Page 1

PXI
NI 8352/8353 User Manual
NI 8352/8353 User Manual
August 2007
372285A-01
Page 2

Support
Worldwide Technical Support and Product Information
ni.com
National Instruments Corporate Headquarters
11500 North Mopac Expressway Austin, Texas 78759-3504 USA Tel: 512 683 0100
Worldwide Offices
Australia 1800 300 800, Austria 43 662 457990-0, Belgium 32 (0) 2 757 0020, Brazil 55 11 3262 3599,
Canada 800 433 3488, China 86 21 5050 9800, Czech Republic 420 224 235 774, Denmark 45 45 76 26 00,
Finland 358 (0) 9 725 72511, France 01 57 66 24 24, Germany 49 89 7413130, India 91 80 41190000,
Israel 972 3 6393737, Italy 39 02 413091, Japan 81 3 5472 2970, Korea 82 02 3451 3400,
Lebanon 961 (0) 1 33 28 28, Malaysia 1800 887710, Mexico 01 800 010 0793, Netherlands 31 (0) 348 433 466,
New Zealand 0800 553 322, Norway 47 (0) 66 90 76 60, Poland 48 22 3390150, Portugal 351 210 311 210,
Russia 7 495 783 6851, Singapore 1800 226 5886, Slovenia 386 3 425 42 00, South Africa 27 0 11 805 8197,
Spain 34 91 640 0085, Sweden 46 (0) 8 587 895 00, Switzerland 41 56 2005151, Taiwan 886 02 2377 2222,
Thailand 662 278 6777, Turkey 90 212 279 3031, United Kingdom 44 (0) 1635 523545
For further support information, refer to the Technical Support and Professional Services appendix. To comment
on National Instruments documentation, refer to the National Instruments Web site at
the info code
feedback.
ni.com/info and enter
© 2007 National Instruments Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Important Information
Warranty
The NI 8352/8353 is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of one year from the date of shipment, as evidenced
by receipts or other documentation. National Instruments will, at its option, repair or replace equipment that proves to be defective during the
warranty period. This warranty includes parts and labor.
The media on which you receive National Instruments software are warranted not to fail to execute programming instructions, due to defects in
materials and workmanship, for a period of 90 days from date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National Instruments
will, at its option, repair or replace software media that do not execute programming instruc tions if National Instruments receives notice of such defects
during the warranty period. National Instruments does not warrant that the operation of the software shall be uninterrupted or error free.
A Return Material Authorization (RMA) number must be obtained from the factory and clearly marked on the outside of the package before any
equipment will be accepted for warranty work. National Instruments will pay the shipping costs of returning to the owner parts which are covered by
warranty.
National Instruments believes that the information in this document is accurate. The document has been carefully reviewed for technical accuracy. In
the event that technical or typographical errors exist, National Instruments reserves the right to make changes to subsequent editions of this document
without prior notice to holders of this edition. The reader should consult National Instruments if errors are suspected. In no event shall National
Instruments be liable for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the information contained in it.
E
XCEPT AS SPECIFIED HEREIN, NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTY OF
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. CUSTOMER’S RIGHT TO RECOVER DAMAGES CAUSED BY FAULT OR NEGLIGENCE ON THE PART OF NATIONAL
I
NSTRUMENTS SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE AMOUNT THERETOFORE PAID BY THE CUSTOMER. NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES RESULTING
FROM LOSS OF DATA, PROFITS, USE OF PRODUCTS, OR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF. This limitation of
the liability of National Instruments will apply regardless of the form of action, whether in contract or tort, including negligence. Any action against
National Instruments must be brought within one year after the cause of action accrues. National Instruments shall not be liable for any delay in
performance due to causes beyond its reasonable control. The warranty provided herein does not cover damages, defects, malfunctions, or service
failures caused by owner’s failure to follow the National Instruments installation, operation, or maintenance instructions; owner’s modification of the
product; owner’s abuse, misuse, or negligent acts; and power failure or surges, fire, flood, accident, actions of third parties, or other events outside
reasonable control.
Copyright
Under the copyright laws, this publication may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
recording, storing in an information retrieval system, or translating, in whole or in part, without the prior written consent of National
Instruments Corporation.
National Instruments respects the intellectual property of others, and we ask our users to do the same. NI software is protected by copyright and other
intellectual property laws. Where NI software may be used to reproduce software or other materials belonging to others, you may use NI software only
to reproduce materials that you may reproduce in accordance with the terms of any applicable license or other legal restriction.
Trademarks
National Instruments, NI, ni.com, and LabVIEW are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation. Refer to the Terms of Use section
on
ni.com/legal for more information about National Instruments trademarks.
Other product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies.
Members of the National Instruments Alliance Partner Program are business entities independent from National Instruments and have no agency,
partnership, or joint-venture relationship with National Instruments.
Patents
For patents covering National Instruments products, refer to the appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software, the patents.txt file
on your CD, or ni.com/patents.
WARNING REGARDING USE OF NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS
(1) NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED WITH COMPONENTS AND TESTING FOR A LEVEL OF
RELIABILITY SUITABLE FOR USE IN OR IN CONNECTION WITH SURGICAL IMPLANTS OR AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN
ANY LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS WHOSE FAILURE TO PERFORM CAN REASONABLY BE EXPECTED TO CAUSE SIGNIFICANT
INJURY TO A HUMAN.
(2) IN ANY APPLICATION, INCLUDING THE ABOVE, RELIABILITY OF OPERATION OF THE SOFTWARE PRODUCTS CAN BE
IMPAIRED BY ADVERSE FACTORS, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO FLUCTUATIONS IN ELECTRICAL POWER SUPPLY,
COMPUTER HARDWARE MALFUNCTIONS, COMPUTER OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE FITNESS, FITNESS OF COMPILERS
AND DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE USED TO DEVELOP AN APPLICATION, INSTALLATION ERRORS, SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE
COMPATIBILITY PROBLEMS, MALFUNCTIONS OR FAILURES OF ELECTRONIC MONITORING OR CONTROL DEVICES,
TRANSIENT FAILURES OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS (HARDWARE AND/OR SOFTWARE), UNANTICIPATED USES OR MISUSES, OR
ERRORS ON THE PART OF THE USER OR APPLICATIONS DESIGNER (ADVERSE FACTORS SUCH AS THESE ARE HEREAFTER
COLLECTIVELY TERMED “SYSTEM FAILURES”). ANY APPLICATION WHERE A SYSTEM FAILURE WOULD CREATE A RISK OF
HARM TO PROPERTY OR PERSONS (INCLUDING THE RISK OF BODILY INJURY AND DEATH) SHOULD NOT BE RELIANT SOLELY
UPON ONE FORM OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEM DUE TO THE RISK OF SYSTEM FAILURE. TO AVOID DAMAGE, INJURY, OR DEATH,
THE USER OR APPLICATION DESIGNER MUST TAKE REASONABLY PRUDENT STEPS TO PROTECT AGAINST SYSTEM FAILURES,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO BACK-UP OR SHUT DOWN MECHANISMS. BECAUSE EACH END-USER SYSTEM IS
CUSTOMIZED AND DIFFERS FROM NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS' TESTING PLATFORMS AND BECAUSE A USER OR APPLICATION
DESIGNER MAY USE NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS IN COMBINATION WITH OTHER PRODUCTS IN A MANNER NOT
EVALUATED OR CONTEMPLATED BY NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS, THE USER OR APPLICATION DESIGNER IS ULTIMATELY
RESPONSIBLE FOR VERIFYING AND VALIDATING THE SUITABILITY OF NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS WHENEVER
NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS ARE INCORPORATED IN A SYSTEM OR APPLICATION, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THE APPROPRIATE DESIGN, PROCESS AND SAFETY LEVEL OF SUCH SYSTEM OR APPLICATION.
Page 4

Compliance
Compliance with FCC/Canada Radio Frequency Interference
Regulations
Determining FCC Class
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has rules to protect wireless communications from interference. The FCC
places digital electronics into two classes. These classes are known as Class A (for use in industrial-commercial locations only)
or Class B (for use in residential or commercial locations). All National Instruments (NI) products are FCC Class A products.
Depending on where it is operated, this Class A product could be subject to restrictions in the FCC rules. (In Canada, the
Department of Communications (DOC), of Industry Canada, regulates wireless interference in much the same way.) Digital
electronics emit weak signals during normal operation that can affect radio, television, or other wireless products.
All Class A products display a simple warning statement of one paragraph in length regarding interference and undesired
operation. The FCC rules have restrictions regarding the locations where FCC Class A products can be operated.
Consult the FCC Web site at
FCC/DOC Warnings
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in strict accordance with the instructions
in this manual and the CE marking Declaration of Conformity*, may cause interference to radio and television reception.
Classification requirements are the same for the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Department
of Communications (DOC).
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by NI could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment under the
FCC Rules.
Class A
Federal Communications Commission
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated
in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user is required to correct the interference
at their own expense.
www.fcc.gov for more information.
Canadian Department of Communications
This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur du Canada.
Compliance with EU Directives
Users in the European Union (EU) should refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for information* pertaining to the
CE marking. Refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for this product for any additional regulatory compliance
information. To obtain the DoC for this product, visit
and click the appropriate link in the Certification column.
* The CE marking Declaration of Conformity contains important supplementary information and instructions for the user or
installer.
ni.com/certification, search by model number or product line,
Page 5

Contents
About This Manual
Conventions ...................................................................................................................ix
Related Documentation..................................................................................................x
Chapter 1
Getting Started
Unpacking......................................................................................................................1-1
What You Need to Get Started ......................................................................................1-1
Key Features ..................................................................................................................1-2
Mainboard Features .........................................................................................1-2
NI 8352/8353 Description .............................................................................................1-5
Optional Equipment.......................................................................................................1-6
Memory Upgrades...........................................................................................1-6
Rack Mount Kit ...............................................................................................1-6
USB Floppy Disk Drive ..................................................................................1-6
NI 8352/8353 Overview ................................................................................................1-6
National Instruments Software ......................................................................................1-7
CPU...................................................................................................1-2
Chipset ..............................................................................................1-2
Memory.............................................................................................1-2
Slots...................................................................................................1-3
Video.................................................................................................1-3
HDD ..................................................................................................1-3
DVD-ROM........................................................................................1-3
Onboard LAN ...................................................................................1-3
Onboard I/O ......................................................................................1-3
Power Management Features ............................................................1-3
Front Panel LEDs..............................................................................1-4
System Management .........................................................................1-4
Chapter 2
Installation and BIOS Setup
Safety Information .........................................................................................................2-1
Chassis Cooling Considerations ....................................................................................2-2
Providing Adequate Clearance ........................................................................2-2
Installation .....................................................................................................................2-2
Connecting Safety Ground.............................................................................................2-3
Connecting to Power Source..........................................................................................2-3
© National Instruments Corporation v NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 6

Contents
BIOS Setup.................................................................................................................... 2-3
Main BIOS Setup Menu.................................................................................. 2-4
Main Setup Features ......................................................................... 2-4
Advanced Setup .............................................................................................. 2-7
Boot Features.................................................................................... 2-7
Memory Cache ................................................................................. 2-8
PCI Configuration............................................................................. 2-10
Slot1 PCI 32, Slot6 PCI-X 133 MHz, and Slot6 PCI-Exp. x8 ......... 2-10
Advanced Processor Options............................................................ 2-12
I/O Device Configuration ................................................................. 2-14
DMI Event Logging.......................................................................... 2-15
Console Redirection ......................................................................... 2-16
Hardware Monitor Logic .................................................................. 2-17
IPMI.................................................................................................. 2-18
System Event Log/System Event Log (List Mode).......................... 2-20
Realtime Sensor Data ....................................................................... 2-20
Security ........................................................................................................... 2-20
Boot................................................................................................................. 2-21
Exit .................................................................................................................. 2-21
Rack Mounting .............................................................................................................. 2-22
Installing Inner Slides ..................................................................................... 2-23
Installing Outer Slides..................................................................................... 2-24
Installing the Slide Assemblies in the Rack....................................................2-25
Installing the Chassis into the Rack ................................................................ 2-26
Hard Drive Recovery..................................................................................................... 2-28
Installing an OS ............................................................................................................. 2-28
Cleaning......................................................................................................................... 2-28
Exterior Cleaning ............................................................................................ 2-28
Chapter 3
I/O Information
Rear Panel Connectors .................................................................................................. 3-1
PS/2 ................................................................................................................. 3-2
Universal Serial Bus........................................................................................ 3-3
Serial ...............................................................................................................3-4
VGA ................................................................................................................ 3-5
Ethernet ........................................................................................................... 3-7
MXI-Express Connectors ..............................................................................................3-8
NI 8352/8353 User Manual vi ni.com
Page 7

Chapter 4
Common Configuration Questions
General Questions..........................................................................................................4-1
Boot Options ..................................................................................................................4-1
Chassis Configuration....................................................................................................4-2
Upgrade Information......................................................................................................4-4
Chapter 5
Troubleshooting
Appendix A
Specifications
Appendix B
Hardware Configuration
Appendix C
Intel SATA RAID Utility for Intel ICH7R
Contents
Appendix D
Technical Support and Professional Services
Glossary
Index
© National Instruments Corporation vii NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 8

About This Manual
The NI 8352/8353 User Manual contains information about installing,
configuring, using, and maintaining the NI 8352/8353.
Conventions
The following conventions appear in this manual:
» The » symbol leads you through nested menu items and dialog box options
to a final action. The sequence File»Page Setup»Options directs you to
pull down the File menu, select the Page Setup item, and select Options
from the last dialog box.
This icon denotes a note, which alerts you to important information.
This icon denotes a caution, which advises you of precautions to take to
avoid injury, data loss, or a system crash. When this symbol is marked on a
product, refer to the Read Me First: Safety and Radio-Frequency
Interference for information about precautions to take.
bold Bold text denotes items that you must select or click in the software, such
as menu items and dialog box options. Bold text also denotes parameter
names.
italic Italic text denotes variables, emphasis, a cross-reference, or an introduction
to a key concept. Italic text also denotes text that is a placeholder for a word
or value that you must supply.
monospace Text in this font denotes text or characters that you should enter from the
keyboard, sections of code, programming examples, and syntax examples.
This font is also used for the proper names of disk drives, paths, directories,
programs, subprograms, subroutines, device names, functions, operations,
variables, filenames, and extensions.
monospace bold Bold text in this font denotes the messages and responses that the computer
automatically prints to the screen. This font also emphasizes lines of code
that are different from the other examples.
© National Instruments Corporation ix NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 9

About This Manual
Related Documentation
The following documents contain information that you may find helpful as
you read this manual:
• CompactPCI Specification PICMG 2.0 R 3.0
• PXI Hardware Specification, Revision 2.1
• PXI Software Specification, Revision 2.1
• ANSI/IEEE Standard 1014-1987, IEEE Standard for a Versatile
Backplane Bus: VMEbus
• ANSI/VITA 1-1994, VME64
• NI-VISA User Manual
• NI-VISA Programmer Reference Manual
• Read Me First: Safety and Radio-Frequency Interference, National
Instruments
NI 8352/8353 User Manual x ni.com
Page 10

Getting Started
This chapter describes the key features of the NI 8352/8353 and lists the kit
contents and optional equipment you can order from National Instruments.
Unpacking
Carefully inspect the shipping container and the NI 8352/8353 for damage.
Check for visible damage to the metal work. Check to make sure all
hardware and switches are undamaged. If damage appears to have been
caused during shipment, file a claim with the carrier. Retain the packing
material for possible inspection and/or reshipment.
What You Need to Get Started
The NI 8352/8353 kit contains the following items:
❑ NI 8352/8353 rack mount controller
1
❑ NI 8352/8353 User Manual
❑ Windows recovery CD/DVD
❑ NI driver CD
❑ Rack mount kit
❑ AC power cable (refer to Table 1-1 for a list of AC power cables)
© National Instruments Corporation 1-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 11

Chapter 1 Getting Started
Key Features
Table 1-1. AC Power Cables
Power Cable Reference Standards
Standard 120 V (USA) ANSI C73.11/NEMA 5-15-P/IEC83
Switzerland 220 V SEV
Australia 240 V AS C112
Universal Euro 230 V CEE (7), II, IV, VII IEC83
North America 240 V ANSI C73.20/NEMA 5-15-P/IEC83
United Kingdom 230 V BS 1363/IEC83
Japan 100 V ANSI C73.11/NEMA 5-15-P/IEC83
If you are missing any of the above items, or if you have the incorrect
AC power cable, contact National Instruments.
The NI 8352/8353 combines the performance of a PC with a National
Instruments remote controller for PXI in a rack-mountable compact
1U form factor.
Mainboard Features
CPU
• Intel Core2 Duo 2.4 GHz/Core2 Quad 2.4 GHz CPU with 800 MHz
FSB and 4/8 MB L2 cache
Chipset
• Intel 3000 chipset
• Intel ICH7R chipset
•Intel PXH-V
Memory
• 1 GB memory standard (2 × 512 MB ECC (32 M × 64 bit),
unbuffered, DDR-II)
• Maximum memory supported: 8 GB 533/667 DDR-II SDRAM in
4 DIMM sockets (240 pin)
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 1-2 ni.com
Page 12

Chapter 1 Getting Started
Slots
• PCI Express x8 slot
• PCI-X 64-bit 133 MHz
Video
• ATI ES 1000 with 16 MB SDRAM
HDD
•2 × 250 GB (or greater) SATA hard drive RAID0
•4 × 3.5 in. expansion bay SATA
DVD-ROM
• Slim DVD-ROM drive
Onboard LAN
•2 × Intel 82573V/L Gigabit Ethernet controller
Onboard I/O
• PS/2 keyboard port
• PS/2 mouse port
•Serial port
• VGA port
• Two USB 2.0 ports (rear)
• Two USB 2.0 ports (front)
• Two RJ-45 ports
Power Management Features
• RTC alarm and wake up
• Wake up on LAN (WOL)
• Wake up on serial ring
• Wake up on keyboard/mouse from sleep (S1)
• Wake up on USB from sleep (S1)
© National Instruments Corporation 1-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 13

Chapter 1 Getting Started
• Wake up on PCI
• Supports ACPI S1/S4/S5 functions
Front Panel LEDs
•Power
• LAN activity
• HDD activity
• Thermal trip LED
System Management
•SMB (I2C)
• Temperature, voltage, and fan monitors
• Chassis intrusion
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 1-4 ni.com
Page 14
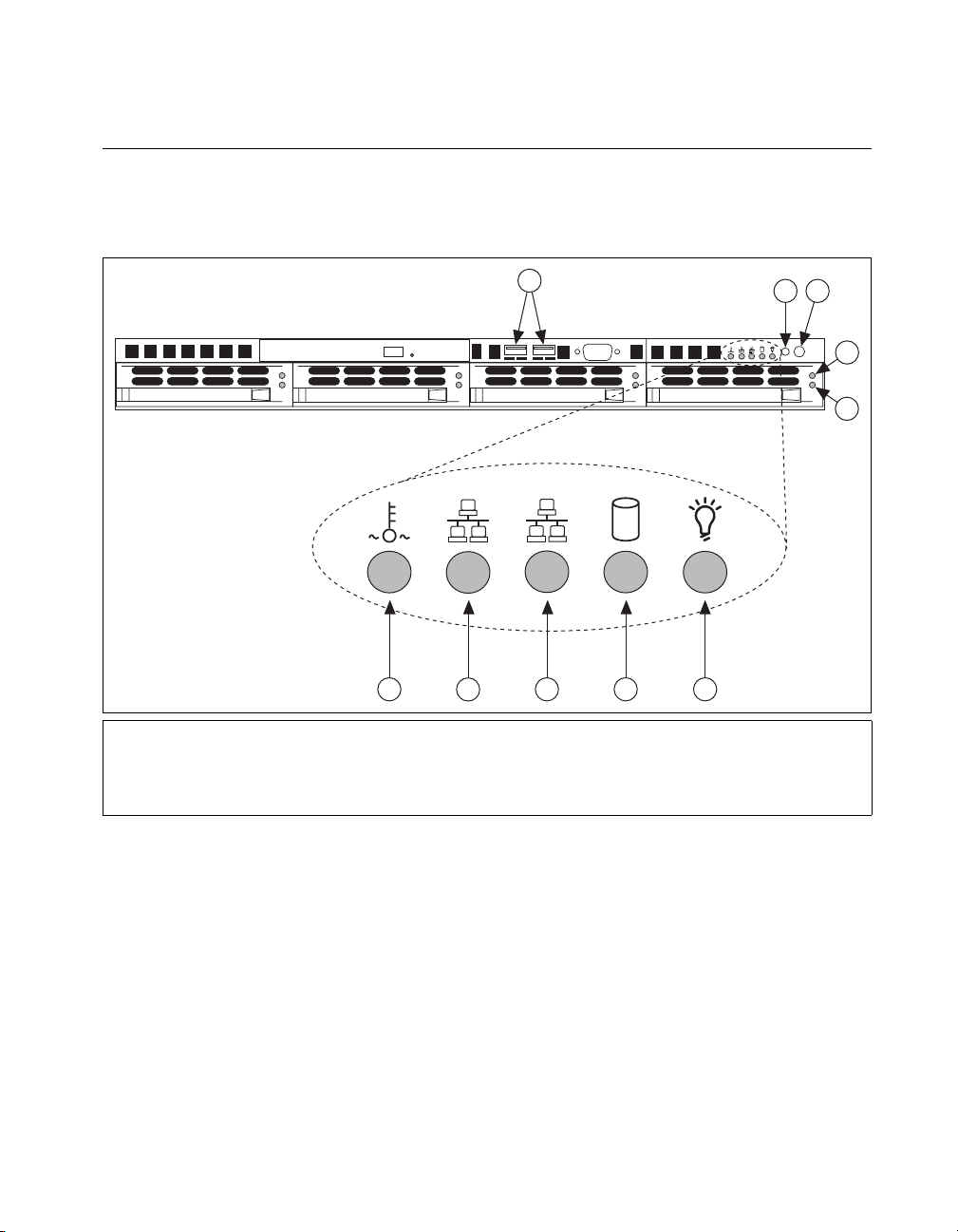
NI 8352/8353 Description
Figure 1-1 shows the key features of the NI 8352/8353 front panel. For
detailed information about the NI 8352/8353 rear panel, refer to Chapter 3,
I/O Information.
Chapter 1 Getting Started
1USB Ports
2Reset Switch
3 Power Switch
4 Hard Drive Activity Indicator
5 Hard Drive Error Indicator
10
1
9
8 7
6 Power Indicator
7 HDD Indicator
8 LAN1 Status Indicator
9 LAN2 Status Indicator
10 System Temp and Fan Warning Indicator
6
2
3
RESET
4
5
Figure 1-1. Front View of the NI 8352/8353
The front panel includes the following LEDs:
• Power indicator—glows when the NI 8352/8353 is powered on.
• LAN status indicators—flash when there is activity on LAN1 or
LAN2.
• Overheat/FanFail LED
– Off—Normal
– On—Overheat
– Flashing—Fan
© National Instruments Corporation 1-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 15

Chapter 1 Getting Started
Optional Equipment
Memory Upgrades
You can upgrade the NI 8352/8353 memory to a maximum of 8 GB.
Note A 32-bit operating system such as Windows XP Pro addresses a maximum of 4 GB.
The NI 8352/8353 supports dual-channel DDR-II SDRAM unbuffered
memory in four 240-pin DIMM sockets. The NI 8352/8353 supports
ECC memory.
Note National Instruments has tested and verified that the DDR-II DIMMs we sell work
with the NI 8352/8353. We recommend you purchase your DDR-II DIMM modules from
National Instruments. Other off-the-shelf DDR-II DIMM modules are not guaranteed to
work properly.
Rack Mount Kit
A rack mount kit is included for mounting the NI 8352/8353 chassis into a
19 in. instrument cabinet.
USB Floppy Disk Drive
A USB floppy drive is available from National Instruments, part number
778492-02.
NI 8352/8353 Overview
The NI 8352/8353 is a 1U PC-server-based controller for
MXI-Express-based control of PXI chassis. The controller provides
leading-edge processing power with Intel Pentium Core2 Duo and
Core2 Quad processors, high disk bandwidth with hardware RAID support,
high I/O bandwidth with a PCI Express x8 slot or an option for a PCI-X
slot, and up to 8 GB of memory. The server fits in a 26 in. rack.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 1-6 ni.com
Page 16

National Instruments Software
National Instruments has developed several software kits you can use with
the NI 8352/8353.
National Instruments hardware and software work together to help you
make the most of your PXI Express system. The LabVIEW, Measurement
Studio, and LabWindows™/CVI™ application development environments
combine with leading hardware drivers such as NI-DAQmx to provide
exceptional control of NI hardware. Instrument drivers are available at
ni.com/idnet to simplify communication with instruments over a variety
of buses.
LabVIEW is a powerful and easy-to-use graphical programming
environment you can use to acquire data from thousands of different
instruments including USB, IEEE 488.2, VXI, serial, PLCs, and plug-in
boards. LabVIEW helps you convert acquired data into meaningful results
using powerful data analysis routines. Add-on tools provide additional
specialized functionality. For more information, visit
and
ni.com/toolkits.
If you prefer to use Microsoft’s Visual Basic, Visual C++, and Visual
Studio .NET for the core of your application, Measurement Studio adds
tools for measurement and automation to each language. For more
information, visit
ni.com/mstudio.
Chapter 1 Getting Started
ni.com/labview
LabWindows/CVI is an interactive ANSI C programming environment
designed for building virtual instrument applications. LabWindows/CVI
includes a drag-and-drop editor for building user interfaces, a complete
ANSI C environment for building your test program logic, and a collection
of automated code generation tools, as well as utilities for building
automated test systems, monitoring applications, or laboratory
experiments. For more information, visit
ni.com/lwcvi.
NI-DAQmx provides an extensive library of functions you can call from
your application development environment or interactive environment,
such as NI Signal Express. These functions provide an intuitive API for
National Instruments multifunction DAQ products. Features include analog
input (A/D conversion), buffered data acquisition (high-speed A/D
conversion), analog output (D/A conversion), waveform generation, digital
I/O, counter/timer operations, SCXI signal conditioning, RTSI or PXI
synchronization, self-calibration, messaging, and acquiring data to
extended memory. For more information, visit
© National Instruments Corporation 1-7 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
ni.com/daq.
Page 17

Chapter 1 Getting Started
National Instruments modular instruments use specialized drivers suited to
each product’s specialization. Express VIs provide customized, interactive
programming of instruments in a single interface, and soft front panels
provide an interface for testing the functionality of each instrument with
no programming required. NI switches, DMMs, high-speed DIO,
high-speed digitizers, and sources each have customized drivers for
high-end modular instrumentation systems. RF applications leverage
two drivers, NI-RFSG and NI-RFSA, and dynamic signal acquisition is
available through NI-DAQmx. For more information, visit
modularinstruments
.
ni.com/
You can expand the timing and triggering functionality of your PXI system
with PXI timing and synchronization products. These products provide
precision clock sources, custom routing of triggers for multichassis
synchronization, clock sharing, and more, and are programmed with
NI-Sync. For more information, visit
ni.com/pxi.
NI-VISA is the National Instruments implementation of the VISA
specification. VISA is a uniform API for communicating and controlling
USB, Serial, GPIB, PXI, VXI, and various other types of instruments. This
API aids in the creation of portable applications and instrument drivers. For
information about writing your own PXI instrument driver with NI-VISA,
refer to the NI-VISA Help and the
directory. For more information, visit
readme.txt file in the NI-VISA
ni.com/visa.
With LabVIEW for Linux and support for more than 200 devices on Linux
with the NI-DAQmx driver, you can now create virtual instruments based
on the Linux OS. The NI-VISA driver for Linux has improved instrument
control in Linux, and NI modular instruments are partially supported. For
more information, visit
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 1-8 ni.com
ni.com/linux.
Page 18

Installation and BIOS Setup
This chapter describes how to install, configure, and use the NI 8352/8353.
Before connecting the NI 8352/8353 to a power source, read this chapter
and the Read Me First: Safety and Radio-Frequency Interference
document included with your NI 8352/8353.
Safety Information
Caution Before undertaking any troubleshooting, maintenance, or exploratory procedure,
carefully read the following caution notices.
This equipment contains voltage hazardous to human life and safety, and is
capable of inflicting personal injury.
• Chassis Grounding—The NI 8352/8353 requires a connection from
the premise wire safety ground to the NI 8352/8353 chassis ground.
The earth safety ground must be connected during use of this
equipment to minimize shock hazards. Refer to the Connecting Safety
Ground section for instructions on connecting safety ground.
• Live Circuits—Operating personnel and service personnel must
not remove protective covers when operating or servicing the
NI 8352/8353. Adjustments and service to internal components must
be undertaken by qualified service technicians. During service of
this product, the mains connector to the premise wiring must be
disconnected. Dangerous voltages may be present under certain
conditions; use extreme caution.
• Explosive Atmosphere—Do not operate the chassis in conditions
where flammable gases are present. Under such conditions, this
equipment is unsafe and may ignite the gases or gas fumes.
• Parts Replacement—Service this equipment only with parts that
are exact replacements, both electrically and mechanically. Contact
National Instruments for replacement part information. Installation of
parts with those that are not direct replacements may cause harm to
personnel operating the chassis. Furthermore, damage or fire may
occur if replacement parts are unsuitable.
2
© National Instruments Corporation 2-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 19

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
• Modification—Do not modify any part of the NI 8352/8353 from
its original condition. Unsuitable modifications may result in safety
hazards.
Chassis Cooling Considerations
The NI 8352/8353 is designed to operate on a bench or in an instrument
rack. Determine how you want to use the NI 8352/8353 and follow the
appropriate installation instructions.
Providing Adequate Clearance
Apertures in the front, top, rear, and along both sides of the chassis
facilitate power supply and motherboard cooling. Air enters through the
front and top inlets of the chassis and exits through the fans on the rear of
the chassis. Place the NI 8352/8353 on a bench top or in an instrument rack
so that the fans (air outlets) and the air inlet apertures along the top and
front of the chassis have adequate ventilation. Keep other equipment a
minimum of 76.2 mm (3 in.) away from the air outlets on the rear of the
chassis.
Installation
Follow these steps to connect devices to the NI 8352/8353:
1. Connect a keyboard and mouse to the appropriate connectors on the
NI 8352/8353 rear panel.
2. Connect the VGA monitor video cable to the VGA connector on the
rear panel.
3. (Optional) To boot into LabVIEW RT, connect the network cable to
LAN jack 1 on the rear panel. (Refer to Figure 3-1, NI 8352/8353 Rear
Panel Layout, for the location of LAN jack 1.)
4. Connect the USB, serial, and parallel devices as necessary to the
NI 8352/8353 front and rear panel ports.
Caution To minimize shock hazard, make sure the electrical power outlet you use to power
the NI 8352/8353 has an appropriate earth safety ground. Refer to the Connecting Safety
Ground section for more information.
5. Connect the AC power cable to the AC inlet on the rear panel and to an
AC power outlet. For more information, refer to Connecting to Power
Source section.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-2 ni.com
Page 20

6. Connect the MXI-Express port on the rear of the NI 8352/8353 to the
PXI chassis and power on the chassis.
7. Power on the NI 8352/8353.
8. Verify that the NI 8352/8353 boots. If it does not boot, refer to the
What if the NI 8352/8353 does not boot? section of Chapter 5,
Troubleshooting.
Connecting Safety Ground
The NI 8352/8353 is designed with a three-position NEMA 5-15 style plug
for the U.S. that connects the ground line to the chassis ground. To
minimize shock hazard, make sure the electrical power outlet you use to
power the chassis has an appropriate earth safety ground.
Connecting to Power Source
Attach input power through the rear AC inlet using the appropriate
AC power cable supplied.
Caution To completely remove power, you must disconnect the AC power cable.
Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
The power switch allows you to power on the chassis or place it in standby
mode. Push the power switch to the On position (if not already on). Observe
that all fans become operational and the power indicator is lit.
BIOS Setup
This section describes all main BIOS setup options.
Use the up/down arrow keys to move among the different settings in each
menu. Use the left/right arrow keys to change the options for each setting.
Press <Esc> to exit the CMOS setup menu. The next section describes in
detail how to navigate through the menus.
To access submenus, highlight a menu item and press <Enter>.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 21

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Main BIOS Setup Menu
Main Setup Features
System Time
To set the system date and time, enter the correct information in the
appropriate fields. Press <Enter> to save the data.
System Date
Using the arrow keys, highlight the month, day, and year fields, and enter
the correct data. Press <Enter> to save the data.
BIOS Date
This field displays the date when this BIOS version was built.
Legacy Diskette A
Use this setting to set the type of floppy disk drive installed as diskette A.
The options are Disabled, 360 KB 5.25 in., 1.2 MB 5.25 in., 720 KB
3.5 in., 1.44/1.25 MB 3.5 in. (default), and 2.88 MB 3.5 in.
Parallel ATA
Use this setting to enable or disable the function of Parallel ATA. The
options are Disabled, Channel 0 (default), Channel 1, and Both.
Serial ATA
Use this setting to enable or disable the function of Serial ATA. The options
are Disabled and Enabled (default).
Native Mode Operation
Select the native mode for ATA. The options are Parallel ATA, Serial
ATA, Both, and Auto (default).
SATA Controller Mode
Select Compatible to allow the BIOS to detect the SATA and PATA drives
automatically and place them in Legacy Mode. Select Enhanced to allow
the BIOS to detect the SATA and PATA drives automatically and place
them in the Native IDE Mode.
Note The Enhanced mode requires Windows 2000 or later.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-4 ni.com
Page 22

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
When the SATA Controller Mode is set to Enhanced, the following items
display.
Serial ATA (SATA) RAID
Select Enabled to enable Serial ATA RAID functions. (For Windows, use
the RAID driver if this feature is set to Enabled. When this item is set to
Enabled, the ICH RAID Code Base item is available for you to select
activation of either Intel or Adaptec Host RAID firmware. If this item is set
to Disabled, the SATA AHCI Enable item is available.) The options are
Enabled and Disabled (default).
SATA AHCI
Select Enabled to enable the Serial ATA Advanced Host Interface
function. (Be careful when using this function. This feature is for advanced
programmers only.) The options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
ICH RAID Code Base
Select Intel to enable the Intel SATA RAID firmware. Select Adaptec to
use Adaptec's HostRAID firmware. The options are Intel (default) and
Adaptec.
IDE Primary Master/Slave, IDE Secondary Master/Slave,
SATA Port3, and SATA Port4
Use these settings to set the parameters of IDE Primary Master/Slave,
IDE Secondary Master/Slave, and SATA Port3/SATA Port4 slots. Press
<Enter> to access the following submenu items. Set the correct
configurations accordingly.
Type
Use this option to select the IDE hard drive type. The Auto (default) option
allows the BIOS to automatically configure the parameters of the HDD
installed at the connection. Enter a number between 1 to 39 to select a
predetermined HDD type. Select User to enter the parameters of the HDD
installed. Select CDROM if a CDROM drive is installed. Select ATAPI if
a removable disk drive is installed.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
CHS Format
In this format, the BIOS displays the following items:
TYPE: This item displays the IDE or SATA device type.
Cylinders: This item indicates the status of cylinders.
Headers: This item indicates the number of headers.
Sectors: This item displays the number of sectors.
Maximum Capacity: This item displays the maximum system storage
capacity.
LBA Format
In this format, the BIOS displays the following items:
Total Sectors: This item displays the number of total sectors available in
the LBA format.
Maximum Capacity: This item displays the maximum capacity in the
LBA format.
Multi-Sector Transfers
Use this item to specify the number of sectors per block to be used in
multisector transfer. The options are Disabled (default), 4 Sectors,
8 Sectors, and 16 Sectors.
LBA Mode Control
This item determines whether the Phoenix BIOS accesses the IDE Primary
Master Device via the LBA mode. The options are Enabled and Disabled
(default).
32 Bit I/O
Use this option to enable or disable the 32-bit data transfer function. The
options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
Transfer Mode
Use this option to set the transfer mode. The options are Standard
(default), Fast PIO1, Fast PIO2, Fast PIO3, Fast PIO4, FPIO3/DMA1,
and FPIO4/DMA2.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-6 ni.com
Page 24

Advanced Setup
Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Ultra DMA Mode
Use this option to select Ultra DMA Mode. The options are Disabled
(default), Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3, Mode 4, and Mode 5.
System Memory
This display shows the amount of system memory.
Extended Memory
This display shows the amount of extended memory.
Choose Advanced from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility main menu with
the arrow keys. To access submenus, highlight a menu item and press
<Enter>.
Boot Features
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
QuickBoot Mode
If enabled, this feature speeds up the Power On Self Test (POST) routine
by skipping certain tests after the computer is turned on. The settings are
Enabled (default) and Disabled. If disabled, the POST routine runs at
normal speed.
Quiet Boot
Use this setting to enable or disable the graphic logo screen during bootup.
The settings are Enabled (default) and Disabled.
ACPI Mode
Use this setting to employ Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
(ACPI) power management on your system. The options are Yes (default)
and No.
Power Button Behavior
If set to Instant-Off, the system powers off immediately when you press
the power button. If set to 4-sec override, the system powers off when you
press the power button for 4 seconds or longer. The options are Instant-Off
(default) and 4-sec override.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-7 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 25

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Resume on Modem Ring
Select On to “wake up” your system when your modem receives an
incoming call. The options are On (default) and Off.
Power Loss Control
Use this setting to choose how the system reacts when power returns after
an unexpected power loss. The options are Stay Off, Power On, and Last
State (default).
Watchdog
If enabled, this option automatically resets the system if the system is not
active for more than 5 minutes. The options are Enabled and Disabled
(default).
Summary Screen
Use this setting to enable or disable the summary screen that displays the
system configuration during bootup. The options are Enabled (default) and
Disabled.
Memory Cache
Cache System BIOS Area
Use this setting to designate a reserve area in the system memory as a
system BIOS buffer. This allows the BIOS to write (cache) data into this
reserved memory area. Select Write Protect (default) to enable this
function and reserve this area for BIOS ROM access only. Select
Uncached to disable this function and make this area available for other
devices.
Cache Video BIOS Area
Use this setting to designate a reserve area in the system memory as a video
BIOS buffer. This allows the BIOS to write (cache) data into this reserved
memory area. Select Write Protect (default) to enable the function and
reserve this area for video BIOS ROM access only. Select Uncached to
disable this function and make this area available for other devices.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-8 ni.com
Page 26

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Cache Base 0–512K
If enabled, this feature allows the data stored in the 0 –512K memory
area to be cached (written) into a buffer, a storage area in static DROM
(SDROM), or written into L1, L2 cache inside the CPU to increase CPU
operation speed. Select Uncached to disable this function. Select Write
Through to allow data to be cached into the buffer and written into the
system memory at the same time. Select Write Protect to prevent data
from being written into the base memory area of Block 0–512K. Select
Write Back to allow the CPU to write back data directly from the buffer
without writing data to the system memory for fast CPU data processing
and operation. The options are Uncached, Write Through, Write
Protect, and Write Back (default).
Cache Base 512K–640K
If enabled, this feature allows the data stored in the 512K–640K memory
area to be cached (written) into a buffer, a storage area in the static DROM
(SDROM), or written into L1, L2, L3 cache inside the CPU to increase
CPU operation speed. Select Uncached to disable this function. Select
Write Through to allow data to be cached into the buffer and written into
the system memory at the same time. Select Write Protect to prevent data
from being written into the base memory area of Block 512–640K. Select
Write Back to allow the CPU to write back data directly from the buffer
without writing data to the System Memory for fast CPU data processing
and operation. The options are Uncached, Write Through, Write
Protect, and Write Back (default).
Cache Extended Memory
If enabled, this feature allows the data stored in the extended memory
area to be cached (written) into a buffer, a storage area in static DROM
(SDROM), or written into L1, L2, L3 cache inside the CPU to increase
CPU operation speed. Select Uncached to disable this function. Select
Write Through to allow data to be cached into the buffer and written into
the system memory at the same time. Select Write Protect to prevent data
from being written into the system memory area above 1 MB. Select Write
Back to allow the CPU to write back data directly from the buffer without
writing data to the System Memory for fast CPU data processing and
operation. The options are Uncached, Write Through, Write Protect,
and Write Back (default).
© National Instruments Corporation 2-9 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 27

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Discrete MTRR Allocation
If enabled, Memory Type Range Registers (MTRRs) are configured as
distinct, separate units and cannot be overlapped. If enabled, you can
achieve better graphic effects when using a Linux graphic driver that
requires the write-combining configuration with 4 GB or more memory.
The options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
PCI Configuration
Access this submenu to make changes to the following PCI device settings.
Onboard GLAN1/Onboard GLAN2 (Gigabit-LAN) OPROM
Configure
Enable this option to boot from GLAN. The options are Disabled and
Enabled (default).
Reset Configuration Data
If set to Yes, this setting clears the Extended System Configuration Data
(ESCD) area. The options are Yes and No (default).
Frequency for PCI-X
Use this option to change the bus frequency for the devices installed in the
slot indicated. The options are Auto (default), PCI 33 MHz, PCI 66 MHz,
PCI-X 66 MHz, PCI-X 100 MHz, and PCI-X 133 MHz.
Slot1 PCI 32, Slot6 PCI-X 133 MHz, and Slot6 PCI-Exp. x8
Access these submenus to change the following settings.
Option ROM Scan
When enabled, this setting initializes the device expansion ROM. The
options are Enabled (default) and Disabled.
Enable Master
Use this setting to enable the selected device as the PCI bus master. The
options are Enabled (default) and Disabled.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-10 ni.com
Page 28

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Latency Timer
Use this setting to set the clock rate for Bus Master. A high-priority,
high-throughout device may benefit from a greater clock rate. The options
are Default, 0020h, 0040h, 0060h, 0080h, 00A0h, 00C0h, and 00E0h. For
Unix, Novell, and other operating systems, select the other option. If a
drive fails after installing new software, you may want to change this
setting and try again. A different OS requires a different Bus Master
clock rate.
Large Disk Access Mode
This setting determines how large hard drives are accessed. The options are
DOS (default) or Other (for Unix, Novell NetWare, and other operating
systems).
Advanced Chipset Control
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
Caution Be careful when changing the advanced settings. Incorrect values may cause
system malfunction. Also, a very high DRAM frequency or incorrect DRAM timing may
cause system instability. When this occurs, revert to the default setting.
Clock Spectrum Feature
If enabled, the BIOS monitors the level of electromagnetic interference
caused by the components and attempts to decrease the interference
whenever needed. The options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
ECC Conditions
This setting specifies the ECC error conditions treated as ECC Error Events
by the system. The options are None, Single Bit, Multiple Bit (default),
and Both.
Note This item is available only when memory supports it.
ECC Error Handler
Use this setting to select the type of interrupt activated as a result of an
ECC error. The options are None, NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt),
SMI (System Management Interrupt) (default), and SCI (System
Control Interrupt).
Note This item is available only when memory supports it.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-11 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 29

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Route Port 80h Cycles to
Use this feature to select the bus where debug information is sent. The
options are Disabled, PCI (default), and LPC.
USB Function
Select Enabled to enable the function of specified USB devices. The
settings are Enabled (default) and Disabled.
Legacy USB Support
Use this setting to enable support for legacy USB devices. The settings are
Enabled (default) and Disabled.
Advanced Processor Options
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
CPU Speed
This display indicates the installed processor speed.
Frequency Ratio
Use this feature to set the CPU internal frequency multiplier. The options
are Default, x12, x13, x14, x15, x16, x17, and x18.
Hyperthreading
Set to Enabled to use hyperthreading for increased CPU performance. The
options are Disabled and Enabled (default).
Machine Checking
Set to Enabled to activate machine checking, which allows the CPU to
detect and report hardware (machine) errors via a set of model-specific
registers (MSRs). The options are Disabled (default) and Enabled.
L3 Cache
Set to Enabled to enable the L3 cache function, which optimizes system
and CPU performance. The options are Disabled and Enabled (default).
1
Available when the CPU supports this feature.
1
1
1
1
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-12 ni.com
Page 30

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Thermal Management 2
1
Set to Enabled to use thermal management 2 (TM2), which lowers CPU
voltage and frequency when the CPU temperature reaches a predefined
overheat threshold. Set to Disabled to use thermal management 1 (TM1),
which regulates CPU clocking via CPU internal clock modulation when the
CPU temperature reaches the overheat threshold. The options are Disabled
and Enabled (default).
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
1
The CPU fetches the cache line for 64 bytes if this option is set to Disabled.
The CPU fetches both cache lines for 128 bytes as comprised if set to
Enabled. The options are Disabled and Enabled (default).
C1 Enhanced Mode
1
Set to Enabled to enable Enhanced Halt State, which lowers CPU
voltage/frequency to prevent overheating. The options are Enabled and
Disabled (default).
Note Refer to the Intel Web site for detailed information.
Intel Virtualization Technology
1
Set to Enabled to use virtualization technology, which allows one platform
to run multiple operating systems and applications in independent
partitions, creating multiple “virtual” systems on one physical computer.
The options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
Note When changing this setting, you must power off and restart the system for the
change to take effect. Refer to the Intel Web site for detailed information.
No Execute Mode Memory Protection
2
Set to Enabled to enable Execute Disable Bit, which allows the processor
to classify areas in memory where an application code can execute and
where it cannot. This prevents a worm or virus from creating a flood of
codes to overwhelm the processor or damage the system during an attack.
The options are Disabled and Enabled (default).
1
Available only when the CPU supports this feature.
2
Available only when the OS and CPU support this feature. For more information about hardware/software support for this
function, refer to the Intel and Microsoft Web sites.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-13 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 31

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Processor Power Management
Use this feature to choose the processor power management mode. The
options are Disabled (default) and C States Only. If set to Disabled,
C states and GV1/GV3 are disabled. If set to C States Only, the processor
power is controlled through CPU power states in the APCI setting.
1
I/O Device Configuration
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
KBC Clock Input
Use this setting to select KBC clock frequency. The options are 6 MHz,
8MHz, 12 MHz (default), and 16 MHz.
Serial Port A
Use this setting to assign control of serial port A. The options are Enabled
(user defined, default), Disabled, and Auto (BIOS or OS controlled).
Base I/O Address
Use this setting to select the base I/O address for serial port A. The options
are 3F8 (default), 2F8, 3E8, and 2E8.
Interrupt
Use this setting to select the interrupt request (IRQ) for serial port A. The
options are IRQ3 and IRQ4 (default).
Serial Port B
Use this setting to assign control of serial port B. The options are Enabled
(user defined, default), Disabled, Auto (BIOS controlled) and OS
Controlled.
Mode
Use this setting to set the type of device connected to serial port B. The
options are Normal (default) and IR (for an infrared device).
Base I/O Address
Use this setting to select the base I/O address for serial port B. The options
are 3F8, 2F8 (default), 3E8, and 2E8.
1
Available only when the CPU supports this feature.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-14 ni.com
Page 32

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Interrupt
Use this setting to select the interrupt request (IRQ) for serial port B. The
options are IRQ3 (default) and IRQ4.
Parallel Port
Use this setting to assign parallel port control. The options are Enabled
(user defined, default), Disabled, and Auto (BIOS or OS controlled).
Base I/O Address
Use this setting to select the parallel port base I/O address. The options are
378 (default), 278, and 3BC.
Interrupt
Use this setting to select the parallel port interrupt request (IRQ). The
options are IRQ5 and IRQ7 (default).
Mode
Use this setting to specify the parallel port mode. The options are Output
only, Bi-Directional, EPP, and ECP (default).
DMA Channel
Use this setting to specify the parallel port DMA channel. The options are
DMA1 and DMA3 (default).
Floppy Disk Controller
Use this setting to assign control of the floppy disk controller. The options
are Enabled (user defined, default), Disabled, and Auto (BIOS and
OS controlled).
Base I/O Address
Use this setting to select the floppy port base I/O address. The options are
Primary (default) and Secondary.
DMI Event Logging
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
Event Log Validity
This display informs you of the event log validity. It is not a setting.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-15 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 33

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Event Log Capacity
This display informs you of the event log capacity. It is not a setting.
View DMI Event Log
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to view the event log contents.
Event Logging
Use this setting to enable or disable event logging. The options are Enable
(default) and Disable.
ECC Event Logging
Use this setting to enable or disable ECC event logging. The options are
Enable (default) and Disable.
Mark DMI Events as Read
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to mark the DMI events as read.
Clear All DMI Event Logs
Select Yes and press <Enter> to clear all DMI event logs. The options are
Yes and No (default).
Console Redirection
Access this submenu to change the following settings.
COM Port Address
Use this setting to redirect the console to Onboard COM A or Onboard
COM B. The options are Enable and Disable (default).
BAUD Rate
Use this setting to select the BAUD rate for console redirection. The
options are 300, 1200, 2400, 9600, 19.2K (default), 38.4K, 57.6K, and
115.2K.
Console Type
Use this setting to select the console type for console redirection. The
options are VT100, VT100 8bit, PC-ANSI 7bit, PC ANSI (default),
VT100+, and VT-UTF8.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-16 ni.com
Page 34

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Flow Control
Use this setting to select the fl ow control for console redirection. The
options are None, XON/XOFF, and CTS/RTS (default).
Console Connection
Use this setting to select the console connection. The options are Direct
(default) or Via Modem.
Continue CR after POST
Use this setting to choose whether to continue with console redirection
after the POST routine. The options are On and Off (default).
Hardware Monitor Logic
CPU Temperature Threshold
Use this option to set a CPU temperature threshold that activates the alarm
system when the CPU temperature reaches this threshold. The options are
70 °C, 75 °C, 80 °C (default), and 85 °C.
Highlight this option and press <Enter> to see monitor data for the
following items.
CPU Temperature
This item displays the CPU temperature.
System Temperature
This item displays the system temperature.
Fan1–Fan6 Speeds
If Auto Fan Control is enabled, the BIOS automatically displays the status
of the fans indicated in this item.
Fan Speed Control Modes
Use this feature to decide how the system controls the onboard fan speed.
The CPU temperature and fan speed are correlative. When the CPU on-die
temperature increases, the fan speed also increases, and vice versa. If the
option is set to 3-pin fan, voltage controls the fan speed. If the option is set
to 4-pin, Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls the fan speed. Select
3-pin if your chassis came with 3-pin fan headers. Select 4-pin if your
chassis came with 4-pin fan headers. Select Workstation if your system is
© National Instruments Corporation 2-17 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 35

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
used as a workstation. Select Server if your system is used as a server.
Select Disable to disable the fan speed control function and allow the
onboard fans to run constantly at full speed (12 V). Select 4-pin Quiet
(or Super Quiet) to lower the fan speed and noise. The options are Disable
(default), 3-pin (Server), 3-pin (Workstation), 4-pin (Server), and 4-pin
(Workstation),
Voltage Monitoring
The following items are monitored and displayed:
• Vcore: 1.25 V
• 1.5 V
• –12 V
•Vdimm
• +3.3 V
• +12 V
•5 Vsb
• 5 VDD
•P_VTT
• Vbat
IPMI
Access this submenu to change the following settings. (This option is
available only when an IPMI card is installed in the system.)
IPMI Specification Version
This item displays the current IPMI version.
Firmware Version
This item displays the current firmware version.
System Event Logging
Select Enabled to enable IPMI event logging. When this function is set to
Disabled, the system continues to log events received via system interface.
The options are Enabled (default) and Disabled.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-18 ni.com
Page 36

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Clear System Event Logging
Select Enabled to force the BIOS to clear the system event logs during the
next cold boot. The options are Enabled and Disabled (default).
Existing Event Log Number
This item displays the existing event log number.
Event Log Control
System Firmware Progress
Select Enabled to log POST progress. The options are Enabled and
Disabled (default).
BIOS POST Errors
Select Enabled to log POST errors. The options are Enabled and Disabled
(default).
BIOS POST Watchdog
Select Enabled to enable POST Watchdog. The options are Enabled and
Disabled (default).
OS Boot Watchdog
Select Enabled to enable OS Boot Watchdog. The options are Enabled
and Disabled (default).
Timer for Loading OS (Minutes)
Use this setting to set the time value (in minutes) for OS Boot Watchdog by
entering a desired number. The default setting is 10 (minutes). (Ignore this
option when OS Boot Watchdog is set to Disabled.)
Time Out Option
Use this setting to determine what action to take in an event of a system
boot failure. The options are No Action (default), Reset, Power Off, and
Power Cycles.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-19 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 37

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
System Event Log/System Event Log (List Mode)
These options display the System Event (SEL) Log and System Event
(SEL) Log in List Mode. The options are SEL (System Event Log) Entry
Number, SEL Record ID, SEL Record Type, Time Stamp, Generator
ID, SEL Message Revision, Sensor Type, Sensor Number, SEL Event
Type, Event Description, and SEL Event Data.
Realtime Sensor Data
This feature displays information from motherboard sensors, such as
temperatures, fan speeds, and voltages of various components.
Security
Use the arrow keys to choose Security from the Phoenix BIOS Setup
Utility main menu. To display security setting options, highlight the setting
using the arrow keys and press <Enter>. This section describes all security
BIOS settings.
Supervisor Password Is:
This item indicates if a supervisor password has been entered for the
system. Clear means such a password has not been used, and Set means
a supervisor password has been entered.
User Password Is:
This item indicates whether a user password has been entered for the
system. Clear means such a password has not been used, and Set means
a user password has been entered.
Set Supervisor Password
To set a supervisor password, highlight Set Supervisor Password and
press <Enter>. When prompted, enter the supervisor password in the
dialogue box, which allows access to the BIOS.
Set User Password
To set a user password, highlight Set User Password and press <Enter>.
When prompted, enter the user password in the dialogue box, which allows
access to the system at bootup.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-20 ni.com
Page 38

Boot
Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Fixed Disk Boot Sector
This setting may offer protection against viruses when set to Write
Protect, which protects the boot sector on the hard drive from having a
virus written to it. The options are Write Protect and Normal (default).
Password on Boot
Use this setting to decide whether a password is required during bootup.
The options are Enabled (password required, default) and Disabled
(password not required).
Use the arrow keys to choose Boot from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
main menu. For details on how to change the order and specs of boot
devices, refer to the Item Specific Help window. This section describes
all boot BIOS settings.
Boot Priority Order/Excluded from Boot Orders
The items in the boot list section are bootable devices listed in the sequence
of boot order as specified. The items included in the candidate list are
currently not bootable. Press <+> or <–> to move the device up or down.
Press <F> or <R> to specify the type of an USB device, either fixed or
removable. You can select one item from the boot list and press <X> to
remove it from the list of bootable devices (to make its resource available
for other bootable devices). Conversely, you can select an item from the
candidate list and press <X> to remove it from the candidate list and place
it in the boot list to make it bootable. For details on how to change the
priority of boot order of devices, refer to the Item Specific Help window.
Exit
Use the arrow keys to choose Exit from the Phoenix BIOS Setup Utility
main menu. This section describes all Exit BIOS settings.
Exit Saving Changes
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to save any changes you made and
exit the BIOS Setup utility.
Exit Discarding Changes
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to exit the BIOS Setup utility without
saving any changes you may have made.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-21 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 39

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Load Setup Defaults
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to load the default settings for all
items in the BIOS Setup. These are the safest settings to use.
Discard Changes
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to discard (cancel) any changes you
made. You will remain in the setup utility.
Save Changes
Highlight this item and press <Enter> to save any changes you made. You
will remain in the setup utility.
Rack Mounting
Note To rack mount the NI 8352/8353, the chassis must be at least 26 in. deep.
The rack mounting hardware includes:
• One pair of inner slides to be installed on the chassis.
• One pair of outer slides to be installed in the rack.
• Two pairs of short brackets for the front of the outer slides.
Note One pair of short brackets includes screw threads, and the other pair does not.
Use the pair that fits into your rack.
• One pair of long brackets for the rear of the outer slides.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-22 ni.com
Page 40

Installing Inner Slides
Follow these steps to install the inner slides:
1. Locate the right inner slide (the slide used on the right side of the
2. Align the four square holes on the right inner slide against the hooks
3. Securely attach the slide to the chassis with two M4 flathead screws.
Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
chassis when facing the chassis front panel).
on the right side of the chassis, as shown in Figure 2-1.
Repeat steps 1–3 to install the left inner slide to the left side of the
chassis.
1
2
3
1 Hooks on Chassis 2 Square Holes on Right Inner Slide 3 Holes for M4 Screws
Figure 2-1. Installing Inner Slides
© National Instruments Corporation 2-23 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 41

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Installing Outer Slides
Follow these steps to install the outer slides:
1. Measure the distance from the front rail of the rack to the rear rail of
2. Attach a short bracket to the rear of the right outer slide and a long
3. Adjust the short and long brackets to the proper distance so that the
4. Repeat steps 1–3 for the left outer slide.
the rack.
bracket to the front of the right outer slide, as shown in Figure 2-2.
chassis fits snugly into the rack.
2
1
1 Long Bracket 2 Short Bracket
Figure 2-2. Installing Outer Slides
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-24 ni.com
Page 42
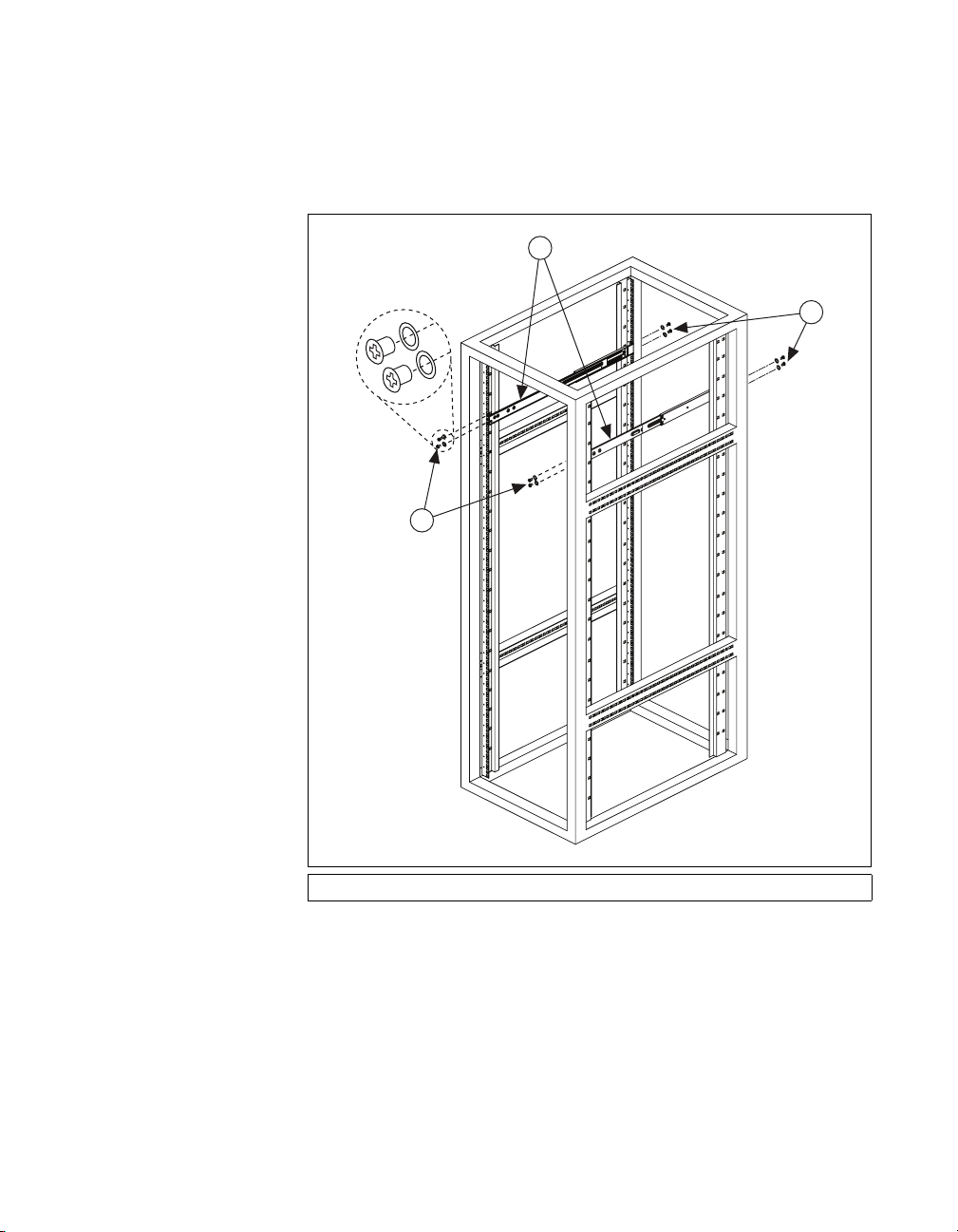
Installing the Slide Assemblies in the Rack
Use the M5 screws and washers to secure the slide assemblies to the rack,
as shown in Figure 2-3.
2
1
Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
1
1 M5 Screws and Washers 2 Slide Assemblies
Figure 2-3. Installing Slide Assemblies into Rack
© National Instruments Corporation 2-25 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 43

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Installing the Chassis into the Rack
Follow these steps to install the chassis in the rack:
1. Push the inner slides, attached to the chassis, into the grooves of the
outer slide assemblies installed in the rack, as shown in Figure 2-4.
2
1
1 Inner Slides 2 Grooves of Outer Slide Assemblies
Figure 2-4. Installing Inner Slides into Outer Slides
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-26 ni.com
Page 44

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
2. Push the chassis all the way to the back of the outer slide assemblies,
as shown in Figure 2-5. (The plastic bezel is not included in the kit.)
Figure 2-5. Installing Chassis Into Rack
© National Instruments Corporation 2-27 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 45

Chapter 2 Installation and BIOS Setup
Hard Drive Recovery
The NI 8352/8353 includes two methods of restoring the original factory
condition of your hard drive. Hard drive-based recovery stores a factory
backup on a separate part of your hard drive, allowing you to restore your
controller without additional media. The NI 8352/8353 also ships with an
OS Recovery CD that allows you to reinstall your operating system onto
your hard drive via an external CD-ROM. For more information about
these tools, refer to KnowledgeBase 2ZKC02OK at
Note Recovering the OS erases the contents of your hard disk. Back up any files you want
to keep.
Installing an OS
The NI 8352/8353 includes a preinstalled OS. In some cases, you may want
to reinstall the OS or install a different OS from the integrated CD-ROM
drive. To install from the CD-ROM drive, you must change the boot
device; refer to the Boot Priority Order/Excluded from Boot Orders section
for more information.
ni.com/support.
Cleaning
Caution Always disconnect the AC power cable before cleaning or servicing the chassis.
Exterior Cleaning
Cautions Avoid getting moisture inside the chassis during exterior cleaning, especially
through the top vents.
Do not wash the front- or rear-panel connectors or switches. Cover these components while
cleaning the chassis.
Do not use harsh chemical cleaning agents; they may damage the chassis. Avoid chemicals
that contain benzene, toluene, xylene, acetone, or similar solvents.
Clean the exterior surfaces of the chassis with a dry lint-free cloth or a
soft-bristle brush. Do not use abrasive compounds on any part of the
chassis.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 2-28 ni.com
Page 46

I/O Information
This chapter describes the NI 8352/8353 I/O connectors.
Rear Panel Connectors
Table 3-1 lists various peripherals and their corresponding NI 8352/8353
external connectors, bus interfaces, and functions.
Table 3-1. NI 8352/8353 Peripherals Overview
Peripheral External Connector Description
Keyboard PS/2 (5-pin Din) PS/2-style keyboard
Mouse PS/2 (5-pin Din) PS/2-style mouse
3
USB USB 4-pin Series A stacked
receptacle
USB USB 4-pin Series A stacked
receptacle
Serial COM1 (9-pin DSUB) 16550 RS-232 serial port
Video VGA (15-pin DSUB) Intel Extreme Graphics controller
Ethernet LAN (RJ45) 10/100/1000 Ethernet connection
Ethernet LAN (RJ45) 10/100/1000 Ethernet connection
USB 2.0 capable
USB 2.0 capable
© National Instruments Corporation 3-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 47

Chapter 3 I/O Information
Figure 3-1 shows the rear panel layout of the NI 8352/8353.
1
2
3
4
65
7
1 PS/2 Mouse Connector
2 PS/2 Keyboard Connector
PS/2
3 USB Ports
4 Serial Port
5VGA Port
6LAN 1
7LAN 2
Figure 3-1. NI 8352/8353 Rear Panel Layout
Figure 3-2 shows the location and pinouts for the PS/2 keyboard and mouse
connectors on the NI 8352/8353. Table 3-2 lists and describes the PS/2
connector signals.
P
S/2
6
4
5
3
1
2
Figure 3-2. PS/2 Connector Location and Pinout
Table 3-2. PS/2 Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 DATA Data Keyboard
2 NC Data Mouse
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 3-2 ni.com
Page 48

Universal Serial Bus
Figure 3-3 shows the location and pinouts for the Universal Serial Bus
(USB) connectors on the NI 8352/8353. Table 3-3 lists and describes the
USB connector signals.
AMP manufactures a USB mating connector, part number 787633.
Chapter 3 I/O Information
Table 3-2. PS/2 Connector Signals (Continued)
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
3 GND Ground
4 VCC VCC
5 CLK Clock Keyboard
6 NC Clock Mouse
1
4
USB
Figure 3-3. USB Connector Location and Pinout
Table 3-3. USB Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 VCC Cable Power (+5 V)
2 –Data USB Data–
3 +Data USB Data+
4 GND Ground
© National Instruments Corporation 3-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 49

Chapter 3 I/O Information
Serial
Figure 3-4 shows the location and pinouts for the serial connector on the
NI 8352/8353. Table 3-4 lists and describes the serial connector signal.
AMP manufactures a serial port mating connector, part number 745491-5.
1
6
Serial
Figure 3-4. Serial Connector Location and Pinout
Table 3-4. Serial Connector Signals
5
9
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 DCD* Data Carrier Detect
2 SIN* Receive Data
3 SOUT* Transmit Data
4 DTR* Data Terminal Ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR* Data Set Ready
7 RTS * Ready to Send
8 CTS* Clear to Send
9 RI* Ring Indicator
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 3-4 ni.com
Page 50

VGA
Chapter 3 I/O Information
Figure 3-5 shows the location and pinouts for the VGA connector on the
NI 8352/8353. Table 3-5 lists and describes the VGA connector signals.
AMP manufactures a mating connector with part numbers 748364-1
(housing) and 748333-2 (pin contact).
11
6
1
VGA
15
10
5
Figure 3-5. VGA Connector Location and Pinout
© National Instruments Corporation 3-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 51

Chapter 3 I/O Information
Table 3-5. VGA Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 R Red
2 G Green
3 B Blue
4 NC Not Connected
5 GND Ground
6 GND Ground
7 GND Ground
8 GND Ground
9 +5V 5 V
10 GND Ground
11 NC Not Connected
12 SD Serial Data
13 HSync Horizontal Sync
14 VSync Vertical Sync
15 SC Serial Clock
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 3-6 ni.com
Page 52
Ethernet
Chapter 3 I/O Information
Figure 3-6 shows the location and pinouts for the Ethernet connectors
on the NI 8352/8353. Table 3-6 lists and describes the Ethernet connector
signals.
AMP manufactures a mating connector, part number 554739-1.
8
Ethernet
Figure 3-6. Ethernet Connector Location and Pinout
1
© National Instruments Corporation 3-7 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 53

Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 D0P Differential Pair 0+
2 D0N Differential Pair 0–
3 D1P Differential Pair 1+
4 D2P Differential Pair 2+
5 D2N Differential Pair 2–
6 D1N Differential Pair 1–
7 D3P Differential Pair 3+
8 D3N Differential Pair 3–
MXI-Express Connectors
Refer to your MXI-Express hardware user manual for connector
information.
Table 3-6. Ethernet Connector Signals
Page 54

Common Configuration
Questions
This chapter answers common configuration questions you may have when
using the NI 8352/8353.
General Questions
What do the LEDs on the NI 8352/8353 front panel mean?
The power indicator lights when the main power is turned on. The LAN
status LEDs flash to when there is activity on LAN1 and LAN2. The hard
drive LED lights when there is hard drive activity on the NI 8352/8353. For
more information, refer to Figure 1-1, Front View of the NI 8352/8353.
How do I check the configuration of the memory, hard drive,
time/date, and so on?
You can view these parameters in the BIOS setup. To enter the BIOS setup,
reboot the NI 8352/8353 and press <Delete> during the memory tests.
Refer to the BIOS Setup section of Chapter 2, Installation and BIOS Setup,
for more information.
4
Can I use the internal SATA drive and an external hard drive at the
same time?
Ye s.
Boot Options
What devices can I boot from?
The NI 8352/8353 can boot from the following devices:
• The internal SATA hard drive
• The internal CD-ROM drive
• A network PXE server on the same subnet
© National Instruments Corporation 4-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 55

Chapter 4 Common Configuration Questions
• An external USB mass storage device such as a USB hard drive or
CD-ROM
Note You should enable Legacy USB support to boot from USB devices. Refer to the
BIOS Setup section of Chapter 2, Installation and BIOS Setup, for more information.
• An external USB floppy drive
Note There are some limitations when booting from a USB device. Windows XP
can be installed from a USB CD-ROM, but earlier versions of Windows cannot. The
NI 8352/8353 BIOS configures the USB devices so that they will work in a DOS
environment.
How do I configure the controller to boot from these devices?
Press <Delete>, enter the BIOS, and select Boot. You can set the boot order
using <+> and <–>. Set the order by device type and set the order for the
devices listed within the device type. Refer to BIOS Setup in Chapter 2,
Installation and BIOS Setup, for more information.
Chassis Configuration
How do I set up the NI 8352/8353 to work with my PXI chassis?
Configuration of the PXI system is handled through Measurement &
Automation Explorer (MAX), included with the software pre-installed
on your NI 8352/8353. MAX creates the
the layout and parameters of your PXI system.
The configuration steps for single or multiple-chassis systems are the same.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 4-2 ni.com
pxisys.ini file, which defines
Page 56

Chapter 4 Common Configuration Questions
Figure 4-1. Multichassis Configuration in MAX
Basic PXI System Configuration
1. Launch MAX.
2. In the Configuration tree, click the Devices and Interfaces branch to
expand it.
3. If the PXI system controller has not yet been configured, it is labeled
PXI System (Unidentified). Right-click this entry to display the
pop-up menu, then select the appropriate controller model from the
Identify As submenu.
4. Click the PXI System controller. The chassis (or multiple chassis in a
multichassis configuration) is listed below it. Identify each chassis by
right-clicking its entry, then selecting the appropriate chassis model
through the Identify As submenu. Further expanding the PXI System
branch shows all devices in the system that can be recognized by
NI-VISA. When your controller and all your chassis are identified,
the required
© National Instruments Corporation 4-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
pxisys.ini file is complete.
Page 57

Chapter 4 Common Configuration Questions
The PXI specification allows many combinations of PXI chassis and
system modules. To assist system integrators, the manufacturers of
PXI chassis and system modules must document the capabilities of their
products. The minimum documentation requirements are contained in
.ini files, which consist of ASCII text. System integrators, configuration
utilities, and device drivers can use these
The capability documentation for the chassis is contained in a
chassis.ini file provided by the chassis manufacturer. The information
in this file is combined with information about the system controller to
create a single system initialization file called
Initialization). The NI 8352/8353 uses MAX to generate the
file from the
.ini files.
pxisys.ini (PXI System
pxisys.ini
chassis.ini file.
Device drivers and other utility software read the
obtain system information. For detailed information about initialization
files, refer to the PXI specification at
Upgrade Information
How do I upgrade system memory?
Refer to Upgrading Memory in Appendix B, Hardware Configuration.
How do I flash a new BIOS?
You can download the new BIOS from
For more information, refer to KnowledgeBase 3H3COSD8 at
Where do I get the latest software drivers?
The latest National Instruments software is available from
downloads/
at
ni.com.
My NI 8352/8353 does not have an internal floppy drive. Is there a way
to use an external drive?
Yes. The NI 8352/8353 controller supports and can boot from USB floppy
drives. A USB floppy drive will not work with Windows NT4, but will
work with Windows 2000 or Windows XP. Refer to the Boot Options
section for more information.
pxisys.ini file to
www.pxisa.org.
ftp.ni.com/support/pxi/.
ni.com.
ni.com/
. For peripheral drivers, refer to KnowledgeBase 3H3COSD8
A USB floppy drive is available from National Instruments, part number
778492-02.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 4-4 ni.com
Page 58

Troubleshooting
This chapter answers common troubleshooting questions you may have
when using the NI 8352/8353.
What if the NI 8352/8353 does not boot?
Several problems can cause a controller not to boot. Here are some things
to look for and possible solutions.
Things to Notice:
• Which LEDs come on? The power indicator LED should stay lit. The
hard disk drive LEDs should blink during boot as the disk is accessed.
• What appears on the display? Does it hang at some particular point
(BIOS, Operating System, and so on)? If nothing appears on the
screen, try a different monitor. Does your monitor work with a
different PC? If it hangs, note the last screen output that you saw for
reference when consulting National Instruments technical support.
• What has changed about the system? Did you recently move the
system? Was there electrical storm activity? Did you recently add
a new module, memory chip, or piece of software?
• Has the system overheated? If the Overheat/FanFail LED is lit, this
indicates overheating. Unplug the AC power cord from the server and
allow it to cool down before powering it on again.
5
Things to Try:
• Make sure the NI 8352/8353 is plugged in to a working power source.
• Remove any nonessential cables or devices.
• Make sure the CPU and memory modules are properly seated in their
slots.
• Clear the CMOS. (Refer to the Clear CMOS Jumper: JBT1 section of
Appendix B, Hardware Configuration.)
• Recover the hard drive on the NI 8352/8353. (Refer to the Hard Drive
Recovery section of Chapter 2, Installation and BIOS Setup.)
© National Instruments Corporation 5-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 59

Chapter 5 Troubleshooting
My NI 8352/8353 boots fine until I get to Windows, at which point I
cannot read the screen. This may include garbled output, white screen,
black screen, or an out of synch message from the monitor.
This problem usually results from having the video card output set past the
limits of the monitor. You will need to boot Windows in Safe Mode. To do
this, reboot the NI 8352/8353. As Windows begins to boot, hold down
<F8>. You should now be able to reset the video driver to lower settings.
Try setting the resolution to 640 × 480 and the refresh rate to 60 Hz. Once
you reboot, you can raise these values again, using the test option in
Windows. These settings are accessible through the Advanced tab of the
Display item in the Control Panel. Alternately, you can try a different
monitor, preferably a newer and larger one.
My system boots fine as long as a particular module is not in my
chassis.
The most common cause of this is a damaged module. Try the module in a
different chassis or with a different controller. Also, remove any external
cables or terminal blocks connected to the system. If the module does not
work in these cases, it is likely damaged. Contact the module manufacturer
for further troubleshooting.
Refer to the KnowledgeBase or product manuals section at
ni.com for
more information specific to the chassis and module with which you are
having difficulties.
How do I set Windows to prompt me before shutting down when I press
the power button?
Select Start»Control Panel»Power Options to open the Power Options
Properties window. Select the Advanced tab. In the Power buttons
section, select Ask me what to do from the pull-down menu. When this is
selected, Windows prompts you to cancel, shut down, or restart when you
press the power button.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual 5-2 ni.com
Page 60

Specifications
This appendix lists the NI 8352/8353 electrical, mechanical, and
environmental specifications.
Electrical
AC Input
Input voltage range................................. 100 –240 VAC
A
Mainboard
Operating voltage range
Input frequency ......................................50/60 Hz
Operating frequency range
Input current rating................................. 5 A max
Power disconnect ................................... The AC power cable provides
Socket..................................................... LGA 775
Chipset ................................................... Intel 3000 chipset, supports
Memory Slots......................................... Four 240-pin DIMM slots,
1
........................ 90 –264 VAC
1
................... 47–63 Hz
main power disconnect.
Depressing the front panel power
switch enables or inhibits the
internal power supply.
533/800/1066 MHz FSB, 8 GB
dual-channel DDR-II memory
two per channel
1
Operating range is guaranteed by design.
© National Instruments Corporation A-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 61

Appendix A Specifications
PCI/PCI Express .....................................One PCI Express x8 slot or
one PCI 32-bit slot
(both risers included)
SATA......................................................Four SATA ports compliant with
the Serial-ATA 2.0 specification.
Maximum data rate of 300 MB/s.
IDE..........................................................One primary IDE connector and
one CompactFlash card IDE
connector. (If the CompactFlash
card connector is populated, the
primary connector is available for
one device only; otherwise, the
primary connector can connect
multiple devices.)
USB ports ...............................................Four USB 2.0 ports
Keyboard ................................................PS/2 keyboard port
Mouse .....................................................PS/2 mouse port
Video ......................................................VGA port, onboard ATI ES 1000
with 16 MB SDRAM
Serial.......................................................One RS-232 serial port
LAN ........................................................Two RJ45 LAN jacks
Onboard LAN controller ........................Intel 82573V/L Gigabit Ethernet
controller
CPU
CPU ........................................................Intel Core2 Duo/Core 2 Quad
Clock speed.............................................2.40 GHz
Front side bus speed ...............................1066 MHz
L2 cache..................................................4/8 MB
Package...................................................LGA 775
NI 8352/8353 User Manual A-2 ni.com
Page 62

Hard Disk Drive
Memory
Appendix A Specifications
Capacity .................................................250 GB in one, two, or four-drive
configurations for maximum
capacity of 1 TB
Interface ................................................. Serial-ATA
Standard memory ................................... 2 × 512 MB (32 M × 64 bit),
DDR-II SDRAM, ECC 667 MHz,
unbuffered, 240-pin DIMMs
2 GB memory upgrade........................... Standard memory plus 2 × 1 GB
(128 M × 64 bit), DDR-II
SDRAM, ECC 533 MHz,
unbuffered, 240-pin DIMMs
4 GB memory upgrade........................... 4 × 1 GB (128 M × 64 bit),
DDR-II SDRAM, ECC 667 MHz,
unbuffered, 240-pin DIMMs,
Mechanical
Overall dimensions (standard chassis)
Height.............................................. 43 mm (1.70 in.)
Width .............................................. 437 mm (17.2 in.)
Depth............................................... 503 mm (19.8 in.)
Weight.................................................... 8.6 kg (19.0 lbs)
Environmental
Operating temperature for NI 8352........ 5 to 40 °C
Operating temperature for NI 8353........ 5 to 35 °C
Storage temperature ............................... –10 to 60 °C
Relative humidity
Operating ........................................ 10 to 90% noncondensing
Nonoperational (storage) ................ 5 to 95% nonconducting
Operating location..................................Indoor use
© National Instruments Corporation A-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 63

Appendix A Specifications
Altitude ...................................................2,000 m
Installation Category...............................II
Pollution Degree .....................................2
Safety
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of safety for electrical equipment for measurement, control,
and laboratory use:
• IEC 60950-1, EN-60950-1
• UL 60950-1, CSA 60950-1
Note For UL, Demko, and other safety certifications, refer to the product label or
visit
ni.com/certification, search by model number or product line, and click the
appropriate link in the Certification column.
Electromagnetic Compatibility
This product is designed to meet the requirements of the following
standards of EMC for electrical equipment for measurement, control,
and laboratory use:
• EN 55024, CISPR 24 EMC requirements
• EN 55022, CISPR 22 Emissions; Class A
• CE, C-Tick, ICES, and FCC Part 15 Emissions; Class A
Note For EMC compliance, operate this device with shielded cabling.
CE Compliance
This product meets the essential requirements of applicable European
Directives, as amended for CE marking, as follows:
• 2006/95/EC; Low-Voltage Directive (safety)
• 2004/108/EC; Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive (EMC)
Note Refer to the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) for this product for any additional
regulatory compliance information. To obtain the DoC for this product, visit
certification
in the Certification column.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual A-4 ni.com
, search by model number or product line, and click the appropriate link
ni.com/
Page 64

Environmental Management
⬉ᄤֵᙃѻક∵ᶧࠊㅵ⧚ࡲ⊩ ˄Ё
˅
Ёᅶ᠋
National Instruments is committed to designing and manufacturing
products in an environmentally responsible manner. NI recognizes that
eliminating certain hazardous substances from our products is beneficial
not only to the environment but also to NI customers.
For additional environmental information, refer to the NI and the
Environment Web page at
environmental regulations and directives with which NI complies, as well
as other environmental information not included in this document.
Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
EU Customers At the end of their life cycle, all products must be sent to a WEEE recycling
center. For more information about WEEE recycling centers and National Instruments
WEEE initiatives, visit
National Instruments
݇Ѣ
National Instruments
(For information about China RoHS compliance, go to
ni.com/environment/weee.htm.
Ё
Appendix A Specifications
ni.com/environment. This page contains the
RoHS
ヺড়Ё⬉ᄤֵᙃѻકЁ䰤ࠊՓ⫼ᶤѯ᳝ᆇ⠽䋼ᣛҸ
ড়㾘ᗻֵᙃˈ䇋ⱏᔩ
RoHS
ni.com/environment/rohs_china
ni.com/environment/rohs_china
(RoHS)
DŽ
DŽ
.)
© National Instruments Corporation A-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 65

Hardware Configuration
This appendix describes how to configure and upgrade the NI 8352/8353
hardware.
Caution Hazardous Voltage Area
No user (operator) serviceable parts are inside the NI 8352/8353.
The hardware configuration and upgrade procedures described in this appendix must be
performed only by a qualified service technician.
Disconnect the power cord before servicing.
Figure B-1 shows the key features of the NI 8352/8353 mainboard.
B
© National Instruments Corporation B-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 66

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
1
454647
44
2
3
4
5 6 7
31 28
32
3334353637383940414243
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
2930
1 Intel 3000 North Bridge
2 24-Pin ATX PWR/
JPW1
3 Fan6/CPU Fan
4 PXH-V
5 Pentium Core2 Duo
CPU LGA 775
6Fan1
78-Pin PWR/JPW2
8JPR1
9PW3
10 DIMM 1A/DIMM 1
11 DIMM 1B/DIMM 2
12 DIMM 2A/DIMM 3
13 DIMM 2B/DIMM 4
14 JLED
15 FP CTRL/JF1
16 PCI-X 133 MHz/Slot6
17 Fan2
18 Fan3
19 JWD
20 JPF
21 WOL
22 BIOS
23 SATA3
24 SATA2
25 SATA1
26 SATA0/JS1
27 Fan4
28 IDE1/J3
29 JP3
30 Buzzer
31 JWF1
32 JL1
33 JWOR
34 LE1
35 Battery
36 USB5/6 J46
37 JBT1
38 USB3/4 J45
39 J4 IDE (Compact Flash
Card Only)
40 ICH7R South Bridge
41 J9
42 J27/Floppy
43 COM2
44 PCI 32-Bit 33 MHz/Slot1
45 J30/Printer
46 JPG1
47 S I/O
48 LE 4
49 LE 3
50 VGA CTRL
51 LAN CTRL
52 JPL2
53 JPL1
54 IPMI
2
55 JI
C2
2
C1
56 JI
57 LAN CTRL
58 Fan5
59 GLAN2
60 GLAN1
61 SXB-E1 PCI-Ex8/J42
62 VGA/J6
63 COM1/J31
64 USB 1/2/J15
65 PS/2 KB/Mouse/J28
Figure B-1. NI 8352/8353 Mainboard Layout
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-2 ni.com
Page 67

Jumper Settings
Figure B-2 shows the jumper locations on the NI 8352/8353.
1
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
9
8
1JI2C1
2
C2
2JI
3JPL1
2
3
4
5 6 7
4JPL2
5JPG1
6JBT1
7JP3
8JPF
9JWD
Figure B-2. NI 8352/8353 Jumper Locations
© National Instruments Corporation B-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 68

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
r
Enable/Disable SMBus to PCI/PCI Express Slots Jumper: JI2C1/JI2C2
Use jumpers JI2C1/JI2C2 to connect PCI/PCI Express slots to the system
management bus. The default setting is open to disable the connection.
Enable SMBus to
PCI/PCI Express Slots
PCI/PCI Express Slots
Figure B-3. Enable/Disable SMBus to PCI/PCI Express Slots Jumper: JI2C1/JI2C2
Enable/Disable GLAN1/GLAN2 Jumper: JPL1/JPL2
Use JPL1 to enable or disable the GLAN1 port and JPL2 to enable or
disable the GLAN2 port on the motherboard. The default setting is enabled.
3
2
1
Enable GLAN1/
GLAN2 (Default)
Figure B-4. Enable/Disable GLAN1/GLAN2 Jumper: JPL1/JPL2
Disable GLAN1/
Enable/Disable VGA Connector Jumper: JPG1
Use JPG1 to enable or disable the VGA connector on the motherboard. The
default setting is enabled.
Disable SMBus to
(Default)
2
3
1
GLAN2
2
3
3
2
1
Enable VGA Connector
(Default)
Disable VGA Connecto
1
Figure B-5. Enable/Disable VGA Connector Jumper: JPG1
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-4 ni.com
Page 69

Clear CMOS Jumper: JBT1
Caution Always remove the AC power cord from the system before clearing CMOS.
Caution For an ATX power supply, you must completely shut down the system, remove
the AC power cord, and then short JBT1 to clear CMOS. Do not use the PW_ON connector
to clear CMOS.
Use JBT1 to clear CMOS. Instead of pins, this “jumper” consists of contact
pads to prevent accidental CMOS clearing. To clear CMOS, use a metal
object such as a small screwdriver to touch both pads at the same time to
short the connection.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Figure B-6. Clear CMOS Jumper: JBT1
CompactFlash Master/Slave Select Jumper: JP3
Use JP3 to select CompactFlash master (primary) or slave (secondary)
mode. Close this jumper to enable a CompactFlash card (master/primary
mode). For the CompactFlash card to work properly, you must connect the
CompactFlash card power cable to JWF1 and close this jumper to enable it.
The default setting is disabled.
Master (Primary)/
Enable CompactFlash Card
Figure B-7. CompactFlash Master/Slave Select Jumper: JP3
Disable CompactFlash Card
Slave (Secondary)/
(Default)
© National Instruments Corporation B-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 70

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Enable/Disable Power Force On Jumper: JPF
Use JPF to enable or disable the Power Force On function. If enabled, the
power always stays on automatically. If disabled, you must press the power
button to power on the system. The default setting is disabled.
Enable Power Force On Disable Power Force On
Figure B-8. Enable/Disable Power Force On Jumper: JPF
Enable/Disable Watchdog Jumper: JWD
JWD controls the watchdog, a system monitor that takes action when a
software application hangs. Closing pins 1–2 allows the watchdog to reset
the system if a program hangs. Closing pins 2–3 generates a nonmaskable
interrupt for the program that hangs.
Note This function requires software support.
Note The watchdog must also be enabled in the BIOS.
3
2
1
Enable Watchdog Reset Enable Watchdog
Figure B-9. Enable/Disable Power Force On Jumper: JPF
(Default)
2
3
1
Nonmaskable Interrupt
2
3
1
Disable Watchdog
(Default)
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-6 ni.com
Page 71

Other Connectors
Figure B-10 shows the locations of other connectors on the NI 8352/8353.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
12
11
1
2
3
4
5
6
8
1 Fan6
2 Fan1
3FP CTRL JF1
4Fan2
5Fan3
6Fan4
910
7JL1
8 USB5/6 J46
9 USB3/4 J45
7
10 COM2
11 SXB-E1 PCI-Ex8 J42
12 Fan5
Figure B-10. NI 8352/8353 Other Connector Locations
© National Instruments Corporation B-7 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 72

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Chassis Intrusion Switch Connector: JL1
JL1 is the chassis intrusion header. Attach the appropriate cable to be
informed of a chassis intrusion.
Figure B-11. Chassis Intrusion Switch Connector (JL1)
Table B-1. Chassis Intrusion Switch Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name
1 CINTRU
2 GND
Front Panel Connector: JF1
JF1 contains header pins for various buttons and indicators on the control
panel at the front of the chassis. These connectors are designed specifically
for use with this chassis.
1
2
19
20
1
2
Figure B-12. Front Panel Connector (JF1)
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-8 ni.com
Page 73

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Table B-2. Front Panel Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 PWR Power button signal
2 GND Power button +3 V standby
3 Reset Reset button reset
4 GND Reset button ground
5 — —
6 — —
7 Vcc Overheat/fan fail LED Vcc
8 GND Overheat/fan fail LED ground
9 Vcc NIC2 LED Vcc
10 GND NIC2 LED ground
11 Vcc NIC1 LED Vcc
12 GND NIC1 LED ground
13 Vcc HDD LED +5 V
14 GND HD active
15 Vcc Power LED +5 V
16 GND Power LED ground
17 — —
18 — —
19 NMI Nonmaskable interrupt button
control
20 GND Nonmaskable interrupt button
ground
© National Instruments Corporation B-9 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 74

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Front USB Connectors: USB 3/4 and USB 5/6
Two Universal Serial Bus ports (USB 1/2) are on the I/O back panel. In
addition, four USB ports (USB 3/4 and USB 5/6) are at J45 and J46 on the
motherboard. You can use these ports to provide front chassis USB access
(cables not included).
Figure B-13. Front USB Connectors (USB 3/4 and USB 5/6)
Table B-3. Front USB Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name Pin Signal Name
1 VCC 6 USB1+
2 VCC 7 GND
3 USB0– 8 GND
4 USB1– 9 Key
5 USB0+ 10 NC
Power Saving Switch Connector: JGS1
Attach a power saving switch to this connector. Press the switch once to
have the system enter the Sleep/Suspend state. Press any key to wake up the
system.
10
9
1
2
Figure B-14. Power Saving Switch Connector (JGS1)
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-10 ni.com
Page 75

Fan Power Connectors: Fan1 to Fan6
The NI 8352/8353 has six fan connectors (Fan1 to Fan6). Fan6 is
designated as the CPU fan.
Note All fans are 4-pin fans. However, pins 1–3 of the fan headers are backward
compatible with traditional 3-pin fans.
The onboard fan speeds are controlled by the Fan Speed Mode (Thermal
Management) in the BIOS Hardware Monitoring section. When using
Thermal Management settings, use all 3-pin fans or all 4-pin fans on the
motherboard. Do not use 3-pin fans and 4-pin fans on the same board. The
default setting is disabled, which allows the onboard fans to run at full
speed.
4
2
3
1
FAN1/2/3/6
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
1
2
3
4
FAN4/5
Figure B-15. Fan Power Connectors (Fan1 to Fan6)
Table B-4. Fan Power Connector Signals
Pin Signal Name
1 GND
2 +12 V
3 Tachometer
4 PWM_Control
© National Instruments Corporation B-11 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 76

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Serial Port Header: COM2
The motherboard includes two serial headers, COM1 (J31) and COM2.
COM1 is a port located next to VGA port.
2
PCI Express Slot
1
Figure B-16. Serial Port Header (COM2)
Table B-5. Serial Port Header Connector Signals
9
Pin Signal Name Signal Description
1 CD Data carry detect
2 RD Serial in or receive data
3 TD Serial out of transmit data
4 DTR Data terminal ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data set ready
7 RTS Request to send
8 CTS Clear to send
9 RI Ring indicate
The mainboard provides one PCI Express x8 slot. This PCIE_1 slot accepts
x8 cards and runs at x8 speeds, with an extra PCIE_3 slot for riser cards.
The slot is PCI Express Specification v1.0a compliant. (You cannot
directly plug in a PCI Express board. The riser card is required to provide
power to the board.)
Figure B-17. PCI Express Slot
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-12 ni.com
Page 77

Upgrading Memory
The mainboard includes four 240-pin ECC DDR-II SDRAM slots with
maximum memory size of 8 GB. Install at least one memory module in
the slots.
Figure B-18 shows the DIMM location on the main board. DIMM1 is on
the top; DIMM4 is on the bottom.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
© National Instruments Corporation B-13 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 78

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
1
2
3
4
Figure B-18. DIMM Location
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-14 ni.com
Page 79

Dual-Channel Memory Configuration
For optimum memory performance, you can use dual-channel memory
configurations. In these configurations, identical memory is installed
in channels A and B. Figures B-19, B-20, and B-21 show allowed
configurations for dual-channel memory mode.
Note Due to chipset limitations, only the following operating systems support 8 GB
memory:
• 32-bit: Windows 2000 Advanced Server, Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition
• 64-bit: Windows Server 2003 Standard x64 Edition, Windows XP Professional x64
Edition, Windows Server 2003 Enterprise x64 Edition
You can install a maximum of 2 GB DIMMs on each slot. However, only
DDR2 667 MHz 2 GB density modules are available for this configuration.
Some older versions of DDR2-667 may not match the Intel on-die
temperature requirement and are automatically downgraded to run at
533 MHz. If this occurs, contact your memory vendor to check the
ODT value.
Due to memory allocation to system devices, memory available for
operational use is reduced when you use 4 GB of RAM. Refer to
Table B-6 for details.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Table B-6. Possible System Memory Allocation and Availability
Physical Memory Available
System Device Size
Firmware hub flash memory
1 MB 3.99
(4 GB Total System Memory)
(system BIOS)
Local APIC 4 KB 3.99
Area reserved for the chipset 2 MB 3.99
I/O APIC (4 KB) 4 KB 3.99
PCI enumeration area 1 256 MB 3.76
PCI Express (256 MB) 256 MB 3.51
PCI enumeration area 2 (if needed)
512 MB 3.01
(aligned on 256 MB boundary)
© National Instruments Corporation B-15 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 80

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Table B-6. Possible System Memory Allocation and Availability (Continued)
Physical Memory Available
System Device Size
(4 GB Total System Memory)
VGA memory 16 MB 2.85
TSEG 1 MB 2.84
Memory available to OS and other
— 2.84
applications
Table B-7 shows all possible memory module combinations.
Table B-7. Memory Module Combinations
DIMM1
(Channel A)
DIMM2
(Channel B)
DIMM3
(Channel A)
DIMM4
(Channel B)
Total Memory
256 MB–2 GB 256 MB–2 GB — — 512 MB–4 GB
— — 256 MB–2 GB 256 MB–2 GB 512 MB– 4 GB
512 MB–1 GB 512 MB–1 GB — — 1–2 GB
512 MB–1 GB 512 MB–1 GB 512 MB–1 GB 512 MB–1 GB 2–4 GB
Installing memory with different speeds is allowed, but the faster memory
downshifts to the speed of the slower memory.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-16 ni.com
Page 81

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Figure B-19 shows two identical DIMMs in DIMM 1 and DIMM 2. You
can also install identical DIMMs in DIMM 3 and DIMM 4.
1
2
3
4
1 Two Identical DIMMs
Figure B-19. Two Identical DIMMs in DIMM 1 and DIMM 2
1
© National Instruments Corporation B-17 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 82

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Figure B-20 shows two different pairs of identical DIMMS—two identical
DIMMs in DIMM 1 an DIMM 2 and two identical DIMMs in DIMM 3 and
DIMM 4.
1
2
3
4
1 First Pair of Identical DIMMs 2 Second Pair of Identical DIMMs
Figure B-20. Two Different Pairs of Identical DIMMs
Figure B-21 shows four identical DIMMs installed in DIMM 1 through
DIMM 4.
1
2
3
4
1
2
1
1 Four Identical DIMMs
Figure B-21. Four Identical DIMMs
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-18 ni.com
Page 83

Installing DDR Modules
Follow these steps to install DDR modules:
1. Press the cover release buttons on the top of the NI 8352/8353.
2. Push the cover backward to remove it.
3. Align the notch in the center of the DDR DIMM module with the key
on the DIMM slot. Insert the module vertically into the slot and push
it in until the pins are fully inserted, as shown below.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
1 2
1Notch 2Key
4. When the module is fully inserted, the plastic clip at each side of the
slot automatically closes, as shown below.
5. Replace the NI 8352/8353 cover by sliding the cover forward. Make
sure the safety lock fits firmly.
© National Instruments Corporation B-19 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 84

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Removing DDR Modules
Follow these steps to remove DDR modules:
1. Open the plastic clips on both sides of the module.
2. Remove the module from the slot.
Upgrading and Replacing Hard Disk Drives
Figure B-22 shows the NI 8352/8353 IDE and SATA connector locations.
1
2
3
4
5
1 SATA3 2 SATA2 3 SATA1 4SATA0 5IDE1
Figure B-22. NI 8352/8353 IDE and SATA Connectors
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-20 ni.com
Page 85

DVD-ROM Connector: IDE1
The mainboard has a 32-bit Enhanced PCI IDE and Ultra DMA 66/100
controller that provides PIO mode 0~4, Bus Master, and Ultra DMA 66/100
functions. You can connect a DVD-ROM or other IDE devices.
Figure B-23 shows the IDE1 connector.
SATA Connectors: SATA0–SATA3
The ICH7R south bridge supports four Serial ATA connectors
(SATA0–SATA3).
SATA connectors are high-speed Serial ATA interface ports. Each supports
Serial ATA data rates of 300 MB/s. All connectors are fully compliant with
Serial ATA 2.0 specifications. Each Serial ATA connector can connect to
one hard disk.
Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Figure B-23. IDE1 Connector
Figure B-24 shows the SATA0–SATA3 connector.
1
7
Figure B-24. SATA0–SATA3 Connector
© National Instruments Corporation B-21 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 86

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
Hard Disk Installation
Caution Before removing or installing a hard disk drive, be sure the NI 8352/8353 is
powered off and not connected to AC power.
Follow these steps to install a hard disk drive:
1. Press the release tab to release the SCA drive tray from its locking
2. Pull the SCA drive tray out from the chassis, as shown in Figure B-25.
position.
Figure B-25. Removing SCA Drive Tray
3. Remove the two screws that attach to the sides of the dummy tray.
Remove the tray, as shown in Figure B-26.
Figure B-26. Removing Dummy Tray
NI 8352/8353 User Manual B-22 ni.com
Page 87

Appendix B Hardware Configuration
4. Slide a hard disk drive into the SCA drive tray. Secure the drive
to the tray with three screws on each side of the tray, as shown in
Figure B-27.
Figure B-27. Sliding Hard Disk Drive into SCA Drive Tray
5. Once the hard disk drive is securely installed in the SCA tray, you can
reinstall the SCA drive tray in the chassis.
Installing a PCI Express Expansion Card
Follow these steps to install a PCI Express expansion card:
1. Locate the riser card bracket on the NI 8352/8353 chassis.
2. Lift the bracket from the chassis.
3. Unscrew the cover plates on the bracket and set them aside for
later use.
4. Insert the PCI Express expansion card into the PCI Express slot on the
riser card bracket.
5. Screw the expansion card firmly to the riser card bracket.
6. Align the riser card bracket with the PCI Express slot on the chassis.
Carefully push down the bracket with even force on both sides until it
is firmly seated in the slot.
© National Instruments Corporation B-23 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 88

Intel SATA RAID Utility for Intel
ICH7R
This appendix describes the Intel SATA RAID utility for Intel ICH7R.
Intel RAID Configuration Utility
The Intel RAID Configuration utility is an embedded BIOS utility for
creating, managing, and deleting arrays from the controller BIOS and
initializing drives.
To run the Intel RAID Configuration utility, press <Ctrl-I> when the
following message appears during system startup:
Press <CTRL-I> to enter Configuration Utility...
The main menu appears. To select an option from this or any menu, browse
with the arrow keys to highlight an option and press <Enter>. In some
cases, selecting an option displays another menu. To return to the previous
menu at any time, press <Esc>.
C
Creating a RAID0 Volume
Follow these steps to create a RAID0 volume:
1. Select Create RAID Volume from the main menu and press <Enter>.
The Create Volume Menu screen appears.
2. Specify a name for the RAID 0 set and press <Tab> or <Enter> to go
to the next field.
3. When RAID Level is highlighted, press the up and down arrow keys
to select RAID0(Stripe) and press <Enter>.
4. When Disks is highlighted, press <Enter> to select the HDD to
configure as RAID. The Select Disks screen appears.
5. Use the up and down arrow keys to highlight a drive and press the
space bar to select it. A triangle appears, confirming the drive
selection.
© National Instruments Corporation C-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 89

Appendix C Intel SATA RAID Utility for Intel ICH7R
6. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the RAID0 array stripe size
(4–128 KB). Press <Enter>.
Note For a server, use a lower stripe size. For a multimedia system, use a higher stripe
size. The default size is 128 KB.
7. Press <Enter> when Create Volume is highlighted. A warning
message displays.
8. When asked
(Y/N)
, press <Y> to create the RAID volume or <N> to return to the
Create Volume menu.
Creating a RAID1 Volume
Follow these steps to create a RAID1 volume:
1. Select Create RAID Volume from the main menu and press <Enter>.
The Create Volume Menu screen appears.
2. Specify a name for the RAID1 set and press <Tab> or <Enter> to go to
the next field.
3. When RAID Level is highlighted, press the up and down arrow keys
to select RAID1(Mirror) and press <Enter>.
4. When Capacity is highlighted, enter your RAID volume capacity and
press <Enter>. The default setting is the maximum capacity allowed.
5. Press <Enter> when Create Volume is highlighted. A warning
message displays.
6. When asked
(Y/N)
, press <Y> to create the RAID volume or <N> to return to the
Create Volume menu.
Are you sure you want to create this volume
Are you sure you want to create this volume
Creating a RAID10 (RAID1+ RAID0)
Follow these steps to create a RAID10 volume:
1. Select Create RAID Volume from the main menu and press <Enter>.
The Create Volume Menu screen appears:
2. Specify a name for the RAID10 set and press <Enter>.
3. When RAID Level is highlighted, use the up and down arrow keys to
select RAID10(RAID0+1) and press <Enter>.
4. When Stripe Size is highlighted, use the up and down arrow keys to
select the RAID10 stripe size (4–128 KB). Press <Enter>.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual C-2 ni.com
Page 90

Note For a server, use a lower stripe size. For a multimedia system, use a higher stripe
size. The default setting is 64 KB.
5. When Capacity is highlighted, enter your RAID volume capacity and
press <Enter>. The default setting is the maximum capacity allowed.
6. Press <Enter> when Create Volume is highlighted. A warning
message displays.
7. When asked
(Y/N)
, press <Y> to create the RAID volume or <N> to return to the
Create Volume menu.
Creating a RAID5 Set (Parity)
Follow these steps to create a RAID5 set:
1. Select Create RAID Volume from the main menu and press <Enter>.
The Create Volume Menu Screen appears.
2. Specify a name for the RAID5 set and press <Enter>.
3. When Raid Level is highlighted, use the up and down arrow keys to
select RAID5(Parity) and press <Enter>.
4. When Disk is highlighted, press <Enter> to select the HDD to
configure as RAID. The Select Disk screen appears.
5. Use the up and down arrow keys to highlight a drive and press the
space bar to select it. A triangle appears, confirming the drive
selection.
6. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the RAID5 array stripe size
(4–128 KB). Press <Enter>.
Appendix C Intel SATA RAID Utility for Intel ICH7R
Are you sure you want to create this volume
Note For a server, use a lower stripe size. For a multimedia system, use a higher stripe
size. The default size is 128 KB.
7. Enter your desired RAID volume capacity and press <Enter> when the
capacity item is highlighted. The default setting is the maximum
capacity allowed.
8. Press <Enter> when Create Volume is highlighted. A warning
message displays.
9. When asked
(Y/N)
Are you sure you want to create this volume
, press <Y> to create the RAID volume or <N> to return to the
Create Volume menu.
© National Instruments Corporation C-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 91

Appendix C Intel SATA RAID Utility for Intel ICH7R
Deleting a RAID Volume
Caution Be sure to back up your data before deleting a RAID set. You will lose all data on
the disk drives when deleting a RAID set.
Follow these steps to delete a RAID volume:
1. From the main menu, select Delete RAID Volume and press <Enter>.
2. Use the up and down arrow keys to select the RAID set to delete and
press <Delete>. A warning message displays.
3. When asked
(Y/N)
Delete Volume menu.
Are you sure you want to delete this volume
, press <Y> to delete the RAID volume or <N> to return to the
Resetting to Non-RAID and Resetting a RAID HDD
Caution Be careful when you reset a RAID volume HDD to non-RAID or reset a RAID
HDD. Resetting reformats the HDD and deletes all internal RAID structure on the drive.
Follow these steps to reset to non-RAID or reset a RAID HDD:
1. From the main menu, select Reset Disks to Non-RAID and press
<Enter>. The Reset RAID Data screen appears.
2. Use the up and down arrow keys to highlight the RAID set drive to
reset and press the space bar to select the drive.
3. Press <Enter> to reset the RAID set drive. A warning message appears.
4. Press <Y> to reset the drive or <N> to return to the main menu.
Exiting the Intel Matrix Storage Manager Utility
Follow these steps to exit the Intel Matrix Storage Manager utility:
1. From the main menu, select Exit and press <Enter>. A warning
message appears.
2. Press <Y> to reset the drive or <N> to return to the main menu.
NI 8352/8353 User Manual C-4 ni.com
Page 92

Technical Support and
Professional Services
Visit the following sections of the National Instruments Web site at
ni.com for technical support and professional services:
• Support—Online technical support resources at
include the following:
– Self-Help Resources—For answers and solutions, visit the
award-winning National Instruments Web site for software drivers
and updates, a searchable KnowledgeBase, product manuals,
step-by-step troubleshooting wizards, thousands of example
programs, tutorials, application notes, instrument drivers, and
so on.
– Free Technical Support—All registered users receive free Basic
Service, which includes access to hundreds of Application
Engineers worldwide in the NI Discussion Forums at
ni.com/forums. National Instruments Application Engineers
make sure every question receives an answer.
For information about other technical support options in your
area, visit
ni.com/contact.
• Training and Certification—Visit
self-paced training, eLearning virtual classrooms, interactive CDs,
and Certification program information. You also can register for
instructor-led, hands-on courses at locations around the world.
• System Integration—If you have time constraints, limited in-house
technical resources, or other project challenges, National Instruments
Alliance Partner members can help. To learn more, call your local
NI office or visit
ni.com/services or contact your local office at
ni.com/alliance.
D
ni.com/support
ni.com/training for
If you searched
your local office or NI corporate headquarters. Phone numbers for our
worldwide offices are listed at the front of this manual. You also can visit
the Worldwide Offices section of
office Web sites, which provide up-to-date contact information, support
phone numbers, email addresses, and current events.
© National Instruments Corporation D-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
ni.com and could not find the answers you need, contact
ni.com/niglobal to access the branch
Page 93

Glossary
Symbol Prefix Value
ppico10
nnano10
μ micro 10
m milli 10
k kilo 10
Mmega10
Ggiga10
Ttera10
Symbols
• Degrees
–12
–9
–6
–3
3
6
9
12
Ω Ohms
% Percent
A
A Amperes
A/D
AC Alternating Current
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Management Interface
ANSI
API Application Programming Interface—A standardized set of subroutines or
© National Instruments Corporation G-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Analog-to-digital. Most often used as A/D converter.
American National Standards Institute
functions along with the parameters that a program can call.
Page 94

Glossary
APIC Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
ASCII
ASIC Application-Specific Integrated Circuit
ATA
American Standard Code for Information Exchange
The specification formulated in the 1980s that defines the IDE drive
interface.
B
BBytes
BIOS Basic Input/Output System—BIOS functions are the fundamental level
of any PC or compatible computer. BIOS functions embody the basic
operations needed for successful use of the computer’s hardware resources.
C
CCelsius
CAS Column Address Strobe
CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor—A process used in making
chips.
COM Communications port
CPU Central Processing Unit
CSA
Carrier Serving Area
D
D/A
DC Direct Current
DDR Double Data Rate
DIMM Dual In-line Memory Module
NI 8352/8353 User Manual G-2 ni.com
Digital-to-analog—Most often used as an abbreviation for a D/A converter
(also known as DAC).
Page 95

Glossary
DMA Direct Memory Access—A method by which data is transferred between
devices and internal memory without intervention of the central processing
unit.
DMI Desktop Management Interface
DRAM Dynamic RAM (Random Access Memory)—Storage that the computer
must refresh at frequent intervals.
E
ECC Error-Correcting Code
EDO RAM Extended Data Output RAM--A type of random access memory (RAM)
chip that improves the time to read from memory on faster microprocessors
such as the Intel Pentium.
EEPROM Electronically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory
EMC Electromagnetic Compatibility
EMI Electromagnetic Interference
EPP Enhanced Parallel Port
F
FCC Federal Communications Commission
G
GB Gigabytes of memory
GPIB General Purpose Interface Bus (IEEE 488)
H
HDD Hard Disk Drive
Hz Hertz; cycles per second
© National Instruments Corporation G-3 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 96

Glossary
I
I/O Input/output—The techniques, media, and devices used to achieve
communication between machines and users.
IDE Integrated Drive Electronics—Hard disk and built-in controller.
IEEE Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IRQ* Interrupt signal
ISA Industry Standard Architecture—The original PC bus architecture,
specifically the 16-bit AT bus.
K
KB Kilobytes of memory
L
LAN Local Area Network—Communications network that serves users within
a confined geographical area. It is made up of servers, workstations, a
network operating system, and a communications link.
LCD
LED Light-emitting diode
Liquid Crystal Display—A display technology using polarizing filters and
liquid crystal cells.
M
MAX Measurement & Automation Explorer
MB Megabytes of memory
MPS Multiprocessor Specification
MTBF Mean Time Between Failure
MTTR Mean Time to Repair
MXI
Multisystem eXtension Interface
NI 8352/8353 User Manual G-4 ni.com
Page 97

Glossary
N
NI-DAQ The National Instruments software for data acquisition instruments.
NI-VISA The National Instruments implementation of the VISA standard—An
interface-independent software that provides a unified programming
interface for VXI, GPIB, and serial instruments.
P
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect. The PCI bus is a high-performance
32-bit or 64-bit bus with multiplexed address and data lines.
PEF Platform Event Filter
PIO Programmed Input/Output
POSC Power On Self Configuration
POST Power On Self Test
PXI PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation—An open implementation of
CompactPCI that adds electrical features that meet the high-performance
requirements of instrumentation applications by providing triggering,
local buses, and system clock capabilities. PXI also offers two-way
interoperability with CompactPCI products.
R
RAM Random Access Memory—The computer’s primary workspace.
RAS Row Address Strobe
RMS Root Mean Squared
RTC Real Time Clock—An electronic circuit that maintains the time of day and
also can provide timing signals for timesharing operations.
© National Instruments Corporation G-5 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 98

Glossary
S
SATA Serial-ATA. See also ATA.
SCSI Small Computer System Inteface
SDRAM
SO-DIMM Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module
SPD Serial Presence Detect EEPROM
SRAM Static RAM—A memory chip that requires power to hold its content. It
A form of dynamic RAM memory that is about 20% faster than EDO
RAM. SDRAM interleaves two or more internal memory arrays so that
while one array is being accessed, the next one is being prepared for access.
SDRAM-II is a faster version of SDRAM technology.
does not require refresh circuitry as a dynamic RAM chip, but it does take
up more space and uses more power.
U
UDMA Ultra Direct Memory Access. See also DMA.
USB Universal Serial Bus
V
VVolts
VGA Video Graphics Array—The minimum video display standard for all PCs.
VISA Virtual Instrument Software Architecture—A single interface library for
controlling GPIB, VXI, RS232, and other types of instruments. VISA has
been standardized by the VXI Plug&Play Systems Alliance.
VME Versa Module Eurocard
VXI
NI 8352/8353 User Manual G-6 ni.com
VME eXtensions for Instrumentation
Page 99

W
W Watts
WDT Watchdog Timer
Glossary
© National Instruments Corporation G-7 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
Page 100

Index
Numerics
32 Bit I/O, 2-6
A
AC power cables (table), 1-2
ACPI Mode, 2-7
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch, 2-13
advanced BIOS setup, 2-7
Advanced Chipset Control, 2-11
Advanced Processor Options, 2-12
B
Base I/O Address, 2-14, 2-15
BAUD Rate, 2-16
BIOS
32 Bit I/O, 2-6
ACPI Mode, 2-7
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch, 2-13
Advanced Chipset Control, 2-11
Advanced Processor Options, 2-12
advanced setup, 2-7
Base I/O Address, 2-14, 2-15
BAUD Rate, 2-16
BIOS Date, 2-4
BIOS POST Errors, 2-19
BIOS POST Watchdog, 2-19
Boot, 2-21
Boot Features, 2-7
Boot Priority Order, 2-21
C1 Enhance Mode, 2-13
Cache Base 0–512K, 2-9
Cache Base 512K–640K, 2-9
Cache Extended Memory, 2-9
Cache System BIOS Area, 2-8
Cache Video BIOS Area, 2-8
checking settings, 4-1
CHS Format, 2-6
Clear All DMI Event Logs, 2-16
Clear System Event Logging, 2-19
Clock Spectrum Feature, 2-11
COM Port Address, 2-16
Console Connection, 2-17
Console Redirection, 2-16
Console Type, 2-16
Continue CR after POST, 2-17
CPU Speed, 2-12
CPU Temperature, 2-17
CPU Temperature Threshold, 2-17
Discard Changes, 2-22
Discrete MTRR Allocation, 2-10
DMA Channel, 2-15
DMI Event Logging, 2-15
ECC Conditions, 2-11
ECC Error Handler, 2-11
ECC Event Logging, 2-16
Enable Master, 2-10
Event Log Capacity, 2-16
Event Log Control, 2-19
Event Log Validity, 2-15
Event Logging, 2-16
Excluded from Boot Orders, 2-21
Existing Event Log Number, 2-19
Exit, 2-21
Exit Discarding Changes, 2-21
Exit Saving Changes, 2-21
Extended Memory, 2-7
Fan Speed Control Modes, 2-17
Fan1–Fan6 Speeds, 2-17
Firmware Version, 2-18
Fixed Disk Boot Sector, 2-21
flashing new BIOS, 4-4
Floppy Disk Controller, 2-15
© National Instruments Corporation I-1 NI 8352/8353 User Manual
 Loading...
Loading...