查询DS90CF563供应商
DS90CF563/DS90CF564
LVDS 18-Bit Color Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link—
65 MHz
DS90CF563/DS90CF564 LVDS 18-Bit Color Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link—65 MHz
July 1997
General Description
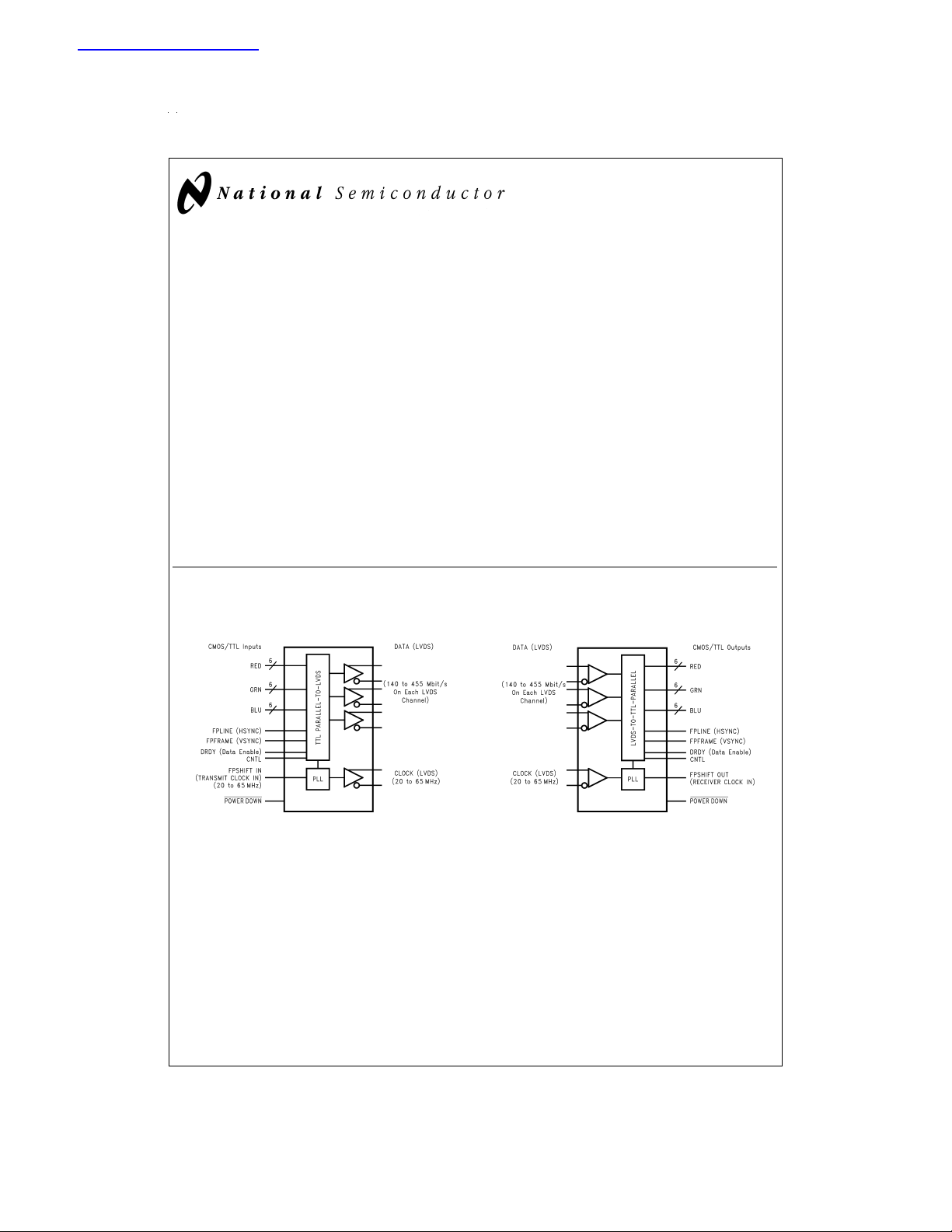
The DS90CF563 transmitter converts 21 bits of CMOS/TTL
data into three LVDS (Low Voltage Differential Signaling)
data streams. A phase-lockedtransmit clock is transmitted in
parallel with the data streams over a fourth LVDSlink. Every
cycle of the transmit clock 21 bits of input data are sampled
and transmitted. The DS90CF564 receiver converts the
LVDS data streams back into 21 bits of CMOS/TTL data. At
a transmit clock frequency of 65 MHz, 18 bits of RGB data
and 3 bits of LCD timing and control data (FPLINE,
FPFRAME, DRDY) are transmitted ata rate of 455 Mbps per
LVDSdata channel. Usinga 65 MHz clock, thedata throughput is 171 Mbytes per second. These devices are offered
with falling edge data strobes for convenient interface with a
variety of graphics and LCD panel controllers.
This chipset is an ideal means to solve EMI and cable size
problems associated with wide, high speed TTL interfaces.
Block Diagrams
DS90CF563
Features
n 20 to 65 MHz shift clk support
n Up to 171 Mbytes/s bandwidth
n Cable size is reduced to save cost
n 290 mV swing LVDS devices for low EMI
n Low power CMOS design (
n Power-down mode saves power (
n PLL requires no external components
n Low profile 48-lead TSSOP package
n Falling edge data strobe
n Compatible with TIA/EIA-644 LVDS standard
n Single pixel per clock XGA (1024 x 768)
n Supports VGA, SVGA, XGA and higher
n 1.3 Gbps throughput
<
550 mW typ)
DS90CF564
<
0.25 mW)
DS012615-2
Order Number DS90CF563MTD
See NS Package Number MTD48
TRI-STATE®is a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
© 1998 National Semiconductor Corporation DS012615 www.national.com
Order Number DS90CF564MTD
See NS Package Number MTD48
DS012615-1
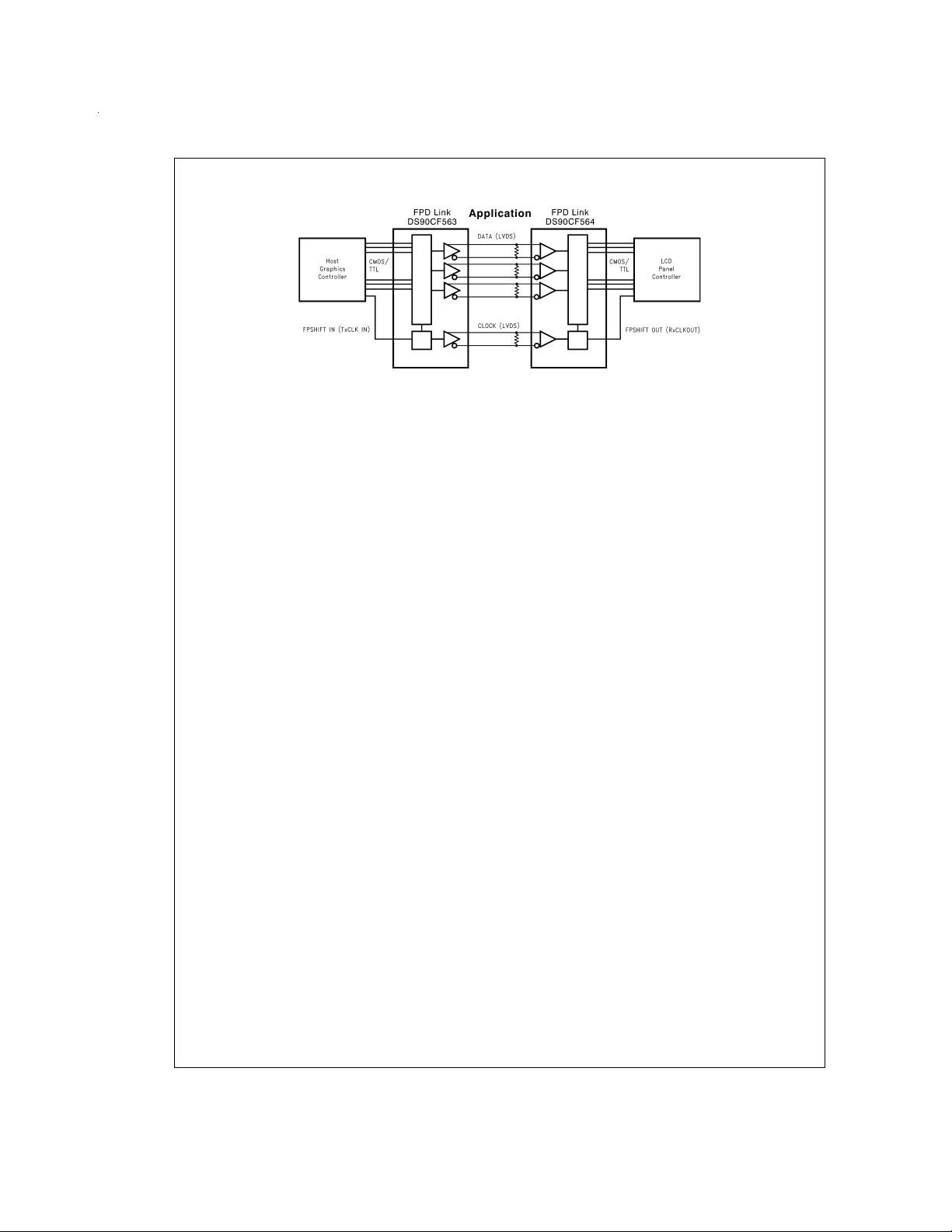
Block Diagrams (Continued)
DS012615-3
www.national.com 2
Absolute Maximum Ratings (Note 1)
If Military/Aerospace specified devices are required,
please contact the National SemiconductorSales Office/
Distributors for availability and specifications.
Supply Voltage (V
CMOS/TTL Input Voltage −0.3V to (V
CMOS/TTL Output Voltage −0.3V to (V
LVDS Receiver Input Voltage −0.3V to (V
LVDS Driver Output Voltage −0.3V to (V
LVDS Output Short Circuit
Duration Continuous
Junction Temperature +150˚C
Storage Temperature −65˚C to +150˚C
Lead Temperature
(Soldering, 4 sec) +260˚C
Maximum Package Power Dissipation
MTD48 (TSSOP) Package:
) −0.3V to +6V
CC
@
CC
CC
CC
CC
+25˚C
+ 0.3V)
+ 0.3V)
+ 0.3V)
+ 0.3V)
DS90CF563 1.98W
DS90CF564 1.89W
Package Derating:
DS90CF563 16 mW/˚C above +25˚C
DS90CF564 15 mW/˚C above +25˚C
This device does not meet 2000V ESD rating (Note 4) .
Recommended Operating
Conditions
Supply Voltage (V
) 4.75 5.0 5.25 V
CC
Operating Free Air −10 +25 +70 ˚C
Temperature (T
)
A
Receiver Input Range 0 2.4 V
Supply Noise Voltage (V
Min Nom Max Units
) 100 mV
CC
Electrical Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
CMOS/TTL DC SPECIFICATIONS
V
High Level Input Voltage 2.0 V
IH
V
Low Level Input Voltage GND 0.8 V
IL
V
High Level Output Voltage I
OH
V
Low Level Output Voltage I
OL
V
Input Clamp Voltage I
CL
I
Input Current V
IN
I
Output Short Circuit Current V
OS
=
−0.4 mA 3.8 4.9 V
OH
=
2 mA 0.1 0.3 V
OL
=
−18 mA −0.79 −1.5 V
CL
=
, GND, 2.5V or 0.4V
V
IN
CC
=
0V −120 mA
OUT
LVDS DRIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS
V
Differential Output Voltage R
OD
∆V
Change in VODbetween
OD
Complementary Output States
Common Mode Voltage 1.1 1.25 1.375 V
V
CM
∆V
Change in VCMbetween
CM
Complementary Output States
High Level Output Voltage 1.3 1.6 V
V
OH
V
Low Level Output Voltage 0.9 1.01 V
OL
I
Output Short Circuit Current V
OS
I
Output TRI-STATE®Current Power Down=0V, V
OZ
=
100Ω 250 290 450 mV
L
OUT
=
0V, R
=
100Ω −2.9 −5 mA
L
OUT
=
0V or V
CC
LVDS RECEIVER DC SPECIFICATIONS
V
Differential Input High
TH
Threshold
Differential Input Low Threshold −100 mV
V
TL
I
Input Current V
IN
=
V
+1.2V +100 mV
CM
=
+2.4V V
IN
=
V
0V
IN
=
5.5V
CC
TRANSMITTER SUPPLY CURRENT
I
CCTW
I
CCTG
Transmitter Supply Current,
Worst Case
Transmitter Supply Current,
16 Grayscale
=
R
100Ω,C
L
Worst Case Pattern
Figure 1,Figure 3
(
=
R
100Ω,C
L
16 Grayscale Pattern
Figure 2,Figure 3
(
=
5 pF,
L
)
=
5 pF,
L
)
f=32.5 MHz 49 63 mA
f=37.5 MHz 51 64 mA
f=65 MHz 70 84 mA
f=32.5 MHz 40 55 mA
f=37.5 MHz 41 55 mA
f=65 MHz 55 67 mA
±
5.1±10 µA
±1±
CC
35 mV
35 mV
10 µA
±
10 µA
±
10 µA
V
P-P
www.national.com3

Electrical Characteristics (Continued)
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
TRANSMITTER SUPPLY CURRENT
I
Transmitter Supply Current,
CCTZ
Power Down
Power Down=Low
125µA
RECEIVER SUPPLY CURRENT
I
CCRW
Receiver Supply Current, C
=
8 pF, f=32.5 MHz 64 77 mA
L
Worst Case Worst Case Pattern f=37.5 MHz 70 85 mA
=
65 MHz 110 140 mA
I
CCRG
Receiver Supply Current, C
(
Figure 1,Figure 4
=
8 pF, f=32.5 MHz 35 55 mA
L
)f
16 Grayscale 16 Grayscale Pattern f=37.5 MHz 37 55 mA
=
65 MHz 55 67 mA
I
CCRZ
(
Figure 2,Figure 4
)f
Receiver Supply Current, Power Down=Low 110µA
Power Down
Note 1: “Absolute Maximum Ratings” are those values beyond which the safety of the device cannot be guaranteed. They are not meant to imply that the device
should be operated at these limits. The tables of “Electrical Characteristics” specify conditions for device operation.
Note 2: Typical values are given for V
Note 3: Current into device pins is defined as positive. Current out of device pinsis defined as negative. Voltagesarereferenced to ground unless otherwise speci-
fied (except V
Note 4: ESD Rating: HBM (1.5 kΩ, 100 pF)
and ∆VOD).
OD
PLL V
≥ 1000V
CC
All other pins ≥ 2000V
EIAJ (0Ω, 200 pF) ≥ 150V
CC
=
5.0V and T
=
+25˚C.
A
Transmitter Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
Figure 3
LLHT LVDS Low-to-High Transition Time (
LHLT LVDS High-to-Low Transition Time (
TCIT TxCLK IN Transition Time (
Figure 5
TCCS TxOUT Channel-to-Channel Skew (Note 5) (
TCCD TxCLK IN to TxCLK OUT Delay
(
Figure 9
)
TCIP TxCLK IN Period (
TCIH TxCLK IN High Time (
TCIL TxCLK IN Low Time (
Figure 7
Figure 7
Figure 7
TSTC TxIN Setup to TxCLK IN (
THTC TxIN Hold to TxCLK IN (
TPDD Transmitter Powerdown Delay (
@
) 15 T 50 ns
) 0.35T 0.5T 0.65T ns
) 0.35T 0.5T 0.65T ns
Figure 7
)f
Figure 7
) 2.5 1.5 ns
Figure 18
TPLLS Transmitter Phase Lock Loop Set (
TPPos0 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 0 (
TPPos1 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 1 1.70 1/7 T
TPPos2 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 2 3.60 2/7 T
TPPos3 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 3 5.90 3/7 T
TPPos4 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 4 8.30 4/7 T
TPPos5 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 5 10.40 5/7 T
TPPos6 Transmitter Output Pulse Position 6 12.70 6/7 T
Note 5: This limit based on bench characterization.
) 0.75 1.5 ns
Figure 3
) 0.75 1.5 ns
)8ns
Figure 6
) 350 ps
25˚C, V
=
5.0V 3.5 8.5 ns
CC
=
65 MHz 5 3.5 ns
) 100 ns
Figure 11
)10ms
Figure 13
) −0.30 0 0.30 ns
2.50 ns
clk
4.50 ns
clk
6.75 ns
clk
9.00 ns
clk
11.10 ns
clk
13.40 ns
clk
www.national.com 4

Receiver Switching Characteristics
Over recommended operating supply and temperature ranges unless otherwise specified.
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units
Figure 4
CLHT CMOS/TTL Low-to-High Transition Time (
CHLT CMOS/TTL High-to-Low Transition Time (
) 2.5 4.0 ns
Figure 4
) 2.0 3.5 ns
RCOP RxCLK OUT Period 15 T 50 ns
RCOH RxCLK OUT High Time f=65 MHz 7.8 9 ns
RCOL RxCLK OUT Low Time f=65 MHz 3.8 5 ns
RSRC RxOUT Setup to RxCLK OUT f=65 MHz 2.5 4.2 ns
RHRC RxOUT Hold to RxCLK OUT f=65 MHz 4.0 5.2 ns
RCCD RxCLK IN to RxCLK OUT Delay
(
Figure 10
)
RPLLS Receiver Phase Lock Loop Set (
RSKM RxIN Skew Margin (Note 6) (
RPDD Receiver Powerdown (
Note 6: Receiver Skew Margin is defined as the valid data sampling region at the receiver inputs. This margin takes into account transmitter output skew (TCCS)
and the setup and hold time (internal data sampling window), allowing for LVDS cable skew dependent on type/length and source clock (TxCLK IN) jitter.
RSKM ≥ cable skew (type, length) + source clock jitter (cycle to cycle)
Figure 17
@
25˚C, V
Figure 12
Figure 14
)1µs
=
5.0V 6.4 10.7 ns
CC
)10ms
=
)V
CC
=
5V, T
25˚C 600 ps
A
AC Timing Diagrams
FIGURE 1. “Worst Case” Test Pattern
DS012615-4
www.national.com5

AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
DS012615-5
FIGURE 2. “16 Grayscale” Test Pattern
Note 7: The worst case test pattern produces a maximum toggling of digital circuits, LVDS I/O and CMOS/TTL I/O.
Note 8: The 16 grayscale test pattern tests device power consumption for a “typical” LCD display pattern. The test pattern approximates signal switching needed
to produce groups of 16 vertical stripes across the display.
Note 9:
Figure 1
and
Figure 2
Note 10: Recommended pin to signal mapping. Customer may choose to define differently.
show a falling edge data strobe (TxCLK IN/RxCLK OUT).
FIGURE 3. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) LVDS Output Load and Transition Times
FIGURE 4. DS90CF564 (Receiver) CMOS/TTL Output Load and Transition Times
FIGURE 5. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) Input Clock Transition Time
www.national.com 6
DS012615-6
DS012615-7
DS012615-8

AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
Note: Measurements at Vdiff=0V
Note: TCSS measured between earliest and latest LVDS edges.
Note: TxCLK Differential High→Low Edge
FIGURE 6. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) Channel-to-Channel Skew and Pulse Width
FIGURE 7. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) Setup/Hold and High/Low Times
FIGURE 8. DS90CF564 (Receiver) Clock In to Clock Out Delay
DS012615-9
DS012615-10
DS012615-11
DS012615-12
FIGURE 9. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) Clock In to Clock Out Delay
www.national.com7

AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
FIGURE 10. DS90CF564 (Receiver) Clock In to Clock Out Delay
FIGURE 11. DS90CF563 (Transmitter) Phase Lock Loop Set Time
DS012615-13
DS012615-14
FIGURE 12. DS90CF564 (Receiver) Phase Lock Loop Set Time
www.national.com 8
DS012615-15

AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
FIGURE 13. Transmitter LVDS Output Pulse Position Measurement
DS012615-16
SW—Setup and Hold Time (Internal Data Sampling Window)
TCCS—Transmitter Output Skew
RSKM ≥ Cable Skew (type, length) + Source Clock Jitter (cycle to cycle)
Cable Skew — typically 10 ps–40 ps per foot
FIGURE 14. Receiver LVDS Input Skew Margin
FIGURE 15. Seven Bits of LVDS in One Clock Cycle
DS012615-17
DS012615-18
www.national.com9

AC Timing Diagrams (Continued)
FIGURE 16. 21 Parallel TTL Data Inputs Mapped to LVDS Outputs (DS90CF563)
FIGURE 17. Receiver Powerdown Delay
DS012615-19
DS012615-20
DS012615-21
FIGURE 18. Transmitter Powerdown Delay
DS90CF563 Pin Descriptions—FPD Link Transmitter
Pin Name I/O No. Description
TxIN I 21 TTL level input. This includes: 6 Red, 6 Green, 6 Blue, and 3 control lines—FPLINE,
TxOUT+ O 3 Positive LVDS differential data output
TxOUT− O 3 Negative LVDS differential data output
FPSHIFT IN I 1 TTL level clock input. The falling edge acts as data strobe
TxCLK OUT+ O 1 Positive LVDS differential clock output
TxCLK OUT− O 1 Negative LVDS differential clock output
PWR DOWN
V
CC
I 1 TTL level input. Assertion (low input) TRI-STATES the outputs, ensuring low current at power
I 4 Power supply pins for TTL inputs
GND I 5 Ground pins for TTL inputs
PLL V
CC
www.national.com 10
I 1 Power supply pin for PLL
FPFRAME, DRDY (also referred to as HSYNC, VSYNC, Data Enable)
down

DS90CF563 Pin Descriptions—FPD Link Transmitter (Continued)
Pin Name I/O No. Description
PLL GND I 2 Ground pins for PLL
LVDS V
CC
I 1 Power supply pin for LVDS outputs
LVDS GND I 3 Ground pins for LVDS outputs
DS90CF564 Pin Descriptions—FPD Link Receiver
Pin Name I/O No. Description
RxIN+ I 3 Positive LVDS differential data inputs
RxIN− I 3 Negative LVDS differential data inputs
RxOUT O 21 TTL level data outputs. This includes: 6 Red, 6 Green, 6 Blue, and 3 control lines—FPLINE,
FPFRAME, DRDY(also referred to as HSYNC, VSYNC, Data Enable)
RxCLK IN+ I 1 Positive LVDS differential clock input
RxCLK IN− I 1 Negative LVDS differential clock input
FPSHIFT
O 1 TTL level clock output. The falling edge acts as data strobe
OUT
PWR DOWN
V
CC
I 1 TTL level input. Assertion (low input) maintains the receiver outputs in the previous state
I 4 Power supply pins for TTL outputs
GND I 5 Ground pins for TTL outputs
PLL V
CC
I 1 Power supply for PLL
PLL GND I 2 Ground pin for PLL
LVDS V
CC
I 1 Power supply pin for LVDS inputs
LVDS GND I 3 Ground pins for LVDS inputs
Connection Diagrams
DS90CF563
DS012615-22
DS90CF564
DS012615-23
www.national.com11

Physical Dimensions inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
48-Lead Molded Thin Shrink Small Outline Package, JEDEC
NS Package Number MTD48
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
NATIONAL’S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE EXPRESS WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT OF NATIONAL SEMICONDUCTOR CORPORATION. As used herein:
1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems which, (a) are intended for surgical implant into
the body, or (b) support or sustainlife, andwhose fail-
DS90CF563/DS90CF564 LVDS 18-Bit Color Flat Panel Display (FPD) Link—65 MHz
ure to perform when properly used in accordance
2. A critical component in any component of a life support
device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably expected to cause the failure of the lifesupport
device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness.
with instructions for use provided in the labeling, can
be reasonably expected to result in a significant injury
to the user.
National Semiconductor
Corporation
Americas
Tel: 1-800-272-9959
Fax: 1-800-737-7018
Email: support@nsc.com
www.national.com
National Semiconductor
Europe
Fax: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 86
Email: europe.support@nsc.com
Deutsch Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-530 85 85
English Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 78 32
Français Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-532 93 58
Italiano Tel: +49 (0) 1 80-534 16 80
National Semiconductor
Asia Pacific Customer
Response Group
Tel: 65-2544466
Fax: 65-2504466
Email: sea.support@nsc.com
National Semiconductor
Japan Ltd.
Tel: 81-3-5620-6175
Fax: 81-3-5620-6179
National does not assume any responsibility for use of any circuitry described, no circuit patent licenses are implied and National reserves the right at any time without notice to change said circuitry and specifications.
 Loading...
Loading...