Page 1

USER GUIDE AND SPECIFICATIONS
NI cDAQ-9172
DeutschFrançais
ni.com/manuals
Contents
Introduction.............................................................................................4
Safety Guidelines .................................................................................... 5
Safety Guidelines for Hazardous Voltages...................................... 5
Related Documentation........................................................................... 6
Device Documentation and Specifications ...................................... 9
Training Courses.............................................................................. 9
Technical Support on the Web......................................................... 9
Installing the Software ............................................................................ 10
Installing NI-DAQmx ...................................................................... 10
Installing Other Software................................................................. 10
Installing the NI cDAQ-9172.................................................................. 11
Mounting the NI cDAQ-9172.......................................................... 12
NI 9901 Desktop Mounting Kit................................................ 12
NI 9910 DIN-Rail Kit............................................................... 13
NI 9905 Panel Mount Kit ......................................................... 13
Setting Up the NI cDAQ-9172................................................................15
Understanding LED Indications.............................................................. 17
Active LED ...................................................................................... 17
Ready LED ...................................................................................... 17
Using the NI cDAQ-9172 ....................................................................... 18
C Series I/O Modules....................................................................... 18
Correlated vs. Static DIO Modules...........................................19
cDAQ Module Interface .................................................................. 19
USB-STC2 ....................................................................................... 19
AI and AO Sample Timing....................................................... 19
Triggering Modes .....................................................................19
Independent Data Streams ........................................................19
PFI Signals................................................................................ 20
Flexible Counter/Timers........................................................... 20
Page 2

Analog Input ............................................................................................20
Analog Input Triggering...................................................................20
AI Start Trigger Signal..............................................................21
AI Reference Trigger Signal .....................................................22
AI Pause Trigger Signal ............................................................24
Analog Input Timing Signals ...........................................................24
AI Sample Clock .......................................................................24
AI Sample Clock Timebase.......................................................25
Convert Behavior For Analog Input Modules...........................25
Getting Started with AI Applications in Software ...........................28
Analog Output .........................................................................................28
Analog Output Data Generation Methods ........................................28
Software-Timed Generations ....................................................29
Hardware-Timed Generations ...................................................29
Analog Output Triggering ................................................................30
Analog Output Timing Signals.........................................................31
AO Sample Clock......................................................................31
AO Start Trigger Signal ............................................................31
AO Pause Trigger Signal...........................................................33
Minimizing Glitches on the Output Signal.......................................34
Getting Started with AO Applications in Software..........................34
Digital I/O................................................................................................35
Correlated vs. Static DIO Modules ..................................................35
Static DIO.........................................................................................36
Digital Waveform Acquisition (Correlated Input) ...........................36
DI Sample Clock Signal............................................................36
Digital Waveform Generation (Correlated Output) .........................37
Buffered Digital Waveform Generation....................................38
Change Detection Event ...................................................................39
Routing Change Detection Event to an Output Terminal .........39
Change Detection Acquisition..........................................................39
Digital Input/Output Configuration for NI 9401 ..............................39
PFI ...........................................................................................................40
Counters...................................................................................................40
Counter Input Applications ..............................................................42
Counting Edges .........................................................................42
Pulse-Width Measurement ........................................................44
Period Measurement..................................................................46
Semi-Period Measurement ........................................................48
Frequency Measurement ...........................................................49
Position Measurement ...............................................................54
Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement..............................57
Counter Output Applications............................................................59
Simple Pulse Generation ...........................................................59
Pulse Train Generation..............................................................61
Frequency Generation ...............................................................62
Frequency Division ...................................................................63
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 2 ni.com
Page 3

Counter Timing Signals................................................................... 63
Counter n Source Signal ........................................................... 64
Counter n Gate Signal............................................................... 65
Counter n Aux Signal ............................................................... 65
Counter n A, Counter n B, and Counter n Z Signals ................ 66
Counter n Up_Down Signal ..................................................... 66
Counter n HW Arm Signal .......................................................66
Counter n Internal Output and Counter n TC Signals ..............67
Frequency Output Signal .......................................................... 67
Default Counter/Timer Routing.......................................................68
Counter Triggering .......................................................................... 68
Other Counter Features.................................................................... 69
Cascading Counters .................................................................. 69
Counter Filters .......................................................................... 69
Prescaling.................................................................................. 70
Duplicate Count Prevention...................................................... 71
Synchronization Modes ............................................................73
Digital Routing and Clock Generation.................................................... 75
Clock Routing .................................................................................. 76
80 MHz Timebase .................................................................... 76
20 MHz Timebase .................................................................... 76
100 kHz Timebase .................................................................... 76
Specifications .......................................................................................... 77
Analog Input .................................................................................... 77
Analog Output.................................................................................. 77
Digital Waveform Characteristics (Slots 1 through 4 Only) ........... 78
PFI Characteristics (Slots 5 and 6 Only) ......................................... 78
General-Purpose Counter/Timers (Slots 5 and 6 Only)................... 79
Frequency Generator (Slots 5 and 6 Only) ...................................... 80
External Digital Triggers (Slots 5 and 6 or with Some
AI Modules) .................................................................................. 80
Module I/O States ............................................................................ 80
Power Requirements ........................................................................ 80
Bus Interface ....................................................................................81
Physical Characteristics ................................................................... 81
Safety ...............................................................................................81
Environmental..................................................................................82
Shock and Vibration ........................................................................82
Electromagnetic Compatibility ........................................................ 83
CE Compliance ................................................................................ 83
Environmental Management............................................................ 83
Where to Go for Support......................................................................... 84
© National Instruments Corporation 3 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 4

Introduction
This user guide describes how to use the National Instruments cDAQ-9172
chassis and lists specifications. For an interactive demonstration of how to
install the NI cDAQ-9172, go to
ni.com/info and enter daqinstall.
The NI cDAQ-9172 is an eight-slot USB chassis designed for use
with C Series I/O modules. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is capable of
measuring a broad range of analog and digital I/O signals and sensors using
a Hi-Speed USB 2.0 interface. For module specifications, refer to the
documentation included with your C Series I/O module(s) or go to
ni.com/manuals.
1
2
NI cDAQ-9172
Ready
Active
3
11-30 VDC
15 W
1 Power Switch
2 Ready/Active LEDs
3 Power Connector
4 USB Connector
ON
OFF
12345
4 5 6
5 Empty Module Slots
6 Installed C Series I/O Modules
7 Screw for Ground Connection
Figure 1. NI cDAQ-9172 Chassis
7
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 4 ni.com
Page 5

Safety Guidelines
Operate the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis only as described in this user guide.
Note Because some C Series I/O modules may have more stringent certification standards
than the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, the combined system may be limited by individual
component restrictions. Refer to the Using the NI cDAQ-9172 section of this document for
more details.
Caution The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is not certified for use in hazardous locations.
Hot Surface This icon denotes that the component may be hot. Touching this component
may result in bodily injury.
Safety Guidelines for Hazardous Voltages
If hazardous voltages are connected to the module, take the following
precautions. A hazardous voltage is a voltage greater than 42.4 V
60 VDC to earth ground.
Caution Ensure that hazardous voltage wiring is performed only by qualified personnel
adhering to local electrical standards.
Caution Do not mix hazardous voltage circuits and human-accessible circuits on the same
module.
or
pk
Caution Make sure that chassis and circuits connected to the module are properly
insulated from human contact.
Caution The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis provides no isolation, but some modules offer
isolation. Follow the safety guidelines for each module when using hazardous voltage.
© National Instruments Corporation 5 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 6

Related Documentation
Each application software package and driver includes information about
writing applications for taking measurements and controlling measurement
devices. Check
documentation, and refer to Table 1 for a list of locations for driver and
application software documentation. The following document location
references assume you have NI-DAQmx 8.8 or later, and where applicable,
version 7.1 or later of the NI application software.
Table 1. NI Driver and Application Software Documentation
Software Document/Description Location/Topic
ni.com/manuals for the most recent hardware
NI-DAQmx for Windows DAQ Getting Started
Guide—describes how to
install and use the
NI-DAQmx driver software
for Windows and your data
acquisition (DAQ) device,
how to confirm the device is
operating properly, and how
to take an NI-DAQmx
measurement.
NI-DAQ Readme—includes
information about
NI-DAQmx and Traditional
NI-DAQ (Legacy).
Describes how to choose
the API to use, new
features, and a list of known
issues, supported devices,
and devices not supported.
Also provides details about
system requirements.
NI-DAQmx Help—explains
how to get started in your
OS and ADE; provides an
NI-DAQmx overview;
includes information about
programming the most
common measurement
tasks with references to
examples in CVI/C, C++,
.NET.
Start»Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»DAQ Getting Started
Guide
Start»Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQ Readme
Start»Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 6 ni.com
Page 7

Table 1. NI Driver and Application Software Documentation (Continued)
Software Document/Description Location/Topic
LabVIEW Getting Started with
LabVIEW—describes the
LabVIEW graphical
programming environment
and the basic LabVIEW
features you use to build
data acquisition and
instrument control
application.
LabVIEW Help—provides
information about
LabVIEW programming
concepts, step-by-step
instructions for using
LabVIEW, and reference
information about
LabVIEW VIs, functions,
palettes, menus, and tools.
LabVIEW Help Topics Specific to NI-DAQmx
Includes overview
information and a tutorial to
learn how to take an
NI-DAQmx measurement
in LabVIEW using the
DAQ Assistant.
Start»All Programs»
National Instruments»
LabVIEW»LabVIEW Manuals or
navigate to the
labview\manuals
directory and opening
LV_Getting_Started.pdf
Help»Search the LabVIEW Help
From the Contents tab, Getting
Started»Getting Started with DAQ
Describes the LabVIEW
NI-DAQmx VIs and
properties.
From the Contents tab, VI and
Function Reference»
Measurement I/O VIs and
Functions
Contains the conceptual
and how-to information you
From the Contents tab, Taking
Measurements
need to acquire and analyze
measurement data in
LabVIEW, including
common measurements,
measurement
fundamentals, NI-DAQmx
key concepts, and device
considerations.
© National Instruments Corporation 7 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 8

Table 1. NI Driver and Application Software Documentation (Continued)
Software Document/Description Location/Topic
LabWindows™/CVI
™
LabWindows/CVI Help
Data Acquisition
book—contains
NI-DAQmx measurement
concepts and step-by-step
Help»Contents, then select Using
LabWindows/CVI»
Data Acquisition»Taking an
NI-DAQmx Measurement in
LabWindows/CVI
instructions about creating
a measurement task using
the DAQ Assistant.
Measurement
Studio/Microsoft Visual
Studio .NET
ANSI C without
NI Application Software
LabWindows/CVI Help
NI-DAQmx Library
LibraryReference»
NI-DAQmx Library
book—contains
NI-DAQmx API overviews
and function reference.
Microsoft Visual Studio
.NET Help/NI
Measurement Studio
Help—contains
NI-DAQmx methods and
Measurement Studio»
NI Measurement Studio Help and
select NI-DAQmx .NET Class
Library or NI-DAQmx Visual C++
Class Library
properties.
NI-DAQmx Help Start»All Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help
NI-DAQmx C Reference
Help—describes the
NI-DAQmx Library
functions.
Start»All Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx C Reference
Help
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 8 ni.com
Page 9

Table 1. NI Driver and Application Software Documentation (Continued)
Software Document/Description Location/Topic
.NET Languages without
NI Application Software
NI-DAQmx .NET
*
Help—contains conceptual
topics for using NI-DAQmx
with Visual C# and Visual
Basic .NET.
Start»All Programs»
National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx .NET
Reference Help. Expand
NI Measurement Studio Help»
NI Measurement Studio .NET
Class Library»Reference to view
the function reference. Expand
NI Measurement Studio Help»
NI Measurement Studio .NET
Class Library»Using the
Measurement Studio .NET Class
Libraries
Visual Studio .NET
Help—contains conceptual
topics for using NI-DAQmx
with Visual C# and Visual
Basic .NET.
*
With the Microsoft .NET Framework version 1.1 or later, you can use NI-DAQmx to create applications using Visual C#
and Visual Basic .NET without Measurement Studio. You need Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 2003 or Microsoft Visual
Studio 2005 for the API documentation to be installed.
Help»Contents. Select
Measurement Studio from the
Filtered By drop-down list and
follow the location instructions for
the NI-DAQmx .NET Help.
Device Documentation and Specifications
Check ni.com/manuals for the most recent device and software
documentation. If you do not have Web access, NI-DAQmx includes a
Documentation CD that includes documentation available when
NI-DAQmx released.
Training Courses
If you need more help getting started developing an application with
NI products, NI offers training courses. To enroll in a course or obtain
a detailed course outline, refer to
ni.com/training.
Technical Support on the Web
For additional support, refer to ni.com/support or zone.ni.com.
© National Instruments Corporation 9 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 10

Installing the Software
Installing NI-DAQmx
The DAQ Getting Started Guide, which you can download at ni.com/
manuals
software and hardware, configuring channels and tasks, and getting started
developing an application.
Installing Other Software
If you are using other software, refer to the installation instructions that
accompany your software.
, offers NI-DAQmx users step-by-step instructions for installing
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 10 ni.com
Page 11

Installing the NI cDAQ-9172
Figure 2 shows the dimensions of the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis.
88.1 mm
(3.50 in.)
46.0 mm
(1.81 in.)
24.8 mm
(0.98 in.)
59.6 mm
(2.35 in.)
NI cDAQ-9172
Ready
Active
11-30 VDC
15 W
53.8 mm
(2.12 in.)
165.1 mm
(6.50 in.)
ON
OFF
254.0 mm
(10.00 in.)
23.7 mm
(0.94 in.)
20.3 mm
(0.80 in.)
25.0 mm
(0.98 in.)
44.1 mm
(1.74 in.)
63.1 mm
(2.49 in.)
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
19.0 mm
(0.75 in.)
36.4 mm
(1.43 in.)
51.7 mm
(2.04 in.)
4.10 mm
(0.16 in.)
44.1 mm
(1.74 in.)
58.9 mm
(2.32 in.)
31.7 mm
(1.25 in.)
19.1 mm
(0.75 in.)
23.2 mm
(0.91 in.)
Figure 2. NI cDAQ-9172 with Dimensions in Millimeters (Inches)
© National Instruments Corporation 11 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 12

Mounting the NI cDAQ-9172
You can mount the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis using a desktop, a 35 mm
DIN-Rail, or a panel mount accessory kit. For accessory ordering
information, refer to
Caution Your installation must meet the following requirements:
• Allows 25.4 mm (1 in.) of clearance above and below the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis for
air circulation.
• Allows at least 50.8 mm (2 in.) of clearance in front of the modules for common
connector cabling such as the 10-terminal detachable screw terminal connector and, as
needed, up to 88.9 mm (3.5 in.) of clearance in front of the modules for other types of
cabling. For more information about mechanical dimensions, refer to
info
and enter the info code cDAQMechanical. For more information about cable
dimensions, refer to
ni.com/info and enter the info code cDAQCable.
NI 9901 Desktop Mounting Kit
The NI 9901 Desktop Mounting Kit includes two metal feet you can install
on the sides of the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis for desktop use. With this kit,
you can tilt the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis for convenient access to the I/O
module connectors. When you install the two metal feet, the two existing
screws on the power switch side of the chassis must be removed. After
removing the screws, replace them with the two longer screws included in
the NI 9901 Desktop Mounting Kit.
ni.com.
ni.com/
Figure 3. NI 9901 Desktop Mounting Kit
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 12 ni.com
Page 13

NI 9910 DIN-Rail Kit
The NI 9910 DIN-Rail Kit contains one clip for mounting the chassis on a
standard 35 mm DIN-Rail. To mount the chassis on a DIN-Rail, fasten the
DIN-Rail clip to the chassis using a number 2 Phillips screwdriver and
two M4 × 17 screws. The screws are included in the DIN-Rail kit. Make
sure the DIN-Rail kit is installed as illustrated in Figure 4, with the larger
lip of the DIN-RAIL positioned up. When the DIN-Rail kit is properly
installed, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is centered on the DIN-Rail.
Caution Remove the I/O modules before removing the chassis from the DIN-Rail.
Figure 4. DIN-Rail Installation on the NI cDAQ-9172
NI 9905 Panel Mount Kit
To mount the chassis on a panel, align the chassis on the panel mount
accessory. Attach the chassis to the panel mount kit using two M4 × 17
screws (as shown in Figure 5). National Instruments provides these screws
with the panel mount kit. You must use these screws because they are the
correct depth and thread for the panel. These slots in the panel mount kit
© National Instruments Corporation 13 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 14

can be used with M4, M5, No. 8, or No.10 panhead screws. Figure 5
illustrates the panel dimensions and installation on the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis. Refer to the documentation included with the NI 9905 Panel
Mount Kit for more detailed dimensions.
330.2 mm
(13.00 in.)
NATIONAL
INSTRUMENTS
NI cDAQ-9172
11-30 VDC
Ready
Active
15 W
ON
OFF
48.1 mm
(1.90 in.)
28.1 mm
(1.11 in.)
87654321
88.1 mm
(3.47 in.)
Figure 5. Panel Mount Dimensions and Installation on the NI cDAQ-9172
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 14 ni.com
Page 15

Setting Up the NI cDAQ-9172
Complete the following steps to prepare the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis for use:
1. Before connecting the hardware, install the NI-DAQmx software.
Refer to the DAQ Getting Started Guide for more information about
software installation.
Note The NI-DAQmx software is included on the CD shipped with your kit and is
available for download at
after installation from Start»All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»DAQ
Getting Started Guide. Other NI documentation is available from
2. If you are not using any mounting accessories, attach the provided
3. Make sure the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis power switch is turned off.
4. Attach a ring lug to a 14 AWG (1.6 mm) wire. Connect the ring lug to
ni.com/support. The DAQ Getting Started Guide is available
rubber standoffs to the back of the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis.
the ground terminal on the side of the chassis using the ground screw.
Attach the other end of the wire to the system safety ground.
ni.com/manuals.
1
1 Attached to System Ground
Figure 6. Ring Lug Attached to Ground Terminal
Note
Additionally, attach a wire with a ring lug to all other C Series I/O module cable
shields. You must connect this wire to the ground terminal of the chassis using the ground
screw.
5. Remove the plastic cover from the connector in any empty module slot.
© National Instruments Corporation 15 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 16

6. Squeeze both C Series I/O module latches, insert the I/O module into
the module slot, and press until both latches lock the module in place.
7. Connect the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis with the supplied USB cable to
any available USB port on your computer.
8. Connect the power source to the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. The
NI cDAQ-9172 chassis requires an external power supply that meets
the specifications in the Power Requirements section.
Note The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis uses a DC input jack with a locking ring. Use only this
connector with the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. Refer to the Specifications section for more
information about the connector.
9. Secure the power supply and USB cables, as depicted in Figure 7,
using the two tie wraps and adhesive tie wrap mounts included in the
shipping kit. The tie wraps and adhesive mounts help secure the
non-latching USB connection. They can also be used to route the
cables to a desirable position.
NI cDAQ-9172
Figure 7. cDAQ Chassis With Secured Cables
10. Power on the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis.
11. Double-click the Measurement & Automation icon, shown at left,
on the desktop to open MAX.
12. Expand Devices and Interfaces, and then expand NI-DAQmx
Devices.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 16 ni.com
Page 17

13. Check that your device appears under Devices and Interfaces. If your
device does not appear, press <F5> to refresh the view in MAX. If your
device is still not recognized, refer to
troubleshooting information.
14. Right-click your device and select Self-Test.
If you need help during the self-test, select Help»Help Topics»
NI-DAQmx and click MAX Help for NI-DAQmx.
When the self-test finishes, a message indicates successful verification
or an error. If an error occurs, refer to
for troubleshooting information.
Note When in use, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis may become warm to the touch. This is
normal.
Understanding LED Indications
Active LED
The Active LED indicates whether the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is
communicating over the USB bus.
ni.com/support/install for
ni.com/support/install
Table 2. Active LED
Ready LED
LED Definition
Amber Power is applied, but USB connection is not
established
Green USB traffic present
Off No USB traffic present
The Ready LED is lit when the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is ready for use. The
color indicates whether the USB connection is Full-Speed or Hi-Speed.
Table 3. Ready LED
LED Definition
Amber Hi-Speed (480 Mbit/sec)
Green Full-Speed (12 Mbit/sec)
Off USB connection is not established
© National Instruments Corporation 17 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 18

Using the NI cDAQ-9172
The cDAQ system consists of three parts: C Series I/O modules, the cDAQ
module interface, and the USB-STC2. These components digitize signals,
perform D/A conversions to generate analog output signals, measure and
control digital I/O signals, and provide signal conditioning.
C Series
I/O Module
cDAQ Module
Interface
C Series
I/O Module
C Series
I/O Module
USB-
STC2
Figure 8. NI cDAQ-9172 Block Diagram
USB
2.0
C Series I/O Modules
National Instruments C Series I/O modules provide built-in signal
conditioning and screw terminal, spring terminal, BNC, D-SUB, or
RJ-50 connectors. A wide variety of I/O types are available, allowing
you to customize the cDAQ system to meet your application needs.
C Series I/O modules are hot-swappable and automatically detected by the
NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. I/O channels are accessible using the NI-DAQmx
driver software.
Because the modules contain built-in signal conditioning for extended
voltage ranges or industrial signal types, you can usually make your
wiring connections directly from the C Series I/O modules to your
sensors/actuators. In most cases, the C Series I/O modules provide isolation
from channel-to-earth ground.
For more information about which C Series I/O modules are compatible
with the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, refer to the KnowledgeBase document,
C Series Modules Supported in the NI cDAQ-9172 CompactDAQ.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 18 ni.com
Page 19

To access this KnowledgeBase, go to ni.com/info and enter the info
code
Correlated vs. Static DIO Modules
Digital I/O module capabilities are determined by the type of digital signals
that the module is capable of measuring or generating. Static digital I/O
modules are designed for signals that change slowly and are accessed by
software-timed reads and writes. Correlated digital I/O modules are for
signals that change rapidly and are updated by either software-timed or
hardware-timed reads and writes. For more information about Digital I/O
modules, refer to the Digital I/O section.
cDAQ Module Interface
The cDAQ Module Interface manages data transfers between the
USB-STC2 and the C Series I/O modules. The interface also handles
autodetection, signal routing, and synchronization.
USB-STC2
The USB-STC2 features independent high-speed data streams; flexible
AI and AO sample timing; triggering; PFI signals for multi-device
synchronization; flexible counter/timers with hardware gating; digital
waveform acquisition and generation; and static DIO.
rdcdaq.
AI and AO Sample Timing
The USB-STC2 contains advanced analog input and analog output timing
engines. A wide range of timing and synchronization signals are available
through the PFI lines. Refer to the Analog Input Timing Signals and
Analog Output Timing Signals sections for more information about the
configuration of these signals.
Triggering Modes
The NI cDAQ-9172 supports different trigger modes, such as start trigger,
reference trigger, and pause trigger with analog, digital, or software
sources. Refer to the Analog Input Triggering and Analog Output
Triggering sections for more information.
Independent Data Streams
The NI cDAQ-9172 supports four independent high-speed data streams;
allowing for up to four simultaneous hardware timed tasks, such as analog
input, analog output, buffered counter/timers, and correlated digital
input/output.
© National Instruments Corporation 19 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 20

Analog Input
PFI Signals
The PFI signals, available through correlated digital input and output
modules installed in slots 5 and/or 6, provide access to advanced features
such as triggering, synchronization, and counter/timers. Refer to the PFI
section for more information.
The PFI pins have a digital filter circuit at the inputs that is configurable on
a per-line basis. The filters allow the rejection of noise caused by noisy
environments, bounces on switches, and so on.
Flexible Counter/Timers
The NI cDAQ-9172 includes two general-purpose 32-bit counter/timers
that can be used to count edges, measure pulse-widths, measure periods and
frequencies, and perform position measurements (encoding). In addition,
the counter/timers can generate pulses, pulse trains, and square waves with
adjustable frequencies. You can access the counter inputs and outputs using
correlated digital I/O modules in slots 5 and/or 6. Refer to the Counters
section for more information.
To perform analog input measurements, insert a supported analog input
C Series I/O module into any slot on the cDAQ chassis. The measurement
specifications, such as number of channels, channel configuration, sample
rate, and gain, are determined by the type of C Series I/O module used. For
more information and wiring diagrams, refer to the documentation included
with your C Series I/O modules.
The NI cDAQ-9172 has one AI timing engine, which means that only
one analog input task can be running at a time on a chassis. However, the
analog input task can include channels from multiple analog input modules.
Analog Input Triggering
A trigger is a signal that causes an action, such as starting or stopping the
acquisition of data. When you configure a trigger, you must decide how
you want to produce the trigger and the action you want the trigger to cause.
The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis supports internal software, external digital
triggering, and analog triggering.
Three triggers are available: start trigger, reference trigger, and pause
trigger. An analog or digital trigger can initiate these three trigger actions.
Any C Series correlated digital input module can supply a digital trigger
when installed in slots 5 or 6, and some C Series analog modules can supply
an analog or digital trigger in any slot. The start, reference, and pause
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 20 ni.com
Page 21

triggers can come from three separate modules if desired. To find your
module triggering options, refer to the documentation included with your
C Series I/O modules. For more information about using digital modules
for triggering, refer to the Digital I/O section.
AI Start Trigger Signal
Use the AI Start Trigger (ai/StartTrigger) signal to begin a measurement
acquisition. A measurement acquisition consists of one or more samples. If
you do not use triggers, begin a measurement with a software command.
Once the acquisition begins, configure the acquisition to stop in one of the
following ways:
• When a certain number of points is sampled (in finite mode)
• After a hardware reference trigger (in finite mode)
• With a software command (in continuous mode)
An acquisition that uses a start trigger (but not a reference trigger) is
sometimes referred to as a posttriggered acquisition. That is, samples are
measured only after the trigger.
When you are using an internal sample clock, you can specify a delay from
the start trigger to the first sample.
Using a Digital Source
To use ai/StartTrigger with a digital source, specify a source and an edge.
Use the following signals as the source:
•Any PFI terminal.
• Counter n Internal Output
The source also can be one of several other internal signals on your
NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. Refer to the Device Routing in MAX topic in the
NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help in version 8.0 or later for more
information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
You also can specify whether the measurement acquisition begins on the
rising edge or falling edge of ai/StartTrigger.
© National Instruments Corporation 21 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
ni.com/manuals.
Page 22

Using an Analog Source
Some C Series I/O modules can generate a trigger based on an analog
signal. In NI-DAQmx, this is called the Analog Comparison Event.
When you use an analog trigger source for ai/StartTrigger, the acquisition
begins on the first rising edge of the Analog Comparison Event signal.
Routing AI Start Trigger to an Output Terminal
You can route ai/StartTrigger to any output PFI terminal. The output is an
active high pulse.
AI Reference Trigger Signal
Use a reference trigger (ai/ReferenceTrigger) signal to stop a measurement
acquisition. To use a reference trigger, specify a buffer of finite size and
a number of pretrigger samples (samples that occur before the reference
trigger). The number of posttrigger samples (samples that occur after the
reference trigger) desired is the buffer size minus the number of pretrigger
samples.
Once the acquisition begins, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis writes samples to
the buffer. After the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis captures the specified number
of pretrigger samples, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis begins to look for the
reference trigger condition. If the reference trigger condition occurs before
the NI cDAQ-9172 captures the specified number of pretrigger samples, the
NI cDAQ-9172 ignores the condition.
If the buffer becomes full, the NI cDAQ-9172 continuously discards the
oldest samples in the buffer to make space for the next sample. This data
can be accessed (with some limitations) before the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis
discards it. Refer to the KnowledgeBase document, Can a Pretriggered
Acquisition be Continuous?, for more information. To access this
KnowledgeBase, go to
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 22 ni.com
ni.com/info and enter the info code rdcanq.
Page 23

When the reference trigger occurs, the NI cDAQ-9172 continues to write
samples to the buffer until the buffer contains the number of posttrigger
samples desired. Figure 9 shows the final buffer.
Reference Trigger
Pretrigger Samples
Complete Buffer
Figure 9. Reference Trigger Final Buffer
Posttrigger Samples
Using a Digital Source
To use ai/ReferenceTrigger with a digital source, specify a source and an
edge. Either PFI or one of several internal signals on the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis can provide the source. Refer to the Device Routing in MAX topic
in the NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help in version 8.0 or later for
more information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
You also can specify whether the measurement acquisition stops on the
rising edge or falling edge of ai/ReferenceTrigger.
ni.com/manuals.
Using an Analog Source
Some C Series I/O modules can generate a trigger based on an analog
signal. In NI-DAQmx, this is called the Analog Comparison Event.
When you use an analog trigger source, the acquisition stops on the first
rising or falling edge of the Analog Comparison Event signal, depending
on the trigger properties.
Routing AI Reference Trigger Signal to an Output Terminal
You can route ai/ReferenceTrigger to any output PFI terminal.
© National Instruments Corporation 23 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 24

AI Pause Trigger Signal
You can use the AI Pause Trigger (ai/PauseTrigger) signal to pause and
resume a measurement acquisition. The internal sample clock pauses while
the external trigger signal is active and resumes when the signal is inactive.
You can program the active level of the pause trigger to be high or low.
Using a Digital Source
To use ai/PauseTrigger, specify a source and a polarity. The source
can be either from PFI or one of several other internal signals on
your NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. Refer to the Device Routing in MAX topic in
the NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help in version 8.0 or later for more
information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
Using an Analog Source
Some C Series I/O modules can generate a trigger based on an analog
signal. In NI-DAQmx, this is called the Analog Comparison Event.
ni.com/manuals.
When you use an analog trigger source, the internal sample clock pauses
when the Analog Comparison Event signal is low and resumes when the
signal goes high (or vice versa).
Note Pause triggers are only sensitive to the level of the source, not the edge.
Analog Input Timing Signals
AI Sample Clock
A sample consists of one reading from each channel in the AI task.
ai/SampleClock signals the start of a sample of all analog input channels
in the task. ai/SampleClock can be generated from external or internal
sources.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 24 ni.com
Page 25

k
PFI
Analog Comparison
Event
20 MHz Timebase
100 kHz Timebase
PFI
Analog Comparison Event
Ctr
n
Sigma-Delta Module Internal Output
ai/SampleClock
Timebase
Programmable
Divider
Figure 10. Sample Clock Timing Options
Internal Output
Clock
ai/SampleCloc
Routing AI Sample Clock to an Output Terminal
You can route ai/SampleClock to any output PFI terminal.
AI Sample Clock Timebase
The AI Sample Clock Timebase (ai/SampleClockTimebase) signal is
divided down to provide a source for ai/SampleClock. ai/SampleClock
Timebase can be generated from external or internal sources.
ai/SampleClockTimebase is not available as an output from the chassis.
Convert Behavior For Analog Input Modules
Scanned
Scanned C Series analog input modules contain a single A/D converter and
a multiplexer to select between multiple input channels. When the cDAQ
Module Interface receives a Sample Clock pulse, it begins generating a
Convert Clock for each scanned module in the current task. Each Convert
Clock signals the acquisition of a single channel from that module. The
Convert Clock rate depends on the module being used, the number of
channels used on that module, and the system Sample Clock rate.
The driver chooses the fastest conversion rate possible based on the speed
of the A/D converter for each module and adds 10 µs of padding between
each channel to allow for adequate settling time. This scheme enables the
channels to approximate simultaneous sampling. If the AI Sample Clock
rate is too fast to allow for 10 µs of padding, NI-DAQmx selects a
conversion rate that spaces the AI Convert Clock pulses evenly throughout
the sample. NI-DAQmx uses the same amount of padding for all the
modules in the task. To explicitly specify the conversion rate, use the
© National Instruments Corporation 25 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 26

ActiveDevs and AI Convert Clock Rate properties using the DAQmx
Timing property node or functions.
Simultaneous Sample-and-Hold
Simultaneous sample-and-hold (SSH) C Series analog input modules
contain multiple A/D converters or circuitry that allows all the input
channels to be sampled at the same time. These modules sample their
inputs on every Sample Clock pulse.
Sigma-Delta
Sigma-delta C Series analog input modules function much like SSH
modules, but use A/D converters that require a high-frequency oversample
clock to produce accurate, synchronized data. Sigma-delta modules in
the cDAQ chassis automatically share a single oversample clock to
synchronize data from all sigma-delta modules.
This clock is used as the AI Sample Clock Timebase. While most modules
supply a common oversample clock frequency (12.8 MHz), some modules,
such as the NI 9234, supply a different frequency. When sigma-delta
modules with different oversample clock frequencies are used in an analog
input task, the AI Sample Clock Timebase can use any of the available
frequencies; by default, the fastest available is used. The sampling
rate of all modules in the system is an integer divisor of the frequency
of the AI Sample Clock Timebase.
When one or more sigma-delta modules are in an analog input task, the
sigma-delta modules also provide the signal used as the AI Sample Clock.
This signal is used to cause A/D conversion for other modules in the
system, just as the AI Sample Clock does when a sigma-delta module is not
being used.
When sigma-delta modules are in an AI task, the chassis automatically
issues a synchronization pulse to each sigma-delta modules that resets their
ADCs at the same time. Both the synchronization pulse and the oversample
clock can be routed from or to any PFI line to allow synchronization
between multiple chassis. Because of the filtering used in sigma-delta A/D
converters, these modules usually exhibit a fixed input delay relative to
non-sigma-delta modules in the system. This input delay is specified in the
C Series I/O module documentation.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 26 ni.com
Page 27

ai/StartTrigger
Data from
A/D Conversion
(Slow Module)
ai/SampleClock
Slow Sample Rate Modules
Some C Series analog input modules are specifically designed for
measuring signals that vary slowly, such as temperature. Because of their
slow rate, it is not appropriate for these modules to constrain the AI Sample
Clock to operate at or slower than their maximum rate. When using such a
module in the cDAQ chassis, the maximum Sample Clock rate can run
faster than the maximum rate for the module. When operating at a rate
faster than these slow rate modules can support, the slow rate module
returns the same point repeatedly, until a new conversion completes. The
first point is acquired when the task is committed. The second point is
acquired after the start trigger.
1st A/D Conversion 2nd A/D Conversion 3rd A/D Conversion
A
B C
Data Returned
to AI Task
A A A B B B C
Figure 11. Sample Clock Timing Example
For example, if running an AI task at 1 kHz using a module with a
maximum rate of 10 Hz, the slow module returns 100 samples of the first
point, followed by 100 samples of the second point, etc. Other modules in
the task will return 1,000 new data points per second, which is normal.
When performing a single-point acquisition, no points are repeated.
Refer to the KnowledgeBase document, C Series Modules Supported in the
NI cDAQ-9172 CompactDAQ, for more information. To access this
KnowledgeBase, go to
© National Instruments Corporation 27 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
ni.com/info and enter the info code rdcdaq.
Page 28

Getting Started with AI Applications in Software
You can use the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis in the following analog input
applications:
• Single-Point
•Finite
• Continuous
For more information about programming analog input applications and
triggers in software, Refer to the NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help in
version 8.0 or later for more information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
ni.com/manuals.
Analog Output
To generate analog output, insert an analog output C Series I/O module in
any slot on the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. The generation specifications, such
as the number of channels, channel configuration, update rate, and output
range, are determined by the type of C Series I/O module used. For more
information, refer to the documentation included with your C Series I/O
modules.
You can run one hardware-timed (waveform) analog output task at a time
on the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, with up to 16 waveform channels. At the
same time, you can also run one or more software-timed (single-point or
immediate) tasks.
For each analog output module, you can either:
• Assign all of the channels on the module to the hardware-timed task.
• Assign all of the channels on the module to one or more
software-timed tasks.
On a single AO module, you cannot assign some channels to a
hardware-timed task and other channels (on the same module) to
a software-timed task.
Analog Output Data Generation Methods
When performing an analog output operation, you either can perform
software-timed or hardware-timed generations. Hardware-timed
generations must be buffered.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 28 ni.com
Page 29

Software-Timed Generations
With a software-timed generation, software controls the rate at which data
is generated. Software sends a separate command to the hardware to initiate
each DAC conversion. In NI-DAQmx, software-timed generations are
referred to as on-demand timing. Software-timed generations are also
referred to as immediate or static operations. They are typically used for
writing out a single value, such as a constant DC voltage.
The following considerations apply to software-timed generations:
• If any AO channel on a module is used in a hardware-timed
(waveform) task, no channels on that module can be used in a
software-timed task.
• You can configure software-timed generation to simultaneously
update.
• Only one simultaneous update task can run at a time.
• Simultaneous update is not restricted to 16 channels.
• A hardware-timed AO task and a simultaneous update AO task cannot
run at the same time.
Hardware-Timed Generations
With a hardware-timed generation, a digital hardware signal controls the
rate of the generation. This signal can be generated internally on the chassis
or provided externally.
Hardware-timed generations have several advantages over software-timed
acquisitions:
• The time between samples can be much shorter.
• The timing between samples is deterministic.
• Hardware-timed acquisitions can use hardware triggering.
Hardware-timed AO operations on the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis must be
buffered.
Buffered Analog Output
A buffer is a temporary storage in computer memory for generated
samples. In a buffered generation, data is moved from a host buffer to the
NI cDAQ-9172 onboard FIFO before it is written to the C Series I/O
modules.
© National Instruments Corporation 29 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 30

One property of buffered I/O operations is sample mode. The sample mode
can be either finite or continuous:
• Finite—Finite sample mode generation refers to the generation of a
specific, predetermined number of data samples. After the specified
number of samples is written out, the generation stops.
• Continuous—Continuous generation refers to the generation of an
unspecified number of samples. Instead of generating a set number of
data samples and stopping, a continuous generation continues until
you stop the operation. There are three different continuous generation
modes that control how the data is written. These modes are
regeneration, onboard regeneration, and non-regeneration:
– In regeneration mode, you define a buffer in host memory. The
data from the buffer is continually downloaded to the FIFO to be
written out. New data can be written to the host buffer at any time
without disrupting the output.
– With onboard regeneration, the entire buffer is downloaded to the
FIFO and regenerated from there. After the data is downloaded,
new data cannot be written to the FIFO. To use onboard
regeneration, the entire buffer must fit within the FIFO size. The
advantage of using onboard regeneration is that it does not require
communication with the main host memory once the operation is
started, which prevents problems that may occur due to excessive
bus traffic or operating system latency.
– With non-regeneration, old data is not repeated. New data must
continually be written to the buffer. If the program does not write
new data to the buffer at a fast enough rate to keep up with the
generation, the buffer underflows and causes an error.
Analog Output Triggering
Analog output supports two different triggering actions:
• Start trigger
• Pause trigger
An analog or digital trigger can initiate these actions. Any C Series
correlated digital module in slots 5 and/or 6 can supply a digital trigger, and
some C Series analog modules can supply an analog trigger. For more
information refer to the AO Start Trigger Signal section of this document
or to the documentation included with your C Series I/O module(s).
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 30 ni.com
Page 31

Analog Output Timing Signals
The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis features the following AO (waveform
generation) timing signals:
• AO Sample Clock
•AO Start Trigger
• AO Pause Trigger
AO Sample Clock
The AO sample clock (ao/SampleClock) signals when all the analog output
channels in the task update. ao/SampleClock can be generated from
external or internal sources.
PFI
Analog Comparison
Event
20 MHz Timebase
ao/SampleClock
Timebase
PFI
Analog Comparison Event
Ctr
n
Internal Output
Programmable
Clock
Divider
ao/SampleClock
100 kHz Timebase
Figure 12. Analog Output Timing Options
Routing AO Sample Clock to an Output Terminal
You can route ao/SampleClock to any output PFI terminal.
AO Sample Clock Timebase Signal
The AO Sample Clock Timebase (ao/SampleClockTimebase)
signal is divided down to provide a source for ao/SampleClock.
ao/SampleClockTimebase can be generated from external or internal
sources, and is not available as an output from the chassis.
AO Start Trigger Signal
Use the AO Start Trigger (ao/StartTrigger) signal to initiate a waveform
generation. If you do not use triggers, you can begin a generation
with a software command. If you are using an internal sample clock,
you can specify a delay from the start trigger to the first sample. For
© National Instruments Corporation 31 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 32

more information, refer to the NI-DAQmx Help. The NI-DAQmx Help
is available after installation from Start»All Programs»National
Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
Using a Digital Source
To use ao/StartTrigger, specify a source and a rising or falling edge.
The source can be one of the following signals:
• A pulse initiated by host software
• Any PFI terminal
• ai/ReferenceTrigger
• ai/StartTrigger
The source also can be one of several internal signals on the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis. Refer to the Device Routing in MAX topic in the NI-DAQmx Help
or the LabVIEW Help in version 8.0 or later for more information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
You also can specify whether the waveform generation begins on the rising
edge or falling edge of ao/StartTrigger.
ni.com/manuals.
Using an Analog Source
Some C Series I/O modules can generate a trigger based on an analog
signal. In NI-DAQmx, this is called the Analog Comparison Event,
depending on the trigger properties.
When you use an analog trigger source, the waveform generation begins on
the first rising or falling edge of the Analog Comparison Event signal,
depending on the trigger properties. The analog trigger circuit must be
configured by a simultaneously running analog input task.
Routing AO Start Trigger Signal to an Output Terminal
You can route ao/StartTrigger to any output PFI terminal. The output is an
active high pulse.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 32 ni.com
Page 33

AO Pause Trigger Signal
Use the AO Pause trigger signal (ao/PauseTrigger) to mask off samples in
a DAQ sequence. When ao/PauseTrigger is active, no samples occur, but
ao/PauseTrigger does not stop a sample that is in progress. The pause does
not take effect until the beginning of the next sample.
When you generate analog output signals, the generation pauses as soon as
the pause trigger is asserted. If the source of the sample clock is the onboard
clock, the generation resumes as soon as the pause trigger is deasserted,
as shown in Figure 13.
Pause Trigger
Sample Clock
Figure 13. ao/PauseTrigger with the Onboard Clock Source
If you are using any signal other than the onboard clock as the source of
the sample clock, the generation resumes as soon as the pause trigger is
deasserted and another edge of the sample clock is received, as shown in
Figure 14.
Pause Trigger
Sample Clock
Figure 14. ao/PauseTrigger with Other Signal Source
Using a Digital Source
To use ao/PauseTrigger, specify a source and a polarity. The source can be
a PFI signal or one of several other internal signals on the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis.
You also can specify whether the samples are paused when ao/PauseTrigger
is at a logic high or low level. Refer to the Device Routing in MAX topic in
the NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help in version 8.0 or later for more
information.
© National Instruments Corporation 33 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 34

The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To v iew th e LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»Search the
LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download the LabVIEW
Help, go to
ni.com/manuals.
Using an Analog Source
Some C Series I/O modules can generate a trigger based on an analog
signal. In NI-DAQmx, this is called the Analog Comparison Event,
depending on the trigger properties.
When you use an analog trigger source, the samples are paused when the
Analog Comparison Event signal is at a high or low level, depending on
the trigger properties. The analog trigger circuit must be configured by
a simultaneously running analog input task.
Minimizing Glitches on the Output Signal
When you use a DAC to generate a waveform, you may observe glitches
on the output signal. These glitches are normal; when a DAC switches from
one voltage to another, it produces glitches due to released charges. The
largest glitches occur when the most significant bit of the DAC code
changes. You can build a lowpass deglitching filter to remove some of
these glitches, depending on the frequency and nature of the output signal.
Go to
ni.com/support for more information about minimizing glitches.
Getting Started with AO Applications in Software
You can use the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis in the following analog output
applications:
• Single-Point (On-Demand) Generation
• Finite Generation
• Continuous Generation
• Waveform Generation
For more information about programming analog output applications and
triggers in software, refer the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, or to
the NI-DAQmx Help.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 34 ni.com
ni.com/manuals.
Page 35

Digital I/O
To use digital I/O, insert a digital I/O C Series module into any slot on
the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis. The I/O specifications, such as number of lines,
logic levels, update rate, and line direction, are determined by the type
of C Series I/O module used. For more information, refer to the
documentation included with your C Series I/O modules.
Correlated vs. Static DIO Modules
Digital I/O module capabilities are determined by the type of digital signals
that the module is capable of measuring or generating. Static digital I/O
modules are designed for signals that change slowly and are accessed by
software-timed reads and writes. Correlated digital I/O modules are
for signals that change rapidly and are updated by either software-timed or
hardware-timed reads and writes. Correlated digital I/O modules can
perform the following tasks:
• Used in any slot—Software-timed reads and writes
• Used in slots 1 though 4—Digital waveform generation and
acquisition (correlated input/output)
• Used in slots 5 and 6—Counter/timer
• Used in slots 5 and 6—Access PFI signals
To determine the capability of digital I/O modules supported by the
NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, refer to the KnowledgeBase document,
C Series Modules Supported in the NI cDAQ-9172 CompactDAQ.
To access this KnowledgeBase document, go to
the info code
rdcdaq.
ni.com/info and enter
Available features, such as trigger and counter/timer, are determined by the
slot containing the digital I/O C Series module and the capabilities of the
module.
Table 4. Digital Module Slot Features
Digital
Waveform/Change
Slots Static DIO PFI
1
Counter/Timer
1
Detection
1
1 Ye s — — Ye s
2 Ye s — — Ye s
3 Ye s — — Ye s
4 Ye s — — Ye s
© National Instruments Corporation 35 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 36

Table 4. Digital Module Slot Features (Continued)
Slots Static DIO PFI
5 Ye s Ye s Ye s —
6 Ye s Ye s Ye s —
7 Ye s — — —
8 Ye s — — —
1
Requires the use of a correlated digital I/O module.
Static DIO
Each of the DIO lines can be used as a static DI or DO line. You can use
static DIO lines to monitor or control digital signals on some C Series I/O
modules. Each DIO line can be individually configured as a digital input
(DI) or digital output (DO), depending on the C Series I/O module being
used.
All samples of static DI lines and updates of static DO lines are
software-timed.
Digital
Waveform/Change
1
Counter/Timer
1
Detection
1
Digital Waveform Acquisition (Correlated Input)
You can acquire digital waveforms using correlated digital modules in
slots 1 through 4. The DI waveform acquisition FIFO stores the digital
samples. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis samples the DIO lines on each rising
or falling edge of the di/SampleClock signal.
DI Sample Clock Signal
Use the DI Sample Clock (di/SampleClock) signal to sample digital I/O on
slots 1 through 4, using correlated digital modules, and store the result in
the DI waveform acquisition FIFO. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis does not
have an independent DI Sample Clock circuit. Therefore, you must route
an external signal or one of many internal signals from another subsystem
to function as the DI Sample Clock. For example, you can correlate digital
and analog samples in time by setting the AI Sample Clock or AO Sample
Clock as the source of the DI Sample Clock. To sample a digital signal
independent of an AI, AO, or DO operation, you can configure a counter
to generate the desired DI Sample Clock or use an external signal as the
source of the DI Sample Clock.
If the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis receives a di/SampleClock signal when the
FIFO is full, it reports an overflow error to the host software.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 36 ni.com
Page 37

Using an Internal Source
To use di/SampleClock with an internal source, specify the signal source
and the polarity of the signal. Use the following signals as the source:
• AI Sample Clock
• AI Convert Clock
• AO Sample Clock
• Counter n Internal Output
•Frequency Output
• DI Change Detection Output
Several other internal signals can be routed to di/SampleClock. Refer to the
Device Routing in MAX topic in the NI-DAQmx Help or the LabVIEW Help
in version 8.0 or later for more information.
The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
To view the LabVIEW Help, in version 8.0 or later, select Help»
Search the LabVIEW Help in LabVIEW. Alternately, to download
the LabVIEW Help, go to
ni.com/manuals.
Using an External Source
You can route the following signals as di/SampleClock:
•Any PFI terminal
• Analog Comparison Event (an analog trigger)
You can sample data on the rising or falling edge of di/SampleClock.
Routing DI Sample Clock to an Output Terminal
You can route di/SampleClock to any output PFI terminal. The PFI
circuitry inverts the polarity of di/SampleClock before driving the PFI
terminal.
Digital Waveform Generation (Correlated Output)
With a hardware-timed generation, a digital hardware signal controls the
rate of the generation. This signal can be generated internally on the chassis
or provided externally.
Hardware-timed generations have several advantages over software-timed
acquisitions:
• The time between samples can be much shorter.
• The timing between samples can be deterministic.
Hardware-timed operations must be buffered.
© National Instruments Corporation 37 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 38

Buffered Digital Waveform Generation
A buffer is a temporary storage in computer memory for generated
samples. In a buffered generation, data is moved from a host buffer to the
NI cDAQ-9172 onboard FIFO before it is written to the C Series I/O
modules. Buffered generations typically allow for much faster transfer
rates than nonbuffered generations because data is moved in large blocks,
rather than one point at a time. The DO sample clock causes all lines in the
task to update at the same time.
One property of buffered I/O operations is the sample mode. The sample
mode can be either finite or continuous:
• Finite—Finite sample mode generation refers to the generation of a
specific, predetermined number of data samples. After the specified
number of samples has been written out, the generation stops.
• Continuous—Continuous generation refers to the generation of an
unspecified number of samples. Instead of generating a set number of
data samples and stopping, a continuous generation continues until
you stop the operation. There are several different methods of
continuous generation that control what data is written. These methods
are regeneration, onboard regeneration, and non-regeneration modes:
– In regeneration mode, you define a buffer in host memory. The
data from the buffer is continually downloaded to the FIFO to be
written out. New data can be written to the host buffer at any time
without disrupting the output.
– With onboard regeneration, the entire buffer is downloaded to the
FIFO and regenerated from there. After the data is downloaded,
new data cannot be written to the FIFO. To use onboard
regeneration, the entire buffer must fit within the FIFO size. The
advantage of using on board regeneration is that it does not require
communication with the main host memory once the operation is
started, thereby preventing any problems that may occur due to
excessive bus traffic or operating system latency.
– With non-regeneration, old data is not repeated. New data must be
continually written to the buffer. If the program does not write new
data to the buffer at a fast enough rate to keep up with the
generation, the buffer underflows and causes an error.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 38 ni.com
Page 39

Change Detection Event
The Change Detection Event is the signal generated when a change on the
rising or falling edge lines is detected by the change detection task.
Routing Change Detection Event to an Output Terminal
You can route ChangeDetectionEvent to any output PFI terminal.
Change Detection Acquisition
You can configure lines on correlated digital modules in slots 1 through 4
to detect rising or falling edges. When one or more of these lines sees the
edge specified for that line, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis samples all the lines
in the task. The rising and falling edge lines do not necessarily have to be
in the task.
Change detection acquisitions can be buffered or nonbuffered:
• Nonbuffered Change Detection Acquisition—In nonbuffered
acquisitions, correlated digital input modules in any slot may be in the
task, but the rising/falling edge detection lines must be in slots 1
through 4.
• Buffered Change Detection Acquisition—A buffer is a temporary
storage in computer memory for acquired samples. In a buffered
acquisition, data is stored in the NI cDAQ-9172 onboard FIFO then
transferred to a PC buffer. Buffered acquisitions typically allow for
much faster transfer rates than nonbuffered acquisitions because data
accumulates and is transferred in blocks, rather than one sample at a
time. With buffered acquisitions, all modules in the task must be in
slots 1 through 4.
Digital Input/Output Configuration for NI 9401
When you change the configuration of lines on a NI 9401 digital I/O
module between input and output, NI-DAQmx temporarily reserves all
of the lines on the module for communication to send the module a line
configuration command. If another task or route is actively using the
module, to avoid interfering with the other task, NI-DAQmx generates an
error instead of sending the line configuration command. During the line
configuration command, the output lines are maintained without glitching.
© National Instruments Corporation 39 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 40

PFI
Counters
You can configure channels of a correlated digital module in slots 5 and 6
as Programmable Function Interface (PFI) terminals.
You can configure each PFI individually as the following:
• Static digital input
• Static digital output
• Timing input signal for AI, AO, DI, DO, or counter/timer functions
• Timing output signal from AI, AO, DI, DO, or counter/timer functions
Each PFI input also has a programmable digital filter circuit that is
configurable on a per-line basis. The filters allow the rejection of noise
caused by noisy environments, bounces on switches, and so on. Refer to the
NI-DAQmx Help for more information. The NI-DAQmx Help is available
after installation from Start»All Programs»National Instruments»
NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis has two general-purpose 32-bit counter/timers
and one frequency generator, as shown in Figure 15. The general-purpose
counter/timers can be used for many measurement and pulse generation
applications.
Some counter/timer signals may be routed to PFI signals. To access
PFI signals, you must use a correlated digital I/O C Series module in
slot 5 and/or 6.
Note For more information about C Series signal connections for counters, refer to
the NI-DAQmx Help. The NI-DAQmx Help is available after installation from Start»
All Programs»National Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 40 ni.com
Page 41

Input Selection Muxes
Counter 0
Counter 0 Source (Counter 0 Timebase)
Input Selection Muxes
Input Selection Muxes
Counter 0 Gate
Counter 0 Aux
Counter 0 HW Arm
Counter 0 A
Counter 0 B (Counter 0 Up_Down)
Counter 0 Z
Counter 1 Source (Counter 1 Timebase)
Counter 1 Gate
Counter 1 Aux
Counter 1 HW Arm
Counter 1 A
Counter 1 B (Counter 1 Up_Down)
Counter 1 Z
Frequency Generator
Counter 0 Internal Output
Counter 1
Counter 1 Internal Output
Counter 0 TC
Counter 1 TC
Frequency Output Timebase Freq Out
Figure 15. NI cDAQ-9172 Counters
Counters have seven input signals, although in most applications only a few
inputs are used.
For information about connecting the counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section. The following sections describe various
counter applications.
© National Instruments Corporation 41 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 42

Counter Input Applications
Counting Edges
In edge counting applications, the counter counts edges on its Source after
the counter is armed. You can configure the counter to count rising or
falling edges on its Source input. You also can control the direction of
counting (up or down).
The counter values can be read on demand or with a sample clock.
Single-Point (On-Demand) Edge Counting
With single-point (on-demand) edge counting, the counter counts the
number of edges on the Source input after the counter is armed. On-demand
refers to the fact that software can read the counter contents at any time
without disturbing the counting process. Figure 16 shows an example of
single-point edge counting.
Counter Value 1 0 5 4 3 2
Counter Armed
SOURCE
Figure 16. Single-Point (On-Demand) Edge Counting
You also can use a pause trigger to pause (or gate) the counter. When the
pause trigger is active, the counter ignores edges on its Source input. When
the pause trigger is inactive, the counter counts edges normally.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 42 ni.com
Page 43

You can route the pause trigger to the Gate input of the counter. You can
C
configure the counter to pause counting when the pause trigger is high or
when it is low. Figure 17 shows an example of on-demand edge counting
with a pause trigger.
Counter Armed
Pause Trigger
(Pause When Low)
SOURCE
Counter Value
1 0 0 5 4 3 2
Figure 17. Single-Point (On-Demand) Edge Counting with Pause Trigger
Buffered (Sample Clock) Edge Counting
With buffered edge counting (edge counting using a sample clock), the
counter counts the number of edges on the Source input after the counter is
armed. The value of the counter is sampled on each active edge of a sample
clock. The NI cDAQ-9172 transfers the sampled values to host memory.
The count values returned are the cumulative counts since the counter
armed event. That is, the sample clock does not reset the counter.
You can route the counter sample clock to the Gate input of the counter. You
can configure the counter to sample on the rising or falling edge of the
sample clock.
Figure 18 shows an example of buffered edge counting. Notice that
counting begins when the counter is armed, which occurs before the
first active edge on Gate.
ounter Armed
(Sample on Rising Edge)
Sample Clock
SOURCE
Counter Value
Buffer
1 0 7 6 3 4 5 2
3
3
6
Figure 18. Buffered (Sample Clock) Edge Counting
© National Instruments Corporation 43 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 44

Controlling the Direction of Counting
In edge counting applications, the counter can count up or down. You can
configure the counter to do the following:
• Always count up
• Always count down
• Count up when the Counter n B input is high; count down when
it is low
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Pulse-Width Measurement
In pulse-width measurements, the counter measures the width of a pulse on
its Gate input signal. You can configure the counter to measure the width
of high pulses or low pulses on the Gate signal.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known
period) to the Source input of the counter. The counter counts the number
of rising (or falling) edges on the Source signal while the pulse on the Gate
signal is active.
You can calculate the pulse width by multiplying the period of the Source
signal by the number of edges returned by the counter.
A pulse-width measurement is accurate even if the counter is armed while
a pulse train is in progress. If a counter is armed while the pulse is in the
active state, it waits for the next transition to the active state to begin the
measurement.
Single Pulse-Width Measurement
With single pulse-width measurement, the counter counts the number of
edges on the Source input while the Gate input remains active. When the
Gate input goes inactive, the counter stores the count in a hardware save
register and ignores other edges on the Gate and Source inputs. The
software then reads the stored count.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 44 ni.com
Page 45

Figure 19 shows an example of a single pulse-width measurement.
GATE
SOURCE
1 0
Counter Value
2
GATE
SOURCE
HW Save Register
2
Figure 19. Single Pulse-Width Measurement
Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
Buffered pulse-width measurement is similar to single pulse-width
measurement, but buffered pulse-width measurement takes measurements
over multiple pulses.
The counter counts the number of edges on the Source input while the Gate
input remains active. On each trailing edge of the Gate signal, the counter
stores the count in a hardware save register. The NI cDAQ-9172 transfers
the stored values to host memory.
Figure 20 shows an example of a buffered pulse-width measurement.
Counter Value
Buffer
1 0 3
3 3
3
2 1 2
2
2
Figure 20. Buffered Pulse-Width Measurement
© National Instruments Corporation 45 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 46

Note If you are using an external signal as the Source, at least one Source pulse should
occur between each active edge of the Gate signal. This condition ensures that correct
values are returned by the counter. If this condition is not met, consider using duplicate
count prevention, described in the Duplicate Count Prevention section.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Period Measurement
In period measurements, the counter measures a period on its Gate input
signal after the counter is armed. You can configure the counter to measure
the period between two rising edges or two falling edges of the Gate input
signal.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a known
period) to the Source input of the counter. The counter counts the number
of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the Source input between the
two active edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the period of the Gate input by multiplying the period of
the Source signal by the number of edges returned by the counter.
Single Period Measurement
With single period measurement, the counter counts the number of rising
(or falling) edges on the Source input occurring between two active edges
of the Gate input. On the second active edge of the Gate input, the counter
stores the count in a hardware save register and ignores other edges on the
Gate and Source inputs. The software then reads the stored count.
Figure 21 shows an example of a single period measurement.
GATE
SOURCE
103
Counter Value
HW Save Register
Figure 21. Single Period Measurement
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 46 ni.com
2
4
5
5
Page 47

GATE
SOURCE
Buffered Period Measurement
Buffered period measurement is similar to single period measurement,
but buffered period measurement measures multiple periods.
The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges on the Source
input between each pair of active edges on the Gate input. At the end of
each period on the Gate signal, the counter stores the count in a hardware
save register. The NI cDAQ-9172 transfers the stored values to host
memory.
The counter begins when it is armed. The arm usually occurs in the middle
of a period of the Gate input. So the first value stored in the hardware save
register does not reflect a full period of the Gate input. In most applications,
this first point should be discarded.
Figure 22 shows an example of a buffered period measurement.
Counter Armed
Counter Value
Buffer
1 1 2 3
2
(Discard) (Discard) (Discard)
3 2
2
3
3 1 1
2
3
2
3
3
2
Figure 22. Buffered Period Measurement
Note
If you are using an external signal as the Source, at least one Source pulse should
occur between each active edge of the Gate signal. This condition ensures that correct
values are returned by the counter. If this condition is not met, consider using duplicate
count prevention, described in the Duplicate Count Prevention section.
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
© National Instruments Corporation 47 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 48

Semi-Period Measurement
In semi-period measurements, the counter measures a semi-period on its
Gate input signal after the counter is armed. A semi-period is the time
between any two consecutive edges on the Gate input.
You can route an internal or external periodic clock signal (with a
known period) to the Source input of the counter. The counter counts
the number of rising (or falling) edges occurring on the Source input
between two edges of the Gate signal.
You can calculate the semi-period of the Gate input by multiplying the
period of the Source signal by the number of edges returned by the counter.
Single Semi-Period Measurement
Single semi-period measurement is equivalent to single pulse-width
measurement.
Buffered Semi-Period Measurement
In buffered semi-period measurement, on each edge of the Gate signal, the
counter stores the count in a hardware save register. The NI cDAQ-9172
transfers the stored values to host memory.
The counter begins counting when it is armed. The arm usually occurs
between edges on the Gate input, which means that the first value stored in
the hardware save register does not reflect a full semi-period of the Gate
input. In most applications, this first point should be discarded.
Figure 23 shows an example of a buffered semi-period measurement.
Counter Armed
GATE
SOURCE
Counter Value
Buffer
1 3
2
2
3
Figure 23. Buffered Semi-Period Measurement
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 48 ni.com
1 1
1 2 1 0 2
2
2
1 3 2
2
2
3
3
1
1
2
Page 49

Note If you are using an external signal as the Source, at least one Source pulse should
occur between each active edge of the Gate signal. This condition ensures that correct
values are returned by the counter. If this condition is not met, consider using duplicate
count prevention, described in the Duplicate Count Prevention section.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Frequency Measurement
You can use the counters to measure frequency in several different ways.
You can choose one of the following methods depending on your
application: Method 1, Method 1b, Method 2, and Method 3.
Method 1—Measure Low Frequency With One Counter
This method is good for low frequency signals. Use this method to measure
one period of your signal using a known timebase. Figure 24 illustrates this
method.
Interval Measured
F1
Ft
Gate
Source
Single Period
Measurement
You can route the signal to measure (F1) to the Gate of a counter. You can
route a known timebase (Ft) to the Source of the counter. The known
timebase can be 80MHzTimebase. For signals that might be slower than
0.02 Hz, use a slower known timebase.
You can configure the counter to measure one period of the gate signal. The
frequency of F1 is the inverse of the period.
F1
1 2 3 … N
Ft
Period of F1 =
Frequency of F1 =
Figure 24. Frequency Measurement—Method 1
…
N
Ft
Ft
N
© National Instruments Corporation 49 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 50

Method 1b—Measure Low Frequency With One Counter
(Averaged)
This method is good for low to medium frequency signals. Use this method
to measure several periods of your signal using a known timebase.
Figure 25 illustrates this method.
Intervals Measured
T
T
1
… T
2
K
F1
Ft
Gate
Source
Buffered Period
Measurement
F1
1
2 ...N
1... ...N2 … 1... ...N
1
Ft
Average Period of F 1 =
Frequency of F1 =
N
1
+ N2 + …N
N
1
K × Ft
+ N2 + …N
K
1
K
×
K
K
Ft
Figure 25. Frequency Measurement—Method 1b
You can route the signal to measure (F1) to the Gate of a counter. You can
route a known timebase (Ft) to the Source of the counter. The known
timebase can be 80MHzTimebase. For signals that might be slower than
0.02 Hz, use a slower known timebase.
You can configure the counter to make K + 1 buffered period
measurements. Recall that the first period measurement in the buffer
should be discarded.
Average the remaining K period measurements to determine the average
period of F1. The frequency of F1 is the inverse of the average period.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 50 ni.com
Page 51

Method 2—Measure High Frequency With Two Counters
This method is good for high frequency signals. Use this method to
measure one pulse of a known width using your signal and derive the
frequency of your signal from the result. Figure 26 illustrates this method.
Width of Pulse (T)
Pulse
F1
Pulse
Gate
1 2 … N
Source
Pulse-Width
Measurement
F1
Width of
Pulse
Frequency of F1 =
Figure 26. Frequency Measurement—Method 2
T =
N
F1
N
T
In this method, you route a pulse of known duration (T) to the Gate of a
counter. You can generate the pulse using a second counter. You also can
generate the pulse externally and connect it to a PFI terminal. You only
need to use one counter if you generate the pulse externally.
Route the signal to measure (F1) to the Source of the counter. Configure the
counter for a single pulse-width measurement. Suppose you measure the
width of pulse T to be N periods of F1. Then the frequency of F1 is N/T.
Another option would be to measure the width of a known period instead
of a known pulse.
Method 3—Measure Large Range of Frequencies Using
Two Counters
By using two counters, you can accurately measure a signal that might
be high or low frequency. This technique is called reciprocal frequency
measurement. In this method, you generate a long pulse using the signal to
measure. You then measure the long pulse with a known timebase. The
NI cDAQ-9172 chassis can measure this long pulse more accurately than
the faster input signal.
© National Instruments Corporation 51 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 52

You can route the signal to measure to the Source input of Counter 0,
as shown in Figure 27. Assume this signal to measure has frequency F1.
Configure Counter 0 to generate a single pulse that is the width of N periods
of the source input signal.
Signal to
Measure (F1)
Signal of Known
Frequency (F2)
CTR_0_SOURCE
(Signal to Measure)
CTR_0_OUT
(CTR_1_GATE)
CTR_1_SOURCE
SOURCE OUT
COUNTER 0
SOURCE
COUNTER 1
GATE
0 1 2 3 … N
Interval to
Measure
OUT
Figure 27. Frequency Measurement—Method 3
Then route the Counter 0 Internal Output signal to the Gate input of
Counter 1. You can route a signal of known frequency (F2) to the Counter 1
Source input. F2 can be 80MHzTimebase. For signals that might be slower
than 0.02 Hz, use a slower known timebase. Configure Counter 1 to
perform a single pulse-width measurement. Suppose the result is that the
pulse width is J periods of the F2 clock.
From Counter 0, the length of the pulse is N/F1. From Counter 1, the length
of the same pulse is J/F2. Therefore, the frequency of F1 is given by
F1 = F2 * (N/J).
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 52 ni.com
Page 53

Choosing a Method for Measuring Frequency
The best method to measure frequency depends on several factors
including the expected frequency of the signal to measures, the desired
accuracy, how many counters are available and how long the measurement
can take.
• Method 1 uses only one counter. It is a good method for many
applications. However, the accuracy of the measurement decreases
as the frequency increases.
Consider a frequency measurement on a 50 kHz signal using an
80 MHz Timebase. This frequency corresponds to 1600 cycles of the
80 MHz Timebase. Your measurement may return 1600 ±1 cycles
depending on the phase of the signal with respect to the timebase. As
your frequency becomes larger, this error of ±1 cycle becomes more
significant, as Table 5 illustrates.
Table 5. Frequency Measurement Method 1
Task Equation Example 1 Example 2
Actual Frequency to Measure F1 50 kHz 5MHz
Timebase Frequency Ft 80 MHz 80 MHz
Actual Number of Timebase
Ft/F1 1600 16
Periods
Worst Case Measured Number
(Ft/F1) – 1 1599 15
of Timebase Periods
Measured Frequency Ft F1/(Ft – F1) 50.031 kHz 5.33 MHz
Error [Ft F1/(Ft – F1)] – F1 31 Hz 333 kHz
Error % [Ft/(Ft – F1)] – 1 0.06% 6.67%
• Method 1b (measuring K periods of F1) improves the accuracy
of the measurement. A disadvantage of Method 1b is that K + 1
measurements are required. These measurements take more time
and consume some of the available USB bandwidth.
• Method 2 is accurate for high frequency signals. However, the
accuracy decreases as the frequency of the signal to measure
decreases. At very low frequencies, Method 2 may be too inaccurate
for your application. Another disadvantage of Method 2 is that it
requires two counters (if you cannot provide an external signal of
known width). An advantage of Method 2 is that the measurement
completes in a known amount of time.
• Method 3 measures high and low frequency signals accurately.
However, it requires two counters.
© National Instruments Corporation 53 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 54

Table 6 summarizes some of the differences in methods of measuring
frequency.
Table 6. Frequency Measurement Method Comparison
Measures High
Number of
Number of
Method
1 1 1 Poor Good
1b 1 Many Fair Good
2 1 or 2 1 Good Poor
3 2 1 Good Good
Counters Used
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Measurements
Returned
Frequency
Signals
Accurately
Measures Low
Frequency
Accurately
Position Measurement
You can use the counters to perform position measurements with
quadrature encoders or two-pulse encoders. You can measure angular
position with X1, X2, and X4 angular encoders. Linear position can be
measured with two-pulse encoders. You can choose to do a single-point
(on-demand) position measurement or a buffered (sample clock) position
measurement. You must arm a counter to begin position measurements.
Measurements Using Quadrature Encoders
The counters can perform measurements of quadrature encoders that
use X1, X2, or X4 encoding. A quadrature encoder can have up to
three channels—channels A, B, and Z.
Signals
X1 Encoding
When channel A leads channel B in a quadrature cycle, the counter
increments. When channel B leads channel A in a quadrature cycle, the
counter decrements. The amount of increments and decrements per cycle
depends on the type of encoding—X1, X2, or X4.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 54 ni.com
Page 55

Figure 28 shows a quadrature cycle and the resulting increments and
decrements for X1 encoding. When channel A leads channel B, the
increment occurs on the rising edge of channel A. When channel B leads
channel A, the decrement occurs on the falling edge of channel A.
Ch A
Ch B
Counter Value
5
6
7
7
6
5
Figure 28. X1 Encoding
X2 Encoding
The same behavior holds for X2 encoding except the counter increments or
decrements on each edge of channel A, depending on which channel leads
the other. Each cycle results in two increments or decrements, as shown in
Figure 29.
Ch A
Ch B
Counter Value
5 6 8
7
Figure 29. X2 Encoding
9
9
7
8
6
5
X4 Encoding
The counter increments or decrements similarly on each edge of
channels A and B for X4 encoding. Whether the counter increments or
decrements depends on which channel leads the other. Each cycle results in
four increments or decrements, as shown in Figure 30.
Ch A
Ch B
Counter Value 5 6 8 9 10 10 11 11 12 12 13 13 7
5 6 8 7 9
Figure 30. X4 Encoding
© National Instruments Corporation 55 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 56
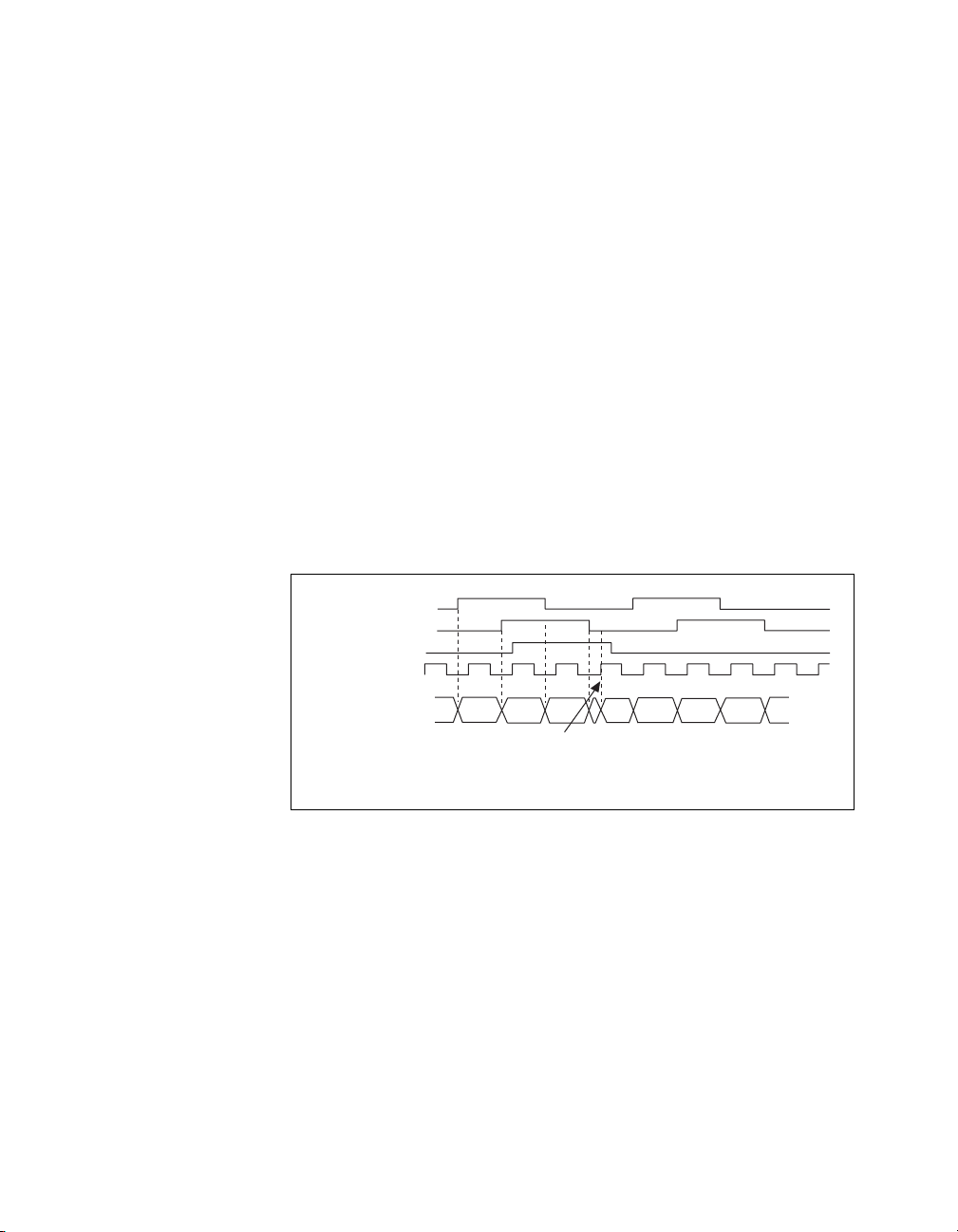
Channel Z Behavior
Some quadrature encoders have a third channel, channel Z, which is also
referred to as the index channel. A high level on channel Z causes the
counter to be reloaded with a specified value in a specified phase of the
quadrature cycle. You can program this reload to occur in any one of the
four phases in a quadrature cycle.
Channel Z behavior—when it goes high and how long it stays
high—differs with quadrature encoder designs. You must refer to the
documentation for your quadrature encoder to obtain timing of channel Z
with respect to channels A and B. You must then ensure that channel Z is
high during at least a portion of the phase you specify for reload. For
example, in Figure 31, channel Z is never high when channel A is high
and channel B is low. Thus, the reload must occur in some other phase.
In Figure 31, the reload phase is when both channel A and channel B are
low. The reload occurs when this phase is true and channel Z is high.
Incrementing and decrementing takes priority over reloading. Thus, when
the channel B goes low to enter the reload phase, the increment occurs first.
The reload occurs within one maximum timebase period after the reload
phase becomes true. After the reload occurs, the counter continues counting
as before. The figure illustrates channel Z reload with X4 decoding.
Ch A
Ch B
Ch Z
Max Timebase
Counter Value
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 56 ni.com
5 6
Figure 31. Channel Z Reload with X4 Decoding
8 9 0 2 1 7 4 3
A = 0
B = 0
Z = 1
Page 57

Measurements Using Two Pulse Encoders
The counter supports two pulse encoders that have two channels—channels
A and B.
The counter increments on each rising edge of channel A. The counter
decrements on each rising edge of channel B, as shown in Figure 32.
Ch A
Ch B
Counter Value 2 3 5 4 3 4 4
Figure 32. Measurements Using Two Pulse Encoders
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement
Two-signal edge-separation measurement is similar to pulse-width
measurement, except that there are two measurement signals—AUX and
Gate. An active edge on the AUX input starts the counting and an active
edge on the Gate input stops the counting. You must arm a counter to begin
a two edge separation measurement.
After the counter has been armed and an active edge occurs on the AUX
input, the counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges on the
Source. The counter ignores additional edges on the AUX input.
The counter stops counting upon receiving an active edge on the Gate input.
The counter stores the count in a hardware save register.
You can configure the rising or falling edge of the AUX input or the Gate
input to be the active edge.
Use this type of measurement to count events or measure the time that
occurs between edges on two signals. This type of measurement is
sometimes referred to as start/stop trigger measurement, second gate
measurement, or A-to-B measurement.
Single Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement
With single two-signal edge-separation measurement, the counter counts
the number of rising (or falling) edges on the Source input occurring
between an active edge of the Gate signal and an active edge of the AUX
signal. The counter then stores the count in a hardware save register and
ignores other edges on its inputs. Software then reads the stored count.
© National Instruments Corporation 57 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 58

Figure 33 shows an example of a single two-signal edge-separation
measurement.
Counter
AUX
GATE
SOURCE
Counter Value
HW Save Register
Armed
0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 8 8
Measured Interval
8
Figure 33. Single Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement
Buffered Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement
Buffered and single two-signal edge-separation measurements are similar,
but buffered measurement measures multiple intervals.
The counter counts the number of rising (or falling) edges on the Source
input occurring between an active edge of the Gate signal and an active
edge of the AUX signal. The counter then stores the count in a hardware
save register. On the next active edge of the Gate signal, the counter begins
another measurement. The NI cDAQ-9172 transfers the stored values to
host memory.
Figure 34 shows an example of a buffered two-signal edge-separation
measurement.
AUX
GATE
SOURCE
Counter Value
Buffer
1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3
3 3 3 3
3
3
Figure 34. Buffered Two-Signal Edge-Separation Measurement
For information about connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 58 ni.com
Page 59

Counter Output Applications
C
Simple Pulse Generation
The counter can output a single pulse. The pulse appears on the Counter n
Internal Output signal of the counter.
You can specify a delay from when the counter is armed to the beginning
of the pulse. The delay is measured in terms of a number of active edges of
the Source input.
You can specify a pulse width. The pulse width is also measured in terms
of a number of active edges of the Source input. You also can specify the
active edge of the Source input (rising or falling).
Figure 35 shows a generation of a pulse with a pulse delay of four and a
pulse width of three (using the rising edge of Source).
SOURCE
ounter Armed
OUT
Figure 35. Single Pulse Generation
Single Pulse Generation with Start Trigger
The counter can output a single pulse in response to one pulse on a
hardware Start Trigger signal. The pulse appears on the Counter n Internal
Output signal of the counter.
You can route the Start Trigger signal to the Gate input of the counter. You
can specify a delay from the Start Trigger to the beginning of the pulse. You
also can specify the pulse width. The delay and pulse width are measured
in terms of a number of active edges of the Source input.
After the Start Trigger signal pulses once, the counter ignores the Gate
input.
© National Instruments Corporation 59 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 60

Figure 36 shows a generation of a pulse with a pulse delay of four and a
pulse width of three (using the rising edge of Source).
GATE
(Start Trigger)
SOURCE
OUT
Figure 36. Single Pulse Generation with Start Trigger
Retriggerable Single Pulse Generation
The counter can output a single pulse in response to each pulse on a
hardware Start Trigger signal. The pulses appear on the Counter n Internal
Output signal of the counter.
You can route the Start Trigger signal to the Gate input of the counter. You
can specify a delay from the Start Trigger to the beginning of each pulse.
You also can specify the pulse width. The delay and pulse width are
measured in terms of a number of active edges of the Source input.
The counter ignores the Gate input while a pulse generation is in progress.
After the pulse generation is finished, the counter waits for another Start
Trigger signal to begin another pulse generation.
Figure 37 shows a generation of two pulses with a pulse delay of five and a
pulse width of three (using the rising edge of Source).
GATE
(Start Trigger)
SOURCE
OUT
Figure 37. Retriggerable Single Pulse Generation
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 60 ni.com
Page 61

Pulse Train Generation
Continuous Pulse Train Generation
This function generates a train of pulses with programmable frequency and
duty cycle. The pulses appear on the Counter n Internal Output signal of the
counter.
You can specify a delay from when the counter is armed to the beginning
of the pulse train. The delay is measured in terms of a number of active
edges of the Source input.
You specify the high and low pulse widths of the output signal. The pulse
widths are also measured in terms of a number of active edges of the Source
input. You also can specify the active edge of the Source input (rising or
falling).
The counter can begin the pulse train generation as soon as the counter is
armed, or in response to a hardware Start Trigger. You can route the Start
Trigger to the Gate input of the counter.
You also can use the Gate input of the counter as a Pause Trigger (if it is not
used as a Start Trigger). The counter pauses pulse generation when the
Pause Trigger is active.
Figure 38 shows a continuous pulse train generation (using the rising edge
of Source).
SOURCE
OUT
Counter Armed
Figure 38. Continuous Pulse Train Generation
Continuous pulse train generation is sometimes called frequency division.
If the high and low pulse widths of the output signal are M and N periods,
then the frequency of the Counter n Internal Output signal is equal to the
frequency of the Source input divided by M + N.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
© National Instruments Corporation 61 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 62

20 MHz Timebase
F
100 kHz Timebase
Frequency Generation
You can generate a frequency by using a counter in pulse train generation
mode or by using the frequency generator circuit.
Using the Frequency Generator
The frequency generator can output a square wave at many different
frequencies. The frequency generator is independent of the two
general-purpose 32-bit counter/timer modules on the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis.
Figure 39 shows a block diagram of the frequency generator.
Frequency
÷ 2
The frequency generator generates the Frequency Output signal. The
Frequency Output signal is the Frequency Output Timebase divided by a
number you select from 1 to 16. The Frequency Output Timebase can be
either the 20 MHz Timebase divided by 2 or the 100 kHz Timebase.
Output
Timebase
Frequency Generator
Divisor
(1–16)
Figure 39. Frequency Generator Block Diagram
Freq Out
The duty cycle of Frequency Output is 50% if the divider is either one or an
even number. For an odd divider, suppose the divider is set to D. In this
case, Frequency Output is low for (D + 1)/2 cycles and high for (D – 1)/2
cycles of the Frequency Output Timebase.
Figure 40 shows the output waveform of the frequency generator when the
divider is set to 5.
requency
Output
Timebase
FREQ OUT
(Divisor = 5)
Figure 40. Frequency Generator Output Waveform
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 62 ni.com
Page 63

Frequency Output can be routed to any output PFI terminal. The FREQ
OUT signal also can be routed to DO Sample Clock and DI Sample Clock.
In software, program the frequency generator as you would program one of
the counters for pulse train generation.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Frequency Division
The counters can generate a signal with a frequency that is a fraction
of an input signal. This function is equivalent to continuous pulse train
generation.
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the Default
Counter/Timer Routing section.
Counter Timing Signals
In slots 5 and/or 6 of the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, you can configure
C Series correlated digital input/output modules as one of the following
counter timing signals:
• Counter n Source
• Counter n Gate
• Counter n Aux
• Counter n A
• Counter n B
• Counter n Z
• Counter n Up_Down
• Counter n HW Arm
• Counter n Internal Output
• Counter n TC
•Frequency Output
In this section, n refers to either Counter 0 or 1. For example,
Counter n Source refers to two signals—Counter 0 Source (the source
input to Counter 0) and Counter 1 Source (the source input to Counter 1).
© National Instruments Corporation 63 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 64

Counter n Source Signal
The selected edge of the Counter n Source signal increments and
decrements the counter value, depending upon the application the counter
is performing. Table 7 lists how this terminal is used in various
applications. Table 8 lists Counter n Source minimum pulse width.
Table 7. Counter Applications and Counter n Source
Application Purpose of Source Terminal
Pulse Generation Counter Timebase
One Counter Time Measurements Counter Timebase
Two Counter Time Measurements Input Terminal
Nonbuffered Edge Counting Input Terminal
Buffered Edge Counting Input Terminal
Two-Edge Separation Counter Timebase
Table 8. Counter n Source Timing
Synchronization
†
Description
Counter n Source
Pulse Width
Mode
Min (ns)
80 MHz Source 6.2 —
Other Internal Source 12.5 —
*
Max (ns)
External Source 16.0 —
*
The times in this table are measured at the pin of the device.
†
Actual performance depends on the module in use.
Routing a Signal to Counter n Source
Each counter has independent input selectors for the Counter n Source
signal. You can route the following signals to the Counter n Source input:
•80MHz Timebase
•20MHz Timebase
• 100 kHz Timebase
• Any PFI terminal
• Analog Comparison Event
In addition, you can route Counter 1 TC or Counter 1 Gate to
Counter 0 Source. You can also route Counter 0 TC or Counter 0 Gate to
Counter 1 Source.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 64 ni.com
Page 65

Routing Counter n Source to an Output Terminal
You can route Counter n Source to any output PFI terminal.
Counter n Gate Signal
The Counter n Gate signal can perform many different operations
depending on the application including starting and stopping the counter,
and saving the counter contents.
Routing a Signal to Counter n Gate
Each counter has independent input selectors for the Counter n Gate signal.
You can route the following signals to the Counter n Gate input:
•Any PFI terminal
• ai/ReferenceTrigger
• ai/StartTrigger
• ai/SampleClock
• ai/ConvertClock
• ao/SampleClock
• di/SampleClock
• do/SampleClock
• Change Detection Event
• Analog Comparison Event
In addition, you can route Counter 1 Internal Output or Counter 1 Source
to Counter 0 Gate. You can also route Counter 0 Internal Output or
Counter 0 Source to Counter 1 Gate.
Some of these options may not be available in some driver software.
Routing Counter n Gate to an Output Terminal
You can route Counter n Gate to any output PFI terminal.
Counter n Aux Signal
The Counter n Aux signal indicates the first edge in a two-signal
edge-separation measurement.
© National Instruments Corporation 65 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 66

Routing a Signal to Counter n Aux
Each counter has independent input selectors for the Counter n Aux signal.
You can route the following signals to the Counter n Aux input:
• Any PFI terminal
• ai/ReferenceTrigger
• ai/StartTrigger
• Analog Comparison Event
In addition, you can route Counter 1 Internal Output, Counter 1 Gate,
Counter 1 Source, or Counter 0 Gate to Counter 0 Aux. You can also
route Counter 0 Internal Output, Counter 0 Gate, Counter 0 Source, or
Counter 1 Gate to Counter 1 Aux.
Some of these options may not be available in some driver software.
Counter n A, Counter n B, and Counter n Z Signals
Counter n B can control the direction of counting in edge counting
applications. Use the A, B, and Z inputs to each counter when measuring
quadrature encoders or measuring two pulse encoders.
Routing Signals to A, B, and Z Counter Inputs
Each counter has independent input selectors for each of the A, B, and Z
inputs. You can route the following signals to each input:
• Any PFI terminal
• Analog Comparison Event
Routing Counter n Z Signal to an Output Terminal
You can route Counter n Z to any output PFI terminal.
Counter n Up_Down Signal
Counter n Up_Down is another name for the Counter n B signal.
Counter n HW Arm Signal
The Counter n HW Arm signal enables a counter to begin an input or output
function.
To begin any counter input or output function, you must first enable,
or arm, the counter. In some applications, such as buffered semi-period
measurement, the counter begins counting when armed. In other
applications, such as single pulse-width measurement, the counter begins
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 66 ni.com
Page 67

waiting for the Gate signal when it is armed. Counter output operations can
use the arm signal in addition to a start trigger.
Software can arm a counter or configure counters to be armed on a
hardware signal. Software calls this hardware signal the Arm Start Trigger.
Neutrally software routes the Arm Start Trigger to the Counter n HW Arm
input of the counter.
Routing Signals to Counter n HW Arm Input
You can route the following signals to the Counter n HW Arm input:
•Any PFI terminal
• ai/ReferenceTrigger
• ai/StartTrigger
• Analog Comparison Event
You can route Counter 1 Internal Output to Counter 0 HW Arm. You can
also route Counter 0 Internal Output to Counter 1 HW Arm.
Some of these options may not be available in some driver software.
Counter n Internal Output and Counter n TC Signals
Counter n TC is an internal signal that asserts when the counter value is 0.
The Counter n Internal Output signal changes in response to Counter n TC.
The two software-selectable output options are pulse output on TC and
toggle output on TC. The output polarity is software-selectable for both
options.
Routing Counter n Internal Output to an Output Terminal
You can route Counter n Internal Output to any output PFI terminal.
Frequency Output Signal
The Frequency Output (FREQ OUT) signal is the output of the frequency
output generator.
Routing Frequency Output to a Terminal
You can route Frequency Output to any output PFI terminal. The FREQ
OUT signal can also route to DO Sample Clock and DI Sample Clock.
© National Instruments Corporation 67 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 68

Default Counter/Timer Routing
Counter/timer signals are available to correlated digital I/O C Series
modules in slots 5 and/or 6. To determine the signal routing options for
modules installed in your system, refer to the Device Routes tab in MAX.
Counter Triggering
Counters support three different triggering actions:
• Arm Start Trigger—to begin any counter input or output function, you
must first enable, or arm, the counter. Software can arm a counter or
configure counters to be armed on a hardware signal. Software calls
this hardware signal the Arm Start Trigger. Internally, software routes
the Arm Start Trigger to the Counter n HW Arm input of the counter.
For counter output operations, you can use the arm start trigger to have
start trigger-like behavior. The arm start trigger can be used for
synchronizing multiple counter input and output tasks.
• Start Trigger—for counter output operations, you can configure a start
trigger to begin a finite or continuous pulse generation. Once a
continuous generation triggers, the pulses continue to generate until
you stop the operation in software. For finite generations, the specified
number of pulses is generated and the generation stops unless you use
the retriggerable attribute. When you use this attribute, subsequent
start triggers cause the generation to restart.
When using a start trigger, the start trigger source routes to the
Counter n Gate signal input of the counter.
For counter input operations, the arm start trigger can imitate
trigger-like behavior.
• Pause Trigger—you can use pause triggers in edge counting and
continuous pulse generation applications. For edge counting
acquisitions, the counter stops counting edges while the external
trigger signal is low and resumes when the signal goes high or vice
versa. For continuous pulse generations, the counter stops generating
pulses while the external trigger signal is low and resumes when the
signal goes high or vice versa.
When using a pause trigger, the pause trigger source routes to the
Counter n Gate signal input of the counter.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 68 ni.com
Page 69

Other Counter Features
Cascading Counters
You can internally route the Counter n Internal Output and Counter n TC
signals of each counter to the Gate inputs of the other counter. By cascading
two counters together, you can effectively create a 64-bit counter. By
cascading counters, you also can enable other applications. For example,
to improve the accuracy of frequency measurements, use reciprocal
frequency measurement, as described in the Method 3—Measure Large
Range of Frequencies Using Two Counters section.
Counter Filters
You can enable a programmable debouncing filter on each PFI signal.
When the filters are enabled, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis samples the input
on each rising edge of a filter clock. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis uses an
onboard oscillator to generate the filter clock with a 40 MHz frequency.
For more information, refer to the NI-DAQmx Help. The NI-DAQmx Help
is available after installation from Start»All Programs»National
Instruments»NI-DAQ»NI-DAQmx Help.
Note NI-DAQmx only supports filters on counter inputs.
The following is an example of low to high transitions of the input signal.
High to low transitions work similarly.
Assume that an input terminal has been low for a long time. The input
terminal then changes from low to high, but glitches several times. When
the filter clock samples the signal high on N consecutive edges, the low to
high transition is propagated to the rest of the circuit. The value of N
depends on the filter setting, as listed in Table 9.
Table 9. Counter Input Filters
N (Filter Clocks
Needed to
Filter Setting
125 ns 5 125 ns 100 ns
6.425 µs 257 6.425 µs 6.400 µs
2.56 ms ~101,800 2.56 ms 2.54 ms
Disabled — — —
© National Instruments Corporation 69 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Pass Signal)
Pulse Width
Guaranteed to
Pass Filter
Pulse Width
Guaranteed to
Not Pass Filter
Page 70

You can configure the filter setting for each input independently. On power
up, the filters are disabled. Figure 41 shows an example of a low to high
transition on an input with its filter set to 125 ns (N = 5).
PFI Terminal
Filter Clock
(40 MHz)
Filtered Input
Filtered input goes high
1 2 3 1 4 1 2 3 4 5
Figure 41. Filter Example
when terminal is sampled
high on five consecutive
filter clocks.
Enabling filters introduces jitter on the input signal. For the 125 ns and
6.425 µs filter settings, the jitter is up to 25 ns. On the 2.56 ms setting, the
jitter is up to 10.025 µs.
Prescaling
Prescaling allows the counter to count a signal that is faster than the
maximum timebase of the counter. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis offers
8X and 2X prescaling on each counter (prescaling can be disabled). Each
prescaler consists of a small, simple counter that counts to eight (or two)
and rolls over. This counter can run faster than the larger counters, which
simply count the rollovers of this smaller counter. Thus, the prescaler acts
as a frequency divider on the Source and puts out a frequency that is
one-eighth (or one-half) of what it is accepting.
External Signal
Prescaler Rollover
(Used as Source
by Counter)
Counter Value
0 1
Figure 42. Prescaling
Prescaling is intended for frequency measurement where the measurement
is made on a continuous, repetitive signal. The prescaling counter cannot
be read; therefore, you cannot determine how many edges have occurred
since the previous rollover. You can use prescaling for event counting
provided it is acceptable to have an error of up to seven (or one). You can
use prescaling when the counter Source is an external signal. Prescaling
is not available if the counter Source is one of the internal timebases
(80MHzTimebase, 20MHzTimebase, or 100kHzTimebase).
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 70 ni.com
Page 71

Duplicate Count Prevention
Risi
Duplicate count prevention (or synchronous counting mode) ensures that a
counter returns correct data in applications that use a slow or non-periodic
external source. Duplicate count prevention applies only to buffered
counter applications such as measuring frequency or period. In such
buffered applications, the counter stores the number of times an external
Source pulses between rising edges on the Gate signal.
Example Application That Works Correctly
(No Duplicate Counting)
Figure 43 shows an external buffered signal as the period measurement
Source.
ng Edge
of Gate
Counter detects rising edge
of Gate on the next rising
edge of Source.
Gate
Source
Counter Value
Buffer
6 7 1 2 1
7
Figure 43. Duplicate Count Prevention Example
2
7
On the first rising edge of the Gate, the current count of seven is stored.
On the next rising edge of the Gate, the counter stores a two because
two Source pulses occurred after the previous rising edge of Gate.
The counter synchronizes or samples the Gate signal with the Source
signal, which means that the counter does not detect a rising edge in the
Gate until the next Source pulse. In this example, the counter stores the
values in the buffer on the first rising Source edge after the rising edge of
Gate. The details of when exactly the counter synchronizes the Gate signal
vary depending on the synchronization mode. Synchronization modes are
described in the Synchronization Modes section.
© National Instruments Corporation 71 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 72

Example Application That Works Incorrectly
(Duplicate Counting)
In Figure 44, after the first rising edge of Gate, no Source pulses occur,
which means that the counter does not write the correct data to the buffer.
No Source edge, so no
value written to buffer.
Gate
Source
Counter Value
Gate
Source
80 MHz Timebase
6 7 1
Buffer
7
Figure 44. Duplicate Count Example
Example Application That Prevents Duplicate Count
With duplicate count prevention enabled, the counter synchronizes both the
Source and Gate signals to the 80 MHz Timebase. By synchronizing to the
timebase, the counter detects edges on the Gate even if the Source does not
pulse. This enables the correct current count to be stored in the buffer even
if no Source edges occur between Gate signals, as shown in Figure 45.
Counter detects
rising Gate edge.
Counter value
increments only
one time for each
Source pulse.
Counter Value
Buffer
6 7 0 1
7
0
7
Figure 45. Duplicate Count Prevention Example
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 72 ni.com
Page 73

Even if the Source pulses are long, the counter increments only once for
each Source pulse.
Normally, the counter value and Counter n Internal Output signals change
synchronously to the Source signal. With duplicate count prevention, the
counter value and Counter n Internal Output signals change synchronously
to the 80 MHz Timebase.
Note Duplicate count prevention should only be used if the frequency of the Source signal
is 20 MHz or less.
When To Use Duplicate Count Prevention
Use duplicate count prevention if the following conditions are true:
• You are making a counter measurement.
• You are using an external signal (such as PFI x) as the counter Source.
• The frequency of the external source is 20 MHz or less.
• You can have the counter value and output to change synchronously
with the 80 MHz Timebase.
In all other cases, you should not use duplicate count prevention.
Enabling Duplicate Count Prevention in NI-DAQmx
You enable duplicate count prevention in NI-DAQmx by setting the
Enable Duplicate Count Prevention attribute/property. For specific
information on finding the Enable Duplicate Count Prevention
attribute/property, refer to the help file for the API you are using.
Synchronization Modes
The 32-bit counter counts up or down synchronously with the Source
signal. The Gate signal and other counter inputs are asynchronous to the
Source signal. The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis synchronizes these signals
before presenting them to the internal counter.
The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis uses one of three synchronization methods:
• 80 MHz source mode
• Other internal source mode
• External source mode
In NI-DAQmx, the chassis uses 80 MHz source mode if you perform the
following:
• Perform a position measurement
• Select duplicate count prevention
© National Instruments Corporation 73 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 74

Otherwise, the mode depends on the signal that drives Counter n Source.
Table 10 describes the conditions for each mode.
Table 10. Synchronization Mode Conditions
Duplicate Count
Prevention Enabled
Ye s Any Any 80 MHz Source
No Position Measurement Any 80 MHz Source
No Any 80 MHz Timebase 80 MHz Source
No All Except Position
No All Except Position
Type of
Measurement
Measurement
Measurement
Signal Driving
Counter n Source
20 MHz Timebase,
100 kHz Timebase
Any Other Signal
(such as PFI)
Synchronization
Mode
Other Internal Source
External Source
80 MHz Source Mode
In 80 MHz source mode, the NI cDAQ-9172 synchronizes signals on the
rising edge of the source, and counts on the following rising edge of the
source, as shown in Figure 46.
Source
Synchronize Count
Figure 46. 80 MHz Source Mode
Other Internal Source Mode
In other internal source mode, the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis synchronizes
signals on the falling edge of the source and counts on the following rising
edge of the source, as shown in Figure 47.
Source
Synchronize Count
Figure 47. Other Internal Source Mode
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 74 ni.com
Page 75

External Source Mode
In external source mode, the chassis generates a delayed Source signal by
delaying the Source signal by several nanoseconds. The NI cDAQ-9172
chassis synchronizes signals on the rising edge of the delayed Source signal
and counts on the following rising edge of the source, as shown in
Figure 48.
Source
Delayed Source
Figure 48. External Source Mode
Digital Routing and Clock Generation
The digital routing circuitry has the following functions:
• Manages the flow of data between the bus interface and the
acquisition/generation sub-systems (analog input, analog output,
digital I/O, and the counters). The digital routing circuitry uses FIFOs
(if present) in each sub-system to ensure efficient data movement.
• Routes timing and control signals. The acquisition/generation
sub-systems use these signals to manage acquisitions and generations.
These signals can come from the following sources:
– Your C Series I/O modules
– User input through the PFI terminals using correlated digital
C Series I/O modules in slots 5 and/or 6
• Routes and generates the main clock signals for the NI cDAQ-9172
chassis.
To determine the signal routing options for C Series I/O modules
installed in the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis, refer to the Device Routes tab
in MAX.
Synchronize
Count
© National Instruments Corporation 75 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 76

Clock Routing
Figure 49 shows the clock routing circuitry of the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis.
Onboard
80 MHz
Oscillator
÷ 4
÷ 200
Figure 49. NI cDAQ-9172 Clock Routing Circuitry
80 MHz Timebase
20 MHz Timebase
100 kHz Timebase
80 MHz Timebase
You can use the 80 MHz Timebase as the Source input to the 32-bit
general-purpose counter/timers.
The 80 MHz Timebase can be generated from the following sources:
• Onboard oscillator
• External signal (by using the external reference clock)
20 MHz Timebase
The 20 MHz Timebase normally generates many of the AI and AO timing
signals. The 20 MHz Timebase can function as the Source input to the
32-bit general-purpose counter/timers.
The 20 MHz Timebase is generated by dividing down the
80 MHz Timebase.
100 kHz Timebase
You can use the 100 kHz Timebase to generate many of the AI and AO
timing signals. The 100 kHz Timebase can also function as the Source
input to the 32-bit general-purpose counter/timers.
The 100 kHz Timebase is generated by dividing down the 20 MHz
Timebase by 200.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 76 ni.com
Page 77

Specifications
Analog Input
These specifications are for the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis only. These
specifications are typical at 25 °C unless otherwise noted. For the C Series
I/O module specifications, refer to the documentation for the C Series I/O
modules you are using.
Input FIFO size ...................................... 2,047 samples
Analog Output
Sample rate
1
Maximum........................................ 3.2 MS/s
(multi-channel, aggregate)
Minimum ........................................ 0 S/s
Timing accuracy
Timing resolution
2
................................... 50 ppm of sample rate
2
................................. 50 ns
Number of channels supported .............. Determined by the C Series
I/O modules
Numbers of channels supported
In hardware-timed task ...................16
In non-hardware-timed task ............ Determined by the C Series
I/O modules
Maximum update rate ............................ 1.6 MS/s
(multi-channel, aggregate)
Timing accuracy..................................... 50 ppm of sample rate
Timing resolution................................... 50 ns
Output FIFO size.................................... 8,191 samples shared among
channels used
1
Performance dependent on type of installed C Series I/O modules and number of channels in the task.
2
Does not include group delay. Refer to C Series I/O module documentation for more information.
© National Instruments Corporation 77 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 78

AO waveform modes..............................Non-periodic waveform,
periodic waveform regeneration
mode from onboard memory,
periodic waveform regeneration
from host buffer including
dynamic update
Digital Waveform Characteristics (Slots 1 through 4 Only)
Waveform acquisition (DI)
FIFO........................................................2,047 samples
Waveform generation (DO)
FIFO........................................................2,047 samples
Digital input sample clock frequency
Streaming to application
memory............................................0 to 8 MHz, system dependent
Finite................................................0 to 10 MHz
Digital output sample clock frequency
Streaming from application
memory............................................0 to 8 MHz, system dependent
Regenerate from FIFO.....................0 to 10 MHz
Finite................................................0 to 10 MHz
Digital output or digital input
sample clock source................................Any PFI, analog sample or
convert clock, analog output
sample clock, Ctr n Internal
Output, and many other sources
1
PFI Characteristics (Slots 5 and 6 Only)
1
Functionality...........................................Static digital input, static digital
output, timing input, and timing
output
Timing output sources ............................Many analog input, analog
output, counter, digital input, and
digital output timing signals
1
Requires correlated digital I/O modules installed on the appropriate slot(s).
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 78 ni.com
Page 79

Debounce filter settings ......................... Selectable per input:
125 ns, 6.425 µs, 2.56 ms, disable,
high and low transitions
Timing input frequency.......................... 0 to 20 MHz
Timing output frequency........................ 0 to 20 MHz
General-Purpose Counter/Timers (Slots 5 and 6 Only)
Number of counter/timers ...................... 2
Resolution .............................................. 32 bits
Counter measurements........................... Edge counting, pulse,
semi-period, period,
two-edge separation
Position measurements........................... X1, X2, X4 quadrature encoding
with Channel Z reloading;
two-pulse encoding
Output applications ................................ Pulse, pulse train with dynamic
updates, frequency division,
equivalent time sampling
Internal base clocks................................ 80 MHz, 20 MHz, 100 kHz
External base clock frequency ............... 0 to 20 MHz
Base clock accuracy ............................... 50 ppm
Output frequency....................................0 to 20 MHz
1
Inputs...................................................... Gate, Source, HW_Arm, Aux,
A, B, Z, Up_Down
Routing options for inputs...................... Any PFI, analog trigger,
many internal signals
FIFO ....................................................... 2 samples
Data transfers ......................................... High-speed data stream,
programmed I/O
1
Requires correlated digital I/O modules installed in the appropriate slot(s).
© National Instruments Corporation 79 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 80

Frequency Generator (Slots 5 and 6 Only)
Number of channels................................1
Base clocks .............................................10 MHz, 100 kHz
Divisors...................................................1 to 16 (integers)
Base clock accuracy................................50 ppm
Output is available on any PFI terminal.
External Digital Triggers (Slots 5 and 6 or with Some AI Modules)
Source .....................................................Any PFI terminal
Polarity....................................................Software-selectable for most
signals
Analog input function.............................Start Trigger, Reference Trigger,
Pause Trigger, Sample Clock,
Sample Clock Timebase
Analog output function...........................Start Trigger, Pause Trigger,
Sample Clock, Sample Clock
Timebase
Counter/timer functions..........................Gate, Source, HW_Arm, Aux,
A, B, Z, Up_Down
Module I/O States
At power-on............................................Module-dependent. Refer to the
documentation included with the
C Series I/O module(s).
With USB cable removed .......................Reverts to power-on state
Power Requirements
You must use a National Electric Code (NEC) Class 2 power source with
the NI cDAQ-9172 chassis.
Note Some I/O modules have additional power requirements. For more information about
C Series I/O module(s) power requirements, refer to documentation included with the
C Series I/O module(s).
Note Sleep mode for C Series I/O modules is not supported in the NI cDAQ-9172.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 80 ni.com
Page 81

Input voltage range................................. 11 V to 30 V
Maximum required input power ............ 15 W
Power input connector ........................... DC input jack with locking,
Power input mating connector ............... Switchcraft S760K
Bus Interface
USB specification .................................. USB 2.0 Hi-Speed
Power from USB
4.10 to 5.25 V ................................. 500 µA maximum
High-performance data streams ............. 4
Types available ............................... Analog input, analog output,
Physical Characteristics
Chassis weight (unloaded) ..................... Approx. 840 g
threaded ring 0.8 in. (2 mm)
center pin
digital input, digital output,
counter/timer input
(1 lb 13 oz)
Chassis dimensions (unloaded) .............. 25.4 cm × 8.81 cm × 5.89 cm
(10.0 in. × 3.5 in. × 2.3 in.)
Safety
If you need to clean the chassis, wipe it with a dry towel.
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of safety for electrical equipment for measurement, control,
and laboratory use:
• IEC 61010-1, EN-61010-1
• UL 61010-1, CSA 61010-1
Note For UL and other safety certifications, refer to the product label or visit ni.com/
certification, search by model number or product line, and click the appropriate link
in the Certification column.
© National Instruments Corporation 81 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
Page 82

Environmental
The NI cDAQ-9172 chassis is intended for indoor use only. For outdoor
use, mount the system in a suitably rated enclosure.
Shock and Vibration
Operating temperature
1
(IEC-60068-2-1 and IEC-60068-2-2) .....–20 to 55 °C
Storage temperature
(IEC-60068-2-1 and IEC-60068-2-2) .....– 40 to 85 °C
Ingress protection ...................................IP 30
Operating humidity
(IEC-60068-2-56) ...................................10 to 90% RH, noncondensing
Storage humidity
(IEC-60068-2-56) ...................................5 to 95% RH, noncondensing
Maximum altitude...................................2,000 m
Pollution Degree (IEC 60664) ................2
To meet these specifications, you must panel mount the NI cDAQ-9172
system and affix ferrules to the ends of the terminal lines.
Operational shock ...................................30 g peak, half-sine, 11 ms pulse
(Tested in accordance with
IEC-60068-2-27. Test profile
developed in accordance with
MIL-PRF-28800F.)
Random vibration
Operating .........................................5 to 500 Hz, 0.3 g
Nonoperating ...................................5 to 500 Hz, 2.4 g
rms
rms
(Tested in accordance
with IEC-60068-2-64.
Nonoperating test profile
exceeds the requirements of
MIL-PRF-28800F, Class 3.)
1
When operated in temperatures below 0 °C, you must use the PS-5 power supply, or another power supply rated for below 0 °C.
NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications 82 ni.com
Page 83

Electromagnetic Compatibility
⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩ ˄Ё
˅
Ёᅶ᠋
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of EMC for electrical equipment for measurement, control,
and laboratory use:
• EN 61326 EMC requirements; Minimum Immunity
• EN 55011 Emissions; Group 1, Class A
• CE, C-Tick, ICES, and FCC Part 15 Emissions; Class A
Note For EMC compliance, operate this device according to product documentation.
CE Compliance
This product meets the essential requirements of applicable European
Directives, as amended for CE marking, as follows:
• 2006/95/EC; Low-Voltage Directive (safety)
• 2004/108/EC; Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC)
Note Refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for this product for any additional
regulatory compliance information. To obtain the DoC for this product, visit
certification
in the Certification column.
, search by model number or product line, and click the appropriate link
ni.com/
Environmental Management
National Instruments is committed to designing and manufacturing
products in an environmentally responsible manner. NI recognizes that
eliminating certain hazardous substances from our products is beneficial
not only to the environment but also to NI customers.
For additional environmental information, refer to the NI and the
Environment Web page at
ni.com/environment. This page contains the
environmental regulations and directives with which NI complies, as well
as other environmental information not included in this document.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
EU Customers At the end of their life cycle, all products must be sent to a WEEE recycling
center. For more information about WEEE recycling centers and National Instruments
WEEE initiatives, visit
ni.com/environment/weee.htm.
RoHS
National Instruments
݇Ѣ
National Instruments
(For information about China RoHS compliance, go to
© National Instruments Corporation 83 NI cDAQ-9172 User Guide and Specifications
ヺড়Ё⬉ᄤֵᙃѻકЁ䰤ࠊՓ⫼ᶤѯ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼ᣛҸ
Ё
ড়㾘ᗻֵᙃˈ䇋ⱏᔩ
RoHS
ni.com/environment/rohs_china
ni.com/environment/rohs_china
(RoHS)
DŽ
DŽ
.)
Page 84

Where to Go for Support
The National Instruments Web site is your complete resource for technical
support. At
troubleshooting and application development self-help resources to email
and phone assistance from NI Application Engineers.
National Instruments corporate headquarters is located at
11500 North Mopac Expressway, Austin, Texas, 78759-3504.
National Instruments also has offices located around the world to help
address your support needs. For telephone support in the United States,
create your service request at
instructions or dial 512 795 8248. For telephone support outside the United
States, contact your local branch office:
Australia 1800 300 800, Austria 43 662 457990-0,
Belgium 32 (0) 2 757 0020, Brazil 55 11 3262 3599,
Canada 800 433 3488, China 86 21 5050 9800,
Czech Republic 420 224 235 774, Denmark 45 45 76 26 00,
Finland 358 (0) 9 725 72511, France 01 57 66 24 24,
Germany 49 89 7413130, India 91 80 41190000, Israel 972 3 6393737,
Italy 39 02 41309277, Japan 0120-527196, Korea 82 02 3451 3400,
Lebanon 961 (0) 1 33 28 28, Malaysia 1800 887710,
Mexico 01 800 010 0793, Netherlands 31 (0) 348 433 466,
New Zealand 0800 553 322, Norway 47 (0) 66 90 76 60,
Poland 48 22 3390150, Portugal 351 210 3 11 210, Russia 7 495 783 6851,
Singapore 1800 226 5886, Slovenia 386 3 425 42 00,
South Africa 27 0 11 805 8197, Spain 34 91 640 0085,
Sweden 46 (0) 8 587 895 00, Switzerland 41 56 2005151,
Taiwan 886 02 2377 2222, Thailand 662 278 6777,
Turkey 90 212 279 3031, United Kingdom 44 (0) 1635 5235455
ni.com/support you have access to everything from
ni.com/support and follow the calling
National Instruments, NI, ni.com, and LabVIEW are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation.
Refer to the Terms of Use section on ni.com/legal for more information about National
Instruments trademarks. Other product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trad e
names of their respective companies. For patents covering National Instruments products, refer to the
appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software, the patents.txt file on your media, or
ni.com/patents.
© 2006–2008 National Instruments Corporation. All rights reserved.
371747F-01 Jun08
 Loading...
Loading...