Page 1

Measurement Studio
User Manual
Subtitle
Measurement Studio User Manual
TM
April 2008
373392C-01
Page 2

Support
Worldwide Technical Support and Product Information
ni.com
National Instruments Corporate Headquarters
11500 North Mopac Expressway Austin, Texas 78759-3504 USA Tel: 512 683 0100
Worldwide Offices
Australia 1800 300 800, Austria 43 662 457990-0, Belgium 32 (0) 2 757 0020, Brazil 55 11 3262 3599,
Canada 800 433 3488, China 86 21 5050 9800, Czech Republic 420 224 235 774, Denmark 45 45 76 26 00,
Finland 358 (0) 9 725 72511, France 01 57 66 24 24, Germany 49 89 7413130, India 91 80 41190000,
Israel 972 3 6393737, Italy 39 02 41309277, Japan 0120-527196, Korea 82 02 3451 3400,
Lebanon 961 (0) 1 33 28 28, Malaysia 1800 887710, Mexico 01 800 010 0793, Netherlands 31 (0) 348 433 466,
New Zealand 0800 553 322, Norway 47 (0) 66 90 76 60, Poland 48 22 3390150, Portugal 351 210 311 210,
Russia 7 495 783 6851, Singapore 1800 226 5886, Slovenia 386 3 425 42 00, South Africa 27 0 11 805 8197,
Spain 34 91 640 0085, Sweden 46 (0) 8 587 895 00, Switzerland 41 56 2005151, Taiwan 886 02 2377 2222,
Thailand 662 278 6777, Turkey 90 212 279 3031, United Kingdom 44 (0) 1635 523545
For further support information, refer to the Technical Support and Professional Services appendix. To comment
on National Instruments documentation, refer to the National Instruments Web site at
the info code
feedback.
ni.com/info and enter
© 2004–2008 National Instruments Corporation. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Important Information
Warranty
The media on which you receive National Instruments software are warranted not to fail to execute programming instructions, due to defects
in materials and workmanship, for a period of 90 days from date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National
Instruments will, at its option, repair or replace software media that do not execute programming instructions if National Instruments receives
notice of such defects during the warranty period. National Instruments does not warrant that the operation of the software shall be
uninterrupted or error free.
A Return Material Authorization (RMA) number must be obtained from the factory and clearly marked on the outside of the package before any
equipment will be accepted for warranty work. National Instruments will pay the shipping costs of returning to the owner parts which are covered by
warranty.
National Instruments believes that the information in this document is accurate. The document has been carefully reviewed for technical accuracy. In
the event that technical or typographical errors exist, National Instruments reserves the right to make changes to subsequent editions of this document
without prior notice to holders of this edition. The reader should consult National Instruments if errors are suspected. In no event shall National
Instruments be liable for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the information contained in it.
XCEPT AS SPECIFIED HEREIN, NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTY OF
E
MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. CUSTOMER’S RIGHT TO RECOVER DAMAGES CAUSED BY FAULT OR NEGLIGENCE ON THE PART OF NATIONAL
I
NSTRUMENTS SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE AMOUNT THERETOFORE PAID BY THE CUSTOMER. NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES RESULTING
FROM LOSS OF DATA, PROFITS, USE OF PRODUCTS, OR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF. This limitation of
the liability of National Instruments will apply regardless of the form of action, whether in contract or tort, including negligence. Any action against
National Instruments must be brought within one year after the cause of action accrues. National Instruments shall not be liable for any delay in
performance due to causes beyond its reasonable control. The warranty provided herein does not cover damages, defects, malfunctions, or service
failures caused by owner’s failure to follow the National Instruments installation, operation, or maintenance instructions; owner’s modification of the
product; owner’s abuse, misuse, or negligent acts; and power failure or surges, fire, flood, accident, actions of third parties, or other events outside
reasonable control.
Copyright
Under the copyright laws, this publication may not be reproduced or transmitted in any form, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying,
recording, storing in an information retrieval system, or translating, in whole or in part, without the prior written consent of National
Instruments Corporation.
National Instruments respects the intellectual property of others, and we ask our users to do the same. NI software is protected by copyright and other
intellectual property laws. Where NI software may be used to reproduce software or other materials belonging to others, you may use NI software only
to reproduce materials that you may reproduce in accordance with the terms of any applicable license or other legal restriction.
Trademarks
National Instruments, NI, ni.com, and LabVIEW are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation. Refer to the Terms of Use section
on ni.com/legal for more information about National Instruments trademarks.
®
FireWire
is the registered trademark of Apple Computer, Inc. Other product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names
of their respective companies.
Members of the National Instruments Alliance Partner Program are business entities independent from National Instruments and have no agency,
partnership, or joint-venture relationship with National Instruments.
Patents
For patents covering National Instruments products, refer to the appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software, the patents.txt file
on your media, or ni.com/patents.
WARNING REGARDING USE OF NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS
(1) NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED WITH COMPONENTS AND TESTING FOR A LEVEL OF
RELIABILITY SUITABLE FOR USE IN OR IN CONNECTION WITH SURGICAL IMPLANTS OR AS CRITICAL COMPONENTS IN
ANY LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS WHOSE FAILURE TO PERFORM CAN REASONABLY BE EXPECTED TO CAUSE SIGNIFICANT
INJURY TO A HUMAN.
(2) IN ANY APPLICATION, INCLUDING THE ABOVE, RELIABILITY OF OPERATION OF THE SOFTWARE PRODUCTS CAN BE
IMPAIRED BY ADVERSE FACTORS, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO FLUCTUATIONS IN ELECTRICAL POWER SUPPLY,
COMPUTER HARDWARE MALFUNCTIONS, COMPUTER OPERATING SYSTEM SOFTWARE FITNESS, FITNESS OF COMPILERS
AND DEVELOPMENT SOFTWARE USED TO DEVELOP AN APPLICATION, INSTALLATION ERRORS, SOFTWARE AND HARDWARE
COMPATIBILITY PROBLEMS, MALFUNCTIONS OR FAILURES OF ELECTRONIC MONITORING OR CONTROL DEVICES,
TRANSIENT FAILURES OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS (HARDWARE AND/OR SOFTWARE), UNANTICIPATED USES OR MISUSES, OR
ERRORS ON THE PART OF THE USER OR APPLICATIONS DESIGNER (ADVERSE FACTORS SUCH AS THESE ARE HEREAFTER
COLLECTIVELY TERMED “SYSTEM FAILURES”). ANY APPLICATION WHERE A SYSTEM FAILURE WOULD CREATE A RISK OF
HARM TO PROPERTY OR PERSONS (INCLUDING THE RISK OF BODILY INJURY AND DEATH) SHOULD NOT BE RELIANT SOLELY
UPON ONE FORM OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEM DUE TO THE RISK OF SYSTEM FAILURE. TO AVOID DAMAGE, INJURY, OR DEATH,
THE USER OR APPLICATION DESIGNER MUST TAKE REASONABLY PRUDENT STEPS TO PROTECT AGAINST SYSTEM FAILURES,
INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO BACK-UP OR SHUT DOWN MECHANISMS. BECAUSE EACH END-USER SYSTEM IS
CUSTOMIZED AND DIFFERS FROM NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS' TESTING PLATFORMS AND BECAUSE A USER OR APPLICATION
DESIGNER MAY USE NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS IN COMBINATION WITH OTHER PRODUCTS IN A MANNER NOT
EVALUATED OR CONTEMPLATED BY NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS, THE USER OR APPLICATION DESIGNER IS ULTIMATELY
RESPONSIBLE FOR VERIFYING AND VALIDATING THE SUITABILITY OF NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS WHENEVER
NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS PRODUCTS ARE INCORPORATED IN A SYSTEM OR APPLICATION, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THE APPROPRIATE DESIGN, PROCESS AND SAFETY LEVEL OF SUCH SYSTEM OR APPLICATION.
Page 4

Contents
About This Manual
How To Use This Manual..............................................................................................ix
Conventions ...................................................................................................................x
Chapter 1
Introduction to Measurement Studio
Installation Requirements ..............................................................................................1-2
Driver Support.................................................................................................1-3
Deployment Requirements ............................................................................................1-3
Installation Instructions..................................................................................................1-3
Installing Hardware Drivers for Visual Studio 2008 Support .........................1-4
Installing Hardware Drivers for Visual Studio 2005 Support .........................1-5
Installing the Current Version of Measurement Studio over
Previous Versions of Measurement Studio ..................................................1-6
Measurement Studio Package Comparison Chart .........................................................1-6
Learning Measurement Studio.......................................................................................1-9
Chapter 2
Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Measurement Studio Support for Visual Studio .NET Class Library Overview ...........2-1
Analysis .........................................................................................................................2-2
Standard Analysis............................................................................................2-2
Professional Analysis ......................................................................................2-2
Enterprise Analysis..........................................................................................2-3
Common.........................................................................................................................2-13
Data Transfer .................................................................................................................2-14
Network Variable ............................................................................................2-14
DataSocket.......................................................................................................2-15
NI-488.2.........................................................................................................................2-16
NI-DAQmx ....................................................................................................................2-16
NI-SCOPE .....................................................................................................................2-17
NI-VISA.........................................................................................................................2-17
User Interface.................................................................................................................2-18
Windows Forms Controls ..............................................................................................2-19
Waveform Graph and Scatter Graph Controls ................................................2-20
Digital Waveform Graph Control....................................................................2-23
Complex Graph Control ..................................................................................2-25
Legend Control................................................................................................2-27
© National Instruments Corporation v Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 5

Contents
Numeric Controls............................................................................................ 2-27
Numeric Edit Control...................................................................................... 2-29
Switch and LED Controls ............................................................................... 2-30
Property Editor Control................................................................................... 2-32
Windows Forms Array Controls ................................................................................... 2-33
Switch and LED Array Controls ..................................................................... 2-33
Numeric Edit Array Control ........................................................................... 2-34
InstrumentControlStrip Control ...................................................................... 2-35
ASP.NET Web Forms Controls .................................................................................... 2-37
Waveform Graph and Scatter Graph Controls................................................2-38
Digital Waveform Graph Control ................................................................... 2-40
Complex Graph Control.................................................................................. 2-42
Legend Control ............................................................................................... 2-44
Numeric Controls............................................................................................ 2-44
Numeric Edit Control...................................................................................... 2-47
Switch and LED Controls ............................................................................... 2-48
AutoRefresh Control ....................................................................................... 2-49
AutoRefresh Callback ..................................................................................... 2-49
Chapter 3
Measurement Studio Visual C++ Class Libraries
Measurement Studio Visual C++ Class Library Overview........................................... 3-1
ActiveX Controls in Visual C++ ................................................................................... 3-2
3D Graph Control .......................................................................................................... 3-2
Plot Operations................................................................................................ 3-3
Additional Operations ..................................................................................... 3-3
Analysis ......................................................................................................................... 3-3
Standard Analysis ........................................................................................... 3-4
Professional Analysis...................................................................................... 3-4
Enterprise Analysis ......................................................................................... 3-4
Common ........................................................................................................................ 3-15
DataSocket..................................................................................................................... 3-15
Microsoft Excel Interface .............................................................................................. 3-16
Microsoft Word Interface .............................................................................................. 3-16
NI-488.2......................................................................................................................... 3-17
NI-DAQmx.................................................................................................................... 3-17
NI-Reports ..................................................................................................................... 3-18
NI-VISA ........................................................................................................................ 3-18
User Interface ................................................................................................................ 3-19
Button Control................................................................................................. 3-19
Graph Control ................................................................................................. 3-20
Plot Operations ................................................................................. 3-20
Axis Operations ................................................................................ 3-21
Measurement Studio User Manual vi ni.com
Page 6

Additional Operations .......................................................................3-21
Knob Control ...................................................................................................3-21
Numeric Edit Control ......................................................................................3-22
Slide Control....................................................................................................3-23
Utility .............................................................................................................................3-24
Chapter 4
Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
Measurement Studio Menu............................................................................................4-1
Creating a Measurement Studio Project ........................................................................4-4
Adding or Removing Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries ................................4-5
Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application ............................................4-6
Creating an NI-DAQmx User Interface ..........................................................4-8
Creating NI-DAQmx User Code in Visual C++ .............................................4-9
Creating an Instrument Control Application .................................................................4-9
Selecting a Measurement Studio Parameter Value........................................................4-11
Using the Instrument Driver Wizard .............................................................................4-12
Chapter 5
Getting Started with Measurement Studio
Measurement Studio Walkthroughs...............................................................................5-1
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Application
with Windows Forms Controls and Analysis ............................................................5-2
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Application
with Web Forms Controls and Analysis ....................................................................5-11
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Application
with Windows Forms Controls and Network Variable ..............................................5-22
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Application
with Web Forms Controls and Network Variable ......................................................5-31
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application .....................5-42
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Instrument I/O Application ................5-52
Contents
Appendix A
Technical Support and Professional Services
Glossary
Index
© National Instruments Corporation vii Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 7

About This Manual
The Measurement Studio User Manual introduces the concepts associated
with the Measurement Studio class libraries and development tools. This
manual assumes that you have a general working knowledge of Microsoft
Visual Studio and the .NET Framework for .NET application development
or MFC for unmanaged C++ application development.
How To Use This Manual
Measurement Studio 8.5 includes two Visual Studio support CDs—one
with support for Visual Studio .NET 2003, Visual Studio 2005, and Visual
Studio 2008 and one with support for Visual Studio 6.0. This manual
documents Measurement Studio for Visual Studio 2005/2008. The
Measurement Studio support for Visual Studio .NET 2003, Visual
Studio 2005, and Visual Studio 2008 CD includes separate, parallel sets
of class libraries, integration features, and support documentation for
developing with Visual Studio .NET 2003, Visual Studio 2005, and Visual
Studio 2008. For help with Visual Studio 6.0, refer to the Measurement
Studio Support for Visual Studio 6.0 Readme located on the Measurement
Studio for Visual Studio 6.0 CD.
The Measurement Studio User Manual is organized into five chapters.
Chapter 1, Introduction to Measurement Studio, is an overview of
Measurement Studio. This chapter includes installation and deployment
requirements, installation instructions, and a list of Measurement Studio
resources. Chapter 2, Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries, and
Chapter 3, Measurement Studio Visual C++ Class Libraries, include
information about the .NET class libraries and the Visual C++ class
libraries, respectively. Chapter 4, Measurement Studio Integrated Tools
and Features, includes information on using the Measurement Studio tools
and features integrated into the Visual Studio environment. Chapter 5,
Getting Started with Measurement Studio, includes walkthroughs that
guide you through step-by-step instructions on how to develop with
Measurement Studio features.
Note Refer to the Measurement Studio Release Notes for updates or changes to the
Measurement Studio User Manual.
© National Instruments Corporation ix Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 8

About This Manual
Use this manual as a starting point to learn about Measurement Studio.
Refer to the NI Measurement Studio Help within the Visual Studio
environment for function reference and detailed information about the
Measurement Studio class libraries, wizards, assistants, and other features.
Conventions
The following conventions appear in this manual:
<> Text enclosed in angle brackets represents directory names and parts of
paths that may vary on different computers, such as <
» The » symbol leads you through nested menu items and dialog box options
to a final action. The sequence File»Page Setup»Options directs you to
pull down the File menu, select the Page Setup item, and select Options
from the last dialog box.
This icon denotes a tip, which alerts you to advisory information.
This icon denotes a note, which alerts you to important information.
bold Bold text denotes items that you must select or click on in the software,
such as menu items and dialog box options. Bold text also denotes class
library member names or emphasis.
Windows\System>.
italic Italic text denotes parameters, variables, cross-references, or an
introduction to a key concept. Italic text also denotes text that is a
placeholder for a word or value that you must supply.
monospace Text in this font denotes text or characters that you enter from the keyboard,
sections of code, programming examples, and syntax examples. This font
also is used for the proper names of disk drives, paths, directories,
programs, device names, filenames and extensions, and code excerpts.
Measurement Studio User Manual x ni.com
Page 9
Introduction to Measurement
Studio
Measurement Studio is an integrated suite of tools and class libraries that
are designed for developers using Microsoft Visual Basic .NET, Visual C#,
ASP.NET, and Visual C++ to develop measurement and automation
applications.
Measurement Studio dramatically reduces application development time
through object-oriented measurement hardware interfaces, advanced
analysis libraries, scientific user interface controls for Windows and Web
applications, measurement data networking, wizards, interactive code
designers, and highly extensible .NET and Visual C++ classes. You can use
Measurement Studio to develop a complete measurement and automation
application that includes data acquisition, analysis, and presentation
functionalities.
Measurement Studio 8.5 Professional and Enterprise packages include
two Visual Studio support CDs—one CD with support for Visual Studio
.NET 2003, Visual Studio 2005, and Visual Studio 2008 and one CD with
support for Visual Studio 6.0. The Measurement Studio 8.5 Standard
package includes one CD with support for Visual Studio .NET 2003, Visual
Studio 2005, and Visual Studio 2008. Visual Studio 6.0 support includes
ActiveX controls for use in Visual Basic 6.0 and MFC class libraries and
ActiveX controls for use in Visual C++ 6.0. Visual Studio .NET 2003
support and Visual Studio 2005 support includes .NET class libraries and
controls for use with .NET languages and MFC class libraries and ActiveX
controls for use with Visual C++. Visual Studio 2008 support includes
only .NET class libraries and controls for use with .NET languages.
Measurement Studio 8.5 does not include MFC class libraries or ActiveX
controls for use in Visual C++ in Visual Studio 2008.
1
Note Measurement Studio 8.5 support for Visual Studio .NET 2003 includes updates to
the ActiveX controls; however, no new features for Visual Studio .NET 2003 are included
in Measurement Studio 8.5.
© National Instruments Corporation 1-1 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 10

Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
This manual documents Measurement Studio for Visual Studio 2005 and
Visual Studio 2008. For help with Visual Studio 6.0 support, refer to the
Measurement Studio Support for Visual Studio 6.0 Readme located on the
Measurement Studio for Visual Studio 6.0 CD. For help with Visual Studio
.NET 2003 support, refer to the Measurement Studio Support for Visual
Studio .NET 2003 Readme located on the CD for Measurement Studio for
Visual Studio .NET 2003. After installing Visual Studio .NET 2003
support, you can refer to the Measurement Studio User Manual by selecting
Start»All Programs»National Instruments»<Measurement Studio for
.NET 2003>»User Manual.
Note Refer to the Measurement Studio Release Notes for updates or changes to the
Measurement Studio User Manual.
Installation Requirements
To use Measurement Studio, your computer must have the following:
• Microsoft Windows Vista/XP/2000 for Visual Studio 2005 or
Microsoft Windows Vista/XP for Visual Studio 2008
Note If you have Windows Vista installed you must also have both Visual Studio 2005
Service Pack 1 and Visual Studio Service Pack 1 Update for Windows Vista installed on
your machine for Measurement Studio to function properly.
• Microsoft .NET Framework 2.0 for Visual Studio 2005 or Microsoft
.NET Framework 3.5 for Visual Studio 2008 (required only for the
Measurement Studio .NET class libraries)
• Standard, Professional, or Team System edition of Microsoft Visual
Studio 2005 or Standard, Professional, or Team System edition of
Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 (required to use the Measurement Studio
integrated tools) or Visual C#, Visual Basic .NET, or Visual C++
Express editions of Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 or Microsoft Visual
Studio 2008
• Intel Pentium III class processor, 1 GHz or higher
• Video display—1024 × 768, 256 colors (16-bit color recommended for
user interface controls)
• Minimum of 256 MB of RAM (512 MB or higher recommended)
• Minimum of 385 MB of free hard disk space for Visual Studio 2005
support or minimum of 200 MB of free hard disk space for Visual
Studio 2008 support
Measurement Studio User Manual 1-2 ni.com
Page 11

• Microsoft-compatible mouse
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 6.0 or later
Optional Installation—In order for links from Measurement Studio help
topics to .NET Framework help topics to work, you must install the
Microsoft .NET Framework SDK 2.0 or Microsoft .NET Framework
SDK 3.5.
Driver Support
To use .NET class libraries that interface to National Instruments device
drivers, NI-DAQmx, NI-VISA and NI-488.2, and the MAX (Measurement
& Automation Explorer) configuration utility, you must install the
underlying device drivers in addition to the .NET class libraries. You can
run the underlying device driver installers from the NI Device Drivers CD
included with Measurement Studio. Alternatively, refer to NI Drivers and
Updates on
download the latest version of the NI Device Drivers CD.
ni.com and enter Device Drivers into the search field to
Deployment Requirements
Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
To deploy an application built with Measurement Studio .NET class
libraries, the target computer must have a Windows Vista/XP/2000
operating system and the .NET Framework version 2.0 for Visual Studio
2005 or the .NET Framework version 3.5 for Visual Studio 2008.
To deploy an application built with Measurement Studio Visual C++ class
libraries, the target computer must have a Windows Vista/XP/2000
operating system.
Installation Instructions
Complete the following steps to install Measurement Studio. These steps
describe a typical installation. Please carefully review all additional
licensing and warning dialog boxes.
National Instruments recommends that you exit all programs before
running the Measurement Studio installer. Applications that run in the
background, such as virus scanning utilities, might cause the installer to
take longer than average to complete.
© National Instruments Corporation 1-3 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 12

Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
Note There are separate installers for Measurement Studio support for Visual Studio 2005
and Measurement Studio support for Visual Studio 2008. Repeat the installation
instructions to install support for both. When installing support for more than one version
of Visual Studio, you can reduce installation time by running the Device Drivers CD
installer only once. To do this, ensure that the Device Drivers CD feature is enabled only
for the last Measurement Studio Visual Studio support installer that you run.
The option to browse for an installation location is valid only if you have
not already installed any Measurement Studio features for the version of
Visual Studio or the .NET Framework that you are installing. If you have
any Measurement Studio features installed, then Measurement Studio
installs to the same root directory to which you installed other
Measurement Studio features.
Complete the following steps to install Measurement Studio:
1. Log on as an administrator or as a user with administrator privileges.
2. Launch
location to which you extracted the downloaded CD image.
3. Select the version of Visual Studio you want to install support for.
4. Follow the instructions that appear on the screen.
Autorun.exe, either from the installation CD or from the
Note If you want to upgrade a Windows XP machine to Windows Vista, National
Instruments recommends first uninstalling all NI software, including both application
software and drivers.
Installing Hardware Drivers for Visual Studio 2008 Support
Visual Studio 2008 .NET class library support for National Instruments
hardware drivers is included on the Measurement Studio 8.5 CD, under the
VS2008 Driver Support feature in the feature tree. To install support for
NI-DAQmx, NI-VISA, NI-488.2, or MAX, you must install the appropriate
feature from the Measurement Studio 8.5 CD and you must install the
underlying device driver from the NI Device Drivers CD or from a
product-specific driver installer. Refer to the Driver Support section for
information on obtaining device driver installers.
Measurement Studio User Manual 1-4 ni.com
Page 13

Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
To install support for NI-DAQmx:
1. In the NI Measurement Studio 8.5 installer, enable the VS2008 Driver
Support».NET Framework 3.5 Languages Support for
NI-DAQmx feature.
2. In the NI Device Drivers installer, enable the Data Acquisition»
NI-DAQmx feature.
To install support for NI-VISA:
1. In the NI Measurement Studio 8.5 installer, enable the VS2008 Driver
Support».NET Framework 3.5 Languages Support for NI-VISA
feature. If you want to use the Instrument I/O Assistant inside Visual
Studio 2008, enable the VS2008 Driver Support»VS2008 DotNET
IIOAssistant Support feature.
2. In the NI Device Drivers installer, enable the Instrument Control»
NI-VISA feature.
To install support for NI-488.2:
1. In the NI Measurement Studio 8.5 installer, enable the VS2008 Driver
Support».NET Framework 3.5 Languages Support for NI-488.2
feature.
2. In the NI Device Drivers installer, enable the Instrument Control»
NI-488.2 feature.
To install support for MAX:
1. In the NI Measurement Studio 8.5 installer, enable the VS2008 Driver
Support».NET Framework 3.5 Languages Support for NI MAX
feature.
2. In the NI Device Drivers installer, enable the NI Measurement and
Automation Explorer feature.
Installing Hardware Drivers for Visual Studio 2005 Support
The .NET and C++ class libraries for Visual Studio 2005 support for
National Instruments hardware drivers are included in the Driver CD
installer.
© National Instruments Corporation 1-5 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 14

Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
Installing the Current Version of Measurement Studio over Previous Versions of Measurement Studio
Note You can have only one version of Measurement Studio installed on a system for each
version of Visual Studio or the .NET Framework installed on the system. For example,
you can have Measurement Studio 8.1.2 for Visual Studio 2005 installed on the
same system as Measurement Studio 8.5 for Visual Studio 2008, but you cannot have
Measurement Studio 8.1.2 for Visual Studio 2005 installed on the same system as
Measurement Studio 8.5 for Visual Studio 2005.
If you install a newer version of Measurement Studio on a machine that has
a prior version of Measurement Studio installed, the newer version installer
replaces the prior version functionality, including class libraries. However,
the prior version assemblies remain in the global assembly cache (GAC);
therefore, applications that reference the prior version continue to use the
prior version .NET assemblies.
Note This does not apply to NationalInstruments.Common.dll.
NationalInstruments.Common.dll uses a publisher policy file to redirect
applications to always use the newest version of
installed on the system, for each version of the .NET Framework.
NationalInstruments.Common.dll is backward-compatible.
NationalInstruments.Common.dll
Measurement Studio Package Comparison Chart
The following table lists the features included in the Standard,
Professional, and Enterprise packages of Measurement Studio. Refer to
ni.com/mstudio for more information about the functionality and
features included with each Measurement Studio package, including Visual
C++ functionality.
Measurement Studio User Manual 1-6 ni.com
Page 15
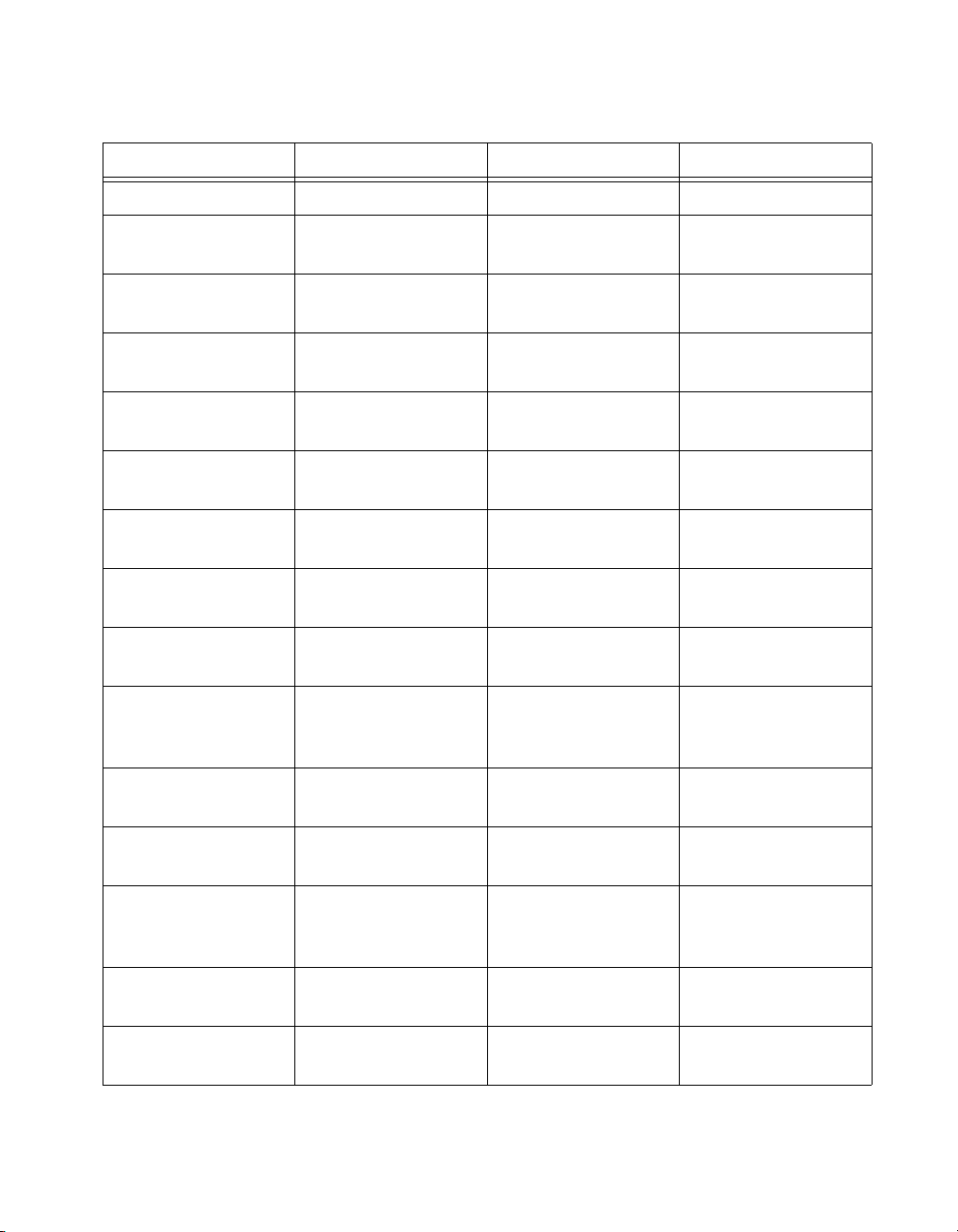
Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
Table 1-1. Measurement Studio Package Comparison Chart for Visual C# and Visual Basic .NET
Feature Standard Edition Professional Edition Enterprise Edition
Project Wizards ✔ ✔ ✔
Windows Forms User
Interface Controls
Standard Analysis
Libraries
1
NI-488.2 Class
Libraries
2
NI-VISA Class
Libraries
2
NI-DAQmx Class
Libraries
2
.NET Instrument
Driver Wizard
User Interface
DataSocket Binding
Web Forms User
Interface Controls
MFC and ActiveX
Controls for
Visual C++ 6.0
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔ ✔
✔ ✔
✔ ✔
Professional Analysis
Libraries
3
3D Graph ActiveX
✔ ✔
✔ ✔
Control
User Interface
✔ ✔
Network Variable
Binding
Network Variable
✔ ✔
Class Library
Network Variable
✔ ✔
Data Source
© National Instruments Corporation 1-7 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 16
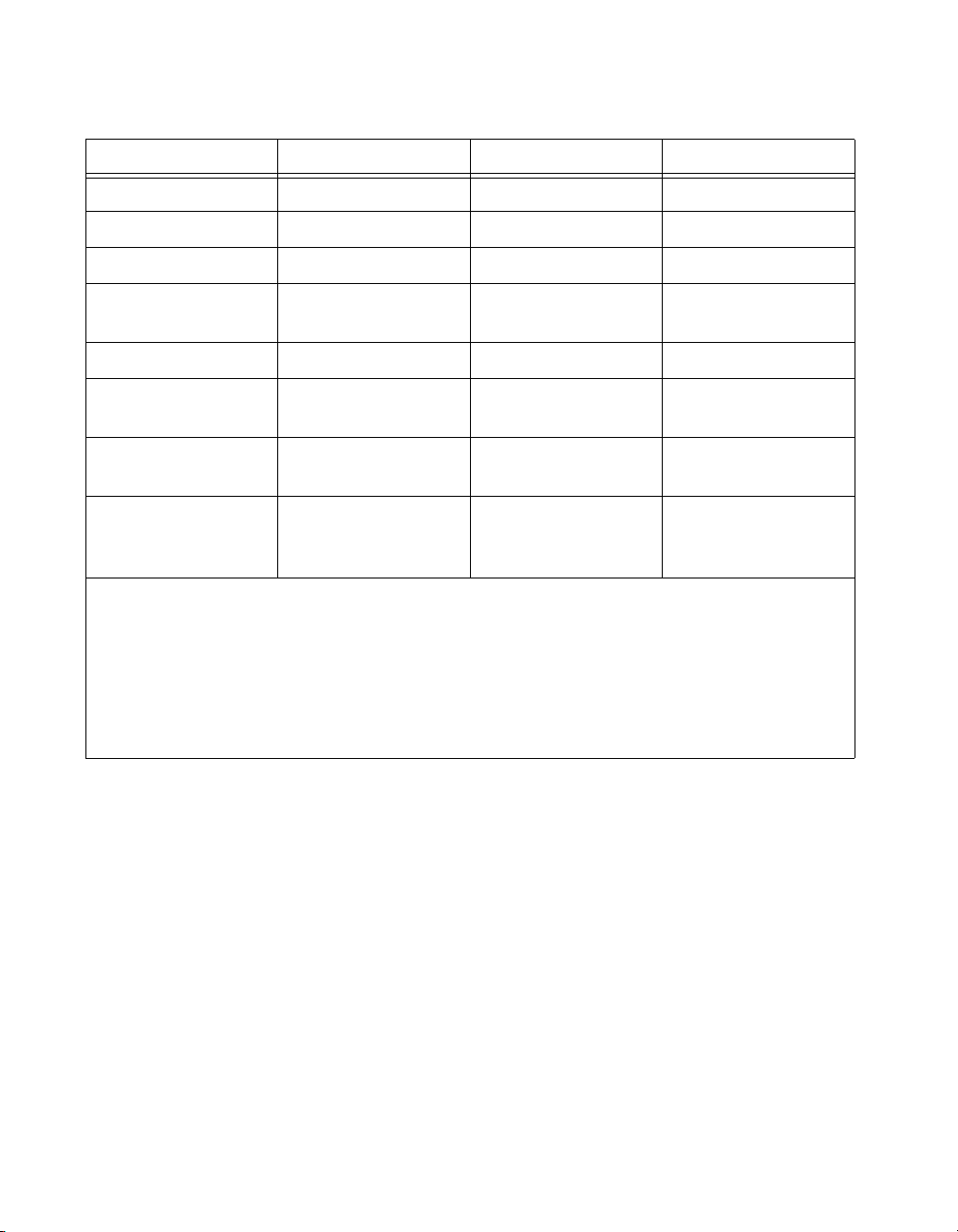
Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
Table 1-1. Measurement Studio Package Comparison Chart for Visual C# and Visual Basic .NET (Continued)
Feature Standard Edition Professional Edition Enterprise Edition
DataSocket Server ✔ ✔
DataSocket Library ✔ ✔
Parameter Assistant ✔ ✔
Instrument I/O
Assistant
DAQ Assistant
2
2
Enterprise Analysis
Libraries
4
NI TestStand
✔ ✔
✔ ✔
✔
✔
Integration
LabWindows™/CVI™
✔
Full Development
System (FDS)
1
Refer to the Standard Analysis section of Chapter 2, Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries, for a list of the
functionality included in the Standard Analysis class library.
2
Included with the Device Drivers CD.
3
Refer to the Professional Analysis section of Chapter 2, Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries, for a list of the
functionality included in the Professional Analysis class library.
4
Refer to the Enterprise Analysis section of Chapter 2, Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries, for a list of the
functionality included in the Enterprise Analysis class library.
Measurement Studio User Manual 1-8 ni.com
Page 17

Learning Measurement Studio
As you work with Measurement Studio, you might need to consult
additional resources. For detailed Measurement Studio help, including
function reference and in-depth documentation on developing with
Measurement Studio, refer to the NI Measurement Studio Help within the
Visual Studio environment. The NI Measurement Studio Help is fully
integrated with the Visual Studio help. You must have Visual Studio
installed to view the online help, and you must have the Microsoft .NET
Framework SDK 2.0 for Visual Studio 2005 or the Microsoft .NET
Framework SDK 3.5 for Visual Studio 2008 installed in order for links
from Measurement Studio help topics to .NET Framework help topics to
work. You can launch the NI Measurement Studio Help in the following
ways:
• From the Windows Start menu, select Start»All Programs»National
Instruments»<Measurement Studio>»Measurement Studio
Documentation. The help launches in a stand-alone help viewer.
• From Visual Studio, select Help»Contents to view the Visual Studio
table of contents. The NI Measurement Studio Help is listed in the table
of contents.
• From Visual Studio, select Measurement Studio»NI Measurement
Studio Help. The help launches within the application.
Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
Tip As you work through this manual, you will see italicized references to relevant help
topics. To find these topics, use the table of contents in the NI Measurement Studio Help
installed on your machine.
The following resources also are available to provide you with information
about Measurement Studio.
• Getting Started information—Refer to the Measurement Studio Core
Overview topic and the Getting Started with the Measurement Studio
Class Libraries section in the NI Measurement Studio Help for an
introduction to Measurement Studio and for walkthroughs that guide
you step-by-step in learning how to develop Measurement Studio
applications. For an introduction to Measurement Studio resources,
refer to the Using the Measurement Studio Help topic in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
• Examples—Measurement Studio installs examples organized by class
library, depending on the component, the version of Visual Studio or
the .NET Framework that the example supports, the version of
Measurement Studio installed on the system, and the operating system.
© National Instruments Corporation 1-9 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 18

Chapter 1 Introduction to Measurement Studio
For more information on example locations, refer to Where To Find
Examples.
• NI Technical Support—Refer to Appendix A, Technical Support and
Professional Services, for more information.
• Measurement Studio Web site,
Measurement Studio news, support, downloads, white papers, product
tutorials, and evaluation software.
• NI Developer Zone,
example programs, tutorials, technical news, and a Measurement
Studio Discussion Forum where you can participate in discussion
forums for Visual Basic 6.0, Visual C++, and .NET Languages.
• Measurement Studio .NET Class Hierarchy Chart and Measurement
Studio Visual C++ Class Hierarchy Chart—Provide overviews of
class relationships within class libraries. Charts are included with all
Measurement Studio packages and are posted online at
manuals
• Review the information from the Microsoft Web site on using Visual
Studio.
ni.com/mstudio—Contains
zone.ni.com—Provides access to online
ni.com/
.
Measurement Studio User Manual 1-10 ni.com
Page 19

2
Measurement Studio .NET Class
Libraries
This chapter provides overview information about the .NET class libraries
included with Measurement Studio support for Visual Studio 2005 and
Visual Studio 2008. Refer to the Using the Measurement Studio .NET Class
Libraries section of the NI Measurement Studio Help for detailed
information about these libraries. Refer to Chapter 5, Getting Started with
Measurement Studio, for step-by-step instructions on developing
applications with these libraries.
Measurement Studio Support for Visual Studio .NET Class Library Overview
Measurement Studio provides .NET class libraries that you can use to
develop complete measurement and automation applications in Visual
Basic .NET and Visual C#.
Measurement Studio includes the following .NET class libraries:
• Analysis
• Common
• DataSocket
• Network Variable
• NI-488.2
•NI-DAQmx
•NI-SCOPE
•NI-VISA
• User Interface
Refer to the following sections for information about each Measurement
Studio .NET class library.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-1 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 20

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Analysis
The Measurement Studio Analysis .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.Analysis namespace. The Analysis class
library includes a set of classes that provides digital signal processing,
signal filtering, signal generation, peak detection, and other general
mathematical functionality. Use this library to analyze acquired data or to
generate data. Additionally, the documentation for the Analysis class
library includes analysis code snippets that you can copy and paste into an
application and use immediately.
The functionality included in the Analysis library varies based on the
Measurement Studio package you purchase. Refer to the following sections
for information about the Standard, Professional, and Enterprise Analysis
class libraries.
Standard Analysis
The Standard Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement Studio
Standard Edition, includes the sawtooth, sine, square, triangle, and basic
function wave generators.
Professional Analysis
The Professional Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement
Studio Professional Edition, includes the Standard Analysis functionality
as well as the following functionality:
• Bessel, Chebyshev, Inverse Chebyshev, Windowed, Kaiser, and
Elliptic Low, High, Bandpass, and Bandstop filters
• Signal processing functions such as convolution, deconvolution,
correlation, decimation, integration, and differentiation
• FFT, Inverse FFT, Real FFT, Fast Hartley, Inverse Fast Hartley, Fast
Hilbert, Inverse Fast Hilbert, DST, Inverse DST, DCT, and Inverse
DCT transformations
• Linear algebra functions such as determinant, check positive
definiteness, calculate dot product, and other various matrix functions
• Scaled and unscaled windowing classes
• Common statistical functions such as mean, median, mode, and
variance
• Exponential, linear, and polynomial curve fitting functions
• Signal generation functions
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-2 ni.com
Page 21
Enterprise Analysis
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
The Enterprise Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement
Studio Enterprise Edition, includes the Standard and Professional Analysis
functionality as well as the following advanced functionality:
• EquiRipple filters
• Linear algebra functions such as forward and back substitution,
LU factorization, Cholesky factorization, Schur decomposition,
and Hessenberg decomposition
• Probability and analysis of variance
• Sinc, impulse, pulse, ramp, and chirp patterns
• General least square curve fit, power fit, log fit, Gauss fit, cubic spline
fit, and interpolation functions
• Measurement functions such as transition measurements, pulse
measurements, and cycle RMS average functions
• Special functions
Refer to Table 2-1 to determine the type of measurements available in the
Professional and Enterprise Analysis .NET libraries.
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Measurements
AC and DC Estimator ✔
Amplitude and Phase
✔
Spectrum
Auto Power Spectrum ✔
Cross Power Spectrum ✔
Cycle RMS Average ✔
Harmonic Analyzer ✔
Harmonic Analyzer Using
✔
Signal
Impulse Response Function ✔ ✔
Network Functions (avg) ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-3 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 22
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Power and Frequency Estimate ✔
Pulse Measurements ✔
Scaled Time Domain Window ✔
Single Tone Information ✔
Spectrum Unit Conversion ✔
State Levels ✔
Transfer Function ✔
Transition Measurements ✔
Signal Generation
Arbitrary Wave ✔ ✔
Chirp Pattern ✔
Gaussian White Noise ✔ ✔
Impulse Pattern ✔
Pulse Pattern ✔
Ramp Pattern ✔
Sawtooth Wave ✔
Sinc Pattern ✔
Sine Pattern ✔ ✔
Sine Wave ✔ ✔
Square Wave ✔ ✔
Triangle Wave ✔ ✔
Uniform White Noise ✔ ✔
Windowing
Blackman Window ✔ ✔
Blackman-Harris Window ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-4 ni.com
Page 23
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Blackman-Nuttall Window ✔ ✔
Cosine Tapered Window ✔ ✔
Dolph-Chebyshev Window ✔ ✔
Exact Blackman Window ✔ ✔
Exponential Window ✔ ✔
Flat Top Window ✔ ✔
Force Window ✔ ✔
Gauss Window ✔ ✔
General Cosine Window ✔ ✔
Hamming Window ✔ ✔
Hanning Window ✔ ✔
Kaiser-Bessel Window ✔ ✔
Scaled Time Domain Windows ✔ ✔
Symmetric Time Domain
✔ ✔
Windows
Triangle Window ✔ ✔
Filters
Bessel ✔ ✔
Butterworth ✔ ✔
Cascade ✔ ✔
Chebyshev ✔ ✔
Elliptic ✔ ✔
Equiripple ✔
FIR ✔ ✔
FIR Windowed ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-5 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 24
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
IIR Cascade ✔ ✔
IIR ✔ ✔
Inverse Chebyshev ✔ ✔
Kaiser ✔ ✔
Signal Processing
Autocorrelation ✔ ✔
Convolution ✔ ✔
Cross Power ✔ ✔
Cross Correlation ✔ ✔
Decimate ✔ ✔
Deconvolution ✔ ✔
Derivative x(t) ✔ ✔
Discrete Cosine Transform ✔ ✔
Discrete Sine Transform ✔ ✔
Fast Hilbert Transform ✔ ✔
Fast Hartley Transform ✔ ✔
Integral x(t) ✔ ✔
Inverse Real and Complex Fast
✔ ✔
Fourier Transform (FFT)
Inverse Fast Hilbert Transform ✔ ✔
Inverse Fast Hartley Transform ✔ ✔
Peak Detection ✔ ✔
Power Spectrum ✔ ✔
Pulse Parameters ✔ ✔
Real and Complex FFT ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-6 ni.com
Page 25
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Threshold Peak Detector ✔ ✔
Unwrap Phase ✔ ✔
Linear Algebra
Back Transform Eigen Vectors ✔
Backward Substitution ✔
Cholesky Factorization ✔
Complex Back Transform
✔
Eigen Vectors
Complex Cholesky
✔
Factorization
Complex Determinant ✔ ✔
Complex Dot Product ✔ ✔
Complex Eigen Vectors and
✔
Eigen Values
Complex General Eigen AB ✔
Complex Hessenberg
✔
Decomposition
Complex Inverse Matrix ✔
Complex Linear Equations ✔
Complex LU Factorization ✔
Complex Matrix Balance ✔
Complex Matrix Condition
✔ ✔
Number
Complex Matrix Norm ✔ ✔
Complex Matrix Rank ✔ ✔
Complex Outer Product ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-7 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 26
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Complex Pseudo Inverse
✔ ✔
Matrix
Complex QR Factorization ✔
Complex QR Factorization
✔
with Pivot Matrix
Complex QR Factorization
✔
with Pivot Vector
Complex QZ Decomposition ✔
Complex Schur
✔
Decomposition
Complex Solve Linear
✔
Equations (Multiple Right
Hand)
Complex Solve Linear
✔
Equations (Single Right Hand)
Complex SVD Factorization ✔
Complex Vector Norm ✔
Determinant ✔ ✔
Dot Product ✔ ✔
Forward Substitution ✔
General Eigen AB ✔
Hessenberg Decomposition ✔
Inverse Matrix ✔ ✔
Linear Equations ✔
LU Factorization ✔
Matrix Balance ✔
Matrix Condition Number ✔ ✔
Matrix Multiplication ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-8 ni.com
Page 27
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Matrix Norm ✔ ✔
Matrix Rank ✔ ✔
Outer Product ✔ ✔
Pseudo Inverse Matrix ✔ ✔
QR Factorization ✔
QR Factorization with Pivot
✔
Matrix
QR Factorization with Pivot
✔
Vector
QZ Decomposition ✔
Schur Decomposition ✔
Solve Linear Equations
✔
(Multiple Right Hand)
Solve Linear Equations
✔
(Single Right Hand)
Special Matrix ✔ ✔
SVD Factorization ✔
Test Positive Definite Matrix ✔ ✔
Trace ✔ ✔
Transpose ✔ ✔
Array and Numeric Operations
1D and 2D Array Arithmetic ✔ ✔
1D and 2D Linear Evaluation ✔ ✔
1D and 2D Polynomial
✔ ✔
Evaluation
1D Polar to Rectangular ✔ ✔
1D Rectangular to Polar ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-9 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 28
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Complex Number Arithmetic ✔ ✔
Find Polynomial Roots ✔ ✔
Scale 1D and 2D ✔ ✔
Curve Fitting
Cubic Spline Fit ✔
Exponential Fit ✔ ✔
Exponential Fit Interval ✔
Gauss Fit ✔
Gauss Fit Interval ✔
General Least Squares
✔
Linear Fit
General Polynomial Fit ✔ ✔
Goodness of Fit ✔
Linear Fit ✔ ✔
Linear Fit Interval ✔
Logarithm Fit ✔
Logarithm Fit Interval ✔
Nonlinear Fit ✔
Power Fit ✔
Power Fit Interval ✔
Remove Outliers ✔
Statistics
1D, 2D, and 3D ANOVA ✔
Chi-Square Distribution ✔
erf(x) and erfc(x) ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-10 ni.com
Page 29
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
F-Distribution ✔
Histogram ✔ ✔
Inverse Chi-Square
✔
Distribution
Inverse F-Distribution ✔
Inverse Normal Distribution ✔
Inverse T-Distribution ✔
Mean ✔ ✔
Median and Mode ✔ ✔
Moment about Mean ✔ ✔
Normal Distribution ✔
Polynomial Interpolation ✔
Root-Mean-Square (RMS) ✔ ✔
Spline Interpolant ✔
Spline Interpolation ✔
Standard Deviation ✔ ✔
T-Distribution ✔
Variance ✔
Special Functions
Airy ✔
Bessel 1st ✔
Bessel 2nd ✔
Beta ✔
Complimentary Gamma ✔
Cosine Integral ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-11 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 30
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Dawson’s Integral ✔
Dilogarithm ✔
Elliptic 1st ✔
Elliptic 2nd ✔
Exponential Integral ✔
Factorial ✔
Fresnel Integrals ✔
Gamma ✔
Gauss Hypergeometric ✔
Hyperbolic Cosine Integral ✔
Hyperbolic Sine Integral ✔
Incomplete Beta ✔
Incomplete Elliptic 1st ✔
Incomplete Elliptic 2nd ✔
Incomplete Gamma ✔
Jacobian Elliptic Function ✔
Kelvin 1st ✔
Kelvin 2nd ✔
Kummer ✔
Logarithm of Factorial ✔
Modified Bessel 1st ✔
Modified Bessel 2nd ✔
Parabolic Cylinder ✔
Psi ✔
Sine Integral ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-12 ni.com
Page 31

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-1. Analysis .NET Library Measurement Types included in
the Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis .NET Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Spherical Bessel 1st ✔
Spherical Bessel 2nd ✔
Stirling ✔
Struve ✔
Tricomi ✔
Zeta ✔
Tip For more information about analyzing or generating data with the Analysis class
library, refer to the Using the Measurement Studio Analysis .NET Library topic in the
NI Measurement Studio Help. For more information about the functionality included in the
Analysis class library, visit
ni.com/analysis and select Visual Basic, Visual Basic
.NET, C++, and C# with Measurement Studio.
Common
The Measurement Studio Common .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments namespace. The Common class library provides
a set of classes that facilitates the exchange of data between the acquisition,
analysis, and user interface portions of your application. The Common
class library includes the following features:
ComplexDouble data type. This data type represents a complex
•A
number of type
Double that is composed of a real part and an
imaginary part.
•A
DigitalWaveform data type. This data type represents a set of
digital states that are grouped by samples or signals.
•A
ComplexWaveform data type. This data type represents an analog
signal that varies over time and is composed of complex data values.
•An
AnalogWaveform data type. This data type represents an analog
signal that varies over time.
•A
DataConverter class that converts data from one data type to
another data type, such as converting an array of integers to an array of
doubles.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-13 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 32

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
•An EngineeringFormatInfo class that defines a custom formatter
to format numeric values as strings with engineering notation and
International System of Units (SI) prefixes and symbols.
•A
PrecisionWaveformTiming class that you can use to represent
the timing of an analog or digital waveform that is accurate to the
nearest 2-64 second.
•An
AnalogWaveformCollection class that contains a strongly
typed collection of
each channel and record combination. You can access these objects
through the 1D indexer or the 2D indexer.
Tip For more detailed information about the Common class library, refer to the
National Instruments section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Data Transfer
You can use the NetworkVariable class library or the DataSocket class
library to transfer live measurement data between applications over a
network. You can use NetworkVariable or DataSocket to exchange
different types of data between Measurement Studio, LabVIEW,
LabWindows/CVI, and other applications that support NI-Publish
Subscribe Protocol (
transferring data between these applications, and, in these cases,
NetworkVariable supersedes DataSocket. You can also use
NetworkVariable and DataSocket to exchange different types of data
between OLE for Process Control (
between Measurement Studio applications and OPC servers with
NetworkVariable requires LabVIEW DSC Run-Time System. Use
DataSocket to communicate directly with an OPC server.
AnalogWaveform<TData> objects; one object for
psp:). NetworkVariable is the preferred method for
opc:) servers. Exchanging data
Network Variable
The Measurement Studio Network Variable .NET class library includes
three namespaces:
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.WindowsForms, and
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.WebForms. You use the
Network Variable class library to transfer live measurement data between
applications and servers over the network. You use WindowsForms and
WebForms data sources to expose Network Variable data items that you
can bind to properties of a Windows Forms or a Web Forms control.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-14 ni.com
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable,
Page 33

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Use the features in the Network Variable class library to perform the
following operations:
• Exchange different types of data between Measurement Studio,
LabVIEW, LabWindows/CVI, and other applications that support
NI-Publish Subscribe Protocol (
opc:) servers. Exchanging data between Measurement Studio
(
psp:) and OLE for Process Control
applications and OPC servers requires LabVIEW DSC.
Note Measurement Studio and LabWindows/CVI refer to variables as network variables
and LabVIEW refers to variables as shared variables. However, you can read to and write
from Measurement Studio and LabWindows/CVI network variables with LabVIEW
shared variables.
• Use Windows Forms and Web Forms data sources to expose Network
Variable data items that you can bind to properties of a Windows
Forms or a Web Forms control.
•Use the
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.Browser
classes to discover network variables and processes.
•Use the
ServerProcess
ServerProcessInfo
NetworkVariable.ServerVariable
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.
ServerVariableInfo
NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.
, NationalInstruments.NetworkVariable.
, NationalInstruments.
, and
classes to explicitly create network variables.
• Use the Network Variable Browser dialog box to quickly locate and
select data items on other computers and servers. The Browser Dialog
is included in the WindowsForms class.
Tip For more detailed information about the Network Variable class library, refer to the
Using the Measurement Studio Network Variable .NET Library section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
DataSocket
The Measurement Studio DataSocket .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.Net namespace. Use the DataSocket class
library to transfer live measurement data over the Internet or an intranet,
between applications on the same computer, and to and from files. Use the
classes in the DataSocket class library to perform the following operations:
• Read and write data between different data sources and targets.
• Use a single, simple API to communicate with several types of servers,
including DataSocket Servers (
© National Instruments Corporation 2-15 Measurement Studio User Manual
dstp:), Web servers (http:), file
Page 34

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
transfer protocol servers (ftp:), file systems (file:), and OLE for
Process Control (
• Specify data sources and targets using a URL, the same way you access
Web pages in a Web browser.
• Use DataSocket Transfer Protocol (DSTP) to exchange different types
of data.
• Expose DataSocket data items as data sources that you can bind to
properties of a Windows Forms control.
• Interactively browse to quickly locate and select data items on other
computers and servers.
Tip For more detailed information about the DataSocket class library, refer to the Using
the Measurement Studio DataSocket .NET Library section in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
NI-488.2
The Measurement Studio NI-488.2 .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.NI4882 namespace. This class library is
included when you install the NI-488.2 driver. The NI-488.2 driver is
available at
of classes for communicating with GPIB instruments, controlling GPIB
devices, and acquiring GPIB status information. Use this library to design
code that communicates with and controls instruments on a GPIB interface.
Use the NI-488.2 class library to configure and communicate with GPIB
devices using the
ni.com/downloads. The NI-488.2 class library includes a set
opc:) servers.
Device and Board classes.
Tip For more information about the NI-488.2 class library, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio NI-488.2 .NET Library topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
For more information about GPIB visit
ni.com/gpib.
NI-DAQmx
The Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.DAQmx namespace. This class library is
included when you install the NI-DAQmx driver. The NI-DAQmx driver
is available at
communicate with and control NI data acquisition (DAQ) devices.
Note Some DAQ devices are not currently supported by the NI-DAQmx driver. Refer to
the NI-DAQ Readme for a complete listing of supported hardware.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-16 ni.com
ni.com/downloads. Use the NI-DAQmx class library to
Page 35

Tip For more information about the NI-DAQmx class library, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx.NET Library topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
For more information about DAQ, visit
NI-SCOPE
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Use the NI-DAQmx class library to perform the following types of tasks:
• Analog signal measurement
• Analog signal generation
• Digital I/O
• Counting and timing
• Pulse generation
• Signal switching
ni.com/dataacquisition.
The .NET class libraries for NI-SCOPE include .NET APIs for NI-Scope,
NI-TClk, and NI-ModInst instrument drivers. These class libraries provide
a .NET interface to the underlying driver API. You can use the .NET class
libraries to create and configure NI-SCOPE components programmatically
and at design time.
Tip For further information on NI-SCOPE .NET driver support and to download the
NI-SCOPE .NET class libraries, refer to NI-SCOPE .NET Driver Support at NI Developer
ni.com/devzone.
Zone,
NI-VISA
The Measurement Studio NI-VISA .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.VisaNS namespace. This class library is
included when you install the NI-VISA driver. The NI-VISA driver is
available at
of classes that provides a rich, object-oriented interface to the NI-VISA
driver. Use this library to quickly create bus-independent or bus-specific
instrument control applications.
The NI-VISA class library supports formatted I/O operations, locking,
event handling, and interface-specific extensions. With this class library
you can access the functionality available in NI-VISA for communicating
with message-based and register-based instruments using the following
interfaces:
•GPIB
• IEEE 1394
© National Instruments Corporation 2-17 Measurement Studio User Manual
ni.com/downloads. The NI-VISA class library includes a set
Page 36

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
•PXI
• Serial (RS-232 and RS-485)
•TCP/IP
•USB
• VXI
Tip For information about creating a Measurement Studio NI-VISA application using the
Instrument I/O Assistant, refer to the Creating an Instrument Control Application section
in Chapter 4, Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features or the Walkthrough:
Creating a Measurement Studio Instrument I/O Application in Chapter 5, Getting Started
with Measurement Studio. For more information about NI-VISA, visit
User Interface
The Measurement Studio user interface controls are in the Windows Forms
and Web Forms .NET class libraries. The following sections list the
functionality included with the Measurement Studio Windows Forms and
Web Forms controls.
Refer to Table 2-2 for the UI controls provided by Measurement Studio.
ni.com/visa.
Table 2-2. Measurement Studio User Interface Controls
User Interface Controls Windows Forms Web Forms
Waveform graph ✔ ✔
Scatter graph ✔ ✔
Digital waveform graph ✔ ✔
Complex graph ✔ ✔
Legend ✔ ✔
Knob ✔ ✔
Gauge ✔ ✔
Meter ✔ ✔
Slide ✔ ✔
Thermometer ✔ ✔
Tank ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-18 ni.com
Page 37

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Table 2-2. Measurement Studio User Interface Controls (Continued)
User Interface Controls Windows Forms Web Form s
Numeric edit ✔ ✔
Switch ✔ ✔
LED ✔ ✔
Property editor ✔
Array controls ✔
AutoRefresh control ✔
InstrumentControlStrip
control
Windows Forms Controls
The Windows Forms .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.UI.WindowsForms namespace. The Windows
Forms class library encapsulates the following Measurement Studio user
interface controls:
• Waveform graph
• Scatter graph
• Digital waveform graph
• Complex graph
•Legend
• Knob
•Gauge
• Meter
•Slide
• Thermometer
•Tank
• Numeric edit
• Switch
•LED
• Property editor
• Array controls
✔
© National Instruments Corporation 2-19 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 38

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Use this class library to add measurement-specific user interface controls
to your application. You can configure the controls programmatically at
design time, through the Properties window in the Windows Forms
Designer, or at run time with the property editor control. The following
sections describe each of the Measurement Studio Windows Forms user
interface controls.
Tip For more information about using the .NET user interface controls, refer to the Using
the Measurement Studio Windows Forms .NET Controls section in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
Waveform Graph and Scatter Graph Controls
Use the Measurement Studio waveform graph and scatter graph controls, as
shown in Figure 2-1, to display two-dimensional data on a Windows Forms
user interface. Use the waveform graph to display two-dimensional linear
data. You explicitly specify each value in one dimension and provide an
initial value and interval to implicitly specify the values in the other
dimension. Use the scatter graph to display two-dimensional linear or
nonlinear data: you explicitly specify each value in both dimensions.
Figure 2-1. Waveform Graph Windows Forms Control with Cursors and
Scatter Graph Windows Forms Control with XY Point Annotation; Both Graphs Have
Corresponding Legends
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-20 ni.com
Page 39

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
With the waveform graph and scatter graph controls and the classes that
interface with the controls, you can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot and chart arrays of double-precision floating point values, analog
waveforms, and complex waveforms.
• Configure a graph to contain multiple plots to show separate but
related data on the same graph.
• Draw lines or fills from a plot to an X value, Y value, or another plot.
• Specify plots in the scatter graph control as X and Y data. Specify plots
in the waveform graph control as X or Y data and optionally with date
and time scaling.
• Use the extensible plot and plot area drawing capabilities and events to
customize the graph appearance.
• Use plot data tooltips to display X and Y coordinates when a user
hovers the mouse over a data point.
• Create custom point and line styles for plots.
• Specify anti-aliased plots for plot lines.
• Calculate and display error bands.
Axis Operations
• Configure a graph to include multiple axes or independent ranges so
that plot data fits the graph plot area.
• Configure the axis modes to: fixed; autoscaling, including autoscaling
based on the visible data only; strip chart; or scope chart.
• Use logarithmic axes with configurable bases.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display origin lines.
• Display captions on the axis.
• Display grid lines.
• Position the axis to display on one or both sides of the graph’s plot
area.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions and origin lines.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-21 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 40

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Cursor Operations
• Use cursors to identify key points in plots and the plot area.
• Configure cursor snap modes to be fixed, floating, nearest point, or
to plot.
• Use cursor labels to display X and Y data coordinates in a customized
format that the cursor crosshair points to, and customize the text font
and colors of the label.
• Create custom point and line styles for cursors.
• Interactively move the cursor by clicking and dragging the vertical or
horizontal crosshair or the center of the cursor.
• Programmatically move the cursor to previous or next position or to a
specified coordinate.
Annotation Operations
• Configure text labels, arrows, and drawing shapes to annotate a point
anywhere in the plot area of the graph.
• Configure range area, text labels, and arrows to annotate a range in the
plot area of the graph.
• Show tooltips configured to display data or other custom text.
Additional Operations
• Pan and zoom interactively, as well as programatically.
• Copy the graph as a BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG image to the clipboard
or a file.
• Perform hit testing of mouse cursor coordinates.
• Bind a plot to a data source on the waveform graph.
Tip For more information about using the waveform and scatter graph controls, refer to
the Using the Measurement Studio Windows Forms Scatter and Waveform Graph .NET
Controls section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-22 ni.com
Page 41

Digital Waveform Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio digital waveform graph control, as shown in
Figure 2-2, to display
interface.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
DigitalWaveform data on a Windows Forms user
Figure 2-2. Digital Graph Windows Forms Control
With the digital waveform graph control and the classes that interface with
the control, you can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot digital waveform data. Data values can represent up to eight
different digital states.
• Configure plot labels on the y-axis.
• Configure plot templates to customize plots that are implicitly created
from plotted data.
• Specify anti-aliased digital plots.
• Expand and collapse signal plots interactively or programmatically.
• Display tooltips.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-23 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 42

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Waveform Sample and Signal State Operations
• Simultaneously display waveforms and signals or display signals only.
• Create custom waveform sample and signal state styles.
• Configure the appearance of sample and state labels.
• Create custom waveform sample and signal state labels.
Axis Operations
• Configure the axis modes to fixed, exact autoscaling, or loose
autoscaling.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display captions on the axis.
• Display grid lines.
• Position the axis to display on one or both sides of the graph’s plot
area.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions.
Additional Operations
• Display data in sample or time mode.
• Perform hit testing of mouse cursor coordinates.
• Pan with scroll bars.
• Configure the style and mode of scroll bars.
• Create custom scroll bars.
• Pan and zoom interactively and programmatically.
• Copy the graph as a BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG image to the clipboard
or a file.
Tip For more information about using the digital waveform graph control, refer to the
Using the Measurement Studio Windows Forms Digital Waveform Graph .NET Control
section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-24 ni.com
Page 43

Complex Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio complex graph control, as shown in
Figure 2-3, to display
interface. A
You can use a waveform graph to plot complex waveform data.
With the complex graph control and the classes that interface with the
control, you can perform the following operations:
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
ComplexDouble data on a Windows Forms user
ComplexDouble consists of a real part and an imaginary part.
Figure 2-3. Complex Graph Windows Forms Control
Plot Operations
• Plot and chart ComplexDouble data.
• Configure a graph to contain multiple plots to show separate but
related data on the same graph.
• Draw lines or fills from a plot to an X value, Y value, or another plot.
• Use the extensible plot and plot area drawing capabilities and events to
customize the graph appearance.
• Configure the plot to display arrows. The arrows indicate the direction
of the complex data.
• Create custom point and line styles for plots.
• Specify anti-aliased plots for plot lines.
• Calculate and display error bands.
• Display tooltips.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-25 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 44

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Axis Operations
• Configure a graph to include multiple axes or independent ranges so
that plot data fits the graph plot area.
• Configure the axis modes to: fixed; autoscaling, including autoscaling
based on the visible data only; strip chart; or scope chart.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display origin lines and grid lines.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions and origin lines.
• Position the axis to display on one or both sides of the graph’s plot
area.
• Display captions on the axis.
Cursor Operations
• Use cursors to identify key points in plots and the plot area.
• Configure cursor snap modes to be fixed, floating, nearest point, or to
plot.
• Use cursor labels to display X and Y data coordinates that the cursor
crosshair points to, and customize the text font and colors of the label.
• Create custom point and line styles for cursors.
• Configure the graph to display cursors that are used to determine the
real, imaginary, magnitude, and phase data coordinates of a point on
the plot area.
Annotation Operations
• Configure text labels, arrows, and drawing shapes to annotate a point
anywhere in the plot area of the graph.
• Configure range area, text labels, and arrows to annotate a range in the
plot area of the graph.
• Annotate points and ranges of real, imaginary, and magnitude values.
• Annotate and label a range of magnitude values for a particular phase.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-26 ni.com
Page 45

Tip For more information about using the complex graph control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Windows Forms Complex Graph .NET Control section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Legend Control
Tip For more information about using the legend control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Windows Forms Legend .NET Control section in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Additional Operations
• Pan and zoom interactively.
• Copy the graph as a BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG image to the clipboard
or a file.
Use the Measurement Studio legend control, as shown in Figure 2-1, to
display symbols and descriptions for a specific set of elements of another
object, such as the plots or cursors of a graph. When you associate the
legend control with another object, any changes you make to that object are
automatically reflected in the legend. For example, if you associate the
legend control with the plots of a graph, any changes you make in the plots
collection editor are automatically reflected in the legend.
Numeric Controls
Use the Measurement Studio numeric controls to display numerical
information, on a Windows Forms user interface, with the look of scientific
instruments. The numeric controls include a knob, gauge, meter, slide,
thermometer, and tank. The following sections describe operations
available with the controls and the classes that interface with them.
With all of the numeric controls and the classes that interface with them,
you can perform the following operations:
• Configure the scale to be linear or logarithmic and toggle the visibility
of the scale.
• Fill the scale and configure the range, color, dimensions, and style of
the fill.
• Connect to the Measurement Studio .NET numeric edit control so that
if you change the value of one control, it changes the value of the other
control.
• Customize the appearance of the control using 3D lab styles or classic
2D styles and change the color and length of ticks and labels.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-27 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 46

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Configure the format of value labels to engineering or date/time.
• Display tooltips reflecting the current value of the pointer.
• Interactively change the value of the control by clicking or dragging
and moving the pointer with the mouse.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Programmatically move the pointer to previous or next value.
• Perform hit testing of mouse cursor coordinates.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
Use the Measurement Studio knob, gauge, and meter controls, as shown in
Figure 2-4, to input and display numeric data on your user interface.
Figure 2-4. Knob, Gauge, and Meter Windows Forms Controls
With the knob, gauge, and meter controls and the classes that interface with
the controls, you can perform the following operations:
• Specify the start and sweep angle of the arc programmatically or from
the Properties window.
• Use automatic division spacing, custom divisions, and invert the scale.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-28 ni.com
Page 47

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Use the Measurement Studio slide, tank, and thermometer controls, as
shown in Figure 2-5, to input and display numeric data on your interface.
Figure 2-5. .NET Slide, Tank, and Thermometer Controls
With the slide, tank, and thermometer controls and the classes that interface
with them, you can perform the following operations:
• Fill to the minimum or maximum value of the scale.
• Position the scale horizontally with left, right, or both and position the
scale vertically with top, bottom, or both.
Tip For more information about using the Windows Forms knob, gauge, meter, slide,
tank, or thermometer controls, refer to the Knob, Gauge, Meter, Slide, Tank, or
Thermometer Class sections in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Numeric Edit Control
Use the Measurement Studio numeric edit control, as shown in Figure 2-6,
to display numeric values and to provide a way by which end users can edit
numeric values. Typically, you use a numeric edit control to input or
display double numerical data instead of using a Windows Forms TextBox
or NumericUpDown control.
Figure 2-6. Numeric Edit Windows Forms Control
© National Instruments Corporation 2-29 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 48

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
With the numeric edit control and the classes that interface with the control
you can perform the following operations:
• Use up and down buttons for easy incrementing and decrementing.
• Perform range checking.
• Set the minimum range value to negative infinity and the maximum
range value to positive infinity.
• Create custom formats or use built-in numeric formats including
generic, engineering, and simple double. You can use these numeric
formats with other Measurement Studio user interface controls, such
as the waveform graph and numeric pointer controls.
• Connect to a Measurement Studio numeric control so that if you
change the value of one control, it changes the value of the other
control.
• Set the coercion mode property to discrete or continuous values. This
property configures the control to allow entry or display of either a
discrete set of values or any value.
• Set the interaction mode to keyboard and mouse, keyboard only,
mouse only, or none.
Tip For more information about using the Windows Forms numeric edit control, refer to
the NumericEdit Class section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Switch and LED Controls
Use the Measurement Studio switch and LED controls as Boolean controls
on a Windows Forms user interface. You typically use a switch control, as
shown in Figure 2-7, to receive and control Boolean input on an application
user interface.
Figure 2-7. Switch Windows Forms Control in Vertical Toggle 3D Style
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-30 ni.com
Page 49

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
You typically use an LED control, as shown in Figure 2-8, to indicate a
Boolean value on an application user interface.
Figure 2-8. LED Windows Forms Control in Square 3D Style
With the switch and LED controls and the classes that interface with the
controls, you can perform the following operations:
• Receive notification before or after the state of the control changes.
• Configure how the control behaves when you click it with the mouse
or press the spacebar when the control has focus.
• Configure the appearance of the control.
• Make the control background transparent.
• Configure the LED control to blink while it is on or off and configure
the rate at which the LED control blinks.
Tip For more information about using the switch and LED controls, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Windows Forms Switch and LED .NET Controls section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-31 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 50

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Property Editor Control
Use the Measurement Studio property editor control, as shown in
Figure 2-9, to configure properties for Windows Forms controls at run
time.
Figure 2-9. Property Editor Windows Forms Control for the Knob Control
Scale Arc Property
With the property editor control and the classes that interface with the
control, you can perform the following operations:
• Edit any .NET type at run time, including collections.
• Edit expandable properties that represent nested properties of another
object, such as major divisions of an axis.
• Display custom editors and type converters for properties.
• Connect to a Windows Forms control so that if you change the value
of a property of the control, the Property Editor updates to reflect the
change.
• Configure the display mode as a visual representation of the value,
text-only, or both.
• Set the interaction mode to edit values or indicator.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-32 ni.com
Page 51

Tip For more information about using the property editor control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Property Editor Control topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Windows Forms Array Controls
You can create an array of Measurement Studio controls that behave as a
single unit. For example, you can use these array controls to visualize and
control ports of a digital line or values of an array. Measurement Studio
includes switch, LED, and numeric edit array controls. You can create
control arrays of other controls if those controls meet the constraints of the
generic type parameter
Switch and LED Array Controls
Use the Measurement Studio switch and LED array controls as an array of
Boolean controls on a Windows Forms user interface. You typically use a
switch array control, as shown in Figure 2-10, to control ports of a digital
line or values of an array. You typically use an LED array control, as shown
in Figure 2-10, to visualize ports of a digital line or values of an array.
TControl.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Figure 2-10. Switch and LED Array Controls
With the switch and LED array controls and the classes that interface with
the controls, you can perform the following operations:
• Set values by passing an array of data.
• Modify the number of controls displayed based on the length of the
specified values.
• Receive notification before or after the state of the control changes.
• Configure how the control behaves when you click it with the mouse
or press the spacebar when the control has focus.
• Configure the appearance of the control.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-33 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 52

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Make the control background transparent.
• Configure the LED controls to blink while they are on or off and
configure the rate at which the LED controls blink.
• Configure the layout of the control to be horizontal or vertical.
• Bind the value of the control to a data source.
• Mark an array of Boolean controls so that only one can be true at a
time.
Tip For more information about using the switch and LED array controls, refer to the
Using the Measurement Studio Control Array .NET Controls topic in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
Numeric Edit Array Control
Use the Measurement Studio numeric edit array control, as shown in
Figure 2-11 to control and visualize values of an array of
With the numeric edit array control and the classes that interface with the
control you can perform the following operations:
double values.
Figure 2-11. Numeric Edit Array control
• Set values by passing an array of data.
• Modify the number of controls displayed based on the length of the
array of values you specify.
• Use up and down buttons for easy incrementing and decrementing.
• Perform range checking.
• Set the minimum range value to negative infinity and the maximum
range value to positive infinity.
• Create custom formats or use built-in numeric formats including
generic, engineering, and simple double.
• Connect to a numeric control so that if you change the value of one
control, it changes the value of the other control.
• Set the coercion mode property to discrete or continuous values. This
property configures the control to allow entry or display of either a
discrete set of values or any value.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-34 ni.com
Page 53

• Set the interaction mode to keyboard and mouse, keyboard only,
mouse only, or none.
• Use the edit box to select text programmatically and to validate text
values.
• Configure the layout of the control to be horizontal or vertical.
• Bind the value of the control to a data source.
Tip For more information about using the numeric edit array control, refer to the Using
the Measurement Studio Control Array .NET Controls topic in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
InstrumentControlStrip Control
You can use the InstrumentControlStrip control as a toolbar for editing
property values of another control through the associated editors at run
time. For example, you can populate the InstrumentControlStrip with
ToolStripPropertyEditor items that edit property values of a waveform
graph through the associated editors at run time. The editor displayed by
the ToolStripPropertyEditor is the same editor that displays when you edit
the property at design time.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
© National Instruments Corporation 2-35 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 54

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Figure 2-12. InstrumentControlStrip Control
Tip
For more information about the InstrumentControlStrip control, refer to Using the
Measurement Studio Windows Forms Instrument Control Strip .NET Control topic in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-36 ni.com
Page 55

ASP.NET Web Forms Controls
The Measurement Studio ASP.NET user interface controls are in the Web
Forms .NET class library. The Web Forms .NET class library is in the
NationalInstruments.UI.WebForms namespace. The Web Forms
class library encapsulates the following Measurement Studio user interface
controls:
• Waveform graph
• Scatter graph
• Digital waveform graph
• Complex graph
•Legend
• Knob
•Gauge
• Meter
•Slide
• Thermometer
•Tank
• Numeric edit
• Switch
•LED
• AutoRefresh
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Note All Measurement Studio ASP.NET Web Forms controls for Visual Studio 2008 are
designed to work with ASP.NET AJAX controls. The Measurement Studio ASP.NET Web
Forms controls for Visual Studio 2005 are not designed to work with Microsoft ASP.NET
AJAX controls.
Use this class library to add measurement-specific user interface controls
to your Web application. You can configure the controls programmatically
at design time or through the Properties window in the Web Forms
Designer. The following sections describe each of the Measurement Studio
Web Forms user interface controls.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-37 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 56

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Waveform Graph and Scatter Graph Controls
Use the Measurement Studio waveform graph and scatter graph controls,
as shown in Figure 2-13, to display two-dimensional data on a Web-based
user interface. Use the waveform graph to display two-dimensional linear
data. You explicitly specify each value in one dimension and provide an
initial value and interval to implicitly specify the values in the other
dimension. Use the scatter graph to display two-dimensional linear or
nonlinear data: you explicitly specify each value in both dimensions.
Figure 2-13. Waveform Graph and Scatter Graph Web Forms Controls;
Both Graphs Have Corresponding Legends
With the waveform graph and scatter graph controls and the classes that
interface with the controls, you can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot and chart arrays of double-precision floating point values, analog
waveforms, and complex waveforms.
• Configure a graph to contain multiple plots to show separate but
related data on the same graph.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-38 ni.com
Page 57

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Draw lines or fills from a plot to an X value, Y value, or another plot.
• Specify plots in the scatter graph control as X and Y data. Specify plots
in the waveform graph control as X or Y data and optionally with date
and time scaling.
• Use the extensible plot and plot area drawing capabilities and events to
customize the graph appearance.
• Create custom point and line styles for plots.
• Specify anti-aliased plots for plot lines.
• Calculate and display error bands.
• Configure plot to specify how data is saved and restored across HTTP
requests.
Axis Operations
• Configure a graph to include multiple axes or independent ranges so
that plot data fits the graph plot area.
• Configure the axis modes to: fixed; autoscaling, including autoscaling
based on the visible data only; strip chart; or scope chart.
• Use logarithmic axes with configurable bases.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions and origin lines.
Cursor Operations
• Use cursors to identify key points in plots and the plot area.
• Configure cursor snap modes to be floating, nearest point, or to plot.
• Use cursor labels to display X and Y data coordinates in a customized
format that the cursor crosshair points to, and customize the text font
and colors of the label.
• Create custom point and line styles for cursors.
• Interactively move the cursor by clicking and dragging the vertical or
horizontal crosshair or the center of the cursor.
• Programmatically move the cursor to previous or next position or to a
specified coordinate.
Annotation Operations
• Configure text labels, arrows, and drawing shapes to annotate a point
anywhere in the plot area of the graph.
• Configure range area, text labels, and arrows to annotate a range in the
plot area of the graph.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-39 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 58

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Additional Operations
• Zoom interactively as well as programatically.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
Tip For more information about using the waveform and scatter graph controls, refer to
the Using the Measurement Studio Web Forms Scatter and Waveform Graph .NET Controls
section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Digital Waveform Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio digital waveform graph control, as shown in
Figure 2-14, to display
application.
DigitalWaveform data in an ASP.NET Web
Figure 2-14. Digital Waveform Graph Web Forms Control
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-40 ni.com
Page 59

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
With the digital waveform graph control and the classes that interface with
the control, you can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot digital waveform data, including digital signal state data and
timing information.
• Configure plot labels on the y-axis.
• Configure plot templates to customize plots that are implicitly created
from plotted data.
• Specify anti-aliased digital plots.
• Expand and collapse signal plots interactively as well as
programmatically.
Waveform Sample and Signal State Operations
• Simultaneously display waveforms and signals or display signals only.
• Create custom waveform sample and signal state styles.
• Configure the appearance of sample and state labels.
• Create custom waveform sample and signal state labels.
Axis Operations
• Configure the axis modes to fixed, exact autoscaling, or loose
autoscaling.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display captions on the axis and grid lines.
• Position the axis to display on one or both sides of the graph’s plot
area.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions.
Additional Operations
• Display data in sample or time mode.
• Configure the style and mode of scroll bars.
• Create custom scroll bars.
• Zoom interactively as well as programmatically.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-41 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 60
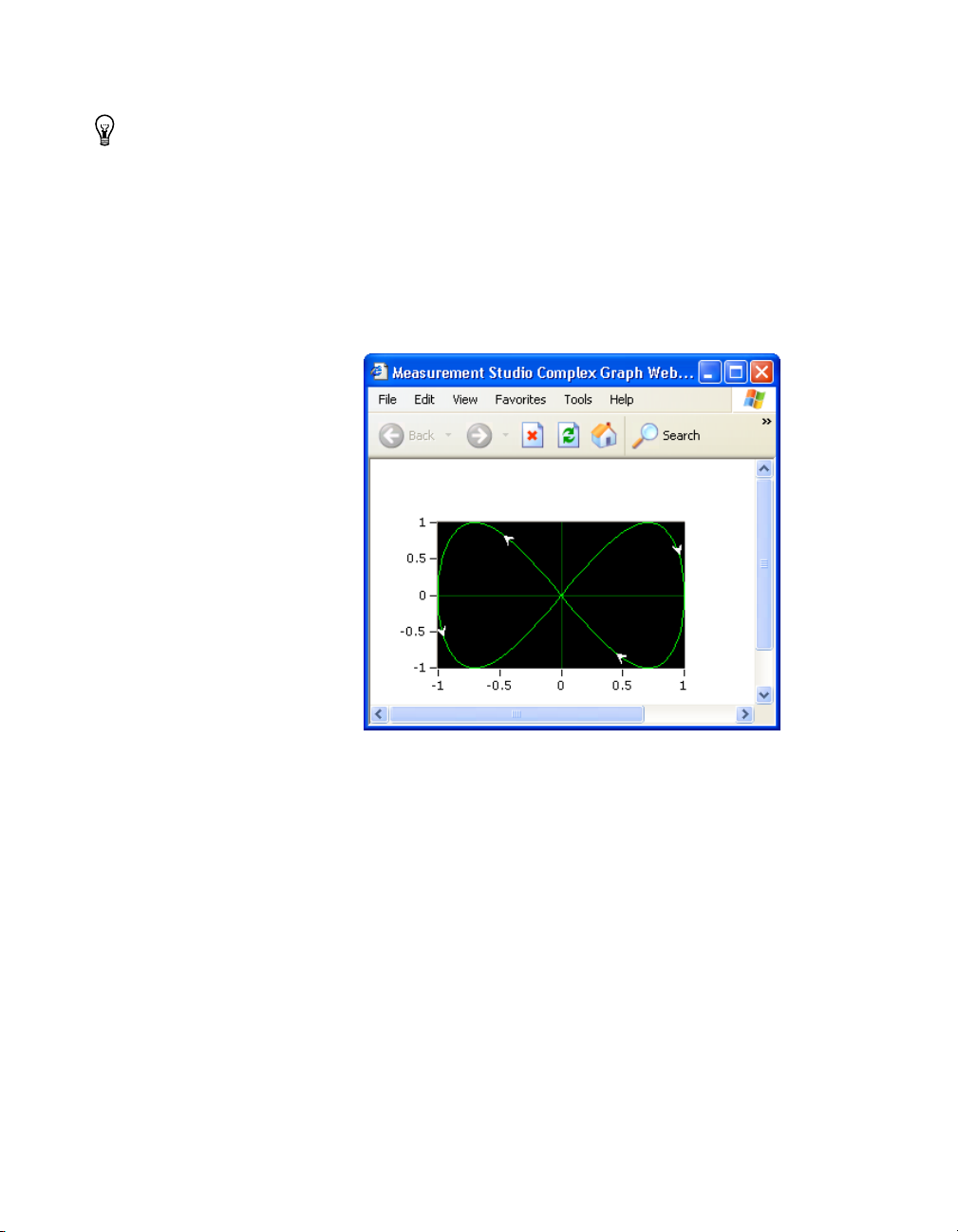
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Tip For more information about using the digital waveform graph control, refer to the
Using the Measurement Studio Web Forms Digital Waveform Graph .NET Control section
in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Complex Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio complex graph control, as shown in
Figure 2-15, to display
application. A
part. You can use a waveform graph to plot complex waveform data.
ComplexDouble consists of a real part and an imaginary
ComplexDouble data on a ASP.NET Web
Figure 2-15. Complex Graph Web Forms Control
With the complex graph control and the classes that interface with the
control, you can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot and chart ComplexDouble data.
• Configure a graph to contain multiple plots to show separate but
related data on the same graph.
• Draw lines or fills from a plot to an X value, Y value, or another plot.
• Use the extensible plot and plot area drawing capabilities and events to
customize the graph appearance.
• Configure the plot to display arrows. The arrows indicate the direction
of the complex data.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-42 ni.com
Page 61

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Create custom point and line styles for plots.
• Specify anti-aliased plots for plot lines.
• Calculate and display error bands.
• Configure plot to specify how data is saved and restored across HTTP
requests.
Axis Operations
• Configure a graph to include multiple axes or independent ranges so
that plot data fits the graph plot area.
• Configure the axis modes to: fixed; autoscaling, including autoscaling
based on the visible data only; strip chart; or scope chart.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display origin lines, captions on the axis, and grid lines.
• Position the axis to display on one or both sides of the graph’s plot
area.
• Configure major, minor, and custom divisions and origin lines.
Cursor Operations
• Use cursors to identify key points in plots and the plot area.
• Configure cursor snap modes to be floating, nearest point, or to plot.
• Use cursor labels to display real, imaginary, magnitude, or phase data
that the cursor crosshair points to, and customize the text font and
colors of the label.
• Create custom point and line styles for cursors.
• Interactively move the cursor by clicking and dragging the vertical or
horizontal crosshair or the center of the cursor.
• Programmatically move the cursor to previous or next position or to a
specified coordinate.
Annotation Operations
• Configure text labels, arrows, and drawing shapes to annotate a point
anywhere in the plot area of the graph.
• Configure range area, text labels, and arrows to annotate a range in the
plot area of the graph.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-43 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 62

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Annotate and label a magnitude value.
• Annotate and label a range of magnitude values for a particular phase.
Additional Operations
• Zoom interactively as well as programmatically.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
Tip For more information about using the complex graph control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Web Forms Complex Graph .NET Control section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Legend Control
Use the Measurement Studio legend control, as shown in Figure 2-13, to
display symbols and descriptions for a specific set of elements of another
object, such as the plots or cursors of a graph. When you associate the
legend control with another object, any changes you make to that object are
automatically reflected in the legend. For example, if you associate the
legend control with the plots of a graph, any changes you make in the plots
collection editor are automatically reflected in the legend.
Tip For more information about using the legend control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Web Forms Legend .NET Control section in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
Numeric Controls
Use the Measurement Studio numeric controls to display numerical
information in an ASP.NET Web application with the look of scientific
instruments. The numeric controls include a knob, gauge, meter, slide,
thermometer, and tank. The following sections describe operations
available with the controls and the classes that interface with them.
With all of the numeric controls and the classes that interface with them,
you can perform the following operations:
• Configure the scale to be linear or logarithmic and toggle the visibility
of the scale.
• Fill the scale and configure the range, color, dimensions, and style of
the fill.
• Connect to a Measurement Studio .NET numeric edit control so that if
you change the value of one control, it changes the value of the other
control.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-44 ni.com
Page 63

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Customize the appearance of the control using 3D lab styles or classic
2D styles and change the color and length of ticks and labels.
• Configure the format of value labels to engineering or date/time.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
• Interactively change the range of an axis and invert the axis at run time
by clicking on the axis end labels.
• Display tooltips reflecting the current value of the pointer.
• Interactively change the value of the control by clicking the pointer
with the mouse.
• Programmatically move the pointer to previous or next value.
Use the Measurement Studio knob, gauge, and meter controls, as shown in
Figure 2-16, to input and display numeric data on your user interface.
Figure 2-16. Knob, Gauge, and Meter Web Forms Controls
With the knob, gauge, and meter controls and the classes that interface with
the controls, you can perform the following operations:
• Specify the start and sweep angle of the arc programmatically or from
the Properties window.
• Use automatic division spacing, custom divisions, and invert the scale.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-45 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 64

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Use the Measurement Studio slide, tank, and thermometer controls, as
shown in Figure 2-17, to input and display numeric data on your interface.
Figure 2-17. Slide, Tank, and Thermometer Web Forms Controls
With the slide, tank, and thermometer controls and the classes that interface
with them, you can perform the following operations:
• Fill to the minimum or maximum value of the scale.
• Position the scale horizontally with left, right, or both and position the
scale vertically with top, bottom, or both.
Tip For more information about using the Web Forms knob, gauge, meter, slide, tank, or
thermometer controls, refer to the Knob, Gauge, Meter, Slide, Ta nk , or Thermometer Class
sections in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-46 ni.com
Page 65

Numeric Edit Control
Use the Measurement Studio numeric edit control, as shown in
Figure 2-18, to display numeric values and to provide a way by which end
users can edit numeric values. Typically, you use a numeric edit control to
input or display double numerical data instead of using a Web Forms
TextBox control.
With the numeric edit control and the classes that interface with the control
you can perform the following operations:
• Perform range checking.
• Set the minimum range value to negative infinity and the maximum
• Create custom formats or use built-in numeric formats including
• Connect to a Measurement Studio numeric control so that if you
• Set the coercion mode property to discrete or continuous values. This
• Validate and format data without posting back to the Web server.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Figure 2-18. Numeric Edit Web Forms Control
range value to positive infinity.
generic, engineering, and simple double. You can use these numeric
formats with other Measurement Studio user interface controls, such
as the waveform graph and numeric pointer controls.
change the value of one control, it changes the value of the other
control.
property configures the control to allow entry or display of either a
discrete set of values or any value.
Tip For more information about using the Web Forms numeric edit control, refer to the
NumericEdit Class section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
© National Instruments Corporation 2-47 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 66

Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
Switch and LED Controls
Use the Measurement Studio switch and LED controls as Boolean controls
in an ASP.NET Web application. You typically use a switch control to
receive and control Boolean input in an ASP.NET Web application. You
typically use an LED control to indicate a Boolean value on an ASP.NET
Web application. The switch and LED controls are shown in Figure 2-19.
Figure 2-19. Switch Web Forms Control in Vertical Toggle 3D Style and
LED Web Forms Control in Square 3D Style
With the switch and LED controls and the classes that interface with the
controls, you can perform the following operations:
• Receive notification before or after the state of the control changes.
• Specify the image format of the control as BMP, GIF, JPEG, or PNG.
• Configure the appearance of the control.
• Configure the LED control to blink while it is on or off and configure
the rate at which the LED control blinks.
Tip For more information about using the switch and LED controls, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Web Forms Switch and LED .NET Controls section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 2-48 ni.com
Page 67

AutoRefresh Control
Use the AutoRefresh control to update a Web control or a group of Web
controls on the client at a specified interval.
The AutoRefresh control uses the ASP.NET client callback architecture to
update a control or a group of controls at a specified interval. The
AutoRefresh control sets up a timer inside the browser using Javascript.
When the timer elapses, the AutoRefresh updates the controls in the
AutoRefresh group. For down-level browsers, the controls update when the
page posts back to the server. If the client browser supports client callbacks,
the client-side script rendered by the AutoRefresh control uses a client
callback to update the associated controls on the client without posting the
page back to the server.
Note The AutoRefresh control is designed to work with the ASP.NET AJAX UpdatePanel
and Timer controls in Visual Studio 2008.
AutoRefresh Callback
This feature provides a mechanism for updating the
RefreshManager.Enabled and AutoRefresh.Interval properties
for
allowing you to turn off the AutoRefresh or change the Interval during an
asynchronous HTTP request without causing a postback.
Chapter 2 Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
AutoRefresh from within the AutoRefresh.Refresh callback,
© National Instruments Corporation 2-49 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 68

3
Measurement Studio Visual C++
Class Libraries
This chapter provides overview information about the Visual C++ class
libraries that are available with Measurement Studio. Measurement Studio
Visual C++ support for Visual Studio .NET 2003 and Visual Studio 2005 is
the same, except where noted. Refer to the Using the Measurement Studio
Visual C++ Class Libraries section of the NI Measurement Studio Help for
detailed information about these libraries.
Note Measurement Studio 8.5 support for Visual Studio 2008 does not include Visual
C++ class libraries.
Measurement Studio Visual C++ Class Library Overview
Measurement Studio provides libraries of MFC-based classes that you can
use to develop complete measurement and automation applications in
Visual C++.
Measurement Studio includes the following Visual C++ class libraries:
• 3D Graph
• Analysis
• Common
• DataSocket
• Microsoft Excel Interface
• Microsoft Word Interface
• NI-488.2
•NI-DAQmx
• NI-Reports
•NI-VISA
• User Interface
• Utility
© National Instruments Corporation 3-1 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 69

Chapter 3
Refer to the following sections for information about each Measurement
Studio Visual C++ class library.
ActiveX Controls in Visual C++
ActiveX controls are specialized COM servers that implement a specific set
of interfaces. The Measurement Studio Visual C++ button, graph, knob,
numeric edit, slide, and 3D graph are ActiveX controls. Measurement
Studio includes classes that provide native C++ interfaces to the ActiveX
controls. For example, the
CWGraph ActiveX graph control.
The Measurement Studio classes that provide interfaces to the
Measurement Studio ActiveX controls simplify using ActiveX controls in
Visual C++ interfaces and programs. The features that simplify this process
include overloaded functions, the ability to call the control from any thread,
and automatic data type translations.
3D Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX 3D graph control, as shown in
Figure 3-1, to plot three-dimensional data. The 3D graph is included only
in the Measurement Studio Enterprise and Professional packages.
CNiGraph class provides an interface to the
Figure 3-1. ActiveX 3D Graph Control
With the Measurement Studio ActiveX 3D graph control and the classes
that interface with the control, you can perform the following operations:
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-2 ni.com
Page 70

Plot Operations
• Plot three-dimensional data, including curves and surfaces.
• Use multiple plot styles—point-line, line-point, hidden-line, contour,
• Create multiple plots with individual properties, such as name, line and
• Configure the control to render directly to OpenGL-enabled hardware
• Bind the control to a DataSocket Server to enable automatic read and
Additional Operations
• Configure the axes using customizable ticks, labels, value pairs, and
• Use legends and plane projections.
• Use cartesian, cylindrical, and spherical coordinate systems.
• Customize the control using color maps, transparency, and lighting.
• Display in orthographic and perspective views.
• Use built-in format styles for labels including scientific, symbolic
• Rotate, pan, and zoom interactively.
Chapter 3
surface, surface-line, surface-contour, and surface-normal.
point style, width, and base value.
accelerator cards.
write functionality.
captions.
engineering, scaling, time, and date.
Tip For information about easily creating graphs with the 3D graph control library, refer
to the 3D Graph Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
Analysis
The Analysis class library includes a set of classes that provides various
digital signal processing, signal filtering, signal generation, peak detection,
and other general mathematical functionality. Use this library to analyze
acquired data or to generate data.
The functionality included in the Analysis library varies based on the
Measurement Studio package you purchased. Refer to the following
sections for information about the Standard, Professional, and Enterprise
Analysis class libraries.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-3 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 71

Chapter 3
Standard Analysis
The Standard Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement Studio
Standard Edition, includes the sawtooth, sine, square, triangle, and basic
function wave generators.
Professional Analysis
The Professional Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement
Studio Professional Edition, includes the Standard Analysis functionality
as well as the following functionality:
• Bessel, Chebyshev, Inverse Chebyshev, Windowed, Kaiser, and
• Signal processing functions such as convolution, deconvolution,
• FFT, Inverse FFT, Real FFT, Fast Hartley, Inverse Fast Hartley, Fast
• Linear algebra functions such as determinant, check positive
• Scaled and unscaled windowing classes
• Common statistical functions such as mean, median, mode, and
• Exponential, linear, and polynomial curve fitting functions
• Signal generation functions
Elliptic Low, High, Bandpass, and Bandstop filters
correlation, decimation, integration, and differentiation
Hilbert, Inverse Fast Hilbert, DST, Inverse DST, DCT, and Inverse
DCT transformations
definiteness, calculate dot product, and other various matrix methods
variance
Enterprise Analysis
The Enterprise Analysis class library, which ships with Measurement
Studio Enterprise Edition, includes the Standard and Professional Analysis
functionality as well as the following advanced functionality:
• EquiRipple filters
• Linear algebra functions such as forward and back substitution,
LU factorization, Cholesky factorization, Schur decomposition, and
Hessenberg decomposition
• Probability and analysis of variance
• Sinc, impulse, pulse, ramp, and chirp patterns
• General least squares fit, power fit, log fit, Gauss Fit, cubic spline fit,
and interpolation functions
• Special functions
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-4 ni.com
Page 72

Refer to Table 3-1 to determine the type of measurements available in the
Professional and Enterprise Analysis Visual C++ libraries.
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Measurements
AC and DC Estimator ✔
Chapter 3
Amplitude and Phase
✔
Spectrum
Auto Power Spectrum ✔
Cross Power Spectrum ✔
Harmonic Analyzer ✔
Impulse Response Function ✔ ✔
Network Functions (avg) ✔ ✔
Power and Frequency Estimate ✔
Scaled Time Domain Window ✔
Spectrum Unit Conversion ✔
Transfer Function ✔
Signal Generation
Arbitrary Wave ✔ ✔
Chirp Wave ✔
Gaussian White Noise ✔ ✔
Impulse Pattern ✔
Pulse Pattern ✔
Ramp Pattern ✔
Sawtooth Wave ✔
Sinc Pattern ✔
Sine Pattern ✔
Sine Wave ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 3-5 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 73

Chapter 3
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Square Wave ✔ ✔
Triangle Wave ✔ ✔
Uniform White Noise ✔ ✔
Windowing
Blackman Window ✔ ✔
Blackman-Harris Window ✔ ✔
Blackman-Nuttall Window ✔ ✔
Cosine Tapered Window ✔ ✔
Dolph-Chebyshev Window ✔ ✔
Exact Blackman Window ✔ ✔
Exponential Window ✔ ✔
Flat Top Window ✔ ✔
Force Window ✔ ✔
Gauss Window ✔ ✔
General Cosine Window ✔ ✔
Hamming Window ✔ ✔
Hanning Window ✔ ✔
Kaiser-Bessel Window ✔ ✔
Scaled Time Domain Windows ✔ ✔
Symmetric Time Domain
✔ ✔
Windows
Triangle Window ✔ ✔
Filters
Bessel ✔ ✔
Butterworth ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-6 ni.com
Page 74
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Cascade ✔ ✔
Chebyshev ✔ ✔
Elliptic ✔ ✔
Equiripple ✔
FIR ✔ ✔
FIR Windowed ✔ ✔
IIR Cascade ✔ ✔
IIR ✔ ✔
Inverse Chebyshev ✔ ✔
Kaiser ✔ ✔
Signal Processing
Chapter 3
Autocorrelation ✔ ✔
Convolution ✔ ✔
Cross Power ✔ ✔
Cross Correlation ✔ ✔
Decimate ✔ ✔
Deconvolution ✔ ✔
Derivative x(t) ✔ ✔
Discrete Cosine Transform ✔ ✔
Discrete Sine Transform ✔ ✔
Fast Hilbert Transform ✔ ✔
Fast Hartley Transform ✔ ✔
Integral x(t) ✔ ✔
Inverse Real and Complex Fast
✔ ✔
Fourier Transform (FFT)
© National Instruments Corporation 3-7 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 75

Chapter 3
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Inverse Fast Hilbert Transform ✔ ✔
Inverse Fast Hartley Transform ✔ ✔
Peak Detection ✔ ✔
Power Spectrum ✔ ✔
Pulse Parameters ✔ ✔
Real and Complex FFT ✔ ✔
Threshold Peak Detector ✔ ✔
Unwrap Phase ✔ ✔
Linear Algebra
Back Transform Eigen Vectors ✔
Backward Substitution ✔
Cholesky Factorization ✔
Complex Back Transform
✔
Eigen Vectors
Complex Cholesky
✔
Factorization
Complex Determinant ✔ ✔
Complex Dot Product ✔ ✔
Complex Eigen Vectors and
✔
Eigen Values
Complex General Eigen AB ✔
Complex Hessenberg
✔
Decomposition
Complex Inverse Matrix ✔
Complex Linear Equations ✔
Complex LU Factorization ✔
Complex Matrix Balance ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-8 ni.com
Page 76

Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Chapter 3
Complex Matrix Condition
✔ ✔
Number
Complex Matrix Norm ✔ ✔
Complex Matrix Rank ✔ ✔
Complex Outer Product ✔ ✔
Complex Pseudo Inverse
✔ ✔
Matrix
Complex QR Factorization ✔
Complex QR Factorization
✔
with Pivot Matrix
Complex QR Factorization
✔
with Pivot Vector
Complex QZ Decomposition ✔
Complex Schur
✔
Decomposition
Complex Solve Linear
✔
Equations (Multiple Right
Hand)
Complex Solve Linear
✔
Equations (Single Right Hand)
Complex SVD Factorization ✔
Complex Vector Norm ✔
Determinant ✔ ✔
Dot Product ✔ ✔
Forward Substitution ✔
General Eigen AB ✔
Hessenberg Decomposition ✔
Inverse Matrix ✔ ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 3-9 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 77

Chapter 3
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Linear Equations ✔
LU Factorization ✔
Matrix Balance ✔
Matrix Condition Number ✔ ✔
Matrix Multiplication ✔ ✔
Matrix Norm ✔ ✔
Matrix Rank ✔ ✔
Outer Product ✔ ✔
Pseudo Inverse Matrix ✔ ✔
QR Factorization ✔
QR Factorization with Pivot
✔
Matrix
QR Factorization with Pivot
✔
Vector
QZ Decomposition ✔
Schur Decomposition ✔
Solve Linear Equations
✔
(Multiple Right Hand)
Solve Linear Equations
✔
(Single Right Hand)
Special Matrix ✔ ✔
SVD Factorization ✔
Test Positive Definite Matrix ✔ ✔
Trace ✔ ✔
Transpose ✔ ✔
Array and Numeric Operations
1D and 2D Array Arithmetic ✔ ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-10 ni.com
Page 78

Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
1D and 2D Linear Evaluation ✔ ✔
Chapter 3
1D and 2D Polynomial
✔ ✔
Evaluation
1D Polar to Rectangular ✔ ✔
1D Rectangular to Polar ✔ ✔
Complex Number Arithmetic ✔ ✔
Find Polynomial Roots ✔ ✔
Scale 1D and 2D ✔ ✔
Curve Fitting
Cubic Spline Fit ✔
Exponential Fit ✔ ✔
Exponential Fit Interval ✔
Gauss Fit ✔
Gauss Fit Interval ✔
General Least Squares
✔
Linear Fit
General Polynomial Fit ✔ ✔
Goodness of Fit ✔
Linear Fit ✔ ✔
Linear Fit Interval ✔
Logarithm Fit ✔
Logarithm Fit Interval ✔
Nonlinear Fit ✔
Polynomial Fit ✔ ✔
Power Fit ✔
Power Fit Interval ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 3-11 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 79

Chapter 3
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Remove Outliers ✔
Statistics
1D, 2D, and 3D ANOVA ✔
Chi-Square Distribution ✔
erf(x) and erfc(x) ✔
F-Distribution ✔
Histogram ✔ ✔
Inverse Chi-Square
✔
Distribution
Inverse F-Distribution ✔
Inverse Normal Distribution ✔
Inverse T-Distribution ✔
Mean ✔ ✔
Median and Mode ✔ ✔
Moment about Mean ✔ ✔
Normal Distribution ✔
Polynomial Interpolation ✔
Root-Mean-Square (RMS) ✔ ✔
Spline Interpolant ✔
Spline Interpolation ✔
Standard Deviation ✔ ✔
T-Distribution ✔
Variance ✔
Special Functions
Airy ✔
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-12 ni.com
Page 80

Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Bessel 1st ✔
Bessel 2nd ✔
Beta ✔
Complimentary Gamma ✔
Cosine Integral ✔
Dawson’s Integral ✔
Dilogarithm ✔
Elliptic 1st ✔
Elliptic 2nd ✔
Exponential Integral ✔
Factorial ✔
Chapter 3
Fresnel Integrals ✔
Gamma ✔
Gauss HyperGeometric ✔
Hyperbolic Cosine Integral ✔
Hyperbolic Sine Integral ✔
Incomplete Beta ✔
Incomplete Elliptic 1st ✔
Incomplete Elliptic 2nd ✔
Incomplete Gamma ✔
Jacobian Elliptic Function ✔
Kelvin 1st ✔
Kelvin 2nd ✔
Kummer ✔
Logarithm of Factorial ✔
© National Instruments Corporation 3-13 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 81

Chapter 3
Table 3-1. Analysis Visual C++ Library Measurement Types Included in the
Professional and Enterprise Packages (Continued)
Analysis Visual C++ Library Professional Package Enterprise Package
Modified Bessel 1st ✔
Modified Bessel 2nd ✔
Parabolic Cylinder ✔
Psi ✔
Sine Integral ✔
Spherical Bessel 1st ✔
Spherical Bessel 2nd ✔
Stirling ✔
Struve ✔
Tricomi ✔
Zeta ✔
Tip For more information about analyzing or generating data with the Analysis class
library, refer to the Analysis Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the
NI Measurement Studio Help. For more information about the functionality included in the
Analysis class library, visit
ni.com/analysis and select Visual Basic, Visual Basic
.NET, C++, and C# with Measurement Studio.
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-14 ni.com
Page 82

Common
Chapter 3
The Measurement Studio Common Visual C++ class library provides data
types and classes that other Measurement Studio Visual C++ class libraries
use. The classes that are implemented natively in Visual C++ include the
CNiVector and CNiMatrix classes.
The Common class library includes the following data types:
•
CNiScalarVector—Implements a vector object that contains scalar
numbers.
•
CNiScalarMatrix—Implements a matrix object that contains scalar
numbers.
•
CNiString—Extends the MFC CString class with streaming
operators for a variety of data types and with various other string
manipulation functions.
•
CNiScalarVector—Implements a vector object that contains scalar
numbers.
•
CNiVariant—Extends the MFC COleVariant class with additional
constructors and assignment operators for CNiComplex-, CNiVector-,
and CNiMatrix-derived objects and with cast operators to convert
CNiVariant objects to a variety of other object types.
CNiException—Extends the MFC CException class and serves as
•
the base class for many Measurement Studio exceptions.
•
CNiRegKey—Encapsulates the interface to the Windows registry. Use
this class and related classes to open and create keys, get keys, and get
values associated with those keys.
Tip For more detailed information about the Common class library, refer to the Common
Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
DataSocket
Use the Measurement Studio DataSocket Visual C++ class library to
transfer live measurement data over the Internet or an intranet, between
applications on the same computer, and to and from files. Use the classes
in the DataSocket Visual C++ class library to perform the following
operations:
• Read and write data between different data sources and targets.
• Use a single, simple API to communicate with several types of servers,
including DataSocket Servers (
© National Instruments Corporation 3-15 Measurement Studio User Manual
dstp:), Web servers (http:), file
Page 83

Chapter 3
transfer protocol servers (ftp:), file systems (file:), and OLE for
Process Control (
• Specify data sources and targets using a URL, the same way you access
Web pages in a Web browser.
• Use DataSocket Transfer Protocol (DSTP) to exchange different types
of data.
• Interactively browse to quickly locate and select data items on other
computers and servers.
Tip For more information about using DataSocket, refer to the DataSocket Visual C++
Class Library Overview topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Microsoft Excel Interface
Use the Measurement Studio Excel Visual C++ class library to
automatically create Excel spreadsheets and charts from within
measurement and automation applications. Use the Microsoft Excel
Interface class library to perform offline processing of the measurement
and automation data you acquire and analyze using other Measurement
Studio Visual C++ classes. This class library is included only in the
Measurement Studio Enterprise package.
opc:) servers.
Tip For more information about using the Measurement Studio Excel Visual C++
class library to create applications that present data in Microsoft Excel format, refer to
the Microsoft Excel Interface Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Microsoft Word Interface
Use the Measurement Studio Microsoft Word Interface Visual C++ class
library to automatically create Word documents from within measurement
and automation applications. Use the Microsoft Word Interface class
library to perform offline processing of the measurement and automation
data you acquire and analyze using other Measurement Studio Visual C++
classes. This class library is included only in the Measurement Studio
Enterprise package.
Tip For more information about using the Measurement Studio Word Visual C++ class
library to create applications that present data in Microsoft Word, refer to the Microsoft
Word Interface Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-16 ni.com
Page 84

NI-488.2
Tip For information about easily creating a Measurement Studio NI-488.2 application
using the Instrument I/O Assistant, refer to the Creating an Instrument Control Application
section of Chapter 4, Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features. You can create
Measurement Studio NI-488.2 applications with the Instrument I/O Assistant in Visual
Studio .NET 2003 only. For more information about GPIB, visit
NI-DAQmx
Chapter 3
Use the Measurement Studio NI-488.2 Visual C++ class library to
communicate with and control instruments on a GPIB interface. This class
library is included when you install the NI-488.2 driver. Use this class
library to configure and communicate with GPIB devices using the
CNi4882Device and CNi4882Board classes.
You can use the NI-488.2 class library to create programs that interface
with a device that is using GPIB and programs that interface with the GPIB
device directly.
ni.com/gpib.
Use the Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Visual C++ class library to
communicate with and control an NI data acquisition (DAQ) device. This
class library is included when you install the NI-DAQmx driver.
Note Some DAQ devices are not currently supported by the NI-DAQmx driver. Refer to
the NI-DAQ Readme for a complete listing of supported hardware.
Use the NI-DAQmx class library to perform the following types of tasks:
• Analog signal measurement
• Analog signal generation
• Digital I/O
• Counting and timing
• Pulse generation
• Signal switching
Tip For information about easily creating an NI-DAQmx application using the DAQ
Assistant, refer to the Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application section of
Chapter 4, Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features, or the Walkthrough:
Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application section of Chapter 5, Getting
Started with Measurement Studio. For more information about DAQ, visit
© National Instruments Corporation 3-17 Measurement Studio User Manual
ni.com/daq.
Page 85

Chapter 3
NI-Reports
Tip For information about generating printed reports using the NI-Reports class library,
refer to the NI-Reports Visual C++ Class Library Overview topic in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
NI-VISA
Use the Measurement Studio NI-Reports Visual C++ class library to
generate printed reports from Measurement Studio Visual C++
applications. This class library is included only in the Measurement Studio
Enterprise package.
The Measurement Studio NI-VISA Visual C++ class library includes
Visual C++ classes that provide an object-oriented interface to the
NI-VISA driver. This class library is included when you install the
NI-VISA driver. Use the NI-VISA class library to quickly create
bus-independent and bus-specific instrument control applications.
The NI-VISA class library supports I/O operations, locking, event
handling, and interface-specific extensions. With this class library, you can
access the functionality available in NI-VISA for communicating with
message-based and register-based instruments using the following
interfaces:
•GPIB
•PXI
• Serial (RS-232 and RS-485)
•TCP/IP
•USB
• VXI
Tip For information about easily creating a Measurement Studio NI-VISA application
using the Instrument I/O Assistant, refer to the Creating an Instrument Control Application
section of Chapter 4, Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features, or the
Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio Instrument I/O Application section of
Chapter 5, and Getting Started with Measurement Studio. For more information about
NI-VISA, visit
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-18 ni.com
ni.com/visa.
Page 86

User Interface
Button Control
Chapter 3
Use the Measurement Studio User Interface Visual C++ class library to add
user interface controls to your application. You can configure the user
interface controls programmatically or through the property pages in the
Visual C++ resource editor. Measurement Studio includes the following
Visual C++ user interface controls:
• Button
•Graph
• Knob
• Numeric edit
•Slide
The following sections describe each of the Measurement Studio Visual
C++ user interface controls.
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX button control, as shown in
Figure 3-2, for different Boolean displays, such as on or off or true or false.
Typically, you use buttons to input or display Boolean information or
initiate an action in a program. The
C++ interface to the ActiveX button control.
CNiButton class provides the Visual
Figure 3-2. ActiveX Button Control
With the button control and the classes that interface with the control, you
can perform the following operations:
• Configure how the control behaves when you click it with the mouse
or press the spacebar when the control has focus.
• Configure how the button control appears using button styles. You can
configure the button control to appear as a push button, LED, or
switch.
• Bind properties to a DataSocket source or target. You use binding to
read property values from a source and write property values to a
target.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-19 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 87

Chapter 3
Tip For more information about using the button control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Button Visual C++ Control section in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
Graph Control
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX graph control, as shown in
Figure 3-3, to plot and chart two-dimensional data. The
provides the Visual C++ interface to the ActiveX graph control.
CNiGraph class
Figure 3-3. ActiveX Graph Control
With the graph control and the classes that interface with the control, you
can perform the following operations:
Plot Operations
• Plot and chart data.
• Configure a graph to contain multiple plots to show separate but
related data on the same graph.
• Configure a graph to include multiple Y axes so that plot data fits the
graph plot area.
• Use cursors and annotations to identify key points in plots and the plot
area.
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-20 ni.com
Page 88

Chapter 3
Axis Operations
•Use the CNiAxis class to interface to a single axis of a graph control.
This feature allows you to modify the appearance and behavior of the
axis.
• Automatically label axes with log or inverted numeric scales.
• Configure the axis modes for manual scaling or autoscaling.
Additional Operations
• Configure cursor snap modes to be fixed, floating, nearest point, and
to plot.
• Pan and zoom interactively.
• Configure the graph for fixed, strip, or scope charting.
• Customize the graph by using ticks, labels, and value pairs.
• Bind properties to a DataSocket source or target. You use binding to
read property values from a source and write property values to a
target.
Tip For more information about easily using the graph control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Graph Visual C++ Control section in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
Knob Control
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX knob control, as shown in
Figure 3-4, to display numerical information. The
provides the Visual C++ interface to the ActiveX knob control.
Figure 3-4. ActiveX Knob Control with Knob, Dial, and Meter Styles
© National Instruments Corporation 3-21 Measurement Studio User Manual
CNiKnob class
Page 89

Chapter 3
With the knob control and the classes that interface with the control, you
can perform the following operations:
• Use different display styles—knobs, dials, and meters.
• Use multiple control pointers, each representing one scalar value.
A control pointer indicates the current value of the knob.
•Use the
CNiAxis class to interface to a single axis of a knob control.
This feature allows you to modify the appearance and behavior of the
axis.
• Automatically label axes with log or inverted numeric scales and
continuous or discrete values.
• Customize the knob by using ticks, labels, and value pairs.
• Bind properties to a DataSocket source or target. You use binding to
read property values from a source and write property values to a
target.
Tip For more information about easily using the knob control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Knob Visual C++ Control section in the NI Measurement Studio
Help.
Numeric Edit Control
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX numeric edit control, as shown in
Figure 3-5, to display numeric values and provide a way by which end
users can edit numeric values. Typically, you use a numeric edit control to
input or display numerical data instead of using a text box. The
CNiNumEdit class provides the Visual C++ interface to the ActiveX
numeric edit control.
With the numeric edit control and the classes that interface with the control,
you can perform the following operations:
• Use built-in numeric format styles, including scientific, symbolic
• Perform range checking.
• Bind properties to a DataSocket source or target. You use binding to
Figure 3-5. ActiveX Numeric Edit Control
engineering, scaling, time, and date.
read property values from a source and write property values to a
target.
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-22 ni.com
Page 90

Tip For more information about easily using the numeric edit control, refer to the Using
the Measurement Studio Numeric Edit Visual C++ Control section in the NI Measurement
Studio Help.
Slide Control
Use the Measurement Studio ActiveX slide control, as shown in
Figure 3-6, to display numerical data.
CNiSlide is the class that
provides the Visual C++ interface to the ActiveX slide control.
Chapter 3
Figure 3-6. ActiveX Slide Control
With the slide control and the classes that interface with the control, you
can perform the following operations:
• Use different display styles—vertical, horizontal, tank, and
thermometer.
•Use the
CNiAxis class to interface to a single axis of a slide control.
This ability allows you to modify the appearance and behavior of the
axis.
• Use multiple control pointers, each one representing one scalar value.
• Automatically label axes with log or inverted numeric scales and
continuous or discrete values.
• Customize the slide by using ticks, labels, and value pairs.
• Bind properties to a DataSocket source or target. You use binding to
read property values from a source and write property values to a
target.
Tip For more information about easily using the slide control, refer to the Using the
Measurement Studio Slide Visual C++ Control section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-23 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 91

Chapter 3
Utility
Use the Measurement Studio Utility Visual C++ class library to easily
access Windows operating system functionality. Table 3-2 lists classes in
the Utility class library and their functionality.
Table 3-2. Utility Class Names and Functionalities
Utility Class Functionality
CNiFile CNiFile extends the MFC CStdioFile class by adding
streaming operators for standard Visual C++ data types. In
addition, a variety of class static functions add the ability to
manipulate file, path, directory, and drive attributes.
CNiSound CNiSound encapsulates an interface for generating synchronous
and asynchronous tones at specific frequencies.
CNiSystem CNiSystem provides the following functionality:
• Getting and setting system preferences
• Displaying help files
• Getting input for the keyboard
CNiSystemTrayIcon CNiSystemTrayIcon encapsulates the interface to the system
tray area that displays changes in the status of an application. The
CNiSystemTrayIcon class includes the following features:
• Icons—You can place an icon in the system tray to notify the
user of changes in an application status.
• String tooltips—You can associate a string tooltip with an icon
and display the tooltip when the user hovers over the icon.
• Shortcut menus—You can associate a shortcut menu with an
icon and display the shortcut menu when the user right-clicks
the icon.
• Overridable event handling.
Measurement Studio User Manual 3-24 ni.com
Page 92

Chapter 3
Table 3-2. Utility Class Names and Functionalities (Continued)
Utility Class Functionality
CNiTempFile CNiTempFile extends the functionality of CNiFile to add
temporary file creation and manipulation.
CNiTimer CNiTimer objects use the Windows multimedia timer to generate
high-resolution, asynchronous tick events. Respond to tick events
when you want to perform an action at a discrete interval.
Additionally, you can count the tick events to calculate elapsed
time. The
CNiTimer class also contains static functions you can
use to delay for a period of time or to determine elapsed time
between two points in your program.
Tip For more information about using the Utility class library, refer to the Utility Visual
C++ Class Library Overview section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-25 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 93

Measurement Studio Integrated
Tools and Features
When you use Measurement Studio in the Visual Studio environment, you
have access to measurement and automation tools and features for Visual
Basic .NET, Visual C#, ASP.NET, and Visual C++. These integrated tools
and features are designed to help you quickly and easily build measurement
and automation applications. These integrated tools and features are
included in support for both Visual Studio 2005 and Visual Studio 2008.
This chapter includes the following sections to help you develop
applications with Measurement Studio:
• Measurement Studio Menu
• Creating a Measurement Studio Project
• Adding or Removing Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
• Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application
• Creating an Instrument Control Application
• Selecting a Measurement Studio Parameter Value
• Using the Instrument Driver Wizard
4
Refer to the Developing with Measurement Studio section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help for more information about the functionality
of these tools and features.
Measurement Studio Menu
The Measurement Studio Menu provides an easy way to access the
following National Instruments resources and tools:
• Parameter Assistant—Use the Measurement Studio Parameter
Assistant to discover and insert valid parameter values for various
Measurement Studio class libraries, such as NI-DAQmx, NI-488.2,
and NI-VISA methods. The Parameter Assistant is available only if
you have Measurement Studio class libraries installed that use
parameter values.
© National Instruments Corporation 4-1 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 94

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
• Add/Remove .NET Class Libraries Wizard—Use the Measurement
Studio Add/Remove Class Libraries wizard to add or remove
Measurement Studio class libraries or assemblies in existing Visual
Basic .NET, Visual C#, or Visual C++ projects.
• Refresh Project License File—Use the Refresh Project License File
to update the
licenses.licx file in a Measurement Studio project to
the currently referenced Measurement Studio assemblies. The Refresh
Project process works by going through the
by line for the active project and removing each Measurement Studio
licensed type that matches the Measurement Studio
PublicKeyToken. After all Measurement Studio licensed types are
removed from the
Studio licensed types that are referenced by the project are added to the
licenses.licx file. This ensures all Measurement Studio licensed
types used by the project are added to the
• Add 64-Bit Protection to Project—Updates your project’s platform
target to x86 and updates your project to protect it from build error
LC0000. Refer to Using Measurement Studio on 64-Bit Operating
Systems and Protecting Your Project from LC0000 Build Error in the
NI Measurement Studio Help for more information. This menu item is
only available in Visual Studio 2005 on a 64-bit Windows OS. Visual
Studio 2008 projects function correctly without this protection.
• Remove 64-Bit Protection from Project—Removes protection for
build error LC0000 from your project. Refer to Using Measurement
Studio on 64-Bit Operating Systems and Protecting Your Project from
LC0000 Build Error in the NI Measurement Studio Help for more
information. This menu item is only available in Visual Studio 2005 on
a 64-bit Windows OS. Visual Studio 2008 projects function correctly
without this protection.
• Update Measurement Studio Project References—Updates any
outdated Measurement Studio references to the latest version installed
on the system.
• NI Tools»Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX)—Use
MAX to configure NI hardware; add new channels, interfaces, and
tasks; execute system diagnostics; and view devices and instruments
connected to the system. Select NI Tools»Measurement &
Automation Explorer (MAX) to access this menu item. The MAX
menu option is available only if you have MAX installed.
• NI Tools»NI Spy—Use NI Spy to monitor, record, and display
National Instruments API calls made by instrument connectivity
applications. Use NI Spy to quickly locate and analyze any erroneous
National Instruments API calls that an application makes and verify
licenses.licx file line
licenses.licx file, the current Measurement
licenses.licx file.
Measurement Studio User Manual 4-2 ni.com
Page 95

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
that the communication with an instrument is correct. Select
NI Tools»NI Spy to access this menu item. The NI Spy menu item is
available only if you have NI Spy installed.
• NI Tools»Variable Manager—Use Variable Manager to create new
processes and variables, delete existing processes and variables, start
and stop processes, create variables with specific data types or the
variant data type, allow multiple writers or restrict write access to a
single client, and configure server buffering. Select NI Tools»Variable
Manager to access this menu item.
• NI Measurement Studio Help—Use the NI Measurement Studio
Help to access detailed Measurement Studio help, including function
reference, walkthroughs, and conceptual topic documentation on
developing with Measurement Studio.
• Measurement Studio Online Resources»Measurement Studio
Home Page—Use the Measurement Studio Web site at
ni.com/mstudio to find Measurement Studio news, support,
downloads, and evaluation software. Select Measurement Studio
Online Resources»Measurement Studio Home Page to access this
menu item.
• Measurement Studio Online Resources»Instrument Driver
Network—Use the NI Instrument Driver Network at
ni.com/idnet
as a central resource for downloading, developing, and submitting
instrument drivers. Select Measurement Studio Online
Resources»Instrument Driver Network to access this menu item.
• Measurement Studio Online Resources»Discussion Forums—Use
the NI Discussion Forums at
forums.ni.com to participate in
discussion forums and exchange code with measurement and
automation developers around the world. Select Measurement Studio
Online Resources»Discussion Forums to access this menu item.
• Measurement Studio Online Resources»Search Technical
Support—Use NI Technical Support at
ni.com/support to find
support resources available for most products, including software
drivers and updates, KnowledgeBase articles, product manuals,
step-by-step troubleshooting wizards, conformity documentation,
example code, tutorials and application notes, instrument drivers,
discussion forums, and a measurement glossary. Select Measurement
Studio Online Resources»Search Technical Support to access this
menu item.
© National Instruments Corporation 4-3 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 96

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
• Measurement Studio Online Resources»NI Developer
Zone—NI Developer Zone,
example programs, tutorials, technical news, and a Measurement
Studio Discussion Forum where you can participate in discussion
forums for Visual Basic 6.0, Visual C++, and .NET Languages. Select
Measurement Studio Online Resources»NI Developer Zone to
access this menu item.
• Patents—Use the Patents dialog box to view information about
NI patents.
• Licenses—Use the Licenses dialog box to view information about
NI licenses.
• About Measurement Studio—Use the Measurement Studio About
box to view version information.
• Preferences—Use the Measurement Studio Preferences dialog box to
configure Measurement Studio settings, such as conversion options
and add-in preferences. Select Tools»Options to access this menu
item.
Tip For more information about the resources included in the Measurement Studio Menu,
refer to the Measurement Studio Menu topic in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
zone.ni.com, provides access to online
Creating a Measurement Studio Project
Measurement Studio includes class library and application templates that
you can use to quickly create measurement applications with Visual Basic
.NET, Visual C#, ASP.NET, and Visual C++. Refer to the following
sections, Walkthrough: Creating an Application with Windows Forms
Controls and Analysis or Walkthrough: Creating an Application with Web
Forms Controls and Analysis, for step-by-step instructions on how to
create a Measurement Studio project. Use the Visual Studio New Project
dialog box, as shown in Figure 4-1, to access these templates and to create
projects. You can create the following projects in Measurement Studio:
• Measurement Studio Visual Basic .NET project
• Measurement Studio Visual C# project
• Measurement Studio ASP.NET project
• Measurement Studio Visual C++ project (Visual Studio 2005 only)
• Measurement Studio Visual C++ project with LabWindows/CVI
libraries (Visual Studio 2005 only)
Measurement Studio User Manual 4-4 ni.com
Page 97

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
Figure 4-1. New Project Dialog Box in Visual Studio 2005
Tip
For more information about using project templates to create a new Measurement
Studio project, refer to the Creating a New Measurement Studio Project section in the
NI Measurement Studio Help.
Note For information about converting Measurement Studio projects, refer to the
Converting Measurement Studio Projects section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Adding or Removing Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries
To add or remove Measurement Studio .NET class libraries from a project,
use the Measurement Studio Add/Remove .NET Class Libraries wizard on
the Measurement Studio menu. This wizard provides an interface, as shown
in Figure 4-2, that you can use to select the Measurement Studio .NET class
libraries you want to add to or remove from a project.
© National Instruments Corporation 4-5 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 98
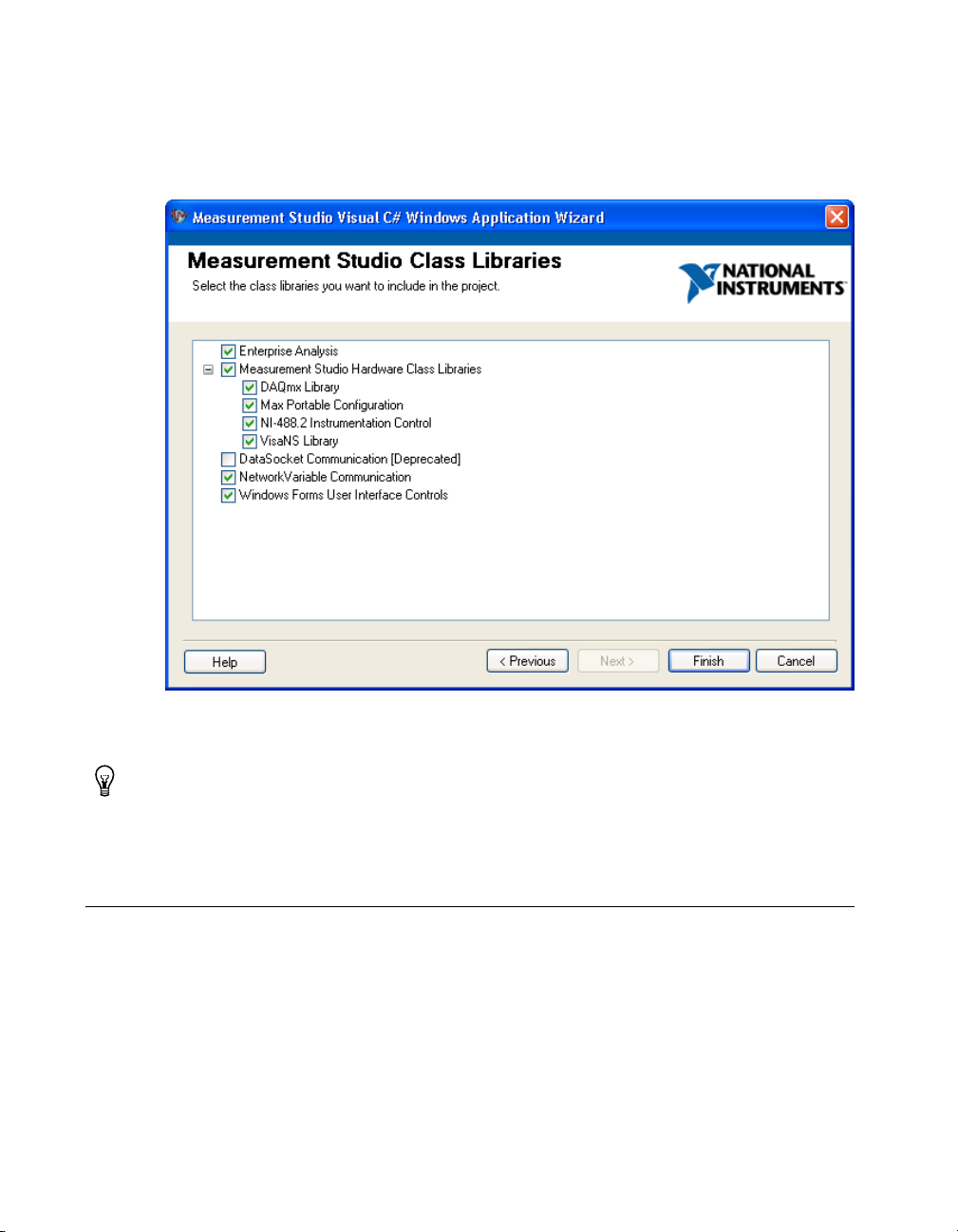
Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
When you exit the wizard, the wizard adds or removes the appropriate
references to or from the project, thus adding or removing the functionality
associated with the class library.
Figure 4-2. Measurement Studio Add/Remove Class Libraries Wizard for
Visual Studio 2005
Tip
For more information about using the Add/Remove .NET Class Libraries wizard to
add or remove Measurement Studio .NET class libraries, refer to the Adding or Removing
Measurement Studio .NET Class Libraries section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx Application
To create a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx application, use the DAQ
Assistant. The DAQ Assistant integrates into Visual Studio as a code
designer. Use the Add New Item wizard to add an NI-DAQmx task to your
project, and use the DAQ Assistant user interface, as shown in Figure 4-3,
to interactively create and configure the NI-DAQmx task. The DAQ
Assistant automatically generates a Visual Basic .NET, Visual C#, or
Visual C++ (Visual Studio 2005 only) class that includes the functionality
you configure in the user interface.
Measurement Studio User Manual 4-6 ni.com
Page 99

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
Note The DAQ Assistant is available only if you have installed NI-DAQmx and either the
Measurement Studio Professional or Measurement Studio Enterprise package.
Refer to Chapter 5, the Walkthrough: Creating a Measurement Studio
NI-DAQmx Application section, for step-by-step instructions on how to
create DAQ applications.
Figure 4-3. DAQ Assistant
© National Instruments Corporation 4-7 Measurement Studio User Manual
Page 100

Chapter 4 Measurement Studio Integrated Tools and Features
The DAQ Assistant interactively assists you in performing the following
operations:
• Creating an NI-DAQmx task class
• Configuring an NI-DAQmx task class
• Generating a Visual Basic .NET, Visual C#, or Visual C++ class that
includes the functionality you configure in the user interface
• Generating code that uses an NI-DAQmx task class
• Using an NI-DAQmx task class in a project
• Generating a DAQ component that uses the task to provide appropriate
operations for your measurement type.
Tip For more information about using the DAQ Assistant to create a Measurement Studio
NI-DAQmx application, refer to the Creating a Measurement Studio NI-DAQmx
Application section in the NI Measurement Studio Help.
Creating an NI-DAQmx User Interface
Using the Configure DAQ Component UI wizard, as shown in Figure 4-4,
you can customize and preview a user interface and code for your task. The
wizard also generates event handlers and code to acquire data and present
it on your generated user interface.
Figure 4-4. Configure DAQ Component UI Wizard
Measurement Studio User Manual 4-8 ni.com
 Loading...
Loading...