Page 1

GPIB-100A
User Manual
March 1990 Edition
Part Number 320063-01
© Copyright 1985, 1991 National Instruments Corporation.
All Rights Reserved.
Page 2

National Instruments Corporation
6504 Bridge Point Parkway
Austin, TX 78730-5039
(512) 794-0100
(800) IEEE-488 (toll-free U.S. and Canada)
Technical support fax: (512) 794-5678
Page 3

Limited Warranty
The GPIB-100A is warranted against defects in materials and workmanship for a period of two years from the
date of shipment, as evidenced by receipts or other documentation. National Instruments will, at its option,
repair or replace equipment that proves to be defective during the warranty period. This warranty includes
parts and labor.
A Return Material Authorization (RMA) number must be obtained from the factory and clearly marked on the
outside of the package before any equipment will be accepted for warranty work. National Instruments will
pay the shipping costs of returning to the owner parts which are covered by warranty.
National Instruments believes that the information in this manual is accurate. The document has been
carefully reviewed for technical accuracy. In the event that technical or typographical errors exist, National
Instruments reserves the right to make changes to subsequent editions of this document without prior notice to
holders of this edition. The reader should consult National Instruments if errors are suspected. In no event
shall National Instruments be liable for any damages arising out of or related to this document or the
information contained in it.
EXCEPT AS SPECIFIED HEREIN, NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS MAKES NO WARRANTIES , EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED
PARTICULAR PURPOSE
ON THE PART OF
THE CUSTOMER
OF DATA
OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF
the form of action, whether in contract or tort, including negligence. Any action against National Instrument
must be brought within one year after the cause of action accrues. National Instruments shall not be liable for
any delay in performance due to causes beyond its reasonable control. The warranty provided herein does not
cover damages, defects, malfunctions, or service failures caused by owner's failure to follow the National
Instruments installation, operation, or maintenance instructions; owner's modification of the product; owner's
abuse, misuse, or negligent acts; and power failure or surges, fire, flood, accident, actions of third parties, or
other events outside reasonable control.
, AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
. CUSTOMER'S RIGHT TO RECOVER DAMAGES CAUSED BY FAULT OR NEGLIGENCE
NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS SHALL BE LIMITED TO THE AMOUNT THERETOFORE PAID BY
. NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR DAMAGES RESULTING FROM LOSS
, PROFITS, USE OF PRODUCTS, OR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, EVEN IF ADVISED
. This limitation of the liability of National Instruments will apply regardless of
Copyright
Under the copyright laws, this book may not be copied, photocopied, reproduced, or translated, in whole or in
part, without the prior written consent of National Instruments Corporation.
Trademarks
Product names listed are trademarks of their respective manufacturers. Company names listed are trademarks
or trade names of their respective companies.
Page 4

FCC/DOC Radio Frequency Interference Compliance
This equipment generates and uses radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in strict
accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause interference to radio and television
reception. This equipment has been tested and found to comply with (1) the limits for a Class A
computing device, in accordance with the specifications in Subpart J of Part 15 of U.S. Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) Rules, and (2) the limits for radio noise emissions from
digital apparatus set out in the Radio Interference Regulations of the Canadian Department of
Communication (DOC). These regulations are designed to provide reasonable protection against
interference from the equipment to radio and television reception in commercial areas.
There is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. However, the
chances of interference are much less if the equipment is used according to this instruction manual.
If the equipment does cause interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined
by turning the equipment on and off, one or more of the following suggestions may reduce or
eliminate the problem.
• Operate the equipment and the receiver on different branches of your AC electrical system.
• Move the equipment away from the receiver with which it is interfering.
• Relocate the equipment with respect to the receiver.
• Reorient the receiver's antenna.
• Be sure that the equipment is plugged into a grounded outlet and that the grounding has not
been defeated with a cheater plug.
If necessary, consult National Instruments or an experienced radio/television technician for
additional suggestions. The following booklet prepared by the FCC may also be helpful: How to
Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems. This booklet is available from the U.S.
Government Printing Office, Washington, DC 20402, Stock Number 004-000-00345-4.
Page 5

Preface
Organization of the Manual
This manual is divided into the following chapters:
Chapter 1, Description of the GPIB-100A, contains a brief description of the GPIB-100A Bus
Extender and how it is used. This section also lists all components and accessories. In addition, it
provides system configuration, performance, operating, electrical, environmental, and physical
specifications for the GPIB-100A.
Chapter 2, Installation, contains instructions for configuring and connecting the GPIB-100A into
your system at your operating voltage.
Chapter 3, Configuration and Operation, describes how to configure and operate a GPIB-100A
system.
Chapter 4, Theory of Operation, contains descriptions of how the GPIB-100A circuitry operates.
Appendix A, Operation of the GPIB, describes GPIB terminology and protocol for users
unfamiliar with the GPIB.
Appendix B, Schematic Diagram, contains a detailed schematic diagram of the GPIB-100A.
Appendix C, GPIB-100A Parts Locator Diagram, contains the parts locator diagram for the
GPIB-100A.
Appendix D, Cable Assembly Wire List, contains the listing of wire connections for the
GPIB-100A transmission cable.
Appendix E, Multiline Interface Messages, contains an ASCII chart and a list of the corresponding
GPIB messages.
Appendix F, Mnemonics Key, contains a mnemonics key that defines the mnemonics used
throughout the manual.
Related Document
The following document is a reference that covers in greater detail specific topics introduced in this
manual:
• ANSI/IEEE Standard 488-1978, IEEE Standard Digital Interface for Programmable
Instrumentation.
© National Instruments Corporation v GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 6

Preface
Abbreviations Used in the Manual
The following abbreviations are used in the text of this manual.
C centigrade
F Fahrenheit
Hz hertz
in. inch
kbytes thousand bytes
m meter
mA milliamperes
Mbytes million bytes
mm millimeter
µsec microsecond
nsec nanosecond
sec second
V volts
VAC Volts Alternating Current
W watt
GPIB-100A User Manual v i © National Instruments Corporation
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1
Description of the GPIB-100A
Introduction...................................................................................................................... 1-1
GPIB-100A Specifications.............................................................................................. 1-3
Chapter 2
Installation
Inspection......................................................................................................................... 2-1
Power Connection............................................................................................................ 2-1
Grounding Configuration................................................................................................. 2-2
Mounting......................................................................................................................... 2-2
Connecting to Hewlett-Packard Controllers..................................................................... 2-2
Chapter 3
Configuration and Operation
Operating Modes............................................................................................................. 3-1
Parallel Poll Response (PPR) Modes............................................................................... 3-2
Mixed Mode Operation.................................................................................................... 3-4
Operating the GPIB-100A System.................................................................................. 3-4
............................................................................................................................. 2-1
Disassembly........................................................................................................ 2-2
Talker/Listener/Controller (TLC) Mode............................................................... 3-1
Talker/Listener (TL) Mode................................................................................... 3-2
Setting the Operating Mode................................................................................. 3-2
Buffered PPR Mode (Approach 1)...................................................................... 3-3
Unbuffered PPR Mode (Approach 2).................................................................. 3-3
....................................................................................... 1-1
.......................................................................................... 3-1
Chapter 4
Theory of Operation
Diagrams......................................................................................................................... 4-1
Power-On........................................................................................................................ 4-1
System Controller Detection............................................................................................ 4-2
Active Controller Detection.............................................................................................. 4-2
Source Handshake Detection........................................................................................... 4-2
Parallel Polling..................................................................................................... 4-3
Data Direction Control......................................................................................... 4-4
EOI.................................................................................................................................. 4-4
© National Instruments Corporation vii GPIB-100A User Manual
........................................................................................................... 4-1
Page 8

Contents
Appendix A
Operation of the GPIB
History of the GPIB......................................................................................................... A-1
Types of Messages.......................................................................................................... A-1
Talkers, Listeners, and Controllers................................................................................... A-1
System Controller and Active Controller......................................................................... A-2
GPIB Signals................................................................................................................... A-2
Data Lines........................................................................................................................ A-3
Handshake Lines.............................................................................................................. A-3
NRFD (not ready for data)................................................................................... A-3
NDAC (not data accepted)................................................................................... A-4
DAV (data valid)................................................................................................. A-4
Interface Management Lines............................................................................................ A-4
ATN (attention).................................................................................................... A-4
IFC (interface clear)............................................................................................. A-4
REN (remote enable)........................................................................................... A-4
SRQ (service request).......................................................................................... A-4
EOI (end or identify)........................................................................................... A-4
Physical and Electrical Characteristics............................................................................. A-5
Configuration Restrictions............................................................................................... A-7
....................................................................................................... A-1
Appendix B
Schematic Diagram
............................................................................................................ B-1
Appendix C
GPIB-100A Parts Locator Diagram
Appendix D
Cable Assembly Wire List
............................................................................................... D-1
Appendix E
Multiline Interface Messages
......................................................................................... E-1
Appendix F
Mnemonics Key
.................................................................................................................... F-1
............................................................................. C-1
GPIB-100A User Manual viii © National Instruments Corporation
Page 9

Contents
Figures
Figure 1-1. The Model GPIB-100A Bus Extender.................................................................. 1-1
Figure 1-2. Typical GPIB-100A Extension System (Physical Configuration)........................ 1-2
Figure 1-3. Typical GPIB-100A Extension System (Logical Configuration).......................... 1-2
Figure 2-1. Voltage Selection.................................................................................................... 2-1
Figure 3-1. Switch Settings for Operating Mode...................................................................... 3-2
Figure 3-2. Switch Settings for Parallel Poll Response Mode................................................... 3-4
Figure 4-1. GPIB-100A Block Diagram................................................................................... 4-1
Figure A-1. GPIB Cable Connector.......................................................................................... A-3
Figure A-2. Linear Configuration of the GPIB Devices............................................................ A-5
Figure A-3. Star Configuration of GPIB Devices..................................................................... A-6
Figure C-1. GPIB-100A Parts Locator Diagram...................................................................... C-1
Tables
Table 1-1. System Configuration Characteristics...................................................................... 1-3
Table 1-2. Performance Characteristics..................................................................................... 1-4
Table 1-3. Operating Characteristics......................................................................................... 1-4
Table 1-4. Electrical Characteristics.......................................................................................... 1-5
Table 1-5. Environmental Characteristics................................................................................. 1-5
Table 1-6. Physical Characteristics............................................................................................ 1-6
Table 1-7. Components and Accessories.................................................................................. 1-6
Table D-1. Cable Assembly Wire List...................................................................................... D-1
© National Instruments Corporation ix GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 10

Chapter 1 Description of the GPIB-100A
Introduction
The high-speed GPIB-100A Bus Extender (Figure 1-1) is used in pairs with a special parallel data
transmission cable to connect two separate GPIB or IEEE-488 bus systems in a functionally
transparent manner.
Figure 1-1. The Model GPIB-100A Bus Extender
While the two bus systems are physically separate, as shown in Figure 1-2, devices logically
appear to be located on the same bus as shown in Figure 1-3. Thus, with the GPIB-100A it is
possible to overcome two configuration restrictions imposed by ANSI/IEEE Standard 488-l978,
namely:
• Cable length limit of 20 m total per contiguous bus or 2 m times the number of devices on the
bus, whichever is smaller.
• Electrical loading limit of 15 devices per contiguous bus.
Each GPIB-100A system extends the distance limit by 300 m and the loading limit to 30 devices
including the extenders, without sacrificing speed or performance. These point-to-point extender
systems can be connected in series for longer distances or in star patterns for additional loading.
At short distances, the data transfer rate over the extension can exceed 250 kbytes/sec, degrading
with distance only by the propagation delay along the cable. Furthermore, regardless of the
distance, there is no speed degradation at all for transfers between devices on the same side of the
© National Instruments Corporation 1-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 11
Description of the GPIB-100A Chapter 1
extension. And because the GPIB-100A is a functionally transparent extender, the same GPIB
communications and control programs that work with an unextended system will work
unmodified with an extended system. There is one minor exception to this transparency in
conducting parallel polls, as explained in Chapter 3 in the paragraph Parallel Poll Response (PPR)
Modes.
RS-232 Compatible
Transmission
GPIB #1 GPIB-100A
Lines
GPIB-100A
GPIB #2
Computer
(System Controller,
Talker, and Listener)
Figure 1-2. Typical GPIB-100A Extension System (Physical Configuration)
Computer
(System Controller,
Talker, and Listener)
Printer
(Listener)
(Listener)
Printer
(Talker and Listener)
GPIB
Multimeter
(Talker and Listener)
Multimeter
Unit Under Test
Signal Generator
(Listener)
Signal Generator
(Listener)
Unit Under Test
Figure 1-3. Typical GPIB-100A Extension System (Logical Configuration)
GPIB-100A User Manual 1-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 12
Chapter 1 Description of the GPIB-100A
GPIB-100A Specifications
The following tables show the system configuration; the performance, operating, electrical,
environmental, and physical characteristics of the GPIB-100A, as well as providing a list of
available GPIB-100A components and accessories.
Table 1-1. System Configuration Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
distance per extension up to 300 m
loading per extension up to 14 additional devices
multiple extensions permitted in any combination of star or linear pattern
GPIB driver output no restrictions (automatic conversion to 2 µsec
circuit and T1 timing T1 delay on remote side is built in)
of source device
Note: T1 is the data settling time (DIO valid to DAV) and varies according to the type of
drivers and the system configuration used.
© National Instruments Corporation 1-3 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 13

Description of the GPIB-100A Chapter 1
Table 1-2. Performance Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
speed 250 to 135 kbytes/sec (approximately 4 µsec per byte
degraded at 10.5 nsec per meter of distance) no
limitation to device speeds when there are no
listeners on remote side of extension
functionality transparent GPIB operation except for pulsed parallel
polls
interlocked maintained across the extension
IEEE-488 handshake (message-grams not used)
IEEE-488 capability SH1 complete Source Handshake
identification AH1 complete Acceptor Handshake
codes T5,TE5 complete Talker
L3,LE3 complete Listener
SR1 complete Service Request
RL1 complete Remote Local
PP1,2 complete Parallel Poll
DC1 complete Device Clear
DT1 complete Device Trigger
C1-5 complete Controller
E1 open collector GPIB drivers
Table 1-3. Operating Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
architecture asynchronous (no clock) parallel design
point-to-point (not multi-drop) transmission
operating modes Talker/Listener/Controller or
Talker/Listener (Talk Only)
Parallel Poll Response Buffered Parallel Poll Response or
modes Unbuffered Parallel Poll Response
GPIB-100A User Manual 1-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 14

Chapter 1 Description of the GPIB-100A
Table 1-4. Electrical Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
GPIB interface circuit duplex transceivers with open
collector drivers (MC3441A)
transmission interface RS-422 drivers and receivers
circuit (MC3487 and AM26LS32) connected with patented
data transmission cable for minimum skewing
(<= 3%) between any two pairs
power supply 50 to 60 Hz
selectable (fuse) 110 V, 160 mA (250 mA, 250 V, Slow Blow)
220 V, 80 mA (200 mA, 250 V, Slow Blow)
GPIB interface load one standard load, AC and DC
power 18 W typical
Table 1-5. Environmental Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
operating temperature 0 to 55 C
humidity 5 to 95% non-condensing conditions
FCC Class A verified
110V Version UL Listed
220V Version UL Listed and also classified by Underwriters
Laboratories Inc. in accordance with International
Electrotechnical Commission publication 950
© National Instruments Corporation 1-5 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 15

Description of the GPIB-100A Chapter 1
Table 1-6. Physical Characteristics
Characteristic Specification
case style CS2
size 3.5 x 8.5 x 13 in. (89 x 216 x 330 mm)
case material UL94V-0 flame retardant polystyrene
Dow 60875 F or equivalent
rack mounting single or dual kits available
GPIB cable Hewlett Packard 10833 style or equivalent
Transmission cable Dynatronics D-200-24 cable with
AMP Amplimite connectors AMP HDP-20 50 pin
connector with RFI/EMI shield
Table 1-7. Components and Accessories
Item Part Number
Model GPIB-100A Bus Extender (110V) 776107-01
(two required per extension)
Model GPIB-100A Bus Extender (220V) 776107-31
(two required per extension)
Type T2 Transmission Cable 178056-xxx
(xxx = length in meters)
Type X2 GPIB Cable
1 meter 763061-01
2 meters 763061-02
4 meters 763061-03
Single Rack-Mount Kit 180304-01
Dual Rack-Mount Kit 180304-02
Note: All part numbers in this table are National Instruments part numbers.
GPIB-100A User Manual 1-6 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 16

Chapter 2 Installation
Inspection
Inspect the shipping container and contents for evidence of physical damage or stress. If damage
is discovered and appears to have been caused in shipment, file a claim with the carrier. If the
equipment is damaged, do not attempt to operate it before contacting National Instruments for
instructions. Retain the shipping material for possible inspection by carrier or reshipment of the
equipment.
Power Connection
The GPIB-100A Bus Extender is shipped from the factory set at a certain operating voltage, either
110 VAC or 220 VAC. Verify that the voltage you are using is the same as that selected on the
rear panel of the GPIB-100A. Operating at a voltage other than the one selected may damage the
unit. If the GPIB-100A is set at a voltage other than the one you are using, follow the steps below
to change the operating voltage.
1. Remove the power cord from the unit.
2. Pull out the fuse holder and replace the fuse with one that has the type and rating specified in
Table 1-4 for your operating voltage.
3. Using a small flat-head screwdriver, rotate the voltage selector to point to your operating
voltage.
Figure 2-1. Voltage Selection
© National Instruments Corporation 2-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 17

Installation Chapter 2
Grounding Configuration
A U.S. standard three-wire power cable is provided with the GPIB-100A. When connected to a
power source, this cable connects the equipment chassis to the power ground.
The GPIB-100A is shipped from the factory with chassis and power grounds connected to the
logic ground of the digital circuitry and the shields of the interfacing cables. If it is necessary to
isolate these grounds to prevent current loops between units, disassemble the unit according to the
following instructions and remove jumper W1 located on the circuit card assembly near the back
panel.
Disassembly
The case consists of two identical sections. Before disassembling, remove power from the unit.
Then remove the two screws on each side of the case and lift the top section. When reassembling,
it may be necessary to adjust the two trim panels on the case side for proper fit in their grooves.
Mounting
The GPIB-100A enclosure is designed for table top operation or for rack mounting. Single and
dual unit rack mounting kits are available from National Instruments for field installation.
Connecting to Hewlett-Packard Controllers
To achieve very high data transfer rates and long cable spans between devices, many HewlettPackard (HP) controllers and computers, such as the 64000 series, use a preload technique on the
unit designated Master Controller. When preloaded, the GPIB lines of the Master Controller are
terminated to represent six device loads. HP has two types of preloading: Class A, in which all 16
GPIB lines are loaded, and Class B, in which all lines except Not Ready For Data (NRFD) and
Not Data Accepted (NDAC) are loaded.
Preloading increases ringing on signal transitions and may cause improper operation of the GPIB100As. If this happens, all signals on the Master Controller should be set to normal (1 unit) load.
This is done by means of a back panel switch when working from the exterior. In addition, the
cabling rule of no more than 2m/device must be strictly enforced.
GPIB-100A User Manual 2-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 18

Chapter 3 Configuration and Operation
Users who are unfamiliar with the GPIB should first read Appendix A, Operation of the GPIB, to
become familiar with GPIB terminology and protocol.
In the following discussions, the terms local and remote refer to certain states of the two GPIB100A Bus Extenders in the system. When one extender is in a local state, meaning that the state in
question originated on the local state's side, the other extender is in the corresponding remote state.
The three states in question are the System Controller, Active Controller, and Source Handshake
states.
Operating Modes
The GPIB-100A has two operating modes: Talker/Listener/Controller mode and Talker/Listener
mode. Both units in the extension system must be set to the same mode.
Talker/Listener/Controller (TLC) Mode
The GPIB-100A is set at the factory to the more common TLC operating mode. The TLC mode
requires a System Controller on one side of the extension. There may be any number of Talkers,
Listeners, and other Controllers in the system.
In the TLC mode, the two GPIB-100As expect to see in order: first the Interface Clear (IFC)
signal from the System Controller; second the Attention (ATN) signal from the Active Controller;
and third the Data Valid (DAV) signal from the Active Controller or Talker. A brief description of
this mode is in the following paragraph.
Both units power up in a quiescent condition with no local or remote state active. They remain that
way until one unit detects an IFC pulse from the System Controller which is on the same
contiguous bus. That unit enters the Local System Controller (LSC) state and causes the other unit
to enter the Remote System Controller (RSC) state. The IFC and Remote Enable (REN) signals
are switched to flow from the local to the remote unit. Next, one unit detects the ATN signal from
the Active Controller, enters the Local Active Controller (LAC) state, and places the other unit in
the Remote Active Controller (RAC) state. The ATN signal is switched to flow from local to
remote side and the Service Request (SRQ) is switched to flow in the opposite direction. Finally,
one unit detects the DAV from the Source Handshake function of the Talker or Active Controller.
That unit enters the Local Source (LS) state and places the other unit in the Remote Source (RS)
state. The DAV and Data (DIO) signals are switched to flow from local to remote side, and the
Not Ready for Data (NRFD) and Not Data Accepted (NDAC) signals are switched to flow from
remote to local side.
As the source side for these three key signals–IFC, ATN, and DAV–change, the local/remote
states of each extender and the directions of the other GPIB signals change accordingly. Chapter 4,
Theory of Operation, contains a more thorough discussion of this.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 19

Configuration and Operation Chapter 3
Talker/Listener (TL) Mode
There is no Controller and only one Talker in the TL mode of operation, sometimes called talk only
mode. Usually, there is just one Listener as well. In the TL mode, the System and Active
Controller states remain inactive and the IFC, REN, ATN, and SRQ signals are unused. The
directions of the other signals are set the first time the Talker asserts DAV.
Setting the Operating Mode
Both GPIB-100As in the extension system must be set to the same operating mode. Use switch
S1, position 1, on the back panel of each GPIB-100A to set the operating mode. Set the switches
as shown in Figure 3-1.
T/L/C
O
N
A. Talker/Listener/Controller Mode B. Talker/Listener Mode
123
O
N
T/L
represents the side of the switch you press down
123
Figure 3-1. Switch Settings for Operating Mode
Parallel Poll Response (PPR) Modes
According to ANSI/IEEE Standard 488-l978, devices must respond to a parallel poll within 200
nsec after the Identify (IDY) message (Attention (ATN) and End Or Identify (EOI)) is asserted by
the Active Controller, which then waits until 2 µsec or more to read the Parallel Poll Response
(PPR). It is not possible for a remote device on an extended system to respond to this quickly
because of cable propagation delay. GPIB extender manufacturers have approached this in three
ways:
Approach 1: Respond to IDY within 200 nsec with the results of the previous poll of the
remote bus.
Approach 2: Ignore the 200 nsec rule and assume the Controller will wait sufficiently long to
capture the response.
Approach 3: Do not support parallel polling at all.
The GPIB-100A uses either Approach 1 or 2, selected at switch S1, position 3. Set this switch as
shown in Figure 3-2.
GPIB-100A User Manual 3-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 20

Chapter 3 Configuration and Operation
Buffered PPR Mode (Approach 1)
Most Controllers pulse the IDY signal for a period of time exceeding 2 µsec and expect a response
within that time. When used with this type of Controller, the GPIB-100A should be left in the
Buffered PPR mode as set at the factory.
In this mode, the local GPIB-100A extender responds to IDY by outputting the contents of the
PPR data register. At the same time, a parallel poll message is sent to the remote bus and the poll
response is returned to the local unit in due course. When the local IDY signal is unasserted, the
register is loaded with the new remote response. Consequently the register contains the response
of the previous poll. To obtain the response of both local and remote buses, the control program
executes two parallel polls back-to-back and uses the second response.
The software driver library of most Controllers contains an easy-to-use parallel poll function. If,
for example, the function is called PPOLL and the control program is written in BASIC, the
sequence to conduct a poll in Buffered PPR mode might be like this:
CALL PPOLL(PPR)
CALL PPOLL(PPR)
IF PPR > 0 GOTO NNN
If two GPIB extender systems are connected in series, three polls are necessary to get responses
from the local, middle, and far buses.
Unbuffered PPR Mode (Approach 2)
Many Hewlett-Packard GPIB Controllers remain in a parallel poll state with IDY asserted
whenever they are not performing another function. A change in the response causes an interrupt
of the control program. In other Controllers, the IDY signal is toggled on and off and the duration
of the signal can be varied to accommodate delayed responses over extenders. When used with
these types of Controllers, the GPIB-100A should be set to Unbuffered PPR mode. This means
that the IDY message is sent to the remote bus and the response is returned as fast as propagation
delays allow. The Controller must allow time to receive the response.
© National Instruments Corporation 3-3 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 21

Configuration and Operation Chapter 3
Mixed Mode Operation
If there are multiple Controllers and all of the same type are located on the same side of the
extension, the two GPIB-100A units can be set to Unbuffered and Buffered PPR modes
accordingly.
BUF
O
N
123
P
P
R
123
O
N
A. Unbuffered PPR Mode B. Buffered PPR Mode
P
P
R
UNBUF
represents the side of the switch you press down
Figure 3-2. Switch Settings for Parallel Poll Response Mode
Operating the GPIB-100A System
The GPIB-100A extension system is fully operational when power is applied to both units. In
TLC mode, it is sometimes necessary to power on the System Controller last, after the extenders
and all other devices are operating. This is necessary if the System Controller executes only one
IFC shortly after power-on.
The preferred operating mode is to keep both extenders and at least two-thirds of the devices on
both buses powered on when there is any GPIB activity.
GPIB-100A User Manual 3-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 22

Chapter 4 Theory of Operation
Diagrams
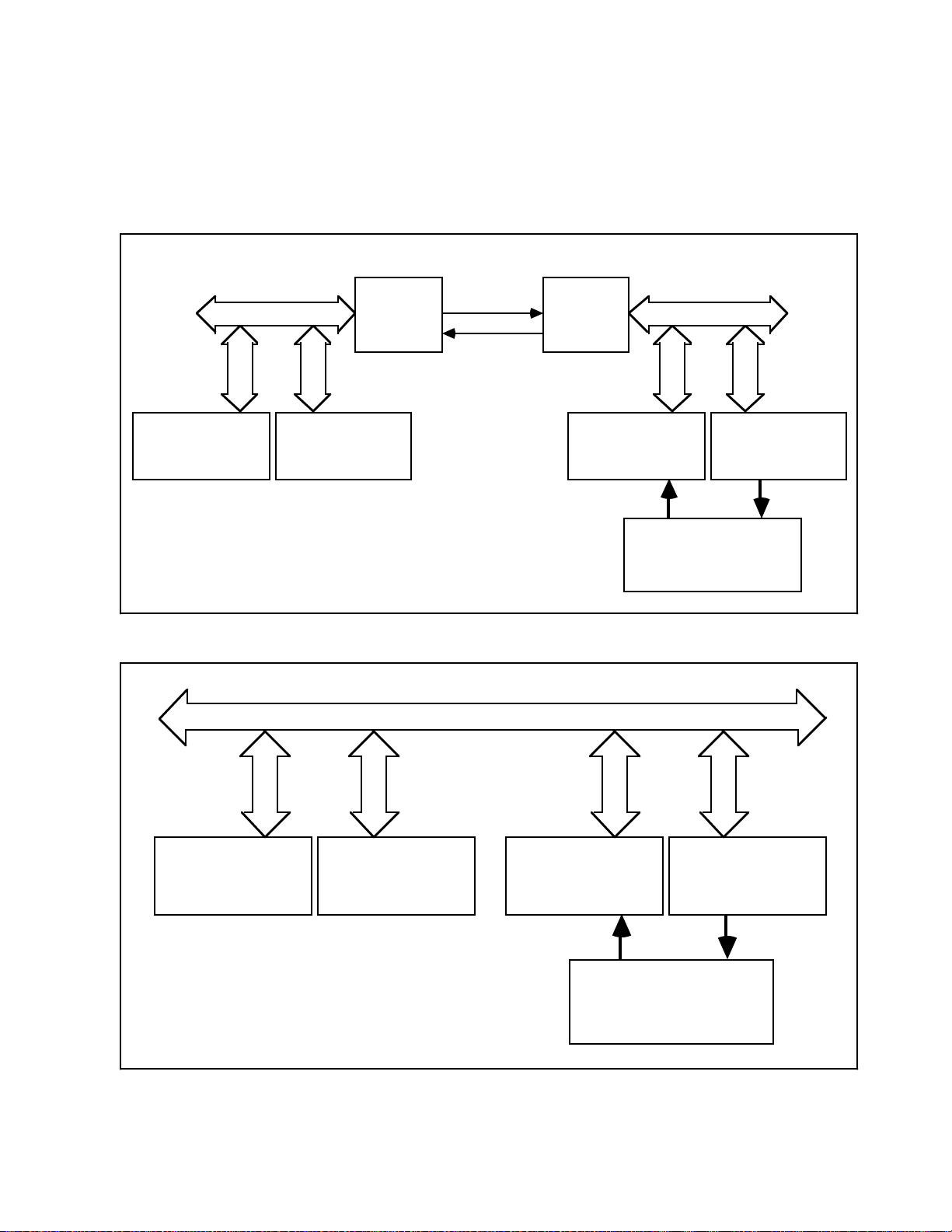
Figure 4-1 shows a block diagram for the GPIB-100A. Refer to Appendix B for GPIB-100A
schematic diagrams and Appendix C for the GPIB-100A parts locator diagram.
Figure 4-1. GPIB-100A Block Diagram
Power-On
When the GPIB-100A is powered on, a reset pulse (PON) created by U48F, U28A/D and
associated Register/Capacitor Delay (RCD) network directly or indirectly clears all flip-flops (FFs)
to an initialized state. PON remains active until both units in the extension are powered on.
© National Instruments Corporation 4-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 23

Theory of Operation Chapter 4
System Controller Detection
PON initializes FFs U22A and U12A to clear the Remote System Controller (RSC) and Local
System Controller (LSC) signals.
When Interface Clear (IFC) is received from the local side via GPIB transceiver U2B, the LSC FF
is set on the leading edge of IFC and after a delay through U21B/C/D/E, IFC is enabled (U35D) to
the remote unit as XIFC through driver U29A. LSC enables the local unit to transmit Remote
Enable (REN) to the remote unit through driver U8A.
XIFC becomes RIFC on the remote side and is received through U10D and propagated to the
remote GPIB through transceiver U2B, where the bus signal is received back to clock the RSC FF
U22A. RSC enables REN (U32C) to be driven on the remote GPIB through transceiver U2D.
Active Controller Detection
The Remote Active Controller (RAC) and Local Active Controller (LAC) FFs U22B and U12B
remain cleared until either RSC or LSC is set via U41B–that is, until the System Controller has
been located. After a short delay (U21A/F and U31B/F), the Attention (ATN) receiver on the local
side (U32D) is enabled. This delay allows the LAC FF to be set if ATN is already asserted when
IFC occurs.
When ATN is received from the local side via transceiver U2C, the LAC FF is set on the leading
edge of ATN and, after a delay through U11B/C/D/E, ATN is enabled (U32A and U43D) to the
remote unit as XATN through driver U29B. LAC enables the local unit to receive Service Request
(SRQ) from the remote unit through receiver U10B, U32B, and transceiver U2A.
XATN becomes RATN on the remote side and is received through U20B and propagated to the
remote GPIB through transceiver U2C, where the bus signal is received to clock RAC FF U22B.
When RAC is set, drivers U8C/D, which transmit SRQ and parallel poll handshake signal BUS
PP to the local unit, are enabled (that is, toward the Active Controller).
Source Handshake Detection
The Local Source (LS) handshake FF U45A is cleared via U33C on the following events:
• Before the Active Controller is identified (TLC mode only)
• Whenever a change in the state of the local ATN signal is caused by a pulse created via U38D,
U24A/D, and associated RC network.
• While ATN or Data Valid (DAV) is received from the remote unit (U34B).
• During a parallel poll (U46C).
The Remote Source (RS) handshake FF U36B is cleared via U33B on the following events:
• Before the Active Controller is identified (TLC mode (U33A) only).
GPIB-100A User Manual 4-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 24

Chapter 4 Theory of Operation
• Whenever a change in the state of the local ATN signal is caused by a pulse created via U38E,
U24B/C, and associated RC network.
• While ATN or DAV is received from the local side (U34A/D).
• During a parallel poll (U38F and U34A).
Before the LS FF is set and unless a parallel poll is in progress, the unit drives the local Not Ready
for Data (NRFD) signal passively false (U42C and U41C). After the Active Controller is
identified and before the Source Handshake is identified, the unit drives Not Data Accepted
(NDAC) signals (U42B and U41D) true. Thus, the unit appears in a normal RFD/NDAC state to
the local GPIB which is awaiting the first data or command byte.
When DAV is received, it is first delayed slightly by U23A, U48E, and associated RCD network
and enabled (U25A) to the LS FF. Setting the FF causes the Local Source Handshake to wait until
ATN changes have propagated and any parallel poll completes fully. The purpose of the DAV
delay is to filter tail-end unstable transitions from a fast rising edge. DAV is further delayed
through U23B/C/E/F before being enabled at U25C by LS to be transmitted to the remote side as
XDAV through driver U30B.
XDAV is received as RDAV on the remote side through U19D. The signal sets the RS FF after
all clearing conditions are removed (U35B). DAV is delayed 2 µsec or more through U38C,
U48B, and associated RCD network to ensure proper data setup time (T1) on the remote side.
Once RS is set and the remote GPIB is ready for data (U46A), DAV is allowed to propagate
(U46D and U36C) to the remote GPIB through U47D, U27C, and GPIB transceiver U1B, and
NRFD is transmitted to the other side through driver U30A (XRFD).
Once the LS FF is set, the propagation of NRFD from the remote side sets FF U36A via receiver
U19A, U44C, and U35A. At this point, the unit drives the NRFD and NDAC lines according to
the levels sensed at the remote unit (via U42C,U41A/D, and GPIB transceiver U1C for NDAC).
Parallel Polling
When the local unit detects ATN and End Or Identify (EOI) asserted at the same time, regardless
of which occurs first, FF U45D is set via U26A, U44E, U48D, and U43C. This causes EOI to be
transmitted to the remote side as XEOI through U46B and driver U30C. ATN is also transmitted
to the remote side as XATN through U43D and driver U29B. XEOI and XATN remain asserted
until the poll signals propagate to the remote unit and a response is returned, even if the local
signals become unasserted in the meantime. To prevent the local side from further non-poll
activity, NRFD is asserted via U46C, U41C, and transceiver U1D.
If the Buffered PPR mode is selected, the contents of the PPR register (U16) are routed through
the A side of multiplexers U13 and U14 to the local GPIB. The A side is selected whenever the
local unit is not being polled from the other side (U27B) and the RS FF is cleared (U47A).
XEOI and XATN are received on the remote side as REOI and RATN through receivers U19B
and U20B and propagated to the remote GPIB. Two microseconds later, a parallel poll handshake
signal (U27C, U38A, and associated RCD network) is transmitted back to the local side through
driver U8C as the signal BUS PP.
BUS PP is received at the local unit through U10C. When the local poll is over (ATN or EOI
unasserted), FF U45B is cleared and U36D is set (via U37B/C and U26A). Setting U36D latches
© National Instruments Corporation 4-3 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 25

Theory of Operation Chapter 4
the remote poll response into register U16. Clearing U45B unasserts XEOI and XATN, and after
they propagate to the remote side, BUS PP is also unasserted. This causes FF U36D to be cleared
as well, terminating the parallel poll process and removing the NRFD condition of the local
extender.
To recap, FF U45B is set from the start of the local poll until the remote response is available and
the local poll is over. FF U36D is set from the time U45B is cleared until the remote poll
handshake is over. While either is set, the local unit remains in an NRFD holdoff.
Data Direction Control
The unit drives the GPIB data lines DI01 to DI08 through transceivers U3 and U4 if there is a
local parallel poll in progress (U47B and U26A) or if the RS FF is set and a remote parallel poll is
not in progress (U47A and U27B). Otherwise, these lines are not driven.
The source for these data lines when they are driven is the remote unit through receivers U15 and
U17 when Unbuffered PPR mode is selected (Switch S1, position 3 open) or when the RS FF is
set and a remote parallel poll is not in progress (U47A and U27B). Otherwise, the source is the
Buffered PPR register U16.
The unit drives the transmission data lines BUS DIO1-8 through drivers U5 and U7 if there is a
remote parallel poll in progress (U37D and U27B) or if the LS FF is set and a local parallel poll is
not in progress (U47C and U26A). Otherwise, these lines are not driven.
EOI
The local unit transmits EOI to the remote side as XEOI if the LS FF is set (transceiver U1A,
U25B, U46B,and driver U30C). Furthermore, XEOI is asserted from the start of a local parallel
poll until the poll handshake signal BUS PP is received from the remote unit and the local poll
stops.
XEOI is received as REOI at the remote unit through receiver U19B. It propagates to the remote
GPIB if the local unit is conducting a parallel poll (U27A/B, U37A and transceiver U1A) or if the
RS remote response (RR) is set and the local unit is not conducting a poll (U47A).
GPIB-100A User Manual 4-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 26

Appendix A Operation of the GPIB
History of the GPIB
The GPIB is a link, bus, or interface system through which interconnected electronic devices
communicate. Hewlett-Packard invented the GPIB, which they call the HP-IB, to connect and
control programmable instruments manufactured by them. Because of its high system data rate
ceilings of from 250 kbytes/sec to 1 Mbytes/sec per second, the GPIB quickly became popular in
other applications such as intercomputer communication and peripheral control. It was later
accepted as the industry standard IEEE-488. The versatility of the system prompted the name
General Purpose Interface Bus.
Types of Messages
Devices on the GPIB communicate by passing messages through the interface system. There are
two types of messages:
• Device-dependent messages, often called data or data messages, contain device-specific
information such as programming instructions, measurement results, machine status, and data
files.
• Interface messages manage the bus itself. They are usually called commands or command
messages. Interface messages perform such functions as initializing the bus, addressing and
unaddressing devices, and setting devices for remote or local programming.
Note: The term command as used here should not be confused with some device instructions
which are also referred to as commands. Such device-specific instructions are actually data
messages.
Talkers, Listeners, and Controllers
There are three types of GPIB communicators. A Talker sends data messages to one or more
Listeners. The Controller manages the flow of information on the GPIB by sending commands to
all devices.
Devices can be Talkers, Listeners, and/or Controllers. A digital multimeter, for example, is a
Talker and may also be a Listener. A printer or plotter is usually only a Listener. A computer on
the GPIB often combines all three roles to manage the bus and communicate with other devices.
The GPIB is a bus like a typical computer bus except that the computer has its circuit cards
interconnected via a backplane bus whereas the GPIB has standalone devices interconnected via a
cable bus.
© National Instruments Corporation A-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 27

Operation of the GPIB Appendix A
The role of the GPIB Controller can also be compared to the role of the computer's CPU, but a
better analogy is to the switching center of a city telephone system.
The switching center (Controller) monitors the communications network (GPIB). When the
center (Controller) notices that a party (device) wants to make a call (send a data message), it
connects the caller (Talker) to the receiver (Listener).
The Controller usually addresses a Talker and a Listener before the Talker can send its message to
the Listener. After the message is transmitted, the Controller usually unaddresses both devices.
Some bus configurations do not require a Controller. For example, one device may only be a
Talker (called a Talk-only device) and there may be one or more Listen-only devices.
A Controller is necessary when the active or addressed Talker or Listener must be changed. The
Controller function is usually handled by a computer.
System Controller and Active Controller
Although there can be multiple Controllers on the GPIB, only one Controller at a time is Active
Controller or Controller-in-Charge (CIC). Active control can be passed from the current Active
Controller to an idle Controller. Only one device on the bus, the System Controller, can make
itself the Active Controller.
GPIB Signals
The interface bus consists of 16 signal lines and 8 ground return or shield drain lines. The 16
signal lines are divided into three groups:
• 8 data lines
• 3 handshake lines
• 5 interface management lines
GPIB-100A User Manual A-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 28

Appendix A Operation of the GPIB
Figure A-1 shows the arrangement of these signals on the GPIB cable connector.
13
DIO1*
DIO2*
DIO3*
DIO4*
EOI*
DAV*
NRFD*
NDAC*
IFC*
SRQ*
ATN*
SHIELD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
DIO5*
14
DIO6*
15
DIO7*
16
DIO8*
17
REN*
18
GND (TW PAIR W/DAV*)
19
GND (TW PAIR W/NRFD*)
20
GND (TW PAIR W/NDAC*)
21
GND (TW PAIR W/IFC*)
22
GND (TW PAIR W/SRQ*)
23
GND (TW PAIR W/ATN*)
24
SIGNAL GROUND
Figure A-1. GPIB Cable Connector
Data Lines
The eight data lines, DIO1 through DIO8, carry both data and command messages. All
commands and most data use the 7-bit ASCII or ISO code set, in which case the eighth bit, DIO8,
is unused or used for parity.
Appendix E lists the GPIB command messages.
Handshake Lines
Three lines asynchronously control the transfer of message bytes among devices. The process is
called a three-wire interlocked handshake and it guarantees that message bytes on the data lines are
sent and received without transmission error.
NRFD (not ready for data)
NRFD indicates when a device is ready or not ready to receive a message byte. The line is driven
by all devices when receiving commands and by Listeners when receiving data messages.
© National Instruments Corporation A-3 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 29

Operation of the GPIB Appendix A
NDAC (not data accepted)
NDAC indicates when a device has or has not accepted a message byte. The line is driven by all
devices when receiving commands and by Listeners when receiving data messages.
DAV (data valid)
DAV tells when the signals on the data lines are stable (valid) and can be accepted safely by
devices. The Controller drives DAV when sending commands, and the Talker drives it when
sending data messages.
The way in which NRFD and NDAC are used by the receiving device is called the Acceptor
Handshake. Likewise, the sending device uses DAV in the Source Handshake.
Interface Management Lines
Five lines are used to manage the flow of information across the interface.
ATN (attention)
The Controller drives ATN true when it uses the data lines to send commands and false when it
allows a Talker to send data messages.
IFC (interface clear)
The System Controller drives the IFC line to initialize the bus to become Controller-In-Charge.
REN (remote enable)
The System Controller drives the REN line, which is used to place devices in remote or local
program mode.
SRQ (service request)
Any device can drive the SRQ line to asynchronously request service from the Active Controller
with the SRQ line.
EOI (end or identify)
The EOI line has two purposes. The Talker uses the EOI line to mark the end of a message string.
The Active Controller uses the EOI line to tell devices to identify their responses in a parallel poll.
GPIB-100A User Manual A-4 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 30

Appendix A Operation of the GPIB
Physical and Electrical Characteristics
Devices are usually connected with a cable assembly consisting of a shielded 24-conductor cable
with both a plug and receptacle at each end. This design allows devices to be connected in either a
linear or a star configuration, or a combination of the two. See Figures A-2 and A-3.
Figure A-2. Linear Configuration of the GPIB Devices
© National Instruments Corporation A-5 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 31

Operation of the GPIB Appendix A
Figure A-3. Star Configuration of GPIB Devices
The standard connector is the Amphenol or Cinch Series 57 MICRORIBBON or AMP CHAMP
type. An adapter cable using non-standard cable and/or connector is used for special interconnect
applications.
The GPIB uses negative logic with standard TTL logic levels. When DAV is true, for example, it
is a TTL low level (≤ 0.8 V), and when DAV is false, it is a TTL high level (≥ 2.0 V).
GPIB-100A User Manual A-6 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 32

Appendix A Operation of the GPIB
Configuration Restrictions
To achieve the high data transfer rate that the GPIB is designed for, the physical distance between
devices and the number of devices on the bus is limited.
The following restrictions are typical:
• A maximum separation of 4 m between any two devices and an average separation of 2 m
over the entire bus.
• A maximum total cable length of 20 m.
• No more than 15 devices connected to each bus, with at least two-thirds powered-on.
It is usually possible to connect a cluster of lab instruments without exceeding these restrictions. But
many applications require longer cable spans or additional loading. From the time the GPIB was
invented, the need has existed for bus extenders and expanders (repeaters).
Extenders connect two separate buses via a transmission medium and the distance between the buses
can be quite long. Expanders allow up to 14 additional devices to be connected to the bus and 20
meters of cable length to be added to the system.
National Instruments provides two extenders which allow longer cable spans. These products are the
GPIB-100A and the GPIB-110. Both must be used in pairs, one at each end of the extension cable.
The GPIB-100A, a parallel extender, relays the instantaneous status of all GPIB signals over an RS422-compatible cable. The GPIB-100A allows up to a 300-meter extension. The GPIB-110, a serial
extender, samples the GPIB signals, encodes the information into small packets, and transmits the
packets on either a low-cost coaxial cable, or a high performance electrically isolated fiber-optic cable.
The GPIB-110 allows up to a 2-kilometer extension.
The GPIB-100A is the only parallel extender on the market today. The instantaneous status of all
GPIB signals on one side are relayed over individual RS-422 circuits to the other side. This
approach makes the GPIB-100A the fastest and most transparent of all extenders available. The
parallel design however, requires bulkier and more costly cable than serial designs.
© National Instruments Corporation A-7 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 33

Appendix B Schematic Diagram
This appendix contains the schematic diagram for the GPIB-100A.
© National Instruments Corporation B-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 34

Page 35

Appendix C GPIB-100A Parts Locator Diagram
This appendix contains the parts locator diagram for the GPIB-100A. The parts locator diagram
shows the locations of the GPIB-100A configuration jumpers and switches.
Figure C-1. GPIB-100A Parts Locator Diagram
© National Instruments Corporation C-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 36

Appendix D Cable Assembly Wire List
This appendix contains the wire list for the GPIB-100A Transmission Cable.
© National Instruments Corporation D-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 37

Table D-1. Cable Assembly Wire List
Page 38

Appendix E Multiline Interface Command Messages
The following tables are multiline interface messages (sent and received with ATN TRUE).
© National Instruments Corporation E-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 39

Multiline Interface Command Messages Appendix E
Multiline Interface Messages
Hex Oct De c ASCII Msg He x Oct D ec ASCII Msg
00 000 0 NUL 20 040 32 SP MLA0
01 001 1 SO H GTL 21 041 33 ! MLA1
02 002 2 STX 22 042 34 " MLA2
03 003 3 ETX 23 043 35 # MLA3
04 004 4 EOT SDC 24 044 36 $ MLA4
05 005 5 EN Q PPC 25 045 37 % MLA5
06 006 6 ACK 26 046 38 & MLA6
07 007 7 BEL 27 047 39 ' MLA7
08 010 8 BS GET 28 050 40 ( MLA8
09 011 9 HT TCT 29 051 41 ) MLA9
0A 012 10 LF 2A 052 42 * MLA10
0B 013 11 VT 2B 053 43 + MLA11
0C 014 12 F F 2C 054 44 , MLA12
0D 015 13 CR 2D 055 45 - MLA13
0E 016 14 SO 2E 056 46 . MLA14
0F 017 15 SI 2F 057 47 / MLA15
10 020 16 DLE 30 060 48 0 MLA16
11 021 17 DC1 LLO 31 061 49 1 MLA17
12 022 18 DC2 32 062 50 2 MLA18
13 023 19 DC3 33 063 51 3 MLA19
14 024 20 DC4 DCL 34 064 52 4 MLA20
15 025 21 NAK PPU 35 065 53 5 MLA21
16 026 22 SYN 36 066 54 6 MLA22
17 027 23 ETB 37 067 55 7 MLA23
18 030 24 CAN SPE 38 070 56 8 MLA24
19 031 25 EM SPD 39 071 57 9 MLA25
1A 032 26 SUB 3A 072 58 : MLA26
1B 033 27 ESC 3B 073 59 ; MLA27
1C 034 28 FS 3C 074 60 < MLA28
1D 035 29 GS 3D 075 61 = MLA29
1E 036 30 RS 3E 076 62 > MLA30
1F 037 31 US 3F 077 63 ? UNL
Message Definitions
DCL Device Clear
GET Group Execute Trigger
GTL Go To Local
LLO Local Lockout
MLA My Listen Address
MSA My Secondary Address
MTA My Talk Address
PPC Parallel Poll Configure
PPD Parallel Poll Disable
GPIB-100A User Manual E-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 40

Appendix E Multiline Interface Command Messages
Multiline Interface Messages
Hex Oct De c ASCII Msg Hex Oct De c ASCII Msg
40 100 64 @ MTA0 60 140 96 ` MSA0,PPE
41 101 65 A MTA1 61 141 97 a MSA1,PPE
42 102 66 B MTA2 62 142 98 b MSA2,PPE
43 103 67 C MTA3 63 143 99 c MSA3,PPE
44 104 68 D MTA4 64 144 100 d MSA4,PPE
45 105 69 E MTA5 65 145 101 e MSA5,PPE
46 106 70 F MTA6 66 146 102 f MSA6,PPE
47 107 71 G MTA7 67 147 103 g MSA7,PPE
48 110 72 H MTA8 68 150 104 h MSA8,PPE
49 111 73 I MTA9 69 151 105 i MSA9,PPE
4A 112 74 J MTA10 6A 152 106 j MSA10,PPE
4B 113 75 K MTA11 6B 153 107 k MSA11,PPE
4C 114 76 L MTA12 6C 154 108 l MSA12,PPE
4D 115 77 M MTA13 6D 155 109 m MSA13,PPE
4E 116 78 N MTA14 6 E 156 110 n MSA14,PPE
4F 117 79 O MTA15 6F 157 111 o MSA15,PPE
50 120 80 P MTA16 70 160 112 p MSA16,PPD
51 121 81 Q MTA17 71 161 113 q MSA17,PPD
52 122 82 R MTA18 72 162 114 r MSA18,PPD
53 123 83 S MTA19 73 163 115 s MSA19,PPD
54 124 84 T MTA20 74 164 116 t MSA20,PPD
55 125 85 U MTA21 75 165 117 u MSA21,PPD
56 126 86 V MTA22 76 166 118 v MSA22,PPD
57 127 87 W MTA23 77 167 119 w MSA23,PPD
58 130 88 X MTA24 78 170 120 x MSA24,PPD
59 131 89 Y MTA25 79 171 121 y MSA25,PPD
5A 132 90 Z MTA26 7A 172 122 z MSA26,PPD
5B 133 91 [ MTA27 7B 173 123 { MSA27,PPD
5C 134 92 \ MTA28 7C 174 124 | MSA28,PPD
5D 135 93 ] MTA29 7D 175 125 } MSA29,PPD
5E 136 94 ^ MTA30 7 E 176 126 ~ MSA30,PPD
5F 137 95 _ UNT 7F 177 127 DEL
PPE Parallel Poll Enable
PPU Parallel Poll Unconfigure
SDC Selected Device Clear
SPD Serial Poll Disable
SPE Serial Poll Enable
TCT Take Control
UNL Unlisten
UNT Untalk
© National Instruments Corporation E-3 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 41

Appendix F Mnemonics Key
This appendix contains a mnemonics key that defines the mnemonics (abbreviations) used
throughout this manual.
Mnemonic Definition
ASCII American Standard Code for Information Interchange
ATN Attention
C Controller
CIC Controller-In-Charge Bit
DAV Data Valid
DIO Data
EOI End or Identify Bit
FF Flip-flop
IDY Identify
IFC Interface Clear
ISO International Standard code set
L Listener
LAC Local Active Controller
LS Local Source
LSC Local System Controller
NDAC GPIB Not Data Accepted line status Bit
NRFD GPIB Not Ready For Data line status Bit
PON Power-On Reset Pulse
PP Parallel Poll (scan all status flags)
PPR Parallel Poll Response
RAC Remote Active Controller
RCD Resistor/Capacitor Delay
© National Instruments Corporation F-1 GPIB-100A User Manual
Page 42

Mnemonics Key Appendix F
Mnemonic Definition
REN Remote Enable
RFD Ready for Data
RR Remote Response
RS Remote Source
RSC Remote System Controller
SRQ Service Request
T Talker
TL Talker/Listener
TLC Talker/Listener/Controller (GPIB Adapter)
TTL Transistor/Transistor Logic
GPIB-100A User Manual F-2 © National Instruments Corporation
Page 43

User Comment Form
National Instruments encourages you to comment on the documentation supplied with our
products. This information helps us provide quality products to meet your needs.
Title: GPIB-100A User Manual
Edition Date March 1990
Part Number: 320063-01
Please comment on the completeness, clarity, and organization of the manual.
If you find errors in the manual, please record the page numbers and describe the errors.
Thank you for your help.
Name
Title
Company
Address
Phone ( )
Mail to: Technical Publications
National Instruments Corporation
6504 Bridge Point Parkway, MS 53-02
Austin, TX 78730-5039
 Loading...
Loading...