查询74VHC943供应商
74VHC943 300 Baud Modem (5V Supply)
74VHC943
300 Baud Modem (5V Supply)
General Description
The 74VHC943 is a full duplex low speed modem. It provides a 300 baud bidirectional serial interface for data communication over telephone lines and other narrow bandwidth channels. It is Bell 103 compatible.
The 74VHC943 utilizes advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. Switched capacitor techniques are used to perform
analog signal processing.
MODULATOR SECTION
The modulator contains a frequency synthesizer and a sine
wave synthesizer. It produces a phase coherent frequency
shift keyed (FSK) output.
LINE DRIVER AND HYBRID SECTION
The line driver and hybrid are designed to facilitate connection to a 600X phone line. They can perform two to four wire
conversion and drive the line at a maximum of
DEMODULATOR SECTION
The demodulator incorporates anti-aliasing filters, a receive
filter, limiter, discriminator, and carrier detect circuit. The
nine-pole receive filter provides 60 dB of transmitted tone
rejection. The discriminator is fully balanced for stable
operation.
b
9 dBm.
PRELIMINARY
October 1995
Features
Y
5V supply
Y
Drives 600X atb9 dBm
Y
All filters on chip
Y
Transmit level adjustment compatible with universal
service order code
Y
TTL and CMOS compatible logic
Y
All inputs protected against static damage
Y
Low power consumption
Y
Full duplex answer or originate operation
Y
Analog loopback for self test
Y
Power down mode
Y
Direct Pin and function replacement for the 74HC943
Applications
Y
Built-in low speed modems
Y
Remote data collection
Y
Radio telemetry
Y
Credit verification
Y
Stand-alone modems
Y
Point-of-sale terminals
Y
Tone signaling systems
Y
Remote process control
Commercial Package Number Package Description
74VHC943WM M20B 20-Lead Molded JEDEC SOIC (0.300×Wide)
74VHC943N N20A 20-Lead Molded DIP
Note: Surface mount packages are also available on Tape and Reel. Specify by appending the suffix letter
‘‘X’’ to the ordering code.
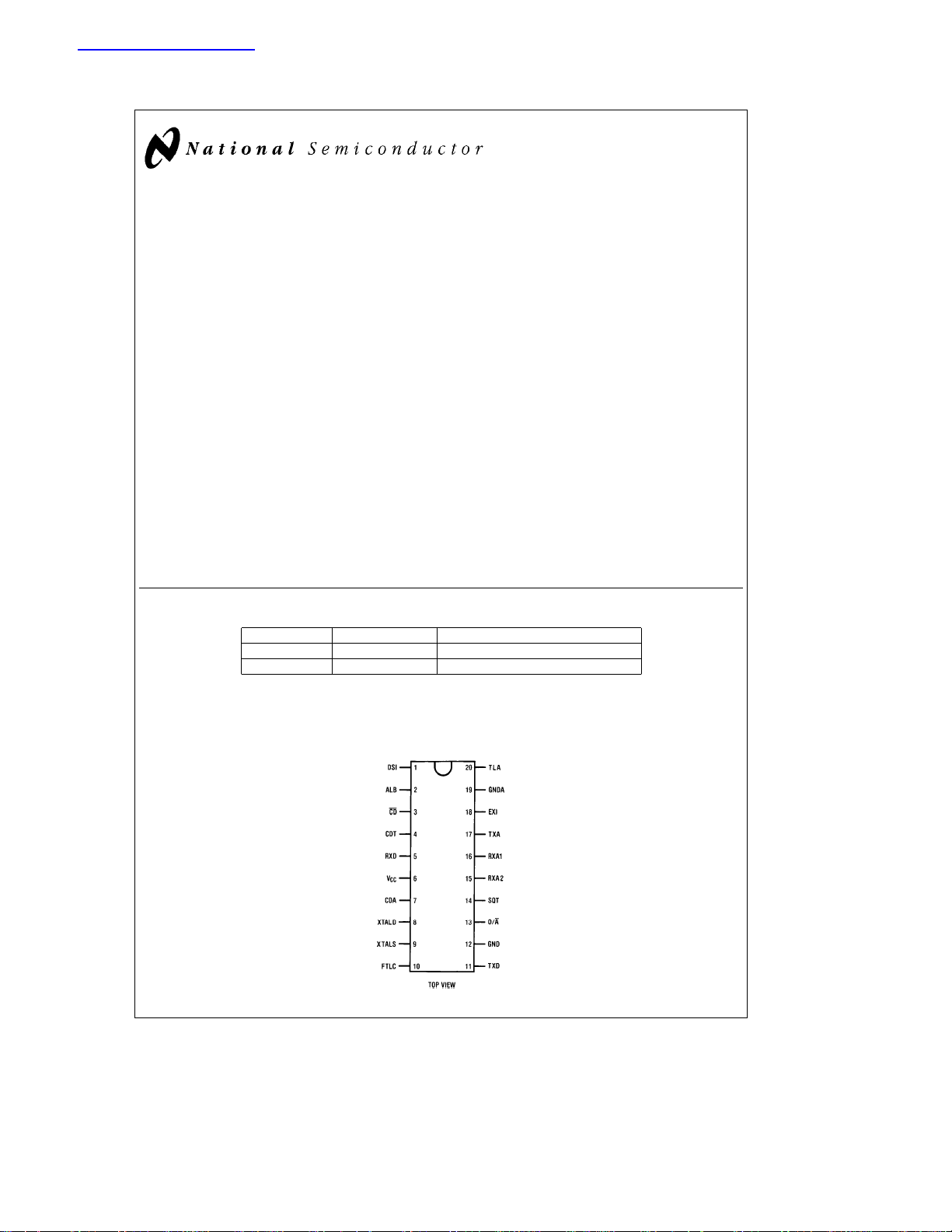
Connection Diagram
Pin Assignments for
SOIC and PDIP
TRI-STATEÉis a registered trademark of National Semiconductor Corporation.
C
1995 National Semiconductor Corporation RRD-B30M125/Printed in U. S. A.
TL/F/11679
TL/F/11679– 1

Block Diagram
TL/F/11679– 2
2

Description of Pin Functions
Pin
Name Function
No.
1 DSI Driver Summing Input: This input may be
2 ALB Analog Loop Back: A logic high on this pin
3CD
4 CDT Carrier Detect Timing: A capacitor on this
5 RXD Received Data: This is the data output pin.
6VCCPositive Supply Pin: Aa5V supply is recom-
7 CDA Carrier Detect Adjust: This is used for ad-
8 XTALD Crystal Drive: XTALD and XTALS connect
9 XTALS Crystal Sense: Refer to pin 8 for details.
used to transmit externally generated tones
such as dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) dialing signals.
causes the modulator output to be connected to the demodulator input so that data is
looped back through the entire chip. This is
used as a chip self test. If ALB and SQT are
simultaneously held high the chip powers
down.
Carrier Detect: This pin goes to a logic low
when carrier is sensed by the carrier detect
circuit.
pin sets the time interval that the carrier
must be present before the CD
mended.
justment of the carrier detect threshold. Carrier detect hysteresis is set at 3 dB.
to a 3.5795 MHz crystal to generate a crystal locked clock for the chip. If an external
circuit requires this clock XTALD should be
sensed. If a suitable clock is already available in the system. XTALD can be driven.
goes low.
Pin
Name Function
No.
10 FTLC Filter Test/Limiter Capacitor: This is con-
11 TXD Transmitted Data: This is the data input.
12 GND Ground: This defines the chip 0V.
13 O/A
14 SQT Squelch Transmitter: This disables the mod-
15 RXA2 Receive Analog
16 RXA1 Receive Analog
17 TXA Transmit Analog: This is the output of the
18 EXI External Input: This is a high impedance in-
19 GNDA Analog Ground: Analog signals within the
20 TLA Transmit Level Adjust: A resistor from this
nected to a high impedance output of the
receiver filter. It may thus be used to evaluate filter performance. This pin may also be
driven to evaluate the demodulator. RXA1
and RXA2 must be grounded during this
test.
For normal modem operation FTLC is AC
grounded via a 0.1 mF bypass capacitor.
Originate/Answer mode select: When logic
high this pin selects the originate mode of
operation.
ulator when held high. The EXI input remains active. If SQT and ALB are simultaneously held high the chip powers down.
Ý
analog inputs. When connected as recommended they produce a 600X hybrid.
line driver.
put to the line driver. This input may be used
to transmit externally generated tones.
When not used for this purpose it should be
grounded to GNDA.
chip are referred to this pin.
pin to V
CC
2: RXA2 and RXA1 are
Ý
1: See RXA2 for details.
sets the transmit level.
3

Functional Description
INTRODUCTION
A modem is a device for transmitting and receiving serial
data over a narrow bandwidth communication channel. The
74VHC943 uses frequency shift keying (FSK) of audio frequency tone. The tone may be transmitted over the
switched telephone network and other voice grade channels. The 74VHC943 is also capable of demodulating FSK
signals. By suitable tone allocation and considerable signal
processing the 74VHC943 is capable of transmitting and
receiving data simultaneously.
The tone allocation used by the 74VHC943 and other Bell
103 compatible modems is shown in Table I. The terms
‘‘originate’’ and ‘‘answer’’ which define the frequency allocation come from use with telephones. The modem on the
end of the line which initiates the call is called the originate
modem. The other modem is the answer modem.
TABLE I. Bell 103 Tone Allocation
Data
Space 1070 Hz 2025 Hz 2025 Hz 1070 Hz
Mark 1270 Hz 2225 Hz 2225 Hz 1270 Hz
THE LINE INTERFACE
The line interface section performs two to four wire conversion and provides impedance matching between the modem and the phone line.
THE LINE DRIVER
The line driver is a power amplifier for driving the line. If the
modem is operating as an originate modem, the second harmonics of the transmitted tones fall close to the frequencies
of the received tones and degrade the received signal to
noise ratio (SNR). The line driver must thus produce low
second harmonic distortion.
THE HYBRID
The voltage on the telephone line is the sum of the transmitted and received signals. The hybrid subtracts the transmitted voltage from the voltage on the telephone line. If the
telephone line was matched to the hybrid impedance, the
output of the hybrid would be only the received signal. This
rarely happens because telephone line characteristic impedances vary considerably. The hybrid output is thus a
mixture of transmitted and received signals.
THE DEMODULATOR SECTION
The Receive Filter
The demodulator recovers the data from the received signals. The signal from the hybrid is a mixture of transmitted
signal, received signals and noise. The first stage of the
Originate Modem Answer Modem
Transmit Receive Transmit Receive
receive filter is an anti-alias filter which attenuates high frequency noise before sampling occurs. The signal then goes
to the second stage of the receive filter where the transmitted tones and other noise are filtered from the received signal. This is a switch capacitor nine pole filter providing at
least 60 dB of transmitted tone rejection. This also provides
high attenuation at 60 Hz, a common noise component.
The Discriminator
The first stage of the discriminator is a hard limiter. The hard
limiter removes from the received signal any amplitude
modulation which may bias the demodulator toward a mark
or a space. It compares the output of the receive filter to the
voltage on the 0.1 mF capacitor on the FTLC pin.
The hard limiter output connects to two parallel bandpass
filters in the discriminator. One filter is tuned to the mark
frequency and the other to the space frequency. The outputs of these filters are rectified, filtered and compared. If
the output of the mark path exceeds the output of the space
path the RXD output goes high. The opposite case sends
RXD low.
The demodulator is implemented using precision switched
capacitor techniques The highly critical comparators in the
limiter and discriminator are auto-zeroed for low offset.
Carrier Detector
The output of the discriminator is meaningful only if there is
sufficient carrier being received. This is established in the
carrier detection circuit which measures the signal on the
line. If this exceeds a certain level for a preset period (adjustable by the CDT pin) the CD
that carrier is present. Then the carrier detect threshold is
lowered by 3 dB. This provides hysteresis ensuring the CD
output remains stable. If carrier is lost CD goes high after
the preset delay and the threshold is increased by 3 dB.
MODULATOR SECTION
The modulator consists of a frequency synthesizer and a
sine wave synthesizer. The frequency synthesizer produces
one of four tones depending on the O/A
frequencies are synthesized to high precision using a crystal
oscillator and variable dual modulus counter.
The counters used respond quickly to data changes, introducing negligible bit jitter while maintaining phase coherence.
The sine wave synthesizer uses switched capacitors to
‘‘look up’’ the voltages of the sine wave. This sampled signal is then further processed by switched capacitor and
continuous filters to ensure the high spectral purity required
by FCC regulations.
output goes low indicating
and TXD pins. The
4
 Loading...
Loading...