
查询LMH6622供应商
LMH6622
Dual Wideband, Low Noise, 160MHz, Operational
Amplifiers
LMH6622 Dual Wideband, Low Noise, 160MHz, Operational Amplifiers
February 2002
General Description
The LMH6622 is a dual high speed voltage feedback operational amplifier specifically optimized for lownoise.A voltage
noise specification of 1.6nV/
cation 1.5pA/
distortion specificationthat exceeds 90dBc combineto make
the LMH6622 an ideal choice for the receive channel amplifier in ADSL, VDSL, or other xDSL designs. The LMH6622
operates from
+5V to +12V in single supply configuration. The LMH6622 is
stable for A
on National Semiconductor’s advanced VIP10 process enables excellent (160MHz) bandwidth at a current consumption of only 4.3mA/amplifier. Packages for this dual amplifier
are the 8-lead SOIC and the 8-lead MSOP.
, abandwidth of 160MHz,and a harmonic
±
2.5V to±6V in dual supply mode and from
≥ 2orAV≤−1. The fabrication of the LMH6622
V
, a current noise specifi-
Features
VS=±6V, TA= 25˚C, Typical values unless specified
n Bandwidth (A
n Supply Voltage Range
n Slew rate 85V/µs
n Supply current 4.3mA/amp
n Input common mode voltage −4.75V to +5.7V
n Output Voltage Swing (R
n Input voltage noise 1.6nV/
n Input current noise 1.5pA/
n Linear output current 90mA
n Excellent harmonic distortion 90dBc
= +2) 160MHz
V
±
2.5V to±6V +5V to +12
= 100Ω)
L
±
4.6V
Applications
n xDSL receiver
n Low noise instrumentation front end
n Ultrasound preamp
n Active filters
n Cellphone basestation
xDSL Analog Front End
© 2002 National Semiconductor Corporation DS200292 www.national.com
20029226

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
LMH6622
Distributors for availability and specifications.
ESD Tolerance
Human Body Model 2kV (Note 2)
Machine Model 200V (Note 2)
V
Differential
IN
Supply Voltage (V
Voltage at Input Pins V
Soldering Information
Infrared or Convection (20 sec) 235˚C
±
6V Electrical Characteristics
+–V−
) 13.2V
+
+0.5V, V−−0.5V
±
1.2V
Wave Soldering (10 sec) 260˚C
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Junction Temperature (Note 4) +150˚C
Operating Ratings (Note 1)
Supply Voltage (V
+–V−
)
Junction Temperature Range
(Note 3), (Note 4)
Package Thermal Resistance (Note 4) (θ
8-pin SOIC 166˚C/W
8-pin MSOP 211˚C/W
±
2.25V to±6V
−40˚C to +85˚C
)
JA
Unless otherwise specified, TJ= 25˚C, V+= 6V, V−= −6V, VCM= 0V, AV= +2, RF= 500Ω,RL= 100Ω. Boldface limits apply
at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
Dynamic Performance
f
CL
BW
0.1dB
SR Slew Rate (Note 8) V
TS Settling Time V
Tr Rise Time V
Tf Fall Time V
−3dB BW VO= 200mV
0.1dB Gain Flatness VO= 200mV
=2V
O
PP
=2VPPto±0.1% 40
O
=2VPPto±1.0% 35
V
O
= 0.2V Step, 10% to 90% 2.3 ns
O
= 0.2V Step, 10% to 90% 2.3 ns
O
PP
PP
160 MHz
30 MHz
85 V/µs
Distortion and Noise Response
e
n
i
n
Input Referred Voltage Noise f = 100kHz 1.6 nV/
Input Referred Current Noise f = 100kHz 1.5 pA/
DG Differential Gain RL= 150Ω,RF= 470Ω, NTSC 0.03 %
DP Differential Phase R
HD2 2
HD3 3
nd
Harmonic Distortion fc= 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 100Ω −90
rd
Harmonic Distortion fc= 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 100Ω −94
MTPR Upstream V
= 150Ω,RF= 470Ω, NTSC 0.03 deg
L
= 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 500Ω −100
f
c
= 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 500Ω −100
f
c
= 0.6 V
O
, 26kHz to 132kHz
RMS
−78
(see test circuit 5)
Downstream V
= 0.6 V
O
, 144kHz to 1.1MHz
RMS
−70
(see test circuit 5)
Input Characteristics
V
OS
TC V
I
OS
I
B
Input Offset Voltage VCM= 0V −1.2
+0.2 +1.2
−2
Input Offset Average Drift VCM= 0V (Note 7) −2.5 µV/˚C
OS
Input Offset Current VCM=0V −1
−0.04 1
−1.5
Input Bias Current VCM= 0V 4.7 10
+2
1.5
15
R
IN
Input Resistance Common Mode 17 MΩ
Differential Mode 12 kΩ
C
IN
Input Capacitance Common Mode 0.9 pF
Differential Mode 1.0 pF
Units
ns
dBc
dBc
dBc
mV
µA
µA
www.national.com 2
±
6V Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, TJ= 25˚C, V+= 6V, V−= −6V, VCM= 0V, AV= +2, RF= 500Ω,RL= 100Ω. Boldface limits apply
at the temperature extremes.
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
CMVR Input Common Mode Voltage
CMRR ≥ 60dB −4.75 −4.5
Range
CMRR Common-Mode Rejection Ratio Input Referred,
V
= −4.2 to +5.2V
CM
5.5 +5.7
80
75
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
100 dB
Units
Transfer Characteristics
A
VOL
Large Signal Voltage Gain VO=4V
PP
74
83 dB
70
X
t
Crosstalk f = 1MHz −75 dB
Output Characteristics
V
O
Output Swing No Load, Positive Swing 4.8
5.2
4.6
No Load, Negative Swing −5.0 −4.6
−4.4
R
= 100Ω, Positive Swing 4.0
L
4.6
3.8
R
= 100Ω, Negative Swing −4.6 −4
L
−3.8
R
I
I
O
SC
OUT
Output Impedance f = 1MHz 0.08 Ω
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing to Ground
= 200mV (Note 3), (Note 9)
∆V
IN
Sinking to Ground
∆V
= −200mV (Note 3), (Note 9)
IN
Output Current Sourcing, VO= +4.3V
Sinking, V
= −4.3V
O
100 135
100 130
90 mA
Power Supply
+PSRR Positive Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
−PSRR Negative Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
I
S
Supply Current (per amplifier) No Load 4.3 6
Input Referred,
V
= +5V to +6V
S
Input Referred,
V
= −5V to −6V
S
80
74
75
69
95
90
6.5
LMH6622
V
V
mA
dB
mA
±
2.5V Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.5V, V−= −2.5V, VCM= 0V, AV= +2, RF= 500Ω,
R
= 100Ω. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
L
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
Dynamic Performance
f
CL
BW
0.1dB
SR Slew Rate (Note 8) V
T
S
T
r
T
f
−3dB BW VO= 200mV
0.1dB Gain Flatness VO= 200mV
=2V
O
PP
PP
PP
150 MHz
20 MHz
80 V/µs
Settling Time VO=2VPPto±0.1% 45
=2VPPto±1.0% 40
V
O
Rise Time VO= 0.2V Step, 10% to 90% 2.5 ns
Fall Time VO= 0.2V Step, 10% to 90% 2.5 ns
Distortion and Noise Response
e
n
i
n
Input Referred Voltage Noise f = 100kHz 1.7 nV/
Input Referred Current Noise f = 100kHz 1.5 pA/
Units
ns
www.national.com3
±
2.5V Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.5V, V−= −2.5V, VCM= 0V, AV= +2, RF= 500Ω,
LMH6622
R
= 100Ω. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
L
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
HD2 2
HD3 3
MTPR Upstream V
nd
Harmonic Distortion fc = 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 100Ω −88
rd
Harmonic Distortion fc = 1MHz, VO=2VPP,RL= 100Ω −92
fc = 1MHz, V
= 0.4V
O
fc = 1MHz, V
=2VPP,RL= 500Ω −98
O
=2VPP,RL= 500Ω −100
O
,26kHz to 132kHz
RMS
Typ
(Note 5)
−76
(see test circuit 5)
Downstream V
= 0.4V
O
,144kHz to 1.1MHz
RMS
−68
(see test circuit 5)
Input Characteristics
V
OS
Input Offset Voltage VCM= 0V −1.5
+0.3 +1.5
−2.3
TC V
I
OS
Input Offset Average Drift VCM= 0V (Note 7) −2.5 µV/˚C
OS
Input Offset Current VCM= 0V −1.5
+0.01 1.5
−2.5
I
B
R
IN
Input Bias Current VCM= 0V 4.6 10
Input Resistance Common Mode 17 MΩ
Differential Mode 12 kΩ
C
IN
Input Capacitance Common Mode 0.9 pF
Differential Mode 1.0 pF
CMVR Input Common Mode Voltage
Range
CMRR Common Mode Rejection Ratio Input Referred,
CMRR ≥ 60dB −1.25 −1
2 +2.2
V
= −0.7 to +1.7V
CM
80
75
100 dB
Transfer Characteristics
A
VOL
X
t
Large Signal Voltage Gain VO=1V
PP
74 82 dB
Crosstalk f = 1MHz −75 dB
Output Characteristics
V
O
Output Swing No Load, Positive Swing 1.4
1.7
1.2
No Load, Negative Swing −1.5 −1.2
R
= 100Ω, Positive Swing 1.2
L
1.5
1
R
= 100Ω, Negative Swing −1.4 −1.1
L
R
I
I
O
SC
OUT
Output Impedance f = 1MHz 0.1 Ω
Output Short Circuit Current Sourcing to Ground
= 200mV (Note 3), (Note 9)
∆V
IN
Sinking to Ground
∆V
= −200mV (Note 3), (Note 9)
IN
Output Current Sourcing, VO= +0.8V
Sinking, V
= −0.8V
O
100 137
100 134
90 mA
Power Supply
+PSRR Positive Power Supply Rejection
Ratio
−PSRR Negative Power Supply
Rejection Ratio
Input Referred,
V
= +2.5V to +3V
S
Input Referred,
V
= −2.5V to −3V
S
78
72
75
70
93
88 dB
Max
(Note 6)
+2.3
2.5
15
−1
−0.9
Units
dBc
dBc
dBc
mV
µA
µA
V
V
mA
dB
www.national.com 4

±
2.5V Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for TJ= 25˚C, V+= 2.5V, V−= −2.5V, VCM= 0V, AV= +2, RF= 500Ω,
R
= 100Ω. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
L
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min
(Note 6)
I
S
Supply Current (per amplifier) No Load 4.1 5.8
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 6)
mA
6.4
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 1.5kΩ in series with 100pF. Machine model, 0Ω in series with 200pF.
Note 3: Applies to both single-supply and split-supply operation. Continuous short circuit operation at elevated ambient temperature can result in exceeding the
maximum allowed junction temperature of 150˚C.
Note 4: The maximum power dissipation is a function of T
(T
J(MAX)−TA
Note 5: Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 6: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
Note 7: Offset voltage average drift is determined by dividing the change in V
Note 8: Slew rate is the slowest of the rising and falling slew rates.
Note 9: Short circuit test is a momentary test.Output short circuitduration is infinitefor V
circuit duration is 1.5ms.
)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly onto a PC board.
, θJAand TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is PD=
J(MAX)
at temperature extremes into the total temperature change.
OS
>
≤±2.5V,atroom temperature andbelow.For V
S
±
2.5V,allowableshort
S
LMH6622
Units
www.national.com5
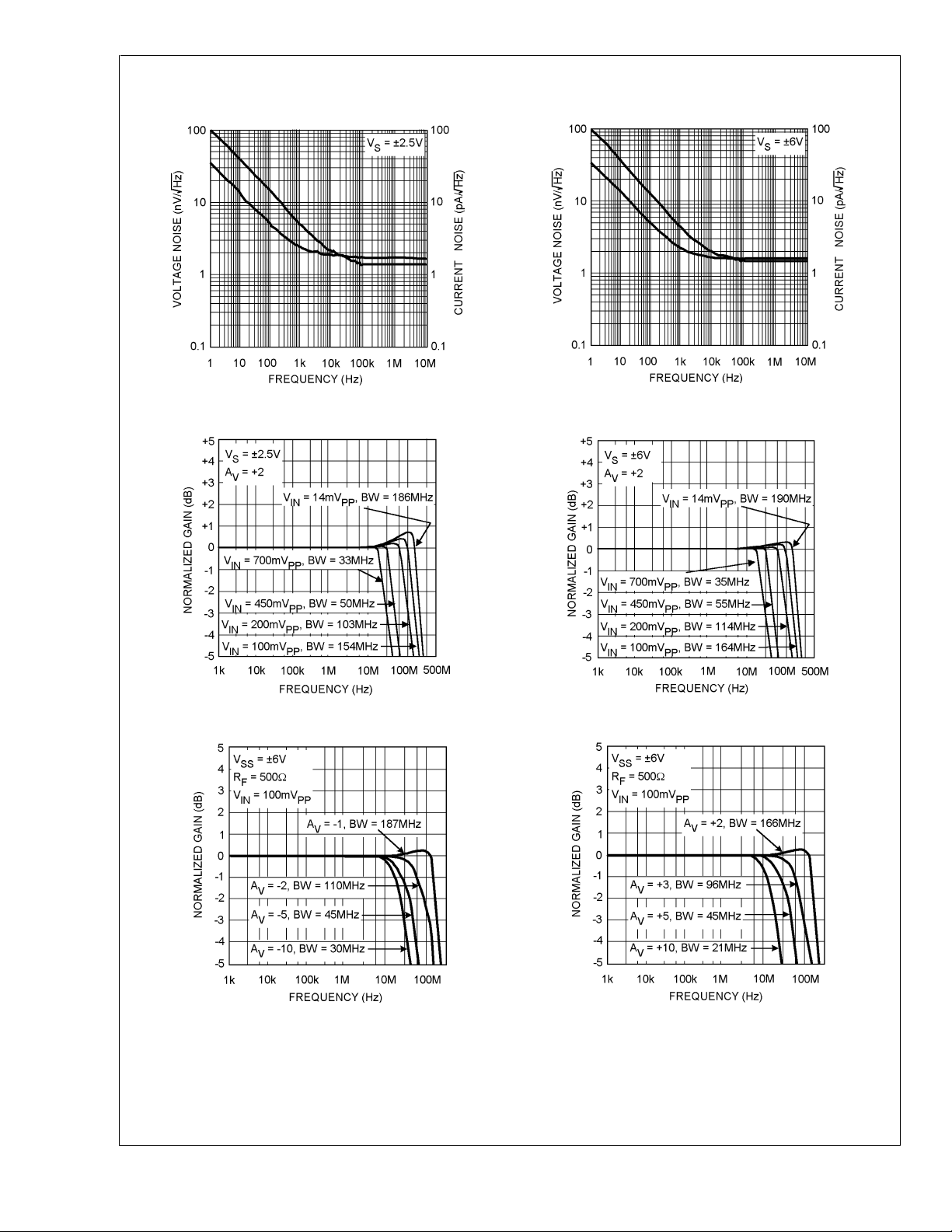
Typical Performance Characteristics
LMH6622
Current and Voltage Noise vs. Frequency Current and Voltage Noise vs. Frequency
20029224
20029225
Frequency Response vs. Input Signal Level Frequency Response vs. Input Signal Level
20029202 20029203
Inverting Amplifier Frequency Response Non-Inverting Amplifier Frequency Response
20029246 20029247
www.national.com 6

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Open Loop Gain and Phase Response Crosstalk vs. Frequency
LMH6622
20029205
20029201
PSRR vs. Frequency CMRR vs. Frequency
20029204
20029206
Positive Output Swing vs. Source Current Negative Output Swing vs. Sink Current
20029248 20029249
www.national.com7

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
LMH6622
Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
V
=±2.5V, RL= 100Ω,AV= +2, RF= 500Ω
S
20029207 20029209
Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
V
=±2.5V, RL= 100Ω,AV= +2, RF= 500Ω
S
Non-Inverting Small Signal Pulse Response
VS=±6V, RL= 100Ω,AV= +2, RF= 500Ω
Non-Inverting Large Signal Pulse Response
VS=±6V, RL= 100Ω,AV= +2, RF= 500Ω
20029208 20029210
Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Signal Level Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Signal Level
20029212 20029213
www.national.com 8

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency
20029214 20029215
Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Signal Level Harmonic Distortion vs. input Signal Level
LMH6622
20029216 20029217
Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Frequency Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Frequency
20029218 20029219
www.national.com9

Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
LMH6622
Full Rate ADSL (DMT) Upstream MTPR
Full Rate ADSL (DMT) Upstream MTPR@VS=±6V Full Rate ADSL (DMT) Downstream MTPR@VS=±6V
@
VS=±2.5V Full Rate ADSL (DMT) Downstream MTPR@VS=±2.5V
20029256 20029258
20029257 20029259
www.national.com 10

Connection Diagram
LMH6622
8-Pin SOIC/MSOP
Top View
20029211
Ordering Information
Package Part Number Package Marking Transport Media NSC Drawing
8-Pin SOIC LMH6622MA LMH6622MA 95 Units per Rail M08A
LMH6622MAX 2.5k Units Tape and Reel
8-Pin MSOP LMH6622MM A80A 1k Units Tape and Reel MUA08A
LMH6622MMX 3.5k Units Tape and Reel
Test Circuits
3) Voltage Noise
R
=1Ωfor f ≤ 100kHz, RG=20Ωfor f>100kHz
1) Non-Inverting Amplifier
20029250
G
20029253
2) CMRR
20029251
4) Current Noise
R
=1Ωfor f ≤ 100kHz, RG=20Ωfor f>100kHz
G
20029252
www.national.com11

Test Circuits (Continued)
LMH6622
5) Multitone Power Ratio, RF= 500Ω,RG= 174Ω,RL=
20029255
437Ω
DSL Receive Channel Applications
FIGURE 1. ADSL Signal Description
The LMH6622 is a dual, wideband operational amplifier designed for use as a DSL line receiver. In the receive band of
a Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) ADSL modem it is
possible that as many as 255 Discrete Multi-Tone (DMT)
QAM signals will be present, each with its own carrier frequency, modulation, and signal level. The ADSL standard
requires a line referred noise power density of -140dBm/Hz
within theCPE receive bandof 100KHz to 1.1MHz. The CPE
driver output signal will leak into the receive path because of
full duplex operation and the imperfections of the hybrid
coupler circuit. The DSL analog front end must incorporate a
20029223
receiver pre-amp which is both low noise and highly linear
for ADSL-standard operation. The LMH6622 is designed for
the twin performance parameters of low noise and high
linearity.
Figure 2
±
2.5V to±6V are
, theLMH6622 is
Applications ranging from +5V to +12V or
fully supportedby the LMH6622.In
used as an inverting summing amplifier to provide both
received pre-amp channel gain and driver output signal cancellation, i.e., the function of a hybrid coupler.
www.national.com 12

DSL Receive Channel Applications (Continued)
LMH6622
FIGURE 2. ADSL Receive Applications Circuit
20029227
www.national.com13

DSL Receive Channel Applications
(Continued)
LMH6622
The two R
ing through the 1:N transformer.
Where RLis the impedance of the twisted pair line.
The resistors R
the pre-amp. The receive gain is selected to meet the ADC
full-scale requirement of a DSL chipset.
Resistor R
cancellation of the output driver signal at the output of the
receiver.
Since the LMH6622 is configured as an inverting summing
amplifier, V
The expression for V1and V2can be found by using superposition principle.
When V
resistors are used to provide impedance match-
S
N is the turns ratio of the transformer.
and RFare used to set the receive gain of
2
and R2along with RFare used to achieve
1
is found to be,
OUT
=0,
S
Receive Channel Noise Calculation
The circuit of
Figure 2
also has the characteristic that it
cancels noise power from the drive channel.
The noise gain of the receive pre-amp is found to be:
Noise power at each of the output of LMH6622:
where
V
n
i
n
i
non-inv
i
inv
k Boltzmann’s constant, K = 1.38 x 10
Input referred voltage noise
Input referred current noise
Input referred non-inverting current noise
Input referred inverting current noise
−23
T Resistor temperature in k
R
+
Source resistance at the non-inverting input
to balance offset voltage, typically very small
for this inverting summing applications
When VA=0,
Therefore,
And then,
Setting R1= 2*R2to cancel unwanted driver signal in the
receive path, then we have
We can also find that,
And then
For a voltage feedback amplifier,
Therefore, total output noise from the differentialpre-amp is:
The factor ’2 ’ appears here because of differential output.
Differential Analog-to-Digital Driver
20029239
In conclusion, the peak-to-peak voltage to the ADC would
be,
www.national.com 14
FIGURE 3. Circuit for Differential A/D Driver

DSL Receive Channel Applications
(Continued)
The LMH6622 is a low noise, low distortion high speed
operational amplifier. The LMH6622 comes in either SOIC-8
or MSOP-8 packages. Because two channels are available
in each package the LMH6622 can be used as a high
dynamic rangedifferential amplifier for the purpose of driving
a high speed analog-to-digital converter.Driving a 1kΩ load,
the differentialamplifier of
frequency response up to 6MHz, and harmonic distortion
that is lower than 80dBc. This circuit makes use of a transformer to convert a single-ended signal to a differential signal. The input resistor R
tion,
Figure 3
IN
provides 20dBgain, a flat
is chosen by the following equa-
LMH6622
20029222
The gain of this differential amplifier can be adjusted by R
and RF,
20029221
FIGURE 4. Frequency Response
C
FIGURE 5. Total Output Referred Noise Density
www.national.com15

DSL Receive Channel Applications
(Continued)
LMH6622
Circuit Layout Considerations
National Semiconductorsuggests the copperpatterns on the
evaluation boards listed below as a guide for high frequency
layout. These boards are also useful as an aid in device
testing and characterization. As is the case with all highspeed amplifiers, accepted-practice R
the PCB layout is mandatory. Generally, a good high frequency layout exhibits a separation of power supply and
ground traces from theinverting input and output pins. Parasitic capacitances between these nodes and ground will
cause frequency response peaking and possible circuit oscillations (see Application Note OA-15 for more information).
High quality chip capacitors with values in the range of
1000pF to 0.1µF should be used for power supply bypassing. One terminal of each chip capacitor is connected to the
ground plane and the other terminal is connected to a point
that is as close as possible to each supply pin as allowed by
the manufacturer’s design rules. In addition, a tantalum capacitor with a value between 4.7µF and 10µF should be
connected in parallel with the chip capacitor. Signal lines
connecting the feedback and gain resistors should be as
short as possible to minimize inductance and microstrip line
effect. Input and output termination resistors should be
placed as close as possible to the input/output pins. Traces
greater than 1 inch in length should be impedance matched
to the corresponding load termination.
Symmetry between the positive and negative paths in the
layout of differential circuitry should be maintained so as to
minimize the imbalance of amplitude and phase of the differential signal.
design technique on
F
Device Package Evaluation Board P/N
LMH6622MA SOIC-8 CLC730036
LMH6622MM MSOP-8 CLC730123
These free evaluation boards are shipped when a device
sample request is placed with National Semiconductor.
Component value selection is another important parameter
in working with high speed/high performance amplifiers.
Choosing external resistorsthat are large in value compared
to thevalue of other criticalcomponents will affectthe closed
loop behavior of the stage because of the interaction of
these resistors with parasitic capacitances. These parasitic
capacitors could either be inherent to the device or be a
by-product of the board layout and component placement.
Moreover,a large resistor will alsoadd more thermalnoise to
the signal path. Either way, keeping the resistor values low
will diminish this interaction. On the other hand, choosing
very low value resistors could load down nodes and will
contribute to higher overall power dissipation and worse
distortion.
Driving Capacitive Load
Capacitive Loads decrease the phase marginof all op amps.
The output impedance of a feedback amplifier becomes
inductive at high frequencies, creating a resonant circuit
when the load is capacitive. This can lead to overshoot,
ringing and oscillation. To eliminate oscillation or reduce
ringing, an isolation resistor can be placed between the load
and the output. In general, the bigger the isolation resistor,
the more damped the pulse response becomes. For initial
evaluation, a 50Ω isolation resistor is recommended.
www.national.com 16

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters)
unless otherwise noted
NS Package Number M08A
LMH6622
8-Pin SOIC
8-Pin MSOP
NS Package Number MUA08A
www.national.com17

Notes
LMH6622 Dual Wideband, Low Noise, 160MHz, Operational Amplifiers
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
 Loading...
Loading...