National Semiconductor LM2622 Technical data
LM2622
600kHz/1.3MHz Step-up PWM DC/DC Converter
LM2622 600kHz/1.3MHz Step-up PWM DC/DC Converter
May 2004
General Description
The LM2622 is a step-up DC/DC converter with a 1.6A, 0.2Ω
internal switch and pin selectable operating frequency. With
the ability to convert 3.3V to multiple outputs of 8V, -8V, and
23V, the LM2622 is an ideal part for biasing TFT displays.
The LM2622 can be operated at switching frequencies of
600kHz and 1.3MHz allowing for easy filtering and low noise.
An external compensation pin gives the user flexibility in
setting frequency compensation, which makes possible the
use of small, low ESR ceramic capacitors at the output. The
LM2622 is available in a low profile 8-lead MSOP package.
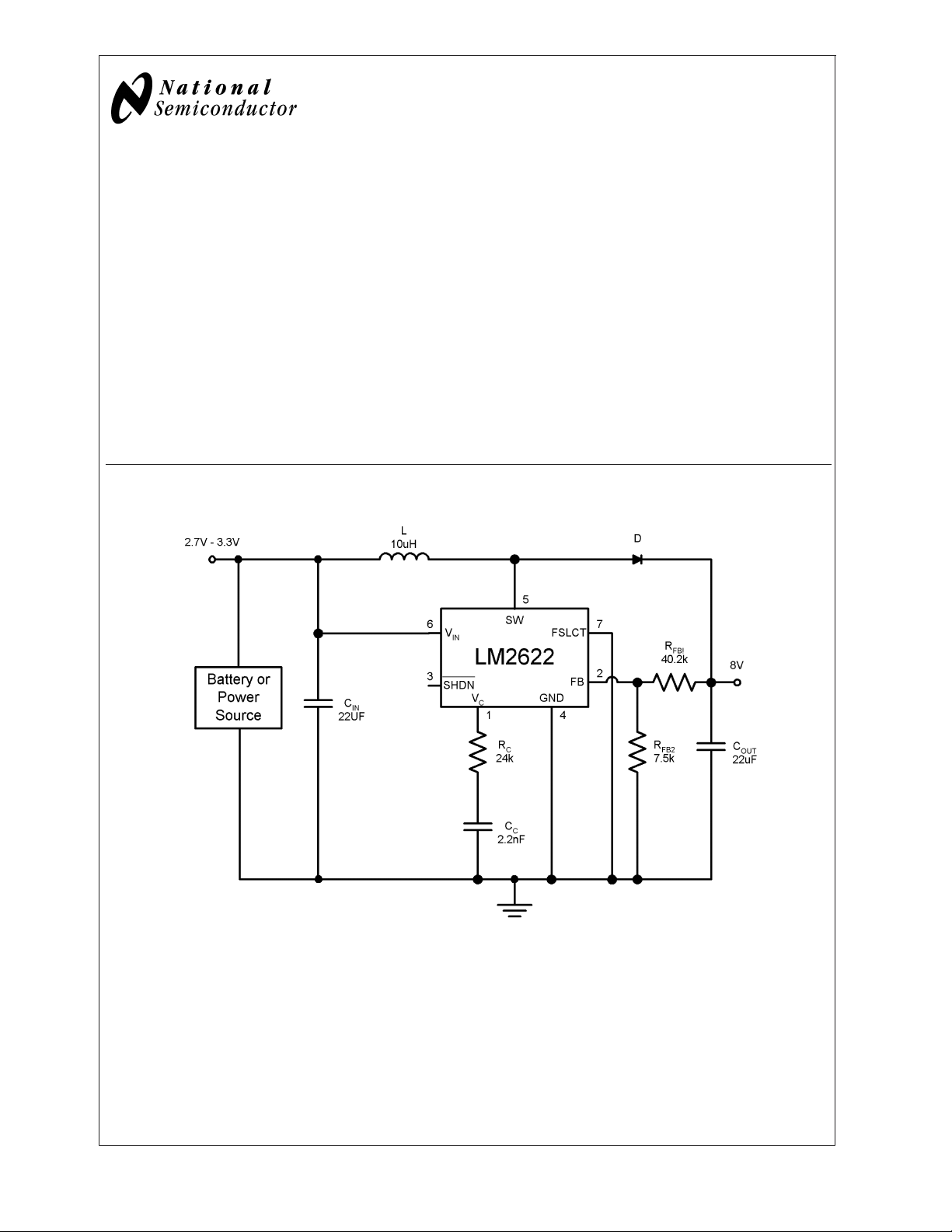
Typical Application Circuit
Features
n 1.6A, 0.2Ω, internal switch
n Operating voltage as low as 2.0V
n 600kHz/1.3MHz pin selectable frequency operation
n Over temperature protection
n 8-Lead MSOP package
Applications
n TFT Bias Supplies
n Handheld Devices
n Portable Applications
n GSM/CDMA Phones
n Digital Cameras
600 kHz Operation
© 2004 National Semiconductor Corporation DS101273 www.national.com
10127331
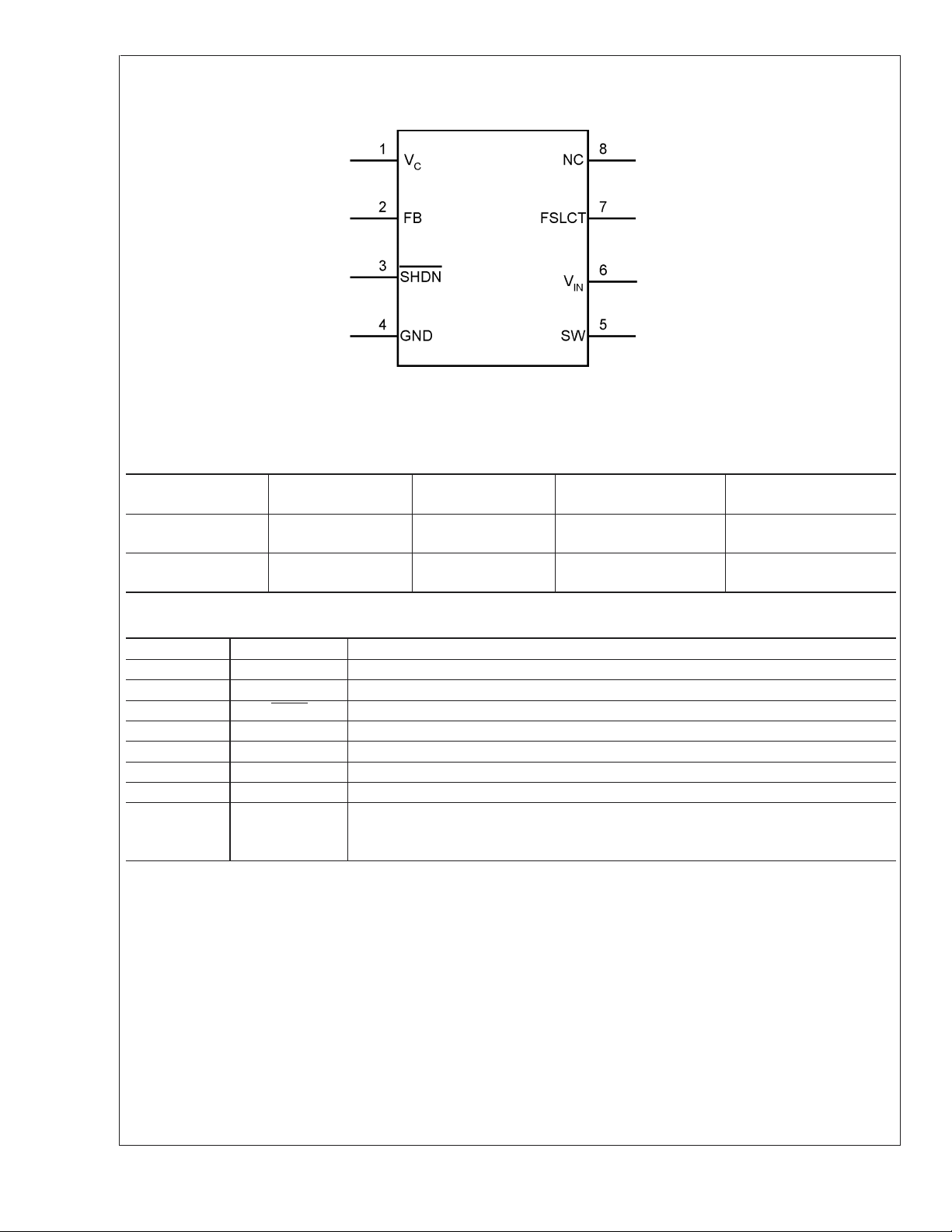
Connection Diagram
LM2622
Top View
8-Lead Plastic MSOP
NS Package Number MUA08A
10127304
Ordering Information
Order Number Package Type NSC Package
Drawing
LM2622MM-ADJ MSOP-8 MUA08A 1000 Units, Tape and
LM2622MMX-ADJ MSOP-8 MUA08A 3500 Units, Tape and
Supplied As Package ID
S18B
Reel
S18B
Reel
Pin Description
Pin Name Function
1V
2 FB Output voltage feedback input.
3 SHDN
4 GND Analog and power ground.
5 SW Power switch input. Switch connected between SW pin and GND pin.
6V
7 FSLCT Switching frequency select input. V
8 NC Connect to ground or leave open. Connect to GND pin directly beneath the device if
C
IN
Compensation network connection. Connected to the output of the voltage error amplifier.
Shutdown control input, active low.
Analog power input.
= 1.3MHz. Ground = 600kHz.
IN
possible. If other traces are in the way or it is otherwise not possible to directly connect it
to GND leave this pin open and shield it from sources of EMI.
www.national.com 2
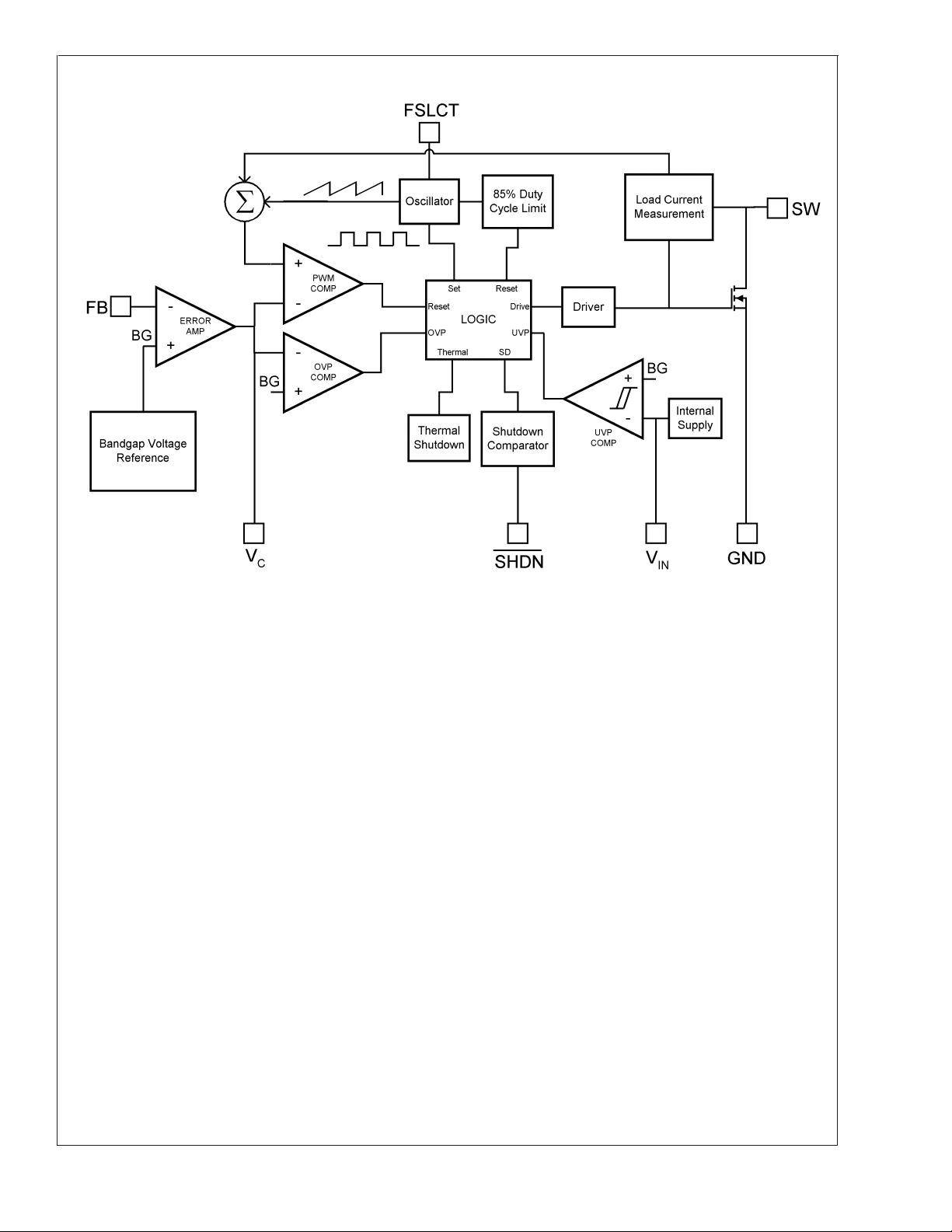
Block Diagram
LM2622
10127303
www.national.com3

Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
LM2622
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
V
IN
SW Voltage 18V
12V
Vapor Phase (60 sec.) 215˚C
Infrared (15 sec.) 220˚C
ESD Susceptibility
(Note 3)
Human Body Model 2kV
Machine Model 200V
FB Voltage 7V
V
Voltage 7V
C
SHDN Voltage
7V
FSLCT 12V
Maximum Junction
150˚C
Temperature
Power Dissipation(Note 2) Internally Limited
Operating Conditions
Operating Junction
Temperature Range (Note 4) −40˚C to +125˚C
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
Supply Voltage 2V to 12V
Lead Temperature 300˚C
Electrical Characteristics
Specifications in standard type face are for TJ= 25˚C and those with boldface type apply over the full Operating Temperature Range (T
Symbol Parameter Conditions
I
Q
V
FB
I
(Note 6) Switch Current Limit VIN= 2.7V (Note 7) 1.0 1.65 2.3 A
CL
∆V
/∆I
O
LOAD
%V
/∆VINFeedback Voltage Line
FB
I
B
V
IN
g
m
A
V
D
MAX
f
S
I
SHDN
I
L
R
DSON
Th
SHDN
UVP On Threshold 1.8 1.92 2.0 V
θ
JA
Note 1: Absolute maximum ratings are limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings are conditions for which the device is intended to
be functional, but device parameter specifications may not be guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: The maximum allowable power dissipation is a function of the maximum junction temperature, T
and the ambient temperature, T
at any ambient temperature is calculated using: P
temperature, and the regulator will go into thermal shutdown.
Note 3: The human body model is a 100 pF capacitor discharged through a 1.5kΩ resistor into each pin. The machine model is a 200pF capacitor discharged
directly into each pin.
= −40˚C to +125˚C)Unless otherwise specified. VIN=2.0V and IL= 0A, unless otherwise specified.
J
Min
(Note 4)
Typ
(Note 5)
Max
(Note 4)
Quiescent Current FB = 0V (Not Switching) 1.3 2.0 mA
V
=0V 5 10 µA
SHDN
Feedback Voltage 1.2285 1.26 1.2915 V
Load Regulation VIN= 3.3V 6.7 mV/A
2.0V ≤ VIN≤ 12.0V 0.013 0.1 %/V
Regulation
FB Pin Bias Current (Note 8) 0.5 20 nA
Input Voltage Range 212V
Error Amp Transconductance ∆I = 5µA 40 135 290 µmho
Error Amp Voltage Gain 135 V/V
Maximum Duty Cycle 78 85 %
Switching Frequency FSLCT = Ground 480 600 720 kHz
Shutdown Pin Current V
FSLCT = V
SHDN=VIN
V
SHDN
IN
=0V −0.5 -1
1 1.25 1.5 MHz
0.01 0.1 µA
Switch Leakage Current VSW= 18V 0.01 3 µA
Switch R
DSON
VIN= 2.7V, ISW= 1A 0.2 0.4 Ω
SHDN Threshold Output High 0.9 0.6 V
Output Low 0.6 0.3 V
Off Threshold 1.7 1.82 1.9 V
Thermal Resistance Junction to Ambient(Note 9) 235 ˚C/W
Junction to Ambient(Note 10) 225
Junction to Ambient(Note 11) 220
Junction to Ambient(Note 12) 200
Junction to Ambient(Note 13) 195
(MAX), the junction-to-ambient thermal resistance, θJA,
. See the Electrical Characteristics table for the thermal resistance of various layouts. The maximum allowable power dissipation
A
(MAX) = (T
D
J(MAX)−TA
)/θJA. Exceeding the maximum allowable power dissipation will cause excessive die
J
Units
www.national.com 4
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Note 4: All limits guaranteed at room temperature (standard typeface) and at temperature extremes (bold typeface). All room temperature limits are 100%
production tested. All limits at temperature extremes are guaranteed via correlation using standard Statistical Quality Control (SQC) methods. All limits are used to
calculate Average Outgoing Quality Level (AOQL).
Note 5: Typical numbers are at 25˚C and represent the most likely norm.
Note 6: Duty cycle affects current limit due to ramp generator.
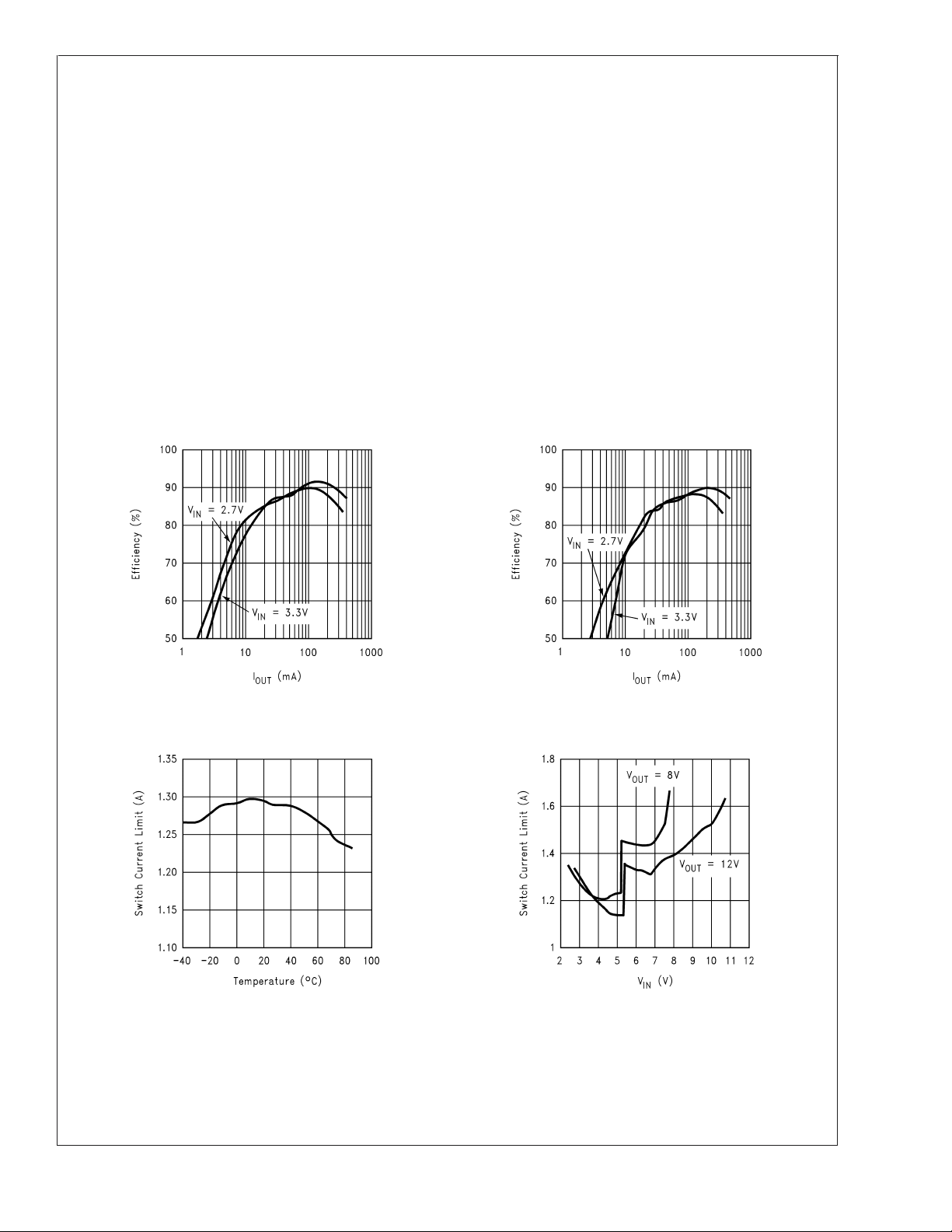
Note 7: Current limit at 0% duty cycle. See TYPICAL PERFORMANCE section for Switch Current Limit vs. V
Note 8: Bias current flows into FB pin.
Note 9: Junction to ambient thermal resistance (no external heat sink) for the MSO8 package with minimal trace widths (0.010 inches) from the pins to the circuit.
See "Scenario ’A’" in the Power Dissipation section.
Note 10: Junction to ambient thermal resistance for the MSO8 package with minimal trace widths (0.010 inches) from the pins to the circuit and approximately
0.0191 sq. in. of copper heat sinking. See "Scenario ’B’" in the Power Dissipation section.
Note 11: Junction to ambient thermal resistance for the MSO8 package with minimal trace widths (0.010 inches) from the pins to the circuit and approximately
0.0465 sq. in. of copper heat sinking. See "Scenario ’C’" in the Power Dissipation section.
Note 12: Junction to ambient thermal resistance for the MSO8 package with minimal trace widths (0.010 inches) from the pins to the circuit and approximately
0.2523 sq. in. of copper heat sinking. See "Scenario ’D’" in the Power Dissipation section.
Note 13: Junction to ambient thermal resistance for the MSO8 package with minimal trace widths (0.010 inches) from the pins to the circuit and approximately
0.0098 sq. in. of copper heat sinking on the top layer and 0.0760 sq. in. of copper heat sinking on the bottom layer, with three 0.020 in. vias connecting the planes.
See "Scenario ’E’" in the Power Dissipation section.
IN
Typical Performance Characteristics
LM2622
Efficiency vs. Load Current
= 8V, fS= 600 kHz)
(V
OUT
10127326 10127325
Switch Current Limit vs. Temperature
(V
IN
= 3.3V, V
= 8V) Switch Current Limit vs. V
OUT
Efficiency vs. Load Current
(V
= 8V, fS= 1.3 MHz)
OUT
IN
10127320
10127322
www.national.com5
 Loading...
Loading...