查询LMC6042供应商
LMC6042
CMOS Dual Micropower Operational Amplifier
LMC6042 CMOS Dual Micropower Operational Amplifier
August 1999
General Description
Ultra-low power consumption and low input-leakage current
are the hallmarks of the LMC6042. Providing input currents
of only 2 fA typical, the LMC6042 can operate from a single
supply, has output swing extending to each supply rail, and
an input voltage range that includes ground.
The LMC6042 is ideal for use in systems requiring ultra-low
power consumption. In addition, the insensitivity to latch-up,
high output drive, and output swing to ground without requiring external pull-down resistors make it ideal for
single-supply battery-powered systems.
Other applications for the LMC6042 include bar code reader
amplifiers, magnetic and electric field detectors, and
hand-held electrometers.
This device is built with National’s advanced Double-Poly
Silicon-Gate CMOS process.
See the LMC6041 for a single, and the LMC6044 for a quad
amplifier with these features.
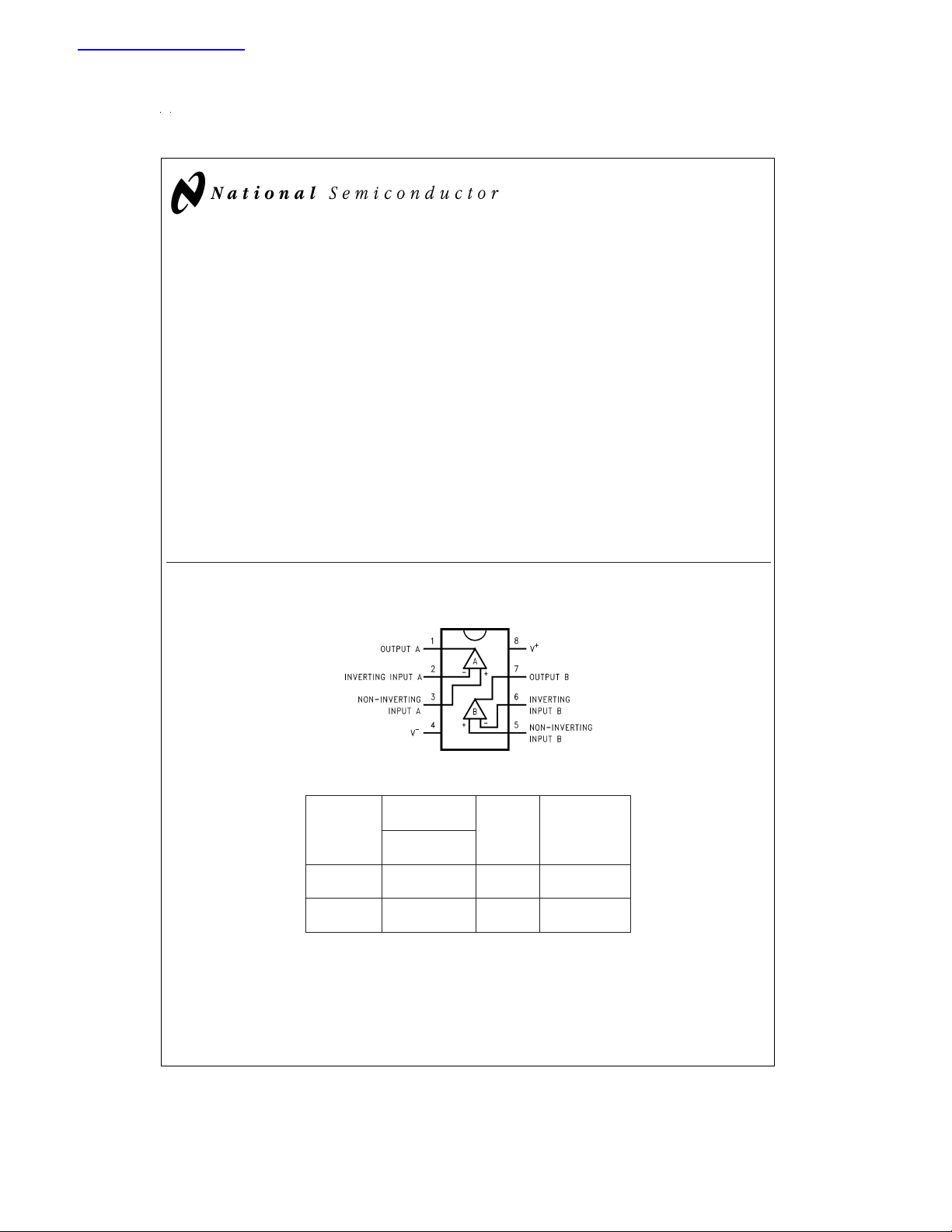
Connection Diagram
8-Pin DIP/SO
Ordering Information
Temperature
Package
8-Pin LMC6042AIM M08A Rail
Small Outline LMC6042IM Tape and Reel
8-Pin LMC6042AIN N08E Rail
Molded DIP LMC6042IN
Range NSC
Industrial Drawing
−40˚C to +85˚C
Features
n Low supply current: 10 µA/Amp (typ)
n Operates from 4.5V to 15V single supply
n Ultra low input current: 2 fA (typ)
n Rail-to-rail output swing
n Input common-mode range includes ground
Applications
n Battery monitoring and power conditioning
n Photodiode and infrared detector preamplifier
n Silicon based transducer systems
n Hand-held analytic instruments
n pH probe buffer amplifier
n Fire and smoke detection systems
n Charge amplifier for piezoelectric transducers
DS011137-1
Transport
Media
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS011137 www.national.com
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Differential Input Voltage
Supply Voltage (V
Output Short Circuit to V
Output Short Circuit to V
+−V−
) 16V
+
−
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 10 seconds) 260˚C
Current at Input Pin
Current at Output Pin
Current at Power Supply Pin 35 mA
Power Dissipation (Note 3)
±
Supply Voltage
(Note 12)
(Note 2)
±
±
18 mA
5mA
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C
Junction Temperature (Note 3) 110˚C
ESD Tolerance (Note 4) 500V
Voltage at Input/Output Pin (V
+
) + 0.3V, (V−) − 0.3V
Operating Ratings
Temperature Range
LMC6042AI, LMC6042I −40˚C ≤ T
Supply Voltage 4.5V ≤ V
Power Dissipation (Note 10)
Thermal Resistance (θ
), (Note 11)
JA
8-Pin DIP 101˚C/W
8-Pin SO 165˚C/W
≤ +85˚C
J
+
≤ 15.5V
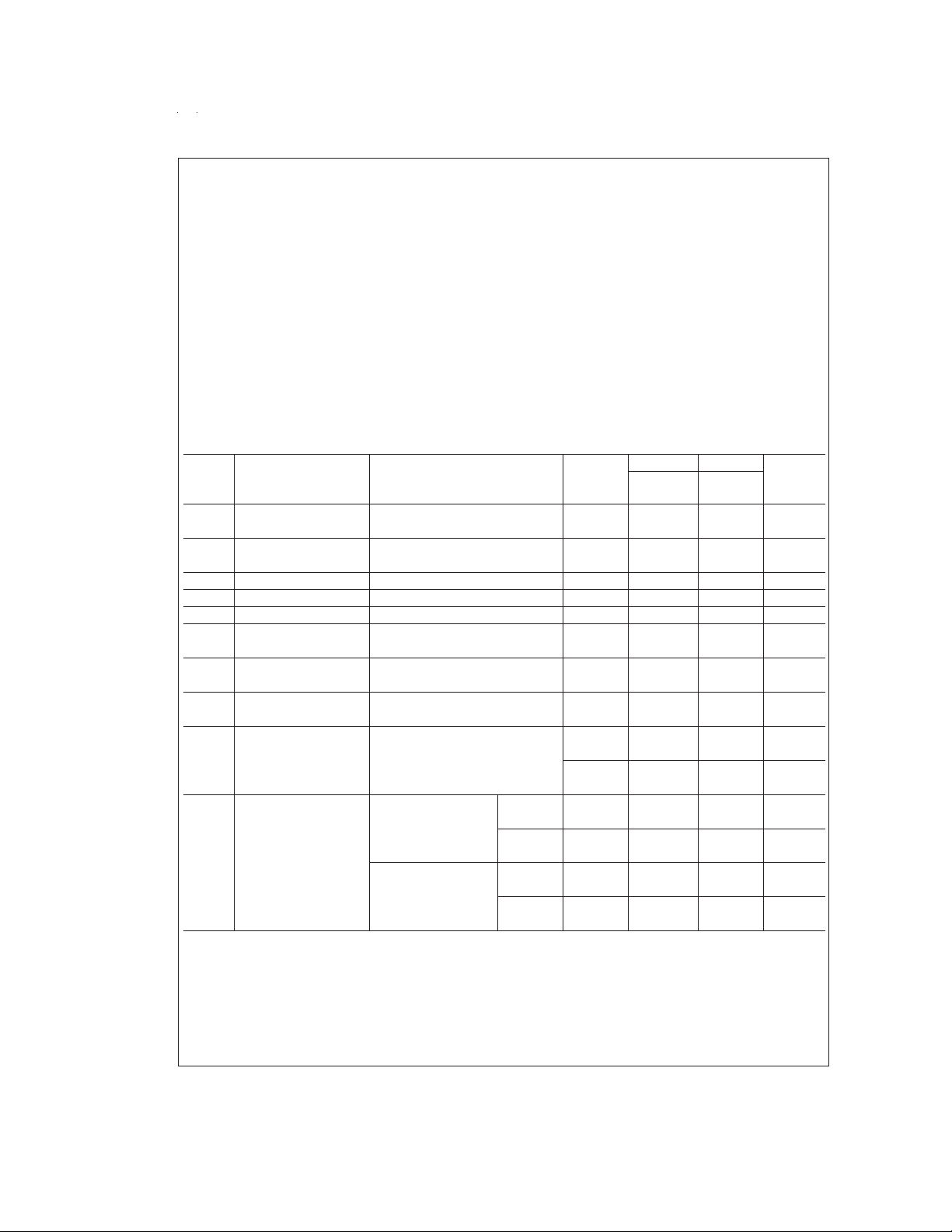
Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise spec ified, all limits guaranteed for T
5V, V
−
=
0V, V
=
1.5V, V
CM
+
=
/2 and R
V
O
>
1M unless otherwise specified.
L
=
=
T
A
25˚C. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes. V
J
+
Typical LMC6042AI LMC6042I Units
Symbol Parameter Conditions (Note 5) Limit Limit (Limit)
(Note 6) (Note 6)
V
Input Offset Voltage 1 3 6 mV
OS
3.3 6.3 Max
TCV
Input Offset Voltage 1.3 µV/˚C
OS
Average Drift
I
B
I
OS
R
CMRR Common Mode 0V ≤ V
+PSRR Positive Power Supply 5V ≤ V
−PSRR Negative Power Supply 0V ≤ V
CMR Input Common-Mode V
Input Bias Current 0.002 44pA (Max)
Input Offset Current 0.001 22pA (Max)
Input Resistance
IN
Rejection Ratio V
Rejection Ratio V
Rejection Ratio V
≤ 12.0V 75 68 62 dB
CM
+
=
15V 66 60 Min
+
≤ 15V 75 68 62 dB
=
2.5V 66 60 Min
O
−
≤ −10V 94 84 74 dB
=
2.5V 83 73 Min
O
+
=
5V and 15V −0.4 −0.1 −0.1 V
>
10 TeraΩ
Voltage Range For CMRR ≥ 50 dB 00Max
+
V
−1.9V V+− 2.3V V+− 2.3V V
A
Large Signal R
V
=
100 kΩ (Note 7) Sourcing 1000 400 300 V/mV
L
+
V
− 2.5V V+− 2.4V Min
Voltage Gain 300 200 Min
Sinking 500 180 90 V/mV
120 70 Min
=
R
25 kΩ (Note 7) Sourcing 1000 200 100 V/mV
L
160 80 Min
Sinking 250 100 50 V/mV
60 40 Min
=
www.national.com 2
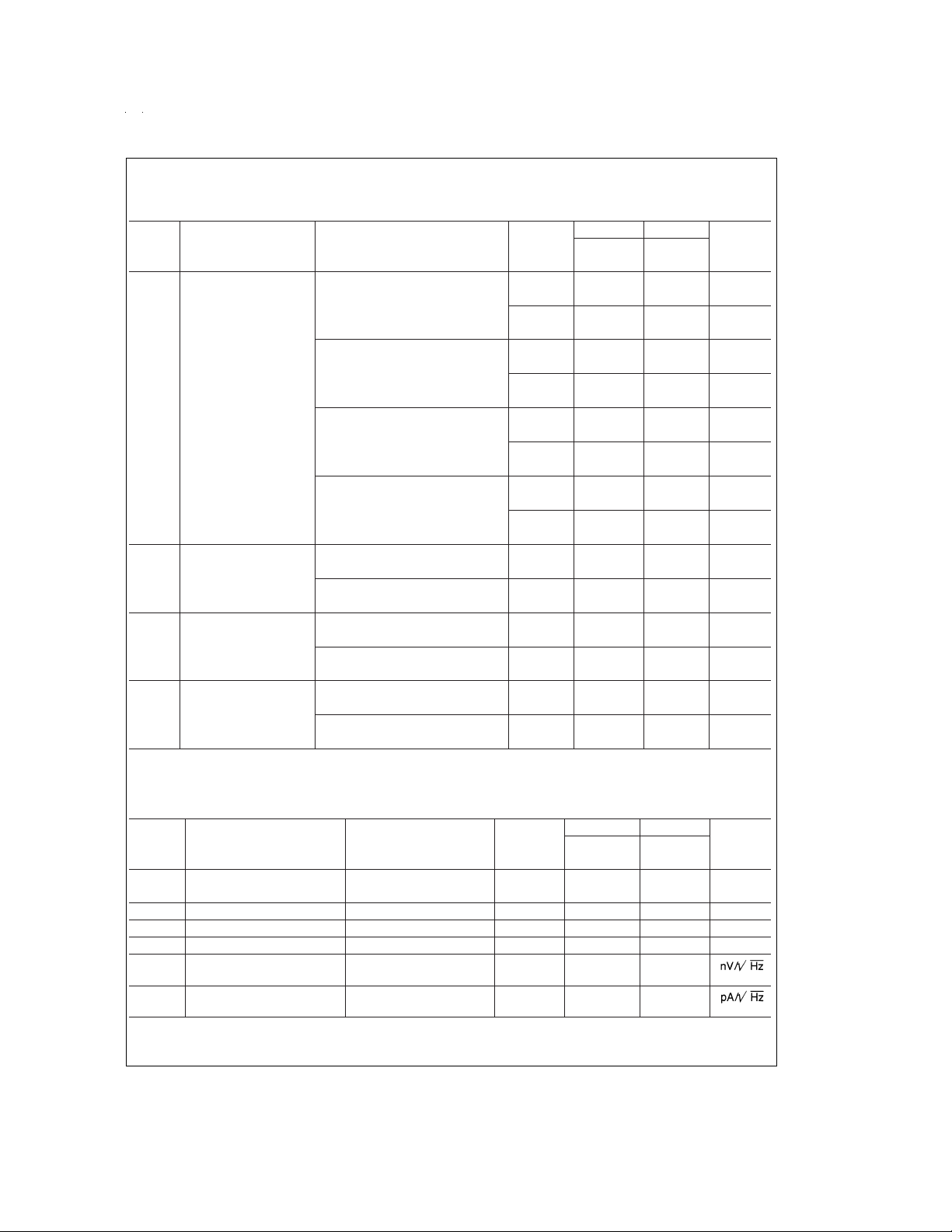
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
=
Unless otherwise spec ified, all limits guaranteed for T
5V, V
−
=
0V, V
=
1.5V, V
CM
+
=
/2 and R
V
O
>
1M unless otherwise specified.
L
=
T
25˚C. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes. V
A
J
Typical LMC6042AI LMC6042I Units
Symbol Parameter Conditions (Note 5) Limit Limit (Limit)
(Note 6) (Note 6)
+
V
O
Output Swing V
=
5V 4.987 4.970 4.940 V
=
R
100 kΩ to V
L
+
/2 4.950 4.910 Min
0.004 0.030 0.060 V
0.050 0.090 Max
+
=
V
5V 4.980 4.920 4.870 V
=
R
25 kΩ to V
L
+
/2 4.870 4.820 Min
0.010 0.080 0.130 V
0.130 0.180 Max
+
=
V
15V 14.970 14.920 14.880 V
=
R
100 kΩ to V
L
+
/2 14.880 14.820 Min
0.007 0.030 0.060 V
0.050 0.090 Max
+
=
V
15V 14.950 14.900 14.850 V
=
R
25 kΩ to V
L
+
/2 14.850 14.800 Min
0.022 0.100 0.150 V
0.150 0.200 Max
I
SC
Output Current Sourcing, V
+
=
V
5V 10 8 Min
Sinking, V
=
0V 22 16 13 mA
O
=
5V 21 16 13 mA
O
88Min
I
SC
Output Current Sourcing, V
+
=
V
15V 10 10 Min
Sinking, V
=
0V 40 15 15 mA
O
=
13V 39 24 21 mA
O
(Note 12) 88Min
I
S
Supply Current Both Amplifiers 20 34 45 µA
=
V
1.5V 39 50 Max
O
Both Amplifiers 26 44 56 µA
+
=
V
15V 51 65 Max
+
=
AC Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
5V, V
−
=
0V, V
=
1.5V, V
CM
+
=
/2 and R
V
O
>
1M unless otherwise specified.
L
=
=
T
25˚C. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes. V
A
J
+
Typ LMC6042AI LMC6042I Units
Symbol Parameter Conditions (Note 5) Limit Limit (Limit)
(Note 6) (Note 6)
SR Slew Rate (Note 8) 0.02 0.015 0.010 V/µs
0.010 0.007 Min
GBW Gain-Bandwidth Product 100 kHz
φ
m
Phase Margin 60 Deg
Amp-to-Amp Isolation (Note 9) 115 dB
e
Input-Referred
n
Voltage Noise
i
n
Input-Referred
Current Noise
f=1 kHz 83
f=1 kHz 0.0002
www.national.com3
=
AC Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
=
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T
5V, V
−
=
0V, V
=
1.5V, V
CM
+
=
/2 and R
V
O
>
1M unless otherwise specified.
L
=
T
25˚C. Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes. V
A
J
Typ LMC6042AI LMC6042I Units
Symbol Parameter Conditions (Note 5) Limit Limit (Limit)
(Note 6) (Note 6)
=
T.H.D. Total Harmonic Distortion f=1 kHz, A
=
R
100 kΩ,V
L
±
5V Supply
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Conditions indicate conditions for which the device is
intended to be functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics. The
guaranteed specifications apply only for the test conditions listed.
Note 2: Applies to both single-supply operation. Continuous short circuit operation at elevated ambient temperature can result in exceeding the maximum allowed
junction temperature of 110˚C. Output currents in excess of
Note 3: The maximum powerdissipationisa function of T
−TA)/θJA.
Note 4: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF.
Note 5: Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 6: All limits are guaranteed at room temperature (standard type face) or at operating temperature extremes (bold face type).
+
Note 7: V
Note 8: V
Note 9: Input referred V
Note 10: For operating at elevated temperatures the device must be derated based on the thermal resistance θ
Note 11: All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
Note 12: Do not connect output to V
=
+
=
=
15V, V
15V. Connected as Voltage Follower with 10V step input. Number specified is the slower of the positive and negative slew rates.
CM
7.5V and R
+
=
connected to 7.5V. For Sourcing tests, 7.5V ≤ VO≤ 11.5V. For Sinking tests, 2.5V ≤ VO≤ 7.5V.
L
15V and R
=
100 kΩ connected to V
L
+
when V+is greater than 13V or reliability may be adversely affected.
±
30 mA over long term may adversely affect reliability.
, θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is P
J(Max)
−5
V
=
2V
O
PP
+
/2. Each amp excited in turn with 100 Hz to produce V
0.01
JA
with P
=
.
12 V
O
PP
=
)/θJA.
(T
D
J−TA
+
%
=
(T
D
J(Max)
=
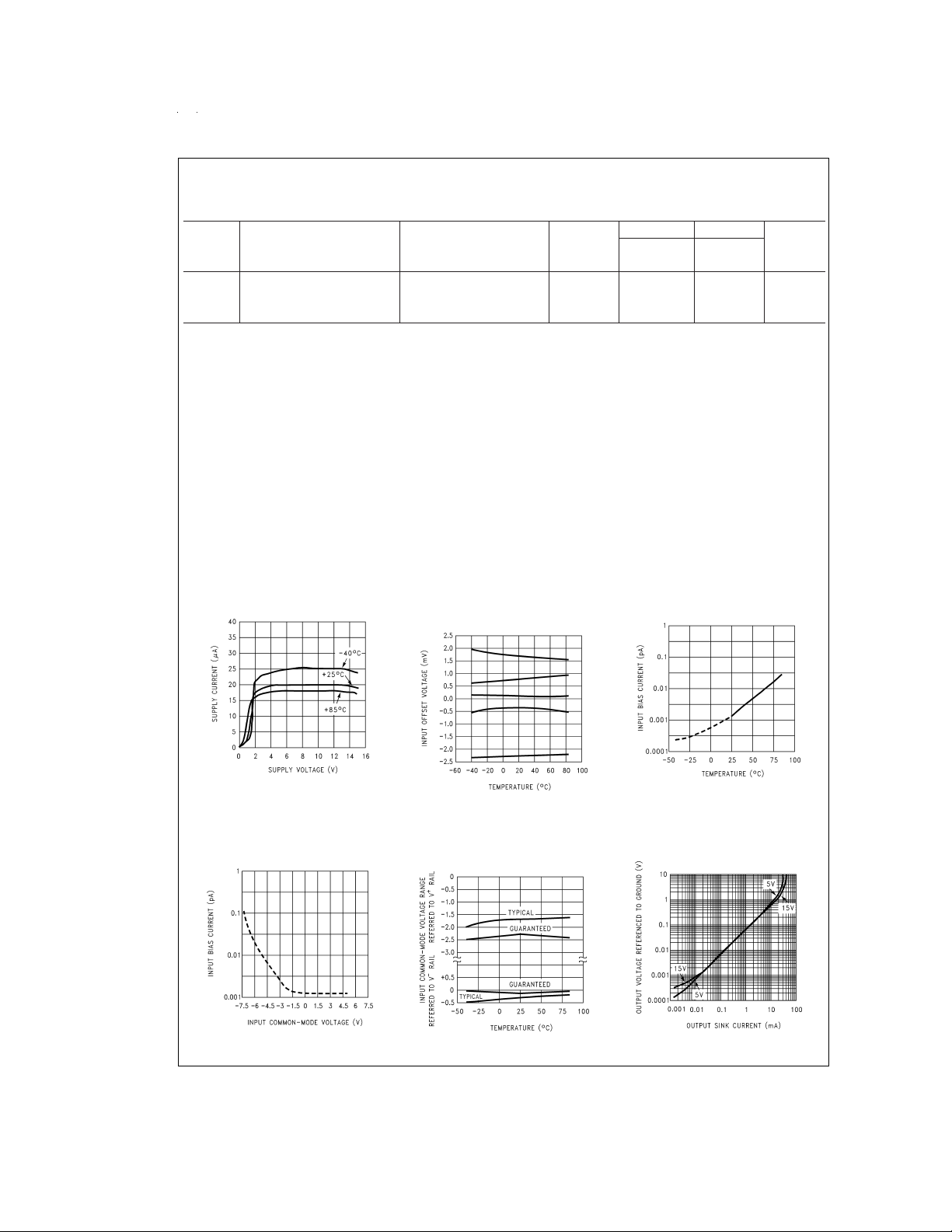
Typical Performance Characteristics V
Supply Current vs
Supply Voltage
DS011137-19
Input Bias Current
vs Input Common-Mode
Voltage
Offset Voltage vs
Temperature of Five
Representative Units
Input Common-Mode
Voltage Range
vs Temperature
=
±
S
7.5V, T
=
25˚C unless otherwise specified
A
Input Bias Current
vs Temperature
DS011137-20
DS011137-21
Output Characteristics
Current Sinking
DS011137-22
www.national.com 4
DS011137-23
DS011137-24

Typical Performance Characteristics V
=
±
S
7.5V, T
=
25˚C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Output Characteristics
Current Sourcing
CMRR vs Frequency
Open-Loop Voltage
Gain vs Temperature
DS011137-25
DS011137-28
Input Voltage Noise
vs Frequency
CMRR vs Temperature
Open-Loop
Frequency Response
DS011137-26
DS011137-29
Crosstalk Rejection
vs Frequency
DS011137-27
Power Supply Rejection
Ratio vs Frequency
DS011137-30
Gain and Phase
Responses vs
Load Capacitance
DS011137-31
DS011137-32
DS011137-33
www.national.com5
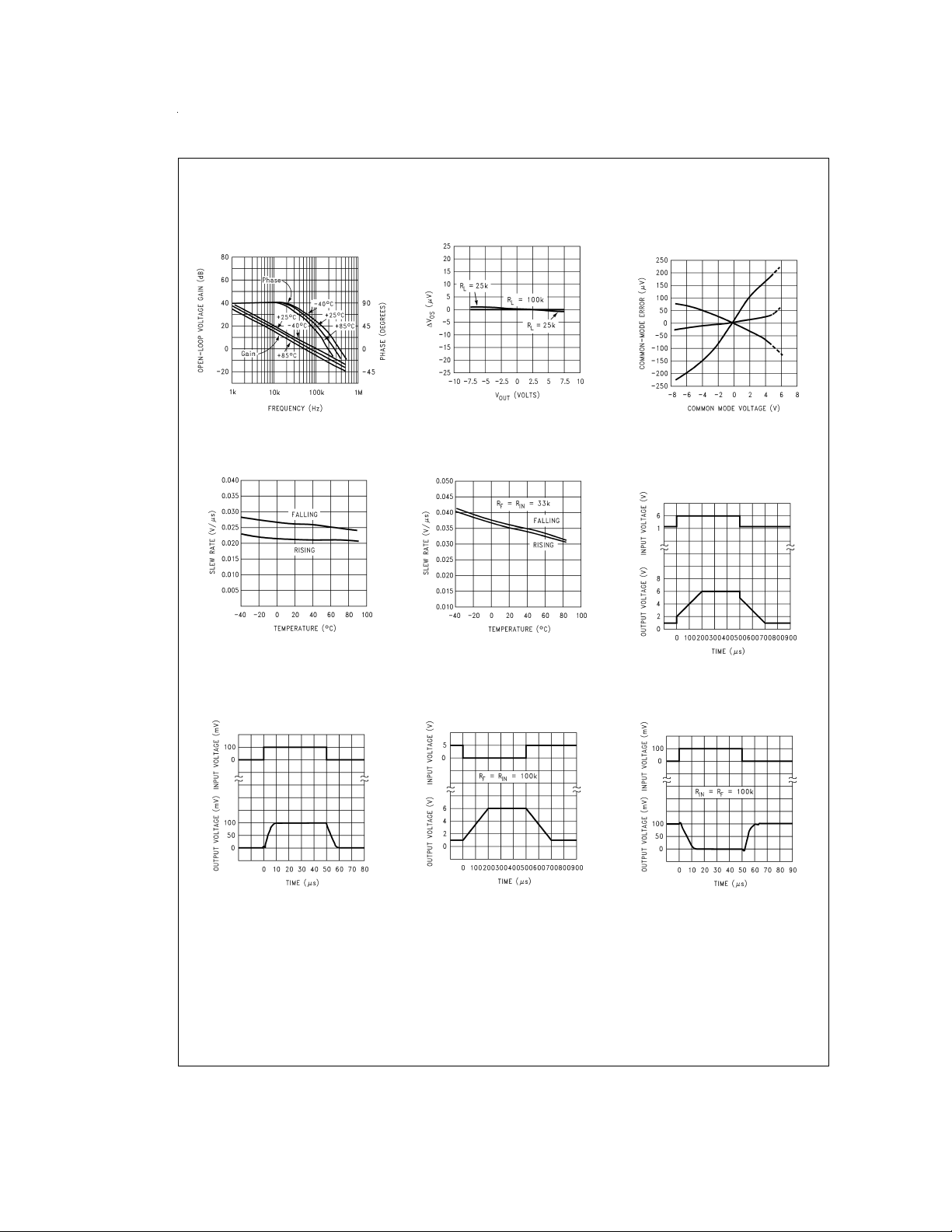
Typical Performance Characteristics V
=
±
S
7.5V, T
=
25˚C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Gain and Phase
Response vs
Temperature
Non-Inverting Slew
Rate vs Temperature
DS011137-34
DS011137-37
Gain Error
(V
vs V
OUT
)
OS
Inverting Slew Rate
vs Temperature
DS011137-35
DS011137-38
Common-Mode Error vs
Common-Mode Voltage of
3 Representative Units
Non-Inverting Large
Signal Pulse Response
=
(A
+1)
V
DS011137-36
DS011137-39
Non-Inverting Small
Signal Pulse Response
DS011137-40
www.national.com 6
Inverting Large-Signal
Pulse Response
DS011137-41
Inverting Small Signal
Pulse Response
DS011137-42

Typical Performance Characteristics V
=
±
S
7.5V, T
=
25˚C unless otherwise specified (Continued)
A
Stability vs Capacitive Load
DS011137-43
Applications Hints
AMPLIFIER TOPOLOGY
The LMC6042 incorporates a novel op-amp design topology
that enables it to maintain rail-to-rail output swing even when
driving a large load. Instead of relying on a push-pull unity
gain output buffer stage, the output stage is taken directly
from the internal integrator, which provides both low output
impedance and large gain. Special feed-forward compensation design techniques are incorporated to maintain stability
over a wider range of operating conditions than traditional
micropower op-amps. These features make the LMC6042
both easier to design with, and provide higher speed than
products typically found in this ultra-low power class.
COMPENSATING FOR INPUT CAPACITANCE
It is quite common to use large values of feedback resistance with amplifiers with ultra-low input curent, like the
LMC6042.
Although the LMC6042 is highly stable over a wide range of
operating conditions, certain precautions must be met to
achieve the desired pulse response when a large feedback
resistor is used. Large feedback resistors and even small
values of input capacitance, due to transducers, photodiodes, and circuit board parasitics, reduce phase margins.
When high input impedances are demanded, guarding of the
LMC6042 is suggested. Guarding input lines will not only reduce leakage, but lowers stray input capacitance as well.
(See Printed-Circuit-Board Layout for High Impedance
Work).
Stability vs Capacitive Load
DS011137-44
The effect of input capacitance can be compensated for by
adding a capacitor. Place a capacitor, C
back resistor (as in
Figure 1
) such that:
, around the feed-
f
or
≤ R2 C
R1 C
IN
f
Since it is often difficult to know the exact value of CIN,Cfcan
be experimentally adjusted so that the desired pulse response is achieved. Refer to the LMC660 and the LMC662
for a more detailed discussion on compensating for input capacitance.
CAPACITIVE LOAD TOLERANCE
Direct capacitive loading will reduce the phase margin of
many op-amps. A pole in the feedback loop is created by the
combination of the op-amp’s output impedance and the capacitive load. This pole induces phase lag at the unity-gain
crossover frequency of the amplifier resulting in either an oscillatory or underdamped pulse response. With a few external components, op amps can easily indirectly drive capacitive loads, as shown in
Figure 2
.
DS011137-5
FIGURE 1. Cancelling the Effect of Input Capacitance
DS011137-6
FIGURE 2. LMC6042 Noninverting Gain of 10 Amplifier,
Compensated to Handle Capacitive Loads
Figure 2
In the circuit of
, R1 and C1 serve to counteract the
loss of phase margin by feeding the high frequency compo-
www.national.com7

Applications Hints (Continued)
nent of the output signal back to the amplifier’s inverting input, thereby preserving phase margin in the overall feedback
loop.
Capacitive load driving capability is enhanced by using a
pull up resistor to V
conducting 10 µA or more will significantly improve capacitive load responses. The value of the pull up resistor must be
determined based on the current sinking capability of the
amplifier with respect to the desired output swing. Open loop
gain of the amplifier can also be affected by the pull up resistor (see Electrical Characteristics).
+
(
Figure 3
). Typically a pull up resistor
DS011137-18
FIGURE 3. Compensating for Large
Capacitive Loads with a Pull Up Resistor
PRINTED-CIRCUIT-BOARD LAYOUT FOR
HIGH-IMPEDANCE WORK
It is generally recognized that any circuit which must operate
with less than 1000 pA of leakage current requires special
layout of the PC board. When one wishes to take advantage
of the ultra-low bias current of the LMC6042, typically less
than 2 fA, it is essential to have an excellent layout. Fortunately, the techniques of obtaining low leakages are quite
simple. First, the user must not ignore the surface leakage of
the PC board, even though it may sometimes appear acceptably low, because under conditions of high humidity or dust
or contamination, the surface leakage will be appreciable.
To minimize the effect of any surface leakage, lay out a ring
of foil completely surrounding the LMC6042’s inputs and the
terminals of capacitors, diodes, conductors, resistors, relay
terminals etc. connected to the op-amp’s inputs, as in
4
. To have a significant effect, guard rings should be placed
Figure
on both the top and bottom of the PC board. This PC foil
must then be connected to a voltage which is at the same
voltage as the amplifier inputs, since no leakage current can
flow between two points at the same potential. For example,
a PC board trace-to-pad resistance of 10
12
Ω, which is normally considered a very large resistance, could leak 5 pA if
the trace were a 5V bus adjacent to the pad of the input. This
would cause a 100 times degradation from the LMC6042’s
actual performance. However, if a guard ring is held within 5
mV of the inputs, then even a resistance of 10
cause only 0.05 pA of leakage current. See
Figure 5
11
Ω would
for typical connections of guard rings for standard op-amp
configurations.
DS011137-7
FIGURE 4. Example of Guard Ring
in P.C. Board Layout
DS011137-8
Inverting Amplifier
DS011137-10
Non-Inverting Amplifier
DS011137-9
Follower
FIGURE 5. Typical Connections of Guard Rings
www.national.com 8

Applications Hints (Continued)
The designer should be aware that when it is inappropriate
to lay out a PC board for the sake of just a few circuits, there
is another technique which is even better than a guard ring
on a PC board: Don’t insert the amplifier’s input pin into the
board at all, but bend it up in the air and use only air as an insulator. Air is an excellent insulator. In this case you may
have to forego some of the advantages of PC board construction, but the advantages are sometimes well worth the
effort of using point-to-point up-in-the-air wiring. See
6
.
Figure
probes, analytic medical instruments, magnetic field detectors, gas detectors, and silicon based pressure transducers.
The circuit in
Figure 7
is recommended for applications
where the common-mode input range is relatively low and
the differential gain will be in the range of 10 to 1000. This
two op-amp instrumentation amplifier features an independent adjustment of the gain and common-mode rejection
trim, and a total quiescent supply current of less than 20 µA.
To maintain ultra-high input impedance, it is advisable to use
ground rings and consider PC board layout an important part
of the overall system design (see Printed-Circuit-Board Layout for High Impedance Work). Referring to
put voltages are represented as a common-mode input V
plus a differential input VD.
Figure 7
, the in-
CM
Rejection of the common-mode component of the input is
accomplished by making the ratio of R1/R2 equal to R3/R4.
So that where,
(Input pins are lifted out of PC board and soldered directly to components.
All other pins connected to PC board.)
DS011137-11
FIGURE 6. Air Wiring
Typical Single-Supply Applications
+
=
(V
5.0 V
)
DC
The extremely high input impedance, and low power consumption, of the LMC6042 make it ideal for applications that
require battery-powered instrumentation amplifiers. Examples of these types of applications are hand-held pH
FIGURE 7. Two Op-Amp Instrumentation Amplifier
Asuggested design guideline is to minimize the difference of
value between R1 through R4. This will often result in improved resistor tempco, amplifier gain, and CMRR over temperature. If RN=R1=R2=R3=R4 then the gain equation
can be simplified:
Due to the “zero-in, zero-out” performance of the LMC6042,
and output swing rail-rail, the dynamic range is only limited to
the input common-mode range of 0V to V
case at room temperature. This feature of the LMC6042
− 2.3V, worst
S
makes it an ideal choice for low-power instrumentation systems.
A complete instrumentation amplifier designed for a gain of
100 is shown in
Figure 8
. Provisions have been made for low
sensitivity trimming of CMRR and gain.
DS011137-12
www.national.com9

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
FIGURE 8. Low-Power Two-Op-Amp
Instrumentation Amplifier
FIGURE 9. Low-Leakage Sample and Hold
+
=
5.0 V
) (Continued)
DC
DS011137-13
DS011137-14
FIGURE 10. Instrumentation Amplifier
www.national.com 10
DS011137-15

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
FIGURE 11. 1 Hz Square Wave Oscillator
FIGURE 12. AC Coupled Power Amplifier
+
=
5.0 V
) (Continued)
DC
DS011137-16
DS011137-17
www.national.com11
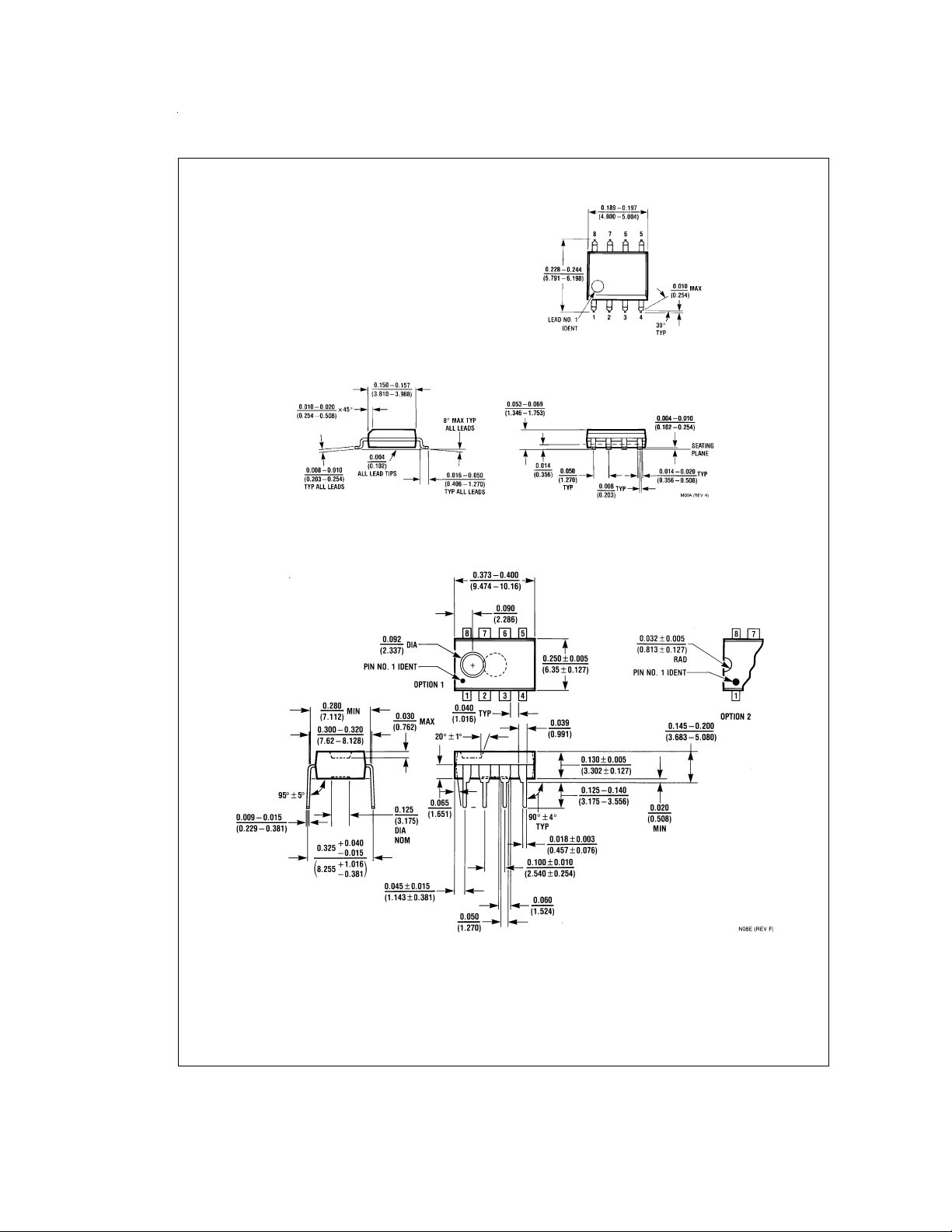
Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
8-Pin Small Outline Package
Order Number LMC6042AIM or LMC6042IM
NS Package Number M08A
8-Pin Molded Dual-In-Line Package
Order Number LMC6042AIN or LMC6042IN
NS Package Number N08E
www.national.com 12
Notes
LMC6042 CMOS Dual Micropower Operational Amplifier
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT
DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or
systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life, and
whose failure to perform when properly used in
accordance with instructions for use provided in the
2. A critical component is any component of a life
support device or system whose failure to perform
can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of
the life support device or system, or to affect its
safety or effectiveness.
labeling, can be reasonably expected to result in a
significant injury to the user.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
 Loading...
Loading...