National Datacomm 0650S02 Users manual

High Speed Access Point
For Small Business
User’s Guide
NDC Communications, Inc.
265 Santa Ana Court
Sunnyvale, CA 94086, USA
Tel: +1 (408) 730-0888
Fax: +1 (408) 730-0889
P/N.: 85-506600-01
Rev.X1
May 2000
Technical Support
E-mail: support@ndclan.com (US only)
Toll-Free (US only): 800-632-1118
Europe and Asia Pacific
E-mail: techsupt@ndc.com.tw
NDC World Wide Web
www.ndclan.com

TRADEMARKS
NDC and SOHOware are trademarks of NDC Communications, Inc. All other
names mentioned in this document are trademarks/registered trademarks of their
respective owners.
NDC provides this document "as is," without warranty of any kind, neither
expressed nor implied, including, but not limited to, the particular purpose. NDC
may make improvements and/or changes in this manual or in the product(s) and/or
the program(s) described in this manual at any time. This document could include
technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
FCC WARNING
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
Digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
Ÿ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna
Ÿ Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
Ÿ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected
Ÿ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
You are cautioned that changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void your authority to operate the
equipment.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that
may cause undesired operation
WARING
This device should be located at a separation distance 20cm or more to the person.
The antenna should not be operated next to a person’s body.
ii InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business

Table Of Contents
PACKING LIST........................................................................................................................................................................VIII
INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................................................................................................................1
INSTANTWAVE HIGH SPEED FAMILY.....................................................................1
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS .............................................................................................1
CABLING..............................................................................................................................1
GLOSSARY .........................................................................................................................................................................................2
HOW TO USE THIS GUIDE..............................................................................................................................................3
PLANNING YOUR NETWORK ....................................................................................................................................4
INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK TYPES.....................................................................4
PLANNING AN INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK....................................................6
Single AP Installation..................................................................................................6
Multiple APs Installation.............................................................................................6
ROAMING.............................................................................................................................7
ACCESS POINT PLACEMENT GUIDELINES............................................................8
Placing For Performance.............................................................................................8
Placement Tools ............................................................................................................8
MOUNTING THE AP.........................................................................................................8
GETTING STARTED.................................................................................................................................................................9
ACCESS POINT HARDWARE INSTALLATION.......................................................9
LED INDICATORS...........................................................................................................10
AP MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INSTALLATION / UNINSTALLATION....10
Installation....................................................................................................................10
Uninstallation...............................................................................................................11
AP COMFIG TOOL .................................................................................................................................................................12
USING THE AP COMFIG TOOL...................................................................................12
AP COMFig Password...............................................................................................12
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business iii

iv InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
AP COMFig Service...................................................................................................13
Perform AP Self Diagnostic Test.............................................................................20
Update AP Firmware..................................................................................................20
Reset AP Configurations...........................................................................................21
Manage APMS Host Table .......................................................................................21
AP MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (APMS)..............................................................................................................22
When Do I Need the APMS Program?....................................................................22
What Does the APMS Program do?........................................................................22
CONFIGURATION REQUIREMENTS FOR APMS.................................................23
NETWORK MANAGEMENT CONNECTION TO THE AP...................................23
MAKING AN ETHERNET CONNECTION................................................................24
TCP/IP Setup ...............................................................................................................24
THE APMS TOOL.....................................................................................................................................................................25
ASSIGNING AN IP ADDRESS TO THE AP..............................................................25
ASSIGNING A NETWORK ID TO THE AP...............................................................25
Network ID ...................................................................................................................25
Host ID..........................................................................................................................26
ASSIGNING A SUBNET MASK TO THE AP............................................................26
USING THE APMS TOOL...............................................................................................26
Adding an AP(s).........................................................................................................27
Create New AP............................................................................................................27
Connecting to an AP..................................................................................................27
MANAGING INSTANTWAVE HIGH SPEED CONFIGURATIONS...................28
Config............................................................................................................................28
VIEWING INSTANTWAVE HIGH SPEED INFORMATION AND STATISTICS
................................................................................................................................................33
View..............................................................................................................................33
SAVING AND LOADING AP CONFIGURATION...................................................35
Saving the AP’s Configuration to File ....................................................................35
Opening an AP’s Configuration File for Loading.................................................35

Import Host Table.......................................................................................................35
Password ......................................................................................................................36
TROUBLESHOOTING........................................................................................................................................................37
HOW TO REACH OUR TECHNICAL SUPPORT ..................................................................................38
NDC LIMITED WARRANTY ........................................................................................................................................39
INDEX....................................................................................................................................................................................................43
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business v

vi InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
List of Figures
FIGURE 1. SIMPLE WIRELESS INFRASTRUCTURE NETWORK.......................4
FIGURE 2. AP TO WIRED ETHERNET BRIDGE ................................................5
FIGURE 3. MULTIPLE AP NETWORK...............................................................5
FIGURE 4. ACCESS POINT .................................................................................9
FIGURE 5. ACCESS POINT .................................................................................9
FIGURE 6. ACCESS POINT LEDS .....................................................................10
FIGURE 7. LED FUNCTIONS............................................................................10
FIGURE 8. AP COMFIG TOOL/SERVICE .......................................................13
FIGURE 9. CONFIGURATION/GENERAL.........................................................13
FIGURE 10. WEP SECURITY.............................................................................16
FIGURE 11. CONFIGURATION/IP......................................................................17
FIGURE 12. CONFIGURATION/FILTER.............................................................18
FIGURE 13. CONFIGURATION/ACCESS CONTROL .........................................19
FIGURE 14. NEW ENTRY..................................................................................19
FIGURE 15. HARDWARE DIAGNOSIS...............................................................20
FIGURE 16. APMS TABLE...............................................................................21
FIGURE 17. IP ADDRESS RESTRICTIONS........................................................26
FIGURE 18. INSTANTWAVE APMS.................................................................26
FIGURE 19. APMS WITH CONNECTION MADE.............................................27
FIGURE 20. AP PROPERTIES............................................................................28
FIGURE 21. CONFIG/AP SETTING ...................................................................28
FIGURE 22. AP SETTING/IP.............................................................................29
FIGURE 23. AP SETTING/ACCESS CONTROL.................................................30
FIGURE 24. V IEW MENU ..................................................................................33
FIGURE 25. AP INFORMATION........................................................................34
FIGURE 26. CONNECTED WIRELESS STATIONS.............................................34

FIGURE 27. SAVE AP CONFIGURATION.........................................................35
FIGURE 28. IMPORT HOST TABLE...................................................................35
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business vii

viii InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
Packing List
The package should contain the following items:
• One Access Point or one NetBlaster
• One Antenna
• Three InstantWave High Speed Access Point System Manager Diskettes
• One AC Power Adapter
• This User’s Guide
• One Wall-fixing Template and Screws

Introduction
Congratulations on choosing one of NDC s InstantWave High Speed wireless
networking product s family. InstantWave High Speed was one of the first IEEE
802.11b wireless standard compliant products in the industry and was designed
with a “Maximizing the Convenience of Networking” philosophy in mind. You
will find InstantWave High Speed products very easy to setup and use.
The User’s Guide gives comprehensive instructions on installing and using the
InstantWave High Speed Access Point (AP). The AP provides a transparent
bridged connection between a wired network and a wireless network and allows
your wireless stations to communicate with devices attached to your wired network.
It manages the flow of data packets from the wired LAN to the wireless LAN, and
vice versa. The Access Point Management System (APMS) performs wireless
network configuration management and diagnostic functions.
InstantWave High Speed Family
The InstantWave High Speed Access Point is part of a family of easy to use high
performance wireless communication products. The family products include:
• InstantWave High Speed Access Point (NWH660, NWH650)
• InstantWave High Speed PCI card (NWH630)
• InstantWave High Speed PC card (NWH610)
System Requirements
System requirements to install and operate the InstantWave High Speed Access
Point are:
• A RS-232 cable
• An Ethernet drop (UTP)
• A PC (only used when the configuration of AP s Network properties is
necessary)
Cabling
Connecting the AP to an Ethernet network requires an Unshielded Twisted-Pair
cable. The AP fits into the network just as any other node would do. An LED will
light to indicate a connection (UTP cable). The cable length should follow
Ethernet standards in each case.
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business 1

2 InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
Glossary
Group ID/BSSID
A Group ID (the 802.11 standard uses the term BSSID) is the ID of a wireless cell.
A wireless cell is usually made up of stations in an area that the radio signal can
comfortably cover. In other words, any wireless station in the cell can
communicate with any other within reach of the radio signal.
Domain Name/ESSID
A “Domain” is most commonly used to refer to a group of computers whose
hostnames share a common suffix. The domain is usually defined by the network
administrator as a segment/subnet of a large network and may be made up of
overlapping wireless cells. Wireless nodes can roam freely within the same
domain without disconnecting from the network.
Roaming
The convenience of a mobile PC is the ability to move freely. The concept is
similar to that of a cellular phone moving from one base station to another.
InstantWave High Speed offers built-in high performance and seamless roaming
capabilities.
Carrier Set
InstantWave High Speed products use the unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific,
Medical) band to communicate through radio waves. Different countries offer
different radio frequencies to be used as the ISM band. There are four frequency
bands defined by 802.11: Japan (2.471GHz 2.497 GHz), USA, Extended Japan,
Canada, and Europe (2.4 GHz 2.4835 GHz), Spain (2.445 GHz
and France (2.4465 GHz 2.4835 GHz). If a user wants to use InstantWave High
Speed in a country not listed above, he/she needs to check with their government
regulating body to find the correct frequency band to use. All InstantWave High
Speed products are supplied preset to the country of sale s frequency band.

How to Use this Guide
InstantWave High Speed is extremely versatile in providing varying levels of
network management. For Small Office/Home Office users, setup and
configuration is a quick, four-step process. For these users the Access Point
Hardware Installation Access Point Hardware Installation Access Point Hardware
Installation section, on page 9, provides simple instructions to get your network up
and running within minutes. Go to the Access Point Hardware Installation section
if your network will meet the following criteria:
• You will accept all default values
• Your network will have only one Access Point
The AP COMFig Tool, see page 12, permits AP configuration from a PC via a
COM port connection. The program enables the user to change the default Access
Point IP configuration settings before introducing a new AP to an already
established wireless network.
For System Administrators, with advanced networking requirements, the AP
Management System (APMS) section, on page22, covers configuring for advanced
management and explains how to make a network management connection. The
APMS program is a simple to use, yet extremely powerful, network management
tool.
Whichever setup method you intend to use, you should read through the next
section “Planning Your Network,” in order to get the best possible performance
from your InstantWave High Speed wireless network.
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business 3

4 InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
Planning Your Network
Infrastructure Network Types
An Infrastructure network is formed by several stations and one or more Access
Points (APs), with the stations within a set distance from the AP. Figure 1 depicts
a typical Infrastructure network topology.
There are three infrastructure network setups that are commonly used. It is a good
idea to understand the possible network setups and configuration requirements
before planning your wireless network.
Type 1. The simplest wireless infrastructure network is composed of one
Access Point (AP) and a few wireless Stations communicating via
radio waves (Figure 1). This setup enables mobile stations to
communicate with each other. The main benefit of this type of
network is to extend the range of the network. If an AP is placed
between Station-1 and Station-2, the radio transmission distance is
effectively doubled since Station-1 can talk to Station-2 through the
AP. The drawback of this configuration is that the effective
bandwidth is halved since all communication is relayed by the AP.
Figure 1. Simple Wireless Infrastructure Network
Type 2. The next simplest wireless network is very similar to the Type 1
network. This time the AP is connected to a wired Ethernet network
as a node. In this configuration the AP is effectively performing as a
bridge between the wired Ethernet and the wireless networks (Figure
2).
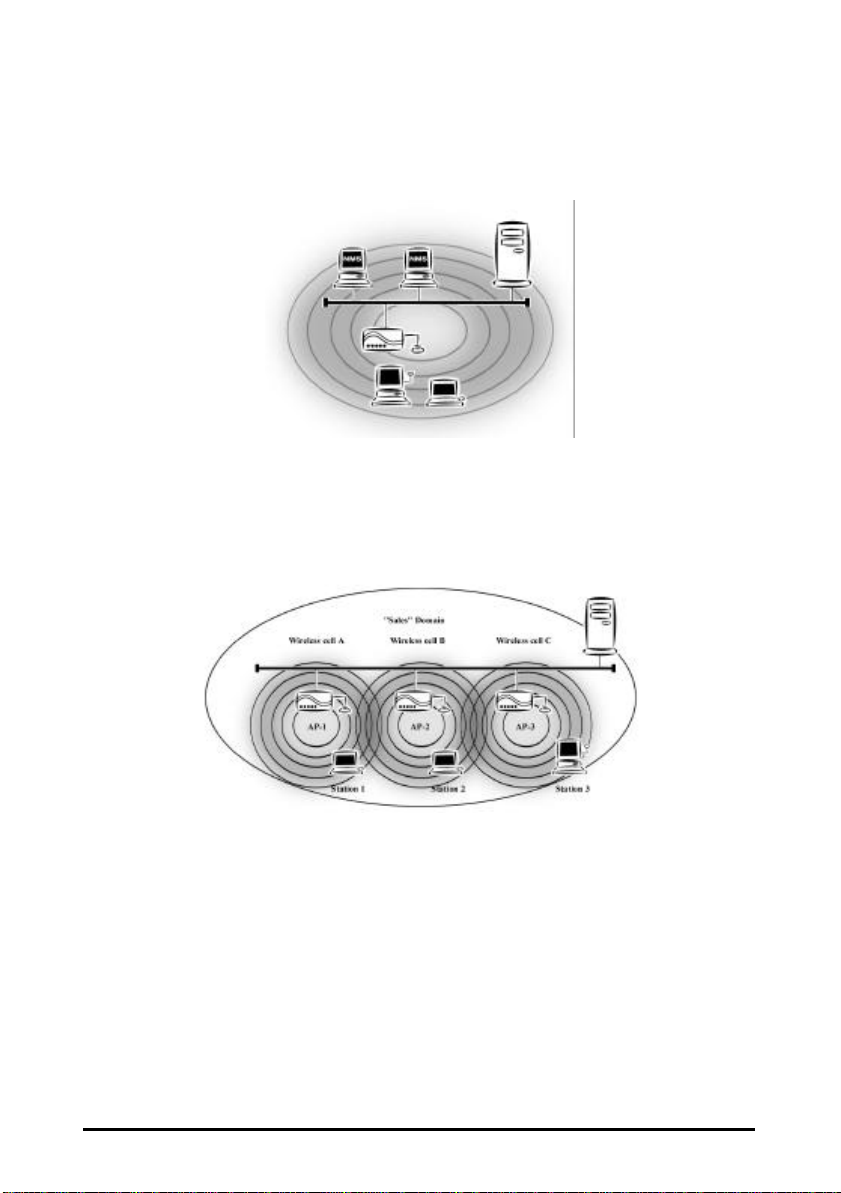
Wireless users have the same access to the network resources as they
would have if they were wired. This type of network is usually used
to extend an existing network into a difficult to wire or a roaming
environment.
Server
Figure 2. AP to Wired Ethernet Bridge
Type 3. The third type of network is composed of multiple APs and multiple
Stations (Figure 3). The APs could also be connected to servers on
the wired Ethernet network. The shadowed area represents signal
overlap between subnet1 (AP-1) and subnet2 (AP-3).
Figure 3. Multiple AP Network
The reasons for having multiple APs installed are:
1. To increase bandwidth in order to boost overall network performance
2. To extend the coverage range
Any other type of configuration is usually a mix of these commonly used types.
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business 5

6 InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
Planning an Infrastructure Network
This section explains some of the things you need to consider in planning an
Infrastructure network. Setting up is a two step process.
1. Install and configure the InstantWave High Speed products
2. Decide the best physical location of the InstantWave High Speed products so
as to optimize performance
The following sections give quick guidelines for these two steps. Before we go
into detail, the network planner should first decide whether to have a single AP
wireless network or a multiple AP network
Single AP Installation
If you are setting up a simple network with only one AP and a few Stations (a Type
1 or Type 2 network configuration as described in Infrastructure Network , page 4),
the installation can be performed painlessly. All you need to do is make sure the
AP and all the wireless Stations hold the same
configuration.
Adding a new Station to an existing Infrastructure Network is easy. Again, all you
need to do is to set the newly added Station to be the same as
Multiple APs Installation
Install multiple APs in the same network (or Domain) with an overlapping signal
(Figure 3)
• Use the same Domain Name
• The roaming function in the Station if roaming is desired.
Note: A Station will automatically connect to whichever AP in the same domain is
offering the best signal

Roaming
InstantWave High Speed products are equipped with seamless roaming capabilities.
Roaming is necessary to prevent mobile Stations from being disconnected from the
network as they move around.
InstantWave High Speed is designed to allow wireless Stations to roam freely
within an infrastructure domain composed of multiple APs with overlapping signal
coverage (as in the Type-3 network configuration described in the previous
section). For example, roaming enables Station-1 to move from the AP-1 signal
coverage area to the AP-2 signal coverage area without disconnecting from the
network. The handover is achieved transparently; the Station-1 user would not
realize he had moved from AP-1 to AP-2.
The requirements for a roaming environment are:
a) Multiple APs with overlapping signal coverage (see Multiple APs
Installation, page 6)
b) The APs must be configured to have the same Domain name (see AP
Setting, page 29)
c) The mobile Stations must have the same Domain name as the APs
d) *It is advisable that APs on different TCP/IP subnets be given different
Domain names to avoid roaming confusion (see AP Setting, page 29)
Note: If you want to move your mobile PC between different APs without
terminating the existing networking link, you need to enable the roaming
function on the Mobile Station. The APs that a Mobile Station will roam to
must also be configured with the same domain name (reference page 2). If a
Station detects that the signal quality with the current linked AP is weak, it
will search for an AP in the same domain with a better signal quality and
automatically establishes a new connection with it. “ When a Station is
roaming, it will always use the same IP address. The TCP/IP router will not
route information packets to a Mobile Station if it re-associates with a AP
that is in a different TCP/IP subnet. In other words, if your network consists
of two subnets connected by a router, a Mobile Station may roam to a
different subnet with the same domain name and then fails to communicate
with other network devices in TCP/IP. To avoid running into such an
awkward situation, you must assign different domain names to different
TCP/IP subnets.”
InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business 7

8 InstantWave High Speed Access Point For Small Business
Access Point Placement Guidelines
A characteristic of radio communication is the problem. Radio is
receptive to interference. Therefore, the more interference you can avoid, the
better performance you will get from wireless products. The following section
describes how the InstantWave High Speed AP should be placed to reduce possible
interference.
A few tips to mention that are particularly significant in a radio wave
communications system:
1. Radio waves reflect or refract from buildings, walls, metal furniture, or other
objects. This could result in performance degradation due to the fluctuation of
the received signal
2. Microwave ovens use the 2.45 GHz frequency band. InstantWave High Speed
also functions in the 2.4 ~ 2.5 GHz band, and therefore shares some of the
band with microwave ovens. This means that when a nearby microwave oven
is in use it may interfere with InstantWave High Speed, resulting in
performance degradation on the wireless network
Placing For Performance
For the best performance, it is advisable that users follow the guidelines below in
placing the product:
• Place the AP as high as possible, in as open an area as possible
• Avoid placing the AP (especially the antenna) close to metal objects (e.g., file
cabinets, metal cubicles, …etc.)
• Keep APs and Stations as far away as possible from microwave ovens (10
meters min. is advisable)
Placement Tools
InstantWave High Speed includes a Station utility program to help users find the
best location in which to place the AP relative to the location of the Stations.
1. Start the AP
2. Allow a wireless Station to connect with the AP
3. From the Station, run the InstantWave High Speed Station Monitor RF Signal
Quality Program
4. Move the AP and the APs antenna to find the best signal quality
Mounting the AP
The AP may be either freestanding or wall-mounted. Screws and a paper template
are provided for easy installation.
 Loading...
Loading...