
Wireless LAN USB
Adapter
USER’S MANUAL
VERSION 1.1
2008/02/28

This manual provides the necessary information for first -time users to successfully
install the Atheros network driver interface specification (NDIS) driver, for the purpose of
evaluating and / or operating the Atheros WLAN 11n ISM Band Dongle STA Reference Design
in a Microsoft Windows environment and the Atheros Client Utility (ACU) .
This guide describes the steps required to install NDIS drivers for the WLAN 11n ISM
Band Dongle in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows XP 64, Windows Vista, Windows Vista
64. This guide also includes the detailed instructions for configuring the network adapter to
interact with an access point (AP) in infrastructure mode. Read this before installing the
Atheros WLAN 11n ISM Band Dongle and NDIS driver in the targeted operating system (OS)
environment.
© All rights reserved.
All trade names are registered trademarks of respective manufacturers listed.
This manual may not be copied in any media or form without the written consent of original maker.

Information To User ..................................................…… .. I
1. Introduction .........................................................… .. 1
2. Wireless LAN Basics ................................................…… ..3
3. IP ADDRESS ..........................................................…… ..4
4. Install Driver/Utility ...............................................…… ..5
5. Wireless Network Conf iguration in Station Mode .................. 9
5.1 TRAY ICON ................................………… .…………………… 9
5.2 GENERAL CONNECTION SETTING .............................. 11
5.2.1 Current Status . . . ………………………………………………… 11
5.2.2 Profile Management ………………………………………… . 15
5.2.3 Diagnostics ……………………………………………………… ….17
5.3 SECURITY ...............................................…………… 19
5.3.1 WPA/WPA2 …………………………………………………………… ..19
5.3.2 802.1x ………………………………………………………………… .30
5.3.3 WPA Pass phrase ……………………………………………………… .30
5.3.4 Pre -Shared Key (Static WEP) …………………………………… 31
5.3.5 None ……………………………………………………………………… 31
5.4 JumpStart for Wireless …………………………………………………… ..31
6. Install VISTA Driver ............................................... ....…. 37
7. Technical Specifications ...........................................… .. 41
8. Troubleshooting ....................................................…… . 42
9. Glossary ..............................................................… . 43

INFORMATION TO USER
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits
for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference in a residential installation.
This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communi cations. However, there
is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or
television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by
one of the following measures:
* Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
* Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
* Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different fr om
that to which the receiver is connected.
* Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved
by the party responsible for compliance could void the use r's authority to
operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
* This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set
forth for an uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be
installed and operated with minimum distance 20cm between the
radiator & your body.
* This transmitter must not be co -located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
i

REGULATORY INFORMATION
WLAN Mini USB Adapter must be installed and used in strict
accordance wit h the instructions. This device complies with the
following radio frequency and safety standards.
USA - Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC Rules. Operation is
subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference.
2. This device must accept any interference that may cause undesired
operation.
Europe - R&TTE Directive
This device complies with the specifications listed below
EN 300 328 V1.6.1 (2004 -11)
EN 301 489 -1 V1.4.1 (20 02-08), EN 301 489 -17 V1.2.1 (2002 -08)
EN 60950-1: 2001
The channel identifiers, channel center frequencies, and regulatory domains
of each 22-MHz-wide channel are shown in following Table.
Regulatory Domains
Channel
Identifier
Center
Frequency
(MHZ)
Japan
ETSI
North
America
Israel
France
Mexico
1
2412
ˇˇˇ
2
2417
ˇˇˇ
3
2422
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
4
2427
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
5
2432
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
6
2437
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
7
2442
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
8
2447
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
9
2452
ˇˇˇ
ˇ
10
2457
ˇˇˇˇˇ
11
2462
ˇˇˇˇˇ
12
2467
ˇˇˇ
13
2472
ˇˇˇ
14
2484
ˇ
ii

1
Thank you for your purchase of the WLAN 11n ISM Band Dongle .
Featuring wireless technology, this wireless networking solution has
been designed for both large and small businesses, and it is scalable
so that you can easily add more users and new network features
depending on your business scale.
FEATURES
Support Microsoft Windows 2000 ,XP , Vista.
Indoor up to 100 meters, Outdoor up to 280 meters .
270/240/180/120/90/60/54 /48/36/30/24/22/18/12/11/6/5.5/2/1
Mbps selectable Data Rate and maximum of 300Mbps.
Support USB 2.0 interface.
64-bit, 128-bit or WEP , TKIP, AES.
2.400GHz ISM Frequency Band.
Modulation Method : BPSK/QPSK/16 -QAM/64-QAM
Spread Spectrum :
IEEE 802.11b : DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum).
IEEE 802.11g / n: OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing).
Easy operation and setting up.
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
Windows System : Windows 2000 , XP , Vista
PCs must have a device driver installed . It allows you to communicate
with WLAN Mini USB Adapter.

2
BEFORE YOU START
1. Confirm Box Contents
CONNECTING YOUR WLAN USB ADAPTER TO PC
Quick Start Guide
Connect your WLAN USB dongle to
your PC.
Install driver.
GETTING TO KNOW WIRELESS LAN USB ADAPTER
LED
LED turns on when POWER is applied to the WLAN Mini USB Adapter.
LED is blinking when PC is sending data through WLAN Mini USB Adapter.

3
Wireless LAN network defined by IEEE 802.11 n/b/g standard committee
could be configured as :
Ad Hoc wireless LAN, or
Infrastructure wireless LAN.
Ad Hoc network is a group of PCs installed with wireless LAN cards, this
group of PCs is called a BSS (Basic Service Set). PCs in this group can use
their wireless LAN cards to comm unicate with each other, but can not
connect to the Internet.
Ad Hoc Wireless Network Infrastructure Wireless Network
The most obvious difference between Infrastructure wireless network
and Ad Hoc wireless network is that the PCs in Infrastructu re wireless
network can access the resource in the Internet through Access Point .
Depending on your requirement, you can easily set up your PC’s
network to be a “ Ad Hoc” or “Infrastructure ” wireless network. Generally
speaking, if in your network, there is an Access Point in it, we recommend
you to set your network as an “ Infrastructure ”, so it can connect to
the Internet.

4
To use the WLAN Mini USB Adapter with a computing device, the WLAN
Mini USB Adapter must be equipped with an USB 1.1 or 2.0 In terface. All
drivers and supporting software for the WLAN Mini USB Adapter must be
installed and configured first.
Ask your system administrator for the following information, which you
may need to provide during driver installation :
using a DHCP server.
Any computer on a network is identified by a unique network address.
There are two methods to assign a network address to a computer on a
TCP/IP network :
In network with static IP addressing, the netwo rk administrator manually
assigns an IP address to each computer. Once a static IP address is
assigned, a computer uses the same IP address every time it reboots and
logs on to the network. You may manually change the IP address in the
Network Properties d ialog box. Network using static IP address is easy to
set up and do not require additional network management software.
In network with dynamic IP addressing, a DHCP server in the network
dynamically assigns IP addresses to all clients every time they log on to
the network. Network using dynamic IP address requires setting up and
running a DHCP Server.

5
The installation driver CD will automatically activate the autorun
installation program after you insert the disk into your CD drive.
Step 1 :
Insert the installation driver
CD into your CD-ROM, chose
your language and click Next to
continue.
Step 2 :
Click Next to continue.

6
Step 3 :
Choose accept and click Next to
continue.
Step 4 :
Choose the installation type. To
install the client utilities and
driver, select the appropriate
button and click Next.
Step 5 :
Insert WLAN USB adapter
into USB port and click OK to
continue.

7
Step 6 :
Click Next to install at the
designated folder. Or, click
“Browse” to select different
folder.
Step 7 :
Click Next to continue.
Step 8 :
If you have multiple computers to
access, choose SSO(Single sign on)
feature set. Or you can choose “Do
not install SSO feature set ” and
Click Next to continue.

8
Step 9 :
Start copying files until it finishes the
installation.
Step 10 :
Click Finish to complete
installation.

9
WLAN USB Adapter uses its own management software. All functions
controlled by users are provi ded by this application. When you insert the
WLAN USB Adapter into the USB port of your PC, a new icon should
appear in the Windows System Tray automatically.
5.1 TRAY ICON
The tray icon appears at the bottom of the screen, and shows the signal
strength using colors and the received signal strength indication (RSSI).
Hold the mouse cursor over the tray icon to display the current configuration
profile name and association, as well as transmit and receive speed and the
wireless adapter name and IP add ress.
Right-click on the tray icon to:
Help
Open the online help.
Open Atheros Client
Utility
Launch the Atheros Client Utility
(ACU). Use the ACU to configur e the
profile or view status and statistics
information.
Client Managed Test
Run the Client Managed Test Utility.

10
Preferences
Set the startup options and menu options for
the ACU. Check whether the program
should start automatically when Windows
starts, and check the menu items that should
appear on the popup menu.
Enable/Disable Radio
Enable or disable the RF Signal.
Manual LEAP Login
Log in to LEAP manually, if LEAP is set to
manually prompt for user name and
password on each login.
Reauthenticate
Reauthenticate to the access point.
Select Profile
Click a configuration profile name to switc h
to it. If no configuration profile exists for a
connection, add a profile first.
Show Connection Status
Display the Connection Status
window. This window displays
information about the connection:
Active Profile
Displays the name of the
active configuration profile.
Auto Profile
Selection
Shows whether auto profile
selection is enabled.
Connection
Status
Displays whether the
adapter is connected to a
wireless network.
Link Quality
Lists the quality of the link
connection.
SSID
Displays the SSID of t he
associated network.
Access Point
Name
Shows the name of the
access point the wireless
adapter is connected to.
Access Point
IP Address
Shows the IP address of the
access point the wireless
adapter is connected to.
Current
Receive Rate
Shows the current receive
rate in Mbps.

11
Current
Transmit Rate
Shows the current transmit
rate in Mbps.
Client
Adapter IP
Address
Displays the IP address of
the wireless adapter.
Exit
Exit the Atheros Client Utility application.
The colors are defined as follows:
Color
Quality
RSSI*
Green
Excellent
20 dB +
Green
Good
10-20 dB +
Yellow
Poor
5-10 dB
Red
Poor
< 5 dB
Gray
No Connection
No Connection
*Received signal strength indication RSSI. Displayed in dB or percentage.
Enable or disable the tray icon in the Action menu.
5.2 GENERAL CONNECTION SETTING
5.2.1 Current Status
The Current Status tab contains
general information about the
program and its operations. The
Current Status tab does not
require any configuration.
The following table describes the items found on the Current Status screen.

12
Profile Name
The name of the current selected configuration
profile. Set up the configuration name on the
General tab.
Link Status
Shows whether the station is associated to the
wireless network.
Wireless Mode
Displays the wireless mode. Configure the
wireless mode on the Advanced tab.
IP Address
Displays the computer's IP address.
Network Type
The type of network the station is connected
to. The options include:
Infrastructure (access point)
AdHoc
Configure the network type on the Advanced tab.
Current
Channel
Shows the currently connected channel.
Control
Channel
Shows the control channel. Available for 802.11n
devices only.
Extension
Channel
Shows the extension channel. Displayed only ifthe
STA is connected in a 40 MHz channel. Available
for 802.11n devices only.
Server Based
Authentication
Shows whether server based authentication is used.
Data
Encryption
Displays the encryption type the driver is
using. Configure the encryption type on the
Security tab.
Signal Strength
Shows the strength of the signal.
Click the Advanced button to see the advanced status diagnostics.
The following table describes the items found on the Advanced Status screen.
Network Name
Displays the wireless network name.

13
(SSID)
Configure the network name on theGeneral tab.
Server Based
Authentication
Shows whether server based authentication is used.
Data
Encryption
Displays the encryption type the driver is
using. Configure the encryption type on theSecurity
tab.
Authentication
Type
Displays the authentication mode.
Configure the authentication mode on the General tab.
Message
Integrity Check
Shows whether MICis enabled. MIC prevents bit-flip
attacks on encrypted packets.
Associated AP
Name
Displays the name of the access point the wireless
adapter is associated to.
Associated AP
IP Address
Shows the IP address of the access point the wireless
adapter is associated to.
Associated AP
MAC Address
Displays the MAC address of the access point the
wireless adapter is associated to.
11n MIMO
Power Save
Shows theMIMO power save mode status. Available
for 802.11n devices only.
Power Save
Mode
Shows the power save mode. Power management is
disabled in ad hoc mode.
Configure the power save mode on theAdvanced tab.
Current Power
Level
Displays thetransmit power level rate in mW.
Configure the transmit power level on theAdvanced
tab.
Available
Power Levels
Shows the 5 GHz and/or 2.4 GHz available power
levels.
Current Signal
Strength
Shows the current signal strength in dBm.
Current Noise
Level
Displays the current noise level in dBm.
Up Time
Shows how long the client adapter has been receiving
power (in hours:minutes:seconds). If the adapter runs
for more than 24 hours, the display shows in
days:hours:minutes:seconds.

14
802.11b
Preamble
Displays the802.11b preamble format.
Configure the preamble format on theAdvanced tab.
Current
Receive Rate
Shows the current receive rate in Mbps.
Current
Transmit Rate
Displays the current transmit rate in Mbps.
Channel
Shows the currently connected channel.
Control
Channel
Shows the current control channel. Available for
802.11n devices only.
Extension
Channel
Shows the extension channel. Displayed only if the
STA is connected in a 40 MHz channel. Available for
802.11n devices only.
Frequency
Displays frequency the station is using.
Control
Frequency
Displays control frequency the station is using.
Available for 802.11n devices only.
Extension
Frequency
Displays extension frequency the station is using.
Available for 802.11n devices only.
Channel Set
Shows the current channel set.
Channel Width
Shows the channel width. Available for 802.11n devices
only.
QoS
The type of quality of service that is currently being
used by your client adapter. QoS on wireless LANS
(WLAN) provides prioritization of traffic from the
access point over the WLAN based on traffic
classification.
A value of None represents that the WMM standard
QoS is not enabled. A value of WMM represents that a
component of the IEEE 802.11e WLAN standard for
QoS is enabled.

15
5.2.2 Profile Management
Configure the wireless network
adapter (wireless card) from the
Profile Management tab of the
Atheros Client Utility.
a. Create or Modify a Configuration Profile
To add a new configuration profile, click New on the Profile Management tab.
To modify a configuration profile, select the configuration from the Profile
list and click the Modify button.
To configure a profile for ad hoc or access point (infrastructure) mode, edit
the Network Type field on the Advanced tab.
Note that the ACU only allows the creation of 16 configuration
profiles. After the creation of 16 profiles , clicking the New button displays
an error message. Remove an old profile or modify an existing profile for a
new use.
b. Remove a Configuration Profile
1. Go to the Profile Management tab.
2. Select the profile to remove from the list of configuration profi les.
3. Click the Remove button.
c. Activate a Configuration Profile
1. To switch to a different profile, go to the Profile Management tab.
2. Click on the profile name in the Profile List.
3. Click the Activate button.

16
The Profile List provides icons that spe cify the operational state for that
profile. The list also provides icons that specify the signal strength for that
profile.
d. Import and Export Profiles
Importing a Profile :
1. From the Profile Management tab, click the Import button. The Import
Profile window appears.
2. Browse to the directory where the profile is located.
3. Highlight the profile name.
4. Click Open. The imported profile appears in the profiles list.
Exporting a Profile :
1. From the Profile Management tab, highlight the profile to export.
2. Click the Export button. The Export Profile window appears.
3. Browse to the directory to export the profile to.
4. Click Save. The profile is exported to the specified location.
e. Ordering Profiles
Including a profile in the auto selection feature allows the wi reless adapter to
automatically select that profile from the list of profiles and use it to connect
to the network.
Including a profile in auto profile selection:
1. On the Profile Management tab, click the Order Profiles button.
2. The Auto Profile Selection Management window appears, with a list of
all created profiles in the Available Profiles box.
3. Highlight the profiles to add to auto profile selection, then click Add.
The profiles appear in the Auto Selected Profiles box.
Ordering the auto selected pr ofiles:

17
1. Highlight a profile in the Auto Selected Profiles box.
2. Click Move Up, Move Down, or Remove as appropriate.
The first profile in the Auto Selected Profiles box has highest priority,
and the last profile has lowest priority.
3. Click OK.
4. Check the Auto Select Profiles box.
5. Save the modified configuration file.
When auto profile selection is enabled by checking Auto Select Profiles
on the Profile Management tab, the client adapter scans for an
available network. The profile with the highest priority and the same
SSID as one of the found networks is the one that is used to connect to
the network. If the connection fails, the client adapter tries the next
highest priority profile that matches the SSID, and so on.
With auto profile selection enabled, th e wireless adapter scans for available
networks. The highest priority profile with the same SSID as a found network
is used to connect to the network. On a failed connection, the client adapter
tries with the next highest priority profile.
5.2.3 Diagnostics
The Diagnostics tab of the Atheros Client Utility provides buttons used to
retrieve receive and transmit statistics. The Diagnostics tab does not require
any configuration.
The Diagnostics tab lists the following receive and transmit diagnostics for
frames received by or transmitted by the wireless network adapter:
Multicast packets transmitted and received
Broadcast packets transmitted and received
Unicast packets transmitted and received
Total bytes transmitted and received
Click the Adapter Information button for more general information about the
the wireless network adapter and the network driver interface specification
(NDIS) driver.

18
Click the Advanced Statistics button on the Diagnostics tab to also show
receive and transmit statistical info rmation for the following receive and
transmit diagnostics for frames received by or transmitted to the wireless
network adapter:
Transmitted Frames
Frames transmitted
OK
Frames retried
Frames dropped
No ACK frames
ACK frames
RTS frames
Clear-to-send (CTS)
frames
No CTS frames
Retried RTS frames
Retried data frames
Received Frames
Frames received OK
Beacons Received
Frames Received with errors
CRC errors
Encryption errors
Duplicate frames
AP mismatches
Data rate mismatches
Authentication time-out
Authentication rejects: the
number of AP authentication
failures received by the wireless
network adapter
Association time-out
Association rejects: the number
of access point authentication
rejects received by the wireless
network adapter
Standard MIC OK
Standard MIC errors
CKIP MIC OK
CKIP MIC errors
5.3 Security

19
In the Atheros Client Utility, access the Security tab by clicking New or Modify
on the Profile Management tab. Click the Security tab in the Profile
Management window.
Edit the fields in the Security tab of Profile Management to configure the
profile. To define the security mode, select the radio button of the desired
security mode. Make sure to also edit the General and Advanced tabs.
Note: If the Profile Locked checkbox is checked, Profile cannot be removed or
modified. However the password fields can be edited. Contact your system
administrator.
The type of security mode the station is using. The options include the
following:
5.3.1 WPA/WPA2
Enables the use of Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA).
Choosing WPA/WPA2 opens the WPA/WPA2 EAP drop -down menu. The
options include:
EAP-FAST
To use EAP-FAST security, the machine must already support EAP -FAST.
Check with the IT manager.
1. Click the Security tab from the Profile Editor window.
2. Click Configure. The Define EAP-FAST window appears.
3. Choose an EAP-FAST authentication method from the EAP -FAST
Authentication Method drop -down list.
4. Click Configure.
o If you chose GTC Token/Password from the EAP-FAST
Authentication Method drop-down list and clicked Configure,

20
the Define PEAP (EAP-GTC) Configuration window appears. To
know more about this option refer Using PEAP (EAP-GTC)
security.
o If you chose MSCHAPv2 Username and Password from the
EAP-FAST Authentication Method dr op-down list and clicked
Configure, the Configure Username and Password window
appears. To know more about this option refer Using
PEAP-MSCHAP V2 security.
o If you chose TLS Client Certificate from the EAP-FAST
Authentication Method drop -down list and clicked Configure,
the Define Certificate window appears. When configuring
EAP-TLS for EAP-FAST, you can check the Authenticate Server
Identity check box to force the system to authenticate the
identity of the server as an added level of security. This option
is available only when configuring EAP -FAST. To know more
about this option refer Using EAP-TLS security.
5. If you want to force the client adapter to disassociate after you log off
so that another user cannot gain access to the wireless network using
your credentials, check the No Network Connection Unless User is
Logged In check box. The default setting is checked.
6. Perform one of the following:
o If you want to enable automatic PAC provisioning, make sure
the Allow Automatic PAC Provisioning for this Prof ile check box
is checked. A protected access credentials (PAC) file is obtained
automatically as needed (for instance, when a PAC expires,
when the client adapter accesses a different server, when the
EAP-FAST username cannot be matched to a previously
provisioned PAC, etc.). This is the default setting.
o If you want to enable manual PAC provisioning, uncheck the
Allow Automatic PAC Provisioning for this Profile check box.
This option requires you to choose a PAC authority or manually
import a PAC file.

21
7. From the Select one or more PAC Authority to use with this Profile list,
highlight the PAC authorities associated with the network defined by
the profile's SSID. The list contains the names of all the authentication
servers from which you have previously pr ovisioned a PAC.
8. Click Manage. The Select EAP-FAST PAC window appears.
This window lets you group PAC authorities to facilitate authentication
while roaming. For example, if there are three PAC authorities at a
certain site covering different areas of the site, you can create a group
containing these authorities and select one of them in the PAC list. In
this way, if you're roaming around the site, the other authorities in the
group will allow you access to the network.
A group consists of one or more aut horities. Each authority may have
one or more PAC files. A PAC authority can belong to only one group.
9. To create a new group, click New Group. A group consists of one or
more authority servers that the user trusts. To rename the group,
right-click the group and choose Rename. You can also rename the
group by clicking it and typing the new name.
When you create a new group, you can either import a PAC file into it
using the Import button or you can move a PAC from another group to
the new group.
10.To import a PAC, click Import. The PAC Import window appears. Do the
following:
a. Click Browse and select a PAC file to import. The default
location is C:/Program Files/Atheros.
b. Click the PAC file (*.pac) so that it appears in the File name box
at the bottom of the w indow.
c. Click Open.
d.If the Enter Password window appears, enter the PAC file
password, which can be obtained from your system
administrator, and click OK.
Note:PAC file passwords are optional. The PAC authority determines
whether to issue PAC files that require user-supplied passwords.
Nevertheless, all PAC files (even those without passwords) are encrypted

22
and protected. PAC file passwords are different from EAP-FAST
passwords and need to be entered only once, at the time a PAC is imported.
e. If you try to import a PAC file with the same PAC ID as a
previously imported PAC file, you are asked to update the
existing PAC. If you click Yes, the existing PAC is replaced by the
new one from the imported file.
f. If the PAC file was imported successfully, the follo wing message
appears: "EAP-FAST PAC file was imported and is ready for use."
Click OK to return to the PAC Import window.
g. Click one of these PAC store options to determine where the
imported PAC file will be stored and by whom it will be
accessible:
Global - PACs that are stored in the global PAC store can be
accessed and used by any user at any logon stage. Global PACs
are available before or during logon or after the user is logged
off if the profile is not configured with the No Network
Connection Unless User is Logged In option.
Private - PACS that are stored in the private store can be
accessed and used only by the user who provisioned them or the
system administrator. They are not accessible until the user is
logged onto the local system. This is the default option.
h. Click Import. The PAC file appears under the selected group.
11.To delete a group, select the group and click Delete. You can also
delete the group by right -clicking the group and choosing Delete.
12.To close the Select EAP -FAST PAC window, click Close.
13.To automatically use PACs belonging to the same PAC authority group,
check the Use Any PAC Belonging to the Same Group check box.
14.Check the Use Machine PAC for Domain Logon check box if you want
the client to attempt to log into a domain using m achine
authentication with user credentials rather than user authentication.
Doing so enables your computer to connect to the network prior to
user logon. The default setting is unchecked.
15. Click OK when done configuring EAP -FAST.
EAP-TLS

23
To use EAP-TLS security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the Security
tab in the Profile Management window.
1. On the Security tab, choose the WPA radio button.
OR: On the Security tab, choose the 802.1x radio button.
2.Choose EAP-TLS from the drop-down menu.
Enabling EAP -TLS security:
To use EAP-TLS security, the machine must already have the EAP -TLS
certificates downloaded onto it. Check with the IT manager.
1. If EAP-TLS is supported, choose EAP-TLS from the drop-down menu on
the right, then click the Configure but ton.
2. Click Configure. The Define Certificate window appears.
3.Check the Use Machine Information for Domain Login check box if you
want the client to attempt to log into a domain using machine
authentication with a machine certificate and machine credentials
rather than user authentication. Doing so enables your computer to
connect to the network prior to user logon. The default setting is
unchecked.
Note: If you do not check theUse Machine Information for Domain Logon check
box, machine authentication is not performed. Authentication does not occur until
you log on.
4. Check the Validate Server Identity check box to force the system to
authenticate the identity of the server as an added level of security.
5.If you checked the Use Machine Information For Domain Logon check
box in the previous step, the Always Do User Authentication check box
at the bottom of the window becomes active. Perform one of the
following:
o Check the Always Do User Authentication check box if you want
the client to switch from using mach ine authentication to using
user authentication after you log on using your username and
password. This is the default setting.

24
o Uncheck the Always Do User Authentication check box if you
want the client to continue to use machine authentication after
the user's computer logs into the domain.
6. Choose your server certificate in the Select a Certificate drop -down
list.
7. Choose the certificate authority from which the server certificate was
downloaded in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities drop -down
list.
8.Perform one of the following:
o Leave the Server/Domain Name field blank to allow the client
to accept a certificate from any server that supplies a
certificate signed by the certificate authority listed in the
Trusted Root Certification Authorities drop -down list
(recommended ).
o In the Server/Domain Name field, enter the domain name of the
server from which the client will accept a certificate.
9. If the Login Name is filled in automatically, enter your username in
this format: username@domain.
10.Click OK to save your changes and return to the Profile Management
(Security) window.
11.Click OK.
12.Activate the profile.
EAP-TTLS
To use EAP security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the Security tab in
the Profile Management window.
1. On the Security tab, choo se the WPA/WPA2 radio button.
OR: On the Security tab, choose the 802.1x radio button.

25
2. Choose EAP-TTLS from the drop-down menu.
Enabling EAP -TTLS security:
To use EAP-TTLS security, the machine must already have the EAP -TTLS
certificates downloaded ont o it. Check with the IT manager.
1. If EAP-TTLS is supported, choose EAP-TTLS from the drop-down menu
on the right, then click the Configure button.
2. Select the appropriate certificate from the drop -down list and click
OK.
3. Specify a user name for EAP authent ication:
o Check Use Windows User Name to use the Windows user name as
the EAP user name.
o OR: Enter a EAP user name in the User Name field to use a
separate user name and password and start the EAP
authentication process.
4. Click Settings and:
o Leave the server name field blank for the client to accept a
certificate from any server with a certificate signed by the
authority listed in the Network Certificate Authority drop -down
list. (recommended)
o Enter the domain name of the server from which the client wil l
accept a certificate.
o Change the login name if needed.
5. Click OK.
6. Enable the profile.
PEAP (EAP-GTC)
To use PEAP (EAP-GTC) security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the
Security tab in the Profile Management window.
1. On the Security tab, cho ose the WPA radio button.
OR: On the Security tab, choose the 802.1x radio button.
2. Choose PEAP (EAP-GTC) from the drop-down menu.

26
To use PEAP (EAP -GTC) security, the server must have WPA -PEAP
certificates, and the server properties must already be set. Check with the IT
manager.
1. Click the Configure button.
2. To resume connection without providing credentials again after a
temporary loss of connection, check Always Resume the Secure
Session.
3. Select the appropriate network certificate authority from the
drop-down list.
4. Specify a user name for inner PEAP tunnel authentication:
o Check Use Windows User Name to use the Windows user name as
the PEAP user name.
o OR: Enter a PEAP user name in the User Name field to use a
separate user name and start the PEAP aut hentication process.
5. Check the Validate Server Identity check box to force the system to
authenticate the identity of the server as an added level of security.
6. Choose the certificate authority from which the server certificate was
downloaded in the Trust ed Root Certification Authorities drop -down
box.
7.Choose Token or Static Password , depending on the user database.
Note that Token uses a hardware token device or the Secure Computing SofToken
program (version 1.3 or later) to obtain and enter a one-time password during
authentication.
8. Click Settings and:
o Leave the Specific Server or Domain field blank to allow the
client to accept a certificate from any server that supplies a
certificate signed by the certificate authority listed in the
Trusted Root Certification Authorities drop -down box on the
Define PEAP (EAP-GTC) Configuration window (recommended)
or enter the domain name of the server from which the client
will accept a certificate.
o If the Login Name field is not filled in automatically, enter you r
username.
o Click OK to save your settings and return to the Profile
Management (Security) window.
9. Click OK.
10.Enable the profile.

27
PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2)
To use PEAP-MSCHAP V2 security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the
Security tab in the Profile Management window.
1. On the Security tab, choose the WPA radio button.
OR: On the Security tab, choose the 802.1x radio button.
2. Choose PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2) from the drop -down menu.
To use PEAP (EAP -MSCHAP V2) security , the server must have WPA -PEAP
certificates, and the server properties must already be set. Check with the IT
manager.
1. Click the Configure button.
2. Check the Validate Server Identity check box to force the system to
authenticate the identity of the server as an added level of security.
3. Choose the certificate authority from which the server certificate was
downloaded in the Trusted Root Certification Authorities drop -down
box.
4. Perform one of the following to specify how you want to establish a
network connection.
o If you want to connect using a username and password, choose
User Name and Password.
o If you want to connect using a user certificate installed on your
computer, choose Certificate, select a certificate from the
drop-down box and go to Step 6.
5. Specify the username and password for inner PEAP tunnel
authentication:

28
o Check Use Windows User Name to use the Windows user name as
the PEAP user name.
o OR: Enter a PEAP user name in the User Name field to use a
separate user name for the PEAP authentication process.
6. Click Settings. The Configuration Setting window appears.
7. Leave the Specific Server or Domain field blank to allow the client to
accept a certificate from any server that supplies a certificate signed
by the certificate authority listed in the Trusted Root Certification
Authorities drop-down box on the Define PEAP (EAP -MSCHAP V2)
Configuration window (this is the recommended option) or enter the
domain name of the server from which the client will accept a
certificate.
8. If the Login Name field is not filled in automaticall y, enter your
username with nothing after it.
9. Click OK.
10.Enable the profile.
LEAP
To use security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the Security tab in the
Profile Management window.
LEAP security requires that all infrastructure devices (e.g. acce ss points and
servers) are configured for LEAP authentication. Check with the IT manager.
Configuring LEAP
Enabling LEAP

29
Configuring LEAP:
On the Security tab, choose the WPA radio button. Choose WPA-LEAP
from the drop-down menu.
OR: On the Security tab, choose the 802.1x radio button. Choose LEAP
from the drop-down menu.
1. Click the Configure button.
2. To resume connection without providing credentials again after a
temporary loss of connection, check Always Resume the Secure
Session.
3. Specify a user name and password:
Select to Use Temporary User Name and Password by choosing the
radio button:
o Check Use Windows User Name to use the Windows user name as
the LEAP user name.
o OR: Check Manually Prompt for LEAP User Name and Password
to manually login and start the LEAP authentication process.
Select to Use Saved User Name and Password by choosing the radio
button:
o Specify the LEAP user name, password, and domain to save and
use.
4. Enter the user name and password.
5. Confirm the password.
6.Specify a domain name:
o Check the Include Windows Logon Domain with User Name
setting to pass the Windows login domain and user name to the
RADIUS server. (default)
o OR: Enter a specific domain name.
7. If desired, check No Network Connection Unless User Is Logged In to
force the wireless adapter to disassociate after logging off.
8. Enter the LEAP authentication timeout time (between 30 and 500
seconds) to specify how long LEAP should wait before declaring
authentication failed, and sending an error message. The default is
90 seconds.
9. Click OK.

30
10.Enable the profile.
5.3.2 802.1x
Enables 802.1x security. This option requires IT administration.
Choosing 802.1x opens the 802.1x EAP type drop -down menu. The options
include:
EAP-FAST
EAP-TLS
EAP-TTLS
PEAP (EAP-GTC)
PEAP (EAP-MSCHAP V2)
LEAP
Please refer to 5.3.1 WPA/WPA2
If the access point that the wireless adapter is associating to has WEP set to
Optional and the client has WEP enabled, make sure that Allow Association to
Mixed Cells is checked on the Security Tab to allow association.
5.3.3 WPA Passphrase
To use WPA Passphrase security In the Atheros Client Utility, access the
Security tab in the Profile Management window.
1.On the Security tab, choose the WPA Passphrase radio button.
2. Click on the Configure button.
3. Fill in the WPA Passphrase.
4. Click OK.
5.3.4 Pre-Shared Key (Static WEP)

31
Enables the use of pre -shared keys that are defined on both the access point
and the station.
To define pre-shared encryption keys, choose the Pre -Shared Key radio
button and click the Configure button to fill in the Define Pre-Shared Keys
window.
If the access point that the wireless adapter is associating to has WEP set to
Optional and the client has WEP enabled, make sure that Allow Association to
Mixed Cells is checked on the Security Tab to allow association.
5.3.5 None
No security (not recommended).
5.4 JumpStart for Wireless
Jumpstart is an application for configuring the wireless network (Access
Point/wireless router). After a successful configuratio n, it also creates
profiles for the wireless network's client applications (like Microsoft’s
Wireless Zero Configuration and Atheros Client Utility), so that clients can
successfully connect to the wireless network.It enables the users to easily
setup a secured wireless network. This application is based on the Wi -Fi
Protected setup specification.

32
Step 1:
Run Setup.exe in “JSW_Install_CD” folder, after installation complete,
Start “Jumpstart” program from Windows Start Programs Atheros
Jumpstart or an icon called “Jumpstart” on desktop.
Step 2 :
Choose “Join a wireless
network” and click Next to
continue.
Step 3 :
Users have three ways to connect to an AP :
a. Push Button Configuration :
1. Click “Push Button Configuration ” in the configuration web page of your
AP that you want to connect.

33
2. Within two minutes, choose
the first option and click Next
to continue.
3. Search for the AP.
4. Connect Successfully.

34
b. Enter a Pin code into AP :
1. Choose the second option
and you’ll get a Pin number.
2. Enter the Pin number in the configuration web page into the Client
PIN Number blank and click “Start PIN”.

35
3. Click Next to continue.
4.Connect Successfully.
c. Enter a Pin from AP :
1. Choose the third option and
enter PIN number from the
configuration web page of
your AP.
2. Click Next and continue.

36
3.Connect Successfully.

37
6.1
The installation driver CD will automatically activate the autorun installation
program after you insert the disk into your CD drive. Please refer to page 1
“INSTALL DRIVER/UTILITY”
6.2
Install Manually :
Plug your USB dongle into USB interface, windows Vista will search for
compatible driver to install.
Step 1 :
Select “Locate and install the
driver software”, Windows will
guide you through the process of
installing driver software for your
device.
Step 2 :
Insert the installation disc into the
CD-ROM and click “next” to
continue installation.

38
Step 3 :
Windows Vista search for the
software and it will be installed
successfully.
Step 4 :
After installation, right click the
network icon on the Windows Vista
System Tray, and click “Connect to a
network”.

39
Step 5 :
Select a network to connect to and
click “Connect”.
Step 6 :
Click “Connect Anyway” if the
network is an unsecured network.
40
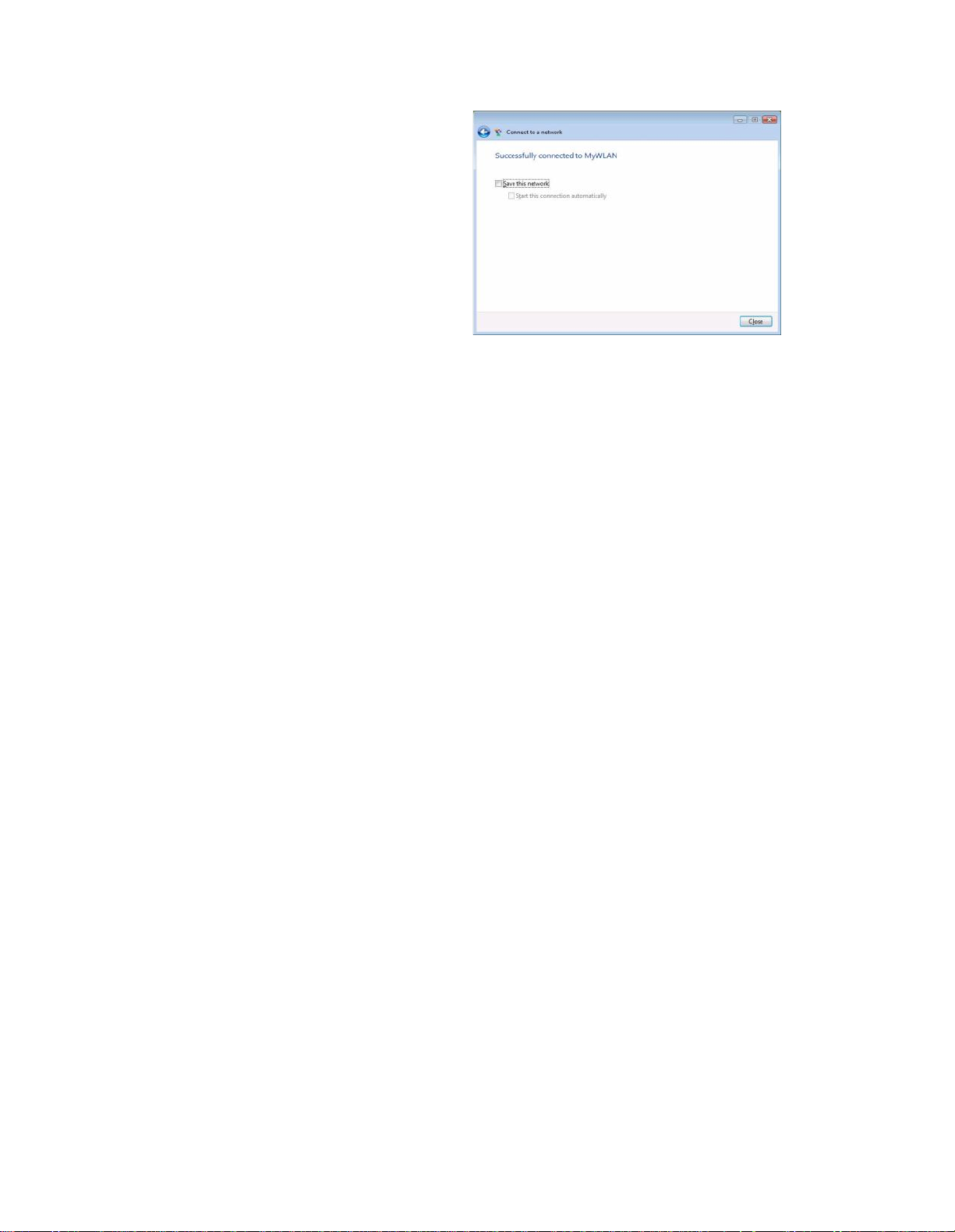
Step 7:
USB Dongle successfully connected
to network, Click “Close”

41
Product
Name
WLAN 11n ISM Band Dongle
Standard
IEEE802.11n/b/g , 802.3, 802.3u
Frequency
Band
2.400GHz ISM band
Modulation
method
BPSK/QPSK/16-QAM/64-QAM
802.11b : DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum)
802.11g/n : OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
Spread
Spectrum
Data Rate
270/240/180/120/90/60/ 54/48/36/30/24/22/18/12/11/6/5.5/
2/1Mbps and Maximum of 300Mbps.
Ad hoc
Operation
mode
Infrastructure (Access Poin ts is needed)
Transmitter
Output
Power
< 14 dBm@11n, < 17 dBm@11b, < 14 dBm@11g
Operating at 11Mbps: @ –80dBm
Operating at 54Mbps: @ –70dBm
Receiver
Sensitivity
Operating at 300Mbps: @ –64dBm
Operating
Range
Indoor Up to 100 m, Outdoor Up to 280 m
Security
64-bit, 128-bit or WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy); TKIP, AES
I/O Interface
USB 2.0
LED
Link/Active
Operating
system
supported
Windows 2000, XP and Vista
Management
Windows-based configuration utility and status monitoring
Regulation
FCC for North America
CE/ETSI for European
Dimension
90 x 26 x 10.95 mm

42
Symptom :
The LED is off.
Remedy :
Make sure the PC Card is inserted properly. Otherwise contact your vendor.
Symptom :
The LED is always on not blinking.
Remedy :
Make sure that you have installed the driver from attached CD. Otherwise
contact your vendor.
Symptom :
The LED is blinking but the PC Card ic on does not appear in your icon tray.
Remedy :
Make sure that you have installed the Utility from the attached CD.
Symptom :
The PC Card is linking, but can’t share files with others.
Remedy :
Make sure the file and printer sharing function is enabled. Yo u can
enable the function by checking the icon of My Computer -> Control
Panel -> Network -> file and printer sharing -> I want to be able to give
others to access to my files .
Symptom :
Slow or poor performance .
Remedy :
Try to select another channel for the communicating group or move your
device closer to the Access Point.
Operating
Temperature
0 ~ 50 ℃
Storage
Temperature
-10 ~ 70 ℃
Humidity
5 ~ 90% maximum (non-condensing)

43
IEEE 802.11 Standard
The IEEE 802.11 Wireless LAN standards subcommittee, which is formulating
a standard for the industry.
Access Point
An internetworking device that seamlessly connects wired and wireless
networks together.
Ad Hoc
An Ad Hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with a WLAN
adapter, connected as an independent wireless LAN. Ad Hoc wireless LAN
is applicable at a departmental scale for a branch or SOHO operati on.
BSSID
A specific Ad Hoc LAN is called a Basic Service Set (BSS). Computers in a
BSS must be configured with the same BSSID.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - a method in which IP addresses are
assigned by server dynamically to clients on the n etwork. DHCP is used for
Dynamic IP Addressing and requires a dedicated DHCP server on the
network.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum
This is the method the wireless cards use to transmit data over the frequency
spectrum. The other method is frequency hoppin g. Direct sequence
spreads the data over one frequency range (channel) while frequency
hopping jumps from one narrow frequency band to another many
times per second.
ESSID
An Infrastructure configuration could also support roaming capability for
mobile workers. More than one BSS can be configured as an Extended
Service Set (ESS). Users within an ESS could roam freely between BSSs
while served as a continuous connection to the network wireless stations
and Access Points within an ESS must be configured with the same ESSID
and the same radio channel.

44
Ethernet
Ethernet is a 10/100Mbps network that runs over dedicated home/office
wiring. Users must be wired to the network at all times to gain access.
Gateway
A gateway is a hardware and software devi ce that connects two dissimilar
systems, such as a LAN and a mainframe. In Internet terminology, a gateway
is another name for a router. Generally a gateway is used as a funnel
for all traffic to the Internet.
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics E ngineers
Infrastructure
An integrated wireless and wired LAN is called an Infrastructure
configuration. Infrastructure is applicable to enterprise scale for wireless
access to central database, or wireless application for mobile workers .
ISM Band
The FCC and their counterparts outside of the U.S. have set aside bandwidth
for unlicensed use in the so -called ISM (Industrial, Scientific and
Medical) band. Spectrum in the vicinity of 2.4 GHz, in particular, is being
made available worldwide. This presents a tru ly revolutionary opportunity
to place convenient high -speed wireless capabilities in the hands of users
around the globe.
Local Area Network (LAN)
A LAN is a group of computers, each equipped with the appropriate network
adapter card connected by cable/air , that share applications, data,
and peripherals. All connections are made via cable or wireless media,
but a LAN does not use telephone services. It typically spans a single
building or campus.
Network
A network is a system of computers that is connected. Data, files, and
messages can be transmitted over this network. Networks may be local or
wide area networks.
Protocol
A protocol is a standardized set of rules that specify how a conversation
is to take place, including the format, timing, sequencing and / or error
checking.

45
Roaming
In an infrastructure network, this is when a wireless PC moves out of
range of the previously connected access point and connects to a newly
connected access point. Throughout the network environment where
access point is deployed, PCs can always be connected regardless of
where they are located or roam.
SSID
A Network ID unique to a network. Only clients and Access Points that
share the same SSID are able to communicate with each other. This string
is case-sensitive.
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
Simple Network Management Protocol is the network management protocol
of TCP/IP. In SNMP, agents -which can be hardware as well as software monitor the activity in the various devices on the network and
report to the network console workstation. Control information about
each device is maintained in a structure known as a management information
block.
Static IP Addressing
A method of assigning IP addresses to clients on the network. In networks
with Static IP address, the ne twork administrator manually assigns an IP
address to each computer. Once a Static IP address is assigned, a computer
uses the same IP address every time it reboots and logs on to the
network, unless it is manually changed.
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The Temporal Key Integrity Protocol, pronounced tee -kip, is part of the
IEEE 802.11i encryption standard for wireless LANs. TKIP is the next
generation of WEP, the Wired Equivalency Protocol, which is used to
secure 802.11 wireless LANs. TKIP provid es per-packet key mixing, a
message integrity check and a re -keying mechanism, thus fixing the
flaws of WEP.
Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
TCP/IP is the protocol suite developed by the Advanced Research
Projects Agency (ARPA). It is widely used in corporate Internet works,
because of its superior design for WANs. TCP governs how packet is
sequenced for transmission the network. The term “TCP/IP” is often
used generically to refer to the entire suite of related protocols.

46
Transmit / Receive
The wireless throughput in Bytes per second averaged over two seconds.
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a nonprofit international association formed in 1999
to certify interoperability of wireless Local Area Network products based
on IEEE 802.11 specification. The goal of the Wi -Fi Alliance’s members is
to enhance the user experience through product interoperability. The
organization is formerly known as WECA.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
The Wi-Fi Alliance put together WPA as a data encryption method for
802.11 wireless LANs. WPA is an industry -supported, pre-standard version
of 802.11i utilizing the Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP),
which fixes the problems of WEP, including using dynamic keys.
Wide Area Network (WAN)
A WAN consists of multiple LANs that are tied together via telephone
services and / or fiber optic cabling. WANs may span a city, a state, a
country, or even the world.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WE P)
Now widely recognized as flawed, WEP was a data encryption method
used to protect the transmission between 802.11 wireless clients and
APs. However, it used the same key among all communicating devices.
WEP’s problems are well -known, including an insuff icient key length and
no automated method for distributing the keys. WEP can be easily
cracked in a couple of hours with off -the-shelf tools.
Wireless LAN (WLAN)
A wireless LAN does not use cable to transmit signals, but rather uses
radio or infrared to transmit packets through the air. Radio Frequency
(RF) and infrared are the commonly used types of wireless transmission.
Most wireless LANs use spread spectrum technology. It offers limited
bandwidth, usually under 11Mbps, and users share the bandwidth with
other devices in the spectrum; however, users can operate a spread
spectrum device without licensing from the Federal Communications
Commission (FCC).

47
One Year Limited Warranty
This device is guaranteed against manufacturing defects for one full year
from the original date of purchase.
This warranty is valid at the time of purchase and is non -transferable.
This warranty must be presented to the service facility before any repair
can be made.
Sales slip or other authentic evidence is required to validate warranty.
and/or
uncertified repairs is not covered by this warranty.
All mail or transportation costs inclu ding insurance are at the expense
of the owner.
Do not send any product to service center for warranty without a RMA
(Return Merchandise Authorization) and proof of purchase. Ensure a
trackable method of delivery is used (keep tracking number).
y is valid only in the country of purchase.
We assumes no liability that may result directly or indirectly from the
use or misuse of these products.
IMPORTANT
" This warranty will be voided if the device is tampered with, improperly
serviced, or the security seals are broken or removed"
 Loading...
Loading...