Nanni 5.280HE, 4.200HE, 4.220HE, 4.195HE, D1503-M Workshop Manual
...
60300075
Mis à jour 01/2013
Diesel Marine Engine
5.280HE—4.200HE—4.220HE—4.195HE
WORKSHOP MANUAL

TO THE READER
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
This Workshop Manual has been prepared to provide servicing personnel with
information on the mechanism, service and maintenance of KUBOTA Diesel Engine 03M Series. It is divided into two parts, “Mechanism” and “Servicing” for each section.
Q Mechanism
Information on the Features and New Mechanisms are described. This information
should be understood before proceeding with troubleshooting, disassembling and
servicing.
Q Servicing
The heading “General” includes general precautions, check and maintenance and
special tools. There are troubleshooting, checking and adjusting, disassembling and
assembling, and servicing which cover procedures, precautions, factory specifications
and allowable limits.
All information illustrations and specifications contained in this manual are based on
the latest product information available at the time of publication. The right is reserved
to make changes in all information at any time without notice.
Due to covering many models of this manual, illustration being used, have not been
specified as one model.
July 2001
© KUBOTA Corporation 2001
03-M Series, WSM
SAFETY FIRST
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This symbol, the industry’s “Safety Alert Symbol”, is used throughout this manual and on labels on
the machine itself to warn of the possibility of personal injury. Read these instructions carefully.
It is essential that you read the instructions and safety regulations before you attempt to repair or use
this unit.
DANGER : Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in
death or serious injury.
WARNING : Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in
death or serious injury.
CAUTION : Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury.
Q IMPORTANT : Indicates that equipment or property damage could result if instructions are not
followed.
Q NOTE : Gives helpful information.
BEFORE SERVICING AND REPAIRING
• Read all instructions and safety instructions in this
manual and on your engine safety decals.
• Clean the work area and engine.
• Park the machine on a firm and level ground.
• Allow the engine to cool before proceeding.
• Stop the engine, and remove the key.
• Disconnect the battery negative cable.
1
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
SAFETY STARTING
• Do not start the engine by shorting across starter
terminals or bypassing the safety start switch.
• Unauthorized modifications to the engine may impair
the function and / or safety and affect engine life.
SAFETY WORKING
• Do not work on the machine while under the influence
of alcohol, medication, or other substances or while
fatigued.
• Wear close fitting clothing and safety equipment
appropriate to the job.
• Use tools appropriate to the work. Makeshift tools,
parts, and procedures are not recommended.
• When servicing is performed together by two or more
persons, take care to perform all work safely.
• Do not touch the rotating or hot parts while the engine
is running.
• Never remove the radiator cap while the engine is
running, or immediately after stopping. Otherwise, hot
water will spout out from radiator. Only remove
radiator cap when cool enough to touch with bare
hands. Slowly loosen the cap to first stop to relieve
pressure before removing completely.
• Escaping fluid (fuel or hydraulic oil) under pressure
can penetrate the skin causing serious injury. Relieve
pressure before disconnecting hydraulic or fuel lines.
Tighten all connections before applying pressure.
• Wear a suitable hearing protective device such as
earmuffs or earplugs to protect against objectionable
or uncomfortable loud noises.
AVOID FIRES
• Fuel is extremely flammable and explosive under
certain conditions. Do not smoke or allow flames or
sparks in your working area.
• To avoid sparks from an accidental short circuit,
always disconnect the battery negative cable first and
connect it last.
• Battery gas can explode. Keep sparks and open
flame away from the top of battery, especially when
charging the battery.
• Make sure that no fuel has been spilled on the engine.
2
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
VENTILATE WORK AREA
• If the engine must be running to do some work, make
sure the area is well ventilated. Never run the engine
in a closed area. The exhaust gas contains poisonous
carbon monoxide.
DISPOSE OF FLUIDS PROPERLY
• Do not pour fluids into the ground, down a drain, or
into a stream, pond, or lake. Observe relevant
environmental protection regulations when disposing
of oil, fuel, coolant, electrolyte and other harmful
waste.
PREVENT ACID BURNS
• Sulfuric acid in battery electrolyte is poisonous. It is
strong enough to burn skin, clothing and cause
blindness if splashed into eyes. Keep electrolyte
away from eyes, hands and clothing. If you spill
electrolyte on yourself, flush with water, and get
medical attention immediately.
PREPARE FOR EMERGENCIES
• Keep a first aid kit and fire extinguisher handy at all
times.
• Keep emergency numbers for doctors, ambulance
service, hospital and fire department near your
telephone.
3
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
SPECIFICATIONS
SPECIFICATIONS
Model D1503-M D1703-M D1803-M
Number of Cylinders 3
Type Vertical, Water-cooled, 4 cycle diesel engine
Bore × Stroke 83 × 92.4 mm (3.27 × 3.64 in.) 87 × 92.4 mm (3.43 × 3.64 in.) 87 × 102.4 mm (3.43 × 4.03 in.)
Total Displacement 1499 cm
ISO Net Cont. 20.4 kW / 2800 min
(27.4 HP / 2800 min
ISO/SAE Net Intermittent 23.5 kW / 2800 min
(31.5 HP / 2800 min
SAE Gross Intermittent 24.9 kW / 2800 min
(33.4 HP / 2800 min
Maximum Bare Speed 3000 min
Minimum Bore Idling Speed 750 to 850 min
Combustion Chamber Spherical Type (E-TVCS)
Fuel Injection Pump Bosch Type Mini Pump
Governor All speed mechanical governor
Direction of Rotation Counter-Clockwise (viewed from flywheel side)
Injection Nozzle Bosch Throttle Type Mini Nozzle (OPD)
Injection Timing 0.314 rad (18 °) before T.D.C.
Firing Order 1-2-3
Injection Pressure 13.73 MPa (140 kgf/cm
Compression Ratio 23 : 1 22.6 : 1 23.8 : 1
Lubricating System Forced Lubrication by Trochoid Pump
Oil Pressure Indicating Electrical type switch
Lubricating Filter Full flow paper filter (cartridge type)
Cooling System Pressurized radiator, forced circulation with water pump
Starting System Electric Starting with Starter
Starting Motor 12 V, 1.4 kW 12 V, 2.0 kW
Starting Support Device By Glow Plug in Combustion Chamber
Battery 12 V, 60 AH, equivalent 12 V, 88 AH, equivalent
Charging Alternator 12 V, 480 W
Fuel Diesel Fuel No.2-D (ASTM D975)
Lubricating Oil Class CF lubricating oil as per API classification is recommended.
Lubricating Oil
Capacity
Oil Pan Depth
90 mm (3.54 in.)
Oil Pan Depth
124 mm (4.88 in.)
Weight (Dry) 148 kg (326 lbs) 151 kg (333 lbs)
* The specification described above is of the standard engine of each model.
* Conversion Formula : HP = 0.746 kW, PS = 0.7355 kW
3
(91.47 cu.in.) 1647 cm3 (100.51 cu.in.) 1826 cm3 (111.43 cu.in.)
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
22.4 kW / 2800 min
(30.0 HP / 2800 min
25.7 kW / 2800 min
(34.5 HP / 2800 min
27.4 kW / 2800 min
(36.7 HP / 2800 min
-1
(rpm) 2800 min-1 (rpm)
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
2
, 1991 psi)
23.3 kW / 2600 min
(31.2 HP / 2600 min
26.9 kW / 2600 min
(36.1 HP / 2600 min
28.4 kW / 2600 min
(38.1 HP / 2600 min
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
If this class of lubricating oil is not available, preferably use Class CD or CE lubricating oil.
For details on recommended lubricating oils, see page S-17, 20.
5.6 L (1.48 U.S.gals)
7.0 L (1.85 U.S.gals)
W10275180
4
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
SPECIFICATIONS
Model V2203-M V2403-M
Number of Cylinders 4
Type Vertical, Water-cooled, 4 cycle diesel engine
Bore × Stroke 87 × 92.4 mm (3.43 × 3.64 in.) 87 × 102.4 mm (3.43 × 4.03 in.)
Total Displacement 2197 cm
ISO Net Cont. 29.8 kW / 2800 min
(40.0 HP / 2800 min
ISO/SAE Net Intermittent 34.3 kW / 2800 min
(46.0 HP / 2800 min
SAE Gross Intermittent 36.4 kW / 2800 min
(48.8 HP / 2800 min
Maximum Bare Speed 3000 min
Minimum Bore Idling Speed 750 to 850 min
3
(134.07 cu.in.) 2434 cm3 (148.53 cu.in.)
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm) 2800 min-1 (rpm)
31.0 kW / 2800 min
(41.6 HP / 2600 min
35.8 kW / 2600 min
(48.0 HP / 2600 min
38.0 kW / 2600 min
(51.0 HP / 2600 min
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
-1
(rpm)
-1
(rpm))
Combustion Chamber Spherical Type (E-TVCS)
Fuel Injection Pump Bosch Type Mini Pump
Governor All speed mechanical governor
Direction of Rotation Counter-Clockwise (viewed from flywheel side)
Injection Nozzle Bosch Throttle Type Mini Nozzle (OPD)
Injection Timing 0.314 rad (18 °) before T.D.C.
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Injection Pressure 13.73 MPa (140 kgf/cm
2
, 1991 psi)
Compression Ratio 22.6 : 1 23.8 : 1
Lubricating System Forced Lubrication by Trochoid Pump
Oil Pressure Indicating Electrical type switch
Lubricating Filter Full flow paper filter (cartridge type)
Cooling System Pressurized radiator, forced circulation with water pump
Starting System Electric Starting with Starter
Starting Motor 12 V, 1.4 kW 12 V, 2.0 kW
Starting Support Device By Glow Plug in Combustion Chamber
Battery 12 V, 88 AH, equivalent 12 V, 92 AH, equivalent
Charging Alternator 12 V, 480 W
Fuel Diesel Fuel No.2-D (ASTM D975)
Lubricating Oil Class CF lubricating oil as per API classification is recommended.
If this class of lubricating oil is not available, preferably use Class CD or CE lubricating oil.
For details on recommended lubricating oils, see page S-17, 20.
Lubricating Oil
Capacity
Oil Pan Depth
90 mm (3.54 in.)
Oil Pan Depth
124 mm (4.88 in.)
7.6 L (2.01 U.S.gals)
9.5 L (2.51 U.S.gals)
Weight (Dry) 180 kg (397 lbs) 184 kg (406 lbs)
* The specification described above is of the standard engine of each model.
* Conversion Formula : HP = 0.746 kW, PS = 0.7355 kW
W10309670
5

03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
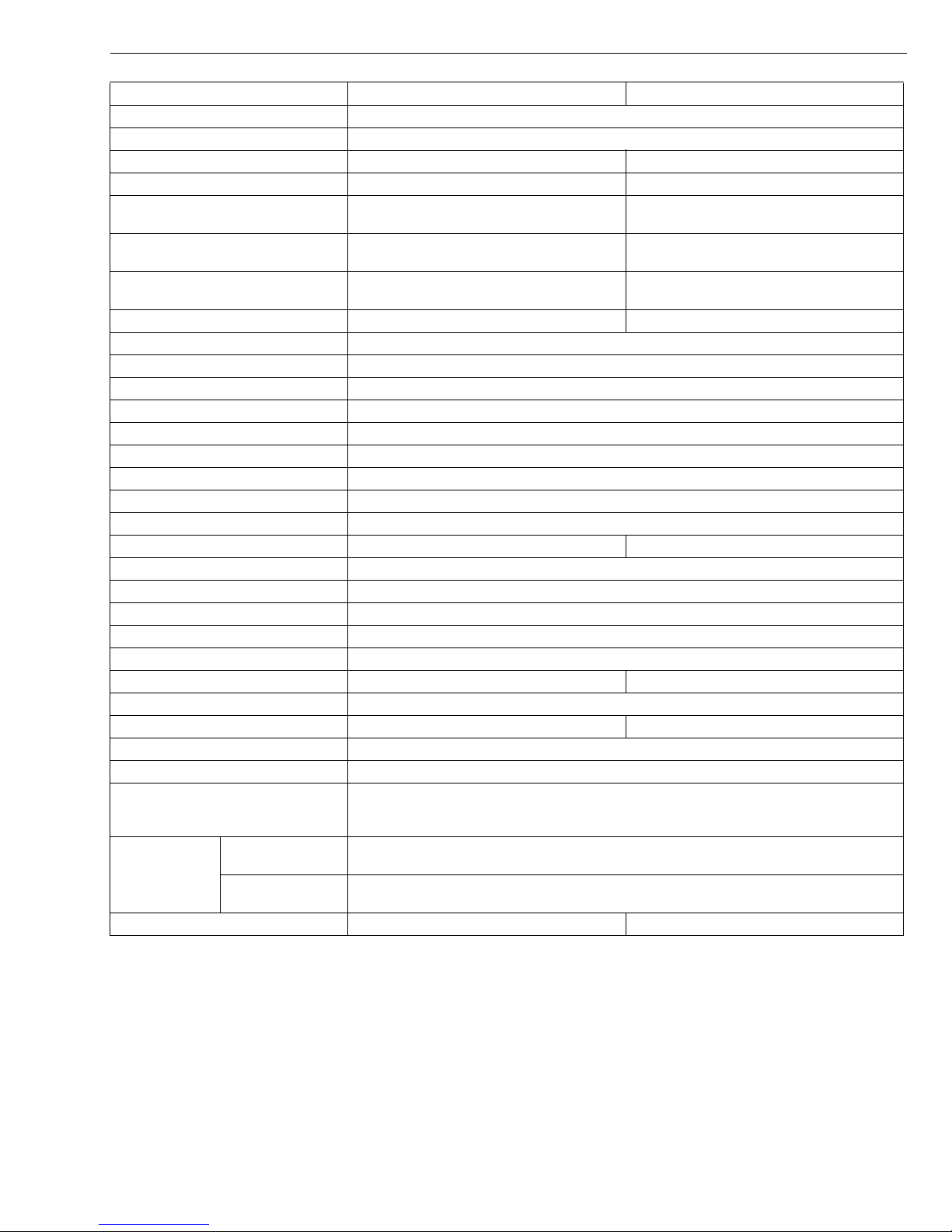
DIMENSIONS
DIMENSIONS
6
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
DIMENSIONS
7

MECHANISM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
CONTENTS
1. ENGINE BODY ............................................................................................... M-1
[1] HOLLOW CORE ....................................................................................... M-1
[2] PISTON...................................................................................................... M-1
[3] BUILT-IN DYNAMIC BALANCER (BALANCER MODEL ONLY) ......... M-1
[4] HALF-FLOATING HEAD COVER ............................................................ M-2
2. COOLING SYSTEM........................................................................................ M-3
[1] BOTTOM BYPASS SYSTEM................................................................... M-3
3. FUEL SYSTEM ............................................................................................... M-4
[1] GOVERNOR .............................................................................................. M-4
NOTICE
For not above-mentioned engine mechanism information, please refer ENGINE MECHANISM
WSM (97897-01870).
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
1. ENGINE BODY
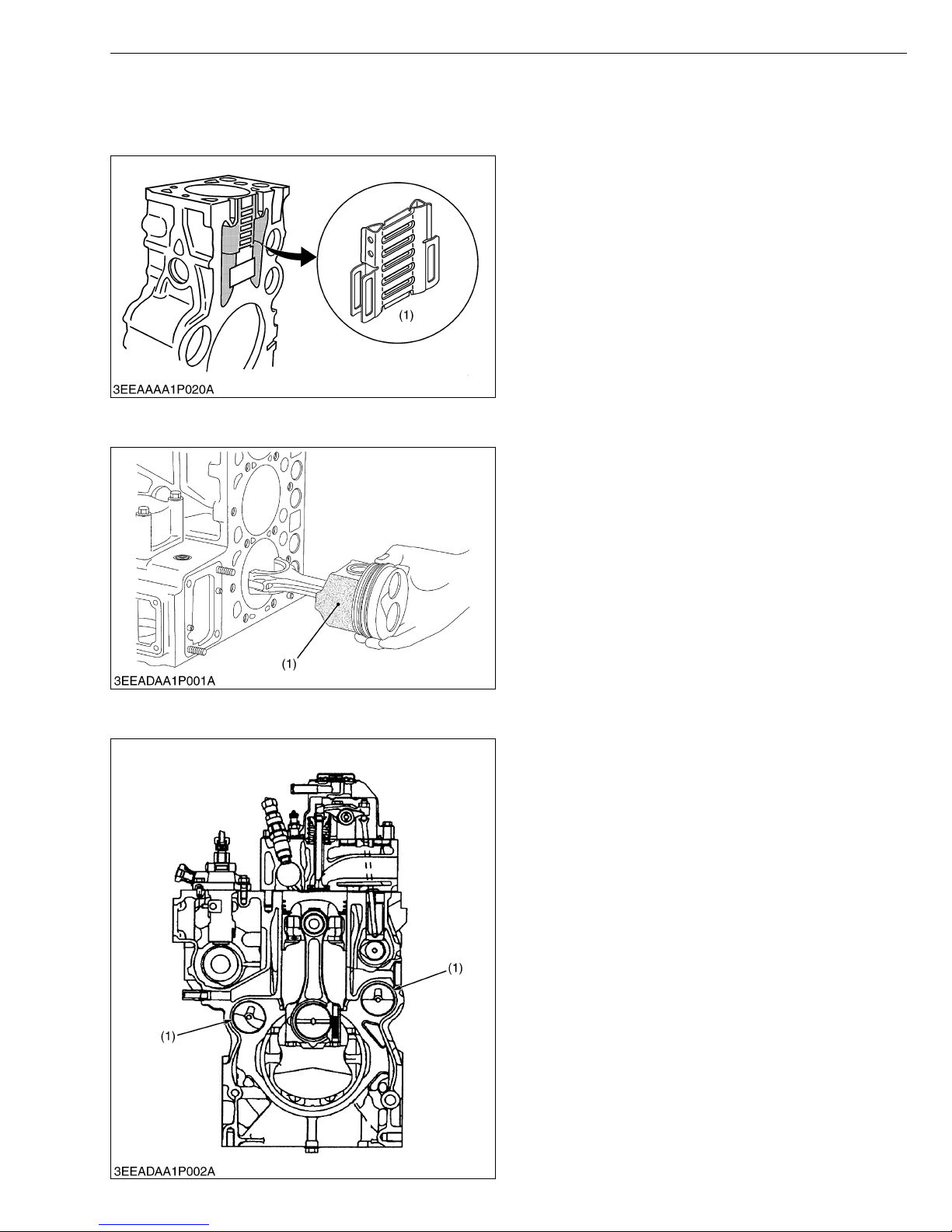
[1] HOLLOW CORE
[2] PISTON
DIESEL ENGINE
The cylinder block has a hollow core (1) already cast
inside the cylinder-to-cylinder water jacket.
In this core, there is a pair of vertical cooling
passages (right and left) as well as multiple horizontal
cooling channels that interconnect these cooling
passages. This design allows smoother cooling water
flow through the cylinder block, which cools down a wider
range between the cylinders more effectively.
(1) Hollow Core
W1013048
Piston’s skirt is coated with molybdenum
disulfied+, which reduces the piston slap noise and
thus the entire operating noise.
+Molybdenum disulfide (MoS
2)
The molybdenum disulfide (1) serves as a solid
lubricant, like a Graphite or Teflon. This material helps
resist metal wears even with little lube oil.
(1) Molybdenum Disulfide
[3] BUILT-IN DYNAMIC BALANCER (BALANCER MODEL ONLY)
Engine are sure to vibrate by piston’s reciprocation.
Theoretically, three-cylinder engines are much less
prone to cause vibration than four-cylinder ones (second
inertia, etc.). However, any engine has many moving
parts in addition to its pistons and cannot be completely
free from vibration.
The four cylinders engine V2203 and V2403 can be
fitted with balance weight on crankcase to absorb the
second inertia mentioned above and reduce vibration.
This engine is internally provide with two balancers
(1), one at the suction side and the other at the exhaust
side.
(1) Balancer
W1013114
W1013221
M-1
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
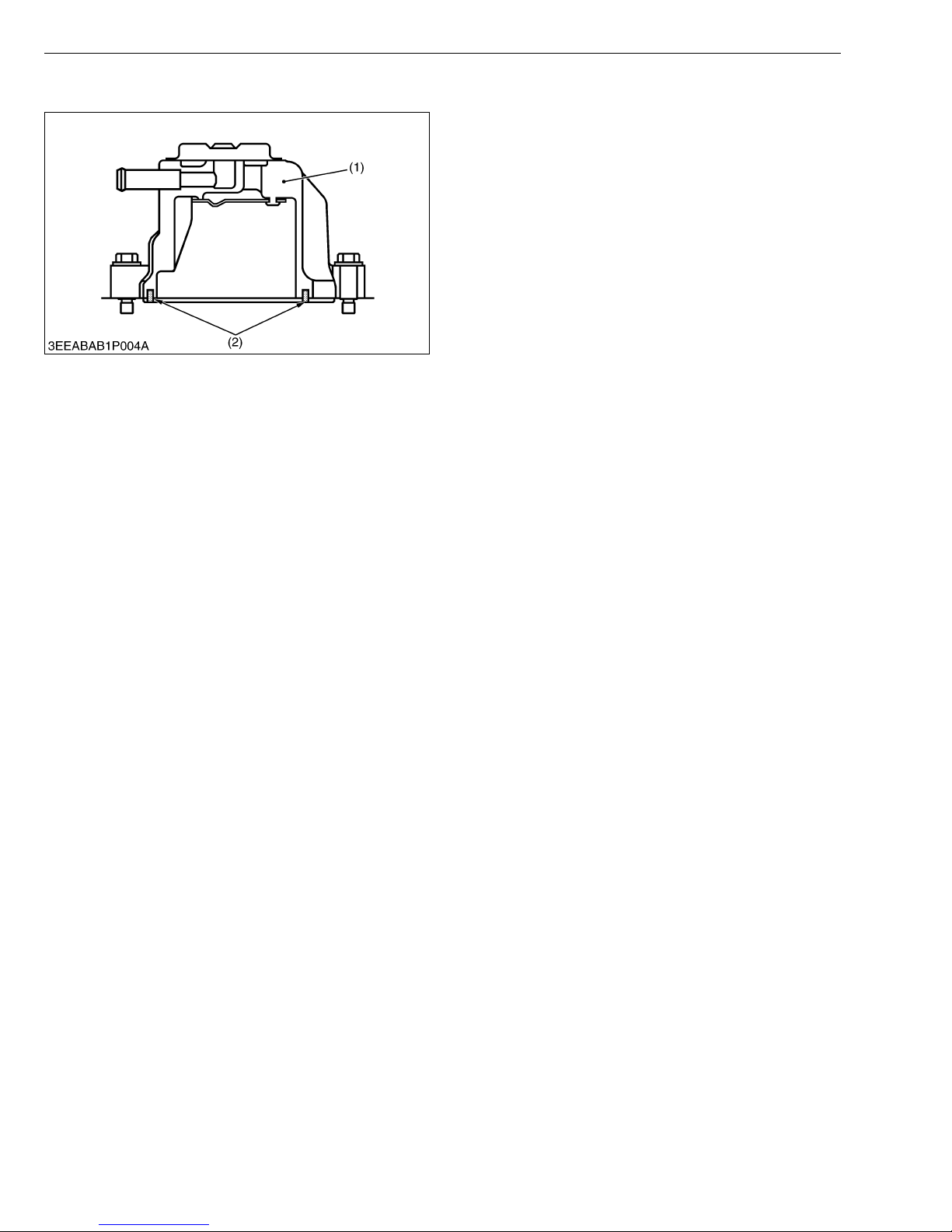
[4] HALF-FLOATING HEAD COVER
DIESEL ENGINE
The rubber packing (2) is fitted in to maintain the
cylinder head cover (1) 0.5 mm (0.02 in.) or so off the
cylinder head (1). This arrangement helps reduce noise
coming from the cylinder head.
(1) Cylinder Head Cover (2) Rubber Packing
W1013327
M-2
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
2. COOLING SYSTEM
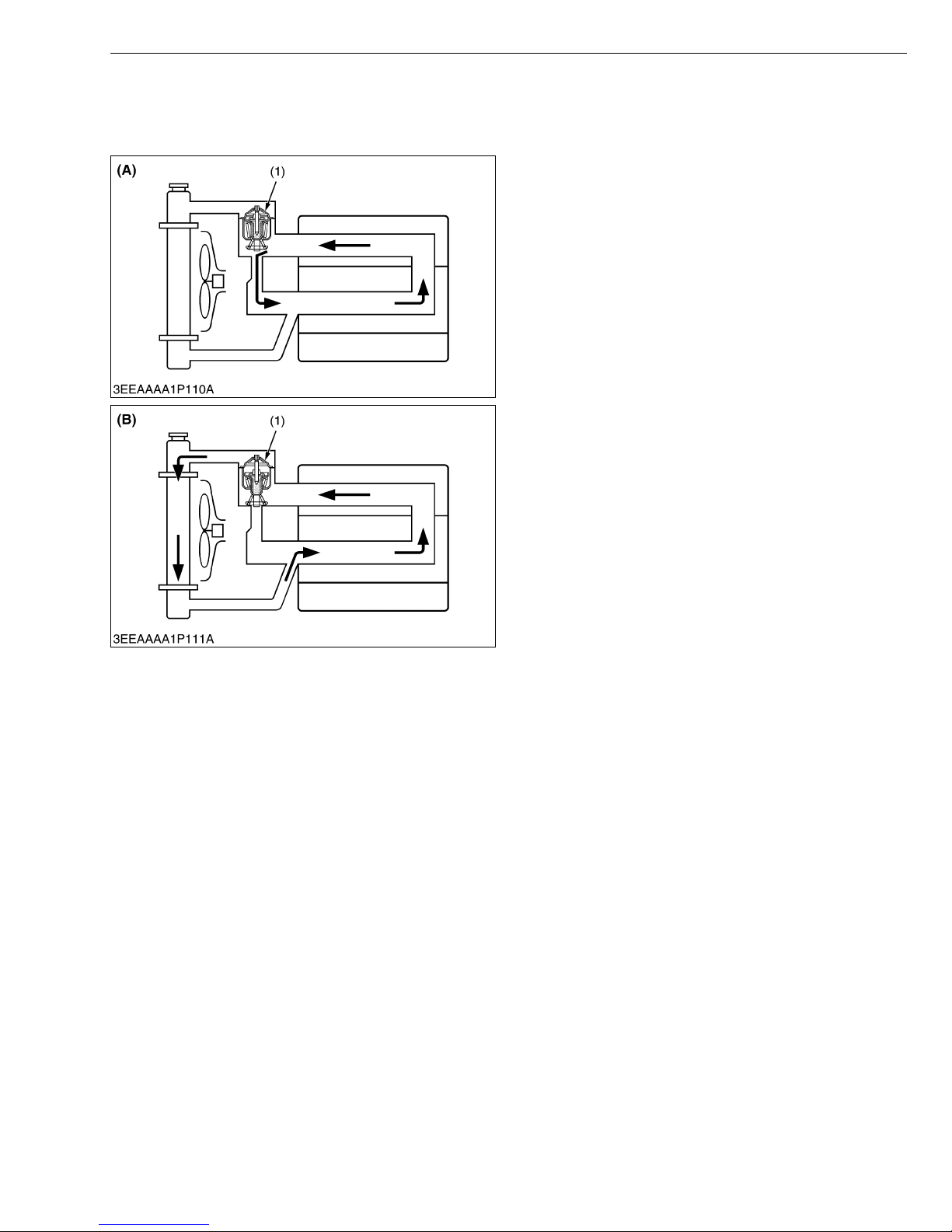
[1] BOTTOM BYPASS SYSTEM
DIESEL ENGINE
Bottom bypass system is introduced in 03-M Series
for improving the cooling performance of the radiator.
While the temperature of coolant in the engine is low,
the thermostat is held closed and the coolant is allowed
to flow through the bypass pipe and to circulate in the
engine.
When the temperature exceeds the thermostat valve
opening level, the thermostat fully opens itself to prevent
the hot coolant from flowing through the bypass into the
engine.
In this way, the radiator can increase its cooling
performance.
(1) Thermostat (A) Bypass Opened
(B) Bypass Closed
W1013406
M-3
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
3. FUEL SYSTEM
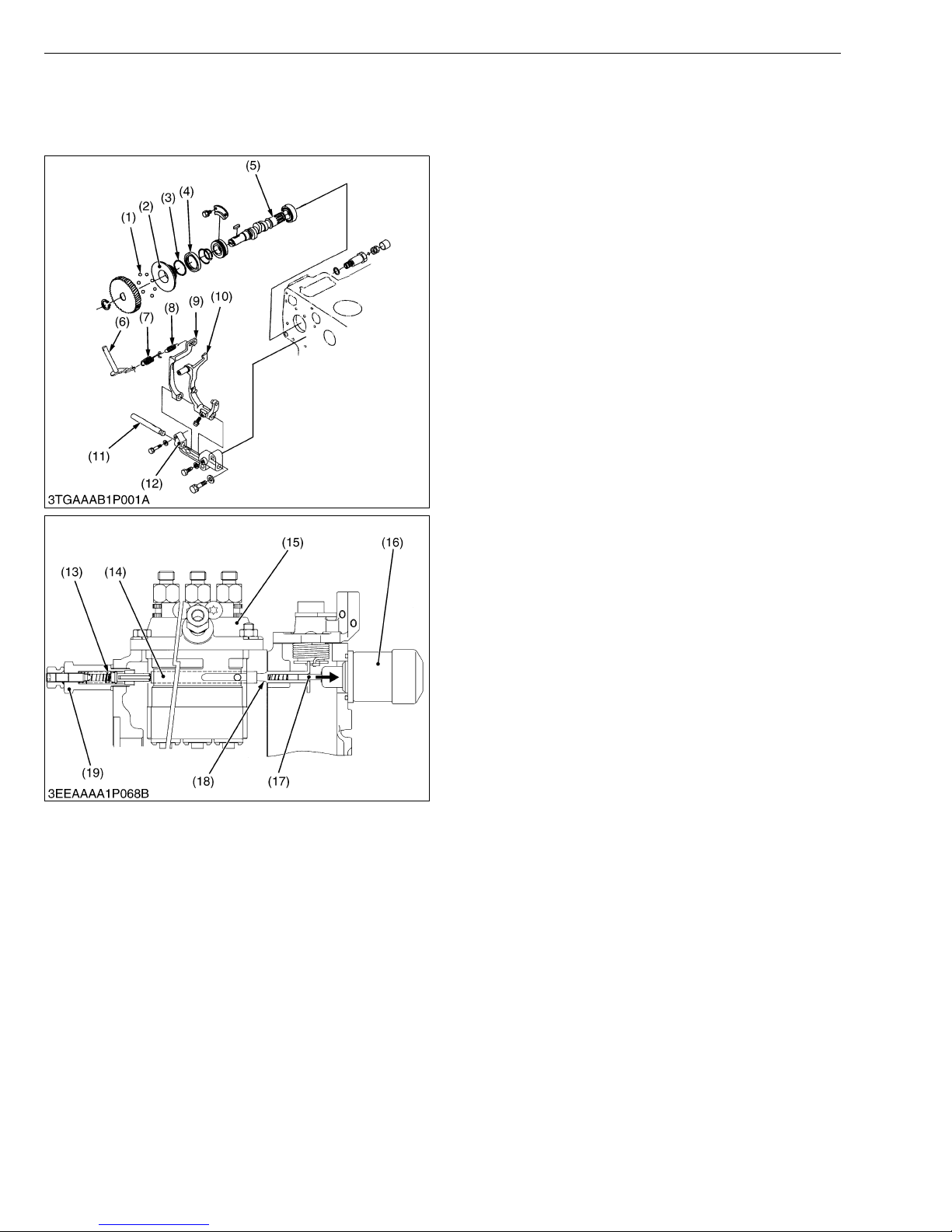
[1] GOVERNOR
DIESEL ENGINE
The governor serves to keep engine speed constant
by automatically adjusting the amount of fuel supplied to
the engine according to changes in the load. This engine
employs an all-speed governor which controls the
centrifugal force of the steel ball (1) weight, produced by
rotation of the fuel camshaft (5), and the tension of the
governor spring 1 (7) and 2 (8) are balanced.
(1) Steel Ball
(2) Governor Sleeve
(3) Steel Ball
(4) Governor Ball Case
(5) Fuel Camshaft
(6) Governor Lever
(7) Governor Spring 1
(8) Governor Spring 2
(9) Fork Lever 2
(10) Fork Lever 1
(11) Fork Lever Shaft
(12) Fork Lever Holder
W1017186
Q At Start
Flowing of the battery current into the engine stop
solenoid (16), the plunger (17) is actuated to arrow
direction.
Since the steel ball (1) have no centrifugal force, the
control rack (14) is pushed to the right by the start spring
(13). Accordingly, the control rack (14) moves to the
maximum injection position to assure easy starting.
(13) Start Spring
(14) Control Rack
(15) Injection Pump
(16) Engine Stop Solenoid
(17) Plunger
(18) Guide
(19) Idling Apparatus
W1017215
M-4
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
DIESEL ENGINE
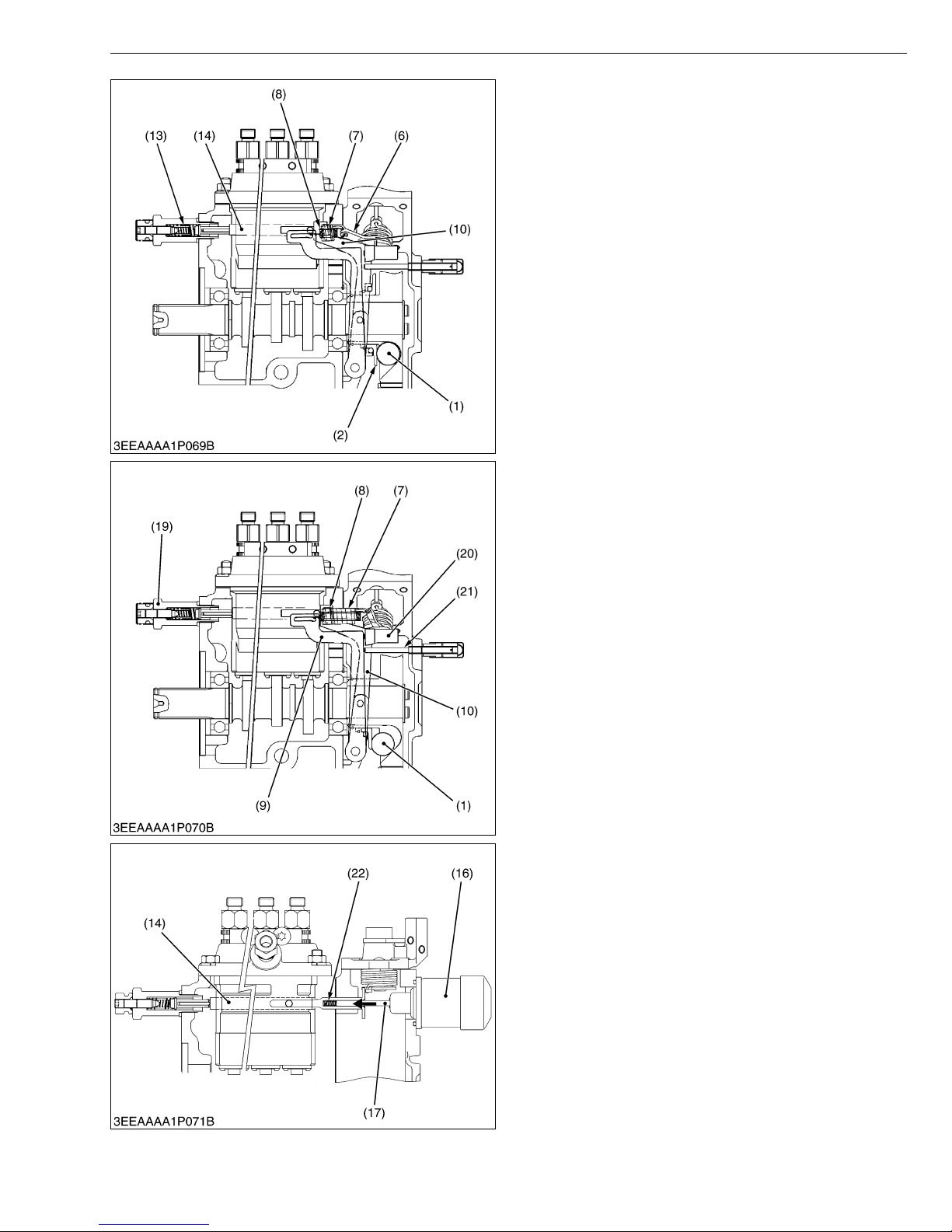
Q At Idling
When the speed control lever is set at the idling
position after the engine starts, the governor spring 1 (7)
does not work at all and the governor spring 2 (8) does
only act slightly. The governor sleeve (2) is pushed
leftward by a centrifugal force of steel ball (1).
Therefore, the fork lever 1 (10) and control rack (14)
are moved to the left by the governor sleeve (2) and then
the start spring (13) is compressed by the control rack
(14). As a result, the control rack (14) is kept at a position
where a centrifugal force of steel ball (1) and forces of
start spring (13), governor spring 2 (8) are balanced,
providing stable idling.
(1) Steel Ball
(2) Governor Sleeve
(6) Governor Lever
(7) Governor Spring 1
(8) Governor Spring 2
(10) Fork Lever 1
(13) Start Spring
(14) Control Rack
W1017317
Q At High Speed Running with Overload
When an overload is applied to the engine running at
a high speed, the centrifugal force of steel ball (1)
becomes small as the engine speed is dropped, and fork
lever 2 (9) is pulled to the right by the governor springs 1
(7) and 2 (8), increasing fuel injection. Though, fork lever
2 (9) becomes ineffective in increasing fuel injection
when it is stopped by the adjusting screw (21).
After that, when the force of torque spring (20)
becomes greater than the centrifugal force of the steel
ball (1), fork lever 1 (10) moves rightward to increase fuel
injection, causing the engine to run continuously at a high
torque.
(1) Steel Ball
(7) Governor Spring 1
(8) Governor Spring 2
(9) Fork Lever 2
(10) Fork Lever 1
(19) Idling Apparatus
(20) Torque Spring
(21) Adjusting Screw
W1017384
Q To Stop Engine
When the battery current stops, the plunger (17) of
engine stop solenoid (16) is returned to the original
position, the spring (22) to keep the control rack (14) in
“No fuel injection” position.
(14) Control Rack
(16) Engine Stop Solenoid
(17) Plunger
(22) Spring
M-5
W1018007

SERVICING
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
CONTENTS
1. GENERAL .........................................................................................................S-1
[1] ENGINE IDENTIFICATION ........................................................................S-1
(1) Model Name and Engine Serial Number ..............................................S-1
(2) Cylinder Number ...................................................................................S-2
[2] GENERAL PRECAUTION .........................................................................S-3
[3] TIGHTENING TORQUES ..........................................................................S-4
(1) Tightening Torques for Special Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts ...............S-4
(2) Tightening Torques for General Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts ..............S-4
[4] TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................................................S-5
[5] SERVICING SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................ S-8
[6] MAINTENANCE CHECK LIST ................................................................S-16
[7] CHECK AND MAINTENANCE ................................................................S-18
(1) Daily Check Points ..............................................................................S-18
(2) Check Points of Initial 50 Hours..........................................................S-20
(3) Check Points of Every 50 Hours .........................................................S-21
(4) Check Points of Every 100 Hours .......................................................S-22
(5) Check Point of Every 150 Hours.........................................................S-24
(6) Check Points of Every 200 Hours .......................................................S-26
(7) Check Points of Every 400 hours........................................................ S-28
(8) Check Points of Every 500 Hours .......................................................S-29
(9) Check Points of Every 1 or 2 Months..................................................S-32
(10)Check Point of Every Year..................................................................S-33
(11)Check Point of Every 800 Hours.........................................................S-34
(12)Check Points of Every 1500 Hours.....................................................S-35
(13)Check Points of Every 3000 Hours.....................................................S-37
(14)Check Points of Every 2 Years ...........................................................S-38
[8] SPECIAL TOOLS.....................................................................................S-42
2. ENGINE BODY ..............................................................................................S-50
[1] CHECKING AND ADJUSTING ...............................................................S-50
[2] DISASSEMBLING AND ASSEMBLING..................................................S-52
(1) Draining Oil and Coolant .....................................................................S-52
(2) External Components .........................................................................S-52
(3) Cylinder Head and Valves ..................................................................S-53
(4) Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft......................................S-57
(5) Piston and Connecting Rod ................................................................S-63
(6) Crankshaft...........................................................................................S-66
[3] SERVICING ..............................................................................................S-69
(1) Cylinder Head and Valves ..................................................................S-69
(2) Timing Gears, Camshaft and Fuel Camshaft......................................S-75
(3) Piston and Connecting Rod ................................................................S-79
(4) Crankshaft...........................................................................................S-82
(5) Cylinder ...............................................................................................S-88
3. LUBRICATING SYSTEM ...............................................................................S-90
[1] CHECKING ...............................................................................................S-90
[2] SERVICING ..............................................................................................S-91
4. COOLING SYSTEM.......................................................................................S-92
[1] CHECKING AND ADJUSTING ...............................................................S-92

[2] DISASSEMBLING AND ASSEMBLING .................................................. S-94
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
5. FUEL SYSTEM.............................................................................................. S-95
[1] CHECKING AND ADJUSTING .............................................................. S-95
(1) Injection Pump.................................................................................... S-95
(2) Injection Nozzle .................................................................................. S-97
6. ELECTRICAL SYSTEM................................................................................. S-99
[1] CHECKING .............................................................................................. S-99
(1) Starter................................................................................................. S-99
(2) Alternator.......................................................................................... S-100
(3) Glow Plug ......................................................................................... S-100
(4) Engine Stop Solenoid....................................................................... S-101
[2] DISASSEMBLING AND ASSEMBLING ............................................... S-102
(1) Starter............................................................................................... S-102
(2) Alternator.......................................................................................... S-103
[3] SERVICING............................................................................................ S-104
(1) Starter............................................................................................... S-104
(2) Alternator.......................................................................................... S-106

03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
1. GENERAL
[1] ENGINE IDENTIFICATION
(1) Model Name and Engine Serial Number
DIESEL ENGINE
When contacting the manufacture, always specify your engine
model name and serial number.
The engine model and its serial number need to be identified
before the engine can be serviced or parts replaced.
Q Engine Serial Number
The engine serial number is an identified number for the engine.
It is marked after the engine model number.
It indicates month and year of manufacture as follows.
• Year of manufacture
Alphabet or
Number
1 2001 F 2015
2 2002 G 2016
3 2003 H 2017
4 2004 J 2018
5 2005 K 2019
6 2006 L 2020
7 2007 M 2021
8 2008 N 2022
9 2009 P 2023
A 2010 R 2024
B 2011 S 2025
C 2012 T 2026
D 2013 V 2027
E 2014
Year
Alphabet or
Number
Yea r
• Month of manufacture
Month
January A0001 ~ A9999 B0001 ~
February C0001 ~ C9999 D0001 ~
March E0001 ~ E9999 F0001 ~
April G0001 ~ G9999 H0001 ~
May J0001 ~ J9999 K0001 ~
June L0001 ~ L9999 M0001 ~
July N0001 ~ N9999 P0001 ~
August Q0001 ~ Q9999 R0001 ~
September S0001 ~ S9999 T0001 ~
October U0001 ~ U9999 V0001 ~
November W0001 ~ W9999 X0001 ~
December Y0001 ~ Y9999 Z0001 ~
0001 ~ 9999 10000 ~
Engine Serial Number
e.g. D1803-1A0001
“1” indicates 2001 and “A” indicates January.
So, 1A indicates that the engine was manufactured in January,
2001.
(1) Engine Model Name and Serial
Number
W1010477
S-1
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
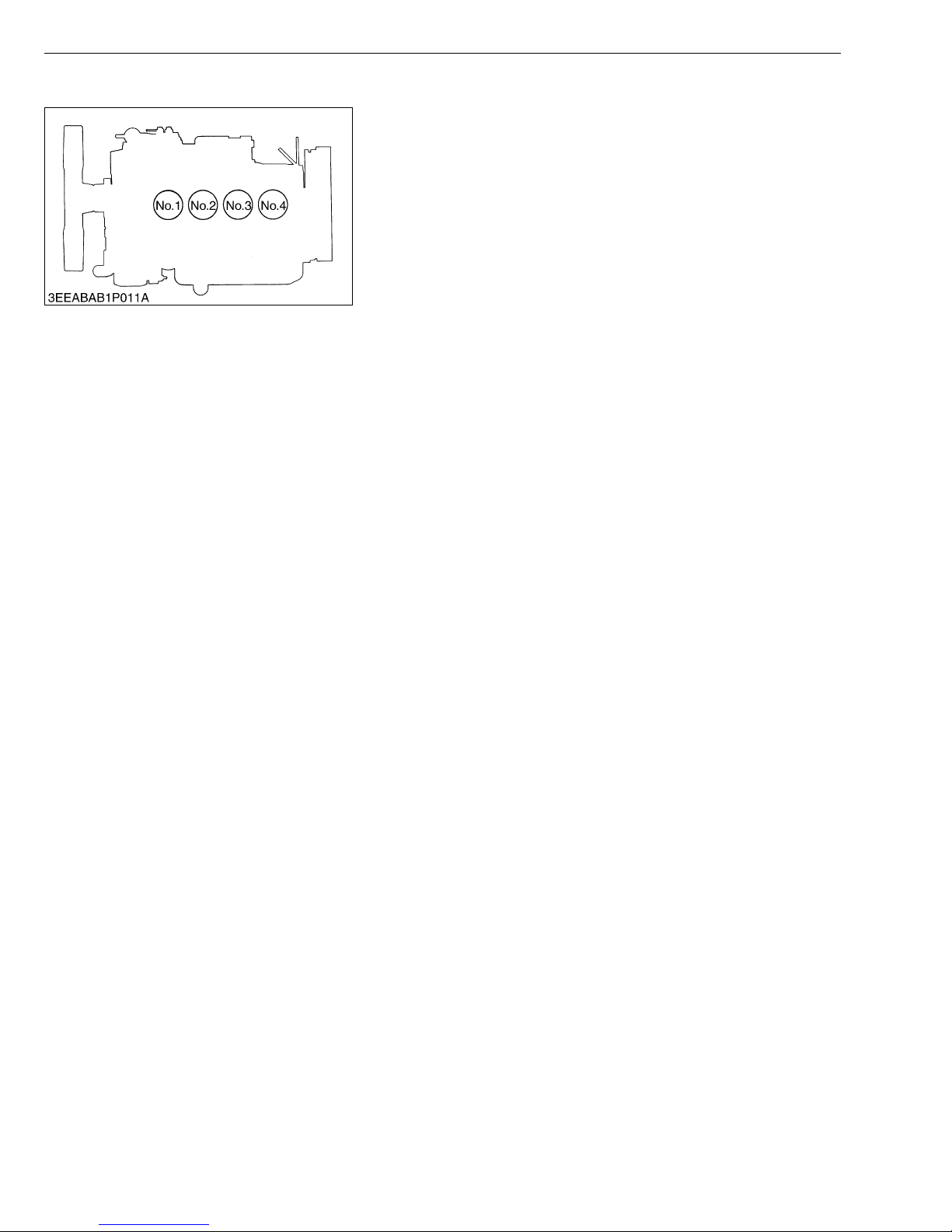
(2) Cylinder Number
DIESEL ENGINE
The cylinder numbers of 03-M Series diesel engine are
designated as shown in the figure.
The sequence of cylinder numbers is given as No.1, No.2, No.3
and No.4 starting from the gear case side.
W1011077
S-2
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
[2] GENERAL PRECAUTION
DIESEL ENGINE
• During disassembly, carefully arrange removed parts in a clean
area to prevent confusion later. Screws, bolts and nuts should be
replaced in their original position to prevent reassembly errors.
• When special tools are required, use KUBOTA genuine special
tools. Special tools which are not frequently used should be
made according to the drawings provided.
• Before disassembling or servicing live wires, make sure to
always disconnect the grounding cable from the battery first.
• Remove oil and dirt from parts before measuring.
• Use only KUBOTA genuine parts for parts replacement to
maintain engine performance and to ensure safety.
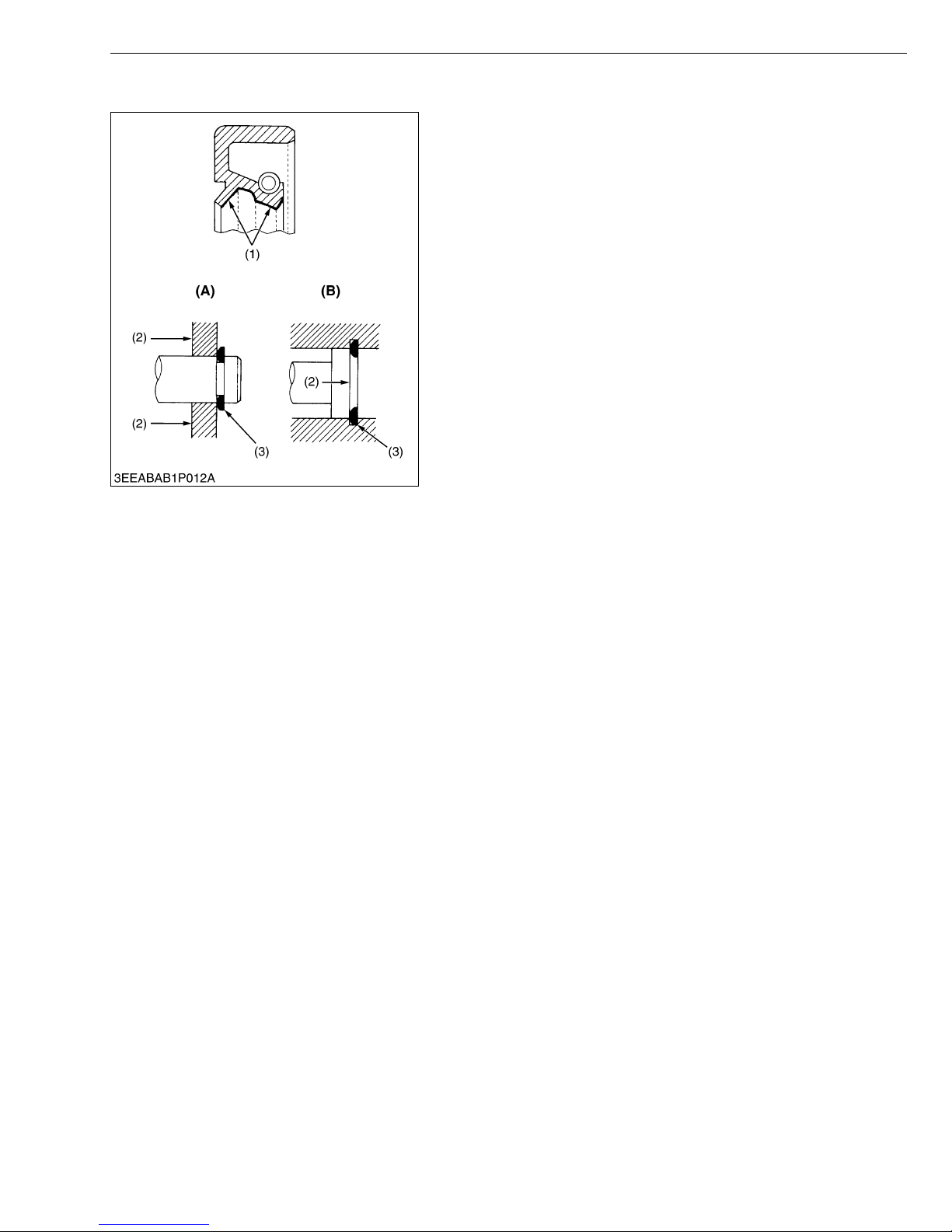
• Gaskets and O-rings must be replaced during reassembly.
Apply grease to new O-rings or oil seals before assembling.
• When reassembling external or internal snap rings, position them
so that the sharp edge faces against the direction from which
force is applied.
• Be sure to perform run-in the serviced or reassembled engine.
Do not attempt to give heavy load at once, or serious damage
may result to the engine.
(1) Grease
(2) Force
(3) Place the Sharp Edge against the
Direction of Force
(A) External Snap Ring
(B) Internal Snap Ring
W1011734
S-3
03-M Series, WSM
NOTEQ
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
DIESEL ENGINE
[3] TIGHTENING TORQUES
Screws, bolts and nuts must be tightened to the specified torque using a torque wrench, several screws, bolts and
nuts such as those used on the cylinder head must be tightened in proper sequence and the proper torque.
(1) Tightening Torques for Special Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts
• For “*” marked screws, bolts and nuts on the table, apply engine oil to their threads and seats before
tightening.
• The letter “M” in Size x Pitch means that the screw, bolt or nut dimension stands for metric. The size is
the nominal outside diameter in mm of the threads. The pitch is the nominal distance in mm between two
threads.
Item Size x Pitch N·m kgf·m ft-lbs
Cylinder head cover screw
* Cylinder head screw
* Main bearing case screw 1
* Main bearing case screw 2
* Flywheel screw
* Connecting rod screw
* Rocker arm bracket screw
* Idle gear shaft screw
Fan drive pulley mounting nut
* Bearing case cover screw
Glow plug
Nozzle holder assembly
Oil Switch taper screw
Injection pipe retaining nut
Overflow pipe assembly retaining nut
Camshaft set screw
Hi-idling body
Balancer shaft set bolt
M6 × 1.0
M11 × 1.25
M9 × 1.25
M10 × 1.25
M12 × 1.25
M8 × 1.0
M8 × 1.25
M8 × 1.25
M30 × 1.5
M8 × 1.25
M10 × 1.25
M20 × 1.5
PT 1/8
M12 × 1.5
–
M8 × 1.25
M14 × 1.0
M8 × 1.25
6.9 to 11.3
93.2 to 98.1
46.1 to 51.0
68.6 to 73.5
98.1 to 107.9
44.1 to 49.0
23.5 to 27.5
23.5 to 27.5
137.3 to 156.9
23.5 to 27.5
19.6 to 24.5
49.0 to 68.6
14.7 to 19.6
24.5 to 34.3
19.6 to 24.5
23.5 to 27.5
44.1 to 49.0
23.5 to 27.5
0.7 to 1.15
9.5 to 10.0
4.7 to 5.2
7.0 to 7.5
10.0 to 11.0
4.5 to 5.0
2.4 to 2.8
2.4 to 2.8
14.0 to 16.0
2.4 to 2.8
2.0 to 2.5
5.0 to 7.0
1.5 to 2.0
2.5 to 3.5
2.0 to 2.5
2.4 to 2.8
4.5 to 5.0
2.4 to 2.8
5.1 to 8.32
68.7 to 72.3
34.0 to 37.6
50.6 to 54.2
72.3 to 79.6
32.5 to 36.2
17.4 to 20.3
17.4 to 20.3
101.3 to 115.7
17.4 to 20.3
14.5 to 18.1
36.2 to 50.6
10.8 to 14.5
18.1 to 25.3
14.5 to 18.1
17.4 to 20.3
32.6 to 36.3
17.4 to 20.3
W1013236
(2) Tightening Torques for General Use Screws, Bolts and Nuts
Grade
Nominal Unit
Diameter
M6 7.9 to 9.3 0.80 to 0.95 5.8 to 6.9 9.8 to 11.3 1.00 to 1.15 7.23 to 8.32
M8 17.7 to 20.6 1.8 to 2.1 13.0 to 15.2 23.5 to 27.5 2.4 to 2.8 17.4 to 20.3
M10 39.2 to 45.1 4.0 to 4.6 28.9 to 33.3 48.1 to 55.9 4.9 to 5.7 35.4 to 41.2
M12 62.8 to 72.6 6.4 to 7.4 46.3 to 53.5 77.5 to 90.2 7.9 to 9.2 57.1 to 66.5
Screw and bolt material grades are shown by numbers punched on the screw and bolt heads. Prior to
tightening, be sure to check out the numbers as shown below.
Punched number Screw and bolt material grade
None or 4 Standard screw and bolt SS400, S20C
7 Special screw and bolt S43C, S48C (Refined)
Standard Screw and Bolt
Special Screw and Bolt
N·m kgf·m ft-lbs N·m kgf·m ft-lbs
W10371750
W1012705
S-4
S-5
03-M Series, WSM
DIESEL ENGINE
[4] TROUBLESHOOTING
W1014322
Symptom Probable Cause Solution
Reference
Page
Engine Does Not
Start
No fuel Replenish fuel –
Air in the fuel system Vent air S-21
Water in the fuel system Change fuel and
repair or replace fuel
system
S-21, 28
Fuel hose clogged Clean or replace S-21
Fuel filter clogged Replace S-28
Excessively high viscosity of fuel or engine oil at
low temperature
Use specified fuel or
engine oil
–
Fuel with low cetane number Use specified fuel –
Fuel leak due to loose injection pipe retaining nut Tighten retaining nut S-53
Incorrect injection timing Adjust S-95
Fuel camshaft worn Replace S-62
Injection nozzle clogged Clean or replace S-54, 97
Injection pump malfunctioning Repair or replace S-57, 96
Seizure of crankshaft, camshaft, piston, cylinder
or bearing
Repair or replace –
Compression leak from cylinder Replace head
gasket, tighten
cylinder head screw,
glow plug and nozzle
holder
–
Improper valve timing Correct or replace
timing gear
S-61
Piston ring and cylinder worn Replace S-50, 64,
65, 80,
81, 88
Excessive valve clearance Adjust S-51
Stop solenoid mulfunctining Replace –
(Starter Does Not
Run)
Battery discharged Charge S-32, 33
Starter malfunctioning Replace S-52, 99,
102, 104,
105
Key switch malfunctioning Repair or replace –
Wiring disconnected Connect –
Engine Revolution Is
Not Smooth
Fuel filter clogged or dirty Replace S-28
Air cleaner clogged Clean or replace S-22, 27,
33
Fuel leak due to loose injection pipe retaining nut Tighten retaining nut S-53
Injection pump malfunctioning Repair or replace S-57, 96
Incorrect nozzle injection pressure Adjust S-54, 97
Injection nozzle stuck or clogged Repair or replace S-54, 97
Governor malfunctioning Repair S-58, 62
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
S-6
03-M Series, WSM
DIESEL ENGINE
W1014322
Symptom Probable Cause Solution
Reference
Page
Either White or Blue
Exhaust Gas Is
Observed
Excessive engine oil Reduce to specified
level
S-18
Piston ring and liner worn or stuck Repair or replace S-50, 64,
65, 80,
81, 88
Incorrect injection timing Adjust S-95
Either Black or Dark
Gray Exhaust Gas Is
Observed
Overload Lessen the load –
Low grade fuel used Use specified fuel –
Fuel filter clogged Replace S-28
Air cleaner clogged Clean or replace S-22, 27,
33
Deficient nozzle injection Repair or replace
nozzle
S-54, 97
Deficient Output Incorrect injection timing Adjust S-95
Engine’s moving parts seem to be seizing Repair or replace –
Injection pump malfunctioning Repair or replace S-57, 96
Deficient nozzle injection Repair or replace
nozzle
S-54, 97
Compression leak Check the
compression
pressure and repair
S-50
Air cleaner dirty or clogged Clean or replace S-22, 27,
33
Excessive Lubricant
Oil Consumption
Piston ring’s gap facing the same direction Shift ring gap
direction
S-64
Oil ring worn or stuck Replace S-65, 80,
81
Piston ring groove worn Replace piston S-65, 81
Valve stem and valve guide worn Replace S-56, 70,
71
Crankshaft bearing, and crank pin bearing worn Replace –
Oil leaking due to defective seals or packing Replace –
Fuel Mixed into
Lubricant Oil
Injection pump’s plunger worn Repair or replace S-57, 96
Deficient nozzle injection Repair or replace
nozzle
S-54, 97,
98
Injection pump broken Replace S-57
Water Mixed into
Lubricant Oil
Head gasket defective Replace S-55
Cylinder block or cylinder head flawed Replace S-55, 69
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
S-7
03-M Series, WSM
DIESEL ENGINE
W1014322
Symptom Probable Cause Solution
Reference
Page
Low Oil Pressure Engine oil insufficient Replenish S-18
Oil strainer clogged Clean S-63
Relief valve stuck with dirt Clean –
Relief valve spring weaken or broken Replace –
Excessive oil clearance of crankshaft bearing Replace S-67, 84,
85, 86,
87
Excessive oil clearance of crankpin bearing Replace S-64, 83
Excessive oil clearance of rocker arm Replace S-54, 73
Oil passage clogged Clean –
Different type of oil Use specified type of
oil
S-20
Oil pump defective Replace S-62, 90,
91
High Oil Pressure Different type of oil Use specified type of
oil
S-20
Relief valve defective Replace –
Engine Overheated Engine oil insufficient Replenish S-20
Fan belt broken or elongated Replace or adjust S-23, 31
Coolant insufficient Replenish S-19
Radiator net and radiator fin clogged with dust Clean –
Inside of radiator corroded Clean or replace S-29
Coolant flow route corroded Clean or replace S-29, 30
Radiator cap defective Replace S-92
Overload running Reduce the load –
Head gasket defective Replace S-55
Incorrect injection timing Adjust S-95
Unsuitable fuel used Use specified fuel –
Battery Quickly
Discharge
Battery electrolyte insufficient Replenish distilled
water and charge
S-22, 32
Fan belt slips Adjust belt tension or
change
S-22, 23,
31
Wiring disconnected Connect –
Rectifier defective Replace S-103, 107
Alternator defective Replace S-103, 106,
107
Battery defective Replace –
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
DIESEL ENGINE
[5] SERVICING SPECIFICATIONS
ENGINE BODY
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Cylinder Head Surface Flatness – 0.05 mm / 500 mm
0.0020 in. /
19.69 in.
Compression Pressure
(When Cranking with Starting Motor)
3.53 to 4.02 MPa /
290 min
36 to 41 kgf/cm
290 min
512 to 583 psi /
290 min
−1
(rpm)
−1
(rpm)
−1
(rpm)
2
/
2.55 MPa /
290 min
26 kgf/cm
290 min
370 psi /
290 min
−1
(rpm)
−1
(rpm)
−1
(rpm)
2
/
Difference among Cylinders
–
Top Clearance 0.55 to 0.70 mm
0.0217 to 0.0276 in.
Valve Clearance (When Cold) 0.18 to 0.22 mm
0.0071 to 0.0087 in.
Valve Seat Width (Intake)
2.12 mm
0.0835 in.
Width (Exhaust)
2.12 mm
0.0835 in.
Valve Seat Angle (Intake)
1.047 rad
60 °
Angle (Exhaust)
0.785 rad
45 °
Valve Face Angle (Intake)
1.047 rad
60 °
Angle (Exhaust)
0.785 rad
45 °
Valve Stem to Valve Guide
Clearance
0.040 to 0.070 mm
0.00157 to 0.00276 in.
10 % or less
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
Valve Stem
Valve Guide
Valve Recessing Protrusion
O.D.
I.D.
Recessing
S-8
7.960 to 7.975 mm
0.31339 to 0.31398 in.
8.015 to 8.030 mm
0.31555 to 0.31614 in.
0.05 mm
0.0020 in.
to
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
–
–
–
0.4 mm
0.0157 in.
W1013874
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
ENGINE BODY (Continued)
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Valve Timing (Intake Valve) D1503-M Open
0.14 rad (8 °)
before T.D.C.
DIESEL ENGINE
–
Close
D1703-M
Open
D1803-M
V2203-M
V2403-M
Close
Valve Timing (Exhaust Valve) D1503-M Open
Close
D1703-M
Open
D1803-M
V2203-M
V2403-M
Close
Valve Spring Free Length
Setting Load /
Setting Length
0.35 rad (20 °)
after B.D.C.
0.21 rad (12 °)
before T.D.C.
0.63 rad (36 °)
after B.D.C.
1.05 rad (60 °)
before B.D.C.
0.21 rad (12 °)
after T.D.C.
0.99 rad (57 °)
before B.D.C.
0.21 rad (12 °)
after T.D.C.
41.7 to 42.2 mm
1.6417 to 1.6614 in.
117.6 N / 35.0 mm
12.0 kgf / 35.0 mm
26.4 lbs / 1.3780 in.
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
41.2 mm
1.6220 in.
100.0 N /35.0 mm
10.2 kgf /35.0 mm
22.5 lbs /1.3780 in.
Tilt
–
1.0 mm
0.039 in.
Rocker Arm Shaft to Rocker Arm
Rocker Arm Shaft
Clearance
O.D.
0.016 to 0.045 mm
0.00063 to 0.00177 in.
13.973 to 13.984 mm
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
–
0.55012 to 0.55055 in.
Rocker Arm
I.D.
14.000 to 14.018 mm
–
0.55118 to 0.55189 in.
Push Rod Alignment – 0.25 mm
0.0098 in.
Tappet to Tappet Guide
Tappet
Clearance
O.D.
0.020 to 0.062 mm
0.00079 to 0.00244 in.
23.959 to 23.980 mm
0.07 mm
0.0028 in.
–
0.94327 to 0.94410 in.
Tappet Guide
I.D.
24.000 to 24.021 mm
–
0.94488 to 0.94571 in.
W1013874
S-9
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
ENGINE BODY (Continued)
Timing Gear
Crank Gear to Idle Gear
DIESEL ENGINE
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Backlash
0.0415 to 0.1122 mm
0.00163 to 0.00442 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
Idle Gear to Cam Gear
Idle Gear to Injection Pump Gear
Crank Gear to Oil Pump Gear
Idle Gear to Balancer Gear
(Balancer Model Only)
Idle Gear Side Clearance 0.12 to 0.48 mm
Idle Gear Shaft to Idle Gear Bushing
Idle Gear Shaft
Backlash
Backlash
Backlash
Backlash
(Intake side)
Backlash
(Exhaust side)
Clearance
O.D.
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.00163 to 0.00454 in.
0.0415 to 0.1154 mm
0.00163 to 0.00454 in.
0.0415 to 0.1090 mm
0.00163 to 0.00429 in.
0.0350 to 0.1160 mm
0.00138 to 0.00457 in.
0.0350 to 0.1160 mm
0.00138 to 0.00457 in.
0.0047 to 0.0189 in.
0.025 to 0.066 mm
0.00098 to 0.00260 in.
37.959 to 37.975 mm
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
0.9 mm
0.0354 in.
0.10 mm
0.0039 in.
–
1.49445 to 1.49508 in.
Idle Gear Bushing
I.D.
38.000 to 38.025 mm
–
1.49606 to 1.49705 in.
Camshaft Side Clearance 0.07 to 0.22 mm
0.0028 to 0.0087 in.
0.30 mm
0.0118 in.
Camshaft Alignment – 0.01 mm
0.0004 in.
Cam Height
(Intake / Exhaust)
Camshaft Journal to Cylinder Block Bore
Clearance
33.90 mm
1.3346 in.
0.050 to 0.091 mm
0.00197 to 0.00358 in.
33.85 mm
1.3327 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
Camshaft Journal
Cylinder Block Bore
Balancer Shaft
(Balancer Model Only)
Balancer Shaft
(Balancer Model Only)
O.D.
39.934 to 39.950 mm
–
1.57221 to 1.57284 in.
I.D.
40.000 to 40.025 mm
–
1.57480 to 1.57579 in.
Side Clearance 0.07 to 0.22 mm
0.0028 to 0.0087 in.
0.30 mm
0.0118 in.
Alignment – 0.02 mm
0.0008 in.
W1013874
S-10
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
ENGINE BODY (Continued)
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Balancer Shaft Journal 1 to Balancer Shaft
Bearing 1 (Balancer Model Only)
Clearance
0.030 to 0.111 mm
0.00118 to 0.00437 in.
DIESEL ENGINE
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
Balancer Shaft Journal 1
O.D.
43.934 to 43.950 mm
1.72969 to 1.73032 in.
Balancer Shaft Bearing 1
I.D.
43.980 to 44.045 mm
1.73150 to 1.73406 in.
Balancer Shaft Journal 2 to Balancer Shaft
Bearing 2 (Balancer Model Only)
Balancer Shaft Journal 2
Clearance
O.D.
0.030 to 0.111 mm
0.00118 to 0.00437 in.
41.934 to 41.950 mm
1.65095 to 1.65158 in.
Balancer Shaft Bearing 2
I.D.
41.980 to 42.045 mm
1.65276 to 1.65532 in.
Balancer Shaft Journal 3 to Balancer Shaft
Bearing 3 (Balancer Model Only)
Balancer Shaft Journal 3
Clearance
O.D.
0.020 to 0.094 mm
0.00079 to 0.00370 in.
21.947 to 21.960 mm
0.86406 to 0.86457 in.
Balancer Shaft Bearing 3
I.D.
21.980 to 22.041 mm
0.86535 to 0.86776 in.
Piston Pin Bore I.D. 25.000 to 25.013 mm
0.98425 to 0.98476 in.
Second Ring to Ring Groove D1503-M
Clearance 0.093 to 0.120 mm
0.0037 to 0.0047 in.
–
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
25.05 mm
0.9862 in.
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
D1703-M
D1803-M
0.093 to 0.128 mm
0.0037 to 0.0050 in.
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
V2203-M
V2403-M
Oil Ring to Ring Groove Clearance 0.020 to 0.060 mm
0.0008 to 0.0024 in.
Top Ring D1503-M
Ring Gap 0.20to 0.35 mm
0.0079 to 0.0138 in.
D1703-M
D1803-M
0.20 to 0.40 mm
0.0079 to 0.0157 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
V2203-M
V2403-M
Second Ring Ring Gap 0.30 to 0.45 mm
0.0118 to 0.0177 in.
Oil Ring Ring Gap 0.25 to 0.45 mm
0.0098 to 0.0177 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
1.25 mm
0.0492 in.
Connecting Rod Alignment – 0.05 mm
0.0020 in.
W1013874
S-11
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
ENGINE BODY (Continued)
Piston Pin to Small End Bushing
DIESEL ENGINE
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Clearance
0.014 to 0.038 mm
0.00055 to 0.00150 in.
0.15 mm
0.0059 in.
Piston Pin
O.D.
25.002 to 25.011 mm
–
0.98433 to 0.98469 in.
Small End Bushing
I.D.
25.025 to 25.040 mm
–
0.98524 to 0.98583 in.
Crankshaft Alignment – 0.02 mm
0.00079 in.
Crankshaft Journal to
Crankshaft Bearing 1
Oil Clearance
0.040 to 0.118 mm
0.00157 to 0.00465 in.
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
(Serial No.: below 3R9999)
Crankshaft Journal
D1503-M
D1703-M
O.D.
51.921 to 51.940 mm
2.04413 to 2.04488 in.
–
V2203-M
Crankshaft Bearing 1
D1803-M
V2403-M
D1503-M
D1703-M
I.D.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.35910 to 2.35984 in.
51.980 to 52.039 mm
2.04646 to 2.04878 in.
–
–
V2203-M
D1803-M
V2403-M
Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing
1 (Serial No.: above 3S0001)
Oil Clearance
59.980 to 60.039 mm
2.36142 to 2.36374 in.
0.040 to 0.118 mm
0.00157 to 0.00465 in.
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
Crankshaft Journal
Crankshaft Bearing 1
Crankshaft Journal to
Crankshaft Bearing 2
(Serial No.: below 3R9999)
Crankshaft Journal
Crankshaft Bearing 2
D1503-M
D1703-M
V2203-M
D1803-M
V2403-M
D1503-M
D1703-M
V2203-M
D1803-M
V2403-M
O.D.
I.D.
Oil Clearance
O.D.
I.D.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.35910 to 2.35984 in.
59.980 to 60.039 mm
2.36142 to 2.36374 in.
0.040 to 0.104 mm
0.00157 to 0.00409 in.
51.921 to 51.940 mm
2.04413 to 2.04488 in.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.35910 to 2.35984 in.
51.980 to 52.025 mm
2.04646 to 2.04823 in.
59.980 to 60.025 mm
2.36142 to 2.36319 in.
–
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
–
–
W1029676
S-12
03-M Series, WSM
KiSC issued 08, 2012 A
ENGINE BODY (Continued)
Item Factory Specification Allowable Limit
Crankshaft Journal to Crankshaft Bearing
2 (Serial No.: above 3S0001)
Oil Clearance
0.040 to 0.104 mm
0.00157 to 0.00409 in.
DIESEL ENGINE
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
Crankshaft Journal
O.D.
59.921 to 59.940 mm
2.35910 to 2.35984 in.
Crankshaft Bearing 2
I.D.
59.980 to 60.025 mm
2.36142 to 2.36319 in.
Crankpin to Crankpin Bearing
Oil Clearance
0.025 to 0.087 mm
0.00098 to 0.00343 in.
Crankpin
O.D.
46.959 to 46.975 mm
1.84878 to 1.84941 in.
Crankpin Bearing
I.D.
47.000 to 47.046 mm
1.85039 to 1.85221 in.
Crankshaft
(Serial No.: below 3R9999)
D1503-M
D1703-M
Side Clearance 0.15 to 0.35 mm
0.0059 to 0.0138 in.
V2203-M
D1803-M
V2403-M
0.15 to 0.31 mm
0.0059 to 0.0122 in.
Crankshaft (Serial No.: above 3S0001) Side Clearance 0.15 to 0.31 mm
0.0059 to 0.0122 in.
Cylinder Bore
[Standard]
D1503-M
I.D.
83.000 to 83.022 mm
3.26772 to 3.26858 in.
–
–
0.20 mm
0.0079 in.
–
–
0.5 mm
0.0197 in.
0.5 mm
0.0197 in.
0.5 mm
0.0197 in.
83.150 mm
3.2736 in.
[Oversize]
D1703-M
D1803-M
V2203-M
V2403-M
D1503-M
D1703-M
D1803-M
V2203-M
V2403-M
I.D.
87.000 to 87.022 mm
3.42520 to 3.42606 in.
83.250 to 83.272 mm
3.27756 to 3.27843 in.
87.250 to 87.272 mm
3.43504 to 3.43591 in.
87.150 mm
3.4311 in.
83.400 mm
3.2835 in.
87.400 mm
3.4409 in.
W1013874
S-13
 Loading...
Loading...