现货库存、技术资料、百科信息、热点资讯,精彩尽在鼎好!
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers
October 2005
General Description
The LM158 series consists of two independent, high gain,
internally frequency compensated operational amplifiers
which were designed specifically to operate from a single
power supply over a wide range of voltages. Operation from
split power supplies is also possible and the low power
supply current drain is independent of the magnitude of the
power supply voltage.
Application areas include transducer amplifiers, dc gain
blocks and all the conventional op amp circuits which now
can be more easily implemented in single power supply
systems. For example, the LM158 series can be directly
operated off of the standard +5V power supply voltage which
is used in digital systems and will easily provide the required
interface electronics without requiring the additional
power supplies.
The LM358 and LM2904 are available in a chip sized package (8-Bump micro SMD) using National’s micro SMD package technology.
±
15V
Unique Characteristics
n In the linear mode the input common-mode voltage
range includes ground and the output voltage can also
swing to ground, even though operated from only a
single power supply voltage.
n The unity gain cross frequency is temperature
compensated.
n The input bias current is also temperature compensated.
Advantages
n Two internally compensated op amps
n Eliminates need for dual supplies
n Allows direct sensing near GND and V
GND
n Compatible with all forms of logic
n Power drain suitable for battery operation
also goes to
OUT
Features
n Available in 8-Bump micro SMD chip sized package,
(See AN-1112)
n Internally frequency compensated for unity gain
n Large dc voltage gain: 100 dB
n Wide bandwidth (unity gain): 1 MHz
(temperature compensated)
n Wide power supply range:
— Single supply: 3V to 32V
— or dual supplies:
n Very low supply current drain (500 µA) — essentially
independent of supply voltage
n Low input offset voltage: 2 mV
n Input common-mode voltage range includes ground
n Differential input voltage range equal to the power
supply voltage
n Large output voltage swing
±
1.5V to±16V
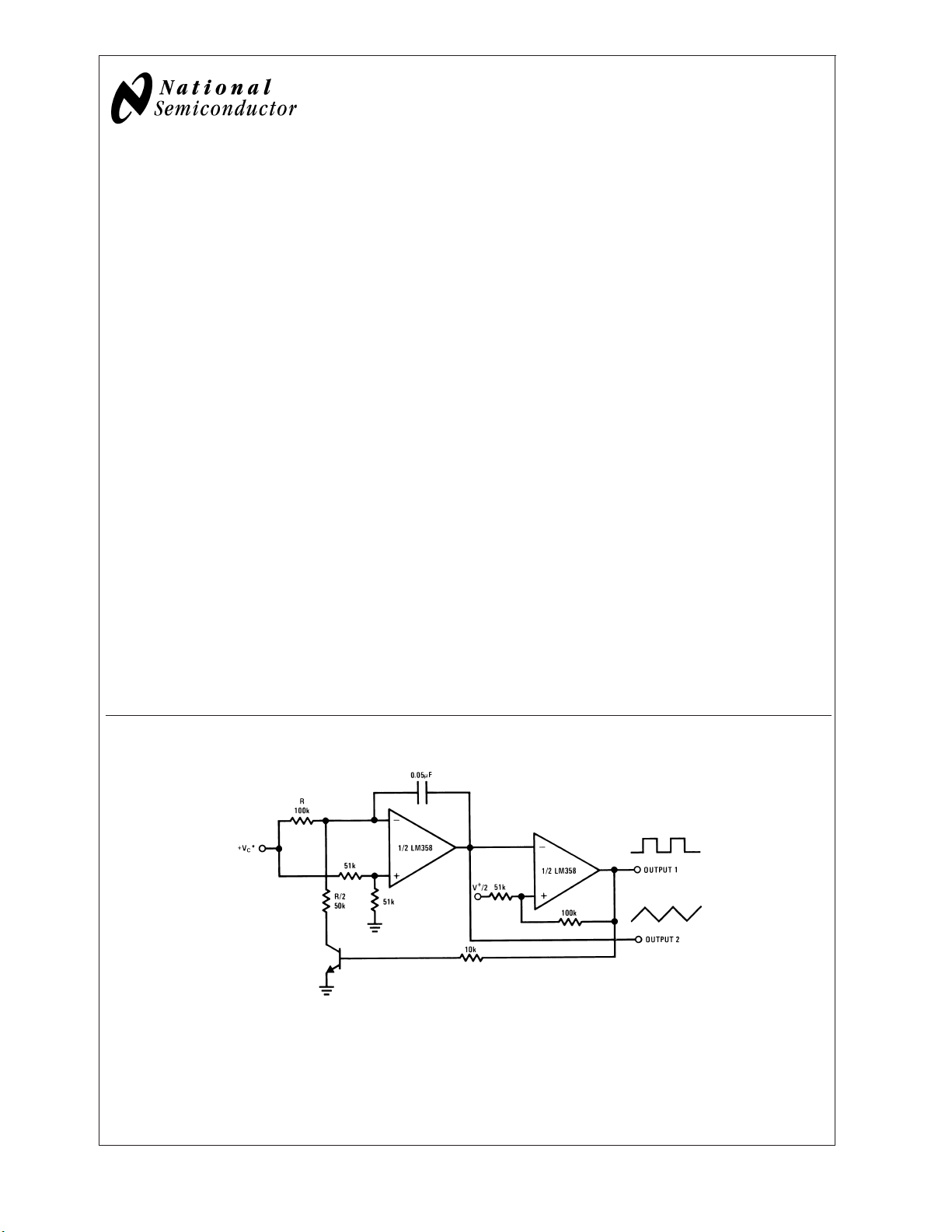
Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
00778723
© 2005 National Semiconductor Corporation DS007787 www.national.com
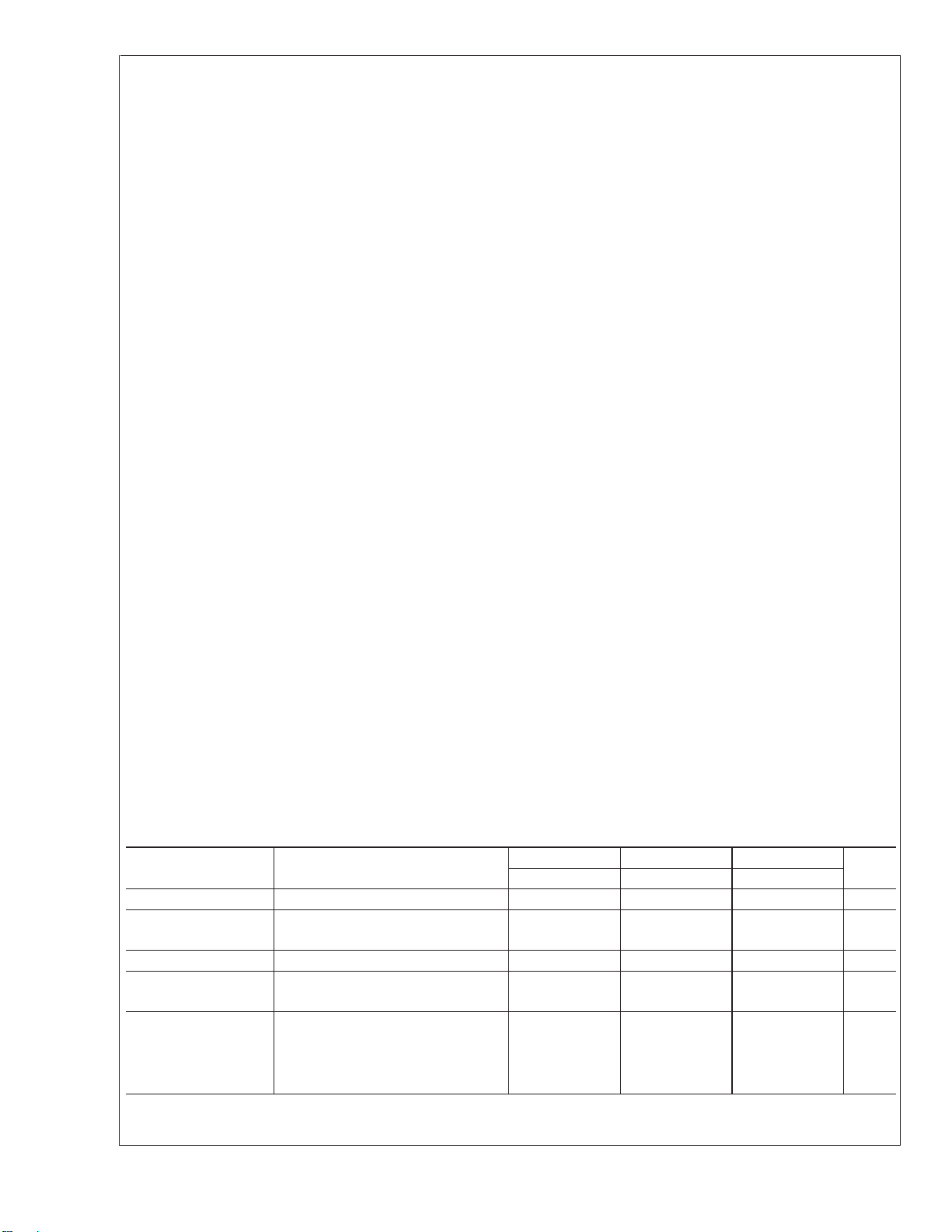
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 9)
Distributors for availability and specifications.
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National Semiconductor Sales Office/
LM158/LM258/LM358 LM2904
LM158A/LM258A/LM358A
Supply Voltage, V
+
32V 26V
Differential Input Voltage 32V 26V
Input Voltage −0.3V to +32V −0.3V to +26V
Power Dissipation (Note 1)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Molded DIP 830 mW 830 mW
Metal Can 550 mW
Small Outline Package (M) 530 mW 530 mW
micro SMD 435mW
Output Short-Circuit to GND
(One Amplifier) (Note 2)
+
V
≤ 15V and TA= 25˚C Continuous Continuous
Input Current (V
<
−0.3V) (Note 3) 50 mA 50 mA
IN
Operating Temperature Range
LM358 0˚C to +70˚C −40˚C to +85˚C
LM258 −25˚C to +85˚C
LM158 −55˚C to +125˚C
Storage Temperature Range −65˚C to +150˚C −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature, DIP
(Soldering, 10 seconds) 260˚C 260˚C
Lead Temperature, Metal Can
(Soldering, 10 seconds) 300˚C 300˚C
Soldering Information
Dual-In-Line Package
Soldering (10 seconds) 260˚C 260˚C
Small Outline Package
Vapor Phase (60 seconds) 215˚C 215˚C
Infrared (15 seconds) 220˚C 220˚C
See AN-450 “Surface Mounting Methods and Their Effect on Product Reliability” for other methods of soldering
surface mount devices.
ESD Tolerance (Note 10) 250V 250V
Electrical Characteristics
V+= +5.0V, unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions LM158A LM358A LM158/LM258 Units
Input Offset Voltage (Note 5), T
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
Input Common-Mode V
IN(+)
V
CM
IN(+)−IIN(−),VCM
+
= 30V, (Note 7) 0 V+−1.5 0 V+−1.5 0 V+−1.5 V
Voltage Range (LM2904, V
Supply Current Over Full Temperature Range
R
=∞on All Op Amps
L
+
V
= 30V (LM2904 V+= 26V) 1 2 1 2 1 2 mA
+
V
= 5V 0.5 1.2 0.5 1.2 0.5 1.2 mA
www.national.com 2
= 25˚C 1 2 2 3 2 5 mV
A
or I
IN(−),TA
= 25˚C, 20 50 45 100 45 150 nA
= 0V, (Note 6)
= 0V, TA= 25˚C 2 10 5 30 3 30 nA
+
= 26V), TA= 25˚C
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
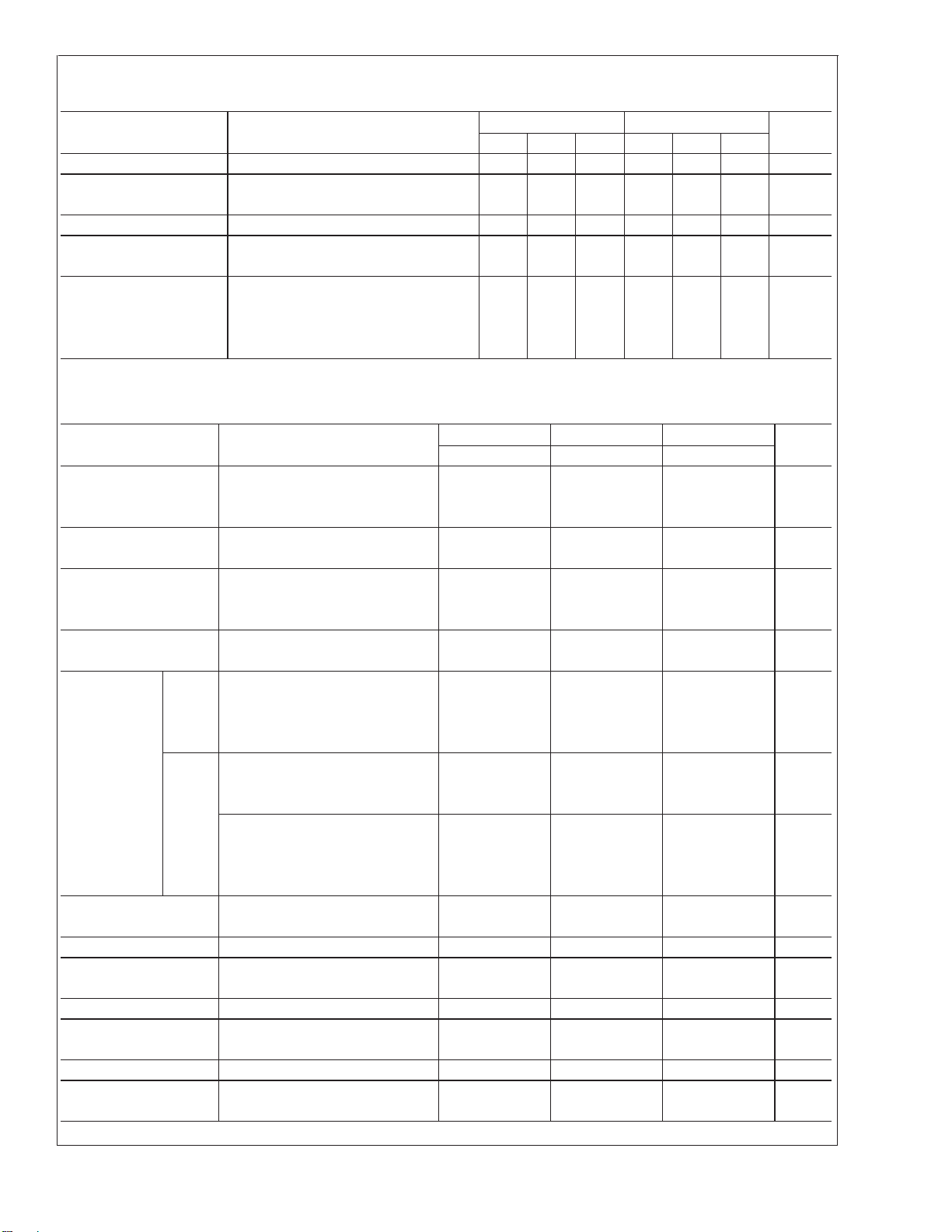
Electrical Characteristics
V+= +5.0V, unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions LM358 LM2904 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Input Offset Voltage (Note 5) , T
Input Bias Current I
Input Offset Current I
Input Common-Mode V
or I
IN(+)
V
= 0V, (Note 6)
CM
IN(+)−IIN(−),VCM
+
= 30V, (Note 7) 0 V+−1.5 0 V+−1.5 V
Voltage Range (LM2904, V
= 25˚C 2 7 2 7 mV
A
IN(−),TA
= 25˚C, 45 250 45 250 nA
= 0V, TA= 25˚C 5 50 5 50 nA
+
= 26V), TA= 25˚C
Supply Current Over Full Temperature Range
R
=∞on All Op Amps
L
+
V
= 30V (LM2904 V+= 26V) 1 2 1 2 mA
+
V
= 5V 0.5 1.2 0.5 1.2 mA
Electrical Characteristics
V+= +5.0V, (Note 4), unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions
Large Signal Voltage V
Gain R
+
= 15V, TA= 25˚C,
≥ 2kΩ, (For VO= 1V 50 100 25 100 50 100 V/mV
L
to 11V)
Common-Mode T
Rejection Ratio V
Power Supply V
Rejection Ratio (LM2904, V
Amplifier-to-Amplifier f = 1 kHz to 20 kHz, T
= 25˚C,
A
=0VtoV+−1.5V
CM
+
=5Vto30V
to 26V), T
+
= 5V 65 100 65 100 65 100 dB
= 25˚C
A
= 25˚C
A
Coupling (Input Referred), (Note 8)
Output Current Source V
Sink V
Short Circuit to Ground T
+
= 1V,
IN
−
V
= 0V,
IN
+
V
= 15V,
V
= 2V, TA= 25˚C
O
−
= 1V, V
IN
+
V
= 15V, TA= 25˚C, 10 20 10 20 10 20 mA
V
=2V
O
−
V
= 1V,
IN
+
V
=0V
IN
T
= 25˚C, VO= 200 mV,
A
+
V
= 15V
= 25˚C, (Note 2),
A
+
V
= 15V
IN
+
=0V
Input Offset Voltage (Note 5) 4 5 7 mV
Input Offset Voltage R
S
=0Ω
Drift
Input Offset Current I
Input Offset Current R
IN(+)−IIN(−)
=0Ω
S
Drift
Input Bias Current I
Input Common-Mode V
Voltage Range (LM2904, V
or I
IN(+)
IN(−)
+
= 30 V, (Note 7)
+
= 26V)
LM158A LM358A LM158/LM258 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
70 85 65 85 70 85 dB
−120 −120 −120 dB
20 40 20 40 20 40 mA
12 50 12 50 12 50 µA
40 60 40 60 40 60 mA
7 15 7 20 7 µV/˚C
30 75 100 nA
10 200 10 300 10 pA/˚C
40 100 40 200 40 300 nA
0V
+
−2 0 V+−2 0 V+−2 V
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
www.national.com3
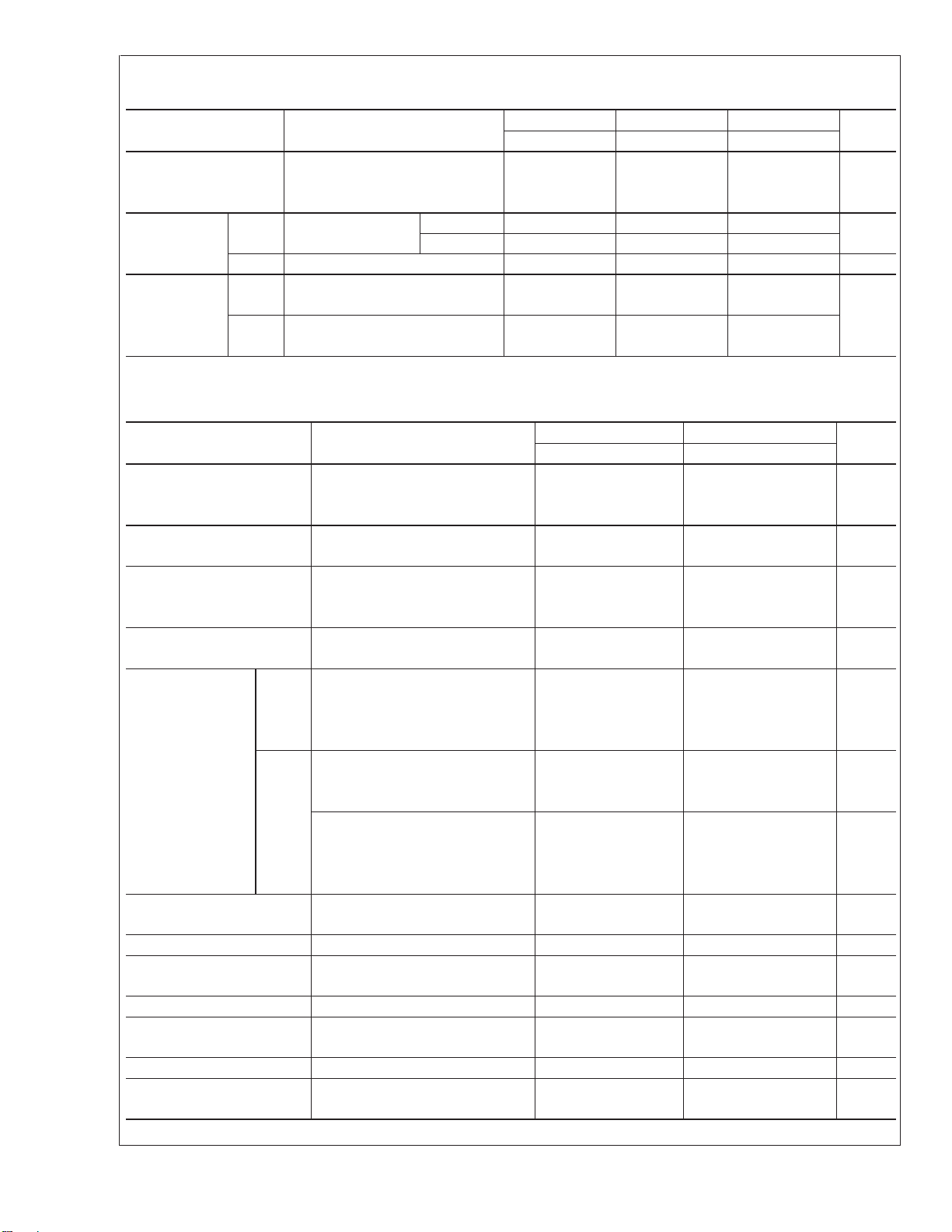
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
V+= +5.0V, (Note 4), unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions
Large Signal Voltage V
Output V
+
= +15V
= 1V to 11V)
O
R
≥ 2kΩ
L
V+= +30V RL=2kΩ 26 26 26 V
OH
Voltage (LM2904, V
Swing V
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Output Current Source V
V+= 5V, RL=10kΩ 520 520 520 mV
OL
+
= +1V, V
IN
+
V
= 15V, VO=2V
Sink V
−
= +1V, V
IN
+
V
= 15V, VO=2V
+
= 26V) RL=10kΩ 27 28 27 28 27 28 V
−
= 0V,
IN
+
= 0V,
IN
LM158A LM358A LM158/LM258 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
25 15 25 V/mVGain (V
10 20 10 20 10 20 mA
10 15 5 8 5 8 mA
Electrical Characteristics
V+= +5.0V, (Note 4), unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions
Large Signal Voltage V
Gain R
+
= 15V, TA= 25˚C,
≥ 2kΩ, (For VO= 1V 25 100 25 100 V/mV
L
to 11V)
Common-Mode T
Rejection Ratio V
Power Supply V
Rejection Ratio (LM2904, V
Amplifier-to-Amplifier f = 1 kHz to 20 kHz, T
= 25˚C,
A
=0VtoV+−1.5V
CM
+
=5Vto30V
to 26V), T
+
= 5V 65 100 50 100 dB
= 25˚C
A
= 25˚C
A
Coupling (Input Referred), (Note 8)
Output Current Source V
Sink V
Short Circuit to Ground T
+
= 1V,
IN
−
V
= 0V,
IN
+
V
= 15V,
V
= 2V, TA= 25˚C
O
−
= 1V, V
IN
+
V
= 15V, TA= 25˚C, 10 20 10 20 mA
V
=2V
O
−
V
= 1V,
IN
+
V
=0V
IN
T
= 25˚C, VO= 200 mV,
A
+
V
= 15V
= 25˚C, (Note 2),
A
+
V
= 15V
+
=0V
IN
Input Offset Voltage (Note 5) 9 10 mV
Input Offset Voltage R
S
=0Ω
Drift
Input Offset Current I
Input Offset Current R
IN(+)−IIN(−)
=0Ω
S
Drift
Input Bias Current I
Input Common-Mode V
Voltage Range (LM2904, V
or I
IN(+)
IN(−)
+
= 30 V, (Note 7)
+
= 26V)
LM358 LM2904 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
65 85 50 70 dB
−120 −120 dB
20 40 20 40 mA
12 50 12 50 µA
40 60 40 60 mA
7 7 µV/˚C
150 45 200 nA
10 10 pA/˚C
40 500 40 500 nA
0V
+
−2 0 V+−2 V
www.national.com 4
Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
V+= +5.0V, (Note 4), unless otherwise stated
Parameter Conditions
Large Signal Voltage V
Output V
Voltage (LM2904, V
Swing V
Output Current Source V
Note 1: For operating at high temperatures, the LM358/LM358A, LM2904 must be derated based on a +125˚C maximum junction temperature and a thermal
resistance of 120˚C/W for MDIP, 182˚C/W for Metal Can, 189˚C/W for Small Outline package, and 230˚C/W for micro SMD, which applies for the device soldered
in a printed circuit board, operating in a still air ambient. The LM258/LM258Aand LM158/LM158A can be derated based on a +150˚C maximum junction temperature.
The dissipation is the total of both amplifiers —use external resistors, where possible, to allow the amplifier to saturate or to reduce the power which is dissipated
in the integrated circuit.
Note 2: Short circuits from the output to V
current is approximately 40 mA independent of the magnitude of V
dissipation ratings and cause eventual destruction. Destructive dissipation can result from simultaneous shorts on all amplifiers.
Note 3: This input current will only exist when the voltage at any of the input leads is driven negative. It is due to the collector-base junction of the input PNP
transistors becoming forward biased and thereby acting as input diode clamps. In addition to this diode action, there is also lateral NPN parasitic transistor action
on the IC chip. This transistor action can cause the output voltages of the op amps to go to the V
that an input is driven negative. This is not destructive and normal output states will re-establish when the input voltage, which was negative, again returns to a value
greater than −0.3V (at 25˚C).
Note 4: These specifications are limited to −55˚C ≤ T
−25˚C ≤ T
+85˚C.
Note 5: V
Note 6: The direction of the input current is out of the IC due to the PNP input stage. This current is essentially constant, independent of the state of the outputso
no loading change exists on the input lines.
Note 7: The input common-mode voltage of either input signal voltage should not be allowed to go negative by more than 0.3V (at 25˚C). The upper end of the
common-mode voltage range is V
+
V
Note 8: Due to proximity of external components, insure that coupling is not originating via stray capacitance between these external parts. This typically can be
detected as this type of capacitance increases at higher frequencies.
Note 9: Refer to RETS158AX for LM158A military specifications and to RETS158X for LM158 military specifications.
Note 10: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF.
≤ +85˚C, the LM358/LM358A temperature specifications are limited to 0˚C ≤ TA≤ +70˚C, and the LM2904 specifications are limited to −40˚C ≤ TA≤
A
. 1.4V, RS=0Ω with V+from 5V to 30V; and over the full input common-mode range (0V to V+−1.5V) at 25˚C. For LM2904, V+from 5V to 26V.
O
.
+
= +15V
= 1V to 11V)
O
R
≥ 2kΩ
L
V+= +30V RL=2kΩ 26 22 V
OH
V+= 5V, RL=10kΩ 5 20 5 100 mV
OL
+
IN
+
V
= 15V, VO=2V
Sink V
−
IN
+
V
= 15V, VO=2V
+
+
−1.5V (at 25˚C), but either or both inputs can go to +32V without damage (+26V for LM2904), independent of the magnitude of
+
= 26V) RL=10kΩ 27 28 23 24 V
= +1V, V
= +1V, V
can cause excessive heating and eventual destruction. When considering short cirucits to ground, the maximum output
−
= 0V,
IN
+
= 0V,
IN
+
. At values of supply voltage in excess of +15V, continuous short-circuits can exceed the power
≤ +125˚C for the LM158/LM158A. With the LM258/LM258A, all temperature specifications are limited to
A
LM358 LM2904 Units
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
15 15 V/mVGain (V
10 20 10 20 mA
58 58 mA
+
voltage level (or to ground for a large overdrive) for the time duration
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
www.national.com5
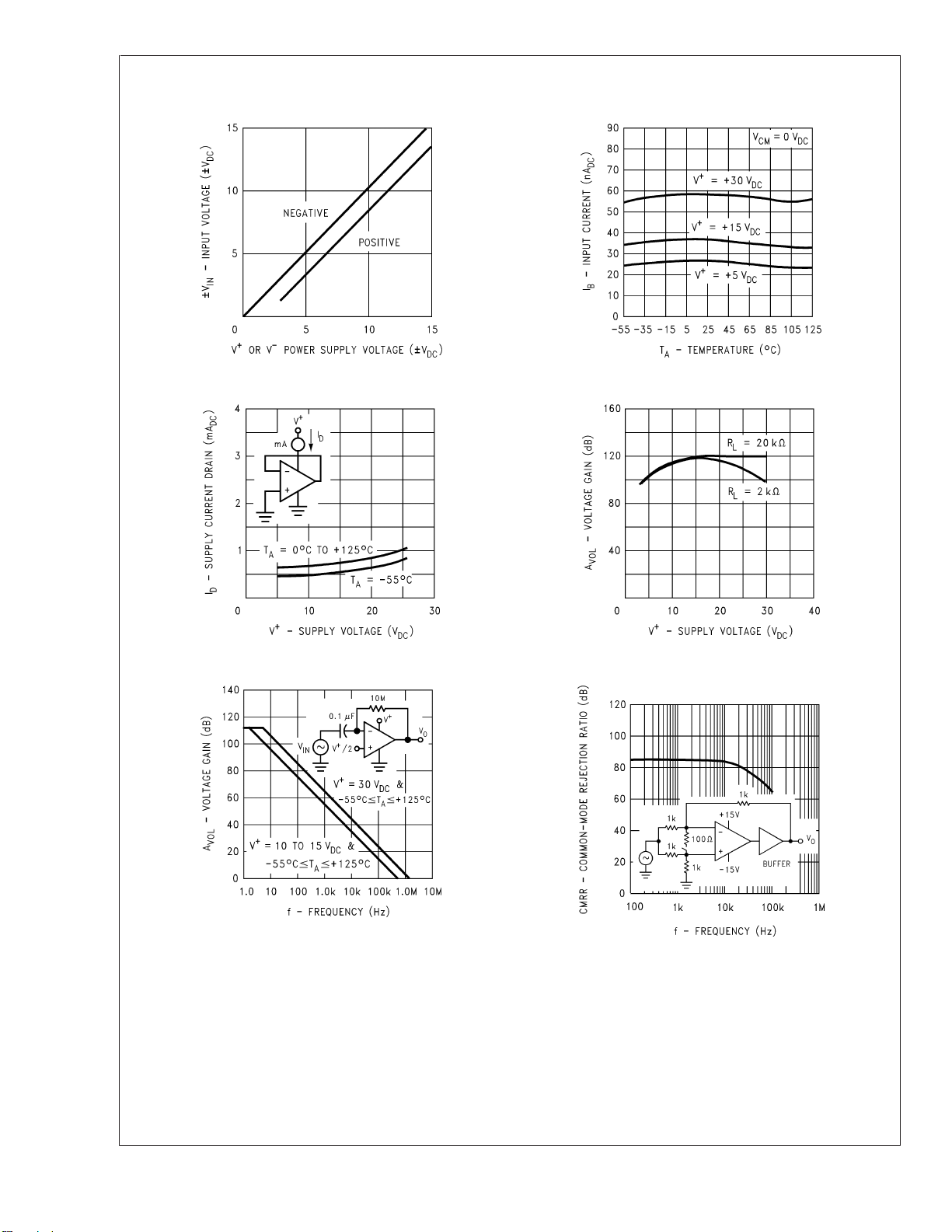
Typical Performance Characteristics
Input Voltage Range Input Current
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778734 00778735
Supply Current Voltage Gain
00778736 00778737
Open Loop Frequency Response Common-Mode Rejection Ratio
00778738
00778739
www.national.com 6
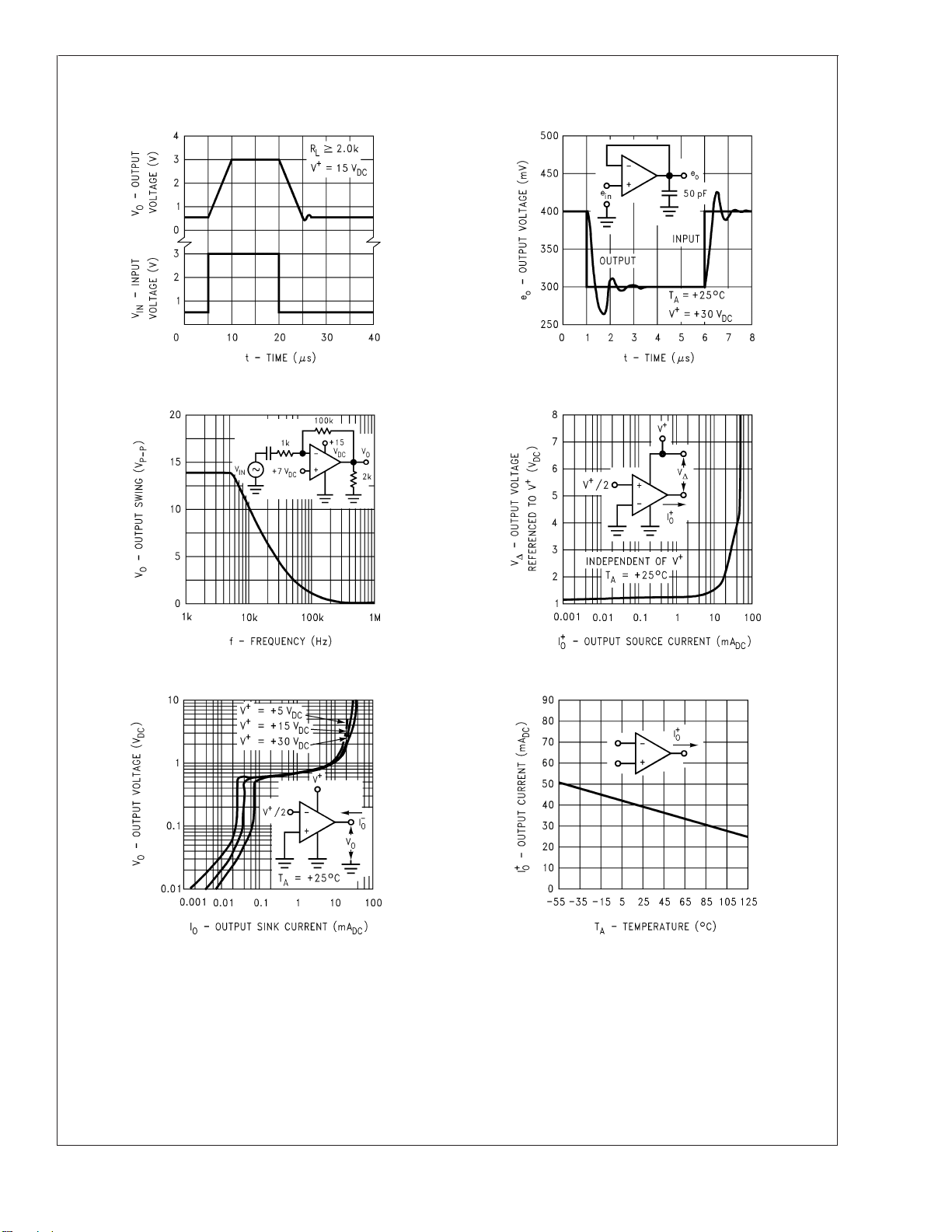
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Voltage Follower Pulse Response Voltage Follower Pulse Response (Small Signal)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778740
Large Signal Frequency Response Output Characteristics Current Sourcing
00778742
Output Characteristics Current Sinking Current Limiting
00778741
00778743
00778744
00778745
www.national.com7
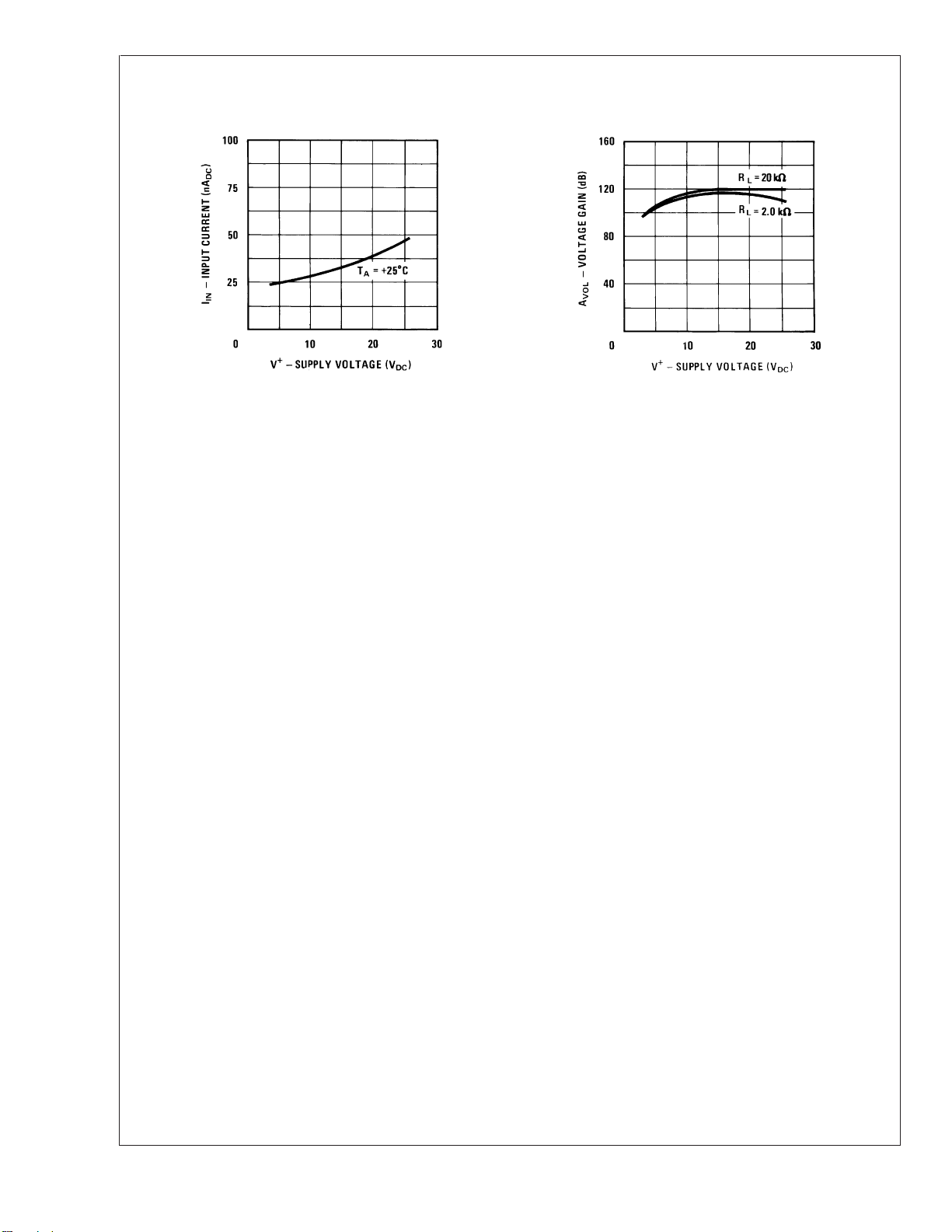
Typical Performance Characteristics (Continued)
Input Current (LM2902 only) Voltage Gain (LM2902 only)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778746
Application Hints
The LM158 series are op amps which operate with only a
single power supply voltage, have true-differential inputs,
and remain in the linear mode with an input common-mode
voltage of 0 V
of power supply voltage with little change in performance
characteristics. At 25˚C amplifier operation is possible down
to a minimum supply voltage of 2.3 V
Precautions should be taken to insure that the power supply
for the integrated circuit never becomes reversed in polarity
or that the unit is not inadvertently installed backwards in a
test socket as an unlimited current surge through the resulting forward diode within the IC could cause fusing of the
internal conductors and result in a destroyed unit.
Large differential input voltages can be easily accomodated
and, as input differential voltage protection diodes are not
needed, no large input currents result from large differential
input voltages. The differential input voltage may be larger
+
than V
provided to prevent the input voltages from going negative
more than −0.3 V
resistor to the IC input terminal can be used.
To reduce the power supply current drain, the amplifiers
have a class A output stage for small signal levels which
converts to class B in a large signal mode. This allows the
amplifiers to both source and sink large output currents.
Therefore both NPN and PNP external current boost transistors can be used to extend the power capability of the basic
amplifiers. The output voltage needs to raise approximately
1 diode drop above ground to bias the on-chip vertical PNP
transistor for output current sinking applications.
For ac applications, where the load is capacitively coupled to
the output of the amplifier, a resistor should be used, from
the output of the amplifier to ground to increase the class A
bias current and prevent crossover distortion. Where the
load is directly coupled, as in dc applications, there is no
crossover distortion.
. These amplifiers operate over a wide range
DC
.
DC
without damaging the device. Protection should be
(at 25˚C). An input clamp diode with a
DC
00778747
Capacitive loads which are applied directly to the output of
the amplifier reduce the loop stability margin. Values of 50
pF can be accomodated using the worst-case non-inverting
unity gain connection. Large closed loop gains or resistive
isolation should be used if larger load capacitance must be
driven by the amplifier.
The bias network of the LM158 establishes a drain current
which is independent of the magnitude of the power supply
voltage over the range of 3 V
to 30 VDC.
DC
Output short circuits either to ground or to the positive power
supply should be of short time duration. Units can be destroyed, not as a result of the short circuit current causing
metal fusing, but rather due to the large increase in IC chip
dissipation which will cause eventual failure due to excessive function temperatures. Putting direct short-circuits on
more than one amplifier at a time will increase the total IC
power dissipation to destructive levels, if not properly protected with external dissipation limiting resistors in series
with the output leads of the amplifiers. The larger value of
output source current which is available at 25˚C provides a
larger output current capability at elevated temperatures
(see typical performance characteristics) than a standard IC
op amp.
The circuits presented in the section on typical applications
emphasize operation on only a single power supply voltage.
If complementary power supplies are available, all of the
standard op amp circuits can be used. In general, introducing a pseudo-ground (a bias voltage reference of V
+
/2) will
allow operation above and below this value in single power
supply systems. Many application circuits are shown which
take advantage of the wide input common-mode voltage
range which includes ground. In most cases, input biasing is
not required and input voltages which range to ground can
easily be accommodated.
www.national.com 8

Connection Diagrams
DIP/SO Package Metal Can Package
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778701
Top View
00778702
Top View
8-Bump micro SMD
Top View
00778755
(Bump Side Down)
LM358BP micro SMD Marking Orientation LM2904IBP micro SMD Marking Orientation
00778757
Top View
00778756
Top View
LM358TP micro SMD Marking Orientation LM2904ITP micro SMD Marking Orientation
Top View
00778758
Top View
00778759
www.national.com9

Ordering Information
Package
−55˚C to 125˚C −25˚C to 85˚C 0˚C to 70˚C −40˚C to 85˚C
SO-8 LM358AM
8-Pin Molded DIP LM358AN
8-Pin Ceramic DIP LM158AJ/883(Note 11)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
LM158J/883(Note 11)
LM158J
LM158AJLQML(Note 12)
LM158AJQMLV(Note 12)
TO-5, 8-Pin Metal
Can
LM158AH/883(Note 11)
LM158H/883(Note 11)
LM158AH
LM158H
LM158AHLQML(Note 12)
LM158AHLQMLV(Note 12)
8-Bump micro
SMD
8-Bump micro
SMD
Lead Free
14-Pin Ceramic
LM158AWG/883
SOIC
Note 11: LM158 is available per SMD#5962-8771001
#
LM158A is available per SMD
Note 12: See STD Mil DWG 5962L87710 for Radiation Tolerant Devices
5962-8771002
Temperature Range
LM258H LM358H
LM358AMX
LM358M
LM358MX
LM358N
LM358BP
LM358BPX
LM358TP
LM358TPX
LM2904M
LM2904MX
LM2904N
LM2904IBP
LM2904IBPX
LM2904ITP
LM2904ITPX
NSC Drawing
M08A
N08E
J08A
H08C
BPA08AAB
0.85 mm Thick
TPA08AAA
0.50 mm Thick
WG10A
www.national.com 10

Typical Single-Supply Applications
(V+= 5.0 VDC)
Non-Inverting DC Gain (0V Output)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
*
R not needed due to temperature independent I
DC Summing Amplifier
≥ 0VDCand VO≥ 0VDC) Power Amplifier
(V
IN’S
Where: VO=V1+V2−V3−V
(V1+V2) ≥ (V3+V4) to keep V
4
>
0V
O
DC
00778706
IN
00778708
VO=0VDCfor VIN=0V
AV=10
DC
00778707
00778709
www.national.com11

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
“BI-QUAD” RC Active Bandpass Filter
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
fo= 1 kHz
Q=50
= 100 (40 dB)
A
v
Fixed Current Sources
00778710
Lamp Driver
00778712
00778711
www.national.com 12

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
LED Driver Current Monitor
00778713
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778714
*
(Increase R1 for ILsmall)
≤ V+−2V
V
L
Driving TTL Voltage Follower
00778715 00778717
VO=V
IN
Pulse Generator
00778716
www.national.com13

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
Squarewave Oscillator Pulse Generator
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
00778718
Low Drift Peak Detector
00778719
HIGH Z
IN
LOW Z
OUT
www.national.com 14
00778720

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
High Compliance Current Sink Comparator with Hysteresis
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778722
IO= 1 amp/volt V
(Increase REfor IOsmall)
IN
00778721
Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
*
WIDE CONTROL VOLTAGE RANGE: 0 VDC≤ VC≤ 2(V+−1.5VDC)
00778723
www.national.com15

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
AC Coupled Inverting Amplifier
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Ground Referencing a Differential Input Signal
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
00778724
www.national.com 16
00778725

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
AC Coupled Non-Inverting Amplifier
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778726
Av= 11 (As Shown)
fo= 1 kHz
Q=1
=2
A
V
DC Coupled Low-Pass RC Active Filter
00778727
www.national.com17

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
Bandpass Active Filter
fo= 1 kHz
Q=25
00778728
High Input Z, DC Differential Amplifier
00778729
www.national.com 18

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
Photo Voltaic-Cell Amplifier Bridge Current Amplifier
00778730
High Input Z Adjustable-Gain
DC Instrumentation Amplifier
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
00778733
00778731
www.national.com19

Typical Single-Supply Applications (V
Using Symmetrical Amplifiers to
Reduce Input Current (General Concept)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
+
= 5.0 VDC) (Continued)
Schematic Diagram (Each Amplifier)
00778732
www.national.com 20
00778703

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Metal Can Package (H)
NS Package Number H08C
Cerdip Package (J)
NS Package Number J08A
www.national.com21

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
SOIC Package (M)
NS Package Number M08A
Molded Dip Package (N)
NS Package Number N08E
www.national.com 22

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
Order Number LM158AWG/883
NS Package Number WG10A
www.national.com23

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
1. EPOXY COATING
2. 63Sn/37Pb EUTECTIC BUMP
3. RECOMMEND NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED LANDING PAD.
4. PIN A1 IS ESTABLISHED BY LOWER LEFT CORNER WITH RESPECT TO TEXT ORIENTATION REMAINING PINS ARE NUMBERED
COUNTERCLOCKWISE.
5. XXX IN DRAWING NUMBER REPRESENTS PACKAGE SIZE VARIATION WHERE X
PACKAGE HEIGHT.
6. REFERENCE JEDEC REGISTRATION MO-211, VARIATION BC.
IS PACKAGE WIDTH, X2IS PACKAGE LENGTH AND X3IS
1
8-Bump micro SMD
NS Package Number BPA08AAB
= 1.285 X2= 1.285 X3= 0.850
X
1
www.national.com 24

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted (Continued)
LM158/LM258/LM358/LM2904 Low Power Dual Operational Amplifiers
NOTES: UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED
1. EPOXY COATING
2. RECOMMEND NON-SOLDER MASK DEFINED LANDING PAD.
3. PIN A1 IS ESTABLISHED BY LOWER LEFT CORNER WITH RESPECT TO TEXT ORIENTATION REMAINING PINS ARE NUMBERED
COUNTERCLOCKWISE.
4. XXX IN DRAWING NUMBER REPRESENTS PACKAGE SIZE VARIATION WHERE X
PACKAGE HEIGHT.
5. REFERENCE JEDEC REGISTRATION MO-211, VARIATION BC.
IS PACKAGE WIDTH, X2IS PACKAGE LENGTH AND X3IS
1
8-Bump micro SMD Lead Free
NS Package Number TPA08AAA
= 1.285 X2= 1.285 X3= 0.500
X
1
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves
the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
For the most current product information visit us at www.national.com.
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS
WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL COUNSEL OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR
CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems
which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the body, or
(b) support or sustain life, and whose failure to perform when
properly used in accordance with instructions for use
2. A critical component is any component of a life support
device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably
expected to cause the failure of the life support device or
system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
provided in the labeling, can be reasonably expected to result
in a significant injury to the user.
BANNED SUBSTANCE COMPLIANCE
National Semiconductor manufactures products and uses packing materials that meet the provisions of the Customer Products
Stewardship Specification (CSP-9-111C2) and the Banned Substances and Materials of Interest Specification (CSP-9-111S2) and contain
no ‘‘Banned Substances’’ as defined in CSP-9-111S2.
Leadfree products are RoHS compliant.
National Semiconductor
Americas Customer
Support Center
Email: new.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Europe Customer Support Center
Fax: +49 (0) 180-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 69 9508 6208
English Tel: +44 (0) 870 24 0 2171
Français Tel: +33 (0) 1 41 91 8790
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Support Center
Email: ap.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Customer Support Center
Fax: 81-3-5639-7507
Email: jpn.feedback@nsc.com
Tel: 81-3-5639-7560
 Loading...
Loading...