
LM3915
Dot/Bar Display Driver
General Description
The LM3915 is a monolithic integrated circuit that senses
analog voltage levels and drives ten LEDs, LCDs or vacuum
fluorescent displays, providing a logarithmic 3 dB/step analog display. One pin changes the display from a bar graph to
a moving dot display. LED current drive is regulated and
programmable, eliminating the need for current limiting resistors. The whole display system can operate from a single
supply as low as 3V or as high as 25V.
The IC contains an adjustable voltage reference and an
accurate ten-step voltage divider. The high-impedance input
buffer accepts signals down to ground and up to within 1.5V
of the positive supply. Further, it needs no protection against
inputs of
parators referenced to the precision divider. Accuracy is
typically better than 1 dB.
The LM3915’s 3 dB/step display is suited for signals with
wide dynamic range, such as audio level, power, light intensity or vibration. Audio applications include average or peak
level indicators, power meters and RF signal strength
meters. Replacing conventional meters with an LED bar
graph results in a faster responding, more rugged display
with high visibility that retains the ease of interpretation of an
analog display.
The LM3915 is extremely easy to apply. A 1.2V full-scale
meter requires only one resistor in addition to the ten LEDs.
One more resistor programs the full-scale anywhere from
1.2V to 12V independent of supply voltage. LED brightness
is easily controlled with a single pot.
±
35V. The input buffer drives 10 individual com-
February 2001
The LM3915 is very versatile. The outputs can drive LCDs,
vacuum fluorescents and incandescent bulbs as well as
LEDs of any color. Multiple devices can be cascaded for a
dot or bar mode display with a range of 60 or 90 dB.
LM3915s can also be cascaded with LM3914s for a linear/
log display or with LM3916s for an extended-range VU
meter.
Features
n 3 dB/step, 30 dB range
n Drives LEDs, LCDs, or vacuum fluorescents
n Bar or dot display mode externally selectable by user
n Expandable to displays of 90 dB
n Internal voltage reference from 1.2V to 12V
n Operates with single supply of 3V to 25V
n Inputs operate down to ground
n Output current programmable from 1 mA to 30 mA
n Input withstands
n Outputs are current regulated, open collectors
n Directly drives TTL or CMOS
n The internal 10-step divider is floating and can be
referenced to a wide range of voltages
The LM3915 is rated for operation from 0˚C to +70˚C. The
LM3915N-1 is available in an 18-lead molded DIP package.
±
35V without damage or false outputs
LM3915 Dot/Bar Display Driver
© 2004 National Semiconductor Corporation DS005104 www.national.com
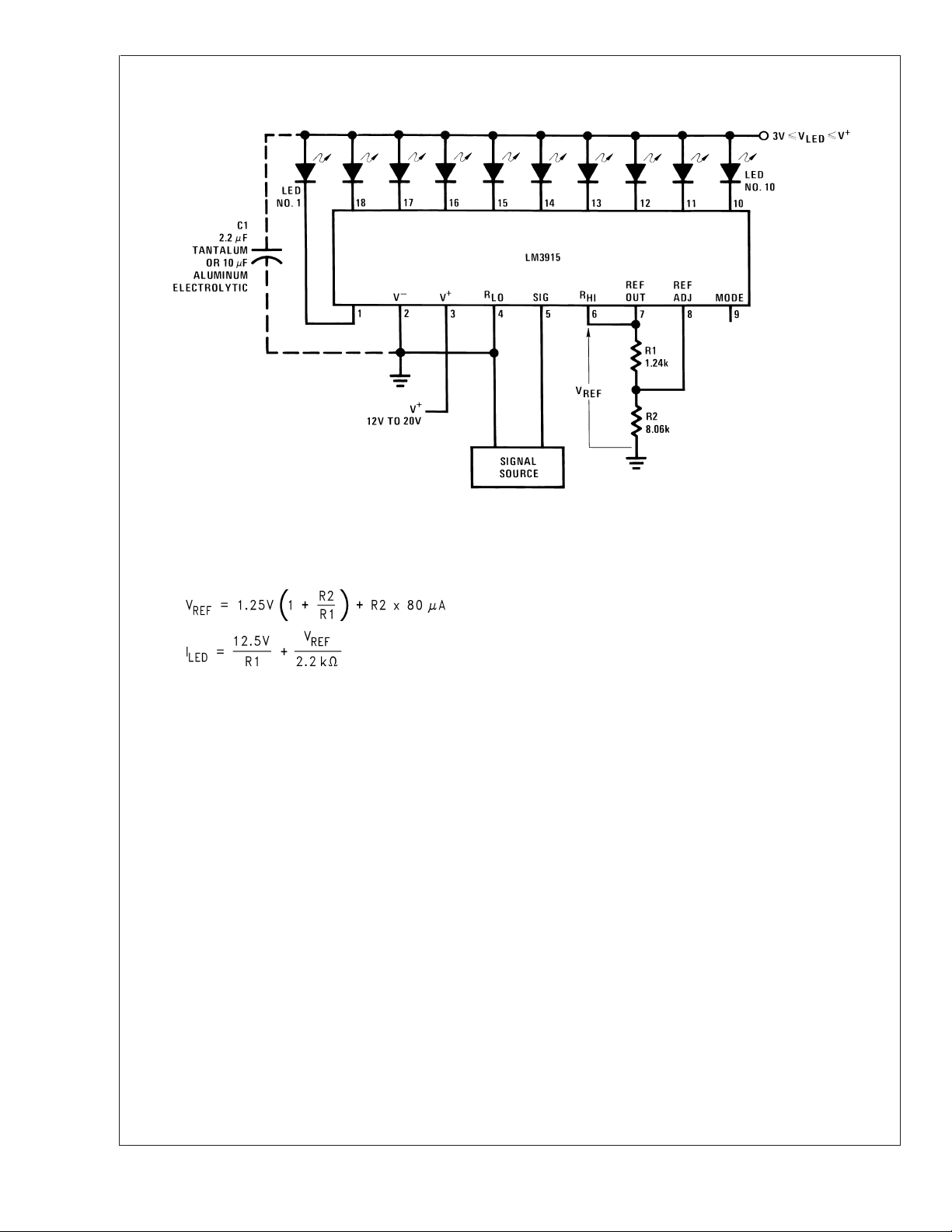
Typical Applications
LM3915
0V to 10V Log Display
Notes: Capacitor C1 is required if leads to the LED supply are 6" or longer.
Circuit as shown is wired for dot mode. For bar mode, connect pin 9 to pin 3. V
dissipation.
00510401
must be kept below 7V or dropping resistor should be used to limit IC power
LED
www.national.com 2
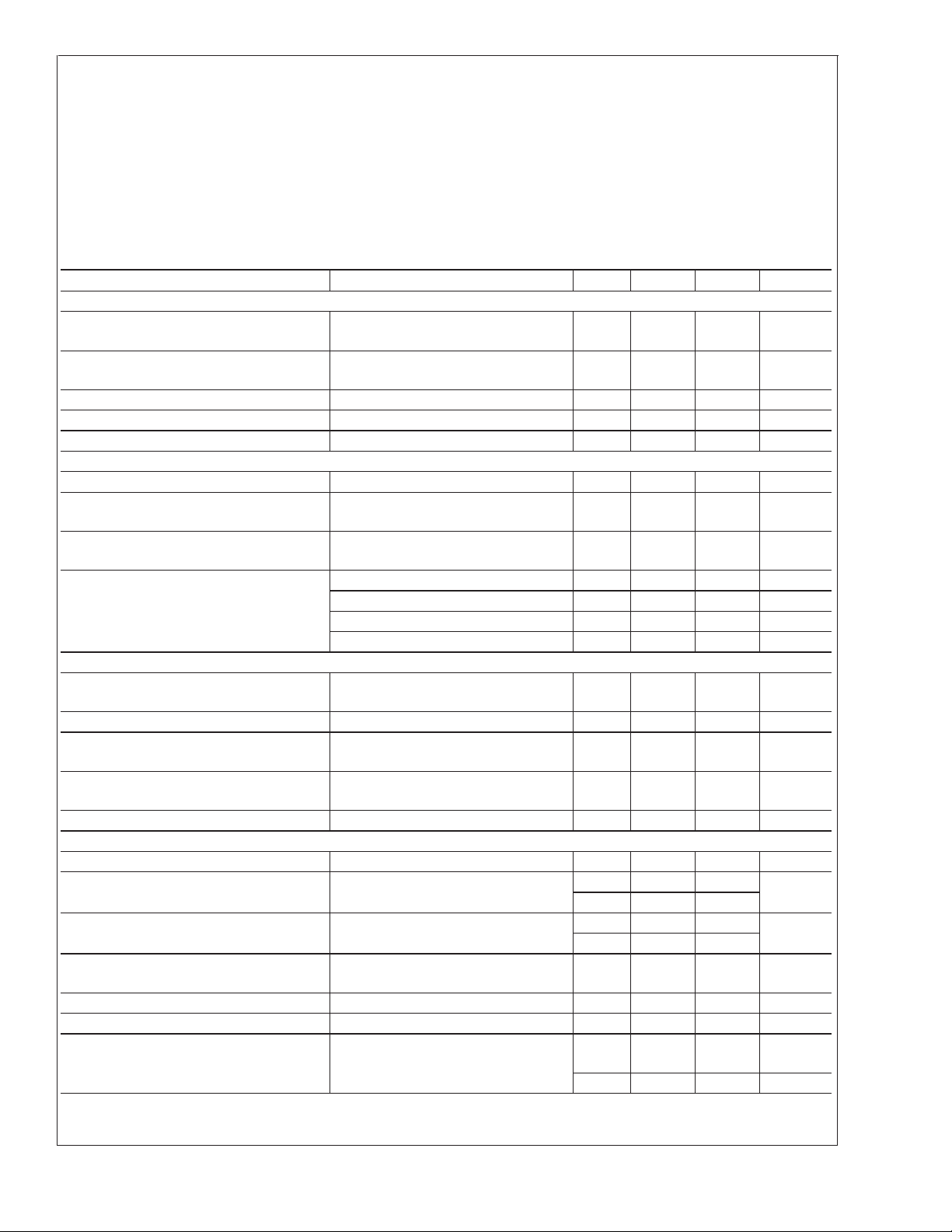
LM3915
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Power Dissipation (Note 6)
Molded DIP(N) 1365 mW
Input Signal Overvoltage (Note 4)
Divider Voltage −100 mV to V
Reference Load Current 10 mA
Storage Temperature Range −55˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 10 sec.) 260˚C
±
35V
Supply Voltage 25V
Voltage on Output Drivers 25V
Electrical Characteristics (Notes 2, 4)
Parameter Conditions (Note 2) Min Typ Max Units
COMPARATOR
Offset Voltage, Buffer and First
Comparator
Offset Voltage, Buffer and Any Other
Comparator
Gain (∆I
/∆VIN)I
LED
Input Bias Current (at Pin 5) 0V ≤ V
Input Signal Overvoltage No Change in Display −35 35 V
VOLTAGE-DIVIDER
Divider Resistance Total, Pin 6 to 4 16 28 36 kΩ
Relative Accuracy (Input Change Between
Any Two Threshold Points)
Absolute Accuracy at Each Threshold
Point
VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage 0.1 mA ≤ I
Line Regulation 3V ≤ V
Load Regulation 0.1 mA ≤ I
Output Voltage Change with
Temperature
Adjust Pin Current 75 120 µA
OUTPUT DRIVERS
LED Current V
LED Current Difference (Between
Largest and Smallest LED Currents)
LED Current Regulation 2V ≤ V
Dropout Voltage I
Saturation Voltage I
Output Leakage, Each Collector (Bar Mode) (Note 5) 0.1 10 µA
Output Leakage
Pins 10– 18
Pin 1 60 150 450 µA
0V ≤ V
=1mA
I
LED
0V ≤ V
=1mA
I
LED
L(REF)
(Note 3)
RLO=VRHI
RLO=VRHI
= 2 mA, I
≤ (V+− 1.5V) 25 100 nA
IN
≤ 12V,
≤ 12V,
= 10 mA 3 8 mA/mV
LED
310mV
315mV
2.0 3.0 4.0 dB
(Note 3)
V
= −3, −6 dB −0.5 +0.5 dB
IN
V
= −9 dB −0.5 +0.65 dB
IN
V
= −12, −15, −18 dB −0.5 +1.0 dB
IN
V
= −21, −24, −27 dB −0.5 +1.5 dB
IH
≤ 4 mA,
+
=V
V
+
=V
V
0˚C ≤ T
+
=V
V
+
=V
V
LED
V
LED
=20mA
I
LED
LED(ON)
∆I
LED
= 2.0 mA, I
LED
L(REF)
=5V
LED
+
≤ 18V 0.01 0.03 %/V
≤ 4 mA,
L(REF)
=5V
LED
≤ +70˚C, I
A
=5V
LED
= 5V, I
LED
= 5V, I
LED
= 5V, I
LED
≤ 17V, I
LED
=20mA,@V
=2mA
20 mA
= 1 mA,
L(REF)
= 1 mA 7 10 13 mA
L(REF)
=2mA
LED
= 5V,
LED
=2mA
= 0.4 mA 0.15 0.4 V
L(REF)
1.2 1.28 1.34 V
0.4 2 %
1%
0.12 0.4
1.2 3
0.1 0.25
13
1.5 V
(Dot Mode) (Note 5)
0.1 10 µA
mA
mA
+
www.national.com3
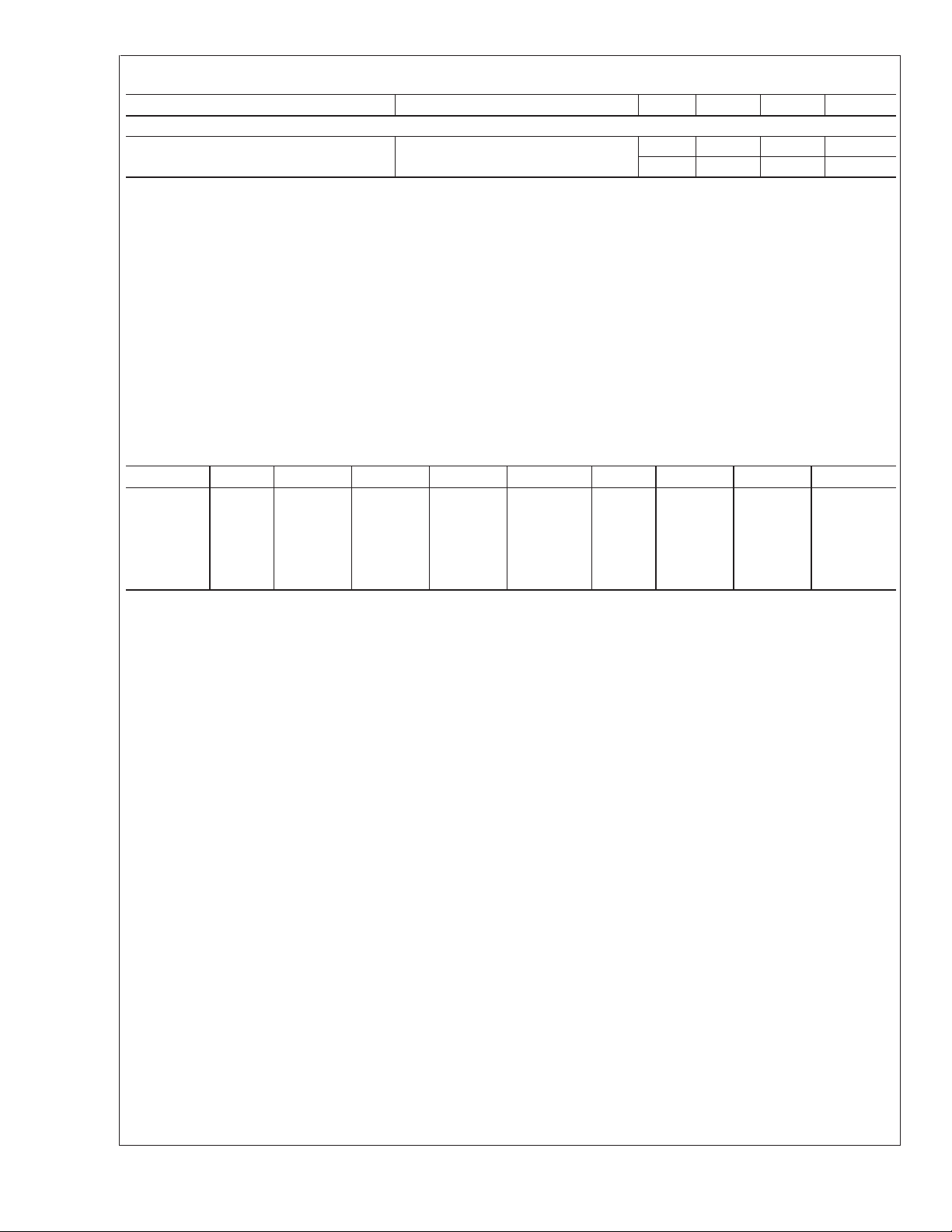
Electrical Characteristics (Notes 2, 4) (Continued)
LM3915
SUPPLY CURRENT
Standby Supply Current
(All Outputs Off)
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is
functional, but do not guarantee specific performance limits. Electrical Characteristics state DC and AC electrical specifications under particular test conditions which
guarantee specific performance limits. This assumes that the device is within the Operating Ratings. Specifications are not guaranteed for parameters where no limit
is given, however, the typical value is a good indication of device performance.
Note 2: Unless otherwise stated, all specifications apply with the following conditions:
3V
≤ V+≤ 20 V
DC
≤ V
3V
DC
−0.015V ≤ V
Note 3: Accuracy is measured referred to 0 dB = + 10.000 V
comparator offset voltage may add significant error. See table for threshold voltages.
Note 4: Pin 5 input current must be limited to
Note 5: Bar mode results when pin 9 is within 20 mV of V
disabled if pin 9 is pulled 0.9V or more below V
Note 6: The maximum junction temperature of the LM3915 is 100˚C. Devices must be derated for operation at elevated temperatures. Junction to ambient thermal
resistance is 55˚C/W for the molded DIP (N package).
Parameter Conditions (Note 2) Min Typ Max Units
+
LED
RHI
≤ V
≤ 12 V
DC
+
−0.015V ≤ V
V
REF,VRHI,VRLO
0V ≤ VIN≤ V+− 1.5V
DC
V
= +5V, I
+
= +20V, I
V
≤ 12 V
RLO
≤ (V+− 1.5V) For higher power dissipations, pulse testing is used.
±
3 mA. The addition of a 39k resistor in series with pin 5 allows±100V signals without damage.
LED
TA= 25˚C, I
DC
at pin 5, with + 10.000 VDCat pin 6, and 0.000 VDCat pin 4. At lower full scale voltages, buffer and
DC
+
. Dot mode results when pin 9 is pulled at least 200 mV below V+. LED #10 (pin 10 output current) is
.
= 0.2 mA
L(REF)
= 1.0 mA
L(REF)
= 0.2 mA, pin 9 connected to pin 3 (bar mode).
L(REF)
2.4 4.2 mA
6.1 9.2 mA
Threshold Voltage (Note 3)
Output dB Min Typ Max Output dB Min Typ Max
1 −27 0.422 0.447 0.531 6 −12 2.372 2.512 2.819
2 −24 0.596 0.631 0.750 7 −9 3.350 3.548 3.825
3 −21 0.841 0.891 1.059 8 −6 4.732 5.012 5.309
4 −18 1.189 1.259 1.413 9 −3 6.683 7.079 7.498
5 −15 1.679 1.778 1.995 10 0 9.985 10 10.015
www.national.com 4
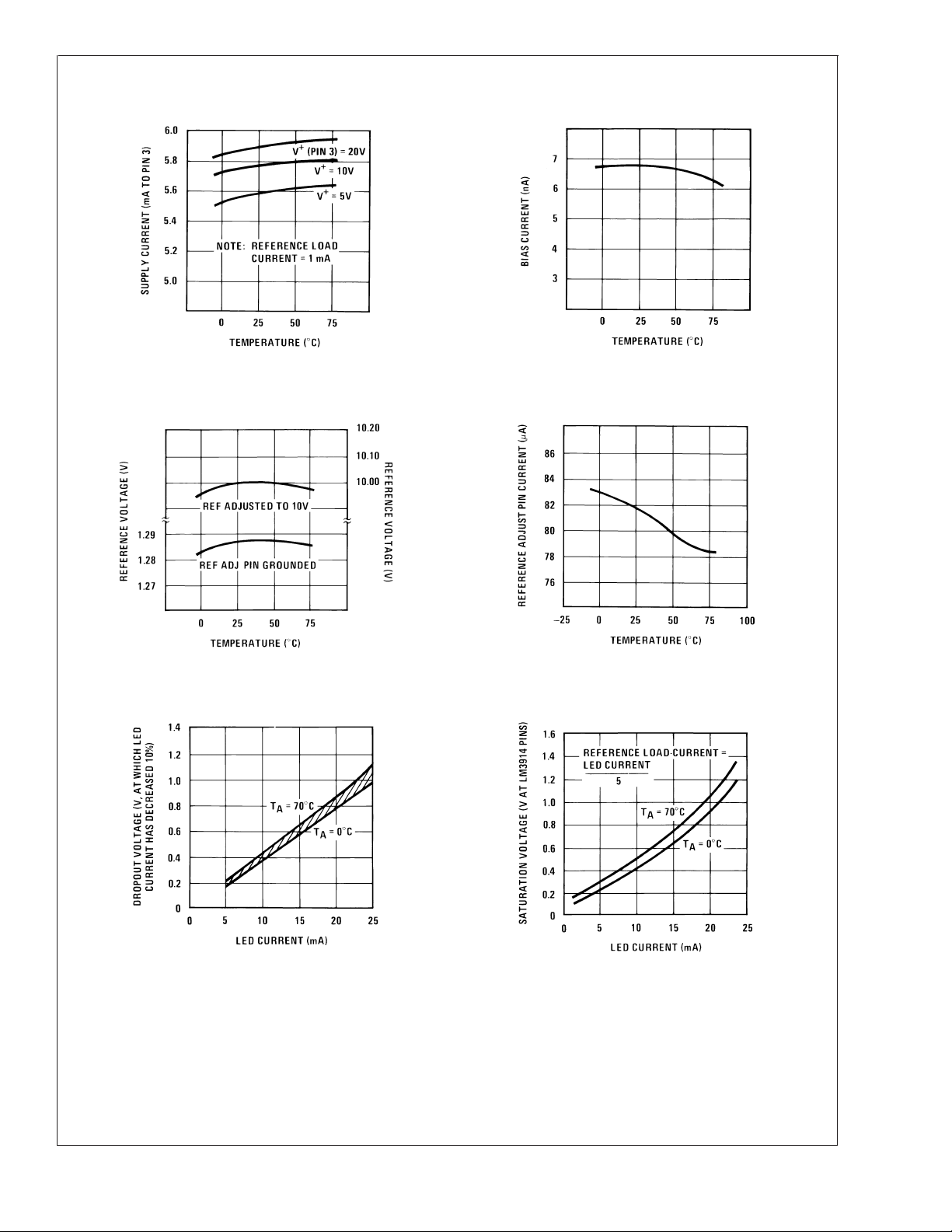
Typical Performance Characteristics
Supply Current vs Temperature Operating Input Bias Current vs Temperature
LM3915
Reference Voltage vs
Temperature
LED Current-Regulation
Dropout
00510434
00510436
00510435
Reference Adjust Pin
Current vs Temperature
00510437
LED Driver Saturation
Voltage
00510438
00510439
www.national.com5
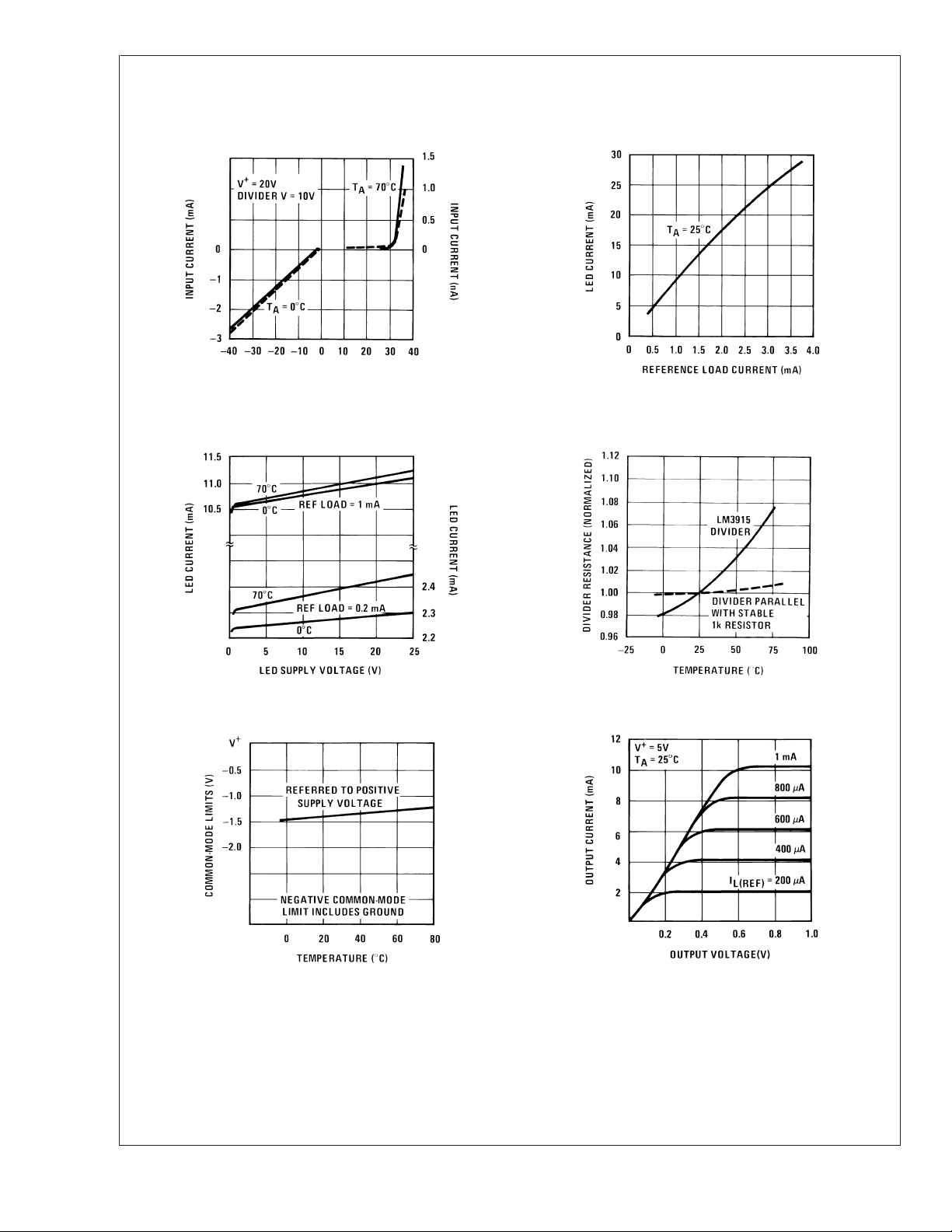
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
LM3915
Input Current Beyond
Signal Range (Pin 5)
LED Driver Current
Regulation
LED Current vs
Reference Loading
00510440
00510441
Total Divider Resistance
vs Temperature
00510442
Common-Mode Limits Output Characteristics
00510444
00510443
00510445
www.national.com 6
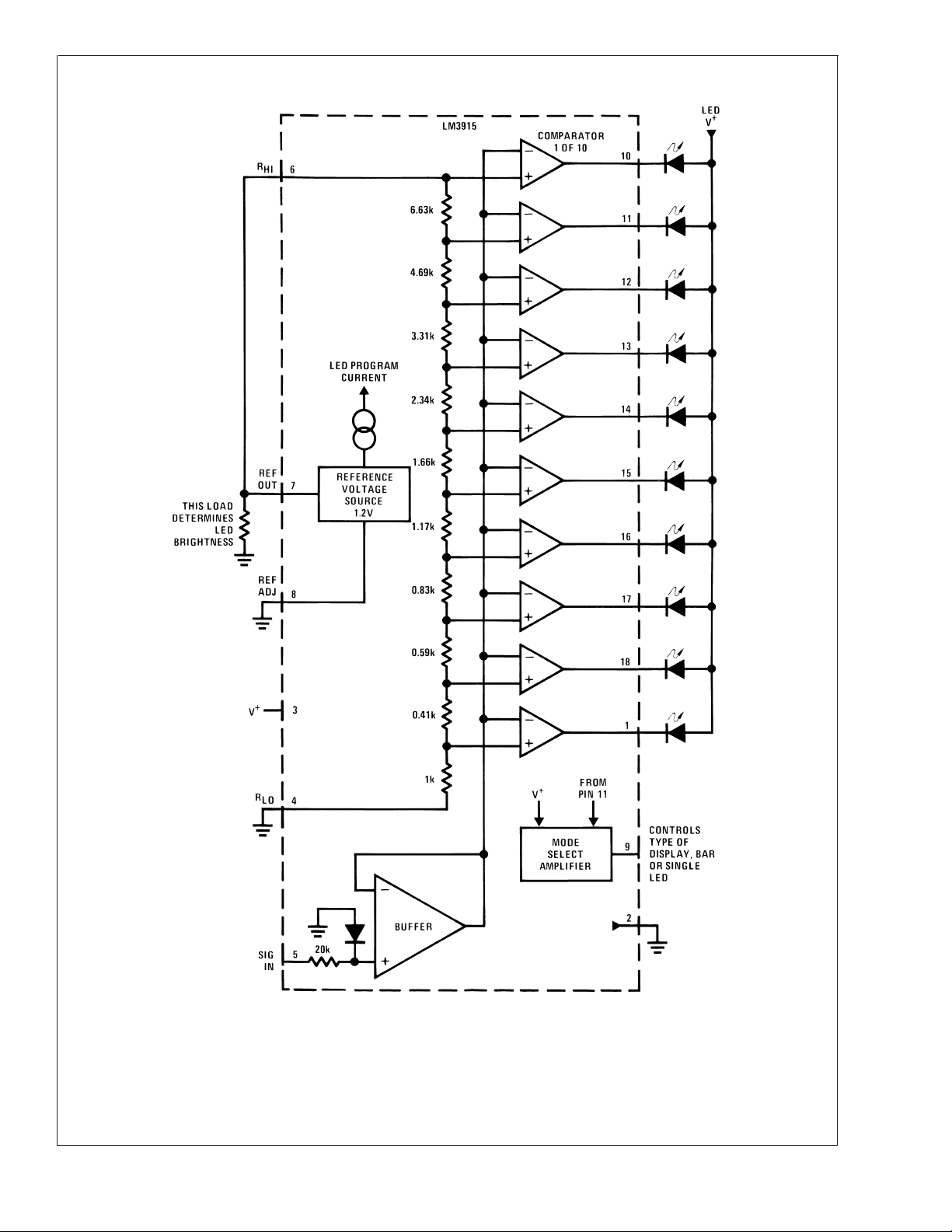
Block Diagram (Showing Simplest Application)
LM3915
00510404
www.national.com7
Functional Description
The simplified LM3915 block diagram is included to give the
LM3915
general idea of the circuit’s operation. A high input impedance buffer operates with signals from ground to 12V, and is
protected against reverse and overvoltage signals. The signal is then applied to a series of 10 comparators; each of
which is biased to a different comparison level by the resistor
string.
In the example illustrated, the resistor string is connected to
the internal 1.25V reference voltage. In this case, for each
3 dB that the input signal increases, a comparator will switch
on another indicating LED. This resistor divider can be connected between any 2 voltages, providing that they are at
least 1.5V below V
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
The reference is designed to be adjustable and develops a
nominal 1.25V between the REF OUT (pin 7) and REF ADJ
(pin 8) terminals. The reference voltage is impressed across
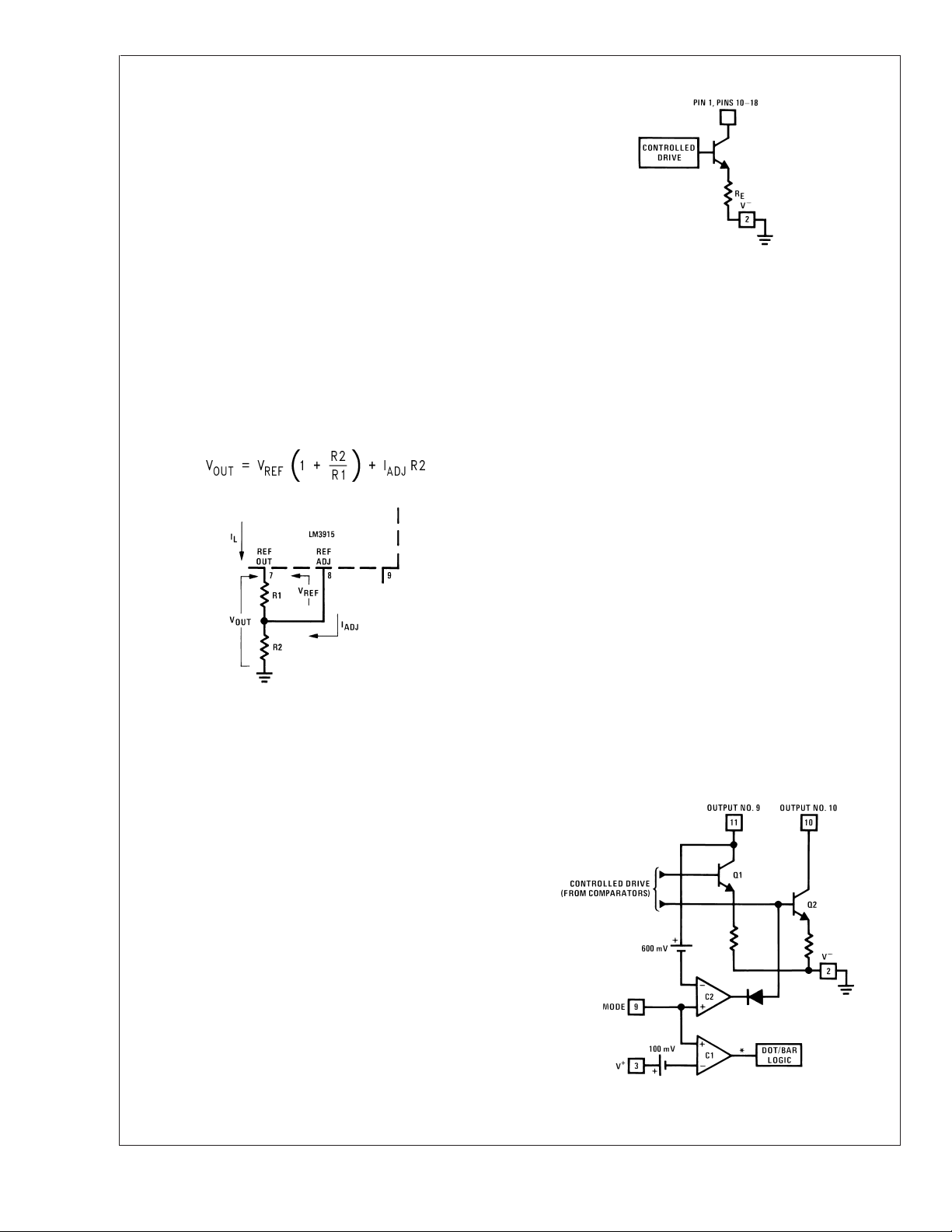
program resistor R1 and, since the voltage is constant, a
constant current I
R2 giving an output voltage of:
Since the 120 µA current (max) from the adjust terminal
represents an error term, the reference was designed to
minimize changes of this current with V
For correct operation, reference load current should be between 80 µA and 5 mA. Load capacitance should be less
than 0.05 µF.
+
and no lower than V−.
then flows through the output set resistor
1
00510405
+
and load changes.
LM3915 Output Circuit
00510406
Outputs may be run in saturation with no adverse effects,
making it possible to directly drive logic. The effective saturation resistance of the output transistors, equal to R
plus
E
the transistors’ collector resistance, is about 50Ω. It’s also
possible to drive LEDs from rectified AC with no filtering. To
avoid oscillations, the LED supply should be bypassed with a
2.2 µF tantalum or 10 µF aluminum electrolytic capacitor.
MODE PIN USE
Pin 9, the Mode Select input, permits chaining of multiple
LM3915s, and controls bar or dot mode operation. The
following tabulation shows the basic ways of using this input.
Other more complex uses will be illustrated in the applications.
Bar Graph Display: Wire Mode Select (pin 9) directly to pin
+
pin).
3(V
Dot Display, Single LM3915 Driver: Leave the Mode Select
pin open circuit.
Dot Display, 20 or More LEDs: Connect pin 9 of the first
driver in the series (i.e., the one with the lowest input voltage
comparison points) to pin 1 of the next higher LM3915 driver.
Continue connecting pin 9 of lower input drivers to pin 1 of
higher input drivers for 30 or more LED displays. The last
LM3915 driver in the chain will have pin 9 left open. All
previous drivers should have a 20k resistor in parallel with
LED #9 (pin 11 to V
LED
).
Mode Pin Functional Description
This pin actually performs two functions. Refer to the simplified block diagram below.
Block Diagram of Mode Pin Function
CURRENT PROGRAMMING
A feature not completely illustrated by the block diagram is
the LED brightness control. The current drawn out of the
reference voltage pin (pin 7) determines LED current. Approximately 10 times this current will be drawn through each
lighted LED, and this current will be relatively constant despite supply voltage and temperature changes. Current
drawn by the internal 10-resistor divider, as well as by the
external current and voltage-setting divider should be included in calculating LED drive current. The ability to modulate LED brightness with time, or in proportion to input voltage and other signals can lead to a number of novel displays
or ways of indicating input overvoltages, alarms, etc.
The LM3915 outputs are current-limited NPN transistors as
shown below. An internal feedback loop regulates the transistor drive. Output current is held at about 10 times the
reference load current, independent of output voltage and
processing variables, as long as the transistor is not saturated.
www.national.com 8
*High for bar
00510407
 Loading...
Loading...