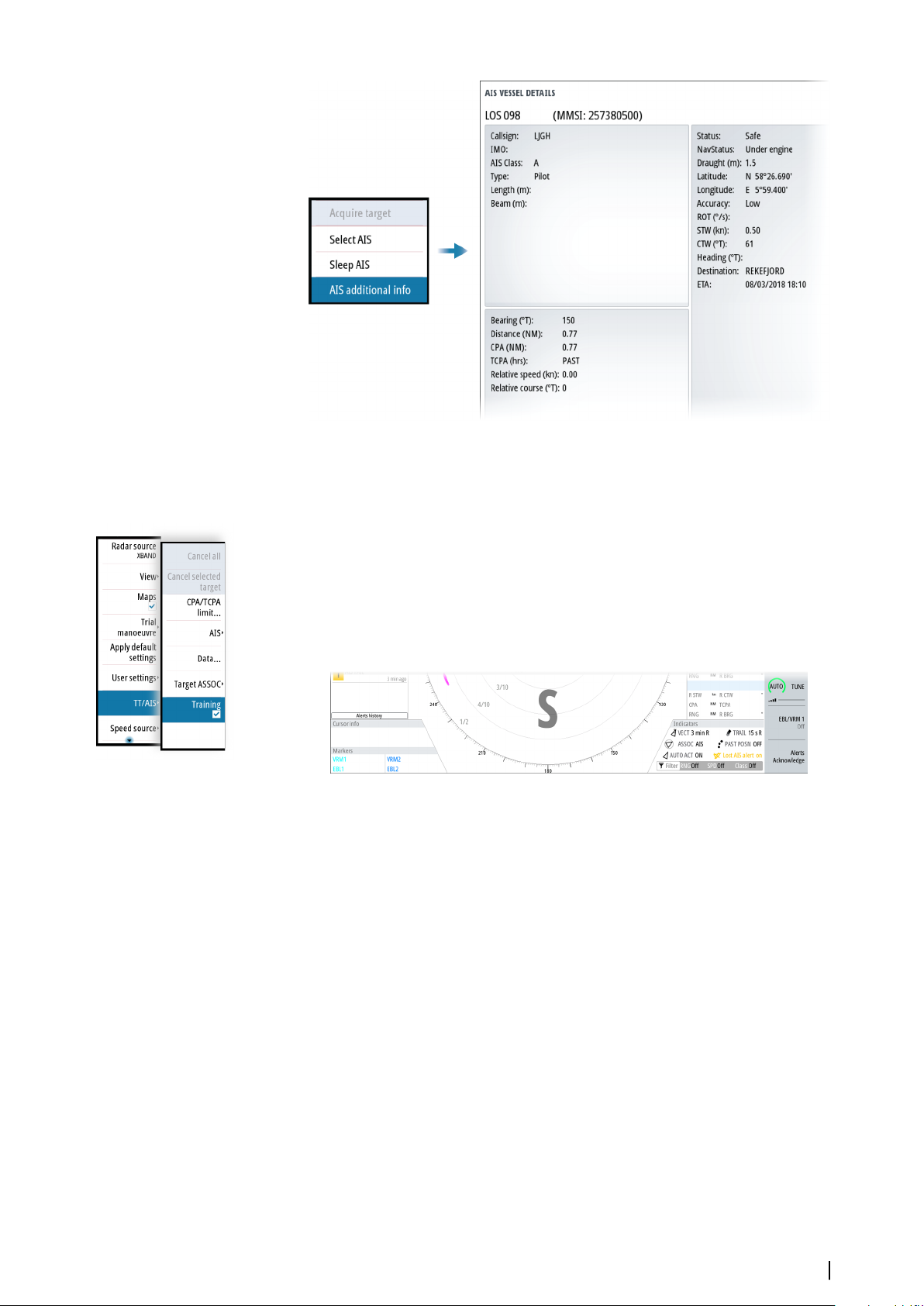
Training simulator
The training function is used to train the operator on manual radar target acquisition, on
target selection and on the tracking procedures.
The function is activated from the menu.
When started the system replays a pre-loaded file, simulating a target with constant speed
and course approaching own vessel. The training target's speed is as per the pre-loaded file,
and it cannot be altered by the user. The CPA and TCPA depends on the simulated target's
speed and own vessel's speed.
A flashing S is shown on the lower part of the screen as long as the function is active to warn
that training simulation is running.
You can perform all tracking operations on the simulated target.
The CPA and TCPA of the training target is automatically tested by the system. Alerts are
raised in case of a malfunctioning of the tracking software:
• Training Tgt CPA Out of Range: if the difference between theoretical and target displayed
CPA is greater than 0.5NM
• Training Tgt TCPA Out of Range: if the difference between theoretical and target displayed
CPA is greater than 30sec
The radar will return to default operation as soon as the training option is turned off from the
menu.
Targets | R5000 Operator manual
43
Navigation tools
A
B
C
D
9
Tracking zones
The tracking zone function allows for automatic acquisition of radar and AIS targets when
they enter a user defined zone ahead or around your vessel.
Two tracking zones can be defined, each with individual settings.
When a target enters a zone, it will automatically be considered as safe or dangerous based
on the CPA/TCPA settings.
Two types of tracking zones are available.
Guard zone
When a target enters a guard zone the following happens:
• radar targets are acquired and AIS targets activated
• warning about new target and warning about target being in zone are activated
• the target icon turns red and flashing
When the warning about new target is acknowledged, the icon stops flashing. The icon
remains red until the target leaves the guard zone.
The color of the border line of a guard zone is defined by the user.
Auto acquisition zone
When a target enters an auto acquisition zone the following happens:
• radar targets are acquired and AIS targets activated
• warning about new target is activated
• the target icon turns red and flashing
When the warning is acknowledged, the target change to basic target icon and color
depending on its status (save or dangerous).
The border line of an auto acquisition zone is white.
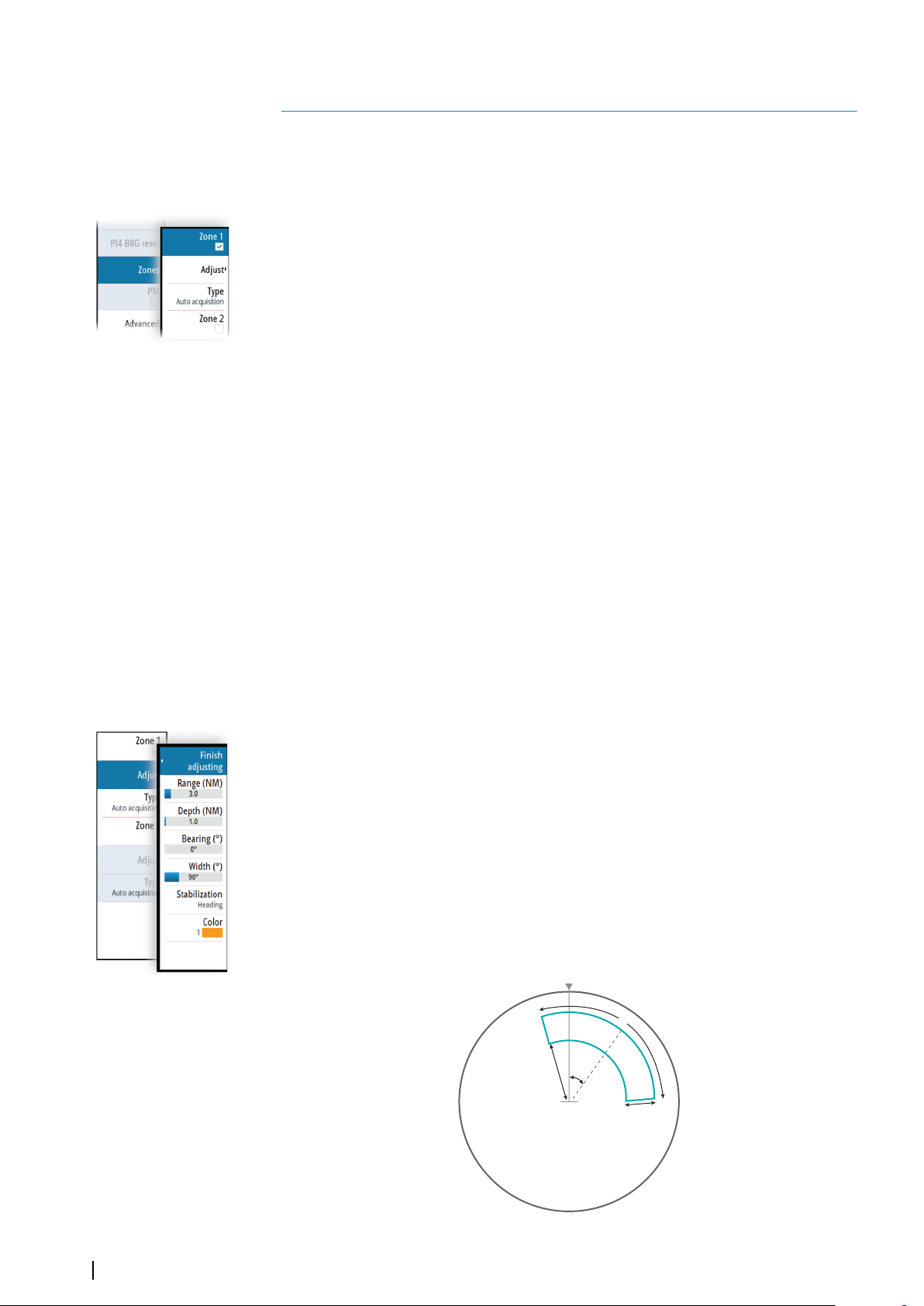
Defining a tracking zone
1 Turn ON the tracking zone you want to define
• The tracking zone lines are displayed on the radar PPI
2 Select the adjust option
• The tracking zone lines turns to dashed lines to indicate that you are in edit
mode
3 Define the guard zone options:
A: Range, relative to vessel center
B: Depth
C: Bearing, relative to vessel heading or to North
D: Width
44
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
4 Select the type for the zone
1 2 3 4
Note: The line color is only applicable when the type is set to guard zone. The line color
Ú
is always white if the type is set to auto acquisition.
5 Save the changes by selecting the finish adjusting option in the menu
Note: If you exit the menu by pressing the exit key, the zone remains in edit mode. The
Ú
lines remain with dashed lines, and the zone is not active.
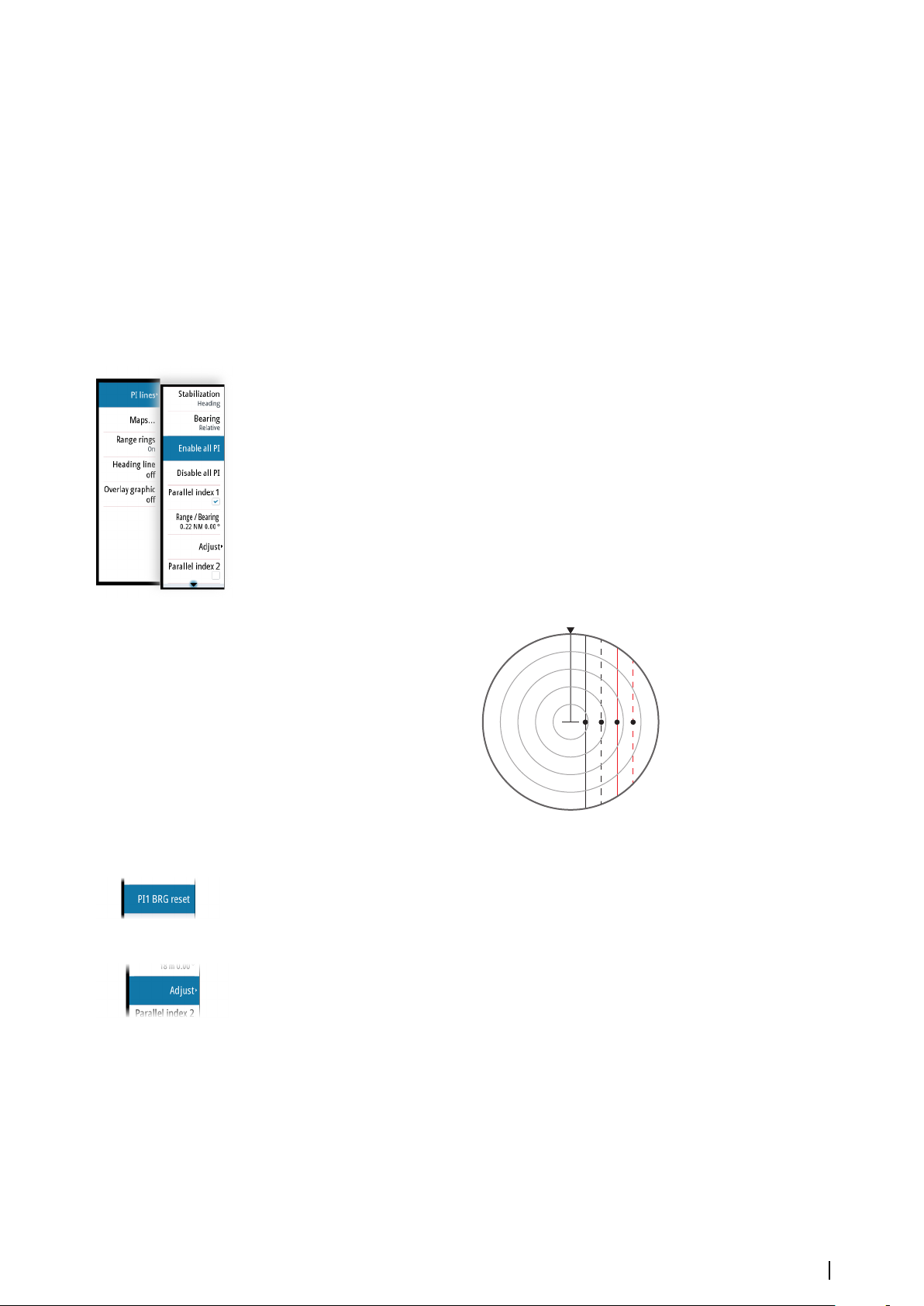
Parallel index lines
Parallel Index (PI) lines are used to visualize the distance to own vessel, other vessels or to
land objects. Two index lines can be used to indicate a corridor - typically used to visualize an
area you want to maneuver within.
The PI lines can be defined with north or heading stabilization, and with true or relative
bearing.
• North stabilization: the line direction is maintained with respect to north
• Heading stabilization: the line rotates with the vessel heading
• True bearings: the parallel index bearing is measured from the geographical north
• Relative bearings: the parallel index bearing is measured from the heading line
You can define four PI lines in the system, and they are identified with different color and
style:
• PI1: Grey solid line
• PI2: Grey dashed line
• PI3: Orange solid line
• PI4: Orange dashed line
You can turn each PI line on and off individually, and the position, bearing and truncating
can be set for each line.
Each PI line can be reset to be parallel to own ship's heading from the main menu.
Adjusting a PI line
Each PI line's range and bearing are shown in PI lines submenu.
You can adjust the line's settings from the selected line's Adjust menu option. The options
described in the next sections are available.
Adjusting range and bearing
1. Select the range or bearing menu options
-
The slider bar is displayed
2. Turn the rotary knob or use the up/down arrow keys to increase or decrease the slider bar
value
- The change is immediately committed and shown on the image
3. Press the exit key or the right arrow key to leave the edit mode
Note: Max range for a bearing line is 12 NM.
Ú
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
45
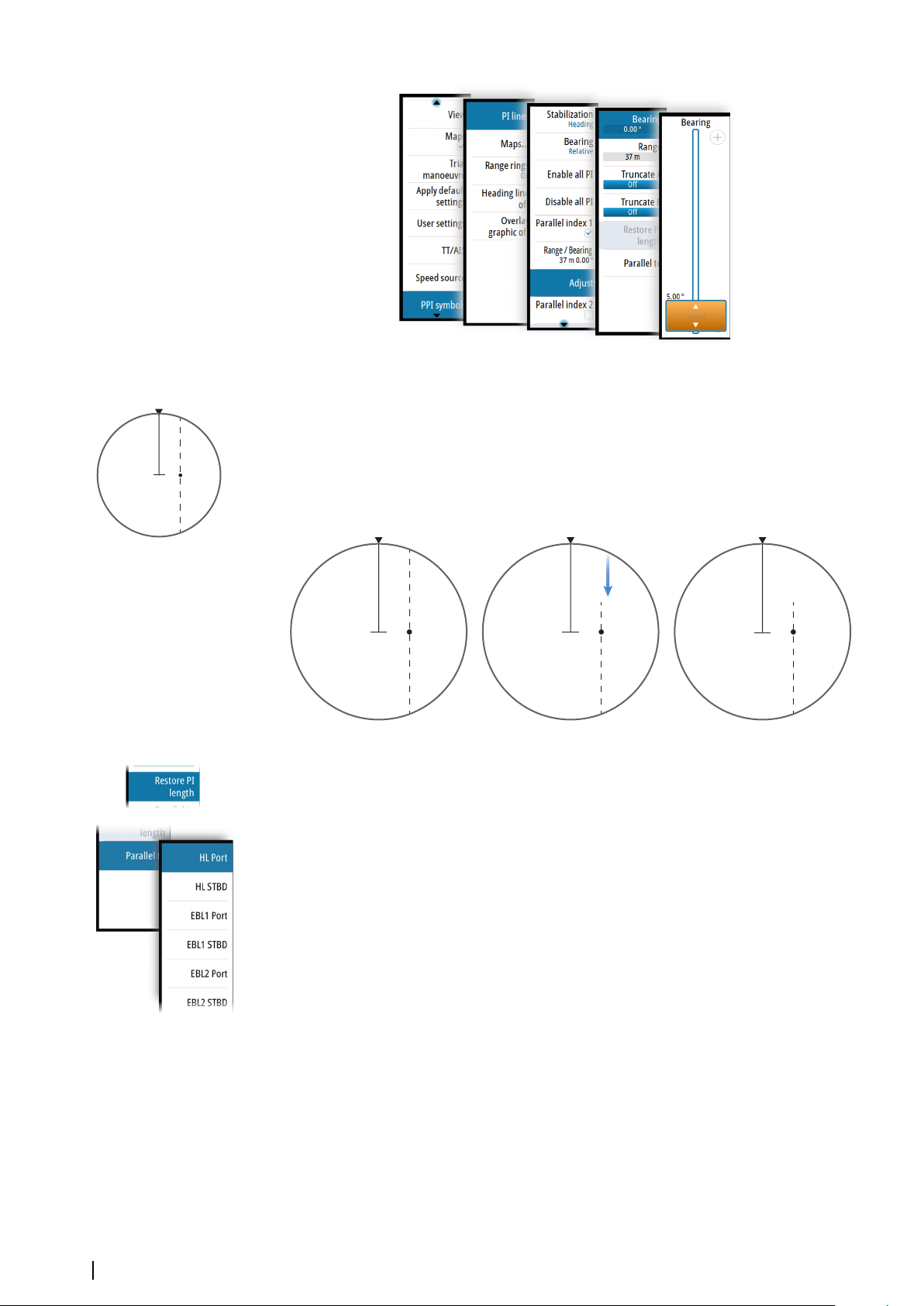
Truncating a PI line
2
2
2
A
B
2
You can use the truncate menu option to extend or reduce an existing PI line. The end points
of the line (A and B) are adjusted individually.
1. Select the truncate A or B option in the menu.
- The slider bar is displayed
2. Turn the rotary knob to extend or reduce the line
3. Press the exit key to confirm the selection
Function activated
End point adjusted
Line truncated
A line remains truncated until the restore length option is selected from the menu.
PI line alignment
A PI line can be parallel to port or starboard of the heading line, or to the port or starboard
side of an EBL.
• If the stabilization is set to heading, the PI line rotates as the vessel heading change
• Parallel to EBL is a way to quickly set the bearing of a PI line parallel to the EBL in use. The
line does not rotate if the EBL is changed later.
EBL/VRM markers
The EBL/VRM markers are a basic tool for collision avoidance. They are used to mark any fixed
or moving radar target, and to measure distances between two objects.
The reference point of an EBL/VRM marker is by default positioned at the center of the vessel.
It is possible to offset the reference point to any selected position on the radar image to
measure the distance between two objects on the PPI, or to fix the marker to a target.
Two different EBL/VRMs can be placed on the radar image. They are identified as dashed
rings/lines with different colors to discriminate them from each other and from the fixed
range rings:
• EBM/VRM1 is cyan
• EBL/VRM2 is blue
46
The EBL presentation can be defined with true or relative presentation:
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
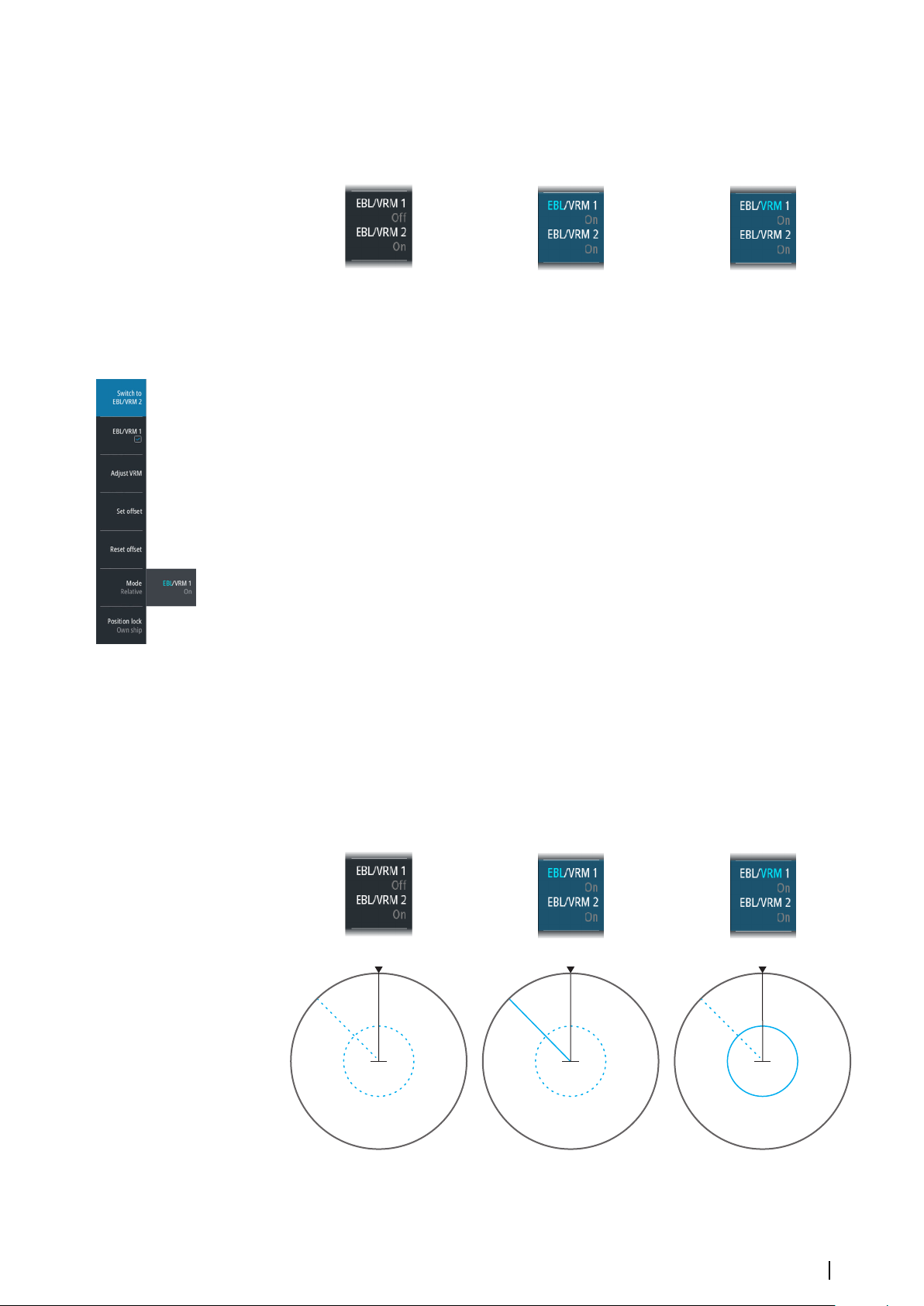
• True motion: the reference is geographic (e.g. a coastal line or current own vessel position)
• Relative motion: the EBL follows a moving reference (own vessel or a moving target)
The marker's line width indicates whether the marker is in edit mode (bold lines) or at a fixed
position (thin lines).
EBL/VRM1 OFF,
function not active
EBL/VRM1 ON,
EBL in edit mode
EBL/VRM1 ON,
VRM in edit mode
The EBL/VRM pop-up
The content of the pop-up depends on status of the active EBL/VRM. The example shows the
pop-up when the active EBL/VRM is offset.
The adjustable parameter is indicated with blue text in the softkey.
From the pop-up you can:
• switch between active EBL/VRM 1 and EBL/VRM 2 marker
• turn ON/OFF displaying of the active marker
• switch between adjusting EBL and VRM for the active marker. You can also switch
between adjustable parameter by pressing the rotary knob
• set EBL presentation (True or Relative)
• set offset for active marker
• reset an offset marker to vessel position
• select whether the EBL/VRM should be locked to own vessel or to a geographical position
Turning the EBL/VRM marker on and off
At system start-up, both EBL/VRM markers are turned off.
• Turn ON EBL/VRM 1 by pressing the EBL/VRM key once
• Switch between EBL/VRM 1 and EBL/VRM 2 from the function's pop-up
• Turn OFF an EBL/VRM from the function's pop-up
Adjusting the EBL/VRM marker
The text in the EBL/VRM short-cut button and the EBL/VRM marker's line width indicate
which item that is in edit mode.
EBL/VRM2 ON,
function not in edit mode
EBL/VRM1 and 2 ON,
EBL1 in edit mode
EBL/VRM1 and 2 ON,
VRM1 in edit mode
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
47

When an EBL/VRM marker is in edit mode, the following options are available for adjusting
the marker:
• Use the arrow keys or mouse to move the EBL/VRM intersection
• Turn the rotary knob or left mouse key/scroll wheel to adjust the adjustable parameter
(bold line and blue text in softkey)
• Press the rotary knob or mouse scroll wheel to switch between adjusting EBL and VRM
Offsetting EBL/VRM markers
1. Press the EBL/VRM key twice to display the pop-up
2. Select the set offset option
- The pop-up closes, and the cursor is positioned in the EBL/VRM center
3. Use the arrow keys to move the EBL/VRM center, then select one of the following options:
Press the enter key to fix the marker to the selected position, then use the arrow keys
to move the EBL/VRM intersection
- Turn the rotary knob to adjust the EBL
- Press the rotary knob to toggle between EBL and VRM, then turn the rotary knob or use
the arrow keys to adjust the item that is editable
You remove the EBL/VRM marker from the radar image by pressing the exit key.
Measuring range and bearing
Different options are available for measuring the position, speed, course, distance and
bearing of radar echoes.
• Cursor position
• Range rings and bearing scale
• EBL (Electronic Bearing Lines) and VRM (Variable Range Markers)
It is important to minimize the range to obtain the best precision for the measurement. In
most cases you can use a higher range if you position the PPI in one of the off-center modes.
Refer to "Offsetting the PPI center" on page 31.
Note: Every measurement made with cursor or EBL/VRM is always referred to the
Ú
Consistent Common Reference Point (CCRP).
Using the cursor
When you position the cursor over a target, the cursor information area will show range and
bearing from the vessel to the cursor position.
This measuring option gives a fast and precise measurement of distance to a target.
Range rings and bearing scale
Range rings and bearing scale are used to measure distance when a fast measurement is
required. This measuring option only gives an approximate distance and speed of a target.
The range scale (A) and the distance between two adjacent range rings (B) are shown in the
System Information area on the radar image.
The range scales, the related distance between the range rings and number of rings are:
Range (NM) Range rings interval (NM) Number of range rings
1/8 (200m) 1/40 (100m) 1
1/4 1/20 4
1/2 1/10 4
3/4 1/4 2
1.5 1/4 5
3 1/2 5
6 1 5
12 2 5
48
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
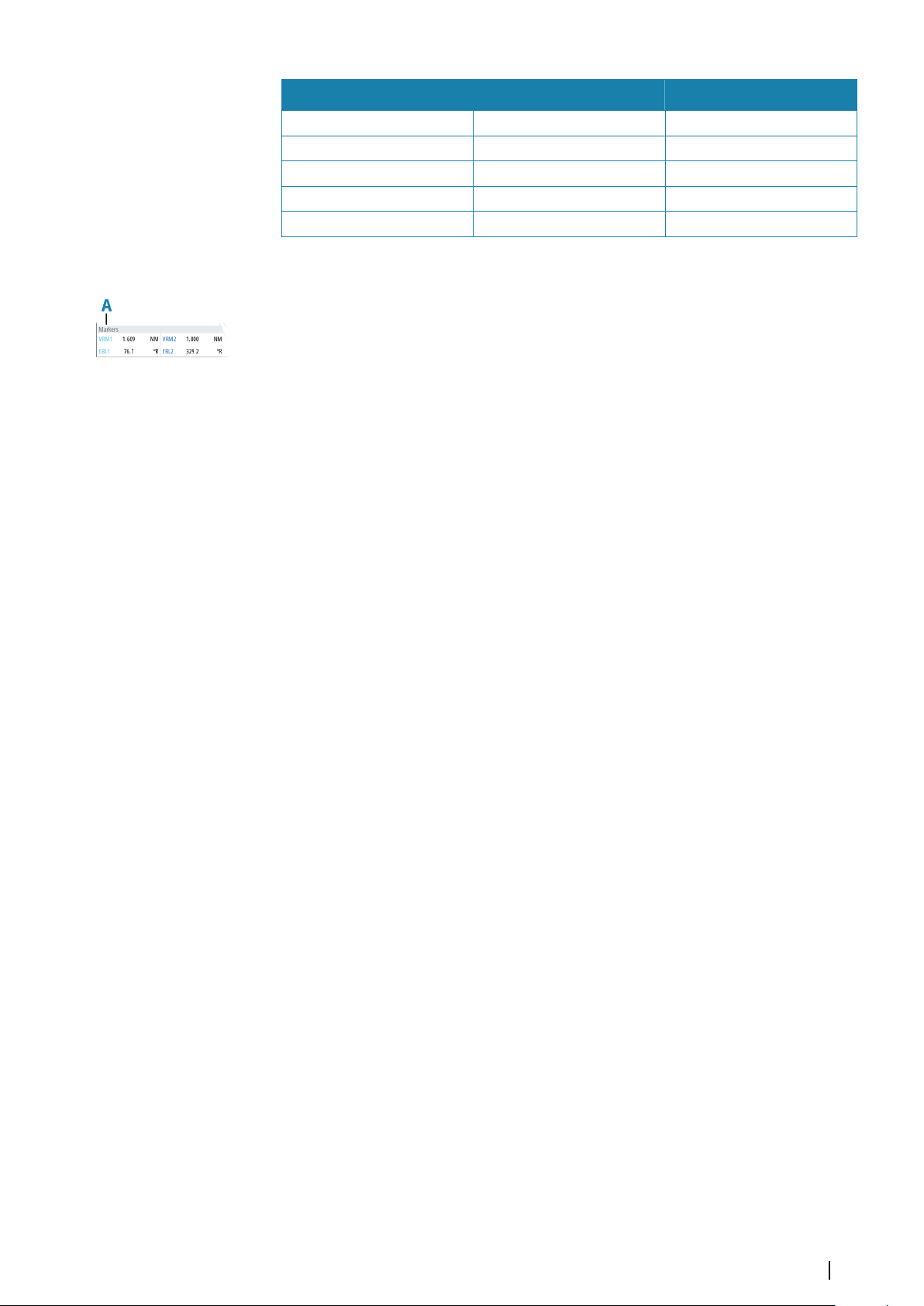
Range (NM) Range rings interval (NM) Number of range rings
24 4 5
36 6 5
48 8 5
64 16 3
72 12 5
Measuring by using EBL/VRM markers
The Electronic Bearing Line (EBL) and Variable Range Marker (VRM) allows quick
measurements of range and bearing from own vessel to a target, or between two targets on
the PPI. Bearing and range are shown in the Markers panel (A).
Measuring distance from own vessel
1. Press the EBL/VRM key to turn the selected EBL/VRM marker on
2. Repress the EBL/VRM key to display the pop-up if you need to:
-
Select the EBL presentation (True or Relative)
-
Reposition the marker to vessel position (if the center of the selected EBL/VRM is offset)
3. Use the arrow keys or turn the rotary knob to position the EBL/VRM on the second
measuring point
Measuring distance between two objects
1. Press the EBL/VRM key twice
- The selected EBL/VRM marker is turned on and the pop-up displayed
2. Select the EBL presentation (true or relative)
3. Select the set offset option
4. Use the arrow keys to reposition the EBL/VRM marker's center on the object from where
you want to measure the distance
5. Press the enter key to confirm the position
- The cursor moves from the marker's center to the EBL/VRM intersection
6. Use the arrow keys or turn the rotary knob to move the EBL/VRM to the second
measuring point
- Range and bearing from the EBL/VRM marker's center to cursor position is now
displayed in the Markers panel
You can reset the EBL/VRM marker's center to vessel position by selecting the reset offset
option in the EBL/VRM pop-up.
Navigation tools | R5000 Operator manual
49
10
Maps
Maps are graphical navigation tools, composed of lines and symbols that can be added to
the radar image. Maps are used to help the operator to increase the definition of the coast,
restricted or dangerous areas.
For maximum number of maps, symbols and segments, refer to "Technical specifications" on page
78.
Note: The maps option must be enabled to be able to work with maps.
Ú
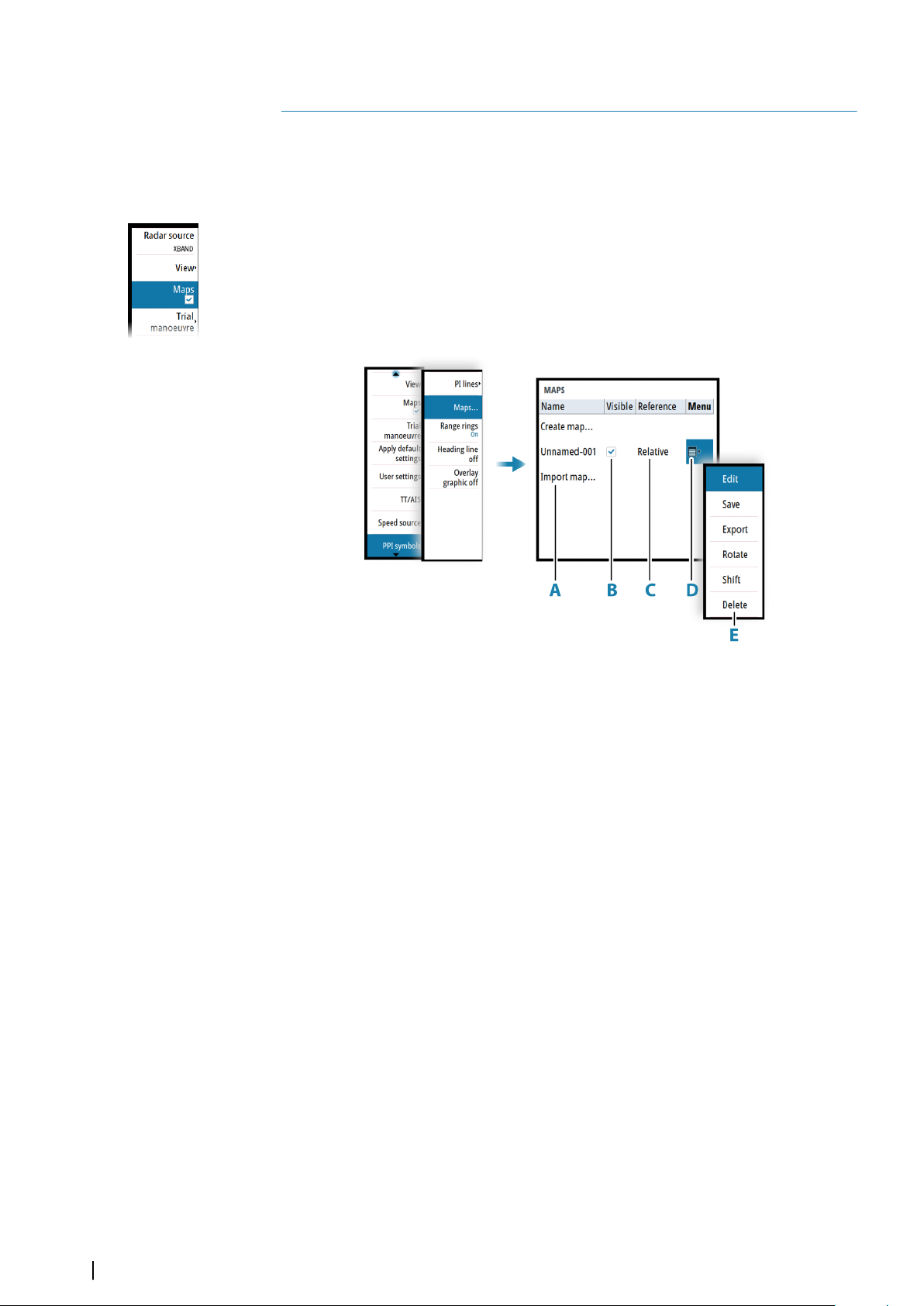
The maps dialog
The maps dialog lists all maps available in the unit's temporary memory and in the nonvolatile memory.
From the maps dialog you can:
• Import stored map files from the unit's internal file system or from an SD card (A)
• Select which maps that are displayed (B)
• Set a map's reference (C)
• Display the maps pop-up from where you can create new maps, edit, save, export and
delete a map (D / E)
Map references
The system includes the follow map types:
• Relative maps, which follows the position and equals the heading of own ship. All relative
map coordinates are stored as distances from own ship
• Geographic maps. The coordinates for this type of maps are stored as geographic
positions, and its elements are always drawn in the same absolute position.
When a map is saved the system automatically calculates both relative and the geographic
details for all map items. When you switch reference the change is immediately committed
without having to save the map.
Note: Relative maps cannot be created or imported if log or gyro is unavailable or failing.
Ú
Note: Geographic maps cannot be created or imported if EPFS (Electronic Position Fixing
Ú
System) or Gyro is unavailable or failing. A geographic map cannot be displayed if the
ship is too far from the area of the map.
50
Maps | R5000 Operator manual
Map colors and symbols
D
?
?
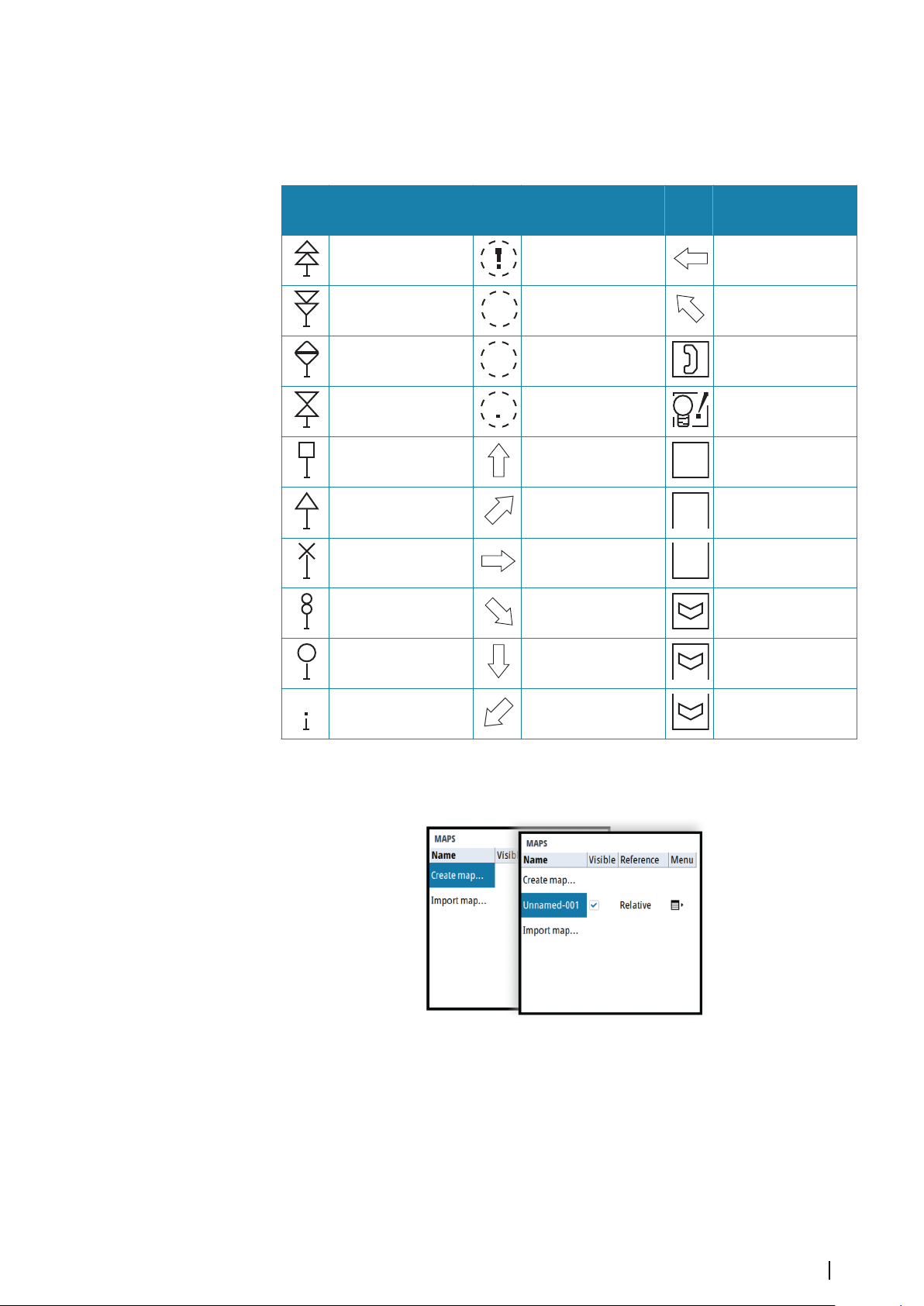
Lines and map symbols can be presented in various colors.
The following map symbols are available:
Sym
bol
Description
Buoy North Area Caution Arrow W
Buoy South
Buoy East Area Empty Sign Call
Buoy West
Buoy Lateral Port Arrow N Nato 1
Buoy Lateral Stbd Arrow NE Nato 2
Buoy Special Arrow E Nato 3
Buoy Danger Arrow SE Nato 4
Sym
bol
Description
Area Depth Arrow NW
Area Ufo Sign Reminder
Sym
bol
Description
Buoy Safe Arrow S Nato 5
Buoy Unknown Arrow SW Nato 6
Creating a new map
When the create map option is selected, a new map is immediately saved to the unit's
temporary memory.
The map name is defined by the system, and the visibility is set to ON.
Note: The new map has at this stage no content.
Ú
• Select the map name to display the keyboard if you want to give the map a unique name
• Set the map reference
• Select the menu option to enter map details. See "Modifying a map" on page 52.
Maps | R5000 Operator manual
51
Saving a map
New maps and edited maps are by default saved to the unit's temporary memory. The maps
must be saved to be available in the unit after a restart.
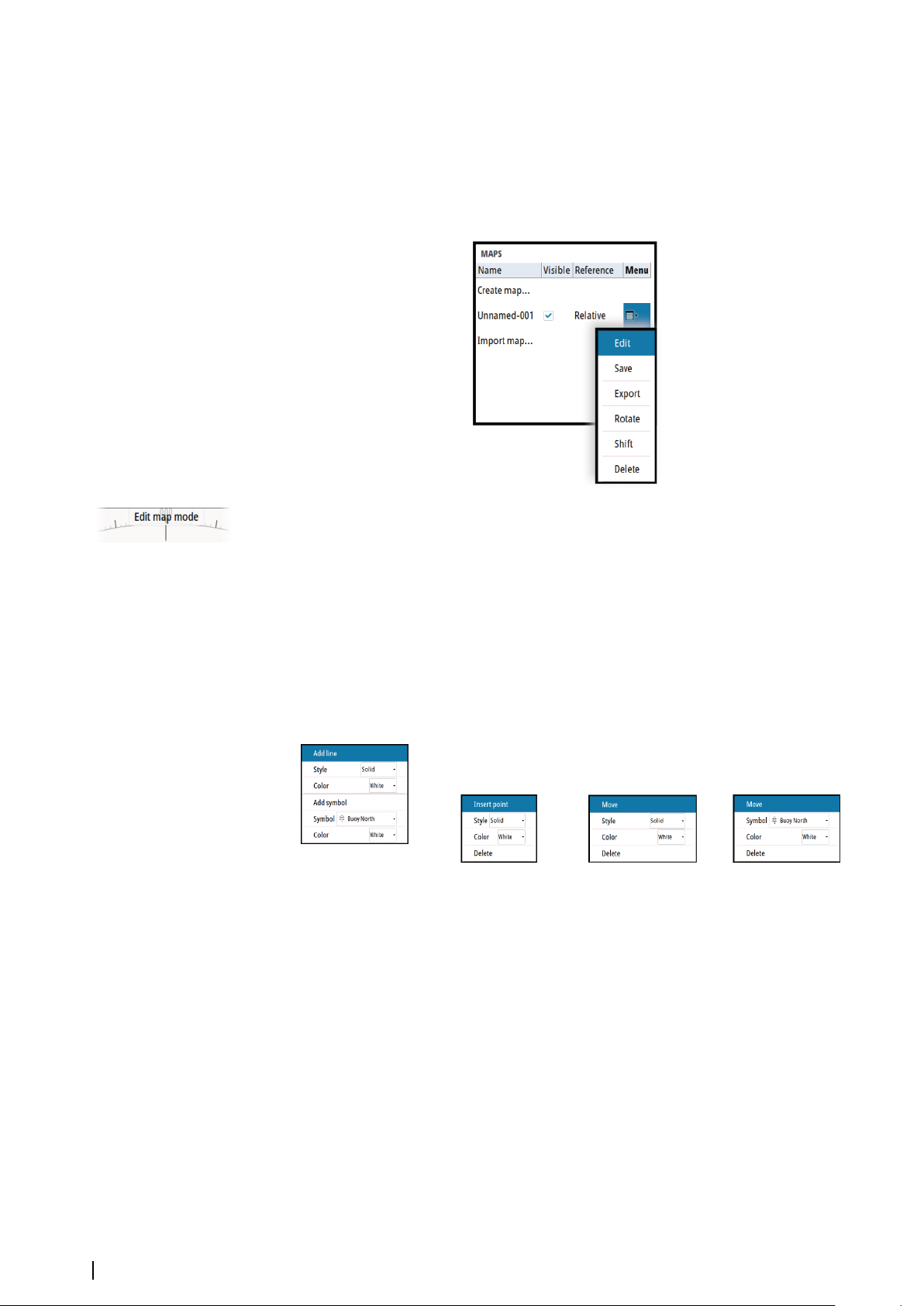
Modifying a map
Any details for a map are added or edited from the maps pop-up menu.
When an edit option is selected in the pop-up menu, the system turns into edit map mode.
This is indicated on the PPI.
To exit edit map mode:
• Press the exit key
Note: When you exit edit mode the changes are automatically saved to the temporary
Ú
memory only. The maps must be saved to be available in the unit after a restart.
Edit map details
Map details are added or edited from the edit map menu. The content of the edit map menu
depends on where the cursor is positioned:
No map details at cursor
position Map line at cursor position Vertex at cursor position Symbol at cursor position
1. Position the cursor where you want to add or edit a map detail
2. Press the enter key or the right mouse key to display the map edit menu, then select the
edit option
3. Continue positioning the cursor and selecting the edit option until all changes are done
4. Press the exit key to leave the edit mode
52
Maps | R5000 Operator manual
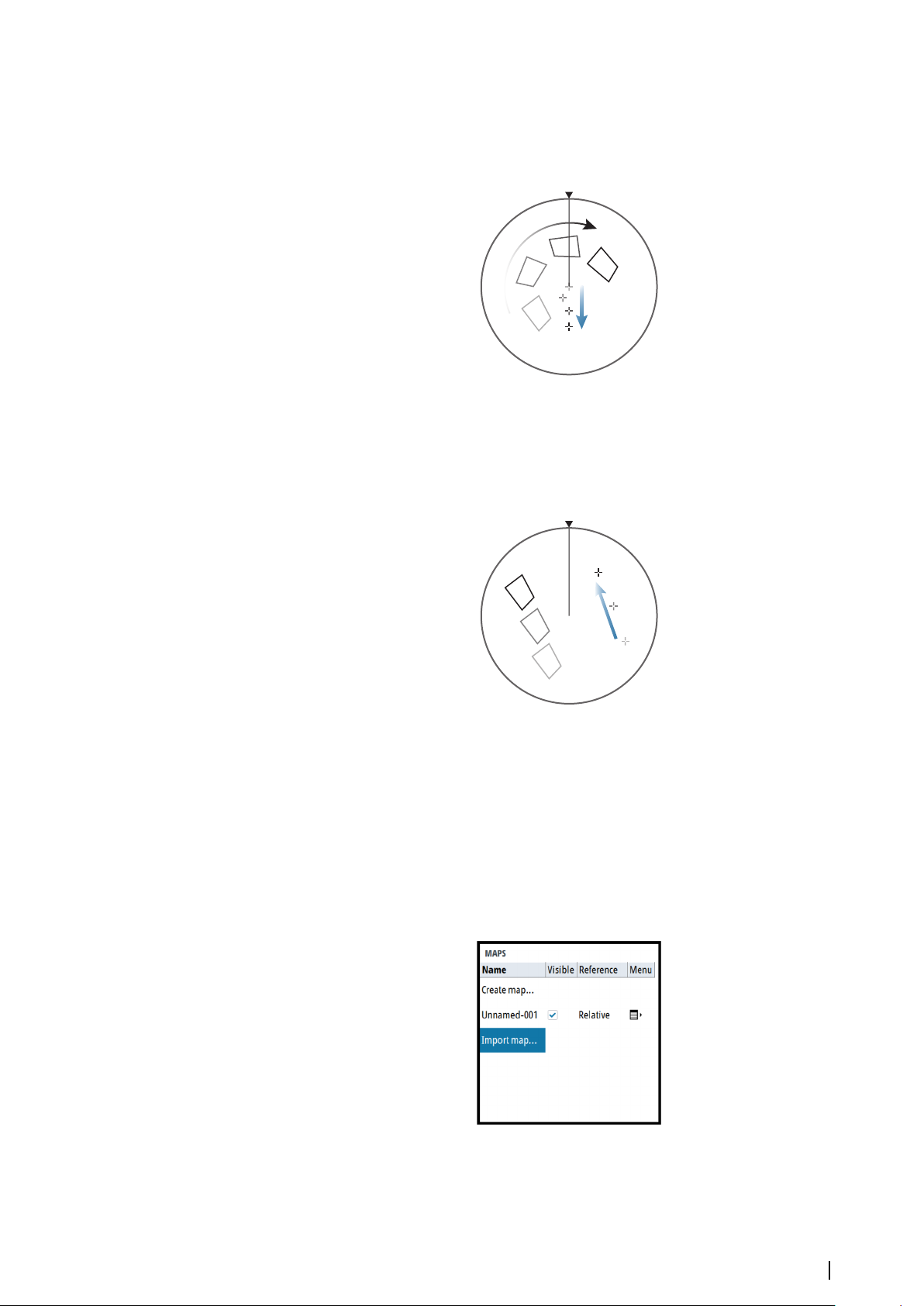
Rotating a map
When the rotate option is selected, the cursor is positioned in the center of the PPI.
• Use the arrow keys to move the cursor and to rotate the map around the vessel's position
• Press the exit key to leave edit mode
Shifting a map position
When the shift option is selected, the cursor is positioned in the center of the PPI, and the
map is anchored to the cursor.
• Use the arrow keys to move the cursor and to shift the map position
• Press the exit key to leave edit mode
Exporting maps
Maps listed in the maps dialog can be exported individually and used on other compatible
radar units.
Saved maps can also be copied from internal memory to a memory card from the files
management system.
Importing maps
Compatible maps created on other units can be imported to the system. Imported maps are
added to the units' non-volatile memory, and the maps are added to the list of loaded maps.
Maps | R5000 Operator manual
53
 Loading...
Loading...