MYSON MTV021N24 Datasheet
TECHNOLOGY
Enhanced Super On-Screen Display
FEATURES GENERAL DESCRIPTION
• Horizontal SYNC input up to 130 KHz.
• On-chip PLL circuitry up to 96 MHz.
• Programmable horizontal resolutions up to 1524 dots per
display row.
• Full-screen display consists of 15 (rows) by 30 (columns)
characters.
• 12 x 18 dot matrices per character.
• Total of 272 characters and graphic fonts, including 256
standard and 16 multi-color mask ROM fonts.
• 8 color-selectable maximum per display character.
• 7 color-selectable maximum for character background.
• Double character height and/or width control.
• Programmable positioning for display screen center.
• Bordering, shadowing and blinking effect.
• Programmable character height (18 to 71 lines) control.
• Row to row spacing register to manipulate the constant
display height.
• 4 programmable background windows with multi-level
operation and shadowing on window effect.
• Software clears bit for full-screen erasing.
• Half tone and fast blanking output.
• Fade-in/fade-out effect.
• 8-channel/8-bit PWM D/A converter output.
• Compatible with SPI bus or I2C interface with slave
address 7AH (slave address is mask option).
• 16-pin, 20-pin or 24-pin PDIP package.
MTV021 is designed for monitor applications to
display built-in characters or fonts onto monitor
screens. The display operation occurs by transferring
data and control information from the micro-controller
to RAM through a serial data interface. It can execute
full-screen display automatically, as well as specific
functions such as character background color, bordering, shadowing, blinking, double height and width,
font by font color control, frame positioning, frame
size control by character height and row-to-row spacing, horizontal display resolution, full-screen erasing,
fade-in/fade-out effect, windowing effect and shadowing on window.
MTV021 provides 256 standard and 16 multi-color
characters and graphic fonts for more efficacious
applications. The full OSD menu is formed by 15
rows x 30 columns, which can be positioned anywhere on the monitor screen by changing vertical or
horizontal delay.
Moreover, MTV021 also provides 8 PWM DAC
channels with 8-bit resolution and a PWM clock output for external digital-to-analog control.
MTV021MYSON
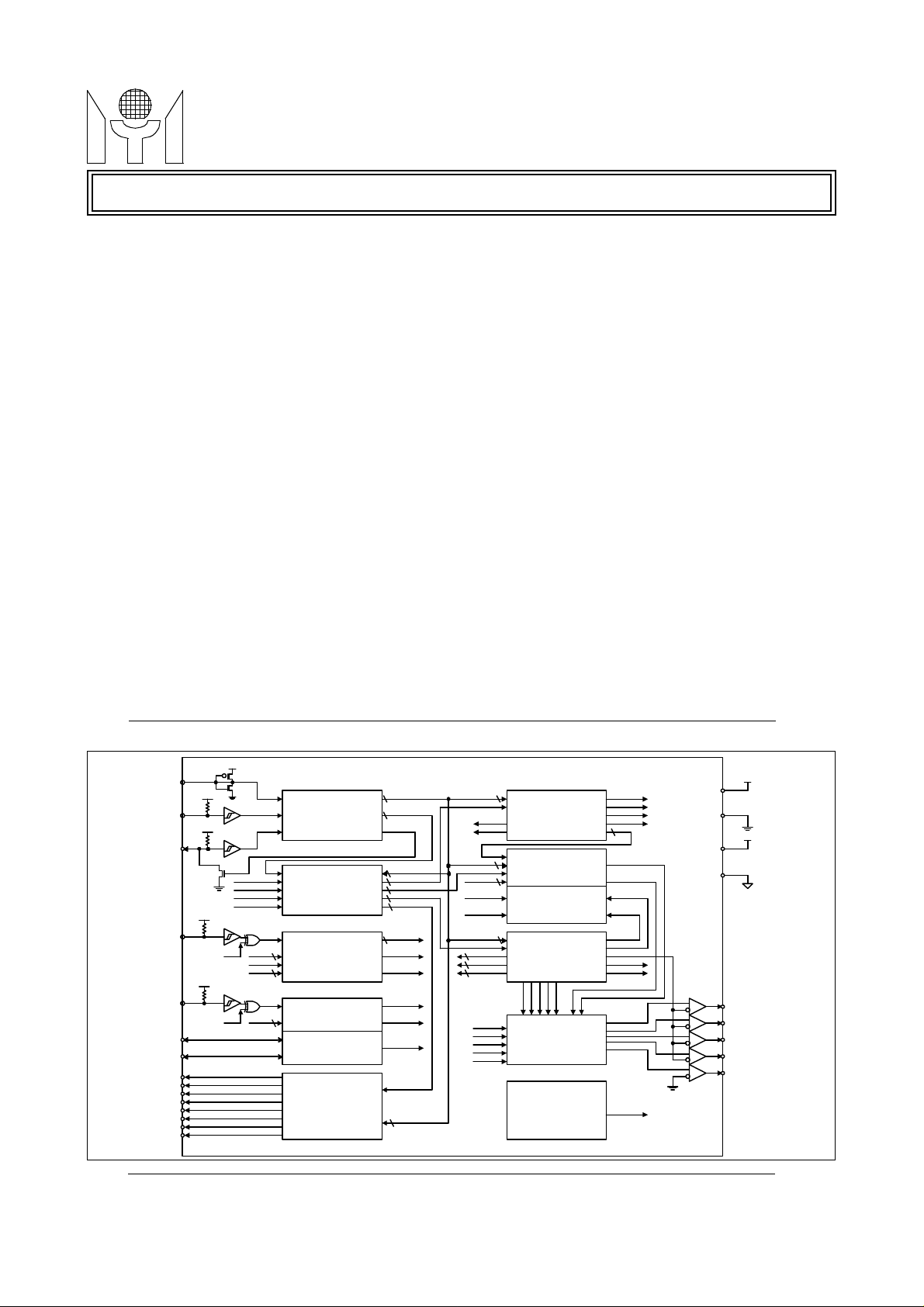
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SSB
SCK
SDA
VFLB
HFLB
VCO
PWM0
PWM1
PWM2
PWM3
PWM4
PWM5
PWM6
PWM7
8
SERIAL DATA
INTERFACE
ARWDB
ADDRESS BUS
HDREN
VDREN
ADMINISTRATOR
NROW
VERTICAL
7
CHS
VERTD
HORD
CH
8
8
DISPLAY
CONTROL
HORIZONTAL
DISPLAY CONTROL
PHASE LOCK LOOP
VSP
HSP
RP
DATA
9
ROW, COL
ACK
5
RCADDR
9
DADDR
9
FONTADDR
5
WINADDR
5
PWMADDR
5
LPN
NROW
VDREN
ARWDB
HDREN
VCLKX
PWM D/A
CONVERTER
8
DATA
8 LUMAR
DATA
DISPLAY & ROW
CWS
DATA
LPN
CWS
VCLKS
8
VERTD
8
HORD
7
LUMAR
LUMAG
LUMAB
BLINK
VCLKX
CHS
DATA
REGISTERS
8
CHARACTER ROM
5
LUMINANCE &
GENERATOR
8
WINDOWS &
CH
CONTROL
WRWGWB
ENCODER
CONTROL
BORDGER
FRAME
FBKGC
BLANK
COLOUR
POWER ON
RESET
LUMAG
LUMAB
BLINK
8
CRADDR
LUMA
BORDER
BSEN
SHADOW
OSDENB
HSP
VSP
PRB
This datasheet contains new product information. Myson Technology reserves the rights to modify the product specification without notice.
No liability is assumed as a result of the use of this product. No rights under any patent accompany the sales of the product.
VDD
VSS
VDDA
VSSA
ROUT
GOUT
BOUT
FBKG
HTONE
1/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999

TECHNOLOGY
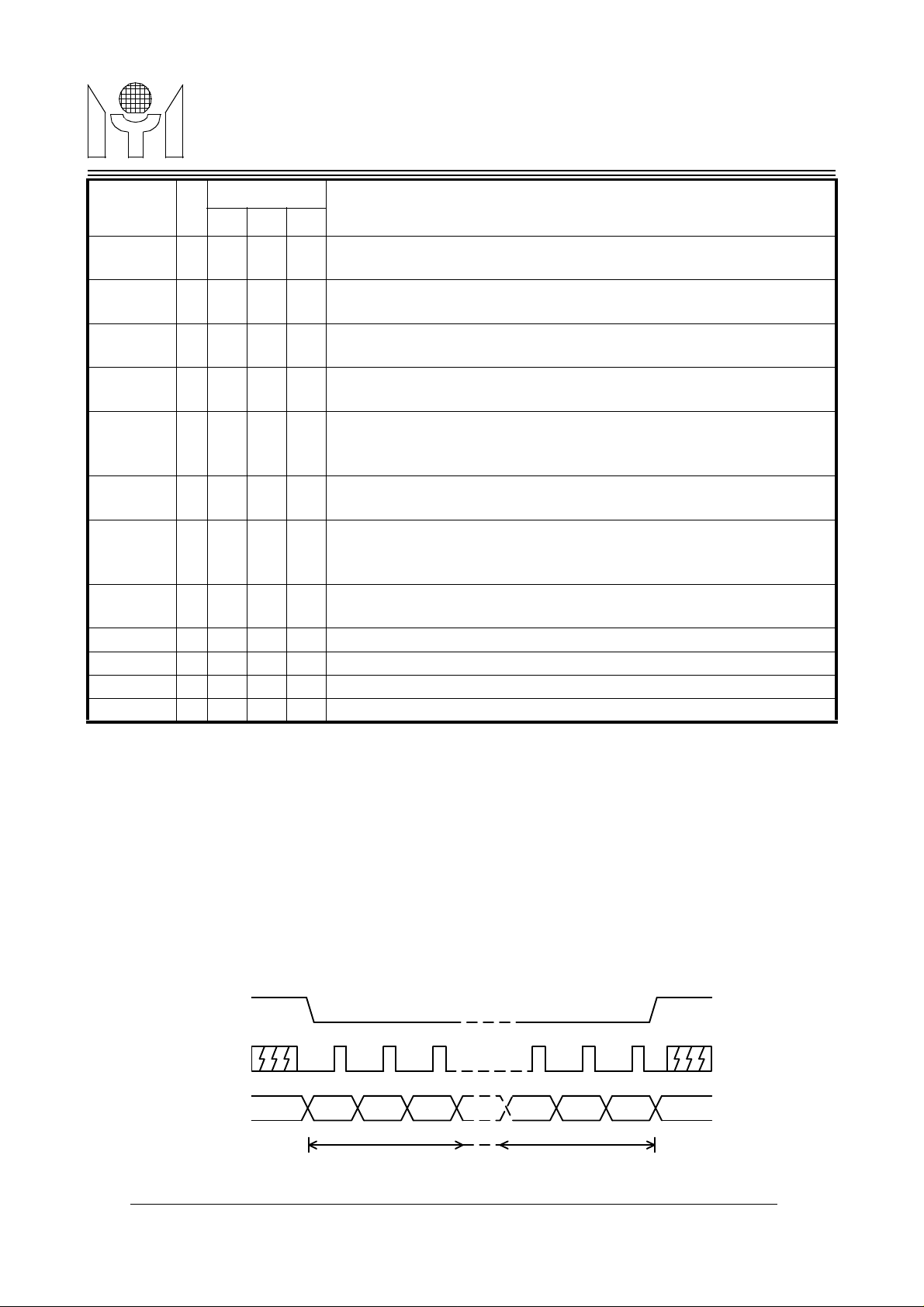
1.0 PIN CONNECTION
MTV021MYSON
VSSA
VCO
RP
VDDA
HFLB
SSB
SDA
SCK
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
MTV021
16
VSS
15
ROUT
14
GOUT
13
BOUT
12
FBKG
11
HTONE/PWMCK
VFLB
10
VDD
9
VSSA
VCO
RP
VDDA
HFLB
SSB
SDA
SCK
PWM0
PWM1
1
2
3
4
5
MTV021N20
6
7
8
9
10
20
VSS
19
ROUT
18
GOUT
17
BOUT
16
FBKG
HTONE/PWMCK
15
14
VFLB
VDD
13
PWM7
12
PWM6
11
VSSA
VCO
RP
VDDA
HFLB
SSB
SDA
SCK
PWM0
PWM1
PWM2
PWM3
1
2
3
4
5
6
MTV021N24
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
VSS
23
ROUT
22
GOUT
21
BOUT
20
FBKG
19
HTONE/PWMCK
VFLB
18
VDD
17
PWM7
16
PWM6
15
PWM5
14
PWM4
13
2.0 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Name I/O
VSSA - 1 1 1 Analog ground. This ground pin is used to internal analog circuitry.
VCO I/O 2 2 2 Voltage Control Oscillator. This pin is used to control the internal oscil-
RP I/O 3 3 3 Bias Resistor. The bias resistor is used to regulate the appropriate bias
VDDA - 4 4 4 Analog power supply. Positive 5 V DC supply for internal analog cir-
HFLB I 5 5 5 Horizontal input. This pin is used to input the horizontal synchronizing
SSB I 6 6 6 Serial interface enable. It is used to enable the serial data and is also
SDA I 7 7 7 Serial data input. The external data transfer through this pin to internal
SCK I 8 8 8 Serial clock input. The clock-input pin is used to synchronize the data
PWM0 O - 9 9 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 0. The output pulse width is program-
PWM1 O - 10 10 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 1. The output pulse width is program-
PWM2 O - - 11 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 2. The output pulse width is program-
PWM3 O - - 12 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 3. The output pulse width is program-
Pin No.
Descriptions
N16 N20 N24
lator frequency by DC voltage input from external low pass filter.
current for internal oscillator to resonate at specific dot frequency.
cuitry. And a 0.1uF decoupling capacitor should be connected across to
VDDA and VSSA.
signal. It is a leading edge triggered and has an internal pull-up resistor.
used to select the operation of I2C or SPI bus. If this pin is left floating, I2C
bus is enabled, otherwise the SPI bus is enabled.
display registers and control registers. It has an internal pull-up resistor.
transfer. It has an internal pull-up resistor.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 23.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 24.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 25.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 26.
2/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999
TECHNOLOGY
MTV021MYSON
Name I/O
PWM4 O - - 13 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 4. The output pulse width is program-
PWM5 O - - 14 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 5. The output pulse width is program-
PWM6 O - 11 15 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 6. The output pulse width is program-
PWM7 O - 12 16 Open-Drain PWM D/A converter 7. The output pulse width is program-
VDD - 9 13 17 Digital power supply. Positive 5 V DC supply for internal digital circuitry
VFLB I 10 14 18 Vertical input. This pin is used to input the vertical synchronizing signal.
HTONE /
PWMCK
FBKG O 12 16 20 Fast Blanking output. It is used to cut off external R, G, B signals of
BOUT O 13 17 21 Blue color output. It is a blue color video signal output.
GOUT O 14 18 22 Green color output. It is a green color video signal output.
ROUT O 15 19 23 Red color output. It is a red color video signal output.
VSS - 16 20 24 Digital ground. This ground pin is used to internal digital circuitry.
O 11 15 19 Half tone output / PWM clock output. This is a multiplexed pin selected
Pin No.
Descriptions
N16 N20 N24
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 27.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 28.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 29.
mable by the register of Row 15, Column 30.
and a 0.1uF decoupling capacitor should be connected across to VDD
and VSS.
It is leading triggered and has an internal pull-up resistor.
by PWMCK bit. This pin can be a PWM clock or used to attenuate R, G, B
gain of VGA for the transparent windowing effect.
VGA while this chip is displaying characters or windows.
3.0 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
3.1 SERIAL DATA INTERFACE
The serial data interface receives data transmitted from an external controller. And there are 2 types of bus
can be accessed through the serial data interface, one is SPI bus and other is I2C bus.
3.1.1 SPI bus
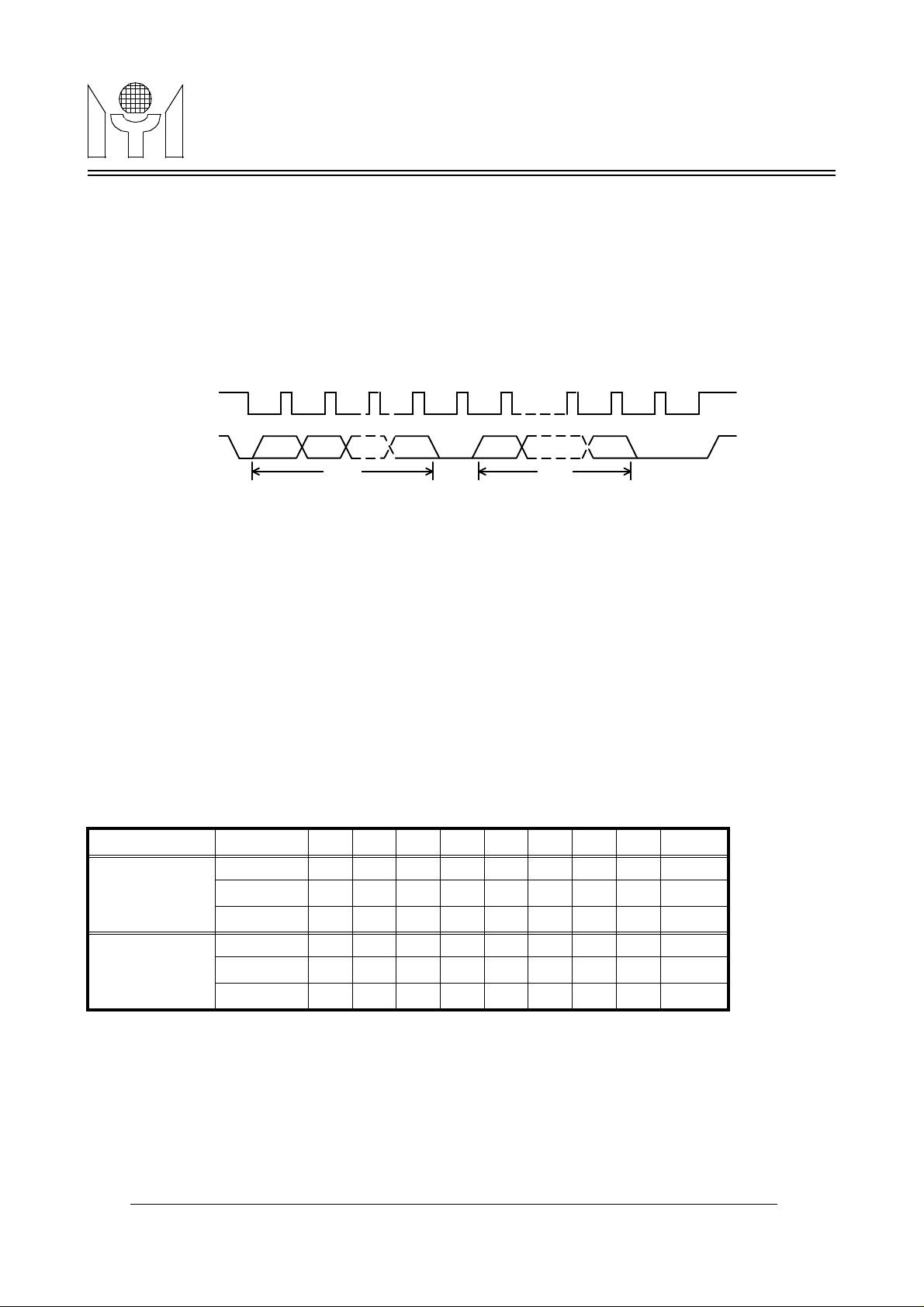
While SSB pin is pulled to "high" or "low" level, the SPI bus operation is selected. And a valid transmission
should be starting from pulling SSB to "low" level, enabling MTV021 to receiving mode, and retain "low" level
until the last cycle for a complete data packet transfer. The protocol is shown in Figure1.
SSB
SCK
SDA
MS
B
first byte last byte
FIGURE 1. Data Transmission Protocol (SPI)
3/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999
LSB
MTV021MYSON
TECHNOLOGY
There are three transmission formats shown as below:
Format (a) R - C - D → R - C - D → R - C - D
Format (b) R - C - D → C - D → C - D → C - D
Format (c) R - C - D → D → D → D → D → D
Where R=Row address, C=Column address, D=Display data
3.1.2 I2C bus
I2C bus operation is only selected when SSB pin is left floating. And a valid transmission should be starting
from writing the slave address 7AH, which is mask option, to MTV021. The protocol is shown in Figure2.
SCK
SDA
START ACK
B7 B6 B0 B7 B0
first byte
second byte last byte
¡@¡@¡@¡@
¡@
ACK STOP
FIGURE 2. Data Transmission Protocol (I2C)
There are three transmission formats shown as below:
Format (a) S - R - C - D → R - C - D → R - C - D
Format (b) S - R - C - D → C - D → C - D → C - D
Format (c) S - R - C - D → D → D → D → D → D
Where S=Slave address, R=Row address, C=Column address, D=Display data
Each arbitrary length of data packet consists of 3 portions viz, Row address (R), Column address (C), and
Display data (D). Format (a) is suitable for updating small amount of data which will be allocated with different
row address and column address. Format (b) is recommended for updating data that has same row address
but different column address. Massive data updating or full screen data change should use format (c) to
increase transmission efficiency. The row and column address will be incremented automatically when the
format (c) is applied. Furthermore, the undefined locations in display or fonts RAM should be filled with
dummy data.
TABLE 1. The configuration of transmission formats.
Address b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0 Format
Row 1 0 0 x R3 R2 R1 R0 a,b,c
Address Bytes
of Display Reg.
Column
Column
0 0 x C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 a,b
ab
0 1 x C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 c
c
Row 1 0 1 x R3 R2 R1 R0 a,b,c
Attribute Bytes
of Display Reg.
Column
Column
0 0 x C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 a,b
ab
0 1 x C4 C3 C2 C1 C0 c
c
There are 2 types of data should be accessed through the serial data interface, one is ADDRESS bytes of display registers, and other is ATTRIBUTE bytes of display registers, the protocol are same for all except the bit5
of row address. The MSB(b7) is used to distinguish row and column addresses when transferring data from
external controller. The bit6 of column address is used to differentiate the column address for format (a), (b)
and format (c) respectively. Bit5 of row address for display register is used to distinguish ADDRESS byte
when it is set to "0" and ATTRIBUTE byte when it is set to "1". See Table 1 on page 4.
4/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999
MTV021MYSON
TECHNOLOGY
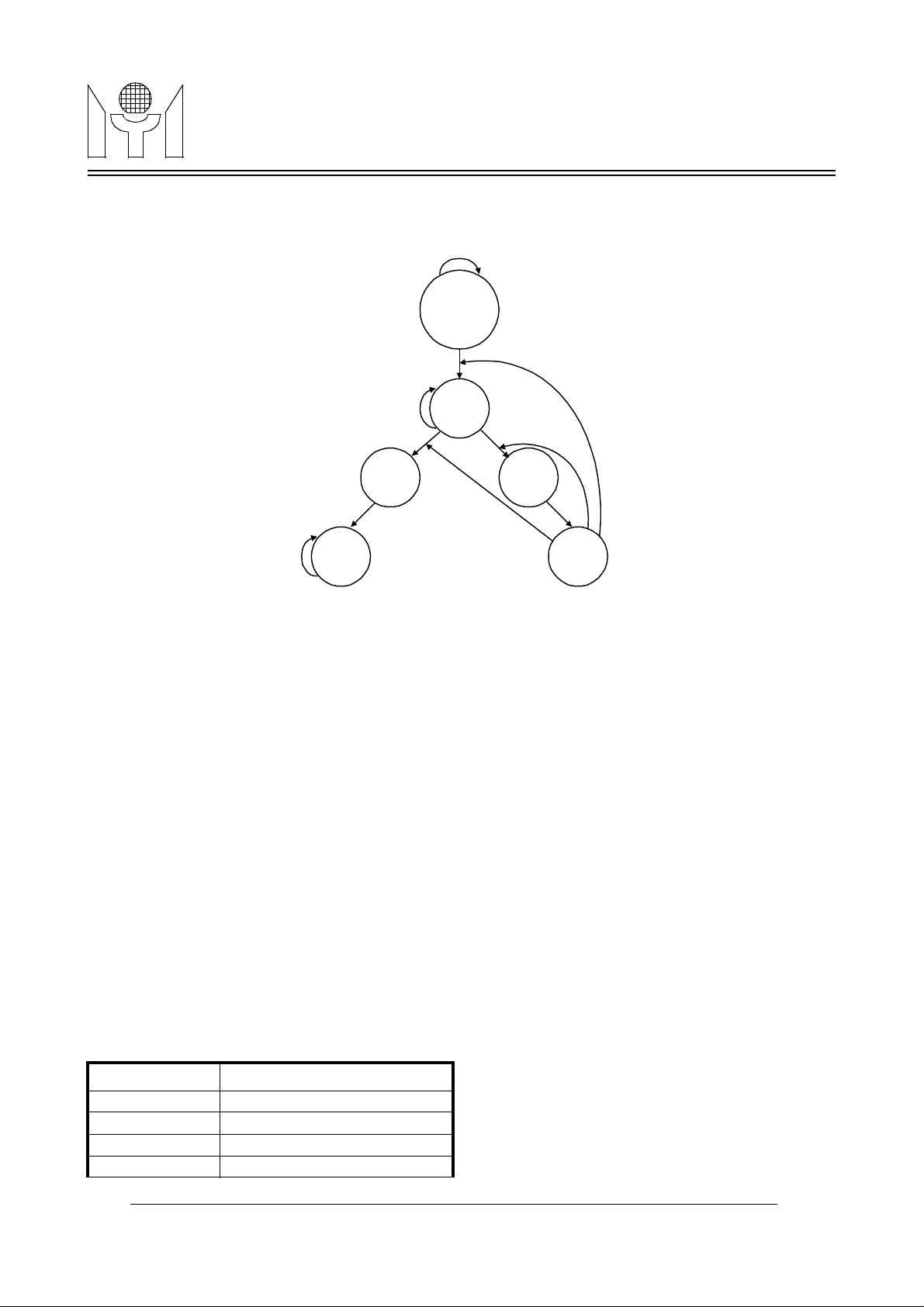
The data transmission is permitted to change from format (a) to format (b) and (c), or from format (b) to format
(a), but not from format (c) back to format (a) and (b). The alternation between transmission formats is configured as the state diagram shown in Figure3.
0, X
0, 0
format (b)
COL
Input = b7, b6
format (a)
0, 0
ab
X, X
DA
1, X
ab
X, X
DA
format (c)
COL
X, X
c
1, X
c
Initiate
1, X
ROW
0, 1
0, 1
FIGURE 3. Transmission State Diagram
3.2 Address bus administrator
The administrator manages bus address arbitration of internal registers or user fonts RAM during external
data write in. The external data write through serial data interface to registers must be synchronized by internal display timing. In addition, the administrator also provides automatic increment to address bus when external write using format (c).
3.3 Vertical display control
The vertical display control can generates different vertical display sizes for most display standards in current
monitors. The vertical display size is calculated with the information of double character height bit(CHS), vertical display height control register(CH6-CH0).The algorithm of repeating character line display are shown as
Table 2 and Table 3. The programmable vertical size range is 270 lines to maximum 2130 lines.
The vertical display center for full screen display could be figured out according to the information of vertical
starting position register (VERTD) and VFLB input. The vertical delay starting from the leading edge of VFLB,
is calculated with the following equation:
Vertical delay time = ( VERTD * 4 + 1 ) * H Where H = one horizontal line display time
TABLE 2. Repeat line weight of character
CH6 - CH0 Repeat Line Weight
CH6,CH5=11 +18*3
CH6,CH5=10 +18*2
CH6,CH5=0x +18
CH4=1 +16
5/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999
TECHNOLOGY
TABLE 2. Repeat line weight of character
CH6 - CH0 Repeat Line Weight
CH3=1 +8
CH2=1 +4
CH1=1 +2
CH0=1 +1
TABLE 3. Repeat line number of character
MTV021MYSON
Repeat Line
Weight
+1 - - - - - - - - v - - - - - - - - +2 - - - - v - - - - - - - v - - - - +4 - - v - - - v - - - v - - - v - - -
+8 - v - v - v - v - v - v - v - v - +16 - v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v +17 v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v +18 v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v v
Note:" v " means the nth line in the character would be repeated once, while " - " means the nth line in the
character would not be repeated.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Repeat Line #
3.4 Horizontal display control
The horizontal display control is used to generate control timing for horizontal display based on double character width bit (CWS), horizontal positioning register (HORD), horizontal resolution register (HORR), and
HFLB input. A horizontal display line consists of (HORR*12) dots which include 360 dots for 30 display characters and the remaining dots for blank region. The horizontal delay starting from HFLB leading edge is calculated with the following equation,
Horizontal delay time = ( HORD * 6 + 49) * P - phase error detection pulse width
Where P = One pixel display time = One horizontal line display time / (HORR*12)
3.5 Phase lock loop (PLL)
On-chip PLL generates system clock timing (VCLK) by tracking the input HFLB and horizontal resolution register (HORR). The frequency of VCLK is determined by the following equation:
VCLK Freq = HFLB Freq * HORR * 12
The VCLK frequency ranges from 6MHz to 96MHz selected by (VCO1, VCO0). In addition, when HFLB input
is not present to MTV021, the PLL will generate a specific system clock, approximately 2.5MHz, by a built-in
oscillator to ensure data integrity.
3.6 Display & Row control registers
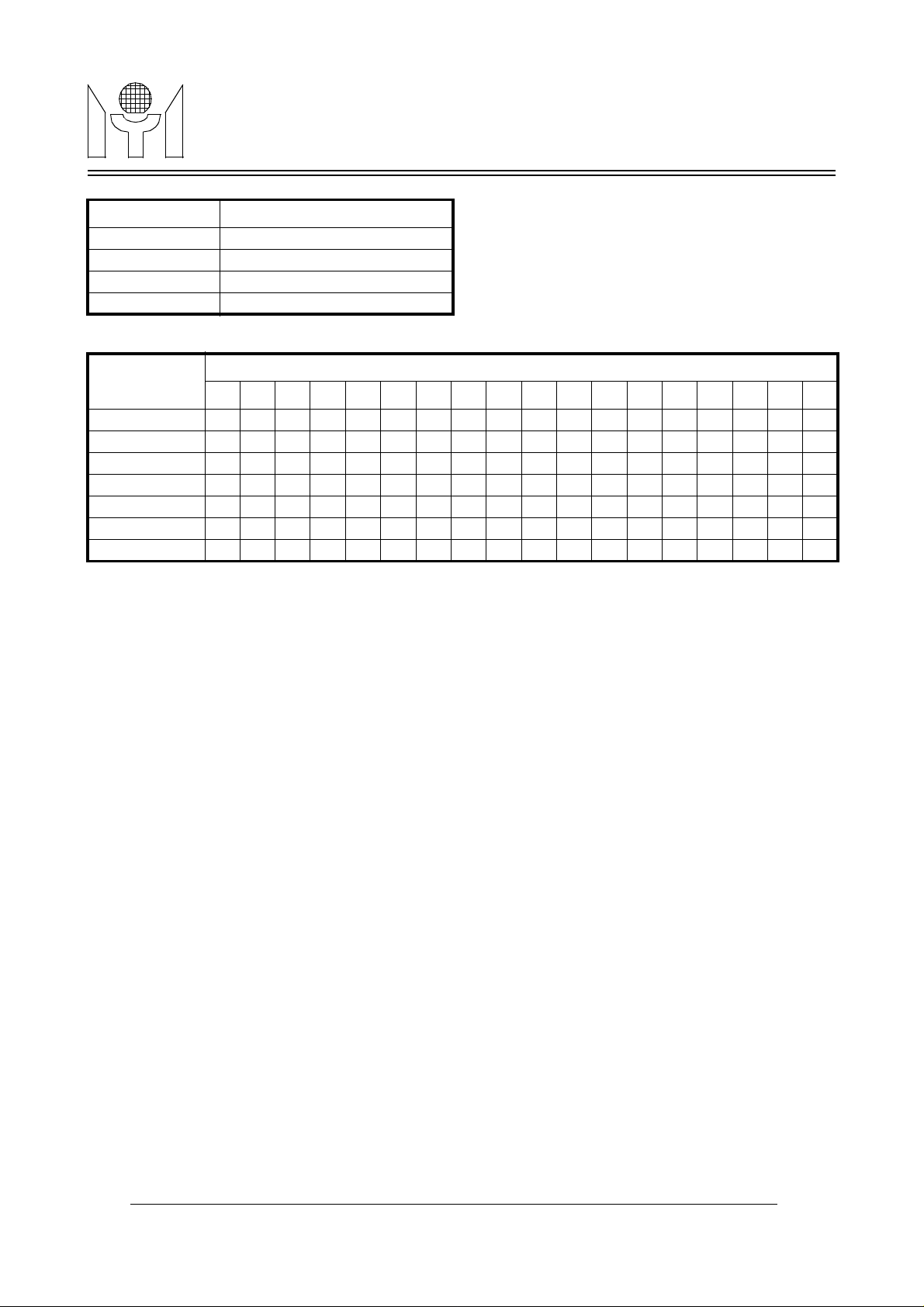
The internal RAM contains display and row control registers. The display registers have 450 locations which
are allocated between (row 0, column 0) to (row 14, column 29), as shown in Figure4. Each display register
has its corresponding character address on ADDRESS byte, its corresponding background color, 1 blink bit
and its corresponding color bits on ATTRIBUTE bytes. The row control register is allocated at column 30 for
6/17 MTV021 Revision 5.0 6/29/1999
 Loading...
Loading...