LMD18245
3A, 55V DMOS Full-Bridge Motor Driver
LMD18245 3A, 55V DMOS Full-Bridge Motor Driver
March 2006
General Description
The LMD18245 full-bridge power amplifier incorporates all
the circuit blocks required to drive and control current in a
brushed type DC motor or one phase of a bipolar stepper
motor. The multi-technology process used to build the device
combines bipolar and CMOS control and protection circuitry
with DMOS power switches on the same monolithic structure. The LMD18245 controls the motor current via a fixed
off-time chopper technique.
An all DMOS H-bridge power stage delivers continuous output currents up to 3A (6A peak) at supply voltages up to 55V.
The DMOS power switches feature low R
efficiency, and a diode intrinsic to the DMOS body structure
eliminates the discrete diodes typically required to clamp
bipolar power stages.
An innovative current sensing method eliminates the power
loss associated with a sense resistor in series with the motor.
A four-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) provides a digital
path for controlling the motor current, and, by extension,
simplifies implementation of full, half and microstep stepper
motor drives. For higher resolution applications, an external
DAC can be used.
DS(ON)
for high
Features
n DMOS power stage rated at 55V and 3A continuous
n Low R
n Internal clamp diodes
n Low-loss current sensing method
n Digital or analog control of motor current
n TTL and CMOS compatible inputs
n Thermal shutdown (outputs off) at T
n Overcurrent protection
n No shoot-through currents
n 15-lead TO-220 molded power package
Applications
n Full, half and microstep stepper motor drives
n Stepper motor and brushed DC motor servo drives
n Automated factory, medical and office equipment
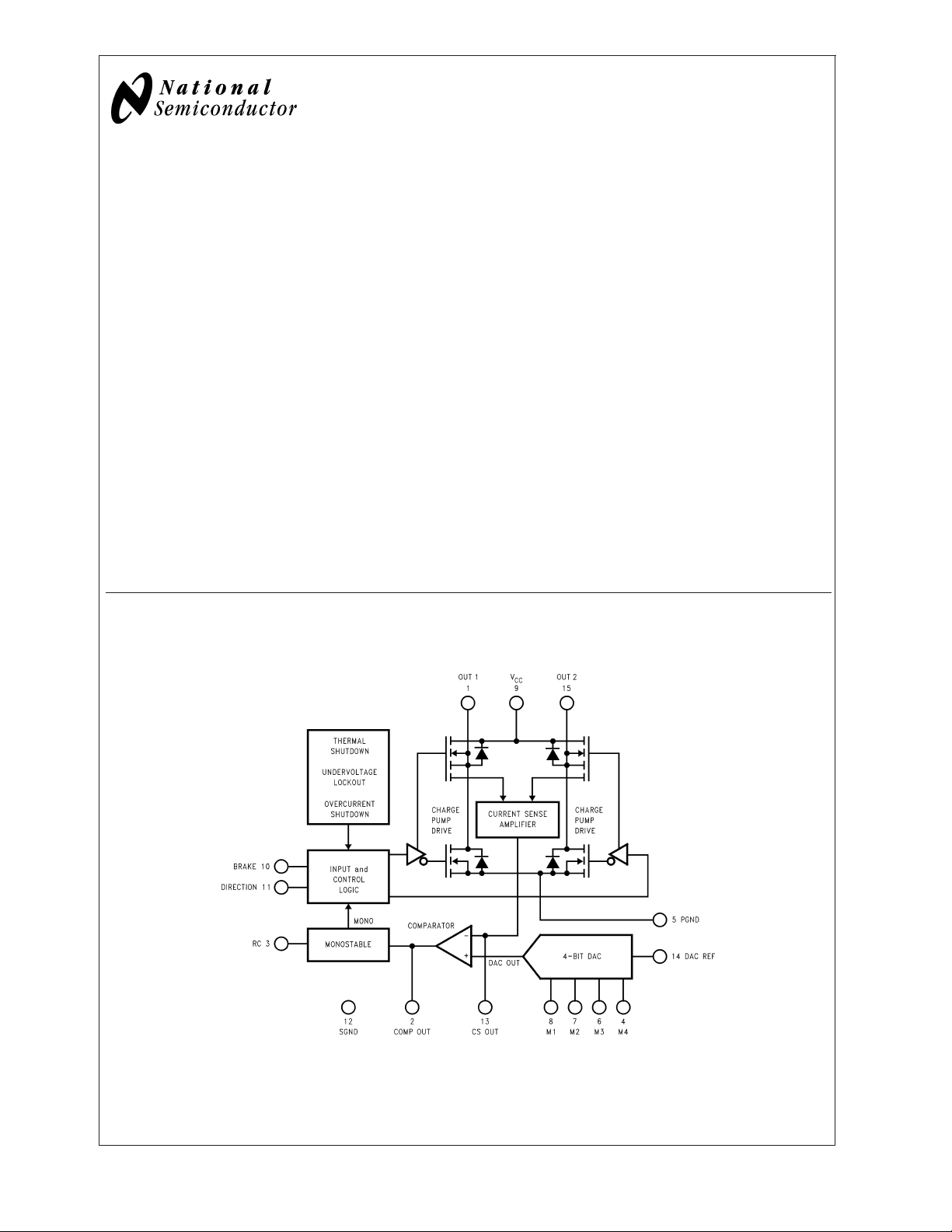
Functional Block and Connection Diagram
(15-Lead TO-220 Molded Power Package (T) )
of typically 0.3Ω per power switch
DS(ON)
= 155˚C
J
Order Number LMD18245T
See NS Package Number TA15A
© 2006 National Semiconductor Corporation DS011878 www.national.com
01187801

Connection Diagram
LMD18245
15-Lead TO-220 Molded Power Package
Order Number LMD18245T
See NS Package Number TA15A
Pinout Descriptions (See Functional Block
and Connection Diagrams)
Pin 1, OUT 1: Output node of the first half H-bridge.
Pin 2, COMP OUT: Output of the comparator. If the voltage
at CS OUT exceeds that provided by the DAC, the comparator triggers the monostable.
Pin 3, RC: Monostable timing node. A parallel resistorcapacitor network connected between this node and ground
sets the monostable timing pulse at about 1.1 RC seconds.
Pin 5, PGND: Ground return node of the power bridge. Bond
wires (internaI) connect PGND to the tab of the TO-220
package.
Pins 4 and 6 through 8, M4 through M1: Digital inputs of
the DAC. These inputs make up a four-bit binary number
with M4 as the most significant bit or MSB. The DAC provides an analog voltage directly proportional to the binary
number applied at M4 through M1.
Pin 9, V
Pin 10, BRAKE: Brake logic input. Pulling the BRAKE input
logic-high activates both sourcing switches of the power
bridge —effectively shorting the load. See Table 1. Shorting
the load in this manner forces the load current to recirculate
and decay to zero.
Pin 11, DIRECTION: Direction logic input. The logic level at
this input dictates the direction of current flow in the load.
See Table 1.
: Power supply node.
CC
Top View
01187802
Pin 12, SGND: Ground return node of all signal level circuits.
Pin 13, CS OUT: Output of the current sense amplifier. The
current sense amplifier sources 250 µA (typical) per ampere
of total forward current conducted by the upper two switches
of the power bridge.
Pin 14, DAC REF: Voltage reference input of the DAC. The
DAC provides an analog voltage equal to V
DAC REF
x D/16,
where D is the decimal equivalent (0–15) of the binary
number applied at M4 through M1.
Pin 15, OUT 2: Output node of the second half H-bridge.
TABLE 1. Switch Control Logic Truth Table
BRAKE DIRECTION MONO Active Switches
H X X Source 1, Source 2
L H L Source 2
L H H Source 2, Sink 1
L L L Source 1
L L H Source 1, Sink 2
X = don’t care
MONO is the output of the monostable.
www.national.com 2

LMD18245
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
DC Voltage at:
OUT 1, V
COMP OUT, RC, M4, M3, M2, M1, BRAKE, +12V
, and OUT 2 +60V
CC
TO-220 (T
TO-220 (T
= 25˚C, Infinite Heatsink) 25W
A
= 25˚C, Free Air) 3.5W
A
ESD Susceptibility (Note 4) 1500V
Storage Temperature Range (T
) −40˚C to +150˚C
S
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 seconds) 300˚C
Operating Conditions (Note 1)
DIRECTION, CS OUT, and DAC REF
DC Voltage PGND to SGND
±
400mV
Continuous Load Current 3A
Peak Load Current (Note 2) 6A
Junction Temperature (T
) +150˚C
J(max)
Power Dissipation (Note 3) :
Temperature Range (T
Supply Voltage Range (V
CS OUT Voltage Range 0V to +5V
DAC REF Voltage Range 0V to +5V
MONOSTABLE Pulse Range 10 µs to 100 ms
) (Note 3) −40˚C to +125˚C
J
) +12V to +55V
CC
Electrical Characteristics (Note 2)
The following specifications apply for VCC= +42V, unless otherwise stated. Boldface limits apply over the operating temperature range, −40˚C ≤ T
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limit Units
I
CC
Quiescent Supply Current DAC REF = 0V, VCC= +20V 8 mA
POWER OUTPUT STAGE
R
V
DIODE
T
rr
Q
t
D(ON)
DS(ON)
rr
Switch ON Resistance I
Body Diode Forward Voltage I
Diode Reverse Recovery Time I
Diode Reverse Recovery Charge I
Output Turn ON Delay Time
Sourcing Outputs I
Sinking Outputs I
t
D(OFF)
Output Turn OFF Delay Time
Sourcing Outputs I
Sinking Outputs I
t
ON
Output Turn ON Switching Time
Sourcing Outputs I
Sinking Outputs I
t
OFF
Output Turn OFF Switching Time
Sourcing Outputs I
Sinking Outputs I
t
pw
t
DB
Minimum Input Pulse Width Pins 10 and 11 2 µs
Minimum Dead Band (Note 6) 40 ns
CURRENT SENSE AMPLIFIER
Current Sense Output I
Current Sense Linearity Error 0.5A ≤ I
≤ +125˚C. All other limits apply for TA=TJ= 25˚C.
J
= 3A 0.3 0.4 Ω (max)
LOAD
I
= 6A 0.3 0.4 Ω (max)
LOAD
= 3A 1.0 V
DIODE
=1A 80 ns
DIODE
=1A 40 nC
DIODE
=3A 5 µs
LOAD
= 3A 900 ns
LOAD
= 3A 600 ns
LOAD
= 3A 400 ns
LOAD
=3A 40 µs
LOAD
=3A 1 µs
LOAD
= 3A 200 ns
LOAD
=3A 80 ns
LOAD
= 1A (Note 7) 200 µA (min)
LOAD
≤ 3A (Note 7)
LOAD
(Note 5) (Note 5) (Limits)
15 mA (max)
0.6 Ω (max)
0.6 Ω (max)
1.5 V(max)
250 175 µA (min)
300 µA (max)
325 µA (max)
±
6%
±
9 %(max)
www.national.com3

Electrical Characteristics (Note 2) (Continued)
The following specifications apply for VCC= +42V, unless otherwise stated. Boldface limits apply over the operating temperature range, −40˚C ≤ T
LMD18245
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Limit Units
CURRENT SENSE AMPLIFIER
Current Sense Offset I
DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER (DAC)
Resolution 4 Bits (min)
Monotonicity 4 Bits (min)
Total Unadjusted Error 0.125 0.25 LSB (max)
Propagation Delay 50 ns
I
REF
DAC REF Input Current DAC REF = +5V −0.5 µA
COMPARATOR AND MONOSTABLE
Comparator High Output Level 6.27 V
Comparator Low Output Level 88 mV
Comparator Output Current
Source 0.2 mA
Sink 3.2 mA
t
DELAY
Monostable Turn OFF Delay (Note 8) 1.2 µs
PROTECTION AND PACKAGE THERMAL RESISTANCES
Undervoltage Lockout, V
T
JSD
Shutdown Temperature, T
Package Thermal Resistances
θ
JC
θ
JA
Junction-to-Case, TO-220 1.5 ˚C/W
Junction-to-Ambient, TO-220 35 ˚C/W
LOGIC INPUTS
V
IL
V
IH
I
IN
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Electrical specifications do not apply when operating the device
outside the rated Operating Conditions.
Note 2: Unless otherwise stated, load currents are pulses with widths less than 2 ms and duty cycles less than 5%.
Note 3: The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is P
operation, T
forcing T
junction-to-case thermal resistance of the package, θ
Note 4: ESD rating is based on the human body model of 100 pF discharged through a 1.5 kΩ resistor. M1, M2, M3 and M4, pins 8, 7, 6 and 4 are protected to
800V.
Note 5: All limits are 100% production tested at 25˚C. Temperature extreme limits are guaranteed via correlation using accepted SQC (Statistical Quality Control)
methods. All limits are used to calculate AOQL (Average Outgoing Quality Level). Typicals are at T
Note 6: Asymmetric turn OFF and ON delay times and switching times ensure a switch turns OFF before the other switch in the same half H-bridge begins to turn
ON (preventing momentary short circuits between the power supply and ground). The transitional period during which both switches are OFF is commonly referred
to as the dead band.
Note 7: (I
The current sense linearity is specified as the slope of the line between the 0.5A and 1A data points minus the slope of the line between the 2A and 3A data points
all divided by the slope of the line between the 0.5A and 1A data points.
Note 8: Turn OFF delay, t
DMOS switch beginning to turn OFF. With V
5V at 1.2V/µs, and t
Low Level Input Voltage −0.1 V (min)
High Level Input Voltage 2 V (min)
Input Current VIN=0Vor12V
is the ambient temperature in ˚C, and θJAis the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance in ˚C/W. Exceeding P
A
above 125˚C. If the junction temperature exceeds 155˚C, internal circuitry disables the power bridge. When a heatsink is used, θJAis the sum of the
J
LOAD,ISENSE
) data points are taken for load currents of 0.5A, 1A, 2A and 3A. The current sense gain is specified as I
DELAY
is measured as the time from the voltage at RC reaching 2V to the time the voltage at OUT 1 reaches 3V.
DELAY
≤ +125˚C. All other limits apply for TA=TJ= 25˚C.
J
(Note 5) (Note 5) (Limits)
=0A 5 µA
LOAD
20 µA (max)
0.5 LSB (max)
±
10 µA (max)
2.0 µs (max)
CC
5 V (min)
8 V (max)
J
155 ˚C
0.8 V (max)
12 V (max)
±
10 µA (max)
= (125 − TA)/θJA, where 125˚C is the maximum junction temperature for
Max
, and the case-to-ambient thermal resistance of the heatsink.
JC
= 25˚C and represent the most likely parametric norm.
J
, is defined as the time from the voltage at the output of the current sense amplifier reaching the DAC output voltage to the lower
= 32V, DIRECTION high, and 200Ω connected between OUT1 and VCC, the voltage at RC is increased from 0V to
CC
voids the Electrical Specifications by
max
SENSE/ILOAD
for the 1A data point.
www.national.com 4
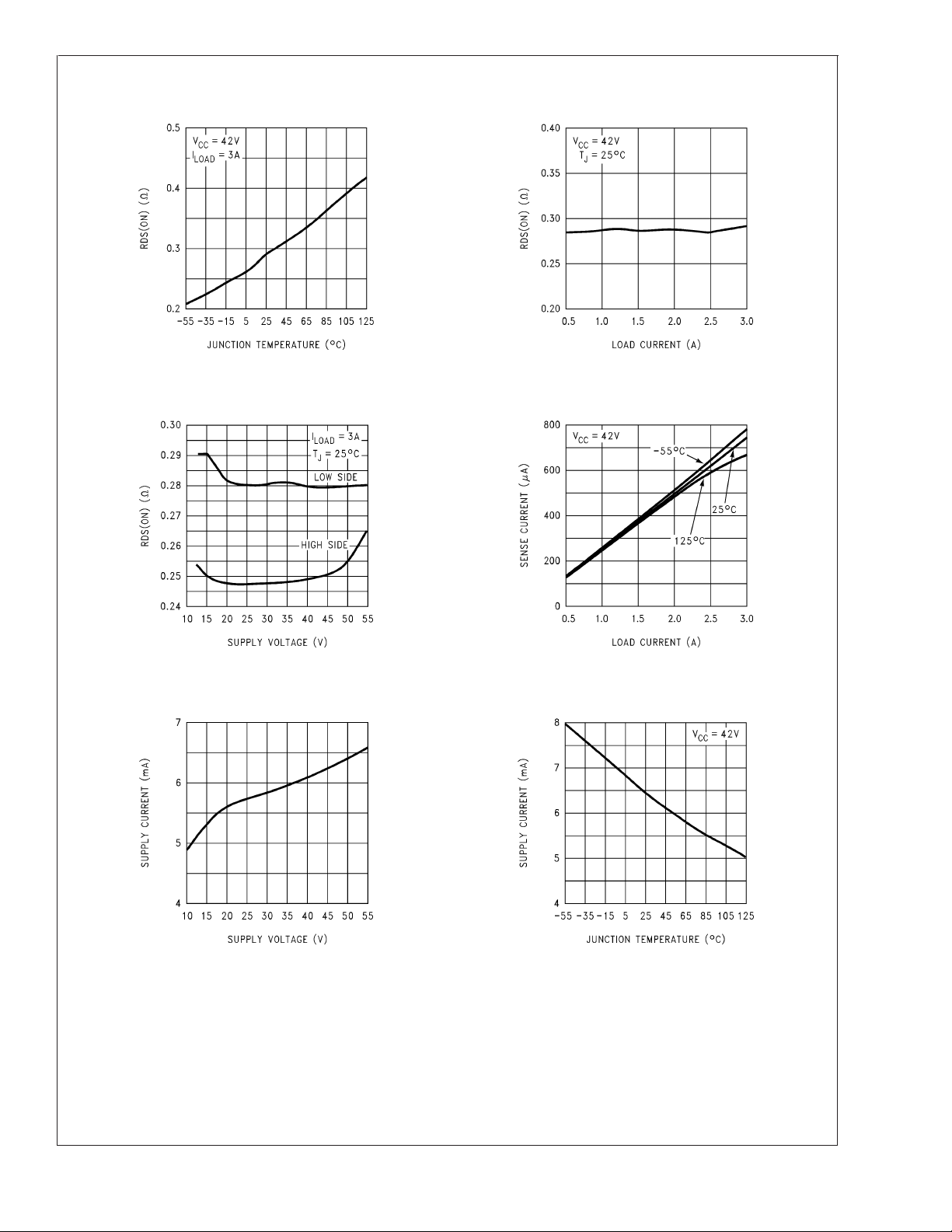
Typical Performance Characteristics
RDS(ON) vs Temperature RDS(ON) vs Load Current
LMD18245
RDS(ON) vs
Supply Voltage
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage
01187829
01187830
Current Sense Output
vs Load Current
01187831 01187832
Supply Current vs
Temperature
01187833
01187834
www.national.com5

Functional Descriptions
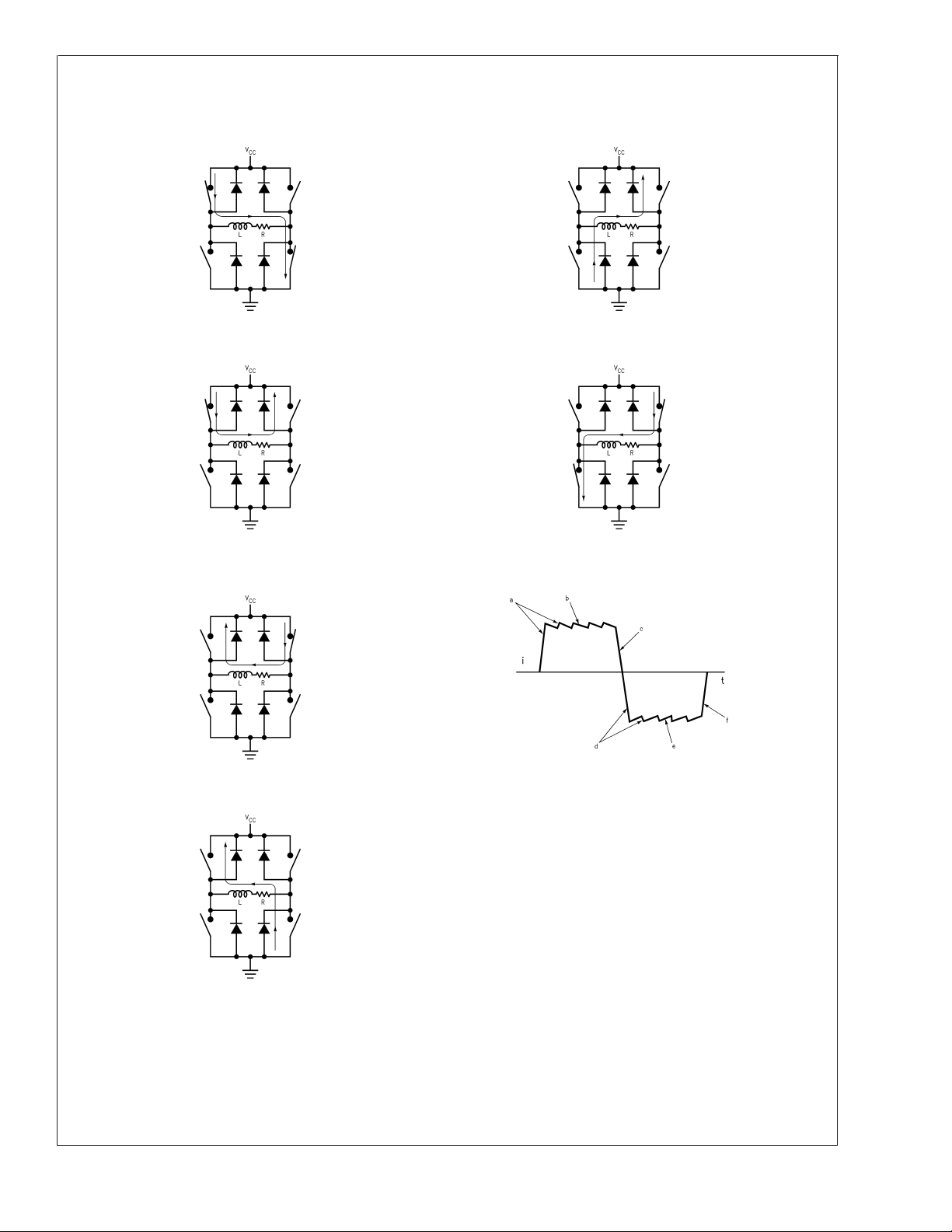
TYPICAL OPERATION OF A CHOPPER AMPLIFIER
LMD18245
Chopper amplifiers employ feedback driven switching of a
power bridge to control and limit current in the winding of a
motor (Figure 1). The bridge consists of four solid state
power switches and four diodes connected in an H configuration. Control circuitry (not shown) monitors the winding
current and compares it to a threshold. While the winding
current remains less than the threshold, a source switch and
a sink switch in opposite halves of the bridge force the
supply voltage across the winding, and the winding current
increases rapidly towards V
As the winding current surpasses the threshold, the control
circuitry turns OFF the sink switch for a fixed period or
/R (Figure 1a and Figure 1d ).
CC
off-time. During the off-time, the source switch and the opposite upper diode short the winding, and the winding current recirculates and decays slowly towards zero (Figure 1b
and Figure 1e ). At the end of the off-time, the control circuitry turns back ON the sink switch, and the winding current
again increases rapidly towards V
/R (Figure 1a and Fig-
CC
ure 1d again). The above sequence repeats to provide a
current chopping action that limits the winding current to the
threshold (Figure 1g ). Chopping only occurs if the winding
current reaches the threshold. During a change in the direction of the winding current, the diodes provide a decay path
for the initial winding current (Figure 1c and Figure 1f ).
Since the bridge shorts the winding for a fixed period, this
type of chopper amplifier is commonly referred to as a fixed
off-time chopper.
www.national.com 6
Functional Descriptions (Continued)
LMD18245
(a)
(b)
(e)
01187803
01187804
(c)
01187805
(d)
01187806
(g)
01187807
01187809
(f)
01187808
FIGURE 1. Chopper Amplifier Chopping States: Full VCCApplied Across the Winding (a) and (d), Shorted Winding (b)
and (e), Winding Current Decays During a Change in the Direction of the Winding Current (c) and (f), and the
Chopped Winding Current (g)
www.national.com7

Functional Descriptions (Continued)
THE LMD18245 CHOPPER AMPLIFIER
The LMD18245 incorporates all the circuit blocks needed to
LMD18245
implement a fixed off-time chopper amplifier. These blocks
include: an all DMOS, full H-bridge with clamp diodes, an
amplifier for sensing the load current, a comparator, a
monostable, and a DAC for digital control of the chopping
threshold. Also incorporated are logic, level shifting and drive
blocks for digital control of the direction of the load current
and braking.
THE H-BRIDGE
The power stage consists of four DMOS power switches and
associated body diodes connected in an H-bridge configuration (Figure 2 ).
The time constant to charge or discharge any inductor, in this
case the motor windings, is defined as:
τ = L/R
where L is the winding inductance, and R is the sum of the
series resistance in the current path including the winding
resistance.
Turning ON a source switch and a sink switch in opposite
halves of the bridge forces the full supply voltage less the
switch drops (I x R
) across the motor winding. While
DS(ON)
the bridge remains in this state, the winding current increases exponentially towards a limit dictated by the supply
voltage, the switch drops (I x R
), and the winding
DS(ON)
resistance. However, the winding current exponential rate of
increase will end when the current chopping circuitry becomes active.
Subsequently turning OFF the sink switch causes a voltage
transient that forward biases the body diode of the other
source switch. The diode clamps the transient at one diode
drop above the supply voltage and provides an alternative
current path. While the bridge remains in this state, it essentially shorts the winding, the winding current recirculates and
decays exponentially towards zero at a rate that is defined
by the L/R time constant.
During a change in the direction of the winding current, both
the switches and the body diodes provide a decay path for
the initial winding current (Figure 3 ).
During actual motor operation there are many variables that
can effect the motor winding magnetic behavior and performance. Resonance, eddy currents, friction, motor loading,
damping, temperature coefficients of the windings, are only a
few. These are all issues that are beyond the scope of the
this data sheet.
www.national.com 8

Functional Descriptions (Continued)
LMD18245
01187810
FIGURE 2. The DMOS H-Bridge
01187811
www.national.com9

Functional Descriptions (Continued)
LMD18245
01187812
FIGURE 3. Decay Paths for Initial Winding Current During a Change in the Direction of the Winding Current
THE CURRENT SENSE AMPLIFIER
Many transistor cells in parallel make up the DMOS power
switches. The current sense amplifier (Figure 5 ) uses a
small fraction of the cells of both upper switches to provide a
unique, low-loss means for sensing the load current. In
practice, each upper switch functions as a 1x sense device
in parallel with a 4000x power device. The current sense
amplifier forces the voltage at the source of the sense device
to equal that at the source of the power device; thus, the
devices share the total drain current in proportion to the
1:4000 cell ratio. Only the current flowing from drain to
source, the forward current, registers at the output of the
current sense amplifier. The current sense amplifier, therefore, sources 250 µA per ampere of total forward current
conducted by the upper two switches of the power bridge.
The sense current develops a potential across R
that is
S
proportional to the load current; for example, per ampere of
www.national.com 10
01187813
load current, the sense current develops one volt across a
4kΩ resistor (the product of 250 µA per ampere and 4 kΩ).
Since chopping of the load current occurs as the voltage at
CS OUT surpasses the threshold (the DAC output voltage),
sets the gain of the chopper amplifier; for example, a
R
S
2kΩ resistor sets the gain at two amperes of load current
per volt of the threshold (the reciprocal of the product of
250 µA per ampere and 2 kΩ). A quarter watt resistor suffices. A low value capacitor connected in parallel with R
filters the effects of switching noise from the current sense
signal.
While the specified maximum DC voltage compliance at CS
OUT is 12V, the specified operating voltage range at CS
OUT is 0V to 5V.
S

LMD18245
Functional Descriptions (Continued)
THE DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER (DAC)
The DAC sets the threshold voltage for chopping at
V
DAC REF
of the binary number applied at M4 through M1, the digital
inputs of the DAC. M4 is the MSB or most significant bit. For
applications that require higher resolution, an external DAC
can drive the DAC REF input. While the specified maximum
DC voltage compliance at DAC REF is 12V, the specified
operating voltage range at DAC REF is 0V to 5V.
THE COMPARATOR, MONOSTABLE AND WINDING CURRENT THRESHOLD FOR CHOPPING
As the voltage at CS OUT surpasses that at the output of the
DAC, the comparator triggers the monostable, and the
monostable, once triggered, provides a timing pulse to the
control logic. During the timing pulse, the power bridge
shorts the motor winding, causing current in the winding to
recirculate and decay slowly towards zero (Figure 1b and
Figure 1e again). A parallel resistor-capacitor network connected between RC (pin #3) and ground sets the timing
pulse or off-time at about 1.1 RC seconds.
Chopping of the winding current occurs as the voltage at CS
OUT exceeds that at the output of the DAC; so chopping
occurs at a winding current threshold of about
The R
the maximum rated current of the LMD18245, withD=15
and V
x D/16, where D is the decimal equivalent (0–15)
(V
DAC REF
S
DAC REF
(5.00V x 15/16) ÷ ((250 x 10
x D/16) ÷ ((250 x 10−6)xRS)) amperes.
value required to set the winding current threshold at
of 5.00V would be:
−6
) x 6.25 kΩ)) = 3.00A
The resulting typical DAC programmable current limit values,
for different values of R
R
D
18.75 kΩ
=
S
, would be:
S
9.375kΩ
RS=
RS=
6.250 kΩ
0 0.00A 0.00A 0.00A
1 0.07A 0.13A 0.20A
2 0.13A 0.27A 0.40A
3 0.20A 0.40A 0.60A
4 0.27A 0.53A 0.80A
5 0.33A 0.67A 1.00A
6 0.40A 0.80A 1.20A
7 0.47A 0.93A 1.40A
8 0.53A 1.07A 1.60A
9 0.60A 1.20A 1.80A
10 0.67A 1.33A 2.00A
11 0.73A 1.47A 2.20A
12 0.80A 1.60A 2.40A
13 0.87A 1.73A 2.60A
14 0.93A 1.87A 2.80A
15 1.00A 2.00A 3.00A
FIGURE 4. D to A winding current thresholds for
V
REF DAC
= 5.00V
01187814
FIGURE 5. The Source Switches of the Power Bridge and the Current Sense Amplifier
www.national.com11

Applications Information
POWER SUPPLY BYPASSING
LMD18245
Step changes in current drawn from the power supply occur
repeatedly during normal operation and may cause large
voltage spikes across inductance in the power supply line.
Care must be taken to limit voltage spikes at V
the 60V Absolute Maximum Rating. At a change in the
direction of the load current, the initial load current tends to
raise the voltage at the power supply rail (Figure 3) again.
Current transients caused by the reverse recovery of the
clamp diodes tend to pull down the voltage at the power
supply rail.
Bypassing the power supply line at V
CC
the device and minimize the adverse effects of normal operation on the power supply rail. Using botha1µFhigh
frequency ceramic capacitor and a large-value aluminum
electrolytic capacitor is highly recommended. A value of
100 µF per ampere of load current usually suffices for the
aluminum electrolytic capacitor. Both capacitors should have
short leads and be located within one half inch of V
OVERCURRENT PROTECTION
If the forward current in either source switch exceeds a 12A
threshold, internal circuitry disables both source switches,
forcing a rapid decay of the fault current (Figure 6). Approximately 3 µs after the fault current reaches zero, the device
restarts. Automatic restart allows an immediate return to
normal operation once the fault condition has been removed.
If the fault persists, the device will begin cycling into and out
of thermal shutdown. Switching large fault currents may
cause potentially destructive voltage spikes across induc-
CC
is required to protect
to less than
.
CC
tance in the power supply line; therefore, the power supply
line must be properly bypassed at V
for the motor driver to
CC
survive an extended overcurrent fault.
In the case of a locked rotor, the inductance of the winding
tends to limit the rate of change of the fault current to a value
easily handled by the protection circuitry. In the case of a low
inductance short from either output to ground or between
outputs, the fault current could surge past the 12A shutdown
threshold, forcing the device to dissipate a substantial
amount of power for the brief period required to disable the
source switches. Because the fault power must be dissipated by only one source switch, a short from output to
ground represents the worst case fault. Any overcurrent fault
is potentially destructive, especially while operating with high
supply voltages (≥30V), so precautions are in order. Sinking
for heat with 1 square inch of 1 ounce copper on the
V
CC
printed circuit board is highly recommended. The sink
switches are not internally protected against shorts to V
CC
THERMAL SHUTDOWN
Internal circuitry senses the junction temperature near the
power bridge and disables the bridge if the junction temperature exceeds about 155˚C. When the junction temperature
cools past the shutdown threshold (lowered by a slight hysteresis), the device automatically restarts.
UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
Internal circuitry disables the power bridge if the power
supply voltage drops below a rough threshold between 8V
and 5V. Should the power supply voltage then exceed the
threshold, the device automatically restarts.
.
Trace: Fault Current at 5A/div
Horizontal: 20 µs/div
FIGURE 6. Fault Current with VCC= 30V, OUT 1 Shorted to OUT 2, and CS OUT Grounded
www.national.com 12
01187815

The Typical Application
Figure 7 shows the typical application, the power stage of a
chopper drive for bipolar stepper motors. The 20 kΩ resistor
and 2.2 nF capacitor connected between RC and ground set
the off-time at about 48 µs, and the 20 kΩ resistor connected
between CS OUT and ground sets the gain at about 200 mA
LMD18245
per volt of the threshold for chopping. Digital signals control
the thresholds for chopping, the directions of the winding
currents, and, by extension, the drive type (full step, half
step, etc.). A µprocessor or µcontroller usually provides the
digital control signals.
FIGURE 7. Typical Application Circuit for Driving Bipolar Stepper Motors
ONE-PHASE-ON FULL STEP DRIVE (WAVE DRIVE)
To make the motor take full steps, windings A and B can be
energized in the sequence
A→B→A*→B*→A→…,
where A represents winding A energized with current in one
direction and A* represents winding A energized with current
in the opposite direction. The motor takes one full step each
time one winding is de-energized and the other is energized.
To make the motor step in the opposite direction, the order of
01187816
the above sequence must be reversed. Figure 8 shows the
winding currents and digital control signals for a wave drive
application of the typical application circuit.
TWO-PHASE-ON FULL STEP DRIVE
To make the motor take full steps, windings A and B can also
be energized in the sequence
AB→A*B→A*B*→AB*→AB→…,
and because both windings are energized at all times, this
sequence produces more torque than that produced with
www.national.com13

The Typical Application (Continued)
wave drive. The motor takes one full step at each change of
direction of either winding current. Figure 9 shows the wind-
LMD18245
ing currents and digital control signals for this application of
the typical application circuit, and Figure 10 shows, for a
single phase, the winding current and voltage at the output of
the associated current sense amplifier.
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase B Winding Current at 1A/div
Horizontal: 1 ms/div
*500 steps/second
01187817
BRAKE A = BRAKEB=0
FIGURE 8. Winding Currents and Digital Control Signals for One-Phase-On Drive (Wave Drive)
www.national.com 14
01187841

The Typical Application (Continued)
LMD18245
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase B Winding Current at 1A/div
Horizontal: 1 ms/div
*500 steps/second
M4 A through M1A=M4Bthrough M1B=1
BRAKE A = BRAKEB=0
FIGURE 9. Winding Currents and Digital Control Signals for Two-Phase-On Drive
01187819
01187842
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase A Sense Voltage at 5V/div
Horizontal: 1 ms/div
*500 steps/second
FIGURE 10. Winding Current and Voltage at the Output of the Associated Current Sense Amplifier
01187821
www.national.com15

The Typical Application (Continued)
HALF STEP DRIVE WITHOUT TORQUE COMPENSATION
LMD18245
To make the motor take half steps, windings A and B can be
energized in the sequence
A→AB→B→A*B→A*
A*B*→B*→AB*→A→…
The motor takes one half step each time the number of
energized windings changes. It is important to note that
→
although half stepping doubles the step resolution, changing
the number of energized windings from two to one decreases (one to two increases) torque by about 40%, resulting in significant torque ripple and possibly noisy operation.
Figure 11 shows the winding currents and digital control
signals for this half step application of the typical application
circuit.
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase B Winding Current at 1A/div
Horizontal: 1 ms/div
*500 steps/second
01187822
BRAKE A = BRAKEB=0
FIGURE 11. Winding Currents and Digital Control Signals for Half Step Drive without Torque Compensation
www.national.com 16
01187843

The Typical Application (Continued)
HALF STEP DRIVE WITH TORQUE COMPENSATION
To make the motor take half steps, the windings can also be
energized with sinusoidal currents (Figure 12). Controlling
the winding currents in the fashion shown doubles the step
resolution without the significant torque ripple of the prior
drive technique. The motor takes one half step each time the
level of either winding current changes. Half step drive with
torque compensation is microstepping drive. Along with the
obvious advantage of increased step resolution, microstepping reduces both full step oscillations and resonances
that occur as the motor and load combination is driven at its
LMD18245
natural resonant frequency or subharmonics thereof. Both of
these advantages are obtained by replacing full steps with
bursts of microsteps. When compared to full step drive, the
motor runs smoother and quieter.
Figure 13 shows the lookup table for this application of the
typical application circuit. Dividing 90˚electrical per full step
by two microsteps per full step yields 45˚ electrical per
microstep. α, therefore, increases from 0 to 315˚ in increments of 45˚. Each full 360˚ cycle comprises eight half steps.
Rounding |cosα| to four bits gives D A, the decimal equivalent of the binary number applied at M4 A through M1 A.
DIRECTION A controls the polarity of the current in winding
A. Figure 12 shows the sinusoidal winding currents.
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase B Winding Current at 1A/div
Horizontal: 2 ms/div
*500 steps/second
01187824
BRAKE A = BRAKEB=0
90˚ ELECTRICAL/FULL STEP ÷ 2 MICROSTEPS/FULL STEP = 45˚ ELECTRICAL/MICROSTEP
FIGURE 12. Winding Currents and Digital Control Signals for Half Step Drive with Torque Compensation
01187844
www.national.com17

The Typical Application (Continued)
LMD18245
FORWARD 45˚ 0.707 11 1 0.707 11 1
REVERSE 270˚ 0 0 1 1 15 0
α |cos(α)| D A DIRECTION A |sin(α)| D B DIRECTlON B
| 0˚ 1 15 1 0 0 1
↓ 90˚ 0 0 0 1 15 1
135˚ 0.707 11 0 0.707 11 1
180˚ 1 15 0 0 0 0
↑
| 315˚ 0.707 11 1 0.707 11 0
225˚ 0.707 11 0 0.707 11 0
REPEAT
FIGURE 13. Lookup Table for Half Step Drive with Torque Compensation
www.national.com 18

The Typical Application (Continued)
QUARTER STEP DRIVE WITH TORQUE COMPENSATION
Figure 14 shows the winding currents and lookup table for a
quarter step drive (four microsteps per full step) with torque
compensation.
LMD18245
Top Trace: Phase A Winding Current at 1A/div
Bottom Trace: Phase B Winding Current at 1A/div
Horizontal: 2ms/div
*250 steps/second
01187826
90˚ ELECTRICAL/FULL STEP ÷ 4 MICROSTEPS/FULL STEP = 22.5˚ ELECTRICAL/MICROSTEP
α |cos(α)| D A DIRECTION A |sin(α)| D B DIRECTION B
| 0.0˚ 1 15 1 0 0 1
FORWARD 22.5˚ 0.924 14 1 0.383 6 1
↓ 45.0˚ 0.707 11 1 0.707 11 1
67.5˚ 0.383 6 1 0.924 14 1
90.0˚ 0 0 0 1 15 1
112.5˚ 0.383 6 0 0.924 14 1
135.0˚ 0.707 11 0 0.707 11 1
157.5˚ 0.924 14 0 0.383 6 1
180.0˚ 1 15 0 0 0 0
202.5˚ 0.924 14 0 0.383 6 0
225.0˚ 0.707 11 0 0.707 11 0
247.5˚ 0.383 6 0 0.924 14 0
270.0˚ 0 0 1 1 15 0
↑
292.5˚ 0.383 6 1 0.924 14 0
REVERSE 315.0˚ 0.707 11 1 0.707 11 0
| 337.5˚ 0.924 14 1 0.383 6 0
REPEAT
BRAKE A = BRAKEB=0
FIGURE 14. Winding Currents and Lookup Table for Quarter Step Drive with Torque Compensation
www.national.com19

Test Circuit and Switching Time Definitions
LMD18245
www.national.com 20
01187828

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
LMD18245 3A, 55V DMOS Full-Bridge Motor Driver
15-Lead TO-220 Power Package (T)
Order Number LMD18245T
NS Package Number TA15A
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves
the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
For the most current product information visit us at www.national.com.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS
WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems
which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or
(b) support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform when
properly used in accordance with instructions for use
2. A critical component is any component of a life support
device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably
expected to cause the failure of the life support device or
system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result
in a significant injury to the user.
BANNED SUBSTANCE COMPLIANCE
National Semiconductor manufactures products and uses packing materials that meet the provisions of the Customer Products
Stewardship Specification (CSP-9-111C2) and the Banned Substances and Materials of Interest Specification (CSP-9-111S2) and contain
no ‘‘Banned Substances’’ as defined in CSP-9-111S2.
Leadfree products are RoHS compliant.
National Semiconductor
Americas Customer
Support Center
Email: new.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Europe Customer Support Center
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Support Center
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Customer Support Center
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
Email: jpn.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
 Loading...
Loading...